
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Immunol., 20 February 2025
Sec. Cytokines and Soluble Mediators in Immunity
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1526081
This article is part of the Research TopicCytokine Network Dynamics: Influence on Autoimmune Disorders and Cancer TherapyView all 8 articles
Background: The airway epithelial barrier is the first defence against aeroallergens. Nasal epithelial cells (NECs) are vital in regulating innate and adaptive mucosal immunity in allergic rhinitis (AR). Tregs produce cytokines essential for the immunomodulatory activities in allergen immunotherapy. Understanding the relationship between NECs and Tregs in the airway hyperresponsiveness network is essential for developing novel treatments.
Methods: Using an in vitro human Treg-NEC co-culture system of AR and health control group, the chemokine expression profiles of NECs were examined using immunohistochemistry, RT-PCR, and ELISA, and functional surface markers of Tregs were detected using flow cytometric analysis. Correlation analysis was performed between cytokines derived from NECs and surface markers of CD4+CD8+Foxp3+ Tregs in the AR group after co-culture, including TSLP/CTLA4, CCL1/CTLA4, TSLP/CTLA4, TSLP/CCR8, and CCL1/CCR8.
Results: CCR8 and CTLA-4 expressions after co-culturing were higher than single culture. Following Derp1 stimulation, TSLP, IL-25 and TGF-β expressions in the AR + Derp1 group were increased. CCL1 mRNA was lower in the AR + Derp1 group than control group. In the AR + Derp1 group, TSLP was higher, and CCL1 protein levels were decreased. There were no significant differences in IL-25, TGF-β and IL-10. When Treg co-culture group added, changes were similar to that observed in pNECs. After co-culture, CCL1/CCR8 was positively correlated in AR.
Conclusion: Human pNECs can communicate with Tregs directly, CCL1/CCR8 may be the pathway between NECs and Tregs in vitro and may play a key role in the immune network of AR.
Allergic rhinitis (AR), characterised by upper airway hyperresponsiveness, is a major allergic disease of global concern. Its incidence has increased dramatically in recent years and is undertreated, even according to guidelines (1, 2). An aberrant type 2 response to aeroallergens may be owing to upregulated pro-allergic pathways and disrupted epithelial barriers. Exposure to allergens could lead to the release of epithelial-derived cytokines, such as thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, and interleukin (IL)-25 (3). Nasal epithelial cells (NECs), as the first mucosal defence against inhaled allergens, are being increasingly studied but remain undefined. Allergen immunotherapy (AIT) remains the only disease-modifying treatment for AR, which induces immunological tolerance characterised by increased Foxp3+ Treg cell count and decreased sensitivity to Treg apoptosis (4, 5). Most studies have examined the effects of NECs on dendritic and T helper cells in the nasal mucosa. However, the relationship between NECs and Tregs in the network of airway hyperresponsiveness remain unexplored.
AR is triggered by the disruption of the nasal epithelium through the production of epithelium-derived cytokines such as TSLP and IL-25 (6). CCL1/I-309 is a member of the CCL chemokine family and is produced by several cellular sources, including airway epithelial cells (7). Previous studies have suggested that CCL1 may play a role in lymphocyte recruitment in allergic disease (8). CCR8 is an essential receptor for CCL1, and intrathecal injection of recombinant CCL1 into naïve mice induces hypersensitivity (9, 10). Notably, Tregs exhibit suppressive activity through CCR8 expression in mice and humans (11).
This study investigated the immunological features of human primary NECs (pNECS) and Foxp3+ Tregs to identify key molecules involved in their interactions. We focused on TSLP, TGF-β, IL-25, and CCL1 derived from NECs and CCR8 and CTLA-4 expressed by Tregs.
The study cohort consisted of 40 patients with dust mite-induced AR (17 females and 23 males, aged 19–49 years, mean age 32.1 ± 6.3 years) and 40 healthy volunteers (15 females and 25 males, aged 26–32 years, mean age 28.9 ± 1.7 years). A clinical interview was conducted before the collection of peripheral blood and NECs. All participants were non-smokers, non-obese, without a diagnosis of an immune disease, and no history of recent infection. This study was approved by the ethics committee of our institute, and informed consent was obtained from all volunteers.
The pNECs were obtained from bilateral inferior turbinate under nasal endoscope by brushing (radius*length: 0.49 mm*1.2 cm, Pestro Healthcare Inc.). NECs were collected from each side, and the brush was gently turned twice and placed in an Eppendorf tube containing 1 ml phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) buffer. Cell suspensions were diluted to 1 × 105/ml with 10% foetal bovine serum-BMGM medium (Lonza, Switzerland) and seeded into 35 mm cell culture dishes (Corning, USA). Once the monolayer of pNECs was confluent, Derp1 (5 ug/ml) recombinant protein or PBS was added to the groups. The adherent cells and cell suspension were collected after 24 h of incubation (37°C, 5% CO2) for subsequent co-culture and detection.
Subsequently, 40 patients with AR (21 males and 19 females, aged 27–45 years, mean age 31.7 ± 5.40 years) with positive house dust mite allergens and 30 healthy volunteers (19 males and 11 females, aged 20–52 years, mean age 30.3 ± 2.50 years) were enrolled. Subsequently, tests and analysis were used to detect: 1) the AR group, with Derp1 (ab73855, abcam), group A; 2) the AR group, with PBS, group B; 3) the healthy control (HC) group, with Derp1, group C; and 4) the HC group, with PBS, group D.
Foxp3+ Tregs were purified from peripheral blood mononuclear cells through magnetic cell selection using a CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Treg Isolation Kit (Miltenyi Biotec, Germany). The purity was approximately 75–80%, identified using flow cytometry with Foxp3-APC (eBioscience, USA). Subsequently, Tregs (3 × 104 cells/dish) were cultured with confluent pNECs from a single donor.
The pNECs-Foxp3+ Tregs co-culture model was established. Closer inspection and analysis were applied to detect these healthy volunteers: 1) NECs-Tregs co-culture group, pNECs were adherent, group A; 2) NECs-Tregs co-culture group, pNECs were suspension, group B; 3) Treg cells cultured in co-culture medium alone, group C; and 4) RPMI-1640 was used as blank control group of Tregs cultured alone, group D.
Foxp3 is a transcription factor involved in Tregs. Immunostaining of Foxp3 in the nasal mucosa (n = 10, 5 in each AR and HC group) was performed. The primary antibody was a rabbit anti-human Foxp3 polyclonal antibody (Wuhan Huamei Biotech Co., LTD, China). All sections were observed and counted under a microscope. Positive staining for Foxp3 was considered tan. Ten high-power fields (400×) were randomly selected from each section, and the percentage of positive cells in each high-power field was recorded. The average value was used to calculate the expression rate of the positive cells.
Flow cytometry was performed on freshly isolated or stimulated Foxp3+ Tregs using the following antibodies: CD4-FITC (eBioscience, USA), CD25-PerCP-cyanine 2.5 (eBioscience, USA), Foxp3-APC (eBioscience, USA), CTLA-4-PE (eBioscience, USA), CCR8-PE (BioLegend, USA), and PerFix-nc Kit (no centrifuge assay kit) (Beckman Co. USA). The cells were analysed using flow cytometry (Accuri C6; BD Biosciences, USA), and 10,000 events in live cell gates were acquired in array analysis. The application settings were applied in each experiment to standardise the flow cytometric readouts over time.
Quantitative real-time PCR was performed on confluent and co-cultured pNECs for TSLP (F 5’-GGCTGCCTTAGCTATCTGG -3’), IL-10 (F 5’-GCATTCTTCACCTGCTCCAC -3’), TGF-β (F 5’-GAGCCTGAGGCCGACTACTA-3’), IL-25 (F 5’-GTAGGGCCAGTGAAGATGGA-3’), CCL1 (F 5’-TTCACCAGGCTCATCAAAGCT-3’) mRNA, and beta-actin (F 5’-AAGAGCTACGAGCTGCCTGA-3’) in AR and HC groups (QIAGEN, German). Data were analysed using a real-time PCR (ABI7300, Applied Biosystems, USA) and ABI Prism 7500 SDS Software.
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was conducted to determine IL-10, TGF-beta, IL-25, and CCL1 expression after Derp1, Tregs, or both, stimulated cell suspension in AR and HC groups using an ELISA kit (eBioscience, USA). The optical density was measured, and the detected protein concentration was calculated according to the standard curve.
Statistical analyses were performed using the chi-square, Mann–Whitney U, or T-test. Statistical significance was set at P <0.05.
In the nasal mucosa of AR and HC inferior turbinates, Foxp3 showed positive expression in the cell nucleus (brown) after immunohistochemical staining, mainly in the nucleated round mononuclear cells. There was no significant difference in the number of Foxp3-positive cells between the AR and HC group (P = 0.256) (Figure 1).
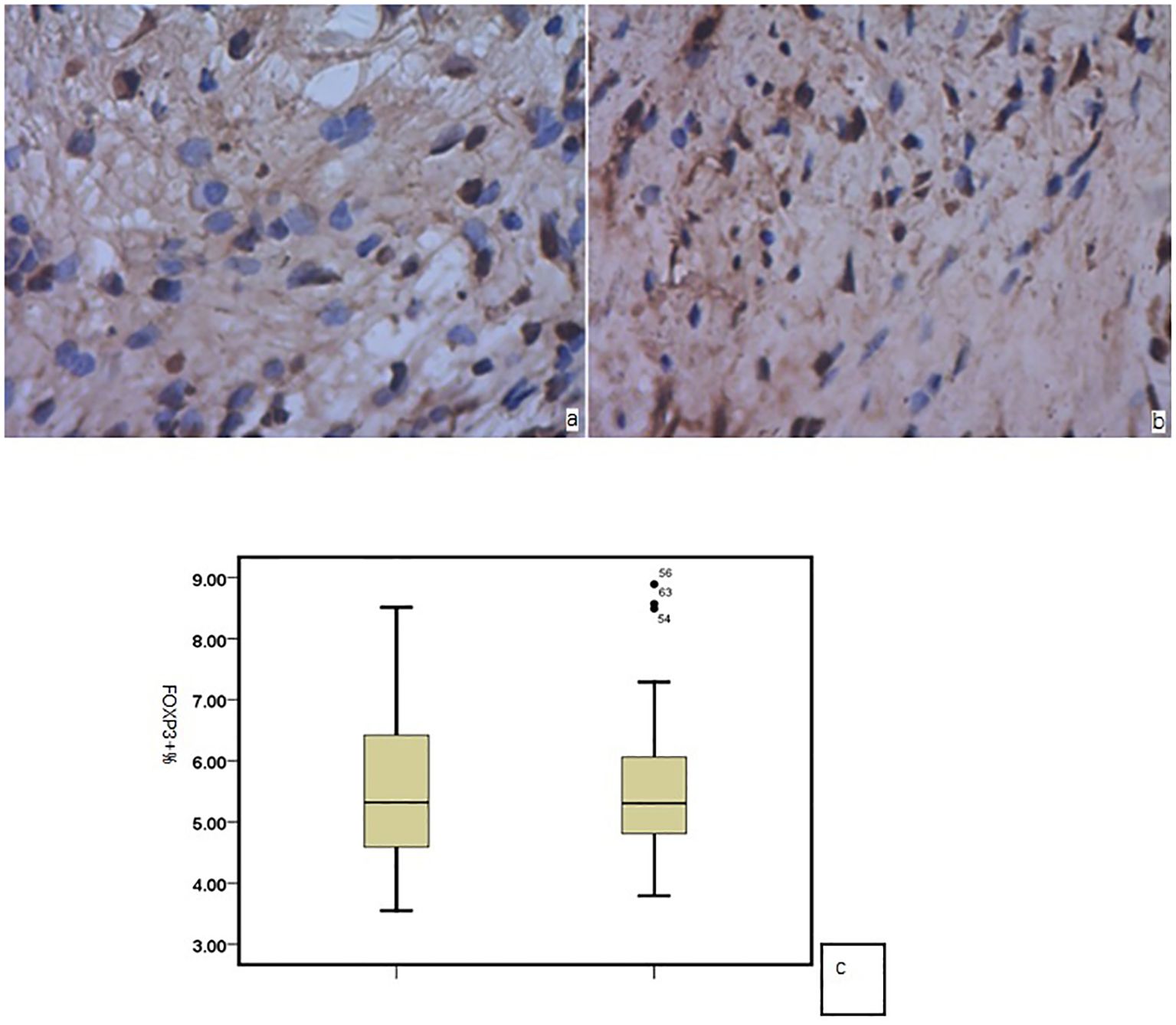
Figure 1. Foxp3 in the nasal mucosa of (a) AR and (b) HC; (c) no significant difference between the two groups.
PNECs were obtained from 40 patients; the mean cell count is (2.84 ± 0.67) × 105 cells per patient before culture. The 80% confluence rate was 40% (n = 40,16/40), and the average time from culture to confluence was 15.2 ± 1.25 days.
The average number of Tregs isolated by immunomagnetic beads in 36 patients was (1.35 ± 0.54) × 105 cells per sample. The co-culture experiment required at least 4 × 3 × 104 and 1.0 × 104 cells. Therefore, the number of Treg cells after isolation was at least 1.3 × 105. Only 16 of 36 patients met the requirement (44.4%, n = 36, 16/36). The purity of CD4+CD25+ Tregs isolated using immunomagnetic beads was 75–80%, as identified by flow cytometry using Foxp3 as a surface marker (Figure 2).
The pNECs-Foxp3+ Tregs co-culture model was successfully established (Figure 3). In the last part of the study, the number of samples with 80% successful confluent NECs was 18 (n = 40) and 19 (n = 40) cases in AR and HC groups, respectively. After co-culture with Tregs from blood collection, co-culture models were successfully established for 16 patients in each group.
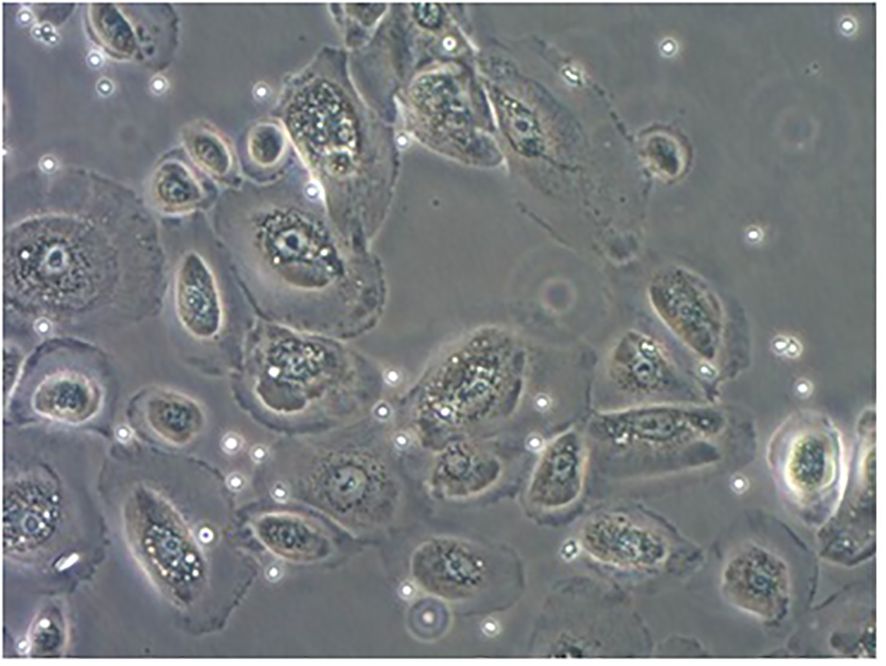
Figure 3. PNECs-Foxp3+ Tregs co-culture model. The adherent cells were nasal mucosa epithelium and the suspension was Foxp3+ Tregs.
Flow cytometry was used to detect HCs in all four groups. The Foxp3, CCR8, and CTLA-4 expression levels were compared between groups. There was no significant difference in the Foxp3 expression between groups A, B, C, and D (P >0.05). CCR8 expression was significantly higher in group A than in groups B, C and D (P <0.05). However, there were no significant differences among groups B, C, and D (P >0.05). CTLA-4 expression was significantly higher in group A than in groups B, C and D (P <0.05). There was no significant difference in CTLA-4 expression among groups B, C, and D (P >0.05) (Tables 1, 2, Figures 4, 5). When adding the disease group after co-culture, CCR8 and CTLA-4 expressions were lower in the AR group than in the HC group (P = 0.011 and P = 0.007, respectively) (Figure 6).
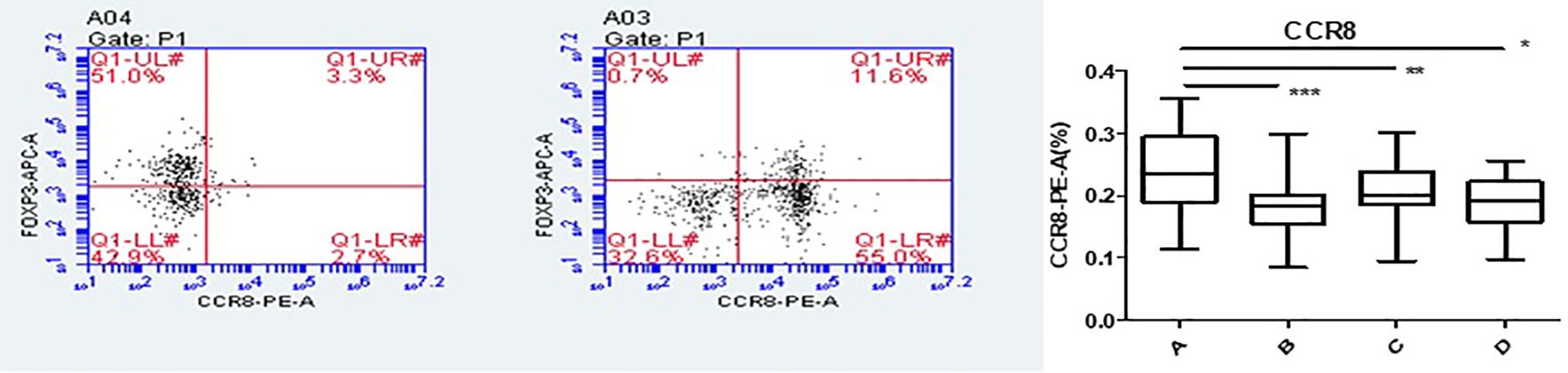
Figure 4. CCR8 expression of Tregs in group A increased following co-culture. *, **, ***p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
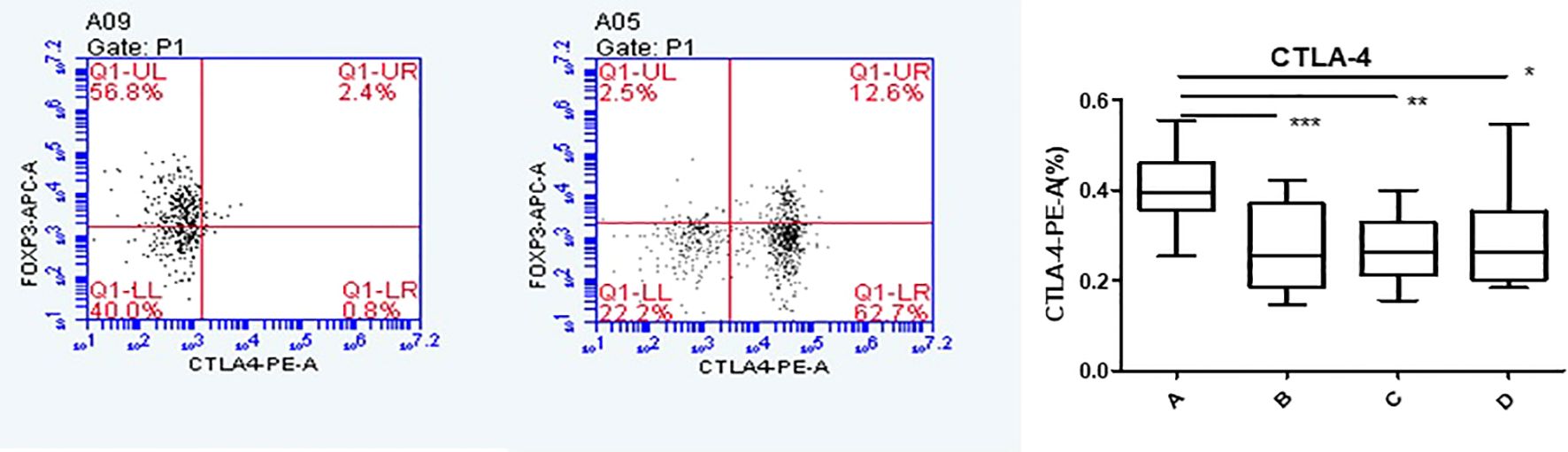
Figure 5. CTLA-4 expression of Tregs in group A increased following co-culture. *, **, ***p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
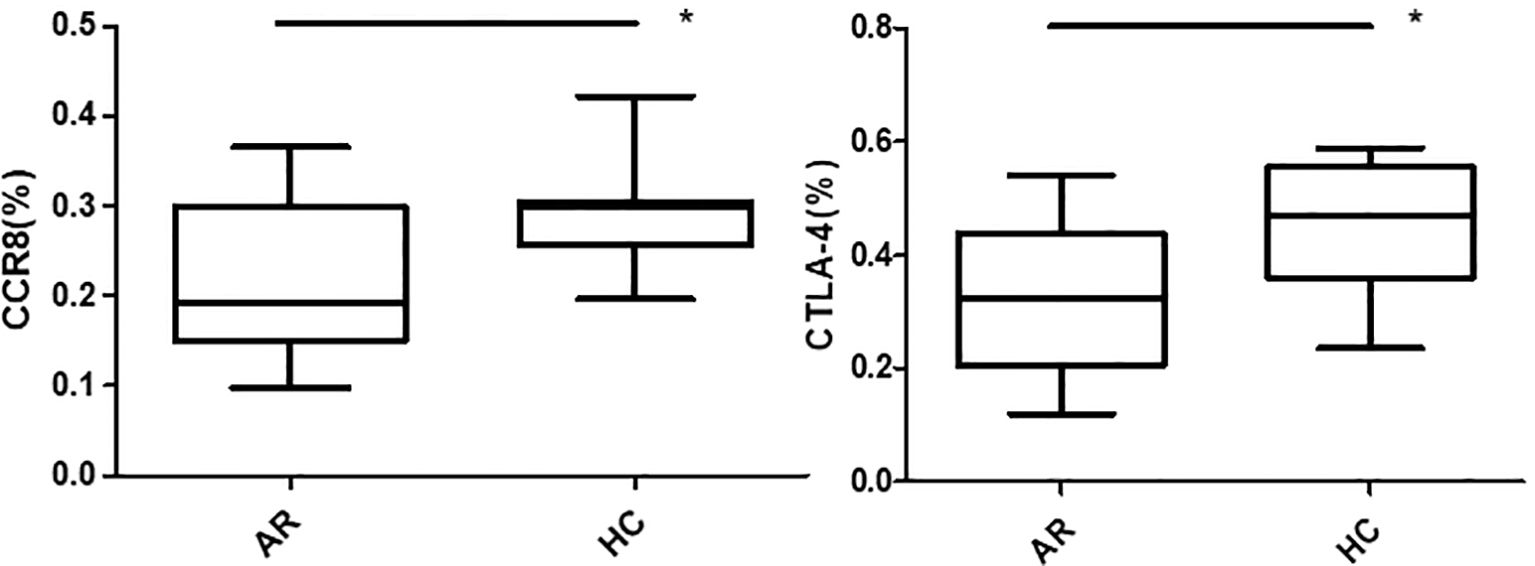
Figure 6. CCR8 and CTLA-4 expressions of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs were lower in the allergic rhinitis group than in the healthy controls (P = 0.011 and P = 0.007, respectively). *P <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
After 24 h of Derp1 stimulation in pNECs, quantitative real-time PCR showed that the expressions of TSLP mRNA (P = 0.001, P = 0.01, and P = 0.000), IL-25 mRNA (P = 0.000, P = 0.006, and P = 0.001), and TGF-β mRNA (P = 0.016, P = 0.023, and P = 0.250) in AR + Derp1 group were increased. CCL1 mRNA was significantly lower in the AR + Derp1 group than in the control groups (P = 0.001, P = 0.023, and P = 0.08). There was no significant difference in IL-10 mRNA expression between the two groups (P = 0.141, P = 0.265, P = 0.358) (Figure 7).
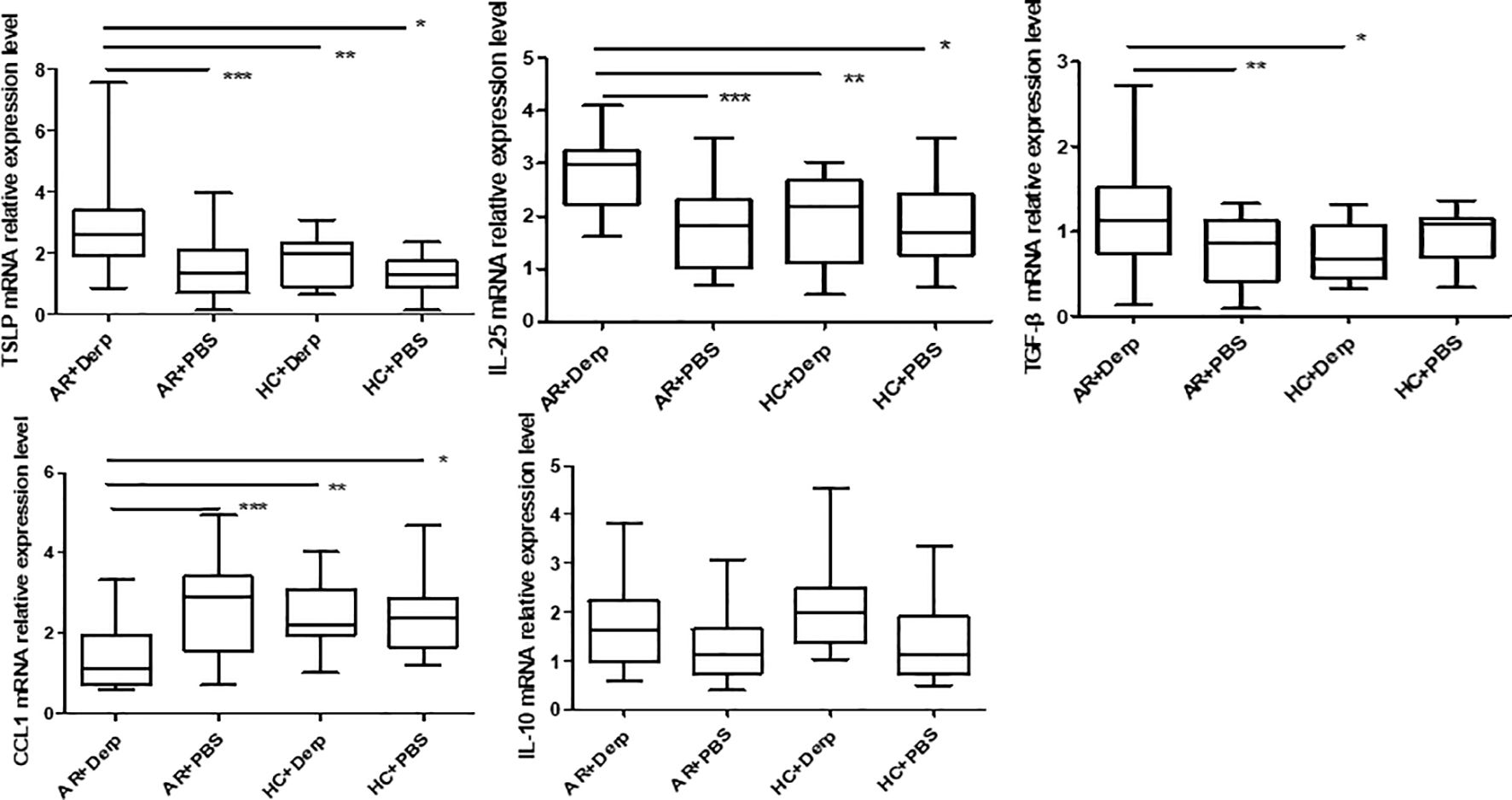
Figure 7. TSLP, IL-25, and TGF-β mRNA in pNECs in the AR + Derp1 group increased after Derp1 stimulation. CCL1 mRNA expression was lower in the AR + Derp1 group than in control groups. No significant difference was found in IL-10 mRNA. *P <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
TSLP, IL-25, and TGF-β mRNA in pNECs in the AR + Derp1 group increased after Derp1 stimulation. CCL1 mRNA expression was lower in the AR + Derp1 group than in control groups. No significant difference was found in IL-10 mRNA.
TSLP, CCL1, IL-25, IL-10 and TGF-β expressions in the pNECs cell suspension were detected by ELISA. The results showed that TSLP concentration was higher in the AR + Derp1 group than in the other three groups (P = 0.000, P = 0.001, and P = 0.000). CCL1 protein expression was decreased (P = 0.058, P = 0.028, and P = 0.012). There were no significant differences in IL-25 (P = 0.904, P = 0.941, and P = 0.846), TGF-β (P = 0.918, P = 0.559, and P = 0.290), and IL-10 (P = 0.681, P = 0.830, and P = 0.746). The mean ± standard deviation of each group is shown in (Table 3) and (Figure 8). After adding the Tregs co-culture group, IL-10, TSLP, CCL1 and TGF-β expressions in the cell suspension of AR and HC groups after co-culture was detected by ELISA. The trend of the change in expression was similar to that observed in pNECs. The expression level of TSLP increased (P = 0.016), whereas that of CCL1 decreased, with a statistically significant difference (P = 0.047). No significant difference was found between the two groups in IL-10 and TGF-β expressions (P = 0.101 and P = 0.432) (Figure 9).

Figure 8. The TSLP concentration in the AR + Derp1 group was higher than that in the other three groups. The CCL1 protein was decreased. There were no significant differences in IL-25, TGF-β, and IL-10. *P <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
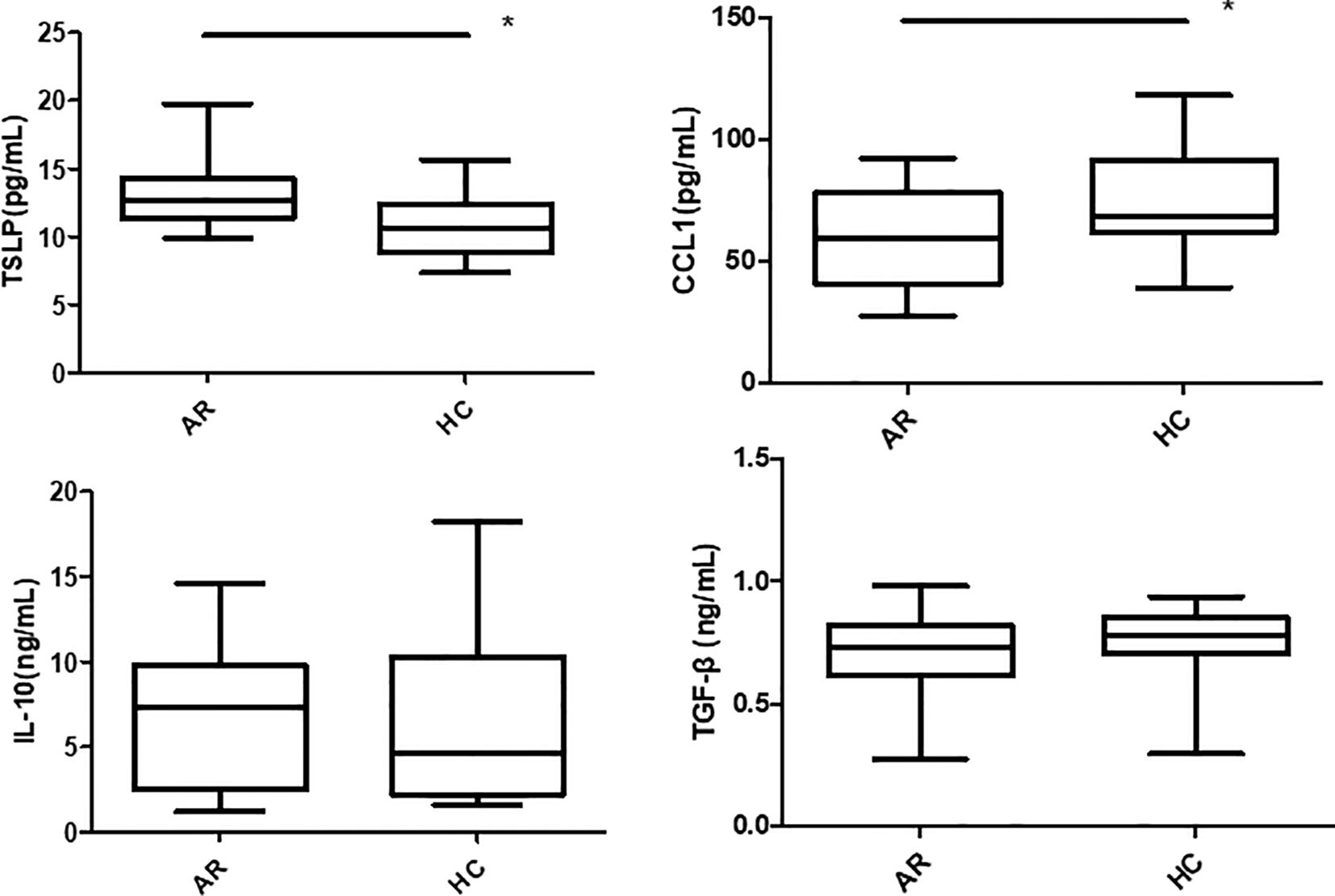
Figure 9. TSLP concentration in the AR group was higher than in the HC group after co-culture. The CCL1 protein was decreased. There were no significant differences in TGF-β and IL-10. *P <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Correlation analysis was performed between cytokines derived from NECs and surface markers of CD4+CD8+Foxp3+ Tregs in the AR group after co-culture (n = 16), including TSLP/CTLA4, CCL1/CTLA4, TSLP/CTLA4, TSLP/CCR8, and CCL1/CCR8. After co-culture, CCL1/CCR8 levels were positively correlated (r = 0.642, P = 0.007) (Figure 10). There were no statistically significant correlations between TSLP/CTLA4 (r = 0.024, P = 0.931), CCL1/CTLA4 (r = 0.344, P = 0.192), and TSLP/CCR8 (r = 0.194, P = 0.471).
AIT is an effective AR treatment that induces clinical tolerance to sensitising allergens, which has been reported for 113 years since 1911 (12). It is administered subcutaneously or sublingually. The immune tolerance mechanisms of AIT are highly complex and far from clear. The induction of Tregs is still considered a pivotal point that can suppress effector T cell responses by early- and late-phase systemic responses (13). However, local tolerance and stability of Tregs in the nasal mucosa remain unexplored. As the first line of the environment, NECs play a vital role in the local immune microenvironment. However, their crosstalk with Tregs is unknown. Understanding the relationship between local Tregs and NECs may improve their therapeutic use for AR.
The nasal mucosa is a local tissue that lacks lymph nodes. The distribution of Foxp3+ Tregs in the nasal mucosa was observed using Foxp3 immunohistochemical staining. Our results revealed that these cells were distributed in the inferior turbinate mucosa of patients with AR and HCs. However, there was no significant difference between the two groups. A previous study showed that patients with AR present low Tregs in the peripheral blood and the nasal mucosa (14). Shirasaki et al. (15) and Sogut et al. (16) suggested that Foxp3+ Tregs play an essential role in the immune microenvironment of the nasal mucosa in AR and can locally regulate the Th1/Th2 balance in the mucosa. Muller et al. (17) also performed immunohistochemical staining on the nasal mucosal tissues of patients with pollen allergy, pollen and dust mite multiple allergies, and HCs and obtained similar results. We conducted a mixed culture of primary NECs and CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Treg cells in vitro. A previous review showed many limitations to animal experiments, especially the small number of epithelial and Treg cells. Therefore, we did not conduct animal experiments.
NECs-derived cytokines modulate innate and acquired immune responses consisting of TSLP and IL-25. Additionally, Treg-associated factors include IL-10 and TGF-β (18, 19). Foxp3+ Tregs infiltrate and expand via chemokine- and cytokine-dependent mechanisms. CCL1 in brain tissue is crucial for Treg accumulation by CCR8 on Tregs (20). TLSP also influences Treg function in tumours (21). This study investigated the potential association between NECs-derived cytokines and Tregs, including TSLP, IL-25, IL-10, TGF-β, and CCL1. Foxp3 and CTLA-4 are vital components of Tregs and are responsible for maintaining immune homeostasis (22, 23). Following co-culture with normal NECs, although there was no difference in Foxp3, which marked the differentiation of Tregs, CCR8 marked the increase in CTLA-4 migration and expression. This indicates that the inhibitory activity was substantially increased. These results suggest that information transmission occurs between NECs and Foxp3+ Tregs by inducing Treg chemotaxis and enhancing their inhibitory activity. Colantonio et al. (24) investigated local Foxp3+ Treg cells in the skin and concluded that the skin exerts its inhibitory activity through chemotaxis toward Tregs via the CCL1/CCR8 pathway. Another study on bile duct sclerosis (25) suggested that IgG-associated CCL1 chemotaxis of Th2 and Foxp3+ Treg cells occurs via the CCL1/CCR8 pathway, although these studies did not focus on airways and allergies.
Furthermore, we investigated the potential association of NEC-derived cytokines with Tregs in NECs of specific house dust mite AR following Derp1 stimulation. CCL1 was detected in NECs and extracellular cells. CCL1 mRNA expression and protein levels in AR cell suspensions decreased after exposure to specific allergens. Although no further evidence supports the involvement of CCL1 derived from the airway mucosal epithelium in allergic reactions in AR pathogenesis, our results indirectly suggest that CCL1 derived from NECs has a regulatory effect on Tregs. IL-10 and TGF-β have a bidirectional regulation effect that regulates the immunosuppressive activity of Foxp3+ Treg. Moreover, although there were no crucial results, they are the main functional cytokines of immunosuppressive activity secreted by Foxp3+ Tregs (26, 27). TSLP suppressed the functional activity of Tregs in the respiratory tract of an animal model (28, 29). Although IL-10, TGF-β, and TSLP are all important cytokines of NECs, our results showed that TSLP expression in NECs increased in the AR group. There was no significant correlation between TSLP, CCR8, and CTLA-4 expressions. Owing to the small number of cells and fixed number of flow cytometry staining channels, we could not detect the expression of the TSLP receptor (TSLPR) on the surface of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs. NECs cannot avoid transmitting information via CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs through TSLP/TSLPR, similar to the lower airway in asthma (30).
Our co-culture results with or without AR stimulated by Derp1 showed that CCL1 derived from NECs was significantly and linearly correlated with CCR8 expression on the surface of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs in patients with AR. CCR8 is specifically expressed in Th2 and Tregs and plays three immunological roles: binding to ligands with high affinity, chemotaxis of Tregs to local tissues, and migration to antigen-presenting cells (31–33). Based on our results, the CCL1/CCR8 pathway is one of the information transmission pathways between NECs and CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs involved in AR pathogenesis. After NECs were exposed to specific allergens, the CCL1 expression level decreased, similar to the CCR8 effect on Tregs. It means that, NECs could enhance the inhibitory function of Tregs via chemotaxis in Th2 immune responses, including but not limited to AR. Local Foxp3+ Tregs in the skin (34) have been investigated, and the results indicated that skin epidermal cells could exert inhibitory activity through chemotaxis to Tregs via the CCL1/CCR8 pathway. Another study on bile duct sclerosis (25) suggested that IgG-associated CCL1 chemotaxis involves Th2 and Foxp3+ Tregs via the CCL1/CCR8 pathway.
Our results suggest that human pNECs could communicate with Tregs directly and that the suppressive function of Tregs was maintained or mounted after co-culture with NECs. This may become a new target for biological therapy in AR. CCL1/CCR8 may be the pathway between NECs and Tregs in vitro and may play a key role in the immune network of AR. These conclusions help identify novel therapeutic targets for AR and airway allergic diseases (Figure 11).
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics committee of China-Japan Union Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin.
JS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MY: Formal analysis, Software, Writing – review & editing. YL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. LS: Software, Writing – review & editing. CM: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. DZ: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82071016). National Clinical Research Center for Otorhinolaryngologic Diseases program (2024KF001).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1526081/full#supplementary-material
1. Zhang Y, Lan F, Zhang L. Advances and highlights in allergic rhinitis. Allergy. (2021) 76:3383–9. doi: 10.1111/all.v76.11
2. Greiner AN, Hellings PW, Rotiroti G, Scadding GK. Allergic rhinitis. Lancet. (2011) 378:2112–22. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60130-X
3. Wipperman MF, Gayvert KM, Atanasio A, Wang CQ, Corren J, Covarrubial A, et al. Differential modulation of allergic rhinitis nasal transcriptome by dupilumab and allergy immunotherapy. Allergy. (2024) 79:894–907. doi: 10.1111/all.16001
4. Pavon-Romero GF, Parra-Vargas MI, Ramirez-Jimenez F, Melgoza-Ruiz E, Serrano-Perez NH, Teran LM, et al. Allergen immunotherapy: current and future trends. Cells. (2022) 11:212. doi: 10.3390/cells11020212
5. Datta A, Moitra S, Das PK, Mondal S, Faruk SMO, Hazra I, et al. Allergen immunotherapy modulates sensitivity of Treg cells to apoptosis in rat model of allergic asthma. Immunotherapy. (2017) 9:1239–51. doi: 10.2217/imt-2017-0038
6. Nur Husna SM, Tan HT, Md Shukri N, Ashari NSM, Wong KK. Nasal epithelial barrier integrity and tight junctions disruption in allergic rhinitis: overview and pathogenic insights. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:663626. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.663626
7. Montes-Vizuet R, Vega-Miranda A, Valencia-Maqueda E, Negrete-Garcia MC, Velasquenz JR, Teran LM. CC chemokine ligand 1 is released into the airways of atopic asthmatics. Eur Respir J. (2006) 28:59–67. doi: 10.1183/09031936.06.00134304
8. Seto T, Yoshitake M, Ogasawara T, Ikari J, Sakamoto A, Hatano M, et al. Bcl6 in pulmonary epithelium coordinately controls the expression of the CC-type chemokine genes and attenuates allergic airway inflammation. Clin Exp Allergy. (2011) 41:1568–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2011.03836.x
9. Pawlik K, Mika J. Targeting members of the chemokine family as a novel approach to treating neuropathic pain. Molecules. (2023) 28:5766–809. doi: 10.3390/molecules28155766
10. Zychowska M, Rouewska E, Piotrowska A, Kreiner G, Nalepa I, Mika J. Spinal CCL1/CCR8 signaling interplay as a potential therapeutic target-evidence from a mouse diabetic neuropathy model. Int Immunopharmacol. (2017) 52:261–71. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.09.021
11. Whiteside SK, Grant FM, Alvisi G, Clarke J, Tang L, Imianowski CJ, et al. Acquisition of suppressive function by conventional T cells limits antitumor immunity upon Treg depletion. Sci Immunol. (2023) 8:eabo5558–5592. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abo5558
12. Shamji MH, Sharif H, Layhadi JA, Zhu R, Kishore U, Renz H. Diverse immune mechanisms of allergen immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis with and without asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2022) 149:791–801. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2022.01.016
13. Martin-Cruz L, Benito-Villalvilla C, Sirvent S, Angelina A, Palomares O. The role of regulatory T cells in allergic disease: collegium internationale allergologicum(CIA) update 2024. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. (2024) 185:503–18. doi: 10.1159/000536335
14. Tsai YG, Yang KD, Wen YS, Huang CH, Chien JW, Lin CY. Allergen-specific immunotherapy enhances CD8+CD25+CD37+ regulatory T cells and decreases nasal nitric oxide. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. (2019) 30:531–9. doi: 10.1111/pai.2019.30.issue-5
15. Shirasaki H, Kanaizumi E, Seki N, Himi T. Correlation of local FOXP3-expressing T cells and Th1-Th2 balance in perennial allergic nasal mucosa. Int J Otolaryngol. (2011) 2011:259867. doi: 10.1155/2011/259867
16. Sogut A, Yilmaz O, Kirmaz C, Ozbilgin K, Onur E, Celik O, et al. Regulatory T, T-helper 1, and T-helper 2 cell differentiation in nasal mucosa of allergic rhinitis with olive pollen sensitivity. In Arch Allergy Immunol. (2012) 157:349–53. doi: 10.1159/000329159
17. Muller B, Reinartz SM, van Egmond D, Groot EJJ, Fokkens WJ, Drunen CM. Mono-allergic and poly-allergic rhinitis patients have comparable numbers of mucosal Foxp3+CD4+T lymphocytes. Rhinology. (2014) 52:260–6. doi: 10.4193/Rhino13.223
18. Huang ZQ, Liu J, Sun LY, Ong HH, Ye J, Xu Y, et al. Update epithelial barrier dysfunction in chronic rhinosinusitis: targeting pathophysiology and treatment response of tight junctions. Allergy. (2024) 79:1146–65. doi: 10.1111/all.16064
19. Yu Hw Wang WW, Jing Q, Pan YL. TSLP induces epithelial-mesnchymal transition in nasal epithelial cells from allergic rhinitis patients through TGF-beta1/Smad2/3 signaling. Am J Rhinol Allergy. (2023) 37:739–50. doi: 10.1177/19458924231193154
20. Ito M, Komai K, Mise-Omata S, Koga MI, Noguchi Y, Kondo T, et al. Brain regulatory T cells suppress astrogliosis and potentiate neurological recovery. Nature. (2019) 565:246–50. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0824-5
21. Obata-Ninomiya K, de Jesus Carrion S, Hu A, Ziegler SF. Emerging role for thymic stromal lymphopoietin-responsive regulatory T cells in colorectal cancer progression in humans and mice. Sci Transl Med. (2022) 14:eabl6960. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abl6960
22. Zong Y, Deng K, Chong WP. Regulation of Treg cells by cytokine signaling and co-stimulatory molecule. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1387975. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1387975
23. Chauhan SK, Bartolome Casado R, Landsverk OJB, Johannessen H, Phung D, Nilsen HR, et al. Human small intestine contains 2 functionally distinct regulatory T-cell subsets. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2023) 152:278–89. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.02.030
24. Colantonio L, lellem A, Sinigagalia F, D’Ambrosio D. Skin-homing CLA+T cells and regulatory CD25+Tregs represent major subsets of human peripheral blood memory T cells migrating in response to CCL/I-309. Eur J Immuol. (2002) 32:3506–14. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200212)32:12<3506::AID-IMMU3506>3.0.CO;2-#
25. Zen Y, Liberal R, Nakanuma Y, Heaton N, Portmann B. Possible involvement of CCL1-CCR8 interaction in lymphocytic recruitment in IgG-related sclerosing cholangitis. J Hepatol. (2013) 59:1059–64. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.06.016
26. Li J, Lin X, Liu X, Ma Z, Li Y. Baicalin regulates Treg/Th17 cell imbalance by inhibiting autophagy in allergic rhinitis. Mol Immunol. (2020) 125:162–71. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2020.07.008
27. Horwitz DA, Wang JH, Kim D, Kang C, Brion K, Bickerton S, et al. Nanoparticles loaded with IL-2 and TGF-beta promote transplantation tolerance to alloantigen. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1329335. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1429335
28. Chauhan A, Singh M, Agarwal A, Paul N. Correlation of TSLP, IL-33, and CD4+CD25+Foxp3+T regulatory (Treg) in pediatric asthma. J Asthma. (2015) 52:868–72. doi: 10.3109/02770903.2015.1026441
29. Kim HJ, Kim YJ, Lee SH, Yu J, Jeong SK, Hong SJ. Effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus on allergic march model by suppressing Th2, Th17, and TSLP responses via CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs. Clin Immunol. (2014) 153:178–86. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2014.04.008
30. Nguyen KD, Vanichsarn C, Nadeau KC. TSLP directly impairs pulmonary Treg function: association with aberrant tolerogenic immunity in asthmatic airway. Allergy Asthma& Clin Immunol. (2010) 6:4–15. doi: 10.1186/1710-1492-6-4
31. Unterman A, Zhao AY, Neumark N, Schupp JC, Ahangari F, Jr CC, et al. Single-cell profiling reveals immune aberrations in progressive idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2024) 210:484–96. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202306-0979OC
32. Wang M, Qin Z, Wan J, Yan Y, Duan X, Yao X, et al. Tumor-derived exosomes drive pre-metastatic niche formation in lung via modulating CCL1+ fibroblast and CCR8+ Treg cell interactions. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2022) 71:2717–30. doi: 10.1007/s00262-022-03196-3
33. Watanabe S, Yamada Y, Murakami H. Expression of Th1/Th2 cell-related chemokine receptors on CD4+lymphocytes under physiological conditions. Int J Lab Hematol. (2020) 42:68–76. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.13141
34. Zen Y, Liberal R, Nakamuna Y, Heaton N, Portmann B. Skin-homing CLA+T cells and regulatory CD25+Tregs represent major subsets of human peripheral blood memory T cells migrating in response to CCL/I-309[J. Eur J Immuol. (2002) 32:3506–14. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200212)32:12<3506::AID-IMMU3506>3.0.CO;2-#
Keywords: allergic rhinitis, nasal epithelial cells, regulatory T cells, cytokines, CC chemokine ligand 1
Citation: Sha J, Yang M, Lei Y, Sun L, Meng C and Zhu D (2025) Interaction between nasal epithelial cells and Tregs in allergic rhinitis responses to allergen via CCL1/CCR8. Front. Immunol. 16:1526081. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1526081
Received: 19 November 2024; Accepted: 21 January 2025;
Published: 20 February 2025.
Edited by:
Takemichi Fukasawa, The University of Tokyo Hospital, JapanReviewed by:
Laura La Paglia, National Research Council (CNR), ItalyCopyright © 2025 Sha, Yang, Lei, Sun, Meng and Zhu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dongdong Zhu, emh1ZGRAamx1LmVkdS5jbg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.