
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Ind. Microbiol., 07 April 2025
Sec. Agriculture
Volume 3 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/finmi.2025.1553472
This article is part of the Research TopicMicrobial-based Inoculants for Agriculture: Production and Improvement of Commercial FormulationsView all 4 articles
The global agricultural sector faces significant challenges due to increasing demands from a growing population, limited arable land and the environmental degradation caused by chemical inputs. As a potential solution, microbial inoculants, particularly arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF), offer an eco-friendly alternative to traditional fertilizers and pesticides. AMF enhance plant growth by improving nutrient and water uptake while protecting against stressors, fostering sustainable agriculture. This study explores the production, development, and application of AMF bioformulations, emphasizing key requirements for their effectiveness, including strain selection, genetic stability, environmental compatibility, other beneficial microbial compatibility, and eco-friendly carriers. Advances in production methods such as substrate-based systems, bioreactors, and solid media are discussed, along with the role of synergistic microbial combinations to enhance agricultural productivity. Additionally, challenges in the stability, shelf-life, and quality control of AMF bioformulations are addressed, with a focus on adjuvants, fillers, and storage methods. Risk evaluation and biosafety concerns related to the use of novel microbial strains are examined, particularly in the context of regulatory frameworks that classify bioformulations as biostimulants or biopesticides. Barriers to widespread adoption, including farmer awareness, product quality, and regulatory constraints, are identified. Despite these obstacles, the potential of mycorrhizal inoculants for sustainable agricultural practices remains high, provided that ongoing research, development, and collaboration between stakeholders can address these challenges.
As of mid-November 2022, the global population reached 8 billion (United Nations, 2022), with 4,781 million hectares of agricultural land, including 1,573 million hectares for cropland and 3,208 million hectares for meadows and pastures (Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations, 2024). Agriculture relies on light, water, and fertile soil, but the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides damages these resources.
In 2022, global fertilizer use was 185 million metric tons, with nitrogen fertilizers making up 58%, phosphates 23%, and potash 18% (Statista, 2024b). Pesticide use also increased to 3.69 million metric tons, raising concerns due to their harmful effects on non-target beneficial species and human health like cancer and endocrine disruption (Statista, 2024a). Chemical fertilizers cause environmental pollution, soil degradation, greenhouse gas emissions, and reduce crop quality. They also contribute to water contamination and biodiversity loss (Phillips, 2022; Das et al., 2023; Jote, 2023). Pesticides, including herbicides, fungicides, insecticides, and rodenticides, harm beneficial insects, birds, and aquatic life, and can lead to health issues (Statista, 2024b). Pesticide overuse, as seen in the case of Punjab’s Malwa region, illustrates the severe health risks faced by farmers and their families, with rising cancer rates as a stark example of the toll chemical dependency can take on public health (Das, 2016). The fact that the government had to intervene with a “cancer train” speaks to the scale of the crisis and emphasizes the urgency of shifting away from harmful agricultural chemicals. There is a growing consensus in the scientific community and agricultural sectors about the necessity of transitioning to practices that minimize chemical input reliance, focusing on sustainable and safer alternatives such as integrated pest management, organic farming, and the use of biological fertilizers and inoculants. This transition is not only crucial for human health but for the future viability of our agricultural systems and the environment at large.
To tackle the environmental issues, eco-friendly solutions like microbial inoculants provide a viable alternative to chemical inputs. These inoculants, which act as biofertilizers, bioherbicides, biopesticides, and biocontrol agents, enhance soil and crop health while supporting effective pest management, ultimately benefiting human health (Chaudhary et al., 2024). Microorganisms are known to help reduce the reliance on fertilizers like nitrogen and phosphorus by improving nutrient acquisition and breaking down organic matter (Kumar and Dubey, 2020). Plants and soil host millions of microorganisms that form the microbiome, which enhances plant growth, nutrient efficiency, and pest management (Ray et al., 2020). Additionally, these microbes bolster plant resilience against various stresses (El-Sharoud, 2019). Research on plant growth-promoting microorganisms, such as mycorrhizal fungi, highlights their importance for plant success across diverse crops and climates (Brundrett and Tedersoo, 2018). This approach not only supports environmental sustainability but also contributes to better human health outcomes by reducing the harmful effects of chemical inputs.
AMF are soil-borne fungi that boost plant growth by enhancing nutrient and water uptake while protecting against various stresses in exchange for photosynthetic products (Sun et al., 2018; Basiru and Hijri, 2022). They belong to the phylum Glomeromycota and form mutualistic relationships with about 80% of terrestrial plants. AMF are a sustainable alternative to chemical fertilizers, with their inoculants containing spores, mycelium, or propagules used in agriculture to enhance growth, health, and nutrient absorption, particularly phosphorus and nitrogen, thereby boosting biomass and photosynthesis (Willis et al., 2012; Berruti et al., 2016; Begum et al., 2019). AMF improve plant resilience to drought, salinity, and heavy metal contamination, and strengthen plant defense mechanisms (Fall et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2024). As a natural biofertilizers, they reduce nutrient loss from soil and support plant establishment, making them vital for sustainable nutrient management (Cavagnaro et al., 2015; Berruti et al., 2016). They also act as phosphate solubilizers, making phosphorus more accessible to plants (Seenivasagan and Babalola, 2021; Anand et al., 2022). AMF are cost-effective and efficient Plant Growth Promoting Microorganisms (PGPM), aiding in nitrogen fixation and plant hormone production (Allouzi et al., 2022; Timofeeva et al., 2022). They serve as bioprotectors against diseases, pests, and weeds by activating plant defense systems and inducing systemic resistance (Nevalainen, 2020). Additionally, AMF enhance plant performance under high salinity, temperature extremes, and heavy metal exposure, making them useful for bioremediation in areas like deserts and mines (Anand et al., 2022). They are promising for improving crop resilience in the face of climate change (Torres et al., 2018). Reintroducing these fungi into the soil, either alone or with other microorganisms, can maximize their benefits. AMF inoculation enhances plant growth and yield by increasing nutrient uptake in Leguminosae crops. While Claroideoglomus boosted colonization, Rhizophagus and Funneliformis contributed more to yield. Soil and climate conditions influence the outcomes, with AMF generally improving productivity based on species and environment (Li et al., 2025). AMF application enhances crop resilience and productivity under water deficiency, reducing yield losses. It improves antioxidant activity, phenols, and ascorbate in tomatoes, boosts soluble proteins and sugars in date palms, increases osmolyte content and antioxidant defenses in quinoa, and raises proline levels in soybeans. AMF promotes better water and nutrient uptake through extended fungal hyphae, improving overall plant health (Lamaizi et al., 2024). AMF inoculation can be used as an effective solution for low-P conditions, improving nutrient acquisition, enhancing physiological responses, and increasing plant dry biomass in low-fertility soils (Souza et al., 2025). AMF inoculation significantly improves infection rates, microbial activity, growth, and grain yield in maize and wheat, making it a key strategy for enhancing salt tolerance and productivity in saline soils (Ahammed & Hajiboland, 2024). AMF inoculation in barley resulted in the highest values for plant height, spike length, spike weight, number of grains/spikes, 1000-grain weight, and grain yield. AMF-treated plants showed a 17.27% increase in grain yield, demonstrating its effectiveness in boosting productivity, improving drought tolerance, and supporting sustainable farming practices under water scarcity (Alotaibi et al., 2024). AMF work synergistically with soil microbiota, including Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) such as Azospirillum, Bacillus, Pseudomonas, etc in amplifying plant growth by promoting nutrient acquisition, producing phytohormones, offering pathogen protection and stress resilience through a complex rhizosphere interaction (Cortivo et al., 2017). PGPR improve AMF colonization by releasing compounds like indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), which stimulate root growth and increase the surface area for AMF attachment. Pseudomonas species solubilize phosphate, benefiting both plants and AMF, thereby supporting better nutrient acquisition and stress tolerance. Some PGPR strains produce siderophores that chelate iron, making it more accessible to plants and mitigating heavy metal toxicity, such as cadmium (Cd) and lead (Pb) (Fatima et al., 2024). Therefore, AMF inoculation represents a viable, eco-friendly solution to enhance agricultural productivity, soil health, and plant resilience, ensuring more sustainable and climate-resilient food production systems (Figure 1).

Figure 1. Global food security is threatened by various challenges, while arbuscular mycorrhizal bioformulations play a vital role in enhancing crop productivity and promoting agricultural sustainability.
The global agricultural sector increasingly confronted with the dual challenges of rising food demand and the environmental degradation caused by conventional farming practices. In response, microbial inoculants, particularly AMF, have emerged as a promising, eco-friendly alternative to chemical fertilizers and pesticides. AMF enhance plant growth by improving nutrient uptake, water absorption, and stress resistance, making them central to the development of sustainable agricultural practices. Recent advances in the commercial formulation of AMF inoculants have focused on optimizing production methods, including substrate-based systems, bioreactors, and solid media, to ensure scalability and cost-effectiveness. Furthermore, strain selection prioritized genetic stability and environmental compatibility, enabling better performance across diverse agricultural conditions. The potential of synergistic microbial combinations, integrating AMF with other beneficial microbes, has also been explored to enhance agricultural productivity. Despite these advancements, challenges remain in ensuring the stability, shelf-life, and quality control of AMF bioformulations, with particular attention to the role of adjuvants, fillers, and storage methods. Additionally, the evolving regulatory frameworks for bioformulations, including their classification as biostimulants or biopesticides, raise important biosafety concerns. This study aims to highlight these recent developments, emphasizing the innovative strides made to overcome existing barriers and the need for continued research and collaboration to realize the full potential of AMF-based inoculants in sustainable agriculture ecosystem.
Inoculants, or biofertilizers, are products containing beneficial microorganisms in solid or liquid forms for agricultural use (Alladi et al., 2017). Ensuring essential requirements are met can enhance the effectiveness of AM inoculants in natural environments. Selecting the right strains is essential for the effectiveness of AM bioinoculants, as different strains have specific environmental needs for optimal performance (Rojas-Sánchez et al., 2022). Bioinoculants must be adapted to local conditions, including soil temperature, pH, salinity, and microbiota, to perform effectively under environmental stressors like UV radiation and extreme temperatures (Chaudhary et al., 2020). Local adaptation of AMF strains is particularly important for optimizing plant growth and biomass (Rúa et al., 2016). For instance, Rhizophagus irregularis has been shown to aid in bioremediation against Cd contamination (Etesami and Glick, 2023), reduce sodium ion content in roots (He et al., 2019), and is more resistant to temperature fluctuations (Püschel et al., 2019). It can also improve the saline-alkali tolerance of switchgrass (Wen et al., 2024).
Co-inoculation with other beneficial microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, protozoa, or endophytes can further enhance plant growth, yield, nutrient availability, soil health, and soil microbial diversity compared to single microbial inoculants (Alladi et al., 2017; Thirumal, 2017; Riaz et al., 2020; Singh et al., 2021; Kamath et al., 2023). However, it is also crucial to maintain the genetic stability of AMF strains to ensure their functional benefits remain consistent and effective over time. Studies show that genetic exchange in the Rhizophagus intraradices, allowing nuclei from different strains to mix negatively impact plant growth and alter fungal colonization (Colard et al., 2011). Therefore, not only the right strain selection is essential for addressing specific environmental challenges but ensuring that the strains remain genetically stable and functionally effective throughout their use is key in maximizing the potential of AMF inoculants in agriculture ecosystem.
The choice of carrier material for AM bioinoculants is critical, as it ensures microbial survival, stability, and effective distribution in the soil, enhancing soil health by promoting nutrient cycling and microbial diversity (Kumar et al., 2022; Poppeliers et al., 2023). The application method—whether via spraying, irrigation, soil inoculation, or seed application—should ensure even distribution and efficient interaction with plant roots to maximize effectiveness. Proper storage conditions, such as managing temperature and humidity, are necessary to preserve microbial viability and extend shelf life (Thirumal, 2017). Quality control during manufacturing ensures genetic stability and prevents contamination.
AMF, as obligate biotrophs, need host plant roots to complete their life cycle (Wipf et al., 2019), which is a significant challenge in cultivating them. Several methods exist for producing AM inoculants, but only a few have been commercially exploited, each with its own pros and cons (Table 1).
This conventional technique for mass-multiplication of AMF involves setting up a trap culture using soil or rhizosphere soil combined with root pieces and sterilized diluents to grow host plants. These hosts promote AMF sporulation by providing a favorable environment, though the process is labor-intensive and prone to contamination with other biological materials (Sakha et al., 2024). These limitations highlight the need for further optimization to minimize contamination risks and improve efficiency, particularly for large-scale production.
Recently, synthetic substrates have offered advantages such as enhanced spore dispersal, higher survival rates, and greater effectiveness. These substrates support AMF inoculum growth by aiding the colonization of spores and mycelium in plant roots, retaining essential nutrients like potassium and calcium, and improving water retention and nutrient availability (Table 2). For instance, perlite, vermiculite, and biochar in constructed wetlands improved AMF colonization and wastewater treatment (Hu et al., 2022). High-peat substrates benefited gardenia plants by improving root growth and nutrient uptake (Papafotiou et al., 2021). Zeolite combined with AMF and superabsorbent enhanced plant establishment and biomass in arid environments (Azimi et al., 2019). Sand, vermiculite, and vermicompost mixtures optimized AMF production and corn growth (Coelho et al., 2014). These studies underscore the potential of synthetic substrates in promoting AMF colonization and improving plant health in both agriculture and environmental management.
Substrate-free systems produce inoculum without substrates, allowing for high-density infective propagules.
Bioreactors provide a controlled environment that enhances the symbiotic relationship between AMF and plant roots, optimizing nutrient uptake and growth (Dewir et al., 2023). They optimize AMF production by controlling pH, temperature, and nutrient composition, ensuring consistent inoculum quality (Vassileva et al., 2021). Various bioreactor types, such as stirred tank, airlift, and packed bed reactors, offer different advantages depending on scalability, cost, and AMF strain requirements but are prone to algae contamination and affected spore production rates (Dubey et al., 2013). Key factors for effective operation include aeration, agitation, growth media, nutrient supplementation, and pH regulation to achieve optimal biomass production (Singh et al., 2019). Quality control throughout production is crucial, including monitoring growth, viability, and genetic stability. As the demand for AMF inoculants grows, scaling up production to industrial levels will require advanced engineering solutions to meet both efficiency and quality standards.
Various cultivation techniques have been developed to improve gas exchange for AMF. These include using thin nutrient layers over roots to address aeration issues in inclined channels (Mosse and Thompson, 1980; Lee and George, 2005), aeroponics, which enhances aeration by exposing roots of host plants and AMF propagules to a nutrient fog and micro-droplets (Jarstfer et al., 1998), and static systems where aerated nutrient solutions are intermittently pumped to prevent oxygen deprivation in roots, reduce nutrient solution flow, and avoid air bubbles damaging delicate extraradical hyphae (Hawkins and George, 1997; IJdo et al., 2010). Ultrasonic nebulizers were found to be more efficient method than Atomizing disks (Mohammad et al., 2000). These advancements point to the critical role in optimizing environmental conditions to maximize AMF productivity and their beneficial impacts on plant growth, yield and soil health.
Experiments with bioreactors using substrates like agar and vermiculite achieved spore yields of 120,000 spores per liter (Fortin et al., 1993). Airlift bioreactors and petri dish cultures with low-salt M-medium yielded 20,000–30,000 spores per liter with 25%–75% colonization and 0.13 g DW per liter biomass (Jolicœur et al., 1999).
A cost-effective, simple, and efficient novel gas-phase (mist) bioreactor has been patented for large-scale aseptic production and in vitro cultivation of AMF, involving growing fungal spores and roots within a transformed plant’s hairy root. This system, featuring a misting device, inoculation system, culture mesh, and nutrient mist recycling, ensures optimal oxygen and nutrient distribution, minimizing shear damage to sensitive transformed roots, resulting in high-quality, contamination-free AMF spores (Adholeya and Mukherjee, 2017). Evologic Technologies GmbH, a bioprocessing company in Vienna, recently developed a novel AMF production method that increases yield by 10–20% and improves stress resistance. The company is scaling this process to be 30.000 times larger than competing methods, aiming to offer an economically feasible AMF product (Evologic Technologies GmbH – Wien, Austria, 2025). The continued refinement of bioreactor technologies holds promise for improving the cost-effectiveness and scalability of AMF production, which could further enhance their use in sustainable agricultural practices.
Various methods have been developed for cultivating AMF using ROC, employing different techniques, substrates, media, and inoculum types, with varying results in spore yield, biomass, and colonization rates. The absence of unwanted microorganisms makes this system ideal for producing high-quality AMF inoculum in large quantities. However, constant monitoring and regulation are required, making it labor-intensive and requiring skilled technicians and laboratory equipment. While the use of ROC for cultivating AMF offers a promising approach to producing high-quality, sterile inoculum in large quantities, the method’s need for skilled technicians and specialized laboratory equipment present significant challenges. Despite these challenges, ROC remains a valuable technique for research and niche applications where quantity and sterility are paramount.
The ROC studies with various host plants have investigated the production of spores from different AMF strains under diverse culture conditions, emphasizing how host plants and methods affect spore concentrations. For example, ROC with Trifolium incarnatum and Arachis hypogaea yielded 2766 ± 1066 spores per liter for Rhizophagus and Gigaspora strains (Wood et al., 1985). A study on Daucus carota produced 500,000 spores per liter (St-Arnaud et al., 1996). Using petri dish cultures and bioreactors to propagate Rhizophagus, Gigaspora, Scutellospora, and Sclerocystis with hosts like Daucus carota and Trifolium pratense resulted in spore concentrations ranging from 48,300 to 120,000 spores per liter (Fortin et al., 1993). Airlift bioreactor and petri dish cultures of R. intraradices with Daucus carota yielded 20,000 to 30,000 spores per liter (Jolicœur et al., 1999). ROC in solid medium with Rhizophagus and Daucus carota achieved 280,000 spores per liter (Declerck et al., 2001). Inoculating Rhizophagus with Solanum tuberosum produced around 400,000 spores per liter (Puri and Adholeya, 2013). Finally, Schüßler (2018) used root organ liquid (ROL)-based ROC with multiple AMF species, such as Acaulospora, Rhizophagus, Scutellospora, and Funneliformis, and host plants like chicory, clover, and bindweed, yielding spore concentrations between 106 ppg and 300,000 spores per liter.
A recent study using a solid medium-based ROC with Daucus carota with 0.23% gellan gum and M-medium achieved over 350,000 spores per liter and more than 2 million propagules per liter. It demonstrated high biomass production (>2 g Dry Weight per liter) and a colonization rate of 60–70% (Ghorui et al., 2023a), marking significant advancement in AMF cultivation methods. The variability in the spore yield, biomass, and colonization rates further suggests that continuous optimization and careful management strategies are essential for achieving consistent, high-quality yields. However, using Ri-transformed roots for AMF propagation could lead to a loss of resilience and effectiveness of AMF strains when applied in natural environments. There is also a risk of gene transfer from genetically modified roots containing AMF propagules to wild crops, potentially causing ecological consequences. Additionally, this approach may result in socio-economic impacts, such as public resistance and market restrictions.
This technique developed by Voets et al. (2009) involved placing the Medicago truncatula plantlets into an actively growing mycelial network derived from a mycorrhizal donor plant. While this technique enables rapid and uniform mycorrhization and eliminates the risks associated with using genetically modified roots, its suitability for large-scale production still requires further investigation.
An autotrophic culture system was developed for in vitro mycorrhization of plantlets of different hosts like Potato, Strawberry, Trifolium, etc, where roots of micro propagated plantlets were associated with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi under controlled conditions, while shoots grew in open air. The system resulted in the production of thousands of spores, extensive extraradical mycelium, and abundant root colonization (Voets et al., 2005). These spores were able to colonize new plantlets under the same conditions. An advancement to the above technique is the in vitro Mycorrhizal Donor Plant (MDP) system enables fast, uniform colonization of a wide variety of photosynthetically active plants, with applications in both basic research and mass production (Lalaymia and Declerck, 2020). This system demonstrates the potential for continuous cultivation of AMF, offering a valuable tool for studying the symbiosis, especially where a source–sink relationship and photosynthetically active tissues are required. The feasibility of this technique for mass cultivation needs further evaluation, as it is labor-intensive and demands significant space for maintaining the entire plants.
Although research on AMF bioformulation development is limited, the global mycorrhizal market is expanding due to the benefits of mycorrhizal bioinoculants, such as enhanced plant growth, improved nutrient uptake, and increased pathogen resistance. Developing effective AM bioinoculants requires selecting the right beneficial microbes, carriers, adjuvants, application methods, and the ability of microbes to thrive in the soil and plant environment (Bargaz et al., 2018; Aamir et al., 2020) such as the ones which are commercially available (Table 3). Desirable traits for bioinoculants include effective host plant colonization, adaptability to the host environment, resilience under harsh conditions, genetic stability, long shelf life, and non-pathogenicity (Chakraborty, 2020). Although challenges remain, the growing recognition of the potential of AM bioinoculants underscores the need for continued research to drive sustainable agricultural practices (Figure 2).
AMF, both as a sole microorganism or used in combination with other microorganisms have proved to be beneficial for the agriculture (Benami et al., 2020; Yadav et al., 2020; Santoyo et al., 2021). Selecting the right AMF strain and compatible microbes is crucial for creating effective bioinoculants. These strains should suit the host plant species, environmental conditions, native microbiota, and intended purpose. Besides AMF, other compatible microbial candidates like beneficial bacteria as nitrogen fixers, phosphorus solubilizers, and disease suppressors should be identified to work synergistically with mycorrhizal fungi (Benami et al., 2020; Yadav et al., 2020; Santoyo et al., 2021). Developing efficient bioinoculants, therefore, requires a holistic approach that considers the complex interactions between these microorganisms.
Key factors in primary selection include plant growth promotion abilities, degradation potential, and compatibility properties like synergistic and antagonistic effects (Wong et al., 2019; Singh et al., 2020). spp. Commonly associated bacteria with AMF include Rhizobium meliloti, Bradyrhizobium japonicum, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Bacillus licheniformis, Azospirillum, and B. subtilis (Srivastava et al., 2021). Co-inoculations with endophytic filamentous fungi (EFF) like Trichoderma viride, T. harzanium, Piriformospora indica, Umbelopsis nana, Mortierella sp., Fusarium oxysporum, and Penicillium pinophilum often enhance each other’s effects (Díaz-Urbano et al., 2023). These microorganisms can be isolated from soil and plant roots, tested for plant growth promotion, and biocontrol properties, and evaluated through in planta trials to ensure effective colonization and growth enhancement. This helps create robust bioinoculants that offer multiple benefits in agriculture.
Mycorrhiza helper bacteria (MHB) enhance the symbiotic relationship between AMF and plant roots which promote AMF spore germination, mycelial growth, and root colonization, improving the fungal ability to access and transfer nutrients to plants (Sangwan and Prasanna, 2021; Yang et al., 2023; Guarnizo et al., 2023). This, in turn, boosts plant growth, nutrient uptake, and resilience to abiotic stresses like drought. MHB achieve this by producing plant growth hormones, solubilizing soil nutrients, or creating a favorable environment for AMF development (Nasslahsen et al., 2022). Dual inoculation with AMF and Bacillus spp. under field conditions showed that reducing NPK fertilizers by 50% had no negative impact on crop growth, nutrition, or yield (Nanjundappa et al., 2019).
A suitable carrier serves as a delivery medium for live microbial strains, facilitating their transition from the lab to the field (Sohaib et al., 2019; Singh et al., 2020; Rojas-Sánchez et al., 2022). Ideal carriers for mycorrhizal bioformulations should:
i. provide a favorable micro-environment for microbial multiplication and survival during storage and planting,
ii. be compatible with microorganisms based on physico-chemical properties,
iii. be non-toxic to both microbes and plants,
iv. ensure successful release of microorganisms after application.
v. reduce losses from micro-fauna degradation in the soil,
vi. support competition with native soil microorganisms,
vii. be chemically stable,
viii. have small particle size for faster dispersibility,
ix. retain high nutrient and moisture (carriers with low C:N ratio),
x. have a neutral pH of 7,
xi. be compatible with the intended delivery method,
xii. be cost-effective and ecologically friendly for commercial production,
xiii. be easy to process and scalable.
Different carriers have varying capacities to hold infective propagules and may affect plants differently. For example, vermiculite was most effective for soybean but negatively impacted corn, whereas phosphorus-enriched peat improved corn growth (Barazetti et al., 2019).
Different types of carriers are used for formulating mycorrhizal inoculants which serve as support materials for the fungi, helping to protect and deliver them to plants in agricultural applications (Table 4). The different commercial formulations of arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculants include solid, liquid, encapsulated, and nanofiber-based forms. Solid formulations are easy to handle and store but may have a short shelf life. Liquid formulations are simple to mix and distribute but can pose inhalation hazards. Encapsulated forms protect microorganisms and provide controlled release, though they are more expensive. Nanofiber formulations offer enhanced stability and targeted delivery but face challenges with scalability. Each formulation type has unique advantages and limitations depending on storage, application, and effectiveness (Table 5).
Adjuvants consist of polysaccharides, polyalcohol derivatives, natural or synthetic polymers, or caseinate salts that enhance microbial stability, adhesion, handling, and mixing, reduce dust, and prevent inoculant dispersion during sowing (Jambhulkar et al., 2016; Pedrini et al., 2016). Common adjuvants used in solid bioformulation include carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), methyl cellulose, gum arabic, skim milk, humic acids, PVP, glycerol, and trehalose. CMC improves shelf life and efficacy (Zhou et al., 2017), gum arabic protects microbes from desiccation (Wani et al., 2007), and skim milk boosts cell viability and release into soil (Bashan et al., 2002). Humic acids support microbial growth and plant development (Young et al., 2006), PVP helps microbes survive desiccation and toxins (Singleton et al., 2002), and starch improves survival and rhizosphere colonization (Bashan et al., 2002). Chitosan, with antibacterial properties, enhances microbial biocontrol and storage (Muxika et al., 2017), while sugars like trehalose protect microbes during drying (Schoebitz et al., 2013). Protein hydrolysates stimulate microbial activity (Colla et al., 2017), with glycerol, silicon, and poly-lactic acid improving microbial viability (Vassilev et al., 2017). Liquid adjuvants like glycerol increases shelf life and stress tolerance in microbes, improving water retention and resistance to high temperature and desiccation (Taurian et al., 2009). PVP also protects microbes in stressful conditions through its water retention capacity (Gopal & Baby, 2016). Therefore, glycerol, PVP, or trehalose-based liquid bioformulations are highly promising for agricultural use.
Fillers are added to bioformulations to enhance properties like stability, microbial survival, and controlled release. Materials such as bentonite, kaolin, and perlite improve the mechanical strength of carriers, protect microbial cells or spores, and regulate their soil release for sustained effectiveness. These fillers also increase carrier porosity, promoting better water retention and nutrient exchange, ultimately supporting microbial colonization in the rhizosphere and enhancing bioformulation performance.
The microbial stability of bioinoculants should ideally range from 6 to 12 months or longer (Berninger et al., 2017). Key factors for enhancing shelf-life and microbial stability include additives and low-temperature storage to protect microbes from harsh environmental conditions such as variations in soil pH, nutrient limitations, and temperature fluctuations (Liu et al., 2014). Methods like freeze-drying, vacuum-drying, spray-drying, fluidized bed-drying, and air-drying, as well as the addition of external protectants, stress adaptation, promoting exopolysaccharide production, and using “helper” microbial strains, enhance shelf-life (Berninger et al., 2017). Trehalose acts as a protectant during desiccation (García, 2011). Drying is a well-established method for long-term storage, as the right drying conditions can improve both product quality and shelf-life. Proper encapsulation materials, temperatures, and packaging are used to maintain microbial activity and control humidity.
Each bioformulation type is associated with specific delivery methods to ensure effective application, considering factors like the bioformulation’s nature, target environment, and intended use (Table 6).
Quality control is essential to ensure the efficacy and safety of AMF bioformulations, building confidence among farmers and consumers. Strong standards are required to address challenges in consistent production, formulation, and maintaining viable microorganisms. Considerations include ecological risks of non-native strains and the need for long-term research on the persistence and effectiveness of AM inoculants. QC starts with evaluating AM inoculants, microbial strains, carriers, and the final product, followed by proper labelling and commercialization.
AMF species or strains must be identified before mass cultivation. The culture should be sterile with high viability, and germination capacity. Regulations, such as those in India and the EU, specify minimum viable spores and acceptable variation in microorganism concentrations (Ghorui et al., 2024). During pre-fermentation and fermentation, the identity and purity of microbial strains must be carefully controlled to prevent contamination. Initially, the flask inoculum’s quality is verified using lab tests like inoculating a Petri dish with PDA medium. Only the intended strain should grow; otherwise, it’s discarded. At the end of the strain’s growth, a sample is taken for microscopic examination to confirm identity and check for contamination. pH, sugars, and PMW levels are also monitored (Volpato, 2020). During fermentation, microorganisms multiply in a bioreactor with controlled parameters like air, temperature, pH, and pressure. Post-growth, an aliquot is tested in the lab. Serial dilutions are plated on selective media, and living cells are counted using spread or drop plate methods. Different media are used for various strains. If no contamination is found and cell concentrations are acceptable, the product proceeds; otherwise, the process restarts (Volpato, 2020). Carriers must be checked for contamination, microbial compatibility, required pH, etc.
The final product must meet specific requirements for microorganism presence (as declared on the label), microbial load, relative humidity, particle size, pH, and absence of contaminants. Samples from each lot are tested for these factors. Granulometry is assessed using a ro-tap sifter, and relative humidity is measured with a humidity analyzer balance. CFU counts check the presence and proportion of microorganisms, ensuring they meet or exceed the labeled microbial counts throughout the product’s shelf life (Volpato, 2020).
Labels must comply with regulations of the country where it is intended to sell, accurately reflect contents, and include the lot number and production date. Verification occurs during label creation and post-packaging.
Once AMF bioformulations pass all quality control checks and validation trials, they move to commercialization, ensuring regulatory compliance and market readiness. This involves developing compliant labels, establishing efficient distribution channels, and educating farmers on the proper use of bioformulations. Additionally, post-market surveillance and ongoing research are crucial for maintaining product effectiveness and safety. Listening to customer feedback and making necessary improvements help build long-term relationships with users, ensuring the bioformulations meet their needs and contribute to sustainable agricultural practices. Post market control involving random sampling of boxes sold to distributors (but not yet to final consumers) can verify that the product quality remains consistent from the company to the farmer. This process also allows assessment of transport and storage conditions in dealers’ warehouses to ensure they maintain the product’s quality and identify any special precautions distributors might need.
In planta trials encompass both greenhouse and field studies to assess the real-world agricultural performance of AMF bioformulations. To ensure the high quality of a microbial consortium, it must be initially tested in soil with reference plants and crops through greenhouse trials. Small-scale testing is necessary to verify its effectiveness and economic viability. This involves comparing treated plants with untreated controls to observe performance differences. Laboratory-proven effectiveness must translate into tangible improvements in crop productivity in real-field conditions. For farmers to adopt and continue using microbial consortia, they must demonstrate efficacy, durability, and consistency, matching the claims on their labels.
After a bioformulation is developed and successfully field-tested, it goes through a verification process for validation. This involves conducting field trials at multiple locations to assess the formulation’s performance. Upon successful validation, the bioformulation must be registered, which includes obtaining a patent and necessary safety and risk approvals before commercial release.
Although various microorganisms can be combined with AMF to create mixed biofertilizers, the following are the two primary microbial partners of AMF.
The AMF-legume-rhizobia complex communicates through shared signaling pathways, resulting in synergistic, neutral, or antagonistic effects on colonization and resource uptake (Saxena et al., 1997; Chalk et al., 2006; Larimer et al., 2013; Primieri et al., 2021). Tripartite mutualism among AMF, FLNF, and plants is driven by nutrient exchange. Co-inoculation with AMF boosts FLNF abundance, likely due to improved P availability via AMF extraradical mycelia (Bagyaraj and Menge, 1978; Mishra et al., 2008). AMF scavenge solubilized P beyond the rhizosphere (Ezawa et al., 2002), which may also support rhizobacteria through hyphal exudation or biofilm transport (Jiang et al., 2021). Meanwhile, FLNF fix atmospheric N2 into bioavailable NH₄+, enhancing plant N uptake. This reciprocal nutrient exchange allows AMF and Free-Living Nitrogen Fixers (FLNF) to supply plants with essential nutrients in return for carbon. Certain FLNF genera, such as Azospirillum and Azotobacter, thrive under co-inoculation, indicating taxon-specific interactions with AMF (Figure 3) (Miyauchi et al., 2008; Welsh et al., 2009; Kasanke et al., 2024). The variability in responses underscores the need for a deeper understanding of species-specific interactions, environmental influences, and mechanistic pathways to optimize their application in field conditions.
In the rhizosphere, interactions between AMF and FLNF influence soil processes, plant nutrient uptake, and growth. Both nodulating and non-nodulating plants exhibit tripartite mutualism with AMF and FLNF, though responses vary significantly, ranging from a 255% increase in total biomass to a 94% reduction in shoot biomass. These effects are highly context-dependent, with FLNF enhancing AMF colonization and AMF promoting FLNF abundance. Key factors influencing outcomes include plant phenology, soil type, nutrient availability, and microbial pairings (Kasanke et al., 2024). Harnessing these interactions could improve soil health and crop productivity. AMF and N2-fixing bacteria complement each other in plant nutrition, jointly influencing plant communities by affecting community structure and function. While AMF enhance species diversity and productivity, N2-fixers tend to reduce productivity. Both microbial groups impact species abundance (Bauer et al., 2012). The impact of AMF-nitrogen fixer interactions on plants varies, with some studies showing positive effects, while others report weak or even negative outcomes under dual inoculation, highlighting inconsistent synergy (Table 7) (Saxena et al., 1997). These variations suggest that AMF and rhizobia may compete for root colonization sites, potentially reducing symbiotic efficiency (Chalk et al., 2006). The efficacy of microbial inoculants is site dependent. In dryland environments, plants exhibited greater reliance on AMF+Rhizobium co-inoculation than on single inoculations. However, microbial inoculants proved less effective in high-fertility soils, low organic matter conditions, and acidic environments (Calderon and Dangi, 2024). These findings emphasize the complex and context-dependent nature of AMF-FLNF-plant interactions, highlighting their potential for sustainable agriculture.
Co-inoculation of AMF and PSB enhances plant growth more effectively than single inoculation, as AMF within plant cells facilitate P uptake from soluble P released by PSB in the rhizosphere. AMF influences PSB, by creating a specialized niche through their hyphal network (Agnolucci et al., 2015; Taktek et al., 2015). Bacterial colonization of AMF hyphae and spores confirms a mutualistic relationship (Toljander et al., 2007; Bharadwaj et al., 2011; Scheublin et al., 2010). AMF enhance PSB activity by transferring plant-derived carbon underground, supporting microbial growth and altering soil bacterial communities (Toljander et al., 2007; Drigo et al., 2010; Zhang et al., 2016). AMF-driven carbon flux alleviates organic carbon limitations, improving microbial P solubilization (Hameeda et al., 2006; Patel et al., 2007; Brucker and Spohn, 2019). Similarly, PSB utilize AMF hyphae to access insoluble P sources and migrate toward the rhizosphere (Gahan and Schmalenberger, 2015; Ordoñez et al., 2016). PSB enhance AMF fitness and ecological functions by promoting AMF establishment, growth, and spore germination, leading to improved plant growth parameters (Scheublin et al., 2010; Ordoñez et al., 2016). They stimulate extraradical hyphal growth, increasing nutrient acquisition by expanding the mycorrhizosphere. Root exudates induced by PSB release enzymes that mineralize phosphorus and decompose organic matter, making nutrients available for AMF and plants (Canarini et al., 2019). Flavonoids in root exudates further facilitate AM formation by influencing hyphal growth and root colonization (Schrey et al., 2014). PSB attachment to AMF hyphae ensures localized P solubilization, optimizing fungal and plant nutrient uptake (Artursson et al., 2005). They also facilitate PSB dispersal, reinforcing their synergistic interaction in nutrient cycling and plant growth (Linderman, 2013; Hodge, 2014). Studies have demonstrated this synergy in maize (Wahid et al., 2016), tomato (Kavatagi and Lakshman, 2014), finger millet (Patil and Lakshman, 2011), linseed (Rahimzadeh and Pirzad, 2017), wheat (Yousefi et al., 2011), carrot, potato (Ordoñez et al., 2016), and broad beans (Nadagouda and Lakshman, 2010). AMF and PSB co-inoculation increased root colonization, plant height, biomass, and leaf area in both pot and field trials, with PSB population and AMF spore density showing a stronger correlation with growth parameters than plant nutrient levels (Nacoon et al., 2021). AMF and PSB reshape microbial communities involved in N and P cycling, enhancing nutrient uptake, altering C:N:P stoichiometry, and influencing ginsenoside composition (Mu et al., 2024). Thus, the synergistic interaction between AMF and PSB enhances plant growth, nutrient acquisition, and soil microbial dynamics, making co-inoculation a promising strategy for sustainable agriculture and improved crop productivity (Table 8).
Rhizobium spp. produce carboxylic acids that solubilize P from iron, aluminium, and calcium complexes (Guimarães et al., 2022). By promoting PSB and nitrogen-fixing bacteria, AMF improve plant nutrient acquisition and stress resistance (Mohammad & Mittra, 2011). Rhizobium Sinorhizobium fixes atmospheric N into ammonium, improving plant N absorption. Farmers have traditionally used single or mixed beneficial strains as biofertilizers to support sustainable crop growth. However, their effectiveness is often limited by competition with native soil and plant microflora, making establishment in the rhizosphere or endosphere challenging.
Biofertilizers encounter several challenges, such as short shelf life, instability under field conditions, inconsistent performance in fluctuating climates, and the requirement for high application rates (Das, 2023). The integration of nanotechnology with biotechnology has paved the way for innovative solutions in agriculture ecosystem.
NBFs, which combine biofertilizers with nanoparticles (NPs), offer an environmentally friendly and cost-effective alternative due to the distinctive properties of NPs, including high surface area, improved solubility, lightweight nature, and versatile application methods (Kah et al., 2019). NBFs are synthesized by encapsulating biofertilizers within nanomaterial coatings, producing nanoscale particles ranging from 1 to 100 nm (Marchiol, 2019). These formulations provide multiple benefits by triggering various biochemical and physiological changes in plant metabolic pathways. Advantages include the controlled and sustained release of nutrients, reduced nutrient loss, enhanced nutrient use efficiency, enrichment of beneficial soil microorganisms, improved crop resistance to diseases, large-scale production feasibility, cost-effectiveness, renewable fertilization, and prolonged shelf life (Sharma et al., 2022). However, despite their considerable potential, NBFs remain underutilized.
The major steps of development of NBFs involves three key steps: (a) cultivation of AMF, (b) encapsulation with nanoparticles, (c) performance evaluation, including assessment of quality, purity, and shelf life (Bairwa et al., 2023). The bioformulation of NBFs primarily follows either a top-down or bottom-up approach (Figures 4A, B). In the top-down method, large raw materials are broken down into nanoscale components using various mechano-physical techniques such as mechanical grinding, ball milling, etching, co-precipitation, sputtering, lithography, phytochemical reduction, laser ablation, and electro-explosion. Conversely, the bottom-up approach involves synthesizing nanoparticles from atoms, molecules, or smaller particles through chemical and biological processes. These include supercritical fluid synthesis, evaporation-condensation, sol-gel processing, spray pyrolysis, laser pyrolysis, electrospinning, and chemical vapor deposition (Jamkhande et al., 2019).
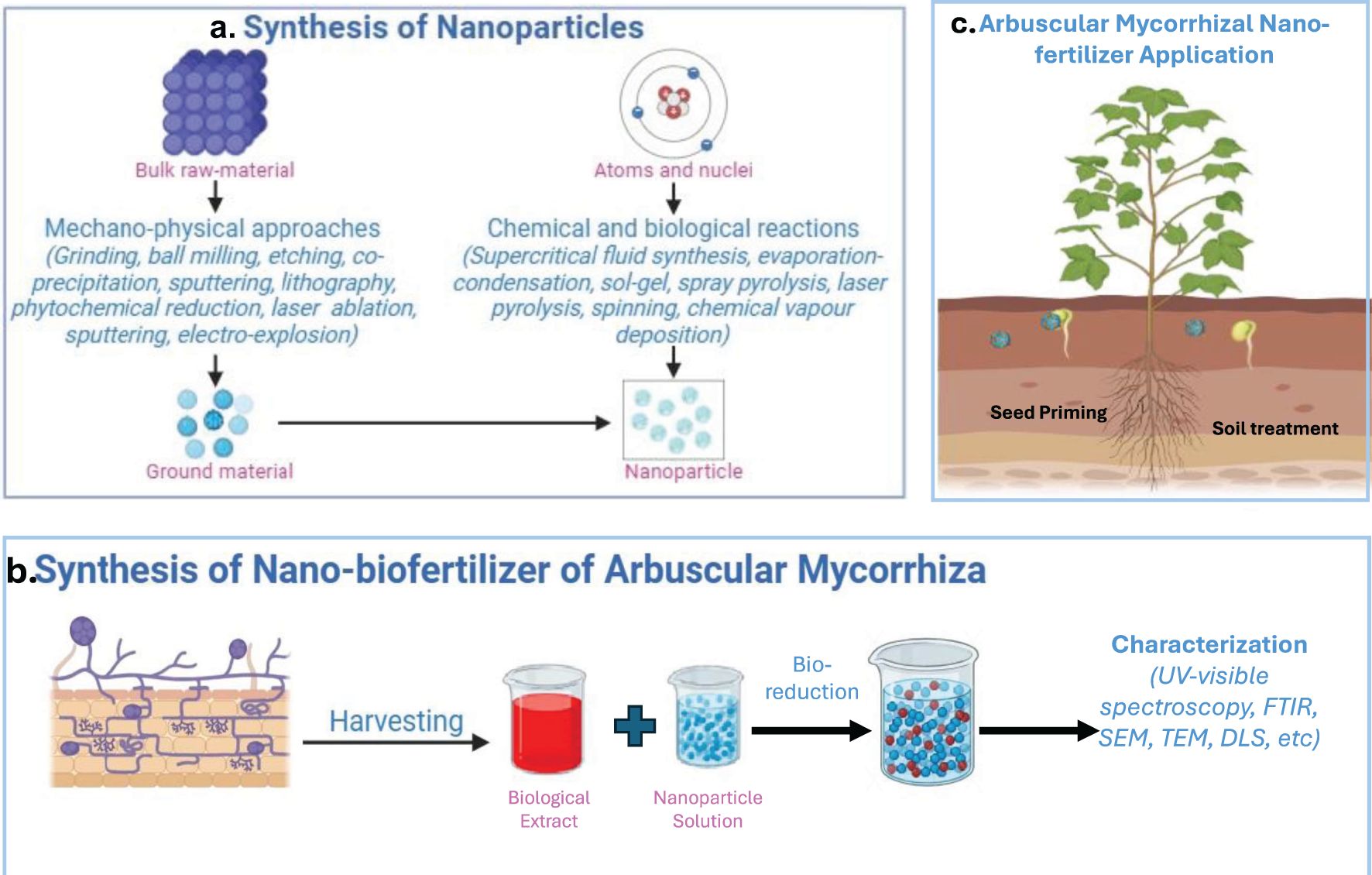
Figure 4. Synthesis of nanoparticles (a), synthesis of nano-biofertilizer of AMF (b), and application of AMF-based biofertilizer (c).
For AMF-based NBFs, application methods include soil application and seed priming (Figure 4C). Soil application enhances plant growth and helps restore soil fertility, while seed priming—a pre-sowing technique—entails soaking seeds in NBFs to promote faster germination, improve seedling establishment, and reduce fertilizer dependency (Table 9). This process stimulates plant growth-promoting hormones and activates stress-resistance genes. Upon contact with roots and seed surfaces, nanoparticles adhere to plant surfaces through electrostatic interactions, hydrophobic forces, and Van der Waals forces. Root uptake of NPs primarily occurs via physiologically active lateral roots and root hairs, with upward transport occurring through the xylem. NPs can penetrate plant cells and move intercellularly through multiple mechanisms, including cell wall pores, endocytosis, plasmodesmata, aquaporins, and ion transporters. The uptake process is influenced by the chemical composition, size, shape, and aggregation state of the NPs, as well as by plant species, since receptor structures vary across different plants (Bairwa et al., 2023).
Nano-enabled agriculture presents several potential limitations, including concerns related to toxicity, environmental impact, and regulatory challenges. In terms of toxicity, nano-based pesticides may pose risks to non-target organisms, such as pollinators and aquatic life. Additionally, NPs can negatively affect seedlings by reducing germination rates and causing phytotoxicity. There are also potential health risks for farm workers and consumers due to exposure to NPs. From an environmental perspective, the behavior of newly developed NPs can be unpredictable, making their monitoring and management challenging. Furthermore, NBFs can undergo physical, chemical, and biological transformations in the environment, potentially altering their effects and interactions within ecosystems (Okeke et al., 2021; Rajput et al., 2021; Muzammil et al., 2023; Ali, 2025).
Despite the promising potential of NBFs in enhancing agricultural sustainability, their widespread adoption remains limited due to concerns surrounding toxicity, environmental interactions, and regulatory challenges. Future research should focus on optimizing NBF formulations to maximize benefits while minimizing ecological and health risks. Advanced studies on nanoparticle behavior in diverse soil and climatic conditions, as well as long-term assessments of their impact on plant-microbe interactions, will be crucial. Additionally, integrating precision agriculture techniques with NBF applications could enhance their efficiency, reducing resource wastage and ensuring targeted nutrient delivery. Collaborative efforts between researchers, policymakers, and industry stakeholders are essential to establish standardized safety protocols and regulatory frameworks, paving the way for the responsible and large-scale implementation of NBFs in modern agriculture.
Farmers traditionally use single or mixed beneficial strains as biofertilizers to support sustainable crop growth. However, their effectiveness is often limited by competition with native soil and plant microflora, leading to inconsistent results (Zakeel and Safeena, 2019). Biofilm biofertilizers offer a solution by forming microbial biofilms embedded in extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). These biofilms adhere to surfaces and provide enhanced protection against environmental stress (Rana et al., 2020). Biofilm-forming microbes, including bacteria, fungi, and algae, communicate via quorum sensing, allowing them to function as cohesive units (Li and Tian, 2012). Compared to single-strain biofertilizers, biofilm-based biofertilizers have demonstrated superior crop productivity (Seneviratne and Jayasinghearachchi, 2003). Multi-strain biofilms are more resilient and sustainable than single-species biofilms, providing microbial protection against biotic and abiotic stresses (Parween et al., 2017; Turhan et al., 2019). Biofilm biofertilizers have shown effectiveness in crops like rice, maize, tea, rubber, and vegetables, reducing chemical fertilizer usage by up to 50% (Seneviratne and Kulasooriya, 2012). Soil microbial biofilms include bacterial, fungal, and fungal-bacterial biofilms (FBBs), each adapting to different surfaces improve nutrient uptake and stress tolerance (Seneviratne et al., 2007). BFBFs contribute to ecosystem sustainability by promoting soil fertility and plant resilience under stress (Vlamakis et al., 2013). Mycorrhizal roots with bacterial-fungal biofilms boost P nutrition (Jayasinghearachchi and Seneviratne, 2005), while fungal-rhizobial BFBFs improve nitrogen use efficiency in Zea mays under drought conditions (Pereira et al., 2020). Mycorrhiza-associated bacteria enhance nutrient availability, produce growth-promoting compounds, and improve resistance to fungal pathogens (Table 10) (Agnolucci et al., 2015).
Biofilm-based biofertilizers represent a significant advancement in sustainable agriculture, offering improved nutrient availability, stress resilience, and reduced dependency on chemical fertilizers. While extensive research exists on bacterial and fungal biofilms, studies on biofilms based on AMF remain limited. Further research is needed to explore their potential in enhancing plant–microbe interactions and promoting soil health.
In advancing research, the beneficial traits of microbial isolates often overshadow the need to assess their pathogenicity at the species level before large-scale applications. There is an assumption that bacteria from natural sources like soil and water are non-pathogenic. However, many biofertilizers are derived from bacteria classified as BSL-2 or higher biohazard groups. These microorganisms, classified as BSL-2, can act as opportunistic pathogens, potentially impacting non-target plants and reducing local biodiversity (Kardol et al., 2007).
The quest for new biofertilizers has identified novel species, but the lack of reference strains for pathogenicity comparison and the presence of similar strains in hospital environments raise safety concerns for commercial use (Uzcátegui-Negrón et al., 2011). Microbial activities of opportunistic pathogens, such as producing antibiotics or growth-regulatory substances, can alter local microbial communities, disrupt nutrient cycles, and change plant biodiversity. Some actinobacteria are linked to serious diseases, necessitating careful use in agriculture (Gneiding et al., 2008). Therefore, it is crucial to conduct thorough pathogenicity assessments of microbial isolates to ensure their safety and prevent unintended ecological consequences when applied in agricultural ecosystem.
Inoculation, which introduces high densities of viable microbes to the host rhizosphere disrupt temporarily the soil microbial community equilibrium (Trabelsi and Mhamdi, 2013). While changes in microbial composition could be undesirable if important native species are lost, ecosystem resilience, driven by plant–soil–biota diversity and interactions, may buffer these effects (Kennedy, 1999). Furthermore, bacterial redundancy, where different species perform the same functions, may ensure system functionality despite species loss (Nannipieri et al., 2003). Recent studies have highlighted that even unsuccessful microbial inoculation can significantly impact native soil microbiota by triggering microbial invasions (Liu et al., 2022). Inoculants, as microbial invaders, can alter native species diversity and community composition, reshaping soil functionality, such as carbon sequestrations (Bannar-Martin et al., 2017; Amor et al., 2020). Microbial inoculations can lead to significant and unforeseen changes in soil microbial communities by initiating secondary succession (Horn, 1974), which in turn can have cascading impacts on the functions and services provided by agroecosystems. The survival of inoculants in soil determines their impact, with longer survival leading to more significant effects (Xing et al., 2020a). Both abiotic factors, like pH and temperature, and biotic factors, such as competition or mutualism, influence inoculant survival (Trexler and Bell, 2019). Microbial communities with higher phylogenetic diversity are more resistant to invasions (Mallon et al., 2018). Additionally, even poor survivors can leave a lasting footprint on native communities (Xing et al., 2020; Reynolds et al., 2017). Inoculation reshapes interspecies interactions through synergism or antagonism or competition or predation and triggers secondary succession in microbial communities by facilitation, tolerance, or inhibition, depending on the suitability of the invaders to the native community (Connell and Slatyer, 1977).
Studies on the potential risks of non-native AMF strains disrupting soil microbiomes have yielded conflicting results. No significant differences were observed in the microbiome of plants exposed to native AMF communities versus those treated with commercial AMF bioinoculants alongside native AMF. Nevertheless, inoculation led to favorable changes in root traits, as well as increased AMF colonization, plant biomass, and leaf nitrogen (Berdeja et al., 2025). In native grassland soils with healthy AMF communities, the use of commercial AMF products was mostly ineffective, and in some cases, led to reduced biomass production and decreased AM fungal root colonization. This suggested that commercial strains could disrupt plant-fungal symbiosis (Duell et al., 2022). Exotic AMF inoculants have been linked to potential disruptions in soil microbial composition and structure (Mummey et al., 2009; Faye et al., 2009). Native AMF species are often considered more mutualistic than non-native strains. Studies comparing local and commercial AMF inoculants found great variability in performance, with some commercial strains failing to form mycorrhizal associations due to poor adaptation to local soil conditions (Corkidi et al., 2004; Rowe et al., 2007; Faye et al., 2013; Salomon et al., 2022)
New EU regulations include only four microorganisms (Azotobacter spp., Mycorrhizal fungi, Rhizobium spp., Azospirillum spp.) under the plant biostimulant category PFC 6(A) (EU Regulation, 2019). Furthermore, the fact that no pathogen has been identified in the above-mentioned 4 species to date does not guarantee that they do not exist. However, safety is not fully guaranteed, as these regulations are based on taxonomic criteria, and genetic variations within species can include both pathogens and harmless strains. The Environmental Hazard Safety Index (EHSI) system, which assesses the safety of microorganisms intended for environmental release, is an improvement over the taxonomic approach but still has shortcomings for fungi, particularly mycorrhizal fungi (Barros-Rodríguez et al., 2020). To ensure the safe and effective selection of PGPR strains for inoculants, advanced and comprehensive methods, such as whole genome sequencing should be used. Environmental and Human Safety Index (EHSI) can help compare isolates with known PGPRs, aiding in the selection process and minimizing risks to the environment and human health (Vílchez et al., 2016). Standardizing these methods will enable more reliable and responsible use of beneficial microorganisms in agriculture.
While the combination of beneficial properties in microbial products is appealing to researchers and end-users, it poses challenges for regulatory authorities. These authorities apply similar regulatory frameworks to agricultural microbial products as they do to chemical products, distinguishing Plant Protection Products (PPPs) and fertilizers. Consequently, microbial inoculants are currently classified only as either biopesticides or biostimulants/plant strengtheners/biofertilizers. This classification is crucial for the registration and market placement of these products, as the procedures differ significantly.
The global agricultural microbials market size was valued at USD 6.17 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow from USD 6.85 billion in 2024 to USD 16.02 billion by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 11.21% during the forecast period (Agricultural Microbials Market Size, Share | Global Report [2032], 2024). Despite such market size of the mycorrhizae-based biofertilizers market, regulatory frameworks may hinder sector growth, particularly during formulation stages.
The new EU regulations introduced in 2019 restrict the marketing of biofertilizers to four types: those that provide nitrogen (symbiotic Rhizobium spp., free-living Azotobacter spp., and Azospirillum spp.) and those that enhance phosphorus nutrition (mycorrhizal fungi). Additionally, only drying or freeze-drying methods are permitted for product formulation, limiting the use of other available technologies (EU Regulation, 2019). In India, mycorrhizal biofertilizers are under the Fertilizer (Organic) (Control) Fifth Amendment Order, 2021, with a spore count of 10 viable spores per gram and a pH range of 5.0–7.0. In Japan, the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries oversees soil conditioners under the Soil Productivity Improvement Act (2019), with a spore count of 25 per gram and a pH range of 4.5–8.0 (MAFF, 2019). Indonesia follows the Law No. 22 of 2019 for biological fertilizers, setting a standard of 2,300 infective propagules per gram for root inoculants. Thailand’s regulations under Fertilizer Act B.E. 2550 (2007) require a spore count of 25 per gram for solid inoculants and 2,300 infective propagules per gram for root inoculants, with pH suitable for both microorganisms and plants. The Philippines enforces regulations under the Fertilizer Act B.E. 2550 (2007), specifying a spore count of 10 per gram for solid inoculants. In the European Union, microbial plant stimulants are governed by Regulation 2019/1009, with specific testing requirements for quality assurance, efficacy trials, and contamination controls, ensuring compliance with heavy metal and pathogen limits (Ghorui et al., 2024).
It is crucial to establish standardized regulations for the control of microbial inoculants, especially biostimulants like AMF. First, they improve global trade and eases market access as producers can adhere to uniform regulatory requirements in several nations, which lowers complexity and expenses. Harmonized regulations may improve product development and result in more dependable product efficacy Additionally, standardizing safety and quality controls can guarantee product reliability, promoting broader adoption by farmers. Such harmonizations can promote the creation of more efficient microbial products suited to particular agricultural requirements by offering defined avenues for innovation. Lastly, by guaranteeing that only safe, non-pathogenic strains are utilized, harmonization would reduce hazards to ecosystems and advance environmental protection.
The primary difficulty in producing AMF inoculum stems from their obligate symbiotic nature, which requires a host plant for growth and life cycle completion, making the cultivation process time- and space-intensive.
It is often assumed that multi-species inoculants are more effective in handling multiple stress conditions, but in contrast, single-species inoculation has been found to more effectively increase shoot biomass (Berruti et al., 2016). Some studies suggest that the composition of species, rather than their diversity, plays a more critical role in determining plant function (Gosling et al., 2015; Wagg et al., 2015). Widely used AMF species such as Rhizophagus intraradices, Funneliformis mosseae, and R. irregularis are versatile generalists, capable of colonizing various host plants and easily propagated for inoculation (Öpik et al., 2010). Moreover, variations in plant responses are typically attributed to differences between isolates of the same species rather than differences between species (Munkvold et al., 2004; Gai et al., 2006; Angelard et al., 2010). This suggests that genetic variability within species might be more influential than species diversity itself.
The market is plagued by counterfeit and low-quality products, particularly in areas with inadequate regulations, which undermines trust and slows growth. Salomon et al. (2022) evaluated 28 commercial AMF inoculants across Australia, Europe, and North America. Greenhouse trials in non-sterile soils showed that most inoculants did not enhance mycorrhizal colonization or plant biomass while 84% failed to colonize roots in sterilized soil. Rhizophagus irregularis cultures showed significant colonization. In North America field trials, metagenomic analysis revealed changes in the mycorrhizal community, with one inoculant increasing biomass. Koziol et al. (2024) conducted a meta-analysis of commercial AMF inoculants over 20 years, finding that 84% resulted in <5% root colonization. In 10 cases, the inoculants caused crop mortality. They estimated that ineffective AMF products waste $876 million USD globally. These varying results raises concerns about the reliability of some commercial inoculants. Rigorous quality control is crucial, as contamination is common, with many commercial biofertilizers failing to meet purity standards (Herrmann and Lesueur, 2013). Inadequate storage facilities and unsuitable carriers can lead to contamination and decreased efficacy. Proper labelling, including expiration dates and clear microorganism identification, is often lacking, undermining credibility (Salomon et al., 2022; Ghorui et al., 2023b; 2024). Absence of clear guidelines on sampling and testing protocols along with no established standards on viability, and infectivity, results in the production of low-quality inoculants.
Although the benefits of AMF in sustainable agriculture are well-established, there are still gaps in understanding their effectiveness and optimal application methods. Some field trials report positive effects, while others present mixed or conflicting results. Berruti et al. (2016) reported that out of 164 inoculation experiments, with 65% conducted in greenhouses and 24% in open-field conditions, the effectiveness of AMF inoculation on shoot biomass, yield, and plant nutrition was consistent across both environments, showing equal success in both greenhouse and field conditions. Hijri (2015) analyzed 231 field trials over four years across North America and Europe, finding a 9.5% increase in marketable potato yield with Rhizophagus irregularis DAOM 197198 inoculation, making it profitable under field conditions. Contradictorily, in native grassland soils with healthy AMF communities, commercial AMF products were mostly ineffective and sometimes reduced biomass and fungal root colonization, indicating potential disruption of plant–fungal symbiosis (Duell et al., 2022). This underscores the importance of additional research to identify the factors contributing to varying results in AMF effectiveness.
The success of commercial AMF formulants in field soil depends on factors like complex interactions with native soil microbes, soil properties (soil texture, pH, organic matter, nutrients, and water retention), environmental conditions, crop types, location, topography, anthropogenic activities, and limited knowledge among end-users about proper application. Additionally, some studies advocate for single inoculation (Li et al., 2025), while others suggest that using diverse AMF communities may yield better results in the field (Madawala, 2021). Loose soils like sand exhibit low biological activity and AMF populations, while compacted soils like clay hinder root penetration and AMF symbiosis (Aziz and Sylvia, 1992; Camel et al., 1991). Soil pH plays a crucial role in composition of rhizosphere microorganisms, including AMF. Neutral soils (pH 6.5) support AMF diversity and promotes AMF growth, while acidic soils (pH < 4.5) reduce spore numbers and activity (Tahat and Sijam, 2012; Guo et al., 2012). Additionally, a negative correlation has been observed between root colonization and organic matter or phosphorus content in the soil. Climatic factors, such as temperature and rainfall, have more variable impacts on AMF than elevated CO2 levels (Bennett and Classen, 2020). AMF species have specific temperature requirements, with extreme temperatures reducing their population. Optimal temperatures for AMF activity align with those of plant vegetation, but different AMF species exhibit varying temperature preferences for spore germination, hyphal infectivity, and sporulation (Lekberg and Koide, 2008). AMF from tropical regions is more resilient to high storage temperatures compared to those from temperate climates (Al-Karaki et al., 2003). Light influences mycorrhizal activity indirectly by regulating photosynthesis, which provides carbohydrates to the roots (Saia et al., 2015). High light intensity enhances root colonization and spore production, while low light can disrupt the nutrient balance and reduce root colonization (Lahrmann et al., 2013). The mycorrhization efficiency fluctuates in annual and winter crops in response to the seasonal changes. Topography also affects the AMF spore populations, linked to nutrient content and water migration (Oehl et al., 2004). AMF species richness is higher in grasslands than in croplands, with species richness increasing with altitude in croplands (Oehl et al., 2017). The distribution of AMF spores is concentrated in the top 15 cm of soil, with populations declining significantly below 30 cm and generally absent below 70 cm (Oehl et al., 2004). However, symbiotic systems can still be present deeper in barren and air-drained soils (Guo et al., 2012). Water availability influences AMF colonization, with excessive water adversely affecting AMF due to a lack of oxygen. AMF spores are seldom found in soils that are periodically flooded (Solaiman and Hirata, 1996). Water deficit, however, leads to smaller biomass losses in mycorrhizal plants compared to non-mycorrhizal ones, along with higher photosynthetic activity and nitrogen assimilation, especially in plants with dual symbiosis (Rhizobium sp. + AMF). Agricultural practices, such as mechanical cultivation and tilling, can damage AMF spores, disrupting mycorrhizal networks and reducing root colonization potential. Frequent cultivation practices that compress the topsoil can lead to a reduction in AMF colonization of plant roots. The season significantly influences AMF spore density and root colonization, with higher spore densities and colonization rates seen in summer, and lower levels during the winter (Sivakumar, 2012). The efficiency of AMF inoculants is also highly dependent on competition with indigenous strains (Jefwa et al., 2010; Tarbell and Koske, 2007). The lack of the optimal factors mentioned above can lead to reduced effectiveness in AMF performance.
While direct comparisons between crop productivity from AMF inoculation and synthetic fertilizers are limited, some studies suggest that AMF can reduce the reliance on chemical fertilizers. One study showed that the combination of AMF and Bacillus sp. formed an effective microbial consortium that significantly enhanced wheat biofortification, grain yield, and soil fertility compared to chemical fertilizers (Yadav et al., 2021). Another study demonstrated that Funneliformis mosseae and Bacillus sonorensis had synergistic effects on plant growth, shoot dry weight, fruit yield, and nutrient content in Chilly. Their large-scale field trial showed that inoculation allowed a 50% reduction in NPK fertilizer without negatively impacting growth, improving soil enzyme activity and organic carbon (Thilagar et al., 2015). Similarly, AMF inoculation improved root colonization and corn yield, with these effects negatively correlated with phosphorus fertilization. The results suggested that phosphorus levels influence native AMF community composition, and that yield benefits from AMF are most prominent when root colonization is low and AMF communities are underdeveloped, providing a potential advantage over chemical fertilizers in such conditions (Bender et al., 2018). Another study found that oil palm seedlings inoculated with AMF responded better to a 500 mg polybag−1 fertilizer dose, while those without AMF required 1000 mg polybag−1, indicating that AMF reduced the necessary fertilizer by 50% (Rini et al., 2022). Furthermore, AMF inoculation with chemical fertilizers improved plant height, dry biomass, total yield, and the number of fruits per plant compared to those solely fertilized with chemicals (Ziane et al., 2021). Mycorrhizal plants with 50% fertilization showed significantly higher fruit mass and organoleptic qualities compared to non-inoculated controls and treatments with varying chemical fertilizer doses (0%, 25%, 75%, 100%). Inoculating with mycorrhizal fungi in the field can reduce chemical fertilizer by 50% without yield loss, while improving fruit quality (Trejo et al., 2021). For commercial AMF inoculants to be adopted by farmers and end-users, they need to outperform chemical fertilizers in both crop yield and cost efficiency.
Farmers often lack awareness and knowledge about the benefits due to limited access to information, socio-economic barriers, and insufficient resources. The other factors include inconsistent performance under varying environmental conditions, limited understanding of their benefits compared to traditional fertilizers, and the need for proper management to optimize their effectiveness. To increase AMF adoption among end-users, it is crucial to focus on effective education and outreach. Organizing training workshops and hands-on demonstrations can help farmers understand AMF’s benefits. Strengthening agricultural extension services will ensure that farmers receive guidance on best practices. Farmer-to-farmer networks can also foster peer learning, allowing early adopters to share their experiences. Additionally, collaborative research and local field trials will showcase AMF’s practical benefits, helping build confidence among farmers to adopt these practices.
Ethical concerns arise from using genetically modified or non-native species. Existing native soil populations may hinder the effectiveness of introduced microbial inoculants. Continuous research, development, and collaboration among scientists, farmers, and policymakers are necessary to address these challenges and advance sustainable agriculture.
The mycorrhizae-based bioformulations are environmentally friendly and sustainable. The commercialization of AMF inoculants has seen a significant advancement, including improvements in production methods, strain selection, and bioformulation strategies with enhanced stability, efficacy, and scalability of AMF-based products.
The market faces several challenges that may hinder its growth. High production costs limit large-scale adoption, necessitating cost reductions for global accessibility. Despite being time-consuming and expensive, thorough studies should be integrated into the strain acquisition process to support registration. Optimizing and controlling production, along with field validation, are essential for ensuring the effectiveness of microbial consortia. Regular feedback from agronomic technicians can help identify strengths and areas for improvement. The presence of counterfeit and substandard products, especially in regions with weak regulations, undermine consumer trust and slows market growth. Performance inconsistencies across different environments, limited knowledge of optimal application methods, and competition with native soil microbes further complicate the reliable benefits of AMF inoculation. Additionally, a major barrier is the lack of farmer awareness regarding biofertilizers, driven by restricted access to information, resources, and socio-economic constraints, limiting widespread adoption. Ensuring genetic stability, quality control, and regulatory consistency remains a key environmental challenge. The potential ecological risks posed by non-native AMF strains require strict biosafety assessments and standardized evaluation methods. Overcoming these obstacles is crucial for the expansion of the market.
Companies must prioritize high-quality production, ensuring superior microbial strains, optimized processes, and effective consortia, while maintaining strict quality control to meet farmers’ needs. Developing improved biofertilizer formulations is crucial for enhancing microbial stability, increasing inoculation potential, and sustaining long-term activity in the soil. To overcome current challenges, further research should focus on optimizing inoculant formulations, refining field management strategies, and improving farmer awareness of their benefits. New technologies like whole genome sequencing (WGS) or next-generation sequencing (NGS), offer valuable insights into AMF interactions with native microbes and aid in screening beneficial microbial candidates. Additionally, classifying diverse AMF species based on host and environmental preferences can help define the most suitable inocula for various crops and climatic conditions. In crops where inoculum compatibility with the host is uncertain, commercial inoculants should prioritize generalist AMF species.
With ongoing advancements, AMF inoculants can contribute significantly to sustainable and cost-effective agriculture, particularly in tropical regions facing high fertilizer costs, environmental risks, and climate change impacts. Strengthening collaboration between researchers and companies, implementing best practices, and improving commercial inoculum functionality will be key to advancing the AMF market and ensuring its long-term success.
Despite the existing challenges, the future of mycorrhizae-based bioformulations appears promising, with increasing global focus on environmental sustainability driving demand. The mycorrhizae-based biofertilizer market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 14.3%, reaching USD 1.087 billion by 2027. This expansion is supported by government and organizational initiatives that promote sustainable farming through stronger regulations and incentives for biofertilizer adoption.
Ongoing advancements in research and technology will enhance the efficacy, shelf life, and affordability of AMF inoculants, making them more accessible to farmers worldwide. Growing interest from agricultural stakeholders highlights their potential to improve soil health, crop productivity, and overall sustainability. With continued efforts to address existing barriers and improve product quality, mycorrhizae-based bioformulations are poised for significant growth, contributing to a more resilient and eco-friendly agricultural future.
MG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft. SC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing. SB: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
MG and SC were employed by Symbiotic Sciences Pvt. Ltd. SB was employed by ATGC Biotech Pvt. Ltd.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Aamir M., Rai K. K., Zehra A., Dubey M. K., Kumar S., Shukla V., et al. (2020). “Microbial bioformulation-based plant biostimulants: a plausible approach toward next generation of sustainable agriculture,” in Microbial Endophytes Functional Biology and Applications (India: Woodhead Publishing), 195–225. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-819654-0.00008-9
Adholeya A., Mukherjee G. (2017). WO2019003240A1 - A novel bioreactor for mass production of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi - Google Patents. Available online at: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2019003240A1/en.
Adholeya A., Tiwari P., Singh R. (2005). “Large-Scale inoculum production of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on root organs and inoculation strategies,” in Soil biology (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer), 315–338. doi: 10.1007/3-540-27331-x_17 (Accessed December 2, 2024).
Agnolucci M., Battini F., Cristani C., Giovannetti M. (2015). Diverse bacterial communities are recruited on spores of different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal isolates. Biol. Fertility Soils 51, 379–389. doi: 10.1007/s00374-014-0989-5
Agricultural Microbials Market Size, Share | Global Report [2032] (2024). Available online at: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/industry-reports/agricultural-microbial-market-100412.
Ahammed G. J., Hajiboland R. (2024). Introduction to arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and higher plant symbiosis: characteristic features, functions, and applications. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Higher Plants (Singapore: Springer), 1–17. doi: 10.1007/978-981-99-8220-2_1
Ali O. (2025). Nanotechnology in agriculture (AZoNano). Available at: https://www.azonano.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=3141:~:text=Potential%20Challenges%20and%20Need%20for,and%20to%20prevent%20unintended%20consequences.
Al-Karaki G., McMichael B., Zak J. (2003). Field response of wheat to arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and drought stress. Mycorrhiza 14, 263–269. doi: 10.1007/s00572-003-0265-2
Alladi A., Kala K. S., Udayasankar A., Thakur K. (2017). Influence of biofertilizers on uptake of NPK in soils and eggplant. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 6, 1259–1263. doi: 10.20546/ijcmas.2017.612.142
Allouzi M. M. A., Allouzi S. M. A., Keng Z. X., Supramaniam C. V., Singh A., Chong S. (2022). Liquid biofertilizers as a sustainable solution for agriculture. Heliyon 8, e12609. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12609
Alotaibi M. M., Aljuaid A., Alharbi M. M., Qumsani A. T., Alzuaibr F. M., Alsubeie M. S., et al. (2024). The effects of bio-fertilizer by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and phosphate solubilizing bacteria on the growth and productivity of barley under deficit of water irrigation conditions. Agronomy 14, 1973. doi: 10.3390/agronomy14091973
Amor D. R., Ratzke C., Gore J. (2020). Transient invaders can induce shifts between alternative stable states of microbial communities. Sci. Adv. 6. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aay8676
Anand K., Pandey G. K., Kaur T., Pericak O., Olson C., Mohan R., et al. (2022). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi as a potential biofertilizers for agricultural sustainability. J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol., 90–107. doi: 10.7324/jabb.2022.10s111
Angelard C., Colard A., Niculita-Hirzel H., Croll D., Sanders I. R. (2010). Segregation in a mycorrhizal fungus alters rice growth and Symbiosis-Specific gene transcription. Curr. Biol. 20, 1216–1221. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.05.031
Artursson V., Finlay R. D., Jansson J. K. (2005). Interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and bacteria and their potential for stimulating plant growth. Environ. Microbiol. 8, 1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00942.x
Azimi R., Heshmati G. A., Farzam M., Goldani M. (2019). Effects of mycorrhiza, zeolite and superabsorbent on growth and primary establishment of agropyron desertorum in mining field (Case study: mashhad′s shargh cement factory, Iran). J. Rangeland Sci. 9, 172–183.
Aziz T., Sylvia D. M. (1992). Mycorrhizal amelioration of the detrimental effect of biodune on plant growth. Proc. Soil Crop Sci. Soc. Florida 51, 20–23.
Bagyaraj D. J., Menge J. A. (1978). Interaction between a VA mycorrhiza and azotobacter and their effects on rhizosphere microflora and plant growth. New Phytol. 80, 567–573. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.1978.tb01588.x
Bairwa P., Kumar N., Devra V., Abd-Elsalam K. (2023). Nano-Biofertilizers Synthesis and applications in agroecosystems. Agrochemicals 2, 118–134. doi: 10.3390/agrochemicals2010009
Bannar-Martin K. H., Kremer C. T., Ernest S. M., Leibold M. A., Auge H., Chase J., et al. (2017). Integrating community assembly and biodiversity to better understand ecosystem function: the Community Assembly and the Functioning of Ecosystems (CAFE) approach. Ecol. Lett. 21, 167–180. doi: 10.1111/ele.12895
Barazetti A. R., Simionato A. S., Navarro M. O. P., Santos I. M. O. D., Modolon F., De Lima Andreata M. F., et al. (2019). Formulations of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculum applied to soybean and corn plants under controlled and field conditions. Appl. Soil Ecol. 142, 25–33. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.05.015
Bargaz A., Lyamlouli K., Chtouki M., Zeroual Y., Dhiba D. (2018). Soil microbial resources for improving fertilizers efficiency in an integrated plant nutrient management system. Front. Microbiol. 9. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01606
Barros-Rodríguez A., Rangseekaew P., Lasudee K., Pathom-Aree W., Manzanera M. (2020). Regulatory risks associated with bacteria as biostimulants and biofertilizers in the frame of the European Regulation (EU) 2019/1009. Sci. Total Environ. 740, 140239. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140239
Bashan Y., De-Bashan L. E., Prabhu S. R., Hernandez J. (2013). Advances in plant growth-promoting bacterial inoculant technology: formulations and practical perspectives, (1998–2013). Plant Soil 378, 1–33. doi: 10.1007/s11104-013-1956-x
Bashan Y., Hernandez J., Leyva L., Bacilio M. (2002). Alginate microbeads as inoculant carriers for plant growth-promoting bacteria. Biol. Fertility Soils 35, 359–368. doi: 10.1007/s00374-002-0481-5
Basiru S., Hijri M. (2022). The potential applications of commercial arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal inoculants and their ecological consequences. Microorganisms 10, 1897. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10101897
Bauer J. T., Kleczewski N. M., Bever J. D., Clay K., Reynolds H. L. (2012). Nitrogen-fixing bacteria, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, and the productivity and structure of prairie grassland communities. Oecologia 170, 1089–1098. doi: 10.1007/s00442-012-2363-3
Begum N., Qin C., Ahanger M. A., Raza S., Khan M. I., Ashraf M., et al. (2019). Role of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in plant Growth Regulation: Implications in abiotic stress Tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01068
Bejarano A., Puopolo G. (2020). Bioformulation of microbial biocontrol agents for a sustainable agriculture. Prog. Biol. control, 275–293. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-53238-3_16
Benami M., Isack Y., Grotsky D., Levy D., Kofman Y. (2020). The economic potential of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in agriculture. Grand challenges Biol. Biotechnol., 239–279. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-29541-7_9
Bender S. F., Schlaeppi K., Held A., Van Der Heijden M. G. (2018). Establishment success and crop growth effects of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus inoculated into Swiss corn fields. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 273, 13–24. doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2018.12.003
Bennett A. E., Classen A. T. (2020). Climate change influences mycorrhizal fungal–plant interactions, but conclusions are limited by geographical study bias. Ecology 101. doi: 10.1002/ecy.2978
Berdeja M. P., Reynolds N. K., Pawlowska T., Vanden Heuvel J. E. (2025). Commercial bioinoculants improve colonization but do not alter the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community of greenhouse-grown grapevine roots. Environ. Microbiome 20. doi: 10.1186/s40793-025-00676-8
Berninger T., López Ó.G., Bejarano A., Preininger C., Sessitsch A. (2017). Maintenance and assessment of cell viability in formulation of non-sporulating bacterial inoculants. Microbial Biotechnol. 11, 277–301. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.12880
Berruti A., Lumini E., Balestrini R., Bianciotto V. (2016). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi as natural biofertilizers: let’s benefit from past successes. Front. Microbiol. 6. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01559
Bharadwaj D. P., Alström S., Lundquist P. (2011). Interactions among Glomus irregulare, arbuscular mycorrhizal spore-associated bacteria, and plant pathogens under in vitro conditions. Mycorrhiza 22, 437–447. doi: 10.1007/s00572-011-0418-7
Bianciotto V., Minerdi D., Perotto S., Bonfante P. (1996). Cellular interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and rhizosphere bacteria. PROTOPLASMA 193, 123–131. doi: 10.1007/bf01276640
Brar S. K., Verma M., Tyagi R., Valéro J. (2005). Recent advances in downstream processing and formulations of Bacillus thuringiensis based biopesticides. Process Biochem. 41, 323–342. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2005.07.015
Brucker E., Spohn M. (2019). Formation of soil phosphorus fractions along a climate and vegetation gradient in the Coastal Cordillera of Chile. CATENA 180, 203–211. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2019.04.022
Brundrett M. C., Tedersoo L. (2018). Evolutionary history of mycorrhizal symbioses and global host plant diversity. New Phytol. 220, 1108–1115. doi: 10.1111/nph.14976
Budi S. W., Bakhtiar Y., May N. L. (2012). Bacteria Associated with Arbuscula Mycorrhizal Spores Gigaspora margarita and Their Potential for Stimulating Root Mycorrhizal Colonization and Neem (Melia azedarach Linn) Seedling Growth. Microbiol. Indonesia 6, 180–188. doi: 10.5454/mi.6.4.6
Calderon R. B., Dangi S. R. (2024). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobium improve nutrient uptake and microbial diversity relative to Dryland Site-Specific soil conditions. Microorganisms 12, 667. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12040667
Camel S. B., Franson R. L., Brown M. S., Bethlenfalvay G. J., Reyes-Solis M. G., Ferrera-Cerrato R. (1991). Growth of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal mycelium through bulk soil. Soil Sci. Soc. America J. 55, 389–393. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1991.03615995005500020016x
Campaña J. M., Arias M. (2020). Nanofibers as a delivery system for arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. ACS Appl. Polymer Materials 2, 5033–5038. doi: 10.1021/acsapm.0c00874
Canarini A., Kaiser C., Merchant A., Richter A., Wanek W. (2019). Root exudation of primary metabolites: Mechanisms and their roles in plant responses to environmental stimuli. Front. Plant Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00157
Cardenas C. I. C., Molina L. X. Z., Cancino G. S., De Los Santos Villalobos S., Anaya E. R., Díaz I. F. C., et al. (2021). Utilización de microorganismos para una agricultura sostenible en México: consideraciones y retos. Rev. Mexicana Cienc. Agrícolas 12, 899–913. doi: 10.29312/remexca.v12i5.2905
Cavagnaro T. R., Bender S. F., Asghari H. R., Van Der Heijden M. G. (2015). The role of arbuscular mycorrhizas in reducing soil nutrient loss. Trends Plant Sci. 20, 283–290. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2015.03.004
CCS Fertilizzanti Micosat F® (2022). Home - micosat F® | CCS. Micosat F® | CCS. Available online at: https://www.micosat.it/ (Accessed December 6, 2024).
Chalk P., Souza R., Urquiaga S., Alves B., Boddey R. (2006). The role of arbuscular mycorrhiza in legume symbiotic performance. Soil Biol. Biochem. 38, 2944–2951. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.05.005
Chaudhary A., Chaudhary P., Fayssal S. A., Singh S., Jaiswal D. K., Tripathi V., et al. (2024). Exploring beneficial microbes and their multifaceted applications: An overview. Microbial Inoculants 1–28. doi: 10.1007/978-981-97-0633-4_1
Chaudhary T., Dixit M., Gera R., Shukla A. K., Prakash A., Gupta G., et al. (2020). Techniques for improving formulations of bioinoculants. 3 Biotech. 10. doi: 10.1007/s13205-020-02182-9
Coelho I. R., Pedone-Bonfim M. V., Silva F. S., Maia L. C. (2014). Optimization of the production of mycorrhizal inoculum on substrate with organic fertilizer. Braz. J. Microbiol. 45, 1173–1178. doi: 10.1590/s1517-83822014000400007
Colard A., Angelard C., Sanders I. R. (2011). Genetic exchange in an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus result in increased rice growth and altered Mycorrhiza-Specific gene transcription. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 6510–6515. doi: 10.1128/aem.05696-11
Colla G., Hoagland L., Ruzzi M., Cardarelli M., Bonini P., Canaguier R., et al. (2017). Biostimulant action of protein hydrolysates: unraveling their effects on plant physiology and microbiome. Front. Plant Sci. 8. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.02202
Connell J. H., Slatyer R. O. (1977). Mechanisms of succession in natural communities and their role in community stability and organization. Am. Nat. 111, 1119–1144. doi: 10.1086/283241
Corkidi L., Allen E. B., Merhaut D., Allen M. F., Downer J., Bohn J., et al. (2004). Assessing the infectivity of commercial mycorrhizal inoculants in plant nursery conditions. J. Environ. Horticulture 22, 149–154. doi: 10.24266/0738-2898-22.3.149
Cortivo C. D., Barion G., Visioli G., Mattarozzi M., Mosca G., Vamerali T. (2017). Increased root growth and nitrogen accumulation in common wheat following PGPR inoculation: Assessment of plant-microbe interactions by ESEM. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 247, 396–408. doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2017.07.006
Cruz A., Ishii T. (2011). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus spores host bacteria and their biofilm efficient in nutrient biodynamics and soil-borne plant pathogen suppression. Nat. Precedings. doi: 10.1038/npre.2011.5544.1
Das P. (2016). The shocking tale of India’s “Cancer Train” | Business Insider India. Business Insider.
Das S. (2023). Nano-biofertilizer for sustainable agriculture. Asia Pacific Biofertilizers and Biopesticides Information Platform. doi: 10.56669/cdma8114
Das H., Devi N. S., Venu N., Borah A. (2023). “Chemical Fertilizer and its Effects on the Soil Environment,” in Research and review in agriculture sciences, vol. 7. (Bright Sky Publications), 31–51. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/372626886_Chemical_Fertilizer_and_its_Effects_on_the_Soil_Environment.
Declerck S., D’or D., Cranenbrouck S., Boulengé L. (2001). Modelling the sporulation dynamics of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in monoxenic culture. Mycorrhiza 11, 225–230. doi: 10.1007/s005720100124
Dewir Y. H., Habib M. M., Alaizari A. A., Malik J. A., Al-Ali A. M., Al-Qarawi A. A., et al. (2023). Promising application of automated liquid culture system and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for Large-Scale micropropagation of red dragon fruit. Plants 12, 1037. doi: 10.3390/plants12051037
Díaz-Urbano M., Goicoechea N., Velasco P., Poveda J. (2023). Development of agricultural bio-inoculants based on mycorrhizal fungi and endophytic filamentous fungi: Co-inoculants for improve plant-physiological responses in sustainable agriculture. Biol. Control 182, 105223. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2023.105223
Drigo B., Pijl A. S., Duyts H., Kielak A. M., Gamper H. A., Houtekamer M. J., et al. (2010). Shifting carbon flow from roots into associated microbial communities in response to elevated atmospheric CO 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 107, 10938–10942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0912421107
Dubey K. K., Kumar D., Kumar P., Haque S., Jawed A. (2013). Evaluation of Packed-Bed reactor and continuous stirred tank reactor for the production of colchicine derivatives. ISRN Chem. Eng. 2013, 1–6. doi: 10.1155/2013/865618
Duell E. B., Cobb A. B., Wilson G. W. T. (2022). Effects of commercial arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculants on plant productivity and Intra-Radical Colonization in Native Grassland: Unintentional De-Coupling of a symbiosis? Plants 11, 2276. doi: 10.3390/plants11172276
El-Sharoud W. (2019). Book Review: Harikesh Singh, Vijai Gupta and Sudisha Jogaiah, New and future developments in microbial biotechnology and bioengineering: microbial genes biochemistry and applications. Sci. Prog. 102, 379. doi: 10.1177/0036850419879612b
Etesami H., Glick B. R. (2023). Exploring the potential: Can mycorrhizal fungi and hyphosphere silicate-solubilizing bacteria synergistically alleviate cadmium stress in plants? Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 6, 100158. doi: 10.1016/j.crbiot.2023.100158
EU Regulation. (2019). 1009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 5 June 2019 laying down rules on the making available on the market of EU fertilising products and amending Regulations (EC) No 1069/2009 and (EC) No 1107/2009 and repealing Regulation (EC) No 2003/2003. 2019. Journal of European Union 170, 1–114. Available online at: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2019/1009/oj.
Evologic Technologies GmbH - Wien, Austria (2025). Available online at: https://www.bionity.com/en/companies/1035666/evologic-technologies-gmbh.html (Accessed February 01, 2025).
Ezawa T., Smith S. E., Smith F. A. (2002). P Metabolism and transport in AM fungi. Plant Soil 244, 221–230. doi: 10.1023/a:1020258325010
Fall A. F., Nakabonge G., Ssekandi J., Founoune-Mboup H., Apori S. O., Ndiaye A., et al. (2022). Roles of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on soil fertility: contribution in the improvement of physical, chemical, and biological properties of the soil. Front. Fungal Biol. 3. doi: 10.3389/ffunb.2022.723892
Fatima R., Basharat U., Safdar A., Haidri I., Fatima A., Mahmood A., et al. (2024). Availability of phosphorus to the soil, their significance for roots of plants and environment. EPH - Int. J. Agric. Environ. Res., 21–34. doi: 10.53555/eijaer.v10i1.97
Faye A., Dalpé Y., Ndung’u-Magiroi K., Jefwa J., Ndoye I., Diouf M., et al. (2013). Evaluation of commercial arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculants. Can. J. Plant Sci. 93, 1201–1208. doi: 10.4141/cjps2013-326
Faye A., Krasova-Wade T., Thiao M., Thioulouse J., Neyra M., Prin Y., et al. (2009). Controlled ectomycorrhization of an exotic legume tree species Acacia holosericea affects the structure of root nodule bacteria community and their symbiotic effectiveness on Faidherbia albida, a native Sahelian Acacia. Soil Biol. Biochem. 41, 1245–1252. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.03.004
Feng Y., Cui X., He S., Dong G., Chen M., Wang J., et al. (2013). The role of metal nanoparticles in influencing arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi effects on plant growth. Environmental Science & Technology. 47(16), 9496–9504. doi: 10.1021/es402109n
Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations. (2024). Land Statistics 2001–2022. In FAOSTAT Analytical Briefs. Rome, Italy: FAO doi: 10.4060/cd1484en
Fortin J. A., St-Arnaud M., Hamel C., Chavarie C., Jolicœur M., De Montreal U. (1993). US5554530A - Aseptic in vitro endomycorrhizal spore mass production - Google Patents. Available online at: https://patents.google.com/patent/US5554530A/en.
Franzini V. I., Azcón R., Mendes F. L., Aroca R. (2009). Interactions between Glomus species and Rhizobium strains affect the nutritional physiology of drought-stressed legume hosts. J. Plant Physiol. 167, 614–619. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2009.11.010
Gahan J., Schmalenberger A. (2015). Arbuscular mycorrhizal hyphae in grassland select for a diverse and abundant hyphospheric bacterial community involved in sulfonate desulfurization. Appl. Soil Ecol. 89, 113–121. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2014.12.008
Gai J. P., Feng G., Christie P., Li X. L. (2006). Screening of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for symbiotic efficiency with sweet potato. J. Plant Nutr. 29, 1085–1094. doi: 10.1080/01904160600689225
García A. H. (2011). Anhydrobiosis in bacteria: From physiology to applications. J. Biosci. 36, 939–950. doi: 10.1007/s12038-011-9107-0
Ghorui M., Chowdhury S., Balu P., Burla S. (2024). Arbuscular Mycorrhizal inoculants and its regulatory landscape. Heliyon 10, e30359. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30359
Ghorui M., Chowdhury S., Das K., Sunar K., Prakash B. (2023a). Optimizing factors for large-scale production of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi consortia using root organ cultures. J. Biol. Methods 10, 1. doi: 10.14440/jbm.2023.410
Ghorui M., Chowdhury S., Jagadeesan M., Preethi N., Das K., Sunar K., et al. (2023b). Comprehensive evaluation of arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculants: A laboratory and greenhouse study. Oxidation Commun. 46, 716–737. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.4653825
Gneiding K., Frodl R., Funke G. (2008). Identities of microbacterium spp. Encountered in human clinical specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 46, 3646–3652. doi: 10.1128/jcm.01202-08
Gopal S., Baby A. (2016). Enhanced shelf-life of Azospirillum and PSB through addition of chemical additives in liquid formulations. Int. J. Science Environ. Technol. 5(4), 2023–2029.
Gosling P., Jones J., Bending G. D. (2015). Evidence for functional redundancy in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and implications for agroecosystem management. Mycorrhiza 26, 77–83. doi: 10.1007/s00572-015-0651-6
Guarnizo Á.L., Navarro-Ródenas A., Calvo-Polanco M., Marqués-Gálvez J. E., Morte A. (2023). A mycorrhizal helper bacterium alleviates drought stress in mycorrhizal Helianthemum almeriense plants by regulating water relations and plant hormones. Environ. Exp. Bot. 207, 105228. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2023.105228
Guimarães G. S., Rondina A. B. L., Santos M. S., Nogueira M. A., Hungria M. (2022). Pointing out opportunities to increase grassland pastures productivity via microbial inoculants: attending the society’s demands for meat production with sustainability. Agronomy 12, 1748. doi: 10.3390/agronomy12081748
Guo N. H. (2012). Spatial distribution of arbuscular mycorrhiza and glomalin in the rhizosphere of Caragana korshinskii Kom. in the Otindag sandy land, China. African Journal of Microbiology Research 6(28). doi: 10.5897/ajmr11.1560
Hack C. M., Porta M., Schäufele R., Grimoldi A. A. (2018). Arbuscular mycorrhiza mediated effects on growth, mineral nutrition and biological nitrogen fixation of Melilotus alba Med. in a subtropical grassland soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 134, 38–44. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2018.10.008
Halmer P. (2008). Seed technology and seed treatment. Acta Hortic. 771, 17–26. doi: 10.17660/actahortic.2008.771.1
Hameeda B., Reddy Y. H. K., Rupela O., Kumar G., Reddy G. (2006). Effect of carbon substrates on rock phosphate solubilization by bacteria from composts and macrofauna. Curr. Microbiol. 53, 298–302. doi: 10.1007/s00284-006-0004-y
Hammond L. L. (1977). Effectiveness of phosphate rocks in Colombian soils as measured by crop response and soil phosphorus levels (Department of Crop and Soil Sciences). Available at: https://books.google.co.in/books/about/Effectiveness_of_Phosphate_Rocks_in_Colo.html?id=OP5tIjheUysC&redir_esc=y.
Hartley E., Gemell L. G., Herridge D. F. (2004). Lime pelleting inoculated serradella (Ornithopus spp.) increases nodulation and yield. Soil Biol. Biochem. 36, 1289–1294. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.04.010
Hawkins H., George E. (1997). Hydroponic culture of the mycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae with linum usitatissimum L., Sorghum bicolor L. and Triticum aestivum l. Plant Soil 196, 143–149. doi: 10.1023/a:1004271417469
He W., Fan X., Zhou Z., Zhang H., Gao X., Song F., et al. (2019). The effect of Rhizophagus irregularis on salt stress tolerance of Elaeagnus angustifolia roots. J. Forestry Res. 31, 2063–2073. doi: 10.1007/s11676-019-01053-1
Herrmann L., Lesueur D. (2013). Challenges of formulation and quality of biofertilizers for successful inoculation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 97, 8859–8873. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-5228-8
Hijri M. (2015). Analysis of a large dataset of mycorrhiza inoculation field trials on potato shows highly significant increases in yield. Mycorrhiza 26, 209–214. doi: 10.1007/s00572-015-0661-4
Hildebrandt U., Ouziad F., Marner F., Bothe H. (2005). The bacterium Paenibacillus Validus stimulates growth of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus intraradices up to the formation of fertile spores. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 254, 258–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2005.00027.x
Hodge A. (2014). Interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and organic material substrates. Adv. Appl. Microbiol., 47–99. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-800259-9.00002-0
Horn H. S. (1974). The ecology of secondary succession. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Systematics 5, 25–37. doi: 10.1146/annurev.es.05.110174.000325
Hu B., Hu S., Vymazal J., Chen Z. (2022). Application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for pharmaceuticals and personal care productions removal in constructed wetlands with different substrate. J. Cleaner Production 339, 130760. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130760
Iffis B., St-Arnaud M., Hijri M. (2014). Bacteria associated with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi within roots of plants growing in a soil highly contaminated with aliphatic and aromatic petroleum hydrocarbons. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 358, 44–54. doi: 10.1111/1574-6968.12533
IJdo M., Cranenbrouck S., Declerck S. (2010). Methods for large-scale production of AM fungi: past, present, and future. Mycorrhiza 21, 1–16. doi: 10.1007/s00572-010-0337-z
Jambhulkar P. P., Sharma P., Yadav R. (2016). “Delivery systems for introduction of microbial inoculants in the field,” in Microbial Inoculants in Sustainable Agricultural Productivity (India, New Delhi: Springer), 199–218. doi: 10.1007/978-81-322-2644-4_13
Jamkhande P. G., Ghule N. W., Bamer A. H., Kalaskar M. G. (2019). Metal nanoparticles synthesis: An overview on methods of preparation, advantages and disadvantages, and applications. J. Drug Delivery Sci. Technol. 53, 101174. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2019.101174
Jarstfer A. G., Farmer-Koppenol P., Sylvia D. M. (1998). Tissue magnesium and calcium affect arbuscular mycorrhiza development and fungal reproduction. Mycorrhiza 7, 237–242. doi: 10.1007/s005720050186
Jayasinghearachchi H., Seneviratne G. (2005). Fungal solubilization of rock phosphate is enhanced by forming fungal–rhizobial biofilms. Soil Biol. Biochem. 38, 405–408. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.06.004
Jefwa J., Vanlauwe B., Coyne D., Van Asten P., Gaidashova S., Rurangwa E., et al. (2010). Benefits and Potential use of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi (AMF) in Banana and Plantain (Musa spp.) systems in Africa. Acta Hortic. 879, 479–486. doi: 10.17660/actahortic.2010.879.52
Jiang H., Li S., Wang T., Chi X., Qi P., Chen G. (2021). Interaction between halotolerant phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (Providencia rettgeri strain TPM23) and rock phosphate improves soil biochemical properties and peanut growth in saline soil. Front. Microbiol. 12. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.777351
Jiang F., Zhang L., Zhou J., George T. S., Feng G. (2020). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi enhance mineralization of organic phosphorus by carrying bacteria along their extraradical hyphae. New Phytol. 230, 304–315. doi: 10.1111/nph.17081
John R. P., Tyagi R. D., Brar S. K., Prévost D. (2010). Development of emulsion from rhizobial fermented starch industry wastewater for application as Medicago sativa seed coat. Eng. Life Sci. 10, 248–256. doi: 10.1002/elsc.201000002
Jolicœur M., Williams R. D., Chavarie C., Fortin J. A., Archambault J. (1999). Production of Glomus intraradices propagules, an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus, in an airlift bioreactor. Biotechnol. Bioengineering 63, 224–232. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0290(19990420)63:2
Joshi D., Chandra R., Suyal D. C., Kumar S., Goel R. (2019). Impacts of Bioinoculants Pseudomonas jesenii MP1 and Rhodococcus qingshengii S10107 on Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) Yield and Soil Nitrogen Status. Pedosphere 29, 388–399. doi: 10.1016/s1002-0160(19)60807-6
Jote C. A. (2023). The impacts of using inorganic chemical fertilizers on the environment and human health. Organic Medicinal Chem. Int. J. 13. doi: 10.19080/OMCIJ.2023.13.555864
Kah M., Tufenkji N., White J. C. (2019). Nano-enabled strategies to enhance crop nutrition and protection. Nat. Nanotechnology 14, 532–540. doi: 10.1038/s41565-019-0439-5
Kamath A., Shukla A., Saiyed T., Bhatt S., Rathod H., Makwana V., et al. (2023). Bioinoculants: the agrarian avengers. Symbiosis 91, 151–166. doi: 10.1007/s13199-023-00953-5
Kardol P., Cornips N. J., Van Kempen M. M. L., Bakx-Schotman J. M. T., Van Der Putten W. H. (2007). Microbe-mediated Plant-Soil feedback causes historical contingency effects in plant community assembly. Ecol. Monogr. 77, 147–162. doi: 10.1890/06-0502
Kasanke S. A., Cheeke T. E., Moran J. J., Roley S. S. (2024). Tripartite interactions among free-living, N-fixing bacteria, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, and plants: Mutualistic benefits and community response to co-inoculation. Soil Sci. Soc. America J. 88, 1000–1013. doi: 10.1002/saj2.20679
Kavatagi P. K., Lakshman H. C. (2014). Interaction between AMF and Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria on two varieties of Solanum lycopersicum L. World Appl. Sci. J., 2054–2062.
Kennedy A. (1999). Bacterial diversity in agroecosystems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 74, 65–76. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8809(99)00030-4
Khan A., Singh A. V., Gautam S. S., Agarwal A., Punetha A., Upadhayay V. K., et al. (2023). Microbial bioformulation: a microbial assisted biostimulating fertilization technique for sustainable agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1270039
Kouadio A. N. M., Nandjui J., Krou S. M., Séry D. J., Nelson P. N., Zézé A. (2017). A native arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus inoculant outcompetes an exotic commercial species under two contrasting yam field conditions. Rhizosphere 4, 112–118. doi: 10.1016/j.rhisph.2017.10.001
Koziol L., McKenna T. P., Bever J. D. (2024). Meta-analysis reveals globally sourced commercial mycorrhizal inoculants fall short. New Phytol. doi: 10.1111/nph.20278
Kumar A., Dubey A. (2020). Rhizosphere microbiome: Engineering bacterial competitiveness for enhancing crop production. J. Advanced Res. 24, 337–352. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.04.014
Kumar P., Singh S., Pranaw K., Kumar S., Singh B., Poria V. (2022). Bioinoculants as mitigators of multiple stresses: A ray of hope for agriculture in the darkness of climate change. Heliyon 8, e11269. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11269
Lahrmann U., Ding Y., Banhara A., Rath M., Hajirezaei M. R., Döhlemann S., et al. (2013). Host-related metabolic cues affect colonization strategies of a root endophyte. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 110, 13965–13970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1301653110
Lalaymia I., Declerck S. (2020). The mycorrhizal Donor Plant (MDP) in vitro culture system for the efficient colonization of whole plants. Methods Mol. Biol., 19–31. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0603-2_2
Lamaizi S., Meddich A., Akensous F., Hafidi M. (2024). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi application: selected case studies corroborating sustainable drought mitigation and enhanced crop productivity. In Sustainable Agriculture under Drought Stress. (UK: Academic Press), 385–399. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-443-23956-4.00023-5
Larimer A. L., Clay K., Bever J. D. (2013). Synergism and context dependency of interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobia with a prairie legume. Ecology 95, 1045–1054. doi: 10.1890/13-0025.1
Ledermann R., Schulte C. C. M., Poole P. S. (2021). How Rhizobia adapt to the nodule environment. J. Bacteriology 203. doi: 10.1128/jb.00539-20
Lee Y., George E. (2005). Development of a nutrient film technique culture system for arbuscular mycorrhizal plants. HortScience 40, 378–380. doi: 10.21273/hortsci.40.2.378
Lekberg Y., Koide R. T. (2008). Effect of soil moisture and temperature during fallow on survival of contrasting isolates of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Botany 86, 1117–1124. doi: 10.1139/b08-077
Li Y., Tian X. (2012). Quorum sensing and bacterial social interactions in biofilms. Sensors 12, 2519–2538. doi: 10.3390/s120302519
Li X., Wu Y., Huang C., Rahman M. A., Argaman E., Xiao Y. (2025). Inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in the field promotes plant colonization rate and yield. Eur. J. Agron. 164, 127503. doi: 10.1016/j.eja.2024.127503
Linderman R. G. (2013). “Vesicular-Arbuscular mycorrhizae and soil microbial interactions,” in Mycorrhizae in Sustainable Agriculture (United States: ASA special publication), 45–70). doi: 10.2134/asaspecpub54.c3
Liu X., Hou C., Zhang J., Zeng X., Qiao S. (2014). Fermentation conditions influence the fatty acid composition of the membranes of Lactobacillus reuteri I5007 and its survival following freeze-drying. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 59, 398–403. doi: 10.1111/lam.12292
Liu X., Roux X. L., Salles J. F. (2022). The legacy of microbial inoculants in agroecosystems and potential for tackling climate change challenges. iScience 25, 103821. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.103821
Liu T., Zhang J., Wang T., Li Z., Liang H., Jiang C., et al. (2024). The novel Pseudomonas thivervalensis strain JI6 promotes growth and controls rusty root rot disease in Panax ginseng. Biol. Control 193, 105514. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2024.105514
Luo L., Zhao C., Wang E., Raza A., Yin C. (2022). Bacillus amyloliquefaciens as an excellent agent for biofertilizer and biocontrol in agriculture: An overview for its mechanisms. Microbiological Res. 259, 127016. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2022.127016
Madawala H. (2021). “Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi as biofertilizers: Current trends, challenges, and future prospects,” in Biofertilizers (India: Woodhead Publishing), 83–93. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-821667-5.00029-4
Magallon-Servín P., Antoun H., Taktek S., Bashan Y., De-Bashan L. (2019). The maize mycorrhizosphere as a source for isolation of arbuscular mycorrhizae-compatible phosphate rock-solubilizing bacteria. Plant Soil 451, 169–186. doi: 10.1007/s11104-019-04226-3
Mallon C. A., Roux X. L., Van Doorn G. S., Dini-Andreote F., Poly F., Salles J. F. (2018). The impact of failure: unsuccessful bacterial invasions steer the soil microbial community away from the invader’s niche. ISME J. 12, 728–741. doi: 10.1038/s41396-017-0003-y
Malusá E., Vassilev N. (2014). A contribution to set a legal framework for biofertilizers. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 98, 6599–6607. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-5828-y
Manceau A., Nagy K. L., Marcus M. A., Lanson M., Geoffroy N., Jacquet T., et al. (2008). Formation of metallic copper nanoparticles at the Soil–Root interface. Environ. Sci. Technol. 42, 1766–1772. doi: 10.1021/es072017o
Marchiol L. (2019). Nanofertilizers. An outlook of crop nutrition in the fourth agricultural revolution. Ital. J. Agron. 14, 183–190. doi: 10.4081/ija.2019.1367
Metwally R. A., Abdelhameed R. E. (2023). Co-application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and nano-ZnFe 2 O 4 improves primary metabolites, enzymes and NPK status of pea (Pisum sativum L.) plants. J. Plant Nutr. 47, 468–486. doi: 10.1080/01904167.2023.2280121
Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Japan. (2019). Soil Productivity Improvement Act. Available online at: http://www.maff.go.jp/e/index.html (Accessed November 22, 2024).
Mishra S., Sharma S., Vasudevan P. (2008). Comparative effect of biofertilizers on fodder production and quality in Guinea grass (Panicum maximum Jacq.). J. Sci. Food Agric. 88, 1667–1673. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.3267
Miyauchi M. Y. H., Lima D. S., Nogueira M. A., Lovato G. M., Murate L. S., Cruz M. F., et al. (2008). Interactions between diazotrophic bacteria and mycorrhizal fungus in maize genotypes. Scientia Agricola 65, 525–531. doi: 10.1590/s0103-90162008000500012
Mohammad A., Khan A. G., Kuek C. (2000). Improved aeroponic culture of inocula of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Mycorrhiza 9, 337–339. doi: 10.1007/s005720050278
Mohammad A., Mittra B. (2011). Effects of inoculation with stress-adapted arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus deserticola on growth of Solanum melogena L. and Sorghum Sudanese Staph. seedlings under salinity and heavy metal stress conditions. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 59, 173–183. doi: 10.1080/03650340.2011.610029
Mosse B., Thompson J. P. (1980). US4294037A - Production of mycorrhizal fungi - Google Patents. U.S. Patent and Trade Office. Available online at: https://patents.google.com/patent/US4294037A/en.
Mu P., Ding G., Zhang Y., Jin Q., Liu Z., Guan Y., et al. (2024). Interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and phosphate-soluble bacteria affect ginsenoside compositions by modulating the C:N:P stoichiometry in Panax ginseng. Front. Microbiol. 15. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1426440
Mummey D. L., Antunes P. M., Rillig M. C. (2009). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi pre-inoculant identity determines community composition in roots. Soil Biol. Biochem. 41, 1173–1179. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.02.027
Munkvold L., Kjøller R., Vestberg M., Rosendahl S., Jakobsen I. (2004). High functional diversity within species of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol. 164, 357–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01169.x
Muxika A., Etxabide A., Uranga J., Guerrero P., De La Caba K. (2017). Chitosan as a bioactive polymer: Processing, properties and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromolecules 105, 1358–1368. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.07.087
Muzammil S., Ashraf A., Siddique M. H., Aslam B., Rasul I., Abbas R., et al. (2023). A review on toxicity of nanomaterials in agriculture: Current scenario and future prospects. Sci. Prog. 106. doi: 10.1177/00368504231221672
Nacoon S., Jogloy S., Riddech N., Mongkolthanaruk W., Ekprasert J., Cooper J., et al. (2021). Combination of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and phosphate solubilizing bacteria on growth and production of Helianthus tuberosus under field condition. Sci. Rep. 11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86042-3
Nacoon S., Jogloy S., Riddech N., Mongkolthanaruk W., Kuyper T. W., Boonlue S. (2020). Interaction between phosphate solubilizing bacteria and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth promotion and tuber inulin content of helianthus tuberosus L. Sci. Rep. 10. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61846-x
Nadagouda M. G., Lakshman H. C. (2010). Microbial solubilization of P and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi use for yield and phosphate uptake in improvement of nodulation and yield of [Vicia Faba L.] [Journal-article. Int. J. Agric. Sci. 1–1, 319–321.
Nanjundappa A., Bagyaraj D. J., Saxena A. K., Kumar M., Chakdar H. (2019). Interaction between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and Bacillus spp. in soil enhancing growth of crop plants. Fungal Biol. Biotechnol. 6. doi: 10.1186/s40694-019-0086-5
Nannipieri P., Ascher J., Ceccherini M. T., Landi L., Pietramellara G., Renella G. (2003). Microbial diversity and soil functions. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 54, 655–670. doi: 10.1046/j.1351-0754.2003.0556.x
Naseer M., Zhu Y., Li F., Yang Y., Wang S., Xiong Y. (2021). Nano-enabled improvements of growth and colonization rate in wheat inoculated with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Environ. pollut. 295, 118724. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118724
Nasslahsen B., Prin Y., Ferhout H., Smouni A., Duponnois R. (2022). Mycorrhizae helper bacteria for managing the mycorrhizal soil infectivity. Front. Soil Sci. 2. doi: 10.3389/fsoil.2022.979246
Nevalainen H. (2020). “Grand challenges in fungal biotechnology,” in Grand challenges in biology and biotechnology. Switzerland: Springer Cham. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-29541-7
Oehl F., Laczko E., Oberholzer H., Jansa J., Egli S. (2017). Diversity and biogeography of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in agricultural soils. Biol. Fertility Soils 53, 777–797. doi: 10.1007/s00374-017-1217-x
Oehl F., Sieverding E., Ineichen K., Ris E., Boller T., Wiemken A. (2004). Community structure of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi at different soil depths in extensively and intensively managed agroecosystems. New Phytol. 165, 273–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01235.x
Okeke E. S., Ezeorba T. P. C., Mao G., Chen Y., Feng W., Wu X. (2021). Nano-enabled agrochemicals/materials: Potential human health impact, risk assessment, management strategies and future prospects. Environ. pollut. 295, 118722. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118722
Öpik M., Vanatoa A., Vanatoa E., Moora M., Davison J., Kalwij J. M., et al. (2010). The online database MaarjAM reveals global and ecosystemic distribution patterns in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (Glomeromycota). New Phytol. 188, 223–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03334.x
Ordoñez Y. M., Fernandez B. R., Lara L. S., Rodriguez A., Uribe-Vélez D., Sanders I. R. (2016). Bacteria with phosphate solubilizing capacity alter mycorrhizal fungal growth both inside and outside the root and in the presence of native microbial communities. PloS One 11, e0154438. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154438
Orru M., Übner M., Orru H. (2011). Chemical properties of peat in three peatlands with balneological potential in Estonia. Proc. Estonian Acad. Sci. Geology 60, 43. doi: 10.3176/earth.2011.1.04
Owen D., Williams A., Griffith G., Withers P. (2014). Use of commercial bio-inoculants to increase agricultural production through improved phosphrous acquisition. Appl. Soil Ecol. 86, 41–54. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2014.09.012
Papafotiou M., Kokotsakis C., Kavadia A., Ehaliotis C. (2021). The effect of inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) and substrate type on growth and flowering of Gardenia jasminoides. Acta Hortic. 1327, 509–514. doi: 10.17660/actahortic.2021.1327.67
Parween T., Bhandari P., Jan S., Mahmooduzzafar N., Fatma T., Raza S. K. (2017). “Role of bioinoculants as Plant Growth-Promoting microbes for Sustainable agriculture,” in Agriculturally Important Microbes for Sustainable Agriculture (Singapore: Springer), 183–206. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-5589-8_9
Patel D. K., Archana G., Kumar G. N. (2007). Variation in the nature of organic acid secretion and mineral phosphate solubilization by citrobacter sp. DHRSS in the presence of different sugars. Curr. Microbiol. 56, 168–174. doi: 10.1007/s00284-007-9053-0
Patil G. B., Lakshman H. C. (2011). Effect of co-inoculation of AM fungi and two beneficial microorganisms on growth and nutrient uptake of eleusine coracana gaertn. (Finger Millet). Asian J. Plant Sci. Res.
Pedrini S., Merritt D. J., Stevens J., Dixon K. (2016). Seed coating: science or marketing spin? Trends Plant Sci. 22, 106–116. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2016.11.002
Pereira S., Abreu D., Moreira H., Vega A., Castro P. (2020). Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) improve the growth and nutrient use efficiency in maize (Zea mays L.) under water deficit conditions. Heliyon 6, e05106. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05106
Phillips S. (2022). “The dangerous effects of chemical fertilizers,” in Msingi afrika magazine. Africa: Msingi Afrika Magazine. Available at: https://www.msingiafrikamagazine.com/2022/11/the-dangerous-effects-of-chemical-fertilizers/.
Poppeliers S. W., Sánchez-Gil J. J., De Jonge R. (2023). Microbes to support plant health: understanding bioinoculant success in complex conditions. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 73, 102286. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2023.102286
Power B., Liu X., Germaine K., Ryan D., Brazil D., Dowling D. (2011). Alginate beads as a storage, delivery and containment system for genetically modified PCB degrader and PCB biosensor derivatives of Pseudomonas fluorescens F113. J. Appl. Microbiol. 110, 1351–1358. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2011.04993.x
Primieri S., Magnoli S. M., Koffel T., Stürmer S. L., Bever J. D. (2021). Perennial, but not annual legumes synergistically benefit from infection with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobia: a meta-analysis. New Phytol. 233, 505–514. doi: 10.1111/nph.17787
Puri A., Adholeya A. (2013). A new system using Solanum tuberosum for the co-cultivation of Glomus intraradices and its potential for mass producing spores of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Symbiosis 59, 87–97. doi: 10.1007/s13199-012-0213-z
Püschel D., Kolaříková Z., Šmilauer P., Rydlová J. (2019). Survival and long-term infectivity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in peat-based substrates stored under different temperature regimes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 140, 98–107. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.04.020
Rahimzadeh S., Pirzad A. (2017). Microorganisms (AMF and PSB) interaction on linseed productivity under water-deficit condition. Int. J. Plant Production 11, 259–274. doi: 10.22069/ijpp.2017.3423
Rajput V. D., Singh A., Minkina T., Rawat S., Mandzhieva S., Sushkova S., et al. (2021). Nano-Enabled Products: challenges and opportunities for sustainable agriculture. Plants 10, 2727. doi: 10.3390/plants10122727
Rana K. L., Kour D., Yadav A. N., Yadav N., Saxena A. K. (2020). “Agriculturally important microbial biofilms: Biodiversity, ecological significances, and biotechnological applications,” in Current Research and Future Trends in Microbial Biofilms. India: Elsevier 221–265. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-444-64279-0.00016-5
Rawat P., Das S., Shankhdhar D., Shankhdhar S. C. (2020). Phosphate-Solubilizing microorganisms: mechanism and their role in phosphate solubilization and uptake. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 21, 49–68. doi: 10.1007/s42729-020-00342-7
Ray P., Lakshmanan V., Labbé J. L., Craven K. D. (2020). Microbe to Microbiome: A Paradigm shift in the application of microorganisms for Sustainable agriculture. Front. Microbiol. 11. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.622926
Reynolds P. L., Glanz J., Yang S., Hann C., Couture J., Grosholz E. (2017). Ghost of invasion past: legacy effects on community disassembly following eradication of an invasive ecosystem engineer. Ecosphere 8. doi: 10.1002/ecs2.1711
Riaz U., Murtaza G., Anum W., Samreen T., Sarfraz M., Nazir M. Z. (2020). “Plant Growth-Promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) as biofertilizers and biopesticides,” in Microbiota and Biofertilizers (Cham: Springer), 181–196. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-48771-3_11
Rini M. V., Yansyah M. P., Arif M. (2022). The application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi reduced the required dose of compound fertilizer for oil palm (Elaeis guineensis jacq.) in nursery. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 1012, 12011. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/1012/1/012011
Rocha I., Ma Y., Souza-Alonso P., Vosátka M., Freitas H., Oliveira R. S. (2019). Seed coating: a tool for delivering beneficial microbes to agricultural crops. Front. Plant Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01357
Rojas-Sánchez B., Guzmán-Guzmán P., Morales-Cedeño L. R., Del Carmen Orozco-Mosqueda M., Saucedo-Martínez B. C., Sánchez-Yáñez J. M., et al. (2022). Bioencapsulation of microbial inoculants: mechanisms, formulation types and application techniques. Appl. Biosci. 1, 198–220. doi: 10.3390/applbiosci1020013
Rowe H. I., Brown C. S., Claassen V. P. (2007). Comparisons of mycorrhizal responsiveness with field soil and commercial inoculum for six native montane species and bromus tectorum. Restor. Ecol. 15, 44–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-100x.2006.00188.x
Rúa M. A., Antoninka A., Antunes P. M., Chaudhary V. B., Gehring C., Lamit L. J., et al. (2016). Home-field advantage? evidence of local adaptation among plants, soil, and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi through meta-analysis. BMC Evolutionary Biol. 16. doi: 10.1186/s12862-016-0698-9
Rumble H., Gange A. C. (2017). Microbial inoculants as a soil remediation tool for extensive green roofs. Ecol. Eng. 102, 188–198. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.01.025
Saia S., Ruisi P., Fileccia V., Di Miceli G., Amato G., Martinelli F. (2015). Metabolomics suggests that soil inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi decreased free amino acid content in roots of durum wheat grown under N-limited, P-rich field conditions. PloS One 10, e0129591. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129591
Sakha M., Jefwa J., Mutua L., Egesa A. O. (2024). Most probable number bioassays and trap culture techniques are promising in estimating quantitative and qualitative arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Int. J. Bioresource Sci. 11. doi: 10.30954/2347-9655.01.2024.1
Salomon M. J., Watts-Williams S. J., McLaughlin M. J., Bücking H., Singh B. K., Hutter I., et al. (2022). Establishing a quality management framework for commercial inoculants containing arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. iScience 25, 104636. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104636
Sangwan S., Prasanna R. (2021). Mycorrhizae helper bacteria: Unlocking their potential as bioenhancers of Plant–Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal associations. Microbial Ecol. 84, 1–10. doi: 10.1007/s00248-021-01831-7
Santoyo G., Gamalero E., Glick B. R. (2021). Mycorrhizal-Bacterial amelioration of plant abiotic and biotic stress. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 5. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2021.672881
Saxena A. K., Rathi S. K., Tilak K. V. B. R. (1997). Differential effect of various endomycorrhizal fungi on nodulating ability of green gram by Bradyrhizobium sp. (Vigna) strain S24. Biol. Fertility Soils 24, 175–178. doi: 10.1007/s003740050227
Scheublin T. R., Sanders I. R., Keel C., Van Der Meer J. R. (2010). Characterization of microbial communities colonizing the hyphal surfaces of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. ISME J. 4, 752–763. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2010.5
Schisler D. A., Slininger P. J., Behle R. W., Jackson M. A. (2004). Formulation of bacillus spp. for biological control of plant diseases. Phytopathology 94, 1267–1271. doi: 10.1094/phyto.2004.94.11.1267
Schrey S. D., Hartmann A., Hampp R. (2014). “Rhizosphere interactions,” in Ecological Biochemistry: Environmental and Interspecies Interactions (John Wiley & Sons, Inc, New Jersey, USA), 292–311. doi: 10.1002/9783527686063.ch15
Schüßler A. (2018). System and methods for continuous propagation and mass production of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in liquid culture, European Patent No. EP3038456B1. Available online at: https://patents.google.com/patent/EP3038456A1/en.
Seenivasagan R., Babalola O. O. (2021). Utilization of microbial consortia as biofertilizers and biopesticides for the production of feasible agricultural product. Biology 10, 1111. doi: 10.3390/biology10111111
Seneviratne G., Jayasinghearachchi H. S. (2003). Mycelial colonization by bradyrhizobia and azorhizobia. J. Biosci. 28, 243–247. doi: 10.1007/bf02706224
Seneviratne G., Kulasooriya S. (2012). Reinstating soil microbial diversity in agroecosystems: The need of the hour for sustainability and health. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 164, 181–182. doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2012.10.002
Seneviratne G., Zavahir J. S., Bandara W. M. M. S., Weerasekara M. L. M. (2007). Fungal-bacterial biofilms: their development for novel biotechnological applications. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 24, 739–743. doi: 10.1007/s11274-007-9539-8
Shah C., Mali H., Kamble V., Mandavgane S., Subramanian R. B. (2022). Multifunctional properties of mycorrhizal helper bacteria: improve mycorrhizal colonization and increase phosphate uptake in Banana. bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory). doi: 10.1101/2022.12.13.520192
Sharma B., Tiwari S., Kumawat K. C., Cardinale M. (2022). Nano-biofertilizers as bio-emerging strategies for sustainable agriculture development: Potentiality and their limitations. Sci. Total Environ. 860, 160476. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160476
Singh M., Bhasin S., Madan N., Suyal D. C., Soni R., Singh D. (2021). “Bioinoculants for agricultural sustainability,” in Microbiological Activity for Soil and Plant Health Management. Singapore: Springer. p. 629–641. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-2922-8_25
Singh R. S., Chauhan K., Pandey A. (2019). Influence of aeration, agitation and process duration on fungal inulinase production from paneer whey in a stirred tank reactor. Bioresource Technol. Rep. 8, 100343. doi: 10.1016/j.biteb.2019.100343
Singh J., Singh A. V., Upadhayay V. K., Khan A. (2020). Comparative evaluation of developed carrier based bioformulations bearing multifarious PGP properties and their effect on shelf life under different storage conditions. Environ. Ecol. 38, 96–103.
Singleton P., Keyser H., Sande E., Herridge D. (2002). Development and evaluation of liquid inoculants. Available online at: https://aciar.gov.au/files/node/2110/pr109echapter07.pdf (Accessed November 28, 2024).
Sivakumar N. (2012). Effect of edaphic factors and seasonal variation on spore density and root colonization of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in sugarcane fields. Ann. Microbiol. 63, 151–160. doi: 10.1007/s13213-012-0455-2
Smith R. S. (1992). Legume inoculant formulation and application. Can. J. Microbiol. 38, 485–492. doi: 10.1139/m92-080
Sohaib M., Zahir Z. A., Khan M. Y., Ans M., Asghar H. N., Yasin S., et al. (2019). Comparative evaluation of different carrier-based multi-strain bacterial formulations to mitigate the salt stress in wheat. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 27, 777–787. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2019.12.034
Solaiman M. Z., Hirata H. (1996). Effectiveness of arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization at nursery-stage on growth and nutrition in wetland rice (Oryza sativaL.) after transplanting under different soil fertility and water regimes. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 42, 561–571. doi: 10.1080/00380768.1996.10416325
Souza T., Santos J. B. L. D., Batista D. S. (2025). An assessment of plant growth and physiological responses in annual crops grown in P deficient soils inoculated with indigenous arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Braz. J. Microbiol. doi: 10.1007/s42770-025-01618-9
Srivastava S., Johny L., Adholeya A. (2021). Review of patents for agricultural use of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Mycorrhiza 31, 127–136. doi: 10.1007/s00572-021-01020-x
Sruthilaxmi C., Babu S. (2017). Microbial bio-inoculants in Indian agriculture: Ecological perspectives for a more optimized use. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 242, 23–25. doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2017.03.019
St-Arnaud M., Hamel C., Vimard B., Caron M., Fortin J. (1996). Enhanced hyphal growth and spore production of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus intraradices in an in vitro system in the absence of host roots. Mycological Res. 100, 328–332. doi: 10.1016/s0953-7562(96)80164-x
Statista (2024a). Global Pesticide Agricultural Use 1990-2022. Available online at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1263077/global-pesticide-agricultural-use/:~:text=From%201990%20to%202022%2C%20the,climate%20change%2C%20and%20population%20growth (Accessed November 28, 2024).
Statista (2024b). Global Fertilizer Consumption 1965-2022. Available online at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/438967/fertilizer-consumption-globally-by-nutrient/:~:text=In%201965%2C%20the%20consumption%20of,increased%20to%20187.92%20million%20tons.
Sun Z., Song J., Xin X., Xie X., Zhao B. (2018). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal 14-3-3 proteins are involved in arbuscule formation and responses to abiotic stresses during AM symbiosis. Front. Microbiol. 9. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00091
Tahat M. M., Sijam K. (2012). Mycorrhizal fungi and abiotic environmental conditions relationship. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 6, 125–133. doi: 10.3923/rjes.2012.125.133
Taktek S., St-Arnaud M., Piché Y., Fortin J. A., Antoun H. (2016). Igneous phosphate rock solubilization by biofilm-forming mycorrhizobacteria and hyphobacteria associated with Rhizoglomus irregulare DAOM 197198. Mycorrhiza 27, 13–22. doi: 10.1007/s00572-016-0726-z
Taktek S., Trépanier M., Servin P. M., St-Arnaud M., Piché Y., Fortin J., et al. (2015). Trapping of phosphate solubilizing bacteria on hyphae of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Rhizophagus irregularis DAOM 197198. Soil Biol. Biochem. 90, 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.07.016
Tarbell T. J., Koske R. E. (2007). Evaluation of commercial arbuscular mycorrhizal inocula in a sand/peat medium. Mycorrhiza 18, 51–56. doi: 10.1007/s00572-007-0152-3
Taurian T., Anzuay M. S., Angelini J. G., Tonelli M. L., Ludueña L., Pena D., et al. (2009). Phosphate-solubilizing peanut associated bacteria: screening for plant growth-promoting activities. Plant Soil 329, 421–431. doi: 10.1007/s11104-009-0168-x
Thilagar G., Bagyaraj D., Rao M. (2015). Selected microbial consortia developed for chilly reduces application of chemical fertilizers by 50% under field conditions. Scientia Hortic. 198, 27–35. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2015.11.021
Thirumal G. (2017). Effects of irradiated carriers, storage temperatures, on rhizobium bioinoculant at different intervals. Int. J. Pure Appl. Bioscience 5, 1240–1246. doi: 10.18782/2320-7051.4072
Timofeeva A., Galyamova M., Sedykh S. (2022). Prospects for using Phosphate-Solubilizing microorganisms as natural fertilizers in agriculture. Plants 11, 2119. doi: 10.3390/plants11162119
Toljander J. F., Lindahl B. D., Paul L. R., Elfstrand M., Finlay R. D. (2007). Influence of arbuscular mycorrhizal mycelial exudates on soil bacterial growth and community structure. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 61, 295–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2007.00337.x
Torres N., Antolín M. C., Goicoechea N. (2018). Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis as a promising resource for improving berry quality in grapevines under changing environments. Front. Plant Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00897
Trabelsi D., Mhamdi R. (2013). Microbial inoculants and their Impact on soil Microbial Communities: a review. BioMed. Res. Int. 2013, 1–11. doi: 10.1155/2013/863240
Trejo D., Sangabriel-Conde W., Gavito-Pardo M. E., Banuelos J. (2021). Mycorrhizal inoculation and chemical fertilizer interactions in pineapple under field conditions. Agriculture 11, 934. doi: 10.3390/agriculture11100934
Trexler R. V., Bell T. H. (2019). Testing sustained soil-to-soil contact as an approach for limiting the abiotic influence of source soils during experimental microbiome transfer. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 366. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnz228
Turhan E.Ü., Erginkaya Z., Korukluoğlu M., Konuray G. (2019). Beneficial biofilm applications in food and agricultural industry. In. Springer eBooks pp. 445–469. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-24903-8_15
United Nations (2022). Population (New York, Manhattan: United Nations). Available at: https://www.un.org/en/global-issues/population.
U.S. Geological Survey. (2024). Mineral commodity summaries 2024. U.S. Geological Survey, U.S. doi: 10.3133/mcs2024
Uzcátegui-Negrón M., Serrano J., Boiron P., Rodriguez-Nava V., Couble A., Moniée D., et al. (2011). Reclassification by molecular methods of actinobacteria strains isolated from clinical cases in Venezuela. J. Mycologie Médicale 21, 100–105. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2011.03.004
Vassilev N., Eichler-Löbermann B., Flor-Peregrin E., Martos V., Reyes A., Vassileva M. (2017). Production of a potential liquid plant bio-stimulant by immobilized Piriformospora indica in repeated-batch fermentation process. AMB Express 7. doi: 10.1186/s13568-017-0408-z
Vassilev N., Vassileva M., Martos V., Del Moral L. F. G., Kowalska J., Tylkowski B., et al. (2020). Formulation of microbial inoculants by encapsulation in natural polysaccharides: Focus on beneficial properties of carrier additives and derivatives. Front. Plant Sci. 11. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00270
Vassileva M., Malusà E., Sas-Paszt L., Trzcinski P., Galvez A., Flor-Peregrin E., et al. (2021). Fermentation strategies to improve Soil Bio-Inoculant production and quality. Microorganisms 9, 1254. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9061254
Vílchez J. I., Navas A., González-López J., Arcos S. C., Manzanera M. (2016). Biosafety test for plant growth-promoting bacteria: proposed environmental and human safety index (EHSI) protocol. Front. Microbiol. 6. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01514
Vlamakis H., Chai Y., Beauregard P., Losick R., Kolter R. (2013). Sticking together: building a biofilm the Bacillus subtilis way. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 11, 157–168. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2960
Voets L., De Boulois H. D., Renard L., Strullu D., Declerck S. (2005). Development of an autotrophic culture system for the in vitro mycorrhization of potato plantlets. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 248, 111–118. doi: 10.1016/j.femsle.2005.05.025
Voets L., de la Providencia I. E., Fernandez K., IJdo M., Cranenbrouck S., Declerck S. (2009). Extraradical mycelium network of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi allows fast colonization of seedlings under in vitro conditions. Mycorrhiza 19, 347–356. doi: 10.1007/s00572-009-0233-6
Volpato S. (2020). Controllo qualità dei microrganismi. Available online at: https://hdl.handle.net/11380/1201052 (Accessed November 27, 2024).
Vosátka M., Látr A., Gianinazzi S., Albrechtová J. (2012). Development of arbuscular mycorrhizal biotechnology and industry: current achievements and bottlenecks. Symbiosis 58, 29–37. doi: 10.1007/s13199-012-0208-9
Wagg C., Barendregt C., Jansa J., Van Der Heijden M. G. (2015). Complementarity in both plant and mycorrhizal fungal communities are not necessarily increased by diversity in the other. J. Ecol. 103, 1233–1244. doi: 10.1111/1365-2745.12452
Wahid F., Sharif M., Steinkellner S., Khan M. A., Marwat K. B., Khan S. A. (2016). Inoculation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and phosphate solubilizing bacteria in the presence of rock phosphate improves phosphorus uptake and growth of maize. Pakistan J. Bot. 48, 739–747.
Wang Q., Liu M., Wang Z., Li J., Liu K., Huang D. (2024). The role of arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis in plant abiotic stress. Front. Microbiol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1323881
Wani P., Khan M., Zaidi A. (2007). Co-inoculation of nitrogen-fixing and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria to promote growth, yield and nutrient uptake in chickpea. Acta Agronomica Hungarica 55, 315–323. doi: 10.1556/aagr.55.2007.3.7
Welsh A. K., Burke D. J., Hamerlynck E. P., Hahn D. (2009). Seasonal analyses of arbuscular mycorrhizae, nitrogen-fixing bacteria and growth performance of the salt marsh grass Spartina patens. Plant Soil 330, 251–266. doi: 10.1007/s11104-009-0197-5
Wen Y., Xu T., Qi D., Chang W., Li K., Fan X., et al. (2024). Rhizophagus irregularis combined with biochar can improve the saline-alkali tolerance and energy quality of switchgrass through osmoregulation and gene expression. Scientia Hortic. 338, 113793. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2024.113793
Willis A., Rodrigues B. F., Harris P. J. C. (2012). The ecology of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 32, 1–20. doi: 10.1080/07352689.2012.683375
Wipf D., Krajinski F., Van Tuinen D., Recorbet G., Courty P. (2019). Trading on the arbuscular mycorrhiza market: from arbuscules to common mycorrhizal networks. New Phytol. 223, 1127–1142. doi: 10.1111/nph.15775
Wong C., Saidi N., Vadamalai G., Teh C., Zulperi D. (2019). Effect of bioformulations on the biocontrol efficacy, microbial viability and storage stability of a consortium of biocontrol agents against Fusarium wilt of banana. J. Appl. Microbiol. 127, 544–555. doi: 10.1111/jam.14310
Wood T., Biermann B., Grainger H., N. P. I., Corp N. (1985). EP0209627A2 - Method for producing axenic vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in association with root organ cultures. Available online at: https://patents.google.com/patent/EP0209627A2/en.
Woomer P., Huising J., Giller K., Baijukya F., Kantengwa S., Vanlauwe B., et al. (2014). N2Africa: Final Report of the first Phase - 2009 - 2013. Available online at: http://library.wur.nl/WebQuery/wurpubs/455445 (Accessed November 30, 2024).
Wu Z., Li X., Liu X., Dong J., Fan D., Xu X., et al. (2020). Membrane shell permeability of Rs-198 microcapsules and their ability for growth promoting bioactivity compound releasing. RSC Adv. 10, 1159–1171. doi: 10.1039/c9ra06935f
Xie M., Zou Y., Wu Q., Zhang Z., Kuča K. (2020). Single or dual inoculation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobia regulates plant growth and nitrogen acquisition in white clover. Plant Soil Environ. 66, 287–294. doi: 10.17221/234/2020-pse
Xing J., Jia X., Wang H., Ma B., Salles J. F., Xu J. (2020). The legacy of bacterial invasions on soil native communities. Environ. Microbiol. 23, 669–681. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.15086
Yadav R., Ror P., Beniwal R., Kumar S., Ramakrishna W. (2021). Bacillus sp. and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi consortia enhance wheat nutrient and yield in the second-year field trial: Superior performance in comparison with chemical fertilizers. J. Appl. Microbiol. 132, 2203–2219. doi: 10.1111/jam.15371
Yadav R., Ror P., Rathore P., Ramakrishna W. (2020). Bacteria from native soil in combination with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi augment wheat yield and biofortification. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 150, 222–233. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.02.039
Yaichi Z. G., Hassanpouraghdam M. B., Rasouli F., Aazami M. A., Mehrabani L. V., Jabbari S. F., et al. (2025). Zinc oxide nanoparticles foliar use and arbuscular mycorrhiza inoculation retrieved salinity tolerance in Dracocephalum moldavica L. by modulating growth responses and essential oil constituents. Sci. Rep. 15. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84198-2
Yang Z., Dong H., Zhang S., Jiang J., Zhu H., Yang H., et al. (2023). Isolation and identification of mycorrhizal helper bacteria of Vaccinium uliginosum and their interaction with mycorrhizal fungi. Front. Microbiol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1180319
Young C., Rekha P., Lai W., Arun A. (2006). Encapsulation of plant growth-promoting bacteria in alginate beads enriched with humic acid. Biotechnol. Bioengineering 95, 76–83. doi: 10.1002/bit.20957
Yousefi A. A., Khavazi K., Moezi A. A., Rejali F., Nadian H. A. (2011). Phosphate solubilizing bacteria and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi impacts on inorganic phosphorus fractions and wheat growth. World Appl. Sci. J. 15, 1310–1318.
Zaidi A., Khan M. S., Saif S., Rizvi A., Ahmed B., Shahid M. (2017). “Role of Nitrogen-Fixing Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria in Sustainable production of Vegetables: Current perspective,” in Microbial Strategies for Vegetable Production. Cham: Springer. p. 49–79. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-54401-4_3
Zakeel M. C. M., Safeena M. I. S. (2019). “Biofilmed biofertilizer for sustainable agriculture,” in Plant Health Under Biotic Stress (Singapore: Springer), 65–82. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-6040-4_3
Zhang L., Xu M., Liu Y., Zhang F., Hodge A., Feng G. (2016). Carbon and phosphorus exchange may enable cooperation between an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and a phosphate-solubilizing bacterium. New Phytol. 210, 1022–1032. doi: 10.1111/nph.13838
Zhou J., Deng B., Zhang Y., Cobb A. B., Zhang Z. (2017). Molybdate in rhizobial Seed-Coat formulations improves the production and nodulation of alfalfa. PloS One 12, e0170179. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170179
Keywords: mycorrhizal inoculants, bioformulations, shelf-life, sustainable agriculture, genetic stability, carrier materials, commercialization, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
Citation: Ghorui M, Chowdhury S and Burla S (2025) Recent advances in the commercial formulation of arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculants. Front. Ind. Microbiol. 3:1553472. doi: 10.3389/finmi.2025.1553472
Received: 30 December 2024; Accepted: 06 March 2025;
Published: 07 April 2025.
Edited by:
Marika Pellegrini, University of L’Aquila, ItalyReviewed by:
Wilgince Apollon, National Polytechnic Institute (IPN), MexicoCopyright © 2025 Ghorui, Chowdhury and Burla. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sashidhar Burla, YnNoYXNoaWRoYXIxMkBnbWFpbC5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.