
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Insect Sci., 11 April 2025
Sec. Insect Health and Pathology
Volume 5 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/finsc.2025.1552694
 Rachid Boulamtat1*
Rachid Boulamtat1* Karim El Fakhouri2
Karim El Fakhouri2 Hassna Jaber1
Hassna Jaber1 Ali Oubayoucef2
Ali Oubayoucef2 Chaimae Ramdani2
Chaimae Ramdani2 Nabil Fikraoui3
Nabil Fikraoui3 Muamar Al-Jaboobi1
Muamar Al-Jaboobi1 Meryem El Fadil2
Meryem El Fadil2 Ilyass Maafa1
Ilyass Maafa1 Abdelhalem Mesfioui4
Abdelhalem Mesfioui4 Seid Ahmed Kemal1
Seid Ahmed Kemal1 Mustapha El Bouhssini2
Mustapha El Bouhssini2The destructive pest of chickpeas, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner), is difficult to control using synthetic insecticides. The current research examined the entomopathogenic and endophytic colonisation effects of three fungal strains of Beauveria bassiana (HASS; RFSL10; SP-IR-566) against H. armigera larvae under laboratory, greenhouse, and field conditions. Four inoculation methods were used in the greenhouse: Root Dipping (RD), Leaf Spraying (LS), Stem Injection (SI), and Seed Coating (SC), while spray application was used for laboratory and field treatments. Under laboratory conditions, the highest entomopathogenic effect was recorded by HASS and RFSL10 strains applied as a direct spray at 108 conidia mL-1 with 100% mortality, followed by SP-IR-566 with 96%, 12 days after treatment. Furthermore, foliar application in the field reduced larval population by an average ranging from 82 to 100%, confirming the significant effects of the three tested strains. In terms of endophytic colonisation under greenhouse setting, both stem injection and root dipping methods expressed low to moderate mortality rates ranging from 32 to 40%, 15 days after application. These findings suggested that B. bassiana strains, investigated as foliar application, had a potential as an effective strategy to control H. armigera. This study also offers new insights into the potential of the endophytic entomopathogens approach as a viable and safe alternative to chemical pesticides.
Climate and farming system changes contribute to the emergence of minor and/or new pests affecting food crops in different regions (1). Among these pests, chickpea pod borer (Helicoverpa armigera), is becoming an important pest in North African countries like Morocco (2, 3). The pest causes significant losses in crops such as chickpeas, cotton, tomatoes, sunflowers, beans, and maize. In Morocco, chickpea pod borer can reduce crop yield up to 31% (4). Currently, the most common method of managing the pest involves the extensive use of synthetic insecticides (4–6). As a result, H. armigera develops resistance to most synthetic insecticides (7, 8). The use of chemical pesticides poses environmental risks, as they contribute to pollution and undesirable side effects on beneficial organisms (9–11). To minimize the impact of excessive use of chemical insecticides to control H. armigera, it is crucial to develop components for Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for sustainable pest management practices (12, 13). Thus far, no reliable sources of resistance to pod borer exist in the primary chickpea gene pool to develop commercial varieties (14, 15). Recent studies have shown that plant extracts and entomopathogenic fungi can play key roles in the management of H. armigera (16–18). The entomopathogenic fungi have several physiological effects, including growth and oviposition perturbation, larval mortality, disruption of reproduction, and regulatory activities (19, 20).
Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) Vuillemin (Hyphomycetes) is one of the most characterized and widely used entomopathogenic fungal species to manage polyphagous pests, such as chickpea pod borer (21, 22). Numerous B. bassiana based formulations are already commercialized in many countries against various agricultural pests (23–26). Besides its ability to parasitize insects, B. bassiana acts as an endophytic agent in several plant species and protects against pathogens (27–31). For example, B. bassiana was effective in controlling Dactylopius opuntiae, which devastates cactus plants in Morocco (26).
The present study aimed to validate the virulence of three B. bassiana strains in controlling H. armigera under laboratory and field conditions.
Helicoverpa armigera larvae were collected from infested chickpea fields between May and June 2021 at the ICARDA (International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas) experimental station in Marchouch, Morocco (33°56’10”N 6°69’21”W). The larvae were reared on an artificial diet according to Boulamtat et al. (17), under 25 ± 2°C temperature, 75 ± 5% relative humidity (RH), and 14:10 L/D photoperiod. Each larva was placed individually in a Petri dish and fed an artificial diet (32), until the pupation. After emergence, adults were maintained in glass cages (90 cm3 volume) with 10% honey solution as an energy source. After oviposition, eggs were collected daily and transferred into Petri dishes. The newly hatched larvae were reared on the artificial diet following the same procedure indicated above. The second instar larvae were used for various bioassays.
Three B. bassiana strains were collected from Syria (two strains) and Iran (one strain), originating from three insect hosts, and were used in this study (Table 1).
B. bassiana inoculum production: The three B. bassiana strains were multiplied on Potato Dextrose Agar medium (PDA) under 25 ± 1 C° temperature, and 14:10 L/D light cycle for 14 days. Spores were harvested by scraping the PDA plates with a sterile scalpel and suspended in 10 mL of sterile distilled water containing Tween-80 (0.01%).
All strains were tested on H. armigera larvae for their pathogenicity. Three conidial concentrations (106, 107, and 108 conidia mL-1) were prepared in sterile distilled water containing Tween-80 (0.01%). Second instar larvae were inoculated by spraying 15 µL of the suspension using a sprayer with a 50 mL capacity, delivering a frequency of 1-2 mL per minute to ensure precise application. the conidia suspension on top of the insect. Five treated larvae were transferred into Petri dishes containing moist sterile filter paper and provided with an artificial diet. The bioassay was conducted using a completely randomized design with five replicates per concentration for each treatment and five larvae were used in each replication. Larvae treated with distilled water containing Tween-80 (0.01%) served as a control. The experiments were conducted under laboratory conditions at 24 ± 1°C temperature, 75 ± 5% RH, and 14:10 L/D cycle light. Larval mortality was recorded daily for 14 days. Mortality was calculated according to Abbott's formula (33):
Chickpea seedlings of Bouchra (cultivar FLIP97-114C) were inoculated with each strain at 108 conidia mL-1 containing Tween-80 (0.01%). Four inoculation methods in five replications were evaluated. Each replication (pot) was planted with five seeds.
a) Root dipping (RD): Three-day-old germinated seeds were dipped in 108 conidia mL-1 suspension containing Tween-80 (0.01%) for 90 min. Control seeds were soaked in a Tween-80 solution (0.01%).
b) Stem injection (SI): Twenty-day-old plants were individually injected at the stem and nodes with 1 mL of 108 conidia mL-1 suspension using a sterile syringe. Control plants were injected by water plus Tween.
c) Fungi-sorghum seed inoculum (FS): Three-day-old germinated seeds were transplanted into a pot containing 2.5 g of sorghum grains pre-infected with the fungus strains. Control seeds were transplanted with 2.5 g sterile sorghum grains.
d) Leaf spray (LS): Twenty-day-old plants were sprayed with a fungal suspension of 1.108 conidia mL-1 using a 500 mL hand-held plastic sprayer. Control plants were sprayed with water.
After inoculation, the plants’ pots were randomized and kept under greenhouse conditions at 22 ± 2°C temperature and 14:10 L/D cycle light and watered as needed.
The seed coating was prepared using sorghum seeds, following a modified method of Nankinga (34). Washed sorghum seeds (200 g) were subdivided into flasks, then boiled in 10 mL of distilled water and sterilized by autoclaving at 121°C at 1 bar for 15 min. After cooling, each flask received 10 mL suspension of 107 conidia mL-1 for each strain, while the control flask received 10 mL of 0.01% (w/v) Tween-80 without the fungus. The flasks were incubated for four weeks in an incubator at 22 ± 2°C and were manually shaken every day. The final product was randomly distributed among the plant replicates.
Second instar larvae were fed with leaves randomly collected from plants of each inoculation method and the control. Larvae were considered dead if no movement was observed after lightly brushed. Dead larvae were removed and living larvae were kept until they pupated. Larvae mortality due to B. bassiana strains was confirmed from the mycosed larvae by placing them on Petri dishes lined with moistened filter paper and incubated for five days, then cultured on PDA and identified. Mortality was calculated according to Abbott’s formula (33).
The presence of B. bassiana was evaluated using three separate treatments for each strain. Sections were cut from leaves and all selected plant parts. Then after, surfaces were sterilized with ethanol (70%) for 30 s, sodium hypochlorite (1.5%) for 90 s, and rinsed with sterilized water for 2 min. The sections were dried and placed on Petri dishes containing PDA medium. Fungal identity was confirmed using morphological techniques.
The field trial was conducted in May 2022 at the ICARDA Marchouch Research Station, Morocco (33°56’10”N 6°69’21”W). The trial was conducted in a randomized complete block design with three replications using the chickpea variety Bouchra (FLIP97-114C). Each plot was planted with four rows of 1 meter length, and 0.6-meter spacing between rows. A 3-meter distance was kept between plots and blocks to prevent spray drift to adjacent plots. Normal agronomic practices were followed for growing the crop using a seeding rate of 100 kg/ha.
Three B. bassiana strains (108 spores per mL), insecticide (emamectin benzoate at 250 g/ha), and control plots sprayed with water plus Tween-80 were applied at economic threshold (one larva per meter row) (35). The non-ionic surfactant Tween-80 (0.01%) was used as an emulsion to mix the spores with water before applying the treatments. The strains were sprayed twice with an interval of one week between the first and the second spray using a two-liter hand sprayer with a frequency of 8 mL/min. Larvae mortality was recorded at 1, 3, and 7 days after each spray application.
Mortality percentages were transformed into angular values (arcsine √P) before the statistical analyses for laboratory and greenhouse bioassays, and the transformed percentages were subjected to a two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). The means were compared by Newman–Keuls tests at p < 0.05, with strains, concentration, exposure time, and method of inoculation as explanatory variables and percentage larval mortality as response variables. Under field conditions, the transformed percentages were subjected to a two-way analysis of variance. Using Henderson and Tilton’s (36) formula, the efficacy of the tested treatments was expressed as a percentage of reduction of H. armigera larvae number, as follows:
n: Insect population, T: treated, Co: Control
Probit analysis was used to calculate the lethal time (LT50) values for each strain, including their 95% confidence limits, using IBM SPSS Statistics 27.0. The computations were carried out using GenStat (22nd Edition, VSN International, UK).
The mortality rates of H. armigera larvae after treatment with different strains of entomopathogenic B. bassiana are shown in Figure 1. All three B. bassiana strains were virulent to H. armigera larvae and their virulence varied significantly compared to the control (p < 0.001). Among the three tested strains, B. bassiana HASS and RFSL10 exhibited the highest virulence compared to SP-IR-566. Six days after treatment (DAT), the highest larval mortality was recorded by B. bassiana RFSL10 then B. bassiana RFSL10 with 76%, and 72%, respectively, at 108 conidia mL-1. Twelve days after treatment, HASS and RFSL10 strains displayed the highest mortality rates (100% mortality), followed by strain SP-IR-566 with 96% mortality at 108 conidia mL-1.

Figure 1. Mean percentage larval mortality of H armigera treatment with three B bassiana strains at three different concentrations under laboratory conditions, DAT, days after treatment. The means that are followed by the different lower-case letters indicate a significant difference among different treatment time, and different capital letters indicate a significant difference between different concentrations (p <0.001).
The mean lethal time (LT50) of all strains is presented in Table 2, based on the daily observation of H. armigera larvae mortality. All strains caused more than 50% mortality, demonstrating this fungus’ efficacity. The effects obtained with the strains RFSL10 and SP-IR-566 were significant at a concentration of 108 conidia mL-1, with LT50 of 2 days. Furthermore, the LT50 was 6 days at a concentration of 107 conidia mL-1. However, the LT50 for the HASS strain was 4 days at a concentration of 108 conidia mL-1 and 7 days at 107 conidia mL-1. No dead insects were observed in the control group.
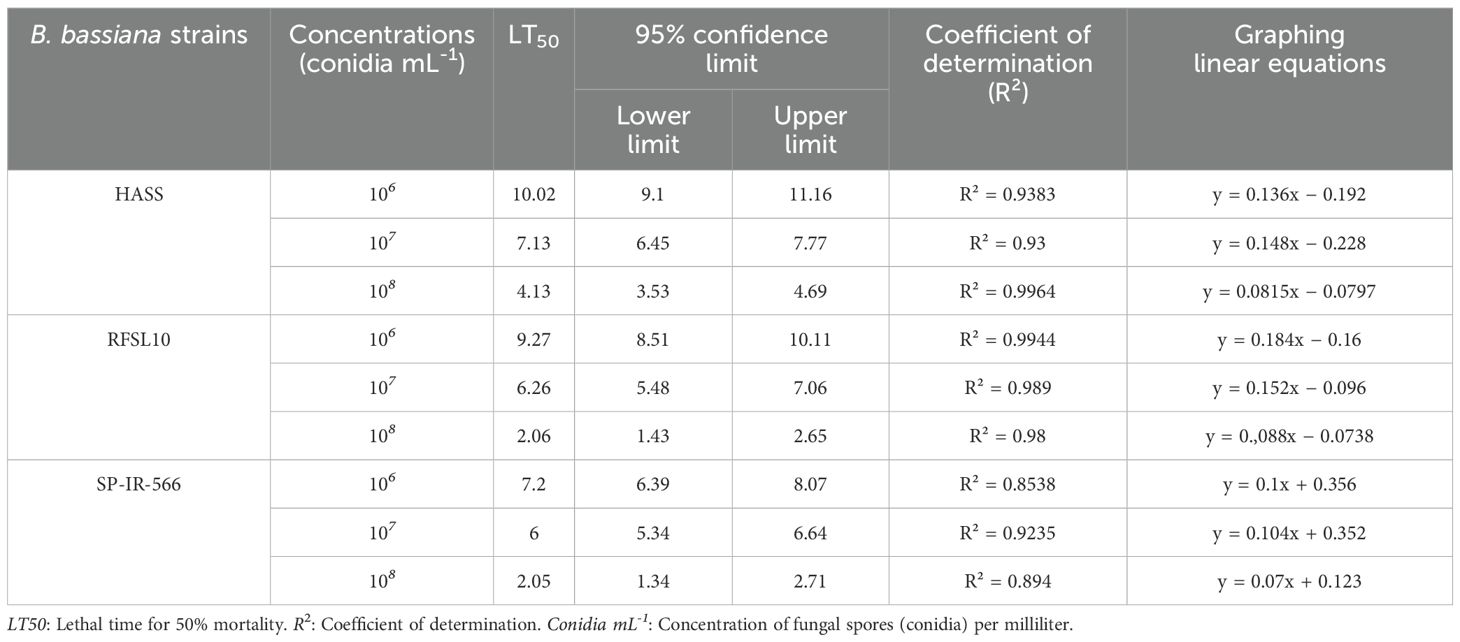
Table 2. Mean lethal time (LT50) and confidence limit values of three B. bassiana strains at three concentrations against H. armigera larvae under Laboratory conditions.
Results (Figures 2, 3) demonstrated that B. bassiana strains were effectively established as endophytes in chickpea tissues, especially after being inoculated in the two methods: Stem Injection (SI) and Root Dipping (RD). All three strains of B. bassiana at 108 conidia mL−1 were pathogenic to H. armigera larvae, and the percentage of larval mortality showed clear endophytic method-dependent as presented in Figure 2. The pathogenicity of B. bassiana was significant compared with the control (p < 0.01), and larval mortality started 5 days after treatment. The percent larval mortality ranged from 24 to 40% for different strains, 15 days after treatment. The highest percentage of mortality was obtained by the injection method, with SP-IR-566 strain reaching 40%, while HASS and RFSL10 strains achieved 36%, 15 days after treatment (Figures 2, 3).
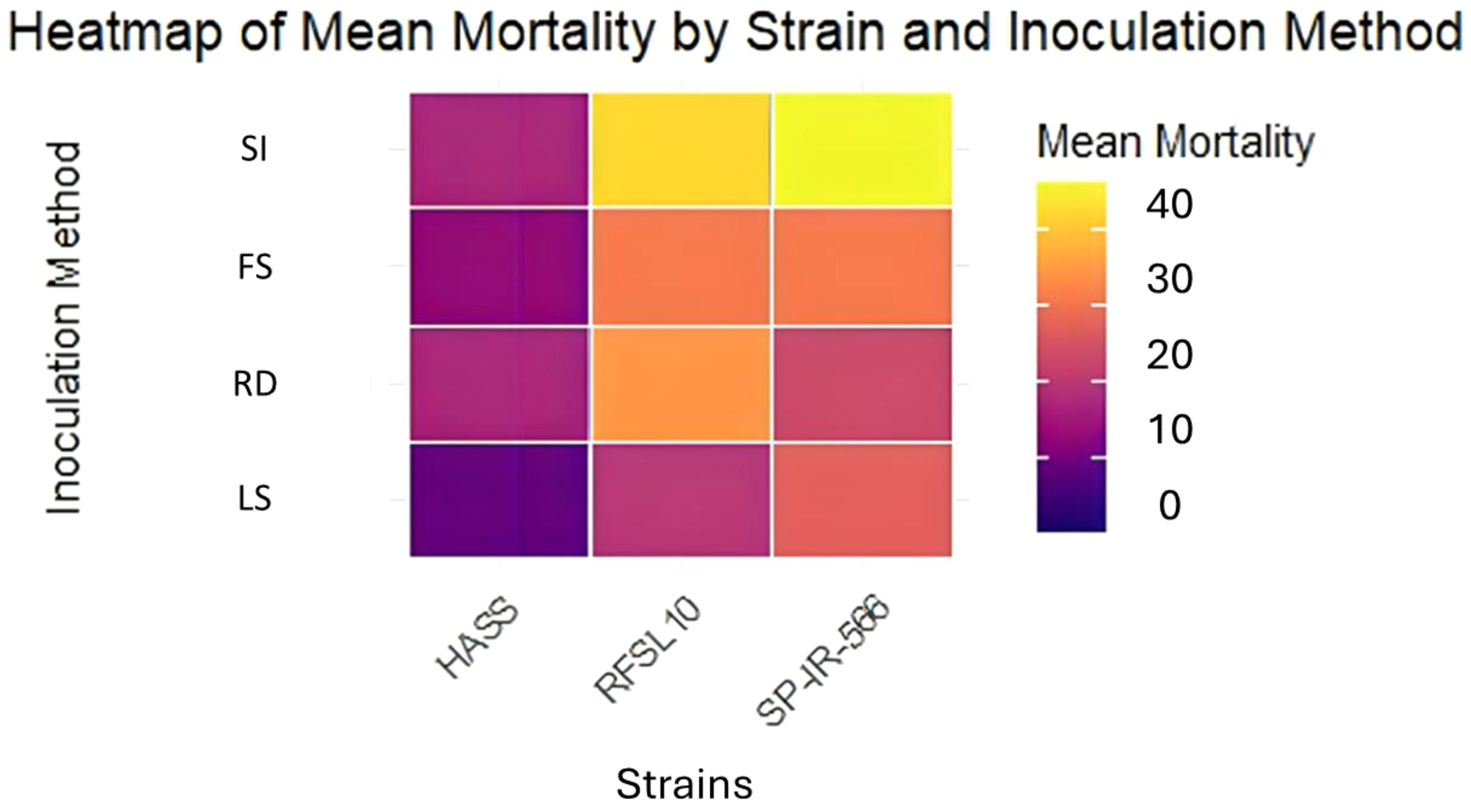
Figure 2. Heatmap representing the endophytic activity of the three strains against the larvae of H. armigera using different inoculation methods under greenhouse conditions. SI, stem injection; FS, fungi-sorghum seed inoculum; RD, root dipping; LS, leaf spray under greenhouse conditions.
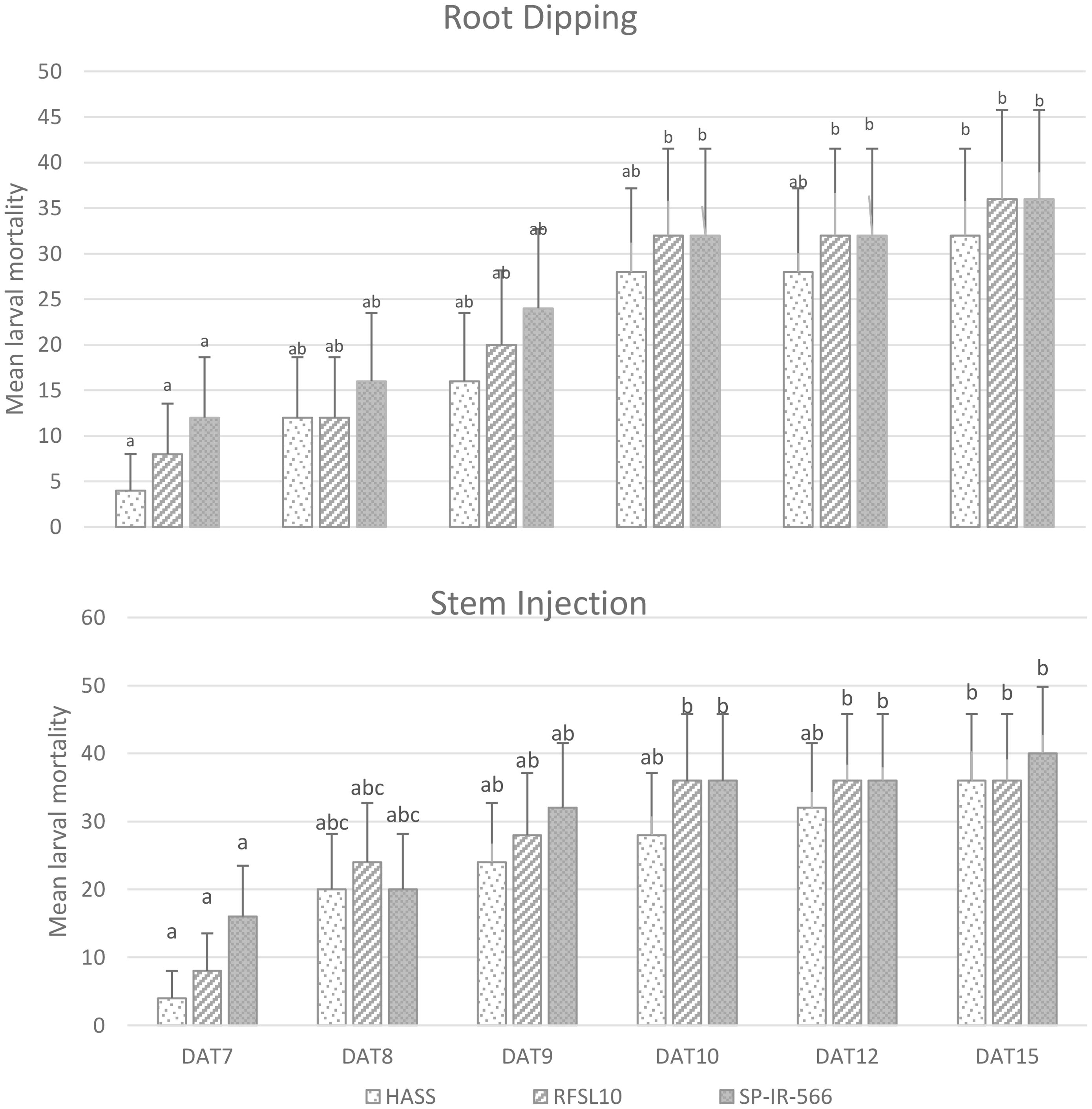
Figure 3. Variation of H armigera larvae mortality at different inoculation methods of B bassiana strains (HASS, RFSL10, and SP-IR-566) at 108 conidia mL-1 under greenhouse conditions. DAT, days after treatment. The means that are followed by the different lower-case letters indicate a significant difference among different treatment time (p <0.01).
Table 3 shows the LT50 recorded for each strain, based on the daily observation of H. armigera mortality. Using different inoculation methods, RFSL10, SP-IR-566, and HASS, strains were effective, and the LT50 was 10 days for RFSL and SP-IR-566 10., and 11 days for HASS, applied using stem injection method. For the root dipping method, the LT50 of RFSL10, SP-IR-566, and HASS was 11 days. Whereas no dead larvae were observed in the check group.
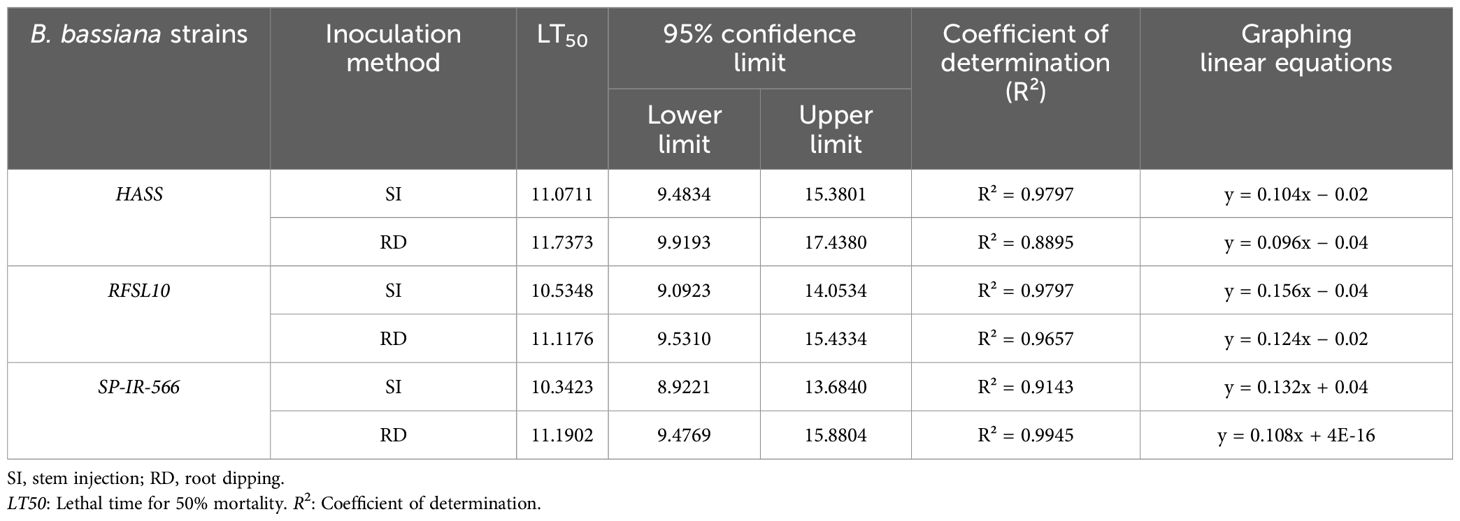
Table 3. Effective mean lethal time (LT50) and confidence limit values of three B. bassiana strains (HASS, RFSL10, and SP-IR-566), using different inoculation methods, against H. armigera larvae under greenhouse conditions.
The ANOVA analysis showed a statistically significant difference in mortality of H. armigera. The difference in the number of live larvae between the treatments, and the control was highly significant (p <0.001) after 3 days of the first application of treatments. The lowest number of larvae with emamectin benzoate (0.89 larvae) was recorded one day after treatment, while the highest number of larvae was recorded in the control (2.67 larvae) on the same day after treatment, followed by B. bassiana strains (Figure 4). All tested treatments were almost equally effective in reducing the number of H. armigera six days after the first application (Figure 4).
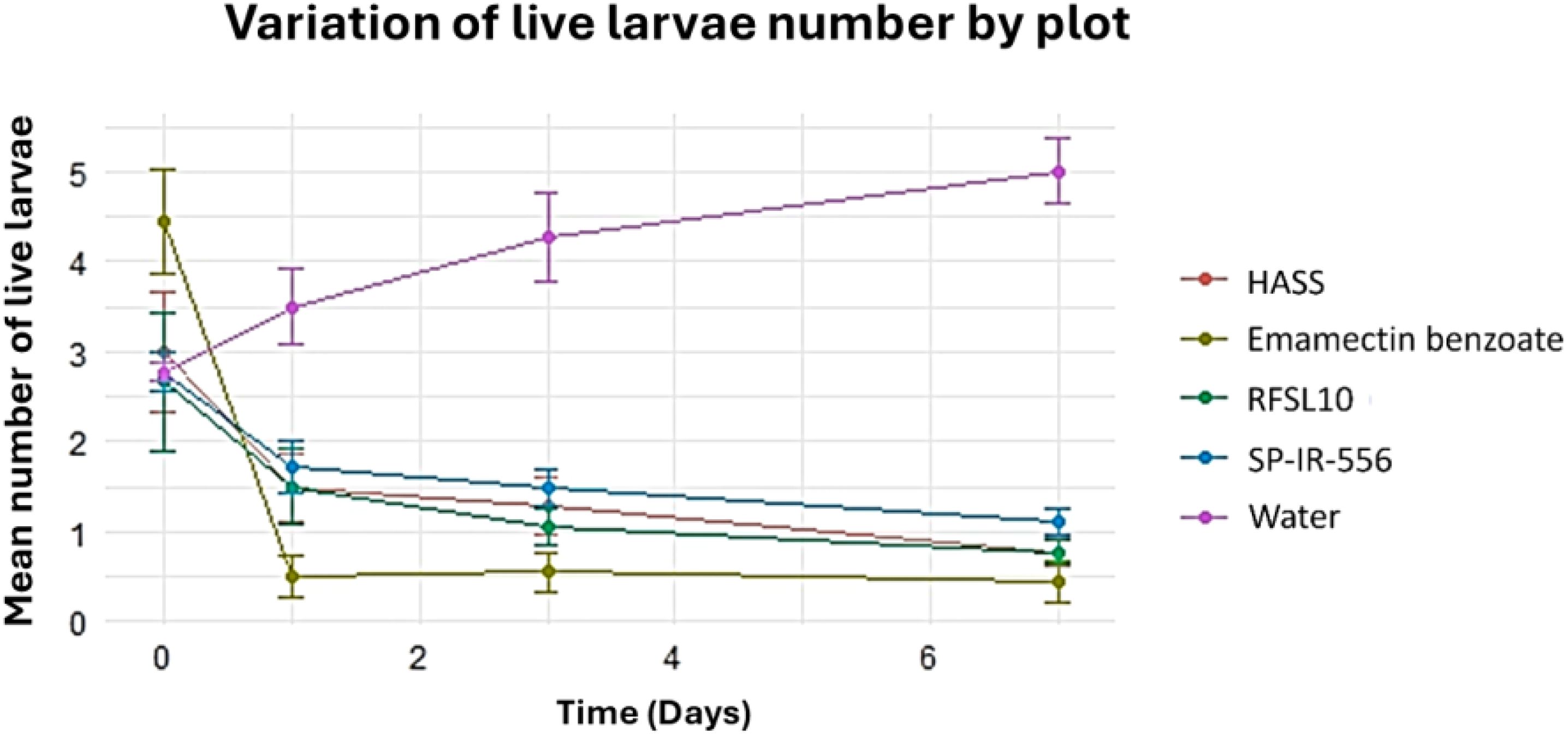
Figure 4. The effect of different strains and controls on the number of live larvae days after application under field conditions.
At the end of the experiment, the results showed that the second spray seemed to differ significantly (p<0.001) in the number of live larvae between the untreated control and all studied treatments. All the evaluated treatments were comparable in their capability to reduce H. armigera larval population.
The application of emamectin benzoate reduced the number of live larvae from 3 larvae before starting the treatment to 0 larvae, seven days after the second treatment. Similarly, the strains HASS and RFSL10 reduced the number of live larvae from 3 and 2 larvae before the treatment to 0.5 larvae, one week after the second treatment. The highest reduction rate was reached by emamectin benzoate with 100%, followed by strains HASS and RFSL10 with 89 and 88%, respectively. Conversely, in the control group (water), live larvae increased from 2 to 5, 14 days after treatment (Figure 5).
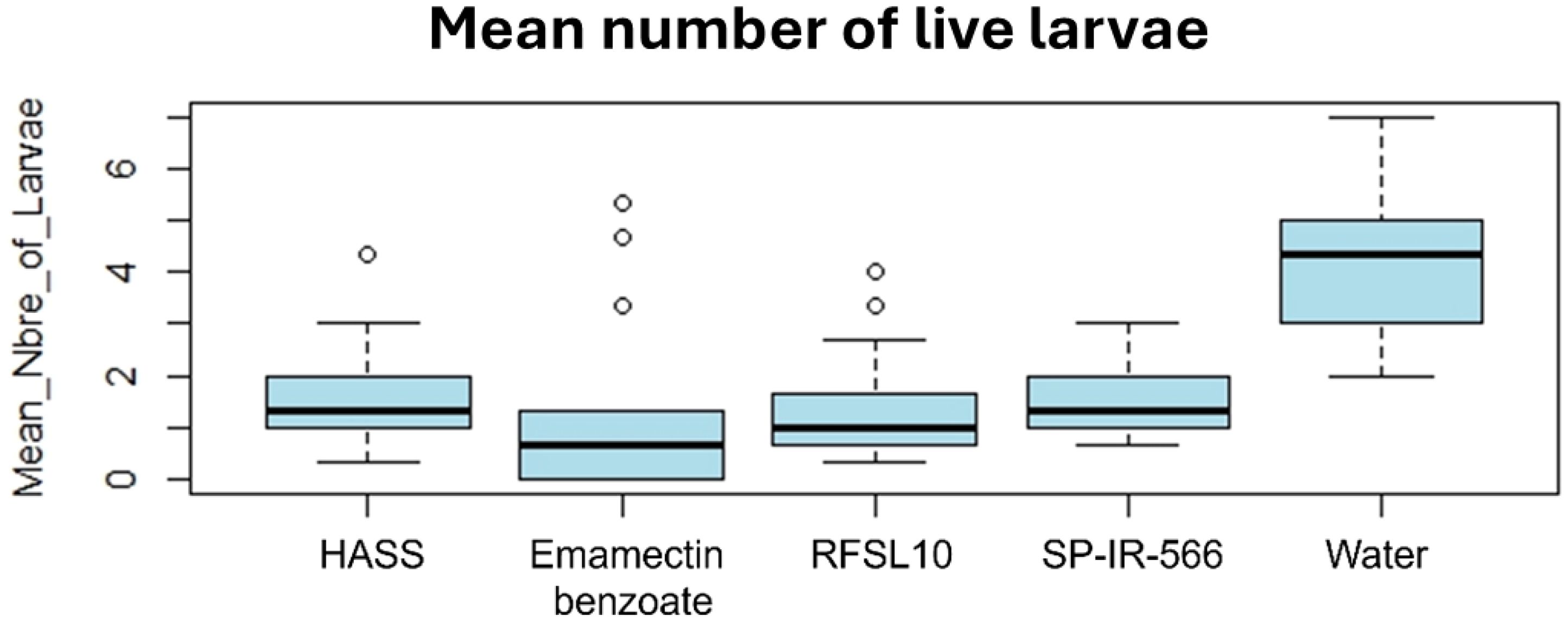
Figure 5. Boxplot of the toxic effect of different strains on the development of H. armigera larvae in comparison to the positive control (emamectin benzoate) under field conditions.
The present research evaluated the potential of three strains of B. bassiana in controlling H. armigera larvae in the laboratory, greenhouse, and field conditions. The current study demonstrated that all B. bassiana strains (RFSL10, SP-IR-566, and HASS), tested at a concentration of 108 conidia mL-1, provided the highest toxicity on H. armigera using mostly direct contact and low to moderate efficacy using endophytic effect. The larval mortality and LT50 of the larvae increased with the increase in fungal concentrations (Figure 1; Table 2). This result is in coordination with the results of Kalvnadi (37) et al., who reported that B. bassiana strain (DC2) reduced the population of the second-instar larvae of H. armigera. Also, Petlamul et al. (38) observed that B. bassiana, applied at a relatively low dose, showed a remarkable efficacy against H. armigera larvae, and this efficacy increased as the spore concentration increased to 1010 conidia mL-1, resulting in 100% mortality. Similarly, a study conducted by Fite et al. (39) confirmed that three strains of B. bassiana (DLCO-EA-56, APPRC-T5, and APPRC-9604) at a concentration of 108 conidia mL-1 were effective against the 3rd instar larvae of H. armigera under laboratory conditions. Moreover, according to Swathi (40) et al., B. bassiana strain-4 caused the highest mortality rate (100%) of second instar H. armigera, five days after treatment. On the other hand, other studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of B. bassiana in controlling several lepidopteran species such as the small cabbage white butterfly Pieris rapae (L.) (Lepidoptera: Pieridae) (41), the diamondback moth Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) (42), and the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) (19, 43).
In fact, according to our results, H. armigera was proven to be susceptible to B. Bassiana strains isolated not only from H. armigera, but also to other strains isolated from different insect species (Table 1). These results align with the findings reported by Suryanarayanan et al. (44) and Uma Devi et al. (45), who showed that B. bassiana was a generalist fungus with no strict host preference.
Furthermore, B. bassiana is likely to be capable of colonizing many other agronomically important crop plants. This study reported the effect of endophytic colonization of chickpea by B. bassiana on the survival of H. armigera larvae, through two different inoculation methods (SI and RD). These findings are consistent with those of Ramakuwela et al. (46), who showed that endophytic B. bassiana can be established in the roots, leaves, and stems of pecan seedlings (Carya illinoinensis), and this capacity may be used to manage pecan pests. The study found that larval mortality and LT50 increased with higher fungal concentrations, while the endophytic effect of B. bassiana on H. armigera larvae was lower with the two inoculation methods compared to direct application. This observation could be explained by the indirect effect of this fungus on chickpea by stimulating the production of secondary metabolites and/or inducing a systemic response (ISR) in the plant (47, 48), which could result in larval antifeedant behavior. Indeed, the capability of B. bassiana to act as an endophyte within several host plants and different plant parts was reported in corn Zea mays (49), tomato (50), cocoa (51), cotton (52), and opium poppy (53). Consistent with our results, Qayyum et al. (54) showed that tomato seedlings may be endophytically colonized by B. bassiana isolate WG-40. In addition, B. bassiana may protect soybean leaves by decreasing plant consumption by Helicoverpa gelotopoeon (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) (55). It has been shown that B. bassiana occurs as an endophyte in maize plants, providing multiple benefits, including negative effects on S. frugiperda and Rachiplusia nu (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Additionally, it functions as a potential protective agent to control S. frugiperda (55, 56).
Several studies reported that this beneficial association has no negative effects on the plant’s development or physiological processes (51, 57). Numerous findings have documented the role of endophytic B. bassiana in promoting the growth of plant biomass. For instance, Jaber and Enkerli (58) showed that B. bassiana, when used as a seed dressing, may systemically colonize several plant parts and enhance plant growth. Furthermore, B. bassiana was able to proliferate and survive in plant tissues after being inoculated into wheat utilizing seed dressing and soil treatment techniques. This supported increased spike production in wheat plants and successfully prevented cotton leafworm (Spodoptera littoralis) infestation (59). The successful re-isolation of the inoculated fungal mycelia from chickpea plants confirmed the success of the colonization trial. However, the used inoculation methods expressed low to moderate mortality rates against H. armigera. However, there is still a lack of solid knowledge about the preferred localization of the strains within plant tissues and other factors that could enhance their performance such as using different types of genetic material.
The present bioassays revealed promising results for using B. bassiana strains (HASS, RFSL10, and SP-IR-566) to effectively control the larvae of H. armigera, mostly when applied as a direct spray. Using various inoculation techniques, B. bassiana strains were able to colonize chickpea plant tissues and reduce H. armigera larvae numbers. These findings show that the use of entomopathogenic fungi, either as biopesticide or endophytic, could be incorporated in the management package for the control of H. armigera as a safe alternative to chemical insecticides. Nevertheless, further research is needed to refine fungal formulations, understand the underlying mechanisms, and assess their compatibility with other biopesticides, such as botanical extracts or oils. These complementary studies will contribute to the establishment of a comprehensive and effective pest management program against H. armigera.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
The manuscript presents research on animals that do not require ethical approval for their study.
RB: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. KF: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HJ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AO: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CR: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. NF: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. MA-J: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. MF: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. IM: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. AM: Writing – review & editing. SK: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. MB: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work is partially supported by CGIAR Plant Health and Rapid Response to Protect Food Security and Livelihoods Initiative (Plant Health Initiative) and by College of Agriculture and Environmental Sciences, Mohammed VI Polytechnic University, Ben Guerir 43150, Morocco.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Heeb L, Jenner E, Cock MJW. Climate-smart pest management: building resilience of farms and landscapes to changing pest threats. J Pest Sci. (2019) 92:951−69. doi: 10.1007/s10340-019-01083-y
2. Hmimina M. Cycle et importance économique de Heliothis armigera Hb. (Noctuidae) sur tomate sur la côte atlantique marocaine. Morocco: AL AWAMIA (MA) (1979) 57, 1–20.
3. CABI. Helicoverpa armigera (cotton bollworm). In: CABI Compendium. Wallingford, UK: CABI (2021). doi: 10.1079/cabicompendium.26757
4. El Fakhouri K, Boulamtat R, Sabraoui A, El Bouhssini M. The chickpea pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner): Yield loss estimation and biorational insecticide assessment in Morocco. Agronomy. (2022) 12:3017. doi: 10.3390/agronomy12123017
5. Muhammad Razaq MR, Anjum Suhail AS, Muhammad Aslam MA, Arif MJ, Saleem MA, Khan MHA. Evaluation of new chemistry and conventional insecticides against Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner) on cotton at Multan (Pakistan). Pak Entomol. (2005) 27(1):71–74. doi: 10.5555/20063205075.
6. Babariya PM, Kabaria BB, Patel VN, Joshi MD. Chemical control of gram pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera Hubner infesting pigeonpea. Legume Res- Int J. (2010) 33:224−6.
7. Joußen N, Heckel DG. Resistance Mechanisms of Helicoverpa armigera. “ Advances in insect control and resistance management. Springer (2016). pp. 241–61. pp. 241–61.
8. Wu C, Ding C, Chen S, Wu X, Zhang L, Song Y, et al. Exposure of Helicoverpa armigera larvae to plant volatile organic compounds induces cytochrome P450 monooxygenases and enhances larval tolerance to the insecticide methomyl. Insects. (2021) 12:238. doi: 10.3390/insects12030238
9. Sabarwal A, Kumar K, Singh RP. Hazardous effects of chemical pesticides on human health–Cancer and other associated disorders. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. (2018) 63:103−14. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2018.08.018
10. Pathak VM, Verma VK, Rawat BS, Kaur B, Babu N, Sharma A, et al. Current status of pesticide effects on environment, human health and it’s eco-friendly management as bioremediation: A comprehensive review. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:962619. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.962619
11. Kaur R, Choudhary D, Bali S, Bandral SS, Singh V, Ahmad MA, et al. Pesticides: An alarming detrimental to health and environment. Sci Total Environ. (2024) 915:170113. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.170113
12. Rahman A, Haque MA, Alam SN, Begum K, Sarker D. Development of integrated pest management approaches against Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner) in tomato. Bangladesh J Agric Res. (2016) 41:287–96. doi: 10.3329/bjar.v41i2.28231
13. Maurya RP, Agnihotri M, Tiwari S, Yadav LB. Validation of integrated pest management module against insect pests of pigeonpea, Cajanus cajan in Tarai region of Uttarakhand. J Appl Nat Sci. (2017) 9:1077−80. doi: 10.31018/jans.v9i2.1324
14. Dua RR, Gowda CL, Kumar S, Saxena KB, Govil JN, Singh BB, et al. Breeding for resistance to Heliothis/Helicoverpa: Effectiveness and limitations. In: Heliothis/helicoverpa management. Boca Raton, FL, USA: CRC Press (2005). p. 235–54.
15. Gupta R, Baruah AM, Acharjee S, Sarmah BK. Compositional analysis of transgenic Bt-chickpea resistant to Helicoverpa armigera. GM Crops Food. (2020) 11:262−74. doi: 10.1080/21645698.2020.1782147
16. Prasad A, Syed N. Evaluating prospects of fungal biopesticide Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) against Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner): An ecosafe strategy for pesticidal pollution. Asian J Exp Biol Sci. (2010) 1:596−601.
17. Boulamtat R, Lhaloui S, Sabraoui A, El-Fakhouri K, Oubayoucef A, Mesfioui A, et al. Antifeedant and larvicidal activities of Mentha pulegium on chickpea pod borer Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Int J Trop Insect Sci. (2020) 40:151−6. doi: 10.1007/s42690-019-00064-z
18. Boulamtat R, Mesfioui A, El-Fakhouri K, Oubayoucef A, Sabraoui A, Aasfar A, et al. Chemical composition, and insecticidal activities of four plant essential oils from Morocco against larvae of Helicoverpa armigera (Hub.) under field and laboratory conditions. Crop Prot. (2021) 144:105607. doi: 10.1016/j.cropro.2021.105607
19. Cruz-Avalos AM, Bivián-Hernández-M-de-los Á, Ibarra JE, Del-Rincón-Castro MC. High virulence of Mexican entomopathogenic fungi against fall armyworm,(Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Econ Entomol. (2019) 112:99−107. doi: 10.1093/jee/toy343
20. Woo RM, Park MG, Choi JY, Park DH, Kim JY, Wang M, et al. Insecticidal and insect growth regulatory activities of secondary metabolites from entomopathogenic fungi, Lecanicillium attenuatum. J Appl Entomol. (2020) 144:655−63. doi: 10.1111/jen.v144.7
21. Alwaneen WS, Tahir M, Avery PB, Wakil W, Kavallieratos NG, Eleftheriadou N, et al. Initial evaluation of the entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium robertsii, and the entomopathogenic nematode Heterorhabditis bacteriophora, individually and in combination against the noxious Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Agronomy. (2024) 14:1395. doi: 10.3390/agronomy14071395
22. Koca AS. Efficacy of native entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) Vuillemin (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae) against Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner, 1808) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Turkish J Entomology. (2025) 48:451–75. doi: 10.16970/entoted.1595065
23. Danfa A, van der Valk HCHG. Laboratory Testing of Metarhizium spp. and Beauveria bassiana on Sahelian non-target arthropods. Biocontrol Sci Technol. (1999) 9:187−98. doi: 10.1080/09583159929776
24. Wu S, Kostromytska OS, Koppenhöfer AM. Synergistic combinations of a pyrethroid insecticide and an emulsifiable oil formulation of Beauveria bassiana to overcome insecticide resistance in Listronotus maculicollis (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J Econ Entomol. (2017) 110:1794−802. doi: 10.1093/jee/tox176
25. Do Nascimento Silva J, Mascarin GM, De Paula Vieira De Castro R, Castilho LR, Freire DM. Novel combination of a biosurfactant with entomopathogenic fungi enhances efficacy against Bemisia whitefly. Pest Manag Sci. (2019) 75:2882−91. doi: 10.1002/ps.v75.11
26. Ramdani C, El Fakhouri K, Boulamtat R, Bouharroud R, Mesfioui A, Al-Jaboobi M, et al. Entomopathogenic fungi as biological control agents of Dactylopius opuntiae (Hemiptera: Dactylopiidae) under laboratory and greenhouse conditions. Front Sustain Food Syst. (2022) 6:997254. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2022.997254
27. Nguyen NTH, Borgemeister C, Poehling HM, Zimmermann G. Laboratory investigations on the potential of entomopathogenic fungi for biocontrol of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae and pupae. Biocontrol Sci Technol. (2007) 17:853−64. doi: 10.1080/09583150701546375
28. Vega FE. Insect pathology and fungal endophytes. J Invertebr Pathol. (2008) 98:277−9. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2008.01.008
29. Hirapara IM, Jethva DM, Patel DS, Desai AV. Bio-efficacy of Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) vuillemin against Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) & Spodoptera litura (Fabricius) in groundnut under laboratory condition. Int J Chem Stud. (2019) 7:2409−12.
30. Mingotti Dias P, de Souza Loureiro E, Amorim Pessoa LG, Mendes de Oliveira Neto F, de Souza Tosta RA, Teodoro PE. Interactions between fungal-infected Helicoverpa armigera and the predator Chrysoperla externa. Insects. (2019) 10:309. doi: 10.3390/insects10100309
31. Tahir M, Wakil W, Ali A, Sahi ST. Pathogenicity of Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae isolates against larvae of the polyphagous pest Helicoverpa armigera. Entomol Gen. (2019) 38:225−42. doi: 10.1127/0171-8177/2019/0460
32. Koul O, Shankar JS, Mehta N, Taneja SC, Tripathi AK, Dhar KL. Bioefficacy of crude extracts of Aglaia species (Meliaceae) and some active fractions against lepidopteran larvae. J Appl Entomol. (1997) 121:245−8. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0418.1997.tb01400.x
33. Abbott WSA. Method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J Econ Entomol. (1925) 18:265–7.
34. Nankinga CM. Characterisation of entomopathogenic fungi and evaluation of delivery systems of beauvaria bassiana for the biological control of the banana weevil, Cosmopolites sordidus. PhD thesis. London, UK: University of Reading (1999).
35. Zahid MA, Islam MM, Reza MH, Prodhan MHZ, Begum MR. Determination of economic injury levels of Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner) in chickpea. Bangladesh J Agric Res. (2008) 33:555−63. doi: 10.3329/bjar.v33i4.2288
36. Henderson CF, Tilton EW. Tests with acaricides against the brown wheat mite. J Econ Entomol. (1955) 48:157–61. doi: 10.1093/jee/48.2.157
37. Kalvnadi E, Mirmoayedi A, Alizadeh M, Pourian HR. Sub-lethal concentrations of the entomopathogenic fungus, Beauveria bassiana increase fitness costs of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) offspring. J Invertebr Pathol. (2018) 158:32−42. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2018.08.012
38. Petlamul W, Boukaew S, Hauxwell C, Prasertsan P. Effects on detoxification enzymes of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) infected by Beauveria bassiana spores and detection of its infection by PCR. ScienceAsia. (2019) 45:581–8. doi: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.2019.45.581
39. Fite T, Tefera T, Negeri M, Damte T, Sori W. Evaluation of Beauveria bassiana, Metarhizium anisopliae, and Bacillus thuringiensis for the management of Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) under laboratory and field conditions. Biocontrol Sci Technol. (2020) 30:278−95. doi: 10.1080/09583157.2019.1707481
40. Swathi P, Ganga P, Visalakshy N, Das SB. Potentiality of Beauveria bassiana strains against Helicoverpa armigera through laboratory bioassay. J Entomol Zool. (2017) 5:463−7.
41. Ding J, Lai Y. Identification of highly pathogenic Beauveria bassiana strain against Pieris rapae larvae. Entomol Res. (2018) 48:339−47. doi: 10.1111/1748-5967.12295
42. Nithya PR, Manimegalai S, Nakkeeran S, Mohankumar S. Comparative study of the ditrophic interaction between Beauveria bassiana and Plutella xylostella. Biotech. (2021) 11:223. doi: 10.1007/s13205-021-02760-5
43. Idrees A, Afzal A, Qadir ZA, Li J. Bioassays of Beauveria bassiana isolates against the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda. J Fungi. (2022) 8:717. doi: 10.3390/jof8070717
44. Suryanarayanan TS, Wittlinger SK, Faeth SH. Endophytic fungi associated with cacti in Arizona. Mycol Res. (2005) 109:635−9. doi: 10.1017/S0953756205002753
45. Uma Devi K, Padmavathi J, Uma Maheswara Rao C, Khan AAP, Mohan MC. A study of host specificity in the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana (Hypocreales, Clavicipitaceae). Biocontrol Sci Technol. (2008) 18:975−89. doi: 10.1080/09583150802450451
46. Ramakuwela T, Hatting J, Bock C, Vega FE, Wells L, Mbata GN, et al. Establishment of Beauveria bassiana as a fungal endophyte in pecan (Carya illinoinensis) seedlings and its virulence against pecan insect pests. Biol Control. (2020) 140:104102. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2019.104102
47. Pieterse CMJ, Zamioudis C, Berendsen RL, Weller DM, Van Wees SCM, Bakker PAHM. Induced systemic resistance by beneficial microbes. Annu Rev Phytopathol. (2014) 52:347−75. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-082712-102340
48. Hartley SE, Eschen R, Horwood JM, Gange AC, Hill EM. Infection by a foliar endophyte elicits novel arabidopside-based plant defence reactions in its host, Cirsium arvense. New Phytol. (2015) 205:816−27. doi: 10.1111/nph.13067
49. Bing LA, Lewis LC. Suppression of Ostrinia nubilalis (Hubner) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) by endophytic Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) vuillemin. Environment Entomol. (1991) 20:1207–11. doi: 10.1093/ee/20.4.1207
50. Sinno M, Ranesi M, Di Lelio I, Iacomino G, Becchimanzi A, Barra E, et al. Selection of endophytic Beauveria bassiana as a dual biocontrol agent of tomato pathogens and pests. Pathogens. (2021) 10:1242. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10101242
51. Posada FJ, Vega FE. A new method to evaluate the biocontrol potential of single spore isolates of fungal entomopathogens. J Insect Sci. (2005) 5:37. doi: 10.1093/jis/5.1.37
52. Lopez DC, Sword GA. The endophytic fungal entomopathogens Beauveria bassiana and Purpureocillium lilacinum enhance the growth of cultivated cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) and negatively affect survival of the cotton bollworm (Helicoverpa zea). Biol Control. (2015) 89:53−60. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2015.03.010
53. Quesada-Moraga E, Landa BB, Muñoz-Ledesma J, Jiménez-Diáz RM, Santiago-Álvarez C. Endophytic colonisation of opium poppy, Papaver somniferum, by an entomopathogenic Beauveria bassiana strain. Mycopathologia. (2006) 161:323−9. doi: 10.1007/s11046-006-0014-0
54. Qayyum MA, Wakil W, Arif MJ, Sahi ST, Dunlap CA. Infection of Helicoverpa armigera by endophytic Beauveria bassiana colonizing tomato plants. Biol Control. (2015) 90:200−7. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2015.04.005
55. Russo ML, Scorsetti AC, Vianna MF, Allegrucci N, Ferreri NA, Cabello MN, et al. Effects of endophytic Beauveria bassiana (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) on biological, reproductive parameters and food preference of the soybean pest Helicoverpa gelotopoeon. J King Saud Univ-Sci. (2019) 31:1077−82. doi: 10.1016/j.jksus.2018.11.009
56. Ramos Y, Taibo AD, Jiménez JA, Portal O. Endophytic establishment of Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae in maize plants and its effect against Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae. Egypt J Biol Pest Control. (2020) 30:20. doi: 10.1186/s41938-020-00223-2
57. Ownley BH, Pereira RM, Klingeman WE, Quigley NB, Leckie BM. Beauveria bassiana, a dual purpose biocontrol organism, with activity against insect pests and plant pathogens. Emerg Concepts Plant Health Manag. (2004) 2004:255−69.
58. Jaber LR, Enkerli J. Effect of seed treatment duration on growth and colonization of Vicia faba by endophytic Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium brunneum. Biol Control. (2016) 103:187−95. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2016.09.008
59. Sánchez-Rodríguez AR, Raya-Díaz S, Zamarreño ÁM, García-Mina JM, del Campillo MC, Quesada-Moraga E. An endophytic Beauveria bassiana strain increases spike production in bread and durum wheat plants and effectively controls cotton leafworm (Spodoptera littoralis) larvae. Biol Control. (2018) 116:90−102. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2017.01.012
Keywords: chickpea pod borer, Beauveria bassiana, virulence, endophyte, chickpea
Citation: Boulamtat R, El Fakhouri K, Jaber H, Oubayoucef A, Ramdani C, Fikraoui N, Al-Jaboobi M, El Fadil M, Maafa I, Mesfioui A, Ahmed Kemal S and El Bouhssini M (2025) Pathogenicity of entomopathogenic Beauveria bassiana strains on Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner). Front. Insect Sci. 5:1552694. doi: 10.3389/finsc.2025.1552694
Received: 28 December 2024; Accepted: 20 March 2025;
Published: 11 April 2025.
Edited by:
Federico Cappa, University of Florence, ItalyReviewed by:
André Rodrigues De Souza, University of São Paulo, BrazilCopyright © 2025 Boulamtat, El Fakhouri, Jaber, Oubayoucef, Ramdani, Fikraoui, Al-Jaboobi, El Fadil, Maafa, Mesfioui, Ahmed Kemal and El Bouhssini. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rachid Boulamtat, ci5ib3VsYW10YXRAY2dpYXIub3Jn
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.