- 1School of Rehabilitation Medicine, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou, China
- 2School of Basic Medicine, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou, China
- 3Key Laboratory of Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases, Ministry of Education, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou, China
The structural and functional integrity of glomerular cells is critical for maintaining normal kidney function. Glomerular diseases, which involve chronic histological damage to the kidney, are related to injury to glomerular cells such as endothelial cells, mesangial cells (MCs), and podocytes. When faced with pathogenic conditions, these cells release pro-inflammatory cytokines such as chemokines, inflammatory factors, and adhesion factors. These substances interact with glomerular cells through specific inflammatory pathways, resulting in damage to the structure and function of the glomeruli, ultimately causing glomerular disease. Although the role of inflammation in chronic kidney diseases is well known, the specific molecular pathways that result in glomerular diseases remain largely unclear. For a long time, it has been believed that only immune cells can secrete inflammatory factors. Therefore, targeted therapies against immune cells were considered the first choice for treating inflammation in glomerular disease. However, emerging research indicates that non-immune cells such as glomerular endothelial cells, MCs, and podocytes can also play a role in renal inflammation by releasing inflammatory factors. Similarly, targeted therapies against glomerular cells should be considered. This review aims to uncover glomerular diseases related to inflammation and pathways in glomerular inflammation, and for the first time summarized that non-immune cells in the glomerulus can participate in glomerular inflammatory damage by secreting inflammatory factors, providing valuable references for future strategies to prevent and treat glomerular diseases. More importantly, we emphasized targeted glomerular cell therapy, which may be a key direction for the future treatment of glomerular diseases.
1 Introduction
Glomerular disease (GD) is divided into two main categories: primary glomerular disease and secondary glomerular disease. The former mainly includes focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), minimal change disease (MCD), IgA nephropathy (IgAN), primary membranous nephropathy (PMN), membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN), and primary crescentic glomerulonephritis, while the latter includes lupus nephritis (LN), HIV-associated nephropathy (HIVAN), diabetic nephropathy (DN), hypertensive nephrosclerosis, post-infectious glomerulonephritis (PIGN), non-IgA membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MesPGN), and hypo-immunoglobular nephritis (1–4). These glomerular diseases result from glomerular injury, severe tubular loss or atrophy, some cystic degeneration, and thickening of the renal vasculature, are considered to be one of the major causes of progressive end-stage renal disease. The glomerular disease can be definitively diagnosed by renal biopsy, histopathologic examination, and laboratory tests. Several studies have shown a multimodal progression of glomerular diseases, which is mainly characterized by inconsistent prevalence of different glomerular diseases in different regions. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS; 19.1%) predominated in North America; lupus nephritis (38.1%) and FSGS (15.8%) predominated in Latin America; IgA nephropathy (IgAN; 22.1%) and FSGS (14.9%) predominated in Europe; and IgAN (39.5%) and lupus nephritis (16.8%) predominated in Asia (5). In China, MCD is the most common glomerular disease, accounting for 28.7% of primary glomerular diseases, while MPGN and IgAN account for 25.8% and 22.1%, respectively, in the second and third places (6). It is safe to assume that LN and DN are the most common secondary glomerular diseases and this finding is prevalent worldwide (2, 7). Despite the fact that the occurrence of glomerular disease varies globally (1), it is known to have an impact on mortality rates associated with chronic kidney disease (8, 9).
The glomerular filtration barrier is composed of three main components: glomerular endothelial cells, MCs and podocytes. Investigating the impairment of those components is a major focus in the study of glomerular diseases. Glomerular endothelial cells have a similar role to other endothelial cells, help maintain tissue perfusion and hemodynamics by constructing a filtration barrier, and regulating the inflammatory process through the expression or binding of various circulating factors, such as endothelin-1 (ET-1), prostacyclin inflammatory receptor, intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM1), vascular cell adhesion protein 1 (VCAM1), E-selectin and membrane cofactor protein 1 (MCP1) among others (10–12). Mohamed A demonstrated that intravenous injection of ET-1 into the glomerulus caused an increase in plasma soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1) and MCP-1 in the glomerulus, as well as an increased in the number of macrophages and lymphocytes in the renal cortex (13). Studies have demonstrated that overexpression of ET-1 in the kidney leads to renal inflammation and fibrosis (14). When glomerular cells are injured, they stimulate the secretion of inflammatory factors. As a kind of stromal cell, in addition to organizing the glomerular structure and maintaining the homeostasis of endothelial cells and podocytes, MCs also participate in the immune response through the production of chemokines (including Col6a3, Mmp14, Mmp17, Col12a1, Cxcl1, Ccl2 and Cx3cl1) (15, 16), which provides the basis for the development of glomerular inflammation. The chemokines Ccl2 and Cx3cl1 have also been found to be involved in the development of inflammation in DN (17). Glomerular disease progression is often linked to inflammation caused by podocyte injury. Inflammatory factors, primarily originating from podocyte injury, are commonly overexpressed in various glomerular diseases. In an experiment by Rachael D. Wright et al., podocytes were exposed to inflammatory factors (IL-1β, TNF-α, IFN-α, and IFN-γ) individually or in combination. The aim was to establish an in vitro renal inflammation model that mirrors the inflammatory conditions observed in patients with lupus nephritis (LN). As a result of this stimulation, there was a rise in the secretion of IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, VEGF, M-CSF, and interferon gamma-inducible protein-10 (IP-10) (18).
Inflammatory factors released after glomerular cell injury may play a crucial role in the progression of glomerular diseases. Studies have shown that oxidative stress can also trigger the release of inflammatory factors from glomerular cells (19, 20). ROS overproduction and impaired antioxidant defense systems are the two leading causes of oxidative stress, which is an imbalance between ROS production and elimination (21) This imbalance is often seen in mitochondria, where excess ROS production can be harmful and cause further damage to mitochondria. This can lead to elevated mtROS levels, reduced ATP production, and ultimately result in mitochondrial metabolic disorders (22–24). Increased levels of ROS in renal tubular epithelial cells can induce the secretion of chemokines and pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), through NOD-like receptors (NLRs), leading to sustained kidney injury (25). High glucose levels induce ROS in glomerular mesangial cells, activating the NF-KB pathway and increasing expression of EGR-1 and PKC-α in MCs of patients with DKD. This activation enhances inflammatory factors MCP-1 and fibrotic markers collagen I and III, promoting localized inflammatory and fibrotic responses in the kidney (26). In glomerular endothelial cells, elevated glucose levels increase the expression of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 (IGFBP5) in endothelial cells, leading to upregulation of EGR1. In addition, it was found that EGR1 enhances the enzymatic function of PFKB3, which leads to the secretion of inflammatory factors such as ICAM-1, TNF-α, IL-6, and MCP-1 from endothelial cells through the enhancement of glycolysis, and ultimately causes inflammatory injury (27). These effects are linked to disruptions in mitochondrial metabolism. Furthermore, when mtROS induce mitochondrial permeability transition pores (mPTP), IMM proteins, such as cytochrome c, are released into the cytosol, resulting in inflammatory response and apoptosis (28).
Inflammatory response caused by glomerular cell injury is a key factor in the progression of glomerular diseases and increase the risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality. While immune cells have long been known to be involved in the development of inflammation, recent studies have shown that non-immune cells such as glomerular endothelial cells, mesangial cells (MCs), and podocytes could also contribute to renal inflammation by releasing inflammatory factors. This article provides a review of research on the molecular mechanisms, prevention, and treatment of inflammatory responses in various types of glomerular diseases. Understanding the signaling pathways involved in triggering glomerular diseases in pathological conditions and implementing strategies to prevent inflammatory responses can help protect against glomerular damage.
2 Structure and function of the glomerulus
The glomerulus is a filtration system consisting of a central capillary bulb and a renal capsule that filters blood and forms primary urine. It consists of an open endothelium layer of endothelial cells, a glomerular basement membrane (GBM) made up of extracellular proteins in the second layer; and the distal layer consists of visceral epithelial. Podocytes contribute to the formation of filtration slit septa, and play a key role in supporting capillary flow and maintaining the integrity of the freestanding capillary loop (29). Glomerular disease can occur due to damage to any of the structures in the glomerular filtration barrier, leading to inflammation. The three types of glomerular cells, including the MCs, have endocrine functions and interact with each other through autocrine and paracrine pathways, which can contribute to the inflammation in the glomerulus (Figure 1).
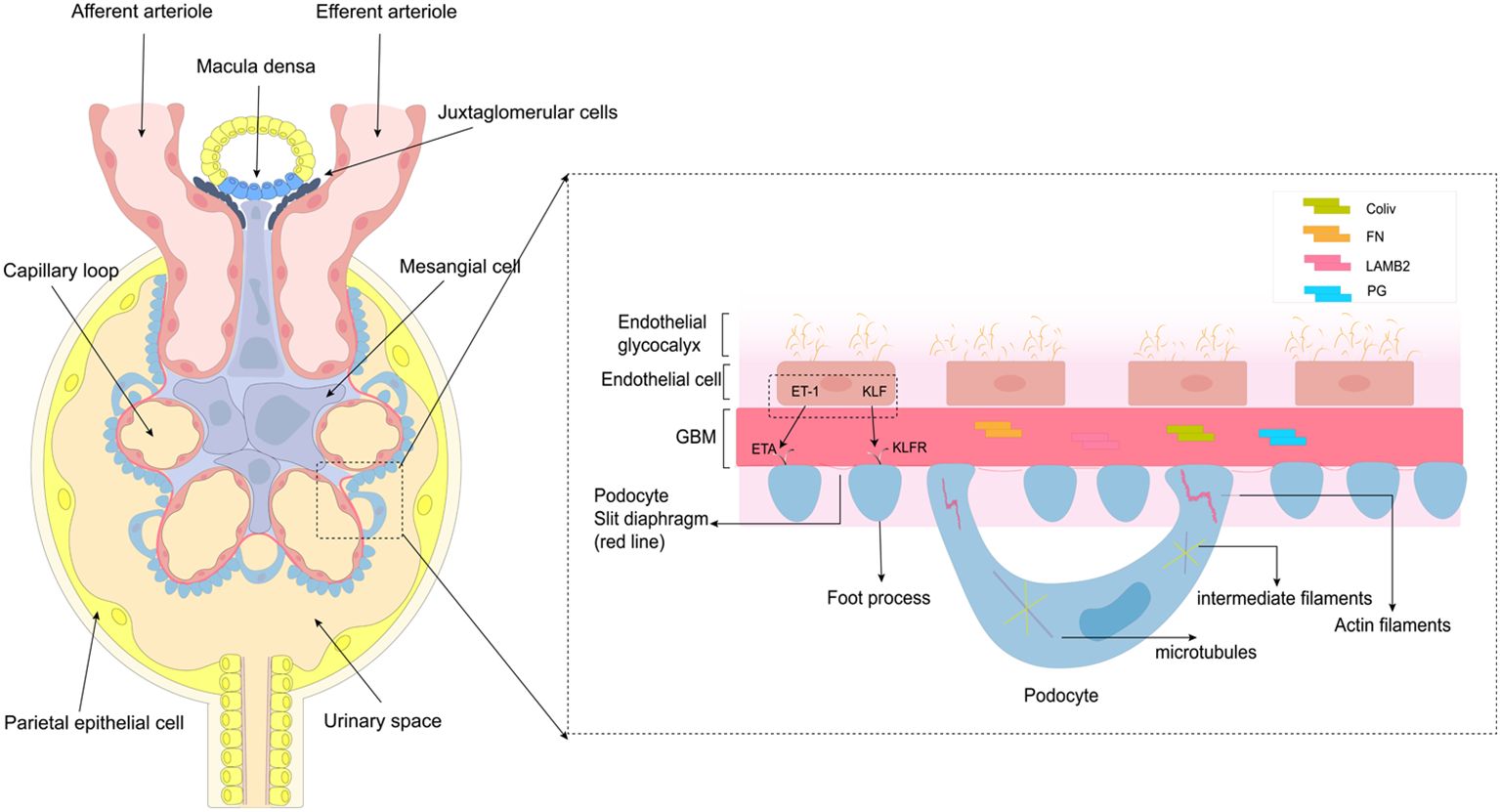
Figure 1. Structure and function of the glomerulus. This diagram depicts the structure and function of glomerular endothelial cells, glomerular basement membrane, and podocytes, primarily podocytes. Podocytes consist of cell bodies, primary processes, and secondary foot processes; adjacent foot processes form the slit diaphragm. The cell bodies and primary processes are based on microtubules and intermediate filaments, while the foot processes mainly depend on the actin filaments.
2.1 Endothelial cell
Glomerular endothelial cells (GEnC) are a vital part of the glomerulus, responsible for maintaining the filtration barrier. These cells are attached to the inner glomerular basement membrane, and are separated from the podocytes by the basement membrane. The open window, found in the cytoplasmic portion of the cytosol, opposite the podocyte pedicle, and passes through the filtration slit of the glomerular basement membrane. This structure not only plays a key role in glomerular permeability but also facilitates communication between GEnC and neighboring cells (30). The glycocalyx, a specialized structure found in GEnC (31), plays a crucial role in limiting the penetration of macromolecular proteins (32). Notably, there is growing evidence that loss of endothelial openings and a decrease in the number of glycocalyx are among the earliest changes in glomerular disease (33), and is also associated with inflammation. A study revealed that in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, serum levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptors 1 and 2 were inversely related to the percentage of open-window GEnC (34). Moreover, dysfunction in GEnC opening and a decrease in glycocalyx quantity can hinder the interaction between GEnC and adjacent glomerular cells, leading to irregular expression of certain cytokines (30, 32). There is evidence that ET-1 and Krüppel-like factor (KLF) mediate communication between endothelial cells and podocytes and bind to corresponding receptors to promote/inhibit inflammation (13, 35). In DN, ET(A) receptor-induced oxidative stress in endothelial mitochondria has been shown to lead to GEnC damage and loss of open windows (36). Mitochondrial oxidative stress induces GEnC dysfunction, causing podocyte injury (37). KLF acts as a transcription factor that inhibits NF-KB activation, resulting in anti-inflammatory effects (38, 39). Endothelial openings and glycocalyx play a key role in the glomerular cell communication and the development of glomerular inflammation.
2.2 Mesangial cells
Mesangial cells (MCs), as resident cells of the kidneys, play an important role in maintaining glomerular function. They are located between the capillary loops of the glomeruli and are adjacent to endothelial cells and the capillary basement membrane (40). Mesangial cells are now recognized to belong in a class of cells known as mesenchymal stromal cells. Consistent with their role as stromal cells, MCs are the main producers of glomerular matrix, which comprises type iv collagen (Col iv), fibronectin (FN), laminin subunit beta 2 (LAMB2), proteoglycans (PG) and other ECM components (41, 42). The main functions of MCs include providing support to the capillary plexus, constricting vascular and secretion of extracellular matrix components, producing cytokines such as Col6a3, Mmp14, and Mmp17, as well as chemokines like Ccl2 and Cx3cl1, and carrying out phagocytosis and clearance of macromolecules (15). MCs can be affected by changes in the glomerular environment, leading to functional transformation. They can act as stromal cells and influence the recruitment of immune cells by altering ECM components and producing chemokines. This can result in a quick response to innate immune stimuli or tissue damage. MCs also have the potential to function as antigen-presenting cells, expressing surface markers like MHC and ICAM-1 when activated. They can interact with CD4 T cells to participate in the local renal immune response (43). Additionally, studies have shown that mast cells (MCs) also express innate immune signaling components such as Toll-like receptors TLR3 and TLR4, as well as intracellular pattern recognition receptors NOD1 and NOD2 (16). In summary, the interaction between MCs and the immune system leads to the production of various chemokines and matrix components that regulate the inflammatory response, aiding in the characterization of inflammation in glomerular disease.
2.3 Podocytes
Podocytes, the glomerular basement membrane (GBM), and endothelial cells make up the glomerular filtration barrier (GFB) (44). The foot process of podocytes can be divided into three specialized membrane regions: the basal, apical, and lacunar septum regions. The apical membrane region plays a crucial role in the negatively charged glomerular barrier; with the slit diaphragm regulating glomerular permeability. In addition, podocytes have a well-organized cytoskeletal structure that includes microtubules (MTs) and intermediate filaments (IFs). It is crucial for maintaining GFB integrity and regulating cell structure, stability, motility, cell adhesion, and slit diaphragm insertion (45). Sijia Ma et al. emphasized the importance of foot cytoskeletal rearrangements in glomerular diseases. The slit diaphragm interacts with various focal adhesion proteins, causing the breakdown of the foot cytoskeletal structure. This includes the involvement of signaling node nephrin, calcium influx through transient receptor potential channel 6 (TRPC6), and regulation of the Rho family, ultimately resulting in the disruption of the initial cytoskeletal framework (46). The slit diaphragm also contains lipid rafts that are abundant in sphingolipids, which serve a structural purpose in cell membranes and possess various bioactive functions (47). Dysregulation in sphingolipid metabolism has been shown to cause podocyte injury and drive the progression of glomerular disease (48). Podocytes, as the critical component of the kidney filtration units, maintain their unique cellular structure through an intricate and coordinated network of cytoskeletons (49). When podocytes suffer direct or indirect injury, it disrupts the cytoskeleton, leading to foot process effacement (FPE), proteinuria, and ultimately kidney inflammation (46, 50).
3 Inflammatory factors in glomerular disease
3.1 Three types of glomerular cells and inflammatory factors
Inflammation plays a significant role in the onset of chronic kidney disease, leading to reduced renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) (51). Glomerular endothelial cells, mesangial cells, and podocytes, as resident cells, function collectively to preserve the structure and function of the glomerulus, and establish communication with one another. When inflammation occurs, renal resident cells become activated and display a pro-inflammatory phenotype (10, 52), this activation involves the release of transcription factors, pro-inflammatory factors, chemokines, and adhesion factors, ultimately resulting in glomerular injury and fibrosis (53, 54). Immune injury, metabolic injury, toxicity, and genetic injury can all lead to the activation of glomerular cells (16). Immune injury is mainly characterized by macrophage recruitment and upregulation of some cytokines, including inflammatory factors, adhesion factors, and chemokines (16, 55). Under these pathological circumstances, glomerular cells crosstalk with each other via signaling and inflammatory mediators, ultimately resulting in glomerular damage (54, 56, 57). In summary, the activation of these three kinds of glomerular cells in pathological conditions leads to the release of pro-inflammatory factors, exacerbating glomerular injury and ultimately causing glomerular disease.
It has been reported that all three types of glomerular cells can express inflammatory factors (Table 1) and lead to glomerular diseases. Here, we will explore the pathophysiological processes of these four glomerular diseases, which are triggered by glomerular cell injury and the inflammatory response.
3.2 Glomerular injury resulting from inflammation
3.2.1 Inflammation associated with diabetic nephropathy can cause damage to the glomeruli
DN is a progressive microvascular diabetic complication and one of the major causes of end-stage renal disease (ESRD), which is clinically characterized by persistent hyper-proteinuria and reduced glomerular filtration (87). Recently, numerous studies have shown that DN may be characterized as a chronic inflammatory kidney disease, with the upregulation of inflammatory signaling pathways and the infiltration of inflammatory cells are associated with kidney injury and the development of DN (88, 89). Reviews have indicated that several inflammatory factors are involved in DN inflammatory processes, such as nuclear transcription factors (NF-κB), pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1, IL-6, IL-18 and TNF), chemokines (MCP-1, CXCL12, CX3CL1 and CX3CR1) adhesion molecules (ICAM1, VCAM1, E-selectin and α-actinin 4), and signaling molecules (STAT1,STAT3 and STAT5) are involved in DN inflammatory processes (17, 90). Yuheng Qiu et al. identified the biological pathways involved in the development of DN by enrichment analysis, revealing that chemokines, cytokines, and inflammation-related pathways were strongly associated with the progression of DN to end-stage renal disease (91). Evidence demonstrated that TNF-α, a pro-inflammatory factor, is necessary for the development of DN (92).
Ioanna et al. found evidence indicating that the TNF-α pathway is activated in the early phases of DN. They observed elevated levels of TNF-α in the urine of patients with early DN compared to those in later stages (93). Elevated levels of TNF-α receptors (TNFR1 and TNFR2) and the kidney injury marker KIM-1 have also been linked to DN (94), TNFR1 and TNFR2 have been recognized as markers for the risk of developing ESRD in people with type 2 diabetes (95). TNF-α is an inflammatory mediator that binds to TNFR1 and TNFR2, leading to the activation of various signaling pathways. This results in the expression of transcription factors, cytokines, growth factors, receptors, cell adhesion molecules, and other inflammatory mediators. When bound to TNFR2, TNF-α, a downstream target of the NF-KB pathway, induces persistent NF-κB activation. It also triggers MCs by releasing chemokines like MCP-1, IL-6, and IL-8 (96),while directly promotes the expression of ICAM-1 on MCs (97). In summary, TNF-α is responsible for initiating and development of DN inflammation, mainly by stimulating the production of adhesion molecules and releasing chemokines when it binds to TNFR. Interestingly, MCP-1 and TNF-α are recognized as novel inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of DN (98).
3.2.2 Lupus nephritis
Systemic lupus erythematosus that affects the kidneys is commonly referred to as LN, which is a serious and frequent complication. Various models have been studied to uncover the cause of LN, and most of these modern models suggest that anti-chromatin antibodies have a significant impact on the initiation of LN, mainly by binding to exposed chromatin in the glomerulus. In the early stages of LN, there is often an accumulation of chromatin fragments and IgG complexes in the mesangial matrix, likely due to the decrease in DNase I enzyme activity. Therefore, the failure to degrade chromatin from secondary necrotic cells leads to its accumulation with IgG complexes in the GBM (99–102). Since the mesangial membrane is one of the major sites of IG deposition, the development of LN inflammation may be associated with MCs (103). It has been demonstrated that anti-dsDNA antibody binds directly to MC membrane connexin II and α-actinin to induce the expression of pro-inflammatory factors in cultured MCs, including TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 (104, 105). A recent study has indicated that IL-6, a well-known pro-inflammatory factor, does not appear to be linked to the emergence of LN (106). Anti-dsDNA antibody also induces MCP-1 secretion and CXCL1 and CX3CL gene expression in cultured MCs through activation of PKC, increased IL-1β secretion, and IκB and NFκB signaling pathways (105, 107, 108). The MCs possess TLR receptors, and upon activation, these receptors initiate pathways that lead to the generation of various adhesion molecules, cytokines, and chemokines (109). Moreover, in the LN mouse model, the adhesion molecules ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 showed an increase in expression in MCs (110). A recent study has shown that the activation of NLRP3 in podocytes may be a contributing factor to LN (111). Moreover, the expression of proinflammatory cytokines (such as IL-1 and IL-6) by classically activated macrophages leads to the proliferation of MCs and the expression of extracellular matrix (112). MCs contribute significantly to IL-6 production in glomeruli and also releases M-CSF, which triggers the recruitment of macrophages in glomeruli (113). Thus, it is evident that macrophages are also involved in the development of LN inflammation. A recent study proposed that macrophages may be a marker for the onset and remission of inflammation in LN (114). Traditional markers for detecting LN, including serum creatinine, urinary protein, anti-dsDNA antibody, and complement C3/4, do not directly reflect the onset of LN or differentiate between active and chronic disease. Some studies have reported that rinary CD11c+ macrophages derived from circulating monocytes are abundant in the urine of patients with active proliferative LN and are significantly associated with the serum anti-dsdsorbutin antibody. significantly associated with the serum anti-dsDNA antibody titer, inflammation and interstitial fibrosis (115). Soluble CD163 is the most discussed macrophage product, and it can be detected in the urine of LN patients (116). Moreover, some studies have reported that patients with active LN have significantly higher levels of urinary soluble CD163 (117). In summary, CD11c+ and CD163 can be used as biomarkers for clinical and pathological features of LN patients (114, 116).
3.2.3 Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
FSGS is characterized by the formation of glomerular scarring and capillary occlusion in specific glomerular clusters due to extracellular matrix deposition (118). Studies have indicated that inflammation can exacerbate glomerulosclerosis and progress to end-stage renal disease. Recently, there have been several new pathogenic mechanisms proposed, such as circulating permeability factors that are able to activate inflammatory factors in glomeruli and subsequently induce glomerulosclerosis (119). Lilian Otalora et al. performed gene-enriched KEGG pathway analysis of glomeruli from FSGS patients and showed that inflammatory pathways including TNF-α, IL-17, and NF-κB were significantly activated by one or more circulating permeability factors (120). Furthermore, they also showed that chemokines such as CCL2, CCL3, CCL20, CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL5, CXCL6, and CXCL12 were activated in the podocytes of FSGS patients. Notably, CCL3 was only rapidly activated when it was exposure to circulating factors present in the serum of FSGS patients (120). Another study revealed that CCL2/CCR2 signaling might contribute to the damage of glomeruli in FSGS (85). The absence of CCL2 has been linked to a reduction in both structural and functional damage to the kidney in glomerulosclerosis. Moreover, individuals with primary FSGS have shown elevated levels of IL-9. Experiments have shown that blocking the attachment of the IL-9 receptor to podocyte membranes can effectively prevent glomerulosclerosis (121). These cytokines not only reflect the degree of inflammation in the disease, but also serve as biomarkers of disease onset and are detected in the patient’s urine (122). As for recurrent FSGS, the mechanism of its occurrence may be related to circulating permeability factors, including soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR), anti-CD40 antibody, cardiolipin-like cytokine 1 (CLCF-1), apolipoprotein A-Ib (ApoA-Ib), calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinases (CASK), microRNAs, and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) (119, 123). Recently, CPF (circulating permeability factor)-containing plasma from FSGS patients was found to induce the accumulation of lipid droplets and perilipin-2 expression in podocytes, and perilipin-2 was proposed to be identified as a potential biomarker (124). Whether these circulating permeability factors can be used as specific biomarkers for the diagnosis of FSGS requires further experimental evidence.
3.2.4 IgAN
IgAN is a chronic inflammatory kidney condition caused by the abnormal presence of galactose-deficient immunoglobulin A1 (Gd-IgA1), resulting in the accumulation of immune complexes in the mesangium, ultimately leading to kidney inflammation and damage (125, 126). According to a recent review, the mechanism of IgAN inflammation may be caused by the elevated levels of renal-derived ICs, such as anti-Gd Ig A1 antibodies and/or Ig M antibodies, leading to the deposition of serum Gd-Ig A1, and these antibodies in the mesangial region of IgAN patients (127). Some of the deposits can form the nephritic immune complex (HIT3) and activate the MCs, which leads to an increase in the production of extracellular matrix components, cytokines, and chemokines (128). The entire process is consistent with the multihit hypothesis of IgA nephropathy, including production of galactose-deficient IgA1 (Gd-IgA1; Hit 1), IgG or IgA autoantibodies that recognize Gd-IgA1 (Hit 2), and their subsequent immune complexes formation (Hit 3) and glomerular deposition (Hit 4), which has been widely supported by many studies. Whichever stage of injury occurs triggers glomerular inflammation, which is regulated by the CCL2/CCR axis (129). Since IgAN is defined by immunohistochemical or immunofluorescent detection of glomerular IgA deposits, the diagnosis can only be made by renal biopsy (130). In addition to the predominantly, mainly mesangial cell IgA deposits (sometimes also visible along the capillary wall), complement C3 can be detected, and rarely other complement components (C4d, C1q) and/or (to a lesser extent) IgG. During the treatment of IgAN patients, the extent of disease progression can be monitored by testing for urinary inflammatory biomarkers, thus avoiding further renal biopsies. Soo-Young Yoon et al. detected inflammation-related biomarkers in the urine of IgAN patients by multiplex enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (131). Compared with normal controls, the IgAN group had higher levels of eight urinary inflammatory biomarkers, including BAFF, MCP-1, CXCL10, GDF-15, IL-6, MBL, TfR, KIM-1, GDF-15 and EGF. Recently, MCP-1 and EGF were proposed as valuable biomarkers of IgAN progression and development of chronic histological lesions (132). Torres et al. demonstrated that the predictive value of the EGF/MCP-1 ratio was significantly higher than that of EGF or MCP-1 alone, histologic grading, creatinine clearance, or proteinuria (132). Ju et al. demonstrated that measurements of urinary EGF improved the prediction of renal outcome (133). Therefore, urinary inflammatory biomarkers can be used as alternative predictive biomarkers in patients with IgAN.
4 Pathways in glomerular inflammation
4.1 JAK/STAT signaling pathway
After being phosphorylated by Janus kinase (JAK) in the cytoplasm, the signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) translocated from the cytoplasm to the nucleus and regulates the expression of relevant genes. This pathway is known as the JAK/STAT signaling pathway (134). Activation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway can be mediated by various factors such as high glucose (135), advanced glycosylation end products (136), and Adriamycin (137). Studies have shown that these substances can induce inflammation by activating the JAK/STAT signaling pathway at the cellular or animal level (138). Moreover, specific cytokines such as TGF-β (139), rIL-6 (140), and IFN (141), can also activate the JAK/STAT signaling pathway.
Extensive research has been conducted on the role of JAK/STAT in various glomerular diseases, including IgAN (142), DN (143), FSGC (144) and LN (142). The overexpression of STAT has been detected in various renal disease caused by glomerular cell injury, including podocytes in DN mice, human glomerular endothelial cells in an in vitro model of LN, and MCs in pediatric FSGS patients (63, 144, 145). Thus, blocking the JAK/STAT signaling pathway is essential for alleviating inflammation in glomerular disease, mainly involving STAT1/3/4.
SOCS, known as suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS), is involved in the negative regulation of glomerular disease and act as the negative feedback regulators of JAK/STAT signaling. SOCS-1, a member of the SOCS family, regulates the intensity and length of JAK/STAT signaling by employing various methods such as kinase inhibition and binding to STAT proteins (146, 147). SOCS-1 has been shown to reduce renal damage in diabetic mice by enhancing MCP-1 expression and controlling JAK/STAT phosphorylation (148). The possible mechanism is that the structure of SOCS-1 contains a 12 amino acid N-terminal kinase inhibitory region (KIR), which is essential for inhibition of JAK tyrosine kinase activity. Carlota and her team studied the renal effects of a peptidomimetic peptide in the KIR region of the SOCS-1 structure. They found that the peptide inhibited STAT1/3 activation, lowered the expression of mediators induced by hyperglycemia and inflammatory diseases, and decreased MCs proliferation (149). A recent study indicated that inhibitors of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) may improve renal injury by reducing renal inflammation and fibrosis via the SOCS/JAK/STAT pathway (150). MiR-145 is able to inactivate the JAK/STAT signaling pathway by directly targeting colony stimulating factor-1(CSF1), thereby inhibiting apoptosis and inflammatory injury in MCs. This ultimately prevents the progression of LN (143).
IL-35, the newest member of the IL-12 family, is composed of IL-12A (p35) and Epstein-Barr virus-induced (EBI)-3 subunits. These subunits bind to the IL-12Rβ2 and gp130 chains, respectively. The gp130 and IL-12Rβ2 chains can form a heterodimer (IL-12Rβ2:gp130), the IL-35 receptor (151). According to a recent study, IL-35 has been proposed to regulate the JAK/STAT signaling pathway in LN model of MCs (152). IL-35 suppresses angiogenesis and also inhibits the mRNA and protein expression levels of TNF-α and IL-6 through the JAK/STAT1 pathway (153). It is possible that STAT1/4 could form a unique heterodimer and bind to the promoter regions of both IL-35 subunits (p35 and EBI3), leading to the mediation of IL35R signaling (154). In addition, the interaction of IL-35 with IL-35R enhanced the inhibitory signaling of leukocyte-associated immunoglobulin (Ig)-like receptor-1 (LAIR1) on the membranes of MCs, leading to the inhibition of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway (152). IL-35 transduces phosphorylation signaling through the JAK/STAT signaling pathway, which in turn enhances the inhibitory effect of LAIR1, reduces the proliferation of MCs, suppresses massive inflammation, and ultimately inhibits the progression of LN.
PTPN2, a non-receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase, is recognized as a key regulator in controlling metabolism and microinflammation (155, 156). There is growing evidence that PTPN is involved in the development and progression of inflammatory diseases (157, 158), and its main mechanism may be to exert anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects through inhibition of the downstream mediator STAT3 signaling pathway (159). TC45 is the predominant form of PTPN2 in most species, which shuttles between the nucleus and cytoplasm in response to growth factor and cytokine receptor signaling to dephosphorylate different substrates, including STAT3 (160, 161). In addition, PTPN2 is the only PTP known to regulate STAT1 other than SHP2. TC45 is the major PTP regulator of STAT1, which is hyperphosphorylated and activated in PTPN2-deficient cells (162). It has been shown that knockdown of PTPN2 in mouse intestinal epithelial cells results in severe colitis and leads to increased inflammation and increased cell proliferation through activation of STAT1 (163). Interestingly, there are studies showing that PTPN2 can improve renal lesions and fibrosis in DN by reducing the expression of pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic cytokines through inhibiting the STAT1/3 signaling pathway (164).The mechanisms involves PTPN2 preventing kidney injury by inhibiting STAT activation, down-regulating STAT-dependent genes, and inhibiting the proliferation of mouse mesangial cells and endothelial cells. Previous research indicated that the recruitment of PTPN11 (SHP-2) could play a role in transmitting negative signals through LAIR-1 molecules involved in transduction (165, 166). Blocking PTPN11 genetically or pharmacologically result in the inhibition of the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway (167). In IL-35-treated lupus mice, it has been suggested that the upregulation of LAIR1 may transmit a negative signal by inhibiting PTPN11 to suppress STAT3 activation in MCs (152). In summary, PTPN may be a potential target for the treatment of inflammation in glomerular diseases, and its mechanism needs to be verified by more experiments.
4.2 CCL2/CCR
Chemokines participate in the adaptive immune response by recruiting small cytokines from different cell types, mainly through chemotaxis (168, 169). Inflammatory chemokines such as CCL2, CCL5 (RANTES), and C-X3-C motif chemokine 1 have the ability to induce the migration of leukocytes to injured tissues (170, 171). CCL2, also known as macrophage chemokine-1 (MCP-1), is involved in the development of glomerular diseases by facilitating the recruitment of macrophages via interaction with type 2 C-C chemokine receptor (CCR2) (172). The glomerular expression levels of CCL2 and its receptor CCR2 were found to be elevated in human glomerulopathies (85), and CCL2/CCR2 signaling may mediate the development of a variety of glomerular diseases.
Anja Wilkening et al. discovered that CCL2 secretion was notably elevated in MCs and mural epithelial cells exposed to adriamycin, while there was no significant increase in podocytes and glomerular endothelial cells (85). Adriamycin was also found to induce TNF production in MCs and mural epithelial cells. Moreover, TNF indirectly induced CCL2 secretion in all glomerular cell lines, but did not alter CCR2 expression in these cells. However, CCR2-deficient mice demonstrated lower renal expression of these inflammatory markers (173). Moreover, further evidence suggested that the absence of CCR2 led to decreased macrophage infiltration in the glomerular and tubulointerstitial areas, leading to enhanced renal injury (174–176). The absence of CCR2 did not seem to impact the adriamycin-induced injury to podocytes or glomerular endothelial cells in FSGS mice, indicating that adriamycin might not directly harm these cell types as previously believed (37, 177, 178). Another study also noted that CCL2 can trigger the inflammatory response by binding in a synergistic manner to glycosaminoglycans located in the glomerular endothelial glycocalyx, such as acetyl-heparin sulfate (HS), chondroitin sulfate, and non-sulfated hyaluronic acid (179). When the N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase-1 enzyme is specifically knocked out in endothelial cells, there is a notable decrease in glomerular endothelial chemokine and leukocyte binding, resulting in diminished inflammatory responses in experimental anti-glomerular basement membrane nephritis mice (180).
In addition to recruiting leukocytes, CCL2 also recruits other cells to infiltrate the kidney to trigger glomerular inflammation, such as γδ1 T cells. Previous research indicates that the extravasation of γδ1 T cells to target organs is primarily facilitated by CCL2 and involves the expression of CCR2 (174, 181, 182). Whereas high expression of CCL2 has been demonstrated in the MCs of IgAN patients (183). A recent study shows that γδ1 T cells in the peripheral blood of IgAN patients can be recruited to the kidney via the CCL2-CCR2 chemokine axis and enhance CCL2-CCR2 axis-mediated chemotaxis via C5a (184). C5a is a potent chemoattractant of immune cells, released by local complement activation of IgAN leading to C5 cleavage, which leads to renal injury in IgAN by promoting migration of γδ1 T cells. Previous studies have shown that activation of C5a-C5aR1 signaling promotes Th9 cell recruitment and IL-9 levels via CCL20-CCL6, leading to IgAN deterioration (185). In summary, the C5a/CCL2/CCR2 pathway may serve as a potential mechanism to ameliorate glomerular inflammation, primarily by decreasing the recruitment of immune cells.
4.3 NLRP3 inflammasome activation
In the innate immune system, inflammatory vesicles are assembled by cell cytoplasm pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) and play a crucial role in responding to pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). Among the five families of PRRs, the NOD-like receptor family, containing the pyrin domain 3 (NLRP3), is the most extensively studied in chronic kidney disease inflammatory vesicles (186). The NLRP3 inflammatory vesicle consists of three proteins: the NLRP3 scaffold, the PYCARD junction protein (ASC), and the active cysteine asparaginase 1 (caspase-1). This structure is crucial for the production of inflammatory factors (187). The NLRP3 protein consists of a C-terminal leucine-rich repeat sequence (LRR), a central nucleotide-binding oligomeric structural domain (NACHT) and an N-terminal pyrin structural domain (PYD). When injury-associated molecules are recognized and bound by the LRR, NACHT will oligomerize, PYD will recruit ASC and pro-Caspase-1 to form NLRP3 inflammatory vesicles, and pro-Caspase-1 will be activated and then cleave pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 to produce mature IL-1β and IL-18 (188, 189). Currently, more and more studies confirm the role of NLRP3 in the kidney, including renal fibrosis, oxidative stress, autophagy and pyroptosis, especially glomerular inflammation (189, 190).
Previous studies have shown that the activation of NLRP3 in renal resident cells plays a role in promoting glomerular disease (111, 191, 192). This pathway can be regulated by NF-κB (193). Zhang Lei et al. found that icariin treatment attenuated renal injury in IgAN rats by inhibiting NF-κB-mediated activation of NLRP3 inflammasome (194). Furthermore, research has revealed that NLRP3 can affect the kidney through non-classical pathways. Wenjie Wang et al. demonstrated that NLRP3 enhances TGF-β1 signaling and Smad activation, promoting renal tubulointerstitial inflammation and fibrosis. Interestingly, these effects were found to be independent on inflammatory vesicle components, such as caspase-1 and the cytokines IL-1β and IL-18 (195). Khurrum Shahzad and his team developed a mouse model with podocytes specifically lacking in NLRP3 or caspase-1. They observed that the absence of NLRP3 or caspase-1 prevented hyperglycemia-induced glomerular injury, although the level of protection differed. Mice with podocyte-specific NLRP3 deficiency were fully protected, whereas those with podocyte-specific caspase-1 deficiency only had partial protection (196). This is in line with earlier findings that NLRP3 operates separately from caspase-1 (197).
Evidence has emerged indicating that the crosstalk between autophagy and NLRP3 inflammatory vesicles is significant in various inflammatory diseases and can be mediated by HDAC6 (168). HDAC6, a class IIb deacetylase, plays a crucial role in the regulation of autophagy and the activation of NLRP3 inflammatory vesicles (198, 199). HDAC6 amplifies pro-IL-1β transcription, raises IL-1β release, and worsens inflammation by promoting NF-κB expression and engaging with NF-κB upstream activators (200–202). At the same time, the caspase-1-mediated signaling intermediate Toll-Interleukin-1 Receptor (TIR) structural domain junction induces interferon-beta (TRIF) cleavage, thereby promoting autophagy (203). HDAC6 could be involved in the crosstalk between inflammatory vesicles and autophagy through its regulation of NF-κB. Furthermore, it has been shown that there is a correlation between increased HDAC6 levels and renal dysfunction (204). Whereas treatment with HDAC6 inhibitors can effectively treat LN in NZB/W mice by reducing α-microtubulin acetylation and NF-κB activation in the glomeruli (205). Additionally, P62 is able to stimulate autophagy by suppressing the deacetylase activity of HDAC6, leading to a higher acetylation levels of α-microtubulin or cortical proteins (206, 207). Hence, it is suggested that the regulation of P62 by HDAC6 may indirectly impact α-microtubulin, potentially playing a role in the crosstalk between inflammation and autophagy in glomerular disease. Future studies should investigate this pathway further.
4.4 Toll-like receptor signaling
Toll-like receptors (TLR) play an important role in kidney inflammation (208). It is known that some resident renal cells, such as podocytes, MCs, and endothelial cells, also express TLR in response to immune stimulation (209). TLRs belong to the PRR family and consist of 10 isoforms, including TLR1-10. TLR1, 2, 4, 5, and 6 are transmembrane proteins with multiple leucine-rich repeats, serving as the recognition domains for PAMP and DAMP. The TLRs on the surface of these cells are in charge of detecting PAMPs and DAMPs, with the latter triggering inflammation by interacting with TLR2 and/or TLR4 (210). The binding results in TLR dimerization and conformational alterations, causing the recruitment of TIRAP, TRIF, and TRAM adaptor proteins, initiating subsequent inflammatory pathways (88). The TLR signaling cascade results in the translocation of NF-κB and the transcription of pro-inflammatory genes, such as IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF (211, 212).
TLRs have the ability to engage in signaling cascades with PRRs, such as NLRP3, which requires precise coordination to trigger a targeted and efficient immune response (213). Activated TLR4 receptors initiate NF-κB and regulate the production of NLRP3, pro-IL-1β, and pro-IL-18, which in turn induce a variety of pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in diabetes-induced inflammatory response and apoptosis, leading to DN (214, 215). Lei Liu et al. found that miR-181a has the potential to reduce injury in CKD patients by suppressing the CRY1 gene and the TLR/NF-κB pathway (216). TLR4 deficiency results in decreased renal inflammation by blocking NF-κB activation induced by angiotensin II therapy (217). Furthermore, in cultured podocytes, high glucose-induced up-regulation of TLR4 expression can be mediated by ROS production and NF-κB activation (218). High glucose-induced increase in TLR2 and TLR4 expression in monocytes is mediated by activation of the protein kinase C (PKC) pathway (219). Inhibition of toll-like receptor 4-mediated STAT3 activation attenuates angiotensin II-induced renal fibrosis and dysfunction (220). Genipin, a major active ingredient in Gardenia jasminoides, is widely used in traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of various cardiovascular diseases, where it inhibits Ang II-induced cell proliferation, ROS generation, and pro-inflammatory responses. These effects may be mediated through the TLR signaling pathway (221). Taken together, TLR can occur by interacting with various signaling pathways, and this interaction could potentially be a mechanism for the development of glomerular inflammation.
The pathways associated with glomerular inflammation mentioned above are succinctly summarized in Figure 2. The full names of the abbreviations are listed in Table 2.

Figure 2. Inflammatory pathways in glomerular disease. This figure depicts the key mechanisms of glomerular disease injury, mainly including the JAK/STAT signaling pathway, CCL2/CCR axis, NLRP3 inflammasome activation, and Toll-like receptor signaling. Several pathological responses, such as oxidative stress, inflammatory response, and fibrosis are among the major causes mediating the activation of these pathways. In addition, several inflammatory factors (including SOCS, IL35, PTPN2, CCL2, NLRP3, etc.) have been found to act on these signaling pathways to modulate glomerular injury.
5 Prevention and treatment
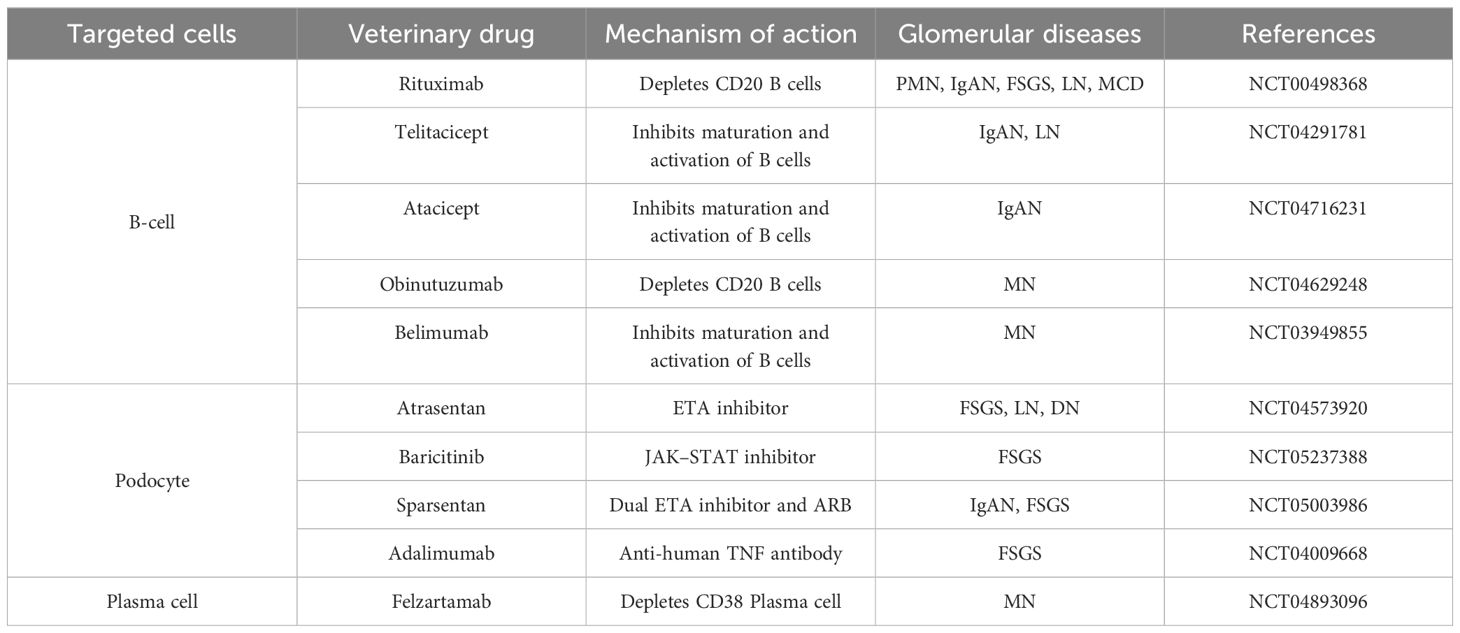
Glomerular diseases are typically classified according to the histological patterns of kidney injury, with various etiologies and pathophysiologic mechanisms linked to different types of glomerular diseases. The primary challenge in treating these diseases lies in their immune-mediated nature, as well as the diverse clinical manifestations and prognosis they present. Recently, targeted therapies have emerged as more precise treatments for glomerular diseases, that focus on the onset and progression of the disease through the influence of specific molecular or cellular processes. These therapies include biologics and small molecule inhibitors that target inflammatory cytokines, immune cells and signaling kinases (Table 3) (222). In a review, Yi-Chan Lin et al. describe relevant targeted therapies for glomerular diseases, including antibody-mediated immune cell exhaustion, complement activation, and signaling (223). However, as we have described, glomerular cells are also involved in the immune response to glomerular disease, and direct targeting of glomerular cells and their signaling is also one of the important options for the treatment of glomerular disease. In recent years, small molecule drugs targeted podocytes have entered clinical trials, offering a glimmer of hope for the treatment of glomerular diseases caused by podocyte injury (224).
Currently, the therapeutic mechanism of commonly used clinical drugs is mainly to prevent rearrangement of the podocyte and podocyte loss. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) can be utilized to treat Ang II-induced renal disease and enhanced podocyte tensile stress, one of the seminal therapeutic breakthroughs in the history of nephrology (225, 226). Signaling mechanisms reported to cause membrane damage in podocytes include Ang II-mediated Rho-ROCK-related disruption of the actin cytoskeleton and transient receptor potential channel 6 (TRPC6)-mediated release of calcium from intracellular stores (227, 228). TRPC6 is mediated by Ang II (229). As previously described, rearrangement of the foot cytoskeleton is regulated by calcium influx in transient receptor potential channel 6 (TRPC6) as well as by the Rho family. Thus, the use of ACE inhibitors and ARBs to treat Ang II-mediated disruption of podocyte structure and homeostasis provides a mechanistic basis for the treatment of glomerular disease. Similar to ACE inhibitors and ARBs, treatment with SGLT2 inhibitor ameliorated mTORC1-related podocyte injury (230), glomerular inflammation, rearrangement of podocyte cytoskeletal (230), and loss of podocyte (230). The first-line treatment for podocytes is glucocorticoids, supported by a large body of efficacy data and evidence of the immunologic basis of podocytosis. Research indicates that glucocorticoids play a role in stabilizing the actin cytoskeleton and the cleft septal complex (231). Calcineurin inhibitors (CNIs) are suggested as second-line induction and/or maintenance agents for treatment of podocytopathies (232). CNIs have been shown to decrease podocyte damage by stabilizing the actin cytoskeleton, which helps maintain RhoA and tight junction protein ZO-1 (233). In the same way, rituximab treatment of podocytosis led to actin stabilization, preservation of podocyte adhesion, and decrease in apoptosis (234). Kristin Meliambro et al. have also suggested various new therapeutic strategies for targeting podocytes, such as harnessing the regenerative capabilities of podocytes, current clinical trials of drug formulations specific to podocytes, and the creation of drug delivery systems that target podocytes (224). In the future, targeted therapies for podocytes focus more on the above approaches.
6 Future prospects
This article reviews studies on the molecular mechanisms, prevention, and treatment of inflammatory responses in various glomerular diseases, especially diabetic nephropathy, lupus nephritis, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, and IgA nephropathy. The development of glomerular disease as a chronic histologic injury to the kidney is often accompanied by structural and functional damage to glomerular cells, such as endothelial cells, mesangial cells and podocytes. This process does not directly depend on the activation of immune cells, instead, it is mediated through a specific pathway that mainly includes the JAK/STAT signaling pathway, the CCL2/CCR axis, NLRP3 inflammasome activation and Toll-like receptor signaling. We discuss some specific structural injuries in glomerular cells that are associated with the development of glomerular diseases. Pro-inflammatory cytokines expressed by glomerular cells under pathogenic conditions are summarized. This article focuses on a review of the molecular mechanisms, preventive and therapeutic studies of the inflammatory response in different types of glomerular diseases, especially diabetic nephropathy, lupus nephritis, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis and IgA nephropathy. These can help us to understand the signaling pathways that trigger glomerular diseases under pathological conditions and prevent glomerular injury caused by inflammatory responses. In the future, research on the inflammatory response in glomerular diseases should not only focus on immune cells, but also pay more attention to the special structure of glomerular cells and the interactions between cells. This may lead to a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms that trigger glomerular diseases in pathological conditions and aid in preventing glomerular injury from inflammatory responses.
Author contributions
YX: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WL: Writing – original draft, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. SJ: Data curation, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. SJW: Investigation, Resources, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. SZW: Investigation, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32460167), Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. 20202ACBL216010, 20224BAB206045), Jiangxi Province Innovative Entrepreneurial Projects for University Students (S202110413002, S202210413006, S202210413042, S202210413021). Scientific Research Fund of Jiangxi Provincial Education Department (GJJ190801; GJJ2201432), Talents′ Start-up Fund of Gannan Medical University (No. QD202018).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Ekrikpo U, Obiagwu P, Chika-Onu U, Yadla M, Karam S, Tannor EK, et al. Epidemiology and outcomes of glomerular diseases in low- and middle-income countries. Semin Nephrol. (2022) 42:151316. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2023.151316
2. AlYousef A, AlSahow A, AlHelal B, Alqallaf A, Abdallah E, Abdellatif M, et al. Glomerulonephritis histopathological pattern change. BMC Nephrol. (2020) 21:186. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-01836-3
3. Kiewisz J, Skowronska A, Winiarska A, Pawlowska A, Kiezun J, Rozicka A, et al. WNT4 expression in primary and secondary kidney diseases: dependence on staging. Kidney Blood Press Res. (2019) 44:200–10. doi: 10.1159/000498989
4. Jelaković B, Corić M, Kos J, Zivko M, Dika Z, Laganović M. Classification of glomerulopathies. Lijec Vjesn. (2014) 136:201–8.
5. O’Shaughnessy MM, Hogan SL, Thompson BD, Coppo R, Fogo AB, Jennette JC. Glomerular disease frequencies by race, sex and region: results from the International Kidney Biopsy Survey. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2018) 33:661–9. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfx189
6. Li Y, Yang Y, Zhuo L, Wu D, Li W, Liu X. Epidemiology of biopsy-proven glomerular diseases in Chinese children: A scoping review. Chronic Dis Transl Med. (2022) 8:271–80. doi: 10.1002/cdt3.v8.4
7. Bandi VK, Nalamati A, Kasinaboina B, Chundru SS. Epidemiologic data of biopsy-proven renal diseases: Experience from a single center in South India. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. (2019) 30:478–91. doi: 10.4103/1319-2442.256855
8. Okpechi IG, Ameh OI, Bello AK, Ronco P, Swanepoel CR, Kengne A. Epidemiology of histologically proven glomerulonephritis in Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PloS One. (2016) 11:e0152203. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152203
9. Agudelo-Botero M, Valdez-Ortiz R, Giraldo-Rodríguez L, González-Robledo MC, Mino-León D, Rosales-Herrera MF, et al. Overview of the burden of chronic kidney disease in Mexico: secondary data analysis based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. BMJ Open. (2020) 10:e035285. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-035285
10. Jourde-Chiche N, Fakhouri F, Dou L, Bellien J, Burtey S, Frimat M, et al. Endothelium structure and function in kidney health and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2019) 15:87–108. doi: 10.1038/s41581-018-0098-z
11. Roumenina LT, Rayes J, Frimat M, Fremeaux-Bacchi V. Endothelial cells: source, barrier, and target of defensive mediators. Immunol Rev. (2016) 274:307–29. doi: 10.1111/imr.2016.274.issue-1
12. Sartain SE, Turner NA, Moake JL. TNF regulates essential alternative complement pathway components and impairs activation of protein C in human glomerular endothelial cells. J Immunol. (2016) 196:832–45. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500960
13. Saleh MA, Boesen EI, Pollock JS, Savin VJ, Pollock DM. Endothelin-1 increases glomerular permeability and inflammation independent of blood pressure in the rat. Hypertension. (2010) 56:942–9. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.156570
14. Hocher B, Schwarz A, Slowinski T, Bachmann S, Pfeilschifter J, Neumayer HH, et al. In-vivo interaction of nitric oxide and endothelin. J Hypertens. (2004) 22:111–9. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200401000-00020
15. Avraham S, Goldstein L, Chen YJ, Lee J, Webster JD, Roose-Girma M, et al. The Mesangial cell - the glomerular stromal cell. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2021) 17:855–64. doi: 10.1038/s41581-021-00474-8
16. Chung JJ, Goldstein L, Chen YJ, Lee J, Webster JD, Roose-Girma M, et al. Single-cell transcriptome profiling of the kidney glomerulus identifies key cell types and reactions to injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2020) 31:2341–54. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020020220
17. Navarro-González JF, Mora-Fernández C, Muros de Fuentes M, García-Pérez J. Inflammatory molecules and pathways in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2011) 7:327–40. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2011.51
18. Wright RD, Beresford MW. Podocytes contribute, and respond, to the inflammatory environment in lupus nephritis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2018) 315:F1683–f1694. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00512.2017
19. Castellani P, Balza E, Rubartelli A. Inflammation, DAMPs, tumor development, and progression: a vicious circle orchestrated by redox signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2014) 20:1086–97. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.5164
20. Samsu N. Diabetic nephropathy: challenges in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. BioMed Res Int. (2021) 2021:1497449. doi: 10.1155/2021/1497449
21. Pizzino G, Irrera N, Cucinotta M, Pallio G, Mannino F, Arcoraci V, et al. Oxidative stress: harms and benefits for human health. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2017) 2017:8416763. doi: 10.1155/2017/8416763
22. Lv W, Booz GW, Fan F, Wang Y, Roman RJ. Oxidative stress and renal fibrosis: recent insights for the development of novel therapeutic strategies. Front Physiol. (2018) 9:105. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00105
23. Fan X, Yang M, Lang Y, Lu S, Kong Z, Gao Y, et al. Mitochondrial metabolic reprogramming in diabetic kidney disease. Cell Death Dis. (2024) 15:442. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06833-0
24. Srivastava A, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress: Role in chronic kidney disease. Life Sci. (2023) 319:121432. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121432
25. Szeto HH, Liu S, Soong Y, Seshan SV, Cohen-Gould L, Manichev V, et al. Mitochondria protection after acute ischemia prevents prolonged upregulation of IL-1β and IL-18 and arrests CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2017) 28:1437–49. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2016070761
26. Jha JC, Dai A, Garzarella J, Charlton A, Urner S, Østergaard JA, et al. Independent of renox, NOX5 promotes renal inflammation and fibrosis in diabetes by activating ROS-sensitive pathways. Diabetes. (2022) 71:1282–98. doi: 10.2337/db21-1079
27. Song C, Wang S, Fu Z, Chi K, Geng X, Liu C, et al. IGFBP5 promotes diabetic kidney disease progression by enhancing PFKFB3-mediated endothelial glycolysis. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:340. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04803-y
28. Kent AC, El Baradie KBY, Hamrick MW. Targeting the mitochondrial permeability transition pore to prevent age-associated cell damage and neurodegeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2021) 2021:6626484. doi: 10.1155/2021/6626484
29. Pollak MR, Quaggin SE, Hoenig MP, Dworkin LD. The glomerulus: the sphere of influence. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. (2014) 9:1461–9. doi: 10.2215/CJN.09400913
30. Fu J, Lee K, Chuang PY, Liu Z, He JC. Glomerular endothelial cell injury and cross talk in diabetic kidney disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2015) 308:F287–97. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00533.2014
31. Jeansson M, Haraldsson B. Morphological and functional evidence for an important role of the endothelial cell glycocalyx in the glomerular barrier. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2006) 290:F111–6. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00173.2005
32. Satchell SC, Braet F. Glomerular endothelial cell fenestrations: an integral component of the glomerular filtration barrier. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2009) 296:F947–56. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.90601.2008
33. Daehn I. Shift in focus-to explore the role of the endothelium in kidney disease. HSOA J Nephrol Ren Ther. (2016) 2:4. doi: 10.24966/NRT-7313/100004
34. Pavkov ME, Weil EJ, Fufaa GD, Nelson RG, Lemley KV, Knowler WC, et al. Tumor necrosis factor receptors 1 and 2 are associated with early glomerular lesions in type 2 diabetes. Kidney Int. (2016) 89:226–34. doi: 10.1038/ki.2015.278
35. Zhang K, Fu Z, Zhang Y, Chen X, Cai G, Hong Q. The role of cellular crosstalk in the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1173933. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1173933
36. Qi H, Casalena G, Shi S, Yu L, Ebefors K, Sun Y, et al. Glomerular endothelial mitochondrial dysfunction is essential and characteristic of diabetic kidney disease susceptibility. Diabetes. (2017) 66:763–78. doi: 10.2337/db16-0695
37. Sun YB, Qu X, Zhang X, Caruana G, Bertram JF, Li J. Glomerular endothelial cell injury and damage precedes that of podocytes in adriamycin-induced nephropathy. PloS One. (2013) 8:e55027. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055027
38. Zahlten J, Steinicke R, Opitz B, Eitel J, N'guessan PD, Vinzing M, et al. TLR2- and nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain 2-dependent Krüppel-like factor 2 expression downregulates NF-kappa B-related gene expression. J Immunol. (2010) 185:597–604. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901798
39. Nayak L, Goduni L, Takami Y, Sharma N, Kapil P, Jain MK, et al. Kruppel-like factor 2 is a transcriptional regulator of chronic and acute inflammation. Am J Pathol. (2013) 182:1696–704. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.01.029
40. Kurihara H, Sakai T. Cell biology of mesangial cells: the third cell that maintains the glomerular capillary. Anat Sci Int. (2017) 92:173–86. doi: 10.1007/s12565-016-0334-1
41. Chaudhari S, Sakai T. Inhibition of interleukin-6 on matrix protein production by glomerular mesangial cells and the pathway involved. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2020) 318:F1478–f1488. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00043.2020
42. Shotorbani PY, et al. Inhibitor of myogenic differentiation family isoform a, a new positive regulator of fibronectin production by glomerular mesangial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2020) 318:F673–f682. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00508.2019
43. Zhao Y, Li Q, Ouyang Q, Wu L, Chen X. Activated mesangial cells acquire the function of antigen presentation. Cell Immunol. (2021) 361:104279. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2020.104279
45. Durvasula RV, Shankland SJ. Podocyte injury and targeting therapy: an update. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. (2006) 15:1–7. doi: 10.1097/01.mnh.0000199012.79670.0b
46. Ma S, Qiu Y, Zhang C. Cytoskeleton rearrangement in podocytopathies: an update. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25(1):647. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010647
47. Hannun YA, Obeid LM. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2008) 9:139–50. doi: 10.1038/nrm2329
48. Tolerico M, Merscher S, Fornoni A. Normal and dysregulated sphingolipid metabolism: contributions to podocyte injury and beyond. Cells. (2024) 13(11):890. doi: 10.3390/cells13110890
49. Blaine J, Dylewski J. Regulation of the actin cytoskeleton in podocytes. Cells. (2020) 9(7):1700. doi: 10.3390/cells9071700
50. Luo Z, Chen Z, Hu J, Ding G. Interplay of lipid metabolism and inflammation in podocyte injury. Metabolism. (2024) 150:155718. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2023.155718
51. Imig JD, Ryan MJ. Immune and inflammatory role in renal disease. Compr Physiol. (2013) 3:957–76. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c120028
52. Kwok SK, Tsokos GC. New insights into the role of renal resident cells in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis. Korean J Intern Med. (2018) 33:284–9. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2017.383
53. Kitching AR, Hutton HL. The players: cells involved in glomerular disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. (2016) 11:1664–74. doi: 10.2215/CJN.13791215
54. Kurts C, Panzer U, Anders HJ, Rees AJ. The immune system and kidney disease: basic concepts and clinical implications. Nat Rev Immunol. (2013) 13:738–53. doi: 10.1038/nri3523
55. Hu S, Hang X, Wei Y, Wang H, Zhang L, Zhao L. Crosstalk among podocytes, glomerular endothelial cells and mesangial cells in diabetic kidney disease: an updated review. Cell Commun Signal. (2024) 22:136. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01502-3
56. Lennon R, Hosawi S. Glomerular cell crosstalk. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. (2016) 25:187–93. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000221
57. Wu Q, Zhou S, Xu D, Meng P, Chen Q, Wang X, et al. The CXCR4-AT1 axis plays a vital role in glomerular injury via mediating the crosstalk between podocyte and mesangial cell. Transl Res. (2023), 15–32. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.4321512
58. Rane MJ, Zhao Y, Cai L. Krϋppel-like factors (KLFs) in renal physiology and disease. EBioMedicine. (2019) 40:743–50. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.01.021
59. Parsamanesh N, Asghari A, Sardari S, Tasbandi A, Jamialahmadi T, Xu S, et al. Resveratrol and endothelial function: A literature review. Pharmacol Res. (2021) 170:105725. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105725
60. Batal I, Wright RD, Budge KL, Midgley A, Satchell SC, Peak M, et al. Glomerular inflammation correlates with endothelial injury and with IL-6 and IL-1β secretion in the peripheral blood. Transplantation. (2014) 97:1034–42. doi: 10.1097/01.TP.0000441096.22471.36
61. Tam FW, Smith J, Karkar AM, Pusey CD, Rees AJ. Interleukin-4 ameliorates experimental glomerulonephritis and up-regulates glomerular gene expression of IL-1 decoy receptor. Kidney Int. (1997) 52:1224–31. doi: 10.1038/ki.1997.447
62. Messmer UK, Briner VA, Pfeilschifter J. Basic fibroblast growth factor selectively enhances TNF-alpha-induced apoptotic cell death in glomerular endothelial cells: effects on apoptotic signaling pathways. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2000) 11:2199–211. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V11122199
63. Dimou P, Wright RD, Budge KL, Midgley A, Satchell SC, Peak M, et al. The human glomerular endothelial cells are potent pro-inflammatory contributors in an in vitro model of lupus nephritis. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:8348. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44868-y
64. Pan Q, Yang XH, Cheng YX. Angiotensin II stimulates MCP-1 production in rat glomerular endothelial cells via NAD(P)H oxidase-dependent nuclear factor-kappa B signaling. Braz J Med Biol Res. (2009) 42:531–6. doi: 10.1590/S0100-879X2009000600009
65. Yokoyama H, Takaeda M, Wada T, Ohta S, Hisada Y, Segawa C, et al. Glomerular ICAM-1 expression related to circulating TNF-alpha in human glomerulonephritis. Nephron. (1997) 76:425–33. doi: 10.1159/000190225
66. He K, Chen Z, Zhao J, He Y, Deng R, Fan X, et al. The role of microRNA-155 in glomerular endothelial cell injury induced by high glucose. Mol Biol Rep. (2022) 49:2915–24. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-07106-1
67. Narumi S, Onozato ML, Tojo A, Sakamoto S, Tamatani T. Tissue-specific induction of E-selectin in glomeruli is augmented following diabetes mellitus. Nephron. (2001) 89:161–71. doi: 10.1159/000046063
68. Guan Z, VanBeusecum JP, Inscho EW. Endothelin and the renal microcirculation. Semin Nephrol. (2015) 35:145–55. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2015.02.004
69. Satriano J, Schlondorff D. Activation and attenuation of transcription factor NF-kB in mouse glomerular mesangial cells in response to tumor necrosis factor-alpha, immunoglobulin G, and adenosine 3’:5’-cyclic monophosphate. Evidence for involvement of reactive oxygen species. J Clin Invest. (1994) 94:1629–36. doi: 10.1172/JCI117505
70. Yang PY, Li PC, Feng B. Protective effects of gliclazide on high glucose and AGEs-induced damage of glomerular mesangial cells and renal tubular epithelial cells via inhibiting RAGE-p22phox-NF-kB pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2019) 23:9099–107. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201910_19313
71. Groza Y, Jemelkova J, Kafkova LR, Maly P, Raska M. IL-6 and its role in IgA nephropathy development. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2022) 66:1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2022.04.001
72. Xia L, Liu Y, Zhang Z, Gong Y, Yu T, Zhao D, et al. Modulation of IL-6 expression by KLF4-mediated transactivation and PCAF-mediated acetylation in sublytic C5b-9-induced rat glomerular mesangial cells. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:779667. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.779667
73. Mezzano S, Burgos ME, Olavarría F, Caorsi I. Immunohistochemical localization of IL-8 and TGF-beta in streptococcal glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. (1997) 8:234–41. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V82234
74. Liu ZH, Striker GE, Stetler-Stevenson M, Fukushima P, Patel A, Striker LJ. TNF-alpha and IL-1 alpha induce mannose receptors and apoptosis in glomerular mesangial but not endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. (1996) 270:C1595–601. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1996.270.6.C1595
75. Liu Q, Imaizumi T, Murakami K, Tanaka H, Wu Y, Yoshizawa T, et al. DEC1 negatively regulates the expression of CXCL10 and CCL5 induced by poly IC in normal human mesangial cells. BioMed Res. (2017) 38:249–55. doi: 10.2220/biomedres.38.249
76. Zahner G, Schaper M, Panzer U, Kluger M, Stahl RA, Thaiss F, et al. Prostaglandin EP2 and EP4 receptors modulate expression of the chemokine CCL2 (MCP-1) in response to LPS-induced renal glomerular inflammation. Biochem J. (2009) 422:563–70. doi: 10.1042/BJ20090420
77. Qing X, Zavadil J, Crosby MB, Hogarth MP, Hahn BH, Mohan C, et al. Nephritogenic anti-DNA antibodies regulate gene expression in MRL/lpr mouse glomerular mesangial cells. Arthritis Rheum. (2006) 54:2198–210. doi: 10.1002/art.21934
78. Chen F, Wei G, Zhou Y, Ma X, Wang Q. The mechanism of miR-192 in regulating high glucose-induced MCP-1 expression in rat glomerular mesangial cells. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. (2019) 19:1055–63. doi: 10.2174/1871530319666190301154640
79. Zou X, Cheng H, Zhang Y, Fang C, Xia Y. The antigen-binding fragment of anti-double-stranded DNA IgG enhances F-actin formation in mesangial cells by binding to alpha-actinin-4. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). (2012) 237:1023–31. doi: 10.1258/ebm.2012.012033
80. Djudjaj S, Lue H, Rong S, Papasotiriou M, Klinkhammer BM, Zok S, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor mediates proliferative GN via CD74. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2016) 27:1650–64. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015020149
81. Hussain S, Romio L, Saleem M, Mathieson P, Serrano M, Moscat J, et al. Nephrin deficiency activates NF-kappaB and promotes glomerular injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2009) 20:1733–43. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2008111219
82. Lee SJ, Borsting E, Declèves AE, Singh P, Cunard R. Podocytes express IL-6 and lipocalin 2/neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute glomerular injury. Nephron Exp Nephrol. (2012) 121:e86–96. doi: 10.1159/000345151
83. Niemir ZI, Stein H, Ciechanowicz A, Olejniczak P, Dworacki G, Ritz E, et al. The in situ expression of interleukin-8 in the normal human kidney and in different morphological forms of glomerulonephritis. Am J Kidney Dis. (2004) 43:983–98. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2004.02.011
84. Nishad R, Mukhi D, Kethavath S, Raviraj S, Paturi ASV, Motrapu M, et al. Podocyte derived TNF-α mediates monocyte differentiation and contributes to glomerular injury. FASEB J. (2022) 36:e22622. doi: 10.1096/fj.202200923R
85. Wilkening A, Krappe J, Mühe AM, Lindenmeyer MT, Eltrich N, Luckow B, et al. C-C chemokine receptor type 2 mediates glomerular injury and interstitial fibrosis in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2020) 35:227–39. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfy380
86. Tseng CC, Zheng RH, Lin TW, Chou CC, Shih YC, Liang SW, et al. [amp]]alpha;-Actinin-4 recruits Shp2 into focal adhesions to potentiate ROCK2 activation in podocytes. Life Sci Alliance. (2022) 5(11):e202201557. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202201557
87. Sahajpal NS, Goel RK, Chaubey A, Aurora R, Jain SK. Pathological perturbations in diabetic retinopathy: hyperglycemia, AGEs, oxidative stress and inflammatory pathways. Curr Protein Pept Sci. (2019) 20:92–110. doi: 10.2174/1389203719666180928123449
88. Tang SCW, Yiu WH. Innate immunity in diabetic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2020) 16:206–22. doi: 10.1038/s41581-019-0234-4
89. Hickey FB, Martin F. Role of the immune system in diabetic kidney disease. Curr Diabetes Rep. (2018) 18:20. doi: 10.1007/s11892-018-0984-6
90. Wada J, Makino H. Inflammation and the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Clin Sci (Lond). (2013) 124:139–52. doi: 10.1042/CS20120198
91. Qiu Y, Tang J, Zhao Q, Jiang Y, Liu YN, Liu WJ. From diabetic nephropathy to end-stage renal disease: the effect of chemokines on the immune system. J Diabetes Res. (2023) 2023:3931043. doi: 10.1155/2023/3931043
92. Navarro JF, Mora C, Gómez M, Muros M, López-Aguilar C, García J. Influence of renal involvement on peripheral blood mononuclear cell expression behaviour of tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 in type 2 diabetic patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2008) 23:919–26. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfm674
93. Lampropoulou IT, Stangou ?, Sarafidis P, Gouliovaki A, Giamalis P, Tsouchnikas I, et al. TNF-α pathway and T-cell immunity are activated early during the development of diabetic nephropathy in Type II Diabetes Mellitus. Clin Immunol. (2020) 215:108423. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108423
94. Waijer SW, Sen T, Arnott C, Neal B, Kosterink JGW, Mahaffey KW, et al. Association between TNF receptors and KIM-1 with kidney outcomes in early-stage diabetic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. (2022) 17:251–9. doi: 10.2215/CJN.08780621
95. Niewczas MA, Gohda T, Skupien J, Smiles AM, Walker WH, Rosetti F, et al. Circulating TNF receptors 1 and 2 predict ESRD in type 2 diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2012) 23:507–15. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2011060627
96. Navarro JF, Mora-Fernández C. The role of TNF-alpha in diabetic nephropathy: pathogenic and therapeutic implications. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2006) 17:441–50. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2006.09.011
97. Brennan DC, Jevnikar AM, Takei F, Reubin-Kelley VE. Mesangial cell accessory functions: mediation by intercellular adhesion molecule-1. Kidney Int. (1990) 38:1039–46. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.310
98. Concepción M, Quiroz J, Suarez J, Paz J, Roseboom P, Ildefonso S, et al. Novel Biomarkers for the diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy. Caspian J Intern Med. (2024) 15:382–91. doi: 10.22088/cjim.15.3.382
99. Rekvig OP, Thiyagarajan D, Pedersen HL, Horvei KD, Seredkina N. Future perspectives on pathogenesis of lupus nephritis: facts, problems, and potential causal therapy modalities. Am J Pathol. (2016) 186:2772–82. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.06.026
100. Fenton K, Fismen S, Hedberg A, Seredkina N, Fenton C, Mortensen ES, et al. Anti-dsDNA antibodies promote initiation, and acquired loss of renal Dnase1 promotes progression of lupus nephritis in autoimmune (NZBxNZW)F1 mice. PloS One. (2009) 4:e8474. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008474
101. Seredkina N, Van Der Vlag J, Berden J, Mortensen E, Rekvig OP. Lupus nephritis: enigmas, conflicting models and an emerging concept. Mol Med. (2013) 19:161–9. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2013.00010
102. Seredkina N, Rekvig OP. Acquired loss of renal nuclease activity is restricted to DNaseI and is an organ-selective feature in murine lupus nephritis. Am J Pathol. (2011) 179:1120–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.05.011
103. Liu M, Zhang L, Wang Y, Hu W, Wang C, Wen Z. Mesangial cell: A hub in lupus nephritis. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1063497. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1063497
104. Yung S, Cheung KF, Zhang Q, Chan TM. Anti-dsDNA antibodies bind to mesangial annexin II in lupus nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2010) 21:1912–27. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2009080805
105. Yung S, Chan TM. Anti-dsDNA antibodies and resident renal cells - Their putative roles in pathogenesis of renal lesions in lupus nephritis. Clin Immunol. (2017) 185:40–50. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2016.09.002
106. Bona N, Pezzarini E, Balbi B, Daniele SM, Rossi MF, Monje AL, et al. Oxidative stress, inflammation and disease activity biomarkers in lupus nephropathy. Lupus. (2020) 29:311–23. doi: 10.1177/0961203320904784
107. Zhang H, Zhao C, Wang S, Huang Y, Wang H, Zhao J, et al. Anti-dsDNA antibodies induce inflammation via endoplasmic reticulum stress in human mesangial cells. J Transl Med. (2015) 13:178. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0536-7
108. Rovin BH, Tan LC. Role of protein kinase pathways in IL-1-induced chemoattractant expression by human mesangial cells. Kidney Int. (1994) 46:1059–68. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.367
109. Satoh T, Akira S. Toll-like receptor signaling and its inducible proteins. Microbiol Spectr. (2016) 4(6):10. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MCHD-0040-2016
110. Abd-Elkareem MI, Al Tamimy HM, Khamis OA, Abdellatif SS, Hussein MR. Increased urinary levels of the leukocyte adhesion molecules ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 in human lupus nephritis with advanced renal histological changes: preliminary findings. Clin Exp Nephrol. (2010) 14:548–57. doi: 10.1007/s10157-010-0322-z
111. Chen FF, Liu XT, Tao J, Mao ZM, Wang H, Tan Y. Renal NLRP3 Inflammasome activation is associated with disease activity in lupus nephritis. Clin Immunol. (2023) 247:109221. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2022.109221
112. Ikezumi Y, Liu XT, Tao J, Mao ZM, Wang H, Tan Y, et al. Adoptive transfer studies demonstrate that macrophages can induce proteinuria and mesangial cell proliferation. Kidney Int. (2003) 63:83–95. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00717.x
113. Sung SJ, Fu SM. Interactions among glomerulus infiltrating macrophages and intrinsic cells via cytokines in chronic lupus glomerulonephritis. J Autoimmun. (2020) 106:102331. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2019.102331
114. Cheng Y, Liu L, Ye Y, He Y, Hu W, Ke H, et al. Roles of macrophages in lupus nephritis. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1477708. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1477708
115. Kim J, Lee JS, Go H, Lim JS, Oh JS, Kim YG, et al. Clinical and histological significance of urinary CD11c(+) macrophages in lupus nephritis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2020) 22:173. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-02265-1
116. Endo N, Tsuboi N, Furuhashi K, Shi Y, Du Q, Abe T, et al. Urinary soluble CD163 level reflects glomerular inflammation in human lupus nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2016) 31:2023–33. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfw214
117. Zhang T, Li H, Vanarsa K, Gidley G, Mok CC, Petri M, et al. Association of urine sCD163 with proliferative lupus nephritis, fibrinoid necrosis, cellular crescents and intrarenal M2 macrophages. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:671. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00671
118. Fogo AB. Causes and pathogenesis of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2015) 11:76–87. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2014.216
119. Salfi G, Casiraghi F, Remuzzi G. Current understanding of the molecular mechanisms of circulating permeability factor in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1247606. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1247606
120. Otalora L, Chavez E, Watford D, Tueros L, Correa M, Nair V, et al. Identification of glomerular and podocyte-specific genes and pathways activated by sera of patients with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. PloS One. (2019) 14:e0222948. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222948
121. Xiong T, Attar M, Gnirck AC, Wunderlich M, Becker M, Rickassel C, et al. Interleukin-9 protects from early podocyte injury and progressive glomerulosclerosis in Adriamycin-induced nephropathy. Kidney Int. (2020) 98:615–29. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.04.036
122. Latt KZ, Heymann J, Jessee JH, Rosenberg AZ, Berthier CC, Arazi A, et al. Urine single-cell RNA sequencing in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis reveals inflammatory signatures. Kidney Int Rep. (2022) 7:289–304. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2021.11.005
123. Hou S, Yang B, Chen Q, Xu Y, Li H. Potential biomarkers of recurrent FSGS: a review. BMC Nephrol. (2024) 25:258. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03695-8
124. den Braanker DJW, Maas RJH, van Mierlo G, Parr NMJ, Bakker-van Bebber M, Deegens JKJ, et al. Primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis plasmas increase lipid droplet formation and perilipin-2 expression in human podocytes. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 24(1):194. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010194
125. Suzuki H, Kiryluk K, Novak J, Moldoveanu Z, Herr AB, Renfrow MB, et al. The pathophysiology of IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2011) 22:1795–803. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2011050464
126. De Vriese AS, Sethi S, Nath KA, Glassock RJ, Fervenza FC. Differentiating primary, genetic, and secondary FSGS in adults: A clinicopathologic approach. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2018) 29:759–74. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2017090958
127. Nihei Y, Suzuki H, Suzuki Y. Current understanding of IgA antibodies in the pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1165394. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1165394
128. Lai KN, Tang SC, Schena FP, Novak J, Tomino Y, Fogo AB, et al. IgA nephropathy. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2016) 2:16001. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.1
129. Shen Y, Zhu Z, Wang R, Yan L, Sun S, Lu L, et al. Chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 2 is associated with the pathological grade and inflammatory response in IgAN children. BMC Nephrol. (2022) 23:215. doi: 10.1186/s12882-022-02839-y
130. Stamellou E, Seikrit C, Tang SCW, Boor P, Tesař V, Floege J, et al. IgA nephropathy. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2023) 9:67. doi: 10.1038/s41572-023-00476-9
131. Yoon SY, Kim JS, Jung SW, Kim YG, Moon JY, Lee SH, et al. Clinical significance of urinary inflammatory biomarkers in patients with IgA nephropathy. BMC Nephrol. (2024) 25:142. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03574-2
132. Schena FP, Rossini M, Abbrescia DI, Zaza G. The molecular mechanisms of inflammation and scarring in the kidneys of immunoglobulin A nephropathy: Gene involvement in the mechanisms of inflammation and scarring in kidney biopsy of IgAN patients. Semin Immunopathol. (2021) 43:691–705. doi: 10.1007/s00281-021-00891-8
133. Ju W, Nair V, Smith S, Zhu L, Shedden K, Song PXK, et al. Tissue transcriptome-driven identification of epidermal growth factor as a chronic kidney disease biomarker. Sci Transl Med. (2015) 7:316ra193. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aac7071
134. Xin P, Xu X, Deng C, Liu S, Wang Y, Zhou X, et al. The role of JAK/STAT signaling pathway and its inhibitors in diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. (2020) 80:106210. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106210
135. Tao Y, Han J, Liu W, An L, Hu W, Wang N, et al. MUC1 promotes mesangial cell proliferation and kidney fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through activating STAT and β-catenin signal pathway. DNA Cell Biol. (2021) 40:1308–16. doi: 10.1089/dna.2021.0098
136. Sun M, Li Y, Bu W, Zhao J, Zhu J, Gu L, et al. DJC suppresses advanced glycation end products-induced JAK-STAT signaling and ROS in mesangial cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2017) 2017:2942830. doi: 10.1155/2017/2942830
137. de Oliveira Santos TC, Pereira G, Coutinho AGG, Dos Santos Silva HP, Lima M MS , Dias FAL, et al. STAT-3 signaling role in an experimental model of nephropathy induced by doxorubicin. Mol Cell Biochem. (2023) 478:981–9. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04574-2
138. Wei Y, Wang D, Wu J, Zhang J. JAK2 inhibitors improve RA combined with pulmonary fibrosis in rats by downregulating SMAD3 phosphorylation. Int J Rheum Dis. (2024) 27:e15164. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.15164
139. Yang Y, Lei Y, Liang Y, Fu S, Yang C, Liu K, et al. Vitamin D protects glomerular mesangial cells from high glucose-induced injury by repressing JAK/STAT signaling. Int Urol Nephrol. (2021) 53:1247–54. doi: 10.1007/s11255-020-02728-z
140. Fang X, Huang W, Sun Q, Zhao Y, Sun R, Liu F, et al. Melatonin attenuates cellular senescence and apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy by regulating STAT3 phosphorylation. Life Sci. (2023) 332:122108. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.122108
141. Shi D, Li Y, Shi X, Yao M, Wu D, Zheng Y, et al. Transcriptional expression of CXCL10 and STAT1 in lupus nephritis and the intervention effect of triptolide. Clin Rheumatol. (2023) 42:539–48. doi: 10.1007/s10067-022-06400-y
142. Tao J, Mariani L, Eddy S, Maecker H, Kambham N, Mehta K, et al. JAK-STAT activity in peripheral blood cells and kidney tissue in igA nephropathy. Clin J Am Soc nephro. (2020) 15:973–82. doi: 10.2215/CJN.11010919
143. Liao W, He XJ, Zhang W, Chen YL, Yang J, Xiang W, et al. MiR-145 participates in the development of lupus nephritis by targeting CSF1 to regulate the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Cytokine. (2022) 154:155877. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2022.155877
144. Pekkucuksen NT, Liu LP, Aly R, Shoemaker LR, Alli AA. Extracellular vesicles from focal segmental glomerulosclerosis pediatric patients induce STAT3 activation and mesangial cell proliferation. PloS One. (2022) 17:e0274598. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274598
145. Zhang H, Nair V, Saha J, Atkins KB, Hodgin JB, Saunders TL, et al. Podocyte-specific JAK2 overexpression worsens diabetic kidney disease in mice. Kidney Int. (2017) 92:909–21. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2017.03.027
146. Linossi EM, Babon JJ, Hilton DJ, Nicholson SE. Suppression of cytokine signaling: the SOCS perspective. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2013) 24:241–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.03.005
147. Yoshimura A, Naka T, Kubo M. SOCS proteins, cytokine signalling and immune regulation. Nat Rev Immunol. (2007) 7:454–65. doi: 10.1038/nri2093
148. Shi Y, Du C, Zhang Y, Ren Y, Hao J, Zhao S, et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 ameliorates expression of MCP-1 in diabetic nephropathy. Am J Nephrol. (2010) 31:380–8. doi: 10.1159/000286559
149. Recio C, Lazaro I, Oguiza A, Lopez-Sanz L, Bernal S, Blanco J, et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 peptidomimetic limits progression of diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2017) 28:575–85. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2016020237
150. Liu J, Zhang Y, Liu M, Shi F, Cheng B. AG1024, an IGF-1 receptor inhibitor, ameliorates renal injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy via the SOCS/JAK2/STAT pathway. Open Med (Wars). (2023) 18:20230683. doi: 10.1515/med-2023-0683
151. Collison LW, Delgoffe GM, Guy CS, Vignali KM, Chaturvedi V, Fairweather D, et al. The composition and signaling of the IL-35 receptor are unconventional. Nat Immunol. (2012) 13:290–9. doi: 10.1038/ni.2227
152. Cai Z, Zhang S, Wu P, Ren Q, Wei P, Hong M, et al. A novel potential target of IL-35-regulated JAK/STAT signaling pathway in lupus nephritis. Clin Transl Med. (2021) 11:e309. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.v11.2
153. Wu S, Li Y, Yao L, Li Y, Jiang S, Gu W, et al. Interleukin-35 inhibits angiogenesis through STAT1 signalling in rheumatoid synoviocytes. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2018) 36:223–7.
154. Cai Z, Wong CK, Kam NW, Dong J, Jiao D, Chu M, et al. Aberrant expression of regulatory cytokine IL-35 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. (2015) 24:1257–66. doi: 10.1177/0961203315585815
155. Xi Y, Liu S, Bettaieb A, Matsuo K, Matsuo I, Hosein E, et al. Pancreatic T cell protein-tyrosine phosphatase deficiency affects beta cell function in mice. Diabetologia. (2015) 58:122–31. doi: 10.1007/s00125-014-3413-7
156. Gurzov EN, Tran M, Fernandez-Rojo MA, Merry TL, Zhang X, Xu Y, et al. Hepatic oxidative stress promotes insulin-STAT-5 signaling and obesity by inactivating protein tyrosine phosphatase N2. Cell Metab. (2014) 20:85–102. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.05.011
157. Spalinger MR, Kasper S, Chassard C, Raselli T, Frey-Wagner I, Gottier C, et al. PTPN2 controls differentiation of CD4+ T cells and limits intestinal inflammation and intestinal dysbiosis. Mucosal Immunol. (2015) 8:918–29. doi: 10.1038/mi.2014.122
158. Spalinger MR, McCole DF, Rogler G, Scharl M. Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 2 and inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol. (2016) 22:1034–44. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1034
159. Lee H, Kim M, Baek M, Morales LD, Jang IS, Slaga TJ. Targeted disruption of TC-PTP in the proliferative compartment augments STAT3 and AKT signaling and skin tumor development. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:45077. doi: 10.1038/srep45077
160. Bourdeau A, Dubé N, Tremblay ML. Cytoplasmic protein tyrosine phosphatases, regulation and function: the roles of PTP1B and TC-PTP. Curr Opin Cell Biol. (2005) 17:203–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2005.02.001
161. Kim M, Morales LD, Jang IS, Cho YY, Kim DJ. Protein tyrosine phosphatases as potential regulators of STAT3 signaling. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19(9):2708. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092708
162. ten Hoeve J, de Jesus Ibarra-Sanchez M, Fu Y, Zhu W, Tremblay M, David M, et al. Identification of a nuclear Stat1 protein tyrosine phosphatase. Mol Cell Biol. (2002) 22:5662–8. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.16.5662-5668.2002
163. Bussières-Marmen S, Vinette V, Gungabeesoon J, Aubry I, Pérez-Quintero LA, Tremblay ML. Loss of T-cell protein tyrosine phosphatase in the intestinal epithelium promotes local inflammation by increasing colonic stem cell proliferation. Cell Mol Immunol. (2018) 15:367–76. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2016.72
164. Li Y, Zhou H, Li Y, Han L, Song M, Chen F, et al. PTPN2 improved renal injury and fibrosis by suppressing STAT-induced inflammation in early diabetic nephropathy. J Cell Mol Med. (2019) 23:4179–95. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.2019.23.issue-6
165. Meyaard L, Adema GJ, Chang C, Woollatt E, Sutherland GR, Lanier LL, et al. LAIR-1, a novel inhibitory receptor expressed on human mononuclear leukocytes. Immunity. (1997) 7:283–90. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80530-0
166. Lebbink RJ, de Ruiter T, Verbrugge A, Bril WS, Meyaard L. The mouse homologue of the leukocyte-associated Ig-like receptor-1 is an inhibitory receptor that recruits Src homology region 2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase (SHP)-2, but not SHP-1. J Immunol. (2004) 172:5535–43. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.9.5535
167. Zehender A, Huang J, Györfi AH, Matei AE, Trinh-Minh T, Xu X, et al. The tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 controls TGFβ-induced STAT3 signaling to regulate fibroblast activation and fibrosis. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:3259. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05768-3
168. Jung SW, Moon JY. The role of inflammation in diabetic kidney disease. Korean J Intern Med. (2021) 36:753–66. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2021.174
169. Shi Y, Wang Y, Li Q, Liu K, Hou J, Shao C, et al. Immunoregulatory mechanisms of mesenchymal stem and stromal cells in inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2018) 14:493–507. doi: 10.1038/s41581-018-0023-5
170. Moser B, Loetscher P. Lymphocyte traffic control by chemokines. Nat Immunol. (2001) 2:123–8. doi: 10.1038/84219
171. Rico-Fontalvo J, Aroca G, Cabrales J, Daza-Arnedo R, Yánez-Rodríguez T, Martínez-Ávila MC, et al. Molecular mechanisms of diabetic kidney disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(15):8668. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158668
172. Chang TT, Chen JW. The role of chemokines and chemokine receptors in diabetic nephropathy. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21(9):3172. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093172
173. Pérez de Lema G, Maier H, Franz TJ, Escribese M, Chilla S, Segerer S, et al. Chemokine receptor Ccr2 deficiency reduces renal disease and prolongs survival in MRL/lpr lupus-prone mice. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2005) 16:3592–601. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2005040426
174. Vielhauer V, Kulkarni O, Reichel CA, Anders HJ. Targeting the recruitment of monocytes and macrophages in renal disease. Semin Nephrol. (2010) 30:318–33. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2010.03.006
175. Zoshima T, Baba T, Tanabe Y, Ishida Y, Nakatani K, Nagata M, et al. CCR2- and CCR5-mediated macrophage infiltration contributes to glomerular endocapillary hypercellularity in antibody-induced lupus nephritis. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2022) 61:3033–48. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab825
176. Giunti S, Barutta F, Perin PC, Gruden G. Targeting the MCP-1/CCR2 System in diabetic kidney disease. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. (2010) 8:849–60. doi: 10.2174/157016110793563816
177. de Mik SM, Hoogduijn MJ, de Bruin RW, Dor FJ. Pathophysiology and treatment of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: the role of animal models. BMC Nephrol. (2013) 14:74. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-14-74
178. Daehn I, Casalena G, Zhang T, Shi S, Fenninger F, Barasch N, et al. Endothelial mitochondrial oxidative stress determines podocyte depletion in segmental glomerulosclerosis. J Clin Invest. (2014) 124:1608–21. doi: 10.1172/JCI71195
179. van Gemst JJ, Kouwenberg M, Rops ALWMM, van Kuppevelt TH, Berden JH, Rabelink TJ. Differential binding of chemokines CXCL1, CXCL2 and CCL2 to mouse glomerular endothelial cells reveals specificity for distinct heparan sulfate domains. PloS One. (2018) 13:e0201560. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201560
180. Rops AL, Loeven MA, van Gemst JJ, Eversen I, Van Wijk XM, Dijkman HB, et al. Modulation of heparan sulfate in the glomerular endothelial glycocalyx decreases leukocyte influx during experimental glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. (2014) 86:932–42. doi: 10.1038/ki.2014.115
181. Torres-Hernandez A, Wang W, Nikiforov Y, Tejada K, Torres L, Kalabin A, et al. [amp]]gamma;δ T cells promote steatohepatitis by orchestrating innate and adaptive immune programming. Hepatology. (2020) 71:477–94. doi: 10.1002/hep.30952
182. Daley D, Zambirinis CP, Seifert L, Akkad N, Mohan N, Werba G, et al. [amp]]gamma;δ T cells support pancreatic oncogenesis by restraining αβ T cell activation. Cell. (2016) 166:1485–99.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.07.046
183. Tang R, Meng T, Lin W, Shen C, Ooi JD, Eggenhuizen PJ, et al. A partial picture of the single-cell transcriptomics of human igA nephropathy. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:645988. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.645988
184. Deng S, Zhou F, Wang F, Jiang Y, Tang J, Hu X, et al. C5a enhances Vδ1 T cells recruitment via the CCL2-CCR2 axis in IgA nephropathy. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 125:111065. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111065
185. Hu X, Feng J, Deng S, Tang J, Liao Z, Luo L, et al. Anaphylatoxins enhance Th9 cell recruitment via the CCL20-CCR6 axis in IgA nephropathy. J Nephrol. (2020) 33:1027–36. doi: 10.1007/s40620-020-00708-1
186. Xiong W, Meng XF, Zhang C. NLRP3 inflammasome in metabolic-associated kidney diseases: an update. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:714340. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.714340
187. Mangan MSJ, Olhava EJ, Roush WR, Seidel HM, Glick GD, Latz E. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. (2018) 17:588–606. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2018.97
188. Yuan Q, Tang B, Zhang C. Signaling pathways of chronic kidney diseases, implications for therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2022) 7:182. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01036-5
189. Huang G, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Ma Y. Chronic kidney disease and NLRP3 inflammasome: Pathogenesis, development and targeted therapeutic strategies. Biochem Biophys Rep. (2023) 33:101417. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101417
190. Lu H, Lu X, Xie Q, Wan H, Sun Y. TTC4 inhibits NLRP3 inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis by HSP70. Int J Rheum Dis. (2023) 26:1751–9. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.14818
191. Shahzad K, Bock F, Al-Dabet MM, Gadi I, Kohli S, Nazir S. Caspase-1, but not caspase-3, promotes diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2016) 27:2270–5. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015060676
192. Wu X, Zhao L, Li K, Yang J. The role of NLRP3 inflammasome in igA nephropathy. Medicina (Kaunas). (2022) 59(1):82. doi: 10.3390/medicina59010082
193. Lorenz G, Darisipudi MN, Anders HJ. Canonical and non-canonical effects of the NLRP3 inflammasome in kidney inflammation and fibrosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2014) 29:41–8. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gft332
194. Zhang L, Wang XZ, Li YS, Zhang L, Hao LR. Icariin ameliorates IgA nephropathy by inhibition of nuclear factor kappa b/Nlrp3 pathway. FEBS Open Bio. (2017) 7:54–63. doi: 10.1002/feb4.2017.7.issue-1
195. Wang W, Wang X, Chun J, Vilaysane A, Clark S, French G, et al. Inflammasome-independent NLRP3 augments TGF-β signaling in kidney epithelium. J Immunol. (2013) 190:1239–49. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201959
196. Shahzad K, Fatima S, Khawaja H, Elwakiel A, Gadi I, Ambreen S, et al. Podocyte-specific Nlrp3 inflammasome activation promotes diabetic kidney disease. Kidney Int. (2022) 102:766–79. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2022.06.010
197. Kim YG, Kim SM, Kim KP, Lee SH, Moon JY. The role of inflammasome-dependent and inflammasome-independent NLRP3 in the kidney. Cells. (2019) 8(11):1389. doi: 10.3390/cells8111389
198. Magupalli VG, Negro R, Tian Y, Hauenstein AV, Di Caprio G, Skillern W, et al. HDAC6 mediates an aggresome-like mechanism for NLRP3 and pyrin inflammasome activation. Science. (2020) 369(6510):eaas8995. doi: 10.1126/science.aas8995
199. Li Z, Liu S, Fu T, Peng Y, Zhang J. Microtubule destabilization caused by silicate via HDAC6 activation contributes to autophagic dysfunction in bone mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2019) 10:351. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1441-4
200. Moreno-Gonzalo O, Ramírez-Huesca M, Blas-Rus N, Cibrián D, Saiz ML, Jorge I, et al. HDAC6 controls innate immune and autophagy responses to TLR-mediated signalling by the intracellular bacteria Listeria monocytogenes. PloS Pathog. (2017) 13:e1006799. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006799
201. Liu L, Zhou X, Shetty S, Hou G, Wang Q, Fu J. HDAC6 inhibition blocks inflammatory signaling and caspase-1 activation in LPS-induced acute lung injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. (2019) 370:178–83. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2019.03.017
202. Youn GS, Lee KW, Choi SY, Park J. Overexpression of HDAC6 induces pro-inflammatory responses by regulating ROS-MAPK-NF-κB/AP-1 signaling pathways in macrophages. Free Radic Biol Med. (2016) 97:14–23. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.05.014
203. Jabir MS, Ritchie ND, Li D, Bayes HK, Tourlomousis P, Puleston D, et al. Caspase-1 cleavage of the TLR adaptor TRIF inhibits autophagy and β-interferon production during Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Cell Host Microbe. (2014) 15:214–27. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.01.010
204. Hu Y, Shang M, Shi Y, Tao M, Yuan W, Tang L, et al. Correlation analysis between expression of histone deacetylase 6 and clinical parameters in IgA nephropathy patients. Ren Fail. (2021) 43:684–97. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2021.1914657
205. Vieson MD, Gojmerac AM, Khan D, Dai R, van Duzer JH, Mazitschek R, et al. Treatment with a selective histone deacetylase 6 inhibitor decreases lupus nephritis in NZB/W mice. Histol Histopathol. (2017) 32:1317–32. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.01.010
206. Chen Q, Yue F, Li W, Zou J, Xu T, Huang C, et al. Potassium bisperoxo(1,10-phenanthroline)oxovanadate (bpV(phen)) induces apoptosis and pyroptosis and disrupts the P62-HDAC6 protein interaction to suppress the acetylated microtubule-dependent degradation of autophagosomes. J Biol Chem. (2015) 290:26051–8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.653568
207. Li W, Dai Y, Shi B, Yue F, Zou J, Xu G. LRPPRC sustains Yap-P27-mediated cell ploidy and P62-HDAC6-mediated autophagy maturation and suppresses genome instability and hepatocellular carcinomas. Oncogene. (2020) 39:3879–92. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-1257-9
208. Gluba A, Banach M, Hannam S, Mikhailidis DP, Sakowicz A, Rysz J. The role of Toll-like receptors in renal diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2010) 6:224–35. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2010.16
209. Lin M, Tang SC. Toll-like receptors: sensing and reacting to diabetic injury in the kidney. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2014) 29:746–54. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gft446
210. Rock KL, Latz E, Ontiveros F, Kono H. The sterile inflammatory response. Annu Rev Immunol. (2010) 28:321–42. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-030409-101311
211. Kawai T, Akira S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol. (2010) 11:373–84. doi: 10.1038/ni.1863
212. De Nardo D. Toll-like receptors: Activation, signalling and transcriptional modulation. Cytokine. (2015) 74:181–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.02.025
213. Kawai T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity. Immunity. (2011) 34:637–50. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.05.006
214. Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D, Sun SC. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2017) 2:17023–. doi: 10.1038/sigtrans.2017.23
215. Elshaer RE, Tawfik MK, Nosseir N, El-Ghaiesh SH, Toraih EA, Elsherbiny NM, et al. Leflunomide-induced liver injury in mice: Involvement of TLR4 mediated activation of PI3K/mTOR/NFκB pathway. Life Sci. (2019) 235:116824. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116824
216. Liu L, Pang XL, Shang WJ, Xie HC, Wang JX, Feng GW, et al. Over-expressed microRNA-181a reduces glomerular sclerosis and renal tubular epithelial injury in rats with chronic kidney disease via down-regulation of the TLR/NF-κB pathway by binding to CRY1. Mol Med. (2018) 24:49. doi: 10.1186/s10020-018-0045-2
217. Milanesi S, Verzola D, Cappadona F, Bonino B, Murugavel A, Pontremoli R, et al. Uric acid and angiotensin II additively promote inflammation and oxidative stress in human proximal tubule cells by activation of toll-like receptor 4. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:10868–76. doi: 10.1002/jcp.v234.7
218. Wei M, Li Z, Xiao L, Yang Z. Effects of ROS-relative NF-κB signaling on high glucose-induced TLR4 and MCP-1 expression in podocyte injury. Mol Immunol. (2015) 68:261–71. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.09.002
219. Dasu MR, et al. High glucose induces toll-like receptor expression in human monocytes: mechanism of activation. Diabetes. (2008) 57:3090–8. doi: 10.2337/db08-0564
220. Xu Z, Zou C, Yu W, Xu S, Huang L, Khan Z, et al. Inhibition of STAT3 activation mediated by toll-like receptor 4 attenuates angiotensin II-induced renal fibrosis and dysfunction. Br J Pharmacol. (2019) 176:2627–41. doi: 10.1111/bph.v176.14
221. Yu D, Shi M, Bao J, Yu X, Li Y, Liu W. Genipin ameliorates hypertension-induced renal damage via the angiotensin II-TLR/MyD88/MAPK pathway. Fitoterapia. (2016) 112:244–53. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2016.06.010
222. Jung SM, Kim WU. Targeted immunotherapy for autoimmune disease. Immune Netw. (2022) 22:e9. doi: 10.4110/in.2022.22.e9
223. Lin YC, Gau TS, Jiang ZH, Chen KY, Tsai YT, Lin KY, et al. Targeted therapy in glomerular diseases. J Formos Med Assoc. (2024) 123:149–58. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2023.06.020
224. Meliambro K, He JC, Campbell KN. Podocyte-targeted therapies - progress and future directions. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2024) 20:643–58. doi: 10.1038/s41581-024-00843-z
225. Casare FA, Thieme K, Costa-Pessoa JM, Rossoni LV, Couto GK, et al. Renovascular remodeling and renal injury after extended angiotensin II infusion. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2016) 310:F1295–307. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00471.2015
226. Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Bain RP, Rohde RD. The effect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition on diabetic nephropathy. The Collaborative Study Group. N Engl J Med. (1993) 329:1456–62. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199311113292004
227. Wang S, Chen C, Su K, Zha D, Liang W, Hillebrands JL, et al. Angiotensin II induces reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and myosin light-chain phosphorylation in podocytes through rho/ROCK-signaling pathway. Ren Fail. (2016) 38:268–75. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2015.1117896
228. Tu P, Gibon J, Bouron A. The TRPC6 channel activator hyperforin induces the release of zinc and calcium from mitochondria. J Neurochem. (2010) 112:204–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06446.x
229. Tao Y, Chaudhari S, Shotorbani PY, Ding Y, Chen Z, Kasetti R, et al. Enhanced Orai1-mediated store-operated Ca(2+) channel/calpain signaling contributes to high glucose-induced podocyte injury. J Biol Chem. (2022) 298:101990. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101990
230. Tomita I, Kume S, Sugahara S, Osawa N, Yamahara K, Yasuda-Yamahara M, et al. SGLT2 inhibition mediates protection from diabetic kidney disease by promoting ketone body-induced mTORC1 inhibition. Cell Metab. (2020) 32:404–419.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.06.020
231. Jiang L, Hindmarch CC, Rogers M, Campbell C, Waterfall C, Coghill J, et al. RNA sequencing analysis of human podocytes reveals glucocorticoid regulated gene networks targeting non-immune pathways. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:35671. doi: 10.1038/srep35671
232. KDIGO 2021 clinical practice guideline for the management of glomerular diseases. Kidney Int. (2021) 100:S1–s276. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2021.05.021
233. Faul C, Donnelly M, Merscher-Gomez S, Chang YH, Franz S, Delfgaauw J. The actin cytoskeleton of kidney podocytes is a direct target of the antiproteinuric effect of cyclosporine A. Nat Med. (2008) 14:931–8. doi: 10.1038/nm.1857
Keywords: glomerular diseases, inflammation, cytokines, glomerular cells, signaling pathway
Citation: Xiong Y, Li W, Jin S, Wan S and Wu S (2025) Inflammation in glomerular diseases. Front. Immunol. 16:1526285. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1526285
Received: 11 November 2024; Accepted: 12 February 2025;
Published: 04 March 2025.
Edited by:
James Cheng-Chung Wei, Chung Shan Medical University Hospital, TaiwanReviewed by:
Guangrui Huang, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, ChinaYao Min Hung, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan
Copyright © 2025 Xiong, Li, Jin, Wan and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Suzhen Wu, d3VzdXpoZW4yMDA1QGdtdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
‡ORCID: Suzhen Wu, orcid.org/0000-0002-0980-3091
 Yongqing Xiong
Yongqing Xiong Wei Li1†
Wei Li1† Suzhen Wu
Suzhen Wu