
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Immunol. , 22 January 2025
Sec. Autoimmune and Autoinflammatory Disorders : Autoimmune Disorders
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1518181
This article is part of the Research Topic Autoimmunity: novel insights and future perspectives View all 38 articles
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a common chronic and systemic autoimmune disease. Numerous clinical studies have indicated a correlation between alterations in gut microbiota and the onset and progression of RA. This research aims to restore intestinal microbiota to a healthy state through the oral administration of Bifidobacterium in the early stages with the goal of delaying the onset and progression of RA.
Methods: Collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) rat model was constructed to assess the development of RA using arthritis clinical scores, paw thickness, pathological analysis of knee joint. The immune response was evaluated by determinating specific antibodies and cytokines in serum and synovial fluid. The expression of intestinal barrier protein was analyzed by qPCR to evaluate the intestinal barrier function. Alterations in gut microbiota and metabolites were assessed by 16S rDNA and non-targeted metabolomics.
Results: The findings reveal that administering Bifidobacterium animalis BD400 orally led to a significant reduction in arthritis clinical scores and paw swelling thickness in CIA rats. Additionally, there was a decrease in osteo-facial fusion and calcified cartilage thickening in the knee joint. Furthermore, the oral administration of B. animalis BD400 resulted in the down-regulation of inflammatory factors TNF-α and collagenase MMP-13 in the knee joint. Levels of specific antibodies (anti-CII IgG, anti-CII IgG1, and anti-CII IgG2a) and cytokine IL-17A in serum, as well as cytokines (TNF-α and IL-1β) in the synovial fluid of B. animalis BD400-treated CIA rats, were significantly reduced (p < 0.05). The gene expression levels of intestinal barrier proteins (occludin-1, MUC-2, and ZO-1) showed a significant increase (p < 0.05) in B. animalis BD400-treated CIA rats. The oral administration of B. animalis BD400 altered the composition of intestinal microorganisms in CIA rats at the phylum and genus levels, particularly affecting the genus HT002. B. animalis BD400 alleviates RA by down-regulating 1-methyl-L-histidine and urocanate in the histidine metabolism, laying a foundation for the RA prevention.
Conclusion: By affecting genus HT002 and histidine metabolism in the gut microbiota of CIA rats, B. animalis BD400 restored intestinal permeability, inhibited systemic inflammatory response, and ultimately slowed down the development of RA.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease characterized by persistent synovial inflammation, cartilage and bone damage, and potential disability (1). The global prevalence rates of RA range from 0.5% to 1.0% (1), with lower rates in China at 0.2% to 0.3% (2). RA is more common in females than in males (3). While the exact pathogenesis of RA remains unclear, certain risk factors such as family history, smoking, air pollution, periodontitis, and hormonal factors are associated with an increased likelihood of developing the disease (4). Studies have shown that RA patients exhibit distinct alterations in gut microbiota compared to healthy individuals (5, 6), which may contribute to systemic immune dysregulation (7, 8). Different strains of gut bacteria can have varying effects on immune system function, potentially influencing the development of RA (9). Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are commonly used in RA treatment and may indirectly impact gut microbiota composition to modulate systemic immunity (9). Considering this therapeutic approach, there is interest in exploring whether early intervention targeting gut microbiota, such as probiotics, could potentially prevent the onset of RA.
Probiotics are defined as “live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host” (10). Probiotics can inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria by competing for nutrition and colonization sites. Meanwhile, metabolites of probiotics can strengthen the intestinal barrier and modulate the host immune responses (11). Three strains of Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus casei, Bifidobacterium bifidum were provided for RA patients in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (12). After 8 weeks, RA patients receiving these probiotics showed improvement in Disease Activity Score of 28 joints (DAS-28) from -0.3 ± 0.4 to -0.1 ± 0.4. Furthermore, insulin levels, homeostatic model assessment-B cell function (HOMA-B), and serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) concentrations decreased significantly, along with improvements in total and low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol levels (12). Given that most studies involve mixed strains of probiotics, the specific effects of a single strain, such as Bifidobacterium, remain unclear. While Bifidobacterium is known for its health benefits, further research is needed to determine if a single strain can replicate the effects of mixed probiotics. In this study, B. animalis BD400 is stored in the lactic acid bacteria species resource bank of the State Key Laboratory of Dairy Biotechnology. Compared with other Bifidobacterium, the B. animalis have good acid resistance, bile salt resistance and oxygen resistance, and have good survival ability in the human gastrointestinal tract. But the biological function of B. animalis BD400 is an unexplored area.
This study aims to protect from RA by taking B. animalis BD400 orally at an early stage to restore the balance of the unbalanced gut microbiota. Clinical scores for arthritis and paw swelling thickness were used to assess arthritis symptoms, while bone damage severity was determined through knee joint pathology and staining in rats. Immune response was evaluated by measuring specific antibodies and cytokines in serum and synovial fluid. The expression of intestinal barrier proteins was analyzed using qPCR to assess intestinal barrier damage. Changes in gut microbiota composition and diversity were assessed through 16S high-throughput sequencing, and metabolomics was used to analyze metabolite production and associated pathways in rat feces. The findings of this study offer valuable insights for the potential use of probiotics in the prevent of RA in daily life.
Bovine type II collagen solution, complete Freund`s adjuvant and incomplete Freund`s adjuvant were purchased from Chondrex (Redmon, WA, USA). Methotrexate (MTX) was purchased from Shanghai Yuanye Bio-Technology Co. (Ltd, Shanghai, China). Anti-TNF-α antibody and anti-MMP-13 antibody were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, United Kingdom). Total CII-IgG ELISA assay kit, CII-IgG1 ELISA assay kit, CII-IgG2a ELISA assay kit and CII-IgG2b ELISA assay kit were purchased from Shanghai MuLuan Biological Technology Co. (Ltd, Shanghai, China). Rat TNF-α ELISA assay kit, rat IL-1β ELISA assay kit and rat IL-17A ELISA assay kit were purchased from Hangzhou Lianke Biotechnology Co. (LTD, Hangzhou, China).
All the probiotics, listed in Table 1, were deposited at State Key Laboratory of Dairy Biotechnology. The twenty strains were cultured in DeManRogosa-Sharpe (MRS) medium at 37°C overnight, and were harvested by centrifugation at 5000g for 10 min at 4°C. The bacterial precipitate was washed twice with saline. The concentration of each strain was re-suspended at 5 × 108 CFU/mL in saline, and stored at –80°C prior to use. The viability of all the probiotics suspensions was measured by colony counting before daily oral administration.
Female Wistar rats (7-8 week-old) (Shanghai SLAC Laboratory Animal Ltd, Shanghai, China) were allowed to acclimatize for seven days before experimentation. The rats were given free access to food and water specific pathogen-free (SPF) standard laboratory conditions at 25 ± 2°C and humidity of 50% ± 5%, with a 12 h light-dark cycle. This study was carried out in accordance with the Regulations for the Administration of Affairs Concerning Experimental Animals in China. Ethical approval for this study was obtained from Animal Ethics Committee of Shanghai Zhanyuan Biological Technology Co., LTD (approval No. 202306261).
The collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) animal model is the most commonly studied autoimmune model of rheumatoid arthritis. CIA was induced and assessed according to the previous method (13). Briefly, bovine type II collagen solution (CII, Chondrex, Redmon, WA, USA) were emulsified with complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA, Chondrex, Redmon, WA, USA) at a ratio of 1:1, and 150 ml emulsion were injected subcutaneously into the tail root of each rat for multi-point immunization at day 1. After seven days, bovine type II collagen solution (CII, Chondrex, Redmon, WA, USA) were emulsified with incomplete Freund’s adjuvant (IFA, Chondrex, Redmon, WA, USA) at a ratio of 1:1, and 150 ml emulsion were injected into the tail root of each rat for a booster immunization. The control rats were subcutaneously injected with 150 ml sterile saline. The experimental rats were subcutaneously injected with same volume of probiotic liquid. The rats were sacrificed on the 63rd day by means of excessive anesthesia with a dose of 0.2 ml 3% pentobarbital sodium per 100 g of rat. The experimental schedule is as Figure 1.
During the experiment, the weight of the rats was measured weekly. Since the arthritic symptoms developed at paw and joint, the paws thickness was measured using calipers and the severity of symptoms was assessed by an arthritis clinical score following the method described previously (13). The quantitative clinical score is as follows: 0, no signs of erythema and swelling; 1, erythema and mild swelling limited to the tarsal bone or ankle joint; 2, erythema and mild swelling extending from the ankle joint to the tarsal bone; 3, Erythema and moderate swelling extending from the ankle joint to the metatarsal joint; 4, erythema and severe swelling of the ankles, feet, and fingers, or stiffness of the limbs.
Clinical condition and symptoms of each rat were evaluated by histological analysis with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and safranin O-fast green staining. At the end of the experiment on the 63rd day, the rats were sacrificed and the knee joints were taken. The joints were fixed in 10% formalin for 48 h, decalcified in 10% EDTA for 30 days, and embedded in paraffin. Tissue sections (5 µm thick) in the sagittal direction along the long axis of the knee were stained using H&E and safranin O-fast green staining.
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples (5 µm thick) were deparaffinized and retrieved with bone tissue antigen retrieval solution was in a wet box at 37°C for 2 h. After sealed at room temperature for 1 h, samples were then incubated with the primary antibody (anti TNF-α and anti MMP-13, respectively) (Abcam, Cambridge, UK) at 4°C overnight, followed by reaction with goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody (FITC) (Abcam, Cambridge, UK) at room temperature for 1 h in the dark. After washing, 4`,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) was applied for re-dyeing and incubated at room temperature for 5 min in the dark, and then the sample was sealed and observed under fluorescence microscope.
Total II collagen-specific IgG (CII-IgG), and its subclasses CII-IgG1, CII-IgG2a and CII-IgG2b were detected by ELISA kits according to the manufacturer`s instructions. Inflammatory factors interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-17A (IL-17A) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in serum and synovial fluid were detected using an ELISA kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Hangzhou LianKe Biological Technology Co., Ltd, Hangzhou, China). OD values were measured by ELIASA.
The transcription levels of ZO-1, Occludin-1, Claudin-1 and MUC-2 in rat ileum were measured via qPCR. Total RNA from rat ileum tissue was extracted using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA). Then, total RNA was analyzed as described previously (14). The primers used are shown in Table 2. Analysis of each sample was repeated three times. β-actin RNA was used as the endogenous control.
Fecal samples were collected at the end of the experiment and stored at –80°C. Total fecal DNA was extracted using the TIANamp Bacteria DNA Kit (TIANGEN Biotech, Beijing, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The V3-V4 region of 16S rDNA was amplified using primer set 341F/806R and sequenced using a MiSeq sequencer (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). The microbial communities were further predicted by PICRUSt.
The fecal samples (25 mg ± 1 mg) were taken, mixed with beads and 500 μL of extraction solution (MeOH: CAN: H2O, 2:2:1 (v/v)). The extraction solution contains deuterated internal standards. The mixed solution was vortexed for 30 s. These soil samples (100 mg ± 1 mg) were taken, mixed with beads and 500 μL of extraction solution (MeOH: CAN: H2O, 2:2:1 (v/v)). The extraction solution contains deuterated internal standards. The mixed solution was vortexed for 30 s.
Then the mixed samples were homogenized (35 Hz, 4 min) and sonicated for 5 min in 4°C water bath, the step repeat for three times. The samples were incubated for 1 h at -40°C to precipitate proteins. Then the samples ware centrifuged at 12000 rpm (RCF=13800(×g), R= 8.6cm) for 15 min at 4°C. The supernatant was transferred to a fresh glass vial for analysis. The quality control (QC) sample was prepared by mixing an equal aliquot of the supernatant of samples.
For polar metabolites, LC-MS/MS analyses were performed using an UHPLC system (Vanquish, Thermo Fisher Scientific) with a Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH Amide (2.1 mm × 50 mm, 1.7 μm) coupled to Orbitrap Exploris 120 mass spectrometer (Orbitrap MS, Thermo). The mobile phase consisted of 25 mmol/L ammonium acetate and 25 ammonia hydroxide in water(pH = 9.75)(A) and acetonitrile (B). The auto-sampler temperature was 4°C, and the injection volume was 2 μL. The Orbitrap Exploris 120 mass spectrometer was used for its ability to acquire MS/MS spectra on information-dependent acquisition (IDA) mode in the control of the acquisition software (Xcalibur, Thermo). In this mode, the acquisition software continuously evaluates the full scan MS spectrum. The ESI source conditions were set as following: sheath gas flow rate as 50 Arb, Aux gas flow rate as 15 Arb, capillary temperature 320°C, full MS resolution as 60000, MS/MS resolution as 15000, collision energy: SNCE 20/30/40, spray voltage as 3.8 kV (positive) or -3.4 kV (negative), respectively.
The raw data were converted to the mzXML format using ProteoWizard and processed with an in-house program. which was developed using R and based on XCMS, for peak detection, extraction, alignment, and integration. The R package and the BiotreeDB(V3.0) were applied in metabolite identification (15).
All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 19.0 statistical software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Statistical differences among the groups were assessed by one-way ANOVA, and multiple comparisons were performed using Tukey HSD test. Values of p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
After a seven-day acclimatization period, Wistar rats were administered either a Bifidobacterium solution or sterile saline orally on day 0. The CIA model group, MTX group, and Bifidobacterium solution group were induced as CIA models with primary immunization on day 14 and booster immunization on day 21. The Bifidobacterium solution group received oral gavage of Bifidobacterium solution (2 × 108 CFU) from day 0 to day 63. The CIA model and control groups were orally gavaged with sterile saline from day 0 to day 63. The MTX group received sterile saline orally from day 0 to day 63 and was treated with MTX twice a week from day 14 to day 63 (Figure 1). Paw photos of each group of rats on day 63 are shown in Figure 2. A comparison between Figures 2G, H reveals significant redness and swelling in the feet and fingers of the CIA rats. The Bifidobacterium intervention demonstrated a reduction in this redness and swelling (Figures 2A–E). In MTX group, before day 35, the clinical score and paw thickness of the rats were lower than those of the CIA model group. After 35 days, the MTX group and the CIA model group had similar results. This result in the MTX group is related to the properties of the drug MTX. Treatment of RA with MTX is often done at an early stage, which is more beneficial for controlling the progression of the disease early on. In addition, in the treatment of MTX, the response rate is 64%-87%. Combined with the above two reasons, MTX showed poor performance in reducing clinical score and paw swelling (16).
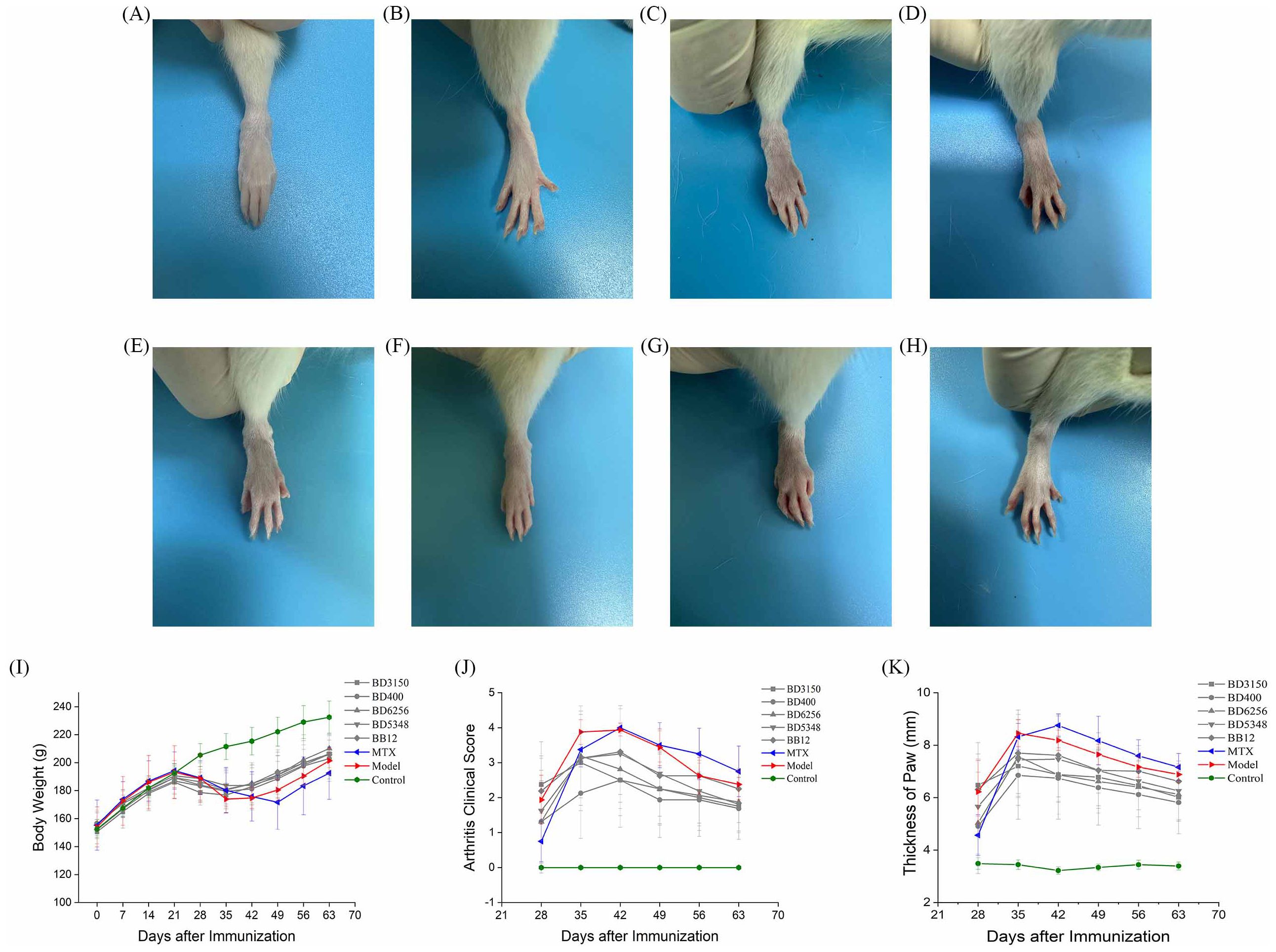
Figure 2. Effect of oral Bifidobacterium on the symptoms of paw arthritis in CIA rats. (A) B. longum BD3150, (B) B. animalis BD400, (C) B. longum BD6256, (D) B. bifidum BD5348, (E) B. breve BB12, (F) MTX, (G) CIA model, (H) Control, (I) Body weight, (J) Arthritis clinical score, (K) Thickness of paw. (n=8).
The study recorded the body weight, clinical scores, and paw thickness of rats to evaluate the severity of arthritis. Prominent symptoms of CIA rats, such as swelling and reddening, appeared on day 21. As depicted in Figure 2I, the weight of CIA rats began to decrease, but by day 35, it had returned to an upward trend as RA stabilized. In contrast, the control group’s rat weight steadily increased. The MTX group’s rat weight hit its lowest point on day 49. Between days 42 and 63, the MTX group’s rat weight was consistently lower than that of the CIA model group, likely due to MTX’s hepatotoxic nature causing gastrointestinal discomfort like vomiting and diarrhea. This resulted in lower body weight compared to the model group. Similarly, the weight of rats in the Bifidobacterium groups (BD3150, BD400, BD6256, BD5348, BB12) exhibited a pattern of initial increase, subsequent decrease, and final rise. There were minimal differences in rat weight among the Bifidobacterium groups.
Arthritis onset was observed in rats one week after booster immunization, with arthritis clinical scores and paw thickness recorded (Figures 2J, K). Paw swelling in CIA rats continued to increase from day 28 to day 42, peaking on day 42 before entering a stable phase with gradual reduction in swelling. While MTX intervention did not show immediate effects in early arthritis stages, it did reduce paw swelling in later stages. Disease activity persisted after MTX treatment, a common scenario in RA management (17). Bifidobacterium administration reduced paw swelling in CIA rats, with the most significant difference seen in the B. animalis BD400 group.
The knee joints of rats were collected for histopathological analysis. Bone erosion in the knee joints was observed through HE staining, while cartilage damage was assessed using safranin O-fast green staining. In Figure 3H, joint staining in normal rats appeared uniform, with round chondrocytes evenly arranged and abundant extracellular collagen fibers. Conversely, the knee bones of CIA rats showed severe damage, with less stained cartilage matrix indicating significant collagen loss, along with damage to the synovial membrane and cartilage (Figure 3G). Rats in the Bifidobacterium and MTX groups exhibited uniformly colored joints and cartilage, suggesting restoration of inflammatory damage and collagen loss in the joints (Figures 3A–F).
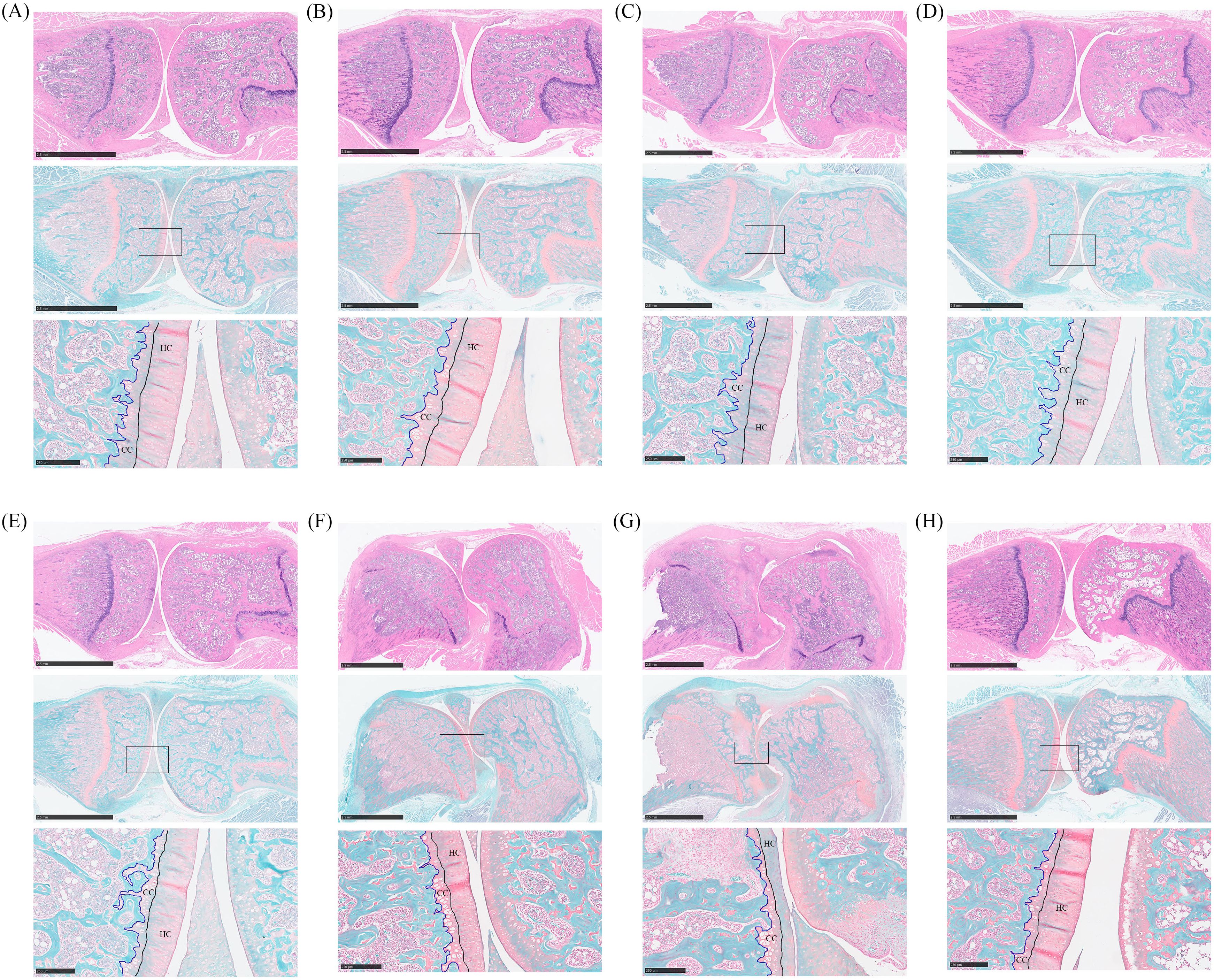
Figure 3. Histopathological analysis of oral treatment with Bifidobacterium in CIA rats. From the top down are the HE staining picture, the safranin O-fast green staining picture, and the enlarged picture at the box of the safranin O-fast green staining picture. (A) B. longum BD3150, (B) B. animalis BD400, (C) B. longum BD6256, (D) B. bifidum BD5348, (E) B. breve BB12, (F) MTX, (G) CIA model, (H) Control.
Safranin O-fast green staining can reveal cartilage damage by coloring normal cartilage layers, hyaline cartilage (HC) and calcified cartilage (CC), in red, while coloring cancellous bone layers in green. HC contains active chondrocytes responsible for repairing the cartilage matrix, whereas CC represents mineralized HC. Thicker CC layers can impede the flow of liquid and small organic molecules into HC, hindering chondrocyte growth (18). In the study, normal rats exhibited thick and intact HC layers with a clearly visible tidal line, along with moderately thick CC layers (Figure 3H). Conversely, rats in the CIA model group showed reduced HC thickness, intensified cartilage matrix degradation, and thickened mineralized CC layers (Figure 3G). Treatment with Bifidobacterium increased HC thickness and decreased CC thickness in CIA rats, indicating a reduction in inflammation levels that promoted chondrocyte biological activity and alleviated RA development (Figures 3A–E). Specifically, the Bifidobacterium group showed knee bone and cartilage conditions similar to those of the normal group, with both B. longum BD3150 and B. animalis BD400 groups exhibiting comparable results.
Immunofluorescence staining was conducted on histopathologic sections of rat knee joints to examine TNF-α and MMP-13 distribution (Figure 4). In the control group, articular cartilage appeared normal with no positive fluorescence. However, in the CIA model group, increased TNF-α and MMP-13 proteins were observed. Treatment with Bifidobacterium led to reduced protein expression, particularly in the B. animalis BD400 group. Quantitative analysis using Image J software showed significantly higher fluorescence in the CIA model group compared to controls (p < 0.05). Bifidobacterium intervention decreased fluorescence significantly (p < 0.05), with no difference between the B. animalis BD400 group and control group (p > 0.05). The details of the comparison of significant differences in the Supplementary Table S3.
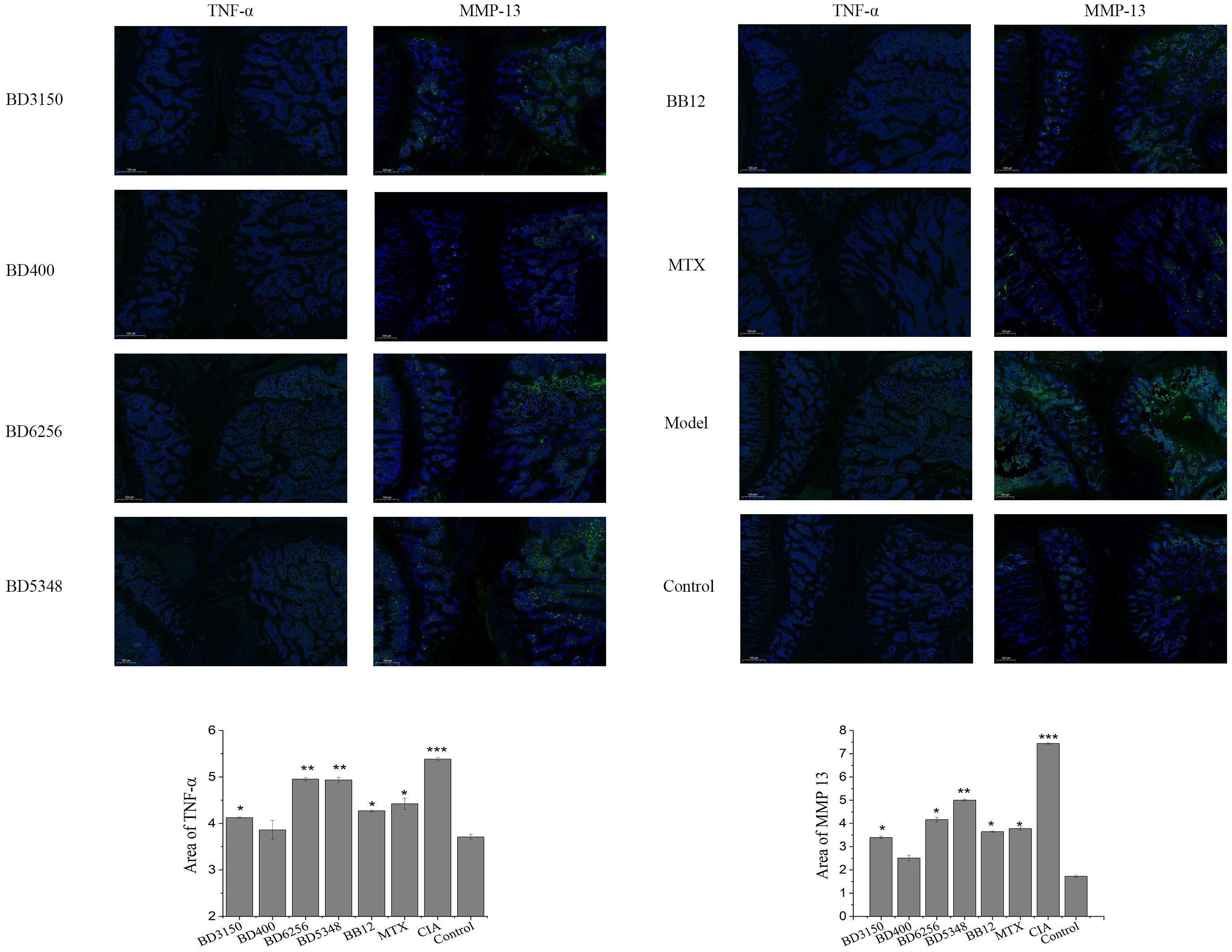
Figure 4. Expression of TNF-α and MMP13 in rat joint tissues. (***p < 0.01, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 against the control group.) (n=8).
Anti-CII IgG is a specific antibody that targets type II collagen and plays a crucial role in the development of arthritis in CIA rats. It is known to induce or worsen arthritis and can be used to evaluate the severity of the disease. Lowering the production of these autoantibodies can effectively halt the progression of arthritis (19). In this study, the impact of Bifidobacterium on the humoral immunity of CIA rats was assessed by measuring the levels of CII-specific antibodies. The study measured the levels of total anti-CII IgG as well as its subtypes (anti-CII IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b) in the serum. Results showed that the levels of these antibodies were significantly higher in the CIA model group compared to the control group (Figures 5A–D). Treatment with MTX reduced these antibody levels to a level comparable to that of normal rats. Oral administration of Bifidobacterium in CIA rats also led to a notable decrease in these antibody levels. Specifically, the B. longum BD3150 and B. animalis BD400 groups showed significantly lower levels of total anti-CII IgG and its subtypes compared to the CIA model group. These findings suggest that B. longum BD3150 and B. animalis BD400 may help alleviate inflammatory damage induced by autoantibodies by reducing the levels of anti-CII IgG, anti-CII IgG1, and anti-CII IgG2a. The details of the comparison of significant differences in the Supplementary Table S3.
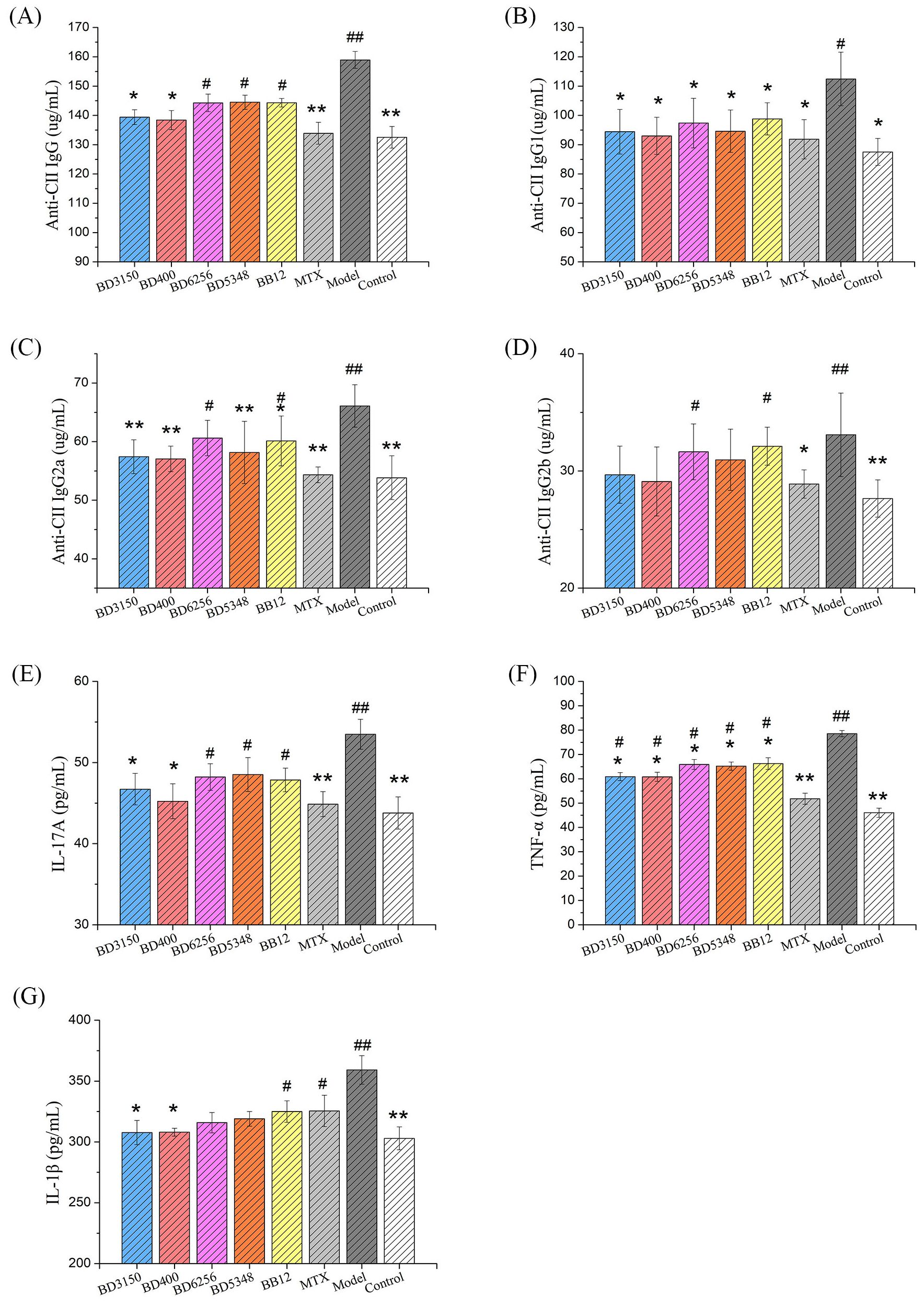
Figure 5. Effects of Bifidobacterium on inflammatory responses in rats. The levels of anti-CII IgG (A), anti-CII IgG1 (B), anti-CII IgG2a (C), anti-CII IgG2b (D) and IL-17A (E) in serum were examined. The levels of TNF-α (F) and IL-1β (G) in the synovial fluid were examined. (##p < 0.01, #p < 0.05 against the control group; **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 against the CIA group as determined by a two-way ANOVA with Tukey`s multiple comparisons.) (n=8).
Cytokine levels in serum serve as indicators of systemic inflammatory immune response, reflecting the overall inflammatory status of the body. Notably, IL-1 and TNF-α are key inflammatory mediators in RA, with IL-17 playing a significant role in promoting the secretion of IL-1 and TNF-α by inflammatory cells. In the study (Figure 5E), levels of IL-17A in the serum of the CIA model group were markedly higher compared to other groups (p < 0.01). Treatment with MTX led to a significant reduction in IL-17A levels in the serum of CIA rats (p < 0.01). Furthermore, administration of B. longum BD3150 and B. animalis BD400 to CIA rats resulted in a significant decrease in IL-17A levels in serum (p < 0.05) (Figures 5F, G). Additionally, analysis of synovial fluid from rats revealed elevated levels of TNF-α and IL-1β in the CIA model group compared to control groups (p < 0.01). Treatment with B. longum BD3150 and B. animalis BD400 significantly lowered TNF-α and IL-1β levels in the synovial fluid of CIA rats (p < 0.05). These findings suggest that B. longum BD3150 and B. animalis BD400 effectively reduce inflammation in both the blood and joint fluid of CIA rats. The details of the comparison of significant differences in the Supplementary Table S3.
Intestinal barrier proteins, such as claudin-1, occludin-1, mucin-2 (MUC-2), and zonula occluden-1 (ZO-1), play a crucial role in maintaining normal intestinal barrier function. Gene expression analysis in a CIA model group revealed a significant decrease in occludin-1 and MUC-2 levels, an increase in claudin-1 expression, and no notable change in ZO-1 levels compared to the control group (Figure 6). Treatment with Bifidobacterium led to a significant increase in occludin-1 and MUC-2 expression, while claudin-1 levels decreased. In the B. animalis BD400 group, there was a significant increase in occludin-1, MUC-2, and ZO-1 expression, with a decrease in claudin-1 levels. Occludin-1 regulates intercellular ion transport, while MUC-2 is a mucin produced by goblet cells in the intestinal wall. The modulation of occludin-1 and MUC-2 by B. animalis BD400 can enhance intestinal selective permeability, reduce the influx of harmful substances into the internal environment, and maintain internal homeostasis. The details of the comparison of significant differences in the Supplementary Table S3.
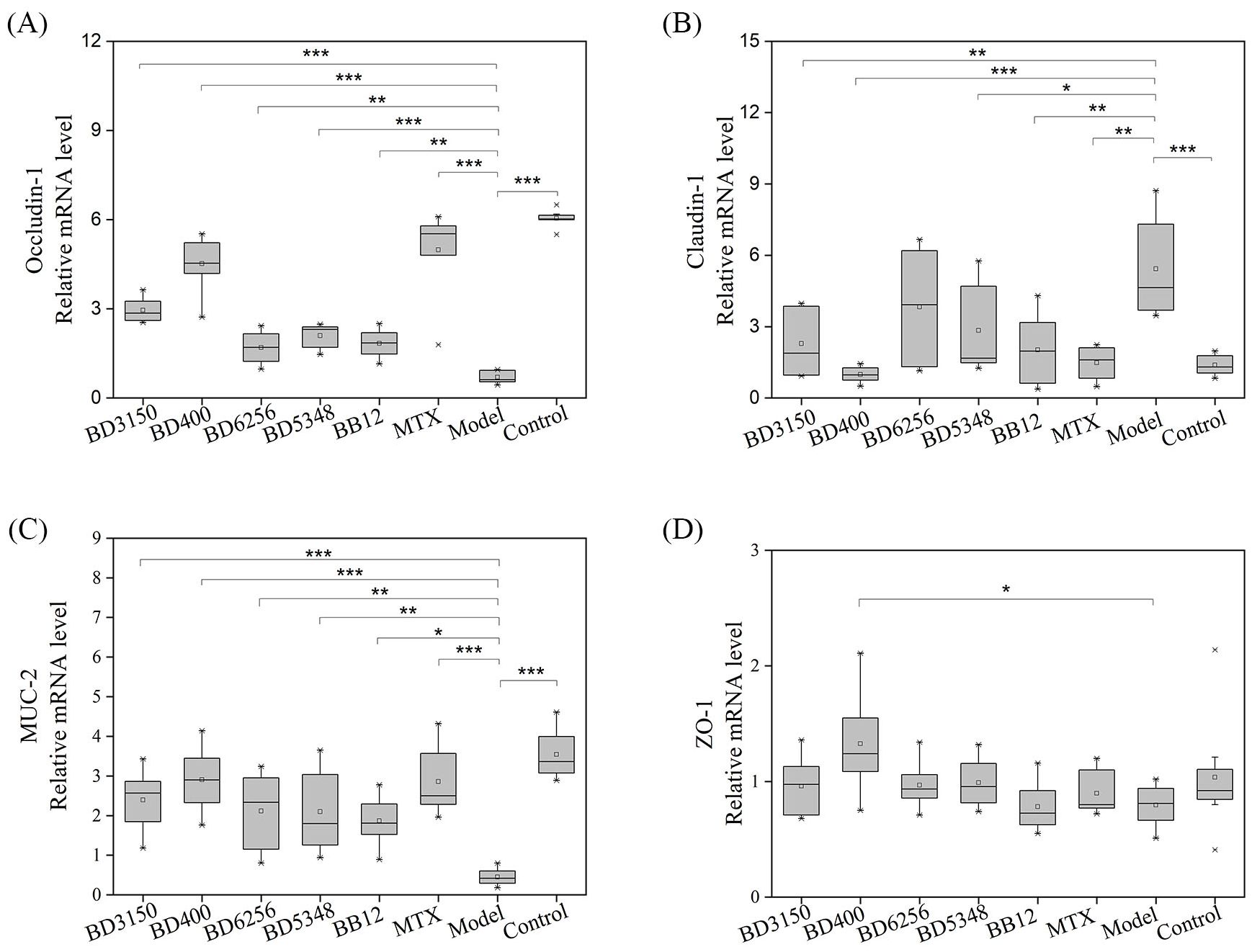
Figure 6. Intestinal barrier protein gene expression in rats. (A) occludin-1, (B) claudin-1, (C) MUC-2, (D) ZO-1. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 against the CIA model group as determined by a two-way ANOVA with Tukey`s multiple comparisons.) (n=8).
Faecal samples were collected to evaluate the impact of Bifidobacterium on the gut microbiota of CIA rats through 16S rDNA V3-V4 sequencing. A total of 3,276,658 valid sequences were obtained after double-end splicing, quality control, and chimera filtering. Through amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) cluster analysis and species annotation, 50,065 ASVs were identified, with an average of 1,043 ASVs per sample. The species accumulation curve in Figure 7A shows a plateau as sample size increases, indicating sufficient sampling. Additionally, the dilution curve in Figure 7B flattens with the increase in sample sequences, suggesting an appropriate amount of sequencing data. Significant differences in Chao1 index, Shannon index, and Simpson index were observed between the CIA model group and the control group (p < 0.05) in Figures 7C–E. Following the intervention of certain Bifidobacterium strains, there was a notable increase in species richness within the gut microbiota of CIA rats (p < 0.05). Specifically, the Chao1 index, Shannon index, and Simpson index significantly increased in the B. longum BD3150 group (p < 0.01), while the Shannon index and Simpson index notably increased in the B. bifidum BD5348 group (p < 0.05). These findings indicate substantial disparities in species diversity within the gut microbiota of CIA rats compared to normal rats, and highlight the potential of B. longum BD3150 and B. bifidum BD5348 interventions in mitigating the reduction in intestinal species diversity induced by arthritis.
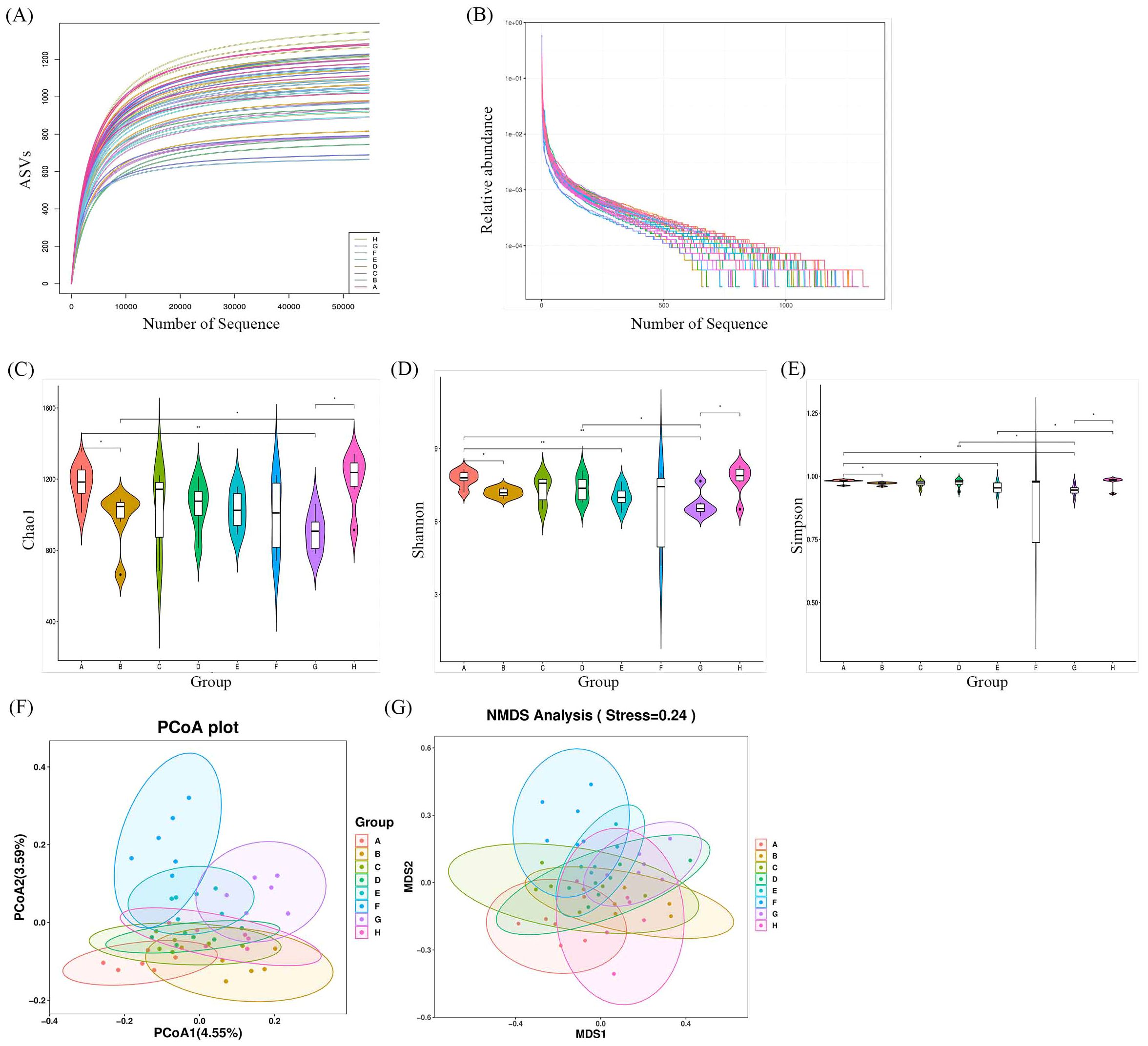
Figure 7. Effects of Bifidobacterium on the relative abundance and diversity of gut microbiota. (A) Specaccum curve, (B) Rank-abundance curve, (C) Chao1, (D) Shannon, (E) Simpson, (F) PCoA, (G) NMDS. Group: (A): B. longum BD3150, (B): B. animalis BD400, (C): B. longum BD6256, (D): B. bifidum BD5348, (E): B. breve BB12, (F): MTX, (G): CIA Model, (H): Control. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, determined by a two-way ANOVA.) (n=6).
Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) and nonmetric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) were utilized to compare the distribution profiles of fecal microorganisms in eight groups. Figures 7F, G demonstrates a significant difference in PCoA and NMDS between the CIA model group (purple circle) and the control group (pink circle). Upon administration of Bifidobacterium, there were significant alterations in the distribution profiles, particularly in the B. longum BD3150 group and the B. animalis BD400 group in PCoA. Adonis analysis revealed a significant difference in the species composition of gut microbiota among the eight groups (p = 0.001) (Table 3).
Based on ASV annotation results and the ASV abundance table for each sample, we generated a species abundance table at various taxonomic levels including kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. Utilizing this information along with species annotation data, we identified the top 30 species for constructing cluster stacked bar charts at the phylum and genus levels. In Figure 8A, Firmicutes and Bacteroidota emerge as the predominant phyla in rat gut bacteria, with a higher proportion observed in the CIA model group compared to the control group. Following intervention with specific strains of Bifidobacterium, the ratio of Firmicutes and Bacteroidota exhibited alterations. Notably, clustering based on Bray-Curtis distance revealed that the B. breve BB12 group closely resembled the control group in terms of Firmicutes and Bacteroidota percentages. Moving to the genus level (Figure 8B), the top 5 species included Clostridia_UCG-014_unclassified, Lactobacillus, Ligilactobacillus, Lachnospiraceae_unclassified, and Firmicutes_unclassified. The proportion of these species differed significantly between the CIA model group (50.72%) and the control group (34.57%) (p < 0.05). Upon Bifidobacterium administration, a decrease in the percentages of these top 5 species was observed, particularly in the B. bifidum BD5348 group.
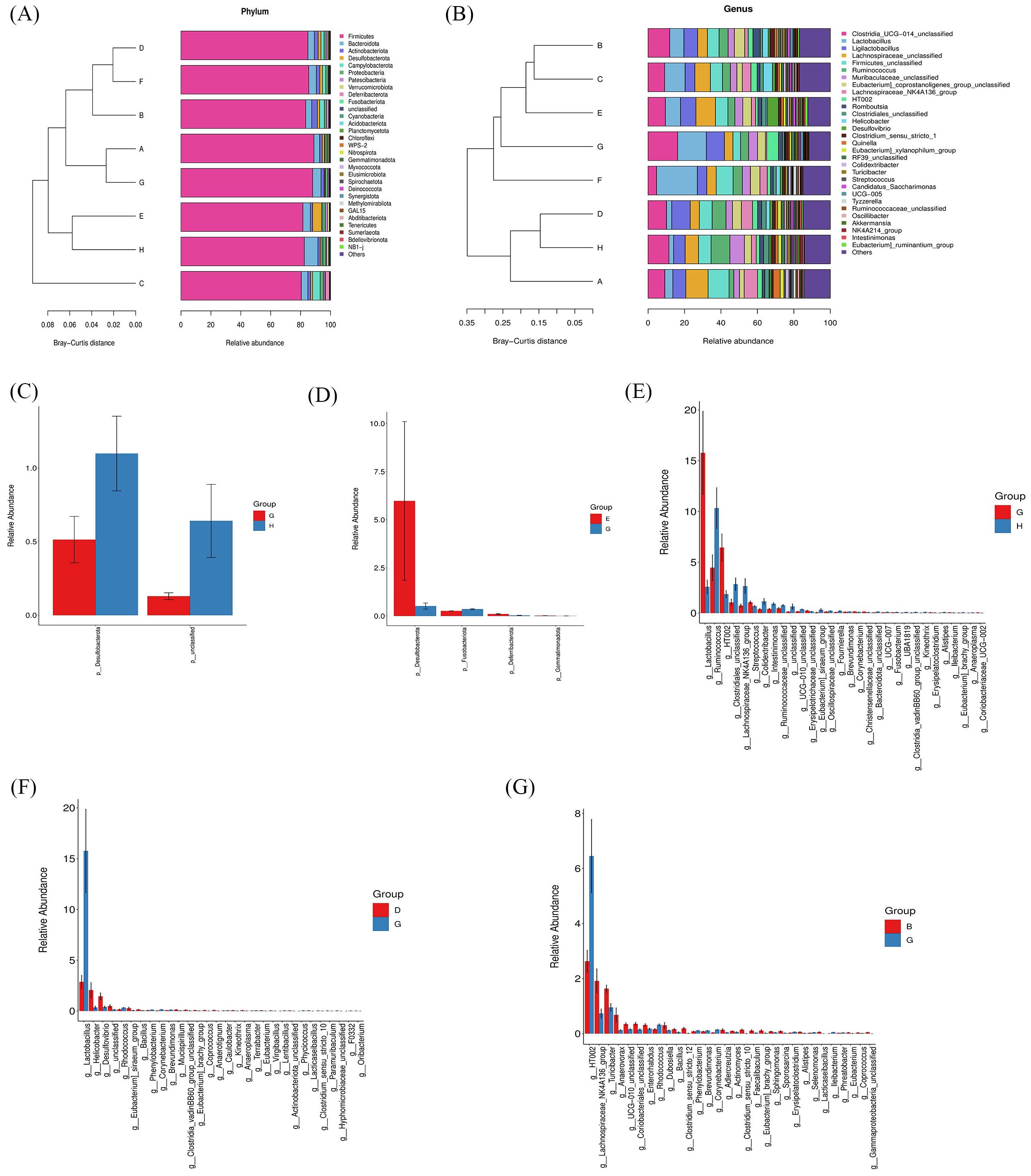
Figure 8. Effects of Bifidobacterium on the species composition of gut microbiota. Species abundance at the phylum level (A), genus level (B), and a relative abundance difference between group G and group H at the phylum level (C), between group E and group G at the phylum level (D), between group G and group H at the genus level (E), between group D and group G at the genus level (F), between group B and group G at the genus level (G). Group: (A): B. longum BD3150, (B): B. animalis BD400, (C): B. longum BD6256, (D): B. bifidum BD5348, (E): B. breve BB12, (F): MTX, (G): CIA Model, (H): Control. (n=6).
To further investigate the species contributing to the differences between groups, a differential abundance analysis was conducted. In Figure 8C, Desulfobacterota at the phylum level exhibited the most significant difference between the CIA model group and the control group. Following the administration of B. breve BB12, there was an increase in the relative abundance of Desulfobacterota (Figure 8D). At the genus level, Lactobacillus showed the most significant difference between the CIA model group and the control group (Figure 8E). Additionally, Ruminococcus and HT002 were also found to differ between the CIA model group and the control group. Notably, there was no observed increase in Ruminococcus with the administration of Bifidobacterium, while B. animalis BD400 reduced the relative abundance of HT002.
The LEfSe tool was utilized to identify biomarkers between groups. In Figures 9A, B, 26 types of bacteria showed significant differences across various classification levels including phylum, class, order, family, and genus in the control group. The top 5 bacteria with notable differences were Ruminococcus_unclassified, Ruminococcus, Ruminococcaceae, Turicibacter_unclassified, and Turicibacter. In the B. bifidum BD5348 group, 7 types of bacteria exhibited significant differences, namely Ruminococcus_bromii, Ruminococcus, Ruminococcaceae, Christensenellales, Christensenellaceae, Christensenellaceae_R_7_group, and Christensenellaceae_R_7_group_unclassified. These results indicate that both the B. bifidum BD5348 group and the control group share biomarkers such as Ruminococcus and Ruminococcaceae, suggesting that the intervention of B. bifidum BD5348 alters the gut microbiota of CIA rats to resemble that of normal rats.
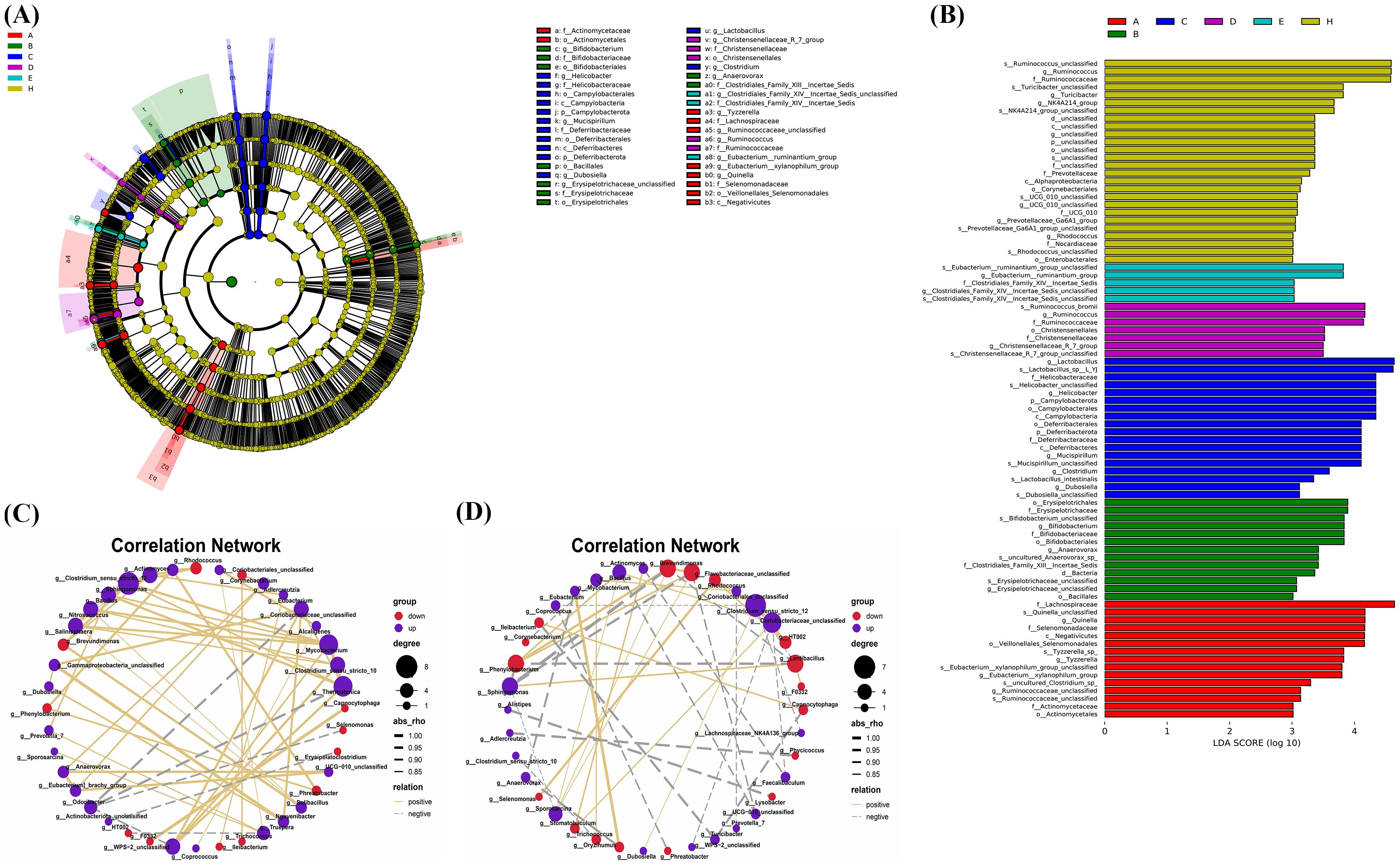
Figure 9. LEfSe analysis and correlation analysis. The cladogram (A) and the bar diagram (B) of LEfSe analysis. The correlation analysis between significantly up-regulated and significantly down-regulated differential species in the B. animalis BD400 group (C) and the CIA model group (D). (n=6).
Figures 9C, D were obtained by Spearman correlation analysis. Comparing the two correlation networks, it was found that most of the significant different bacteria genera in the CIA model group were negatively correlated. After B. animalis BD400 intervention, the correlation was mainly positive. Under the administration of B. animalis BD400, Mycobacterium was positively correlated with Sphingomonas, Bacillus, Nitrosococcus and Salinisphaera. But in the CIA model group, Mycobacterium was only positively correlated with Oryzihumus. In addition, WPS-2_unclassified was positively correlated with Coriobacteriaceae_unclassified, Thermotunica, Clostridium_sensu_stricto_10 and Mycobacterium in the B. animalis BD400 group. WPS-2_unclassified in the CIA model group was only negatively correlated with Coriobacteriaceae_unclassified.
In addition, in the B. animalis BD400 group, genus HT002 was negatively correlated with genus Truepera (Figure 9C). As mentioned above, the relative abundance of HT002 decreases in the B. animalis BD400 group, which means that the relative abundance of Truepera increases. Truperia comes from Deinococcota phylum, Deinococci class, Deinococcales order, Trueperaceae family. Trueperaceae is a relatively newly defined family of bacteria. In 2005, Albuquerque et al. discovered and described a new genus of Trueperaceae family, confirming its taxonomic status and laying the foundation for the establishment of Trueperaceae family (20, 21). Little is known about the physiological role of Truperia. In the CIA model group, genus HT002 was positively correlated with genus Rhodococcus. As mentioned above, the relative abundance of HT002 increases in the CIA model group, which means that the relative abundance of Rhodococcus increases. Rhodococcus comes from Actinobacteriota phylum, Actinobacteria class, Corynebacteriales order, Nocardiaceae family. Some species of Rhodococcus are human and animal pathogens, such as Rhodococcus equi is a pathogen of horses, pigs, cattle and other animals (22). In summary, we hypothesized that HT002 can disrupt the homeostasis of gut microbiota by promoting the growth of harmful bacteria in gut microbiota. B. animalis BD400 can reduce the relative abundance of HT002 and restore gut microbiota homeostasis.
A total of 11632 peaks in positive ion mode and 9769 peaks in negative ion mode were retained after quality control. Differential metabolites between the control and treatment groups were identified based on the variable importance in the projection (VIP) of the OPLS-DA model. Subsequently, a T-test was conducted using SPSS 19.0 statistical software to perform statistical analysis. The criteria for screening differential metabolites included ∣Log2 FOLD CHANGE∣>1, p < 0.01 and VIP > 1. The ratio of each differential metabolite was calculated and transformed logarithmically with a base of 2.
The comparison of differential metabolites between the CIA model group and the control group was presented in Figures 10A, B. Each Bifidobacterium group was compared individually with the control group. The results of each Bifidobacterium group compared with the control group were shown in the Supplementary Figures S2-S5. Notably, the changes in differential metabolites between the B. animalis BD400 group and the control group were found to be opposite to those between the CIA model group and the control group (Figure 10B). For instance, purine nucleosides like crotonoside guanosine, 2’-deoxyuridine, and xanthosine were significantly up-regulated in the CIA model group but down-regulated in the B. animalis BD400 group. Similarly, the fatty acid metabolite 2-ketobutyric acid showed significant up-regulation in the CIA model group but down-regulation in the B. animalis BD400 group. On the other hand, glycerin phospholipids such as 2-O-(4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoyl)-1-O-hexadecylglycero-3-phosphocholine, momordicinin, and botulin were significantly down-regulated in the CIA model group but up-regulated in the B. animalis BD400 group. These contrasting results between the CIA model group and B. animalis BD400 group suggest that B. animalis BD400 may possess the ability to mitigate the abnormal differential metabolite profiles associated with RA.
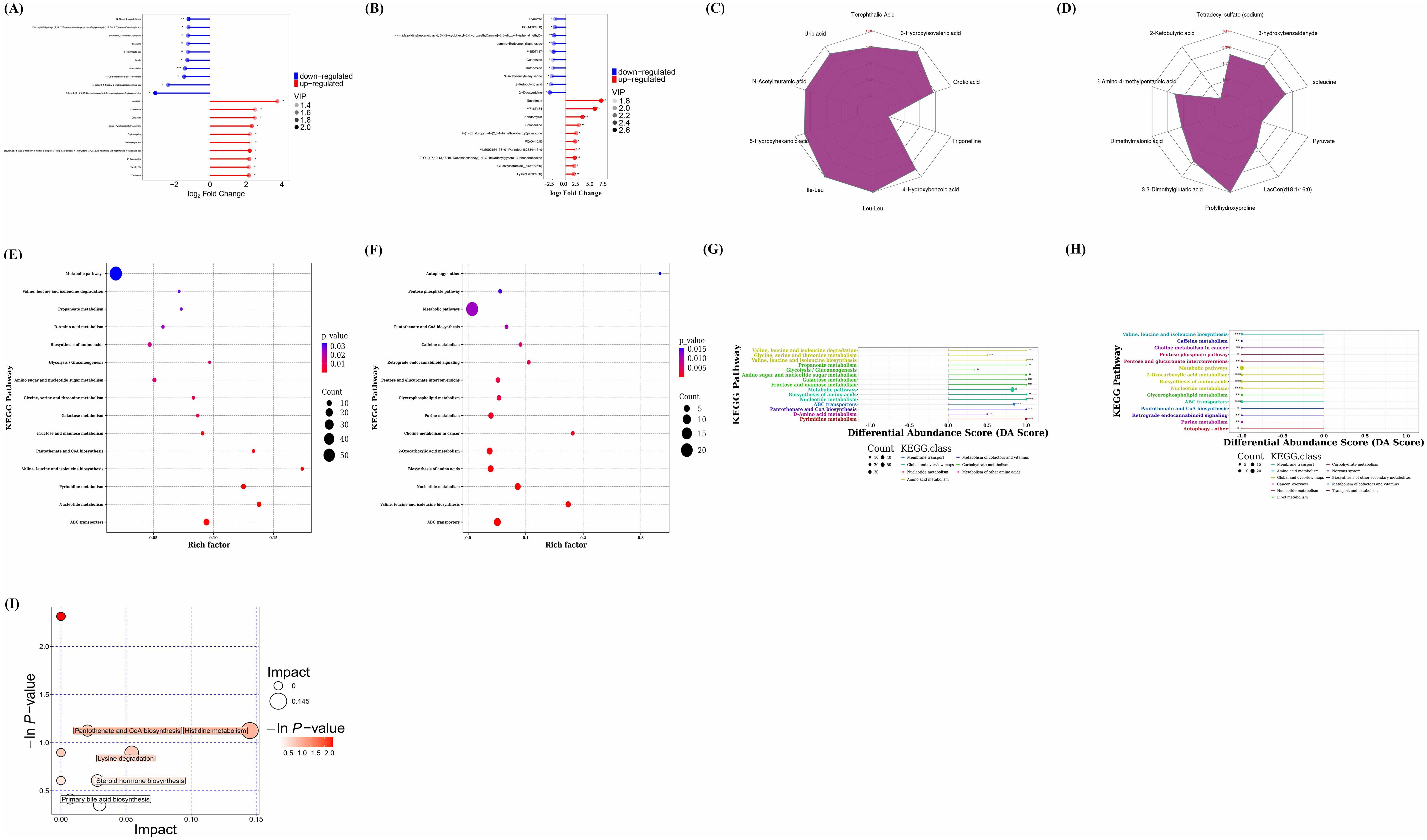
Figure 10. Analysis of differential metabolites and metabolic pathways via non-targeted metabolomics. Matchstick diagram analysis of differential metabolites for CIA model group vs control group (A), for B. animalis BD400 group vs control group (B). Radar chart analysis of differential metabolites for CIA model group vs control group (C), for B. animalis BD400 group vs control group (D). Bubble plot of KEGG Enrichment for CIA model group vs control group (E), for B. animalis BD400 group vs control group (F). Differential Abundance Score for CIA model group vs control group (G), for B. animalis BD400 group vs control group (H). Bubble plot of pathway analysis for CIA model group vs B. animalis BD400 group (I). Rich factor, it refers to the ratio of the number of differential metabolites annotated in a pathway to the number of all metabolites in that pathway; DA score, it refers to the ratio of difference between the number of up-regulated and down-regulated differential metabolites annotated on a pathway to the number of all metabolites on that pathway. (n=6).
A radar chart (Figures 10C, D) was utilized to illustrate the variation trend in the content of differential metabolites. The red font represents the difference multiple for each grid line, while the purple shadow consists of the difference multiple lines for each metabolite. Overall, Figure 10C predominantly shows positive difference multiples, indicating an increasing trend, whereas Figure 10D mostly displays negative difference multiples, suggesting a decreasing trend. Figure 10C compares the content of the same differential metabolite in the CIA model group and the control group, revealing higher levels of certain metabolites in the CIA model group such as orotic acid, 3-hydroxyisovaleric acid, terephthalic acid, uric acid, N-acetylmuramic acid, 5-hydroxyhexanoic acid, Ile-Leu, Leu-Leu, and 4-hydroxybenzoic acid compared to the control group. Conversely, trigonelline was lower in the CIA model group than in the control group. In Figure 10D, prolylhydroxyproline in the B. animalis BD400 group exhibited higher levels compared to the control group, while 3,3-dimethylglutaric acid, dimethylmalonic acid, 3-amino-4-methylpentanic acid, 2-ketobutyric acid, tetradecyl sulfate, 3-hydroxybenzaldehyde, isoleucine, pyruvate, and LacCer(d18:1/16:0) in the B. animalis BD400 group were lower than in the control group. The contrasting trends in difference multiples between the CIA model group and the B. animalis BD400 group demonstrate the potential of B. animalis BD400 to restore intestinal metabolite disturbance.
The role of these differential metabolites was investigated by annotating the metabolic and regulatory pathways they are associated with. Enrichment results (Figures 10E, F) revealed that the differential metabolites primarily belonged to metabolic pathways, suggesting that the CIA model construction significantly impacted the metabolic pathways of rats, and B. animalis BD400 also influenced the metabolic pathways of CIA rats. The differential abundance score (DA score) calculations indicated a positive trend for all metabolites in these pathways (Figure 10G), whereas in the B. animalis BD400 group, metabolites in each pathway exhibited a decreasing trend (Figure 10H).
To pinpoint key metabolic pathways highly correlated with metabolite differences, enrichment analysis and topological analysis were conducted. There were significant differences in histidine metabolism, pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis, lysine degradation, steroid hormone biosynthesis, primary bile acid biosynthesis between the CIA model group and the B. animalis BD400 group (Figure 10I). The differential metabolites were mapped to authoritative metabolite databases such as KEGG and PubChem. After obtaining the matching information of differential metabolites, we searched the pathway database of the corresponding species Rattus norvegicus (rat) and analyzed the metabolic pathway, and obtained Table 3. In Table 4, the metabolic pathway histidine metabolism has the greatest influence, and urocanic acid is the main metabolic substance involved in the histidine metabolism.
We further investigated the expression of metabolites involved in histidine metabolism. Supplementary Figure S1 is a comparison between the CIA model group and the B. animalis BD400 group. In Supplementary Figure S1, the expressions of 1-methyl-L-histidine and urocanate were significantly down-regulated. This result also suggests that B. animalis BD400 may play a preventive role in rheumatoid arthritis through 1-methyl-L-histidine and urocanate in the histidine metabolic pathway. The KEGG ID and KEDD name of the enzyme involved in the Supplementary Figure S1 are arranged in Supplementary Table S1.
RA is a chronic, symmetrical, systemic, inflammatory autoimmune disease with complex etiology and unclear pathogenesis (23). While there are drugs available to treat RA, there is still no effective treatment. In the early stages, RA presents with joint swelling, pain, and dysfunction. As RA progresses, it is marked by different levels of joint stiffness, bone and skeletal muscle atrophy, and can be highly disabling if not treated regularly (1).
Numerous studies conducted worldwide have demonstrated a strong correlation between RA and gut microbiota, especially in the early stage. For instance, a study in the United States utilized 16S sequencing of stool samples taken from 114 RA patients and healthy individuals, revealing an increase in Prevotella copri abundance in RA patients, which was linked to a reduction in Bacteroides levels and a decline in beneficial microbes (24). Similarly, a Japanese study involving 17 early RA patients observed a similar trend with an increase in Prevotella copri abundance and a decrease in Bacteroides (25). Furthermore, researchers Vaahtovuo et al. from Finland employed 16S rRNA hybridization and DNA staining techniques to analyze the fecal microbiota of 51 early RA patients. A comparison with fibromyalgia patients showed a significant decrease in the levels of bacteria within the Bifidobacteria and Bacteroides-Porphyromonas-Prevotella group, Bacteroides fragilis subgroup, and Eubacterium rectale-Clostridium coccoides group among early RA patients (26). Zhang et al. conducted a study in China where they analyzed the oral and gut microbiota of 212 fecal samples from both RA patients and healthy controls using metagenomic shotgun sequencing. Their findings revealed a decrease in Haemophilus spp. in the gut, dental, or saliva microbiome of RA patients, while an increase in Lactobacillus salivarius was observed in these same microbiomes of RA patients (6). Maeda et al. further explored the connection between gut microbiota and RA by transplanting feces from RA patients into germ-free mice. The mice gradually developed ankle swelling two weeks post-transplant and eventually developed RA (25). Additionally, Zeng et al. successfully treated a 20-year-old woman with refractory RA using fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT). By administering fecal suspensions from healthy eight-year-old donors via colonoscopy, they observed no adverse reactions during or after FMT. Notably, the patient’s rheumatic factors significantly decreased (p < 0.05) at 42 days post-FMT, with RA symptoms showing improvement 78 days post-FMT (27). These findings underscore the crucial role of gut microbiota in the pathogenesis and progression of RA.
Bifidobacterium, the predominant microbe in the gastrointestinal tract, plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of gut microbiota and overall host health. Numerous clinical, in vivo, and in vitro studies have demonstrated the beneficial effects of Bifidobacterium on conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, cancer, diarrhea, and lactose intolerance. Bifidobacterium exerts its effects by inhibiting the growth of pathogens, preserving gut microbiota balance, and safeguarding intestinal barrier integrity through the reduction of intestinal pH (28). Moreover, Bifidobacterium produces a variety of metabolites that are advantageous to the host, including vitamins, polyphenols, conjugated linoleic acid, and short-chain fatty acids. These metabolites also have harmful effects on pathogenic microorganisms, such as organic acids, bacteriocins, and bio-surfactants, thereby impeding the proliferation of harmful microorganisms (29). Additionally, Bifidobacterium aids in the breakdown of carbohydrate compounds in the host and from dietary sources through sugar degradation pathways, promoting healthy host metabolism. This feature not only ensures the survival of Bifidobacterium in the mammalian intestine but also provides essential nutrients for the host and other intestinal microorganisms through cross-feeding (30). Jeong et al. identified a novel Bifidobacterium longum RAPO with therapeutic potential from microbiome analysis of RA patients with varying rheumatoid factor (RF) levels. Oral administration of B. longum RAPO significantly reduced RA incidence, arthritis score, inflammation, bone injury, cartilage injury, Th17 cells, and inflammatory cytokine secretion in CIA mice (31). Furthermore, patents suggest that certain Bifidobacterium strains may have preventive or therapeutic effects on RA (32–35). This study demonstrated that oral administration of B. animalis BD400 for nine weeks notably decreased arthritis clinical scores and paw thickness in CIA rats (Figures 2I–K). Histological analysis of knee joint sections and staining of rats revealed that B. animalis BD400 improved the interface between synovium and bone tissue, reduced cell infiltration and synovial hyperplasia, restored the thickness and integrity of the hyaline cartilage layer, ultimately alleviating RA symptoms (Figures 3, 4).
The impact of B. animalis BD400 on RA symptoms prompted further investigation into its effects on specific antibodies and pro-inflammatory factors in the serum and joint fluid of CIA rats. Collagen-induced arthritis, a well-established model for RA, shares key characteristics with human RA, notably immune tolerance breakdown and autoantibody production (13). Autoantibodies, particularly anti-CII IgG antibodies specific to type II collagen, play a crucial role in RA diagnosis and disease progression. High levels of these autoantibodies can be detected in serum well before clinical symptoms manifest (19). In this study, anti-CII IgG and its subtypes (IgG1, IgG2a, and IgG2b) were measured in the serum of CIA rats. Levels of these antibodies were significantly elevated in CIA rats compared to the control group. Treatment with B. longum BD3150 and B. animalis BD400 led to a significant decrease in anti-CII IgG, IgG1, and IgG2a levels (p < 0.05) (Figure 5). Meanwhile, we assessed the production of pro-inflammatory factors, including IL-17A, TNF-α, and IL-1β, in both serum and synovial fluid. The levels of IL-17A in serum, as well as TNF-α and IL-1β in synovial fluid, were significantly reduced with the administration of B. longum BD3150 and B. animalis BD400. These inflammatory factors play a crucial role in cellular communication. Notably, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β are commonly studied in the context of RA. TNF-α, a member of the tumor necrosis factor family, triggers the production of various cytokines and proteases by target cells in RA, primarily through the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways (36). This cascade of inflammatory responses leads to a continuous cycle of inflammation, contributing to bone and joint erosion (37). As a result, the components of the articular cavity, such as synovial cells, synovial tissue fluid, and serum in CIA rats, exhibited an increasing trend compared to healthy controls. The intervention of B. longum BD3150 and B. animalis BD400 reduced the levels of TNF-α in the synovial fluid of CIA rats, suggesting the disruption of this persistent inflammatory cycle. In RA, antigen-presenting cells carrying HLA-DR antigen increase and stimulate CD4+T lymphocytes to secrete numerous cytokines, activating synovial macrophages to release IL-1β and TNF⁃α (38). These cytokines target joint cells, leading to the production of collagen and neutral protease, ultimately causing synovial proliferation and erosion of joint cartilage, worsening the disease (38). While IL⁃1β levels are typically low in the knee fluid of healthy individuals, our study found elevated levels of IL-1β in the joint fluid of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) rats. Treatment with B. longum BD3150 and B. animalis BD400 reduced IL-1β levels in the knee fluid of CIA rats. IL-17A, a key inflammatory mediator in RA, is primarily produced by CD4+Th17 cells, as well as CD8+T cells, NK T cells, γδT cells, neutrophils, and lymphoid tissue inductor-like cells (39). IL-17A works in conjunction with TNF-α to promote osteogenesis, induce PEG production in chondrocytes, stimulate fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) to secrete various inflammatory factors, and activate pathways like PI3K/Akt and NF⁃κB, leading to synovial inflammation and cartilage damage (40). Consequently, IL⁃17A levels are higher in the synovial fluid and surrounding tissues of RA patients compared to healthy individuals. Our study demonstrated a significant decrease in serum IL-17A levels in CIA rats following the oral administration of probiotics, highlighting the potential of B. longum BD3150 and B. animalis BD400 in mitigating RA-related inflammation.
The occurrence and development of RA is closely linked to disruptions in both local and systemic immune responses, stemming from immune sites beyond the joints, known as the “mucosal origin hypothesis” (41–43). The gut, recognized as the largest immune organ, harbors a diverse population of microorganisms that not only provide essential nutrients and energy to the body but also play a role in shaping and regulating the intestinal mucosal immune system (44). These intestinal microorganisms interact with, respond to, and regulate the intestinal mucosa through the intestinal mucosal barrier (45). The tight connection between the mucus barrier and intestinal epithelial cells serves as the primary defense against pathogens (46). Key proteins involved in maintaining the integrity of the intestinal barrier include claudin-1, occludin-1, mucin-2 (MUC-2), and zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1). In a study involving collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) rats, it was found that the expression of occludin-1 and MUC-2 in the gut was significantly reduced compared to control rats (p < 0.001), while the expression of claudin-1 was significantly increased (p < 0.001). Treatment with 5 strains of Bifidobacterium (BD3150, BD400, BD6256, BD5348, BB12) restored the expression of these three proteins (claudin-1, occludin-1, and MUC-2) to normal levels (Figure 6). The relationship between gut microbiota and human health is integral, as gut microbiota are present throughout the human life cycle. Changes in gut microbiota composition result from specific interactions between microorganisms and the gut environment. The evolution and selection process of the gut microbiota remains unclear, but there is growing interest in the co-evolution and mutual interaction between the gut microbiota and the host intestinal immune system. The intestinal microbiota plays a crucial role in supporting the development of the immune system through various mechanisms and helps maintain a balanced intestinal micro-ecology (47, 48). Imbalances in the intestinal micro-ecology have been linked to various diseases, including intestinal and immune disorders (49, 50). This imbalance can lead to the disruption of the intestinal micro-ecology, an increase in pathogenic bacteria, a decrease in beneficial bacteria, triggering local inflammatory responses and cascading effects that impact the immune response of extra-intestinal organs, ultimately posing a threat to the host’s health (51). In our study (Figures 7–9), significant differences were observed in the gut microbiota composition between CIA rats and normal rats (p < 0.05). Desulfobacterota was identified as the phylum with the most significant difference between the CIA model group and the control group (p < 0.05). Treatment with B. breve BB12 led to a restoration in the relative abundance of Desulfobacterota. At the genus level, notable differences were observed in Clostridia_UCG-014_unclassified, Lactobacillus, Ligilactobacillus, Lachnospiraceae_unclassified, and Firmicutes_unclassified (top 5 species). The combined proportion of these top 5 species in the CIA model group was 50.72%, significantly different from the control group’s 34.57%. The percentages of these top 5 species decreased under the administration of B. bifidum BD5348. Through differential abundance analysis, we observed that B. animalis BD400 decreased the relative abundance of HT002. Desulfobacterota, a sulfate-reducing anaerobic bacteria, thrives in the gut and releases hydrogen sulfide. The role of hydrogen sulfide is intricate and at times contradictory. Clinical data suggests an association between hydrogen sulfide and chronic colon disease as well as inflammation of the large intestine (52). However, research has also demonstrated that hydrogen sulfide can directly stimulate angiogenesis, crucial for mending gastrointestinal ulcers (53, 54). Despite the challenging task of elucidating the precise role of Desulfobacterota in the gut, our findings revealed contrasting results in the abundance of Desulfobacterota between the CIA model group and the B. animalis BD400 group, providing insight into the ability of B. animalis BD400 to restore gut microbiota. Furthermore, a separate study on Bifidobacterium adolescentis yielded similar biological outcomes, highlighting Lactobacillus, Ligilactobacillus, and Lachnospiraceae as prominent genera (55). This finding strongly corroborates our own results.
The metabolites of gut microbiota can directly or indirectly impact host health. These metabolites can be categorized based on their synthesis pathway:
1. Metabolites produced by gut microbiota that break down dietary components like short-chain fatty acids, tryptophan, and trimethylamine oxide; 2. Metabolites produced by the host and altered by gut microbiota, such as bile acids; 3. Metabolites synthesized by gut microbiota from scratch, including branched-chain amino acids, polyamines, and vitamins (56). These gut microbiota metabolites play a crucial role in maintaining host intestinal balance and regulating immune function through various mechanisms. They can enter cells through passive diffusion or carrier-mediated transport to regulate processes like protein synthesis, glucose and lipid metabolism, insulin resistance, hepatocyte proliferation, and immunity. Moreover, these metabolites can travel to distant tissues and organs via the bloodstream, influencing the functions of multiple organs (57–60). In this study (Figure 10), metabolites including crotonoside, guanosine, 2`-ketobutyric acid, momordicinin, botulin, trigonelline and so on showed a significant difference in CIA rats. After oral B. animalis BD400, these differences are restored, especially 2`-deoxyuridine, 2`-ketobutyric acid, crotonoside and guanosine. These results also suggest that the role of B. animalis BD400 in protecting from RA is achieved through the regulation of gut microbiota metabolites. So we conducted enrichment and topological analyses to find the key pathways which is the highest correlation to these metabolites. The expression of 1-methyl-L-histidine and urocanate in histidine metabolism was down-regulated in gut microbiota in CIA rats given B. animalis BD400 orally (Supplementary Figure S1). Amino acids are energy sources and substrates for cellular protein and nucleic acid biosynthesis, and a variety of amino acids and their transporters are necessary for T cell activation, differentiation and effector function (61). Histidine, lysine and threonine can inhibit the mTOR signaling pathway and IgE mediated mast cell activation (62). Studies found that lack of histidine or arginine, TGF-β1 extracellular concentration and TGF-β1 mRNA levels decreased, intestinal epithelial cell repair significantly decreased. However, supplementation with 10 µM histidine or 50 µM arginine restored cell repair and TGF-β1 extracellular concentrations. This suggests that the absence of histidine or arginine affects IEC repair by reducing TGF-β1 (63). In our study, reduction in the levels of 1-methyl-L-histidine and urocanate in histidine metabolism leads to the decrease of inflammatory response, highlighting its role in B. animalis BD400 regulation. These results indicate that B. animalis BD400 protect from RA through the regulation of 1-methyl-L-histidine and urocanate in histidine metabolism. The main objective of this study was to screen out a probiotic strain, B. animalis BD400, which has a protective effect on RA. But the key target for B. animalis BD400 to play a role is what we need to study next. As mentioned above, 1-methyl-L-histidine and urocanate in histidine metabolism are significantly down-regulated with the intervention of B. animalis BD400, but the key targets are still unclear. This will also be the key point of our next study.
The clinical treatment of RA focuses on reducing inflammation and alleviating symptoms, as RA is challenging to cure. In our study, the expression of 1-methyl-L-histidine and urocanate in histidine metabolism was reduced by early administration of B. animalis BD400, thus achieving the purpose of protecting from RA. This research is expected to provide a basis for the daily prevention of RA.
The raw sequence data of 16S rDNA gene sequencing were deposited in the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) at NCBI under Bioproject PRJNA1139339 (SUB14619059, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJNA1139339). The data matrix for non-targeted metabolite analysis was supplied in Supplementary Table S2.
The animal study was approved by Animal Ethics Committee of Shanghai Zhanyuan Biological Technology Co., LTD (approval No. 202306261). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
YY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft. QH: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. XZ: Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from the Shanghai State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission Enterprise Innovation Development and Capacity Enhancement Program (No. 2022013) and the National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFD2100704).
The authors are thankful to the State Key Laboratory of Dairy Biotechnology, Shanghai Engineering Research Center of Dairy Biotechnology, Bright Dairy & Food Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China for providing the various resources for the completion of the current article.
Authors YY, QH and ZL were employed by Bright Dairy & Food Co., Ltd.
The remaining author declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1518181/full#supplementary-material
1. Smolen JS, Aletaha D, McInnes IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. (2016) 388:2023–38. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30173-8
2. Felson DT. Comparing the prevalence of rheumatic diseases in China with the rest of the world. Arthritis Res Ther. (2008) 10:106–6. doi: 10.1186/ar2369
3. Crowson CS, Matteson EL, Myasoedova E, Michet CJ, Ernste FC, Warrington KJ, et al. The lifetime risk of adult-onset rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2011) 63:633–9. doi: 10.1002/art.30155
4. Aletaha D, Smolen JS. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis: A review. J Am Med Assoc. (2018) 320:1360–72. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.13103
5. Liu X, Zou Q, Zeng B, Fang Y, Wei H. Analysis of fecal lactobacillus community structure in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Microbiol. (2013) 67:170–6. doi: 10.1007/s00284-013-0338-1
6. Zhang X, Zhang D, Jia H, Feng Q, Wang D, Liang D, et al. The oral and gut microbiomes are perturbed in rheumatoid arthritis and partly normalized after treatment. Nat Med. (2015) 21:895–905. doi: 10.1038/nm.3914
7. Kinashi Y, Hase K. Partners in leaky gut syndrome: intestinal dysbiosis and autoimmunity. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:673708. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.673708
8. Chen B, Sun L, Zhang X. Integration of microbiome and epigenome to decipher the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. J Autoimmun. (2017) 83:31–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2017.03.009
9. Zhao T, Wei Y, Zhu Y, Xie Z, Hai Q, Li Z, et al. Gut microbiota and rheumatoid arthritis: From pathogenesis to novel therapeutic opportunities. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1007165. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1007165
10. Hill C, Guarner F, Reid G, Gibson GR, Merenstein DJ, Pot B, et al. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2014) 11:506–14. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2014.66
11. Ferro M, Charneca S, Dourado E, Guerreiro CS, Fonseca JE. Probiotic supplementation for rheumatoid arthritis: A promising adjuvant therapy in the gut microbiome era. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:711788. doi: 10.3389/FPHAR.2021.711788
12. Zamani B, Golkar HR, Farshbaf S, Emadi-Baygi M, Tajabadi-Ebrahimi M, Jafari P. Clinical and metabolic response to probiotic supplementation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Int J Rheumatic Dis. (2016) 19:869–79. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12888
13. Brand DD, Latham KA, Rosloniec EF. Collagen-induced arthritis. Nat Protoc. (2007) 2:1269–75. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.173
14. Marietta EV, Murray JA, Luckey DH, Jeraldo PR, Lamba A, Patel R. Suppression of inflammatory arthritis by human gut-derived prevotella histicola in humanized mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2016) 68:2878–88. doi: 10.1002/art.39785
15. Zhou Z, Luo M, Zhang H, Yin Y, Cai Y, Zhu ZJ. Metabolite annotation from knowns to unknowns through knowledge-guided multi-layer metabolic networking. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:6656. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34537-6
16. García-González CM, Baker J. Treatment of early rheumatoid arthritis: Methotrexate and beyond. Curr Opin Pharmacol. (2022) 64:102227. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2022.102227
17. O’Dell JR, Mikuls TR, Taylor TH, Ahluwalia V, Brophy M, Warren SR, et al. Therapies for active rheumatoid arthritis after methotrexate failure. N Engl J Med. (2013) 369:307–18. doi: 10.1056NEJMoa1303006
18. Ao Y, Li Z, Zhang C, Duan X. Research progress on calcified cartilage zone. Orthopedic J China. (2019) 27:722–5.
19. Nandakumar KS, Johansson BP, Björck L, Holmdahl R. Blocking of experimental arthritis by cleavage of IgG antibodies in vivo. Arthritis Rheumatism. (2007) 56:3253–60. doi: 10.1002/art.22930
20. Oren A, Garrity GM. Valid publication of the names of forty-two phyla of prokaryotes. Int J systematic evolutionary Microbiol. (2021) 71. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.005056
21. Albuquerque L, Simões C, Fernanda Nobre M, Pino NM, Battista JR, Silva MT, et al. Truepera radiovictrix gen. nov., sp. nov., a new radiation resistant species and the proposal of Trueperaceae fam. nov. FEMS Microbiol Lett. (2005) 247:161–9. doi: 10.1016/j.femsle.2005.05.002
22. Walsh RD, Schochd PE, Cunha BA. Rhodococcus. Infection Control Hosp Epidemiol. (1993) 14:282–7. doi: 10.1086646738
23. Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Barton A, Burmester GR, Emery P, Firestein GS, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2018) 4:18001. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2018.1
24. Scher JU, Sczesnak A, Longman RS, Segata N, Ubeda C, Bielski C, et al. Expansion of intestinal Prevotella copri correlates with enhanced susceptibility to arthritis. eLife. (2013) 2:e01202. doi: 10.7554/eLife.01202
25. Maeda Y, Kurakawa T, Umemoto E, Motooka D, Ito Y, Gotoh K, et al. Dysbiosis contributes to arthritis development via activation of autoreactive T cells in the intestine. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2016) 68:2646–61. doi: 10.1002/art.39783
26. Vaahtovuo J, Munukka E, Korkeamäki M, Luukkainen R, Toivanen P. Fecal microbiota in early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. (2008) 35:1500–5. doi: 10.1097/RHU.0b013e31818277fb
27. Zeng J, Peng L, Zheng W, Huang F, Zhang N, Wu D, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation for rheumatoid arthritis: A case report. Clin Case Rep. (2021) 9:906–9. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.3677
28. Tang Y, Chen C, Jiang B, Zou J. Bifidobacterium bifidum-mediated specific delivery of nanoparticles for tumor therapy. Int J nanomedicine. (2021) 16:4643–59. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S315650
29. Miri ST, Sotoodehnejadnematalahi F, Amiri MM, Pourshafie MR, Rohani M. The impact of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium probiotic cocktail on modulation of gene expression of gap junctions dysregulated by intestinal pathogens. Arch Microbiol. (2022) 204:417. doi: 10.1007/s00203-022-03026-1
30. Levit R, Cortes-Perez NG, Leblanc ADMD, Loiseau J, Aucouturier A, Langella P, et al. Use of genetically modified lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria as live delivery vectors for human and animal health. Gut Microbes. (2022) 14:2110821. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2110821
31. Jeong Y, Jhun J, Lee SY, Na HS, Choi J, Cho KH, et al. Therapeutic potential of a novel bifidobacterium identified through microbiome profiling of RA patients with different RF levels. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:736196. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.736196
32. Dong Y, Gai Z, Wu Z, Chen T, Fang S. Use of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BLa19 used as probiotic agent and composite probiotic for alleviating rheumatoid arthritis in preparation of medicines for preventing, and improving or treating rheumatoid arthritis. Wecare Probiotics Suzhou Co Ltd. CN patent 116606761.
33. Li T, Qin N, Zheng Z. Kit is used for diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis, comprises reagent suitable for detecting at least one strain of first microorganism set and second microorganism set, where first microorganism set comprises Bacteroides strain, and second microorganism set comprises Bifidobacterium strain. Qingdao Ruiyi Precision Medical Testing. CN patent 114317674.
34. Zhang H, Yang B, Ding M, Li B, Chen H, liu X, et al. New strain of Bifidobacterium longum subsp.infantis used for preparing medicine for e.g. preventing and/or treating rheumatoid arthritis, increasing contents of osteoprotegerin and osteocalcin, regulating intestinal flora by increasing relative abundance of Lactobacillus and/or Ruminococcus 1. Univ Jiangnan. CN patent 116574659.
35. Zhang X, Zhu J, Zheng Z. Kit useful for diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis or detecting therapeutic effect of rheumatoid arthritis, comprises reagent for detecting e.g. Acinetobacter johnsonii, Bifidobacterium adolescentis, B.animalis and Brevundimonas diminuta. Shanghai Real Biotechnology Co Ltd. CN patent 11413310.
36. Dostert C, Grusdat M, Letellier E, Brenner D. The TNF family of ligands and receptors: communication modules in the immune system and beyond. Physiol Rev. (2019) 99:115–60. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00045.2017
37. Choy EHS, Panayi GS. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. New Engl J Med. (2001) 344:907–16. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200103223441207
38. Joosten LAB, Helsen MMA, Loo FAJVD, Berg WBVD. Anticytokine treatment of established type II collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1 mice. A comparative study using anti-TNF alpha, anti-IL-1 alpha/beta, and IL-1Ra. . Arthritis Rheumatol. (2010) 39:797–809. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390513
39. Gallego A, Vargas JA, Castejón R, Citores MJ, Durántez A. Production of intracellular IL-2, TNF-alpha, and IFN-gamma by T cells in B-CLL. Cytometry Part B Clin Cytometry. (2010) 56B:23–9. doi: 10.1002/cyto.b.10052
40. Sato K, Suematsu A, Okamoto K, Yamaguchi A, Morishita Y, Kadono Y, et al. Th17 functions as an osteoclastogenic helper T cell subset that links T cell activation and bone destruction. J Exp Med. (2006) 203:2673–82. doi: 10.1084/jem.20061775
41. Zaiss MM, Wu HJJ, Mauro D, Schett G, Ciccia F. The gut–joint axis in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2021) 17:224–37. doi: 10.1038/s41584-021-00585-3
42. Michael HV, Kristen DM, Kuhn KA, Buckner JH, Robinson WH, Yuko O, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis and the mucosal origins hypothesis: protection turns todestruction. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2018) 14:542–57. doi: 10.1038/s41584-018-0070-0
43. Brusca SB, Abramson SB, Scher JU. Microbiome and mucosal inflammation as extra-articular triggers for rheumatoid arthritis and autoimmunity. Curr Opin Rheumatol. (2014) 26:101–7. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000008
44. Lin L, Zhang K, Xiong Q, Zhang J, Cai B, Huang Z, et al. Gut microbiota in pre-clinical rheumatoid arthritis: From pathogenesis to preventing progression. J Autoimmun. (2023) 141:103001. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2023.103001
45. Chelakkot C, Ghim J, Ryu SH. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp Mol Med. (2018) 50:1–9. doi: 10.1038/s12276-018-0126-x
46. Hansson GC, Johansson MEJGM. The inner of the two Muc2 mucin-dependent mucus layers in colon is devoid of bacteria. Gut Microbes. (2008) 105:51–4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803124105
47. Honda K, Littman DRJN. The microbiota in adaptive immune homeostasis and disease. Nature. (2016) 535:75. doi: 10.1038/nature18848
48. Hooper LV, Macpherson AJJNRI. Immune adaptations that maintain homeostasis with the intestinal microbiota. Nat Rev Immunol. (2010) 10:159–69. doi: 10.1038nri2710
49. Sekirov I, Russell SL, Antunes LCM, Finlay BB. Gut microbiota in health and disease. Physiol Rev. (2010) 90:859–904. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00045.2009
50. Jie Z, Xia H, Zhong SL, Feng Q, Kristiansen K. The gut microbiome in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat Commun. (2017) 8:845. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00900-1
51. Opoku YK, Asare KK, Ghartey-Quansah G, Afrifa J, Bentsi-Enchill F, Gyamerahofori E, et al. Intestinal microbiome–rheumatoid arthritis crosstalk: The therapeutic role of probiotics. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:996031. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.996031
52. Maldonado-Arriaga B, Sandoval-Jiménez S, Rodríguez-Silverio J, Lizeth Alcaráz-Estrada S, Cortés-Espinosa T, Pérez-Cabeza de Vaca R, et al. Gut dysbiosis and clinical phases of pancolitis in patients with ulcerative colitis. Microbiol Open. (2021) 10:e1181. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.1181
53. Morbidelli L, Monti M, Terzuoli E. Pharmacological tools for the study of H2S contribution to angiogenesis. Methods Mol Biol. (2019) 2007:151–66. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9528-8_1
54. Köhn C, Dubrovska G, Huang Y, Gollasch M. Hydrogen sulfide: potent regulator of vascular tone and stimulator of angiogenesis. Int J Biomed Sci. (2012) 8:81–6. doi: 10.59566/IJBS.2012.8081
55. Fan Z, Yang B, Ross RP, Stanton C, Shi G, Zhao J, et al. Protective effects of Bifidobacterium adolescentis on collagen-induced arthritis in rats depend on timing of administration. Food Funct. (2020) 11:4499–511. doi: 10.1039/D0FO00077A
56. Yang W, Cong YJ. Gut microbiota-derived metabolites in the regulation of host immune responses and immune-related inflammatory diseases. Cell Mol Immunol. (2021) 18:1–12. doi: 10.1038/s41423-021-00661-4
57. Fusco W, Lorenzo MB, Cintoni M, Porcari S, Rinninella E, Kaitsas F, et al. Short-chain fatty-acid-producing bacteria: key components of the human gut microbiota. Nutrients. (2023) 15:2211. doi: 10.3390/nu15092211
58. Perez-Castro L, Garcia R, Venkateswaran N, Barnes S, Conacci-Sorrell M. Tryptophan and its metabolites in normal physiology and cancer etiology. FEBS J. (2023) 290:7–27. doi: 10.1111/febs.16245
59. Collins SL, Stine J, Bisanz J, Okafor C, Patterson A. Bile acids and the gut microbiota: metabolic interactions and impacts on disease. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2023) 21:236–47. doi: 10.1038/s41579-022-00805
60. Le Couteur DG, Solon-Biet SM, Cogger VC, Ribeiro R, Cabo R, Raubenheimer D, et al. Branched chain amino acids, aging and age-related health. Ageing Res Rev. (2020) 64:101198. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101198
61. Wang W, Zou W. Amino acids and their transporters in T cell immunity and cancer therapy. Mol Cell. (2020) 80:384–95. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.09.006
62. Wu J, Theije CGMD, Silva SLD, Abbring S, Kraneveld AD. Dietary interventions that reduce mTOR activity rescue autistic-like behavioral deficits in mice. Brain Behavior Immun. (2017) 59:273–87. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2016.09.016
Keywords: rheumatoid arthritis, Bifidobacterium, gut microbiota, metabolomics, early intervention
Citation: Yang Y, Hong Q, Zhang X and Liu Z (2025) Bifidobacterium animalis BD400 protects from collagen-induced arthritis through histidine metabolism. Front. Immunol. 16:1518181. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1518181
Received: 28 October 2024; Accepted: 02 January 2025;
Published: 22 January 2025.
Edited by:
Constantin Caruntu, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, RomaniaCopyright © 2025 Yang, Hong, Zhang and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhenmin Liu, bGl1emhlbm1pbkBicmlnaHRkYWlyeS5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.