- 1Hebei University of Engineering School of Medicine, Handan, Hebei, China
- 2Second Department of Urology and Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei Engineering University, Handan, China
Background: This study systematically reviews the efficacy and safety of the single or combined use of programmed factor 1 (PD-1)/programmed factor 1 ligand (PD-L1) inhibitors for treating metastatic or advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Methods: Relevant articles were collected for meta-analysis through searches on PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Clinical Trials, as well as for relevant randomized controlled experiments.
Results: Based on eleven studies, the effectiveness of the experimental group was found to be significantly better than the control in terms of overall survival (OS) [R=0.74, 95%CI: 0.69~0.80, P<0.00001], progression-free survival (PFS) [HR=0.68, 95%CI: 0.57~0.81, P<0.0001], objective response rate (ORR) [RR=1.71, 95%CI: 1.39~2.12, P<0.00001], complete response rate (CR) [RR=2.99 95%CI: 2.34~3.83, P<0.0001], partial response rate (PR) [RR=1.56, 95%CI: 1.20~2.01, P=0.001], and disease control rate (DCR) [RR=1.13, 95%CI: 1.06~1.20, P<0.0001]. No statistical significance was observed between the experimental and control groups in overall adverse reactions (AEs) [RR=1.01, 95%CI: 0.98~1.04, P=0.598], the incidence of stage I~II adverse reactions [RR=1.02, 95%CI: 0.88~1.17, P=0.818], or stage III~V adverse reactions [RR=0.98, 95%CI: 0.81~1.18, P=0.817]. Regarding subgroup analysis, the incidence of dysphonia, rash, hypothyroidism, arthralgia, and pruritus in the experimental group was significantly higher than in the control. Compared with the control group, the incidence of diarrhea, nausea, indigestion, and fatigue in the experimental group was not statistically significant.
Conclusion: A good efficacy was found in treating metastatic or advanced RCC using PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors alone or in combination, which significantly improved and enhanced OS, PFS, ORR, CR, PR, and DCR in patients with RCC. The incidence of adverse reactions in patients was not increased, and adverse reactions were controllable. These findings indicate that the single or combined use of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors shows good efficacy and safety in the treatment of metastatic or advanced RCC.
1 Introduction
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a malignancy of the urinary tract originating in the tubular epithelium, accounting for approximately 80–90% of renal malignancies (1). It is the sixth and eighth most common cancer in both men and women (2). In recent years, its morbidity has increased at a rate of 1.6% per year. A poor prognosis is more common in men (3). At present, surgery remains the main treatment option for patients with RCC. However, about 25% of patients have middle or advanced-stage RCC or distant metastasis at the time of initial diagnosis. In addition, approximately 20–50% of patients with localized renal cell carcinoma eventually develop into metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC), which is insensitive to conventional chemo-radiotherapy and exhibits multi-drug-resistance (4), resulting in a survival rate of less than five years after surgery for over 80% of patients (5).
In recent years, tumor immunotherapy has offered new treatment options for mRCC or advanced renal cell carcinoma (aRCC). Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) is a member of the B7-CD28 co-stimulatory receptor family and is mainly expressed in activated T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, and monocytes, while Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is mainly expressed in tumor cells. These two molecules are specifically combined and showed abnormally high expression in tumor tissues, which is involved in the negative regulation of human immunity. They inhibit the survival and proliferation of T immune cells and the release of killer cytokines in the local microenvironment, as well as inducing cell apoptosis, thereby preventing the immune response against tumor cells and promoting the growth of tumor cells (6). PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors can effectively block this effect, enhance the immune function of T cells, and exert immune function on tumor cells. Additionally, PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, as immune sentinel monoclonal antibodies, have been widely used in treating melanoma, lung cancer, lymphoma and kidney cancer, especially in treating mRCC or aRCC (7). Studies have shown that in renal cell carcinoma, PD-1/PD-L1 alone or in combination with conventional targeted drugs can improve anti-cancer efficacy and significantly extend survival rates (8). At present, based on IMmotion 010, CheckMate 025, CheckMate 214, and KEYNOTE-426 experiments, a multicenter randomized controlled study has been performed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the single or combined use of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in the treatment of mRCC or aRCC. However, its conclusions vary.
In this study, a systematic review of the published research literature on PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors is conducted to comprehensively evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in the treatment of mRCC or aRCC in an attempt to provide a rationale for the immunotherapy of mRCC or aRCC.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 General materials
2.1.1 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
(i) Study subjects: patients with mRCC or aRCC that have been confirmed by histopathology and received no radiotherapy. No requirements regarding age, gender or medication history,but TNM stage required to be metastatic or locally advanced. (ii) study type: stage II or III randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that have been published (English only). (iii) interventions: in the experiment, anti-PD-1 inhibitors or anti-PD-L1 inhibitors were applied alone or in combination with other drugs (either immunological drugs, conventional chemotherapy drugs, or placebo in the case of the control group).
2.1.2 Outcome index
(i) Effective index: overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), objective response rate (ORR), complete response rate (CR), partial response rate (PR), and disease control rate (DCR). (ii) safety index: incidence of treatment-related adverse reactions (AEs) and subgroup analysis (the incidence of adverse events in respiratory, digestive, and other systems).
2.1.3 Exclusion criteria
(i) Duplicates, case reports, and review literature; (ii) retrospective literature; (iii) literature with abstracts only or without results; (iv) non-controlled literature; and (v) non-randomized controlled phase II and III clinical trial research.
2.2 Search methods for the identification of relevant studies
A detailed literature review was conducted using the following electronic databases: PubMed(https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/), Web of Science(https://www.webofscience.com/wos/woscc/basic-search), Embase(https://www.embase.com/landing?status=grey, Cochrane Library(https://www.cochranelibrary.com/), and Clinical Trials(https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/). Manual research methods were used to collect randomized controlled studies of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors for treating renal cell carcinoma. The research period was from the establishment of the database to September 30, 2024. Subject words and free words, search terms included: renal neoplasms, kidney cancers, renal cell carcinomas, collecting duct carcinoma of the kidney, tumor, cancer, PD-1, PD-L1, programmed cell death protein 1, programmed cell death protein 1 inhibitors, immune checkpoint inhibitor, PD-L1 inhibitors, nivolumab, pembrolizumab, lambrolizumab, atezolizumab, tecentriq, durvalumab, imfinzi, bavencio, avelumab, camrelizumab, and sintilimab.
2.3 Study selection and data collection
Two researchers independently screened the literature according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, and relevant information was extracted. Line cross-checking was performed, and third-party discussions were conducted to resolve any discrepancies in extraction. During the literature screening, the title and abstracts were read first. Then, after excluding any unrelated literature, the full text was further read to determine its inclusion. Data extraction mainly included: (i) basic information of the included studies, including the study title, first author, publication journal, country, and time; (ii) baseline characteristics of the study subjects, including the number of included patient cases, histopathological type, gender and age ratio, and follow-up time; (iii) specific details of the interventions; (iv) key elements of risk of bias evaluation; and (v) the outcome indicators and outcome measures of interest, the former of which included ORR, PFS, PR, CR, OS, SD, PD, DCR, and AEs. In addition, further detailed data were collected on the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Combined Database Hazard Score for OS, the PD-L1 expression of PRS, the IMDC score, the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Centre score, and the proportion of common adverse reactions occurring in each system of the AEs.
2.4 Quality assessment and risk of bias
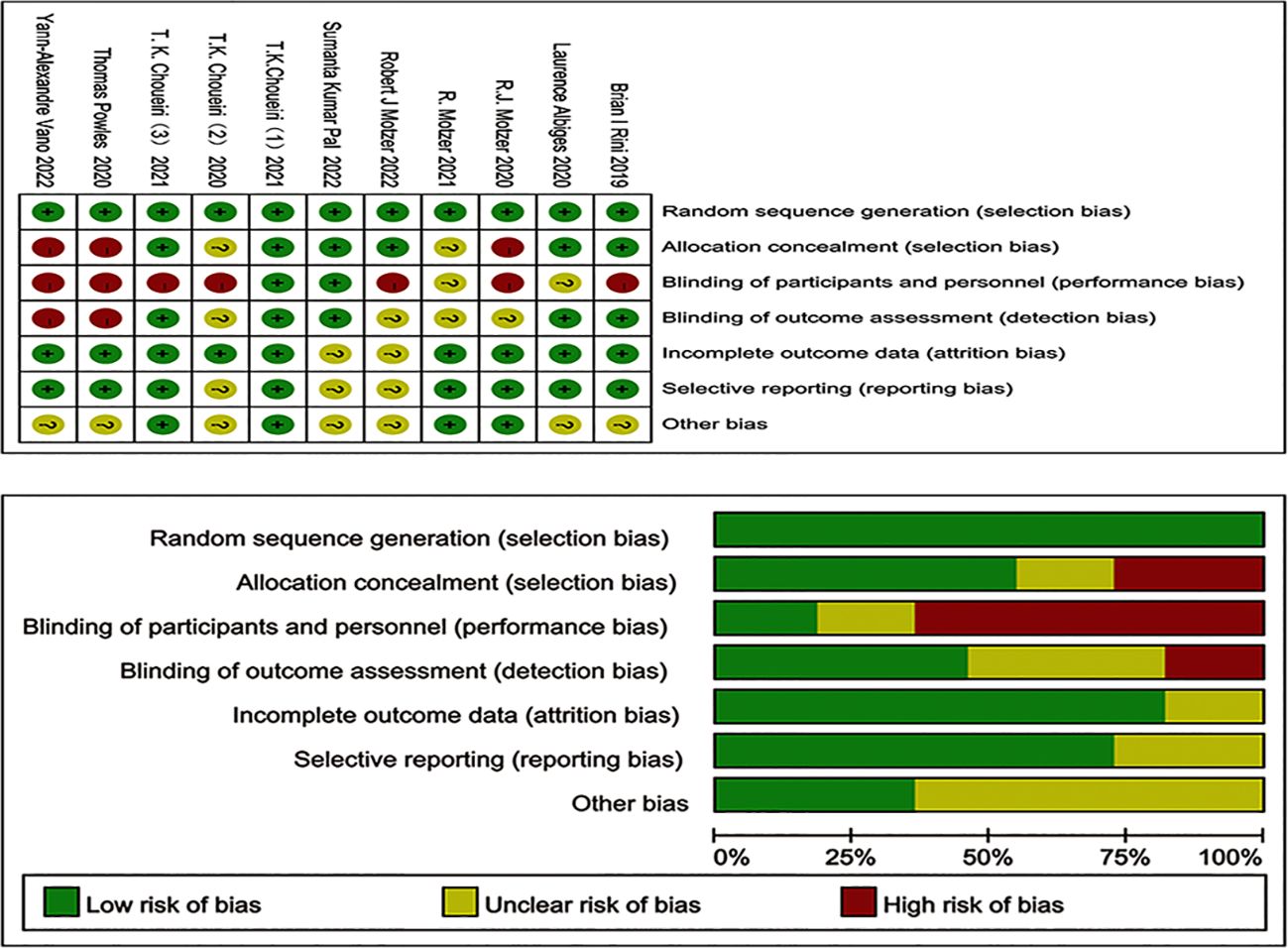
Two researchers assessed the quality of the included studies according to the Cochrane 5.3 manual, and the evaluation criteria included (i) randomization, (ii) group hiding, (iii) blinding, (iv) data integrity, (v) selective reporting, and (vi) other biases.
2.5 Statistical analysis
Stata15.1 software (https://www.stata.com/stata15/) was used for meta-analysis. The risk ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were used to determine effect sizes and evaluate the relevant degree between the experimental group and OS and PFS. The relative risk (RR) and 95% feasible interval (CI) were used as the effect size to assess the degree of association between the experimental group and ORR, PR, CR, DCR, and AEs. According to the recommendations provided by the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/current/chapter-10#section-10-10-4-1), ‘the choice between a fixed-effect and a random-effects meta-analysis should never be made on the basis of a statistical test for heterogeneity.’ In addition, since heterogeneity is always expected for the intervention effects among multiple studies from different groups and geographical locations, a random effects model is encouraged to account for these analyses. α=0.05 was used as the test level for the meta-analysis. α=0.05 was used as the test level for the meta-analysis.
3 Results
3.1 Search results and quality assessment
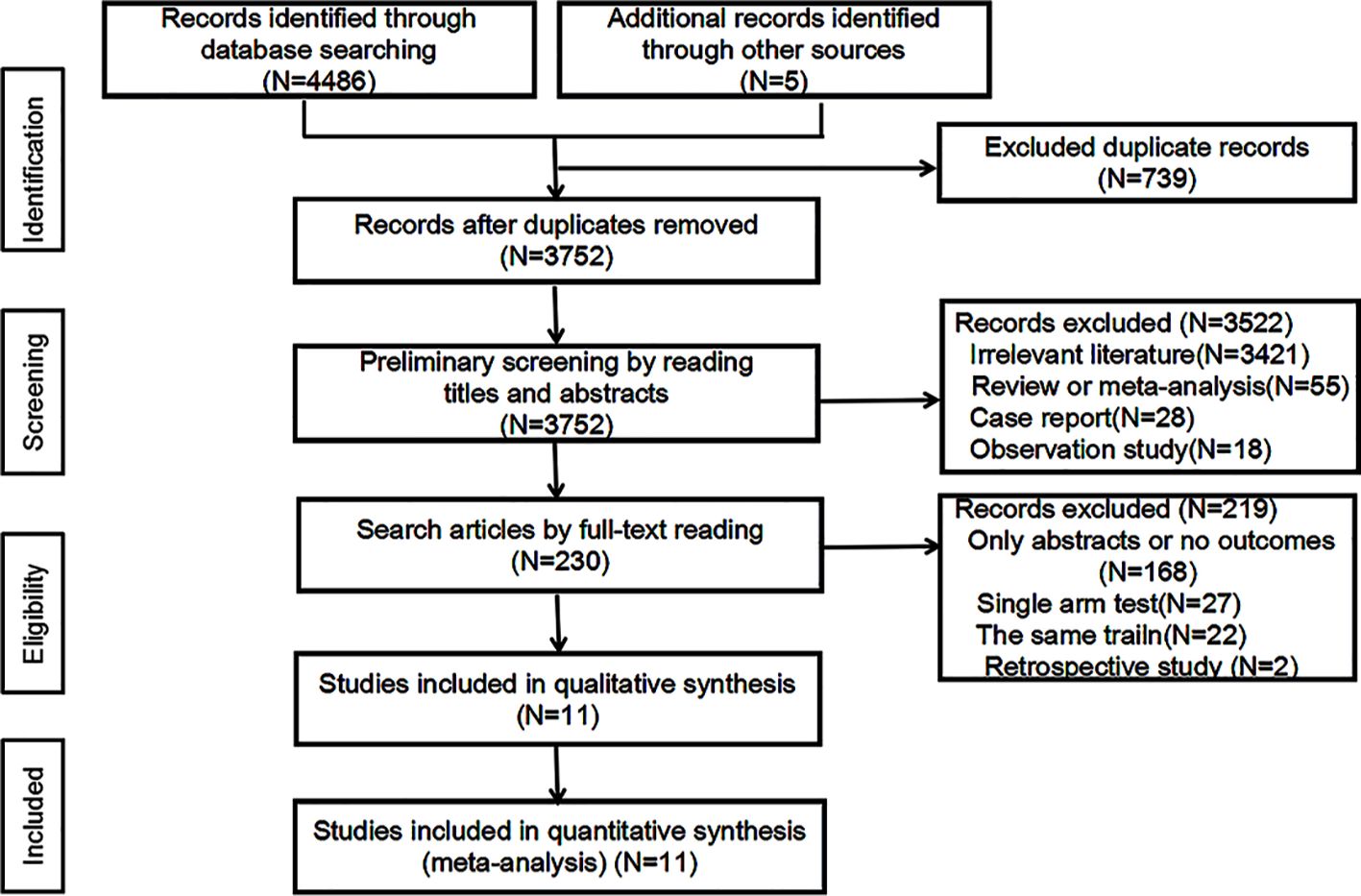
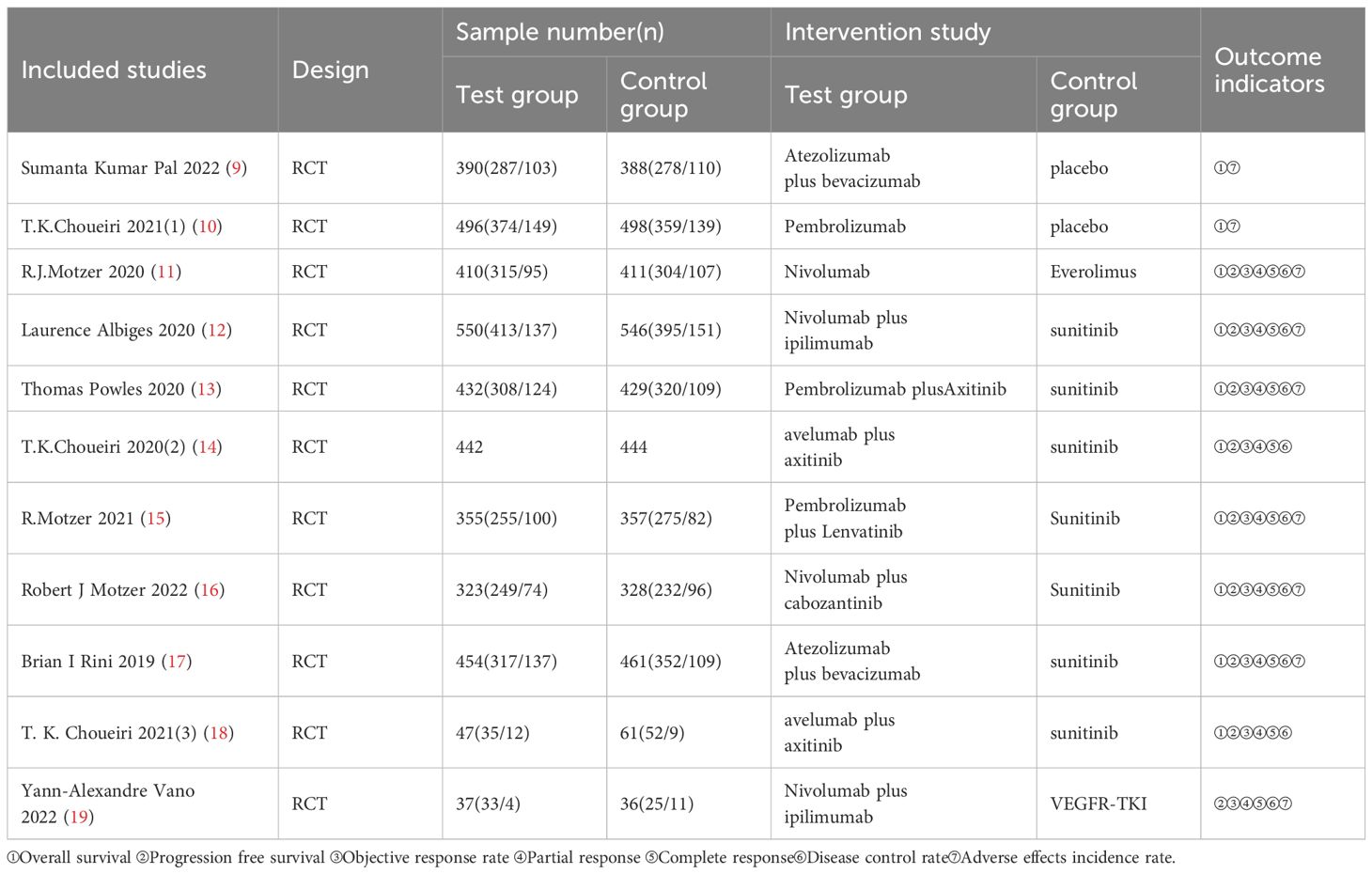
A total of 4491 relevant papers from the preliminary search were identified. After excluding duplicate literature, 11 research articles were included for meta-analysis by analyzing the titles, abstracts, and full text. A flow chart corresponding to this process is provided below (Figure 1). A total of 7895 study subjects were enrolled, with 3936 cases in the experimental group and 3959 cases in the control group. The corresponding characteristics are shown in Table 1, and bias risk evaluation is shown in Figure 2.
3.1.1 Overall survival
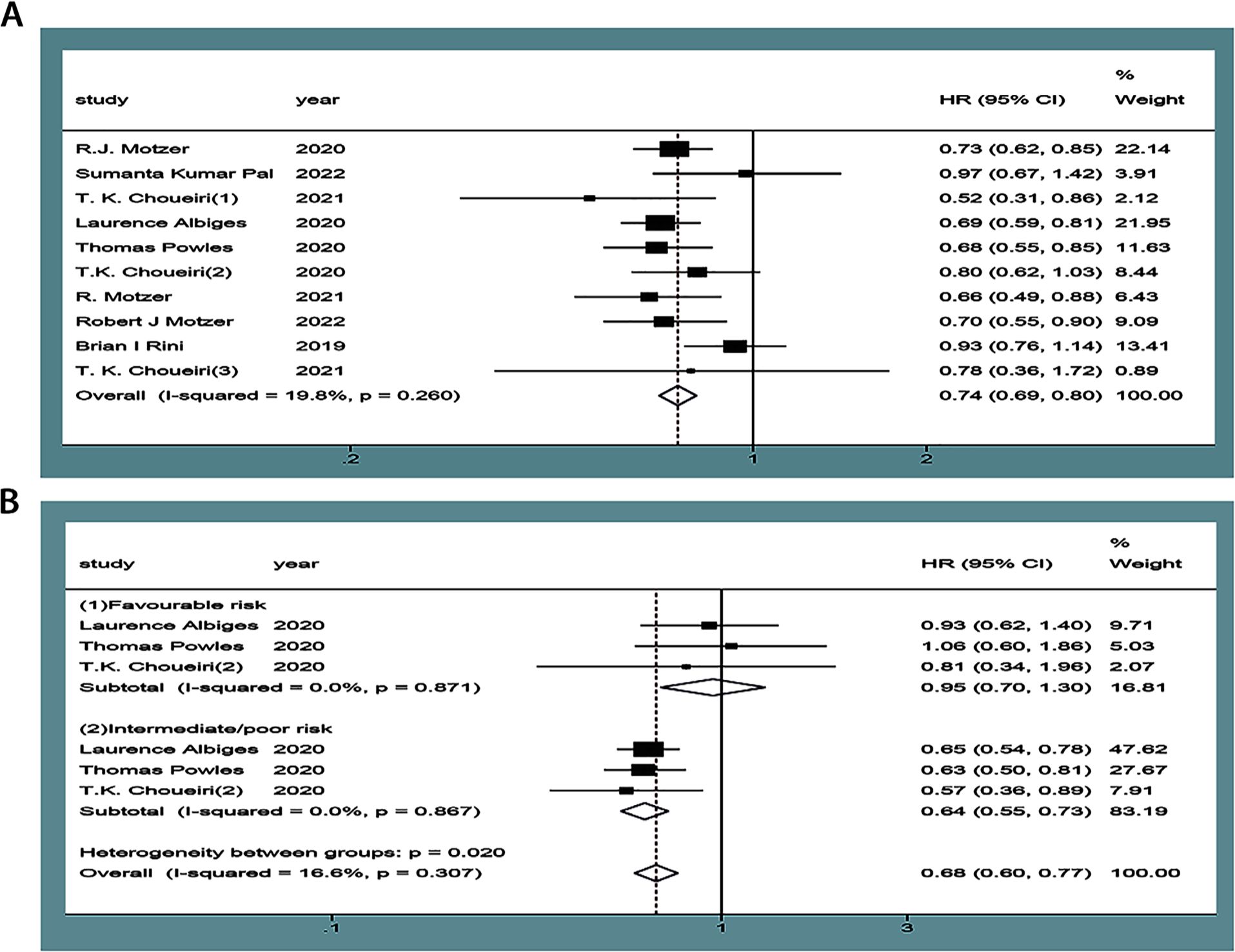
Ten articles reported OS (9–18), of which three (12–14) were used for subgroup analyses based on the risk score of the International Combined Database for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma (IMDC). There was no statistical heterogeneity between the studies (P=0.26, I2 = 19.8% or P=0.31, I2 = 16.6%) with a random-effect model. The results showed that the OS of the experimental group in the treatment of mRCC or aRCC was significantly better than that of the control group, followed by the combined effect size (HR=0.74, 95%CI: 0.68~0.80, P<0.00001). Subgroup analysis showed that the experimental group could improve the IMDC score of the medium/high-risk group (HR=0.69, 95%CI: 0.55~0.73, P<0.00001), and the differences were statistically significant, suggesting that the single or combined use of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors could significantly improve OS in patients with mRCC or aRCC (Figure 3).
3.1.2 Progression-free survival
PFS was reported in nine articles (11–19), among which three articles (14, 15, 17) underwent subgroup analyses based on PD-L1 expression, four (12, 13, 15, 17) underwent subgroup analyses based on IMDC score, and three (14, 15, 17) underwent subgroup analyses based on the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) score. Statistical heterogeneity was observed between the studies (P<0.00001, I2 = 84.6%; P<0.00001, I2 = 79.7%; P<0.00001, I2 = 77.3%; P=0.001, I2 = 69.3%). Random-effects model analysis showed that the PFS of mRCC or aRCC in the experimental group was significantly better than that of the control group, followed by the combined effect size (HR=0.68, 95%CI: 0.57~0.81, P<0.0001). Subgroup analysis showed that the PFS of different subgroup types was improved in the experimental group, PD-L1≥1% (HR=0.59, 95%CI: 0.44~0.80, P=0.001), IMDC score (medium-risk group, high-risk group) (HR=0.66, 95%CI: 0.53~0.82, P<0.0001; HR=0.63, 95%CI: 0.51~0.78, P<0.0001), and MSKCC score (medium-risk group, high-risk group) (HR=0.63, 95%CI: 0.45~0.89, P=0.008; HR=0.37, 95%CI: 0.20~0.67, P=0.001). The difference was statistically significant (P<0.05), suggesting that the PFS of patients with mRCC or aRCC was significantly prolonged by the single or combined use of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors (Figure 4).

Figure 4. Forest plots of PFS (A). Forest plot of pooled PFS basing on expressing PD-L1 subgroup analyses (B). Forest plot of pooled PFS basing on IMDC risk subgroup analyses (C). Forest plot of pooled PFS basing on MSKCC risk subgroup analyses (D).
3.1.3 Objective response rate
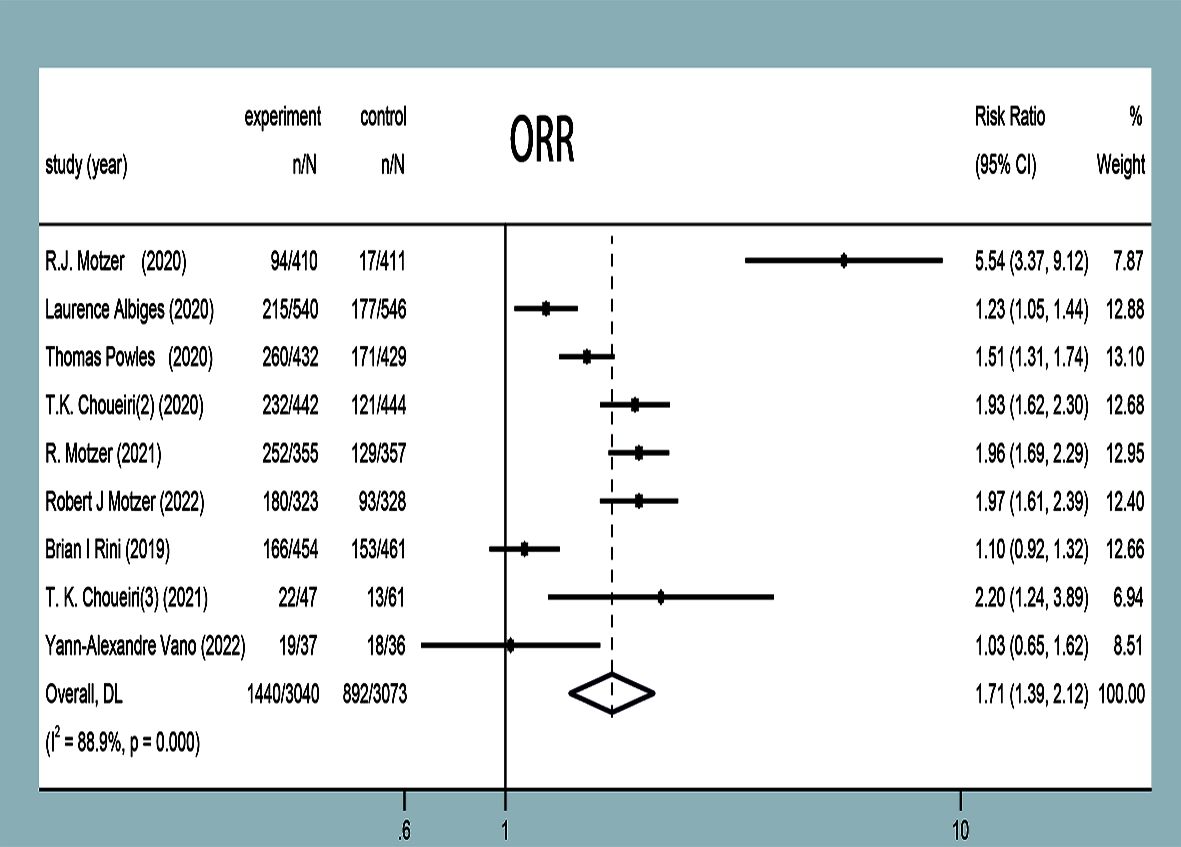
ORR was reported in nine studies (11–19), and statistical heterogeneity was observed between them (P<0.0001, I2 = 88.9%). Random-effects model analysis showed that the ORR of the experimental group was significantly higher than that in the control group in terms of treating mRCC or aRCC, and with the combined effect size (RR=1.71, 95%CI: 1.39~2.12, P<0.00001), the difference was statistically significant (Figure 5).
3.1.4 Partial response rate
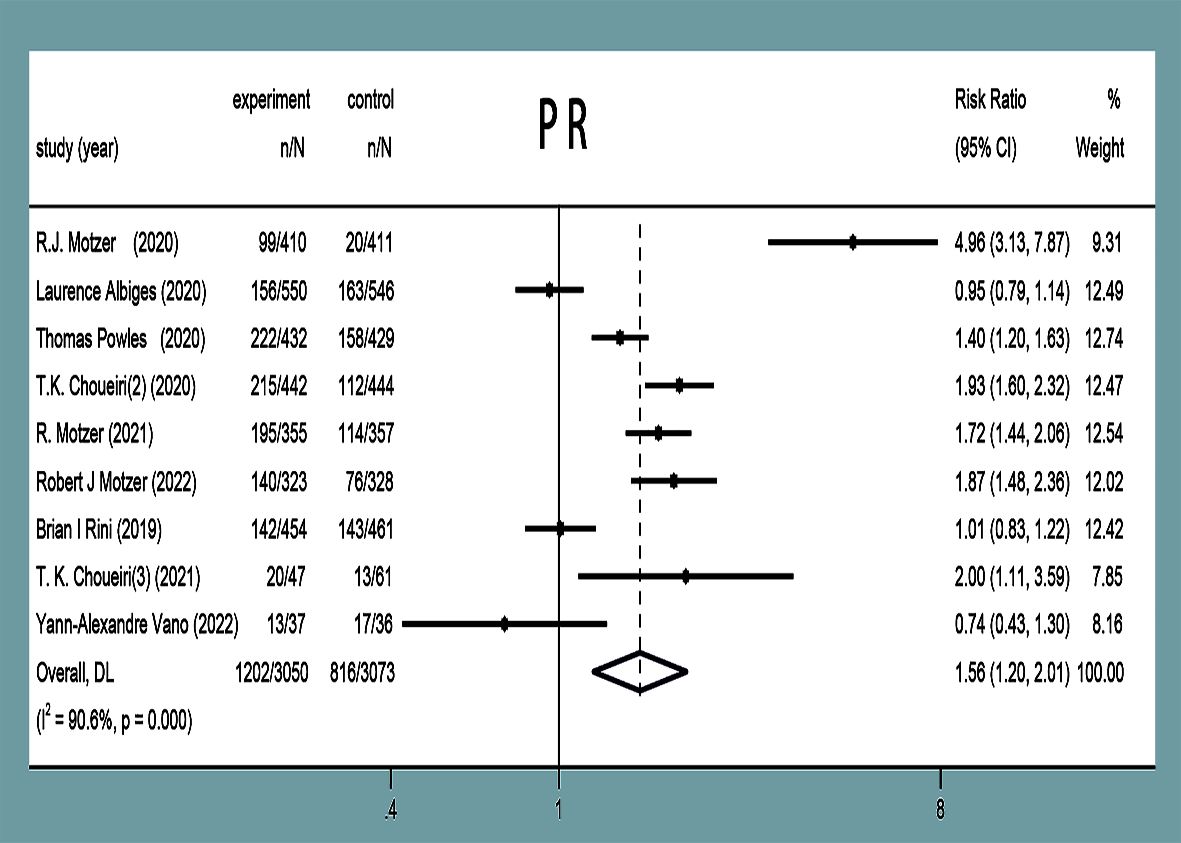
PR was reported in nine studies (11–19), with statistical heterogeneity observed between the studies (P<0.00001, I2 = 90.6%). Random-effects model analysis showed that the PR in the experimental group was higher than that in the control group in the treatment of mRCC or aRCC, and with the combined effect size (RR=1.56, 95%CI: 1.20~2.01, P=0.001), the difference was statistically significant (Figure 6).
3.1.5 Complete response rate
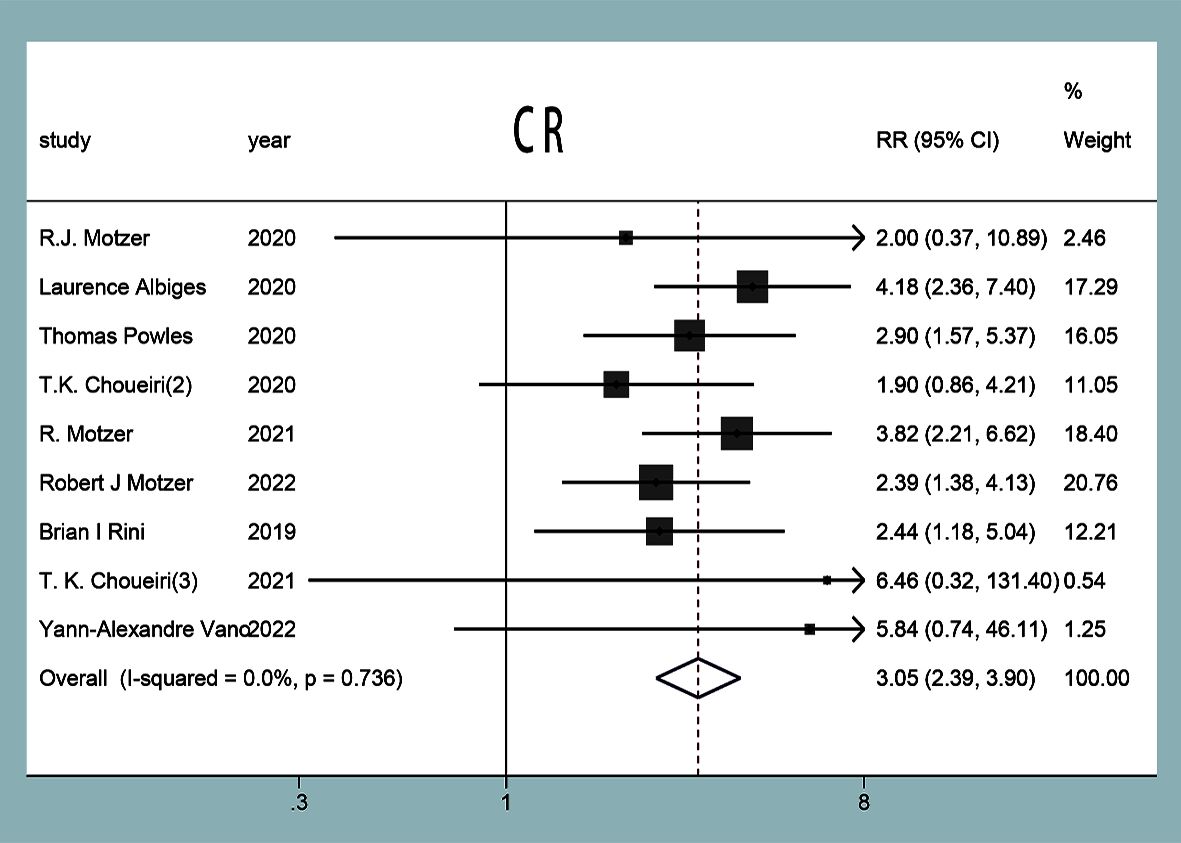
CR was reported in nine studies (11–19), and no statistical heterogeneity was observed between the studies (P=0.74, I2 = 0%). The results of the random-effect model showed that the CR of the experimental group was higher than that in the control group in the treatment of mRCC or aRCC, and with the combined effect size (RR=2.99 95%CI: 2.34~3.83, P<0.0001), the difference was statistically significant (Figure 7).
3.1.6 Disease control rate
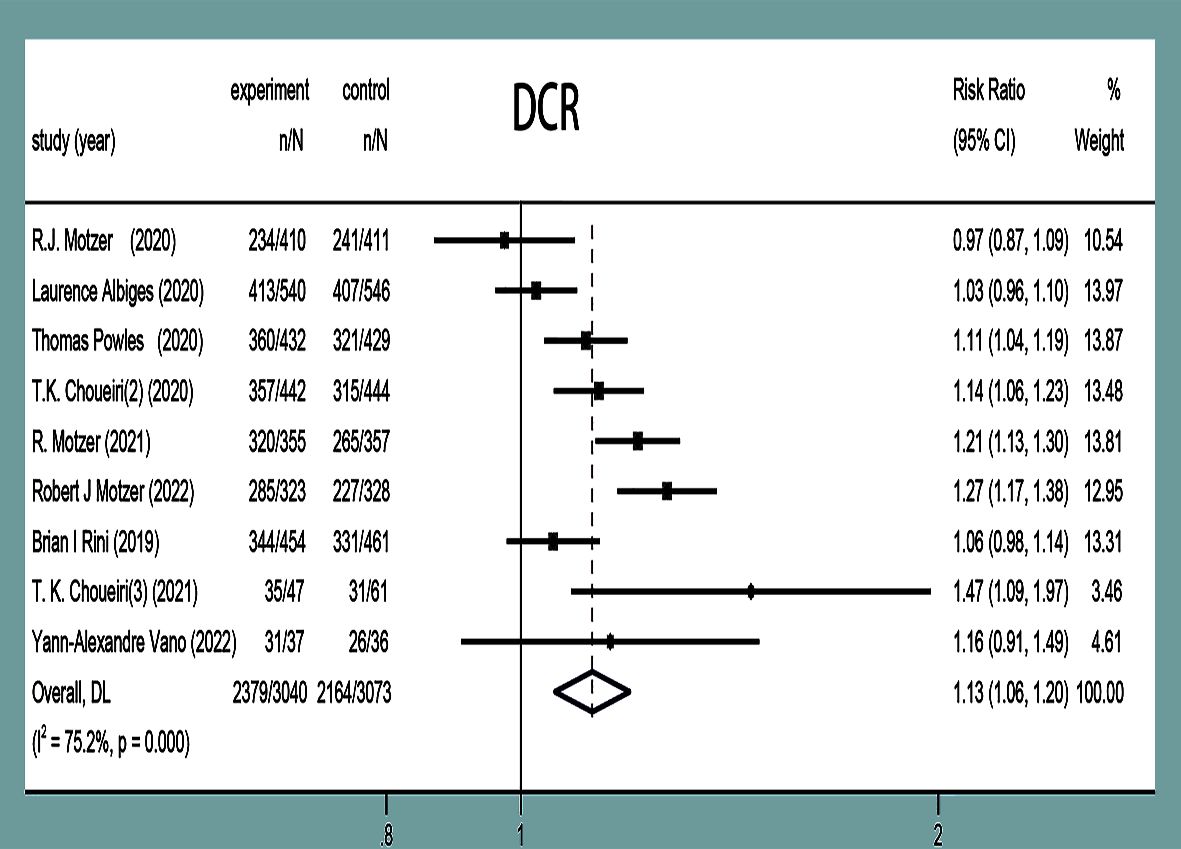
DCR was reported in nine studies (11–19), and there was statistical heterogeneity between the studies (P<0.0001, I2 = 75.2%). Random-effects model analysis showed that the DCR in the experimental group was higher than that in the control group in the treatment of mRCC or aRCC, and with the combined effect size (RR=1.13, 95%CI: 1.06~1.20, P<0.0001), the difference was statistically significant (Figure 8).
3.1.7 Adverse reactions
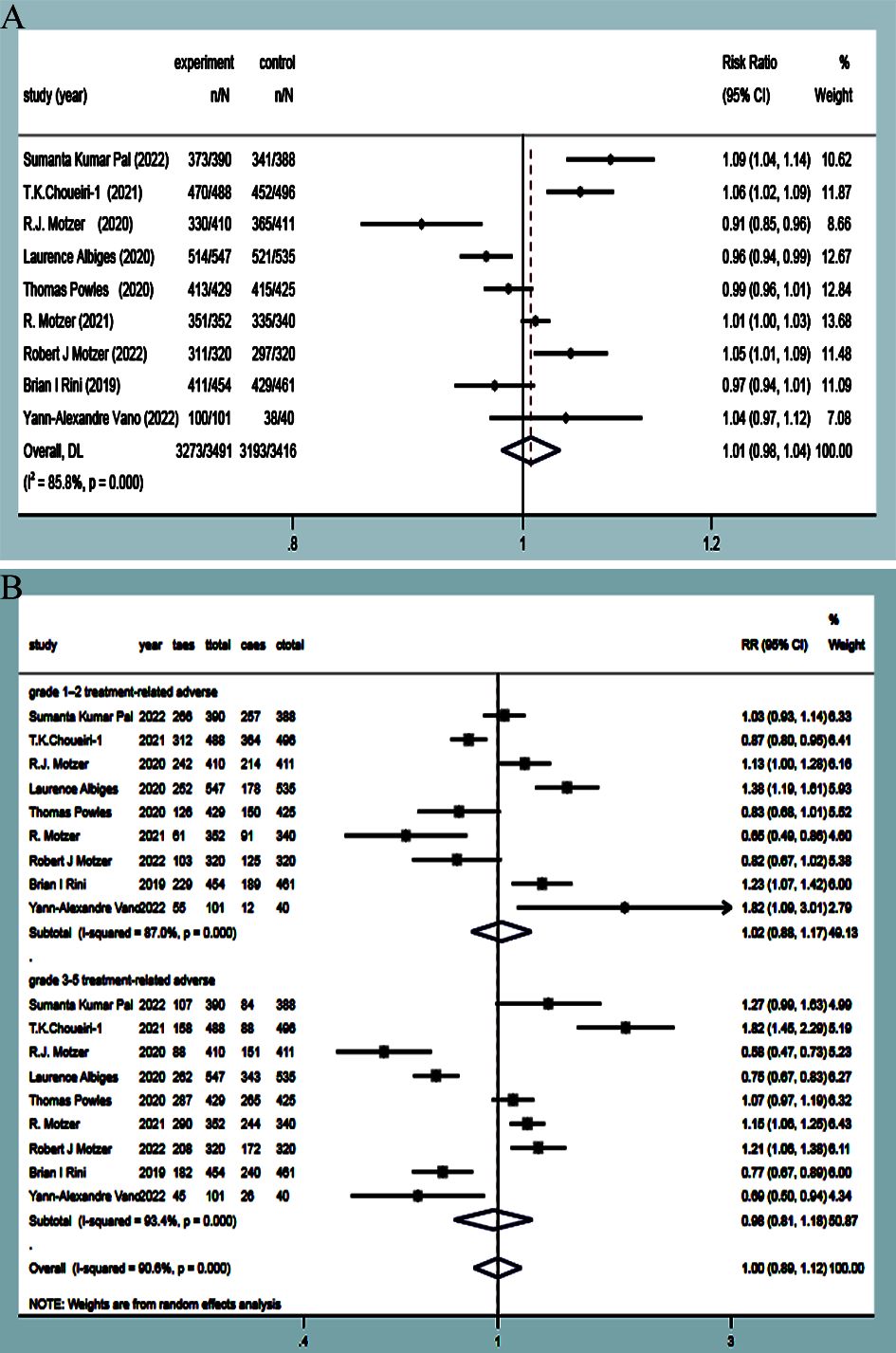
AEs were reported in eleven studies (9–13, 15–17, 19), with statistical heterogeneity observed between the studies (P<0.00001, I2 = 85.8%). Random-effects model analysis revealed that there was no significant difference in AEs between the experimental group and the control group (RR=1.01, 95%CI: 0.98~1.04, P=0.598)(Figure 9A). Subgroup analysis showed that there were no significant differences in the incidence of stage I~II adverse reactions and III~V adverse reactions (RR=1.02, 95%CI: 0.88~1.17, P=0.818; RR=0.98, 95%CI: 0.81~1.18, P=0.817) (Figure 9B). Considering that the heterogeneity in the literature could cause non-statistically significant differences of AEs, subgroup meta-analysis of common adverse reactions was carried out according to the respiratory, digestive, and other systems provided in the studies.
3.1.7.1 Respiratory system
The incidence of dysphonia was higher in the experimental groups by about 21.8%. Dysphonia was reported in three studies (13, 15, 16). No statistical heterogeneity was observed between the studies (P=0.557, I2 = 0.0%), and the results of a random-effect model showed that the incidence of dysphonia in the experimental group was significantly higher than that in the control group. The difference was statistically significant (RR=6.66, 95%CI: 4.72~9.4, P<0.0001) (Figure 10A).
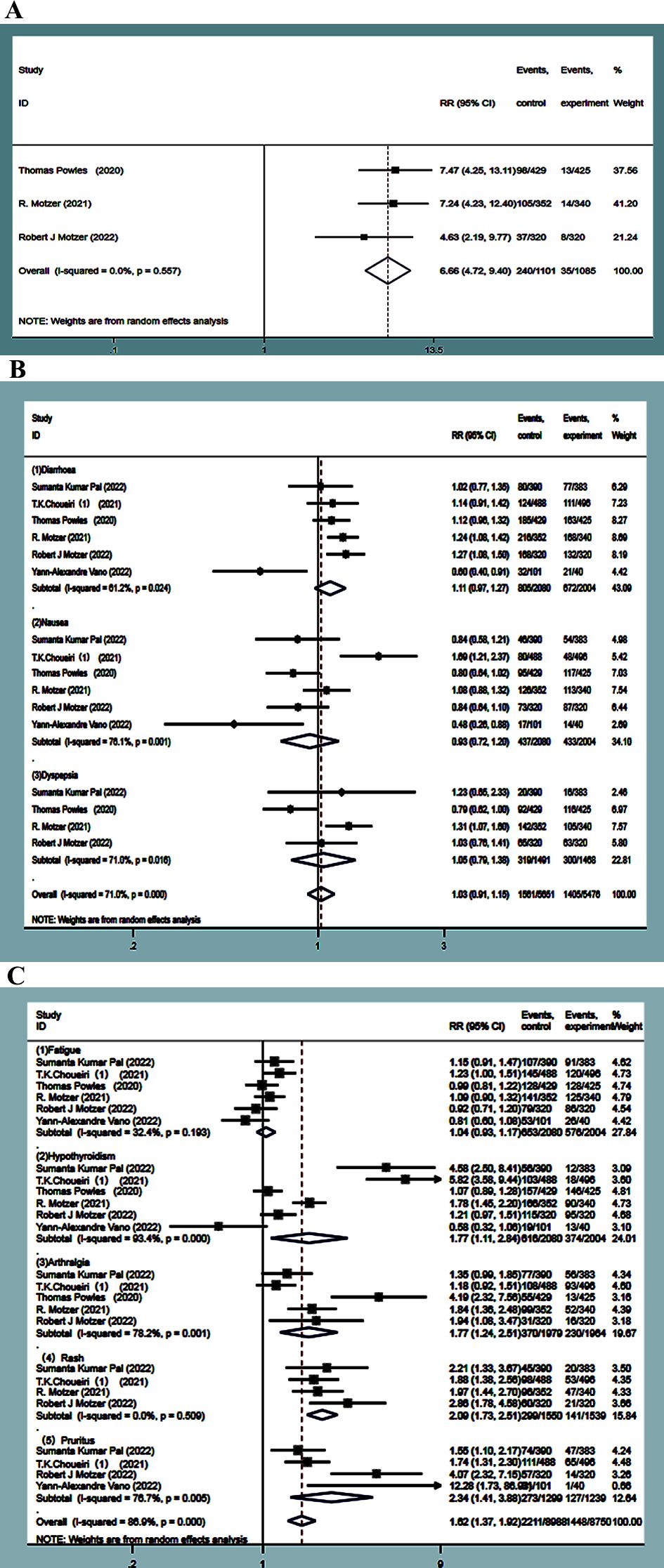
Figure 10. Dysphonia forest plots in experimental group and control group (A). Adverse events of the digestive system forest plots in experimental group and control (B). forest plots about adverse events of other system in experimental group and control (C).
3.1.7.2 Digestive system
The incidence of adverse reactions, such as diarrhea, nausea, and dyspepsia, was much higher in the experimental group, which was about 38.7%, 21%, and 21.3%. Six studies (9, 10, 13, 15, 16, 19) focused on diarrhea and nausea, and four studies (9, 13, 15, 16) reported dyspepsia. Statistical heterogeneity was observed between the studies (P=0.025, I2 = 61.1%; P=0.001, I2 = 76.1%; P=0.016, I2 = 71.0%), and random-effects model analysis showed that the incidence of adverse events, such as diarrhea, nausea, and dyspepsia, in the experimental group was not statistically significant compared to the control group (RR=1.11, 95%CI: 0.97~1.27, P=0.123; RR=0.93, 95%CI: 0.72~1.20, P=0.570; RR=1.05, 95%CI: 0.79~1.38, P=0.742) (Figure 10B).
3.1.7.3 Other systems
The incidence of adverse reactions, such as fatigue, hypothyroidism, pruritus, rash, and arthralgia, was higher in the experimental group by 31.4%, 29.6%, 21.3%, 19.2%, and 18.7%, respectively. Six studies (9, 10, 13, 15, 16, 19) reported fatigue, while four (9, 10, 15, 16) reported rash. No statistical heterogeneity was observed between the studies (P=0.198, I2 = 31.7%; P=0.511, I2 = 0.00%). The random-effect model results showed that the incidence of fatigue had no statistical significance in the experimental group as compared with the control group (RR=1.04, 95%CI: 0.93~1.17, P=0.471), while the incidence of rash in the experimental group was significantly higher than that in the control group, followed by combined effect size (RR=2.09, 95%CI: 1.73~2.51, P<0.0001). Six studies (9, 10, 13, 15, 16, 19) studied hypothyroidism, five (9, 10, 13, 15, 16) reported on arthralgia, and four (9, 10, 16, 19) reported on pruritus, with statistical heterogeneity observed between them (P<0.0001, I2 = 90.3%; P=0.001, I2 = 77.9%; P=0.006, I2 = 75.7%). The random-effects model analysis indicated that the incidence of adverse reactions, such as hypothyroidism, arthralgia, and pruritus, in the experimental group was significantly higher than that in the control group. The difference was statistically significant (RR=1.77, 95%CI:1.12~2.84, P=0.015; RR=1.77, 95%CI: 1.24~2.51, P=0.001; RR=2.34, 95%CI:1.41~3.88, P=0.001) (Figure 10C).
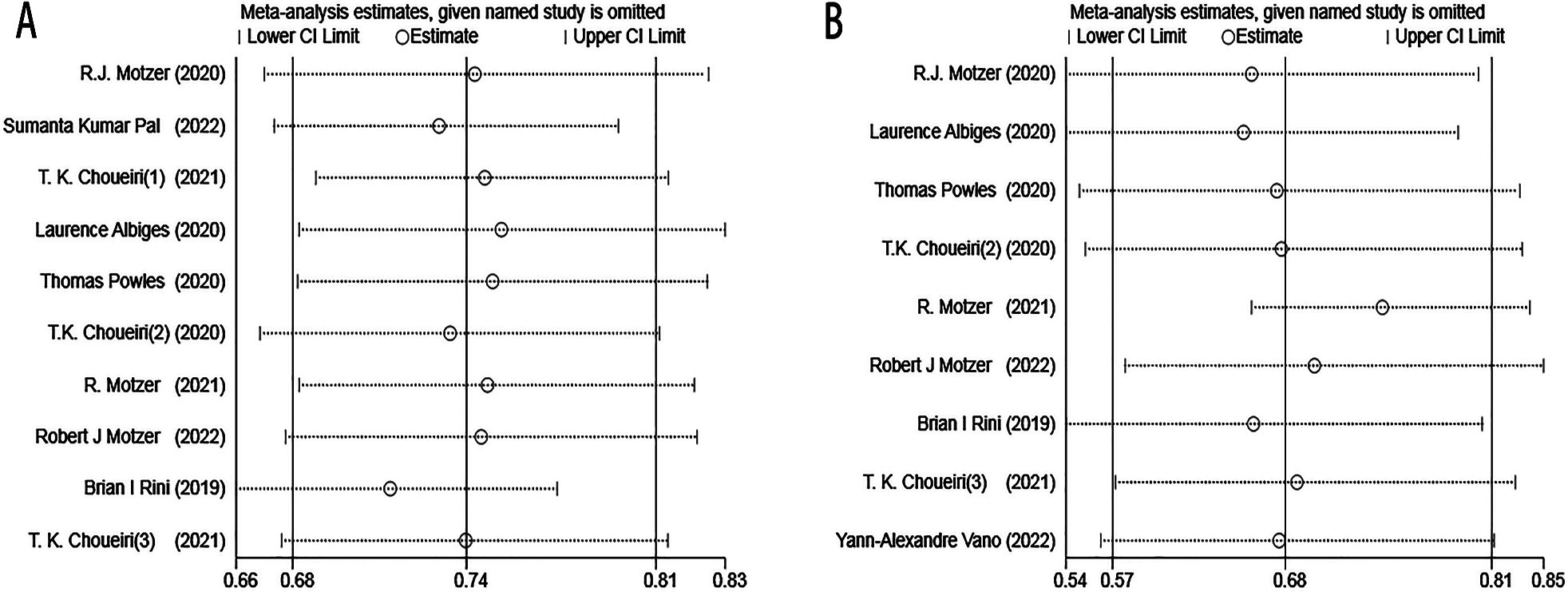
3.2 Sensitivity analysis
Sensitivity analysis was performed using the trim and filling method to assess the potential impact of each included study on combined HR. The results revealed the negligible stability of the comparison results, suggesting that the meta-analysis is reliable (Figure 11).
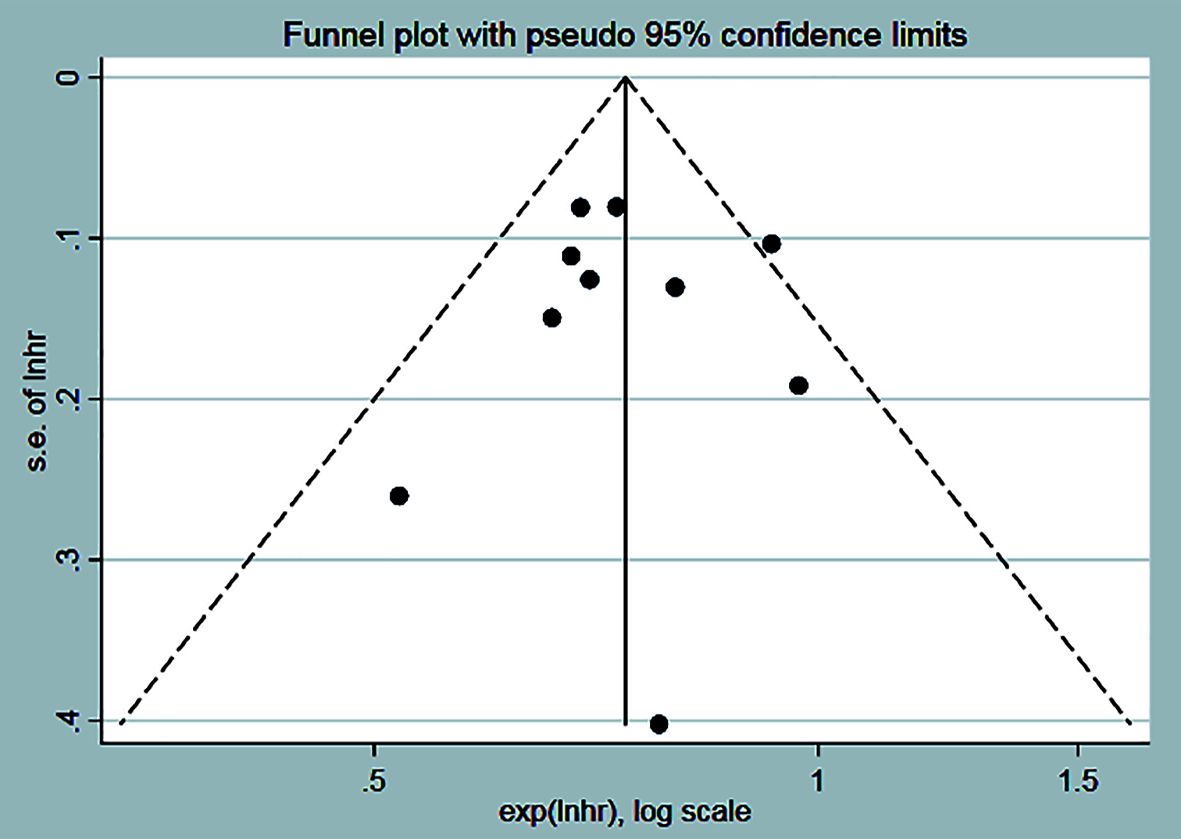
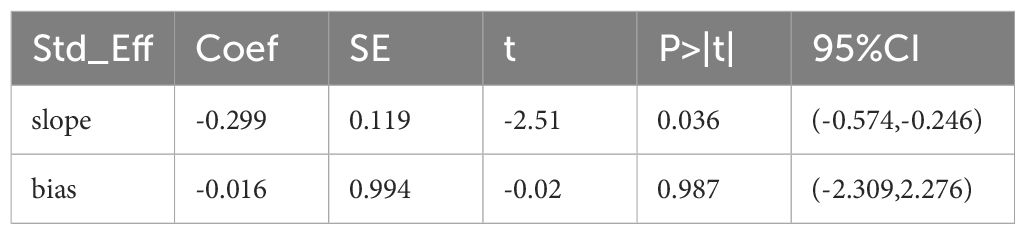
3.3 Assessment of the risks of bias
The funnel plot and Egger test method were used to analyze the publication bias of OS in the experimental group and the control group. The funnel plot showed that the distribution of each study was symmetrical (Figure 12), and Egger’s test indicated that there was a low possibility of publication bias (P=0.987) (Table 2).
4 Discussion
A total of 11 high-quality foreign randomized controlled trials in phase II and III were included in the systematical analysis and evaluation of the clinical efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors alone or in combination in the treatment of mRCC or aRCC, with OS, PFS, ORR, PR, CR, DCR, and AEs as the outcome indicators. Firstly, in terms of total clinical efficacy, it was found that the experimental group was significantly better than the control group in OS, PFS, ORR, PR, CR, and DCR, indicating that the single or combined use of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors can produce better clinical benefits in the treatment of mRCC or aRCC, especially in terms of prolonging the OS and PFS of patients. Secondly, with regards to safety, no statistical significance was observed between the experimental group and the control group in terms of total AEs, stage I~II adverse reactions, or stage III~V adverse reactions, indicating that the PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors alone or in combination did not increase the incidence of adverse reactions in patients, indicative of their safety. Although the incidence of adverse reactions, such as dysphonia, rash, hypothyroidism, arthralgia, and itching, in the experimental group was significantly higher than that in the control group, these reactions were deemed controllable. Therefore, in clinical treatment, these risks should be identified and subsequently avoided when treating mRCC or aRCC when using PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. It has been shown that the safety and tolerability of first-line VEGF inhibitors, including sunitinib, have been demonstrated in the treatment of renal cell carcinoma. And in this study, 7 of them were controlled studies with sunitinib group, and through my study, we found that PD-1/PD-L1 monotherapy or combination therapy group significantly prolonged OS, PFS, and improved ORR compared with sunitinib group, and significantly attenuated the incidence of AEs associated with any level of treatment. There are 2 papers with controlled studies with placebo group, and through my study, I found that there was no increase in grade 3 or higher treatment-related adverse events in the PD-1/PD-L1 mono or combination therapy group compared to the placebo group, which would suggest that combining PD-1/PD-L1 targeted agents is promising and does not increase drug toxicity. Thus, PD-1/PD-L1 monotherapy or combination therapy showed a very good safety profile in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. RCC, the twelfth most common cancer in the world (20), has no characteristic clinical features at the early stage. As a result, as many as 25% to 75% of patients develop distant metastases by the time of diagnosis, missing lifesaving opportunities for surgery. In addition, the prognosis of patients with mRCC or aRCC is always poor, with a five-year survival rate of less than 10% (21). Even with radical renal cancer resection, postoperative recurrence rates range from 10% in low-risk patients to 68% in high-risk patients (22). The widespread application of targeted therapy in cancer has greatly improved prognosis and prolonged the OS and PFS of kidney cancer patients (23). However, the efficacy of targeted drugs like sunitinib as a first-line medicine is not satisfied in the treatment of some mRCCs and aRCCs due to drug resistance (24). PD-1/PD-L1 serves as a common stimulator of the T cell immune response. When the PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway is activated, it can reduce damage to surrounding tissues by the immune response (25). In the tumor microenvironment, signaling overactivation can inhibit the proliferation and activation or apoptosis of CD4 and CD8T cells, thereby promoting the negative regulation of immunity and inhibiting the immune effect of T cells and lymphocytes. This will help tumor cells escape the surveillance of somatic immune response cells, eventually forming immune tolerance. It could mediate the immune escape of tumor cells and promote cellular growth and proliferation without immune prevention and control (26, 27). According to the guidelines of the European Society of Medical Oncology and the European Association of Urology (28), for clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients with medium- or high-risk operation, PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors represented by pembrolizumab can be used to assist in postoperative radical resection or adjuvant immunotherapy with mRCC. This has also been shown to achieve good survival benefits in multicenter, randomized clinical trials of CheckMate 025, CheckMate 214, and KEYNOTE-426 (29, 30).
In this study, after systematically assessing and analyzing the seven outcome indicators of OS, PFS, ORR, PR, CR, DCR, and AEs, it was not difficult to find that, in terms of efficacy and safety, the OS, PFS, ORR, PR, CR, DCR, and AEs of the PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor group, alone or in combination with the PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor group, had a significantly better clinical efficacy and safety in the treatment of mRCC or aRCC than the control group. Significant heterogeneity was found in the analysis of PFS, and subgroup analyses were performed by PD-L1 expression, IMDC score, and the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) score. As a result, it was found that the heterogeneity still existed, which would suggest that the heterogeneity of PFS may come from factors such as race, follow-up time, and sample size, which had less impact on our study in terms of the effectiveness of PFS. On the contrary, in terms of the heterogeneity of AEs, by classifying common adverse reactions by disease system and performing subgroup analyses, the results showed that the heterogeneity of adverse reactions, such as hairiness, rash, and dysphonia, was significantly reduced, and the burden of safety was significantly reduced compared with that of the control group, further indicating that the existence of heterogeneity of AEs could be eliminated by systematic subgroup analyses. It has been shown that racial differences exist in the clinical efficacy of cancer patients receiving targeted therapies in different regions, and the efficiency of patients with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors may vary depending on geographic location, which will likely be another important reason for the presence of heterogeneity. At the same time, we cannot ignore the following reasons for the existence of heterogeneity: (i) the sample size, population distribution, ethnicity, and tumor type of the included studies were quite different; (ii) there were differences in the traditional first-line chemotherapy regimen of patients receiving PD-1/PD-L1 treatment; (iii) most of the literature failed to specifically describe the random allocation method and allocation concealment, causing some non-blind results to the experimenter, investigator and experimental; (iv) in the experiment, the patient withdrew and lost to follow-up due to serious adverse reactions or other reasons. Therefore, we will continue to update the data and collect more high-quality clinical trials, especially in terms of medication regimen, duration of follow-up, type of disease, and ethnicity, to conduct a more detailed analysis to validate the data presented in this paper. But this study has the advantages of a long search time, the most comprehensive outcome indicators, the most recent data from literature studies and a large sample size compared with similar published literature, thus being a more objective and comprehensive outcome indicator for the analysis. At the same time, subgroup analyses were conducted for each outcome indicator, eliminating heterogeneity between studies and providing more objective and reliable guidance for clinical treatment.
In summary, the single or combined use of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors shows significant clinical benefits and safety in treating mRCC or aRCC. However, due to the limited number of articles, more high-quality, multicenter randomized clinical studies are needed to gain more comprehensive and sufficient medical rationales for treating mRCC or aRCC.
Author contributions
DZ: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. CS: Data curation, Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. WZ: Investigation, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HC: Formal analysis, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (H2021402018).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Linehan WM, Ricketts CJ. The cancer genome atlas of renal cell carcinoma: findings and clinical implications. Nat Rev Urol. (2019) 16:539–52. doi: 10.1038/s41585-019-0211-5
2. Siegel RL, Miller Kd and Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. (2019) 69:7–34. doi: 10.3322/caac.21551
3. Gray RE, Harris GT. Renal cell carcinoma: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Phys. (2019) 99:179–84.
4. Serzan MT, Atkins MB. Current and emerging therapies for first line treatment of metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J J Cancer metast Treat. (2021) 7:39. doi: 10.20517/2394-4722.2021.76
5. Choueiri TK, Motzer RJ. Systemic therapy for metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. (2017) 376:354–66. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1601333
6. Han Y, Liu D, Li L. Pd-1/Pd-L1 pathway: current researches in cancer. Am J Cancer Res. (2020) 10:727–42.
7. Mori K, Pradere B, Quhal F, Katayama S, Mostafaei H, Laukhtina E, et al. Differences in oncological and toxicity outcomes between programmed cell death-1 and programmed cell death ligand-1 inhibitors in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Treat Rev. (2021) 99:102242. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2021.102242
8. Rini BI, Plimack ER, Stus V, Gafanov R, Hawkins R, Nosov D, et al. Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. (2019) 380:1116–27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1816714
9. Pal SK, Uzzo R, Karam JA, Master VA, Donskov F, Suarez C, et al. Adjuvant atezolizumab versus placebo for patients with renal cell carcinoma at increased risk of recurrence following resection (immotion010): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet (London England). (2022) 400,10358:1103–16. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01658-0
10. Choueiri TK, Tomczak P, Park SH, Venugopal B, Ferguson T, Chang YH, et al. Adjuvant pembrolizumab after nephrectomy in renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. (2021) 385:683–94. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2106391
11. Motzer RJ, Escudier B, George S, Hammers HJ, Srinivas S, Tykodi SS, et al. Nivolumab versus Everolimus in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: updated results with long-term follow-up of the randomized, open-label, phase 3 checkmate 025 trial. Cancer. (2020) 126:4156–67. doi: 10.1002/cncr.v126.18
12. Albiges L, Tannir NM, Burotto M, McDermott D, Plimack ER, Barthélémy P, et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib for first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma: extended 4-year follow-up of the phase III checkmate 214 trial. ESMO Open. (2020) 5:e001079. doi: 10.1136/esmoopen-2020-001079
13. Powles T, Plimack ER, Soulières D, Waddell T, Stus V, Gafanov R, et al. Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib monotherapy as first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (keynote-426): extended follow-up from a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2020) 21:1563–73. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30436-8
14. Choueiri TK, Motzer RJ, Rini BI, Haanen J, Campbell MT, Venugopal B, et al. Updated efficacy results from the Javelin renal 101 trial: first-line Avelumab plus Axitinib versus Sunitinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol. (2020) 31:1030–9. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.010
15. Motzer R, Alekseev B, Rha SY, Porta C, Eto M, Powles T, et al. Lenvatinib plus Pembrolizumab or Everolimus for advanced renal cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. (2021) 384:1289–300. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2035716
16. Motzer RJ, Powles T, Burotto M, Escudier B, Bourlon MT, Shah AY, et al. Nivolumab plus Cabozantinib versus Sunitinib in first-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma (checkmate 9er): long-term follow-up results from an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2022) 23:888–98. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00290-X
17. Rini BI, Powles T, Atkins MB, Escudier B, McDermott DF, Suarez C, et al. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab versus Sunitinib in patients with previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma (immotion151): a multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. (2019) 393:2404–15. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30723-8
18. Choueiri TK, Larkin J, Pal S, Motzer RJ, Rini BI, Venugopal B, et al. Efficacy and correlative analyses of avelumab plus Axitinib versus Sunitinib in sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma: post hoc analysis of a randomized clinical trial. ESMO Open. (2021) 6:100101. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100101
19. Vano YA, Elaidi R, Bennamoun M, Chevreau C, Borchiellini D, Pannier D, et al. Nivolumab, Nivolumab-Ipilimumab, and Vegfr-tyrosine kinase inhibitors as first-line treatment for metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma (bionikk): a biomarker-driven, open-label, non-comparative, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2022) 23:612–24. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00128-0
20. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
21. Rini BI, Campbell SC, Escudier B. Renal cell carcinoma. Lancet. (2009) 373:1119–32. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60229-4
22. Lam JS, Leppert JT, Figlin RA, Belldegrun AS. Role of molecular markers in the diagnosis and therapy of renal cell carcinoma. Urology. (2005) 66:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2005.06.112
23. Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, et al. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med. (2012) 366:2443–54. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1200690
24. Patel R, Onyechi A, Mohamed MM, Oyenuga M, Sartaj S. Immunotherapy and antiangiogenic therapy for the treatment of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and an updated network meta-analysis of phase III clinical trials. Cureus. (2023) 15:e38838. doi: 10.7759/cureus.38838
25. Burugu S, Dancsok AR, Nielsen TO. Emerging targets in cancer immunotherapy. Semin Cancer Biol. (2018) 52,Pt 2:39–52. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.10.001
26. Carter L, Fouser LA, Jussif J, Fitz L, Deng B, Wood CR, et al. Pd-1:Pd-L inhibitory pathway affects both Cd4(+) and Cd8(+) t cells and is overcome by IL-2. Eur J Immunol. (2002) 32:634–43. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200203)32:3<634::AID-IMMU634>3.0.CO;2-9
27. Philips GK, Atkins M. Therapeutic uses of Anti-Pd-1 and Anti-Pd-L1 antibodies. Int Immunol. (2015) 27:39–46. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxu095
28. Bex A, Albiges L, Ljungberg B, Bensalah K, Dabestani S, Giles RH. Updated European association of urology guidelines regarding adjuvant therapy for renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. (2017) 71:719–22. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.11.034
29. Powles T, Albiges L, Bex A, Grünwald V, Porta C, Procopio G, et al. ESMO clinical practice guideline update on the use of immunotherapy in early stage and advanced renal cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol. (2021) 32:1511–9. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.09.014
30. Bedke J, Albiges L, Capitanio U, Giles RH, Hora M, Lam TB, et al. Updated European Association of Urology guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: Nivolumab plus Cabozantinib joins immune checkpoint inhibition combination therapies for treatment-naïve metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. (2021) 79:339–42. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.12.005
Keywords: renal cell carcinoma, PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor, efficacy, safety, meta-analysis
Citation: Zhang D, Shen C, Zhang W, Chen H and Zhao J (2025) Efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors alone or in combination in the treatment of metastatic or advanced renal cell carcinoma: a network meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 16:1524497. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1524497
Received: 07 November 2024; Accepted: 20 January 2025;
Published: 25 February 2025.
Edited by:
Zodwa Dlamini, Pan African Cancer Research Institute (PACRI), South AfricaReviewed by:
André Filipe Oliveira, Hospital do Divino Espírito Santo, PortugalYuan Tian, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Shen, Zhang, Chen and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianjun Zhao, emhhb2ppYW5qdW4xNjY4QDE2My5jb20=
 Dongli Zhang1
Dongli Zhang1 Chong Shen
Chong Shen Jianjun Zhao
Jianjun Zhao