- 1Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wuhan Third Hospital, Tongren Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
- 2Department of Nephrology, Wuhan Third Hospital, Tongren Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
Objective: This study aims to explore the relationship between body adipose tissue characteristics and clinical outcomes in cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy.
Methods: We conducted an extensive literature search across three major online databases—Embase, PubMed, and the Cochrane Library—to identify studies examining the link between body adipose tissue and treatment outcomes in cancer patients undergoing ICI therapy, from the inception of each database until February 20, 2024. The quality of the included studies was evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. The primary outcomes analyzed were hazard ratios (HRs) for overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS), as well as odds ratios (ORs) for disease control rate (DCR). Pooled estimates and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated.
Results: A total of 23 studies were included, encompassing 2741 cancer patients. The analysis revealed that patients with higher levels of visceral adipose tissue (VAT) exhibited significantly improved OS (HR: 0.72, 95% CI: 0.59–0.89, p < 0.001) and PFS (HR: 0.80, 95% CI: 0.67–0.96, p = 0.015), along with a higher DCR (OR: 1.81, 95% CI: 1.26–2.60, p = 0.001), compared to those with lower VAT levels. Additionally, increased subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) levels were associated with significantly better OS (HR: 0.69, 95% CI: 0.58–0.82, p < 0.001) and PFS (HR: 0.82, 95% CI: 0.68–1.00, p = 0.049), and a higher DCR (OR: 1.99, 95% CI: 1.15–3.44, p = 0.014). Elevated total adipose tissue (TAT) levels were also linked to longer OS (HR: 0.73, 95% CI: 0.55–0.97, p = 0.028). However, a higher visceral-to-subcutaneous adipose tissue ratio (VSR) was associated with a shorter OS (HR: 1.43, 95% CI: 1.09–1.87, p = 0.010). No significant relationship was found between TAT (HR: 0.81, 95% CI: 0.54–1.23, p = 0.332) and VSR (HR: 1.20, 95% CI: 0.95–1.51, p = 0.131) with PFS in ICI-treated patients.
Conclusion: This study highlights the prognostic relevance of VAT and SAT in predicting treatment response and survival outcomes in cancer patients receiving ICIs. These findings suggest that assessments of VAT and SAT should be incorporated into prognostic evaluations for this patient population.
1 Introduction
The phenomenon of immune evasion plays a pivotal role in the onset and progression of cancer and is acknowledged as one of its fundamental attributes (1). Immune checkpoints, encompassing both co-inhibitory and stimulatory signals, modulate the immune system and shield tumor cells from immune surveillance (1–3). In recent years, there has been rapid advancement in medical oncology with the emergence of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) or immunotherapies, such as nivolumab, pembrolizumab, and ipilimumab (4–7). The incorporation of ICIs has become integral in the management of various malignancies, offering an unparalleled survival advantage over conventional therapies like radiation therapy and chemotherapy (4–7). While chemotherapy primarily targets cancer cells to inhibit the cell cycle, ICIs consist of antibodies directed against programmed death 1 (PD-1), programmed death-ligand (PD-L1), or cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4), thus intercepting crucial regulatory signals that suppress immune responses within the tumor microenvironment (4–7). Consequently, ICIs mitigate immune suppression, enabling tumor-reactive T cells to initiate an antitumor response by harnessing the patient’s immune system to combat the malignancy (4–7).
Nonetheless, the response rate to ICI therapy exhibits considerable variability across different cancer types, typically falling within the range of 10% to 40%, with the majority of patients eventually experiencing disease progression despite initial response (8, 9). Additionally, adverse effects related to immune responses from ICI therapy can be severe or even fatal (10). Identifying individuals who are unlikely to respond to ICI therapy early on has emerged as a prominent area of focus in cancer treatment, aiming to avoid ineffective treatments and minimize the risk of adverse effects (11, 12). Currently, intra-tumor PD-L1 assays are often used as biomarkers to guide ICI therapy (13, 14). The predictive capacity of PD-L1 in clinical settings remains unsatisfactory due to the heterogeneous expression in tumor tissues (15). Other immune-related biomarkers utilized for companion diagnostics encompass tumor mutation burden and microsatellite instability (16–19). Nonetheless, their individual utility is limited in predicting outcomes (16, 17). In addition, establishing consistent criteria for quantifying these biomarkers remains challenging. Therefore, the identification of novel prognostic biomarkers capable of enhancing outcomes for cancer patients undergoing ICI treatment is of paramount importance.
The prognostic implications of obesity in different cancer types remain unclear and debated in terms of survival outcomes (20). Although certain earlier investigations have hinted at a potential link between body mass index (BMI) and overall survival (OS) in advanced cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) (21, 22), others have indicated no significant relationship between BMI and clinical outcomes (23). BMI calculation is straightforward and convenient; nonetheless, it represents an imperfect metric that assigns equal weight to all aspects of body composition, resulting in notable diversity in muscle and fat mass among individuals with identical BMI values (24). Consequently, there is growing interest in precise body composition evaluations, including assessments of muscle and fat masses. Currently, the predictive role of body adipose tissue in the prognosis of patients treated with ICI is currently unknown.
Hence, this study aims to make a significant contribution by systematically synthesizing all available evidence, deepening our understanding of the clinical implications of body adipose tissue in predicting prognosis for cancer patients undergoing treatment with ICIs.
2 Methods
2.1 Search strategy
Commencing February 20, 2024, an electronic search was conducted across bibliographic databases, including EMBASE, PubMed, and the Cochrane Library. Specific search terms encompassed “immune checkpoint inhibitors” [Mesh], “ICIs”, “PD-1 Inhibitors”, “PD-L1 Inhibitors”, “CTLA-4 Inhibitors”, “Subcutaneous Adipose Index”, “Subcutaneous Fat Index”, “Visceral Adipose Index”, and “Intramuscular Adipose Index”, covering all fields. The search was restricted to English language human studies. For detailed search strategies, Supplementary Material 1 is provided. Grey literature was sought on Google Scholar, and reference lists of eligible studies were manually scrutinized. Following Cochrane collaboration guidelines, search findings from both manual and electronic sources were consolidated within Covidence software for efficient data management.
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
We established specific inclusion criteria to guide article selection: (i) investigations involving patients diagnosed with cancer; (ii) utilization of ICIs as the therapeutic regimen; (iii) assessment of baseline body adipose tissue’s prognostic relevance (prior to ICI administration); and (iv) documentation of at least one of the following outcome measures: OS, progression-free survival (PFS), or disease control rate (DCR). DCR was defined as the percentage of patients who achieved complete response, partial response, or stable disease. OS was defined as the time from the start of nivolumab treatment to death from any cause. PFS was defined as the time from the start of nivolumab treatment to disease progression or death from any cause.
Exclusion criteria encompassed: (i) studies employing methodologies such as animal experimentation, literature reviews, case studies, or conference abstracts; (ii) the absence of hazard ratios (HRs) or odds ratio (OR) calculations for outcome evaluation based on either text or published data; and (iii) studies in which baseline body adipose tissue data are continuous variables. In cases where studies shared patient cohorts, preference was given to articles presenting comprehensive data and employing rigorous methodologies.
2.3 Data extraction and quality assessment
During the data extraction process, we gathered essential information, including authorship, publication year, study design, study period, study region, cancer type, treatments, sample size, age, gender, outcomes, and parameters related to body adipose tissue (such as assessment techniques, site of measurement, and threshold values). HRs, OR, and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were primarily extracted from multivariate analyses; alternatively, they were obtained from univariate analyses or extracted from survival analysis plots using Engauge Digitizer software (25). The quality of observational studies was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS), with studies scoring six or higher considered to be of high quality (26). Quality-related criteria, totaling nine points, were assigned to domains including patient selection, comparability of studies, and assessment of outcomes. All procedures, from literature retrieval and screening to data extraction and quality assessment, were conducted independently by three researchers, with any discrepancies resolved through consultation with the senior author.
2.4 Statistical methods
The statistical analysis was conducted using Stata 15.0. Visualization of the results was achieved through forest plots. Heterogeneity was assessed using Cochran's Q test and I2 statistics, with significant heterogeneity defined as a p-value of < 0.1 and an I2 value exceeding 50%. When significant heterogeneity was present, a random-effect model utilizing the DerSimonian-Laird method was applied; otherwise, a fixed-effect model employing the Inverse Variance method was utilized. The evaluation of publication bias was carried out using Egger's regression test (27) and Begg's test (28). To ensure the robustness of the results, sensitivity analyses were performed by systematically removing each study. Subgroup analyses were conducted based on methods of body composition analysis. Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed p-value < 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Search results and included studies
The predetermined search strategy and manual exploration yielded 348 potentially pertinent articles. Among these, 55 duplicates were removed, and 252 were excluded based on inadequate alignment with the selection criteria outlined in their titles and abstracts. Following a comprehensive assessment of the full texts of the remaining 41 articles, 18 were excluded due to not meeting the specified criteria. Consequently, a total of 23 studies were considered eligible for inclusion (Figure 1) (29–51).
3.2 Study characteristics
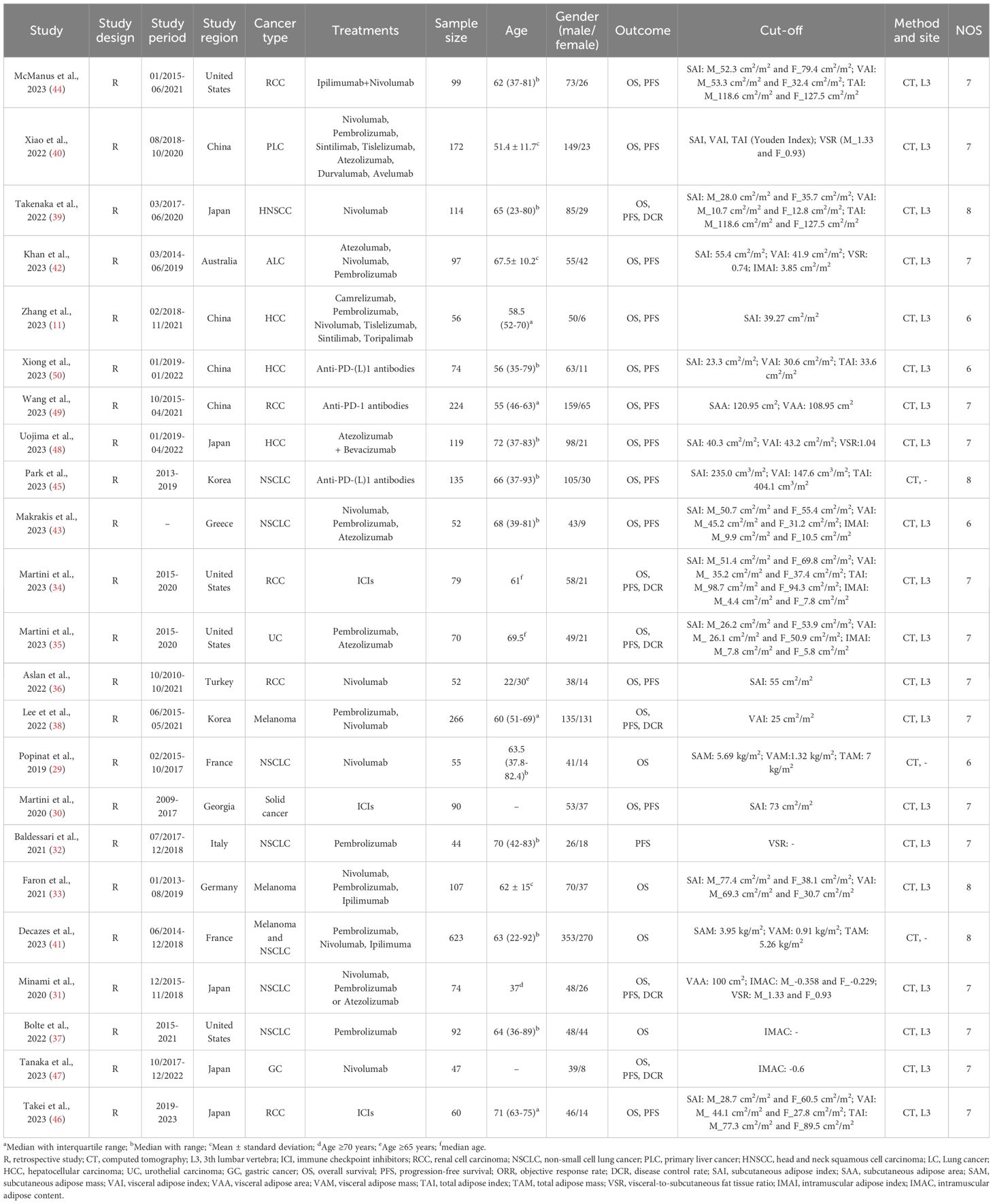
Table 1 presents the primary characteristics of the studies included in this analysis. A total of 2741 patients (68.73% male) with mean or median ages ranging from 51.4 to 72 years were included, with sample sizes varying from 44 to 623 individuals. Among these studies, five were conducted in Japan, four in China, and four in the United States. Computed tomography (CT) was employed in all studies to assess body adipose tissue at the third lumbar vertebra. All studies were retrospective, with Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) scores ranging from 6 to 8, indicating minimal risk of bias (Table 1).
3.3 Baseline visceral adipose tissue and overall survival and progression-free survival
In this analysis, we included a total of 17 studies comprising 2420 patients to investigate the effect of high and low VAT on OS or PFS in cancer patients treated with ICIs. Our findings showed that patients with high VAT had significantly longer OS (HR: 0.72, 95% CI: 0.59–0.89, p < 0.001, Figure 2A) and PFS (HR: 0.80, 95% CI: 0.67–0.96, p = 0.015, Figure 2B) than patients with low VAT. The Cochran Q test and I2 statistics (OS: I2 = 48.4%, p = 0.013; PFS: I2 = 36.7%, p = 0.082) showed that there was significant heterogeneity across studies. Consequently, a random-effects model was employed.
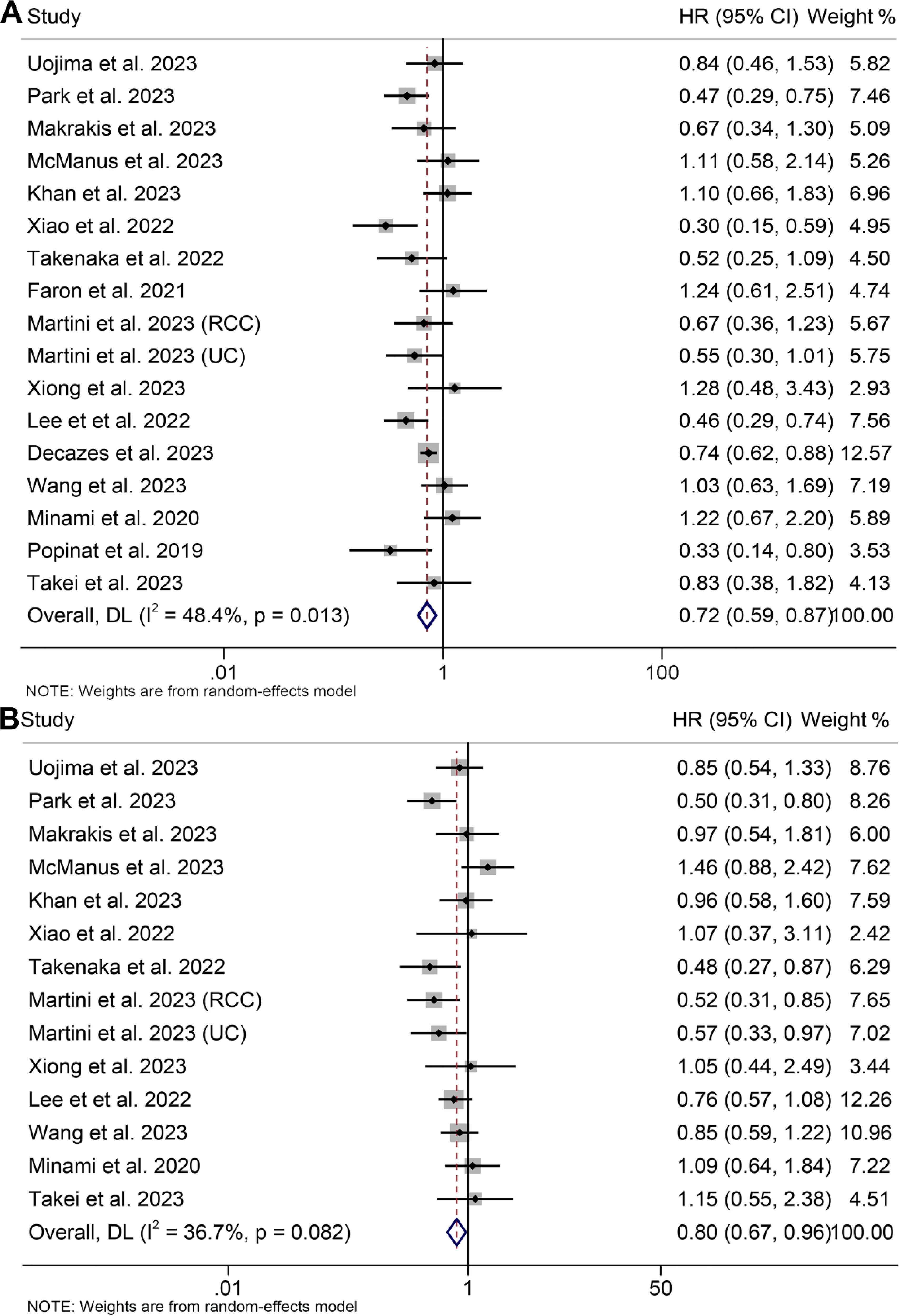
Figure 2. Forest plots of the relationship between visceral adipose tissue and overall survival (A) and progression-free survival (B). HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; DL, DerSimonian and Laird.
Examination of potential publication bias through funnel plots, Begg’s test, and Egger’s test did not yield significant findings concerning OS (Egger’s test: p = 0.881, Begg’s test: p = 0.967, Supplementary Figure S1A) and PFS (Egger’s test: p = 0.546, Begg’s test: p = 0.511, Supplementary Figure S1B). Our sensitivity analysis, involving the systematic exclusion of each study in turn, consistently demonstrated the sustained stability and robustness of the pooled HRs for both OS and PFS (Figures 3A, B). Subgroup analyses confirmed that high visceral fat index was significantly associated with longer OS and PFS, while visceral fat area and mass were not (Table 2).
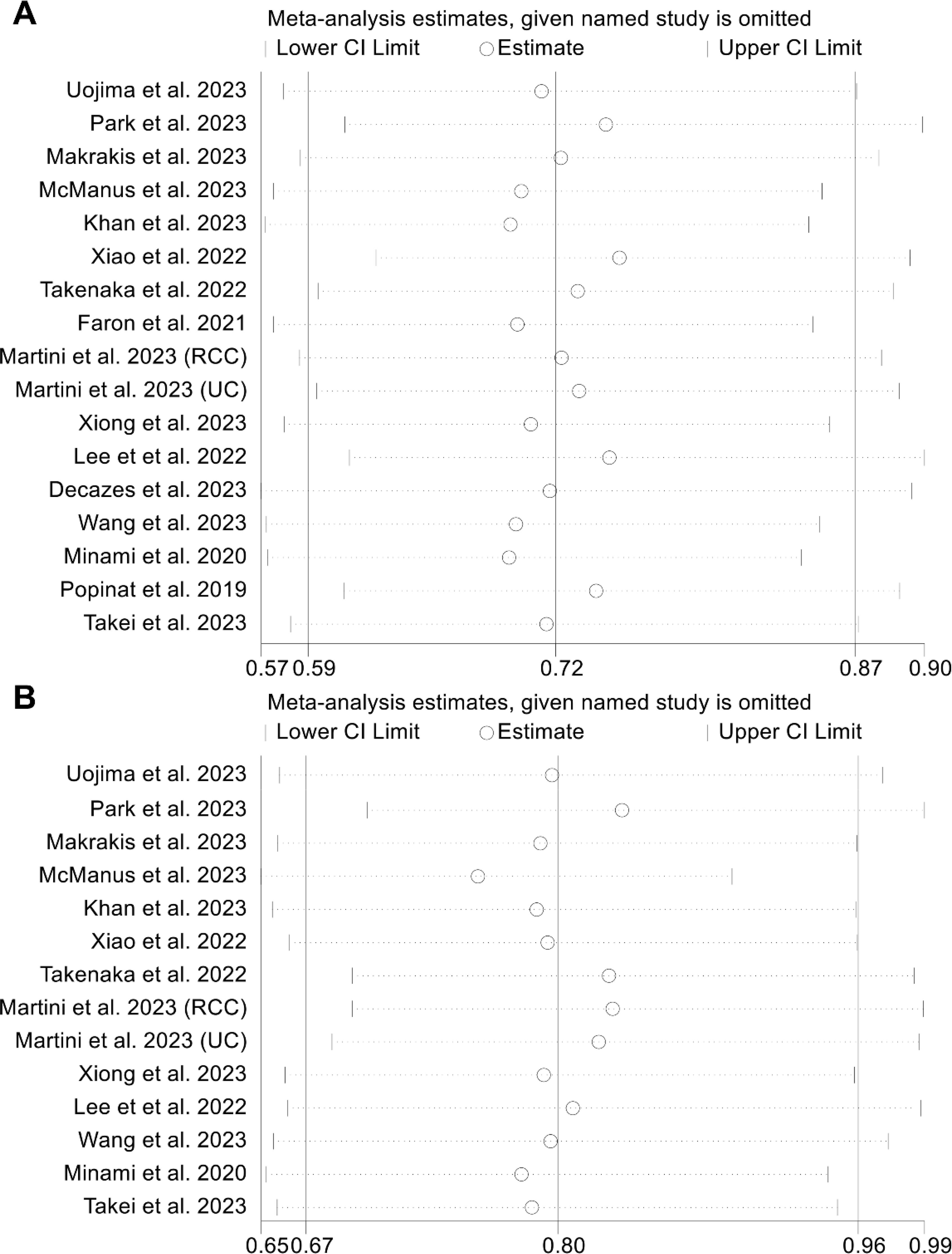
Figure 3. Sensitivity analysis of the association between visceral adipose tissue and overall survival (A) and progression-free survival (B). HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval.
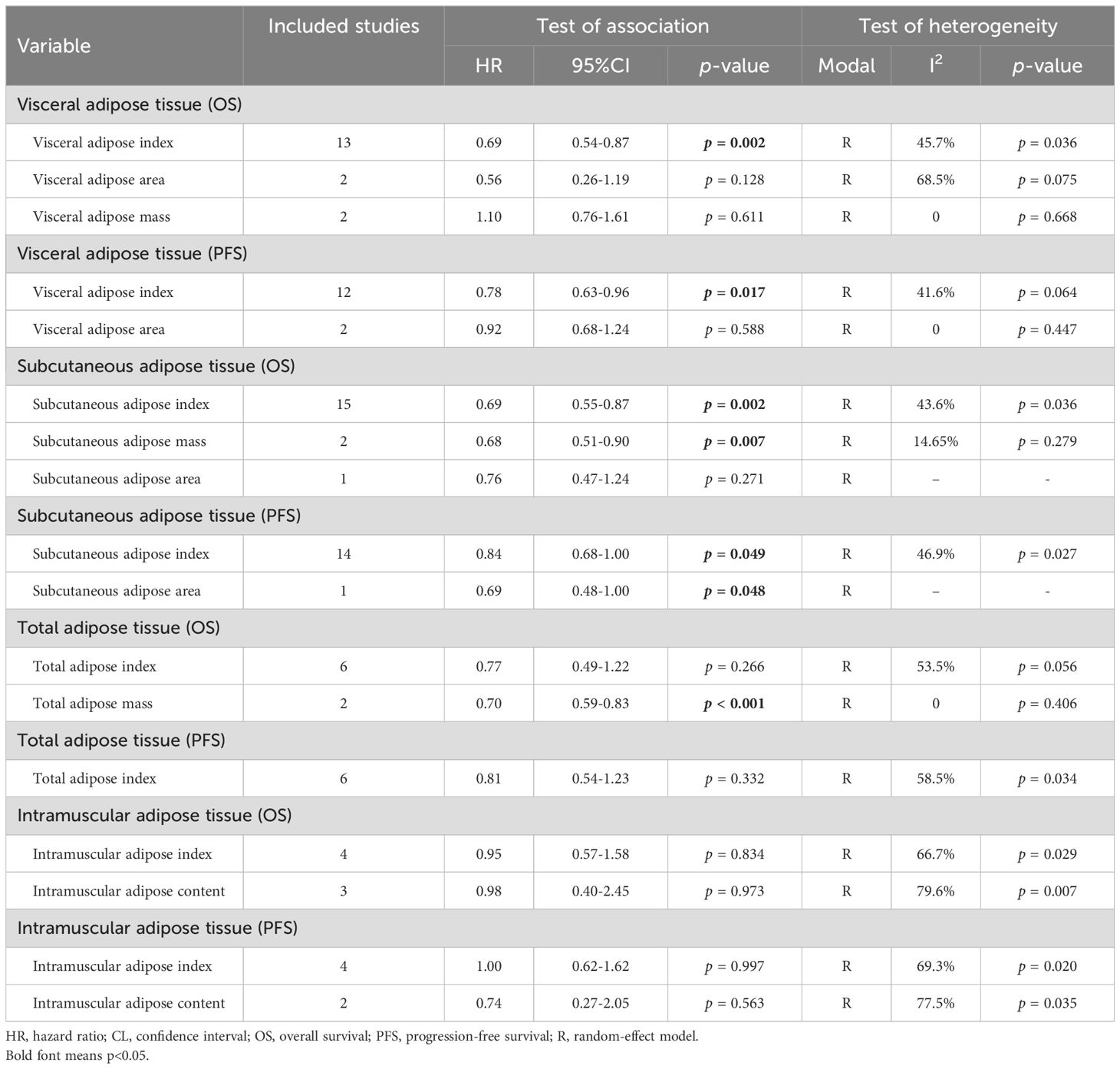
Table 2. Subgroup analysis of the association between body adipose tissue and the outcomes of cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors.
3.4 Baselinevisceral adipose tissue and immunotherapy responses
We conducted an analysis of the association between VAT and DCR in cancer patients (5 studies with 603 patients). It is noteworthy that the included studies exhibited no significant heterogeneity (I2 = 0, p = 0.781), thus warranting the application of a fixed-effects model. The results made it clear that patients with high VAT had a higher DCR (OR: 1.81, 95% CI: 1.26–2.60, p = 0.001, Figure 4A) than people with low VAT. The Egger's test (p = 0.643) and Begg's test (p = 0.806) confirmed the absence of publication bias, while sensitivity analysis revealed the stability of the results (Figure 4B).
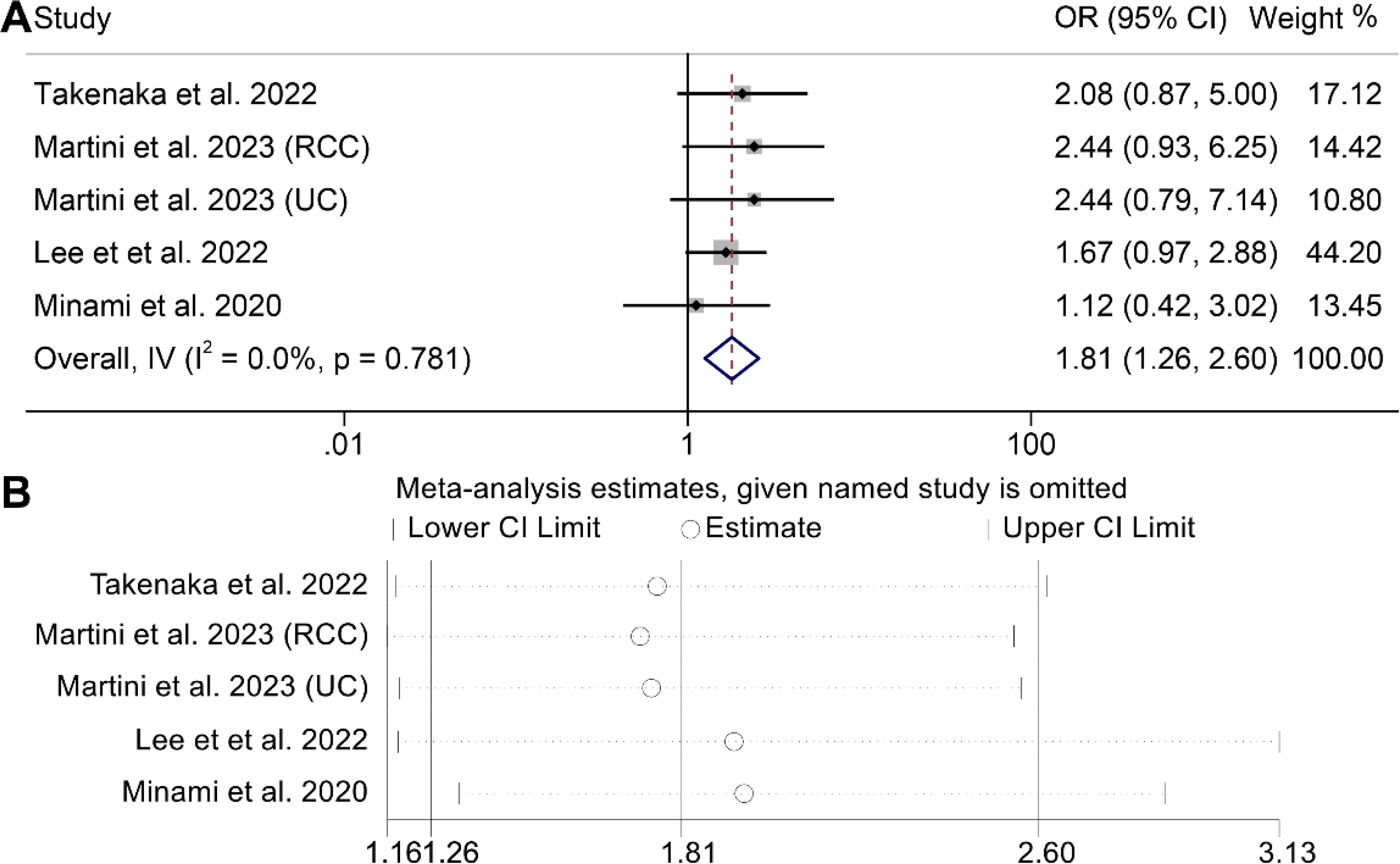
Figure 4. Forest plots of the relationship between visceral adipose tissue and disease control rate (A). Sensitivity analysis of the association between visceral adipose tissue and disease control rate (B). OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; IV, Inverse Variance.
3.5 Pre-immunotherapy subcutaneous adipose tissue and prognosis and response
In the evaluation of the association between subcutaneous adipose tissue and survival outcomes in cancer patients, 18 cohorts comprising 2262 patients were analyzed. A random-effects model revealed that cancer patients with high SAT had a significantly improved OS (I2 = 34.9%, p = 0.073, HR: 0.69, 95% CI: 0.58–0.82, p < 0.001, Figure 5A) and PFS (I2 = 45.6%, p = 0.028, HR: 0.82, 95% CI: 0.68–1.00, p = 0.049, Figure 5B). The results of the subgroup analyses are detailed in Table 2.
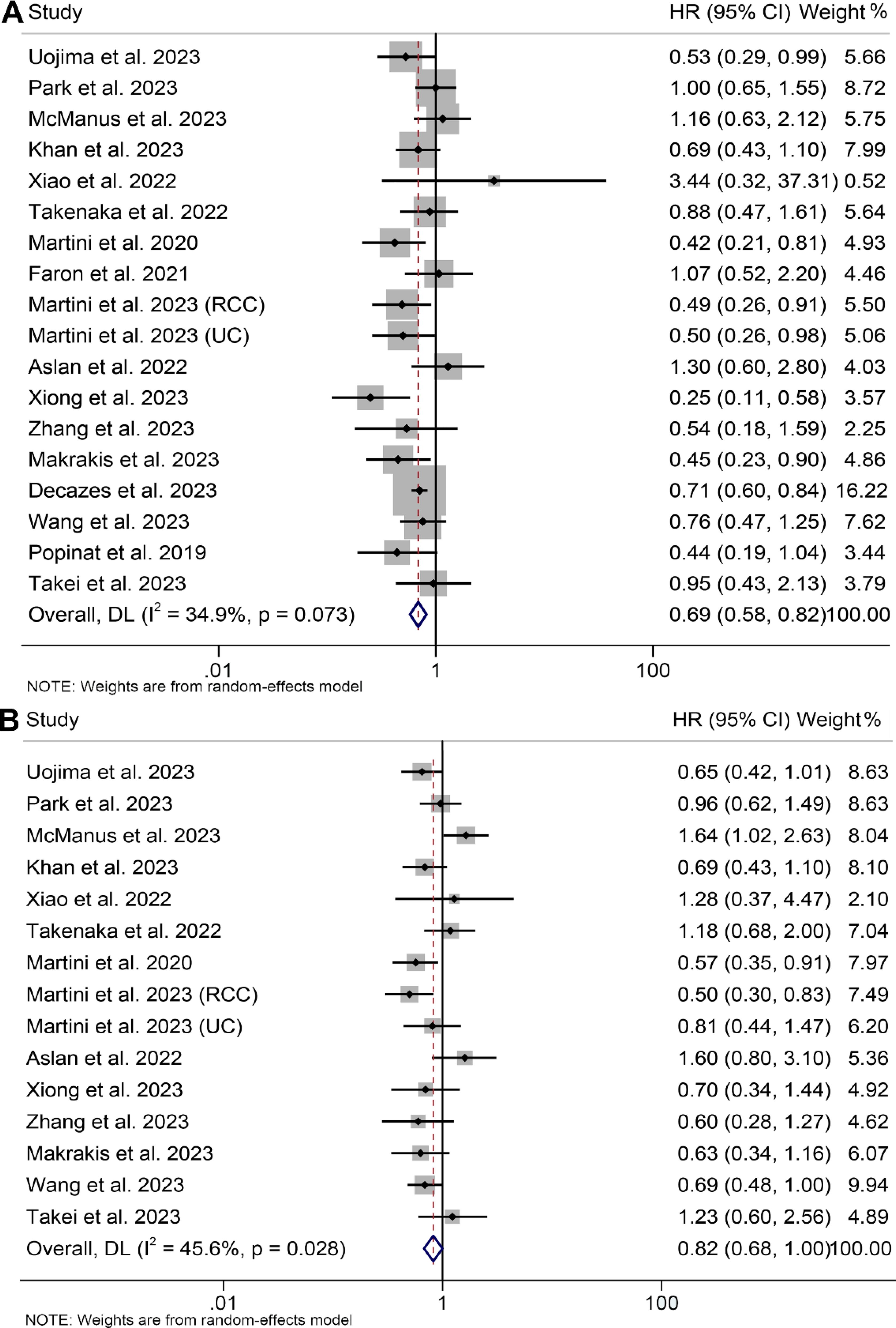
Figure 5. Forest plots of the relationship between subcutaneous adipose tissue and overall survival (A) and progression-free survival (B). HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; DL, DerSimonian and Laird.
Potential publication bias was assessed through funnel plots, Begg's test, and Egger's test, with no significant findings observed for OS (Egger's test: p = 0.771, Begg's test: p = 0.449, Supplementary Figure S2A) or PFS (Egger's test: p = 0.420, Begg's test: p = 0.488, Supplementary Figure S2B). Our sensitivity analyses, involving the systematic exclusion of each study in turn, consistently demonstrated the continued stability and robustness of the combined HRs for OS (Supplementary Figures S3A). However, it is worth noting that the relationship between SAT and PFS became insignificant after excluding some studies (Supplementary Figures S3B).
Besides, three studies involving 263 patients investigated the relationship between SAT and DCR in cancer patients undergoing ICI immunotherapy. There was no notable heterogeneity among the studies (I2 = 38.2%, p = 0.198), leading to the application of a fixed-effect model. The synthesised findings indicated that high SAT correlated with higher DCR (OR: 1.99, 95% CI: 1.15–3.44, p = 0.014, Supplementary Figure S4) compared to patients with lower SAT.
3.6 Baseline total adipose tissue, visceral-to-subcutaneous fat tissue ratio , and overall survival and progression-free survival
Eight studies, involving 1297 patients, and five studies, involving 506 patients, investigated the predictive roles of TAT and VSR on the prognosis of cancer patients, respectively. The results indicated that cancer patients with elevated TAT exhibited significantly longer OS (I2 = 42.4%, p = 0.097, HR: 0.73, 95% CI: 0.55–0.97, p = 0.028, depicted in Figure 6A), while those with high VSR demonstrated a shorter OS (I2 = 0, p = 0.532, HR: 1.43, 95% CI: 1.09–1.87, p = 0.010, Supplementary Figure S5A). However, we found no correlation between the TAT (I2 = 58.5%, p = 0.034, HR: 0.81, 95% CI: 0.54–1.23, p = 0.332, Figure 6B) and VSR (I2 = 0, p = 0.757, HR: 1.20, 95% CI: 0.95–1.51, p = 0.131, Supplementary Figure S5B) and PFS in cancer patients treated with ICIs. The results of the subgroup analyses are detailed in Table 2.
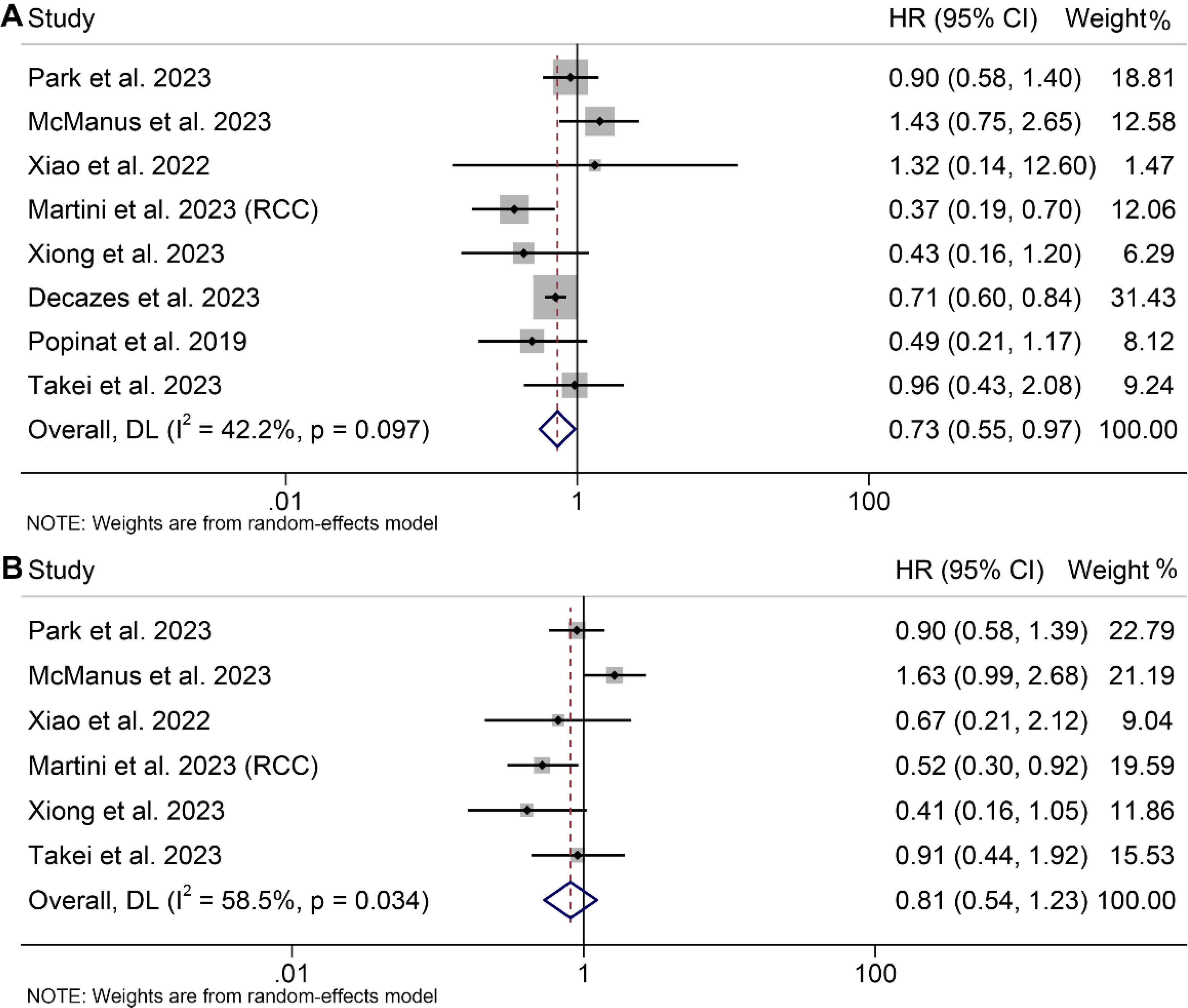
Figure 6. Forest plots of the relationship between total adipose tissue and overall survival (A) and progression-free survival (B). HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; DL, DerSimonian and Laird.
Begg’s test, and Egger’s test did not reveal significant publication bias in OS (TAT, Egger’s test: p = 0.970, Begg’s test: p = 0.536; VSR, Egger’s test: p = 0.636, Begg’s test: p = 0.462) and PFS (TAT, Egger’s test: p = 0.368, Begg’s test: p = 0.452; VSR, Egger’s test: p = 0.785, Begg’s test: p = 1.000). The sensitivity analysis, in which each study was excluded one at a time, demonstrated that the pooled HRs for OS and PFS remained stable and robust (Supplementary Figures S6A–D).
3.7 Baseline intramuscular adipose tissue and prognosis and response
In assessing the correlation between IMAT and prognosis as well as response among cancer patients undergoing ICIs, an analysis was performed on seven cohorts comprising 511 individuals. Utilizing a random-effects model, it revealed no statistically significant differences in OS (I2 = 68.2%, p = 0.004, HR: 0.95, 95% CI: 0.62–1.46, p = 0.827, Supplementary Figure S7A), PFS (I2 = 68.6%, p = 0.007, HR: 0.91, 95% CI: 0.60–1.38, p = 0.654, Supplementary Figure S7B), and DCR (I2 = 63.5%, p = 0.042, HR: 1.03, 95% CI: 0.37–2.68, p = 0.956, Supplementary Figure S7C) between patients with high and low IMAT levels. The results of the subgroup analyses are detailed in Table 2.
Examination for potential publication bias via Begg’s test and Egger’s test did not reveal significant concerns regarding OS (Egger’s test: p = 0.724, Begg’s test: p = 0.548), PFS (Egger’s test: p = 0.880, Begg’s test: p = 1.000), and DCR (Egger’s test: p = 0.473, Begg’s test: p = 0.734). Our sensitivity analysis, involving the systematic exclusion of each study in sequence, consistently indicated the sustained stability and robustness of the pooled HRs for OS, PFS, and DCR (Supplementary Figures S8A–C).
4 Discussion
In the current study, we discovered that patients with high VAT and SAT had significantly longer survival and a higher therapeutic response. In contrast, TAT, VSR, and IMAT are not better predictors of prognosis in cancer patients treated with immunotherapy.
There has been a growing focus on the physiological implications of obesity and its influence on cancer therapy outcomes. The prevalence of obesity in the United States, currently affecting around 40% of the population, reflects a global trend where obesity rates have nearly tripled since 1976 (52). The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have identified obesity as a heightened risk factor for 13 different cancer types (53, 54). Currently, adipose tissue has been identified as a lymphoid tissue, a concept particularly pertinent in understanding its implications in cancer and immunotherapy (55). The accumulation of white fat within the body has been proposed as a primary contributor to obesity and its associated complications (56). It is noteworthy that white adipose tissue serves as a reservoir for memory T cells, contributing to immune regulation (57). Obesity alters the composition and abundance of immune cell populations, including neutrophils, macrophages, B cells, and T cells (58). Immunotherapy directly supports the body's immune response against cancer (59). Considering the interaction between adipose tissue and the immune system, along with the reliance of immunotherapy agents on host immunity, it is plausible that the quantity and types of fat influence clinical responses to immunotherapy treatment. However, the specific impact of different fat depots on clinical outcomes in cancer patients undergoing immunotherapy has not been systematically explored in the literature to our knowledge.
Emerging data indicate a conflicting role of obesity and adipose tissue, along with their associated adipokines, as potential regulators in cancer-related mechanisms, exhibiting both tumor-promoting and tumor-suppressive effects. While adipose tissue is traditionally viewed as an endocrine organ, its role as a crucial modulator of the immune system is gaining recognition (60–62). Fat contributes to inflammation through the release of adipokines, cytokine-like molecules that sustain a state of chronic, low-grade inflammation (60). Among these adipokines, leptin stands out as a well-studied mediator linking metabolism and immune function, enhancing the population and function of regulatory T cells (63). Leptin has also been implicated in promoting immune evasion in lung cancer by upregulating proinflammatory cytokines (64). Obesity contributes to heightened PD-1 expression and increased release of PD-1 protein from T cells, along with elevated secretion of adiponectin and leptin from adipose tissue (65–67). These factors collectively contribute to enhanced T cell exhaustion and dysfunction, thereby facilitating tumor growth and progression (67). Thus, this suggests a potential mechanism for obesity-driven tumor immune escape, which can potentially be reversed through ICI therapy, leading to heightened effector T-cell responses. Collectively, obesity-induced chronic inflammation may contribute to tumorigenesis, yet increased adipose tissue may paradoxically enhance the host immune response to ICIs.
Adipose tissue is distributed in the visceral fat area and the subcutaneous fat area, which have different structural and functional characteristics. Our research findings revealed a significant association between VAT, SAT, and both survival and response. Thus, through the establishment of evidence-based data, it is crucial to consider the favorable impact of VAT on the efficacy of ICI therapy in clinical practice. Further research is warranted to explore whether controlling VAT and SAT improves the effectiveness of ICI therapy.
Certain limitations should be acknowledged in this meta-analysis. Firstly, it is worth mentioning that all investigations incorporated in this analysis were retrospective cohort studies, potentially constraining their statistical robustness. Additionally, due to the limited number of included studies, we were unable to perform subgroup analyses for specific cancer types and ICIs. Finally, the cut-off values for the same diagnostic metric differed among investigations. Hence, to attain more reliable conclusions, there is an urgent requirement for a worldwide, multicenter investigation to explore the impact of body fat tissue on outcomes in cancer patients undergoing ICIs.
5 Conclusion
The predictive effect of VAT and SAT on outcomes in ICI-treated cancer patients is highlighted by this analysis. This finding favors considering the VAT and SAT levels when determining the prognosis for this patient population.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
YL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft. YY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft. KL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft. XX: Conceptualization, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all the medical staff who contributed to the maintenance of the medical record database.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1557726/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. (2011) 144:646–74. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
2. Yuan Q, Deng D, Pan C, Ren J, Wei T, Wu Z, et al. Integration of transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics data to reveal HER2-associated metabolic heterogeneity in gastric cancer with response to immunotherapy and neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:951137. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.951137
3. Pardoll DM. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. (2012) 12:252–64. doi: 10.1038/nrc3239
4. Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, Grob JJ, Rutkowski P, Lao CD, et al. Five-year survival with combined nivolumab and ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med. (2019) 381:1535–46. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1910836
5. Ansell SM, Lesokhin AM, Borrello I, Halwani A, Scott EC, Gutierrez M, et al. PD-1 blockade with nivolumab in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. (2015) 372:311–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1411087
6. Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, Grob JJ, Cowey CL, Lao CD, et al. Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab or monotherapy in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med. (2015) 373:23–34. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1504030
7. Cheng W, Fu D, Xu F, Zhang Z. Unwrapping the genomic characteristics of urothelial bladder cancer and successes with immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Oncogenesis. (2018) 7:2. doi: 10.1038/s41389-017-0013-7
8. Ribas A, Wolchok JD. Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science. (2018) 359:1350–5. doi: 10.1126/science.aar4060
9. O'Donnell JS, Teng MWL, Smyth MJ. Cancer immunoediting and resistance to T cell-based immunotherapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2019) 16:151–67. doi: 10.1038/s41571-018-0142-8
10. Dolladille C, Ederhy S, Sassier M, Cautela J, Thuny F, Cohen AA, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor rechallenge after immune-related adverse events in patients with cancer. JAMA Oncol. (2020) 6:865–71. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.0726
11. Zhang L, Feng J, Kuang T, Chai D, Qiu Z, Deng W, et al. Blood biomarkers predict outcomes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with immune checkpoint Inhibitors: A pooled analysis of 44 retrospective sudies. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 118:110019. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110019
12. Zhao J, Li D, Xie S, Deng X, Wen X, Li J, et al. Nomogram for predicting prognosis of patients with metastatic melanoma after immunotherapy: A Chinese population-based analysis. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1083840. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1083840
13. Ren J, Wang A, Liu J, Yuan Q. Identification and validation of a novel redox-related lncRNA prognostic signature in lung adenocarcinoma. Bioengineered. (2021) 12:4331–48. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1951522
14. Havel JJ, Chowell D, Chan TA. The evolving landscape of biomarkers for checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. (2019) 19:133–50. doi: 10.1038/s41568-019-0116-x
15. Zhou KI, Peterson B, Serritella A, Thomas J, Reizine N, Moya S, et al. Spatial and Temporal Heterogeneity of PD-L1 Expression and Tumor Mutational Burden in Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma at Baseline Diagnosis and after Chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. (2020) 26:6453–63. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2085
16. Jørgensen JT. Companion and complementary diagnostics: clinical and regulatory perspectives. Trends Cancer. (2016) 2:706–12. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2016.10.013
17. Schalper KA, Carleton M, Zhou M, Chen T, Feng Y, Huang SP, et al. Elevated serum interleukin-8 is associated with enhanced intratumor neutrophils and reduced clinical benefit of immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Nat Med. (2020) 26:688–92. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0856-x
18. Wang Y, Wang J, Liu J, Zhu H. Immune-related diagnostic markers for benign prostatic hyperplasia and their potential as drug targets. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1516362. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1516362
19. Pang ZQ, Wang JS, Wang JF, Wang YX, Ji B, Xu YD, et al. JAM3: A prognostic biomarker for bladder cancer via epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulation. Biomol Biomed. (2024) 24:897–911. doi: 10.17305/bb.2024.9979
20. Xiao J, Mazurak VC, Olobatuyi TA, Caan BJ, Prado CM. Visceral adiposity and cancer survival: a review of imaging studies. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). (2018) 27:e12611. doi: 10.1111/ecc.2018.27.issue-2
21. Hu JB, Ravichandran S, Rushing C, Beasley GM, Hanks BA, Jung SH, et al. But not sarcopenia, is associated with pembrolizumab-related toxicity in patients with advanced melanoma. Anticancer Res. (2020) 40:5245–54. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.14528
22. Collet L, Delrieu L, Bouhamama A, Crochet H, Swalduz A, Nerot A, et al. Association between body mass index and survival outcome in metastatic cancer patients treated by immunotherapy: analysis of a french retrospective cohort. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13(9):2200. doi: 10.3390/cancers13092200
23. Crombé A, Kind M, Toulmonde M, Italiano A, Cousin S. Impact of CT-based body composition parameters at baseline, their early changes and response in metastatic cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Eur J Radiol. (2020) 133:109340. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109340
24. Martin L, Birdsell L, Macdonald N, Reiman T, Clandinin MT, McCargar LJ, et al. Cancer cachexia in the age of obesity: skeletal muscle depletion is a powerful prognostic factor, independent of body mass index. J Clin Oncol. (2013) 31:1539–47. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.45.2722
25. Deng J, Huang Y, Yu K, Luo H, Zhou D, Li D. Changes in the gut microbiome of patients with esophageal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis based on 16S gene sequencing technology. Microb Pathog. (2024) 193:106784. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106784
26. Lilong Z, Kuang T, Li M, Li X, Hu P, Deng W, et al. Sarcopenia affects the clinical efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with gastrointestinal cancers. Clin Nutr. (2024) 43:31–41. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2023.11.009
27. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Bmj. (1997) 315:629–34. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
28. Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics. (1994) 50:1088–101. doi: 10.2307/2533446
29. Popinat G, Cousse S, Goldfarb L, Becker S, Gardin I, Salaün M, et al. Sub-cutaneous Fat Mass measured on multislice computed tomography of pretreatment PET/CT is a prognostic factor of stage IV non-small cell lung cancer treated by nivolumab. Oncoimmunology. (2019) 8:e1580128. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2019.1580128
30. Martini DJ, Kline MR, Liu Y, Shabto JM, Williams MA, Khan AI, et al. Adiposity may predict survival in patients with advanced stage cancer treated with immunotherapy in phase 1 clinical trials. Cancer. (2020) 126:575–82. doi: 10.1002/cncr.v126.3
31. Minami S, Ihara S, Tanaka T, Komuta K. Sarcopenia and visceral adiposity did not affect efficacy of immune-checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy for pretreated patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. World J Oncol. (2020) 11:9–22. doi: 10.14740/wjon1225
32. Baldessari C, Pecchi A, Marcheselli R, Guaitoli G, Bonacini R, Valoriani F, et al. Body composition and inflammation impact in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated by first-line immunotherapy. Immunotherapy. (2021) 13:1501–19. doi: 10.2217/imt-2021-0038
33. Faron A, Opheys NS, Nowak S, Sprinkart AM, Isaak A, Theis M, et al. Deep learning-based body composition analysis predicts outcome in melanoma patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Diagn (Basel). (2021) 11(12):2314. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11122314
34. Martini DJ, Olsen TA, Goyal S, Liu Y, Evans ST, Magod B, et al. Body composition variables as radiographic biomarkers of clinical outcomes in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:707050. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.707050
35. Martini DJ, Shabto JM, Goyal S, Liu Y, Olsen TA, Evans ST, et al. Body composition as an independent predictive and prognostic biomarker in advanced urothelial carcinoma patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Oncologist. (2021) 26:1017–25. doi: 10.1002/onco.13922
36. Aslan V, Kılıç ACK, Sütcüoğlu O, Eraslan E, Bayrak A, Öksüzoğlu B, et al. Cachexia index in predicting outcomes among patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Urol Oncol. (2022) 40:494.e1–.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2022.07.018
37. Bolte FJ, McTavish S, Wakefield N, Shantzer L, Hubbard C, Krishnaraj A, et al. Association of sarcopenia with survival in advanced NSCLC patients receiving concurrent immunotherapy and chemotherapy. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:986236. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.986236
38. Lee JH, Hyung S, Lee J, Choi SH. Visceral adiposity and systemic inflammation in the obesity paradox in patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma undergoing immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: a retrospective cohort study. J Immunother Cancer. (2022) 10(8):e005226. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-005226
39. Takenaka Y, Takemoto N, Otsuka T, Nishio M, Tanida M, Fujii T, et al. Predictive significance of body composition indices in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma treated with nivolumab: A multicenter retrospective study. Oral Oncol. (2022) 132:106018. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2022.106018
40. Xiao LS, Li RN, Cui H, Hong C, Huang CY, Li QM, et al. Use of computed tomography-derived body composition to determine the prognosis of patients with primary liver cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Cancer. (2022) 22:737. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09823-7
41. Decazes P, Ammari S, Belkouchi Y, Mottay L, Lawrance L, de Prévia A, et al. Synergic prognostic value of 3D CT scan subcutaneous fat and muscle masses for immunotherapy-treated cancer. J Immunother Cancer. (2023) 11(9):e007315. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-007315
42. Khan A, Welman CJ, Abed A, O'Hanlon S, Redfern A, Azim S, et al. Association of computed tomography measures of muscle and adipose tissue and progressive changes throughout treatment with clinical endpoints in patients with advanced lung cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15(5):1382. doi: 10.3390/cancers15051382
43. Makrakis D, Rounis K, Tsigkas AP, Georgiou A, Galanakis N, Tsakonas G, et al. Effect of body tissue composition on the outcome of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. PloS One. (2023) 18:e0277708. doi: 1371/journal.pone.0277708
44. McManus HD, Zhang D, Schwartz FR, Wu Y, Infield J, Ho E, et al. Relationship between pretreatment body composition and clinical outcomes in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma receiving first-line ipilimumab plus nivolumab. Clin Genitourin Cancer. (2023) 21:e429–e37.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2023.05.006
45. Park JE, Jo J, Youk J, Kim M, Yoon SH, Keam B, et al. Prognostic utility of body composition parameters based on computed tomography analysis of advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Insights Imaging. (2023) 14:182. doi: 10.1186/s13244-023-01532-4
46. Takei K, Kijima T, Okubo N, Kurashina R, Kokubun H, Uematsu T, et al. Association between immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment outcomes and body composition factors in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15(23):5591. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235591
47. Tanaka T, Miwa K, Shimotsuura Y, Nagasu S, Shigyou H, Hirota K, et al. High intramuscular adipose tissue content was a favorable prognostic factor in patients with advanced gastric cancer treated with nivolumab monotherapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 38:1760–7. doi: 10.1111/jgh.v38.10
48. Uojima H, Chuma M, Hidaka H, Tsuda T, Kobayashi S, Hattori N, et al. Impact of body composition for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who received atezolizumab plus bevacizumab therapy. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 35:865–73. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000002581
49. Wang J, Dong P, Qu Y, Xu W, Zhou Z, Ning K, et al. Association of computed tomography-based body composition with survival in metastatic renal cancer patient received immunotherapy: a multicenter, retrospective study. Eur Radiol. (2023) 33:3232–42. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-09345-7
50. Xiong B, Fu B, Wu Y, Gao F, Hou C. Body composition predicts prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients undergoing immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2023) 149:11607–17. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05051-z
51. Zhang J, Yang X, Yang X, Xu J, Wang Y, Wang Y, et al. Prognostic value of SAT volume and density for predicting the outcome of patients with unresectable HCC treated with lenvatinib plus anti-PD-1 antibodies. Am J Cancer Res. (2023) 13:912–21.
52. Colotta F, Allavena P, Sica A, Garlanda C, Mantovani A. Cancer-related inflammation, the seventh hallmark of cancer: links to genetic instability. Carcinogenesis. (2009) 30:1073–81. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp127
53. Budui SL, Rossi AP, Zamboni M. The pathogenetic bases of sarcopenia. Clin cases Miner Bone Metab. (2015) 12:22–6. doi: 10.11138/ccmbm/2015.12.1.022
54. Wang JF, Wang JS, Liu Y, Ji B, Ding BC, Wang YX, et al. Knockdown of integrin β1 inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis in bladder cancer cells. Biofactors. (2025) 51:e2150. doi: 10.1002/biof.v51.1
55. Escobedo N, Oliver G. The lymphatic vasculature: its role in adipose metabolism and obesity. Cell Metab. (2017) 26:598–609. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.07.020
56. Gesta S, Tseng YH, Kahn CR. Developmental origin of fat: tracking obesity to its source. Cell. (2007) 131:242–56. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.004
57. Han SJ, Glatman Zaretsky A, Andrade-Oliveira V, Collins N, Dzutsev A, Shaik J, et al. White adipose tissue is a reservoir for memory T cells and promotes protective memory responses to infection. Immunity. (2017) 47:1154–68.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.11.009
58. Grant RW, Dixit VD. Adipose tissue as an immunological organ. Obes (Silver Spring). (2015) 23:512–8. doi: 10.1002/oby.21003
59. Yang Y. Cancer immunotherapy: harnessing the immune system to battle cancer. J Clin Invest. (2015) 125:3335–7. doi: 10.1172/JCI83871
60. Francisco V, Pino J, Campos-Cabaleiro V, Ruiz-Fernández C, Mera A, Gonzalez-Gay MA, et al. Obesity, fat mass and immune system: role for leptin. Front Physiol. (2018) 9:640. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00640
61. Wang Y, Wang J, He J, Ji B, Pang Z, Wang J, et al. Comprehensive analysis of PRPF19 immune infiltrates, DNA methylation, senescence-associated secretory phenotype and ceRNA network in bladder cancer. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1289198. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1289198
62. Wang Y, Zhu H, Xu H, Qiu Y, Zhu Y, Wang X. Senescence-related gene c-Myc affects bladder cancer cell senescence by interacting with HSP90B1 to regulate cisplatin sensitivity. Aging (Albany NY). (2023) 15:7408–23. doi: 10.18632/aging.204863
63. Matarese G, Procaccini C, De Rosa V, Horvath TL, La Cava A. Regulatory T cells in obesity: the leptin connection. Trends Mol Med. (2010) 16:247–56. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2010.04.002
64. Shen Y, Wang Q, Zhao Q, Zhou J. Leptin promotes the immune escape of lung cancer by inducing proinflammatory cytokines and resistance to apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. (2009) 2:295–9. doi: 10.3892/mmr_00000099
65. Finelli C. Obesity and immunotherapy: the surprisingly positive association! Immunotherapy. (2020) 12:541–4. doi: 10.2217/imt-2019-0143
66. Zhang X, Liu Y, Shao H, Zheng X. Obesity paradox in lung cancer prognosis: evolving biological insights and clinical implications. J Thorac Oncol. (2017) 12:1478–88. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2017.07.022
Keywords: body adipose tissue, visceral adipose tissue, subcutaneous adipose tissue, immune checkpoint inhibitors, cancer
Citation: Li Y, Yu Y, Lv K, Ge R and Xie X (2025) Prognostic value of body adipose tissue parameters in cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front. Immunol. 16:1557726. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1557726
Received: 09 January 2025; Accepted: 24 January 2025;
Published: 12 February 2025.
Edited by:
Minghua Ren, First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Li, Yu, Lv, Ge and Xie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rongjuan Ge, NDk2MTg4Mzg5QHFxLmNvbQ==; Xie Xie, eGlleGllMjAyMjAyMjJAc2luYS5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yan Li
Yan Li Yean Yu2†
Yean Yu2† Xie Xie
Xie Xie