
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Immunol. , 04 February 2025
Sec. Cancer Immunity and Immunotherapy
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1559927
This article is part of the Research Topic Decoding Tumor Plasticity: Integrative Analysis of Epigenetic Regulation and Microenvironmental Adaptation View all 11 articles
This article is a correction to:
A self-assembled nanoparticle vaccine elicits potent neutralizing antibody response against EBV infection
A Corrigendum on
A self-assembled nanoparticle vaccine elicits effective neutralizing antibody response against EBV infection
By Li P, Jiang Z, Shi J, Sha H, Yu Z, Zhao Y, Han S and Ma L (2025) Front. Immunol. 15:1530364. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1530364
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 7 Histopathological analysis of tissues from vaccinated mice as published. We misused an incorrect image of mouse myocardium in the PBS group (Column 1, Row 2) during the selection from our extensive dataset. The corrected Figure 7 Histopathological analysis of tissues from vaccinated mice and its caption Tissues from vaccinated mice were stained by HE, including lungs, myocardium, liver, spleen and kidney. Scale bars represented 100 μm. appear below.
In the published article, there was another error in Figure 3 Characterization of self-assembly of the fusion antigens into ferritin nanoparticles as published. In Figure 3B, we misused the image of Ferritin nanoparticles (1st and 3rd images, Left panel)) during the selection from our extensive dataset. The corrected Figure 3 Characterization of self-assembly of the fusion antigens into ferritin nanoparticles and its caption (A) Dynamic light scattering (DLS) analyzing the particle size of the purified ferritin nanoparticles and L350-Ferritin nanoparticles. The curves of the particle size were drawn by GraphPad Prism 8.3 software. Ferritin nanoparticles (Blue), L350-Ferritin nanoparticles (Red). n = 3 independent repeats. Data are mean ± SD. (B) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analyzing the shape of the purified ferritin nanoparticles and L350-Ferritin nanoparticles. Scale bars represent 100 nm (upper) and 20 nm (Lower) appear below.
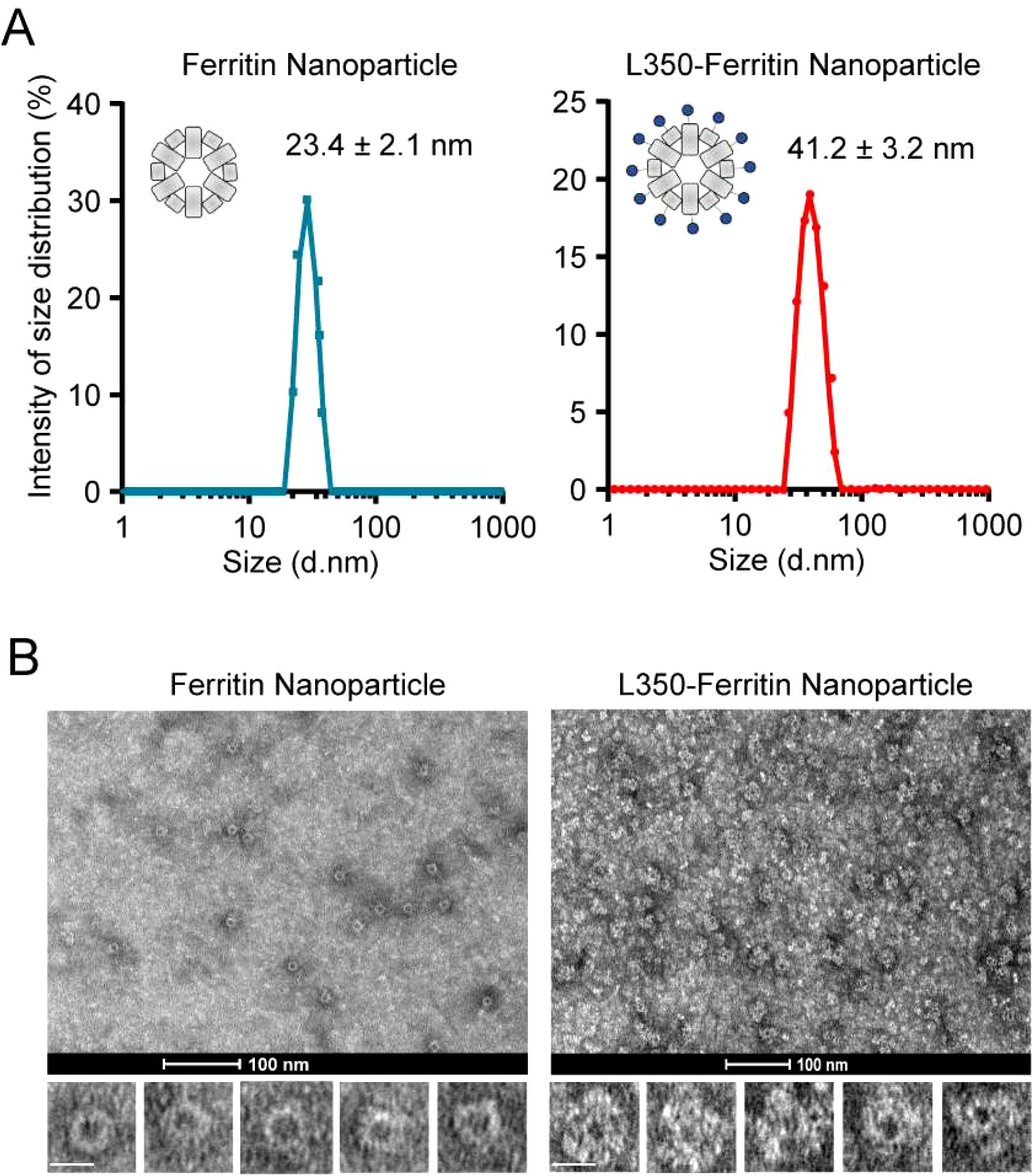
Figure 3. Characterization of self-assembly of the fusion antigens into ferritin nanoparticles. (A) Dynamic light scattering (DLS) analyzing the particle size of the purified ferritin nanoparticles and L350-Ferritin nanoparticles. The curves of the particle size were drawn by GraphPad Prism 8.3 software. Ferritin nanoparticles (Blue), L350-Ferritin nanoparticles (Red). n = 3 independent repeats. Data are mean ± SD. (B) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analyzing the shape of the purified ferritin nanoparticles and L350-Ferritin nanoparticles. Scale bars represent 100 nm (upper) and 20 nm (Lower).
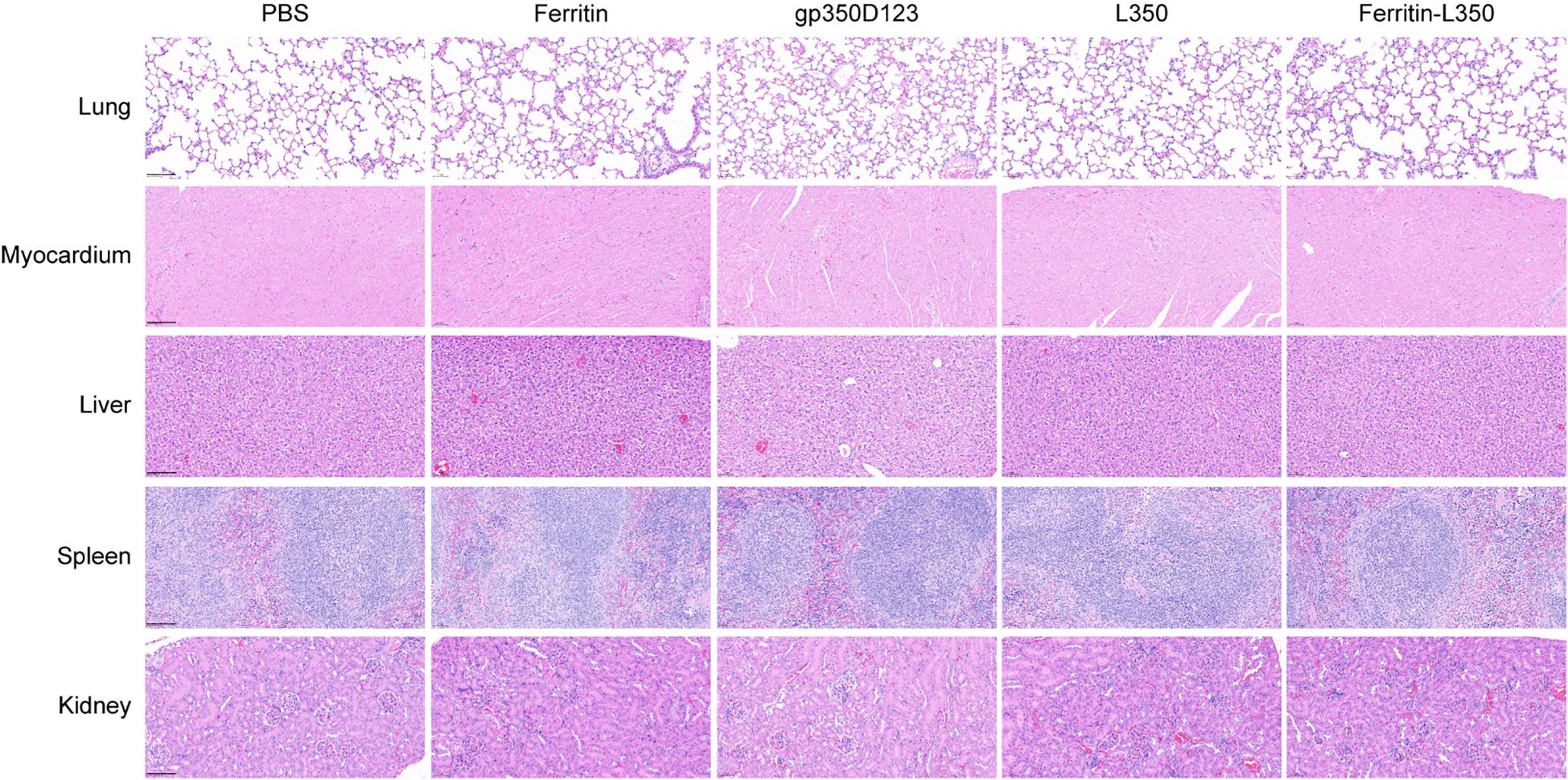
Figure 7. Histopathological analysis of tissues from vaccinated mice. Tissues from vaccinated mice were stained by HE, including lungs, myocardium, liver, spleen and kidney. Scale bars represented 100 μm.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), vaccine, epitope, ferritin, nanoparticle
Citation: Li P, Jiang Z, Shi J, Sha H, Yu Z, Zhao Y, Han S and Ma L (2025) Corrigendum: A self-assembled nanoparticle vaccine elicits effective neutralizing antibody response against EBV infection. Front. Immunol. 16:1559927. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1559927
Received: 13 January 2025; Accepted: 21 January 2025;
Published: 04 February 2025.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Guan-Jun Yang, Ningbo University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Li, Jiang, Shi, Sha, Yu, Zhao, Han and Ma. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lan Ma, bWFsYW5Ac3oudHNpbmdodWEuZWR1LmNu; Sanyang Han, aGFuc2FueWFuZ0Bzei50c2luZ2h1YS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.