
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Immunol. , 05 March 2025
Sec. Cancer Immunity and Immunotherapy
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1557839
Background: Low skeletal muscle mass (LSMM) has been associated with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients receiving systemic therapy. However, its impact across different treatment regimens remains unclear.
Methods: A retrospective study analyzed 714 patients with intermediate and advanced HCC, divided into immunotherapy (I, n=85), target-immunotherapy combination (I+T, n=545), and targeted therapy (T, n=84) groups based on treatment. Skeletal muscle was assessed via computed tomography (CT) at the third lumbar vertebral level (L3) before and after 3 months of treatment. LSMM was evaluated by the third lumbar skeletal muscle index (L3-SMI) using a predefined threshold. Patients were stratified by baseline values and treatment changes. Kaplan-Meier and Cox models were used to compare overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS).
Results: There was no significant difference in the loss of muscle mass among the three groups of LSMM patients; whereas, non-LSMM(NLSMM) patients in group T lost more muscle mass than those in group I (P=0.040).In the I+T group, patients who achieved an objective response (ORR) had less muscle mass loss than those without (P=0.013), while the changes in muscle mass for patients in the I group and T group were unrelated to treatment response. Baseline or post-treatment LSMM was associated with poorer median OS, especially in the I+T group. Progressive LSMM was linked to shorter median PFS (4.9 vs 5.7 months) and OS (9.8 vs 16.5 months), with similar results in the I+T group (mPFS, 4.2 vs. 5.8 months; mOS, 9.7 vs 16.1 months). Patients with LSMM had a higher incidence of treatment-related SAEs, particularly ascites and fatigue.
Conclusion: In patients with combined LSMM in hepatocellular carcinoma, muscle loss did not significantly differ between those treated with I, I+T, and T; however, T treatment contributed to muscle mass loss in NLSMM patients. Greater muscle loss correlated with poorer treatment outcomes and increased SAEs, and baseline, post-treatment, and progressive LSMM were linked to significantly worse prognoses, particularly with combined treatment regimens.
Liver cancer is the sixth most common malignant tumor worldwide and the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most prevalent type of primary liver cancer, accounting for approximately 75%-85% of all liver cancer cases (1). Due to the difficulty in early diagnosis and rapid disease progression, the majority of patients are diagnosed at intermediate to advanced stages, where surgical intervention is no longer an option. For these patients, systemic therapy is the primary treatment choice that offers survival benefits and can be categorized into three types: targeted drug therapy, immunotherapy, and combined treatment strategies (2, 3). Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) include agents targeting programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) and programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1); molecular-targeted therapies primarily consist of multikinase inhibitors (TKI) and more specific small molecule agents, such as anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitors and fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) inhibitors, etc. Combined treatment strategies mainly involve the co-administration of molecular targeted drugs with ICIs (4). Targeted immunotherapy combinations (Atezolizumab + bevacizumab or Durvalumab + tremelimumab) are preferred for first-line treatment, while monotherapy with targeted drugs can be considered for patients with contraindications to ICIs, and dual immunotherapy or monotherapy with immunotherapy can be chosen for patients at high risk of bleeding (5).
The long-term prognosis of HCC patients is related to various factors. In addition to liver function reserve, tumor staging, and treatment methods, maintaining nutritional balance and physical capacity are also important factors in improving the prognosis of advanced HCC patients (6). Sarcopenia is a disease characterized by the loss of muscle mass and a decline in physical function (7). Studies have shown that sarcopenia, characterized by low skeletal muscle mass(LSMM) as defined by computed tomography(CT),independently predicts the overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) of HCC patients (8–10). In the systemic treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma(uHCC), LSMM is associated with adverse clinical outcomes of TKI such as sorafenib and lenvatinib. Similarly, in patients receiving immunotherapy, most studies report that patients with LSMM have poorer OS and PFS (10). Currently, many studies focus on the relationship between LSMM and the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (6–10), however, there is a lack of research on the role of different systemic treatments in skeletal muscle mass loss in patients with mid-to-advanced HCC, as well as the impact of changes in muscle mass on patient prognosis.
Therefore, this study aims to assess the impact of immunotherapy (I), combined immunotherapy and targeted therapy (I+T), and targeted therapy (T) on LSMM in patients with mid-to-advanced HCC, as well as to investigate the relationship between changes in skeletal muscle mass during treatment and treatment response and prognosis.
A retrospective cohort study was conducted on HCC patients who received systematic treatment at Beijing You’an Hospital, affiliated with Capital Medical University, from January 2018 to February 2024. Inclusion criteria: (1) Patients aged ≥18 years; (2) Patients with Child-Pugh Class A or B, and some Child-Pugh C patients from trials on systemic treatment safety and efficacy across liver function levels; (3) Patients with mid-to-advanced HCC who received systematic treatment; (4) Patients who underwent CT assessment within one month before treatment. Patients with any of the following conditions were excluded: (1) Patients without abdominal computed tomography (CT) at baseline and three months after treatment; (2) Patients with other malignancies or severe extrahepatic organ-based diseases; All patient data were retrieved from electronic medical records. A total of 714 cases were included in the final data analysis. Follow-up for all patients continued until August 31, 2024. The study protocol complied with the ethical guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Beijing You’an Hospital(LL-2022-027-K), and exempted from the requirement for informed consent since all data were analyzed retrospectively and anonymously.
Patients were divided into three groups based on treatment regimens: Immunotherapy (I), Combined Therapy (I+T), and Targeted Drug Therapy Group (T). ICIs include inhibitors targeting Programmed Cell Death 1 (PD-1) (sintilimab, tislelizumab, camrelizumab, pembrolizumab) and Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitors (atezolizumab, durvalumab); the T group mainly consists of multi-kinase inhibitors (TKI) (lenvatinib, regorafenib, donafenib, apatinib, sorafenib) and anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitors (bevacizumab and its biosimilars). The combined therapy mainly involves the treatment of molecular targeted drugs in combination with ICIs. All anticancer drugs used in this study, including targeted therapies and immune checkpoint inhibitors, are covered by the China National Reimbursement Drug List (NRDL) or commercial medical insurance drug formularies, ensuring partial or full reimbursement under China’s medical insurance system and commercial health insurance plans.
In our institution, intermediate and advanced-stage HCC treatment is guided by clinical guidelines, tumor staging, Child-Pugh classification, and patient comorbidities. The choice of anticancer drugs is guided by the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system, National Health Commission Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Primary Hepatocellular Carcinoma, and National Comprehensive Cancer Network Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines). First-line options include atezolizumab with bevacizumab, sintilimab with bevacizumab biosimilar, or lenvatinib monotherapy, among others. For patients with contraindications to combination therapy, single-agent treatment (targeted therapy or immunotherapy) is considered. Drug selection is based on availability, patient tolerance, and insurance coverage.
The treatment strategy for all intermediate and advanced HCC patients considers liver function, including cirrhosis staging. Management of underlying cirrhosis follows clinical guidelines, incorporating alcohol cessation, antiviral therapy (HBV/HCV), nutritional support (albumin supplementation), hepatoprotective drugs, and monitoring for complications such as ascites, esophageal varices, and hepatic encephalopathy. Liver function is closely monitored throughout treatment.
Tumor response was assessed using the modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (mRECIST) after three months of treatment, with key indicators including the objective response rate (ORR), representing the proportion of patients with complete response (CR) and partial response (PR) (11). OS (Overall Survival) and PFS (Progression-Free Survival) were calculated from the start of systematic treatment.
All patients underwent abdominal CT scans within one month before treatment and three months after treatment. The CT scans were performed using a US LightSpeed VCT CT 64 scanner. Skeletal Muscle Area (cm²): The cross-sectional area (cm²) of skeletal muscles at the third lumbar vertebra (L3) on CT imaging was used to estimate body skeletal muscle mass, including the psoas major, erector spinae, quadratus lumborum, transversus abdominis, internal oblique, external oblique, and rectus abdominis muscles. The axial images at the L3 level were manually measured on a dedicated workstation (SliceOmatic software, version 5.0) for specific tissues (−29 to +150 Hounsfield units (HU) threshold). The total skeletal muscle area of the L3 cross-section was independently assessed by two radiologists. In case of disagreement, a third doctor intervened and a consensus was reached. The Skeletal Muscle Index (SMI) was calculated as the L3 level skeletal muscle area (cm²) divided by the square of height (m²) to obtain the L3-SMI. An L3-SMI value less than 42 cm²/m² for males and less than 38 cm²/m² for females is considered to have low skeletal muscle mass(LSMM) (12). We assessed only muscle mass, excluding muscle function assessments.
Baseline data of patients were collected, including age, gender, BMI, etiology, history of previous treatments, BCLC staging, ECOG PS, portal vein tumor thrombus (PVTT), extrahepatic metastasis, and Child-Pugh classification. Laboratory data were also collected during the follow-up period, including complete blood count, liver function (total bilirubin, albumin), coagulation, and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) related indicators. The relative change (%) throughout the entire treatment process was calculated as follows: ΔSMI = (SMI at 3 months - baseline SMI)/baseline-SMI * 100%, with the threshold defined as 10%. Progressive LSMM is defined as a decrease in ΔSMI > 10% (13). Body Mass Index (BMI) was calculated using the formula: BMI = weight (kg)/height squared (m²).
Statistical analysis and graphical production were conducted using SPSS version 27.0 (IBM) and RStudio version 2024.09.0 + 375. A P-value of less than 0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. Demographic data and disease characteristics of patients in the immunotherapy group, combined therapy group, and targeted therapy group were compared. Continuous variables are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD), and categorical variables are presented as counts and percentages (%). The T-test was used for intergroup comparison of parametric data, while the Mann-Whitney-U test was used for non-parametric data. The chi-square test (χ2 test) and Kruskal-Wallis H test were used for intergroup comparison of categorical variables. Continuous variables with a normal distribution were compared across multiple groups using one-way ANOVA. Logistic regression analysis was used to study characteristics associated with LSMM. The Kaplan-Meier method was employed to estimate PFS and OS for each group and to plot survival curves. Subsequently, the Cox proportional hazards model was constructed to test for statistically significant differences in survival times between different groups. Patients lost to follow-up were censored at their last known follow-up date in survival analysis.
This study initially included 5,790 patients, of which 5,076 were excluded for various reasons. Ultimately, 714 patients were enrolled and divided into the immunotherapy group (I) with 85 patients, the combined therapy group (I+T) with 545 patients, and the targeted therapy group (T) with 84 patients. Table 1 records the baseline characteristics of the entire cohort. The majority of patients were male (n=606, 84.9%), with an average age of 58.3 (SD ± 10.5) years and an average BMI of 23.92 ± 3.67 kg/m². Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection was the main etiology in this cohort (n=676, 94.7%). Most patients had an ECOG-PS score of 1 (90.9%), Child-Pugh Class A (62.8%), were enrolled at the first-line treatment stage (64.9%), and were at BCLC Stage C at the start of treatment (71.9%), with distant metastasis present in 317 patients(44.4%). Previously, 98 (13.7%) and 566 (79.3%) patients had undergone surgical resection and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) treatment, respectively. Among ICIs, sintilimab (37.8%), tislelizumab (24.8%), and camrelizumab (17%) were the most used, while the most common targeted therapies were lenvatinib (53.5%), bevacizumab (16%), and regorafenib (9.1%). Overall, the average SMI of the study patients was 43.43[38.65,49.9] cm²/m², with 273 (38.2%) diagnosed with LSMM. Radiological assessments showed CR in 53 cases (7.4%), PR in 155 cases (21.7%), SD in 260 cases (36.4%), and PD in 246 cases (34.5%). The objective tumor response rate was 29.1%.
Among the 53 CR patients, as shown in Supplementary Table 1,most received first-line treatment (64.15%) and had a high prevalence of prior TACE treatment (90.57%). Additionally, 37.74% of patients had a history of surgery. Most patients had relatively preserved liver function, with Child-Pugh A (52.83%) and B (41.51%) classifications. The baseline BMI (24.24 ± 3.80) and L3-SMI (44.41 ± 6.91) were higher compared to all patients, with a low proportion of LSMM at 33.96%. The incidence of PVTT and distant metastasis was relatively low, at 7.55% and 26.42%, respectively. These characteristics suggest that CR patients generally have better baseline health status and lower tumor burden, which may contribute to achieving a complete response.
The median survival time for the entire cohort was 15.1 (95% CI, 13.6-16.7) months, and the median PFS was 5.6 (95% CI, 5.2 – 5.8) months. There were no significant differences in median survival and PFS among the three treatment groups. In Group I, 40 (47.1%) patients died, and 67 experienced progression (78.8%). The median survival time was 17.4 (95% CI: 12.1-22.7) months, and the median PFS was 4.5 (95% CI: 3.7 – 5.3) months. In Group I+T, 308 (56.5%) patients died, and 423 experienced progression (77.6%), with a median survival time of 14.9 (95% CI: 13.2-16.7) months and a median PFS of 5.6 (95% CI: 5.2 – 5.9) months. In Group T, 52 (61.9%) patients died, and 65 experienced progression (77.4%), with a median survival time of 15.6 (95% CI: 10.6-20.6) months and a median PFS of 6.0 (95% CI: 5.2 – 6.9) months.
The characteristics of LSMM at baseline among HCC patients were first analyzed. Univariate regression showed that, compared with non-LSMM(NLSMM) patients, among the 273 HCC patients with LSMM, the majority were elderly (aged ≥60 years) (P<0.001), male (P<0.001), and received non-first-line treatment (P<0.001). Incorporating the aforementioned variables into a multivariate logistic regression model revealed that being elderly (aged ≥60 years) (OR=2.227, 95%CI 1.614–3.072), male (OR=2.653, 95%CI 1.713-4.111), and receiving non-first-line treatment (OR=0.465, 95%CI 0.335-0.646) were significantly associated with an increased likelihood of LSMM (P<0.001) (Table 2).
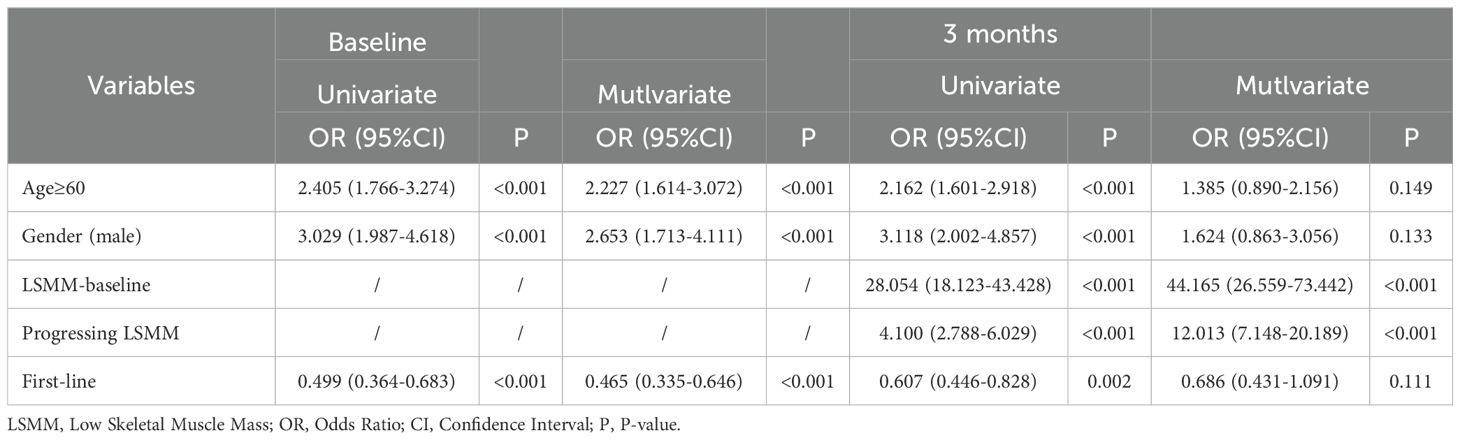
Table 2. Logistic regression analysis of factors associated with LSMM-baseline and LSMM in 3 months.
After systematic treatment for 3 months, 338 patients were diagnosed with LSMM post-treatment, and they shared the same characteristics as patients with LSMM at baseline, predominantly being elderly (aged ≥60 years) (P<0.001), male (P<0.001), and receiving non-first-line treatment (P=0.002). Additionally, baseline LSMM (P<0.001) and the presence of progressive LSMM (P<0.001) were significantly associated with LSMM post-treatment. A multivariate logistic regression model identified baseline LSMM (OR=44.165, 95%CI 26.559–73.442) and the presence of progressive LSMM (OR=12.013, 95%CI 7.148–20.189) as independent risk factors for LSMM post-treatment (P<0.001) (Table 2).
Subsequently, subgroup analyses were conducted on the aforementioned variables. After 3 months of treatment, 44 (51.8%) patients in Group I, 262 (48.1%) in Group I+T, and 32 (38.1%) in Group T were diagnosed with LSMM. Univariate analysis showed that in all three groups, patients with LSMM post-treatment were associated with baseline LSMM (P<0.001) and the presence of progressive LSMM (I P=0.001, I+T P<0.001, T P=0.012). Additionally, LSMM patients in Group I were associated with non-first-line treatment (P=0.023), while those in Group I+T were predominantly aged ≥60 years (P<0.001), male (P<0.001), and receiving non-first-line treatment (P=0.011). Multivariate regression revealed that in all three groups, patients with LSMM post-treatment were significantly associated with baseline LSMM and the presence of progressive LSMM (P<0.001), consistent with the characteristics of the overall group of patients with LSMM (Table 3).
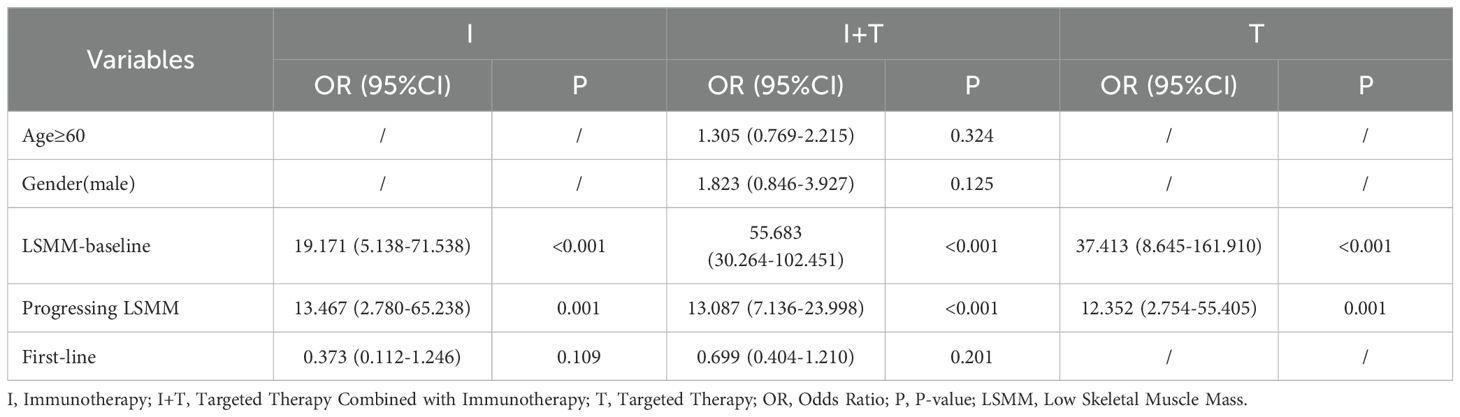
Table 3. Multifactorial logistic regression analysis of factors associated with LSMM 3 months in different groups.
We explored the relationship between LSMM, changes in skeletal muscle mass, and treatment regimens by analyzing the changes in SMI from baseline to 3 months after treatment, denoted as -ΔSMI: As shown in Table 4, there were no significant differences in baseline SMI and ΔSMI among the three groups of patients. Muscle loss did not significantly differ among patients with baseline LSMM across different treatment regimens. However, patients without baseline LSMM in Group I demonstrated less muscle loss compared to those in Group T (p=0.040), with the T regimen resulting in the greatest loss of muscle mass (Figure 1). As shown in Table 5, all LSMM patients exhibited less muscle loss than NLSMM patients (P<0.001), with the same results observable in Group I+T (P<0.001) and Group T (P=0.011) (Figure 2). This indicates that the I+T regimen and T regimen have an impact on muscle changes in patients with different baseline muscle conditions, while the I regimen does not have a significant effect.
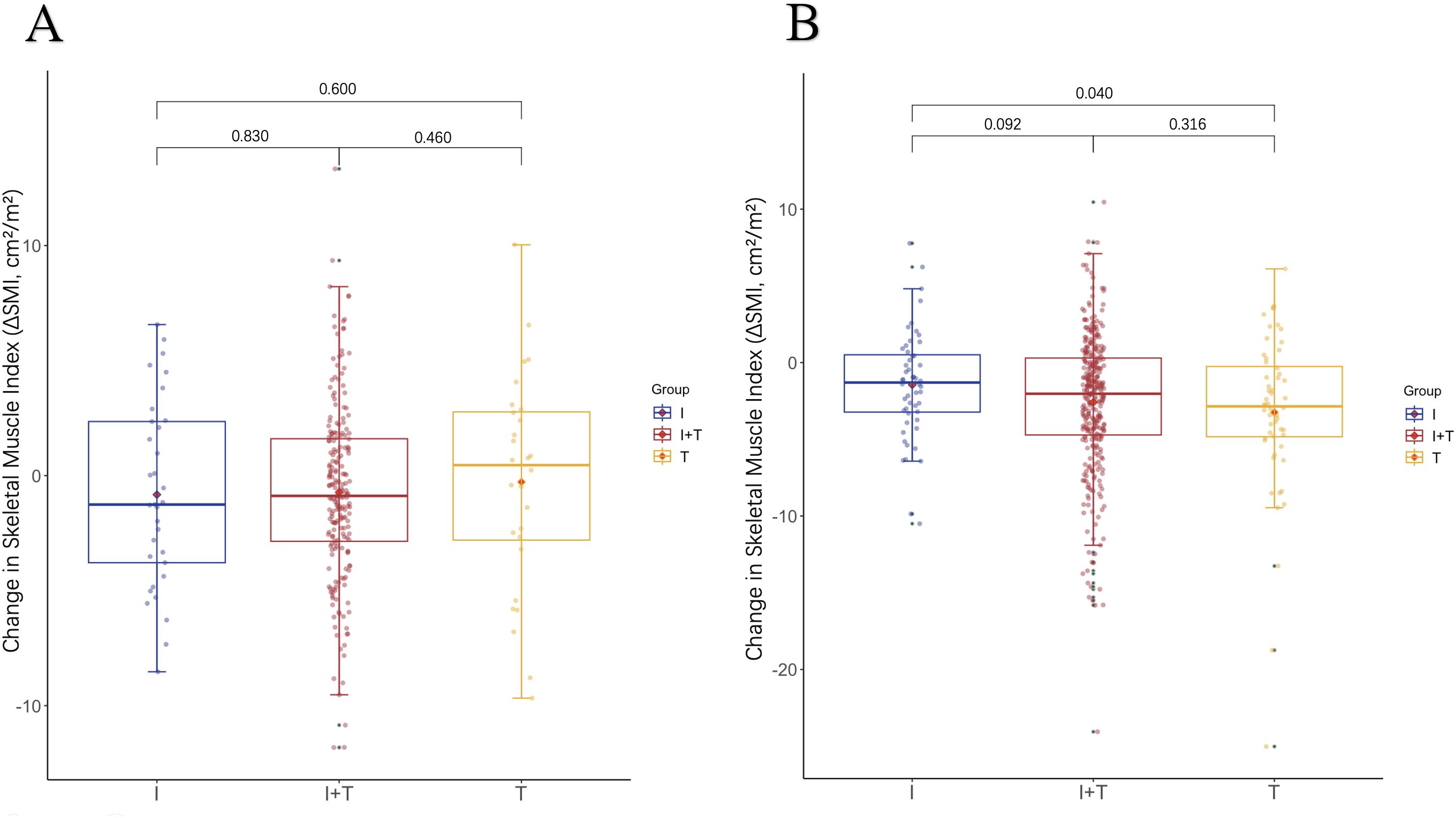
Figure 1. The difference in the change levels of ΔSMI after 3 months of treatment with three therapeutic regimens in patients with (A) LSMM and (B) NLSMM.LSMM,low skeletal muscle;NLSMM, non-low skeletal muscle.

Table 5. The impact of different treatment plans on ΔSMI in patients with different baseline muscle status (intra-group comparison).
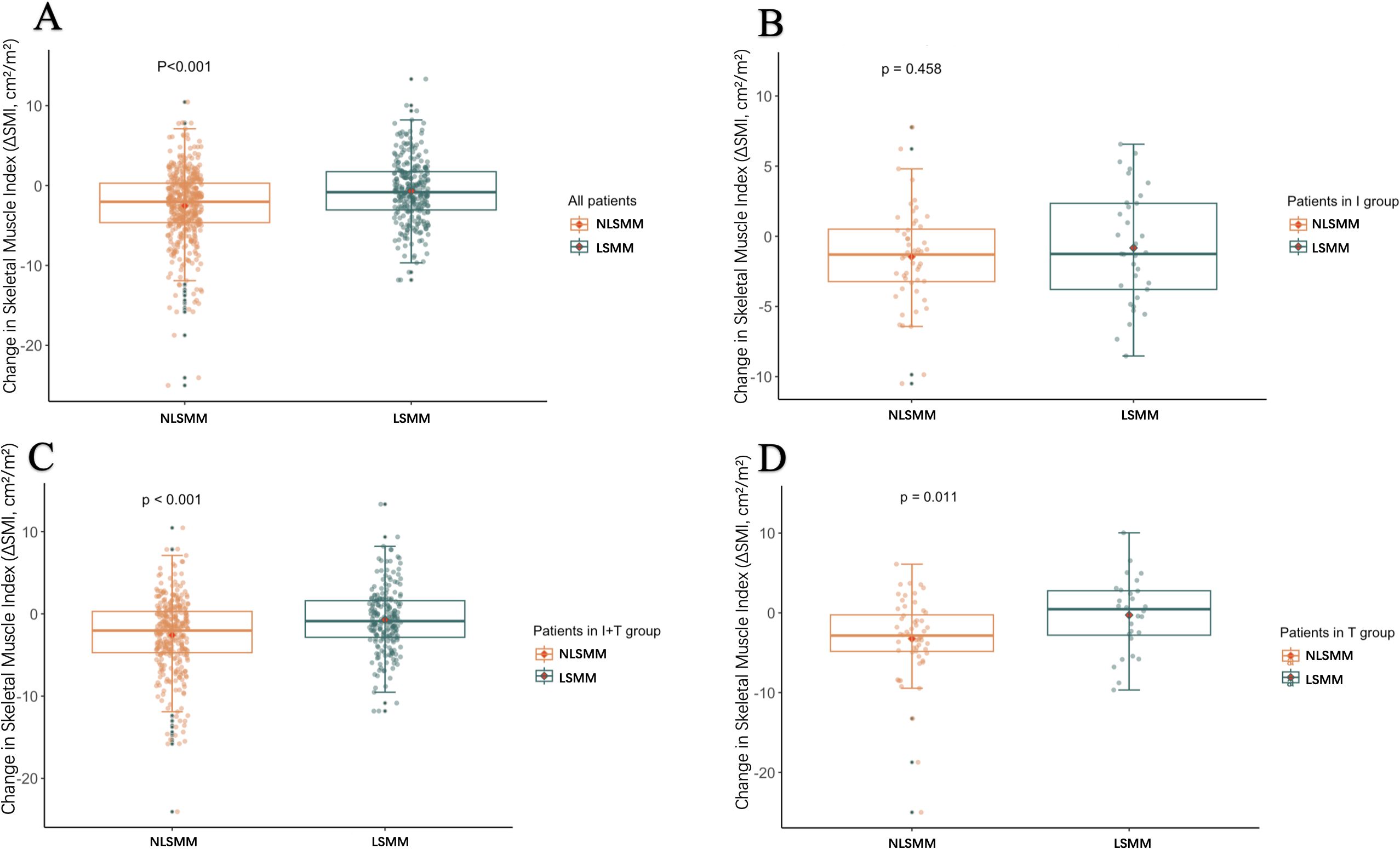
Figure 2. Box plots show the distribution of changes in ΔSMI after 3 months of treatment in patients with LSMM and those without LSMM: all patients (A), immune group/I (B), combined treatment group/I+T (C), and targeted group/T (D). ΔSMI, Skeletal Muscle Index; LSMM, low skeletal muscle.
As shown in Table 6,there were no significant differences in baseline SMI between patients with or without objective response rate (ORR) in the entire cohort, but ORR was associated with the diagnosis of LSMM post-treatment (P=0.048). In the I and T groups, changes in muscle mass were not related to treatment response. However, in the I+T group, patients who achieved ORR had less muscle loss during treatment than those without treatment response (P=0.013), particularly among NLSMM patients(P=0.011)(Figure 3). In summary, patients receiving the combined treatment regimen who achieved ORR had significantly less muscle mass loss compared to those who did not respond to treatment.
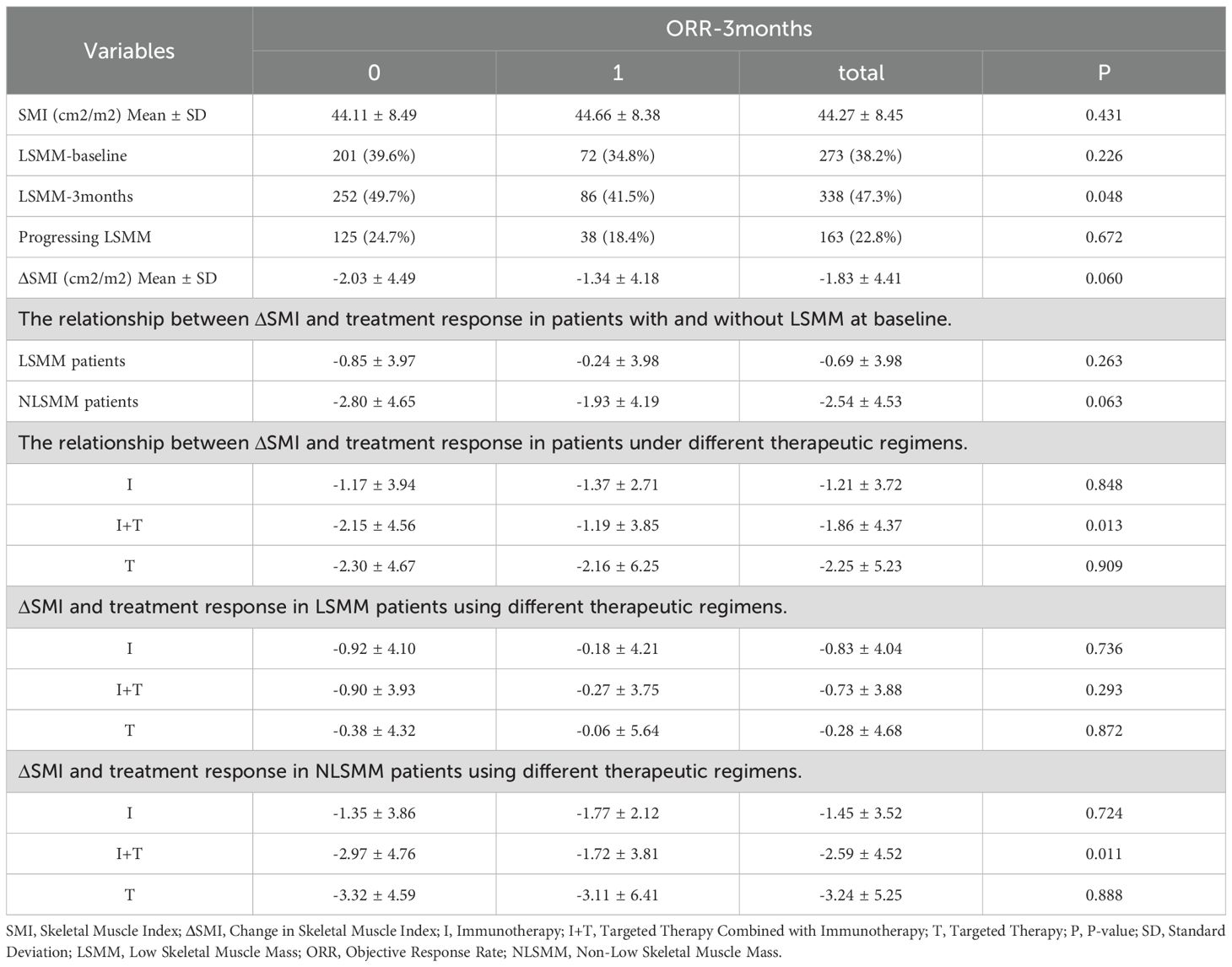
Table 6. The relationship between changes in muscle mass and treatment response among different therapeutic regimens.
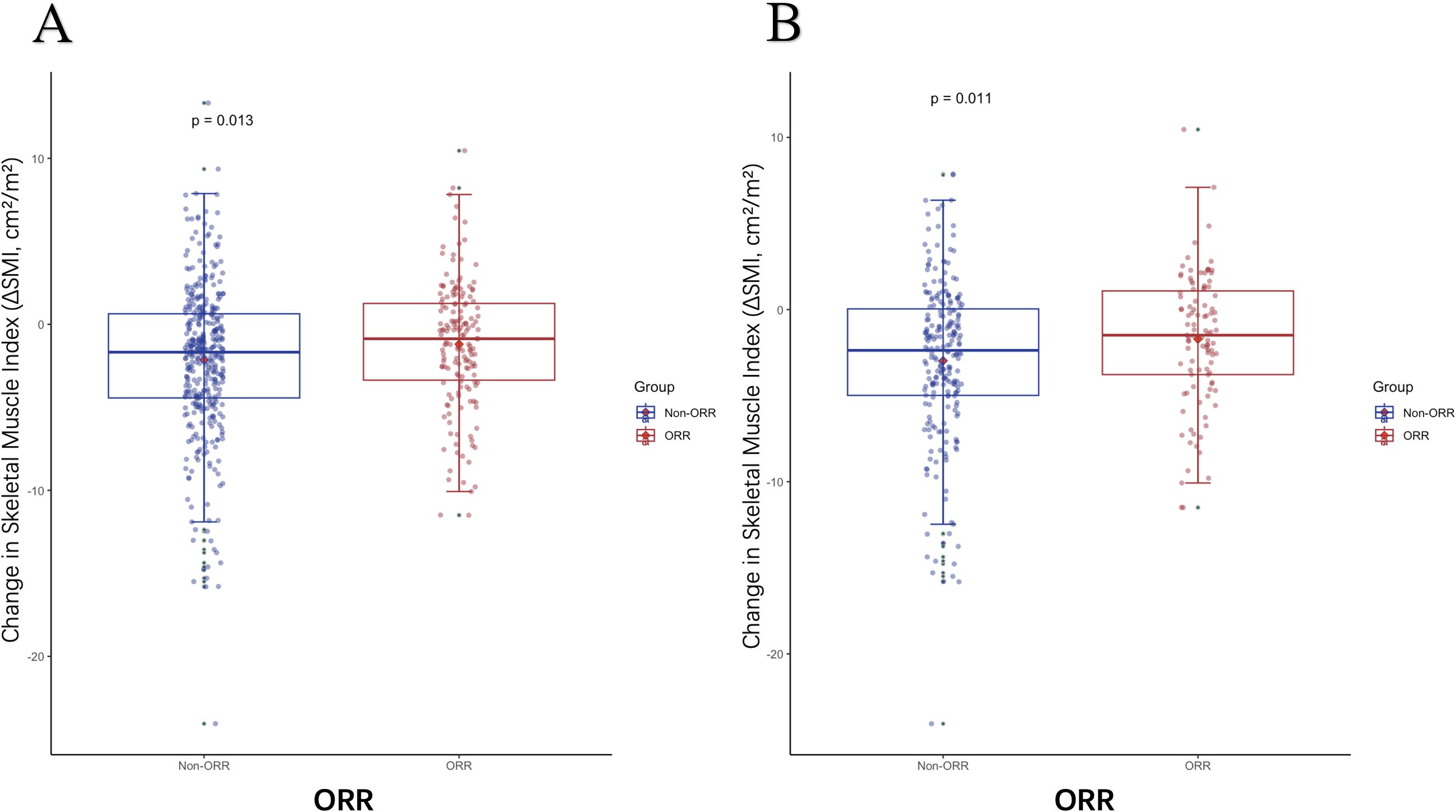
Figure 3. The difference in ΔSMI levels between patients with or without ORR. (A) The difference in ΔSMI between patients with or without ORR in the I+T group (B) The difference in ΔSMI between patients with or without ORR who are NLSMM in the I+T group; ORR, Objective Response Rate; NLSMM, non-low skeletal muscle; ΔSMI, the rate of change in Skeletal Muscle Mass Index; I, Immunotherapy; I+T, Targeted Therapy Combined with Immunotherapy; T, Targeted Therapy.
We stratified the clinical variables that might affect prognosis and used Kaplan-Meier analysis to explore their impact on PFS and OS. As of August 2024, 400 patients (56%) had died, and 555 patients (77.7%) had experienced progression. As shown in Table 7, among the overall patient population, the diagnosis of LSMM, both at baseline and post-treatment, was not associated with PFS. However, the median OS for patients with LSMM at baseline and post-treatment was significantly worse than for those without LSMM (baseline LSMM: median, 12.6 vs. 16.4, P = 0.018; post-treatment LSMM: median, 12.0 vs. 16.9, P = 0.002), with the same results observed in the I+T group (baseline LSMM: median, 12.4 vs. 16.4, P = 0.015; post-treatment LSMM: median, 12.0 vs. 16.9, P < 0.001) (Figure 4).
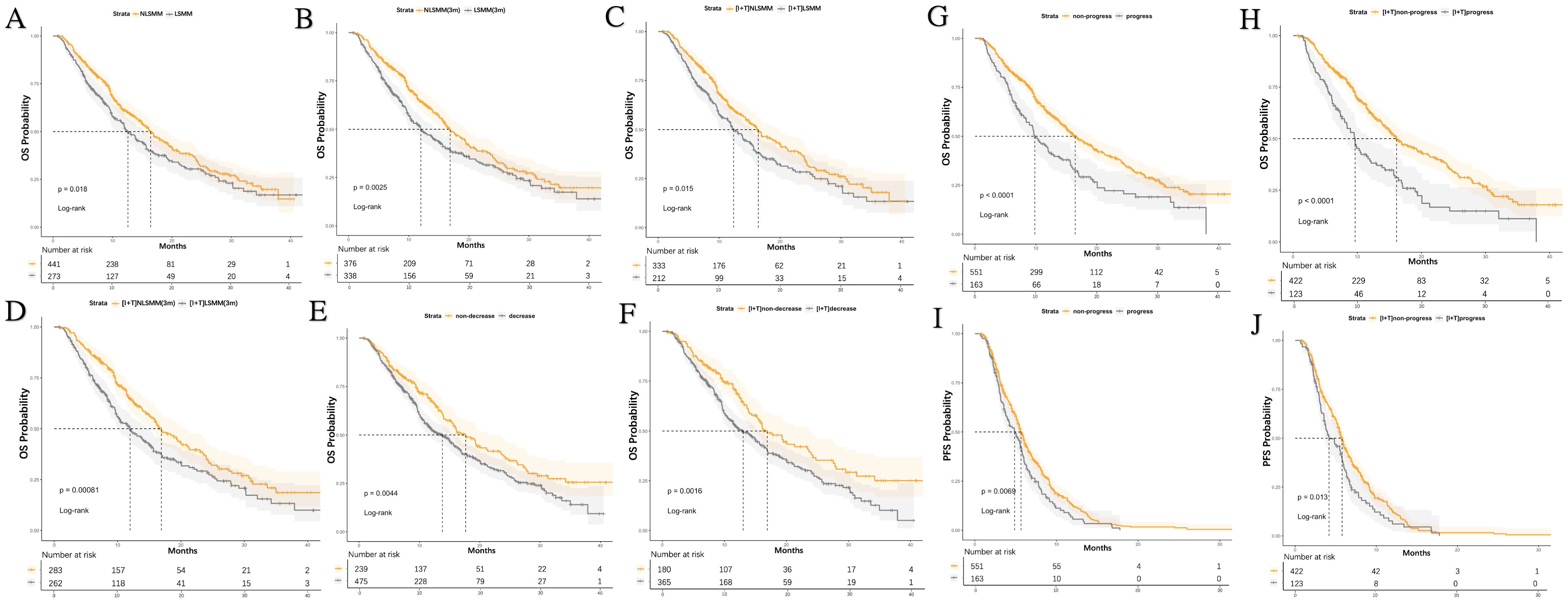
Figure 4. Kaplan-Meier curves for PFS and OS stratified by LSMM status, treatment group, SMI reduction, and progressive LSMM. (A) OS differences based on LSMM at baseline for all patients (B) OS differences based on LSMM status at 3 months; (C) LSMM at baseline in the I+T group (D) OS differences based on LSMM status at 3 months in the I+T group; (E) OS differences based on SMI reduction in all patients (F) OS differences based on SMI reduction in the I+T group; (G) OS differences based on progressive LSMM in all patients (H) OS differences based on progressive LSMM in the I+T group; (I) PFS differences based on progressive LSMM in all patients (J) PFS differences based on progressive LSMM in the I+T group; P-values were calculated using the log-rank test. PFS, progression-free survival; OS, overall survival; SMI, skeletal muscle index; LSMM, low skeletal muscle; NLSMM, non-low skeletal muscle; ΔSMI, the rate of change in Skeletal Muscle Mass Index; I, Immunotherapy; I+T, Targeted Therapy Combined with Immunotherapy; T, Targeted Therapy; 3m, 3months.
At the same time, we analyzed the relationship between the decrease in SMI after 3 months of treatment, progressive LSMM, and survival rates. Notably, compared to patients without a decrease in SMI, those with a decrease in SMI had a shorter OS (median, 13.8 vs 17.6, P=0.004), and this difference was also observed in the I+T group (median, 13.0 vs 17.0, P=0.002). However, a decrease in SMI was not related to PFS. In contrast, patients with progressive LSMM exhibited shorter PFS (median, 4.9 vs 5.7, P=0.007) and OS (median, 9.8 vs 16.5, P<0.001) compared to those without progressive LSMM. Similar differences were observed in the I+T group (PFS: median, 4.2 vs. 5.8, P=0.013;OS: median, 9.7 vs 16.1, P<0.001). (Figure 4). Additionally, age ≥ 60 years (P=0.008), distant metastasis (P=0.018) were associated with a shorter PFS. Pre-TACE treatment (P=0.010), distant metastasis (P=0.009), PVTT (P<0.001), and advanced BCLC staging (P=0.044) were associated with a shorter OS.
After performing multivariate COX regression analysis to control for confounding factors, as shown in Table 8, the presence of progressive LSMM was an independent risk factor for shorter OS and PFS (OS, HR = 1.533 [95% CI: 1.191-1.973], P<0.001; PFS, HR=1.321[95% CI:1.085-1.608], P=0.005). Additionally, age ≥60 years (HR = 1.257 [95% CI: 1.060-1.402], P=0.009) and distant metastasis (HR = 1.185 [95% CI: 1.001-1.402], P=0.049) were also independent risk factors for a lower PFS.
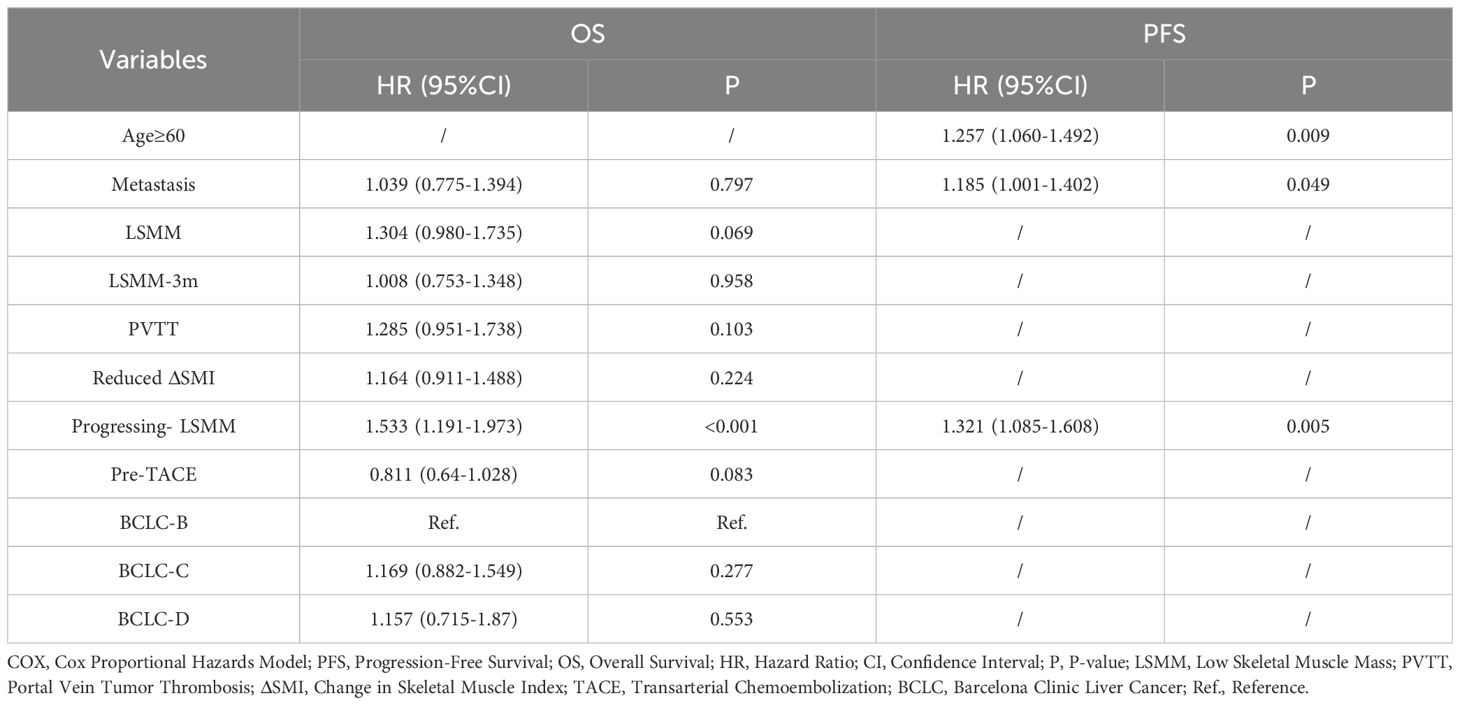
Table 8. Multifactorial COX regression analysis of factors associated with PFS and OS in all patients.
This study included 448 Child-Pugh A patients (48 in the I group, 347 in the I+T group, and 53 in the T group). Baseline characteristics are presented in Supplementary Table 2. The relationship between low muscle mass, changes in skeletal muscle mass, treatment regimens, and treatment response in Child-Pugh A patients was consistent with the overall population. However, unlike the overall cohort, baseline or post-treatment LSMM diagnosis did not significantly affect OS in Child-Pugh A patients.
In Child-Pugh A patients, baseline SMI did not differ significantly among the three groups, and baseline LSMM patients showed no significant difference in muscle loss(Supplementary Table 3). However, among baseline NLSMM patients, those in the I group had less muscle loss than those in the T group (P=0.018)(Supplementary Figure 1). As shown in Supplementary Table 4, muscle loss was significantly lower in LSMM patients than in NLSMM patients (P < 0.001), with the I+T group (P<0.001) and T group (P=0.008) showing similar trends.
In Child-Pugh A patients, the objective response rate (ORR) was significantly associated with post-treatment LSMM diagnosis (P=0.013) (Supplementary Table 5). Patients who achieved ORR with combination therapy exhibited less muscle loss during treatment (P = 0.011).
Unlike the overall cohort, baseline and post-treatment LSMM diagnosis did not significantly impact OS in Child-Pugh A patients. However, The relationship between post-treatment SMI reduction, progressive LSMM, and survival rates in Child-Pugh A patients was consistent with the overall population. Patients with reduced SMI had shorter OS (median, 12.4 vs. 17.6 months, P=0.014; Group I+T: 11.7 vs. 12.3 months, P=0.001). Progressive LSMM was associated with shorter PFS (median, 4.8 vs. 5.9 months, P=0.016; Group I+T: 4.0 vs. 5.8 months, P=0.039) and OS (median, 9.5 vs. 16.5 months, P<0.001; Group I+T: 8.9 vs. 16.5 months, P<0.001) (Supplementary Table 6).
As shown in Supplementary Table 6, progressive LSMM was an independent risk factor for both shorter OS (HR = 1.581, 95% CI: 1.167–2.140, P = 0.003) and PFS (HR = 1.361, 95% CI: 1.066–1.738, P = 0.013). Additionally, Age ≥ 60 years was an independent risk factor for shorter PFS (HR = 1.272, 95% CI: 1.027–1.577, P = 0.028).PVTT was an independent risk factor for shorter OS (HR = 1.426, 95% CI: 1.086–1.874, P = 0.011).
These findings align with the overall cohort, indicating that in Child-Pugh A patients, baseline muscle status—especially L3-SMI and SMI changes—are closely linked to treatment response and prognosis (PFS and OS).
As presented in Table 9, among the 714 patients receiving systemic treatment for HCC, the most common treatment-related SAEs were ascites (19.2%), fatigue (8.7%), and loss of appetite (4.2%), with no significant differences among treatment groups. Additionally, patients with LSMM exhibited a higher overall incidence of SAEs, with fatigue (12.8% vs. 6.1%, P = 0.002) and loss of appetite (6.6% vs. 2.7%, P = 0.012) being significantly more common in the LSMM group (Table 10). This suggests that reduced muscle mass may impact treatment tolerance and quality of life. Other SAEs, including gastrointestinal bleeding, infection, jaundice, liver dysfunction, hypothyroidism, and rash, showed no statistically significant differences across treatment groups or between LSMM and NLSMM patients. These findings indicate that LSMM may increase the risk of treatment-related adverse events, highlighting the need for close monitoring and supportive interventions in these patients.
There were no significant differences in median survival and progression-free survival among the three treatment groups. Subgroup analysis of the aforementioned factors, as shown in Table 11, revealed that the univariate analysis results for PFS and OS in the I+T group were similar to those of the overall patient population. Multivariate analysis showed that progressive LSMM was an independent risk factor for shorter PFS and OS (PFS, HR = 1.338 [95% CI: 1.066-1.680], P=0.012; OS, HR = 1.839 [95% CI: 1.435-2.351], P<0.001); additionally, prior TACE treatment was an independent protective factor for OS (HR = 0.725 [95% CI: 0.562-0.936], P=0.014). Age ≥ 60 years was an independent risk factor for progression (HR = 1.236 [95% CI: 1.014-1.505], P=0.036).
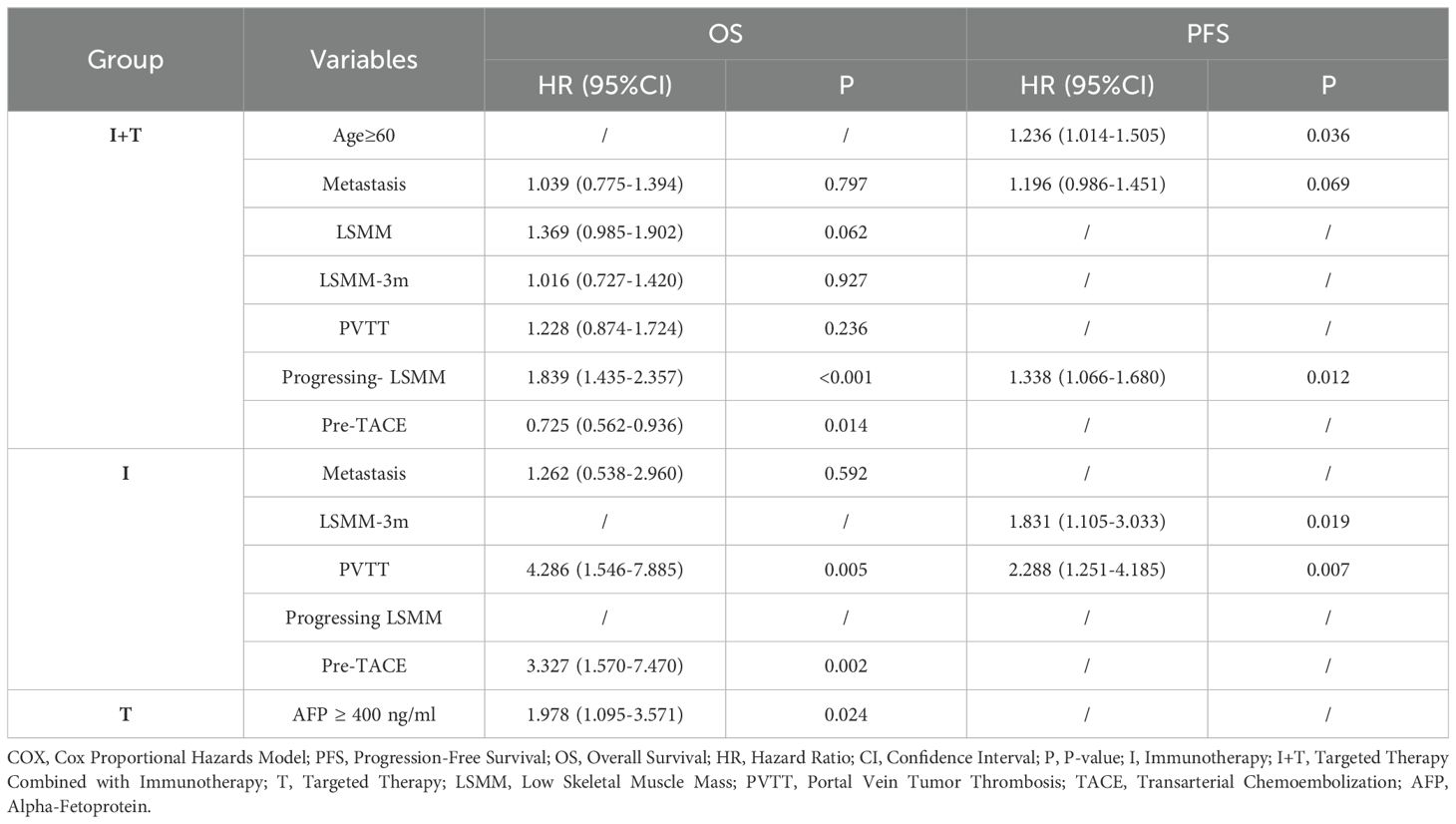
Table 11. Multifactorial COX regression analysis of factors associated with PFS and OS in three groups.
In the univariate analysis of Group I, distant metastasis, PVTT, and prior surgical treatment were significantly associated with OS. Subsequent multivariate analysis identified the presence of PVTT (HR = 4.286 [95% CI: 1.546-7.885], P=0.005) and prior surgical treatment (HR = 3.327 [95% CI: 1.570-7.470], P=0.002) as independent risk factors for OS in HCC patients treated with Group I. The independent risk factors for PFS were PVTT (HR = 1.831 [95% CI: 1.105-3.033], P=0.019) and the diagnosis of LSMM after 3 months of treatment (HR = 2.288 [95% CI: 1.251-4.185], P=0.007).
Among HCC patients treated with Group T, only AFP >400ng/ml was an independent risk factor for OS (HR = 1.978 [95% CI: 1.095-3.571], P=0.024).
This study aimed to assess the impact of I, I+T, and T treatments on skeletal muscle mass changes in patients with intermediate to advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and to explore the influence of LSMM and progressive LSMM on treatment outcomes and prognosis across different treatment groups. The findings revealed no difference in muscle mass loss among LSMM patients receiving I, I+T, and T treatments; however, T treatment appeared to promote muscle loss. Patients with greater muscle loss experienced poorer treatment outcomes, and those with baseline LSMM, post-treatment LSMM, and progressive LSMM had significantly worse prognoses, especially in the I+T group.
In intermediate to advanced HCC patients, specific demographic characteristics and treatment statuses are potential risk factors for LSMM. The first-line treatment was negatively correlated with an increased likelihood of baseline muscle wasting, suggesting that the incidence of muscle wasting is lower in first-line treatment, and patients with muscle wasting are often diagnosed when receiving non-first-line treatments. It has been reported that in cancer patients, the causes of skeletal muscle depletion include reduced physical activity and malnutrition due to disease progression and adverse effects of treatment, as well as increased expression of inflammatory cytokines (14). Regardless of tumor progression, patients receiving systemic treatment lose skeletal muscle (15). There was no significant correlation between different treatment regimens and post-treatment LSMM, and baseline LSMM diagnosis and the presence of progressive muscle wasting were significant correlates of post-treatment muscle wasting. This emphasizes the impact of muscle condition at baseline on the development of LSMM during subsequent treatments and the increased risk of muscle wasting due to the progression of LSMM. This study found that elderly individuals (aged ≥60 years) and males were significantly correlated with baseline LSMM, consistent with previous research findings (16, 17), and possibly related to the decrease in testosterone associated with aging, a hormone that promotes skeletal muscle growth. On the other hand, females are generally more inclined to store a significant amount of fat from fat reserves and generate energy, rather than from skeletal muscle reserves (18), which may make them more resistant to muscle wasting compared to males.
Our observations indicate that there was no significant difference in muscle wasting among patients with baseline LSMM treated with the three regimens, while NLSMM patients in the T group experienced more muscle loss than those in the I group. Comparing muscle loss during treatment between LSMM and NLSMM patients within each group revealed that in the I+T and T groups, LSMM patients lost less muscle mass than NLSMM patients, while the I regimen had no significant impact on muscle changes in patients with different baseline nutritional statuses. This suggests that T may have a promoting effect on muscle loss in NLSMM patients, potentially due to dose toxicity and direct mechanisms that induce muscle wasting, such as alterations in the PI3K/AKT-mTOR signaling pathway. mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) is a key regulator of muscle protein synthesis, with its primary complex, mTORC1, controlling protein synthesis, cell growth, metabolism, and autophagy by phosphorylating downstream targets. Inhibiting mTORC1 enhances autophagy and mitophagy, facilitating the clearance of damaged mitochondria and maintaining muscle homeostasis, while mTORC1 also negatively regulates autophagy to preserve protein synthesis balance (19, 20). Activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway promotes muscle growth (21), whereas T therapy may suppress this pathway, impairing muscle protein synthesis and exacerbating sarcopenia (22). Additionally, TKIs (tyrosine kinase inhibitors) may promote protein degradation by reducing phosphorylation of mTOR downstream targets, such as p70S6K and 4E-BP1, further contributing to muscle loss (23). VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) plays a crucial role in maintaining skeletal muscle blood flow and neovascularization. VEGF inhibitors (such as bevacizumab) may reduce muscle perfusion, leading to diminished nutrient supply and increased muscle wasting. However, in this study, no significant increase in muscle loss was observed in the I+T group due to VEGF inhibition. This may be attributed to the overall physiological effects of combination therapy. For instance, ICIs (immune checkpoint inhibitors) may reduce systemic inflammation (e.g., IL-6, TNF-α), improving metabolic homeostasis and partially counteracting TKI-induced muscle loss. These results indicate that LSMM should be considered a factor in the decision-making for protein kinase inhibitor TKI treatment in HCC patients.
We found that the diagnosis of muscle wasting at baseline was not significantly associated with the effectiveness of tumor treatment both in the entire cohort and in Child-Pugh A patients, while achieving an ORR was related to the diagnosis of LSMM after three months of treatment. A significant decline in SMI was observed in patients treated with I (-2.03), I+T (-1.34), and T (-1.83), and patients with greater muscle loss had poorer treatment outcomes, a phenomenon particularly evident in the I+T group. This is consistent with previous research findings (13, 15).
Current studies on the prognostic impact of LSMM in HCC patients receiving targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and combined therapy show some controversy. Some studies suggest that LSMM is associated with PFS and OS in advanced HCC patients treated with TKIs, including sorafenib and lenvatinib Sun et al. (24–26) believe that LSMM does not determine PFS and OS in advanced HCC patients treated with lenvatinib combined with PD-1 inhibitors (27). Matsumoto et al. found no significant correlation between the presence of LSMM and PFS in HCC patients treated with atezolizumab/becatecarin (16), while Ourak et al. showed that LSMM patients had significantly shorter PFS and OS than NLSMM patients (28). Liu, M et al. indicated that baseline LSMM was not related to PFS and OS in HCC patients treated with ICIs (13). The subgroup analysis in our study provides stronger evidence for the impact of LSMM on OS and PFS in patients receiving the same treatment. The results of this study suggest that in the entire cohort, LSMM is significantly associated with survival time in intermediate to advanced HCC patients, both at baseline and post-treatment, and progressive LSMM is an independent risk factor for shorter OS and PFS, especially in the I+T treatment group. In contrast, baseline LSMM in patients receiving TKI treatment was not related to PFS and OS, which is inconsistent with previous study results (13, 16, 24–26). This may be due to smaller patient sample sizes, selection differences, and different combinations of treatment drugs. In this study, baseline LSMM in patients treated with ICI was not related to PFS and OS, which is consistent with previous research findings (13, 29). We also observed that a diagnosis of LSMM post-treatment in HCC patients treated with ICI was significantly correlated with PFS, supplementing the conclusions of Akce et al. (29).
In the entire cohort, both baseline and post-treatment LSMM were significantly associated with survival in intermediate to advanced HCC. However, in Child-Pugh A patients, LSMM had no significant impact on survival, while progressive LSMM correlated with poorer PFS and OS. This suggests that patients with better liver function tolerate muscle loss better, whereas LSMM has a greater prognostic impact in those with impaired liver function. Future research and interventions should consider liver function stratification, with a focus on dynamic LSMM monitoring to identify high-risk patients and optimize nutritional and rehabilitation strategies.
The adverse impact of LSMM on the effectiveness and prognosis of HCC treatment may be related to the tumor microenvironment (inflammation and immunity) and cytokine activity. It has been reported that skeletal muscle is an organ with immunomodulatory properties, regulating immune function through various soluble factors, cell surface molecules, or cell-to-cell interactions (30, 31). It can produce myokines such as IL-15 to mitigate the harmful effects of pro-inflammatory adipokines, contributing to the suppressive effects on the tumor microenvironment (30, 32). The homeostasis of skeletal muscle is to some extent the cause of healthy immune function, and when muscle atrophy occurs, it reduces the skeletal muscle cell signaling required for immune modulation and maintenance, leading to systemic inflammation and immune disorders (31, 33). On the other hand, skeletal muscle cells can express major histocompatibility complex molecules, delivering antigens to T cells. The reduction in muscle mass may mediate tumor cell immune tolerance to ICIs by affecting T cell function (31). Skeletal muscle wasting can also lead to a decrease in myoglobin levels, which may result in poor responses to immunotherapy (30, 32). In summary, LSMM may affect immune modulation, leading to poorer outcomes in HCC patients.
This study found a higher incidence of SAEs in LSMM patients, particularly fatigue and appetite loss, likely due to metabolic dysfunction, systemic inflammation, and immune dysregulation. SAE rates did not differ significantly between treatment groups, suggesting muscle status may better predict SAE risk than treatment regimen. Increased SAEs in LSMM patients may reduce treatment tolerance, leading to dose adjustments or discontinuation, ultimately impacting survival. Close monitoring, along with nutritional and exercise interventions, may help improve patient outcomes.
Additionally, multivariate analysis also revealed that the elderly (age ≥60 years) and extrahepatic metastasis are independent risk factors for PFS in HCC patients receiving systemic treatment. In subgroup analysis, PVTT and prior surgical treatment were independent risk factors for OS in Group I, while PVTT and post-treatment LSMM were independent risk factors for PFS. In the I+T group, the elderly (age ≥60 years) were independent risk factors for progression, and prior TACE treatment was an independent protective factor for OS. In Group T, only AFP >400ng/ml was an independent risk factor for OS. These results provide specific factors affecting prognosis in different treatment groups.
These results suggest that there is no difference in the impact on muscle mass due to LSMM across different treatment groups, while T treatment has a direct loss effect on muscle mass, which should be an important consideration in treatment decision-making and prognosis assessment. At the same time, they emphasize the significant role of LSMM and progressive LSMM in predicting the prognosis of intermediate to advanced HCC patients, especially in the I+T treatment group, and suggest that clinicians should pay attention to the monitoring and management of LSMM in clinical practice. Exercise and nutritional interventions can enhance the metabolism and function of skeletal muscle (34). Regular resistance training and aerobic exercise are widely recognized as effective strategies for improving muscle mass and function. Supplementing with branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) can help correct hypoalbuminemia, reduce skeletal muscle fat accumulation, maintain muscle mass, and improve glucose sensitivity, thereby preventing sarcopenia in patients with chronic liver disease (35). Additionally, Levocarnitine supplementation has shown potential benefits in improving skeletal muscle mass in HCC patients receiving lenvatinib treatment (36). Integrating multiple muscle-preserving interventions into patient treatment plans—such as personalized resistance training, Levocarnitine, protein, and amino acid supplementation—may help restore muscle function and support immune system health. Furthermore, chemotherapeutic agents and immunosuppressants may cause muscle loss; dose adjustments or alternative therapies could help mitigate this while maintaining treatment efficacy. However, these strategies require strict medical supervision.
This study is a single-center retrospective cohort study and has certain limitations. The study population has a low proportion of females, and the number of patients in the immunotherapy and targeted therapy groups is less than in the combined group. Patients who did not undergo CT scans at our hospital before treatment were not included in this study, which may cause selection bias. Secondly, the specific drugs and dosages of different treatment regimens varied from patient to patient, causing bias. Moreover, after discontinuing the corresponding targeted drugs, immunotherapy drugs, or combined medications, various other anticancer therapies may be used subsequently, which could bias the clinical outcomes of the patients. Finally, the error between manually outlining muscle area and the actual situation cannot be completely eliminated; future studies should validate our results in a broader population and with additional basic research.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
The studies involving humans were approved by BEIJING YOUAN HOSPITAL CAPTAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because The study protocol complied with the ethical guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Beijing You’an Hospital(LL-2022-027-K), and exempted from the requirement for informed consent since all data were analyzed retrospectively and anonymously.
JC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. QW: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Data curation. SL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Data curation. WS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Project administration, Writing – original draft. ML: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Investigation.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Wu Jieping Medical Foundation, WJPMF (Grant Number: 320.6750.2023-20-11).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1557839/full#supplementary-material
1. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
2. Yang C, Zhang H, Zhang L, Zhu AX, Bernards R, Qin W, et al. Evolving therapeutic landscape of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 20:203–22. doi: 10.1038/s41575-022-00704-9
3. Reig M, Forner A, Rimola J, Ferrer-Fàbrega J, Burrel M, Garcia-Criado Á, et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J Hepatol. (2022) 76:681–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.11.018
4. Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A, Singal AG, Pikarsky E, Roayaie S, et al. Author correction: hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2024) 10:10. doi: 10.1038/s41572-024-00500-6
5. Gordan JD, Kennedy EB, Abou-Alfa GK, Beal E, Finn RS, Gade TP, et al. Systemic therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: ASCO guideline update. JCO. (2024) 42:1830–50. doi: 10.1200/JCO.23.02745
6. Chang K-V, Chen J-D, Wu W-T, Huang K-C, Hsu C-T, Han D-S. Association between loss of skeletal muscle mass and mortality and tumor recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Liver Cancer. (2018) 7:90–103. doi: 10.1159/000484950
7. Stuck AK, Basile G, Freystaetter G, De Godoi Rezende Costa Molino C, Lang W, Bischoff-Ferrari HA. Predictive validity of current sarcopenia definitions (EWGSOP2, SDOC, and AWGS2) for clinical outcomes: A scoping review. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2023) 14:71–83. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13161
8. Jiang C, Wang Y, Fu W, Zhang G, Feng X, Wang X, et al. Association between sarcopenia and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:978110. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.978110
9. March C, Omari J, Thormann M, Pech M, Wienke A, Surov A. Prevalence and role of low skeletal muscle mass (LSMM) in hepatocellular carcinoma. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Nutr ESPEN. (2022) 49:103–13. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2022.04.009
10. Kuo M-H, Tseng C-W, Hsu C-S, Chen Y-C, Kao I-T, Wu C-Y, et al. Prevalence and effect of low skeletal muscle mass among hepatocellular carcinoma patients undergoing systemic therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancers. (2023) 15:2426. doi: 10.3390/cancers15092426
11. Lencioni R, Llovet J. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. (2010) 30:052–60. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1247132
12. Nishikawa H, Shiraki M, Hiramatsu A, Moriya K, Hino K, Nishiguchi S. Japan Society of Hepatology guidelines for sarcopenia in liver disease (1st edition): Recommendation from the working group for creation of sarcopenia assessment criteria. Hepatol Res. (2016) 46:951–63. doi: 10.1111/hepr.12774
13. Liu M, Jin Q, Wang H, Li Y. Progressive sarcopenia and myosteatosis predict prognosis of advanced HCC patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1396927. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1396927
14. Fujiwara N, Nakagawa H, Kudo Y, Tateishi R, Taguri M, Watadani T, et al. Sarcopenia, intramuscular fat deposition, and visceral adiposity independently predict the outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. (2015) 63:131–40. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.02.031
15. Uchikawa S, Kawaoka T, Namba M, Kodama K, Ohya K, Morio K, et al. Skeletal muscle loss during tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Liver Cancer. (2020) 9:148–55. doi: 10.1159/000503829
16. Matsumoto H, Tsuchiya K, Nakanishi H, Hayakawa Y, Yasui Y, Uchihara N, et al. Clinical usefulness of monitoring muscle volume during atezolizumab plus bevacizumab therapy in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers. (2022) 14:3551. doi: 10.3390/cancers14143551
17. Imai K, Takai K, Watanabe S, Hanai T, Suetsugu A, Shiraki M, et al. Sarcopenia impairs prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: the role of liver functional reserve and tumor-related factors in loss of skeletal muscle volume. Nutrients. (2017) 9:1054. doi: 10.3390/nu9101054
18. Grossmann M, Hoermann R, Gani L, Chan I, Cheung A, Gow PJ, et al. Low testosterone levels as an independent predictor of mortality in men with chronic liver disease. Clin Endocrinol. (2012) 77:323–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2012.04347.x
19. Zeng Z, Liang J, Wu L, Zhang H, Lv J, Chen N. Exercise-induced autophagy suppresses sarcopenia through Akt/mTOR and Akt/FoxO3a signal pathways and AMPK-mediated mitochondrial quality control. Front Physiol. (2020) 11:583478. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.583478
20. Russell RC, Tian Y, Yuan H, Park HW, Chang YY, Kim J, et al. ULK1 induces autophagy by phosphorylating Beclin-1 and activating VPS34 lipid kinase. Nat Cell Biol. (2013) 15:741–50. doi: 10.1038/ncb2757
21. Edinger AL, Thompson CB. Akt maintains cell size and survival by increasing mTOR-dependent nutrient uptake. MBoC. (2002) 13:2276–88. doi: 10.1091/mbc.01-12-0584
22. Huemer F, Schlintl V, Hecht S, Hackl H, Melchardt T, Rinnerthaler G, et al. Regorafenib is associated with increased skeletal muscle loss compared to TAS-102 in metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. (2019) 18:159–166.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.clcc.2019.04.003
23. Chan SL, Wong CH, Lau CP, Zhou Q, Hui CW, Lui VW, et al. Preclinical evaluation of combined TKI-258 and RAD001 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. (2013) 71:1417–25. doi: 10.1007/s00280-013-2139-4
24. Takada H, Kurosaki M, Nakanishi H, Takahashi Y, Itakura J, Tsuchiya K, et al. Impact of pre-sarcopenia in sorafenib treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. PloS One. (2018) 13:e0198812. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198812
25. Hiraoka A, Kumada T, Kariyama K, Tada T, Tani J, Fukunishi S, et al. Clinical importance of muscle volume in lenvatinib treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma: Analysis adjusted with inverse probability weighting. J Gastro Hepatol. (2021) 36:1812–9. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15336
26. Uojima H, Chuma M, Tanaka Y, Hidaka H, Nakazawa T, Iwabuchi S, et al. Skeletal muscle mass influences tolerability and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with lenvatinib. Liver Cancer. (2020) 9:193–206. doi: 10.1159/000504604
27. Sun W, Yin X, Liu X, Wei J, Yu M, Li W, et al. The clinical significance of sarcopenia in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with lenvatinib and PD-1 inhibitors. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1380477. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1380477
28. Oura K, Morishita A, Manabe T, Takuma K, Nakahara M, Tadokoro T, et al. Relationship between accurate diagnosis of sarcopenia and prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab combination therapy. Cancers. (2023) 15:3243. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123243
29. Akce M, Liu Y, Zakka K, Martini DJ, Draper A, Alese OB, et al. Impact of sarcopenia, BMI, and inflammatory biomarkers on survival in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with anti-PD-1 antibody. Am J Clin Oncol. (2021) 44:74–81. doi: 10.1097/COC.0000000000000787
30. Afzali AM, Müntefering T, Wiendl H, Meuth SG, Ruck T. Skeletal muscle cells actively shape (auto)immune responses. Autoimmun Rev. (2018) 17:518–29. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2017.12.005
31. Nelke C, Dziewas R, Minnerup J, Meuth SG, Ruck T. Skeletal muscle as potential central link between sarcopenia and immune senescence. eBioMedicine. (2019) 49:381–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.10.034
32. Elias R, Hartshorn K, Rahma O, Lin N, Snyder-Cappione JE. Aging, immune senescence, and immunotherapy: A comprehensive review. Semin Oncol. (2018) 45:187–200. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2018.08.006
33. Kim YR, Park S, Han S, Ahn JH, Kim S, Sinn DH, et al. Sarcopenia as a predictor of post-transplant tumor recurrence after living donor liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma beyond the Milan criteria. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:7157. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25628-w
34. Marzetti E, Calvani R, Tosato M, Cesari M, Di Bari M, Cherubini A, et al. Physical activity and exercise as countermeasures to physical frailty and sarcopenia. Aging Clin Exp Res. (2017) 29:35–42. doi: 10.1007/s40520-016-0705-4
35. Kitajima Y, Takahashi H, Akiyama T, Murayama K, Iwane S, Kuwashiro T, et al. Supplementation with branched-chain amino acids ameliorates hypoalbuminemia, prevents sarcopenia, and reduces fat accumulation in the skeletal muscles of patients with liver cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol. (2018) 53:427–37. doi: 10.1007/s00535-017-1370-x
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, systemic therapy, immunotherapy, targeted immunotherapy combination treatment, targeted therapy, low skeletal muscle mass
Citation: Chen J, Huang X, Wei Q, Liu S, Song W and Liu M (2025) The relationship between systemic therapies and low skeletal muscle mass in patients with intermediate and advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 16:1557839. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1557839
Received: 09 January 2025; Accepted: 17 February 2025;
Published: 05 March 2025.
Edited by:
Sachiyo Yoshio, National Center For Global Health and Medicine, JapanReviewed by:
Hiroki Nishikawa, Osaka Medical College, JapanCopyright © 2025 Chen, Huang, Wei, Liu, Song and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mei Liu, bGl1bWVpQGNjbXUuZWR1LmNu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.