
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Immunol., 24 March 2025
Sec. Inflammation
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1523503
This article is part of the Research TopicPost-Transcriptional Modifications in Cancer Immunity and ImmunotherapyView all 5 articles
Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) plays a crucial role in post-transcriptional gene regulation. Substantial evidence links METTL3 to various immune dysfunctions, such as the suppression of antiviral immunity during viral infections and the disruption of immune tolerance in conditions like autoimmune diseases, myeloid leukemia, skin cancers, and anticancer immunotherapy. However, a thorough review and analysis of this evidence is currently missing, which limits the understanding of METTL3’s mechanisms and significance in immune dysfunctions. This review aims to elucidate the roles and mechanisms of METTL3 in these immune issues, highlighting its connections and proposing new insights into its modulation of immune responses. Analysis results in this review suggest that METTL3 hampers antiviral immunity, worsens viral replication and infection, and disrupts immune tolerance; conversely, regulating METTL3 enhances antiviral immunity and facilitates viral clearance. Moreover, clinical data corroborates these findings, showing that METTL3 overexpression is associated with increased susceptibility to viral infections and autoimmune conditions. This review establishes a theoretical basis for considering METTL3 as a novel regulator, an important diagnostic biomarker, and a potential target for treating immune dysfunctions.
The immune system primarily differentiates between healthy and atypical cells to mitigate the risk of infections (1). However, dysfunctions can occur due to a variety of factors, including genetic immunopathology, immunosuppressive infections such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hypersensitivity reactions, and autoimmune disorders (2–4). Consequently, a thorough elucidation of the complex mechanisms that underlie immune system impairments is essential for addressing a range of immunological issues, from infectious diseases to malignancies.
In recent years, RNA N6-methyladenosine (m6A), a dynamic and reversible epigenetic modification, has emerged as a pivotal regulator of immune-related diseases, including viral infections, inflammatory disorders, cancers, and autoimmune dysregulation (5–9). This post-transcriptional mechanism is orchestrated by three classes of proteins: “writers” that install m6A marks, “erasers” that remove them, and “readers” that interpret these modifications to direct RNA fate (10–12). The writer complex, composed of METTL3 (the catalytic core), METTL14, and WTAP, deposits m6A onto RNA, while erasers such as FTO and ALKBH5 erase these marks (13–15). Readers, including YTHDF and IGF2BP proteins, then bind m6A sites to regulate RNA splicing, stability, translation, and other functional outcomes (16, 17). Together, these players fine-tune gene expression, linking m6A to diverse immunological processes (Figure 1).
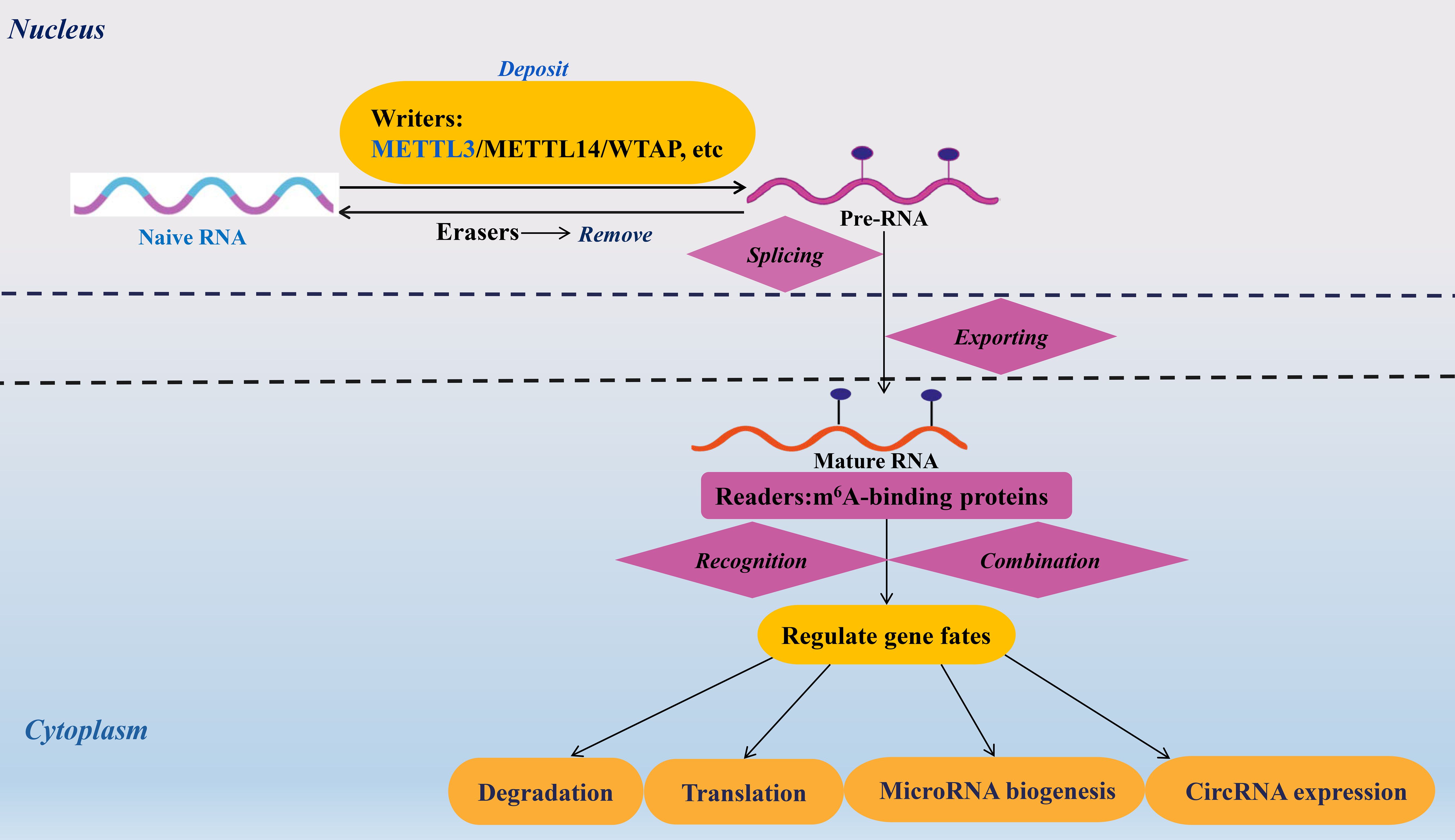
Figure 1. Mechanisms and roles of m6A modification on RNAs. The m6A modification of RNA modulates the fate of target transcripts through the action of m6A methyltransferases, demethylases, and binding proteins. The roles of m6A modification in RNA encompass processes such as splicing, nuclear transport, degradation, translation, microRNA maturation, and the expression of circular RNAs. Methyltransferase-like 3/14(METTL3/14). Wilms tumor 1-associated protein (WTAP). N6-methyladenosine (m6A).
Central to this regulatory system is METTL3, the principal methyltransferase driving m6A deposition (18, 19). An increasing number of investigations have elucidated the involvement of METTL3 in immune dysregulation, encompassing the attenuation of antiviral immunity (in the context of viral infections) and the perturbation of immune tolerance (observed in autoimmune disorders, myeloid leukemia, cutaneous malignancies, and anticancer immunotherapy). Furthermore, the intricate role of METTL3 in modulating immune responses extends beyond mere dysregulation; it also highlights the potential for therapeutic intervention. Recent studies have shown that METTL3 not only influences the expression of immune-related genes but also interacts with various signaling pathways that govern immune cell function. For instance, METTL3 has been implicated in the regulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, which is crucial for the activation of immune responses (20). By modifying the mRNA methylation landscape, METTL3 can alter the stability and translation of mRNAs encoding key proteins involved in inflammation and immune activation, thus shaping the overall immune response (20). In addition to its role in antiviral immunity, METTL3 has been linked to the maintenance of immune tolerance, particularly in the context of autoimmune diseases. For example, its dysregulation can lead to the aberrant activation of T cells, which is a hallmark of autoimmune pathology (21). Recent literature indicates that targeting METTL3 could restore normal immune tolerance mechanisms, offering a novel approach to treat autoimmune conditions. The potential of METTL3 as a therapeutic target is further underscored by investigations exploring the effects of METTL3’s inhibitors, which have demonstrated promising results in preclinical models of autoimmune diseases (22, 23). Moreover, the relationship between METTL3 and immune-related malignancies such as myeloid leukemia and cutaneous malignancies reveals the dual role of METTL3 in both tumor promotion and immune evasion (22, 23). Studies have shown that METTL3 can enhance the expression of oncogenes while simultaneously repressing tumor suppressor genes through mRNA methylation (22, 23). This duality underscores the complexity of METTL3’s function in the tumor microenvironment, where it not only influences cancer cell survival and proliferation but also modulates the immune landscape, potentially leading to immune escape mechanisms. In the context of anticancer immunotherapy, the modulation of METTL3 activity may provide new avenues for enhancing therapeutic efficacy. For instance, by restoring proper METTL3 function, it may be possible to reinvigorate exhausted T cells and enhance their ability to target tumor cells effectively. Recent clinical trials are beginning to explore the combination of METTL3 modulators with existing immunotherapeutic agents, aiming to synergistically improve patient outcomes.
Despite the extensive exploration of METTL3’s functions in immune dysfunctions, a thorough review that examines their interconnections and offers insights into the prospective applications (diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic) of METTL3 remains absent. This review aims to synthesize findings that underscore the roles and mechanisms of METTL3 in modulating immune-related pathological processes to elucidate their interrelations. Additionally, we evaluate the potential of METTL3 as a viable target for immunological diagnostics, therapeutics, and prognostic assessments.
Infections reflect the balance between intracellular virulence factors and host defense mechanisms (24). Virulence factors infection and host defense involve the innate and adaptive immune mechanisms, which are anti-immune responses to inflammation (25). Previous studies have demonstrated that viral RNA contains internal METTL3-mediated m6A modifications. For example, Xu et al. (26) reported that DEAD-box helicase 5 (DDX5) interacts with METTL3 following viral infection to promote the decay of IκB kinase γ and p65 mRNAs in an YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2 (YTHDF2)-dependent manner while promoting DExD/H-box helicase 58 (DHX58) translation and inhibiting the antiviral innate response. Therefore, DDX5 and METTL3 play pivotal roles in reducing antiviral innate immunity through their ability to block the p65 pathway while activating the DHX58/TANK-binding kinase 1 pathway. Chen et al. (27) found that the upregulated expression of METTL3 increases porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) replication, which depends on YTHDF1 modulating the stability of m6A-modified PEDV RNA (27). However, regarding host innate immunity, Zhang et al. (28) suggested that YTHDF3, rather than METTL3, collaborates with poly (A)-binding protein 1(PABP1) and eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 2 (eIF4G2) to facilitate forkhead box O3 (FOXO3) translation by binding to the translation initiation region of FOXO3 mRNA, thereby impeding antiviral immunity under homeostatic conditions (Table 1).
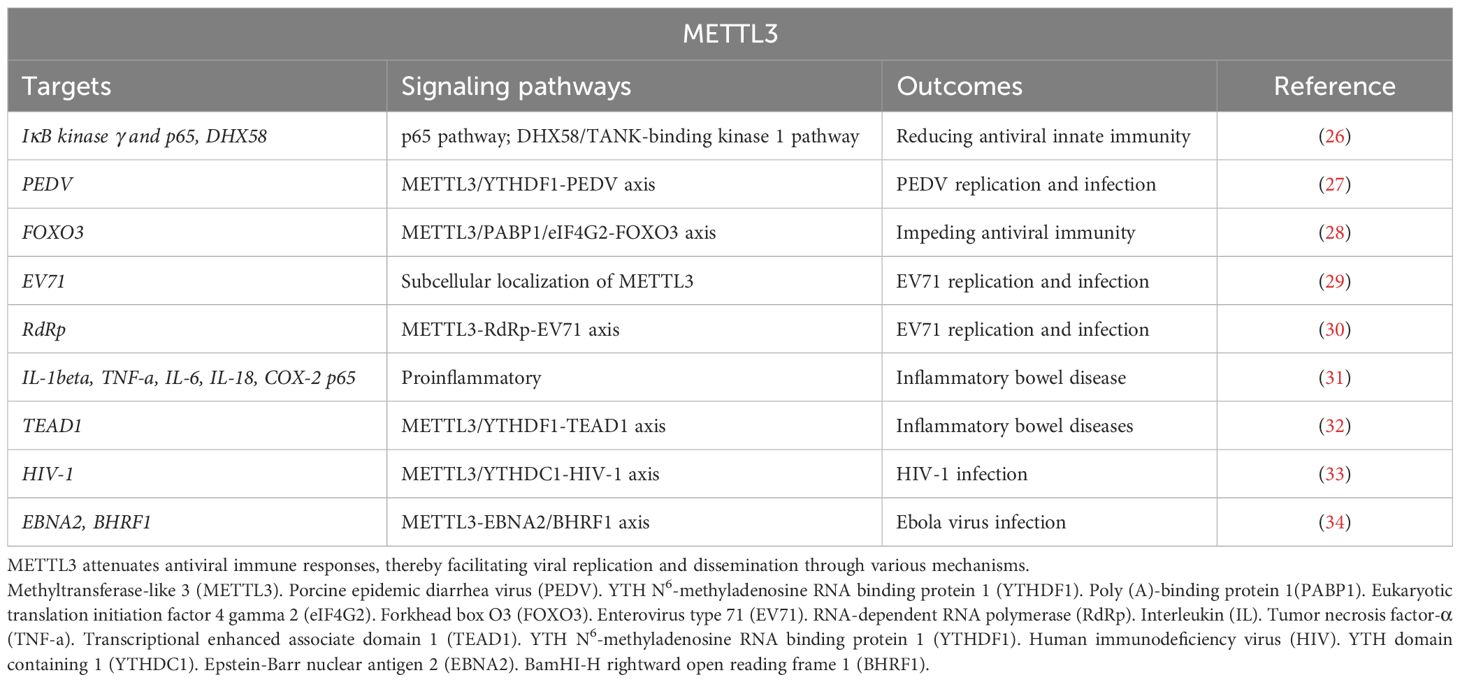
Table 1. Targets and signaling pathways of METTL3’s function in modulating antiviral immune responses and facilitating pathogen invasion.
Another study evaluates the prevalence of m6A modification in the enterovirus type 71 (EV71) genome within human cells and identifies a conserved, preferred site for modification across various viral strains (29). That is, a single m6A modification at the junction between 5’-untranslated regions and rotavirus (RV) subunit VP4 is found to have translational functionality. During EV71 infection, the level of METTL3 expression is upregulated and is specifically localized in the cytoplasm to intermediate viral double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) replication (29). The upregulated expression of METTL3 results in a significant induction of EV71 replication, whereas depletion of the METTL3 results in a significant reduction of EV71 replication. It is noteworthy that both EV71 and METTL3 utilize common nuclear import proteins. The nuclear translocation of METTL3 is facilitated by greater binding to its nuclear localization sequence. The findings of this investigation unveil an intrinsic mechanism through which EV71 modulates the subcellular localization of METTL3 to enhance its gene expression, thereby enhancing our comprehension of RNA epi-transcriptomic during the EV71 replication cycle. Additionally, Hao et al. (30) revealed that METTL3 leads to enhanced sumoylation and ubiquitination of the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) that subsequently promotes EV71 replication. Taken together, these findings demonstrate that the host m6A modification complex interacts with viral proteins to modulate EV71 replication (Table 1).
Intestinal stem cells (IECs) are multipotent adult stem cells that continuously differentiate into specialized cells of the intestinal epithelium to maintain intestinal functions (35). Dysregulated cytokine secretion and signal transduction mechanisms via IECs contribute to inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) (35). Yang et al. (31) reported that the expression of METTL3 is significantly upregulated in IBD. METTL3 upregulation enhances cell viability, suppresses cell apoptosis, reduces cleavage of apoptotic caspase 3 and caspase 9, and increases the production of proinflammatory cytokines (interleukin [IL]-1beta, tumor necrosis factor-α [TNF]-a, IL-6, and IL-18) and inflammatory enzymes (COX-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase), as well as of p65 phosphorylation (31). Furthermore, Jiang et al. (32) found that METTL3 and YTHDF1 inhibit transcriptional-enhanced associate domain 1 (TEAD1) translation in IECs, thereby hindering its differentiation. These findings demonstrate that the METTL3/YTHDF1-TEAD1 axis triggers IEC-induced IBD. Therefore, the abnormally enhanced expression of METTL3 exacerbates IBD (Table 1).
The function of the prototypical immunodeficiency virus, HIV-1, specifically targets T cells and their elimination facilitates secondary infections by other pathogens, is also intricately linked to METTL3-mediated RNA m6A modification (36). A study demonstrated that the activation of the METTL3/METTL14/WTAP RNA methyltransferase complex promotes viral particle production in cells harboring HIV-1 provirus (37). Furthermore, both the m6A methylation level of HIV-1 RNA and the number of m6A residues in the host cell are elevated. Another study revealed that the METTL3/METTL14 methyltransferase complex and cytoplasmic YTHDF2 work in tandem to suppress the abundance of HIV-1 RNAs in infected cells (33). YTH domain containing 1 (YTHDC1) knockdown in HIV-1-producing cells enhances the production of unsliced and incompletely spliced HIV-1 RNAs while leaving the levels of multiply spliced transcripts and the nuclear-cytoplasmic distribution of viral transcripts unaffected (33). YTHDC1 specifically binds to HIV-1 transcripts in a METTL3-dependent manner. Together, these findings suggest that METTL3, YTHDF2, and YTHDC1 are negatively correlated with HIV-1. In addition to their impact on HIV-1, METTL3-mediated RNA m6A modification affects Ebola virus infection. For instance, Zheng et al. (34) demonstrated that following Ebola virus infection, host cellular METTL3-mediated RNA m6A modification significantly enhances the expression of the viral proteins, epstein-barr nuclear antigen 2(EBNA2), and BamHI-H rightward open reading frame 1(BHRF1) (Table 1).
The high level of METTL3 triggers virus replication and inflammatory cascade. Therefore, targeted downregulation of METTL3 might improve the capacity of antiviral immunity and virus clearance (38). Specifically, RV is a nonenveloped icosahedral-structured virus with 11 segments of dsRNA (39). RV encodes multiple viral proteins to inhibit innate immune responses by degrading interferon regulatory factors (IRFs) and mitochondrial antiviral-signaling proteins, thus facilitating efficient virus infection and replication (40). Therefore, the timely induction of an IFN response is key to the host’s successful control of invading viruses. METTL3-mediated RNA m6A modification plays a role in these processes (Table 2).
METTL3 expression is suppressed in response to viral infection or cell stimulation with an inactivated virus, leading to the activation of interferon-beta (IFN-beta), which encodes the primary cytokine responsible for driving type I IFN responses by enhancing its stability (41). Wang et al. (40) discovered that targeted deletion of METTL3 in the IECs not only protects against RV infection but also increases the levels of IFNs and IFN-stimulated genes. Mechanically, METTL3 depletion promotes IRF7 mRNA stability and increases the expression of type I/III interferon. These findings reveal a novel METTL3-IRF7-interferon I/III antiviral signaling cascade that restricts RV infection in vivo (Table 2).
Depletion of METTL3 impedes the replication of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and the beta coronavirus, human coronavirus -OC43 (HCoV-OC43) (42). Furthermore, infection with HCoV-OC43 facilitates the nuclear translocation of METTL3, thereby indicating the potential of targeting the METTL3-mediated m6A modification as a therapeutic approach to impede coronavirus replication (42). Li et al. (43) discovered that in patients with severe coronavirus disease caused by SARS-CoV-2, METTL3 expression is diminished, whereas inflammatory genes are activated. This occurred through the increased retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) binding and subsequent enhancement of downstream innate immune signaling pathways and inflammatory gene expression. Furthermore, METTL3 knockdown in representative members of the Pneumoviridae, Paramyxoviridae, and Rhabdoviridae families significantly increases the levels of type I IFN in a RIG-I-dependent manner (44). These findings collectively suggest that RNA viruses employ METTL3-mediated m6A modification as a common strategy to evade host innate immunity. Thereby rendering METTL3 as a potential intervention target for improving antiviral immunity capacity (Table 2).
METTL3 knockdown in monocytes or hepatocytes facilitates the expression of type I IFN and expedites the clearance of the RNA virus, vesicular stomatitis virus (46). Regarding the METTL3-mediated antiviral innate immune response, Qiu et al. (45) demonstrated that METTL3 translocates into the cytoplasm upon infection by vesicular stomatitis virus to enhance m6A modification on viral transcripts and suppresses viral dsRNA formation, thereby attenuating the virus-sensing efficacy of RIG-like receptors, such as RIG-I and melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 (MDAP5), while reducing antiviral immune signaling. These findings suggest that METTL3-mediated m6A modification on viral RNAs negatively regulates innate sensing pathways of dsRNA and that METTL3 is a potential therapeutic target for modulating antiviral immunity (Table 2).
The immune system is generally tolerant to self-antigens and does not typically attack the cells, tissues, or organs of the body (47). However, the loss of this tolerance, often due to immune deficiencies, leads to disorders such as autoimmune diseases or food allergies (48). Immune tolerance disruption refers to the lack of an immune response against a specific antigen, which occurs when adaptive immune cells that recognize host cells persist unchecked (49). This process is amplified by the recruitment and activation of other immune cells (50). This loss of immune tolerance is detrimental to human health and is linked to METTL3-mediated RNA m6A modification (51).
Autoimmune diseases arise from the breakage of self-tolerance, including autoimmune thyroid disease (AITD) (52), Graves’ disease (53), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) (54), rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (55), primary Sjögren’s syndrome (pSS) (56), autoimmune uveitis (57), and myasthenia gravis (MG) (58), which have a strong genetic basis (59). With advances in gene sequencing, researchers have gained a better understanding of the underlying factors that contribute to autoimmune diseases (60).
Song et al. (61) revealed a significant association between hypothyroidism and the distribution of METTL3 polymorphisms at locus rs3752411 in patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. These findings provide evidence for the correlation between METTL3 mutations and predisposition to AITD and suggest the potential of METTL3 as a therapeutic target for AITD treatment. Another study revealed that both METTL3 and suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) are abnormally expressed in thyroid tissues and CD4+ T cells in Graves’ disease (62). METTL3 knockdown results in the upregulation of SOCS family members (SOCS1, SOCS2, SOCS4, SOCS5, and SOCS6) (62). This study also provides further evidence for the correlation between METTL3-mediated m6A modification and AITD (Table 3).
SLE is a chronic autoimmune disease, which might be triggered by the dysfunction of immune cells such as T cells, B cells, monocytes, neutrophils, and dendritic cells (73). The current perspective from the m6A modification for the pathogenesis and treatment failure of SLE has enhanced the mechanism understanding of SLE. For example, Luo et al. (74) demonstrated that the METTL3 mRNA levels in peripheral blood from patients with SLE are significantly decreased, which suggests a correlation between METTL3 and patients with SLE. Additionally, excessive activation of CD4+T lymphocytes and imbalanced effector T-cell differentiation contribute to SLE pathophysiology (74). Lu et al. (63) found that METTL3 is at a low level in CD4+ T cells of patients with SLE, which promotes the activation of CD4+ T cells and influences the differentiation of effector T cells, predominantly Treg cells. Moreover, METTL3 deficiency promotes antibody production and aggravates the lupus-like phenotype in mice. METTL3 enhances Foxp3 mRNA decay and reduces Foxp3 expression in an m6A-dependent manner, thereby inhibiting Treg cell differentiation. In summary, METTL3 triggers SLE pathogenesis by over-activating CD4+ T cells and dysregulating effector T-cell differentiation via stabilizing Foxp3 mRNA, which could serve as a potential target for therapeutic intervention in SLE. However, Liu et al. (75) reported that METTL3 expressions are elevated in patients with SLE. The upregulated METTL3 promotes IRF4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner, thus causing plasma cell infiltration-mediated kidney damage of SLE (Table 3).
RA is a systematic autoimmune disease characterized by chronic synovitis and joint destruction (76). Abnormal proliferation of synovial fibroblast (SF), also termed fibroblast-like synoviocyte (FLS), in the joints and the formation of granulations that erode and destroy the articular cartilage contributes to RA occurrence (77). The typical pathology of RA is the persistence of inflammation maintained by SF and is driven by multiple epi-modifications (78). In addition, fibroblasts can switch from early immunosuppressive to stimulatory in response to relevant factors to promote RA development (79).
SF are effector cells of synovial hyperplasia of RA and are regarded as tumor-like cells with characteristics such as abnormal proliferation, migration and invasion, resistance to apoptosis, and so on (80). SF plays an important role in the development and progression of RA. While promoting apoptosis or inhibiting proliferation, migration, and invasion of SF efficiently prevents RA occurrence and development. Single-cell analysis and machine learning found that the expression levels and enrichment pathways of METTL3 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 (IGFBP2) are different among SF subgroups (64). Further investigation of receptor-ligand interactions found that NPR3 and GHR may have a role in SF interactions (64). As predicted by machine learning, IGFBP2, and METTL3 are identified as key factors regulating m6A on NPR3 and GHR (64). In summary, NPR3 and GHR, as well as IGFBP2 and METTL3 perform important regulatory functions in RA. This study provides a basis for future studies to identify pathogenic cell subpopulations and molecular mechanisms in RA. As a chronic inflammatory disorder, FA shows synovial hypertrophy, severe joint damage, and loss of joint function (76). The hyper-proliferating FLS releases a large number of pro-inflammatory indicators, such as IL-6, IL-1b, and TNF-a, causing abnormal inflammation in the synovial membrane (81). Moreover, the activated FLS release matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), promote FLS migration and invasion (82). Shi et al. (65) and Su et al. (83) found that METTL3 expression is significantly upregulated in human RA synovial tissues and RA rat models. Inhibition of METTL3 suppresses IL-6, MMP-3, and MMP-9 levels in human RA-FLS and rat RA model-FLS (65). In contrast, METTL3 overexpression reverses these effects. Additionally, in FLS, METTL3 regulates the inflammatory response of FLS by activating the NF-kB signaling pathway (65). These findings collectively suggest that METTL3 triggers FLS activation and inflammatory response by targeting the NF-kB signaling pathway. Similarly, METTL3-mediated methylation of RAC2 contributes to cell motility, oxidative stress, and inflammation in TNF-α-stimulated RA fibroblast-like synovial cells (84). Therefore, targeting METTL3 in FLS is a promising therapeutic strategy for RA. As reported, a high level of TTC4 is associated with poor outcomes in patients with RA, which promotes the production of inflammatory factors and reduces the generation of anti-oxidant factors in the articular tissue of mice with RA (66). Lu et al. (66) demonstrated that inhibition of METTL3 reduces TTC4 mRNA stability and expression in articular tissue of mice with RA, which reduces inflammation and oxidative stress by promoting HSP70 expression that further targets NLRP3. In summary, targeted regulation of METTL3 reduces oxidative response and inflammation in the RA model by regulating the TTC4/HSP70/NLRP3 pathway. Therefore, targeting METTL3 is therapeutic for RA (Table 3).
Furthermore, seeking new drugs that suppress the pathological functions of RA-FLS has become a possible method for RA therapy. Artemisinin (ATT) is a well-known antimalarial drug extracted from the plant Artemisia annua L. with immunomodulatory effects, anti-viral effects, anticancer activities, and so on (85). The ATT derivatives of the natural compound ATT show broad anticancer activities without toxicity on normal tissues (86, 87). Recently, ATT has been reported to have the potential to treat RA. Chen et al. (67) reported that ATT administration restrains RA-FLS migration and invasion via suppressing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), as well as inhibiting RA-FLS proliferation and inducing RA-FLS apoptosis. Moreover, ATT treatment relieves RA in mice. RNA-sequencing analysis and bioinformatics analysis identify intercellular adhesion molecule 2 (ICAM2) as a promoter of RA progression in RA-FLS (67). ATT inhibits RA progression by suppressing ICAM2/PI3K/AKT/p300 pathway in RA-FLS. Moreover, ATT inhibits METTL3-mediated m6A methylation on ICAM2 mRNA in RA-FLS (67). Interestingly, p300 directly facilitates METTL3 transcription, which could be restrained by ATT in RA-FLS. Importantly, the expression of METTL3, ICAM2, and p300 in synovium tissues of patients with RA is related to clinical characteristics and therapy response (67). This study provides strong evidence that ATT has therapeutic potential for RA management by suppressing proliferation, migration, and invasion, in addition to inducing RA-FLS apoptosis through modulating the feedback loop of METTL3/ICAM2/PI3K/AKT/p300, supplying the fundamental basis for the clinical application of ATT in RA therapy. Moreover, METTL3, ICAM2, and p300 might serve as biomarkers for the therapy response of patients with RA (Table 3).
Primary pSS is a chronic autoimmune disorder defined by xerostomia and keratoconjunctivitis sicca, genetic and epigenetic factors have been considered to affect pSS development (56). Glandular inflammation and tissue impairment eventually give rise to disturbances of secretory and clinical manifestations of dryness, including dry eye and xerostomia (88). pSS is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease and is characterized by exocrine gland impairment, such as the salivary and lacrimal glands, which could result in dry mouth and eye (89). Dysregulation of m6A modification is closely associated with pSS.
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) are the effector cells of autoimmune disorders (90). Ma et al. (68) found that the expression level of m6A is markedly increased in the PBMCs of patients with pSS and dry eye. The relative mRNA and protein levels of METTL3 and YTHDF1 are markedly elevated in pSS patients with dry eye. The m6A RNA level is found to be positively related to METTL3 expression in patients with pSS. The m6A RNA level is associated with C4, while METTL3 mRNA expression is associated with C3. This work reveals that the upregulation of m6A and METTL3 is associated with the performance of serological indicators and dry eye signs in patients with pSS. METTL3 may contribute to the pathogenesis of pSS-related dry eye (Table 3).
Autoimmune uveitis, a chronic and unpredictable autoimmune disease, is characterized by inflammatory cell infiltration affecting the retina and uvea, which leads to visual disability and even blindness (91). Study has demonstrated that autoreactive Th17 cells are the main drivers of autoimmune uveitis (92). Th17 cells can be categorized into two functionally distinct subsets: non-pathogenic and pathogenic Th17 cells (93). Th17 cells, generated in the presence of TGF-beta, IL-6, IL-17, and IL-10, are largely nonpathogenic (94). In contrast, IL-23 alone or together with IL-6 induces highly pathogenic Th17 cells, which express signature genes including IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-23 receptor (IL-23R), IL-1R1, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (93). METTL3 maintains the homeostasis of Th17 cells. Zhao et al. (69) found that the expression of METTL3 is decreased, along with reduced m6A levels, in eyeballs and T cells of experimental autoimmune uveitis. Overexpression of METTL3 ameliorates the development of experimental autoimmune uveitis and suppresses pathogenic Th17 cell responses in vivo and in vitro. Mechanistically, METTL3 promotes the expression of ASH1L via enhancing its stability in an YTHDC2-dependent manner, which further decreases the expression of IL-17 and IL-23R, resulting in reduced pathogenic Th17 responses. Together, these data reveal a pivotal role of METTL3 in regulating pathogenic Th17 responses, which may contribute to human uveitis therapy (Table 3).
Pathogenic Th17 cells are critical drivers of autoimmune uveitis (95). Wei et al. (70) showed that miR-338-3p endows dendritic cells (DCs) with an increased ability to activate IRBP 1-20-specific Th17 cells by promoting the production of IL-6, IL-1beta, and IL-23. In vivo, administration of miR-338-infected DCs promotes pathogenic Th17 responses and exacerbates uveitis development. Dual-specificity phosphatase 16 (Dusp16) is a target of miR-338-3p (70). miR-338-3p represses Dusp16 and thereby strengthening the p38 signaling, resulting in increased production of Th17-polarizing cytokines and subsequent pathogenic Th17 responses (70). In addition, METTL3 mediates miR-338-3p upregulation in activated DCs. Together, these findings identify a vital role for METTL3/miR-338-3p/Dusp16/p38 signaling in DC-driven pathogenic Th17 responses and suggest a potential therapeutic avenue for uveitis and other Th17 cell-related autoimmune disorders (Table 3).
MG is an autoantibodies-mediated autoimmune disease with complications of deregulated levels of immune factors that are associated with anti-inflammation and pro-inflammation (58). Previous study indicates that the aberrant regulation of immune T cells and inflammatory factors are linked to MG occurrence (58). The NLRP3 inflammasome is present primarily in immune and inflammatory cells following activation by inflammatory stimuli (71). These cells include macrophages, monocytes, DCs, and splenic neutrophils. METTL3 has been reported to regulate the normal function of these immune cells, as well as involved in the regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome. Consistently, Li et al. (72) found that the serum expression level of PTX3 in patients with MG is up-regulated compared to the normal group. METTL3-mediated m6A modification decreases PTX3 stability to enhance its expression level, which subsequently induces the STAT3/NLRP3 inflammasome and promotes STAT3 synthesis, promoting inflammation and pyroptosis in patients with MG, as well as in MG mouse model. This study suggests that PTX3 promotes inflammation and pyroptosis by regulating the STAT3/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway, which requires the modification of METTL3. Therefore, targeting METTL3 might be therapeutic for PTX3-induced MG (Table 3).
Collectively, these findings suggest that METTL3 is involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. Therefore, we propose that METTL3 may be a valuable diagnostic biomarker and a promising therapeutic target for autoimmune diseases. Nonetheless, additional fundamental and clinical studies are warranted to consolidate the evidence supporting their association and clinical potential.
Some types of cancer directly result from the uncontrolled proliferation of immune cells. For instance, leukemia is caused by white blood cells, which are immune cells (96). Whereas lymphoma arises from lymphocytes, which are adaptive B or T cells (97). Abnormal expression of METTL3 has been extensively implicated in leukemia, including chronic myelocytic leukemia (CML) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML), where it functions as an oncogene or regulates other oncogenes.
Abnormally upregulated METTL3 promotes oncogene pescadillo homolog 1 (PES1) translation directly, which enhances the proliferation, sensitivity to imatinib (a tyrosine kinase inhibitor), and resistance of CML cells (98). METTL3, acting as an oncoprotein in CML, specifically modifies PES1 transcripts through its cytoplasmic localization ability rather than its catalytic activity (98). This finding suggests that targeting METTL3 may be a promising therapeutic strategy for tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant CML. Lai et al. (99) demonstrated that METTL3 functions indirectly as a downstream target of LINC00470 to modify the oncogene PTEN, thereby suppressing CML cell autophagy and resulting in chemo-resistance. Besides, Yao et al. (100) demonstrated that METTL3-mediated m6A modification on the long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) effectively downregulates NEAT1 expression in CML, thereby promoting the proliferation and inhibiting the apoptosis of CML cells. Interestingly, the upregulation of miR-766-5p expression is observed in CML PBMCs, which potentially abolishes NEAT1 functions in CML cells (100). miR-766-5p exerts its function by inhibiting the expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (CDKN1A) in CML PBMCs. These findings suggest that in CML, METTL3 acts as an oncoprotein by directly targeting the NEAT1/miR-766-5p/CDKN1A axis to promote CML progression (Figure 2).
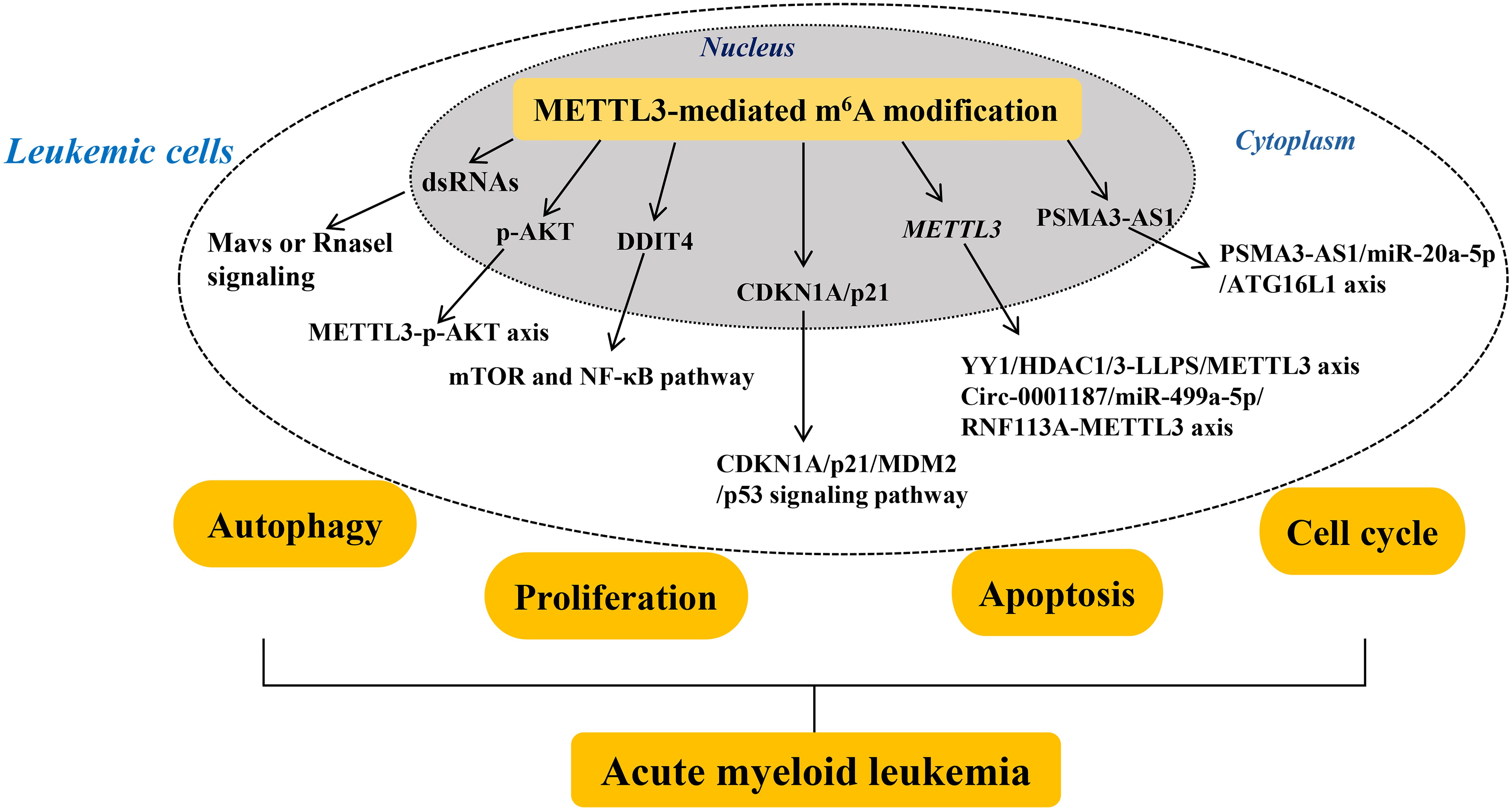
Figure 2. Mechanisms of METTL3’s role in myeloid leukemia. The roles and mechanisms of METTL3 in chronic and acute myeloid leukemia are thoroughly summarized. In summary, METTL3 contributes to the development of myeloid leukemia with different mechanism. Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3). Double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs). Protein kinase B (AKT). Damage-inducible transcript 4 (DDIT4). Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (CDKN1A). Mouse double minute 2 (MDM2). Yin Yang 1 (YY1). YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 1 (YTHDF1).
In summary, the overexpressed level of METTL3 is associated with CML by its direct or indirect oncogenic functions, suggesting that METTL3 is a promising biomarker for CML diagnosis or prognosis, as well as a potential therapeutic target for CML treatment.
AML is a hematologic malignancy characterized by dysregulated proliferation and accumulation of leukemic cells in the hematopoietic system (101). Gao et al. (102) reported that the deletion of METTL3 conditionally in murine fetal liver brings about hematopoietic failure and perinatal lethality. Importantly, loss of METTL3 induces the formation of endogenous dsRNAs that are characterized by high m6A modification in their native state, which further activates the aberrant innate immune response and results in hematopoietic defects by triggering the Mavs or Rnasel signaling (102). Furthermore, inhibition of Mavs or Rnasel signaling prevents the aberrant immune response and partially rescues the hematopoietic defects observed in METTL3-deficient cells in vitro and in vivo. These results suggest that METTL3-mediated m6A modification regulates the innate immune response during mammalian hematopoietic development (Figure 2).
Additionally, the abnormal differentiation of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSPCs) is a common feature of AML, which relates to the aberrantly low level of METTL3 (103). Loss of METTL3 enhances the p-AKT level, which contributes to the abnormal differentiation of HSPCs. Overall, METTL3 contributes to HSPC-induced AML by regulating p-AKT, providing a rationale for the therapeutic targeting of METTL3 in AML. As reported, Sun et al. (104) found that the downregulated level of METTL3 represents a novel prognostic factor and a promising therapeutic target for patients with ETV6/RUNX1-positive AML. Targeted suppression of METTL3 in the myeloid lineage reportedly confers protection against age-related and diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and obesity in mice and is accompanied by improved inflammatory and metabolic phenotypes (105). Loss of METTL3 leads to a marked elevation in the mRNA level of DNA damage-inducible transcript 4 (DDIT4) and a strong suppression of mTOR and NF-κB pathway in macrophages in response to cellular stress and cytokine stimulation (105). This indicates that METTL3-mediated m6A modification on DDIT4 mRNA results in macrophage metabolic reprogramming during NAFLD and obesity. These findings suggest that METTL3 is actively involved in leukemia (Figure 2).
Furthermore, the abnormally overexpressed METTL3 plays a critical role in AML progression, which relates to different development stages of AML. For example, Sang et al. (106) demonstrated that METTL3 expression is significantly upregulated in most patients with AML. Moreover, METTL3 overexpression is associated with shorter survival time in patients with AML because of its ability to promote cell proliferation and cell cycle progression. Conversely, suppression of METTL3 results in the upregulation of CDKN1A/p21 and reduces mouse double minute 2 (MDM2) mRNA stability, thereby activating the tumor protein 53 (p53) signaling pathway to promote cell proliferation while also facilitating apoptosis and differentiation. These findings suggest that elevated levels of METTL3 play an oncogenic role by targeting the CDKN1A/p21/MDM2/p53 signaling pathway in AML. Similarly, Li et al. (107) uncovered that Yin Yang 1 (YY1) is a transcription factor of METTL3 that interacts with the HDAC1/3 promoter region of METTL3 to promote METTL3 expression in a moderate liquid-liquid phase separation manner, which further enhances the proliferation of AML cells. Therefore, METTL3 acts as the oncogene for AML progression by regulating AML cell proliferation, which might be a biomarker for the developed AML diagnosis. Besides, Wu et al. (108) indicated that METTL3-mediated m6A modification on PSMA3-AS1 enhances the stability and level of PSMA3-AS1 in patients with FLT3-ITD+ AML, which in turn promotes AML cell autophagy by targeting miR-20a-5p that further downregulates ATG16L1 mRNA expression, ultimately promotes AML progression. Therefore, METTL3 enhances AML progression by promoting AML cell autophagy via the PSMA3-AS1/miR-20a-5p/ATG16L1 axis, which provides new horizons for early screening and targeted therapy of FLT3-ITD+ AML by targeting METTL3. Furthermore, circular RNAs (circRNAs), a class of non-coding RNAs, serve as important epigenetic regulators in AML progression (109). Large-scale sample detection found that circ-0001187 is only significantly downregulated in newly diagnosed patients with AML whereas is increased in patients with hematological complete remission compared with controls (110). Circ-0001187 sponges miR-499a- 5p to enhance the expression of E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF113A, which further mediates METTL3 ubiquitin/proteasome-dependent degradation to reduce METTL3 expression via K48-linked polyubiquitin chains. The inhibited level of METTL3 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of AML cells in vitro and in vivo. Therefore, METTL3 serves as the oncogenic target in AML, which is regulated by the circ-0001187/miR-499a-5p/RNF113A axis (Figure 2).
In summary, METTL3 contributes to the development of AML, suggesting its potential for AML diagnosis and classification.
Although great advances have been made in AML therapy, treatment failure occurs in many patients with poor outcomes. Therefore, further investigation of the underlying mechanism for AML treatment failure is required, which might be helpful in exploring new methods to improve AML treatment outcomes.
AML is a distinct hematologic malignancy that targets a specific subpopulation of blood-forming stem/progenitor cells (111). Specifically, AML is characterized by the malignant proliferation of immature bone marrow stem cells in the bone marrow and peripheral blood (112). The adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) confers chemoresistance to AML cells (111, 113). METTL3 plays a vital role in the sensitivity of AML cells to Cytarabine through its interaction with immune-infiltrating cells and autophagy (114). Besides, Pan et al. (115) observed a conspicuous reduction in METTL3 expression in BMSCs obtained from patients with AML, which stimulates BMSC adipogenesis and contributes to AML pathogenesis. The reduced level of METTL3 in BMSCs functions by mediating m6A modification on AKT1 transcripts to increase its mRNA stability and induce AKT1 protein expression, thereby activating the PI3K/AKT pathway that causes BMSC adipogenesis and chemoresistance in AML cells. These findings suggest that the METTL3-mediated m6A modification on AKT1 is responsible for AML chemoresistance induced by BMSC adipogenesis, hinting at the possibility of targeting METTL3 for BMSC adipogenesis regulation and AML chemoresistance removal. The homing/engraftment in bone marrow (BM) is a crucial step for AML cells to acquire chemoresistance by interacting with stromal cell components, which relates to the upregulated expression of METTL3 in chemoresistant cells (116). Specifically, METTL3-mediated m6A modification on ITGA4 mRNA induces ITGA4 expression, which further enhances the homing/engraftment of AML cell chemoresistance in vitro and in vivo. Importantly, inhibition of METTL3 improves homing/engraftment chemoresistance in AML cells. These results suggest that METTL3-mediated m6A modification functions in the interaction between AML cells and BM niches and clarify the relationship between METTL3 and AML homing/engraftment, suggesting a therapeutic strategy for the treatment of refractory/relapsed AML with METTL3 inhibitors (Figure 2).
Adriamycin chemoresistance poses a great threat in AML therapy (117). Transcriptome-wide analysis of RNA m6A modification in Adriamycin-resistant AML cells found that the expression level of METTL3 is elevated, which modifies m6A on genes that are enriched in pathways of the FoxO signaling pathway, p53 signaling pathway, and Notch signaling pathway (118). After a combined treatment of STM2457 (an inhibitor of METTL3) and Adriamycin, the proliferation of AML cells is inhibited. Thus, the abnormality of METTL3-mediated m6A modification plays an important role in AML Adriamycin resistance. Similarly, low levels of lncRNA maternally expressed gene 3 (MEG3) and miR-493-5p are associated with Adriamycin resistance and poor prognosis in patients with AML (119). Wang et al. (119) found that MEG3 leads to elevated expression of miR-493-5p that further targets METTL3. Subsequently, METTL3 elevates the m6A level of MYC to increase MYC expression, leading to Adriamycin resistance in AML cells. Importantly, suppression of METTL3 inhibits AML cell proliferation and promotes their apoptosis, improving Adriamycin sensitivity in AML cells. Collectively, MEG3 and miR-493-5p promote the Adriamycin resistance of AML cells by inactivating the METTL3/MYC axis (Figure 2).
In summary, METTL3 plays an oncogenic role in AML chemoresistance and is associated with poor outcomes in patients with AML. Therefore, we propose that targeting METTL3 represents a rational and promising therapeutic strategy for improving AML treatment failure.
The skin serves as a primary barrier against microbial invasion via the production and secretion of vital antimicrobial proteins by skin cells and the presence of immune cells in specific layers (120). It has been demonstrated that the monoclonal proliferation of T lymphocytes in the skin contributes to the onset of cutaneous T cell lymphomas (CTCL) (121). Wang et al. (122) reported that METTL3 is significantly downregulated in CTCL cells, which is responsible for CTCL cell proliferation and migration by promoting CDKN2A mRNA degradation in an m6A reader IGF2BP2 dependent way. This study suggests the participation of METTL3-mediated m6A modification in regulating the function of skin immune cells that trigger the onset and progression of skin cancers. However, the exact mechanism is still unclear and needs further exploration. Generally, uncontrolled cell proliferation and migration, cell cycle progression, as well as EMT, are indicative of aggressive processes for tumorigenesis and metastasis (123). Exploring the molecular mechanism for these processes from the perspective of METTL3-mediated m6A modification has been reported in skin cancers, which are highly aggressive malignancies originating in the skin and occur during the immunosuppression process, including melanoma, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC), acral melanoma, and keratinocyte transformation (124) (Table 4).
METTL3 functions in these skin cancers either directly as the oncogene or indirectly by mediating RNA m6A modification on RNAs to regulate their fate and functions, including mRNA stability, nuclear processing, transport, localization, translation, primary microRNA processing, and RNA-protein interactions. Chang et al. (125) demonstrated that METTL3 is a direct target gene of miR-302a-3p in melanoma cells, which upregulates METTL3 expression. The extensive expression of METTL3 further activates the PI3K/AKT pathway in melanoma cells, which subsequently facilitates cell proliferation, invasion, and cell cycle progression, as well as EMT marker expression, while suppressing apoptosis. These findings suggest that METTL3 functions directly as the oncogene to facilitate melanoma metastasis by regulating the METTL3-PI3K/AKT axis. Moreover, uridine cytidine kinase 2 (UCK2) is an oncogene that is associated with poor survival in patients with melanoma. Wu et al. (126) reported that the extensively increased expression of METTL3 enhances UCK2 mRNA stability and expression by mediating m6A modification on UCK2 transcripts; this subsequently promotes melanoma progression by regulating the WNT/beta-catenin pathway. Therefore, METTL3 functions indirectly by targeting oncogene UCK2, which is a promising target for preventing and treating melanoma. In addition, the MMP family contributes to the metastasis of melanoma cells. Dahal et al. (127) reported that the elevated levels of METTL3 in melanoma cells typically facilitate the accumulation of MMP family members such as MMP2 and N-cadherin. Remarkably, the upregulation of METTL3 with a catalytic site mutation result in increased expression of MMP2 and N-cadherin, thereby indicating that the METTL3-mediated m6A modification of MMP2 and N-cadherin contributes to colony formation and invasion of melanoma cells. These findings highlight that METTL3 plays an important role in human melanoma invasion by targeting oncogenes MMP2 and N-cadherin (Table 4).
Furthermore, Zhou et al. (128) found that METTL3-mediated RNA m6A modification plays an oncogenic role in cSCC, and the same is evidenced by the upregulation of both METTL3 and m6A, together with DNp63 expression. This highlights that METTL3 has a critical role in regulating cSCC tumorigenesis by targeting DNp63. Another study revealed that METTL3 expression is upregulated via direct methylation on thioredoxin domain-containing protein 5 (TXNDC5) mRNA in acral melanoma tissues and this upregulation is associated with advanced stages in patients with primary acral melanoma (129). This suggests that METTL3 promotes acral melanoma progression by targeting TXNDC5 and highlights the m6A-dependent METTL3 signaling pathway as a promising therapeutic strategy for treating patients under this condition. Additionally, Zhao et al. (130) demonstrated that an elevated level of METTL3 triggers the transformation of human keratinocytes through p53 pathway deactivation. METTL3 collaborates with YTHDF1 to facilitate the degradation of PR/SET domain 2 (PRDM2) mRNA (a positive regulator of p53) and with YTHDF1 to augment the translation of YY1 and MDM2 mRNA (a negative regulator of p53). Briefly, METTL3 facilitates p53 signaling in human keratinocytes by deactivating the YTHDF2/PRDM2 axis and activating the YTHDF1/YY1-MDM2A axis (Table 4).
An emerging concept posits that cancer progression may be partially attributable to the escape of cancer cells from immune surveillance (131). Immune evasion may arise from an overabundance of inhibitory immune cells or cytokines and other poorly understood factors (132). A comprehensive pan-cancer analysis suggests that a high level of METTL3 in most cancers usually is indicative of poor outcomes and low disease-free survival rates (133). Importantly, METTL3 levels are strongly linked to immune cell infiltration and immune checkpoint gene levels, which regulate the tumor immune microenvironments and EMT via modulating RNA modification and metabolism (133). Specifically, METTL3 plays a vital role in the sensitivity of AML cells to Cytarabine through its interaction with immune-infiltrating cells and autophagy (114). Therefore, METTL3 serves as an oncogene in most cancers and shows potential as a prognostic biomarker and a potential therapeutic target. As reported, the knockdown of METTL3 and METTL14 augments the efficacy of PD-L1 treatment in colorectal cancer and melanoma, boosting the infiltration of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells into tumor tissues and elevating the secretion of IFN-c, CXCL9, and CXCL10 within the tumor-associated macrophages (134). Mechanistically, knockdown of either METTL3 or METTL14 promotes IFN-C/IFN-C/STAT1/IRF1 signaling by stabilizing STAT1 and IRF1 mRNAs via an YTHDF2-dependent mechanism. Moreover, m6A-related lncRNA TRAF3IP2-AS1 predicts prognosis and designs immunotherapy in patients with AML (135). Therefore, METTL3-mediated RNA m6A modification plays a crucial role in adaptive immunity and is a novel mechanism underlying the failure of cancer immunotherapy. Targeting METTL3 may hold promise as a potential therapeutic strategy for improving anticancer immunotherapy.
METTL3 and its role in RNA m6A modification are intricately linked to the development and progression of immune dysfunctions in humans (136). This review aims to provide a thorough overview, categorization, and analysis of research surrounding METTL3, elucidating its functions, underlying mechanisms, applications, and future prospects in immune disorders, which encompass antiviral immune suppression (due to viral infections) and disruptions in immune tolerance (related to autoimmune diseases, myeloid leukemia, skin cancers, and anticancer immunotherapy).
The findings suggest that METTL3-mediated RNA m6A modification plays a significant role in immune system irregularities. Elevated levels of METTL3 are associated with infections during periods of antiviral immune suppression, particularly enhancing the replication of enteroviruses such as PEDV, rotavirus, and EV71. In this context, METTL3 mainly influences inflammation and creates a supportive microenvironment, while its downregulation aids in the recovery of antiviral innate immunity and the clearance of viruses. Consequently, heightened METTL3 levels may act as both a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker and represent a promising target in the context of infections. Conversely, during immune tolerance breakdown, METTL3 can function as an oncogene, either directly or indirectly targeting other oncogenes, thereby driving the onset and advancement of autoimmune diseases, myelocytic leukemia, and skin cancers, as well as contributing to the ineffectiveness of anticancer immunotherapy. The mechanisms through which METTL3 operates in immune dysfunction include the modulation of inflammation, oxidative stress, autophagy, cell proliferation, apoptosis, and the cell cycle. Overall, this review underscores METTL3 as a significant factor in triggering immune dysfunctions.
However, research by Barbieri et al. (137) indicates that METTL3 is essential for the proliferation of AML cells, with its downregulation hindering the cell cycle and differentiation of these cells. This effect is mediated through its association with chromatin and its localization to the transcription start site of active genes that bind the CAATT-box binding protein CEBPZ. Collectively, these contrasting observations suggest that METTL3 regulates a novel chromatin-based pathway vital for sustaining the AML state and highlights it as a promising therapeutic target for preventing AML progression. Additionally, the findings concerning METTL3’s expression and function in the pathogenesis of CML and AML exhibit inconsistencies, likely due to differences in sample selection. Notwithstanding these disparities, the majority of studies support the oncogenic role of METTL3 in the progression of myelocytic leukemia. In terms of its implications in abnormal immune conditions, METTL3 holds potential as both a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for distinguishing between CML and AML, as well as representing a promising therapeutic target for myelocytic leukemia. Nonetheless, further extensive data from both basic and clinical research are necessary to strengthen the evidence supporting their association and clinical significance.
Exploring the dual roles of METTL3 in both diagnostic and therapeutic contexts opens a wealth of research opportunities. One significant avenue for future research is the development of METTL3-targeting therapies. Given its implication in various cancers and autoimmune diseases, targeted inhibition or modulation of METTL3 activity could provide a novel therapeutic strategy. For instance, small molecule inhibitors or RNA-based therapies could be designed to specifically target METTL3, potentially halting the progression of diseases where METTL3 acts as an oncogene (138–141). Moreover, the precise mechanisms by which METTL3 contributes to the breakdown of immune tolerance and subsequent disease progression warrant further investigation. Understanding these pathways could reveal additional therapeutic targets and refine existing treatments. For example, identifying co-factors or downstream effectors of METTL3 could help in developing combination therapies that enhance the efficacy of current treatments or mitigate side effects. Another critical research direction involves the validation of METTL3 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker. Large-scale clinical trials are essential to establish the reliability and specificity of METTL3 levels in predicting disease onset, progression, and patient outcomes. Such trials should encompass a diverse patient population to ensure the generalizability of the findings. Furthermore, incorporating advanced techniques such as single-cell RNA sequencing and CRISPR-based gene editing could provide deeper insights into the role of METTL3 at the cellular and molecular levels. Beyond oncology and autoimmune diseases, the role of METTL3 in infectious diseases presents another promising research frontier. Investigating how METTL3 modulates the host immune response to various pathogens could uncover novel therapeutic targets and improve our understanding of host-pathogen interactions. For instance, exploring the interplay between METTL3 and viral replication mechanisms could lead to the development of antiviral therapies that exploit this relationship. In addition to these specific areas, there is a broader need to understand the context-dependent functions of METTL3. Its role as both an oncogene and a regulator of immune response highlights the complexity of its functions and necessitates a nuanced approach to therapeutic development. Research should aim to delineate the conditions under which METTL3 acts beneficially versus detrimentally, potentially leading to personalized medicine approaches where METTL3-targeting therapies are tailored to individual patients based on their specific disease context and METTL3 expression profiles. Furthermore, the potential off-target effects and long-term consequences of METTL3 inhibition need to be thoroughly evaluated. Preclinical studies in animal models and subsequent phase I/II clinical trials will be crucial for assessing the safety and efficacy of METTL3-targeting therapies. These studies should also explore the potential for resistance development and identify biomarkers that can predict patient response to treatment. In conclusion, METTL3 represents a multifaceted target with significant implications for both diagnostics and therapeutics. Expanding our understanding of its roles across different diseases and contexts will be key to unlocking its full potential. Future research should focus on elucidating the detailed mechanisms of METTL3 action, validating it as a biomarker in clinical settings, and developing targeted therapies that can be integrated into personalized treatment regimens. Through these efforts, we can better harness the power of METTL3 to improve patient outcomes across a range of diseases.
In summary, this review offers an in-depth interpretation of the connection between METTL3 and immune-related pathological events, while also underscoring its potential clinical applications. Therefore, it sheds light on existing gaps in the literature that need to be addressed, serving as a valuable reference for both researchers and clinicians.
DZ: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. TX: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. XG: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. YQ: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. XS: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 82371717) and a Grant from the Science and Technology Bureau of Sichuan Province (2024NSFSC0047).
We would like to thank Edit age (www.editage.cn) for English language editing.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1523503/full#supplementary-material
1. Futata EA, Fusaro AE, de Brito CA, Sato MN. The neonatal immune system: immunomodulation of infections in early life. Expert Rev anti-infective Ther. (2012) 10:289–98. doi: 10.1586/eri.12.9
2. Marshall GD Jr. Psychological stress, immune dysfunction, and allergy: Opportunities for improved patient health. Ann allergy Asthma immunology: Off Publ Am Coll Allergy Asthma Immunol. (2020) 125:365–6. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2020.08.020
3. James C, Bernstein DI. Allergen immunotherapy: an updated review of safety. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. (2017) 17:55–9. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000335
4. Dumas G, Arabi YM, Bartz R, Ranzani O, Scheibe F, Darmon M, et al. Diagnosis and management of autoimmune diseases in the ICU. Intensive Care Med. (2024) 50:17–35. doi: 10.1007/s00134-023-07266-7
5. Cui L, Ma R, Cai J, Guo C, Chen Z, Yao L, et al. RNA modifications: importance in immune cell biology and related diseases. Signal transduction targeted Ther. (2022) 7:334. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01175-9
6. Wang X, Lu Z, Gomez A, Hon GC, Yue Y, Han D, et al. N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature. (2014) 505:117–20. doi: 10.1038/nature12730
7. Tang Y, Chen K, Song B, Ma J, Wu X, Xu Q, et al. m6A-Atlas: a comprehensive knowledgebase for unraveling the N6-methyladenosine (m6A) epitranscriptome. Nucleic Acids Res. (2021) 49:D134–d43. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa692
8. He PC, He C. m(6) A RNA methylation: from mechanisms to therapeutic potential. EMBO J. (2021) 40:e105977. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020105977
9. Su X, Feng Y, Qu Y, Mu D. Association between methyltransferase-like 3 and non-small cell lung cancer: pathogenesis, therapeutic resistance, and clinical applications. Trans Lung Cancer Res. (2024) 13:1121–36. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-85
10. Meyer KD, Jaffrey SR. Rethinking m(6)A readers, writers, and erasers. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. (2017) 33:319–42. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100616-060758
11. Shen D, Wang B, Gao Y, Zhao L, Bi Y, Zhang J, et al. Detailed resume of RNA m(6)A demethylases. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2022) 12:2193–205. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.01.003
12. Zhao Y, Shi Y, Shen H, Xie W. m(6)A-binding proteins: the emerging crucial performers in epigenetics. J Hematol Oncol. (2020) 13:35. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00872-8
13. Fang Z, Mei W, Qu C, Lu J, Shang L, Cao F, et al. Role of m6A writers, erasers and readers in cancer. Exp Hematol Oncol. (2022) 11:45. doi: 10.1186/s40164-022-00298-7
14. Bayoumi M, Munir M. Structural insights into m6A-erasers: A step toward understanding molecule specificity and potential antiviral targeting. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2020) 8:587108. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.587108
15. Feng H, Yuan X, Wu S, Yuan Y, Cui L, Lin D, et al. Effects of writers, erasers and readers within miRNA-related m6A modification in cancers. Cell proliferation. (2023) 56:e13340. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13340
16. You SY, Su XJ, Ying JJ, Li SP, Qu Y, Mu DZ. Research progress on the role of RNA m6A modification in glial cells in the regulation of neurological diseases. Biomolecules. (2022) 12:1158. doi: 10.3390/biom12081158
17. Wang JF, Cai W, Qiu FS, Yu CH. Pathogenic roles of m6A modification in viral infection and virus-driven carcinogenesis. Endocrine Metab Immune Disord Drug targets. (2022) 22:1009–17. doi: 10.2174/2772432817666220412112759
18. Su X, Qu Y, Mu D. The regulatory network of METTL3 in the nervous system: diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Biomolecules. (2023) 13:664. doi: 10.3390/biom13040664
19. Liu S, Zhuo L, Wang J, Zhang Q, Li Q, Li G, et al. METTL3 plays multiple functions in biological processes. Am J Cancer Res. (2020) 10:1631–46.
20. Liu X, Wang H, Yuan M, Zhang T, Wang Q, Chen N, et al. m6A-modified RIOK3 activated the NF-κB-signaling pathway by CDC42, promoting the replication and proliferation of enterovirus. Int J Biol Macromol. (2025) 305:140988. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.140988
21. Wang X, Chen C, Sun H, Mao K, Yao J, Zhang W, et al. m6A mRNA modification potentiates Th17 functions to inflame autoimmunity. Sci China Life Sci. (2023) 66:2543–52. doi: 10.1007/s11427-022-2323-4
22. Ganguly M, Gupta R, Roychowdhury A, Hazra D. De novo drug designing coupled with brute force screening and structure guided lead optimization gives highly specific inhibitor of METTL3: a potential cure for Acute Myeloid Leukaemia. J Biomol Struct Dyn. (2025) 43:1038–51. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2291162
23. Dutheuil G, Oukoloff K, Korac J, Lenoir F, El Bousmaqui M, Probst N, et al. Discovery, optimization, and preclinical pharmacology of EP652, a METTL3 inhibitor with efficacy in liquid and solid tumor models. J Med Chem. (2025) 68:2981–3003. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c02225
24. Taebnia N, Römling U, Lauschke VM. In vitro and ex vivo modeling of enteric bacterial infections. Gut Microbes. (2023) 15:2158034. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2158034
25. Kaltsas A, Sepkowitz K. Community acquired respiratory and gastrointestinal viral infections: challenges in the immunocompromised host. Curr Opin Infect diseases. (2012) 25:423–30. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0b013e328355660b
26. Xu J, Cai Y, Ma Z, Jiang B, Liu W, Cheng J, et al. The RNA helicase DDX5 promotes viral infection via regulating N6-methyladenosine levels on the DHX58 and NFkappaB transcripts to dampen antiviral innate immunity. PLoS pathogens. (2021) 17:e1009530. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009530
27. Chen J, Jin L, Wang Z, Wang L, Chen Q, Cui Y, et al. N6-methyladenosine regulates PEDV replication and host gene expression. Virology. (2020) 548:59–72. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2020.06.008
28. Zhang Y, Wang X, Zhang X, Wang J, Ma Y, Zhang L, et al. RNA-binding protein YTHDF3 suppresses interferon-dependent antiviral responses by promoting FOXO3 translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2019) 116:976–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1812536116
29. Yao M, Dong Y, Wang Y, Liu H, Ma H, Zhang H, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine modifications enhance enterovirus 71 ORF translation through METTL3 cytoplasmic distribution. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2020) 527:297–304. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.04.088
30. Hao H, Hao S, Chen H, Chen Z, Zhang Y, Wang J, et al. N6-methyladenosine modification and METTL3 modulate enterovirus 71 replication. Nucleic Acids Res. (2019) 47:362–74. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1007
31. Yang L, Wu G, Wu Q, Peng L, Yuan L. METTL3 overexpression aggravates LPS-induced cellular inflammation in mouse intestinal epithelial cells and DSS-induced IBD in mice. Cell Death discovery. (2022) 8:62. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-00849-1
32. Jiang D, Hou J, Qian Y, Gao Y, Gao X, Wei S. YTHDF1-regulated expression of TEAD1 contributes to the maintenance of intestinal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2021) 557:85–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.03.175
33. N’Da Konan S, Segeral E, Bejjani F, Bendoumou M, Ait Said M, Gallois-Montbrun S, et al. YTHDC1 regulates distinct post-integration steps of HIV-1 replication and is important for viral infectivity. Retrovirology. (2022) 19:4. doi: 10.1186/s12977-022-00589-1
34. Zheng X, Wang J, Zhang X, Fu Y, Peng Q, Lu J, et al. RNA m(6) A methylation regulates virus-host interaction and EBNA2 expression during Epstein-Barr virus infection. Immunity Inflammation disease. (2021) 9:351–62. doi: 10.1002/iid3.v9.2
35. Gehart H, Clevers H. Tales from the crypt: new insights into intestinal stem cells. Nat Rev Gastroenterol hepatology. (2019) 16:19–34. doi: 10.1038/s41575-018-0081-y
36. Gallo RC. Some reflections on HIV/AIDS research after 40 years. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. (2021) 321:L1057–L8. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00442.2021
37. Selberg S, Zusinaite E, Herodes K, Seli N, Kankuri E, Merits A, et al. HIV replication is increased by RNA methylation METTL3/METTL14/WTAP complex activators. ACS omega. (2021) 6:15957–63. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c01626
38. Akar-Ghibril N. Defects of the innate immune system and related immune deficiencies. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. (2022) 63:36–54. doi: 10.1007/s12016-021-08885-y
39. Papa G, Burrone OR. Rotavirus reverse genetics: A tool for understanding virus biology. Virus Res. (2021) 305:198576. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2021.198576
40. Wang A, Tao W, Tong J, Gao J, Wang J, Hou G, et al. m6A modifications regulate intestinal immunity and rotavirus infection. eLife. (2022) 11:e73628. doi: 10.7554/eLife.73628
41. Winkler R, Gillis E, Lasman L, Safra M, Geula S, Soyris C, et al. m(6)A modification controls the innate immune response to infection by targeting type I interferons. Nat Immunol. (2019) 20:173–82. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0275-z
42. Burgess HM, Depledge DP, Thompson L, Srinivas KP, Grande RC, Vink EI, et al. Targeting the m(6)A RNA modification pathway blocks SARS-CoV-2 and HCoV-OC43 replication. Genes Dev. (2021) 35:1005–19. doi: 10.1101/gad.348320.121
43. Li N, Hui H, Bray B, Gonzalez GM, Zeller M, Anderson KG, et al. METTL3 regulates viral m6A RNA modification and host cell innate immune responses during SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell Rep. (2021) 35:109091. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109091
44. Lu M, Xue M, Wang HT, Kairis EL, Ahmad S, Wei J, et al. Nonsegmented negative-sense RNA viruses utilize N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) as a common strategy to evade host innate immunity. J Virol. (2021) 95:e01939-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01939-20
45. Qiu W, Zhang Q, Zhang R, Lu Y, Wang X, Tian H, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine RNA modification suppresses antiviral innate sensing pathways via reshaping double-stranded RNA. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:1582. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21904-y
46. Su X, Lu R, Qu Y, Mu D. Diagnostic and therapeutic potentials of methyltransferase-like 3 in liver diseases. Biomedicine pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine pharmacotherapie. (2024) 172:116157. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116157
47. Yang L, Jin R, Lu D, Ge Q. T cell tolerance in early life. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:576261. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.576261
48. Kucuksezer UC, Ozdemir C, Akdis M, Akdis CA. Influence of innate immunity on immune tolerance. Acta Med academica. (2020) 49:164–80. doi: 10.5644/ama2006-124.295
49. De Luca F, Shoenfeld Y. The microbiome in autoimmune diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. (2019) 195:74–85. doi: 10.1111/cei.13158
50. Munoz CM, Goulden B, Ahmed K, Alijotas-Reig J, Giles I. Risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes prior to the onset of an autoimmune rheumatic disease: a systematic review. Rheumatology. (2023) 62:497–511. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keac417
51. Su X, Qu Y, Mu D. Methyltransferase-like 3 modifications of RNAs: Implications for the pathology in the endocrine system. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol basis disease. (2024) 1870:167010. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.167010
52. Lee HJ, Li CW, Hammerstad SS, Stefan M, Tomer Y. Immunogenetics of autoimmune thyroid diseases: A comprehensive review. J autoimmunity. (2015) 64:82–90. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2015.07.009
53. Antonelli A, Ferrari SM, Ragusa F, Elia G, Paparo SR, Ruffilli I, et al. Graves’ disease: Epidemiology, genetic and environmental risk factors and viruses. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2020) 34:101387. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2020.101387
54. Zucchi D, Silvagni E, Elefante E, Signorini V, Cardelli C, Trentin F, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus: one year in review 2023. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2023) 41:997–1008. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/4uc7e8
55. Jang S, Kwon EJ, Lee JJ. Rheumatoid arthritis: pathogenic roles of diverse immune cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:905. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020905
56. Thorlacius GE, Björk A, Wahren-Herlenius M. Genetics and epigenetics of primary Sjögren syndrome: implications for future therapies. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2023) 19:288–306. doi: 10.1038/s41584-023-00932-6
57. Pandey R, Bakay M, Hakonarson H. SOCS-JAK-STAT inhibitors and SOCS mimetics as treatment options for autoimmune uveitis, psoriasis, lupus, and autoimmune encephalitis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1271102. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1271102
58. Hehir MK, Silvestri NJ. Generalized myasthenia gravis: classification, clinical presentation, natural history, and epidemiology. Neurologic clinics. (2018) 36:253–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ncl.2018.01.002
59. Riddell MC, Peters AL. Exercise in adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinology. (2023) 19:98–111. doi: 10.1038/s41574-022-00756-6
60. Yazar S, Alquicira-Hernandez J, Wing K, Senabouth A, Gordon MG, Andersen S, et al. Single-cell eQTL mapping identifies cell type-specific genetic control of autoimmune disease. Science. (2022) 376:eabf3041. doi: 10.1126/science.abf3041
61. Song RH, Liu XR, Gao CQ, Du P, Zhang JA. METTL3 gene polymorphisms contribute to susceptibility to autoimmune thyroid disease. Endocrine. (2021) 72:495–504. doi: 10.1007/s12020-020-02503-1
62. Song RH, Du P, Gao CQ, Liu XR, Zhang JA. METTL3 Is Involved in the Development of Graves’ Disease by Inducing SOCS mRNA m6A Modification. Front endocrinology. (2021) 12:666393. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.666393
63. Lu S, Wei X, Zhu H, Hu Z, Zheng M, Wu J, et al. m(6)A methyltransferase METTL3 programs CD4(+) T-cell activation and effector T-cell differentiation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol Med (Cambridge Mass). (2023) 29:46. doi: 10.1186/s10020-023-00643-4
64. Xiao J, Cai X, Wang R, Zhou W, Ye Z. Identification of synovial fibroblast-associated neuropeptide genes and m6A factors in rheumatoid arthritis using single-cell analysis and machine learning. Dis markers. (2022) 2022:5114697. doi: 10.1155/2022/5114697
65. Shi W, Zheng Y, Luo S, Li X, Zhang Y, Meng X, et al. METTL3 promotes activation and inflammation of FLSs through the NF-κB signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Med. (2021) 8:607585. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.607585
66. Lu H, Lu X, Xie Q, Wan H, Sun Y. TTC4 inhibits NLRP3 inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis by HSP70. Int J rheumatic diseases. (2023) 26:1751–9. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.14818
67. Chen J, Lin X, He J, Liu D, He L, Zhang M, et al. Artemisitene suppresses rheumatoid arthritis progression via modulating METTL3-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of ICAM2 mRNA in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Clin Trans Med. (2022) 12:e1148. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.v12.12
68. Ma J, Wang X, Yang X, Wang X, Tan T, Fang H, et al. Increased METTL3 expression and m(6)A RNA methylation may contribute to the development of dry eye in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. BMC ophthalmology. (2023) 23:252. doi: 10.1186/s12886-023-02988-0
69. Zhao L, Liu Y, Ma B, Liu X, Wei R, Nian H. METTL3 inhibits autoreactive Th17 cell responses in experimental autoimmune uveitis via stabilizing ASH1L mRNA. FASEB journal: Off Publ Fed Am Societies Exp Biol. (2023) 37:e22803. doi: 10.1096/fj.202201548R
70. Wei Y, Yang C, Liu Y, Sun D, Li X, Wei R, et al. Mettl3 induced miR-338-3p expression in dendritic cells promotes antigen-specific Th17 cell response via regulation of Dusp16. FASEB journal: Off Publ Fed Am Societies Exp Biol. (2023) 37:e23277. doi: 10.1096/fj.202300893R
71. Fu J, Wu H. Structural mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and activation. Annu Rev Immunol. (2023) 41:301–16. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-081022-021207
72. Li Y, Wang S, Liu Y, Zhang Y. Serum pentaxin 3 (PTX3) promotes NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis in patients with up-regulated myasthenia gravis. Front bioscience (Landmark edition). (2023) 28:306. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2811306
73. Ameer MA, Chaudhry H, Mushtaq J, Khan OS, Babar M, Hashim T, et al. An overview of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) pathogenesis, classification, and management. Cureus. (2022) 14:e30330. doi: 10.7759/cureus.30330
74. Luo Q, Fu B, Zhang L, Guo Y, Huang Z, Li J. Decreased peripheral blood ALKBH5 correlates with markers of autoimmune response in systemic lupus erythematosus. Dis markers. (2020) 2020:8193895. doi: 10.1155/2020/8193895
75. Liu Y, Wang X, Huang M, Luo A, Liu S, Cai M, et al. METTL3 facilitates kidney injury through promoting IRF4-mediated plasma cell infiltration via an m6A-dependent manner in systemic lupus erythematosus. BMC Med. (2024) 22:511. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03735-y
76. Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ. The immunology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Immunol. (2021) 22:10–8. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-00816-x
77. Cheng L, Wang Y, Wu R, Ding T, Xue H, Gao C, et al. New insights from single-cell sequencing data: synovial fibroblasts and synovial macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:709178. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.709178
78. Villanueva-Romero R, Gutiérrez-Cañas I, Carrión M, Pérez-García S, Seoane IV, Martínez C, et al. The anti-inflammatory mediator, vasoactive intestinal peptide, modulates the differentiation and function of th subsets in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol Res. (2018) 2018:6043710. doi: 10.1155/2018/6043710
79. Kemble S, Croft AP. Critical role of synovial tissue-resident macrophage and fibroblast subsets in the persistence of joint inflammation. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:715894. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.715894
80. Matsuda K, Shiba N, Hiraoka K. New insights into the role of synovial fibroblasts leading to joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:5173. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065173
81. Chwastek J, Kędziora M, Borczyk M, Korostyński M, Starowicz K. Inflammation-driven secretion potential is upregulated in osteoarthritic fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:11817. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911817
82. Lowin T, Straub RH. Synovial fibroblasts integrate inflammatory and neuroendocrine stimuli to drive rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. (2015) 11:1069–71. doi: 10.1586/1744666X.2015.1066674
83. Su Y, Wu Z, Liu Y, Liu X, Kang J, Jia J, et al. Increased m6A RNA methylation and METTL3 expression may contribute to the synovitis progression of rheumatoid arthritis. Exp Cell Res. (2024) 442:114237. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.114237
84. Ren H, Wei G, Kong Z, Zhang M, Li Y, Liu S, et al. METTL3-mediated methylation of RAC2 contributes to cell motility, oxidative stress and inflammation in TNF-α-stimulated rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synovial cells. J Orthop Surg Res. (2025) 20:180. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05526-4
85. Talman AM, Clain J, Duval R, Ménard R, Ariey F. Artemisinin bioactivity and resistance in malaria parasites. Trends parasitology. (2019) 35:953–63. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2019.09.005
86. Chen GQ, Benthani FA, Wu J, Liang D, Bian ZX, Jiang X. Artemisinin compounds sensitize cancer cells to ferroptosis by regulating iron homeostasis. Cell Death Differ. (2020) 27:242–54. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0352-3
87. Gao F, Sun Z, Kong F, Xiao J. Artemisinin-derived hybrids and their anticancer activity. Eur J medicinal Chem. (2020) 188:112044. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112044
88. Khatri B, Tessneer KL, Rasmussen A, Aghakhanian F, Reksten TR, Adler A, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies Sjögren’s risk loci with functional implications in immune and glandular cells. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:4287. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30773-y
89. Desvaux E, Pers JO. Autoimmune epithelitis in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Joint Bone spine. (2023) 90:105479. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2022.105479
90. Zhong J, Ding R, Jiang H, Li L, Wan J, Feng X, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals the molecular features of peripheral blood immune cells in children, adults and centenarians. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1081889. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1081889
91. Hysa E, Cutolo CA, Gotelli E, Pacini G, Schenone C, Kreps EO, et al. Immunopathophysiology and clinical impact of uveitis in inflammatory rheumatic diseases: An update. Eur J Clin Invest. (2021) 51:e13572. doi: 10.1111/eci.13572
92. Guo K, Zhang X. Cytokines that modulate the differentiation of th17 cells in autoimmune uveitis. J Immunol Res. (2021) 2021:6693542. doi: 10.1155/2021/6693542
93. Yasuda K, Takeuchi Y, Hirota K. The pathogenicity of Th17 cells in autoimmune diseases. Semin immunopathology. (2019) 41:283–97. doi: 10.1007/s00281-019-00733-8
94. Wu B, Wan Y. Molecular control of pathogenic Th17 cells in autoimmune diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. (2020) 80:106187. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106187
95. Zhong Z, Su G, Kijlstra A, Yang P. Activation of the interleukin-23/interleukin-17 signalling pathway in autoinflammatory and autoimmune uveitis. Prog retinal eye Res. (2021) 80:100866. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2020.100866
96. Zoine JT, Moore SE, Velasquez MP. Leukemia’s next top model? Syngeneic models to advance adoptive cellular therapy. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:867103. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.867103
97. Jayavelu AK, Wolf S, Buettner F, Alexe G, Haupl B, Comoglio F, et al. The proteogenomic subtypes of acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell. (2022) 40:301–17.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2022.02.006
98. Ianniello Z, Sorci M, Ginistrelli LC, Iaiza A, Marchioni M, Tito C, et al. New insight into the catalytic -dependent and -independent roles of METTL3 in sustaining aberrant translation in chronic myeloid leukemia. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:870. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04169-7
99. Lai X, Wei J, Gu XZ, Yao XM, Zhang DS, Li F, et al. Dysregulation of LINC00470 and METTL3 promotes chemoresistance and suppresses autophagy of chronic myelocytic leukaemia cells. J Cell Mol Med. (2021) 25:4248–59. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16478
100. Yao FY, Zhao C, Zhong FM, Qin TY, Wen F, Li MY, et al. m(6)A Modification of lncRNA NEAT1 Regulates Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia Progression via miR-766-5p/CDKN1A Axis. Front Oncol. (2021) 11. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.679634
101. Stubbins RJ, Francis A, Kuchenbauer F, Sanford D. Management of acute myeloid leukemia: A review for general practitioners in oncology. Curr Oncol (Toronto Ont). (2022) 29:6245–59. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29090491
102. Gao Y, Vasic R, Song Y, Teng R, Liu C, Gbyli R, et al. m(6)A modification prevents formation of endogenous double-stranded RNAs and deleterious innate immune responses during hematopoietic development. Immunity. (2020) 52:1007–21.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.05.003
103. Vu LP, Pickering BF, Cheng Y, Zaccara S, Nguyen D, Minuesa G, et al. The N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A)-forming enzyme METTL3 controls myeloid differentiation of normal hematopoietic and leukemia cells. Nat Med. (2017) 23:1369–76. doi: 10.1038/nm.4416
104. Sun C, Chang L, Liu C, Chen X, Zhu X. The study of METTL3 and METTL14 expressions in childhood ETV6/RUNX1-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Mol Genet genomic Med. (2019) 7:e00933. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.v7.10
105. Qin Y, Li B, Arumugam S, Lu Q, Mankash SM, Li J, et al. m(6)A mRNA methylation-directed myeloid cell activation controls progression of NAFLD and obesity. Cell Rep. (2021) 37:109968. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109968
106. Sang L, Wu X, Yan T, Naren D, Liu X, Zheng X, et al. The m(6)A RNA methyltransferase METTL3/METTL14 promotes leukemogenesis through the mdm2/p53 pathway in acute myeloid leukemia. J Cancer. (2022) 13:1019–30. doi: 10.7150/jca.60381
107. Li M, Li M, Xia Y, Li G, Su X, Wang D, et al. HDAC1/3-dependent moderate liquid-liquid phase separation of YY1 promotes METTL3 expression and AML cell proliferation. Cell Death disease. (2022) 13:992. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05435-y
108. Wu S, Weng S, Zhou W, Chen Y, Liu Z. METTL3 affects FLT3-ITD+ acute myeloid leukemia by mediating autophagy by regulating PSMA3-AS1 stability. Cell Cycle (Georgetown Tex). (2023) 22:1232–45. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2023.2204770
109. Singh V, Uddin MH, Zonder JA, Azmi AS, Balasubramanian SK. Circular RNAs in acute myeloid leukemia. Mol cancer. (2021) 20:149. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01446-z
110. Yang X, Han F, Hu X, Li G, Wu H, Can C, et al. EIF4A3-induced Circ_0001187 facilitates AML suppression through promoting ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation of METTL3 and decreasing m6A modification level mediated by miR-499a-5p/RNF113A pathway. biomark Res. (2023) 11:59. doi: 10.1186/s40364-023-00495-4
111. Forte D, Garcia-Fernandez M, Sanchez-Aguilera A, Stavropoulou V, Fielding C, Martin-Perez D, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells support acute myeloid leukemia bioenergetics and enhance antioxidant defense and escape from chemotherapy. Cell Metab. (2020) 32:829–43.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.09.001
112. Pei J, Tang J, Hu Y, Wan X, Shi J, Wang H, et al. Effect of blood sampling management on reducing blood transfusions in very preterm infants. Chin Med J (Engl). (2023) 136:2389–91. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002596
113. Liao X, Cai D, Liu J, Hu H, You R, Pan Z, et al. Deletion of Mettl3 in mesenchymal stem cells promotes acute myeloid leukemia resistance to chemotherapy. Cell Death disease. (2023) 14:796. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06325-7
114. Yang J, Li L, Cheng J, Lu J, Zhang S, Wang S, et al. The m6A modulator-mediated cytarabine sensitivity and immune cell infiltration signature in acute myeloid leukemia. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2023) 149:11457–69. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05029-x
115. Pan ZP, Wang B, Hou DY, You RL, Wang XT, Xie WH, et al. METTL3 mediates bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell adipogenesis to promote chemoresistance in acute myeloid leukaemia. FEBS Open bio. (2021) 11:1659–72. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13165
116. Li M, Ye J, Xia Y, Li M, Li G, Hu X, et al. METTL3 mediates chemoresistance by enhancing AML homing and engraftment via ITGA4. Leukemia. (2022) 36:2586–95. doi: 10.1038/s41375-022-01696-w
117. Mattioli R, Ilari A, Colotti B, Mosca L, Fazi F, Colotti G. Doxorubicin and other anthracyclines in cancers: Activity, chemoresistance and its overcoming. Mol aspects Med. (2023) 93:101205. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2023.101205
118. Fang S, Peng B, Wen Y, Yang J, Wang H, Wang Z, et al. Transcriptome-wide analysis of RNA N(6)-methyladenosine modification in adriamycin-resistant acute myeloid leukemia cells. Front Genet. (2022) 13:833694. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.833694
119. Wang A, Chen Y, Shi L, Li M, Li L, Wang S, et al. Tumor-suppressive MEG3 induces microRNA-493-5p expression to reduce arabinocytosine chemoresistance of acute myeloid leukemia cells by downregulating the METTL3/MYC axis. J Trans Med. (2022) 20:288. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03456-x
120. Saheb Kashaf S, Proctor DM, Deming C, Saary P, Holzer M, Program NCS, et al. Integrating cultivation and metagenomics for a multi-kingdom view of skin microbiome diversity and functions. Nat Microbiol. (2022) 7:169–79. doi: 10.1038/s41564-021-01011-w
121. Kempf W, Kazakov DV, Kerl K. Cutaneous lymphomas: an update. Part 1: T-cell and natural killer/t-cell lymphomas and related conditions. Am J dermatopathology. (2014) 36:105–23. doi: 10.1097/DAD.0b013e318289b1db
122. Wang X, Hu M, Yu L, Wang X, Jiang X, Zhang G, et al. The “m6A writer” METTL3 and the “m6A reader” IGF2BP2 regulate cutaneous T-cell lymphomas progression via CDKN2A. Hematological Oncol. (2022) 40:567–76. doi: 10.1002/hon.v40.4
123. Huang Y, Hong W, Wei X. The molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies of EMT in tumor progression and metastasis. J Hematol Oncol. (2022) 15:129. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01347-8
124. Kalaora S, Nagler A, Wargo JA, Samuels Y. Mechanisms of immune activation and regulation: lessons from melanoma. Nat Rev Cancer. (2022) 22:195–207. doi: 10.1038/s41568-022-00442-9
125. Chang X, Lin YY, Bai LN, Zhu W. miR-302a-3p suppresses melanoma cell progression via targeting METTL3. J chemotherapy. (2022) 34:55–66. doi: 10.1080/1120009X.2021.1953886
126. Wu H, Xu H, Jia D, Li T, Xia L. METTL3-induced UCK2 m(6)A hypermethylation promotes melanoma cancer cell metastasis via the WNT/beta-catenin pathway. Ann Trans Med. (2021) 9:1155. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-2906
127. Dahal U, Le K, Gupta M. RNA m6A methyltransferase METTL3 regulates invasiveness of melanoma cells by matrix metallopeptidase 2. Melanoma Res. (2019) 29:382–9. doi: 10.1097/CMR.0000000000000580
128. Zhou R, Gao Y, Lv D, Wang C, Wang D, Li Q. METTL3 mediated m(6)A modification plays an oncogenic role in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by regulating DeltaNp63. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2019) 515:310–7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.05.155
129. Yue Z, Cao M, Hong A, Zhang Q, Zhang G, Jin Z, et al. m(6)A methyltransferase METTL3 promotes the progression of primary acral melanoma via mediating TXNDC5 methylation. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:770325. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.770325
130. Zhao T, Sun D, Zhao M, Lai Y, Liu Y, Zhang Z. N(6)-methyladenosine mediates arsenite-induced human keratinocyte transformation by suppressing p53 activation. Environ pollution. (2020) 259:113908. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113908
131. Simiczyjew A, Dratkiewicz E, Mazurkiewicz J, Zietek M, Matkowski R, Nowak D. The influence of tumor microenvironment on immune escape of melanoma. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:8359. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218359
132. Koymans KJ, Vrieling M, Gorham RD Jr., van Strijp JAG. Staphylococcal immune evasion proteins: structure, function, and host adaptation. Curr topics Microbiol Immunol. (2017) 409:441–89. doi: 10.1007/82_2015_5017
133. Guo Y, Heng Y, Chen H, Huang Q, Wu C, Tao L, et al. Prognostic values of METTL3 and its roles in tumor immune microenvironment in pan-cancer. J Clin Med. (2022) 12:155. doi: 10.3390/jcm12010155
134. Wang L, Hui H, Agrawal K, Kang Y, Li N, Tang R, et al. m(6) A RNA methyltransferases METTL3/14 regulate immune responses to anti-PD-1 therapy. EMBO J. (2020) 39:e104514. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020104514
135. Zhong F, Yao F, Cheng Y, Liu J, Zhang N, Li S, et al. m6A-related lncRNAs predict prognosis and indicate immune microenvironment in acute myeloid leukemia. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:1759. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05797-5
136. Zhang M, Gou Z, Qu Y, Su X. The indispensability of methyltransferase-like 3 in the immune system: from maintaining homeostasis to driving function. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1456891. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1456891
137. Barbieri I, Tzelepis K, Pandolfini L, Shi J, Millan-Zambrano G, Robson SC, et al. Promoter-bound METTL3 maintains myeloid leukaemia by m (6)A-dependent translation control. Nature. (2017) 552:126–31. doi: 10.1038/nature24678
138. Garbo S, Zwergel C, Battistelli C. m6A RNA methylation and beyond - The epigenetic machinery and potential treatment options. Drug Discovery Today. (2021) 26:2559–74. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2021.06.004
139. Oerum S, Meynier V, Catala M, Tisné C. A comprehensive review of m6A/m6Am RNA methyltransferase structures. Nucleic Acids Res. (2021) 49:7239–55. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab378
140. Huang W, Chen TQ, Fang K, Zeng ZC, Ye H, Chen YQ. N6-methyladenosine methyltransferases: functions, regulation, and clinical potential. J Hematol Oncol. (2021) 14:117. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01129-8
Keywords: methyltransferase-like 3, immune dysfunction, antiviral immunity, immune tolerance, diagnostic biomarker, therapeutic target
Citation: Zhang D, Xu T, Gao X, Qu Y and Su X (2025) Methyltransferase-like 3-mediated RNA N6-methyladenosine contributes to immune dysregulation: diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target. Front. Immunol. 16:1523503. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1523503
Received: 07 November 2024; Accepted: 11 March 2025;
Published: 24 March 2025.
Edited by:
Duanwu Zhang, Fudan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Hui Lu, Zhejiang University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Zhang, Xu, Gao, Qu and Su. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaojuan Su, eGlhb2p1YW5zdTIwMTdAMTYzLmNvbQ==; c3V4aWFvanVhbjIwMjNAc2N1LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.