
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Immunol., 03 April 2025
Sec. Cancer Immunity and Immunotherapy
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1528230
This article is part of the Research TopicThe crosstalk between emerging cell death and immune microenvironment remodeling in cancer progression and treatmentView all 12 articles
 Pooya Jalali1
Pooya Jalali1 Arvin Shahmoradi2
Arvin Shahmoradi2 Amir Samii3
Amir Samii3 Radman Mazloomnejad1
Radman Mazloomnejad1 Mohammad Reza Hatamnejad4
Mohammad Reza Hatamnejad4 Anwaar Saeed5
Anwaar Saeed5 Afshin Namdar6
Afshin Namdar6 Zahra Salehi7*†
Zahra Salehi7*†Autophagy is a cellular degradation process that plays a crucial role in maintaining metabolic homeostasis under conditions of stress or nutrient deprivation. This process involves sequestering, breaking down, and recycling intracellular components such as proteins, organelles, and cytoplasmic materials. Autophagy also serves as a mechanism for eliminating pathogens and engulfing apoptotic cells. In the absence of stress, baseline autophagy activity is essential for degrading damaged cellular components and recycling nutrients to maintain cellular vitality. The relationship between autophagy and cancer is well-established; however, the biphasic nature of autophagy, acting as either a tumor growth inhibitor or promoter, has raised concerns regarding the regulation of tumorigenesis without inadvertently activating harmful aspects of autophagy. Consequently, elucidating the mechanisms by which autophagy contributes to cancer pathogenesis and the factors determining its pro- or anti-tumor effects is vital for devising effective therapeutic strategies. Furthermore, precision medicine approaches that tailor interventions to individual patients may enhance the efficacy of autophagy-related cancer treatments. To this end, interventions aimed at modulating the fate of tumor cells by controlling or inducing autophagy substrates necessitate meticulous monitoring of these mediators’ functions within the tumor microenvironment to make informed decisions regarding their activation or inactivation. This review provides an updated perspective on the roles of autophagy in cancer, and discusses the potential challenges associated with autophagy-related cancer treatment. The article also highlights currently available strategies and identifies questions that require further investigation in the future.
Cancer constitutes a critical global health and economic challenge, with projections indicating an intensification in the coming years. The prevalence of cancer surpassed 18 million cases in 2018 and is estimated to escalate to nearly 29 million cases by 2040, primarily due to an aging and growing population. As of 2022, approximately 2 million new cancer cases had been diagnosed, amounting to around 5,500 new cases per day (1). Despite considerable efforts towards prevention and treatment, cancer continues to be the leading cause of death and poses a substantial burden on healthcare systems worldwide.
Despite significant advancements in the field of cancer therapy, there are still numerous challenges that hinder successful treatment outcomes. These challenges primarily arise from an incomplete understanding of the precise mechanisms underlying cancer pathogenesis. Therefore, it is imperative to gain a comprehensive understanding of the physiological and pathophysiological processes occurring at the cellular and molecular levels in order to effectively manage the disease and address its associated complications. Research exploring the mechanisms of cancer initiation has revealed that the accumulation of genetic, epigenetic, and metabolic alterations contributes to the development of malignant cells, ultimately leading to cancer cell invasion and the emergence of drug resistance (2, 3).
In recent years, targeted therapies, particularly cancer immunotherapy, have emerged as promising clinical approaches that have significantly improved overall survival rates for cancer patients (4, 5). Consequently, there has been a growing focus on investigating the role of the immune system in developing effective strategies for cancer diagnosis and immunotherapy-based treatments (6, 7). Given the inherent heterogeneity of cancer, along with variations in the tumor’s site of onset and the composition of immune cells, the precise selection of immunotherapies to specifically target tumor cells becomes imperative.
Autophagy has recently garnered attention as a cellular process that plays a pivotal role in modulating tumorigenesis, acting either as a tumor suppressor or promoter. Autophagy is a catabolic cellular degradation response that is triggered by starvation or stressful conditions. It involves the encapsulation, digestion, and recycling of cellular proteins, organelles, and cytoplasm to sustain cellular metabolism (8, 9). There are three main types of autophagy: macroautophagy, microautophagy, and chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA). Basal autophagy is crucial for preserving cellular homeostasis, serving as a quality control mechanism for proteins and organelles. This process operates in parallel with the ubiquitin-proteasome degradation pathway, preventing the accumulation of polyubiquitinated and aggregated proteins (10–15). Additionally, autophagy plays a role in pathogen removal (16) and apoptotic cell digestion (17). One of autophagy’s critical mechanisms is the execution of an intracellular degradation pathway mediated by double-membrane vesicles called autophagosomes. While general autophagy aggregates cytoplasmic components within autophagosomes and delivers them to lysosomes for degradation, selective autophagy specifically targets damaged organelles, protein aggregates, and intracellular pathogens (18). Disruptions or mutations in ATGs, which regulate the autophagic process, have been implicated in various human diseases, including neurological disorders, autoimmune diseases, metabolic disorders, infectious diseases, and cancer (19–21). Therefore, identifying autophagy mediators and related metabolic pathways is critical for understanding autophagy’s role in tumorigenesis (22).
Autophagy has been a subject of cancer research for several years, with numerous studies demonstrating its association with cancer onset and treatment (23, 24). In particular, autophagy has been shown to regulate various oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes, as evidenced by multiple studies (25, 26). Despite extensive research efforts, the role of autophagy in cancer remains enigmatic and controversial. While some studies suggest that autophagy promotes tumorigenesis, others argue that it inhibits cancer development (27–30). Furthermore, autophagy has displayed dual roles as a pro-metastatic or anti-metastatic effector (31). In the early stages of cancer metastasis, autophagy inhibits metastasis by limiting cancer necrosis, inflammation responses, and reducing cancer cell invasion and migration. However, in advanced stages of metastasis, autophagy plays a pro-metastatic role by promoting cancer cell survival (32, 33). Consequently, the function of autophagy in cancer remains a complex and ongoing area of investigation. In the cancer microenvironment, autophagy provides cellular energy and inhibits cytotoxicity under stressful conditions (34, 35).
Since autophagy impacts tumor cells at various stages (initiation, development, and progression) with conflicting roles, it remains a complex phenomenon concerning cancer treatment. Current evidence suggests that tumor cells may use autophagy as a protective shield to resist numerous anticancer therapies (36). In line with these findings, autophagy suppression has been shown to enhance the benefits of cancer therapies by sensitizing tumor cells to these drugs (37–39). Additionally, autophagy may play a crucial role in maintaining stemness in cancer stem cells and regulating their homeostasis (40, 41). Thus, elucidating the molecular mechanisms of autophagy can help manipulate this process for the benefit of cancer therapy and clarify which strategies should be adopted for clinical interventions to achieve desirable outcomes.
In this review, we aim to present current knowledge on the role of autophagy in cancer and its effects on suppressing or promoting malignancies through interactions with immune system components. By elucidating the role of autophagy in tumor suppression and growth, we seek to provide valuable insights into the context-dependent implementation of therapeutic strategies. Subsequently, we will explore the potential of anticancer therapies based on modulating autophagy as either an inhibitor or promoter. Lastly, we will discuss the current landscape of autophagy inhibitors and the therapeutic approaches employed to regulate autophagy (Figure 1).
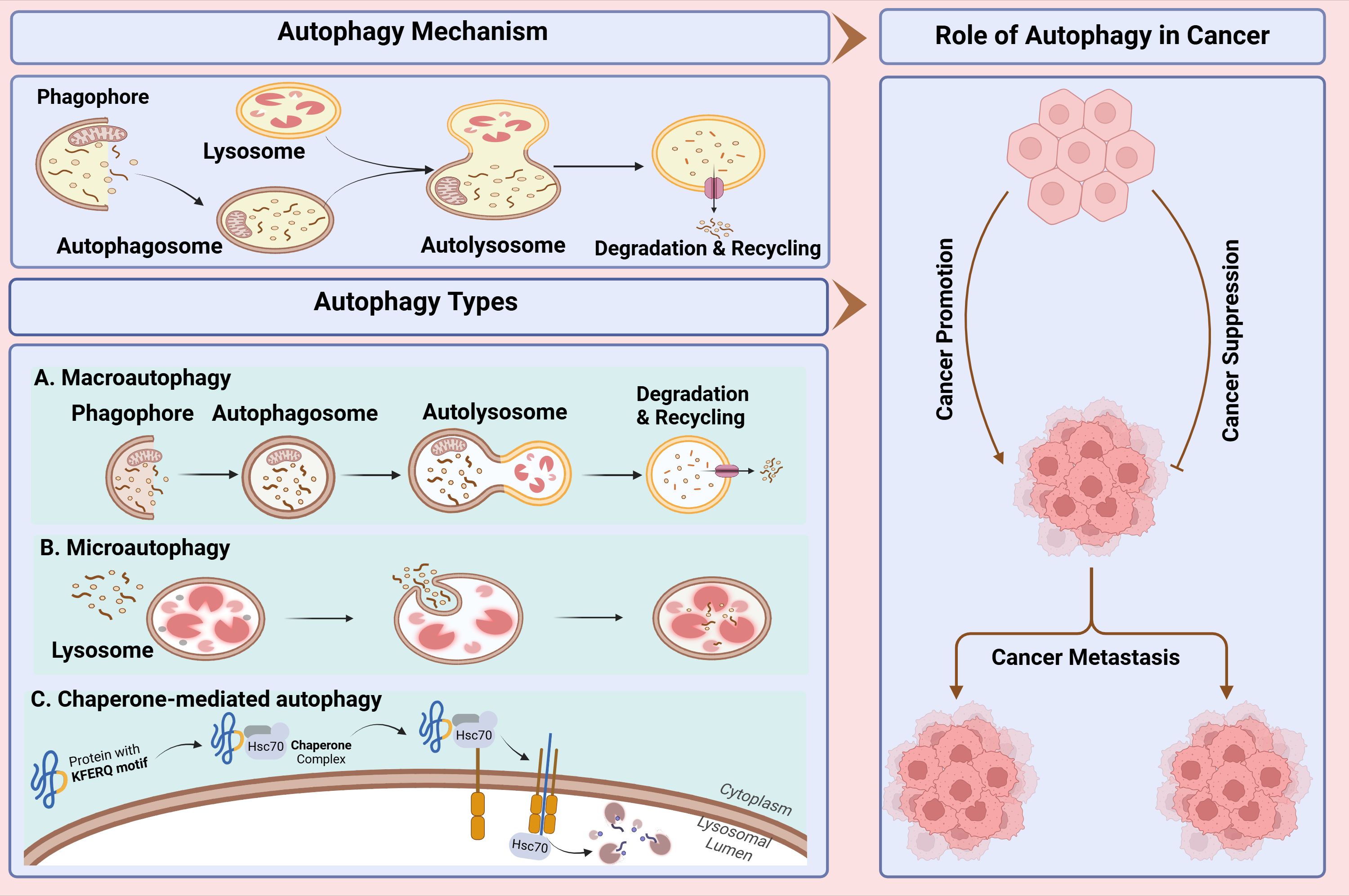
Figure 1. Study workflow for comprehensive study of autophagy and its role in cancer. In this study, first, we present autophagy mechanism and types of autophagy then its dual role in cancer including progression, metastasis and suppression of cancer cells discussed. Lastly, we discussed the current landscape of autophagy inhibitors and the therapeutic approaches employed to regulate autophagy.
Autophagy is a cellular process through which both intracellular and extracellular substrates are delivered to lysosomes for degradation (42). This process is required to maintain cellular homeostasis (43), produce amino acids for sustained viability during periods of starvation (44, 45), and increase protection against pathogens (46). Based on the delivery route and cargo specificity, three different types of autophagy are distinguished: macroautophagy, microautophagy, and chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) (43). Both macro- and micro-autophagy include the dynamic rearrangement of membranes to cover parts of the cytoplasm and have the capacity to sequestrate large structures such as whole organelles.
Macroautophagy involves the sequestration of cytoplasmic components within a de novo double-membrane vesicle called the autophagosome. The autophagosome subsequently fuses with the lysosome or vacuole, releasing its inner single-membrane vesicle into the lumen. The autophagic body membrane is then lysed, allowing the contents to be broken down and the resulting macromolecules to be transported back into the cytosol through membrane permeases for reuse (47) (Figure 2A). Microautophagy is a process by which the cytoplasm is directly engulfed by the lysosome through invagination, protrusion, and septation of the lysosomal membrane (48) (Figure 2B). Unlike microautophagy and macroautophagy, which can non-specifically engulf bulk cytoplasm, CMA selectively targets specific proteins linked to a KFERQ pentapeptide motif. This targeting motif is commonly found in all CMA substrates, making CMA highly specific in its selection of proteins for degradation (49) (Figure 2C).
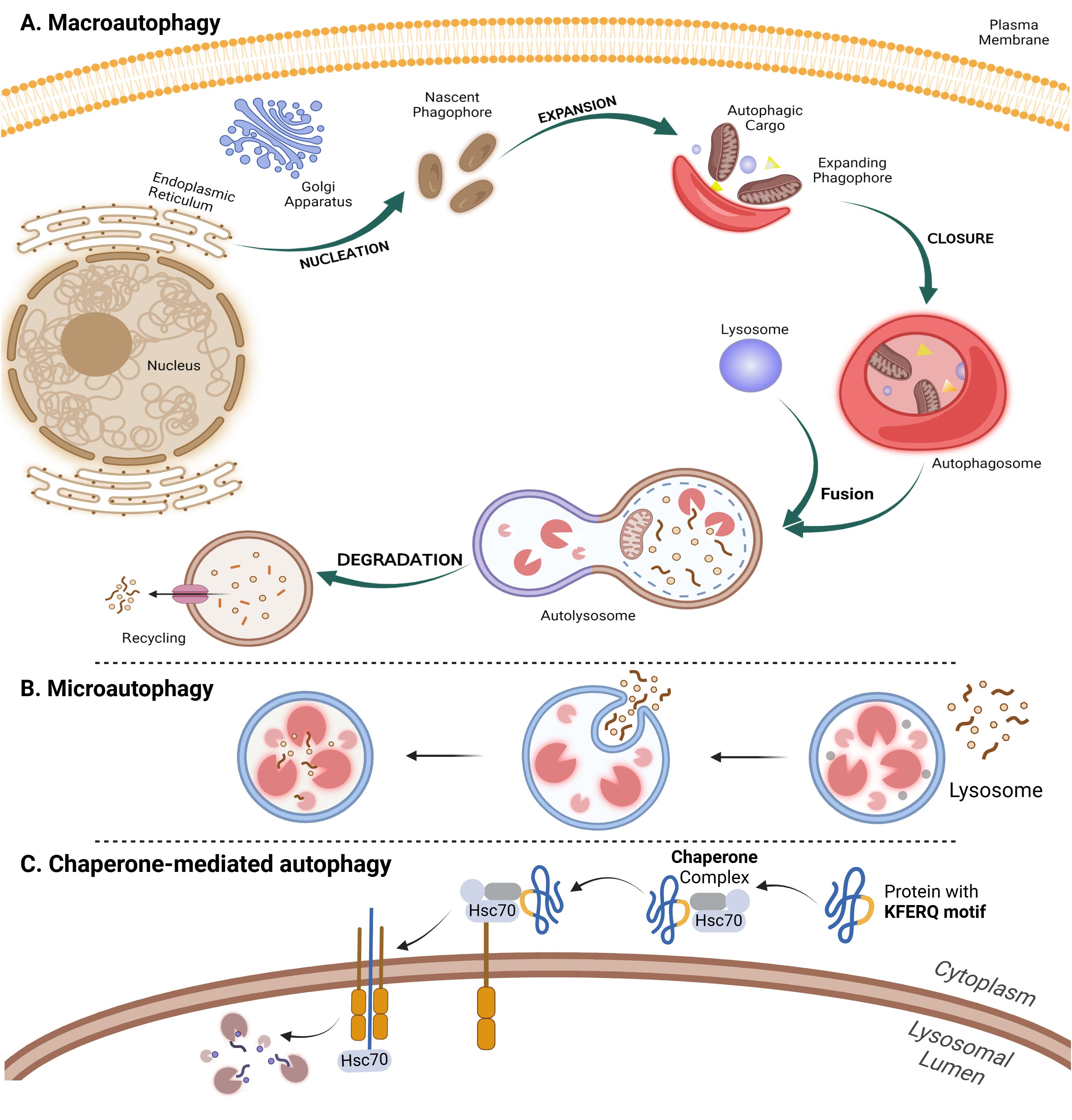
Figure 2. The autophagy mechanism and its three types. The process of autophagy is divided into five distinct stages: initiation, nucleation, expansion and elongation, closure and fusion, and cargo degradation. Once autophagy is induced, ATG proteins are gathered to form autophagy initiation complex. Subsequently, recruitment of other ATG proteins leads to the generation of phagophore which is then matured as a bilayer membrane structure called autophagosome. When autophagosome fuses with lysosome to form autophagolyosome, cellular components undergo enzymatic degradation to be reused by cells. (A) Macroautophagy involves the formation of autophagosome as a double-membrane vesicle that engulfs cytoplasmic material. The autophagosome then fuses with a lysosome in order to degrade and recycle the sequesteredcontents. (B) In microautophagy, lysosomes directly engulf and digest cytoplasmic materials, such as damaged organelles and misfolded proteins. (C) Chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) occurs when specific proteins, containing a KFERQ motif, are selectively recognized by chaperones and transported to the lysosome for degradation.
Autophagy was originally defined as a pathway for bulk degradation that is triggered by glucagon and nutrient scarcity (50, 51). This type of bulk autophagy functions to recycle essential building blocks to make up for a deficiency in nutrients and is generally considered non-selective regarding its substrates, referred to as cargos (52, 53). However, it has become evident that autophagy also plays a vital role in maintaining intracellular homeostasis in cells that are not nutrient-deprived, as it selectively degrades various cargo materials including aggregated proteins, damaged mitochondria, excess peroxisomes, and invading pathogens (54–56). The significance of selective autophagy for cellular homeostasis is underscored by research showing that tissue-specific deletion of autophagy-related genes in mice leads to conditions such as neurodegeneration or liver cancer (10, 57–59). Furthermore, studies have indicated that cells with impaired autophagy are unable to eliminate certain intracellular pathogens (60, 61). Recent evidence also suggests that selective autophagy is crucial for regulating intracellular free iron levels by modulating the amounts of the iron-binding protein ferritin, a process known as ferritinophagy (62–65). Also, the selective autophagy of the endoplasmic reticulum is referred to as “ER-phagy/reticulophagy” (66), and the degradation of ribosomes is called “ribophagy” (67).
In general, autophagy is an essential, ubiquitous, evolutionary, catabolic, and self-destructive process that mediates the elimination of cytoplasmic macromolecules to maintain genomic integrity, achieve cellular metabolism, and ensure cell survival (46, 68–70). It is a natural regulatory mechanism that retains beneficial substances and removes harmful substances from the body while playing a housekeeping role in eliminating misfolded or aggregated proteins, destroying damaged organelles, proteins (71–73), and cancerous substances (18), and eliminating foreign pathogens such as viruses through a destructive lysosomal pathway (58, 74–76).
Studies have shown that autophagy dysfunction is associated with the accumulation of damaged proteins and organelles, which can contribute to a variety of diseases, including cancer, neurodegeneration, and metabolic disorders (58, 77). Additionally, the modulation of autophagy has emerged as a potential therapeutic strategy for such diseases. The potential clinical applications of autophagy modulation are diverse, ranging from cancer therapy to neurodegenerative disease treatment. For example, inducing autophagy has been shown to sensitize cancer cells like colon and breast cancer to chemotherapy (78, 79), while inhibiting autophagy can protect neurons from the toxic effects of misfolded proteins in Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s disease and Huntington disease (80–83).
Autophagy is a well-regulated process coordinated by several protein complexes acting stepwise. The three most important complexes playing roles in the initiation and elongation of autophagy are (1): the ULK1/2 complex, the principal regulator of autophagy induction (2), class III phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase complex (PI3KC3), which contributes to phagophore nucleation, and (3) Atg5-Atg12/Atg16 complex, which contributes to autophagosome elongation.
Of these, the ULK1/2 complex is tasked with sensing upstream signals for autophagy initiation. The complex consists of ULK1, its homolog ULK2, ATG13, ATG101, and FIP200 (RB1CC1). The activity of ULK1 is also tightly controlled by two major nutrient-sensing kinases: AMPK and mTORC1. AMPK activates autophagy by direct phosphorylation and activation of ULK1, whereas mTORC1 inhibits autophagy by phosphorylation of ULK1 at specific sites to inhibit its activation. When activated, the ULK1/2 complex initiates the formation of autophagosomes, augmenting the level of autophagy. When the serine-kinase activity of ULK phosphorylates components of the ULK complex or other members of the core autophagy machinery, it triggers starvation-induced autophagy (84–86). This phosphorylation of components leads to modulation of their catalytic activities and subcellular distribution, which ultimately initiates autophagy. The class III phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase complex (PI3KC3), which contains the Atg14 subunit and Beclin-1/Atg, is another factor that contributes to the initiation and assembly of the phagophore at the onset of autophagy (Figure 3A) (87).
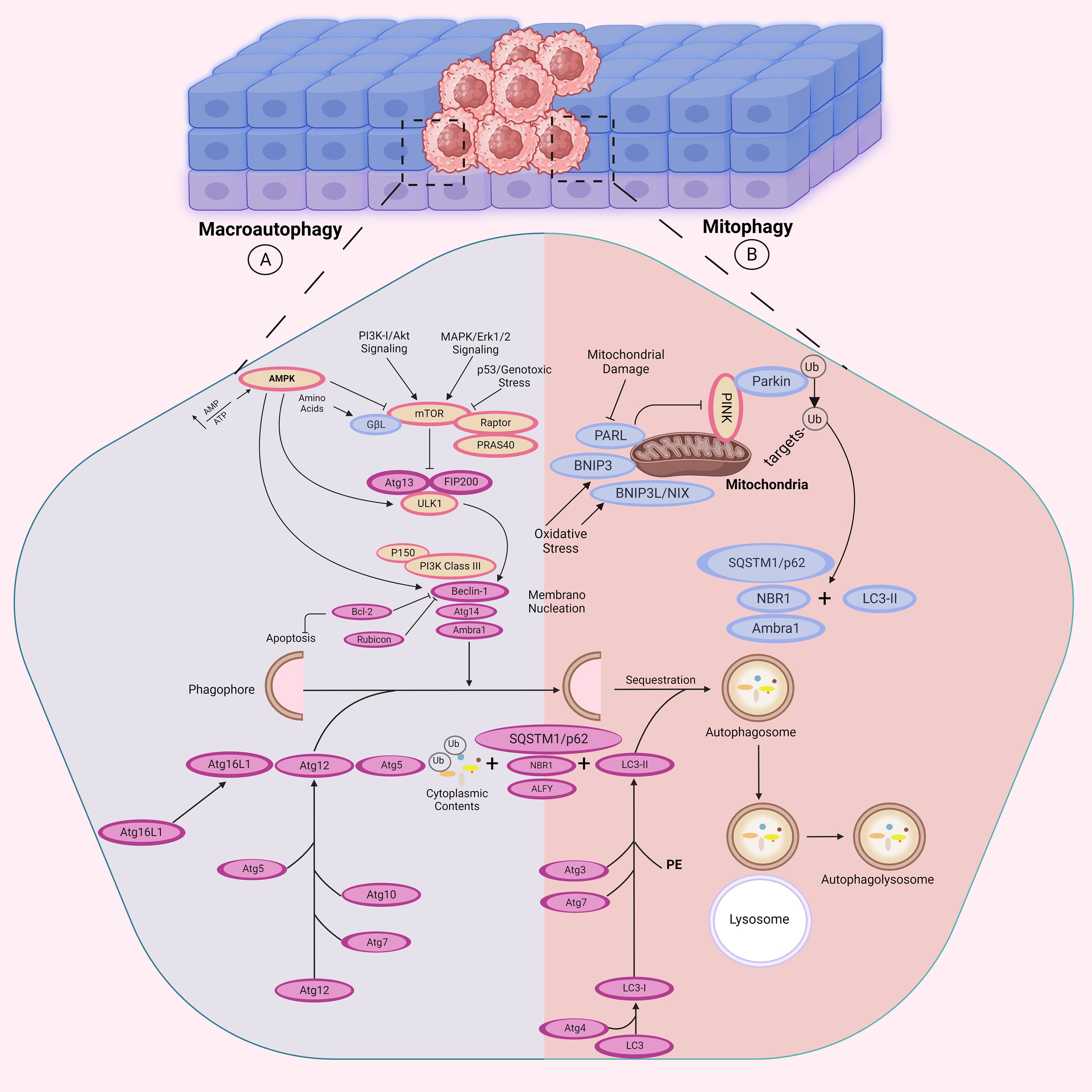
Figure 3. Autophagy-related signaling pathways. The autophagosome formation is mediated by the activities of three complexes: the ULK1, the phosphoinositide 3-kinase catalytic subunit type III (PI3KC3), and the Atg16L1 complexes. (A) In response to cellular ATP reduction, AMPK is activated to inhibit mTOR activity. mTOR downregulation leads to autophagy activation by releasing its inhibitory effect on ULK1 complex (ULK1, ATG13, and FIP200). However, in PI3K/Akt and MAPK/Erk signaling pathways, autophagy is suppressed in response to mTOR activity. The initial phagophore formation requires ULK1 complex to activate PI3KC3 complex which is consisted of Atg14 and Beclin-1/Atg6. Binding of Bcl-2 to Beclin-1 inhibits autophagy by preventing the formation of the PI3KC3. PI3KC3 then recruits two ubiquitin-like conjugation systems: The Atg12 (Atg5, Atg7, Atg10, Atg12 and Atg16) and Atg8 (Atg3, Atg4, Atg7 and Atg8) conjugation systems which participate in autophagosome formation, which further fuses with the lysosome for substrate degradation. AMBRA1 is another protein that directly binds to Beclin-1 to promote autophagy induction. (B) In response to mitochondrial damage, hypoxia or increased ROS production, mitophagy is triggered as a selective process for degradation of mitochondria by autophagy. NBR1 and BNIP3, BNIP3L/NIX and SQSTM1/p62 function as receptors on the mitochondria outer-membrane. BNIP3 competes with Beclin-1 for binding Bcl-2 and thus releases Beclin-1 for participating in mitophagy. Moreover, p62/SQSTM1 protein mediates clearance of ubiquitinated or aggregated proteins by binding them to the autophagy mediators for degradation. LC3 is involved in phagophore elongation and autophagosome-lysosome fusion.
In addition, there are two ubiquitin-like conjugation systems that are crucial for the elongation of phagophore. The first system involves the Atg5-Atg12/Atg16 complex, where Atg12 is conjugated to Atg5 and catalyzed by Atg7 and Atg10 (88, 89). The Atg5-Atg12 conjugate then associates with Atg16 via Atg5 and this complex is recruited to the phagophore by WIPI2 (90, 91). The second system is comprised of the Atg8 proteins, which are divided into two sub-families, LC3 and GABARAP (92). LC3-I, which is a cytosolic ubiquitin-like protein, is cleaved by the cysteine protease Atg4 to expose its C-terminal glycine residue. Atg7 and Atg3 enzymes, along with the Atg5-Atg12/Atg16 complex, then conjugate LC3-I to phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) to form LC3-II, which leads to the formation of autophagosome. Subsequently, autophagosome is fused with lysosome to degrade the sequestered substrates (89, 93, 94).
Selective autophagy or cargo-induced autophagy is a non-starvation, degradative process that has a role to play in cellular homeostasis through the specific degradation of individual cellular components (56). Excluding mitophagy, all other types of selective autophagy in the other categories of selective autophagy also play important roles to ensure cell homeostasis. Ferritinophagy aids in intracellular iron homeostasis by degrading ferritin inside lysosomes. The cargo receptor NCOA4 binds ferritin and facilitates its interaction with autophagosomes, facilitating the release of iron and maintaining cellular balance (62–66). ER-phagy specifically degrades damaged or redundant endoplasmic reticulum (ER) components to maintain ER homeostasis. Receptors such as FAM134B and RTN3 interact with LC3 to facilitate autophagic sequestration and degradation of ER fragments under stress conditions (62–66). To recognize specific cargoes, selective autophagy employs cargo-receptor proteins that are identifiable to the machinery of autophagy. BNIP3L (Nix) is one such protein referred to as Nix that functions as a receptor in mitochondria with recent reports identifying its function to mediate mitophagy. Through the interaction with LC3 via the N-terminal interacting region, Nix plays a role in regulating this process (95).
Mitophagy, a form of selective autophagy, degrades faulty mitochondria to help maintain cellular homeostasis. PINK1 is enriched on faulty mitochondria and recruits Parkin, which facilitates their ubiquitination and subsequent degradation by autophagosomes (96).
Moreover, several recent studies have revealed that the ubiquitin-binding protein p62/SQSTM1 serves as a receptor that links the autophagy machinery to different cargo targets, such as ubiquitinated protein aggregates and bacterial pathogens (97). This protein interacts with LC3 and ubiquitinated cargo through its LC3-interacting region and C-terminal ubiquitin-associated (UBA) domain, respectively (97, 98). Another ubiquitin-binding protein, called NBR1 (neighbor of BRCA1 gene 1), shares similar domain organizations with p62/SQSTM1, and it directly interacts with p62/SQSTM1. NBR1 also functions as a receptor for selective autophagy targeting of ubiquitinated protein aggregates (99) (Figure 3B).
The better understanding of autophagy indicates the ethological relevance of ATG mutations to various cancers. Ultimately, modeling revealed that while autophagy is an anti-tumorigenic process, excessive autophagic activity would have also been linked to neurodegenerative diseases -consistent with the duality that autophagy embodies in health and disease (100).
Autophagy was initially considered as a tumor-suppressor mechanism. Links that connect autophagy to tumors stem from two meager pieces of evidence (101). First, it was found that BECN1, the gene encoding Beclin-1 and the yeast ortholog Atg6, is monoallelically eliminated in breast, ovarian, and prostate cancers (102, 103). It has also been demonstrated that BECN1 deficient mice are more susceptible to develop hepatocellular and lung carcinomas as well as lymphomas (57, 104). However, induction of deficient autophagy through deletion of Atg5 or Atg7 in mice leads to benign liver tumors, indicating that autophagy could play an essential role in inhibiting tumor initiation in liver, which necessitates further research in human cancers (105). In addition, ectopic overexpression of BECN1 in human breast cancer cell line (MCF7 cells), which have very low levels of endogenous Beclin-1, resulted in activation of autophagy, which concurred with reducing proliferation and inhibiting tumorigenesis (103).
Beclin-1 is a highly investigated mammalian-specific autophagy regulator that shares homology with yeast Atg6. It serves as a crucial platform for the recruitment and initiation of PI3KC3 (106). Under normal conditions of mammalian cell growth, Beclin-1 associates with Bcl-2, an anti-apoptotic protein, through an interaction with the Beclin-1 BH3 domain. This interaction inhibits the formation of the Beclin-1/PI3KC3 complex and suppresses autophagy (36). Conversely, exposure to nutrient-deficient conditions disrupts the Beclin-1/Bcl-2 complex, releasing Bcl-2 from Beclin-1 and subsequent autophagy induction (107).
Consistently, ectopic overexpression of BECN1 in colon cancer cell lines leads to growth inhibition, which is attributed to the low endogenous expression of this gene in these cancer cells (108). Other mutations in ATGs such as Atg2B, Atg5, Atg9B, Atg12, and UVRAG have been proved to be associated with gastric and colorectal cancers beyond the BECN1 (109), therefore offering further support to the roles of autophagy in tumor suppression.
Adding to the support of autophagy’s role in cancer, experimental studies in genetically modified mouse models have shown that the loss of key regulators of autophagy increases the incidence of tumors. It was found first in mice hemizygous for BECN1 and later in mice lacking Atg4C and BIF1 that lack of these autophagic factors could lead to increased tumor formation incidence (102, 103, 110). Similarly, in another study, Takamura et al. reported that mice with Atg5 and Atg7 deficiency are more susceptible to develop liver tumor, which could be reversed by concomitant knockout of the p62 gene (57). Collectively, these observations confirmed that autophagy is required for tumor suppression.
Atg5 is a crucial autophagosome-forming protein that acts as an E1-activating enzyme in eukaryotic cells (111, 112). E1-activating enzymes are known as ubiquitin-activating enzymes which are responsible for catalyzing proteins undergoing ubiquitination reaction (111, 112). Atg5 combines with Atg12 through an ubiquitin-like system. Alongside LC3-II, which is a key molecule in autophagosomal membrane formation via the Atg5-Atg12/Atg16 complex, Atg5 also plays an essential role in various biological processes such as viral infection (113, 114), tumor apoptosis (115, 116), and tumor proliferation (117, 118). Several autophagy-specific regulatory genes have been classified in yeast, including several genes with mammalian homologs. Among them, Atg5, a key regulator of autophagosome formation, is one of the most studied ATGs. Furthermore, Atg5 also participates in the regulation of cell death. Ectopic expression of Atg5 can stimulate cells to undergo apoptosis in response to apoptotic stimuli, such as anticancer agents (116). In addition, during cell death, calpain can break down Atg5, and truncated Atg5 leads to mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis (119). This suggests that Atg5 may act as a critical regulator in determining whether cells undergo autophagy or apoptosis.
Another vital component of stress signaling and adaptation is the tumor suppressor p53. A wide range of stressors, such as DNA damage, metabolic stress, and oxidative stress, activate P53 (120). In response to these stressors, p53 regulates gene transcription or acts through non-transcriptional mechanisms to cope with stress adaptation (e.g., cell cycle arrest) or to destroy cells that cannot be repaired by apoptosis or aging. One component of this p53-mediated transcriptional response is autophagy activation (120). Conversely, autophagy has the ability to suppress p53 levels and functions. The p53 and autophagy pathways are intricately intertwined and exert significant influence on stress, metabolism, and cancer responses (120).
The regulation of autophagy can influence the expression of tumor suppressor proteins or oncogenes. Furthermore, autophagy modulation by certain anticancer medications can contribute to either the survival or destruction of cancer cells (29, 30). Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) negatively regulate tumor suppressor factors, which induces autophagy and suppresses cancer onset (121). Conversely, mTOR Class I PI3K and AKT activate oncogenes, suppressing autophagy and promoting cancer formation (122).
Numerous preclinical investigations have demonstrated that targeted treatments and DNA damaging agents have the potential to induce autophagy. However, the majority of studies have found that the autophagy elicited by these anticancer drugs is cytoprotective rather than cytotoxic (123). Currently, some specific autophagy inducers have been introduced. Most agents that induce autophagy either hinder other crucial cellular functions, such as mTOR signaling, or activate additional stress responses, such as the unfolded protein response (124). Tat-Beclin1 is a fusion peptide believed to act as an inducer of autophagy, though the precise mechanism remains undefined (125).
Compound 5e is a newly synthesized fluorescent molecule and a selective mTOR inhibitor by interacting with FKBP12 reducing tumor growth in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. This inhibition subsequently induces autophagy, suggesting that autophagy is a secondary response and not the primary mechanism of action (126). Additionally, some other natural herbal derivatives with anti-tumor activities have been introduced to induce autophagy in cancer cells. Honokiol and Isobavachalcone, respectively, both antitumoral in effect, were later shown to have autophagy as a secondary response in melanoma and myeloma cells. Honokiol targets the Notch signaling pathway, reducing the stemness of melanoma. In contrast, apoptosis triggered by the isobavachalcone was achieved through the activation of caspases and increased LC3-II expression, linking autophagy with death mechanisms of cells (127, 128). HNK is a natural compound that targets notch signaling pathway to maintain melanoma cells stemness and self-renewal via inhibiting the expression of downstream target proteins including Hes-1 and cyclin D1. Furthermore, the treatment of H929 myeloma cells with IBC enhances the expression of LC3-II which is an autophagosome formation marker. IBC-induced cell death is triggered by the activation of apoptosis mediators such as caspases 3,9 and the cleavage of poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) and the proteolytic activation of protein kinase C (PKC) (127, 128). These inducers may be effective for reducing the development of benign lesions such as polyps, but further research is required to find the appropriate targets and chemical agents that may specifically induce autophagy.
There is increasing evidence that inhibiting autophagy may be an effective treatment for advanced cancers (129). Additionally, several research groups have demonstrated that autophagy might support tumor immunity by serving as a tumor protector. For example, RAS proteins are small GTPases that regulate key signaling pathways for metabolism, cell survival, and proliferation. In cancer cells with RAS mutations, autophagy is often upregulated as a means of supporting tumor survival and progression (18, 130–132). The formation of some lethal malignancies, such as lung, colon, and pancreatic, is linked to the occurrence of RAS-activating mutations, which induce autophagy, which promotes tumor development, survival, and oncogenesis (18, 133–136).
Genetically engineered mouse models (GEMMs) studies have shown that autophagy suppresses the formation of early-stage benign tumors but facilitates the progression of advanced malignancies in mouse models of lung adenocarcinoma and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) driven by mutant RAS or BRAF (137–141). Similarly, it was shown in a mouse model of breast cancer that suppression of autophagy by FIP200 inhibits tumor initiation and progression (142). The activation of necrotic cell death and an inflammatory response in tumors with autophagy and apoptosis deficiencies partially explains how the loss of autophagy’s pro-survival role promotes carcinogenesis (143). Preventing starvation-induced survival through autophagy and rerouting apoptosis-defective tumor cells toward a necrotic cell fate can result in the development of chronically necrotic tumors. This process may impair the normal wound-healing response and promote tumor development, suggesting that autophagy defects represent a non-cell-autonomous mechanism for promoting tumorigenesis (144–146).
In contrast to apoptosis, necrosis and cell lysis lead to the release of nuclear high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) from cells, which stimulates the innate immune response, the recruitment of inflammatory cells, cytokine production, and nuclear factor-B (NF-B) activation. In certain cases, these events are associated with increased tumorigenesis (147–149). Inhibition of autophagy by constitutively activating AKT in apoptosis-defective cells results in necrosis in response to metabolic stress in vitro, and in vivo, necrosis coincides with NF-B activation and promotes tumorigenesis (143).
Despite significant investment into this field, the detailed molecular mechanisms by which autophagy drives cancer progression still remain elusive and are therefore poised for further work. Therefore, further studies are needed to investigate the relationship between different processes of cell death and their impact on the immune system and the tumor microenvironment to better understand their relationship and regulate tumor growth. In the following, the dual role of autophagy in tumor promotion and suppression will be discussed.
The primary role of the immune system is to defend the host against external threats like bacteria and toxins and maintain the body’s structural integrity (150). The categorization of the immune response into two distinct parts, namely innate immunity, which provides non-specific resistance to infections, and adaptive immunity, which targets particular pathogens through a highly specialized and adaptable process, has been artificially established (150). Both innate and adaptive immune responses require autophagy, a cellular mechanism, to function properly (29). The progressive and in-depth analysis of the molecular underpinnings of cancer progression, carcinogenesis, and the dissemination of cancer cells to other parts of the body has resulted in more precise, efficacious, and specialized treatment strategies for various forms of solid and hematological malignancies, particularly those with a high propensity for distant metastasis (151). Meanwhile, the recognition of various pathways implicated in the advancement of cancer or, conversely, in the elimination of tumors, emphasized the crucial significance of the immune reaction (151). Researchers can develop more effective cancer treatments by having a better understanding of the autophagy concept, its dual functions, and how it interacts with the immune system.
The complement system and innate immunity are invariably triggered by inflammation, the body’s first line of defense (152). On the other hand, when pathogens or pathogenic peptides are captured and presented by antigen-presenting cells (APCs), such as macrophages, B-cells, or antigen-presenting dendritic cells (DC) they activate T-lymphocytes, which in turn induce cell death (153). Moreover, the promotion of the infiltration of DCs and the recruitment of CD4+ helper and CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes to the tumor microenvironment is seen (154). Additionally, autophagy in dying tumor cells is essential for the induction of immunogenic cell death, which enables the effective detection of tumors by the immune system (6, 155). Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules present antigenic, foreign proteins on antigen-presenting cells, activating CD4+ T-cells and CD8+ T cells, and natural killer (NK) cells create cytolytic granules, which autophagy encourages destruction (29). The cells of many bodily organs occasionally rely on autophagy to enhance their performance. For example, thymic epithelial cells need autophagy to recognize host and foreign antigens via MHC class II (29).
Neoplastic cells exhibit a panel of T-cell-recognizable antigens (156). Tumor antigen presentation is a vital part of anticancer reactions, and a malfunction in this system may lead to tumor leakage from immune surveillance, a factor typically linked with cancer expansion, and inhibiting autophagy can impede the process (156, 157).
A number of investigations have initiated the process of defining the distinct regulation mechanisms of macroautophagy and CMA in peripheral T cells. Initial research has indicated that the induction of macroautophagy in T cells involves specific signals. It has been stated that CD4+ and CD8+ T cells exhibit upregulation of macroautophagy upon engagement of the T cell receptor (TCR) (158–161). The signaling mechanisms underlying the stimulation of macroautophagy in active T cells are still being fully understood (158). The activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) JNK, located downstream of the TCR, has been suggested to play a role in the initiation of macroautophagy (15). This is supported by findings indicating that the inhibition of JNK1 or JNK2 through chemical means or genetic deletion results in a reduction in activation-induced macroautophagy in CD4+ T cells (15). None of these processes, however, have been implicated in the activation of autophagy in T cells as of yet (158). The upregulation of the expression of the lysosomal associate membrane protein 2A (LAMP-2A) in T cells after TCR engagement is in response to the enhanced production of reactive oxygen species in activated cells (162). The production of ROS in CD4+ T cells is regulated by intracellular calcium signaling, which has the transcription factor nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) as one of its key targets (163–165).
Macroautophagy is crucial for preserving the homeostasis of T cells (158). Since T cells must significantly reduce their mitochondrial content as they develop from immature peripheral naive T cells into single-positive thymocytes, mitophagy-regulated mitochondrial recycling is particularly crucial in T cells (158). In T cells lacking essential ATG proteins, organelle turnover—including those of the mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum—is severely impaired (166–168). Proapoptotic protein levels may have increased in T cells due to increased oxidative stress as well as a potential role for autophagy in the turnover of a number of those proteins and this would also increase the likelihood of cell death, which occurs regardless of functional macroautophagy (160, 169).
According to a number of studies, T cells lacking the crucial Atg genes have lowered proliferative reactions to TCR engagement resulting in being unaffected by CD28 or IL2-receptor signaling (158). Defects in activation-induced proliferation are also seen as autophagy is acutely blocked using inducible deletion of ATG genes or using chemical inhibitors, both of which are sure to have a negative effect on the responses to antigens due to the altered metabolic output and mitochondrial dysfunction seen in T cells from Atg-deficient mice (161). In autophagosomes located in resting cells, organelles, and particularly mitochondria, seem to be the preferred cargo. Conversely, in autophagosomes observed in activated cells, cytosolic material is favored over organelles (161). This implies that selective cargo degradation may be involved in the control of T-cell activation-induced responses (158). DeVorkin et al. demonstrated that the elimination of Atg5 or Atg7 in T cells resulted in a remarkable denial of tumor implants in syngeneic mouse tumor models (170). Research conducted by Mgrditchian and colleagues has demonstrated that the suppression of BECN1 gene expression enhances the infiltration of T cells to the immune system’s microenvironment (171).
In addition to macroautophagy, CMA functions in antigen presentation, especially cytoplasmic antigens (153, 172). Antigen processing may include more than one kind of autophagy (153). Antigens produced from outside the cell are destroyed in lysosomes, and autophagy transports antigens destined for destruction and peptides from degraded antigens back to the cell surface for presentation on class II MHC (153).
B-lymphocytes are essential components of the immune system that are responsible for mounting immune reactions against infections and tumors by generating protective antibodies (173). Different B cell populations exhibit the ability to engage in both protective and destructive action (173). In addition to conventional facets of cellular metabolism, B cells rely on autophagy, a mechanism that facilitates the degradation of damaged cellular constituents (173). Autophagy is responsible for preserving metabolic balance in the absence of nutrients and promoting the extended survival of plasma cells (PCs) (174). Autophagy has been observed to facilitate the evasion of autoimmune checkpoints by self-reactive B cells, their activation through innate immune signals, and the presentation of autoantigens to T lymphocytes (175–177). Miller BC et al’s study elucidates the involvement of autophagy in B cell development by demonstrating that the introduction of Atg5-deficient cells into the fetal livers of Rag1–/– mice results in a developmental impediment at the pre-B cell stage (178). The findings suggest that the development of B2 cells requires autophagy, as evidenced by the unaffected splenic and lymph node B cell populations when Atg5 deletion was limited to mature B cells, while peripheral maintenance of these cells does not depend on autophagy (178). Autophagy was found to be a crucial process in the sustenance of mature B cell populations in the peripheral regions (179). Similar to other metabolic processes, autophagy plays a pivotal role in the functioning of B cells following activation. The study revealed that the absence of B cell autophagy did not affect the normal formation of memory cells two weeks post-immunization in mice. However, a significant reduction in the number of memory cells was observed after eight weeks, suggesting that autophagy is not a prerequisite for the formation of memory B cells, but plays a crucial role in their maintenance (180). Recent studies have demonstrated that AMPK regulates mitochondrial autophagy in memory B cells, thereby aiding in the mitigation of oxidative stress (181).
LC3-associated phagocytosis (LAP) is a newly discovered function of autophagy proteins that play a role in immune regulation and inflammation reactions in different cell and tissue types (182). LAP is a process that involves the conjugation of LC3 family proteins to phagosome membranes (182). It utilizes a segment of the conventional autophagy machinery, triggered by the binding of surface receptors that identify different types of cargos such as infectious agents, cell death, soluble ligands, and protein aggregates (182). Phagocytic cells may use LAP, in which the act of phagocytosis causes specific autophagy machinery to become activated and interact with the phagosome, facilitating its fusion with lysosomes (183, 184). LAP needs the same proteins as autophagy, including BECN1, VPS34-generated PI3P, Atg5, and Atg7; however, unlike autophagy, LC3 connects with the single phagosome membrane rather than the double membrane of autophagosomes (184). Additionally, in contrast to autophagy, the lysosomal acid phosphatase process does not require the first autophagy protein complex (ULK1, Atg13, and FIP200) instead, LAP involves a BECN1– VPS34 complex incorporating the Rubicon protein (184). Furthermore, LAP is an essential mechanism of immunosuppression in the microenvironment of tumors (184, 185).
Cytokines are a class of diminutive proteins that are secreted by cells and exert a distinct influence on intercellular interactions and communications (186). The presence of cytokines with pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory properties has been observed (186). The process of autophagy plays a critical role in regulating the synthesis and release of cytokines such as IL-1, IL-18, and TNF-α (187). Specifically, in human macrophages, cytokines such as IL-1, TNF-α, IL-6, IFN-γ, IL-2, and TGF-β have been shown to trigger autophagy, whereas cytokines like IL-4, IL-13, and IL-10 inhibit this process (154). Moreover, the release of cytokines due to the inflammatory response in the tumor microenvironment can lead to the recruitment and absorption of anti-tumor macrophages into the hypoxic region of the tumor (143).
IFN-γ is an essential cytokine that promotes inflammation that is mostly produced by natural killer cells and activated CD4+ or CD8+ T cells and innate and adaptive immunity depend heavily on IFN-γ (188, 189). New research reveals that IFN-γ increases autophagy, which in turn encourages antigen presentation, cellular growth, and the elimination of viruses and bacteria. In a process known as positive feedback, this autophagy activation then increases the release of IFN-γ (190, 191). Moreover, to assist eradicate invasive infections or causing cell death, IFN-γ may promote autophagy (192). Whereas the exact mechanism by which IFN-γ triggers autophagy is unclear, IFN-γ may activate macrophages through a pathway involving the family M member 1 GTPase Irgm1/IRGM1 (192). Autophagy can trigger the production of IFN-γ and promote the inflammatory response (193). As an illustration, conditional Atg5 knockdown significantly reduced IFN-γ induced LC3 conversion and autophagosome formation, which in turn reduced IFN-γ secretion by CD4+ T cells (192). Evidently, autophagy induced IFN-γ inducible inflammatory responses (194).
Endotoxins cause the creation of TNF-α, which hastens the development of several disorders linked to inflammatory responses (192). The idea that TNF-α and autophagy interact is supported by mounting evidence (195). Osteoclasts, epithelial cells, T lymphoblastic leukemic cells, skeletal muscle cells, and vascular smooth muscle cells are only a few of the cells that TNF-α primes for autophagy (195–200). It is unclear how TNF-α causes autophagy in various cell types (192). Depending on the cellular setting, autophagy either appears to up or down-regulate TNF-α production (192). One way that autophagy activation can reduce inflammatory reactions is by preventing the release of TNF-α (192). On the other side, autophagy has the potential to activate the inflammasome and cause the release of proinflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-8, and IL-6 (192).
The inflammatory response is mediated by IL-17, which is largely produced by Th17 cells and plays a role in the formation of the tumor microenvironment (192). In vitro experiments on B cells revealed that IL-17A promoted autophagy (201). Recently, it was revealed that IL-1β can induce autophagosome formation in macrophages and epithelial cells in an inflammatory context, suggesting that IL-1β may induce autophagy as part of a negative feedback loop to reduce excessive inflammation and restore cellular homeostasis (202). This suggests that they may activate autophagy as a component of a negative feedback loop to reduce inflammation (202). According to a recent study by Gao Yung et al, IL-33 appears to suppress both the inflammatory response and the autophagic activation of apoptosis (203) (Figure 4).
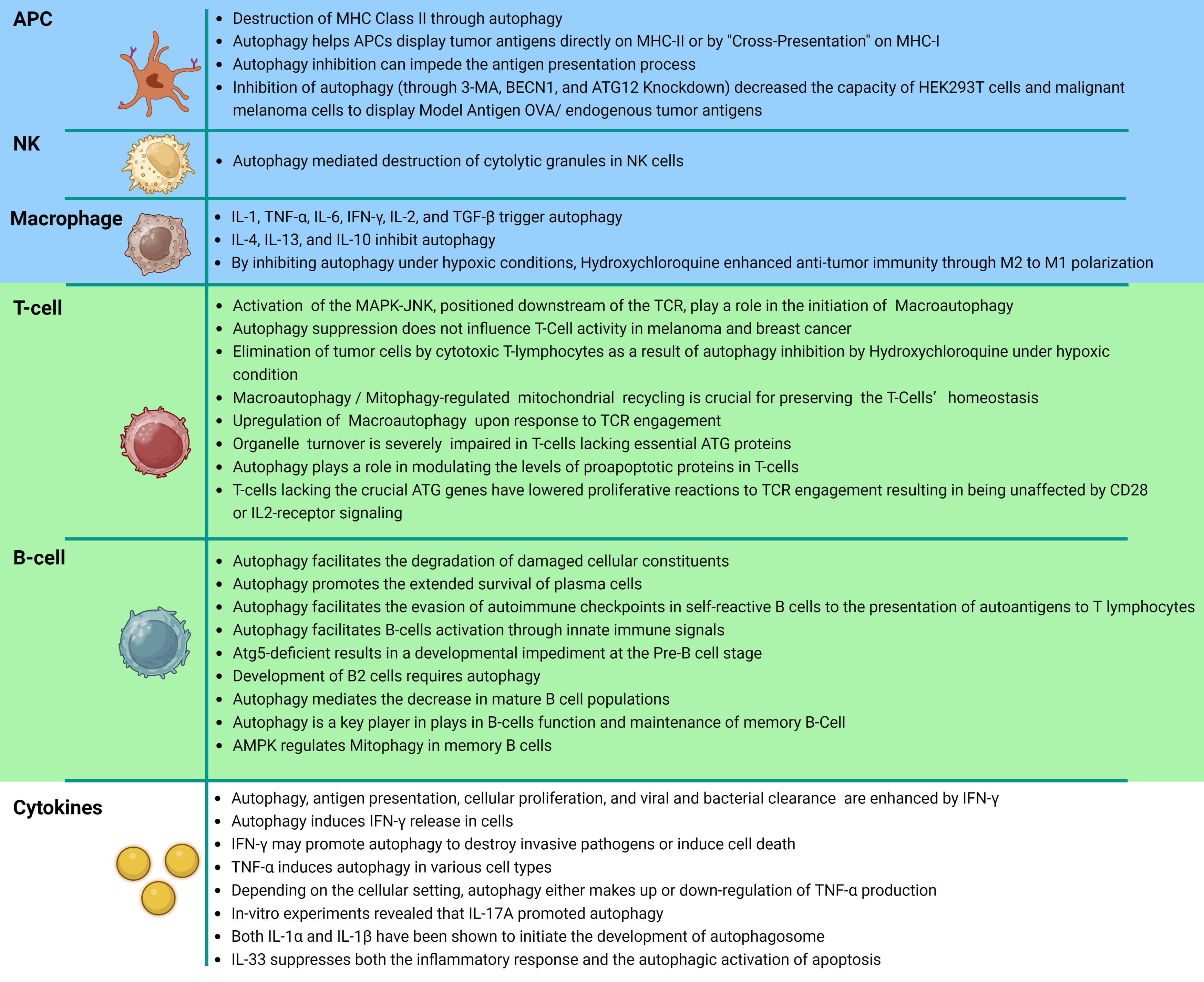
Figure 4. Autophagy related cancer immunity. This diagram represents a tabular structure, wherein the upper section with blue rows illustrates the interplay between innate immune cells, namely antigen-presenting cells, natural killer cells, and macrophages, in relation to autophagy. The central segment, highlighted in green, showcases additional interactions between the specific immune system and autophagy. It presents a detailed depiction and explanation of the involvement of T cells and subsequently B cells. Lastly, the lower section, depicted in white, elucidates the reciprocal interactions and consequential effects between cytokines secreted within the immune system and autophagy.
Limited autophagy has cell-intrinsic implications, including genomic stress, DNA damage, and increased susceptibility to acquiring growth-promoting mutations (204, 205). Besides, autophagy can play a dual role in the cancer process, it regulates and prevents neoplasia, inflammation, and cancer; thus, these factors would be a common cancer trigger and produce a pro-tumorigenic environment (206–208). For instance, Crohn’s disease (CD) involves transmural inflammation of the terminal ileum (small intestine) but may affect the entire GI tract (209). Mouse hypomorphic for Atg16L1 or defective in Atg5 or Atg7 in the gut had significant cellular abnormalities localized to intestinal Paneth cells, similar to CD patients with the Atg16L1 risk gene (210, 211). Chronic intestinal and pancreatic inflammation, cancer risk factors, are characterized by impaired autophagy (29, 212).
As part of the cell’s reaction to xenobiotics, cytokines, and invasion by bacteria, as well as during mitochondrial oxidative metabolism, ROS are produced (213). ROS have been observed to be present at heightened levels in nearly all types of cancers, and are known to facilitate numerous facets of tumor growth and advancement (29, 212). Adequate levels of ROS are essential for the process of autophagy, and ROS accumulation in the tumor microenvironment hinders DC tumor defense action (29, 214). It is mostly derived from the respiratory chain of the mitochondria (29). ROS influences all phases of tumor development (212). Mitophagy is a process by which the cell gets rid of ROS-producing mitochondria that have been damaged (29). Mitophagy has two distinct molecular routes (29). When mitochondria are damaged, phosphatase and tensin homolog-induced kinase 1 recruit the E3 ubiquitin-like ligase PARKIN, which causes the voltage-dependent anion channel 1 (VDAC1) on the membrane of the mitochondria to get ubiquitinated and triggers the recruitment of p62 (215–217). Autophagic degradation is also aided by transferring oxidized proteins to p62 for destruction, and in many cancers, P62 is overexpressed (29, 218). Mathew et al. conducted a significant investigation that demonstrated the crucial requirement of p62 in tumorigenesis, revealing that depletion of p62 through autophagy suppressed tumor development (29, 219). Further molecular pathways supporting tumor growth were activated by persistent p62 expression that further changed nuclear factor-kappa B signaling (220). Oxidative DNA damage and increased tumorigenesis in autophagy-deficient cells are linked to p62’s inability to be properly cleared from the cell (29). Furthermore, mitochondrial BNIP3L may interact with Atg8 homologs and transport mitochondria to autophagosomes (95, 221).
Some studies suggest that it would be better to promote autophagy during cancer treatment to show the favorable effects (222). For instance, in breast cancer patients, the presence of increased LC3 puncta (indicative of autophagosomes) and nuclear HMGB1 correlated with improved overall survival, reduced metastasis, and enhanced tumor immune infiltration (223, 224). Interestingly, studies have demonstrated that suppression of autophagy does not affect T cell activity in preclinical models of melanoma and breast cancer, including cells treated with chemotherapy in the case of melanoma. However, within the hypoxic tumor microenvironment, autophagy upregulation in tumor cells inhibits immunological effector-induced cell death (143, 225). Nonetheless, under hypoxic conditions, treatment with hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) has been shown to improve T-cell death and enhance anti-tumor immunity by inducing a transition from an M2 to M1 polarization state in macrophages. This polarization transition facilitates the elimination of tumor cells by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (226, 227). Notably, despite the distinct mechanisms of action, both class I and II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) processing require activation of autophagy, even though a combination of starvation and rapamycin therapy induces autophagy, which reduces class II protein presentation (153, 228).
Inhibition of autophagy, either through 3-methyladenine treatment or knockdown of Beclin-1 or Atg12, significantly reduces the ability of human embryonic kidney cells (HEK293T) and malignant melanoma cells to present model antigen OVA or endogenous tumor antigens (229). Conversely, induction of autophagy yields the opposite effect (229). Autophagy plays a crucial role in antigen presentation by antigen-presenting cells (APCs) through a direct presentation on class II MHC or through “cross-presentation” on class I MHC (230). Pharmacological induction of autophagy with rapamycin in melanocytes significantly enhances the priming of CD8+ T cells by APCs presenting the melanocyte-derived tumor antigen gp100. Conversely, blocking autophagy with 3-methyladenine (3-MA) reverses this effect (229). Moreover, blocking autophagy by impairing autophagosome turnover increases antigen cross-presentation, indicating that autophagosomes serve as effective transporters of antigens from APCs to T cells. The stabilization of autophagosomes, rather than the initiation and completion of the autophagy process, is critical for cytotoxic T-cell priming (153, 229).
There is evidence that autophagy plays a role in preventing tumorigenesis by several mechanisms. For example, autophagy can remove damaged organelles, particularly mitochondria that produce reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can damage cellular structures and promote genomic instability. Additionally, autophagy can promote the degradation of oncogenic proteins and inhibit their activity, thereby inhibiting their ability to promote carcinogenesis (24).
In cancer cell lines and mouse models, the absence of BECN1 has been shown to decrease autophagy and increase cell proliferation, providing evidence that BECN1 is a tumor suppressor gene (102, 103). Similarly, other proteins that interact with Beclin-1 and positively regulate autophagy, such as AMBRA1 (231), BIF-1 (110), and UVRAG (232), have demonstrated anti-proliferative or tumor-suppressive effects. Reported evidence indicate that AMBRA1 deficient mice models represent accelerated tumor growth, invasiveness, and metastasis in BRAF/PTEN melanoma phenotype via increased activity of Focal Adhesion Kinase 1 (FAK1) (231). UVRAG, as another Beclin1-binding protein, activates the Beclin1–PI3KC3 complex to promote autophagy and suppress the proliferation of human colon cancer cells (232). Furthermore, several studies have reported decreased levels of Beclin-1 in various types of cancer, including cervical squamous cell carcinomas and hepatocellular carcinomas (233–236). Consistent with the tumor suppressor hypothesis, the development of knockout mice for specific ATGs has revealed that deficiencies in certain regulators of autophagy are associated with a tumorigenic phenotype. However, because systemic deletion of Atg3, Atg5, Atg7, Atg9, or Atg16L1 results in neonatal mortality (12, 53, 237–239), the long-term effects of inhibiting autophagy could not be evaluated until mosaic Atg5 deletion mice were generated. In this context, mice with systemic mosaic Atg5 deletion or liver-specific deletion of Atg7 spontaneously develop benign hepatic adenomas (57).
Autophagy-deficient mice accumulate ubiquitinated keratins, the autophagy cargo adaptor p62, and aberrant mitochondria (12, 59, 219). Elevated levels of p62 and phospho-keratin 8 in several tissues and cancers, as well as in mammary tissues and malignancies, are potential biomarkers for autophagy defects (12, 240) aggregates or inclusions and are associated with forming ROS, activating the DNA damage response, cellular damage, and death. This can lead to chronic inflammation, promote degenerative and inflammatory disorders, and contribute to cancer development (9, 143, 210, 219). Chronic tissue injury and inflammation also contribute to the formation of DNA-damaging ROS, which can cause mutations and promote tumor growth (81). Deficient autophagy can lead to the development of p62/SQSTM1 protein aggregates, damaged mitochondria, and misfolded proteins, resulting in the formation of ROS that induces DNA damage and genomic instability (59). Knockdown of p62/SQSTM1 inhibited ROS and DNA damage responses in autophagy-deficient cells, indicating a potential molecular relationship between deficient autophagy and tumorigenesis (59). This association was also observed in p62/SQSTM1/mice, which were protected from Ras-induced lung carcinomas compared to wild-type animals (241). Autophagy may help protect against tumorigenesis by restricting necrosis and chronic inflammation connected with the production of pro-inflammatory HMGB1 (Figure 5A) (242). However, some results suggest a potential dual nature of this process in tumor development and progression. Overall, these findings suggest that autophagy can play a role in suppressing tumorigenesis in the early stages of cancer, but its effects can be complex and multifaceted.
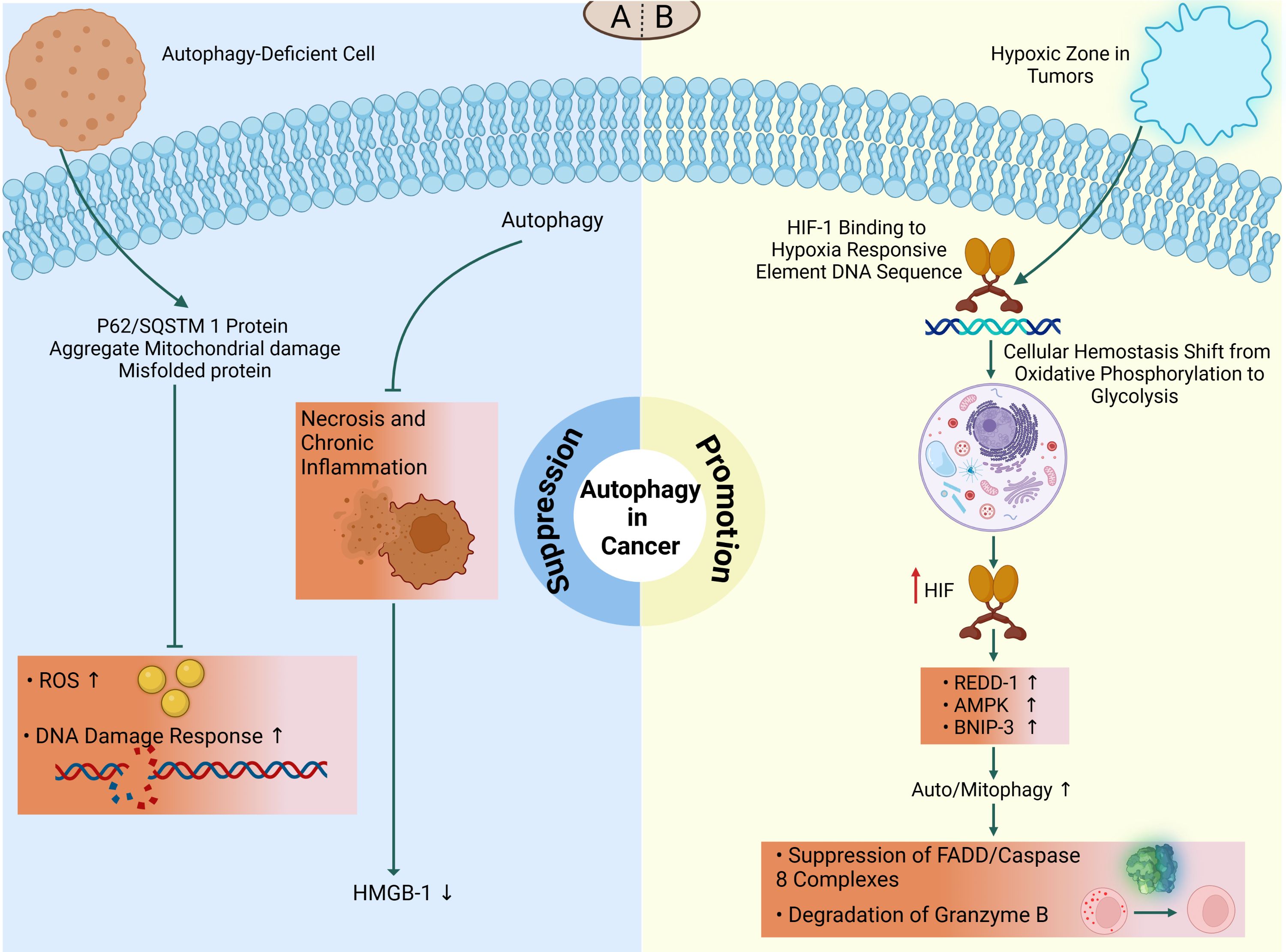
Figure 5. The dual role of autophagy in cancer. The double-edged nature of autophagy in tumor microenvironment demonstrates that it might function as a suppressor or promotor, depending on the type and stage of cancer. (A) On the one hand, autophagy suppresses tumor initiation and its deficiency may lead to tumorigenesis. Impaired autophagy shows increased DNA double-strand breaks and ROS production in defective cells via the accumulation of p62/SQSTM1 and other misfolded proteins which subsequently promotes tumorigenesis. Autophagy may also function in tumor suppression by mitigating tumor-associated necrosis and inflammatory response which is associated with release of HMGB1. (B) On the other hand, in hypoxic microenvironments, HIF-1 triggers hypoxia-induced autophagy to protect tumor cells from death. During this condition, HIF-1/HRE interactions contributes to oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis transition which subsequently increases REDD1, AMPK, and BNIP3 to promote tumorigenesis via suppression of apoptosis-related factors (FADD/caspase-8 complex) or degradation of cellular lysing proteases (granzyme B).
There is a substantial body of evidence indicating that autophagy plays a crucial role in promoting tumor development and survival, particularly in advanced malignancies (243, 244). This process is often triggered by hypoxic conditions within the central regions of solid tumors, which leads to the activation of autophagy. Deletion of the essential autophagy regulator Beclin-1 has been shown to suppress autophagy and increase cellular death (143, 245). Moreover, autophagy also supports the high metabolic and energy demands of rapidly growing malignancies by recycling intracellular components to provide essential metabolic substrates (24, 142).
Oxygen content is a critical metric influenced by the heterogeneity of tumors. Within the tumor, there are regions where oxygen content is less than 2%, creating a hypoxic zone (246). These hypoxic circumstances activate cellular pathways to maintain homeostasis. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) is the major transcriptional regulator under hypoxic settings. HIF-1 is a complex composed of two subunits, α and β. Under normoxic conditions (oxygen-rich), the α subunit degrades (247, 248). However, during hypoxia, the ubiquitylation of the α subunit decreases, leading to increased stability of HIF-1. HIF-1 binds to hypoxia-responsive element DNA sequences, which promotes a metabolic shift from oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) to glycolysis (249). Regardless of oxygen concentration, HIF-1 upregulates the expression of approximately 80 genes essential for glucose metabolism, cell survival, tumor angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis in tumor cells (249). HIF-1 increases AMPK in response to hypoxia or starvation, which further initiates autophagy through BINP3/Beclin-1 or mTOR suppression (250). In hypoxia, HIF-1 also promotes transcription of the regulated in development and DNA damage response 1 (REDD1), which activates the TSC1/2 complex, hence reducing mTOR activity and promoting autophagy (251). HIF-1 also increases the transcription of the gene encoding the Bcl-2/adenovirus E1 19kDa interacting protein 3 (BNIP3) that triggers mitophagy by releasing Beclin-1 from Bcl-2 family members, hence initiating autophagy (247) (Figure 5B). It has been demonstrated that hypoxia-induced autophagy may serve as a protective mechanism against apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells during periods of nutritional restriction, potentially through a Beclin-1-dependent pathway (252).
There are several reports suggesting the implications of autophagy as a preservative mechanism of tumor cells against immune responses. In a recent study, the protective role of autophagy in limiting T cell-mediated killing of tumor cells by TNF-α has been elucidated via suppression of FADD/caspase-8 complex activation (253). In addition, autophagy can limit the anti-tumor effect of NK cells in breast cancer cells via degradation of granzyme B in a hypoxic condition (Figure 5B) (254). Another mechanism of immune invasion is described in pancreatic cancer cells which involves degradation of MHC-I molecules in lysosomes to reduce the presentation of tumor cells following autophagy activation (255).
Autophagy is also enhanced in RAS-mutated cancer cells, which maintain a high basal-level of autophagy. RAS are small GTPases that participate in crucial signaling pathways for proliferation, survival, and metabolism (131, 256, 257). A mutation that activates RAS increases autophagy, which promotes tumor growth, survival, and oncogenesis, and is linked to the emergence of many lethal malignancies, including lung, colon, and pancreatic cancer (133–135, 258). Several studies have demonstrated that RAS-activating mutant cells exhibit an increased level of autophagy, which is essential for their survival during periods of nutrient deprivation (136, 259). Furthermore, inhibition of autophagy-related proteins leads to the accumulation of damaged mitochondria and a subsequent decrease in cell growth (141, 260, 261). Therefore, these findings demonstrate that autophagy plays a significant role in the survival of RAS-dependent tumor cells and can play a significant role in tumor promotion.
In addition to maintenance and differentiation of normal stem cells, autophagy is strongly correlated with cancer stem cell survival and maintenance, leading to tumor progression to secondary metastatic sites and therapy resistance.
Metastasis is influenced by several biological factors encompassing both intrinsic properties of cancer cells, including their migratory, invasive, and intracellular signaling abilities, as well as extrinsic properties of the microenvironment, such as the extracellular matrix (ECM) composition, interactions with other cell types, and vascular access, all of which collectively govern nutrient and oxygen availability (133). Given the many challenges that metastatic tumor cells must overcome in order to successfully establish distant colonies (such as invasion, anoikis resistance, and colonization) and the essential role of autophagy as a response to cellular stress, various roles for autophagy in the metastatic cascade have been hypothesized as mechanisms of tumor cell survival (39). Indeed, several environmental stresses known to promote metastasis, such as hypoxia, as well as those encountered by disseminated tumor cells, such as nutrition deprivation (262) and detachment from the ECM, activate autophagic flux (263–266). Currently, available data supports the notion that autophagy plays two distinct roles in cancer metastasis: either as a promotor or inhibitor, depending on the type of tumor cell, the tumor microenvironment and the steps of metastatic cascade (12, 13).
Despite the fact that we are currently unable to directly quantify autophagic flux in primary human tumor samples, several studies using surrogate markers have shown a relationship between enhanced autophagy and metastasis. Actually, autophagy-mediated metastasis promotion is achieved through two distinct mechanisms: 1. Disassembly of direct cell-to-cell contact 2. Enhanced secretion of pro-invasive factors. The dissemination and migratory abilities of tumor cell could be augmented by the detachment of adhesion molecules between tumor cells and migratory cells. Another important factor is the secretion of soluble components like interleukin 6 (IL-6), matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP2) and Wnt family member 5a (WNT5A) for induction of paracrine effects on recipient cells (267). These data suggest that autophagy is essential for invasive capacity of tumor cells.
Research on human breast and melanoma cancer revealed that higher light chain B (LC3B), as an autophagosome marker, punctate staining was associated with lymph node metastasis and decreased survival (268, 269). While melanoma metastases revealed enhanced LC3B staining as compared to original tumor samples with the same characteristics (268, 270, 271). LC3B expression has been discovered to be associated with metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Specifically, increased LC3B staining has been observed in metastases compared to original tumors, as well as in early metastatic colonies compared to late metastatic colonies (272, 273). Increased expression of an autophagy gene signature was related with a more aggressive and invasive glioblastoma phenotype (274).
Numerous investigations have demonstrated an association between autophagy and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in cancer, a process that facilitates the migratory capacity of tumor cells for invasion when their epithelial characteristics are lost for the acquisition of mesenchymal characteristics. During the metastatic phase, EMT-activated cancer cells have a high amount of autophagy to survive under several stressful situations (260, 261, 275). Another study showed that Cadherin-6, a type 2 cadherin that causes EMT during embryonic development, is abnormally increased in cancer and linked with cancer progression (276).
While autophagy promotes tumor growth and results in therapy resistance, new evidence has surprisingly demonstrated that autophagy suppresses the proliferation of disseminated tumor cells. According to one study, the activation of autophagy by nutrient deprivation and mTOR inhibition decreased glioblastoma cell migration and invasion. In addition, reduction of autophagy-related proteins, including Beclin-1, Atg5, and Atg7, enhanced the migration and invasion of glioblastoma cells with EMT regulators (277). It has been shown that in vitro and in vivo models of breast cancer metastasis could be inhibited through autophagy induction by CLDN6 as a component of actin cytoskeleton (278). Unexpectedly, a mammary cancer model experiment disclosed the contrary impacts of autophagy on cancer cells. While autophagy stimulates primary tumor expansion, metastatic growth is attenuated (279).
Collectively, these findings emphasize that due to the multi-faceted roles of autophagy during cancer progression, the prediction of overall outcome on tumor cells’ fate is dependent on the type of affected cell and the tumor stage, which requires to be evaluated on a context-dependent manner.
Cancer is a prevalent health concern on a global scale, accounting for approximately one-sixth of all fatalities across the world (280). The process of treating cancer has been characterized by a high degree of complexity (280). The treatment of cancer encompasses a diverse range of methods, such as surgical intervention, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy (280, 281). The selection of therapy is contingent upon the classification of neoplasm, its degree of advancement, and the general well-being of the individual (281). Tumors are frequently excised through surgical intervention, whereas cancer cells are targeted for destruction through chemotherapy and radiation therapy (281). Immunotherapy facilitates the recognition and eradication of cancerous cells by the immune system, whereas targeted therapy selectively targets molecules that are essential for the growth and survival of cancer cells (281). Combination therapies, comprising the utilization of multiple treatments, are frequently employed to attain optimal therapeutic results (281). As per the American Cancer Society, enhancements in the treatment of cancer have resulted in better survival rates and enhanced quality of life for individuals diagnosed with cancer (281).
The idea would have been that inhibiting autophagy in addition to conventional chemotherapy would be effective for treating tumors due to the survival benefits of autophagy that were originally shown in vitro (282). Nevertheless, several studies have shown that pharmacologically inhibiting autophagy using chloroquine may be advantageous for the treatment of tumors (283, 284). However, one can argue that promoting autophagy would be the best course of action when we take into account the potential implications this may have on a necrosis-driven pro-tumorigenic inflammatory response or the effects on preventing cellular senescence (282). According to prior research, two fundamentally distinct aspects of inhibiting or stimulating autophagy for the treatment of cancer are reviewed separately in this article.
Autophagy inhibition may be beneficial for cancer therapy, although also raises problems (285). Targeting alternative cell death pathways is an appealing method for enhancing anti-tumor therapy since apoptosis abnormalities are common in many solid tumor cells and can enhance tumor cell resistance to numerous traditional cancer therapies (286). Therefore, in cancer cells, the control of autophagy acts as a defense mechanism against chemotherapy (287). Autophagy inhibition in cancer therapy has drawbacks. For instance, given autophagy’s tumor-suppressive and protective effects in other systems (such as neurodegeneration, aging, and infectious illnesses), there are worries that inhibiting autophagy may increase the occurrence of secondary cancers or other disorders in treated individuals (154).On the other hand, the therapeutic benefits of chemotherapy and radiation are often counteracted by autophagy, which results in drug resistance (288). Restoring the vulnerability of tumor cells thus poses a prospective target for hematological malignancies (288). Autophagy decreases oxidative stress, inflammation, p62 accumulation, and genomic instability, which may suppress tumors in some model systems (285). Human cancer cells treated with HDAC inhibitors, arsenic trioxide, TNF-α, IFN- γ, rapamycin, and antiestrogen hormonal therapy activate autophagy as a pro-survival strategy, suggesting that inhibiting autophagy might make cancer cells more sensitive to these treatments (289–294). Autophagy serves as a cellular protection and defense mechanism that prevents cancer cell death during treatment, induces a state of dormancy in residual cancerous cells following treatment, promotes cancer-related recurrence and metastasis, and impedes cancer therapy and tumor cell eradication (283, 295).
It may not be possible to determine the side effects of systemic autophagy inhibition throughout the course of cancer treatment (154). However, recent research found that inhibiting autophagy might reduce chemotherapeutic responses by obstructing autophagy-dependent immune responses that fight cancer (6). Autophagy enhances tumor-cell survival under metabolic stress but also inhibits carcinogenesis, necrosis, and inflammation in one animal model when tumor cells have a deficiency in the apoptotic pathway, and autophagy regulation is a promising prospective method for improving cancer treatment (296–298). While the biological consequences on tumor cell behavior may change when the autophagy pathway is stopped at different stages of cancer, inducing autophagy may help prevent cancer since it suppresses tumors (222). What is more, Inhibiting autophagy and alkylating drugs enhance apoptosis and cell death (222).
Autophagy plays a cytoprotective or pro-survival role in cancer cells and can be induced by most cancer treatments including radiation therapy, chemotherapy, histone deacetylase inhibitors in colon cancer cells, arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in malignant glioma cells, Temozolomide (TMZ) in malignant glioma cells (299–306). Despite the fact that autophagy is upregulated in both tumor and normal cells exposed to cancer therapy, tumor cells rely more heavily on the cytoprotective benefits of autophagy than normal cells do (307). Certain chemotherapeutic drugs, such as etoposide, fenretinide, and dexamethasone, were discovered to induce autophagic cell death in cancer cells lacking critical apoptotic modulators such as BAX, BAK, or caspases in vitro (308–311). Both in vivo studies have shown that resveratrol and fisetin induce autophagic cell death in prostate cancer and Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia cell lines (312). Studies on malignant glioma cell lines, including U87MG and T98G, along with normal human astrocytes, have demonstrated that sodium selenite can selectively induce mitophagic cell death in glioma cells while sparing normal astrocytes. These observations signal that sodium selenite could become a promising therapeutic strategy for glioblastoma, presenting a mitochondria-selective way of inducing autophagic cell death (313, 314).
As a synthetic guanidine derivative, metformin is used to treat the symptoms of diabetes (287). By activating autophagy in cancer cell lines and animal models, metformin also has anticancer effects (287). In endometrial cancer cells, metformin produces cell cycle arrest, which prevents cell viability and proliferation, and promotes apoptosis by triggering autophagy (315). Additionally, metformin induces the autophagic flow by increasing the levels of LC3-II and decreasing the levels of p62, which leads to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in TRAIL-resistant lung cancer cells (316).
In this section of the article, we have discussed various therapeutic issues in the field of autophagy. We have pointed out the importance of cancer prevention by promoting autophagy. In addition, we have expanded the discussion about the effect of autophagy inhibition on anticancer therapy. Moreover, we have investigated the signaling pathways related to the initiation and inhibition of autophagy. In addition, we have written a detailed discussion on the suppression of autophagy by chloroquine (CQ) and hydroxychloroquine (HCQ). Finally, we have introduced a future prospective view of new medications.
The fact that approximately 70% of clinical studies are dedicated to exploring the role of autophagy in cancer indicates the promising potential of modulating autophagy for cancer treatment. Clinical trials have been designed to investigate the impact of autophagy modulation in combination with conventional therapies (317). Thirty-six genes involved in the autophagy pathway are associated with the risk, diagnosis, and clinical outcome of 30 different types of cancer (318). Therefore, a potentially effective strategy for treating cancer could involve targeting autophagy through a combination of autophagy modulators and chemotherapeutic agents.
Polymorphisms in autophagy genes, including certain ATG SNPs, predispose individuals to develop a wide variety of diseases such as cancer. Notably, PIK3C3 SNPs are more frequently found in different gastrointestinal cancers (319, 320). Similarly, variations in all components of the ATG12 conjugation system are linked to different solid tumors (321–323), highlighting the significance of autophagy in the development of cancer.
Various clinical trials are testing the efficacy of anticancer therapies utilizing autophagy modulators. PI3K and MTOR inhibitors have been implemented in hematological malignancies such as CLL and T-ALL, as well as hepatocellular carcinoma (324–326). Moreover, the interplay between autophagy and apoptosis plays a significant role in multiple myeloma (MM) progression and drug resistance. A potential approach to combat MM cell survival may include inhibiting autophagy to trigger apoptosis (327).
However, predicting the therapeutic response of diseases to autophagy alteration is context-dependent and whether autophagy acts as a tumor suppressor or an oncogenic factor. It is crucial to determine precisely when to regulate to achieve optimal effects as an adjuvant therapy for tumors. Therefore, to achieve more effective personalized treatment responses, further investigation and research into strategies for activating or inhibiting autophagy are necessary under different conditions.
Currently, preventive treatments are important in the management of cancer, including its hereditary types. The development of endocrine resistance poses a significant challenge in the management of breast cancer that is positive for estrogen receptor expression (328). The relationship between autophagy and endocrine resistance is not yet fully understood, despite the growing attention given to autophagy as a potential contributing factor (328). The administration of Tamoxifen (Tam) induces autophagy and influences the lysosomal compartment of MCF7 cells (328). This results in the activation of autophagy, which facilitates the elimination of Tamoxifen-damaged lysosomes through lysophagy (287, 328, 329). The MCF7-TamR cells, which are resistant to 5 µM tamoxifen, exhibit an increased autophagic flux and greater resistance to Tam-induced lysosomal alterations in comparison to the parental cells (328). This indicates a potential correlation between these two phenomena (328). Autophagy inhibition re-sensitizes MCF7-TamR cells, which overexpress metallothionein 2A and ferritin heavy chain mRNAs (328). In parental MCF7 cells, overexpressing these proteins protects lysosomes against Tam-induced damage and retains survival, but suppressing autophagy removes protection (328). Chiara Actisshow and colleagues showed that additional breast cancer cells that overexpress certain iron-binding protein mRNAs are less vulnerable to Tam-induced lysosomal degradation when autophagy is initiated (328).
Nonetheless, it should be noted that there exists solely a correlative association between the decrease in cancer incidence and the implementation of autophagy-promoting strategies (154). If autophagy upregulation has a mechanistic role in the effectiveness of such cancer prevention measures, further research is needed to confirm this (154). If true, using more direct autophagy activators could provide a workable new alternative cancer prevention technique (154).
Anticancer therapies are made more effective in a variety of cancer cells by suppressing autophagy via genetic or pharmacological means (330–332). Different autophagy inhibitors may be used alone or in conjunction with other anticancer medications for the treatment of cancer. In this regard, by increasing caspase activity and decreasing cell survival, the suppression of autophagy by Atg5 and Beclin-1 siRNA improves cisplatin sensitivity in lung cancer cells (333). Similarly, 3-methyladenine (3-MA), an autophagy inhibitor, promotes hypoxia-induced apoptosis in colorectal cancer by suppressing autophagy (334). In addition, the effectiveness of enzalutamide (ENZ) in bladder cancer is limited by the resistance that is induced by an increase in AMPK, Atg5, LC3B, and ULK1 levels due to the stimulation of autophagy (335).
In many cancer cells, the cholesterol-lowering drug atorvastatin (ATO) exhibits anticancer effects (287). The stimulation of apoptosis-related proteins such as caspase-3, PARP, and Bim by ATO reduces cancer development and increases apoptosis in cervical cancer cells (287). Autophagy is induced as a side effect of ATO therapy, which limits the therapeutic impact of cancer medications. Combining ATO with an autophagy inhibitor, such as 3-MA or Bafilomycin A1 (Baf A1), enhances ATO-induced apoptosis in cervical cancer cells (336). Reactivation of p53 and induction of tumor cell apoptosis (RITA) is a small chemical that disrupts the link between p53 and mouse double-minute 2 homolog (MDM2) and exhibits anticancer benefits by exclusively causing apoptosis, however, resistance to the drug is a significant obstacle in the treatment of cancer (287). Through the suppression of autophagy and promotion of apoptosis, the combination therapy with RITA and 3-MA has excellent therapeutic effects on cisplatin- and RITA-resistant head and neck cancer cells (337).
Baf A1 demonstrates autophagy suppression and augmentation of apoptosis (287). However, the therapeutic benefit of Baf A1 is only seen at high doses, and its use is restricted owing to the possibility of toxicity (338). Baf A1 inhibits autophagy, targets mitochondria, and induces apoptosis to have therapeutic benefits in juvenile B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) at low doses (339). In bladder cancer, cisplatin causes autophagy to become activated, which then results in cisplatin resistance (340). By preventing autophagy, Baf A1 therapy enhances the therapeutic effects of cisplatin (287). Because autophagy plays a role in the development of 5-FU resistance in gastric cancer, treating the disease with Baf A1 in combination reduces autophagy, which suppresses autophagy and reduces the capacity of cancer to clone, invades, or migrates (341). Another study found that in BRAF-mutant melanoma, cytoprotective autophagy plays a key role in the development of resistance to BRAF inhibition (342). This result was particularly noteworthy since, despite extensive research on the role autophagy plays in PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling resistance to targeted therapeutics, the role of autophagy in MAPK pathway suppression has received less attention (343, 344).
Signaling pathways are very important in understanding a biological phenomenon, according to changes in these pathways, a disease may start or cure. Today, the main basis of some treatments is based on major or minor changes in biological signaling pathways. A prospective chemotherapeutic target that is often activated in various tumors is the PI3K/mTOR pathway (345, 346). PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling is dysregulated in human cancers, and mTOR inhibition induces autophagy (347). In a mouse model, treatment with mTOR inhibitor rapamycin was connected to a 90% decrease in lung cancers brought on by carcinogens (348). Similarly, in the same tumor model, metformin’s inhibition of mTOR signaling reduced tumorigenesis (349). In addition, ongoing low-dose rapamycin therapy significantly reduced intestinal neoplasia in APCMin/+ mice with increased AKT-mTOR signaling (350).
Through a range of signaling pathways, including the DNA damage response, mTOR and AMP-activated protein kinase signaling, the ER stress response, and others, traditional cytotoxic chemotherapeutics and tailored treatments promote autophagy (351). Unc-51-like kinase 1 (ULK-1) is a small molecule inhibitor of ULK1 that, in response to various stimuli, suppresses both autophagy and autophagy flux (352). There are only two serine/threonine kinases in the autophagy pathway, ULK1, and ULK2, which makes them a great target for therapeutic intervention (353). Inhibitors of ULK1 kinase that compete with ATP include the selective SBI-0206965 (SBI) (353). The combination of SBI and mTOR suppresses and controls autophagy and works in concert with other common chemotherapies, such as mTOR inhibition (353, 354). The mTORC1 inhibitors temsirolimus and everolimus, promote autophagy (18).
SAR405 is a PIK3C3 low molecular mass kinase inhibitor that prevents autophagy by reducing PIK3C3’s catalytic activity (355). SB02024 was demonstrated to successfully inhibit autophagy, decrease breast cancer xenograft models, and work in synergy with other treatments in vitro (356). VPS34 inhibitors have been created, including SB02024 and VPS34-IN1 (357). Inhibitors of ULK1 and VPS34 have also been demonstrated to be efficient in CNS tumor cells that depend on autophagy (358).
To determine autophagy reliance, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations or amplifications have also been used (222). Numerous downstream pathways, including PI3K-AKT-mTOR, STAT3, and RAS family signaling, are regulated by EGFR and have an impact on autophagy (359). Radio resistance is linked to EGFR mutations and amplifications in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas and glioblastoma (GBM) (222). These cancers respond to pharmacological inhibition of autophagy and are highly autophagy-dependent (360).
The least Drugs including rapamycin analogs (mTOR inhibitors), class I PI3K inhibitors, and metformin (an AMPK activator) have been shown to suppress malignant transformation when they pharmacologically activate autophagy (58, 361, 362). Additionally, Atg7 inhibitors might theoretically also be used to target the conjugation machinery (222). It has been demonstrated that Atg7 can be genetically targeted to stop this enzyme in cancer cells (363, 364).
With therapeutic effects on leukemic cell lines and B-cells generated from patients through inhibition of the PI3K/AKT pathway and activation of autophagy, quercetin is a natural flavonol and a multi-kinase inhibitor that restores the sensitivity to ABT-737 (365). ABT-737 and its derivatives (ABT-263 and ABT199) inhibit the interaction between Beclin-1 and Bcl2 to induce autophagic-like cell death, which has anticancer effects on glioblastoma cells (366). As a possible ALK/IGF1R inhibitor, AZD3463 demonstrates an anticancer impact and, via controlling the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, triggers apoptosis and autophagy (367). Through the activation of apoptosis, autophagy, and a decrease in cell proliferation in breast cancer cells, the co-treatment of AZD3463 with rapamycin boosts the effectiveness of anticancer therapy (368).
The flavonoid isoliquiritigenin (ISL), which is produced from Glycyrrhiza glabra, has anticancer properties both in vivo and in vitro (287). By altering the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, ISL causes the suppression of cell development by boosting apoptosis and autophagy (287). By promoting ISL-mediated apoptosis, the autophagy inhibitor HCQ enhances the therapeutic impact of anticancer treatment against HCC (367).
Autophagy was directly suppressed by chloroquine (CQ) and hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), which have previously been used to prevent and cure malaria (369), by altering lysosomal pH, stopping autophagic breakdown, and increasing autophagosomal accumulation (370, 371). The autophagy inhibitors CQ and HCQ are utilized in conjunction with various targeted regulators or chemotherapeutics, such as bortezomib and cyclophosphamide (372). Temsirolimus (CQ: antimalaria agent), everolimus (HCQ: CQ derivative), and hydroxychloroquine (HCQ: CQ derivative) are some of the autophagy regulators and apoptosis triggers utilized in cancer treatment including bladder cancer (369, 373). Similar to CQ, HCQ is a weak basic tertiary amine that may build up in the lysosome’s acidic environment, where it is protonated and prevents lysosome diffusion (374, 375). The lysosome’s pH rises consequently, inhibiting lysosomal activity and autophagy in the process (375). Combining CQ or HCQ with metabolic stresses (such as an angiogenesis inhibitor or 2-deoxyglucose) or targeted therapeutic medications (such as imatinib, a Bcr-Abl inhibitor) has also been shown to increase the risk of cell mortality (376, 377). CQ and HCQ have decreased cancer cell proliferation in the bladder and pancreatic adenocarcinoma preclinical tests (369, 373).
Arsenic trioxide is one example of a common medication that causes autophagy rather than cell survival (372). Therefore, when autophagy acts as a pro-survival mechanism in response to a particular treatment strategy, autophagy inhibitors should be utilized (288).
CQ’s inhibition of autophagy in preclinical models enhances tumor cells’ reactivity to alkylating drugs, indicating that autophagy aids in survival (284). Autophagy induction is similar between HCQ and CQ, despite the fact that HCQ is less toxic (378). Combination therapy with ENZ and CQ enhances the therapeutic efficiency by decreasing tumor growth and inducing apoptosis, which is achieved by genetic suppression of autophagy using Atg5 siRNA (335).
It has also been shown that CQ may increase the apoptosis and the therapeutic benefits of PS-PDT in colorectal cancer cells via inhibiting autophagy (379). CQ and HCQ suppress autophagy by reducing autophagosome/lysosome fusion (380). CQ also has autophagy-independent anti-cancer properties and can sensitize cancer cells to treatment (381–383). Patients’ clinical results were noticeably improved in the first clinical study of CQ for the treatment of GBM patients (384).
Autophagy inhibition changes normal and malignant cell responses to other therapies, hence the maximum tolerable dose (MTD) of HCQ varies with concurrent therapy (222). In studies with HCQ with targeted treatments like vorinostat, the MTD was 600 mg twice daily, whereas, with cytotoxic chemotherapy like temozolomide and radiation in GBM, the MTD was 400 mg twice daily (385). As a single agent, HCQ’s MTD is unknown, and 600 mg twice daily in adults is the greatest dosage studied to date, however, autophagy inhibition was not consistently attained at that level (385).
Pharmacokinetic investigations in dog lymphoma patients utilizing HCQ and doxorubicin showed a 100-fold increase in tumor HCQ compared to plasma concentrations, suggesting a divergence between tumor exposures and evaluating autophagy inhibition in PBMCs as a proxy for efficacy (381).
Examples of completed research include a Phase I study that combined HCQ with bortezomib, a proteasome inhibitor, in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma, and found that the combination had a better impact than bortezomib alone in the past (386, 387). Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) patients who had progressed through multiple lines of therapy and were given only HCQ as monotherapy in a Phase II trial showed no objective responses, but it’s possible that this was due to the fact that these patients were heavily pretreated population and didn’t receive HCQ for a long enough duration to achieve therapeutic doses of the drug (388). Preoperative HCQ and gemcitabine treatment exhibited responsiveness to the CA19-9 tumor marker and improved overall survival when compared to historical controls in Phase I and II trials of HCQ-mediated autophagy suppression in PDAC (389).
In a phase I clinical study, HCQ and chemotherapy drugs together improved 18 patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma’s median progression-free survival (mPFS) and overall survival (OS) (390). A study was conducted to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of combining HCQ with the histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat (VOR) in 19 patients diagnosed with metastatic colorectal cancer (391). In patients with refractory colorectal cancer, the combination therapy demonstrated 2.8 months progression-free survival (mPFS) and 6.7 months OS, confirming its safety and well-tolerance in these patients (287, 391).
Thirty-five patients with borderline resectable pancreatic adenocarcinomas were treated in a phase 1/2 experiment with doses of fixed-dose gemcitabine (1500mg/m2) and HCQ at a dosage of 1200 mg per day until the day of surgery (389). The experiment proved safe and well-tolerated pre-operative autophagy suppression with HCQ with gemcitabine (389). The fact that 29 out of 35 patients received surgical resection and 19 out of 35 patients demonstrated a drop in surrogate biomarker response suggests autophagy inhibition with HCQ might have a beneficial effect (389).
Everolimus, also known as RAD-001, is a rapamycin derivative (287). In endometrial cancer and HEC01A cells, RAD-001 increases susceptibility to paclitaxel-induced apoptosis by inducing autophagy through the downregulation of AKT/mTOR phosphorylation and accumulation of LC3 (392). In pancreatic cancer PC-2 cells, rapamycin generates autophagic vacuoles, which inhibit proliferation and triggers death (393). It also increases the expression of Beclin-1 in a dose-dependent way (393). Everolimus was evaluated in phase I clinical study on women who had lymphangioleiomyomatosis, together with the autophagic flux inhibitor HCQ (287). Patients with advanced cancer have undergone testing combining rapamune (also known as rapamycin; commercial name) with HCQ (287).
It is crucial to highlight that in vivo genetic proof that the effects of CQ in these conditions were via regulation of autophagy has yet to be demonstrated (222). CQ’s effects, however, are not confined to autophagy suppression, causing, among other things, inhibition of lysosomal activity generally (222). In this context, it is noteworthy that a separate investigation into the therapeutic efficacy of CQ found prodeath consequences of autophagy (222). In this situation, the cell death brought on by CQ treatment was decreased by caspase inhibition in an autophagy-deficient background but not in autophagy-competent cells (222). This would suggest that autophagy is somewhat required for cell death downstream of CQ in this environment (222). In Table 1, the clinical trials investigating the effects of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine on various cancers are presented.
Next-generation lysosomal targeted inhibitors that are more effective and selective are now being developed, including Lys05, a bisaminoquinoline, and DQ661, a dimeric quinacrine with the added advantage of concurrent lysosome and mTOR inhibition (394). Lys05, which is around ten times more powerful than CQ, has shown effective in controlling the formation of colorectal adenocarcinoma and melanoma in animal models Due to a larger concentration in and deacidification of the lysosome, Lys05 is a more powerful autophagy inhibitor than HCQ (395). CQ inhibits autophagy by preventing autophagosome-lysosome fusion, unlike Lys05 (380). In melanoma and colon cancer xenograft models, Lys05 demonstrated more anticancer effects than HCQ both in vitro and in vivo (381, 395).
Additionally, DQ661 has demonstrated significant in vivo single-agent effectiveness against melanoma and colorectal cancer, as well as in vivo efficacy against PDAC when combined with gemcitabine as a single treatment, HCQ has demonstrated very modest clinical responses in cancers such as advanced metastatic pancreatic cancer (394).
There exist supplementary techniques to modulate autophagy, such as the utilization of epigenetic modifiers (222). The regulation of autophagy via epigenetic mechanisms has been evidenced by the acetylation of histones, hyper-methylation of CpG islands, and interference with mRNA activity caused by noncoding RNAs in the cytoplasm (396). Histone deacetylase inhibitors used to treat malignant nerve sheath tumors increased autophagy and therapy resistance (397). Consequently, the search for additional CQ analogs like Lys05 and medicines that affect other parts of the autophagic pathway is at an all-time high (398).
Cancer cells may rely on noncanonical mechanisms such as LC3-associated phagocytosis that have been overlooked in the rush to target the canonical autophagic route (399). Some dietary phytochemicals, including quercetin, apigenin, genstein, hesperein, and luteolin have recently been proven to trigger autophagy in normal cells as well as numerous types of cancer cells (400, 401).
Autophagy addiction, also known as autophagy-dependence, is essential because only autophagy-dependent tumors react strongly to autophagy inhibition, even when the same medicines with CQ are tried (402). The effect of other drugs and autophagy inhibitors is additive in autophagy-dependent tumor cells, while these drugs have an antagonistic effect on autophagy-independent tumor cells (402, 403).
BrafV600E-driven lung and melanoma mouse models were among the first to show autophagy dependency and sensitivity to Atg7 deletion (363, 404). Following clinical studies, PDAC patients treated with gemcitabine, nab-paclitaxel, and HCQ had better surgical results (389, 405). Recent studies showed the advantage of inhibiting autophagy together with MEK or ERK to target the RAS pathway (406, 407). Multiple cancer cell lines have been treated with recombinant Bacillus caldovelox arginase mutant (BCA-M), which is effective in anticancer treatment by slowing the proliferation of human cervical cancer cells (408). Through the reduction of growth, an increase in apoptosis, and cell cycle arrest, BCA-M demonstrated beneficial therapeutic effects on cancer cells in phase III clinical study (287). Additionally, by lowering autophagy, combined therapy with BCA-M and CQ enhances the therapeutic benefits of BCA-M (287).
Class III PI3K kinase complexes are removed by proteasomal degradation when Spautin-1, a protein that normally suppresses autophagy, is present (409). Spautin-1’s ability to promote apoptosis is linked to GSK3β, a key downstream effector of PI3K/AKT (409).
SAR405 also inhibits Vps18 and Vps34 kinases, impairing lysosomal function and interfering with the late endosome-lysosome interface (410). The combination of SAR405 with everolimus has been shown to increase the suppression of kidney cancer cell growth (410). Furthermore, Vps34 inhibitor SAR405 has anticancer therapeutic benefits, as shown by these data (18). Everolimus and SAR405 therapy combined results in a synergistic anticancer impact by reducing kidney cancer cell growth (410). By inhibiting autophagy by specifically targeting Vps34, SB02024, a novel, and highly effective selective inhibitor, increases sensitivity to sunitinib and erlotinib (356).
Doxorubicin is a DNA-damaging drug that causes aberrant mitochondrial activity and the creation of superoxide to have an anticancer impact (411). Doxorubicin sensitivity is restored in colorectal cancer stem cells by inhibiting mitophagy by silencing BNIP3L, a key regulator of mitophagy (412).
Foxk proteins (Foxk1 and Foxk2) functioning as transcriptional repressors of autophagy genes have been used to illustrate the transcriptional control of autophagy (413, 414). In nutrient-rich environments, mTOR stimulates Foxk1’s transcriptional activity, which leads to Foxk1 and Sin3A co-localizing at the promoters of 79 known autophagy-associated genes (413). Intriguingly, Foxk1 siRNA ablation led to the overexpression of essential Ulk1 and Vps34 machinery, highlighting the detrimental effect Foxk1 transcriptional activity has on autophagy (414). Studies, that starvation triggers a transcriptional mechanism predominantly controlled by the transcription factor EB (TFEB), which results in the activation of autophagy and lysosomal genes to help the cell survive, autophagy has been connected to lysosomal biogenesis (415). TFEB, when overexpressed, greatly increases the number of autophagosomes in cells (413).
The mice models outlined for examining the potential impact of mutant p53 on the susceptibility to autophagy-based treatment have been supplemented by the discovery that P53 plays a function in the transcription of autophagy genes (413). Global genomic profiling of mouse embryo fibroblasts showed p53 to transcriptionally control a large number of autophagy genes, with p53 transcriptional activity being required for the activation of autophagy in response to DNA damage (416). It is important to note that autophagy has been shown to continue even in the absence of functioning p53, indicating that p53 plays a role in the intricately choreographed symphony that is autophagy rather than just regulating it (417).
In autophagic cells, the epigenetically determined acetylation state of histone H4 lysine 16 (H4K16) controls choices about life and death (418). When autophagy is induced, H4K16 acetylation (H4K16ac) declines, which in turn reduces the expression of ATG genes throughout the whole genome (418). An increase in autophagic cell death is caused by reversing the decrease in H4K16ac that occurs when autophagy is induced (418).
Mitophagy is reduced by mitochondrial division inhibitor 1, or mdivi-1, a specific inhibitor of dynamin I and the mitochondrial division-related protein DRP1 (419). Mdivi-1’s suppression of mitophagy improves silibinin-mediated apoptosis in breast cancer (419) (Table 2).
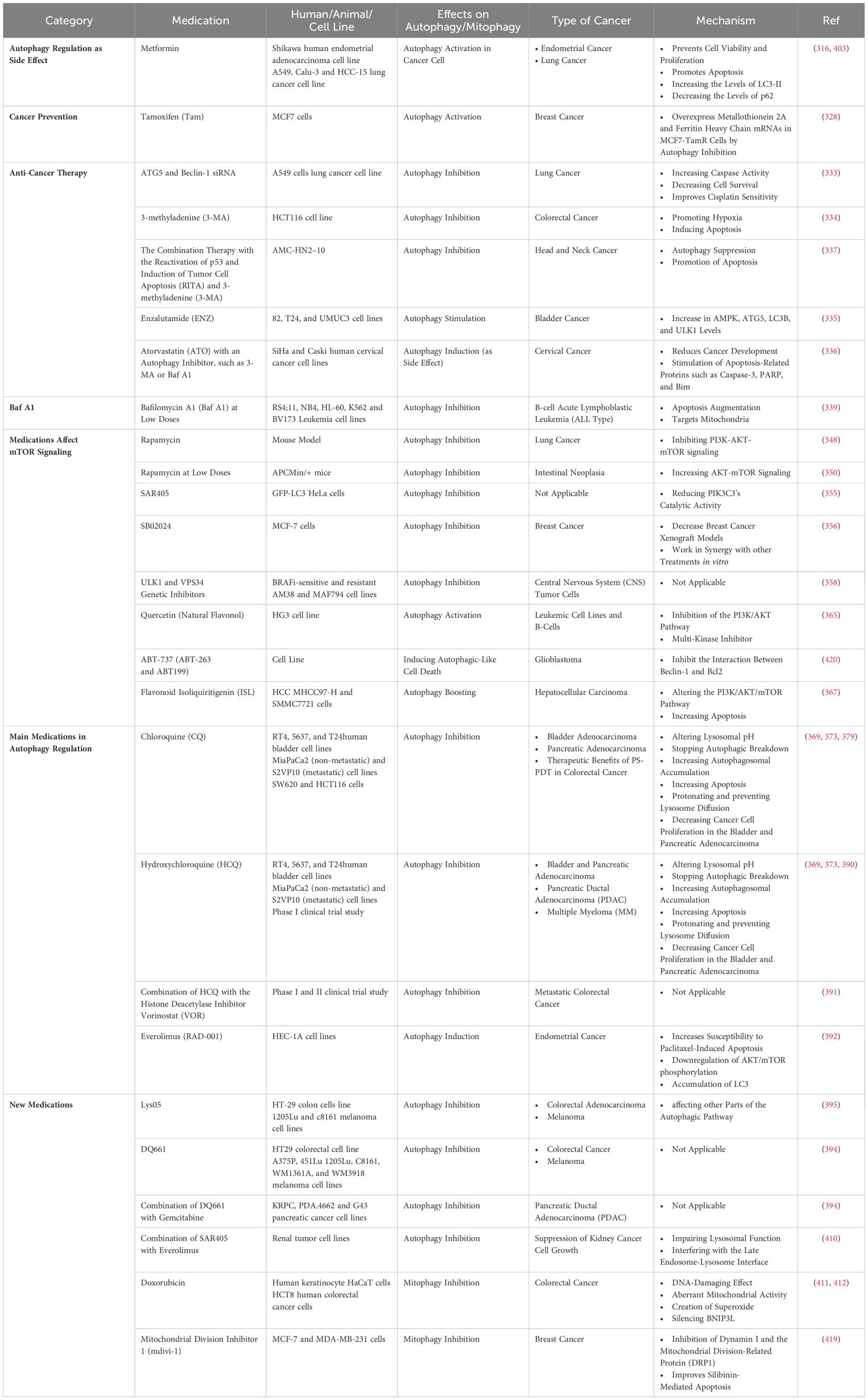
Table 2. the effects of autophagy-mediated medications in different types of cancer and their mechanisms.
Further research is necessary; however, other pharmacological autophagy activators could possibly be helpful for cancer chemoprevention. Most of these medications lack anticancer activity and selectivity (421). Given the many studies demonstrating that autophagy is triggered as a survival response to antineoplastic treatment, the bulk of the trials has combined HCQ with other antineoplastic regimens, such as chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and radiation therapy (386). As a result, new biomarkers and methodologies are needed (386). Autophagy inhibitory effects of CQ and HCQ in clinical studies have yet to be determined, even though these compounds have been shown beneficial in vitro (374). In addition, the pharmacokinetics of HCQ make it difficult to achieve appropriate micromolar dosage levels during short periods (422, 423). Targeting downstream ubiquitin-like conjugation machinery, including Atg7, maybe a potential therapeutic method (374). Autophagy plays a critical part in normal tissue homeostasis; therefore, potency and toxicity must be balanced (374).
In cancer biology, autophagy is crucial for the expansion and multiplication of cancer cells as well as the control of tumor formation (27, 28). The modulation of autophagy has the potential to impact the manifestation of tumor suppressor proteins or oncogenes. In addition, manipulating autophagy through specific anticancer drugs can potentially promote either the viability or demise of malignant cells (29, 424). Autophagy is a cellular process that is activated in response to stress or nutrient-deprivation conditions. This process is essential for maintaining cellular metabolism and can also be utilized to eliminate pathogens and apoptotic cells. Mutations in autophagy-related genes (ATGs) modulate autophagy and have been linked to various diseases affecting humans, such as cancer (19–21). The relationship between autophagy and malignancies has gained widespread recognition. However, the dualistic character of autophagy, which can act as either a promoter or inhibitor of tumor growth, has raised concerns regarding the regulation of tumorigenesis without triggering deleterious aspects of autophagy. The impact of autophagy on tumor cells at different stages (initiation, development, and progression) remains a complex and contentious phenomenon in the context of cancer therapies. Autophagy is believed to have a significant impact on the preservation of stemness in cancer stem cells, as well as the regulation of these cells’ homeostasis (40, 41).
It is of utmost importance to comprehend the mechanisms through which autophagy contributes to the development of cancer and the factors that dictate its pro- or antitumor impacts, in order to devise efficacious therapeutic approaches. Interventions targeting the modification of tumor cell fate through the regulation or induction of autophagy substrates necessitate meticulous monitoring of these mediators’ activities within the tumor microenvironment to enable informed decisions regarding their activation or deactivation. The investigation of the functioning of autophagy in cancer is a complicated and ongoing area of research. Additionally, there are many forms of autophagy that are solely applicable to particular cell organelles. There is a lot of autophagy research going on right now. These novel findings, however, bring up a lot of new issues. Therefore, additional research is required to understand the primary role of autophagy in various disorders, including cancer. However, there have been some recent successes.
Several research studies have been carried out, indicating a correlation between the removal of the BECN1 gene and the development of breast, ovarian, and prostate cancer (102, 103). Furthermore, it has been observed that animal models exhibiting deficient expression of this particular gene display heightened vulnerability to liver and lung tumors as well as lymphoma (57, 104). Furthermore, the upregulation of this particular gene has been associated with a decrease in cellular proliferation and the hindrance of tumorigenesis in cases of breast cancer (103). Mice that are hemizygous for BECN1 and those that lack Atg4C and BIF1 exhibit a heightened likelihood of tumor formation due to the absence of these autophagic factors (102, 103, 110). Additionally, mice with deficiencies in ATG5 and ATG7 are more prone to the development of liver tumors (105). The protein ATG5 has been identified as a potentially crucial modulator in the decision-making process of cells to undergo either autophagy or apoptosis (116, 119). The pathways of p53 and autophagy are closely interconnected and have a notable impact on stress, metabolism, and cancer reactions (120).
Autophagy can potentially supply nutrients to cancer cells and aid in their acclimatization to unfavorable surroundings. While autophagy has been found to inhibit tumorigenesis, it has also been observed to facilitate tumorigenesis and the progression of tumors. The twofold character of autophagy’s property necessitates additional exploration. The induction of hypoxia within the tumor microenvironment via various molecular and cellular mechanisms results in an upregulation of autophagic activity. This, in turn, leads to tumor proliferation via two distinct pathways.
Autophagy is closely associated with the survival and maintenance of cancer stem cells, which can result in the progression of tumors to secondary metastatic sites and resistance to therapy. The present data substantiates the concept that autophagy serves dual functions in the process of cancer metastasis, acting either as a facilitator or a suppressor, contingent upon the tumor cell category, the microenvironment of the tumor, and the stages of the metastatic cascade (12, 13). Although direct quantification of autophagic flux in primary human malignancies samples is currently unfeasible, various studies utilizing surrogate markers have indicated a correlation between increased autophagy and metastasis.
Autophagy, a cellular process, is essential for the proper functioning of immune responses that are both innate and adaptive (29). The autophagy process in tumor cells undergoing apoptosis is a crucial factor in the initiation of immunogenic cell death. This mechanism facilitates the efficient identification of tumors by the immune system, as reported in references (6, 155). The presentation of tumor antigens is a crucial component of anti-cancer responses. A breakdown in this mechanism may result in immune evasion by tumors, a phenomenon commonly associated with cancer progression. It has been observed that inhibiting autophagy may block this process (157, 425). Several studies have been conducted to establish the unique regulatory mechanisms of macroautophagy and CMA in peripheral T cells. Preliminary investigations suggest that the activation of macroautophagy in T lymphocytes entails distinct signaling pathways. Previous studies have indicated that the activation of the T cell receptor (TCR) results in an increase in macroautophagy in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (158–161). The complete comprehension of the signaling mechanisms that trigger macroautophagy stimulation in active T cells is still underway (158). For T cell homeostasis to be maintained, macroautophagy is essential (158). The process of mitophagy-mediated mitochondrial recycling holds significant importance in T cells, as they undergo a substantial reduction in mitochondrial content during their maturation from immature peripheral naive T cells to single-positive thymocytes (158). Autophagy is a crucial mechanism that governs the production and dissemination of cytokines, including IL-1, IL-18, and TNF-α (187). Sufficient levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) play a crucial role in facilitating autophagy, while the buildup of ROS within the tumor microenvironment impedes the ability of dendritic cells to defend against tumors (29, 214). The origin of this is primarily attributed to the respiratory chain located within the mitochondria (29). ROS has an impact on the entire tumor growth process (212). The process of mitophagy involves the elimination of mitochondria that have been impaired and are producing reactive oxygen species (ROS) within the cell (29).
Both inducing and inhibiting autophagy can have both beneficial and detrimental consequences. Autophagy inhibition is a defensive mechanism against chemotherapy, and it can also result in secondary diseases including various malignancies (154). Chemotherapeutic medicines such as etoposide, fenretinide, and dexamethasone produce autophagic cell death in vitro (308–311). Sodium selenite only affects malignant glioma cells via mitophagy resulting in cell death (313, 314). There exist pharmacological agents that do not primarily function to induce or inhibit autophagy, yet have demonstrated the ability to modulate autophagy. One such example is metformin, commonly used for its anti-diabetic properties. Conversely, the administration of ATO, a medication employed for the purpose of diminishing blood cholesterol concentrations, in conjunction with an autophagy inhibitor, has been observed to yield beneficial outcomes in the context of cancer therapy (287). There exists a potential for certain pharmacological agents, including tamoxifen, to impede the proliferation of cancer cells via the augmentation of autophagy (328). However, the precise signaling pathways that elucidate the connection between autophagy and endocrine resistance remain incompletely characterized (328). This topic holds significant potential for future academic investigation. Baf A1 exhibits a reduction of autophagy and enhancement of apoptosis in the treatment of cancer (287). The dysregulation of PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling has been observed in various types of human cancers (347). The administration of rapamycin, an inhibitor of the mTOR, in a mouse model was found to be associated with a significant reduction of 90% in the incidence of lung cancers induced by carcinogens (348). CQ and HCQ directly inhibited autophagy (370, 371). The combination therapy of HQC and QC for cancer treatment is commonly employed, with a focus on the regulation of autophagy. Novel inhibitors with improved selectivity and efficacy are currently under development, specifically targeted toward the next generation’s lysosomes. These inhibitors have demonstrated enhanced anti-cancer properties.
More research is required to understand the molecular mechanisms that govern autophagy in tumor initiation and progression. In view of the complexity of signaling pathways involved, such an extensive characterization of the role of autophagy in cancer should be instrumental in providing insights about therapeutic methods. A more thorough understanding of these mechanisms will help develop targeted therapies that can also overcome the resistance and improve clinical outcomes.
Potential avenues for future research in the realm of autophagy and cancer may encompass a variety of domains such as:
1. Additional research is required to comprehensively comprehend the molecular mechanisms underlying autophagy, which plays a role in the initiation, advancement, and progression of cancer pathogenesis. This information has the potential to offer valuable insights into new therapeutic targets for the treatment of cancer. Moreover, clinical trials are being conducted to examine the effectiveness and safety of autophagy-targeted therapies in diverse cancer patients. The aim is to investigate the potential of such therapies in treating cancer. The aforementioned studies have the potential to furnish significant insights regarding the clinical efficacy of therapies that target autophagy in the context of cancer treatment.
2. For investigating the function of autophagy within the context of the tumors’ microenvironment. The examination of autophagy’s function within the tumor microenvironment, including its impact on tumor suppression, promotion, and interaction with the immune system, may yield valuable information regarding potential therapeutic targets for various forms of cancer.
Future research endeavors should investigate the feasibility of amalgamating autophagy-focused therapeutic interventions with alternative treatment modalities, such as chemotherapy and immunotherapy, to augment their effectiveness and surmount pharmacological resistance.
To summarize, potential avenues for future research in the realm of autophagy and cancer could lead to significant revelations regarding innovative therapeutic targets, treatment methodologies, and the impact of autophagy on cancer, ultimately leading to enhanced outcomes for cancer patients.
PJ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ArS: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. AmS: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. RM: Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. MH: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. AnS: Validation, Writing – review & editing. AN: Validation, Writing – review & editing. ZS: Conceptualization, Investigation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
ALL: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
AMBRA1: Activating molecule in Beclin-1-regulated autophagy
AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase
APC: Antigen-presenting Cells
AS2O3: Arsenic trioxide
ATG: Autophagy-related gene
ATO: Atorvastatin
BAF A1: Bafilomycin A1
BCA-m: Bacillus caldovelox arginase mutant
BNIP3: Bcl-2/adenovirus E1 19kDa interacting protein 3
BNIP3L: BNIP3-like protein
CD: Crohn’s disease
CMA: Chaperone-mediated autophagy
CQ: Chloroquine
DC: Dendritic Cell
ECM: Extracellular matrix
EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor
EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition
ENZ: Enzalutamide
FAK1: Focal adhesion kinase 1
GEMMs: Genetically engineered mouse models
GBM: Glioblastoma
HCQ: Hydroxychloroquine
HEK293T: Human embryonic kidney cell lines
HMGB1: High mobility group box 1
HNK: Honokiol
HIF-1: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1
H4K16: H4 lysine 16
H4K16ac: H4K16 acetylation
IBC: Isobavachalcone
IL6: Interleukin 6
ISL: Isoliquiritigenin
LAMP-2A: Lysosomal associate membrane protein 2A
LAP: LC3-associated phagocytosis
LC3B: Light chain 3B
MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase
mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin
MDM2: Mouse double-minute 2 homolog
MMP2: Matrix metalloproteinase-2
mPFS: Median progression-free survival
MHC: Major histocompatibility complex
NBR1: Neighbor of BRCA1 gene 1
NFAT: Nuclear factor of activated T cells
NF-B: Nuclear Factor-B
NK: Natural Killer
NSCLC: Non-small cell lung cancer
OS: Overall Survival
OXPHOS: Oxidative phosphorylation
PARP: Poly ADP-ribose polymerase
PC: Plasma cells
PDAC: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
PE: Phosphatidylethanolamine
PI3KC3: Class III Phosphatidylinositol 3 Kinase Complex
PKC: Protein kinase C
REDD1: Regulated in development and DNA damage response 1
RITA: Reactivation of p53 and induction of tumor cell apoptosis
ROS: Reactive oxygen species
SBI: SBI-0206965
TAM: Tamoxifen
TCR: T cell receptor
TFEB: transcription factor EB
TMZ: Temozolomide
UBA: ubiquitin-associated
ULK1: Unc-51-like kinase 1
VDAC1: Voltage-dependent anion channel 1
VOR: Vorinostat
WNT5A: Wnt family member 5a
3-MA: 3-methyladenine
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
2. Sharma S, Kelly TK, Jones PA. Epigenetics in cancer. Carcinogenesis. (2010) 31:27–36. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp220
3. Akhavan-Niaki H, Samadani AA. DNA methylation and cancer development: molecular mechanism. Cell Biochem Biophysics. (2013) 67:501–13. doi: 10.1007/s12013-013-9555-2
4. Atkins MB, Plimack ER, Puzanov I, Fishman MN, McDermott DF, Cho DC, et al. Axitinib plus pembrolizumab in patients with advanced renal-cell carcinoma: long-term efficacy and safety from a phase Ib trial. Eur J Cancer. (2021) 145:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.12.009
5. Procopio G, Ratta R, de Braud F, Verzoni E. Combination therapies for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Lancet Oncol. (2018) 19:281–3. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30092-5
6. Michaud M, Martins I, Sukkurwala AQ, Adjemian S, Ma Y, Pellegatti P, et al. Autophagy-dependent anticancer immune responses induced by chemotherapeutic agents in mice. Science. (2011) 334:1573–7. doi: 10.1126/science.1208347
7. Michaud M, Xie X, Bravo-San-Pedro JM, Zitvogel L, White E, Kroemer G. An autophagy-dependent anticancer immune response determines the efficacy of melanoma chemotherapy. Oncoimmunology. (2014) 3:e944047. doi: 10.4161/21624011.2014.944047
8. Levine B, Klionsky DJ. Development by self-digestion: molecular mechanisms and biological functions of autophagy. Dev Cell. (2004) 6:463–77. doi: 10.1016/S1534-5807(04)00099-1
9. Mizushima N. Autophagy: process and function. Genes Dev. (2007) 21:2861–73. doi: 10.1101/gad.1599207
10. Hara T, Nakamura K, Matsui M, Yamamoto A, Nakahara Y, Suzuki-Migishima R, et al. Suppression of basal autophagy in neural cells causes neurodegenerative disease in mice. Nature. (2006) 441:885–9. doi: 10.1038/nature04724
11. Komatsu M, Waguri S, Chiba T, Murata S, J-i I, Tanida I, et al. Loss of autophagy in the central nervous system causes neurodegeneration in mice. Nature. (2006) 441:880–4. doi: 10.1038/nature04723
12. Komatsu M, Waguri S, Ueno T, Iwata J, Murata S, Tanida I, et al. Impairment of starvation-induced and constitutive autophagy in Atg7-deficient mice. J Cell Biol. (2005) 169:425–34. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200412022
13. Ravikumar B, Duden R, Rubinsztein DC. Aggregate-prone proteins with polyglutamine and polyalanine expansions are degraded by autophagy. Hum Mol Genet. (2002) 11:1107–17. doi: 10.1093/hmg/11.9.1107
14. Shibata M, Lu T, Furuya T, Degterev A, Mizushima N, Yoshimori T, et al. Regulation of intracellular accumulation of mutant Huntingtin by Beclin 1. J Biol Chem. (2006) 281:14474–85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600364200
15. Williams A, Jahreiss L, Sarkar S, Saiki S, Menzies FM, Ravikumar B, et al. Aggregate-prone proteins are cleared from the cytosol by autophagy: therapeutic implications. Curr Topics Dev Biol. (2006) 76:89–101. doi: 10.1016/S0070-2153(06)76003-3
16. Colombo MI. Autophagy: a pathogen driven process. IUBMB Life. (2007) 59:238–42. doi: 10.1080/15216540701230503
17. Qu X, Zou Z, Sun Q, Luby-Phelps K, Cheng P, Hogan RN, et al. Autophagy gene-dependent clearance of apoptotic cells during embryonic development. Cell. (2007) 128:931–46. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.12.044
18. Yun CW, Lee SH. The roles of autophagy in cancer. Int J Of Mol Sci. (2018) 19:3466. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113466
19. Xilouri M, Stefanis L. Autophagy in the central nervous system: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. CNS Neurological Disorders-Drug Targets (Formerly Curr Drug Targets-CNS Neurological Disorders). (2010) 9:701–19. doi: 10.2174/187152710793237421
20. Yin H, Wu H, Chen Y, Zhang J, Zheng M, Chen G, et al. The therapeutic and pathogenic role of autophagy in autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:1512. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01512
21. Biasizzo M, Kopitar-Jerala N. Interplay between NLRP3 inflammasome and autophagy. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:591803. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.591803
22. Rubinsztein DC, Codogno P, Levine B. Autophagy modulation as a potential therapeutic target for diverse diseases. Nat Rev Drug discovery. (2012) 11:709–30. doi: 10.1038/nrd3802
23. Lorin S, Hamaï A, Mehrpour M, Codogno P. Autophagy regulation and its role in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. (2013) 23(5):361–79. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2013.06.007
24. White E. Deconvoluting the context-dependent role for autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev cancer. (2012) 12:401–10. doi: 10.1038/nrc3262
25. Maiuri M, Tasdemir E, Criollo A, Morselli E, Vicencio J, Carnuccio R, et al. Control of autophagy by oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Cell Death Differentiation. (2009) 16:87–93. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2008.131
26. Botti J, Djavaheri-Mergny M, Pilatte Y, Codogno P. Autophagy signaling and the cogwheels of cancer. Autophagy. (2006) 2:67–73. doi: 10.4161/auto.2.2.2458
27. Newton K, Dixit VM. Signaling in innate immunity and inflammation. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol. (2012) 4:a006049. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a006049
28. Salminen A, Kaarniranta K, Kauppinen A. Beclin 1 interactome controls the crosstalk between apoptosis, autophagy and inflammasome activation: impact on the aging process. Ageing Res Rev. (2013) 12:520–34. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2012.11.004
29. Rosenfeldt MT, Ryan KM. The multiple roles of autophagy in cancer. Carcinogenesis. (2011) 32:955–63. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgr031
30. Gewirtz DA. The four faces of autophagy: implications for cancer therapyAutophagy and cancer therapy. Cancer Res. (2014) 74:647–51. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-2966
31. Kenific CM, Thorburn A, Debnath J. Autophagy and metastasis: another double-edged sword. Curr Opin Cell Biol. (2009) 22:1–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.10.008
32. Sosa MS, Bragado P, Aguirre-Ghiso JA. Mechanisms of disseminated cancer cell dormancy: an awakening field. Nat Rev Cancer. (2014) 14:611–22. doi: 10.1038/nrc3793
33. Langley RR, Fidler IJ. The seed and soil hypothesis revisited—The role of tumor-stroma interactions in metastasis to different organs. Int J Cancer. (2011) 128:2527–35. doi: 10.1002/ijc.v128.11
34. Daskalaki I, Gkikas I, Tavernarakis N. Hypoxia and selective autophagy in cancer development and therapy. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2018) 6:104. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2018.00104
35. Li Y-Y, Feun LG, Thongkum A, Tu C-H, Chen S-M, Wangpaichitr M, et al. Autophagic mechanism in anti-cancer immunity: its pros and cons for cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci. (2017) 18:1297. doi: 10.3390/ijms18061297
36. Chen N, Karantza-Wadsworth V. Role and regulation of autophagy in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Res. (2009) 1793:1516–23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.12.013
37. Chen S, Rehman SK, Zhang W, Wen A, Yao L, Zhang J. Autophagy is a therapeutic target in anticancer drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) - Rev Cancer. (2010) 1806:220–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2010.07.003
38. Chen Z, Jiang Q, Zhu P, Chen Y, Xie X, Du Z, et al. NPRL2 enhances autophagy and the resistance to Everolimus in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Prostate. (2019) 79:44–53. doi: 10.1002/pros.23709
39. Xiao X, Wang W, Li Y, Yang D, Li X, Shen C, et al. HSP90AA1-mediated autophagy promotes drug resistance in osteosarcoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2018) 37:1–13. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0880-6
40. Pan H, Cai N, Li M, Liu GH, Izpisua Belmonte JC. Autophagic control of cell ‘stemness’. EMBO Mol Med. (2013) 5:327–31. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201201999
41. Hou J, Han Z, Jing Y, Yang X, Zhang S, Sun K, et al. Autophagy prevents irradiation injury and maintains stemness through decreasing ROS generation in mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Death Disease. (2013) 4:e844–e. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.338
42. Dunn Jr. WA. Autophagy and related mechanisms of lysosome-mediated protein degradation. Trends Cell Biol. (1994) 4:139–43. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90069-8
43. Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM, Klionsky DJ. Autophagy fights disease through cellular self-digestion. Nature. (2008) 451:1069–75. doi: 10.1038/nature06639
44. Cuervo AM. Autophagy: in sickness and in health. Trends Cell Biol. (2004) 14:70–7. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2003.12.002
45. Ciechanover A. Proteolysis: from the lysosome to ubiquitin and the proteasome. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2005) 6:79–87. doi: 10.1038/nrm1552
46. Shoji-Kawata S, Levine B. Autophagy, antiviral immunity, and viral countermeasures. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Res. (2009) 1793:1478–84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2009.02.008
47. Yang Z, Klionsky DJ. An overview of the molecular mechanism of autophagy. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. (2009) 335:1–32. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-00302-8_1
48. Mijaljica D, Prescott M, Devenish RJ. Microautophagy in mammalian cells: revisiting a 40-year-old conundrum. Autophagy. (2011) 7:673–82. doi: 10.4161/auto.7.7.14733
49. Dice JF. Peptide sequences that target cytosolic proteins for lysosomal proteolysis. Trends Biochem Sci. (1990) 15:305–9. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90019-8
50. Takeshige K, Baba M, Tsuboi S, Noda T, Ohsumi Y. Autophagy in yeast demonstrated with proteinase-deficient mutants and conditions for its induction. J Cell Biol. (1992) 119:301–11. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.2.301
51. Ashford TP, Porter KR. Cytoplasmic components in hepatic cell lysosomes. J Cell Biol. (1962) 12:198–202. doi: 10.1083/jcb.12.1.198
52. Kopitz J, Kisen GO, Gordon PB, Bohley P, Seglen PO. Nonselective autophagy of cytosolic enzymes by isolated rat hepatocytes. J Cell Biol. (1990) 111:941–53. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.941
53. Kuma A, Hatano M, Matsui M, Yamamoto A, Nakaya H, Yoshimori T, et al. The role of autophagy during the early neonatal starvation period. Nature. (2004) 432:1032–6. doi: 10.1038/nature03029
54. Kraft C, Reggiori F, Peter M. Selective types of autophagy in yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2009) 1793:1404–12. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2009.02.006
55. Khaminets A, Behl C, Dikic I. Ubiquitin-dependent and independent signals in selective autophagy. Trends Cell Biol. (2016) 26:6–16. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2015.08.010
56. Rogov V, Dötsch V, Johansen T, Kirkin V. Interactions between autophagy receptors and ubiquitin-like proteins form the molecular basis for selective autophagy. Mol Cell. (2014) 53:167–78. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.12.014
57. Takamura A, Komatsu M, Hara T, Sakamoto A, Kishi C, Waguri S, et al. Autophagy-deficient mice develop multiple liver tumors. Genes Dev. (2011) 25:795–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2016211
58. Levine B, Kroemer G. Autophagy in the pathogenesis of disease. Cell. (2008) 132:27–42. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.018
59. Komatsu M, Waguri S, Koike M, Sou YS, Ueno T, Hara T, et al. Homeostatic levels of p62 control cytoplasmic inclusion body formation in autophagy-deficient mice. Cell. (2007) 131:1149–63. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.035
60. Randow F, Youle RJ. Self and nonself: how autophagy targets mitochondria and bacteria. Cell Host Microbe. (2014) 15:403–11. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.03.012
61. Deretic V, Saitoh T, Akira S. Autophagy in infection, inflammation and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. (2013) 13:722–37. doi: 10.1038/nri3532
62. Mancias JD, Pontano Vaites L, Nissim S, Biancur DE, Kim AJ, Wang X, et al. Ferritinophagy via NCOA4 is required for erythropoiesis and is regulated by iron dependent HERC2-mediated proteolysis. Elife. (2015) 4:e10308. doi: 10.7554/eLife.10308
63. Kishi-Itakura C, Koyama-Honda I, Itakura E, Mizushima N. Ultrastructural analysis of autophagosome organization using mammalian autophagy-deficient cells. J Cell Sci. (2014) 127:4089–102. doi: 10.1242/jcs.164293
64. Mancias JD, Wang X, Gygi SP, Harper JW, Kimmelman AC. Quantitative proteomics identifies NCOA4 as the cargo receptor mediating ferritinophagy. Nature. (2014) 509:105–9. doi: 10.1038/nature13148
65. Dowdle WE, Nyfeler B, Nagel J, Elling RA, Liu S, Triantafellow E, et al. Selective VPS34 inhibitor blocks autophagy and uncovers a role for NCOA4 in ferritin degradation and iron homeostasis in vivo. Nat Cell Biol. (2014) 16:1069–79. doi: 10.1038/ncb3053
66. Bernales S, Schuck S, Walter P. ER-phagy: selective autophagy of the endoplasmic reticulum. Autophagy. (2007) 3:285–7. doi: 10.4161/auto.3930
67. Kraft C, Deplazes A, Sohrmann M, Peter M. Mature ribosomes are selectively degraded upon starvation by an autophagy pathway requiring the Ubp3p/Bre5p ubiquitin protease. Nat Cell Biol. (2008) 10:602–10. doi: 10.1038/ncb1723
68. Deng Z, Purtell K, Lachance V, Wold MS, Chen S, Yue Z. Autophagy receptors and neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Cell Biol. (2017) 27:491–504. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2017.01.001
69. Lin L-T, Dawson PW, Richardson CD. Viral interactions with macroautophagy: a double-edged sword. Virology. (2010) 402:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2010.03.026
70. Antonioli M, Di Rienzo M, Piacentini M, Fimia GM. Emerging mechanisms in initiating and terminating autophagy. Trends Biochem Sci. (2017) 42:28–41. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2016.09.008
71. Yang Z, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM. Autophagy in autoimmune disease. J Mol Med. (2015) 93:707–17. doi: 10.1007/s00109-015-1297-8
72. Anding AL, Baehrecke EH. Cleaning house: selective autophagy of organelles. Dev Cell. (2017) 41:10–22. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.02.016
73. Shah SZA, Zhao D, Hussain T, Sabir N, Mangi MH, Yang L. p62-Keap1-NRF2-ARE pathway: a contentious player for selective targeting of autophagy, oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in prion diseases. Front Mol Neurosci. (2018) 11:310. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00310
74. Sharma V, Verma S, Seranova E, Sarkar S, Kumar D. Selective autophagy and xenophagy in infection and disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2018) 6:147. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2018.00147
75. Glick D, Barth S, Macleod KF. Autophagy: cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathology. (2010) 221:3–12. doi: 10.1002/path.v221:1
76. Kim HJ, Lee S, Jung JU. When autophagy meets viruses: a double-edged sword with functions in defense and offense. Semin Immunopathol. (2010) 32(4):323–41. doi: 10.1007/s00281-010-0226-8
77. Guo F, Liu X, Cai H, Le W. Autophagy in neurodegenerative diseases: pathogenesis and therapy. Brain Pathol. (2018) 28:3–13. doi: 10.1111/bpa.2018.28.issue-1
78. Selvakumaran M, Amaravadi RK, Vasilevskaya IA, O’Dwyer PJ. Autophagy inhibition sensitizes colon cancer cells to antiangiogenic and cytotoxic therapy. Clin Cancer Res. (2013) 19:2995–3007. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1542
79. Dragowska WH, Weppler SA, Wang JC, Wong LY, Kapanen AI, Rawji JS, et al. Induction of autophagy is an early response to gefitinib and a potential therapeutic target in breast cancer. PloS One. (2013) 8:e76503. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076503
80. Levy JMM, Towers CG, Thorburn A. Targeting autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. (2017) 17:528–42. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2017.53
81. Amaravadi RK, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Yin XM, Weiss WA, Takebe N, Timmer W, et al. Principles and current strategies for targeting autophagy for cancer treatment. Clin Cancer Res. (2011) 17:654–66. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2634
82. Eshraghi M, Ahmadi M, Afshar S, Lorzadeh S, Adlimoghaddam A, Rezvani Jalal N, et al. Enhancing autophagy in Alzheimer’s disease through drug repositioning. Pharmacol Ther. (2022) 237:108171. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108171
83. Cui M, Yoshimori T, Nakamura S. Autophagy system as a potential therapeutic target for neurodegenerative diseases. Neurochem Int. (2022) 155:105308. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2022.105308
84. Egan DF, Shackelford DB, Mihaylova MM, Gelino S, Kohnz RA, Mair W, et al. Phosphorylation of ULK1 (hATG1) by AMP-activated protein kinase connects energy sensing to mitophagy. Science. (2011) 331:456–61. doi: 10.1126/science.1196371
85. Alers S, Löffler AS, Wesselborg S, Stork B. Role of AMPK-mTOR-Ulk1/2 in the regulation of autophagy: cross talk, shortcuts, and feedbacks. Mol Cell Biol. (2012) 32:2–11. doi: 10.1128/MCB.06159-11
86. Jung CH, Jun CB, Ro S-H, Kim Y-M, Otto NM, Cao J, et al. ULK-Atg13-FIP200 complexes mediate mTOR signaling to the autophagy machinery. Mol Biol Of Cell. (2009) 20:1992–2003. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-12-1249
87. Xie Z, Klionsky DJ. Autophagosome formation: core machinery and adaptations. Nat Cell Biol. (2007) 9:1102–9. doi: 10.1038/ncb1007-1102
88. Ohsumi Y. Molecular dissection of autophagy: two ubiquitin-like systems. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2001) 2:211–6. doi: 10.1038/35056522
89. Tanida I, Tanida-Miyake E, Komatsu M, Ueno T, Kominami E. Human Apg3p/Aut1p homologue is an authentic E2 enzyme for multiple substrates, GATE-16, GABARAP, and MAP-LC3, and facilitates the conjugation of hApg12p to hApg5p. J Biol Chem. (2002) 277:13739–44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M200385200
90. Kuma A, Mizushima N, Ishihara N, Ohsumi Y. Formation of the∼ 350-kDa Apg12-Apg5· Apg16 multimeric complex, mediated by Apg16 oligomerization, is essential for autophagy in yeast. J Biol Chem. (2002) 277:18619–25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111889200
91. Dooley HC, Razi M, Polson HE, Girardin SE, Wilson MI, Tooze SA. WIPI2 links LC3 conjugation with PI3P, autophagosome formation, and pathogen clearance by recruiting Atg12–5-16L1. Mol Cell. (2014) 55:238–52. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.05.021
92. Tanida I, Ueno T, Kominami E. LC3 conjugation system in mammalian autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2004) 36:2503–18. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2004.05.009
93. Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A, Kirisako T, Noda T, et al. LC3, a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome membranes after processing. EMBO J. (2000) 19:5720–8. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.21.5720
94. Kirisako T, Ichimura Y, Okada H, Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Yoshimori T, et al. The reversible modification regulates the membrane-binding state of Apg8/Aut7 essential for autophagy and the cytoplasm to vacuole targeting pathway. J Cell Biol. (2000) 151:263–76. doi: 10.1083/jcb.151.2.263
95. Novak I, Kirkin V, McEwan DG, Zhang J, Wild P, Rozenknop A, et al. Nix is a selective autophagy receptor for mitochondrial clearance. EMBO Rep. (2010) 11:45–51. doi: 10.1038/embor.2009.256
96. Nguyen TN, Padman BS, Lazarou M. Deciphering the molecular signals of PINK1/parkin mitophagy. Trends Cell Biol. (2016) 26:733–44. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2016.05.008
97. Pankiv S, Clausen TH, Lamark T, Brech A, Bruun J-A, Outzen H, et al. p62/SQSTM1 binds directly to Atg8/LC3 to facilitate degradation of ubiquitinated protein aggregates by autophagy. J Biol Chem. (2007) 282:24131–45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M702824200
98. Ichimura Y, Kumanomidou T, Sou Y-S, Mizushima T, Ezaki J, Ueno T, et al. Structural basis for sorting mechanism of p62 in selective autophagy. J Biol Chem. (2008) 283:22847–57. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802182200
99. Kirkin V, Lamark T, Sou Y-S, Bjørkøy G, Nunn JL, Bruun J-A, et al. A role for NBR1 in autophagosomal degradation of ubiquitinated substrates. Mol Cell. (2009) 33:505–16. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.01.020
100. Yang Y, Klionsky DJ. Autophagy and disease: unanswered questions. Cell Death Differentiation. (2020) 27:858–71. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0480-9
101. Lim K-H, Staudt LM. Toll-like receptor signaling. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol. (2013) 5:a011247. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a011247
102. Qu X, Yu J, Bhagat G, Furuya N, Hibshoosh H, Troxel A, et al. Promotion of tumorigenesis by heterozygous disruption of the beclin 1 autophagy gene. J Clin Invest. (2003) 112:1809–20. doi: 10.1172/JCI20039
103. Yue Z, Jin S, Yang C, Levine AJ, Heintz N. Beclin 1, an autophagy gene essential for early embryonic development, is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2003) 100:15077–82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2436255100
104. Aita VM, Liang XH, Murty V, Pincus DL, Yu W, Cayanis E, et al. Cloning and genomic organization of beclin 1, a candidate tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 17q21. Genomics. (1999) 59:59–65. doi: 10.1006/geno.1999.5851
105. Liang XH, Jackson S, Seaman M, Brown K, Kempkes B, Hibshoosh H, et al. Induction of autophagy and inhibition of tumorigenesis by beclin 1. Nature. (1999) 402:672–6. doi: 10.1038/45257
106. Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, Garuti R, Liang XH, Mizushima N, et al. Bcl-2 antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell. (2005) 122:927–39. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.07.002
107. Koneri K, Goi T, Hirono Y, Katayama K, Yamaguchi A. Beclin 1 gene inhibits tumor growth in colon cancer cell lines. Anticancer Res. (2007) 27:1453–7.
108. Kim MS, Jeong EG, Ahn CH, Kim SS, Lee SH, Yoo NJ. Frameshift mutation of UVRAG, an autophagy-related gene, in gastric carcinomas with microsatellite instability. Hum Pathology. (2008) 39:1059–63. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2007.11.013
109. Kang MR, Kim MS, Oh JE, Kim YR, Song SY, Kim SS, et al. Frameshift mutations of autophagy-related genes ATG2B, ATG5, ATG9B and ATG12 in gastric and colorectal cancers with microsatellite instability. J Pathology: A J Pathological Soc Great Britain Ireland. (2009) 217:702–6. doi: 10.1002/path.v217:5
110. Takahashi Y, Coppola D, Matsushita N, Cualing HD, Sun M, Sato Y, et al. Bif-1 interacts with Beclin 1 through UVRAG and regulates autophagy and tumorigenesis. Nat Cell Biol. (2007) 9:1142–51. doi: 10.1038/ncb1634
111. Hanada T, Noda NN, Satomi Y, Ichimura Y, Fujioka Y, Takao T, et al. The Atg12-Atg5 conjugate has a novel E3-like activity for protein lipidation in autophagy. J Biol Chem. (2007) 282:37298–302. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C700195200
112. Otomo C, Metlagel Z, Takaesu G, Otomo T. Structure of the human ATG12~ ATG5 conjugate required for LC3 lipidation in autophagy. Nat Struct Mol Biol. (2013) 20:59–66. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2431
113. Jounai N, Takeshita F, Kobiyama K, Sawano A, Miyawaki A, Xin K-Q, et al. The Atg5–Atg12 conjugate associates with innate antiviral immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2007) 104:14050–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704014104
114. Hwang S, Maloney NS, Bruinsma MW, Goel G, Duan E, Zhang L, et al. Nondegradative role of Atg5-Atg12/Atg16L1 autophagy protein complex in antiviral activity of interferon gamma. Cell Host Microbe. (2012) 11:397–409. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.03.002
115. Ndoye A, Budina-Kolomets A, Kugel CH III, Webster MR, Kaur A, Behera R, et al. ATG5 mediates a positive feedback loop between Wnt signaling and autophagy in melanoma. Cancer Res. (2017) 77:5873–85. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0907
116. Pyo J-O, Jang M-H, Kwon Y-K, Lee H-J, Jun J-I, Woo H-N, et al. Essential roles of Atg5 and FADD in autophagic cell death: dissection of autophagic cell death into vacuole formation and cell death. J Biol Chem. (2005) 280:20722–9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413934200
117. O’Sullivan TE, Geary CD, Weizman O-E, Geiger TL, Rapp M, Dorn GW, et al. Atg5 is essential for the development and survival of innate lymphocytes. Cell Rep. (2016) 15:1910–9. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.04.082
118. Xiong X, Wu M, Zhang H, Li J, Lu B, Guo Y, et al. Atg5 siRNA inhibits autophagy and enhances norcantharidin-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. (2015) 47:1321–8. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3103
119. Yousefi S, Perozzo R, Schmid I, Ziemiecki A, Schaffner T, Scapozza L, et al. Calpain-mediated cleavage of Atg5 switches autophagy to apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol. (2006) 8:1124–32. doi: 10.1038/ncb1482
120. White E. Autophagy and p53. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Med. (2016) 6:a026120. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a026120
121. Comel A, Sorrentino G, Capaci V, Del Sal G. The cytoplasmic side of p53’s oncosuppressive activities. FEBS letters. (2014) 588:2600–9. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.04.015
122. Choi AM, Ryter SW, Levine B. Autophagy in human health and disease. N Engl J Med. (2013) 368:1845–6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1205406
123. Katayama M, Kawaguchi T, Berger M, Pieper R. DNA damaging agent-induced autophagy produces a cytoprotective adenosine triphosphate surge in Malignant glioma cells. Cell Death Differentiation. (2007) 14:548–58. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402030
124. Kapuy O, Vinod P, Bánhegyi G. mTOR inhibition increases cell viability via autophagy induction during endoplasmic reticulum stress–An experimental and modeling study. FEBS Open Bio. (2014) 4:704–13. doi: 10.1016/j.fob.2014.07.006
125. Shoji-Kawata S, Sumpter R, Leveno M, Campbell GR, Zou Z, Kinch L, et al. Identification of a candidate therapeutic autophagy-inducing peptide. Nature. (2013) 494:201–6. doi: 10.1038/nature11866
126. Lin Z, Wang Z, Zhou X, Zhang M, Gao D, Zhang L, et al. Discovery of new fluorescent thiazole–pyrazoline derivatives as autophagy inducers by inhibiting mTOR activity in A549 human lung cancer cells. Cell Death Disease. (2020) 11:551. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02746-w
127. Kaushik G, Venugopal A, Ramamoorthy P, Standing D, Subramaniam D, Umar S, et al. Honokiol inhibits melanoma stem cells by targeting notch signaling. Mol Carcinogenesis. (2015) 54:1710–21. doi: 10.1002/mc.v54.12
128. Zhao S, Ma C-M, Liu C-X, Wei W, Sun Y, Yan H, et al. Autophagy inhibition enhances isobavachalcone-induced cell death in multiple myeloma cells. Int J Mol Med. (2012) 30:939–44. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2012.1066
129. Tanida I. Autophagosome formation and molecular mechanism of autophagy. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2011) 14:2201–14. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3482
130. Zhu D, Zhou J, Zhao J, Jiang G, Zhang X, Zhang Y, et al. ZC3H13 suppresses colorectal cancer proliferation and invasion via inactivating Ras-ERK signaling. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:8899–907. doi: 10.1002/jcp.v234.6
131. Su CC. Tanshinone IIA can inhibit MiaPaCa−2 human pancreatic cancer cells by dual blockade of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways. Oncol Rep. (2018) 40:3102–11. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6670
132. Natan S, Tsarfaty G, Horev J, Haklai R, Kloog Y, Tsarfaty I. Interplay between HGF/SF-Met-Ras signaling, tumor metabolism and blood flow as a potential target for breast cancer therapy. Oncoscience. (2014) 1:30–8. doi: 10.18632/oncoscience.v1i1
133. Guo JY, Chen HY, Mathew R, Fan J, Strohecker AM, Karsli-Uzunbas G, et al. Activated Ras requires autophagy to maintain oxidative metabolism and tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. (2011) 25:460–70. doi: 10.1101/gad.2016311
134. Karnoub AE, Weinberg RA. Ras oncogenes: split personalities. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2008) 9:517–31. doi: 10.1038/nrm2438
135. Goel S, Huang J, Klampfer L. K-Ras, intestinal homeostasis and colon cancer. Curr Clin Pharmacol. (2015) 10:73–81. doi: 10.2174/1574884708666131111204440
136. Masliah-Planchon J, Garinet S, Pasmant E. RAS-MAPK pathway epigenetic activation in cancer: miRNAs in action. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:38892–907. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v7i25
137. Strohecker AM, White E. Targeting mitochondrial metabolism by inhibiting autophagy in BRAF-driven cancers. Cancer Discovery. (2014) 4:766–72. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-0196
138. Yang S, Wang X, Contino G, Liesa M, Sahin E, Ying H, et al. Pancreatic cancers require autophagy for tumor growth. Genes Dev. (2011) 25:717–29. doi: 10.1101/gad.2016111
139. Yang A, Kimmelman AC. Inhibition of autophagy attenuates pancreatic cancer growth independent of TP53/TRP53 status. Autophagy. (2014) 10:1683–4. doi: 10.4161/auto.29961
140. Guo JY, Teng X, Laddha SV, Ma S, Van Nostrand SC, Yang Y, et al. Autophagy provides metabolic substrates to maintain energy charge and nucleotide pools in Ras-driven lung cancer cells. Genes Dev. (2016) 30:1704–17. doi: 10.1101/gad.283416.116
141. Guo JY, White E. Autophagy is required for mitochondrial function, lipid metabolism, growth, and fate of KRASG12D-driven lung tumors. Autophagy. (2013) 9:1636–8. doi: 10.4161/auto.26123
142. Wei H, Wei S, Gan B, Peng X, Zou W, Guan J-L. Suppression of autophagy by FIP200 deletion inhibits mammary tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. (2011) 25:1510–27. doi: 10.1101/gad.2051011
143. Degenhardt K, Mathew R, Beaudoin B, Bray K, Anderson D, Chen G, et al. Autophagy promotes tumor cell survival and restricts necrosis, inflammation, and tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. (2006) 10:51–64. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.06.001
144. Balkwill F, Charles KA, Mantovani A. Smoldering and polarized inflammation in the initiation and promotion of Malignant disease. Cancer Cell. (2005) 7:211–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2005.02.013
145. Vakkila J, Lotze MT. Inflammation and necrosis promote tumour growth. Nat Rev Immunol. (2004) 4:641–8. doi: 10.1038/nri1415
146. Zeh HJ III, Lotze MT. Addicted to death: invasive cancer and the immune response to unscheduled cell death. J Immunother. (2005) 28:1–9. doi: 10.1097/00002371-200501000-00001
147. Ellerman JE, Brown CK, De Vera M, Zeh HJ, Billiar T, Rubartelli A, et al. Masquerader: high mobility group box-1 and cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2007) 13:2836–48. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1953
148. Karin M. Nuclear factor-κB in cancer development and progression. Nature. (2006) 441:431–6. doi: 10.1038/nature04870
149. Karin M, Lawrence T, Nizet V. Innate immunity gone awry: linking microbial infections to chronic inflammation and cancer. Cell. (2006) 124:823–35. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.016
150. Schultz KT, Grieder F. Structure and function of the immune system. Toxicol Pathol. (1987) 15:262–4. doi: 10.1177/019262338701500301
151. Mattei F, Alfaro C, Keisari Y. Cancer immunology: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Cells. (2022) 11(3):459. doi: 10.3390/cells11030459
152. Eisenbarth SC, Flavell RA. Innate instruction of adaptive immunity revisited: the inflammasome. EMBO Mol Med. (2009) 1:92–8. doi: 10.1002/emmm.200900014
153. Mah LY, Ryan KM. Autophagy and cancer.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.(2012) 4:a008821. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008821
154. Lorin S, Hamaï A, Mehrpour M, Codogno P. Autophagy regulation and its role in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. (2013) 23:361–79. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2013.06.007
155. Ko A, Kanehisa A, Martins I, Senovilla L, Chargari C, Dugue D, et al. Autophagy inhibition radiosensitizes in vitro, yet reduces radioresponses in vivo due to deficient immunogenic signalling. Cell Death Differ. (2014) 21:92–9. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2013.124
156. Sensi M, Anichini A. Unique tumor antigens: evidence for immune control of genome integrity and immunogenic targets for T cell-mediated patient-specific immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. (2006) 12:5023–32. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2682
157. Garcia-Lora A, Algarra I, Garrido F. MHC class I antigens, immune surveillance, and tumor immune escape. J Cell Physiol. (2003) 195:346–55. doi: 10.1002/jcp.v195:3
158. Macian F. Autophagy in T cell function and aging. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2019) 7:213. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00213
159. Li C, Capan E, Zhao Y, Zhao J, Stolz D, Watkins SC, et al. Autophagy is induced in CD4+ T cells and important for the growth factor-withdrawal cell death. J Immunol. (2006) 177:5163–8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.8.5163
160. Pua HH, Dzhagalov I, Chuck M, Mizushima N, He YW. A critical role for the autophagy gene Atg5 in T cell survival and proliferation. J Exp Med. (2007) 204:25–31. doi: 10.1084/jem.20061303
161. Hubbard VM, Valdor R, Patel B, Singh R, Cuervo AM, Macian F. Macroautophagy regulates energy metabolism during effector T cell activation. J Immunol. (2010) 185:7349–57. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000576
162. Kiffin R, Christian C, Knecht E, Cuervo AM. Activation of chaperone-mediated autophagy during oxidative stress. Mol Biol Cell. (2004) 15:4829–40. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-06-0477
163. Macian F. NFAT proteins: key regulators of T-cell development and function. Nat Rev Immunol. (2005) 5:472–84. doi: 10.1038/nri1632
164. Kwon J, Shatynski KE, Chen H, Morand S, de Deken X, Miot F, et al. The nonphagocytic NADPH oxidase Duox1 mediates a positive feedback loop during T cell receptor signaling. Sci Signal. (2010) 3:ra59. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2000976
165. Sena LA, Li S, Jairaman A, Prakriya M, Ezponda T, Hildeman DA, et al. Mitochondria are required for antigen-specific T cell activation through reactive oxygen species signaling. Immunity. (2013) 38:225–36. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.10.020
166. Pua HH, Guo J, Komatsu M, He YW. Autophagy is essential for mitochondrial clearance in mature T lymphocytes. J Immunol. (2009) 182:4046–55. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0801143
167. Jia W, He YW. Temporal regulation of intracellular organelle homeostasis in T lymphocytes by autophagy. J Immunol. (2011) 186:5313–22. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002404
168. Jia W, Pua HH, Li QJ, He YW. Autophagy regulates endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis and calcium mobilization in T lymphocytes. J Immunol. (2011) 186:1564–74. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001822
169. Kovacs JR, Li C, Yang Q, Li G, Garcia IG, Ju S, et al. Autophagy promotes T-cell survival through degradation of proteins of the cell death machinery. Cell Death Differ. (2012) 19:144–52. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2011.78
170. DeVorkin L, Pavey N, Carleton G, Comber A, Ho C, Lim J, et al. Autophagy regulation of metabolism is required for CD8(+) T cell anti-tumor immunity. Cell Rep. (2019) 27:502–13.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.03.037
171. Mgrditchian T, Arakelian T, Paggetti J, Noman MZ, Viry E, Moussay E, et al. Targeting autophagy inhibits melanoma growth by enhancing NK cells infiltration in a CCL5-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2017) 114:E9271–e9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1703921114
172. Deretic V. Autophagy in innate and adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol. (2005) 26:523–8. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2005.08.003
173. Raza IG, Clarke AJ. B cell metabolism and autophagy in autoimmunity. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:681105. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.681105
174. Pengo N, Scolari M, Oliva L, Milan E, Mainoldi F, Raimondi A, et al. Plasma cells require autophagy for sustainable immunoglobulin production. Nat Immunol. (2013) 14:298–305. doi: 10.1038/ni.2524
175. Morandi E, Jagessar SA, t Hart BA, Gran B. EBV infection empowers human B cells for autoimmunity: role of autophagy and relevance to multiple sclerosis. J Immunol. (2017) 199:435–48. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700178
176. Clarke AJ, Ellinghaus U, Cortini A, Stranks A, Simon AK, Botto M, et al. Autophagy is activated in systemic lupus erythematosus and required for plasmablast development. Ann Rheumatic Diseases. (2015) 74:912–20. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204343
177. Deane JA, Pisitkun P, Barrett RS, Feigenbaum L, Town T, Ward JM, et al. Control of toll-like receptor 7 expression is essential to restrict autoimmunity and dendritic cell proliferation. Immunity. (2007) 27:801–10. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.09.009
178. Miller BC, Zhao Z, Stephenson LM, Cadwell K, Pua HH, Lee HK, et al. The autophagy gene ATG5 plays an essential role in B lymphocyte development. Autophagy. (2008) 4:309–14. doi: 10.4161/auto.5474
179. Arnold J, Murera D, Arbogast F, Fauny J-D, Muller S, Gros F. Autophagy is dispensable for B-cell development but essential for humoral autoimmune responses. Cell Death Differentiation. (2016) 23:853–64. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.149
180. Chen M, Kodali S, Jang A, Kuai L, Wang J. Requirement for autophagy in the long-term persistence but not initial formation of memory B cells. J Immunol. (2015) 194:2607–15. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1403001
181. Brookens SK, Cho SH, Basso PJ, Boothby MR. AMPKα1 in B Cells Dampens primary antibody responses yet promotes mitochondrial homeostasis and persistence of B cell memory. J Immunol. (2020) 205:3011–22. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901474
182. Heckmann BL, Green DR. LC3-associated phagocytosis at a glance. J Cell Sci. (2019) 132(5):jcs231472. doi: 10.1242/jcs.231472
183. Martinez J, Malireddi RK, Lu Q, Cunha LD, Pelletier S, Gingras S, et al. Molecular characterization of LC3-associated phagocytosis reveals distinct roles for Rubicon, NOX2 and autophagy proteins. Nat Cell Biol. (2015) 17:893–906. doi: 10.1038/ncb3192
184. Amaravadi RK, Kimmelman AC, Debnath J. Targeting autophagy in cancer: recent advances and future directions. Cancer Discovery. (2019) 9:1167–81. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0292
185. Cunha LD, Yang M, Carter R, Guy C, Harris L, Crawford JC, et al. LC3-associated phagocytosis in myeloid cells promotes tumor immune tolerance. Cell. (2018) 175:429–41.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.08.061
186. Zhang JM, An J. Cytokines, inflammation, and pain. Int Anesthesiol Clin. (2007) 45:27–37. doi: 10.1097/AIA.0b013e318034194e
188. Wang L, Du F, Wang H, Xie C. Cooperation of CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells and release of IFN-γ are critical for antileukemia responses of recipient mice treated by microtransplantation. Exp Ther Med. (2018) 15:1532–7. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5541
189. Brasseit J, Kwong Chung CK, Noti M, Zysset D, Hoheisel-Dickgreber N, Genitsch V, et al. Divergent roles of interferon-γ and innate lymphoid cells in innate and adaptive immune cell-mediated intestinal inflammation. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:23. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00023
190. Shi C-S, Kehrl JH. TRAF6 and A20 regulate lysine 63–linked ubiquitination of Beclin-1 to control TLR4-induced autophagy. Sci Signaling. (2010) 3:ra42–ra. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2000751
191. Tu SP, Quante M, Bhagat G, Takaishi S, Cui G, Yang XD, et al. IFN-γ Inhibits gastric carcinogenesis by inducing epithelial cell autophagy and T-cell apoptosisIFN-γ Inhibits gastric inflammation and carcinoma. Cancer Res. (2011) 71:4247–59. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4009
192. Ge Y, Huang M, Yao Y-M. Autophagy and proinflammatory cytokines: interactions and clinical implications. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2018) 43:38–46. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2018.07.001
193. Chang Y-P, Tsai C-C, Huang W-C, Wang C-Y, Chen C-L, Lin Y-S, et al. Autophagy facilitates IFN-γ-induced Jak2-STAT1 activation and cellular inflammation. J Biol Chem. (2010) 285:28715–22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.133355
194. Liu E, Van Grol J, Subauste CS. Atg5 but not Atg7 in dendritic cells enhances IL-2 and IFN-γ production by Toxoplasma gondii-reactive CD4+ T cells. Microbes Infection. (2015) 17:275–84. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2014.12.008
195. Lin N-Y, Stefanica A, Distler JH. Autophagy: a key pathway of TNF-induced inflammatory bone loss. Autophagy. (2013) 9:1253–5. doi: 10.4161/auto.25467
196. Keller CW, Fokken C, Turville SG, Lünemann A, Schmidt J, Münz C, et al. TNF-α induces macroautophagy and regulates MHC class II expression in human skeletal muscle cells. J Biol Chem. (2011) 286:3970–80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.159392
197. Wang M-X, Cheng X-Y, Jin M, Cao Y-L, Yang Y-P, Wang J-D, et al. TNF compromises lysosome acidification and reduces α-synuclein degradation via autophagy in dopaminergic cells. Exp Neurology. (2015) 271:112–21. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.05.008
198. Lin N-Y, Beyer C, Gießl A, Kireva T, Scholtysek C, Uderhardt S, et al. Autophagy regulates TNFα-mediated joint destruction in experimental arthritis. Ann Rheumatic Diseases. (2013) 72:761–8. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201671
199. Prokesch A, Blaschitz A, Bauer T, Moser G, Hiden U, Zadora J, et al. Placental DAPK1 and autophagy marker LC3B-II are dysregulated by TNF-α in a gestational age-dependent manner. Histochem Cell Biol. (2017) 147:695–705. doi: 10.1007/s00418-016-1537-1
200. Rodríguez A, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Catalan V, Rotellar F, Valentí V, Silva C, et al. The ghrelin O-acyltransferase–ghrelin system reduces TNF-α-induced apoptosis and autophagy in human visceral adipocytes. Diabetologia. (2012) 55:3038–50. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2671-5
201. Yuan J, Yu M, Li H-H, Long Q, Liang W, Wen S, et al. Autophagy contributes to IL-17-induced plasma cell differentiation in experimental autoimmune myocarditis. Int Immunopharmacology. (2014) 18:98–105. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.11.008
202. Zhang M, Kenny SJ, Ge L, Xu K, Schekman R. Translocation of interleukin-1β into a vesicle intermediate in autophagy-mediated secretion. elife. (2015) 4:e11205. doi: 10.7554/eLife.11205.023
203. Gao Y, Ma L, Luo C-L, Wang T, Zhang M-Y, Shen X, et al. IL-33 exerts neuroprotective effect in mice intracerebral hemorrhage model through suppressing inflammation/apoptotic/autophagic pathway. Mol Neurobiology. (2017) 54:3879–92. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9947-6
204. Karantza-Wadsworth V, Patel S, Kravchuk O, Chen G, Mathew R, Jin S, et al. Autophagy mitigates metabolic stress and genome damage in mammary tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. (2007) 21:1621–35. doi: 10.1101/gad.1565707
205. Mathew R, Kongara S, Beaudoin B, Karp CM, Bray K, Degenhardt K, et al. Autophagy suppresses tumor progression by limiting chromosomal instability. Genes Dev. (2007) 21:1367–81. doi: 10.1101/gad.1545107
206. Li X, He S, Ma B. Autophagy and autophagy-related proteins in cancer. Mol Cancer. (2020) 19:12. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-1138-4
207. Kwong C, Gilman-Sachs A, Beaman K. Tumor-associated a2 vacuolar ATPase acts as a key mediator of cancer-related inflammation by inducing pro-tumorigenic properties in monocytes. J Immunol. (2011) 186:1781–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002998
208. White E, Karp C, Strohecker AM, Guo Y, Mathew R. Role of autophagy in suppression of inflammation and cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol. (2010) 22:212–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.12.008
209. Van Limbergen J, Wilson DC, Satsangi J. The genetics of Crohn’s disease. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. (2009) 10:89–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-082908-150013
210. Cadwell K, Liu JY, Brown SL, Miyoshi H, Loh J, Lennerz JK, et al. A key role for autophagy and the autophagy gene Atg16l1 in mouse and human intestinal Paneth cells. Nature. (2008) 456:259–63. doi: 10.1038/nature07416
211. Cadwell K, Patel KK, Komatsu M, Virgin HW, Stappenbeck TS. A common role for Atg16L1, Atg5 and Atg7 in small intestinal Paneth cells and Crohn disease. Autophagy. (2009) 5:250–2. doi: 10.4161/auto.5.2.7560
212. Reuter S, Gupta SC, Chaturvedi MM, Aggarwal BB. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: how are they linked? Free Radic Biol Med. (2010) 49:1603–16. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.09.006
213. Ray PD, Huang BW, Tsuji Y. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis and redox regulation in cellular signaling. Cell Signal. (2012) 24:981–90. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.01.008
214. Fricke I, Gabrilovich DI. Dendritic cells and tumor microenvironment: a dangerous liaison. Immunol Invest. (2006) 35:459–83. doi: 10.1080/08820130600803429
215. Narendra D, Tanaka A, Suen DF, Youle RJ. Parkin is recruited selectively to impaired mitochondria and promotes their autophagy. J Cell Biol. (2008) 183:795–803. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200809125
216. Narendra DP, Jin SM, Tanaka A, Suen DF, Gautier CA, Shen J, et al. PINK1 is selectively stabilized on impaired mitochondria to activate Parkin. PloS Biol. (2010) 8:e1000298. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000298
217. Suen DF, Narendra DP, Tanaka A, Manfredi G, Youle RJ. Parkin overexpression selects against a deleterious mtDNA mutation in heteroplasmic cybrid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2010) 107:11835–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914569107
218. Moscat J, Diaz-Meco MT. p62 at the crossroads of autophagy, apoptosis, and cancer. Cell. (2009) 137:1001–4. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.023
219. Mathew R, Karp CM, Beaudoin B, Vuong N, Chen G, Chen HY, et al. Autophagy suppresses tumorigenesis through elimination of p62. Cell. (2009) 137:1062–75. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.048
220. Kongara S, Kravchuk O, Teplova I, Lozy F, Schulte J, Moore D, et al. Autophagy regulates keratin 8 homeostasis in mammary epithelial cells and in breast tumors. Mol Cancer Res. (2010) 8:873–84. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0494
221. Sandoval H, Thiagarajan P, Dasgupta SK, Schumacher A, Prchal JT, Chen M, et al. Essential role for Nix in autophagic maturation of erythroid cells. Nature. (2008) 454:232–5. doi: 10.1038/nature07006
222. Mulcahy Levy JM, Thorburn A. Autophagy in cancer: moving from understanding mechanism to improving therapy responses in patients. Cell Death Differ. (2020) 27:843–57. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0474-7
223. Ladoire S, Penault-Llorca F, Senovilla L, Dalban C, Enot D, Locher C, et al. Combined evaluation of LC3B puncta and HMGB1 expression predicts residual risk of relapse after adjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Autophagy. (2015) 11:1878–90. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1082022
224. Ladoire S, Enot D, Senovilla L, Ghiringhelli F, Poirier-Colame V, Chaba K, et al. The presence of LC3B puncta and HMGB1 expression in Malignant cells correlate with the immune infiltrate in breast cancer. Autophagy. (2016) 12:864–75. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1154244
225. Starobinets H, Ye J, Broz M, Barry K, Goldsmith J, Marsh T, et al. Antitumor adaptive immunity remains intact following inhibition of autophagy and antimalarial treatment. J Clin Invest. (2016) 126:4417–29. doi: 10.1172/JCI85705
226. Chen D, Xie J, Fiskesund R, Dong W, Liang X, Lv J, et al. Publisher Correction: Chloroquine modulates antitumor immune response by resetting tumor-associated macrophages toward M1 phenotype. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:1808. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04169-w
227. Frazier JP, Bertout JA, Kerwin WS, Moreno-Gonzalez A, Casalini JR, Grenley MO, et al. Multidrug analyses in patients distinguish efficacious cancer agents based on both tumor cell killing and immunomodulation. Cancer Res. (2017) 77:2869–80. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0084
228. Lee HK, Mattei LM, Steinberg BE, Alberts P, Lee YH, Chervonsky A, et al. In vivo requirement for Atg5 in antigen presentation by dendritic cells. Immunity. (2010) 32:227–39. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.12.006
229. Li Y, Wang LX, Yang G, Hao F, Urba WJ, Hu HM. Efficient cross-presentation depends on autophagy in tumor cells. Cancer Res. (2008) 68:6889–95. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0161
230. Münz C. Antigen processing via autophagy–not only for MHC class II presentation anymore? Curr Opin Immunol. (2010) 22(1):89–93. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2010.01.016
231. Di Leo L, Bodemeyer V, Bosisio FM, Claps G, Carretta M, Rizza S, et al. Loss of Ambra1 promotes melanoma growth and invasion. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:2550. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22772-2
232. Liang C, Feng P, Ku B, Dotan I, Canaani D, Oh B-H, et al. Autophagic and tumour suppressor activity of a novel Beclin1-binding protein UVRAG. Nat Cell Biol. (2006) 8:688–98. doi: 10.1038/ncb1426
233. Cai M, Hu Z, Liu J, Gao J, Liu C, Liu D, et al. Beclin 1 expression in ovarian tissues and its effects on ovarian cancer prognosis. Int J Of Mol Sci. (2014) 15:5292–303. doi: 10.3390/ijms15045292
234. Qiu D-M, Wang G-L, Chen L, Xu Y-Y, He S, Cao X-L, et al. The expression of beclin-1, an autophagic gene, in hepatocellular carcinoma associated with clinical pathological and prognostic significance. BMC Cancer. (2014) 14:1–13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-327
235. Zhang Z, Shao Z, Xiong L, Che B, Deng C, Xu W. Expression of Beclin1 in osteosarcoma and the effects of down-regulation of autophagy on the chemotherapeutic sensitivity. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol. (2009) 29:737–40. doi: 10.1007/s11596-009-0613-3
236. Huang X, Bai H-M, Chen L, Li B, Lu Y-C. Reduced expression of LC3B-II and Beclin 1 in glioblastoma multiforme indicates a down-regulated autophagic capacity that relates to the progression of astrocytic tumors. J Clin Neurosci. (2010) 17:1515–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2010.03.051
237. Saitoh T, Fujita N, Jang MH, Uematsu S, Yang B-G, Satoh T, et al. Loss of the autophagy protein Atg16L1 enhances endotoxin-induced IL-1β production. Nature. (2008) 456:264–8. doi: 10.1038/nature07383
238. Saitoh T, Akira S. Regulation of inflammasomes by autophagy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2016) 138(1):28–36. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.05.009
239. Sou Y-S, Waguri S, Iwata J-I, Ueno T, Fujimura T, Hara T, et al. The Atg8 conjugation system is indispensable for proper development of autophagic isolation membranes in mice. Mol Biol Cell. (2008) 19:4762–75. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-03-0309
240. Kongara S, Kravchuk O, Teplova I, Lozy F, Schulte J, Moore D, et al. Autophagy regulates keratin 8 homeostasis in mammary epithelial cells and in breast tumorsphospho-K8 in mammary cells and breast tumors. Mol Cancer Res. (2010) 8:873–84. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0494
241. Duran A, Linares JF, Galvez AS, Wikenheiser K, Flores JM, Diaz-Meco MT, et al. The signaling adaptor p62 is an important NF-κB mediator in tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. (2008) 13:343–54. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.02.001
242. Tang D, Kang R, Livesey KM, Cheh C-W, Farkas A, Loughran P, et al. Endogenous HMGB1 regulates autophagy. J Cell Biol. (2010) 190:881–92. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200911078
243. Luo T, Fu J, Xu A, Su B, Ren Y, Li N, et al. PSMD10/gankyrin induces autophagy to promote tumor progression through cytoplasmic interaction with ATG7 and nuclear transactivation of ATG7 expression. Autophagy. (2016) 12:1355–71. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1034405
244. Liu M, Jiang L, Fu X, Wang W, Ma J, Tian T, et al. Cytoplasmic liver kinase B1 promotes the growth of human lung adenocarcinoma by enhancing autophagy. Cancer science. (2018) 109:3055–67. doi: 10.1111/cas.2018.109.issue-10
245. White E, DiPaola RS. The double-edged sword of autophagy modulation in cancerAutophagy in cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. (2009) 15:5308–16. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-5023
246. Sanchez-Vega F, Mina M, Armenia J, Chatila WK, Luna A, La KC, et al. Oncogenic signaling pathways in the cancer genome atlas. Cell. (2018) 173:321–37.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.035
247. Semenza GL. HIF-1: upstream and downstream of cancer metabolism. Curr Opin Genet Dev. (2010) 20:51–6. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2009.10.009
248. Semenza GL. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) pathway. Science’s STKE. (2007) 2007:cm8–cm. doi: 10.1126/stke.4072007cm8
249. Pezzuto A, Carico E. Role of HIF-1 in cancer progression: novel insights. A review. Curr Mol Med. (2018) 18:343–51. doi: 10.2174/1566524018666181109121849
250. Lai M-C, Chang C-M, Sun HS. Hypoxia induces autophagy through translational up-regulation of lysosomal proteins in human colon cancer cells. PloS One. (2016) 11:e0153627. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153627
251. Sengupta S, Peterson TR, Sabatini DM. Regulation of the mTOR complex 1 pathway by nutrients, growth factors, and stress. Mol Cell. (2010) 40:310–22. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.026
252. Song J, Guo X, Xie X, Zhao X, Li D, Deng W, et al. Autophagy in hypoxia protects cancer cells against apoptosis induced by nutrient deprivation through a Beclin1-dependent way in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Biochem. (2011) 112:3406–20. doi: 10.1002/jcb.v112.11
253. Young TM, Reyes C, Pasnikowski E, Castanaro C, Wong C, Decker CE, et al. Autophagy protects tumors from T cell–mediated cytotoxicity via inhibition of TNFα-induced apoptosis. Sci Immunol. (2020) 5:eabb9561. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abb9561
254. Baginska J, Viry E, Berchem G, Poli A, Noman MZ, van Moer K, et al. Granzyme B degradation by autophagy decreases tumor cell susceptibility to natural killer-mediated lysis under hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2013) 110:17450–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1304790110
255. Yamamoto K, Venida A, Yano J, Biancur DE, Kakiuchi M, Gupta S, et al. Autophagy promotes immune evasion of pancreatic cancer by degrading MHC-I. Nature. (2020) 581:100–5. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2229-5
256. Peng Y-F, Shi Y-H, Ding Z-B, Ke A-W, Gu C-Y, Hui B, et al. Autophagy inhibition suppresses pulmonary metastasis of HCC in mice via impairing anoikis resistance and colonization of HCC cells. Autophagy. (2013) 9:2056–68. doi: 10.4161/auto.26398
257. Zhu D, Zhou J, Zhao J, Jiang G, Zhang X, Zhang Y, et al. ZC3H13 suppresses colorectal cancer proliferation and invasion via inactivating Ras–ERK signaling. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:8899–907. doi: 10.1002/jcp.v234.6
258. Natan S, Tsarfaty G, Horev J, Haklai R, Kloog Y, Tsarfaty I. Interplay between HGF/SF–Met-Ras signaling, tumor metabolism and blood flow as a potential target for breast cancer therapy. Oncoscience. (2014) 1:30. doi: 10.18632/oncoscience.v1i1
259. Mikhaylova O, Stratton Y, Hall D, Kellner E, Ehmer B, Drew AF, et al. VHL-regulated MiR-204 suppresses tumor growth through inhibition of LC3B-mediated autophagy in renal clear cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell. (2012) 21:532–46. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.02.019
260. Shin JH, Park CW, Yoon G, Hong SM, Choi KY. NNMT depletion contributes to liver cancer cell survival by enhancing autophagy under nutrient starvation. Oncogenesis. (2018) 7:58. doi: 10.1038/s41389-018-0064-4
261. Guo JY, Karsli-Uzunbas G, Mathew R, Aisner SC, Kamphorst JJ, Strohecker AM, et al. Autophagy suppresses progression of K-ras-induced lung tumors to oncocytomas and maintains lipid homeostasis. Genes Dev. (2013) 27:1447–61. doi: 10.1101/gad.219642.113
262. Kalluri R, Weinberg RA. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. (2009) 119:1420–8. doi: 10.1172/JCI39104
263. Polyak K, Weinberg RA. Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states: acquisition of Malignant and stem cell traits. Nat Rev Cancer. (2009) 9:265–73. doi: 10.1038/nrc2620
264. Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell. (2009) 139:871–90. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.11.007
265. Avivar-Valderas A, Bobrovnikova-Marjon E, Alan Diehl J, Bardeesy N, Debnath J, Aguirre-Ghiso J. Regulation of autophagy during ECM detachment is linked to a selective inhibition of mTORC1 by PERK. Oncogene. (2013) 32:4932–40. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.512
266. Cai Q, Yan L, Xu Y. Anoikis resistance is a critical feature of highly aggressive ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene. (2015) 34:3315–24. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.264
267. Lock R, Kenific CM, Leidal AM, Salas E, Debnath J. Autophagy-dependent production of secreted factors facilitates oncogenic RAS-driven invasionAutophagy-dependent secretion and invasion. Cancer discovery. (2014) 4:466–79. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0841
268. Fung C, Lock R, Gao S, Salas E, Debnath J. Induction of autophagy during extracellular matrix detachment promotes cell survival. Mol Biol Cell. (2008) 19:797–806. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-10-1092
269. Lazova R, Camp RL, Klump V, Siddiqui SF, Amaravadi RK, Pawelek JM. Punctate LC3B expression is a common feature of solid tumors and associated with proliferation, metastasis, and poor outcomeAutophagy in solid Malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. (2012) 18:370–9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1282
270. Zhao H, Yang M, Zhao J, Wang J, Zhang Y, Zhang Q. High expression of LC3B is associated with progression and poor outcome in triple-negative breast cancer. Med Oncol. (2013) 30:1–8. doi: 10.1007/s12032-013-0475-1
271. Lazova R, Klump V, Pawelek J. Autophagy in cutaneous Malignant melanoma. J Cutaneous Pathology. (2010) 37:256–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.2009.01359.x
272. Shomit S, Timothy RS. m David, Regulation of mTORC1 complex 1 pathway by nutrients, growth factor and stress. Mol Cell. (2010) 40:310–22. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.026
273. Chaffer CL, Weinberg RA. A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science. (2011) 331:1559–64. doi: 10.1126/science.1203543
274. Valastyan S, Weinberg RA. Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell. (2011) 147:275–92. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.024
275. Gonçalves PR, Rocha-Brito KJ, Fernandes MR, Abrantes JL, Durán N, Ferreira-Halder CV. Violacein induces death of RAS-mutated metastatic melanoma by impairing autophagy process. Tumor Biol. (2016) 37:14049–58. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5265-x
276. Gupta GP, Massagué J. Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell. (2006) 127:679–95. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.001
277. Bryant KL, Mancias JD, Kimmelman AC, Der CJ. KRAS: feeding pancreatic cancer proliferation. Trends Biochem Sci. (2014) 39:91–100. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2013.12.004
278. Dong Y, Jin Q, Sun M, Qi D, Qu H, Wang X, et al. CLDN6 inhibits breast cancer metastasis through WIP-dependent actin cytoskeleton-mediated autophagy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2023) 42:1–17. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02644-x
279. Marsh T, Kenific CM, Suresh D, Gonzalez H, Shamir ER, Mei W, et al. Autophagic degradation of NBR1 restricts metastatic outgrowth during mammary tumor progression. Dev Cell. (2020) 52:591–604.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.01.025
280. Debela DT, Muzazu SG, Heraro KD, Ndalama MT, Mesele BW, Haile DC, et al. New approaches and procedures for cancer treatment: Current perspectives. SAGE Open Med. (2021) 9:20503121211034366. doi: 10.1177/20503121211034366
281. Society A. Cancer treatment & survivorship facts & figures 2019–2021. Atlanta: American Cancer Society (2019).
282. Rosenfeldt MT, Ryan KM. The role of autophagy in tumour development and cancer therapy. Expert Rev Mol Med. (2009) 11:e36. doi: 10.1017/S1462399409001306
283. Lu Z, Luo RZ, Lu Y, Zhang X, Yu Q, Khare S, et al. The tumor suppressor gene ARHI regulates autophagy and tumor dormancy in human ovarian cancer cells. J Clin Invest. (2008) 118:3917–29. doi: 10.1172/JCI35512
284. Amaravadi RK, Yu D, Lum JJ, Bui T, Christophorou MA, Evan GI, et al. Autophagy inhibition enhances therapy-induced apoptosis in a Myc-induced model of lymphoma. J Clin Invest. (2007) 117:326–36. doi: 10.1172/JCI28833
285. White E. The role for autophagy in cancer. J Clin Invest. (2015) 125:42–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI73941
286. Schleicher SM, Moretti L, Varki V, Lu B. Progress in the unraveling of the endoplasmic reticulum stress/autophagy pathway and cancer: implications for future therapeutic approaches. Drug Resist Updat. (2010) 13:79–86. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2010.04.002
287. Yun CW, Jeon J, Go G, Lee JH, Lee SH. The dual role of autophagy in cancer development and a therapeutic strategy for cancer by targeting autophagy. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 22(1):179. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010179
288. Dong Z, Liang S, Hu J, Jin W, Zhan Q, Zhao K. Autophagy as a target for hematological Malignancy therapy. Blood Rev. (2016) 30:369–80. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2016.04.005
289. Carew JS, Nawrocki ST, Kahue CN, Zhang H, Yang C, Chung L, et al. Targeting autophagy augments the anticancer activity of the histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA to overcome Bcr-Abl-mediated drug resistance. Blood. (2007) 110:313–22. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-10-050260
290. Smith DM, Patel S, Raffoul F, Haller E, Mills GB, Nanjundan M. Arsenic trioxide induces a beclin-1-independent autophagic pathway via modulation of SnoN/SkiL expression in ovarian carcinoma cells. Cell Death Differ. (2010) 17:1867–81. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2010.53
291. Wang MC, Wu AG, Huang YZ, Shao GL, Ji SF, Wang RW, et al. Autophagic regulation of cell growth by altered expression of Beclin 1 in triple-negative breast cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med. (2015) 8:7049–58.
292. Nc C, Keane J, Lavelle EC, Hope JC, Harris J. Autophagy in the immune response to tuberculosis: clinical perspectives. Clin Exp Immunol. (2011) 164:291–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04381.x
293. Fan Q-W, Cheng C, Hackett C, Feldman M, Houseman BT, Nicolaides T, et al. Akt and autophagy cooperate to promote survival of drug-resistant glioma. Sci Signaling. (2010) 3(147):ra81. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2001017
294. Qadir MA, Kwok B, Dragowska WH, To KH, Le D, Bally MB, et al. Macroautophagy inhibition sensitizes tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells and enhances mitochondrial depolarization. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2008) 112:389–403. doi: 10.1007/s10549-007-9873-4
295. Kondo Y, Kanzawa T, Sawaya R, Kondo S. The role of autophagy in cancer development and response to therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. (2005) 5:726–34. doi: 10.1038/nrc1692
296. DeNardo DG, Barreto JB, Andreu P, Vasquez L, Tawfik D, Kolhatkar N, et al. CD4(+) T cells regulate pulmonary metastasis of mammary carcinomas by enhancing protumor properties of macrophages. Cancer Cell. (2009) 16:91–102. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.06.018
297. Mukhopadhyay S, Panda PK, Sinha N, Das DN, Bhutia SK. Autophagy and apoptosis: where do they meet? Apoptosis. (2014) 19:555–66. doi: 10.1007/s10495-014-0967-2
299. Tam SY, Wu VW, Law HK. Influence of autophagy on the efficacy of radiotherapy. Radiat Oncol. (2017) 12:57. doi: 10.1186/s13014-017-0795-y
300. Zois CE, Koukourakis MI. Radiation-induced autophagy in normal and cancer cells: towards novel cytoprotection and radio-sensitization policies? Autophagy. (2009) 5:442–50. doi: 10.4161/auto.5.4.7667
301. Garbar C, Mascaux C, Giustiniani J, Merrouche Y, Bensussan A. Chemotherapy treatment induces an increase of autophagy in the luminal breast cancer cell MCF7, but not in the triple-negative MDA-MB231. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:7201. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07489-x
302. Sui X, Chen R, Wang Z, Huang Z, Kong N, Zhang M, et al. Autophagy and chemotherapy resistance: a promising therapeutic target for cancer treatment. Cell Death Dis. (2013) 4:e838. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.350
303. Zhang J, Ng S, Wang J, Zhou J, Tan SH, Yang N, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce autophagy through FOXO1-dependent pathways. Autophagy. (2015) 11:629–42. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1023981
304. Kanzawa T, Kondo Y, Ito H, Kondo S, Germano I. Induction of autophagic cell death in Malignant glioma cells by arsenic trioxide. Cancer Res. (2003) 63:2103–8.
305. Kanzawa T, Zhang L, Xiao L, Germano IM, Kondo Y, Kondo S. Arsenic trioxide induces autophagic cell death in Malignant glioma cells by upregulation of mitochondrial cell death protein BNIP3. Oncogene. (2005) 24:980–91. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208095
306. Kanzawa T, Germano IM, Komata T, Ito H, Kondo Y, Kondo S. Role of autophagy in temozolomide-induced cytotoxicity for Malignant glioma cells. Cell Death Differ. (2004) 11:448–57. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401359
307. White E, DiPaola RS. The double-edged sword of autophagy modulation in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2009) 15:5308–16. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-5023
308. Shimizu S, Kanaseki T, Mizushima N, Mizuta T, Arakawa-Kobayashi S, Thompson CB, et al. Role of Bcl-2 family proteins in a non-apoptotic programmed cell death dependent on autophagy genes. Nat Cell Biol. (2004) 6:1221–8. doi: 10.1038/ncb1192
309. Fazi B, Bursch W, Fimia GM, Nardacci R, Piacentini M, Di Sano F, et al. Fenretinide induces autophagic cell death in caspase-defective breast cancer cells. Autophagy. (2008) 4:435–41. doi: 10.4161/auto.5669
310. Grandér D, Kharaziha P, Laane E, Pokrovskaja K, Panaretakis T. Autophagy as the main means of cytotoxicity by glucocorticoids in hematological Malignancies. Autophagy. (2009) 5:1198–200. doi: 10.4161/auto.5.8.10122
311. Laane E, Tamm KP, Buentke E, Ito K, Kharaziha P, Oscarsson J, et al. Cell death induced by dexamethasone in lymphoid leukemia is mediated through initiation of autophagy. Cell Death Differ. (2009) 16:1018–29. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2009.46
312. Suh Y, Afaq F, Khan N, Johnson JJ, Khusro FH, Mukhtar H. Fisetin induces autophagic cell death through suppression of mTOR signaling pathway in prostate cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. (2010) 31:1424–33. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgq115
313. Kim EH, Sohn S, Kwon HJ, Kim SU, Kim MJ, Lee SJ, et al. Sodium selenite induces superoxide-mediated mitochondrial damage and subsequent autophagic cell death in Malignant glioma cells. Cancer Res. (2007) 67:6314–24. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4217
314. Kim EH, Choi KS. A critical role of superoxide anion in selenite-induced mitophagic cell death. Autophagy. (2008) 4:76–8. doi: 10.4161/auto.5119
315. Takahashi A, Kimura F, Yamanaka A, Takebayashi A, Kita N, Takahashi K, et al. Metformin impairs growth of endometrial cancer cells via cell cycle arrest and concomitant autophagy and apoptosis. Cancer Cell Int. (2014) 14:53. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-14-53
316. Nazim UM, Moon JH, Lee JH, Lee YJ, Seol JW, Eo SK, et al. Activation of autophagy flux by metformin downregulates cellular FLICE-like inhibitory protein and enhances TRAIL- induced apoptosis. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:23468–81. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v7i17
317. Marinković M, Šprung M, Buljubašić M, Novak I. Autophagy modulation in cancer: current knowledge on action and therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2018) 2018:8023821. doi: 10.1155/2018/8023821
318. Grosjean I, Roméo B, Domdom M-A, Belaid A, D’Andréa G, Guillot N, et al. Autophagopathies: From autophagy gene polymorphisms to precision medicine for human diseases. Autophagy. (2022) 18:2519–36. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2039994
319. Abuli A, Fernandez-Rozadilla C, Giraldez M, Munoz J, Gonzalo V, Bessa X, et al. A two-phase case–control study for colorectal cancer genetic susceptibility: candidate genes from chromosomal regions 9q22 and 3q22. Br J Cancer. (2011) 105:870–5. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.296
320. Zhao L-L, Liu H-L, Luo S, Walsh KM, Li W, Wei Q. Associations of novel variants in PIK3C3, INSR and MAP3K4 of the ATM pathway genes with pancreatic cancer risk. Am J Cancer Res. (2020) 10:2128–44.
321. Yang Z, Liu Z. Potentially functional variants of autophagy-related genes are associated with the efficacy and toxicity of radiotherapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Genet Genomic Med. (2019) 7:e1030. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.v7.12
322. Zhou J, Hang D, Jiang Y, Chen J, Han J, Zhou W, et al. Evaluation of genetic variants in autophagy pathway genes as prognostic biomarkers for breast cancer. Gene. (2017) 627:549–55. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.06.053
323. Shen M, Lin L. Functional variants of autophagy-related genes are associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Life Sci. (2019) 235:116675. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116675
324. Thomas HE, Mercer CA, Carnevalli LS, Park J, Andersen JB, Conner EA, et al. mTOR inhibitors synergize on regression, reversal of gene expression, and autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Trans Med. (2012) 4:139ra84–ra84. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003923
325. Furman RR, Sharman JP, Coutre SE, Cheson BD, Pagel JM, Hillmen P, et al. Idelalisib and rituximab in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. New Engl J Med. (2014) 370:997–1007. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1315226
326. Chiarini F, Grimaldi C, Ricci F, Tazzari PL, Evangelisti C, Ognibene A, et al. Activity of the novel dual phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 against T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Res. (2010) 70:8097–107. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1814
327. Al-Odat OS, Guirguis DA, Schmalbach NK, Yao G, Budak-Alpdogan T, Jonnalagadda SC, et al. Autophagy and apoptosis: current challenges of treatment and drug resistance in multiple myeloma. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 24:644. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010644
328. Actis C, Muzio G, Autelli R. Autophagy triggers tamoxifen resistance in human breast cancer cells by preventing drug-induced lysosomal damage. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13(6):1252. doi: 10.3390/cancers13061252
329. Bursch W, Ellinger A, Kienzl H, Török L, Pandey S, Sikorska M, et al. Active cell death induced by the anti-estrogens tamoxifen and ICI 164 384 in human mammary carcinoma cells (MCF-7) in culture: the role of autophagy. Carcinogenesis. (1996) 17:1595–607. doi: 10.1093/carcin/17.8.1595
331. Shen HM, Codogno P. Autophagic cell death: Loch Ness monster or endangered species? Autophagy. (2011) 7:457–65. doi: 10.4161/auto.7.5.14226
332. Kenific CM, Debnath J. Cellular and metabolic functions for autophagy in cancer cells. Trends Cell Biol. (2015) 25:37–45. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2014.09.001
333. Chen J, Zhang L, Zhou H, Wang W, Luo Y, Yang H, et al. Inhibition of autophagy promotes cisplatin-induced apoptotic cell death through Atg5 and Beclin 1 in A549 human lung cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. (2018) 17:6859–65. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8686
334. Dong Y, Wu Y, Zhao GL, Ye ZY, Xing CG, Yang XD. Inhibition of autophagy by 3-MA promotes hypoxia-induced apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2019) 23:1047–54. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201902_16992
335. Quan Y, Lei H, Wahafu W, Liu Y, Ping H, Zhang X. Inhibition of autophagy enhances the anticancer effect of enzalutamide on bladder cancer. BioMed Pharmacother. (2019) 120:109490. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109490
336. Sheng B, Song Y, Zhang J, Li R, Wang Z, Zhu X. Atorvastatin suppresses the progression of cervical cancer via regulation of autophagy. Am J Transl Res. (2020) 12:5252–68.
337. Shin D, Kim EH, Lee J, Roh JL. RITA plus 3-MA overcomes chemoresistance of head and neck cancer cells via dual inhibition of autophagy and antioxidant systems. Redox Biol. (2017) 13:219–27. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.05.025
338. Cheng X, Feng H, Wu H, Jin Z, Shen X, Kuang J, et al. Targeting autophagy enhances apatinib-induced apoptosis via endoplasmic reticulum stress for human colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. (2018) 431:105–14. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.05.046
339. Yuan N, Song L, Zhang S, Lin W, Cao Y, Xu F, et al. Bafilomycin A1 targets both autophagy and apoptosis pathways in pediatric B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. (2015) 100:345–56. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2014.113324
340. Lin JF, Lin YC, Tsai TF, Chen HE, Chou KY, Hwang TI. Cisplatin induces protective autophagy through activation of BECN1 in human bladder cancer cells. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2017) 11:1517–33. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S126464
341. Li LQ, Xie WJ, Pan D, Chen H, Zhang L. Inhibition of autophagy by bafilomycin A1 promotes chemosensitivity of gastric cancer cells. Tumour Biol. (2016) 37:653–9. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3842-z
342. Ma XH, Piao SF, Dey S, McAfee Q, Karakousis G, Villanueva J, et al. Targeting ER stress-induced autophagy overcomes BRAF inhibitor resistance in melanoma. J Clin Invest. (2014) 124:1406–17. doi: 10.1172/JCI70454
343. Cheng Y, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Ren X, Huber-Keener KJ, Liu X, et al. MK-2206, a novel allosteric inhibitor of Akt, synergizes with gefitinib against Malignant glioma via modulating both autophagy and apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther. (2012) 11:154–64. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0606
344. Chang Z, Shi G, Jin J, Guo H, Guo X, Luo F, et al. Dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BEZ235-induced apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines is enhanced by inhibitors of autophagy. Int J Mol Med. (2013) 31:1449–56. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1351
345. Boutouja F, Stiehm CM, Platta HW. mTOR: A cellular regulator interface in health and disease. Cells. (2019) 8(1):18. doi: 10.3390/cells8010018
346. Blagosklonny MV. Rapalogs in cancer prevention: anti-aging or anticancer? Cancer Biol Ther. (2012) 13:1349–54. doi: 10.4161/cbt.22859
347. Takeuchi H, Kondo Y, Fujiwara K, Kanzawa T, Aoki H, Mills GB, et al. Synergistic augmentation of rapamycin-induced autophagy in Malignant glioma cells by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B inhibitors. Cancer Res. (2005) 65:3336–46. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3640
348. Granville CA, Warfel N, Tsurutani J, Hollander MC, Robertson M, Fox SD, et al. Identification of a highly effective rapamycin schedule that markedly reduces the size, multiplicity, and phenotypic progression of tobacco carcinogen-induced murine lung tumors. Clin Cancer Res. (2007) 13:2281–9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2570
349. Memmott RM, Mercado JR, Maier CR, Kawabata S, Fox SD, Dennis PA. Metformin prevents tobacco carcinogen–induced lung tumorigenesis. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). (2010) 3:1066–76. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0055
350. Koehl GE, Spitzner M, Ousingsawat J, Schreiber R, Geissler EK, Kunzelmann K. Rapamycin inhibits oncogenic intestinal ion channels and neoplasia in APC(Min/+) mice. Oncogene. (2010) 29:1553–60. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.435
351. Amaravadi RK, Thompson CB. The roles of therapy-induced autophagy and necrosis in cancer treatment. Clin Cancer Res. (2007) 13:7271–9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1595
352. Martin KR, Celano SL, Solitro AR, Gunaydin H, Scott M, O’Hagan RC, et al. A potent and selective ULK1 inhibitor suppresses autophagy and sensitizes cancer cells to nutrient stress. iScience. (2018) 8:74–84. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2018.09.012
353. Egan DF, Chun MG, Vamos M, Zou H, Rong J, Miller CJ, et al. Small molecule inhibition of the autophagy kinase ULK1 and identification of ULK1 substrates. Mol Cell. (2015) 59:285–97. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.05.031
354. Tang F, Hu P, Yang Z, Xue C, Gong J, Sun S, et al. SBI0206965, a novel inhibitor of Ulk1, suppresses non-small cell lung cancer cell growth by modulating both autophagy and apoptosis pathways. Oncol Rep. (2017) 37:3449–58. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5635
355. Pasquier B. SAR405, a PIK3C3/Vps34 inhibitor that prevents autophagy and synergizes with MTOR inhibition in tumor cells. Autophagy. (2015) 11:725–6. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1033601
356. Dyczynski M, Yu Y, Otrocka M, Parpal S, Braga T, Henley AB, et al. Targeting autophagy by small molecule inhibitors of vacuolar protein sorting 34 (Vps34) improves the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to Sunitinib. Cancer Lett. (2018) 435:32–43. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.07.028
357. Bago R, Malik N, Munson MJ, Prescott AR, Davies P, Sommer E, et al. Characterization of VPS34-IN1, a selective inhibitor of Vps34, reveals that the phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate-binding SGK3 protein kinase is a downstream target of class III phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Biochem J. (2014) 463:413–27. doi: 10.1042/BJ20140889
358. Zahedi S, Fitzwalter BE, Morin A, Grob S, Desmarais M, Nellan A, et al. Effect of early-stage autophagy inhibition in BRAF(V600E) autophagy-dependent brain tumor cells. Cell Death Dis. (2019) 10:679. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1880-y
359. Jutten B, Rouschop KM. EGFR signaling and autophagy dependence for growth, survival, and therapy resistance. Cell Cycle. (2014) 13:42–51. doi: 10.4161/cc.27518
360. Jutten B, Keulers TG, Schaaf MB, Savelkouls K, Theys J, Span PN, et al. EGFR overexpressing cells and tumors are dependent on autophagy for growth and survival. Radiother Oncol. (2013) 108:479–83. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2013.06.033
361. Harrison DE, Strong R, Sharp ZD, Nelson JF, Astle CM, Flurkey K, et al. Rapamycin fed late in life extends lifespan in genetically heterogeneous mice. Nature. (2009) 460:392–5. doi: 10.1038/nature08221
362. Buzzai M, Jones RG, Amaravadi RK, Lum JJ, DeBerardinis RJ, Zhao F, et al. Systemic treatment with the antidiabetic drug metformin selectively impairs p53-deficient tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. (2007) 67:6745–52. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4447
363. Xie X, Koh JY, Price S, White E, Mehnert JM. Atg7 overcomes senescence and promotes growth of brafV600E-driven melanoma. Cancer Discovery. (2015) 5:410–23. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-1473
364. Karvela M, Baquero P, Kuntz EM, Mukhopadhyay A, Mitchell R, Allan EK, et al. ATG7 regulates energy metabolism, differentiation and survival of Philadelphia-chromosome-positive cells. Autophagy. (2016) 12:936–48. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1162359
365. Russo M, Milito A, Spagnuolo C, Carbone V, Rosén A, Minasi P, et al. CK2 and PI3K are direct molecular targets of quercetin in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:42571–87. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17246
366. Pareja F, Macleod D, Shu C, Crary JF, Canoll PD, Ross AH, et al. PI3K and Bcl-2 inhibition primes glioblastoma cells to apoptosis through downregulation of Mcl-1 and Phospho-BAD. Mol Cancer Res. (2014) 12:987–1001. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0650
367. Song L, Luo Y, Li S, Hong M, Wang Q, Chi X, et al. ISL Induces Apoptosis and Autophagy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Downregulation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in vivo and in vitro. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2020) 14:4363–76. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S270124
368. Ozates NP, Soğutlu F, Lerminoglu F, Demir B, Gunduz C, Shademan B, et al. Effects of rapamycin and AZD3463 combination on apoptosis, autophagy, and cell cycle for resistance control in breast cancer. Life Sci. (2021) 264:118643. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118643
369. Lin YC, Lin JF, Wen SI, Yang SC, Tsai TF, Chen HE, et al. Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine inhibit bladder cancer cell growth by targeting basal autophagy and enhancing apoptosis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. (2017) 33:215–23. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2017.01.004
370. Njaria PM, Okombo J, Njuguna NM, Chibale K. Chloroquine-containing compounds: a patent review (2010 - 2014). Expert Opin Ther Pat. (2015) 25:1003–24. doi: 10.1517/13543776.2015.1050791
371. Manic G, Obrist F, Kroemer G, Vitale I, Galluzzi L. Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine for cancer therapy. Mol Cell Oncol. (2014) 1:e29911. doi: 10.4161/mco.29911
372. Qian W, Liu J, Jin J, Ni W, Xu W. Arsenic trioxide induces not only apoptosis but also autophagic cell death in leukemia cell lines via up-regulation of Beclin-1. Leuk Res. (2007) 31:329–39. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2006.06.021
373. Frieboes HB, Huang JS, Yin WC, McNally LR. Chloroquine-mediated cell death in metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma through inhibition of autophagy. Jop. (2014) 15:189–97. doi: 10.6092/1590-8577/1900
374. Santana-Codina N, Mancias JD, Kimmelman AC. The role of autophagy in cancer. Annu Rev Cancer Biol. (2017) 1:19–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cancerbio-041816-122338
375. Homewood CA, Warhurst DC, Peters W, Baggaley VC. Lysosomes, pH and the anti-malarial action of chloroquine. Nature. (1972) 235:50–2. doi: 10.1038/235050a0
376. Ramakrishnan S, Nguyen TM, Subramanian IV, Kelekar A. Autophagy and angiogenesis inhibition. Autophagy. (2007) 3:512–5. doi: 10.4161/auto.4734
377. DiPaola RS, Dvorzhinski D, Thalasila A, Garikapaty V, Doram D, May M, et al. Therapeutic starvation and autophagy in prostate cancer: a new paradigm for targeting metabolism in cancer therapy. Prostate. (2008) 68:1743–52. doi: 10.1002/pros.v68:16
378. McChesney EW, Fitch CD. 4-aminoquinolines. In: Peters W, Richards WHG, editors. Antimalarial Drug II: Current Antimalarial and New Drug Developments. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg (1984). p. 3–60.
379. Xiong L, Liu Z, Ouyang G, Lin L, Huang H, Kang H, et al. Autophagy inhibition enhances photocytotoxicity of Photosan-II in human colorectal cancer cells. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:6419–32. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14117
380. Mauthe M, Orhon I, Rocchi C, Zhou X, Luhr M, Hijlkema KJ, et al. Chloroquine inhibits autophagic flux by decreasing autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Autophagy. (2018) 14:1435–55. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1474314
381. Barnard RA, Wittenburg LA, Amaravadi RK, Gustafson DL, Thorburn A, Thamm DH. Phase I clinical trial and pharmacodynamic evaluation of combination hydroxychloroquine and doxorubicin treatment in pet dogs treated for spontaneously occurring lymphoma. Autophagy. (2014) 10:1415–25. doi: 10.4161/auto.29165
382. Maes H, Kuchnio A, Peric A, Moens S, Nys K, De Bock K, et al. Tumor vessel normalization by chloroquine independent of autophagy. Cancer Cell. (2014) 26:190–206. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.06.025
383. Maycotte P, Aryal S, Cummings CT, Thorburn J, Morgan MJ, Thorburn A. Chloroquine sensitizes breast cancer cells to chemotherapy independent of autophagy. Autophagy. (2012) 8:200–12. doi: 10.4161/auto.8.2.18554
384. Briceño E, Reyes S, Sotelo J. Therapy of glioblastoma multiforme improved by the antimutagenic chloroquine. Neurosurg Focus. (2003) 14:e3. doi: 10.3171/foc.2003.14.2.4
385. Rosenfeld MR, Ye X, Supko JG, Desideri S, Grossman SA, Brem S, et al. A phase I/II trial of hydroxychloroquine in conjunction with radiation therapy and concurrent and adjuvant temozolomide in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. Autophagy. (2014) 10:1359–68. doi: 10.4161/auto.28984
386. Kimmelman AC. The dynamic nature of autophagy in cancer. Genes Dev. (2011) 25:1999–2010. doi: 10.1101/gad.17558811
387. Vogl DT, Stadtmauer EA, Tan KS, Heitjan DF, Davis LE, Pontiggia L, et al. Combined autophagy and proteasome inhibition: a phase 1 trial of hydroxychloroquine and bortezomib in patients with relapsed/refractory myeloma. Autophagy. (2014) 10:1380–90. doi: 10.4161/auto.29264
388. Wolpin BM, Rubinson DA, Wang X, Chan JA, Cleary JM, Enzinger PC, et al. Phase II and pharmacodynamic study of autophagy inhibition using hydroxychloroquine in patients with metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Oncologist. (2014) 19:637–8. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2014-0086
389. Boone BA, Bahary N, Zureikat AH, Moser AJ, Normolle DP, Wu WC, et al. Safety and biologic response of pre-operative autophagy inhibition in combination with gemcitabine in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. (2015) 22:4402–10. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4566-4
390. Scott EC, Maziarz RT, Spurgeon SE, Medvedova E, Gajewski J, Reasor-Heard S, et al. Double autophagy stimulation using chemotherapy and mTOR inhibition combined with hydroxychloroquine for autophagy modulation in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Haematologica. (2017) 102:e261–e5. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2016.162321
391. Patel S, Hurez V, Nawrocki ST, Goros M, Michalek J, Sarantopoulos J, et al. Vorinostat and hydroxychloroquine improve immunity and inhibit autophagy in metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:59087–97. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10824
392. Wang H, Li D, Li X, Ou X, Liu S, Zhang Y, et al. Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor RAD001 sensitizes endometrial cancer cells to paclitaxel-induced apoptosis via the induction of autophagy. Oncol Lett. (2016) 12:5029–35. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.5338
393. Dai ZJ, Gao J, Ma XB, Kang HF, Wang BF, Lu WF, et al. Antitumor effects of rapamycin in pancreatic cancer cells by inducing apoptosis and autophagy. Int J Mol Sci. (2012) 14:273–85. doi: 10.3390/ijms14010273
394. Rebecca VW, Nicastri MC, McLaughlin N, Fennelly C, McAfee Q, Ronghe A, et al. A unified approach to targeting the lysosome’s degradative and growth signaling roles. Cancer Discovery. (2017) 7:1266–83. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0741
395. McAfee Q, Zhang Z, Samanta A, Levi SM, Ma XH, Piao S, et al. Autophagy inhibitor Lys05 has single-agent antitumor activity and reproduces the phenotype of a genetic autophagy deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2012) 109:8253–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1118193109
396. Vidoni C, Ferraresi A, Secomandi E, Vallino L, Dhanasekaran DN, Isidoro C. Epigenetic targeting of autophagy for cancer prevention and treatment by natural compounds. Semin Cancer Biol. (2020) 66:34–44. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.04.006
397. Lopez G, Torres K, Liu J, Hernandez B, Young E, Belousov R, et al. Autophagic survival in resistance to histone deacetylase inhibitors: novel strategies to treat Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Cancer Res. (2011) 71:185–96. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2799
398. Solomon VR, Hu C, Lee H. Design and synthesis of chloroquine analogs with anti-breast cancer property. Eur J Med Chem. (2010) 45:3916–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2010.05.046
399. Kim SE, Overholtzer M. Autophagy proteins regulate cell engulfment mechanisms that participate in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. (2013) 23:329–36. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2013.05.004
400. Singletary K, Milner J. Diet, autophagy, and cancer: a review. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. (2008) 17:1596–610. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-07-2917
401. Hannigan AM, Gorski SM. Macroautophagy: the key ingredient to a healthy diet? Autophagy. (2009) 5:140–51. doi: 10.4161/auto.5.2.7529
402. Maycotte P, Gearheart CM, Barnard R, Aryal S, Mulcahy Levy JM, Fosmire SP, et al. STAT3-mediated autophagy dependence identifies subtypes of breast cancer where autophagy inhibition can be efficacious. Cancer Res. (2014) 74:2579–90. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3470
403. Levy JM, Thompson JC, Griesinger AM, Amani V, Donson AM, Birks DK, et al. Autophagy inhibition improves chemosensitivity in BRAF(V600E) brain tumors. Cancer Discovery. (2014) 4:773–80. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-0049
404. Strohecker AM, Guo JY, Karsli-Uzunbas G, Price SM, Chen GJ, Mathew R, et al. Autophagy sustains mitochondrial glutamine metabolism and growth of BrafV600E-driven lung tumors. Cancer Discovery. (2013) 3:1272–85. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0397
405. La Belle Flynn A, Calhoun BC, Sharma A, Chang JC, Almasan A, Schiemann WP. Autophagy inhibition elicits emergence from metastatic dormancy by inducing and stabilizing Pfkfb3 expression. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:3668. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11640-9
406. Kinsey CG, Camolotto SA, Boespflug AM, Guillen KP, Foth M, Truong A, et al. Protective autophagy elicited by RAF→MEK→ERK inhibition suggests a treatment strategy for RAS-driven cancers. Nat Med. (2019) 25:620–7. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0367-9
407. Finbloom DS, Silver K, Newsome DA, Gunkel R. Comparison of hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine use and the development of retinal toxicity. J Rheumatol. (1985) 12:692–4.
408. Chung SF, Kim CF, Chow HY, Chong HC, Tam SY, Leung YC, et al. Recombinant bacillus caldovelox arginase mutant (BCA-M) induces apoptosis, autophagy, cell cycle arrest and growth inhibition in human cervical cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21(20):7445. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207445
409. Shao S, Li S, Qin Y, Wang X, Yang Y, Bai H, et al. Spautin-1, a novel autophagy inhibitor, enhances imatinib-induced apoptosis in chronic myeloid leukemia. Int J Oncol. (2014) 44:1661–8. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2313
410. Ronan B, Flamand O, Vescovi L, Dureuil C, Durand L, Fassy F, et al. A highly potent and selective Vps34 inhibitor alters vesicle trafficking and autophagy. Nat Chem Biol. (2014) 10:1013–9. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1681
411. Luanpitpong S, Chanvorachote P, Nimmannit U, Leonard SS, Stehlik C, Wang L, et al. Mitochondrial superoxide mediates doxorubicin-induced keratinocyte apoptosis through oxidative modification of ERK and Bcl-2 ubiquitination. Biochem Pharmacol. (2012) 83:1643–54. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.03.010
412. Yan C, Luo L, Guo CY, Goto S, Urata Y, Shao JH, et al. Doxorubicin-induced mitophagy contributes to drug resistance in cancer stem cells from HCT8 human colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Lett. (2017) 388:34–42. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.11.018
413. Rebecca VW, Amaravadi RK. Emerging strategies to effectively target autophagy in cancer. Oncogene. (2016) 35:1–11. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.99
414. Bowman CJ, Ayer DE, Dynlacht BD. Foxk proteins repress the initiation of starvation-induced atrophy and autophagy programs. Nat Cell Biol. (2014) 16:1202–14. doi: 10.1038/ncb3062
415. Settembre C, Di Malta C, Polito VA, Garcia Arencibia M, Vetrini F, Erdin S, et al. TFEB links autophagy to lysosomal biogenesis. Science. (2011) 332:1429–33. doi: 10.1126/science.1204592
416. Kenzelmann Broz D, Spano Mello S, Bieging KT, Jiang D, Dusek RL, Brady CA, et al. Global genomic profiling reveals an extensive p53-regulated autophagy program contributing to key p53 responses. Genes Dev. (2013) 27:1016–31. doi: 10.1101/gad.212282.112
417. Karsli-Uzunbas G, Guo JY, Price S, Teng X, Laddha SV, Khor S, et al. Autophagy is required for glucose homeostasis and lung tumor maintenance. Cancer Discovery. (2014) 4:914–27. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-0363
418. Füllgrabe J, Lynch-Day MA, Heldring N, Li W, Struijk RB, Ma Q, et al. The histone H4 lysine 16 acetyltransferase hMOF regulates the outcome of autophagy. Nature. (2013) 500:468–71. doi: 10.1038/nature12313
419. Si L, Fu J, Liu W, Hayashi T, Mizuno K, Hattori S, et al. Silibinin-induced mitochondria fission leads to mitophagy, which attenuates silibinin-induced apoptosis in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. (2020) 685:108284. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108284
420. Karpel-Massler G, Ishida CT, Zhang Y, Halatsch ME, Westhoff MA, Siegelin MD, et al. Targeting intrinsic apoptosis and other forms of cell death by BH3-mimetics in glioblastoma. Expert Opin Drug Discov. (2017) 12(10).
421. Yang ZJ, Chee CE, Huang S, Sinicrope FA. The role of autophagy in cancer: therapeutic implications. Mol Cancer Ther. (2011) 10:1533–41. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0047
422. Munster T, Gibbs JP, Shen D, Baethge BA, Botstein GR, Caldwell J, et al. Hydroxychloroquine concentration-response relationships in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2002) 46:1460–9. doi: 10.1002/art.10307
423. Tett SE, Day RO, Cutler DJ. Concentration-effect relationship of hydroxychloroquine in rheumatoid arthritis–a cross sectional study. J Rheumatol. (1993) 20:1874–9.
424. Gewirtz DA. The four faces of autophagy: implications for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. (2014) 74:647–51. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-2966
Keywords: autophagy, cancer, immunotherapy, precision-medicine, tumorigenesis
Citation: Jalali P, Shahmoradi A, Samii A, Mazloomnejad R, Hatamnejad MR, Saeed A, Namdar A and Salehi Z (2025) The role of autophagy in cancer: from molecular mechanism to therapeutic window. Front. Immunol. 16:1528230. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1528230
Received: 14 November 2024; Accepted: 12 March 2025;
Published: 03 April 2025.
Edited by:
Weiliang Hou, Naval Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Mariana Pavel-Tanasa, Grigore T. Popa University of Medicine and Pharmacy, RomaniaCopyright © 2025 Jalali, Shahmoradi, Samii, Mazloomnejad, Hatamnejad, Saeed, Namdar and Salehi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zahra Salehi, emFocmEuc2FsZWhpNjQ2M0B5YWhvby5jb20=
†ORCID: Zahra Salehi, orcid.org/0000-0002-0839-2729
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.