- 1Department of Respirology, The Affiliated Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
- 2College of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
- 3Department of Dermatology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Asthma, a complex and heterogeneous respiratory disease, is often accompanied by various comorbidities, notably atopic dermatitis (AD). AD characterized by recurrent eczematous lesions and severe itching, can trigger or exacerbate asthma. Individuals with AD are 2.16 times more likely to develop asthma compared to the reference population. Furthermore, asthmatics with AD experience more severe and frequent emergency department visits and hospital admissions compared to patients with asthma alone. The close connection between asthma and AD indicates there are overlap pathophysiologic mechanisms. It is well-known that dysregulated type 2 (T2) immune inflammation is pivotal in the development of both AD and asthma, traditionally attributed to CD4+ type 2 helper T (Th2) cells. Over the past decade, group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s), as potent innate immune cells, have been demonstrated to be the key drivers of T2 inflammation, playing a crucial role in the pathogenesis of both asthma and AD. ILC2s not only trigger T2 immune-inflammation but also coordinate the recruitment and activation of innate and adaptive immune cells, thereby intensifying the inflammatory response. They are rapidly activated by epithelium alarmins producing copious amounts of T2 cytokines such as interleukin (IL) -5 and IL-13 that mediate the airway inflammation, hyperresponsiveness, and cutaneous inflammation in asthma and AD, respectively. The promising efficiency of targeted ILC2s in asthma and AD has further proven their essential roles in the pathogenesis of both conditions. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is currently no review article specifically exploring the role of ILC2s in asthma combined with AD and their potential as future therapeutic targets. Hence, we hypothesize that ILC2s may play a role in the pathogenesis of asthma combined with AD, and targeting ILC2s could be a promising therapeutic approach for this complex condition in the future. In this review, we discuss recent insights in ILC2s biology, focus on the current knowledge of ILC2s in asthma, AD, particularly in asthma combined with AD, and suggest how this knowledge might be used for improved treatments of asthma combined with AD.
1 Introduction
Over the past decades, the incidence of allergic diseases, such as AD and bronchial asthma (asthma), has significantly increased, affecting approximately 20% of the world’s population, thereby imposing a substantial individual and socioeconomic burden (1, 2). Atopic diseases may evolve from one to another. Intriguingly, AD often serves as the first step indicating the development of other allergic diseases, such as food hypersensitivity, allergic rhinitis, and asthma, namely the “atopic march” (3). The comorbidity of asthma and AD has garnered significant research attention due to the strong association between AD and the development, severity, and risk of exacerbations in asthma (3–5). A comprehensive meta-analysis involving 458,810 participants indicated that individuals with AD were 2.16 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.88-2.48) times more likely to develop asthma compared to those without AD (6). Recent research by Ahn et al. utilized a two-sample bidirectional Mendelian randomization approach to reinforce the causal link between AD and the subsequent development of asthma (7). And the risk for progression to asthma was correlated with the severity of AD that severe AD was significantly (relative risk [RR], 2.40; 95% CI, 1.96-2.94) higher than in mild AD (RR, 1.82; 95% CI, 1.03-3.23) or moderate AD (RR, 1.51; 95% CI, 1.30-1.75) (6). Moreover, asthma combined with AD has worse clinical outcomes compared with asthma only (8). In a population-based cohort study including 65,539 individuals with asthma only and 819 with concomitant asthma and AD, the latter had more emergency department visits (9% vs 7%) and hospital admissions (31% vs 27%) compared to patients with asthma only (8). These results suggested that improvements in management and monitoring AD may reduce unscheduled hospital visits and lower healthcare costs in asthmatics combined with AD. Therefore, McDonald et al. have suggested that AD was an important extrapulmonary treatable traits of asthma since it could be modifiable by targeted treatment to improve the outcomes of asthma (9).
The close connection between AD and asthma indicates that they have overlapping pathogenetic mechanisms. It is clearly that dysregulated T2 immune response is one of the fundamental causes of AD and asthma (10). Although CD4+ Th2 cells undoubtedly play an important role in the pathogenesis of AD and asthma, the discovery of ILC2s has added another layer of complexity to the pathogenesis of these diseases. Increasing evidence suggests that ILC2s as potent innate immune cells are key drivers of T2 inflammation (11). In a freshly released research, Szeto et al. applied the Boolean-ILC2-Cre mice to definitively establish the crucial role of ILC2s in facilitating the initiation of Th2-driven adaptive immunity (12). They are not only initiating T2 immune-inflammation but orchestrating the recruitment and activation of other members of innate and adaptive immunity, further amplifying the inflammatory response (13).
Despite their lower total numbers compared to Th2 cells in the body, ILC2s respond more swiftly and remain unaffected by antigen stimulation (14). ILC2s are rapidly activated by epithelium alarmins producing copious amounts of T2 cytokines such as IL-5 and IL-13 (14). The promising efficacy of targeting ILC2s in AD and asthma (14) has further proved their essential roles in the pathogenesis of AD and asthma. However, their mechanism of action in asthma combined with AD has not yet been completely elucidated. In this review, we explore recent advances in ILC2s biology, emphasizing their role in asthma and AD, especially in the context of asthma combined with AD, and how this knowledge can be leveraged to develop improved treatments for asthma combined with AD.
2 Immunobiology of ILC2s
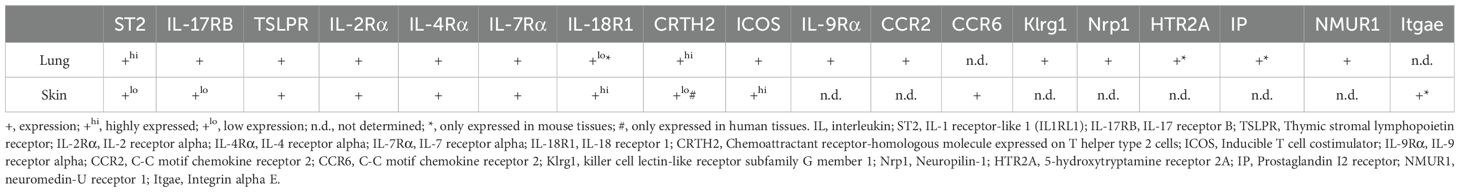
For slightly over a decade, ILC2s, identified as one of the five key members of the innate lymphoid cell (ILC) family, play a crucial role in the body’s initial defense against infections (15). Alongside natural killer (NK) cells, ILC1s, ILC3s, and lymphoid tissue inducer cells (LTi), ILC2s contribute to the innate immune response that precedes the activation of adaptive immune cells (13). ILC2s are abundant in various mucosal tissues, including lung, skin, and intestine, where they exhibit tissue-specific heterogeneity (16). A recent single-cell RNA sequencing study revealed distinct patterns of receptor expression in tissue-specific ILC2 populations. Specifically, cutaneous ILC2s demonstrated low expression levels of IL-33 receptor (ST2), IL-25 receptor (IL17RB), and TSLP receptor (TSLPR), but exhibited marked upregulation of IL-18 receptor. In contrast, lung ILC2 populations showed reciprocal expression profiles, characterized by high ST2 expression coupled with minimal IL-18 receptor detection (17). We have summarized the different expression receptors of ILC2s in lung and skin (see Table 1) (17–19).
Initially, they were considered to be associated with resistance to parasitic infections (15). Nowadays, it is increasingly clear that ILC2s play pivotal roles in the regulation of body’s homeostasis and tissue repair (20). Moreover, they can also regulate the function of other T2 immune cells such as Th2 cells which share key transcription factors and cytokine production profiles with ILC2s (13). Therefore, ILC2s are often considered to be the “mirror cell” of Th2 cells (21). Although their total cell numbers are far less than the numbers of Th2 cells in the body, ILC2s respond faster and are not affected by antigen stimulation (13). This allows ILC2s to be the first responders to allergens that enter the system, producing a large amounts of T2 cytokines including IL-5 and IL-13, driving eosinophilia (22). Dysregulation of ILC2s contributes to T2-skewed immune-mediated inflammatory diseases such as AD and asthma, making ILC2s to be an attractive target for therapeutic interventions (13). However, there are complex regulatory systems to modulate ILC2s functions and plasticity. The abnormal regulatory systems would result in ILC2s dysfunction that leads to unfavorable health problems. In the coming section, we focus on the regulatory systems and molecules that modulate ILC2s’ functions and plasticity (Figure 1).
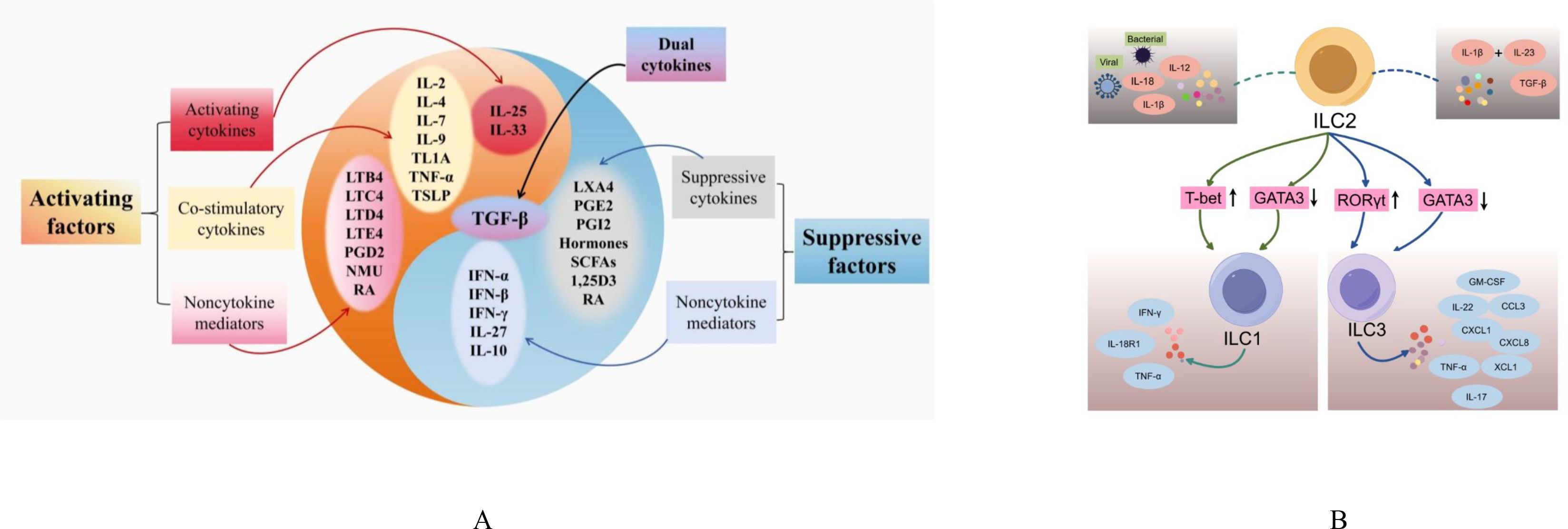
Figure 1. The modulating factors and differentiation of ILC2s. (A) Activating and suppressive factors of ILC2s; (B) ILC2s Plasticity. IL, interleukin; TSLP, thymic stromal lymphopoietin; IFN, interferon; TLA1, tumor necrosis factor-like cytokine 1A; TNF-α, tumor Necrosis Factor alpha; TGF-β, transforming growth factor beta; LT, leukotrienes; PG, prostaglandins; NMU, neuromedin U; RA, the vitamin A metabolite retinoic acid; LXA4, Lipoxin A4; 1,25D3, vitamin D metabolite1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3; SCFA, short-chain fatty acids; INF, Interferon; T-bet, T-box expressed in T cells; GATA3, GATA Binding Protein 3; RORγt, Retinoic Acid Receptor-related Orphan Receptor Gamma t; IL-18R1, IL-18 receptor 1; GM-CSF, Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor; CCL3, Chemokine (C-C motif) Ligand 3; CXCL, Chemokine (C-X-C motif) Ligand; XCL1, X-C motif chemokine ligand 1.
2.1 Activating cytokines and co-stimulatory cytokines
Unlike T cells, ILC2s do not possess antigen-specific receptors, therefore, their activation is mediated by the recognition of epithelial-derived cytokines (alarmins), mainly, IL-25 and IL-33 (22). They are strong activators of ILC2s via mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR)-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) pathways, respectively (23–26). IL-25 belongs to IL-17 family cytokines which is released from epithelium, including tuft cells and brush cells (27). In mouse models, IL-25 can amplify the T2 immune response, significantly induce the expression of the IL-4/5/13 cytokines gene, and causes lesions in the lung and digestive tract (27). And the administration of IL-25 has been shown to induce lung eosinophilia and airway hyperreactivity (AHR), underscoring its critical role in the pathogenesis of asthma (27). IL-33 belongs to the IL-1 family and is released from epithelial cells, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, among others (28). It elicits the activation of ILC2s and stimulates ILC2s to produce IL-5 and IL-13 in mouse and human (29). In humans, endothelial cells and bronchial epithelial cells constitutively express IL-33 and may serve as major sources during airway inflammation (29).
However, mouse and human studies indicate that the application of IL-25 or IL-33 alone has limited effects on activating ILC2s, necessitating additional stimulus signals (30, 31). Common co-stimulators are categorized into two primary groups: the gamma-C (γ-c) cytokine family, comprising IL-2 and IL-15 (32), and the tumor necrosis factor superfamily (TNFSF), which encompasses a range of ligands and receptors involved in various immune and inflammatory processes (33). The γ-c cytokine family, which encompasses IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, and others, activates ILC2s through the Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway (32). These cytokines play a crucial role in the survival, development, and maintenance of ILC2s (32). Mouse studies found that IL-2 and IL-7 can strongly activate STAT5 pathway, and collaborative IL-33-induced ILC2s proliferation and producing T2 cytokines (34–36). Similar to IL-2 and IL-7, IL-4 and IL-9 can amplify cytokines production by activated mouse and human ILC2s in synergy with IL-33 (36, 37). Motomura et al. found that basophil-derived IL-4 facilitated ILC2s effector functions in papain-induced mouse airway inflammation (38). While autocrine IL-9 induces the anti-apoptotic protein to support mouse ILC2s survival (39).
Additionally, the current body of evidence has shown that members of TNFSF possess costimulatory functions, particularly tumor necrosis factor-like cytokine 1A (TL1A) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) (40, 41). TL1A activates ILC2s through its cognate receptor DR3 expressed on mouse and human ILC2s, leading to activation of the nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-кB) and MAPK signaling pathways (42). In synergy with IL-33 and IL-25, TL1A can enhance mice ILC2s functions, mediate papain-induced ILC2s activation and lung inflammation (43, 44). TNF-α binds to its receptor TNFR2 which is expressed on mouse ILC2s, promoting ILC2s activation and survival through the non-canonical NF-кB pathway (41). Furthermore, the IL-33 and A. alternata-challenged asthma mouse model has demonstrated that TNF-α/TNFR2 signaling is crucial for ILC2s survival and function and induction of AHR (41).
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) as one of the alarmins is historically considered to be an activator of ILC2s, but increasing evidence suggest that this factor has costimulatory properties similar to IL-2 and IL-7 (26). TSLP alone does not induce mouse ILC2s to produce cytokines, it acts in synergy with IL-33 to enhance cell viability, proliferation, and cytokine production (36). Moreover, TSLP augments IL-33-induced IL-9 production which can amplify the cytokines production of mouse ILC2s (36). Intriguingly, TSLP is more important for ILC2s survival than IL-33 in humans and plays a critical role in ILC2s mediated steroids resistance (45).
2.2 Suppressive cytokines
Mouse and human ILC2s’ functions can be attenuated by a spectrum of cytokines, such as interferons (IFNs), IL-27, IL-10, and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) (26). In vivo and in vitro studies have demonstrated that IFNs and IL-27 can strongly suppress the proliferation of ILC2s and production of type 2 cytokines by ILC2s through STAT1 pathway (46). Exogenous administration of IFNs (IFN-β or IFN-γ) can inhibit mouse and human ILC2s’ effector functions and relieve the flowing T2 immunopathology (46, 47). IL-27 is another cytokine that directly inhibits mouse ILC2s’ functions in a manner dependent on the STAT1 (46). In the A. alternata-induced asthmatic animal model, administration of IL-27 was not only significantly suppress the number of ILC2s cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and lung, but also attenuate ILC2-driven airway inflammation (48).
IL-10 inhibits mouse ILC2s proliferation and T2 cytokines production in response to IL-33/TSLP stimulation (49). In addition, a recent clinical research suggested that IL-10-producing ILC2s attenuate Th responses and maintain epithelial integrity in modulating grass pollen allergy (50). The role of IL-10+ ILC2s in the disease-regulatory role of allergen immunity is highlighted (50). However, IL-10 failed to inhibit IL-25-activated mouse ILC2s, indicating that its inhibition of ILC2s depends on the stimulator (51, 52). TGF-β is an important cytokine for ILC2s development and maturation, as TGFBR2-deficient mice exhibit reduced numbers of mature ILC2s in various tissues, including the lungs (53). Moreover, a clinical study has shown that TGF-β not only inhibits the production of IL-5 and IL-13 by ILC2s but also increases the production of IL-9 which acts as a costimulator of ILC2s (49). Therefore, compared with other inhibitory cytokines, TGF-β plays a dual role in the activation of ILC2s (54). Further studies are needed to clarify the role of TGF-β in ILC2s’ functions.
2.3 Noncytokine mediators
In addition to cellular mediators, ILC2s are also regulated by non-cytokine mediators, such as lipid mediators, neuropeptides/neurotransmitters, hormones, among others. It is well known that lipid mediators including leukotrienes (LT) and prostaglandins (PG) play crucial roles in homeostasis and inflammation (55). Both human and mouse ILC2s possess a variety of receptors for LT and PG. LTB4, LTC4, LTD4, LTE4, and PGD2 are known to positively regulate ILC2s (56–60). Meanwhile, LXA4, PGE2, and PGI2 are negative regulators of ILC2s (61–63). Neuropeptides produced by peripheral neurons have been suggested could directly affect the function of ILC2s in the lung and intestine (64). As a strong positive regulator, neuromedin U (NMU) rapidly activates human ILC2s through the NMU/NMUR1 axis (65). In addition, the abundance of the neurotransmitter dopamine is negatively correlated with the amount of circulating mouse and human ILC2s, which alleviates allergen-induced ILC2s responses and airway inflammation by impairing the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) pathway of ILC2s (66). In turn to hormones, more and more studies indicate that sex hormone plays an important role in the regulation of ILC2s (67–70). Testosterone and its downstream hormone, 5α-dihydrotestosterone, negatively regulate the proliferation of mouse ILC2s and the production of type 2 cytokines by down-regulating the expression of GATA binding protein 3 (GATA3) and Retinoic Acid-Related Orphan Receptor Alpha (RORα) (69). On the other hand, while estrogen does not affect the lung ILC2s signal, a lack of mice uterine ILC2s reduces estrogen receptors, estrogen-related to maintaining permanent ILC2s uterus (70).
Furthermore, vitamin metabolites and dietary metabolites have demonstrated the ability to regulate ILC2s function, either directly or indirectly (26). The vitamin A metabolite retinoic acid (RA) acts different functions in ILC2s of different species; in humans, RA induces ILC2s to produce T2 cytokines (71), whereas in mice, RA deficiency promotes ILC2s proliferation and cytokine production (72). In addition, the vitamin D metabolite, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, exerts an inhibitory effect on human ILC2s (71). It is well-established that diet plays a crucial role in influencing immune homeostasis and the development of allergic diseases (73). Animal research has found that short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) mainly produced by dietary fiber can reduce ILC2-mediated allergic inflammation (74). Recent research has demonstrated that butyrate, a type of SCFAs, can suppress the production of type 2 cytokines and proliferation of ILC2s by targeting GATA3 in both mice and humans (75). Meanwhile, inhibiting the mouse ILC2s’ functions through the administration of butyrate significantly improved the AHR and airway inflammation mediated by A. alternata and IL-33 (76). Interestingly, programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) as a potent immune inhibitory receptor is well-known in tumor therapy (77), which is also expressed on mouse ILC2s and acts an early checkpoint in ILC2s (78, 79). Recently, PD-1 was reported to limit the viability of ILC2s and attenuated their effector functions by shifting mouse ILC2s metabolism toward glutaminolysis, glycolysis and methionine catabolism (80).
2.4 ILC2s plasticity
For some time, ILC2s were considered to be a homogeneous population of cells because, no phenotypic or functional heterogeneity of ILC2s were found like ILC1s and ILC3s (13). Nowadays, it is clear that ILC2s exhibit high plasticity, as evidenced by their capacity to differentiate into cells with characteristics of ILC1 or ILC3 subsets in response to microenvironmental signals (81). Animal study has shown that IL-1β and IL-12 produced by viral and bacterial infection can drive ILC2s converts to IFN-γ-producing ILC1-like cells which was associated with disease severity and acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (82). Moreover, recent animal research has shown that stimulating ILC2s with a mix of IL-1β, IL-23, and TGF-β leads to the upregulation of RORγt, a key transcription factor for ILC3s, while concurrently downregulating GATA3 and inducing IL-17 production (83). As IL-17 is significantly associated with airway neutrophilia, the transdifferentiation of human ILC2s into ILC3-like cells might contribute to neutrophilic asthma (84). Thus, the unique high plasticity of ILC2s suggests that they may play an important role in multiple immune responses against different types of pathogens/infections (83).
In conclusion, studies examining the stimulators, suppressors, plasticity, and other factors associated with ILC2s have furnished invaluable insights into the understanding of ILC2s and their potential exploitation for developing novel therapeutic strategies to combat allergic diseases.
3 Asthma and ILC2s
Asthma is a very common and heterogeneity chronic respiratory disease characterized by chronic airway inflammation and AHR, affecting more than 300 million people worldwide across all age ranges (85). With the increased understanding of its heterogeneity, many clinical phenotypes of asthma have been identified, such as allergic asthma, non-allergic asthma, late-onset asthma, early-onset asthma, and asthma associated with obesity (2). In terms of causes, manifestations, and treatment response, phenotypes are clinically relevant, however, they do not certainly associate with the underlying disease mechanisms (86). More than two decades ago, Wenzel et al. stratified severe asthmatics into two subtypes according to the presence of airway eosinophilia which might allow for more precise treatment (87). In 2008, Anderson introduced the concept of endotype in asthma, which refers to a functionally and pathologically defined subtype of the disease, characterized by specific molecular features (88). Subsequently, Lötvall and colleagues defined an endotype as “a subtype of a condition, which is defined by a distinct functional or pathophysiological mechanism.” (89). Endotype is considered to be a subtype defined by an unique pathophysiological mechanism at the cellular and molecular level which link molecular mechanisms to phenotype (90). As research deepens, asthma has subsequently been polarized into two major endotypes: T2-high and T2-low, which represent the most established classification, particularly in considering biologic therapy (91). These endotypes are defined based on their level of expression of T2 cytokines, such as IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, which may be secreted by Th2 cells or ILC2s, thus the terminology of subtype shifts from Th2 to T2 (90–93).
ILC2s are essential for eosinophils and T2 inflammation. Since the discovery of ILC2s, they have been shown to mediate airway inflammation and AHR in several asthmatic mouse models (80). And increasing data correlate ILC2s numbers and function with asthma incident and severity in humans (80). Allergens such as house dust mite (HDM) and ovalbumin (OVA) can activate mice ILC2s within a few hours, leading to the production of significant amounts of IL-13 and IL-5 (93–96). This immune response is associated with the development of asthma-like symptoms in mice, characterized by eosinophil infiltration, AHR, and mucus hypersecretion (57, 94–97). In addition to allergens, respiratory viral infections have been reported to enhance ILC2s activation and drive AHR and airway inflammation in mouse models, which demonstrate ILC2s may play an important role in viral-induced asthma exacerbation (98). ILC2-deficient mice, however, had reduced eosinophil numbers and were unable to induce T2 inflammation at homeostasis (99). Recently, Jarick and colleagues used selective and specific ILC2-deficient mice to demonstrate the important role of ILC2s in airway inflammation in allergic asthma models (99). Moreover, ILC2s not only directly induce airway inflammation, but also activate Th2 cell responses through T2 cytokines released by ILC2s as signaling molecules. Particularly, mouse ILC2-derived IL-13 can induce dendritic cells to potentiate the memory Th2 cell response during allergen rechallenge (100). That is, ILC2s enhance T2 inflammation by orchestrating innate and adaptive T2 immunity.
It is clear that sex hormone plays an important role in the pathogenesis of asthma may also associated with ILC2s. Wang et al. have found female mice exhibited more ILC2s and T2 cytokines than male mice in a Rag1-/- asthmatic model (101). In vitro study, treatment of testosterone significantly attenuated the production of ILC2s-derived T2 cytokines and the proliferation of ILC2s in response to IL-25/33 (101). Dopamine has been shown to inhibit mouse and human ILC2s responses by restraining mitochondrial activity (66). Conditional deletion of the ILC2s’ dopamine receptor Drd1 or ablation of lung dopaminergic neurons resulted in excessive ILC2s responses and aggravated airway inflammation in clinical asthma model (66). In recent years, an increasing number of researchers have recognized the crucial roles played by the PD-1/PD-L1 or PD-L2 signaling pathway in modulating inflammatory responses in asthma (66, 80, 102–104). Helou et al. have demonstrated that PD-1 deficiency functions as a metabolic checkpoint in mice ILC2s, influencing their activation and proliferation (80). And PD-1 agonist could ameliorate AHR and suppress lung inflammation in a asthmatic mouse model (80). More importantly, ILC2s were suggested one of the major sources of steroid-resistant IL-4 and IL-13 transcripts in mice models of steroid-resistant asthma exacerbation (105).
In line with animal studies, a growing number of clinical studies have demonstrated the close relationship among ILC2s and asthma (106, 107). Asthmatic patients exhibit significantly elevated levels of ILC2s in their peripheral blood, sputum, and BALF, in contrast to control subjects (108–110). Smith et al. and other researchers have reported that the frequency of ILC2s was positively correlated with disease severity and airway eosinophilic inflammation (sputum and blood eosinophils and fractional exhaled nitric oxide [FeNO] fraction) (111) and negatively correlated with predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1%) (108). Recently, human ILC2s have been reported in mediating resistance to immunosuppression by corticosteroids, a cornerstone drug for asthma (45, 112, 113), however, partial patients fail to response adequately (114, 115).
Considering the critical role of ILC2s in the pathogenesis of asthma, targeting ILC2s emerges as a promising therapeutic strategy for asthma, aligning well with the concept of precision medicine. Tiotropium as an effective long-acting muscarinic antagonist is approved for maintenance treatment of asthma in recent years (116). Adding tiotropium to high-dose inhaled corticosteroids plus long-acting Beta2-agonists has been shown to significantly improve lung function and reduce the risk of exacerbation in patients with moderate to severe asthma (117–120). Matsuyama et al. found tiotropium regulated mouse airway inflammation through ILC2s (121). It attenuated ILC2-dependent airway inflammation by suppressing basophils-derived IL-4 production and modulating ILC2s activation in a papain-induced asthma murine model (121). Moreover, some biological agents targeting ILC2s activators and co-stimulators have demonstrated efficacy in improving airway inflammation, AHR, and asthma symptoms in both animal experiments and clinical trials (122).
Mepolizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody specifically targeting IL-5, has gained global approval as an add-on therapy for severe asthma patients who exhibit an eosinophilic phenotype (123). Across numerous clinical trials and real-world studies, the efficacy of mepolizumab in providing therapeutic benefits to these patients has been consistently demonstrated (124–129). Intriguingly, severe asthmatics treated with mepolizumab exhibited reduced ILC2s proliferation, TSLPR, GATA3 expression, and T2 cytokine secretion, accompanied by clinical improvement in asthma symptoms and a reduction in exacerbation frequency (107). The study suggests that post-treatment reduction in airway inflammation correlates with a diminished infiltration of ILC2s into the lungs (107). Dupilumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody against IL-4Rα, the receptor to IL-4 and IL-13, which was licensed for the treatment of asthma in 2018 (130). Numerous clinical trials have demonstrated significant improvements in asthma control and lung function following dupilumab treatment, resulting in a notable reduction in exacerbation rates (131–134). For instance, in the VENTURE study, dupilumab treatment led to a 70% reduction in the average dose of oral corticosteroids and a 59% reduction in asthma exacerbations among the overall patient population (134). In a murine model indicated IL-4 might facilitate ILC2s cytokine production through IL-4R (38). Dupilumab treatment significantly reduced ILC2s numbers in the blood of asthmatics and inhibited the expression of IL-5 and IL-13 mRNA in ILC2s (135). Thus, these results suggested that dupilumab attenuated ILC2s response in asthmatics and might be involved in the reduced risk of asthma exacerbation (135). Moreover, human ILC2s have been demonstrated to express IL-4Rα that means dupilumab can be a novel treatment targeting ILC2s (37). Tezepelumab, the first biologic targeting TSLP, was approved by the FDA in 2021 for the add-on maintenance treatment of severe asthma, regardless of phenotype or endotype (136). It has been shown to reduce exacerbations, improve lung function, and quality of life in patients with severe asthma (137, 138). As mentioned above, IL-33 and IL1RL1 (encoding ST2) have obvious links to ILC2s biology. The efficiency of biological agents targeting IL-33 (itepekimab) and its receptor (astegolimab) have been confirmed in clinical trials. In a phase 2 clinical trial involving 296 patients with moderate-to-severe asthma, itepekimab demonstrated significant improvements in asthma control, quality of life, and lung function, along with reductions in eosinophil levels and FeNO (139). Astegolimab has demonstrated the potential to reduce the annualized asthma exacerbation rate by up to 43% (140).Anti-IL-25 antibody significantly reduced serum IgE, IL-5, and IL-13 production, eosinophil infiltration (141); abrogated airway smooth muscle hyperplasia; prevented AHR in OVA and HDM induced asthma mouse models (142). Moreover, administration of anti-IL-25 neutralizing antibody attenuated ILC2s proliferation, mucous hypersecretion and AHR in rhinovirus infected mice model (143). SM17 (a humanized antibody of the IgG4/kappa isotype) targeting the IL-25 pathway via specific binding to IL-17RB, a co-receptor for IL-25 expressed on the surface of mouse and human ILC2s cells an other cells (144). The latest research has suggested that SM17 could significantly suppress T2 inflammation in the BALF and infiltration of ILC2s into the lungs in a HDM-induced asthma mouse model (145). Meanwhile SM17 was well tolerated with no drug-related serious adverse events were observed in the Phase I clinical study (145). These results indicates SM17 is a potential therapeutic agent to asthma with a favorable safety profile, and is worthy to further clinical development. Moreover, another anti-IL-25 monoclonal antibody, XKH001, has been evaluated as therapeutic agents in clinical trials for asthma (146).
4 ILC2s and atopic dermatitis
AD is an extremely common relapsing skin disorder characterized by recurrent eczematous lesions and intense itching, affecting individuals of all ages and ethnicities with at least 230 million patients worldwide (1). Moreover, AD is the leading cause of the global socioeconomic burden from skin disease (1, 147). The pathophysiology of AD is complex and multifactorial including genetic mutations, epidermal barrier dysfunction, skin microbiome abnormalities, and immune dysfunction (1). These pathologic drivers can interact with others (148). For example, the mutations of filaggrin gene (FLG) can induce the barrier dysfunction of skin which promotes inflammation and T2-cell infiltration; and local T2 immune responses further attenuate barrier function, and promotes dysbiosis (149). Among the multiple dysregulated immune responses in AD, T2-skewed immune dysregulation, driven by ILC2s and Th2 cells appears to be a dominant mechanism (150). In this section, we will focus on the roles of ILC2s in AD which mediated the skin inflammation by producing T2 cytokines such as IL-5 and IL-13.
ILC2s were found enriched in the skin lesions of AD patients and mice models, particularly in AD patients with FLG mutations and FLG-deficient mice (151, 152). Compared to healthy skin, the frequency of mouse and human ILC2s were significant increased in lesional AD skin, and the increase of IL-5 and IL-13 levels in the lesion area of AD were positively correlated with the number of ILC2s (153–155). Depletion of ILC2s attenuates AD-like dermatitis in mice, reinforcing the role of ILC2s in the development of AD (155). IL-33 as one of the most important alarmins to activate ILC2s is highly expressed in the skin of patients with AD (156). Excessive IL-33 has been demonstrated to cause AD-like inflammation in hK14mIL-33tg mice (transgenic mice for overexpress IL-33 in their skin) by producing large amounts of T2 cytokines, such as IL-4, IL-5,and IL-13, with increasing and activating ILC2s in the skin, lymph nodes, and peripheral blood (157). This was ILC2s-dependent for that hK14mIL-33tg mice with ILC2s deletion completely suppressed dermatitis and normalized the increasing of T2 cytokines (158). IL-25 as another important alarmins to activate ILC2s has been suggested to play an essential role in driving IL-13 expression by skin ILC2s to mediate skin inflammation in mouse AD model, both in acute and chronic phase (159). In terms of TSLP which has emerged as a key epithelium-derived cytokine and activator of skin ILC2s in the AD pathogenesis (157, 160–163). Increased expression of TSLP has been revealed in skin and serum from patients with AD (163, 164). Increasing evidence suggests that the PD-1 (can expressed on ILC2s and and acts an early checkpoint in ILC2s) and its ligands axis are emerging as key regulators of the immune response in allergic diseases including AD (165). The deficiency of PD-L1 leads to severe changes in the thickness of the ears and inflammation in AD murine model that indicates the involvement of PD-L1 in the pathogenesis of this disease (166). However, to date, there are no reports on the use of PD-L1 agonists to treat AD patients.
Given the important role of ILC2s in AD suggests that targeting ILC2s is a promising treatment of AD. Dupilumab as mentioned above is a fully human monoclonal antibody against IL-4Rα, which was the first biologic therapy to be approved for the treatment of moderate-to-severe AD in adults (167). In a clinical study in Japan, 27 AD patients treated with dupilumab had a significant reduction in the number of ILC2s in peripheral blood and total serum IgE, with significantly improvement the patient’s dermatitis (168). As mentioned above, SM17 as a humanized antibody of the IgG4/kappa isotype targets the IL-25 pathway, it could suppress T2 inflammatory response and ameliorate the AD pathology in vitro and in vivo data (143). Etokimab (ANB020), a humanized anti-IL-33 monoclonal antibody, reduced the peripheral eosinophils and skin neutrophil infiltration of AD patients in a proof-of-concept clinical trial (169). However, itepekimab (another anti-IL-33 monoclonal antibody) and astegolimab (anti-IL-33R monoclonal antibody), have recently shown not result in meaningful improvements in eczema area and severity index (EASI) scores versus placebo in a phase II clinical trial for moderate-severe AD patients (170). Recently, anti-TSLPR (ASP7266), a novel antibody, has been found to inhibit ILC2s activation, which almost completely inhibits antigen-specific cutaneous allergic reaction in the allergic experiment of AD monkey model (171). Similarly, inhibition of TSLP production by topical application of celastrol also resulted in the downregulation of ILC2s activation and alleviation of AD symptoms both in vivo and in vitro AD models (172). Tezepelumab (anti-TSLP) was investigated in a phase IIa trial in combination with topical corticosteroids (TCS) in adults with moderate to severe AD for 12 weeks (173). A higher number of patients in tezepelumab plus TCS-treated achieved response rate for ≥50% reduction in the EASI versus placebo plus TCS (64.7% vs 48.2% in the placebo arm; P = 0.091) (173), however, these improvements were not statistically significant. Although the results not statistically significant, numerical improvements versus placebo were found (173). Given the preclinical studies demonstrate the key role for IL-33 and TSLP in AD, additional clinical studies including more severe AD patients are required to validate these findings.
5 ILC2s in asthma combined with AD
AD is frequently present in patients with asthma, shares a strong genetic etiology with asthma, and is believed to be an important early causal factor in the ultimate development of atopic asthma (“atopic march”) (7, 174, 175). Li et al. conducted a meta-analysis with 458,810 participants to explore the link between AD and the progression to asthma (6). The results indicated that AD may be a precursor to asthma, as suggested by the “atopic march” concept (6). And individuals with AD were more than twice as likely to have asthma compared to the reference population (6). Recently, the casual relationship between AD and asthma has been confirmed by a two-sample bidirectional Mendelian randomization study (7). Furthermore, the risk of progressing to asthma was found to be correlated with the severity of AD (6). Amat et al. identified several risk factors for the development and progression of asthma in individuals with AD, including early-onset and severe AD, male gender, a parental history of asthma, and early and multiple sensitization (5). In addition, a population-based cohort study involving 65,539 individuals with asthma only and 819 with both asthma and AD found that patients with both conditions had a higher rate of emergency department visits (9% vs 7%) and hospital admissions (31% vs 27%) compared to those with asthma alone (8). These findings underscore the importance of AD as a significant comorbidity in severe asthma. Researchers emphasized that improved management and monitoring of AD could potentially reduce unscheduled hospital visits and lower healthcare costs (8). More recently, McDonald and colleagues highlighted AD as a crucial extrapulmonary treatable trait of asthma, noting that targeted treatments for AD could modify the condition and improve asthma outcomes (176).
The close link between AD and asthma suggests that they share overlapping pathogenic mechanisms. Notably, dysregulated T2 immune inflammation mediated by ILC2s plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of both conditions, even in atopic march (Figure 2). However, the precise role of ILC2s in asthma combined with AD remains incompletely understood. In this section, we will delve into the current understanding of ILC2s in the context of asthma combined with AD, and explore potential implications for improved treatment strategies. By understanding the mechanisms underlying the role of ILC2s in this complex interplay, we may identify novel therapeutic targets that could benefit patients with asthma combined with AD.
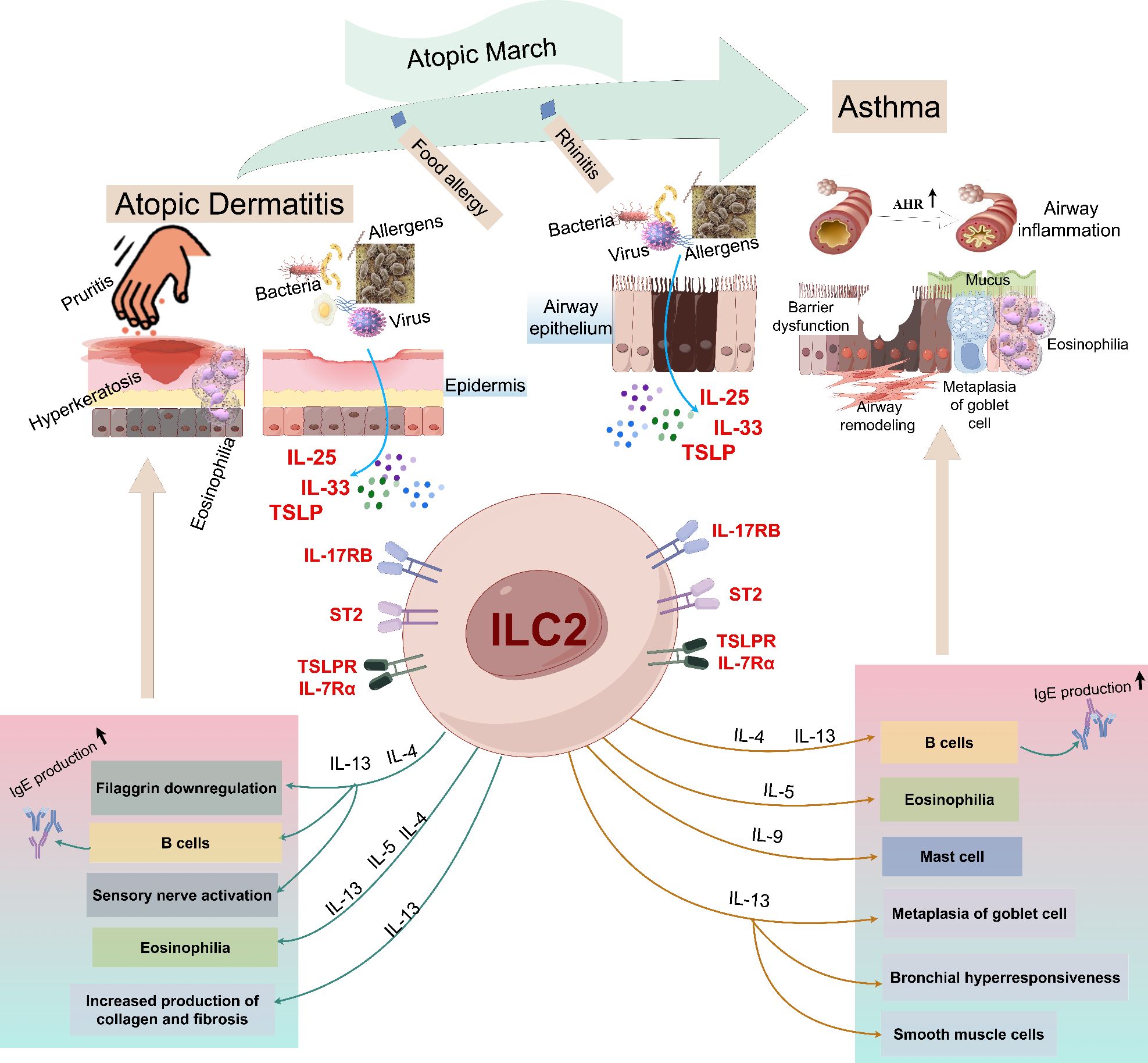
Figure 2. An illustrative overview of the roles of ILC2s in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis and asthma. Allergens enter the skin through the damaged skin barrier, which stimulates epithelial cells to release IL-25, IL-33 and TSLP, and then activates ILC2s, including IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13. These mediators cause the production of IgG1 and IgE, causing itching, skin inflammation and the decrease of skin barrier integrity, thus driving the onset of AD. When the allergen is encountered again, the alarm factors IL-25 and IL-33 released by the injured epithelial cells activate ILC2s, releasing various effector factors (including IL-4, IL-5, IL-9 and IL-13), among which IL-5 induces eosinophilia, IL-9 promotes mast cell growth and goblet cell metaplasia, and IL-4 and IL-13 pass through. IgG, Immunoglobulin G; IL, interleukin; ILC2s, group 2 innate lymphoid cells; AHR, airway hyperreactivity; ST2, IL-1 receptor-like 1 (IL1RL1); TSLP, thymic stromal lymphopoietin.
In animal models, sensitization with allergens such as OVA, cockroach extract, or HDM followed by subsequent challenge successfully induced AD-like skin manifestations as well as airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness (93, 153, 177–179). These findings provided evidence in support of the “outside-in” hypothesis, which posits that exposure to environmental allergens initiates the development of atopic conditions (177, 178). In vivo and in vitro studies have suggested that ILC2s might responsible for airway sensitization after skin exposure to allergens (179–182). Allergens through damaged skin barrier into the skin, stimulate epithelial cells to release alarmins including IL-25, IL-33 and TLSP. These cytokines activate ILC2s producing large amounts of T2 cytokines predominately IL-5 and IL-13, leading to AD when meeting again allergens, and can promote the occurrence of asthma independent of adaptive immunity (179). IL-5 is mainly responsible for the maturation and recruitment of eosinophils in the skin and airway (179). IL-13 damage the epithelial tight barrier and induce barrier leakiness in the skin and airway (180–182). Skin barrier injury sets into motion inflammation if these processes are continuing and the further generation of pro-inflammatory cytokines to establish a vicious cycle (10).
It is clearly that the epithelial and epidermal derived alarmins IL-25, IL-33, and TSLP play crucial roles in the action of allergic inflammation in asthma and AD. In vitro study, IL-25 acts synergistically with T2 cytokines to inhibit filaggrin expression and aggravate skin inflammation (183). And the expression of IL-25 was positively associated with airway inflammation and AHR in mouse study (184). IL-33 is highly expressed in skin or airway epithelial cells of AD or asthma animal models (185–188). IL-33 binds to IL-1 receptor appendages on a variety of cells through long-form serum stimulating factor-2 (ST2) and activates mouse and human ILC2s, leading to the development and aggravation of asthma and AD (188, 189). As a potent activator of ILC2s, TSLP is a key molecule in the progression of AD to asthma (190–192). Zhang and colleagues found that the increased expression of TSLP in skin keratinocytes not only triggered AD but also increased irritability asthma-like airway inflammation in a “atopic march” mice model by using calcipotriol topical, followed by OVA sensitization in the abdominal cavity and the nasal excitation (190). The results indicated that keratinocytic TSLP may act as an important mediator in the link of AD to asthma (190). Similarly, Jiang et al. established a mice model using topically calcipotriol, following by inhalation of HDM to induce asthma (193). It demonstrated that excessive production of TSLP in AD skin promoted airway sensitization, thereby triggered allergic asthma (193). The results indicated that TSLP represented a skin-transmitted signal in AD that promoted sensitivity to inhaled aeroallergens (193).
Given the critical role of ILC2s in asthma and AD, theoretically, biologics are effective by inhibiting ILC2s activation and proliferation in asthmatics combined with AD (Table 2). Excitingly, dupilumab as a human IgG4к monoclonal antibody blocking IL-4 receptor (a shared receptor for IL-4 and IL-13) is the first biologic approved both for AD (FDA in 2017 and EMA in 2019) and asthmatic patients (USA and Europe in 2018) (196). Subsequently, the significant efficiency of dupilumab for asthma combined with AD had been found in many case reports (197–199), and demonstrated by clinical trails (200) and real-world study (201). Boguniewicz et al. evaluated the efficiency of dupilumab for asthma combined with severe AD in four randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trials (200). The results showed statistically and clinically significant improvement in asthma control Questionnaire-5 score and AD-related outcomes (EASI, peak pruritus numerical rating scale, and dermatology life quality index) with acceptable safety (200). In a latest retrospective study, the researchers used dupilumab to treat severe AD patients with asthma, a reduction in the number of ILC2s could improve the two diseases at the same time has a good curative effect (202). This may suggest that we can reduce the number of ILC2s by blocking the effector of ILC2s in the treatment of AD-asthma, thereby improving the disease. These results put in evidence that dupilumab should be give priority to asthmatics combined with AD. As mentioned above, tezepelumab as a human monoclonal antibody that inhibits the action of TSLP has licensed as an add-on maintenance treatment for severe asthmatics regardless of the phenotype (136). Surprisingly, the current available evidence of tezepelumab in treating AD is not satisfactory although TSLP plays an important role in the pathogenesis of AD (173). Since overwhelming basic studies have demonstrated TSLP is a hopeful target against AD, new agents targeting TSLP or TSLPR are still given great expectations. Encouragingly, Adhikary and coworkers have developed a first potent and safe small-molecule TSLP inhibitor (BP79) leveraging an organ-on-chip technology (195). Application of BP79 onto atopic skin models co-cultivated with lung models has demonstrated its potential to effectively suppress immune cell infiltration and cytokine/chemokine secretion, while also upregulating skin barrier proteins (195). These effects suggest that BP79 may be a promising therapeutic option for the treatment of AD, and has a great potential to expand the therapeutic options in other atopic diseases such as asthma (195). The efficiency targeting IL-33 (itepekimab) and its receptor (astegolimab) for asthma have been confirmed in clinical trials (138), while they are failed to reach statistical significance in AD except etokimab (a humanized anti-IL-33 monoclonal antibody). However, there are lack of research of etokimab in treating asthma (169). The promising efficiency of SM17 targeting IL-25 has been reported in pre-clinical studies both in asthma and AD (143, 144), which could be a hopeful biologic for asthma and AD, even asthma combined AD.
6 Concluding remarks
As an important treatable treat of asthma, AD is not only trigger but also exacerbates asthma. This review suggests that ILC2s bridge the pathophysiological mechanisms of asthma combined with AD, and making them a promising target. However, to date, despite the availability of dupilumab for the treatment of asthma combined with AD, further research is still needed for other biologics/therapies targeting ILC2s. Particularly, new agents targeting TSLP or TSLPR such as ASP7266 (a novel recombinant monoclonal antibody against TSLPR) and BP79 (a small- molecular inhibitor against TSLP-TSLPR), which crucial role is demonstrated by overwhelming basic studies are given great expectations in treating asthma combined with AD, although there is no clinical trial supporting the efficacy of TSLP-targeting drugs against AD at present. With the advancement of technology, more and more new technologies, such as organs-on-chips, are facilitating rapid evaluation of new drug development. Undoubtedly, biologic agents serve as highly effective supplementary therapies for severe, refractory asthma and AD. Given their high cost, it is imperative to target their use specifically to patients who are most likely to derive significant benefit from these antibodies.
Furthermore, agents that regulate the functions of ILC2s continue to be anticipated, including activators or inhibitors of PD-1/PD-L1 or PD-L2, SCFAs, dopamine, hormones, and other entities. Fascinatingly, a recent study has unveiled the immunomodulatory function of the Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+ channel components Orai1 and Orai2 in mouse ILC2s (203). Blocking or genetic ablation of Orai1 and Orai2 downregulated mouse ILC2s effector functions and cytokine productions, and attenuated ILC2-mediated airway inflammation and AHR (203). This discovery holds promise for the development of novel therapies aimed at improving asthma and AD, paving the way for potential downstream targets in the treatment of asthma comorbid with AD.
Author contributions
YFL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YD: Writing – review & editing. FY: Writing – review & editing. MD: Writing – review & editing. XX: Writing – review & editing. YLY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SHA: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Supported by Sichuan Science and Technology Program(2022YFS0631) and Sichuan Province Pharmaceutical Administration Program(2023MS426).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to S-HA and Y-LY for generous help in critical revision of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
2. Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention (2024). Available online at: https://ginasthma.org (Accessed January 20, 2025).
3. Dierick BJH, van der Molen T, Flokstra-de-Blok BMJ, Muraro A, Postma MJ, Kocks JWH, et al. Burden and socioeconomics of asthma, allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis and food allergy. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. (2020) 20:437–53. doi: 10.1080/14737167.2020.1819793
4. Ogulur I, Pat Y, Ardicli O, Barletta E, Cevhertas L, Fernandez-Santamaria R, et al. Advances and highlights in biomarkers of allergic diseases. Allergy. (2021) 76:3659–86. doi: 10.1111/all.15089
5. Amat F, Soria A, Tallon P, Bourgoin-Heck M, Lambert N, Deschildre A, et al. New insights into the phenotypes of atopic dermatitis linked with allergies and asthma in children: An overview. Clin Exp Allergy. (2018) 48:919–34. doi: 10.1111/cea.13156
6. Li H, Dai T, Liu C, Liu Q, Tan C. Phenotypes of atopic dermatitis and the risk for subsequent asthma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2022) 86:365–72. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2021.07.064
7. Ahn K, Penn RB, Rattan S, Panettieri RA Jr, Voight BF, An SS. Mendelian randomization analysis reveals a complex genetic interplay among atopic dermatitis, asthma, and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2023) 207:130–7. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202205-0951OC
8. Ali Z, Egeberg A, Thyssen JP, Ulrik CS, Thomsen SF. Adults with concomitant atopic dermatitis and asthma have more frequent urgent healthcare utilization and less frequent scheduled follow-up visits than adults with atopic dermatitis or asthma only: a nationwide cohort study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2022) 36:2406–13. doi: 10.1111/jdv.18415
9. McDonald VM, Gibson PG. Treatable traits in asthma: moving beyond diagnostic labels. Med J Aust. (2022) 216:331–3. doi: 10.5694/mja2.51464
10. Akdis CA, Arkwright PD, Brüggen MC, Busse W, Gadina M, Guttman-Yassky E, et al. Type 2 immunity in the skin and lungs. Allergy. (2020) 75:1582–605. doi: 10.1111/all.14318
11. Kato A. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells in airway diseases. Chest. (2019) 156:141–9. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.04.101
12. Szeto ACH, Clark PA, Ferreira ACF, Heycock M, Griffiths EL, Jou E, et al. Mef2d potentiates type-2 immune responses and allergic lung inflammation. Science. (2024) 384:eadl0370. doi: 10.1126/science.adl0370
13. Spits H, Mjösberg J. Heterogeneity of type 2 innate lymphoid cells. Nat Rev Immunol. (2022) 22:701–12. doi: 10.1038/s41577-022-00704-5
14. Lu HF, Zhou YC, Luo DD, Yang DH, Wang XJ, Cheng BH, et al. ILC2s: Unraveling the innate immune orchestrators in allergic inflammation. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 131:111899. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111899
15. Vivier E, Artis D, Colonna M, Diefenbach A, Di Santo JP, Eberl G, et al. Innate lymphoid cells: 10 years on. Cell. (2018) 174:1054–66. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.07.017
16. Mjösberg JM, Trifari S, Crellin NK, Peters CP, van Drunen CM, Piet B, et al. Human IL-25- and IL-33-responsive type 2 innate lymphoid cells are defined by expression of CRTH2 and CD161. Nat Immunol. (2011) 12:1055–62. doi: 10.1038/ni.2104
17. Ricardo-Gonzalez RR, Van Dyken SJ, Schneider C, Lee J, Nussbaum JC, Liang HE, et al. Tissue signals imprint ILC2 identity with anticipatory function. Nat Immunol. (2018) 19:1093–9. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0201-4
18. Olguín-Martínez E, Ruiz-Medina BE, Licona-Limón P. Tissue-specific molecular markers and heterogeneity in type 2 innate lymphoid cells. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:757967. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.757967
19. Qin M, Fang Y, Zheng Q, Peng M, Wang L, Sang X, et al. Tissue microenvironment induces tissue specificity of ILC2. Cell Death Discovery. (2024) 10:324. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02096-y
20. Yashiro T, Moro K. Crossing the valley of death: Toward translational research regarding ILC2. Allergol Int. (2023) 72:187–93. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2022.12.006
21. Lloyd CM, Snelgrove RJ. Type 2 immunity: Expanding our view. Sci Immunol. (2018) 3:eaat1604. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aat1604
22. Bartemes KR, Kita H. Roles of innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) in allergic diseases: The 10-year anniversary for ILC2s. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2021) 147:1531–47. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2021.03.015
23. Wong CK, Li PW, Lam CW. Intracellular JNK, p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB regulate IL-25 induced release of cytokines and chemokines from costimulated T helper lymphocytes. Immunol Lett. (2007) 112:82–91. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2007.07.002
24. Xu M, Dong C. IL-25 in allergic inflammation. Immunol Rev. (2017) 278:185–91. doi: 10.1111/imr.12558
25. Liew FY, Girard JP, Turnquist HR. Interleukin-33 in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. (2016) 16:676–89. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.95
26. Kabata H, Moro K, Koyasu S. The group 2 innate lymphoid cell (ILC2) regulatory network and its underlying mechanisms. Immunol Rev. (2018) 286:37–52. doi: 10.1111/imr.12706
27. Fort MM, Cheung J, Yen D, Li J, Zurawski SM, Lo S, et al. IL-25 induces IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 and Th2-associated pathologies in vivo. Immunity. (2001) 15:985–95. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(01)00243-6
28. Cayrol C, Girard JP. Interleukin-33 (IL-33): A nuclear cytokine from the IL-1 family. Immunol Rev. (2018) 281:154–68. doi: 10.1111/imr.12619
29. Drake LY, Kita H. IL-33: biological properties, functions, and roles in airway disease. Immunol Rev. (2017) 278:173–84. doi: 10.1111/imr.12552
30. Moro K, Yamada T, Tanabe M, Takeuchi T, Ikawa T, Kawamoto H, et al. Innate production of T(H)2 cytokines by adipose tissue-associated c-Kit(+)Sca-1(+) lymphoid cells. Nature. (2010) 463:540–4. doi: 10.1038/nature08636
31. Neill DR, Wong SH, Bellosi A, Flynn RJ, Daly M, Langford TK, et al. Nuocytes represent a new innate effector leukocyte that mediates type-2 immunity. Nature. (2010) 464:1367–70. doi: 10.1038/nature08900
32. Lin JX, Leonard WJ. The common cytokine receptor γ Chain family of cytokines. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. (2018) 10:a028449. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a028449
33. Dostert C, Grusdat M, Letellier E, Brenner D. The TNF family of ligands and receptors: communication modules in the immune system and beyond. Physiol Rev. (2019) 99:115–60. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00045.2017
34. Spolski R, Gromer D, Leonard WJ. The γ-c family of cytokines: fine-tuning signals from IL-2 and IL-21 in the regulation of the immune response. F1000Res. (2017) 6:1872. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.12202.1
35. Roediger B, Kyle R, Tay SS, Mitchell AJ, Bolton HA, Guy TV, et al. IL-2 is a critical regulator of group 2 innate lymphoid cell function during pulmonary inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2015) 136:1653–1663.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.03.043
36. Mohapatra A, Van Dyken SJ, Schneider C, Nussbaum JC, Liang HE, Locksley RM. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells utilize the IRF4-IL-9 module to coordinate epithelial cell maintenance of lung homeostasis. Mucosal Immunol. (2016) 9:275–86. doi: 10.1038/mi.2015.59
37. Bal SM, Bernink JH, Nagasawa M, Groot J, Shikhagaie MM, Golebski K, et al. IL-1β, IL-4 and IL-12 control the fate of group 2 innate lymphoid cells in human airway inflammation in the lungs. Nat Immunol. (2016) 17:636–45. doi: 10.1038/ni.3444
38. Motomura Y, Morita H, Moro K, Nakae S, Artis D, Endo TA, et al. Basophil-derived interleukin-4 controls the function of natural helper cells, a member of ILC2s, in lung inflammation. Immunity. (2014) 40:758–71. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.04.013
39. Turner JE, Morrison PJ, Wilhelm C, Wilson M, Ahlfors H, Renauld JC, et al. IL-9-mediated survival of type 2 innate lymphoid cells promotes damage control in helminth-induced lung inflammation. J Exp Med. (2013) 210:2951–65. doi: 10.1084/jem.20130071
40. Matsuyama T, Salter BM, Emami Fard N, Machida K, Sehmi R. TNF superfamily and ILC2 activation in asthma. Biomolecules. (2024) 14:294. doi: 10.3390/biom14030294
41. Hurrell BP, Galle-Treger L, Jahani PS, Howard E, Helou DG, Banie H, et al. TNFR2 signaling enhances ILC2 survival, function, and induction of airway hyperreactivity. Cell Rep. (2019) 29:4509–4524.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.11.102
42. Meylan F, Richard AC, Siegel RM. TL1A and DR3, a TNF family ligand-receptor pair that promotes lymphocyte costimulation, mucosal hyperplasia, and autoimmune inflammation. Immunol Rev. (2011) 244:188–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01068.x
43. Richard AC, Tan C, Hawley ET, Gomez-Rodriguez J, Goswami R, Yang XP, et al. The TNF-family ligand TL1A and its receptor DR3 promote T cell-mediated allergic immunopathology by enhancing differentiation and pathogenicity of IL-9-producing T cells. J Immunol. (2015) 194:3567–82. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401220
44. Liu X, Zhang J, Zhang D, Pan Y, Zeng R, Xu C, et al. Necroptosis plays a role in TL1A-induced airway inflammation and barrier damage in asthma. Respir Res. (2024) 25:271. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02900-4
45. Liu S, Verma M, Michalec L, Liu W, Sripada A, Rollins D, et al. Steroid resistance of airway type 2 innate lymphoid cells from patients with severe asthma: The role of thymic stromal lymphopoietin. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2018) 141:257–268.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.03.032
46. Moro K, Kabata H, Tanabe M, Koga S, Takeno N, Mochizuki M, et al. Interferon and IL-27 antagonize the function of group 2 innate lymphoid cells and type 2 innate immune responses. Nat Immunol. (2016) 17:76–86. doi: 10.1038/ni.3309
47. García M, Carrasco García A, Weigel W, Christ W, Lira-Junior R, Wirth L, et al. Innate lymphoid cells are activated in HFRS, and their function can be modulated by hantavirus-induced type I interferons. PloS Pathog. (2024) 20:e1012390. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012390
48. Okuzumi S, Miyata J, Kabata H, Mochimaru T, Kagawa S, Masaki K, et al. TLR7 agonist suppresses group 2 innate lymphoid cell-mediated inflammation via IL-27-producing interstitial macrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2021) 65:309–18. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2021-0042OC
49. Ogasawara N, Poposki JA, Klingler AI, Tan BK, Weibman AR, Hulse KE, et al. IL-10, TGF-β, and glucocorticoid prevent the production of type 2 cytokines in human group 2 innate lymphoid cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2018) 141:1147–1151.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.09.025
50. Golebski K, Layhadi JA, Sahiner U, Steveling-Klein EH, Lenormand MM, Li RCY, et al. Induction of IL-10-producing type 2 innate lymphoid cells by allergen immunotherapy is associated with clinical response. Immunity. (2021) 54:291–307.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.12.013
51. Rigas D, Lewis G, Aron JL, Wang B, Banie H, Sankaranarayanan I, et al. Type 2 innate lymphoid cell suppression by regulatory T cells attenuates airway hyperreactivity and requires inducible T-cell costimulator-inducible T-cell costimulator ligand interaction. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2017) 139:1468–1477.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.08.034
52. Morita H, Arae K, Unno H, Miyauchi K, Toyama S, Nambu A, et al. An interleukin-33-mast cell-interleukin-2 axis suppresses papain-induced allergic inflammation by promoting regulatory T cell numbers. Immunity. (2015) 43:175–86. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.06.021
53. Wang L, Tang J, Yang X, Zanvit P, Cui K, Ku WL, et al. TGF-β induces ST2 and programs ILC2 development. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:35. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13734-w
54. Denney L, Byrne AJ, Shea TJ, Buckley JS, Pease JE, Herledan GM, et al. Pulmonary epithelial cell-derived cytokine TGF-β1 is a critical cofactor for enhanced innate lymphoid cell function. Immunity. (2015) 43:945–58. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.10.012
55. Wang Y, Mou YK, Liu WC, Wang HR, Song XY, Yang T, et al. Genetically predicted immune cell-mediated effect of lipid metabolism on allergic diseases: A two-step, mediation mendelian randomization study. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. (2024) 14:1–15. doi: 10.1159/000542036.
56. Kan LL, Li P, Hon SS, Lai AY, Li A, Wong KC, et al. Deciphering the interplay between the epithelial barrier, immune cells, and metabolic mediators in allergic disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:6913. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136913
57. Ualiyeva S, Lemire E, Aviles EC, Wong C, Boyd AA, Lai J, et al. Tuft cell-produced cysteinyl leukotrienes and IL-25 synergistically initiate lung type 2 inflammation. Sci Immunol. (2021) 6:eabj0474. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abj0474
58. Lund SJ, Portillo A, Cavagnero K, Baum RE, Naji LH, Badrani JH, et al. Leukotriene C4 potentiates IL-33-induced group 2 innate lymphoid cell activation and lung inflammation. J Immunol. (2017) 199:1096–104. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601569
59. Jin J, Sunusi S, Lu H. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) are important in typical type 2 immune-mediated diseases and an essential therapeutic target. J Int Med Res. (2022) 50:3000605211053156. doi: 10.1177/03000605211053156
60. Carstensen S, Gress C, Erpenbeck VJ, Kazani SD, Hohlfeld JM, Sandham DA, et al. Prostaglandin D2 metabolites activate asthmatic patient-derived type 2 innate lymphoid cells and eosinophils via the DP2 receptor. Respir Res. (2021) 22:262. doi: 10.1186/s12931-021-01852-3
61. Liu Y, Wei L, He C, Chen R, Meng L. Lipoxin A4 inhibits ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation and airway remodeling in a mouse model of asthma. Chem Biol Interact. (2021) 349:109660. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2021.109660
62. Robb CT, Zhou Y, Felton JM, Zhang B, Goepp M, Jheeta P, et al. Metabolic regulation by prostaglandin E2 impairs lung group 2 innate lymphoid cell responses. Allergy. (2023) 78:714–30. doi: 10.1111/all.15541
63. Zhou W, Toki S, Zhang J, Goleniewksa K, Newcomb DC, Cephus JY, et al. Prostaglandin I2 signaling and inhibition of group 2 innate lymphoid cell responses. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2016) 193:31–42. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201410-1793OC
64. Chen W, Shu Q, Fan J. Neural regulation of interactions between group 2 innate lymphoid cells and pulmonary immune cells. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:576929. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.576929
65. Ju X, Nagashima A, Dvorkin-Gheva A, Wattie J, Howie K, Whetstone C, et al. Neuromedin-U mediates rapid activation of airway group 2 innate lymphoid cells in mild asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2024) 210:755–65. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202311-2164OC
66. Cao Y, Li Y, Wang X, Liu S, Zhang Y, Liu G, et al. Dopamine inhibits group 2 innate lymphoid cell-driven allergic lung inflammation by dampening mitochondrial activity. Immunity. (2023) 56:320–335.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.12.017
67. Trigunaite A, Dimo J, Jørgensen TN. Suppressive effects of androgens on the immune system. Cell Immunol. (2015) 294:87–94. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2015.02.004
68. Kovats S. Estrogen receptors regulate innate immune cells and signaling pathways. Cell Immunol. (2015) 294:63–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2015.01.018
69. Cephus JY, Stier MT, Fuseini H, Yung JA, Toki S, Bloodworth MH, et al. Testosterone attenuates group 2 innate lymphoid cell-mediated airway inflammation. Cell Rep. (2017) 21:2487–99. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.110
70. Bartemes K, Chen CC, Iijima K, Drake L, Kita H. IL-33-responsive group 2 innate lymphoid cells are regulated by female sex hormones in the uterus. J Immunol. (2018) 200:229–36. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1602085
71. Ruiter B, Patil SU, Shreffler WG. Vitamins A and D have antagonistic effects on expression of effector cytokines and gut-homing integrin in human innate lymphoid cells. Clin Exp Allergy. (2015) 45:1214–25. doi: 10.1111/cea.12568
72. Spencer SP, Wilhelm C, Yang Q, Hall JA, Bouladoux N, Boyd A, et al. Adaptation of innate lymphoid cells to a micronutrient deficiency promotes type 2 barrier immunity. Science. (2014) 343:432–7. doi: 10.1126/science.1247606
73. Julia V, Macia L, Dombrowicz D. The impact of diet on asthma and allergic diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. (2015) 15:308–22. doi: 10.1038/nri3830
74. Trompette A, Gollwitzer ES, Yadava K, Sichelstiel AK, Sprenger N, Ngom-Bru C, et al. Gut microbiota metabolism of dietary fiber influences allergic airway disease and hematopoiesis. Nat Med. (2014) 20:159–66. doi: 10.1038/nm.3444
75. Lewis G, Wang B, Shafiei Jahani P, Hurrell BP, Banie H, Aleman Muench GR, et al. Dietary fiber-induced microbial short chain fatty acids suppress ILC2-dependent airway inflammation. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:2051. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02051
76. Thio CL, Chi PY, Lai AC, Chang YJ. Regulation of type 2 innate lymphoid cell-dependent airway hyperreactivity by butyrate. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2018) 142:1867–1883.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.02.032
77. Lin X, Kang K, Chen P, Zeng Z, Li G, Xiong W, et al. Regulatory mechanisms of PD-1/PD-L1 in cancers. Mol Cancer. (2024) 23:108. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02023-w
78. Yu Y, Tsang JC, Wang C, Clare S, Wang J, Chen X, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq identifies a PD-1hi ILC progenitor and defines its development pathway. Nature. (2016) 539:102–6. doi: 10.1038/nature20105
79. Taylor S, Huang Y, Mallett G, Stathopoulou C, Felizardo TC, Sun MA, et al. PD-1 regulates KLRG1+ group 2 innate lymphoid cells. J Exp Med. (2017) 214:1663–78. doi: 10.1084/jem.20161653
80. Helou DG, Shafiei-Jahani P, Lo R, Howard E, Hurrell BP, Galle-Treger L, et al. PD-1 pathway regulates ILC2 metabolism and PD-1 agonist treatment ameliorates airway hyperreactivity. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:3998. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17813-1
81. Ohne Y, Silver JS, Thompson-Snipes L, Collet MA, Blanck JP, Cantarel BL, et al. IL-1 is a critical regulator of group 2 innate lymphoid cell function and plasticity. Nat Immunol. (2016) 17:646–55. doi: 10.1038/ni.3447
82. Silver JS, Kearley J, Copenhaver AM, Sanden C, Mori M, Yu L, et al. Erratum: Inflammatory triggers associated with exacerbations of COPD orchestrate plasticity of group 2 innate lymphoid cells in the lungs. Nat Immunol. (2016) 17:1005. doi: 10.1038/ni0816-1005c
83. Bernink JH, Ohne Y, Teunissen MBM, Wang J, Wu J, Krabbendam L, et al. c-Kit-positive ILC2s exhibit an ILC3-like signature that may contribute to IL-17-mediated pathologies. Nat Immunol. (2019) 20:992–1003. doi: 10.1038/s41590-019-0423-0
84. Ju X, Fard NE, Bhalla A, Dvorkin-Gheva A, Xiao M, Radford K, et al. A population of c-kit+ IL-17A+ ILC2s in sputum from individuals with severe asthma supports ILC2 to ILC3 trans-differentiation. Sci Transl Med. (2025) 17(781):eado6649. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.ado6649
85. Busse PJ, McDonald VM, Wisnivesky JP, Gibson PG. Asthma across the ages: adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. (2020) 8:1828–38. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.03.044
86. Papi A, Brightling C, Pedersen SE, Reddel HK. Asthma. Lancet. (2018) 391:783–800. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33311-1
87. Wenzel SE, Schwartz LB, Langmack EL, Halliday JL, Trudeau JB, Gibbs RL, et al. Evidence that severe asthma can be divided pathologically into two inflammatory subtypes with distinct physiologic and clinical characteristics. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (1999) 160:1001–8. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.160.3.9812110
88. Anderson GP. Endotyping asthma: new insights into key pathogenic mechanisms in a complex, heterogeneous disease. Lancet. (2008) 372:1107–19. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61452-X
89. Lötvall J, Akdis CA, Bacharier LB, Bjermer L, Casale TB, Custovic A, et al. Asthma endotypes: a new approach to classification of disease entities within the asthma syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2011) 127:355–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.11.037
90. Agache I, Akdis CA. Endotypes of allergic diseases and asthma: An important step in building blocks for the future of precision medicine. Allergol Int. (2016) 65:243–52. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2016.04.011
91. Gans MD, Gavrilova T. Understanding the immunology of asthma: Pathophysiology, biomarkers, and treatments for asthma endotypes. Paediatr Respir Rev. (2020) 36:118–27. doi: 10.1016/j.prrv.2019.08.002
92. Matsuyama T, Machida K, Mizuno K, Matsuyama H, Dotake Y, Shinmura M, et al. The functional role of group 2 innate lymphoid cells in asthma. Biomolecules. (2023) 13:893. doi: 10.3390/biom13060893
93. Peters MC, Ringel L, Dyjack N, Herrin R, Woodruff PG, Rios C, et al. A transcriptomic method to determine airway immune dysfunction in T2-high and T2-low asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2019) 199:465–77. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201807-1291OC
94. Klein Wolterink RG, Kleinjan A, van Nimwegen M, Bergen I, de Bruijn M, Levani Y, et al. Pulmonary innate lymphoid cells are major producers of IL-5 and IL-13 in murine models of allergic asthma. Eur J Immunol. (2012) 42:1106–16. doi: 10.1002/eji.201142018
95. Aldossary H, Karkout R, Couto K, Labrie L, Fixman ED. IL-33-experienced group 2 innate lymphoid cells in the lung are poised to enhance type 2 inflammation selectively in adult female mice. Respir Res. (2024) 25:427. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03043-2
96. Barlow JL, Bellosi A, Hardman CS, Drynan LF, Wong SH, Cruickshank JP, et al. Innate IL-13-producing nuocytes arise during allergic lung inflammation and contribute to airways hyperreactivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2012) 129:191–8.e84. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.09.041
97. Bartemes KR, Iijima K, Kobayashi T, Kephart GM, McKenzie AN, Kita H. IL-33-responsive lineage- CD25+ CD44(hi) lymphoid cells mediate innate type 2 immunity and allergic inflammation in the lungs. J Immunol. (2012) 188:1503–13. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102832
98. Kumar RK, Foster PS, Rosenberg HF. Respiratory viral infection, epithelial cytokines, and innate lymphoid cells in asthma exacerbations. J Leukoc Biol. (2014) 96:391–6. doi: 10.1189/jlb.3RI0314-129R
99. Jarick KJ, Topczewska PM, Jakob MO, Yano H, Arifuzzaman M, Gao X, et al. Non-redundant functions of group 2 innate lymphoid cells. Nature. (2022) 611:794–800. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05395-5
100. Halim TY, Hwang YY, Scanlon ST, Zaghouani H, Garbi N, Fallon PG, et al. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells license dendritic cells to potentiate memory TH2 cell responses. Nat Immunol. (2016) 17:57–64. doi: 10.1038/ni.3294
101. Wang C, Xu ZB, Peng YQ, Zhang HY, Yu QN, Guo YB, et al. Sex differences in group 2 innate lymphoid cell-dominant allergic airway inflammation. Mol Immunol. (2020) 128:89–97. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2020.09.019
102. Singh AK, Stock P, Akbari O. Role of PD-L1 and PD-L2 in allergic diseases and asthma. Allergy. (2011) 66:155–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2010.02458.x
103. McAlees JW, Lajoie S, Dienger K, Sproles AA, Richgels PK, Yang Y, et al. Differential control of CD4(+) T-cell subsets by the PD-1/PD-L1 axis in a mouse model of allergic asthma. Eur J Immunol. (2015) 45:1019–29. doi: 10.1002/eji.201444778
104. Bratke K, Fritz L, Nokodian F, Geißler K, Garbe K, Lommatzsch M, et al. Differential regulation of PD-1 and its ligands in allergic asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. (2017) 47:1417–25. doi: 10.1111/cea.13017
105. Wang L, Netto KG, Zhou L, Liu X, Wang M, Zhang G, et al. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis reveals the immune landscape of lung in steroid-resistant asthma exacerbation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2021) 118:e2005590118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2005590118
106. Kim J, Ham J, Kang HR, Bae YS, Kim T, Kim HY. JAK3 inhibitor suppresses multipotent ILC2s and attenuates steroid-resistant asthma. Sci Adv. (2023) 9:eadi3770. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adi3770
107. Malik B, Bartlett NW, Upham JW, Nichol KS, Harrington J, Wark PAB. Severe asthma ILC2s demonstrate enhanced proliferation that is modified by biologics. Respirology. (2023) 28:758–66. doi: 10.1111/resp.14506
108. Bartemes KR, Kephart GM, Fox SJ, Kita H. Enhanced innate type 2 immune response in peripheral blood from patients with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2014) 134:671–678.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.06.024
109. Liu T, Wu J, Zhao J, Wang J, Zhang Y, Liu L, et al. Type 2 innate lymphoid cells: A novel biomarker of eosinophilic airway inflammation in patients with mild to moderate asthma. Respir Med. (2015) 109:1391–6. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2015.09.016
110. Yu QN, Tan WP, Fan XL, Guo YB, Qin ZL, Li CL, et al. Increased group 2 innate lymphoid cells are correlated with eosinophilic granulocytes in patients with allergic airway inflammation. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. (2018) 176:124–32. doi: 10.1159/000488050
111. Smith SG, Chen R, Kjarsgaard M, Huang C, Oliveria JP, O'Byrne PM, et al. Increased numbers of activated group 2 innate lymphoid cells in the airways of patients with severe asthma and persistent airway eosinophilia. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2016) 137:75–86.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.05.037
112. van der Ploeg EK, Golebski K, van Nimwegen M, Fergusson JR, Heesters BA, Martinez-Gonzalez I, et al. Steroid-resistant human inflammatory ILC2s are marked by CD45RO and elevated in type 2 respiratory diseases. Sci Immunol. (2021) 6:eabd3489. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abd3489
113. Chen R, Smith SG, Salter B, El-Gammal A, Oliveria JP, Obminski C, et al. Allergen-induced increases in sputum levels of group 2 innate lymphoid cells in subjects with asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2017) 196:700–12. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201612-2427OC
114. Barnes PJ. Corticosteroid resistance in patients with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2013) 131:636–45. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.12.1564
115. Wadhwa R, Dua K, Adcock IM, Horvat JC, Kim RY, Hansbro PM. Cellular mechanisms underlying steroid-resistant asthma. Eur Respir Rev. (2019) 28:190096. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0096-2019
116. Mansfield L, Bernstein JA. Tiotropium in asthma: From bench to bedside. Respir Med. (2019) 154:47–55. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2019.06.008
117. Kerstjens HA, Engel M, Dahl R, Paggiaro P, Beck E, Vandewalker M, et al. Tiotropium in asthma poorly controlled with standard combination therapy. N Engl J Med. (2012) 367:1198–207. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1208606
118. Peters SP, Kunselman SJ, Icitovic N, Moore WC, Pascual R, Ameredes BT, et al. Tiotropium bromide step-up therapy for adults with uncontrolled asthma. N Engl J Med. (2010) 363:1715–26. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1008770
119. Kerstjens HA, Moroni-Zentgraf P, Tashkin DP, Dahl R, Paggiaro P, Vandewalker M, et al. Tiotropium improves lung function, exacerbation rate, and asthma control, independent of baseline characteristics including age, degree of airway obstruction, and allergic status. Respir Med. (2016) 117:198–206. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2016.06.013
120. Casale TB, Bateman ED, Vandewalker M, Virchow JC, Schmidt H, Engel M, et al. Tiotropium respimat add-on is efficacious in symptomatic asthma, independent of T2 phenotype. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. (2018) 6:923–935.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2017.08.037
121. Matsuyama T, Machida K, Motomura Y, Takagi K, Doutake Y, Tanoue-Hamu A, et al. Long-acting muscarinic antagonist regulates group 2 innate lymphoid cell-dependent airway eosinophilic inflammation. Allergy. (2021) 76:2785–96. doi: 10.1111/all.14836
122. Williams TC, Loo SL, Nichol KS, Reid AT, Veerati PC, Esneau C, et al. IL-25 blockade augments antiviral immunity during respiratory virus infection. Commun Biol. (2022) 5:415. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03367-z
123. US Food and Drug Administration. Drug trials snapshots: NUCALA (mepolizumab) . Available online at: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases/drug-trials-snapshots-nucala (Accessed January 20, 2025).
124. Nair P, Pizzichini MM, Kjarsgaard M, Inman MD, Efthimiadis A, Pizzichini E, et al. Mepolizumab for prednisone-dependent asthma with sputum eosinophilia. N Engl J Med. (2009) 360:985–93. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0805435
125. Haldar P, Brightling CE, Hargadon B, Gupta S, Monteiro W, Sousa A, et al. Mepolizumab and exacerbations of refractory eosinophilic asthma. N Engl J Med. (2009) 360:973–84. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0808991
126. Ortega HG, Liu MC, Pavord ID, Brusselle GG, FitzGerald JM, Chetta A, et al. Mepolizumab treatment in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma. N Engl J Med. (2014) 371:1198–207. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1403290
127. Pavord ID, Korn S, Howarth P, Bleecker ER, Buhl R, Keene ON, et al. Mepolizumab for severe eosinophilic asthma (DREAM): a multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. (2012) 380:651–9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60988-X
128. Khatri S, Moore W, Gibson PG, Leigh R, Bourdin A, Maspero J, et al. Assessment of the long-term safety of mepolizumab and durability of clinical response in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2019) 143:1742–1751.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.09.033
129. Lee JK, Pollard SJ, Liu MC, Schleich F, Pelaia G, Almonacid C, et al. Mepolizumab real-world effectiveness in severe asthma with an eosinophilic phenotype and overlapping severe allergic asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. (2025) S1081-1206(25)00003-1. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2025.01.002
130. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves asthma indication for Dupixent®(dupilumab) . Available online at: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/761055s007lbl.pdf (Accessed January20, 2025).
131. Ricciardolo FLM, Bertolini F, Carriero V. The role of dupilumab in severe asthma. Biomedicines. (2021) 9:1096. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9091096
132. Scioscia G, Nolasco S, Campisi R, Quarato CMI, Caruso C, Pelaia C, et al. Switching biological therapies in severe asthma. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:9563. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119563
133. Ramírez-Jiménez F, Pavón-Romero GF, Velásquez-Rodríguez JM, López-Garza MI, Lazarini-Ruiz JF, Gutiérrez-Quiroz KV, et al. Biologic therapies for asthma and allergic disease: past, present, and future. Pharm (Basel). (2023) 16:270. doi: 10.3390/ph16020270
134. Rabe KF, Nair P, Brusselle G, Maspero JF, Castro M, Sher L, et al. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in glucocorticoid-dependent severe asthma. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:2475–85. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1804093
135. Patel G, Pan J, Ye L, Shen X, Rosloff D, D'Souza SS, et al. Blockade of IL-4Rα inhibits group 2 innate lymphoid cell responses in asthma patients. Clin Exp Allergy. (2020) 50:267–70. doi: 10.1111/cea.13514
136. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves maintenance treatment Tezspire (tezepelumab-ekko) for severe asthma drug . Available online at: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/news-events-human-drugs/fda-approves-maintenance-treatment-severe-asthma (Accessed January 20, 2025).
137. Corren J, Garcia Gil E, Griffiths JM, Parnes JR, van der Merwe R, Sałapa K, et al. Tezepelumab improves patient-reported outcomes in patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma in PATHWAY. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. (2021) 126:187–93. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2020.10.008
138. Menzies-Gow A, Corren J, Bourdin A, Chupp G, Israel E, Wechsler ME, et al. Tezepelumab in adults and adolescents with severe, uncontrolled asthma. N Engl J Med. (2021) 384:1800–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2034975
139. Wechsler ME, Ruddy MK, Pavord ID, Israel E, Rabe KF, Ford LB, et al. Efficacy and safety of itepekimab in patients with moderate-to-severe asthma. N Engl J Med. (2021) 385:1656–68. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2024257
140. Kelsen SG, Agache IO, Soong W, Israel E, Chupp GL, Cheung DS, et al. Astegolimab (anti-ST2) efficacy and safety in adults with severe asthma: A randomized clinical trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2021) 148:790–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2021.03.044
141. Gregory LG, Jones CP, Walker SA, Sawant D, Gowers KH, Campbell GA, et al. IL-25 drives remodelling in allergic airways disease induced by house dust mite. Thorax. (2013) 68:82–90. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2012-202003
142. Ballantyne SJ, Barlow JL, Jolin HE, Nath P, Williams AS, Chung KF, et al. Blocking IL-25 prevents airway hyperresponsiveness in allergic asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2007) 120:1324–31. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2007.07.051
143. Hong JY, Bentley JK, Chung Y, Lei J, Steenrod JM, Chen Q, et al. Neonatal rhinovirus induces mucous metaplasia and airways hyperresponsiveness through IL-25 and type 2 innate lymphoid cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2014) 134:429–39. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.04.020
144. Lam LH, Li W, Wu WC, Chow KC, Au WYD, Xu G, et al. SM17, a new IL-17RB-targeting antibody, ameliorates disease progression in a mouse model of atopic dermatitis. Allergy. (2024) 79:1625–8. doi: 10.1111/all.16120
145. Xu G, Paglialunga S, Qian X, Ding R, Webster K, van Haarst A, et al. Evaluation of the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of SM17 in healthy volunteers: results from pre-clinical models and a first-in-human, randomized, double blinded clinical trial. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1495540. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1495540
146. Liu J, Qian B, Zhou L, Shen G, Tan Y, Liu S, et al. IL25 enhanced colitis-associated tumorigenesis in mice by upregulating transcription factor GLI1. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:837262. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.837262
147. Ohya Y, Saeki H, Nawata H, Arima K, Inukai M, Rossi AB, et al. The disease burden of pediatric patients with atopic dermatitis in Japan. Pediatr Dermatol. (2023) 40:851–6. doi: 10.1111/pde.15399
148. Savva M, Papadopoulos NG, Gregoriou S, Katsarou S, Papapostolou N, Makris M, et al. Recent advancements in the atopic dermatitis mechanism. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). (2024) 29:84. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2902084
149. Saunders SP, Moran T, Floudas A, Wurlod F, Kaszlikowska A, Salimi M, et al. Spontaneous atopic dermatitis is mediated by innate immunity, with the secondary lung inflammation of the atopic march requiring adaptive immunity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2016) 137:482–91. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.06.045
150. Miraglia del Giudice M, Decimo F, Leonardi S, Maioello N, Amelio R, Capasso A, et al. Immune dysregulation in atopic dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. (2006) 27:451–5. doi: 10.2500/aap.2006.27.2887
151. Jurakic Toncic R, Kezic S, Jakasa I, Ljubojevic Hadzavdic S, Balic A, Petkovic M, et al. Filaggrin loss-of-function mutations and levels of filaggrin degradation products in adult patients with atopic dermatitis in Croatia. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2020) 34:1789–94. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16232
152. Gonzalez JR, Celli A, Weckel A, Dhariwala MO, Merana GR, Ojewumi OT, et al. FLG deficiency in mice alters the early-life CD4+ T-cell response to skin commensal bacteria. J Invest Dermatol. (2023) 143:790–800.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2022.10.019
153. Kim BS, Siracusa MC, Saenz SA, Noti M, Monticelli LA, Sonnenberg GF, et al. TSLP elicits IL-33-independent innate lymphoid cell responses to promote skin inflammation. Sci Transl Med. (2013) 5:170ra16. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3005374
154. Salimi M, Barlow JL, Saunders SP, Xue L, Gutowska-Owsiak D, Wang X, et al. A role for IL-25 and IL-33-driven type-2 innate lymphoid cells in atopic dermatitis. J Exp Med. (2013) 210:2939–50. doi: 10.1084/jem.20130351
155. Mashiko S, Mehta H, Bissonnette R, Sarfati M. Increased frequencies of basophils, type 2 innate lymphoid cells and Th2 cells in skin of patients with atopic dermatitis but not psoriasis. J Dermatol Sci. (2017) 88:167–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2017.07.003
156. Bielecki P, Riesenfeld SJ, Hütter JC, Torlai Triglia E, Kowalczyk MS, Ricardo-Gonzalez RR, et al. Skin-resident innate lymphoid cells converge on a pathogenic effector state. Nature. (2021) 592:128–32. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03188-w
157. Imai Y, Yasuda K, Sakaguchi Y, Haneda T, Mizutani H, Yoshimoto T, et al. Skin-specific expression of IL-33 activates group 2 innate lymphoid cells and elicits atopic dermatitis-like inflammation in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2013) 110:13921–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1307321110
158. Imai Y, Yasuda K, Nagai M, Kusakabe M, Kubo M, Nakanishi K, et al. IL-33-induced atopic dermatitis-like inflammation in mice is mediated by group 2 innate lymphoid cells in concert with basophils. J Invest Dermatol. (2019) 139:2185–2194.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2019.04.016
159. Leyva-Castillo JM, Galand C, Mashiko S, Bissonnette R, McGurk A, Ziegler SF, et al. ILC2 activation by keratinocyte-derived IL-25 drives IL-13 production at sites of allergic skin inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2020) 145:1606–1614.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.02.026
160. Xu M, Li C, Yang J, Ye A, Yan L, Yeoh BS, et al. Activation of CD81+ skin ILC2s by cold-sensing TRPM8+ neuron-derived signals maintains cutaneous thermal homeostasis. Sci Immunol. (2022) 7:eabe0584. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abe0584
161. Kobayashi T, Voisin B, Kim DY, Kennedy EA, Jo JH, Shih HY, et al. Homeostatic control of sebaceous glands by innate lymphoid cells regulates commensal bacteria equilibrium. Cell. (2019) 176:982–997.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.12.031
162. Ebina-Shibuya R, Leonard WJ. Role of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in allergy and beyond. Nat Rev Immunol. (2023) 23:24–37. doi: 10.1038/s41577-022-00735-y
163. García-Reyes MM, Zumaya-Pérez LC, Pastelin-Palacios R, Moreno-Eutimio MA. Serum thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) levels in atopic dermatitis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Exp Med. (2023) 23:4129–39. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01147-5
164. Luo Y, Zhou B, Zhao M, Tang J, Lu Q. Promoter demethylation contributes to TSLP overexpression in skin lesions of patients with atopic dermatitis. Clin Exp Dermatol. (2014) 39:48–53. doi: 10.1111/ced.12206
165. Galván Morales MA, Montero-Vargas JM, Vizuet-de-Rueda JC, Teran LM. New insights into the role of PD-1 and its ligands in allergic disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:11898. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111898
166. Bonamichi-Santos R, Aun MV, Kalil J, Castells MC, Giavina-Bianchi P. PD-L1 blockade during allergen sensitization inhibits the synthesis of specific antibodies and decreases mast cell activation in a murine model of active cutaneous anaphylaxis. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:655958. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.655958
167. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves new eczema drug Dupixent . Available online at: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-eczema-drug-dupixent (Accessed January 20, 2025).
168. Imai Y, Kusakabe M, Nagai M, Yasuda K, Yamanishi K. Dupilumab effects on innate lymphoid cell and helper T cell populations in patients with atopic dermatitis. JID Innov. (2021) 1:100003. doi: 10.1016/j.xjidi.2021.100003
169. Chen YL, Gutowska-Owsiak D, Hardman CS, Westmoreland M, MacKenzie T, Cifuentes L, et al. Proof-of-concept clinical trial of etokimab shows a key role for IL-33 in atopic dermatitis pathogenesis. Sci Transl Med. (2019) 11:eaax2945. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aax2945
170. Kosloski MP, Guttman-Yassky E, Cork MJ, Worm M, Nahm DH, Zhu X, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of itepekimab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: Results from two terminated phase II trials. Clin Transl Sci. (2024) 17:e13874. doi: 10.1111/cts.13874
171. Numazaki M, Abe M, Hanaoka K, Imamura E, Maeda M, Kimura A, et al. ASP7266, a novel antibody against human thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor for the treatment of allergic diseases. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2022) 380:26–33. doi: 10.1124/jpet.121.000686
172. Lee JK, Seok JK, Cho I, Yang G, Kim KB, Kwack SJ, et al. Topical application of celastrol alleviates atopic dermatitis symptoms mediated through the regulation of thymic stromal lymphopoietin and group 2 innate lymphoid cells. J Toxicol Environ Health A. (2021) 84:922–31. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2021.1955785
173. Simpson EL, Parnes JR, She D, Crouch S, Rees W, Mo M, et al. Tezepelumab, an anti-thymic stromal lymphopoietin monoclonal antibody, in the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: A randomized phase 2a clinical trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2019) 80:1013–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.059
174. Zhu Z, Lee PH, Chaffin MD, Chung W, Loh PR, Lu Q, et al. A genome-wide cross-trait analysis from UK Biobank highlights the shared genetic architecture of asthma and allergic diseases. Nat Genet. (2018) 50(6):857–64. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0121-0
175. Davidson WF, Leung DYM, Beck LA, Berin CM, Boguniewicz M, Busse WW, et al. Report from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases workshop on "Atopic dermatitis and the atopic march: Mechanisms and interventions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2019) 143(3):894–913. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.01.003
176. McDonald VM, Hamada Y, Agusti A, Gibson PG. Treatable traits in asthma: the importance of extrapulmonary traits-GERD, CRSwNP, atopic dermatitis, and depression/anxiety. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. (2024) 12:824–37. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2024.01.020
177. Spergel JM, Mizoguchi E, Brewer JP, Martin TR, Bhan AK, Geha RS. Epicutaneous sensitization with protein antigen induces localized allergic dermatitis and hyperresponsiveness to methacholine after single exposure to aerosolized antigen in mice. J Clin Invest. (1998) 101:1614–22. doi: 10.1172/JCI1647
178. Lee MF, Chu YW, Wu CS, Lee MH, Chen YH, Wang NM. Indoor aeroallergens from American cockroaches and mites initiate atopic march via cutaneous contact in a murine model. PloS One. (2023) 18:e0289138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0289138
179. Han H, Roan F, Ziegler SF. The atopic march: current insights into skin barrier dysfunction and epithelial cell-derived cytokines. Immunol Rev. (2017) 278:116–30. doi: 10.1111/imr.12546
180. Furue M. Regulation of filaggrin, loricrin, and involucrin by IL-4, IL-13, IL-17A, IL-22, AHR, and NRF2: pathogenic implications in atopic dermatitis. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:5382. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155382
181. Sugita K, Altunbulakli C, Morita H, Sugita A, Kubo T, Kimura R, et al. Human type 2 innate lymphoid cells disrupt skin keratinocyte tight junction barrier by IL-13. Allergy. (2019) 74:2534–7. doi: 10.1111/all.13935
182. Sugita K, Steer CA, Martinez-Gonzalez I, Altunbulakli C, Morita H, Castro-Giner F, et al. Type 2 innate lymphoid cells disrupt bronchial epithelial barrier integrity by targeting tight junctions through IL-13 in asthmatic patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2018) 141:300–310.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.02.038
183. Kim BE, Bin L, Ye YM, Ramamoorthy P, Leung DYM. IL-25 enhances HSV-1 replication by inhibiting filaggrin expression, and acts synergistically with Th2 cytokines to enhance HSV-1 replication. J Invest Dermatol. (2013) 133:2678–85. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.223
184. Kang CM, Jang AS, Ahn MH, Shin JA, Kim JH, Choi YS, et al. Interleukin-25 and interleukin-13 production by alveolar macrophages in response to particles. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2005) 33:290–6. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0003OC
185. Molofsky AB, Savage AK, Locksley RM. Interleukin-33 in tissue homeostasis, injury, and inflammation. Immunity. (2015) 42:1005–19. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.06.006
186. Savinko T, Karisola P, Lehtimäki S, Lappeteläinen AM, Haapakoski R, Wolff H, et al. ST2 regulates allergic airway inflammation and T-cell polarization in epicutaneously sensitized mice. J Invest Dermatol. (2013) 133:2522–9. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.195
187. Savinko T, Matikainen S, Saarialho-Kere U, Lehto M, Wang G, Lehtimäki S, et al. IL-33 and ST2 in atopic dermatitis: expression profiles and modulation by triggering factors. J Invest Dermatol. (2012) 132:1392–400. doi: 10.1038/jid.2011.446
188. Imai Y. Interleukin-33 in atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol Sci. (2019) 96:2–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2019.08.006
189. Saikumar Jayalatha AK, Hesse L, Ketelaar ME, Koppelman GH, Nawijn MC. The central role of IL-33/IL-1RL1 pathway in asthma: From pathogenesis to intervention. Pharmacol Ther. (2021) 225:107847. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107847
190. Zhang Z, Hener P, Frossard N, Kato S, Metzger D, Li M, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin overproduced by keratinocytes in mouse skin aggravates experimental asthma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2009) 106:1536–41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812668106
191. Zhu Z, Oh MH, Yu J, Liu YJ, Zheng T. The Role of TSLP in IL-13-induced atopic march. Sci Rep. (2011) 1:23. doi: 10.1038/srep00023
192. Demehri S, Morimoto M, Holtzman MJ, Kopan R. Skin-derived TSLP triggers progression from epidermal-barrier defects to asthma. PloS Biol. (2009) 7:e1000067. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000067
193. Jiang H, Hener P, Li J, Li M. Skin thymic stromal lymphopoietin promotes airway sensitization to inhalant house dust mites leading to allergic asthma in mice. Allergy. (2012) 67:1078–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2012.02857.x
194. Kang EG, Narayana PK, Pouliquen IJ, Lopez MC, Ferreira-Cornwell MC, Getsy JA. Efficacy and safety of mepolizumab administered subcutaneously for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. Allergy. (2020) 75:950–3. doi: 10.1111/all.14050
195. Adhikary PP, Idowu T, Tan Z, Hoang C, Shanta S, Dumbani M, et al. Disrupting TSLP-TSLP receptor interactions via putative small molecule inhibitors yields a novel and efficient treatment option for atopic diseases. EMBO Mol Med. (2024) 16:1630–56. doi: 10.1038/s44321-024-00085-3
196. Ratchataswan T, Banzon TM, Thyssen JP, Weidinger S, Guttman-Yassky E, Phipatanakul W. Biologics for treatment of atopic dermatitis: current status and future prospect. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. (2021) 9:1053–65. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.11.034
197. Benzecry V, Pravettoni V, Segatto G, Marzano AV, Ferrucci S. Type 2 inflammation: atopic dermatitis, asthma, and hypereosinophilia successfully treated with dupilumab. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. (2021) 31:261–3. doi: 10.18176/jiaci.0614
198. Ichiyama S, Ito M, Hoashi T, Kanda N, Natsuno T, Saeki H. Severe atopic dermatitis effectively treated with dupilumab changed from interleukin-5 inhibitors for concomitant severe bronchial asthma. J Dermatol. (2021) 48:e76–7. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.15691
199. Tolino E, Proietti I, Sarni A, Bernardini N, Mambrin A, Balduzzi V, et al. Success of dupilumab as a monotherapy in an adult patient affected by severe uncontrolled asthma and atopic dermatitis. Dermatol Ther. (2021) 34(1):e14596. doi: 10.1111/dth.14596
200. Boguniewicz M, Beck LA, Sher L, Guttman-Yassky E, Thaçi D, Blauvelt A, et al. Dupilumab improves asthma and sinonasal outcomes in adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. (2021) 9(3):1212–1223.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.12.059
201. Nettis E, Patella V, Lombardo C, Detoraki A, Macchia L, Di Leo E, et al. Efficacy of dupilumab in atopic comorbidities associated with moderate-to-severe adult atopic dermatitis. Allergy. (2020) 75(10):2653–61. doi: 10.1111/all.14338
202. Pose K, Laorden D, Hernández N, Villamañán E, Quirce S, Domínguez-Ortega J. Efficacy of dupilumab for severe atopic dermatitis co-occurring with asthma in a real-world setting. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. (2023) 33:217–9. doi: 10.18176/jiaci.0837
Keywords: group 2 innate lymphoid cells, asthma, atopic dermatitis, asthma combined with atopic dermatitis, biologics
Citation: Luo Y-f, Deng Y, Yang F, Meiduosiji, Xiong X, Yuan Y-l and Ao S-h (2025) The role of ILC2s in asthma combined with atopic dermatitis: bridging the gap from research to clinical practice. Front. Immunol. 16:1567817. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1567817
Received: 28 January 2025; Accepted: 11 March 2025;
Published: 01 April 2025.
Edited by:
Tetsuro Kobayashi, RIKEN Yokohama, JapanCopyright © 2025 Luo, Deng, Yang, Meiduosiji, Xiong, Yuan and Ao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yu-lai Yuan, NzU5MDA0OTMzQHFxLmNvbQ==; Su-hua Ao, NDYzNzg3MjE2QHFxLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Yan-fang Luo1,2†
Yan-fang Luo1,2† Yu-lai Yuan
Yu-lai Yuan