
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Immunol., 27 March 2025
Sec. Inflammation
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1535823
This article is part of the Research TopicModulation of Pro-Inflammatory Signaling by InterferonsView all 5 articles
Interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) is a critical transcription factor in the IRF family, playing a pivotal role in modulating immune responses, particularly within the innate immune system. IRF5 regulates the expression of type I interferons (IFNs), proinflammatory cytokines, and other immune-related genes, essential for effective host defense against infections and immune surveillance. Its functions, however, are diverse and highly context-dependent, adapting to different immune challenges and tissue environments. Studies have demonstrated that dysregulated IRF5 activation contributes to the pathogenesis of numerous diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, and chronic inflammatory conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This dysregulation underscores the dual role of IRF5, both in immune protection and in driving pathological inflammation. Given its significant involvement in both physiological and pathological processes, IRF5 presents a promising therapeutic target for managing diseases characterized by excessive inflammation and immune dysregulation. However, developing effective molecules to specifically modulate the IRF5 pathway remains challenging, with limited therapeutic agents available for clinical application. In this review, we examine the diverse roles of IRF5 in various disease contexts, the mechanisms by which IRF5 contributes to disease progression, and the potential therapeutic strategies targeting IRF5. Additionally, we discuss potential complications and risks associated with IRF5-targeted therapies, including the balance between dampening pathological inflammation and preserving essential immune functions. This exploration highlights both the therapeutic potential and the complexity of modulating IRF5 activity in clinical settings.
The IRF (interferon regulatory factor) family of transcription factors is essential not only in regulating gene expression and apoptosis but also in modulating cell cycle processes and tumorigenesis (1). This family comprises nine members (IRF1–IRF9), all characterized by a conserved multi-domain structure (2). Each IRF contains an N-terminal DNA-binding domain (DBD), which recognizes specific DNA sequences in interferon-stimulated response elements (3), and a C-terminal IRF-associated domain (IAD), facilitating interactions with other IRFs and proteins to form transcriptional complexes (4).
Among these, IRF5 is pivotal in regulating immune responses, including interferon expression, cellular maturation, differentiation, apoptosis, and the production of proinflammatory cytokines (5). IRF5 is constitutively expressed across various immune cell types, including dendritic cells (DCs), macrophages, and neutrophils (6, 7). The IRF5 gene in humans consists of nine coding exons and at least four alternative non-coding exons (1A, 1B, 1C, and 1D), enabling the production of multiple functional isoforms (5, 8). These isoforms, denoted as V1–V11, are expressed in a cell type-specific manner, each with distinct localization and functions (9). For instance, IRF5 isoforms V2, V9, and V10, which include exon 1B, are linked to increased susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), whereas IRF5 lacking exon 1B does not confer the same risk (10).
Typically, IRF5 remains inactive until it undergoes post-translational modifications, leading to homodimerization and nuclear translocation. In the nucleus, IRF5 interacts with the NF-κB p65 RelA subunit (11), enabling it to polarize macrophages to M1 or M2 phenotypes and drive the expression of proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α (6, 7, 12). This activity is crucial for an effective immune response to pathogens and injuries. However, dysregulated IRF5 activation is implicated in the pathogenesis of cancer, autoimmune systems, and inflammatory diseases. This review will summarize IRF5’s roles in these conditions and examine the therapeutic potential of IRF5-targeted interventions.
Extensive research demonstrates that IRF5 participates in numerous signaling pathways via activation mechanisms like ubiquitination and phosphorylation. Multiple phosphorylation sites have been identified in serine clusters at IRF5’s C-terminus, including T10, S158, S309, S317, S451, S462, S425, S427, S430, and S436 (13–15). These phosphorylation sites serve distinct functions in IRF5 activity. Specifically, S451 and S462 are pivotal for nuclear translocation, transcriptional regulation, and apoptosis (13). Phosphorylation at S436 aids in stabilizing the activated dimer, while modifications at S425, S427, and S430 are crucial for releasing the C-terminal autoinhibitory conformation. High-throughput kinase inhibitor libraries offer a valuable approach for identifying potential candidate kinases. Several kinases have been implicated in IRF5 phosphorylation, including TBK-1, TRAF6, and RIP2, with RIP2—NOD2’s downstream kinase—serving as a potent activator. In human macrophages, NOD2-induced IRF5 phosphorylation activates Akt2, enhancing glycolysis and promoting cytokine expression and macrophage polarization (16).
Ubiquitination, mediated by the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAF6, also promotes IRF5’s nuclear translocation and binding to IFNA4, IFNA13, and IFNB promoters, though polyubiquitination itself is not essential for IRF5’s transcriptional role. Phosphorylation and ubiquitination act independently in regulating IRF5 function (13, 17).
The TLR-MyD88 pathway is well-characterized in IRF5 activation. Ligand binding to TLRs (PAMPs) leads to TLR dimerization and MyD88 recruitment, initiating downstream interactions where IRF5 associates with TRAF6 and MyD88 to activate transcription factors like NF-κB and IRF5 itself (12, 17). Additionally, TLR7/8 stimulation in human monocytes triggers IRAK4-mediated phosphorylation of IRF5 via the IRAK4-TAK1-IKKβ signaling cascade (18). Upon activation, IRF5 forms homodimers through its C-terminal dimerization domain, translocate to the nucleus, and binds to gene promoters in coordination with coactivators. Studies also show that IRF5 modulates IFN-β production in response to C. albicans through the Dectin-1-Syk-IRF5 pathway in dendritic cells (19). Additionally, DNA-damaging agents like CPT and various viral infections, including herpesviruses, can induce IRF5 phosphorylation and transcriptional activation (14, 20–23).
Upon activation and nuclear translocation, IRF5 regulates target genes essential for immune responses by coordination with coactivators. For example, it modulates the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-12, by recruiting the target genes through its interaction with the NF-κB subunit RelA. This supports inflammatory responses and enhances pathogen defense (6, 7, 12). Furthermore, IRF5 modulates chemokines like CXCL10 and CCL5, crucial for immune cell recruitment to infection or inflammation sites (24), and enhances the expression of co-stimulatory molecules, such as CD40 and CD86, on antigen-presenting cells, which are essential for T-cell activation and immune regulation (25).
IRF3 and IRF7 release type I interferons in response to viral infections, while IRF5 boosts pro-inflammatory cytokines such TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-12 (12). IRF5 binds to the promoters of inflammatory genes, while IRF3 and IRF7 trigger IFN-β transcription. IRF7, which shares a close association with IRF3, is a transcription factor that requires activation. IRF7 activation requires the virus-activated domain in human IRF7A (26). IRF7 is inherently located in the cytoplasm, and it is mostly expressed in B cells, plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), and monocytes in the spleen, thymus, and peripheral blood leukocytes (27, 28). Numerous stimuli, such LPS (Lipopolysaccharide), IFN-bet, EBV-latent membrane protein 1 (EBV-LMP1), viral infections, and certain chemical agents like phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) and sodium butyrate, can significantly induce IRF7 synthesis within specific cell lines (28–30). Furthermore, DNA damage, virus infection, and EBV-LMP1 can cause IRF7 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation (26, 30, 31).
During lymphocyte development, IRF4 and IRF8 operate as transcriptional repressors or activators. IRF4 regulates T-cell activity, whereas IRF5 promotes M1 macrophage polarization and inflammatory responses (32). IRF4 is only expressed in immune system cells and responds to a variety of mitogenic stimuli, such as PMA/Ionomycin and T-cell receptor (TCR) cross-linking (33–35). IRF4’s function as a transcriptional activator or suppressor is governed by its interactions with various transcription factors or the DBD on different promoters (36, 37). The human IRF8 gene is located on chromosome 16q24.1, spanning 23 kb and including 9 exons and 8 introns. The IRF8 protein encodes 426 amino acids. IRF8 is primarily found in lymphoid and myeloid cell lines, but it can also be found in the colon, skin, lung, liver, ocular lens, cornea, and heart epithelial cells. IFN-γ stimulates its expression (38–40). IRF8 is abundantly expressed in both progenitor and mature cells within the B cell, conventional DC1 (cDC1), and pDC lineages, and it plays a critical role in their development and activity.
IRF1 is a tumor suppressor that regulates apoptosis and the cell cycle, but IRF5 can suppress tumors and cause cancer based on its biological context (41). The IRF1 gene is expressed at low baseline levels in human cells but can be activated by various stimuli, including IFNs, tumor necrosis factor (TNF), and interleukin-1 (IL-1) (42). Many cell types constitutively produce IRF2, and viruses and IFN can further stimulate its expression.
Building on the structural features of IRF5, including its activation, dimerization, nuclear translocation, and interactions with co-activators, targeting specific binding sites on IRF5 presents a potential avenue for therapeutic intervention. Identifying crucial peptide sequences involved in IRF5–protein interactions is essential. The development of specific small-molecule inhibitors to disrupt these processes offers a promising strategy for precise modulation of IRF5 activity, which will be elaborated on in the following section.
IRF5 plays a critical role in microbial resistance, cell survival, and innate immunity (43, 44), however, dysregulation of IRF5 activation is involved in various diseases including tumors, autoimmune and inflammatory disorders.
High IRF5 expression is closely associated with several autoimmune diseases, notably systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), multiple sclerosis (MS), Sjögren’s syndrome, and rheumatoid arthritis (RA), with particularly strong correlations in SLE and Sjögren’s syndrome (45–49). Extensive research into IRF5’s role in SLE pathogenesis has highlighted elevated inflammatory cytokines and type I interferons (IFNs) as characteristic in SLE patients (46, 50, 51). IRF5 shows high expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of SLE patients and is persistently activated in monocytes (52, 53). Specifically, overexpressed IRF5 isoforms (v2, v9, v10) are linked to increased SLE susceptibility (10). suggesting that IRF5 dysregulation may drive SLE pathogenesis. Recent genome-wide association studies have identified several SLE-risk single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) enriched in the IRF5 locus. Among these, rs4728142 could act as an enhancer to regulate the expression of IRF5 by affecting the binding affinity of zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 3 (ZBTB3), a transcription factor involved in regulation. Furthermore, in monocytes from SLE patients, CRISPR-based interference with the regulation of this enhancer attenuated the production of disease-associated cytokines (54).
Research shows that either genetic IRF5 deficiency (Irf5–/–) or pharmacological inhibition using N5-1, which blocks IRF5 nuclear translocation, effectively protects against SLE onset and severity in murine lupus models (46, 51, 55, 56). Additionally, IRF5 deficiency shields mice from inflammatory damage in both inflammatory and lupus arthritis models (48, 55, 57–59). In antigen-induced arthritis models, Irf5–/– mice show reduced knee swelling and lower levels of proinflammatory cytokine IL-12p40 (57). Further, IRAK4 inhibition, which downregulates IRF5, alleviates joint inflammation in RA by reducing IRF5 activity in macrophages and fibroblasts (60).
The IRF family has nine members (IRF1-IRF9), each with a unique role in immunological regulation, inflammation, and oncogenesis. While numerous IRFs, including IRF3, IRF4, IRF7, and IRF8, have been linked to these processes, IRF5 stands out for its distinct role in increasing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokine. IRF5 is a transcriptional regulator of inflammatory pathways activated through Toll-like receptors (TLRs), leading to the production of cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-12 (12), unlike IRF3 and IRF7, which primarily drive antiviral responses via type I interferon (IFN) signaling (Honda et al., 2006). This renders IRF5 especially important in the development of autoimmune illnesses such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in which increased inflammatory cytokine production drives disease progression (10). Conversely, IRF4 suppresses the polarization of inflammatory macrophage, demonstrating IRF5’s specific pro-inflammatory activity (61).
IRF5 also plays a distinct and context-specific role in cancer, distinguishing it from other IRFs that act primarily as tumor suppressors or oncogenes. Such as IRF1 and IRF8 support the suppression of tumors by promoting apoptosis and improving immune control (41), but IRF5 has a coupled role based on the tumor microenvironment as well. In some malignancies, including breast cancer, IRF5 acts as a tumor suppressor by triggering apoptosis and cell cycle arrest (21). However, in inflammation-driven cancers, IRF5 may promote tumor growth by chronic production of cytokines and immunological regulation (62).
RF5 is critical in initiating proinflammatory cytokine production via Toll-like receptor activation. Immune signaling in response to viral or bacterial infections typically induces type I IFN and inflammatory cytokine production, which helps eliminate pathogens. Upon viral invasion, IRF5 employs a dual mechanism: it promotes the synthesis of interferons (IFNs), powerful signaling molecules with antiviral properties, which in turn activate diverse immune cells to identify and destroy infected cells effectively (21, 63, 64). Studies reveal that Irf5-/- mice show increased susceptibility to viral infections due to reduced IFN production and enhanced viral replication, highlighting IRF5’s essential role in antiviral defense (21). Additionally, emerging research suggests that IRF5’s antiviral functions extend beyond IFN production, potentially enhancing immune cell metabolism, particularly in macrophages, to strengthen antiviral responses (65, 66).
In the context of HIV infection, IRF5 plays a pivotal role by inducing various interferons that inhibit viral processes such as entry, replication, and assembly. IRF5 also stimulates the expression of antiviral genes, including PKR and 2’,5’-oligoadenylate synthetase, which aid in suppressing HIV replication (67), Specific IRF5-TNPO3 polymorphisms, such as rs2004640, rs10954213, rs2280714, and rs10279821, have been linked to enhanced HIV control in long-term non-progressors (LTNPs), suggesting these variants may boost IRF5’s antiviral activity and help maintain lower viral loads (68). However, recent findings indicate that IRF5 may predispose memory CD4+ T cells to Fas-mediated apoptosis and is integral to the Fas/FasL pathway; blocking this pathway with IRF5 inhibitory peptides has shown promise in preventing memory CD4+ T cell loss in HIV patients (69).
Elevated IRF5 expression and tissue damage are hallmarks of chronic inflammatory responses, suggesting that IRF5’s role in HIV-1 infection may extend to other chronic viral infections, including SARS-CoV-2 (64). COVID-19’s hyperinflammatory syndrome—often manifesting one to two weeks post-symptom onset—is termed “macrophage activation syndrome” (70), “cytokine storm” (71) or “acute respiratory distress syndrome” (72). This condition is characterized by excessive proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines (73), and other bioactive molecules, contributing to COVID-19 severity and mortality.
The proposed mechanism suggests that SARS-CoV-2, upon cell entry, may amplify the Hexosamine Biosynthetic Pathway (HBP), leading to increased glucose consumption and rapid viral replication. This heightened HBP activity raises levels of O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT), an enzyme with high binding affinity to IRF5 (74), potentially driving IRF5 overexpression. This overexpression can upregulate inflammatory cytokine genes and provoke detrimental endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, resulting in hyperinflammation, cytokine storm, and multiorgan failure (75).
Additionally, SARS-CoV-2 infection reduces IRF5+ myeloid dendritic cells (mDCs), although IRF5+ plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) remain unaffected (76). The IRAK4-IRF5 pathway significantly contributes to the hyperinflammatory cytokine and chemokine response in COVID-19 (77, 78). IRAK4 inhibitors reduce SARS-CoV-2-induced cytotoxicity in ACE2+ HEK293 cells by targeting IRF5 and IRF7, alongside reducing monokines and cytokines such as IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α, and CCL2, underscoring IRF5’s role in COVID-19 pathogenesis (78, 79).
IRF5 has been widely studied in mouse models of colitis and IBD, and it is reported that it plays an important role in the inflammation of the colon. Research related to IRF5 knockout mice (IRF5-/-) has revealed significant protection against experimental colitis, which includes DSS- and TNBS-induced colitis, mainly attributed to decreased pro-inflammatory polarization of macrophages and reduced levels of cytokines including IL-6, IL-12 and TNF-α (6, 80). These results indicate that IRF5 is an important regulator of the response to inflammation in colitis and a prospective therapeutic target for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Nonetheless, transforming these results into therapeutic implications needs further evidence via human studies.
Various research investigated patient specimens to study IRF5’s role in human IBD. IRF5 polymorphisms have been related to an increased vulnerability to IBD, specifically Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis. For example, particular IRF5 risk alleles have been linked to greater disease severity and inflammatory cytokine production in IBD patients’ colon biopsies (81). Furthermore, IRF5 mRNA and protein levels have been reported to be higher among monocytes and colonic macrophages in IBD patients than in healthy controls, indicating that it plays a role in disease pathophysiology (80). These outcomes are consistent with mouse studies and support the involvement of IRF5 in its role as pro-inflammatory mediator in IBD and colitis.
While preclinical evidence clearly justifies focusing on IRF5 for IBD therapy, comprehensive clinical trials testing IRF5 antagonists in patients with IBD are currently missing. Emerging methods for autoimmune diseases, such as small-molecule antagonists and antisense oligonucleotides inhibiting IRF5 signaling, are currently under development and could lead the pathway for further clinical trials in IBD (46). Furthermore, given IRF5’s contribution to macrophage polarization, IRF5-targeted therapies may provide a more specific approach to modifying colon immune response while maintaining protective immunity. Overall, whereas human samples provide strong evidence supporting IRF5 as a viable option for therapy in IBD, more clinical research and treatment interventions are needed to demonstrate its translational significance.
IRF5 has been identified as a mediator of DNA damage-induced apoptosis and as a regulator of cell migration (21, 23, 82), suggesting that its loss may enhance cell proliferation and migration—traits consistent with cancer hallmarks (83), such as sustained proliferative signaling, invasion, metastasis, and resistance to cell death. Thus, IRF5 dysregulation may contribute to tumor initiation, progression, and metastasis, as well as impact treatment response (84). Extensive evidence shows IRF5 can function as either a tumor suppressor or a proto-oncogene, depending on cell type and tissue specificity.
Research indicates that IRF5 may act as a tumor suppressor, where its loss promotes tumor growth, metastasis, and poor outcomes in cancers such as breast, gastric, colorectal, pancreatic, and lung (82, 85–88). For example, IRF5 expression declines significantly in advanced ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and is nearly absent in invasive ductal carcinoma, with low levels correlating to poorer prognosis in ER/PR-negative breast and non-small cell lung cancers (89–91). High IRF5 expression is linked to improved survival in pancreatic, head and neck squamous, and laryngeal cancers (85, 92, 93). The mechanisms responsible for reduced IRF5 expression in cancer remain largely unclear. A preliminary analysis of TCGA genomics data indicates that IRF5 rarely undergoes gene mutations or loss of heterozygosity. Thus, the reduced expression of IRF5 in tumors is likely attributable to expression loss or inhibition through post-transcriptional modifications rather than gene mutations (84).
The loss of IRF5 drives tumorigenesis through multiple mechanisms, primarily manifested as dysregulation of cell cycle control and apoptosis, activation of oncogenes, immune evasion, and enhanced cell migration and invasion abilities. In cell cycle regulation, IRF5 deficiency impedes the expression of genes such as Bak, caspase 8, Bax, and p21, preventing cells from entering a stagnation state or undergoing apoptosis, thus acquiring the ability for sustained proliferation (21, 23). At the same time, the loss of IRF5 is closely associated with the overexpression of the MYC gene, which not only promotes the generation of cancer stem cells but also correlates with reduced immune cell infiltration and decreased chemotherapy responses. In immune regulation, IRF5, as a core regulator of type I IFN and pro-inflammatory cytokine expression, loses its function, weakening the anti-tumor immune response in the tumor microenvironment, promoting dysregulated angiogenesis and inflammation, and creating conditions for tumor immune evasion (94). Moreover, IRF5 deficiency also leads to dysregulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), significantly enhancing the migration and invasion abilities of tumor cells, and making them more likely to form metastases (95). Notably, the function of IRF5 involves not only transcriptional regulation but also the limitation of cell migration and invasion through the regulation of cytoskeletal molecules (82). Its loss disrupts this crucial mechanism, further promoting tumor progression.
Moreover, IRF5 can also act as a proto-oncogene, with elevated levels in tumors like hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (96), non-metastatic clear cell renal carcinoma (97), endometrial, prostate cancers (98), and primary central nervous system (CNS) tumors (99). While the exact mechanism remains unknown. Study shows IRF5 is overexpressed in HCC and promotes the proliferation and tumorigenic potential of HCC cells by upregulating the expression of lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) and promoting glycolysis (96). High IRF5 levels correlate with increased recurrence and poorer outcomes in prostate cancer (100) and accelerated proliferation in thyroid cancer cells (101). Overall, IRF5’s role as a tumor suppressor or proto-oncogene is context-dependent, varying by cell type and tissue (84).
However, in malignancies characterized by inflammation, such as colorectal and pancreatic cancers, IRF5 may contribute to tumor growth by maintaining a chronic inflammatory state. Research demonstrates that IRF5 controls the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-12, which might result in tumor-associated inflammation and immune evasion (41, 101). In these situations, chronic activation of IRF5-driven inflammation may result in enhanced angiogenesis, tumor cell survival, and resistance to immunotherapy. Furthermore, IRF5 activation in tumor-associated macrophages has been linked to an inflammatory tumor microenvironment that promotes cancer cell proliferation and metastasis (82). These data indicate that, while IRF5 activation may be advantageous in some tumors, it could be a useful therapeutic strategy in others where persistent inflammation drives malignancy.
Depending on the tumor type and immunological environment, IRF5’s dual nature emphasizes the importance of a proficient strategy when targeting this transcription factor for cancer therapy.
Cerebral ischemia initiates a complex inflammatory response, which, while aiding in cell repair, can also exacerbate disease progression. Microglia, as the brain’s resident immune cells, are pivotal in triggering and sustaining post-stroke inflammation, positioning them as central players in this process. Therefore, regulating microglial activation post-stroke holds potential for improving stroke outcomes. Recent findings indicate that central IRF4-IRF5 signaling drives microglial activation and stroke prognosis more significantly than the peripheral IRF4-IRF5 axis in cerebral ischemia (102–104). Conditional IRF5 knockout (CKO) promotes M2 activation, reduces proinflammatory responses, and improves outcomes in cerebral ischemia, spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion (I/R), and neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) models (105–107). Conversely, IRF5 upregulation enhances M1 activation, intensifies proinflammatory responses, and worsens outcomes (102, 105).
Additionally, TLR7/MyD88/IRF5 signaling aggravates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury (108). Silencing IRF5 with siRNA in vivo accelerates inflammation resolution, aids wound and infarct healing, and reduces post-myocardial infarction heart failure, as shown by fluorescence molecular tomography and cardiac MRI (109). In liver ischemia, elevated TLR4/IRF5 mRNA and downstream cytokines were observed three hours post-reperfusion. Pretreatment with N-acetylcysteine, an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, notably reduced TLR4/IRF5 mRNA and cytokine levels, thereby alleviating hepatic injury (110).
Studies have also identified IRF5 as a key factor in diseases such as asthma (111, 112), metabolic diseases (113), vascular diseases (114–116), neuropathic pain (117, 118), and liver fibrosis (119, 120). For instance, severe asthma (SA) is a life-threatening condition often resistant to corticosteroids. Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cells from severe asthmatic patients show elevated IRF5 expression compared to those from individuals with milder asthma or healthy controls. In an SA model, IRF5 knockout mice exhibited reduced IFN-γ and IL-17 responses and an enhanced response to corticosteroids, which suppressed the elevated Th2 response (121).
In summary, these findings highlight IRF5 as a promising therapeutic target, with growing interest in its potential for innovative treatments.
As is known, IRF5 plays an important role throughout the immune system network and factors affecting the IRF5-meidated signaling pathway are numerous and complex, making it challenging to define an effective pathway to target IRF5. Specific strategies to target IRF5 included regulation of gene expression, inhibiting the activation of IRF5, and inhibiting the production of active dimers.
Strategies to regulate IRF5 expression include small interfering RNA (siRNA), CRISPR-Cas9, and locked nucleic acid (LNA) oligonucleotides (ODNs) (Figure 1). Among these, siRNA targeting IRF5 mRNA is widely utilized, with studies demonstrating that lipid-like nanoparticles (LLNs) delivering IRF5-specific siRNA can mitigate post-myocardial infarction inflammation and promote tissue repair (109).
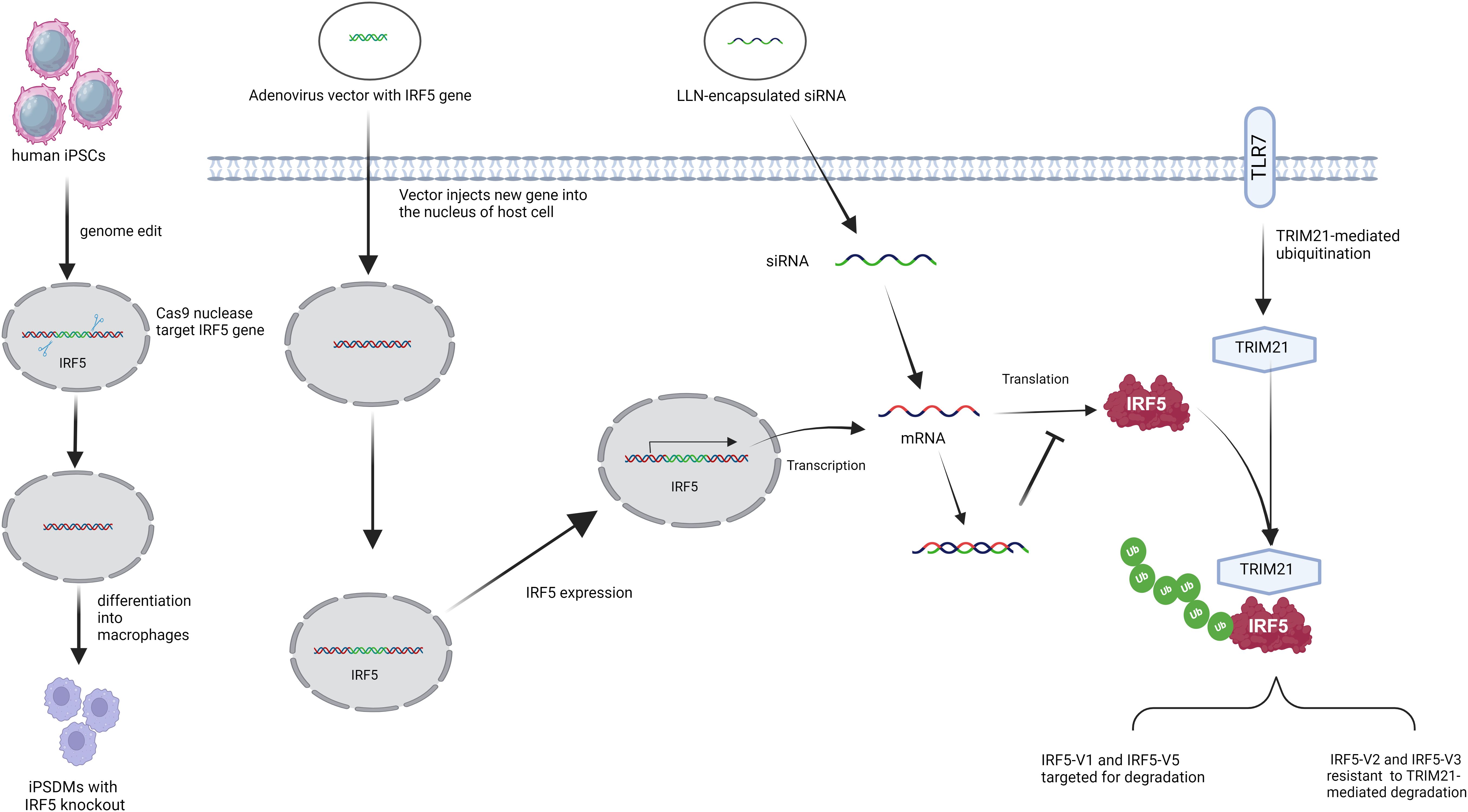
Figure 1. Strategies to regulate the expression of IRF5. (From left to right) IRF5 knockout in human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived macrophages using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Adenoviral vectors delivered IRF5 genes to increase IRF5 expression. IRF5 expression was modulated by RNA interference (RNAi) using small interfering RNA (siRNA) -mediated therapy delivered by lipid-like nanoparticles (LLN). After stimulation with Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7), TRIpartite motif 21 (TRIM21) regulates IRF5 stability and activity in an isotype-specific manner.
CRISPR-Cas9 has shown additional potential, as recent work using this technology to knock out IRF5 in induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived macrophages resulted in reduced resistance to Chlamydia infection, underscoring IRF5’s role in anti-chlamydial immunity (Figure 1) (122).
The E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM21 (Figure 1) also modulates IRF5 levels, targeting degradation primarily of IRF5 isotypes V1 and V5 after TLR7 activation, while sparing isotypes V2 and V3. V1 is mainly found in primary human plasmacytoid dendritic cells, and V5 is prevalent in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (9). Enhancing TRIM21 activity could help regulate immune responses by decreasing IRF5 levels in certain patients, though it may be less effective in V2-associated SLE cases (8, 123).
In contrast, targeted IRF5 overexpression has therapeutic potential. An adenoviral vector delivering IRF5 to the lungs enhanced immune responses following allergen exposure, reducing goblet cell proliferation, mucus production, and improving airway hyperresponsiveness. Additionally, IRF5 overexpression lowered IL-2 levels and eosinophil counts, making localized adenoviral delivery a promising approach for managing eosinophilic asthma without the side effects of systemic IRF5 expression (124, 125).
Collectively, these studies provide insights into therapeutic targeting of IRF5; however, significant challenges remain before these approaches are ready for clinical application.
Phosphorylation activates IRF family members by inducing a conformational shift in their C-terminal autoinhibitory region, prompting dimerization (15). This underscores the importance of targeting kinases responsible for serine phosphorylation in IRF5 activation.
Multiple kinases, including RIP2, TAK1, and members of the IKK family (IKKα and IKKβ), can phosphorylate IRF5 (126–129). However, due to these kinases’ broader roles in other signaling pathways, targeting them for specific IRF5 inhibition is challenging. A novel small-molecule compound, YE6144, has been shown to selectively inhibit IRF5 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation, while only minimally affecting NF-κB activity in human PBMCs. Treatment with YE6144 reduced autoantibody production and slowed disease progression in NZB/W F1 mice, a model for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) (46).
IRAK4 has been identified as a kinase that activates IRF5 through the IRAK4-TAK1-IKKβ pathway in human monocytes. Selective inhibition of IRAK4 (using IRAK4 inhibitors or IRAK4i) disrupts IRF5 nuclear translocation and transcriptional activity without impacting NF-κB (18, 130). Recent studies indicate that IRAK4 inhibition can reduce inflammation and joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) by rebalancing macrophage and fibroblast metabolism, effectively decreasing RA disease activity (60, 131) Additionally, IRAK4 inhibition mitigates SARS-CoV-2-induced cytotoxicity in ACE2+ HEK293 cells (77, 78). and protects neurons by suppressing microglial inflammation following ischemic injury (132). These findings support IRAK4 as a promising therapeutic target.
Preclinical studies have found some possible IRF5 inhibitors that show potential in animal models, notably for autoimmune illnesses like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The following is a summary of significant preclinical experiments (Table 1).
These preclinical studies are promising, indicating that targeting IRF5 may constitute a potential treatment strategy for a variety of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. However, further research is required to create IRF5-targeted treatments acceptable for human clinical trials.
Given IRF5’s extensive protein and DNA interaction regions, peptide inhibitors could serve as effective blockers of protein-protein interactions. However, their clinical application is challenged by low conformational stability, which diminishes binding efficacy (133). In a mouse model of systemic scleroderma, the apoA-I mimetic peptide 4F reduced pro-inflammatory HDL levels and competitively inhibited IRF5 activation, effectively reducing myocardial inflammation (Figure 2). This study also linked immune cell composition to varying inflammation levels (37).
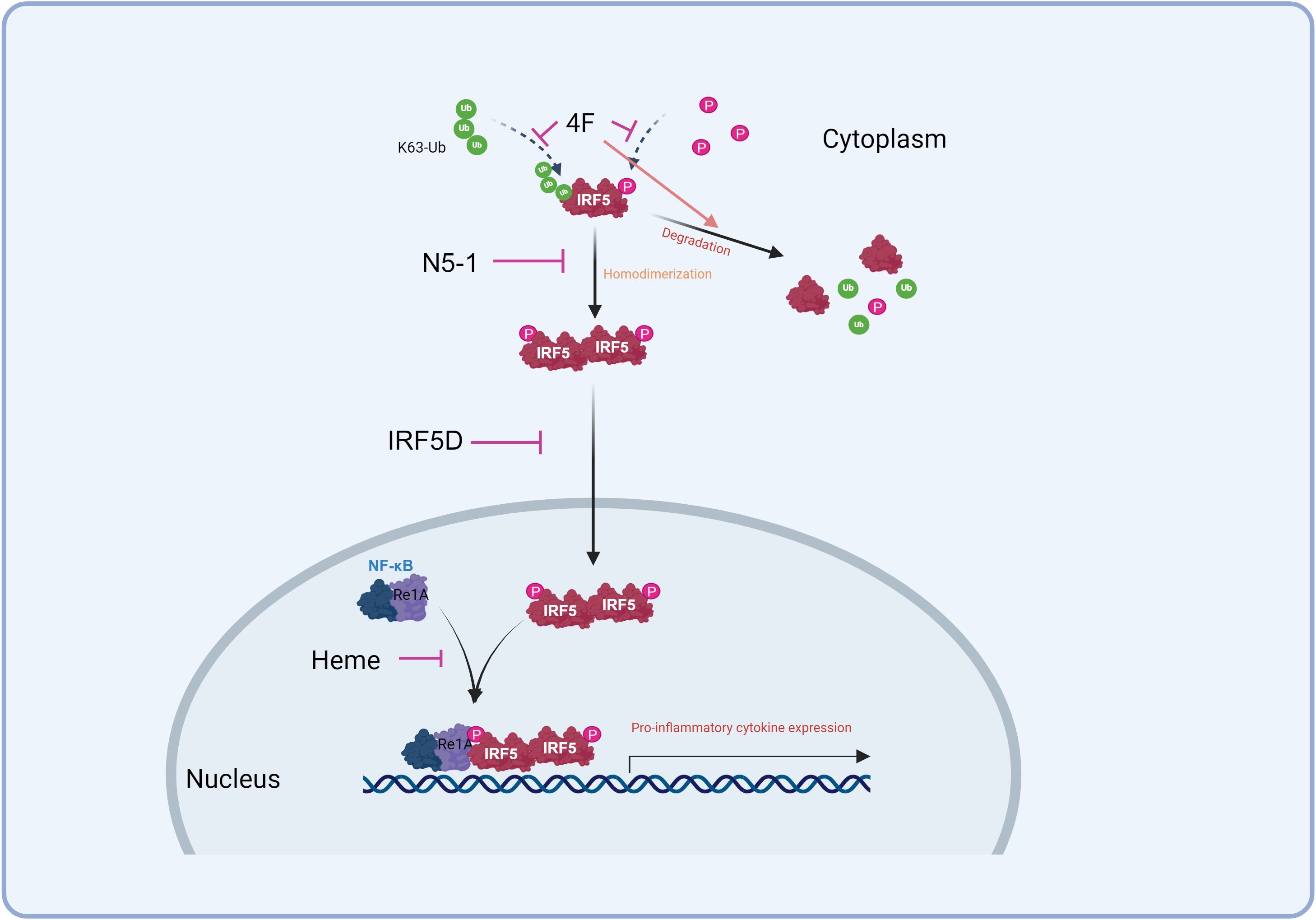
Figure 2. Strategies to inhibit IRF5. 4F competed for access to IRF5 to inhibit its activation and promote its degradation. N5-1 stabilizes the inactive monomer, inhibiting its homodimerization and nuclear translocation. IRF5D targets IRF5 and prevents its nuclear translocation. Heme inhibits the IRF5/RelA interaction to down-regulate inflammation.
Another promising inhibitor, IRF5D, was engineered to prevent IRF5’s nuclear translocation. Derived from IRF5’s C-terminal dimerization domain, IRF5D functions as a decoy by replacing the original target sequence with a 17-amino acid peptide. In a Tsk+/+ mouse model of myocardial inflammation and fibrosis, IRF5D treatment decreased ICAM-1 and IRF5 expression, reduced leukocyte infiltration, and improved vascular endothelial relaxation. These findings, supported by in vitro results, highlight IRF5 as a potential target for managing myocardial inflammation and fibrosis (115, 134). The IRF5D structure sets the foundation for developing future IRF5-specific peptide inhibitors (Figure 2) (15). Furthermore, a new peptide inhibitor, N5-1, shows strong affinity for IRF5, binding to and stabilizing the inactive monomer to prevent nuclear translocation. In lupus-prone mice, N5-1 demonstrated protective effects (Figure 2) (51, 135).
IRF5 is recruited to the TNF-α gene through interaction with the NF-κB subunit RelA, which is essential for activating pro-inflammatory gene expression involving IRF5 (11, 32, 136). Blocking this IRF5-RelA interaction has emerged as a key therapeutic target (11, 137). Specific peptide inhibitors have been developed to spatially inhibit the IRF5/RelA interaction, thereby modulating inflammation. Studies have shown that heme can protect the intestinal mucosal barrier in DSS-induced colitis by regulating macrophage polarization via disruption of the IRF5-RelA complex (Figure 2) (138, 139). Other inhibitors, such as Sedum sarmentosum Bunge extract, Euphorbia Factor L2, and Lipoxin A4, also downregulate IRF5 and RelA activity to reduce inflammation (140–142).
Additionally, the chaperone CSN, specifically its subunit CSN3, binds directly to IRF5, enhancing its stability and transcriptional activity. CSN3 knockdown leads to IRF5 degradation, highlighting the CSN-IRF5 interaction as crucial for IRF5 activation and suggesting it as a potential target for disrupting IRF5 function (143). Targeting these protein binding sites on IRF5 could guide the development of peptide-based inhibitors, emphasizing the need to identify precise IRF5 binding sequences.
The Src kinase family member Lyn also negatively regulates IRF5 through the TLR-MyD88 pathway in a kinase-independent manner. Expressed in immune cells such as monocytes, macrophages, and B cells, Lyn interacts with IRF5, inhibiting its post-translational modifications. Lyn deficiency leads to IRF5 overactivation, exacerbating SLE-like symptoms in mice, while IRF5 deficiency alleviates these symptoms, supporting Lyn’s regulatory role in SLE (46, 144). Interestingly, IRF5’s role differs in asthma (145), where it enhances responses to allergens, modulating airway hyperresponsiveness, mucus secretion, and eosinophilic inflammation. Lyn peptide inhibitors block eosinophil differentiation and airway infiltration in asthma models, indicating that Lyn-IRF5 interaction inhibitors might enhance IRF5’s protective role in asthma (125, 146–148).
Oligodeoxynucleotides (ODNs) mimicking DNA’s immunosuppressive properties are also under investigation as IRF5 inhibitors. The ODN MS19, containing an AAAG-rich sequence that binds IRF5, reduces nuclear translocation and expression of inflammatory markers (iNOS, IL-6, and TNF-α). MS19 has shown efficacy in models of septic peritonitis, acute lung injury (ALI), and myocarditis, alleviating systemic inflammatory responses (149–152). Furthermore, MS19 could attenuate systemic inflammatory responses and decrease IRF5 expression in burn injury skin and myocardial tissues of coxsackie virus B3-infected mice (150, 153). Additionally, MS19’s inhibitory effect on LPS-induced ALI appears to act through the HMGB1-TLR4-NF-κB pathway (154), supporting its potential as a therapeutic target for inflammatory conditions.
While these findings underscore IRF5 as a promising therapeutic target, significant challenges remain in translating these methodologies into clinical applications.
This review highlights the critical roles of IRF5 in various diseases and explores its potential as a therapeutic target. Strategies to regulate IRF5 activity and expression are examined, including approaches to modulate IRF5 levels, disrupt post-translational modifications, and inhibit its interactions with protein chaperones. Emerging therapies such as siRNAs, nanoparticles, CRISPR/Cas9, and adenoviral vectors show promise but require further development to ensure clinical feasibility. At present, kinase inhibitors represent a particularly promising strategy for specifically inhibiting the IRF5 pathway. Ideal kinase inhibitors should target IRF5 selectively, avoiding off-target effects; inhibitors affecting broader pathways (e.g., TAK1 or IKKβ) risk unwanted side effects due to lack of specificity. IRAK4 inhibitors, however, exhibit specific selectivity for the IRF5 pathway and have shown therapeutic potential in RA, ischemia, and SARS-CoV-2 infection models.
Additionally, YE6144 selectively inhibits IRF5 phosphorylation, demonstrating strong therapeutic promise. Lyn peptide inhibitors have shown benefit in asthma models, though further safety evaluations are warranted given potential risks like lupus associated with Lyn suppression. Notably, the novel inhibitor N5-1 binds IRF5 and blocks its nuclear translocation, displaying protective effects in lupus-prone mice. Similarly, small-molecule inhibitors targeting IRF5 interactions with RelA or CSN could suppress pro-inflammatory macrophage activation by inhibiting IRF5’s downstream targets, though further research is needed.
In summary, modulating IRF5 presents a compelling avenue for developing new treatments for inflammatory diseases, tumors, and certain autoimmune disorders.
XY: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Software. AR: Formal Analysis, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. LD: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XZ: Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JL: Data curation, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. XX: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. GC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Writing – original draft. ZJ: Data curation, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82171336 to XX) and Open Project of Sichuan Provincial Key Laboratory for Clinical Immunology Translational Medicine (No. LCMYZHYX-KFKT202203 to XX).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Tamura T, Yanai H, Savitsky D, Taniguchi T. The IRF family transcription factors in immunity and oncogenesis. Annu Rev Immunol. (2008) 26:535–84. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.26.021607.090400
2. Mamane Y, Heylbroeck C, Genin P, Algarte M, Servant MJ, LePage C, et al. Interferon regulatory factors: the next generation. Gene. (1999) 237:1–14. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(99)00262-0
3. Fujii Y, Shimizu T, Kusumoto M, Kyogoku Y, Taniguchi T, Hakoshima T. Crystal structure of an IRF-DNA complex reveals novel DNA recognition and cooperative binding to a tandem repeat of core sequences. EMBO J. (1999) 18:5028–41. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.18.5028
4. Taniguchi T, Ogasawara K, Takaoka A, Tanaka N. IRF family of transcription factors as regulators of host defense. Annu Rev Immunol. (2001) 19:623–55. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.623
5. Kozyrev SV, Alarcon-Riquelme ME. The genetics and biology of Irf5-mediated signaling in lupus. Autoimmunity. (2007) 40:591–601. doi: 10.1080/08916930701510905
6. Krausgruber T, Blazek K, Smallie T, Alzabin S, Lockstone H, Sahgal N, et al. IRF5 promotes inflammatory macrophage polarization and TH1-TH17 responses. Nat Immunol. (2011) 12:231–8. doi: 10.1038/ni.1990
7. Weiss M, Blazek K, Byrne AJ, Perocheau DP, Udalova IA. IRF5 is a specific marker of inflammatory macrophages in vivo. Mediators Inflammation. (2013) 2013:245804. doi: 10.1155/2013/245804
8. Lazzari E, Korczeniewska J, Ni Gabhann J, Smith S, Barnes BJ, Jefferies CA. TRIpartite motif 21 (TRIM21) differentially regulates the stability of interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) isoforms. PloS One. (2014) 9:e103609. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103609
9. Mancl ME, Hu G, Sangster-Guity N, Olshalsky SL, Hoops K, Fitzgerald-Bocarsly P, et al. Two discrete promoters regulate the alternatively spliced human interferon regulatory factor-5 isoforms. Multiple isoforms with distinct cell type-specific expression, localization, regulation, and function. J Biol Chem. (2005) 280:21078–90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500543200
10. Graham RR, Kozyrev SV, Baechler EC, Reddy MV, Plenge RM, Bauer JW, et al. A common haplotype of interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) regulates splicing and expression and is associated with increased risk of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet. (2006) 38:550–5. doi: 10.1038/ng1782
11. Saliba DG, Heger A, Eames HL, Oikonomopoulos S, Teixeira A, Blazek K, et al. IRF5:RelA interaction targets inflammatory genes in macrophages. Cell Rep. (2014) 8:1308–17. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.07.034
12. Takaoka A, Yanai H, Kondo S, Duncan G, Negishi H, Mizutani T, et al. Integral role of IRF-5 in the gene induction programme activated by Toll-like receptors. Nature. (2005) 434:243–9. doi: 10.1038/nature03308
13. Chang Foreman HC, Van Scoy S, Cheng TF, Reich NC. Activation of interferon regulatory factor 5 by site specific phosphorylation. PloS One. (2012) 7:e33098. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033098
14. Barnes BJ, Kellum MJ, Field AE, Pitha PM. Multiple regulatory domains of IRF-5 control activation, cellular localization, and induction of chemokines that mediate recruitment of T lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol. (2002) 22:5721–40. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.16.5721-5740.2002
15. Chen W, Lam SS, Srinath H, Jiang Z, Correia JJ, Schiffer CA, et al. Insights into interferon regulatory factor activation from the crystal structure of dimeric IRF5. Nat Struct Mol Biol. (2008) 15:1213–20. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1496
16. Hedl M, Yan J, Abraham C. IRF5 and IRF5 disease-risk variants increase glycolysis and human M1 macrophage polarization by regulating proximal signaling and akt2 activation. Cell Rep. (2016) 16:2442–55. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.07.060
17. Balkhi MY, Fitzgerald KA, Pitha PM. Functional regulation of MyD88-activated interferon regulatory factor 5 by K63-linked polyubiquitination. Mol Cell Biol. (2008) 28:7296–308. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00662-08
18. Cushing L, Winkler A, Jelinsky SA, Lee K, Korver W, Hawtin R, et al. IRAK4 kinase activity controls Toll-like receptor-induced inflammation through the transcription factor IRF5 in primary human monocytes. J Biol Chem. (2017) 292:18689–98. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.796912
19. del Fresno C, Soulat D, Roth S, Blazek K, Udalova I, Sancho D, et al. Interferon-beta production via Dectin-1-Syk-IRF5 signaling in dendritic cells is crucial for immunity to C. albicans Immun. (2013) 38:1176–86. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.05.010
20. Paun A, Reinert JT, Jiang Z, Medin C, Balkhi MY, Fitzgerald KA, et al. Functional characterization of murine interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF-5) and its role in the innate antiviral response. J Biol Chem. (2008) 283:14295–308. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800501200
21. Yanai H, Chen HM, Inuzuka T, Kondo S, Mak TW, Takaoka A, et al. Role of IFN regulatory factor 5 transcription factor in antiviral immunity and tumor suppression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2007) 104:3402–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611559104
22. Barnes BJ, Moore PA, Pitha PM. Virus-specific activation of a novel interferon regulatory factor, IRF-5, results in the induction of distinct interferon alpha genes. J Biol Chem. (2001) 276:23382–90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M101216200
23. Hu G, Mancl ME, Barnes BJ. Signaling through IFN regulatory factor-5 sensitizes p53-deficient tumors to DNA damage-induced apoptosis and cell death. Cancer Res. (2005) 65:7403–12. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0583
24. Lum FM, Lye DCB, Tan JJL, Lee B, Chia PY, Chua TK, et al. Longitudinal study of cellular and systemic cytokine signatures to define the dynamics of a balanced immune environment during disease manifestation in zika virus-infected patients. J Infect Dis. (2018) 218:814–24. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiy225
25. Yan J, Hedl M, Abraham C. Myeloid cell-intrinsic IRF5 promotes T cell responses through multiple distinct checkpoints in vivo, and IRF5 immune-mediated disease risk variants modulate these myeloid cell functions. J Immunol. (2020) 205:1024–38. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900743
26. Lin R, Mamane Y, Hiscott J. Multiple regulatory domains control IRF-7 activity in response to virus infection. J Biol Chem. (2000) 275:34320–7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M002814200
27. Zhang L, Pagano JS. IRF-7, a new interferon regulatory factor associated with Epstein-Barr virus latency. Mol Cell Biol. (1997) 17(10):48–57. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.10.5748
28. Au W-C, Moore PA, LaFleur DW, Tombal B, Pitha PM. Characterization of the interferon regulatory factor-7 and its potential role in the transcription activation of interferon A genes. J Biol Chem. (1998) 273:29210–7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.44.29210
29. Zhang L, Pagano JS. Interferon regulatory factor 7 mediates activation of Tap-2 by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1. J Virol. (2001) 75:341–50. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.1.341-350.2001
30. Zhang L, Pagano JS. Interferon regulatory factor 7 is induced by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1. J Virol. (2000) 74:1061–8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.74.3.1061-1068.2000
31. Kim TK, Kim T, Kim TY, Lee WG, Yim J. Chemotherapeutic DNA-damaging drugs activate interferon regulatory factor-7 by the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase-4-c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathway. Cancer Res. (2000) 60:1153–6.
32. Krausgruber T, Saliba D, Ryzhakov G, Lanfrancotti A, Blazek K, Udalova IA. IRF5 is required for late-phase TNF secretion by human dendritic cells. Blood. (2010) 115:4421–30. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-01-263020
33. Matsuyama T, Grossman A, Mittrücker H-W, Siderovski DP, Kiefer F, Kawakami T, et al. Molecular cloning of LSIRF, a lymphoid-specific member of the interferon regulatory factor family that binds the interferon-stimulated response element (ISRE). Nucleic Acids Res. (1995) 23:2127–36. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.12.2127
34. Yamagata T, Nishida J, Tanaka T, Sakai R, Mitani K, Yoshida M, et al. A novel interferon regulatory factor family transcription factor, ICSAT/Pip/LSIRF, that negatively regulates the activity of interferon-regulated genes. Mol Cell Biol. (1996) 16:1283–94. doi: 10.1128/MCB.16.4.1283
35. Shindo H, Yasui K, Yamamoto K, Honma K, Yui K, Kohno T, et al. Interferon regulatory factor-4 activates IL-2 and IL-4 promoters in cooperation with c-Rel. Cytokine. (2011) 56:564–72. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2011.08.014
36. De Silva NS, Simonetti G, Heise N, Klein U. The diverse roles of IRF4 in late germinal center B-cell differentiation. Immunol Rev. (2012) 247:73–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01113.x
37. Xu H, Krolikowski JG, Jones DW, Ge ZD, Pagel PS, Pritchard KA Jr., et al. 4F decreases IRF5 expression and activation in hearts of tight skin mice. PloS One. (2012) 7:e52046. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052046
38. Kesper C, Viestenz A, Wiese-Rischke C, Scheller M, Hammer T. Impact of the transcription factor IRF8 on limbal epithelial progenitor cells in a mouse model. Exp Eye Res. (2022) 218:108985. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2022.108985
39. Li W, Nagineni CN, Ge H, Efiok B, Chepelinsky AB, Egwuagu CE. Interferon consensus sequence-binding protein is constitutively expressed and differentially regulated in the ocular lens. J Biol Chem. (1999) 274:9686–91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.14.9686
40. Jiang D-S, Wei X, Zhang X-F, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Chen K, et al. IRF8 suppresses pathological cardiac remodelling by inhibiting calcineurin signalling. Nat Commun. (2014) 5:3303. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4303
41. Yanai H, Negishi H, Taniguchi T. The IRF family of transcription factors: Inception, impact and implications in oncogenesis. Oncoimmunology. (2012) 1:1376–86. doi: 10.4161/onci.22475
42. FuJITA T, Reis L, Watanabe N, KIMuRA Y, Taniguchi T, Vilcek J. Induction of the transcription factor IRF-1 and interferon-beta mRNAs by cytokines and activators of second-messenger pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (1989) 86:9936–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9936
43. Marié I, Durbin JE, Levy DE. Differential viral induction of distinct interferon-alpha genes by positive feedback through interferon regulatory factor-7. EMBO J. (1998) 17:6660–9. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.22.6660
44. Zhang L, Wu L, Hong K, Pagano JS. Intracellular signaling molecules activated by Epstein-Barr virus for induction of interferon regulatory factor 7. J Virol. (2001) 75:12393–401. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.24.12393-12401.2001
45. Matta B, Barnes BJ. Coordination between innate immune cells, type I IFNs and IRF5 drives SLE pathogenesis. Cytokine. (2020) 132:154731. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.05.018
46. Ban T, Kikuchi M, Sato GR, Manabe A, Tagata N, Harita K, et al. Genetic and chemical inhibition of IRF5 suppresses pre-existing mouse lupus-like disease. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:4379. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24609-4
47. Asgari N, Ghaemi EA, Naeimi MH, Tahamtan A, Sechi LA, Zamani S. Cross-reactivity between Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis 4027 peptide and Human IRF5 may contribute to Multiple Sclerosis in Iranian patients. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e22137. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22137
48. Ortíz-Fernández L, Martín J, Alarcón-Riquelme ME. A summary on the genetics of systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic sclerosis, and sjögren’s syndrome. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. (2023) 64:392–411. doi: 10.1007/s12016-022-08951-z
49. Jin L, Dai M, Li C, Wang J, Wu B. Risk factors for primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rheumatol. (2023) 42:327–38. doi: 10.1007/s10067-022-06474-8
50. Banchereau R, Hong S, Cantarel B, Baldwin N, Baisch J, Edens M, et al. Personalized immunomonitoring uncovers molecular networks that stratify lupus patients. Cell. (2016) 165:551–65. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.03.008
51. Song S, De S, Nelson V, Chopra S, LaPan M, Kampta K, et al. Inhibition of IRF5 hyperactivation protects from lupus onset and severity. J Clin Invest. (2020) 130:6700–17. doi: 10.1172/JCI120288
52. Feng D, Sangster-Guity N, Stone R, Korczeniewska J, Mancl ME, Fitzgerald-Bocarsly P, et al. Differential requirement of histone acetylase and deacetylase activities for IRF5-mediated proinflammatory cytokine expression. J Immunol. (2010) 185:6003–12. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000482
53. Stone RC, Feng D, Deng J, Singh S, Yang L, Fitzgerald-Bocarsly P, et al. Interferon regulatory factor 5 activation in monocytes of systemic lupus erythematosus patients is triggered by circulating autoantigens independent of type I interferons. Arthritis Rheum. (2012) 64:788–98. doi: 10.1002/art.33395
54. Hou G, Zhou T, Xu N, Yin Z, Zhu X, Zhang Y, et al. Integrative functional genomics identifies systemic lupus erythematosus causal genetic variant in the IRF5 risk locus. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2023) 75:574–85. doi: 10.1002/art.42390
55. Feng D, Yang L, Bi X, Stone RC, Patel P, Barnes BJ. Irf5-deficient mice are protected from pristane-induced lupus via increased Th2 cytokines and altered IgG class switching. Eur J Immunol. (2012) 42:1477–87. doi: 10.1002/eji.201141642
56. Barnes BJ. Genetic versus non-genetic drivers of SLE: implications of IRF5 dysregulation in both roads leading to SLE. Curr Rheumatol Rep. (2019) 21:2. doi: 10.1007/s11926-019-0803-3
57. Weiss M, Byrne AJ, Blazek K, Saliba DG, Pease JE, Perocheau D, et al. IRF5 controls both acute and chronic inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2015) 112:11001–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1506254112
58. Duffau P, Menn-Josephy H, Cuda CM, Dominguez S, Aprahamian TR, Watkins AA, et al. Promotion of inflammatory arthritis by interferon regulatory factor 5 in a mouse model. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2015) 67:3146–57. doi: 10.1002/art.v67.12
59. Said NM, Ezzeldin N, Said D, Ebaid AM, Atef DM, Atef RM. HLA-DRB1, IRF5, and CD28 gene polymorphisms in Egyptian patients with rheumatoid arthritis: susceptibility and disease activity. Genes Immun. (2021) 22:93–100. doi: 10.1038/s41435-021-00134-8
60. Umar S, Palasiewicz K, Volin MV, Zanotti B, Al-Awqati M, Sweiss N, et al. IRAK4 inhibitor mitigates joint inflammation by rebalancing metabolism malfunction in RA macrophages and fibroblasts. Life Sci. (2021) 287:120114. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.120114
61. Lee KM-C, Achuthan AA, De Souza DP, Lupancu TJ, Binger KJ, Lee MK, et al. Type I interferon antagonism of the JMJD3-IRF4 pathway modulates macrophage activation and polarization. Cell Rep. (2022) 39. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110719
62. Lazzari E, Jefferies CA. IRF5-mediated signaling and implications for SLE. Clin Immunol. (2014) 153:343–52. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2014.06.001
63. Jiang R, Zhu W, Liao Z, Yang C, Su J. TLR7 neo-functionalizes to sense dsRNA and trigger antiviral and antibacterial immunity in non-tetrapod vertebrates. iScience. (2023) 26:108315. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108315
64. Heinz LX, Lee J, Kapoor U, Kartnig F, Sedlyarov V, Papakostas K, et al. TASL is the SLC15A4-associated adaptor for IRF5 activation by TLR7-9. Nature. (2020) 581:316–22. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2282-0
65. Wüst S, Schad P, Burkart S, Binder M. Comparative analysis of six IRF family members in alveolar epithelial cell-intrinsic antiviral responses. Cells. (2021) 10. doi: 10.3390/cells10102600
66. Kaur A, Lee LH, Chow SC, Fang CM. IRF5-mediated immune responses and its implications in immunological disorders. Int Rev Immunol. (2018) 37:229–48. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2018.1469629
67. Klotz D, Gerhauser I. Interferon-stimulated genes-mediators of the innate immune response during canine distemper virus infection. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20. doi: 10.3390/ijms20071620
68. Sepúlveda-Crespo D, Jiménez-Sousa MA, Fernández-Rodíguez A, Muñoz-Fernández MA, Jiménez JL, Moreno S, et al. IRF5-TNOP3 polymorphisms are associated with elite control of HIV infection: A retrospective study. J Med Virol. (2023) 95:e28841. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28841
69. Carmona-Pérez L, Dagenais-Lussier X, Mai LT, Stögerer T, Swaminathan S, Isnard S, et al. The TLR7/IRF-5 axis sensitizes memory CD4+ T cells to Fas-mediated apoptosis during HIV-1 infection. JCI Insight. (2023) 8. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.167329
70. Booz GW, Altara R, Eid AH, Wehbe Z, Fares S, Zaraket H, et al. Macrophage responses associated with COVID-19: A pharmacological perspective. Eur J Pharmacol. (2020) 887:173547. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173547
71. Wang J, Jiang M, Chen X, Montaner LJ. Cytokine storm and leukocyte changes in mild versus severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: Review of 3939 COVID-19 patients in China and emerging pathogenesis and therapy concepts. J Leukoc Biol. (2020) 108:17–41. doi: 10.1002/JLB.3COVR0520-272R
72. Navas-Blanco JR, Dudaryk R. Management of Respiratory Distress Syndrome due to COVID-19 infection. BMC Anesthesiol. (2020) 20:177. doi: 10.1186/s12871-020-01095-7
73. Khalil BA, Elemam NM, Maghazachi AA. Chemokines and chemokine receptors during COVID-19 infection. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. (2021) 19:976–88. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.01.034
74. Chen X, Zhou L, Peng N, Yu H, Li M, Cao Z, et al. MicroRNA-302a suppresses influenza A virus-stimulated interferon regulatory factor-5 expression and cytokine storm induction. J Biol Chem. (2017) 292:21291–303. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.805937
75. Laviada-Molina HA, Leal-Berumen I, Rodriguez-Ayala E, Bastarrachea RA. Working hypothesis for glucose metabolism and SARS-coV-2 replication: interplay between the hexosamine pathway and interferon RF5 triggering hyperinflammation. Role of BCG vaccine? Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2020) 11:514. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00514
76. Matta B, Battaglia J, Barnes BJ. Detection of neutrophil extracellular traps in patient plasma: method development and validation in systemic lupus erythematosus and healthy donors that carry IRF5 genetic risk. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:951254. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.951254
77. Stoy N. Involvement of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 and interferon regulatory factor 5 in the immunopathogenesis of SARS-coV-2 infection: implications for the treatment of COVID-19. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:638446. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.638446
78. Umar S, Palasiewicz K, Meyer A, Kumar P, Prabhakar BS, Volin MV, et al. Inhibition of IRAK4 dysregulates SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-induced macrophage inflammatory and glycolytic reprogramming. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2022) 79:301. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04329-8
79. Cords L, Woost R, Kummer S, Brehm TT, Kluge S, Schmiedel S, et al. Frequency of IRF5+ dendritic cells is associated with the TLR7-induced inflammatory cytokine response in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cytokine. (2023) 162:156109. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2022.156109
80. Yang Y, Zhang C, Jing D, He H, Li X, Wang Y, et al. IRF5 acts as a potential therapeutic marker in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflammatory Bowel Dis. (2021) 27:407–17. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izaa200
81. Kristjánsdóttir GT. Genetic variation and expression of the IRF5 gene in autoimmune diseases. Uppsala: Acta Universitatis Upsaliensis (2009).
82. Pimenta EM, Barnes BJ. A conserved region within interferon regulatory factor 5 controls breast cancer cell migration through a cytoplasmic and transcription-independent mechanism. Mol Cancer. (2015) 14:32. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0305-5
83. Hanahan D. Hallmarks of cancer: new dimensions. Cancer Discovery. (2022) 12:31–46. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1059
84. Roberts BK, Collado G, Barnes BJ. Role of interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) in tumor progression: Prognostic and therapeutic potential. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. (2024) 1879:189061. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.189061
85. D’Angelo A, Sobhani N, Roviello G, Bagby S, Bonazza D, Bottin C, et al. Tumour infiltrating lymphocytes and immune-related genes as predictors of outcome in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. PloS One. (2019) 14:e0219566. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0219566
86. Guo J, Wang X, Wang Y, Wang L, Hua S. A promising role of interferon regulatory factor 5 as an early warning biomarker for the development of human non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. (2019) 135:47–55. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.07.008
87. Zhou Y, Cheng X, Zhang F, Chen Q, Chen X, Shen Y, et al. Integrated multi-omics data analyses for exploring the co-occurring and mutually exclusive gene alteration events in colorectal cancer. Hum Mutat. (2020) 41:1588–99. doi: 10.1002/humu.24059
88. Pimenta EM, De S, Weiss R, Feng D, Hall K, Kilic S, et al. IRF5 is a novel regulator of CXCL13 expression in breast cancer that regulates CXCR5(+) B- and T-cell trafficking to tumor-conditioned media. Immunol Cell Biol. (2015) 93:486–99. doi: 10.1038/icb.2014.110
89. Bi X, Hameed M, Mirani N, Pimenta EM, Anari J, Barnes BJ. Loss of interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) expression in human ductal carcinoma correlates with disease stage and contributes to metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. (2011) 13:R111. doi: 10.1186/bcr3053
90. Feng DD, Cao Q, Zhang DQ, Wu XL, Yang CX, Chen YF, et al. Transcription factor E2F1 positively regulates interferon regulatory factor 5 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Onco Targets Ther. (2019) 12:6907–15. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S215701
91. Liu J, Han X, Chen L, Han D, Mu X, Hu X, et al. TRIM28 is a distinct prognostic biomarker that worsens the tumor immune microenvironment in lung adenocarcinoma. Aging (Albany NY). (2020) 12:20308–31. doi: 10.18632/aging.v12i20
92. Zhang J, Hu X, Liu S, He Y, Lyu L, Jiang L. Clinical value screening, prognostic significance, and key gene identification of trkB in laryngeal carcinoma. Dis Markers. (2022) 2022:1354005. doi: 10.1155/2022/1354005
93. Liu S, Wang Z. Interferon regulatory factor family genes: at the crossroads between immunity and head and neck squamous carcinoma. Dis Markers. (2022) 2022:2561673. doi: 10.1155/2022/2561673
94. Li Q, Tang L, Roberts PC, Kraniak JM, Fridman AL, Kulaeva OI, et al. Interferon regulatory factors IRF5 and IRF7 inhibit growth and induce senescence in immortal Li-Fraumeni fibroblasts. Mol Cancer Res. (2008) 6:770–84. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-07-0114
95. Dongre A, Weinberg RA. New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2019) 20:69–84. doi: 10.1038/s41580-018-0080-4
96. Fang Y, Lu ZH, Liu BZ, Li N, Yang MZ, Wang P. IRF5 promotes glycolysis in the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma and is regulated by TRIM35. J Dig Dis. (2023) 24:480–90. doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.13218
97. Bai Q, Liu L, Xia Y, Wang J, Xi W, Qu Y, et al. IRF5 is associated with adverse postoperative prognosis of patients with non-metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:44186–94. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17777
98. Lu X, Li R, Ying Y, Zhang W. A comprehensive analysis of interferon regulatory factor expression: correlation with immune cell infiltration and patient prognosis in endometrial carcinoma. BioMed Res Int. (2022) 2022:7948898. doi: 10.1155/2022/7948898
99. Lei J, Zhou MH, Zhang FC, Wu K, Liu SW, Niu HQ. Interferon regulatory factor transcript levels correlate with clinical outcomes in human glioma. Aging (Albany NY). (2021) 13:12086–98. doi: 10.18632/aging.202915
100. Lv D, Wu X, Chen X, Yang S, Chen W, Wang M, et al. A novel immune-related gene-based prognostic signature to predict biochemical recurrence in patients with prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2021) 70:3587–602. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-02923-6
101. Massimino M, Vigneri P, Fallica M, Fidilio A, Aloisi A, Frasca F, et al. IRF5 promotes the proliferation of human thyroid cancer cells. Mol Cancer. (2012) 11:21. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-11-21
102. Al Mamun A, Chauhan A, Yu H, Xu Y, Sharmeen R, Liu F. Interferon regulatory factor 4/5 signaling impacts on microglial activation after ischemic stroke in mice. Eur J Neurosci. (2018) 47:140–9. doi: 10.1111/ejn.2018.47.issue-2
103. Wang H, Li J, Zhang H, Wang M, Xiao L, Wang Y, et al. Regulation of microglia polarization after cerebral ischemia. Front Cell Neurosci. (2023) 17:1182621. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1182621
104. Ngwa C, Al Mamun A, Qi S, Sharmeen R, Conesa MPB, Ganesh BP, et al. Central IRF4/5 signaling are critical for microglial activation and impact on stroke outcomes. Transl Stroke Res. (2023) 15(4):831–43. doi: 10.1007/s12975-023-01172-2
105. Al Mamun A, Chauhan A, Qi S, Ngwa C, Xu Y, Sharmeen R, et al. Microglial IRF5-IRF4 regulatory axis regulates neuroinflammation after cerebral ischemia and impacts stroke outcomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2020) 117:1742–52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1914742117
106. Al Mamun A, Yu H, Sharmeen R, McCullough LD, Liu F. IRF5 signaling in phagocytes is detrimental to neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Transl Stroke Res. (2021) 12:602–14. doi: 10.1007/s12975-020-00832-x
107. Fang H, Yang M, Pan Q, Jin HL, Li HF, Wang RR, et al. MicroRNA-22-3p alleviates spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury by modulating M2 macrophage polarization via IRF5. J Neurochem. (2021) 156:106–20. doi: 10.1111/jnc.v156.1
108. Liu Z, Liu Z, Zhou H, Zhou Y, Xu X, Li Z, et al. Increased sympathetic outflow induced by emotional stress aggravates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via activation of TLR7/MyD88/IRF5 signaling pathway. Inflammation Res. (2023) 72:901–13. doi: 10.1007/s00011-023-01708-0
109. Courties G, Heidt T, Sebas M, Iwamoto Y, Jeon D, Truelove J, et al. In vivo silencing of the transcription factor IRF5 reprograms the macrophage phenotype and improves infarct healing. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2014) 63:1556–66. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.11.023
110. Nasiri M, Saadat M, Karimi MH, Azarpira N, Saadat I. Evaluating mRNA expression levels of the TLR4/IRF5 signaling axis during hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injuries. Exp Clin Transplant. (2019) 17:648–52. doi: 10.6002/ect.2017.0007
111. Draijer C, Boorsma CE, Robbe P, Timens W, Hylkema MN, Ten Hacken NH, et al. Human asthma is characterized by more IRF5+ M1 and CD206+ M2 macrophages and less IL-10+ M2-like macrophages around airways compared with healthy airways. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2017) 140:280–283.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.11.020
112. Turan N, van der Veen TA, Draijer C, Fattahi F, Ten Hacken NH, Timens W, et al. Neutrophilic asthma is associated with smoking, high numbers of IRF5+, and low numbers of IL10+ Macrophages. Front Allergy. (2021) 2:676930. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2021.676930
113. Dalmas E, Toubal A, Alzaid F, Blazek K, Eames HL, Lebozec K, et al. Irf5 deficiency in macrophages promotes beneficial adipose tissue expansion and insulin sensitivity during obesity. Nat Med. (2015) 21:610–8. doi: 10.1038/nm.3829
114. Seneviratne AN, Edsfeldt A, Cole JE, Kassiteridi C, Swart M, Park I, et al. Interferon regulatory factor 5 controls necrotic core formation in atherosclerotic lesions by impairing efferocytosis. Circulation. (2017) 136:1140–54. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.027844
115. Weihrauch D, Krolikowski JG, Jones DW, Zaman T, Bamkole O, Struve J, et al. An IRF5 decoy peptide reduces myocardial inflammation and fibrosis and improves endothelial cell function in tight-skin mice. PloS One. (2016) 11:e0151999. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151999
116. Cai H, Yao Z, Li W. IRF-5 accelerates leukocyte adhesion to endothelial cells in ischemia-reperfusion injury through regulating the transcription of VCAM-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2017) 492:192–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.08.044
117. Cao J, Hu C, Ding Z, Chen J, Liu S, Li Q. Mechanism of IRF5-regulated CXCL13/CXCR5 signaling axis in CCI-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Curr Mol Med. (2023) 24(7):940–9. doi: 10.2174/1566524023666230825120836
118. Kong E, Li Y, Ma P, Zhang Y, Ding R, Hua T, et al. Lyn-mediated glycolysis enhancement of microglia contributes to neuropathic pain through facilitating IRF5 nuclear translocation in spinal dorsal horn. J Cell Mol Med. (2023) 27:1664–81. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.v27.12
119. Alzaid F, Lagadec F, Albuquerque M, Ballaire R, Orliaguet L, Hainault I, et al. IRF5 governs liver macrophage activation that promotes hepatic fibrosis in mice and humans. JCI Insight. (2016) 1:e88689. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.88689
120. Saigusa R, Asano Y, Taniguchi T, Yamashita T, Ichimura Y, Takahashi T, et al. Multifaceted contribution of the TLR4-activated IRF5 transcription factor in systemic sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2015) 112:15136–41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1520997112
121. Oriss TB, Raundhal M, Morse C, Huff RE, Das S, Hannum R, et al. IRF5 distinguishes severe asthma in humans and drives Th1 phenotype and airway hyperreactivity in mice. JCI Insight. (2017) 2. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.91019
122. Yeung ATY, Hale C, Lee AH, Gill EE, Bushell W, Parry-Smith D, et al. Exploiting induced pluripotent stem cell-derived macrophages to unravel host factors influencing Chlamydia trachomatis pathogenesis. Nat Commun. (2017) 8:15013. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15013
123. Espinosa A, Dardalhon V, Brauner S, Ambrosi A, Higgs R, Quintana FJ, et al. Loss of the lupus autoantigen Ro52/Trim21 induces tissue inflammation and systemic autoimmunity by disregulating the IL-23-Th17 pathway. J Exp Med. (2009) 206:1661–71. doi: 10.1084/jem.20090585
124. Yamamoto Y, Nagasato M, Yoshida T, Aoki K. Recent advances in genetic modification of adenovirus vectors for cancer treatment. Cancer Sci. (2017) 108:831–7. doi: 10.1111/cas.2017.108.issue-5
125. Byrne AJ, Weiss M, Mathie SA, Walker SA, Eames HL, Saliba D, et al. A critical role for IRF5 in regulating allergic airway inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. (2017) 10:716–26. doi: 10.1038/mi.2016.92
126. Schoenemeyer A, Barnes BJ, Mancl ME, Latz E, Goutagny N, Pitha PM, et al. The interferon regulatory factor, IRF5, is a central mediator of toll-like receptor 7 signaling. J Biol Chem. (2005) 280:17005–12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M412584200
127. Cheng TF, Brzostek S, Ando O, Van Scoy S, Kumar KP, Reich NC. Differential activation of IFN regulatory factor (IRF)-3 and IRF-5 transcription factors during viral infection. J Immunol. (2006) 176:7462–70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.12.7462
128. Balkhi MY, Fitzgerald KA, Pitha PM. IKKalpha negatively regulates IRF-5 function in a MyD88-TRAF6 pathway. Cell Signal. (2010) 22:117–27. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.09.021
129. Bergstrom B, Aune MH, Awuh JA, Kojen JF, Blix KJ, Ryan L, et al. TLR8 Senses Staphylococcus aureus RNA in Human Primary Monocytes and Macrophages and Induces IFN-beta Production via a TAK1-IKKbeta-IRF5 Signaling Pathway. J Immunol. (2015) 195:1100–11. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1403176
130. Wu C, Xu X, Zhi X, Jiang Z, Li Y, Xie X, et al. Identification and functional characterization of IRAK-4 in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2019) 87:438–48. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.01.031
131. Umar S, Palasiewicz K, Van Raemdonck K, Volin MV, Romay B, Amin MA, et al. IRAK4 inhibition: a promising strategy for treating RA joint inflammation and bone erosion. Cell Mol Immunol. (2021) 18:2199–210. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-0433-8
132. Ngwa C, Mamun AA, Xu Y, Sharmeen R, Liu F. Phosphorylation of microglial IRF5 and IRF4 by IRAK4 regulates inflammatory responses to ischemia. Cells. (2021) 10. doi: 10.3390/cells10020276
133. Wojcik P, Berlicki L. Peptide-based inhibitors of protein-protein interactions. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. (2016) 26:707–13. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.12.084
134. Weihrauch D, Krolikowski JG, Jones DW, Zaman T, Bamkole O, Struve J, et al. Vasodilation of isolated vessels and the isolation of the extracellular matrix of tight-skin mice. J Vis Exp. (2017) 121. doi: 10.3791/55036
135. McHugh J. IRF5 inhibitor shows promise in mouse models of SLE. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2020) 16:667. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-00525-7
136. Stein T, Wollschlegel A, Te H, Weiss J, Joshi K, Kinzel B, et al. Interferon regulatory factor 5 and nuclear factor kappa-B exhibit cooperating but also divergent roles in the regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines important for the development of TH1 and TH17 responses. FEBS J. (2018) 285:3097–113. doi: 10.1111/febs.2018.285.issue-16
137. Bidula S. Analysis of putative G-quadruplex forming sequences in inflammatory mediators and their potential as targets for treating inflammatory disorders. Cytokine. (2021) 142:155493. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155493
138. Wu Y, Wu B, Zhang Z, Lu H, Fan C, Qi Q, et al. Heme protects intestinal mucosal barrier in DSS-induced colitis through regulating macrophage polarization in both HO-1-dependent and HO-1-independent way. FASEB J. (2020) 34:8028–43. doi: 10.1096/fj.202000313RR
139. Kayama H, Kohyama M, Okuzaki D, Motooka D, Barman S, Okumura R, et al. Heme ameliorates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis through providing intestinal macrophages with noninflammatory profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2018) 115:8418–23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1808426115
140. Yuan J, Lin F, Chen L, Chen W, Pan X, Bai Y, et al. Lipoxin A4 regulates M1/M2 macrophage polarization via FPR2-IRF pathway. Inflammopharmacology. (2022) 30:487–98. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-00942-y
141. Tang J, Cheng X, Yi S, Zhang Y, Tang Z, Zhong Y, et al. Euphorbia factor L2 ameliorates the progression of K/bxN serum-induced arthritis by blocking TLR7 mediated IRAK4/IKKβ/IRF5 and NF-kB signaling pathways. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:773592. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.773592
142. Lu H, Cheng S, Wu C, Zheng S, Hong W, Liu L, et al. Sedum sarmentosum Bunge extract alleviates inflammation and kidney injury via inhibition of M1-macrophage polarization. Phytomedicine. (2019) 62:152976. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152976
143. Korczeniewska J, Barnes BJ. Corrected and republished from: the COP9 signalosome interacts with and regulates interferon regulatory factor 5 protein stability. Mol Cell Biol. (2018) 38. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00493-17
144. Ban T, Sato GR, Nishiyama A, Akiyama A, Takasuna M, Umehara M, et al. Lyn kinase suppresses the transcriptional activity of IRF5 in the TLR-myD88 pathway to restrain the development of autoimmunity. Immunity. (2016) 45:319–32. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.07.015
145. Wang C, Rose-Zerilli MJ, Koppelman GH, Sandling JK, Holloway JW, Postma DS, et al. Evidence of association between interferon regulatory factor 5 gene polymorphisms and asthma. Gene. (2012) 504:220–5. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.05.021
146. Adachi T, Pazdrak K, Stafford S, Alam R. The mapping of the Lyn kinase binding site of the common beta subunit of IL-3/granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor/IL-5 receptor. J Immunol. (1999) 162:1496–501. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.162.3.1496
147. Gray P, Dagvadorj J, Michelsen KS, Brikos C, Rentsendorj A, Town T, et al. Myeloid differentiation factor-2 interacts with Lyn kinase and is tyrosine phosphorylated following lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of the TLR4 signaling pathway. J Immunol. (2011) 187:4331–7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100890
148. Adachi T, Stafford S, Sur S, Alam R. A novel Lyn-binding peptide inhibitor blocks eosinophil differentiation, survival, and airway eosinophilic inflammation. J Immunol. (1999) 163:939–46. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.163.2.939
149. Fang M, Wan M, Guo S, Sun R, Yang M, Zhao T, et al. An oligodeoxynucleotide capable of lessening acute lung inflammatory injury in mice infected by influenza virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2011) 415:342–7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.10.062
150. Nie S, Dong B, Gao S, Zhou Y, Lu W, Fang M, et al. The protective effect of interfering TLR9-IRF5 signaling pathway on the development of CVB3-induced myocarditis. Clin Immunol. (2019) 207:24–35. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2019.07.002
151. Bayik D, Gursel I, Klinman DM. Structure, mechanism and therapeutic utility of immunosuppressive oligonucleotides. Pharmacol Res. (2016) 105:216–25. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2015.11.010
152. Gao S, Li X, Nie S, Yang L, Tu L, Dong B, et al. An AAAG-rich oligodeoxynucleotide rescues mice from bacterial septic peritonitis by interfering interferon regulatory factor 5. Int J Mol Sci. (2017) 18. doi: 10.3390/ijms18051034
153. Xiao Y, Lu W, Li X, Zhao P, Yao Y, Wang X, et al. An oligodeoxynucleotide with AAAG repeats significantly attenuates burn-induced systemic inflammatory responses via inhibiting interferon regulatory factor 5 pathway. Mol Med. (2017) 23:166–76. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2016.00243
Keywords: IRF5, tumorigenesis, inflammatory diseases, cytokines, autoimmune diseases
Citation: Yu X, Rehman AU, Dang L, Zhang X, Liu J, Xiong X, Chen G and Jian Z (2025) Interferon regulatory factor 5: a potential target for therapeutic intervention in inflammatory diseases. Front. Immunol. 16:1535823. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1535823
Received: 27 November 2024; Accepted: 06 March 2025;
Published: 27 March 2025.
Edited by:
René Huber, Hannover Medical School, GermanyReviewed by:
Sarang Tartey, IGM Biosciences, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Yu, Rehman, Dang, Zhang, Liu, Xiong, Chen and Jian. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Gang Chen, Z2FuZ2NoZW43N0B3aHUuZWR1LmNu; Zhihong Jian, emhpaG9uZ0B3aHUuZWR1LmNu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.