
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Immunol., 13 February 2025
Sec. Cancer Immunity and Immunotherapy
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1508730
This article is part of the Research TopicMetabolism in the Tumour Microenvironment: Implications for Pathogenesis and TherapeuticsView all 5 articles
 Yuchun Jiang1
Yuchun Jiang1 Qing Tao1
Qing Tao1 Xuehan Qiao1
Xuehan Qiao1 Yufei Yang1
Yufei Yang1 Chen Peng1
Chen Peng1 Miao Han1
Miao Han1 Kebin Dong1
Kebin Dong1 Wei Zhang2
Wei Zhang2 Min Xu2
Min Xu2 Deqiang Wang1,2
Deqiang Wang1,2 Wen Zhu1*
Wen Zhu1* Xiaoqin Li1*
Xiaoqin Li1*The incidence of gastric cancer remains high and poses a serious threat to human health. Recent comprehensive investigations into amino acid metabolism and immune system components within the tumor microenvironment have elucidated the functional interactions between tumor cells, immune cells, and amino acid metabolism. This study reviews the characteristics of amino acid metabolism in gastric cancer, with a particular focus on the metabolism of methionine, cysteine, glutamic acid, serine, taurine, and other amino acids. It discusses the relationship between these metabolic processes, tumor development, and the body’s anti-tumor immunity, and analyzes the importance of targeting amino acid metabolism in gastric cancer for chemotherapy and immunotherapy.
Gastric cancer (GC) is a common malignancy of the digestive tract. The early diagnosis rate of gastric cancer is low, with high morbidity and mortality (1). Due to the lack of early detection biomarkers, most patients with GC are already at an advanced stage when diagnosed, losing the opportunity for radical surgical resection. Chemotherapy is still an indispensable treatment for gastric cancer, however, gastric cancer patients often develop resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs in the advanced stages, resulting in poor treatment effects and low survival rates for many patients. For example, conventional chemotherapeutic agents, such as cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil, have reduced sensitivity to GC cells, which limits the therapeutic efficacy of treatment (2), highlighting the need for alternative therapies.
The mechanisms of chemoresistance in GC include the activation of DNA repair mechanisms (3), inhibition of cell death pathways (4), and dysregulation of multiple non-coding RNAs (5, 6). For example, activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR (7) and RAF/MEK/ERK (8) signaling pathways in paclitaxel-resistant GC cells makes them resistant to chemotherapeutic drugs, and the use of pathway inhibitors can improve the therapeutic effect. p53 cell cycle protein defects can also lead to chemotherapeutic drug resistance in cancer cells (9). GC stem cells (GCSCs) maintain their stemness through the WNT and Hippo pathways, which in turn affects chemosensitivity (10, 11)
Amino acid metabolism can also affect chemoresistance through different mechanisms, including providing metabolic feedstock, influencing redox homeostasis, and regulating epigenetic modifications. Understanding the role of these metabolic pathways in chemoresistance can help develop new therapeutic strategies to overcome drug resistance in cancer treatment.
Traditional chemotherapy and targeted therapy have limited efficacy, a high incidence of adverse reactions, and poor patient tolerance; the median survival of patients is mostly less than 1 year. Recently, immunotherapy has brought new therapeutic hope for patients with advanced GC (12).Molecular typing of GC based on high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics analysis revealed the biological features and clinical prognosis of each subtype. Molecular typing has guided the selection of clinical treatment strategies, for example, the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) classified GC into EBV-infected, microsatellite-unstable, chromosome-unstable, and genome-stable types (13, 14). Among them, patients with EBV-infected and microsatellite unstable GC have better responses to immunotherapy (15). Tumor cells as well as immune cells and fibroblasts in the TME influence the efficacy of tumor immunotherapy (16). Most human solid tumors exhibit one of three distinct immune phenotypes: inflammation, exclusion, or desert (17). Several characteristic molecular markers help identify patients for whom immunotherapy is effective, including PD-L1 (18), CPS (19), microsatellite instability (20), TMB (21), deficient mismatch repair, dMMR (22), immune infiltration levels (23), and BRCA2 mutations (24).
Intra-tumor, intra-patient, and inter-patient heterogeneity in GC is a major obstacle to the development of systemic therapeutic agents, and although clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of immunotherapy, the majority of patients with gastric cancer are not susceptible to immune checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy; thus, there is an urgent need to find new therapeutic approaches to overcome the resistance of patients with GC to ICI therapy. Temporal and spatial heterogeneity, invasiveness, and prognosis of GC are closely related to the tumor microenvironment (TME). The TME is mainly composed of endothelial cells, lymphocytes, macrophages, myeloid cells, and cancer-associated fibroblasts that are involved in inflammation, cancer immunosuppression, angiogenesis, and metastasis (25, 26). The TME specifically affects the immunotherapeutic efficacy and survival of gastric cancer patients, and activated fibroblasts, endothelial cells, immunosuppressive myeloid cell subpopulations, and regulatory T cells are closely associated with the establishment of an immunosuppressive TME in GC (27, 28). Moreover, IFNγ-activated T cell subsets and HLA-II-expressing macrophages are associated with better treatment outcomes (29). Amino acid metabolism plays an important role in the TME, affecting the growth of tumor cells, the function of immune cells, and the immune status of the entire microenvironment, including the dysregulation of T lymphocyte metabolism and macrophage metabolism. Targeting amino acid metabolism to enhance immunotherapeutic efficacy is an emerging cancer therapeutic strategy that involves the modulation of specific amino acid metabolic pathways to influence tumor cell growth and immune responses.
Amino acid metabolism plays an important role in the TME. Although amino acids are metabolites that provide energy and carbon for biomass synthesis, they also play a signaling role (30). Amino acid metabolism is associated with chemoresistance and poor immunotherapy outcomes. Immune checkpoints can suppress anti-tumor immunity through amino acid metabolism. Amino acids are involved in multiple steps of anti-tumor immunity in immune cells, and cancer cells are metabolically reprogrammed to obtain sufficient nutrients to meet high metabolic demands (31). The development of anticancer drugs that target the metabolic vulnerability of cancer cells is a therapeutic strategy for cancer treatment (32, 33).
In this article, we review the influence of amino acid metabolism on tumor development in GC, including methionine, cysteine, glutamic acid, serine, and taurine. In addition, we provide guidelines for targeting amino acid metabolism in GC for chemotherapy resistance and immunotherapy.
Methionine is an essential amino acid, and S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) produced during methionine metabolism is involved in the regulation of many biomolecules, affecting the biological functions of tumors and immune cells. Intervention with enzymes involved in methionine metabolism or restricting the uptake of methionine is beneficial for limiting the development of tumors.
Gastric hepatoid adenocarcinoma (HAS) has higher stemness and methionine cycle activity than conventional GC (34). HAS is a subtype of GC with low morbidity, high mortality, and increased epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) activity. Tumor stem cells (TICs), as tumor-initiating cells, are heterogeneous in their metabolism compared to normal tumor cells, which often leads to the development of chemotherapy resistance and even increases the malignancy of the tumor (35). Methionine starvation and backfill experiments demonstrated that tumor-initiating cells are dependent on methionine metabolism, and its main product, SAM, is the source of nucleic acid methylation and histone methylation methyl group, which is catalyzed by Methionine adenosyltransferase IIA(MAT2A). The authors’ study using the MAT2A inhibitor, FIDAS-5, found that it greatly reduced the levels of SAM and SAH in the tumor-initiating cells, and lowered the levels of histone methylation, which resulted in the tumor clonogenic and tumorigenic abilities of the initiating cells were drastically reduced (35). Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of gene expression data from gastric HAS revealed that samples were enriched in biological processes related to folate binding and glycine metabolism, and that the gene expression levels of MAT2A in this pathway differed significantly between the two groups, and could be a potential drug target in HAS (34).
GSEA of gene expression data from gastric HAS revealed that samples were enriched in biological processes related to folate binding and glycine metabolism and that two genes in this pathway, MAT2A and AHCY (SAHH), showed significant differences in gene expression levels between the two groups and may be drug targets for HAS (36). Thus, the development of NNMT inhibitors may contribute to the prevention of GC.
It follows that GC cells may enhance the level of methionine metabolism through the high expression of the key enzyme of methionine metabolism (Figure 1), thereby promoting the malignant biological behavior of GC using the methionine metabolite SAM. Therefore, limiting methionine intake or inhibiting a key enzyme involved in methionine metabolism, MAT2A, is a potential therapeutic approach. However, relevant treatments have not yet been popularized in the clinic; most of these studies are preclinical studies conducted in animal models or at the cellular level, and their safety and efficacy in human patients need to be verified by further clinical trials.
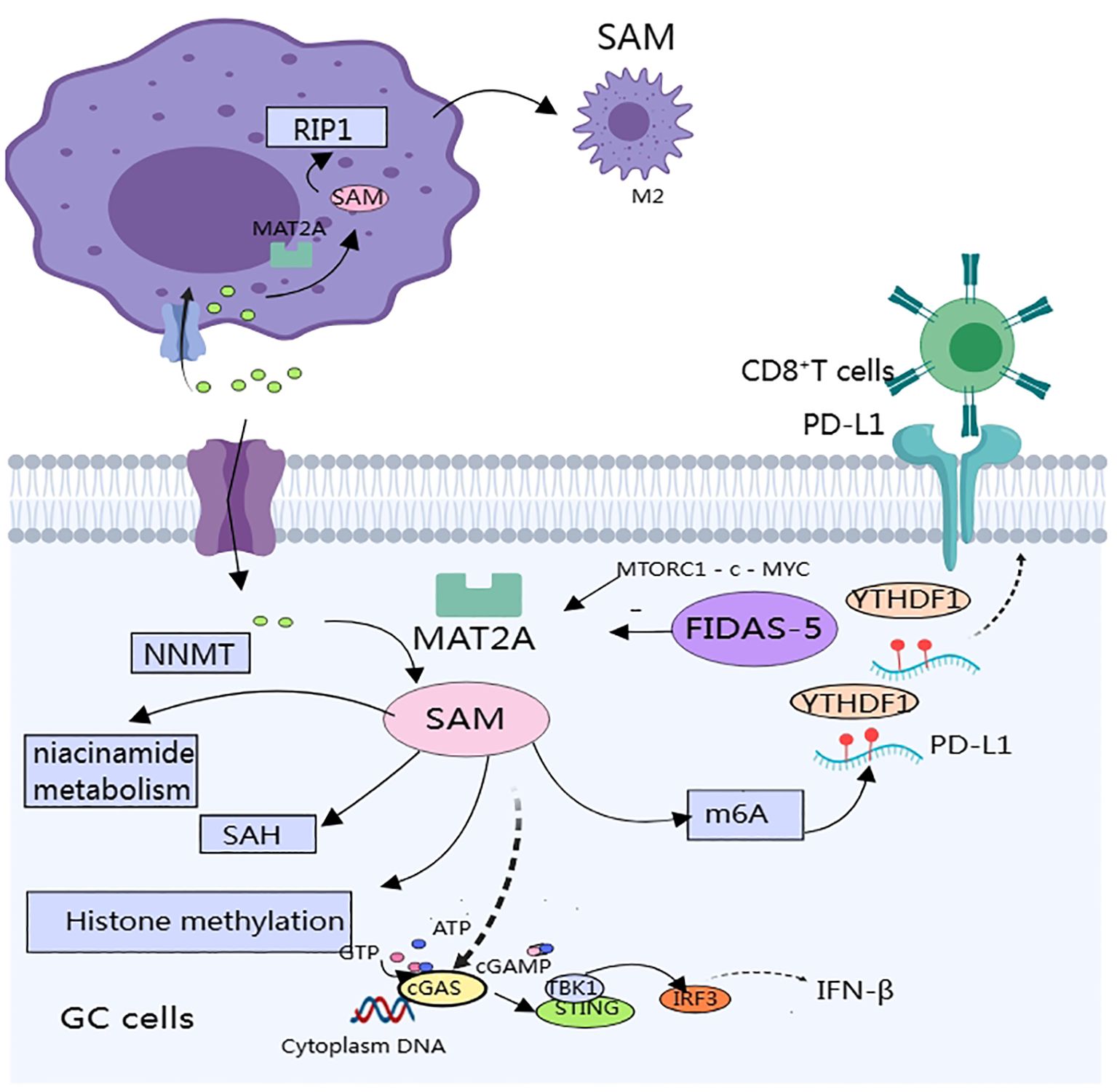
Figure 1. SAM produced by methionine metabolism affects gastric cancer progression and immune components in the tumor microenvironment.
Methionine metabolism affects multiple aspects of antitumor immunity in gastric cancer: including effects on macrophage polarization, expression of immunosuppressive molecules, and activation of immune pathways (Figure 1). Few studies have been published that directly affect the T cells. Targeting the methionine metabolism is expected to enhance the efficacy of immunotherapy and chemotherapy for GC.
Macrophages play multiple roles in antitumor immunity; they are important components of the immune system and key cell types in the TME (37). They recognize and phagocytose pathogens and resist infection while activating other immune cells through the release of signals such as cytokines. Metabolic interactions between tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and malignant cells are critical for maintaining the immunosuppressive nature of the TME.TAMs can be polarized into a pro-inflammatory phenotype M1 and an anti-inflammatory phenotype M2 (38). M1-type TAM mainly exerts antitumor effects, whereas M2-type TAM promotes tumor progression by secreting interleukin (IL)-10 and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) (39). In hepatocellular carcinoma, M2 TAMs are the main immune cells that express the immunosuppressive molecule PD-L1 (40). In GC, TAMs trigger regulatory T cells by secreting chemokines, inhibiting the anti-tumor response of T cells, and disrupting immune cell interactions, ultimately leading to the immune escape of GC tumor cells (41). Amino acid metabolism is involved in mediating macrophage polarization, which affects anti-tumor immunity (42), therefore targeting amino acid metabolism to modulate anti-tumor immunity is a promising therapeutic tool.
TAMs in the GC microenvironment predominantly exhibit the M2 phenotype and promote cancer progression through immune escape. Reprogramming of methionine metabolism is tightly linked to the maintenance of the M2 phenotype. TMAs in the GC microenvironment overexpress methionine adenosyltransferase IIA (MAT2A), which increases intracellular levels of SAM and alters the epigenetic pattern of TAMs, thereby inducing the expression of receptor-interacting protein 1 (RIP1), and the RIP1 upregulation promotes macrophage polarization to M2 type (43). Therefore, targeting the MAT2A-PIP1 axis is expected to improve the efficacy of immunotherapy.MAT2A-related inhibitors include: substrate-competitive inhibitors and denaturing inhibitors. Only two compounds of this inhibitor have entered clinical studies, and the reasons for the difficulty in applying related inhibitors include poor specificity, difficulty in crossing the blood-brain barrier, and other side effects (44, 45).
SAM produced during methionine metabolism also affects the expression of immune checkpoints in the TME. In vitro and in vivo experiments have revealed that SAM produced by methionine metabolism promotes the expression of immune checkpoints (PD-L1) and V-domain lg suppressor of T cell activation (VISTA) in tumor cells, which ultimately inhibits T cell activation (46). Specific mechanism: SAM promotes m6A modification of PD-L1 mRNA in tumor cells, and the specific binding protein YTH structural domain family protein 1 (YTHDF1) recognizes and binds to m6A-modified PD-L1 mRNA and promotes PD-L1 expression, methionine dietary restriction or targeting of YTHDF1 enhances the therapeutic effects of PD-L1 blockade (46). In a mouse model of GC, the authors significantly inhibited tumor growth and metastasis by engineering small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) to deliver siRNA targeting m’A reader YTHDF1 (47). Unfortunately, no investigators have yet verified whether inhibition of methionine metabolism has the same effect in GC.
SAM also attenuates the activation of the STING pathway by promoting the methylation of cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS), resulting in a weakened anti-tumor immune response. cGAS is a genome resistance-associated protein that is associated with genome stability. cGAS is a key molecule of the immune system that is located in the endoplasmic reticulum in the inactivated state and senses cytoplasmic DNA, thereby activating the expression of interferon genes. STING is a key molecule of the immune system, located in the endoplasmic reticulum in the inactivated state, and can sense cytoplasmic DNA to activate interferon gene expression and regulate immune cells to exert anti-tumor effects (48). In a study of intestinal cancer, methionine deprivation promoted the cGAS-sting-interferon pathway and inhibited tumor growth. cGAS is located in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. cGAS, which is located in the cytoplasm, is the main receptor for cytoplasmic DNA; when stimulated, cGAS produces the second messenger cGAMP, which in turn activates the STING-TBK1-IRF3-INF signaling pathway. Thus, it plays a key role in anti-tumor immunity. SAM methylates cGAS and promotes its cytosolic localization, which decreases its activity. Methionine restriction blocks cGAS methylation, which enhances its cytoplasmic localization and strengthens anti-tumor immunity (49). In vitro and in vivo experiments have demonstrated that methionine restriction enhances the efficacy of radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy by potentiating the activation of the cGAS-STING pathway. Activation of STING could shift STING to the vicinity of the nucleus and promote macrophage polarization towards pro-inflammatory phenotypes depending on the IL6R - JAK - IL24 pathway, enhance anti-tumor immune responses, and induce apoptosis in GC cells (50). However, no study has linked methionine metabolism to the activation of the STING pathway in GC, and further studies are warranted.
SAM produced by methionine metabolism promotes the malignant biological behavior of tumor cells and inhibits the differentiation and functional roles of immune cells, so targeting MAT2A is expected to be a promising target to promote gastric cancer therapy. However, it has not yet been shown that methionine enters gastric cancer cells and macrophages through which transporter protein specifically, so it is not easy to achieve by restricting transporter proteins to specifically restrict methionine entry into gastric cancer cells or macrophages
Cys is a semi-essential amino acid (51), and in vivo Cys that can be interconverted in vivo. Cys is a key component in the synthesis of glutathione (GSH), which is closely associated with the maintenance of a stable cellular redox state.
Glutamate-cysteine ligase (GCL), the rate-limiting enzyme in GSH synthesis, consists of a catalytic subunit (GCLC) and a modifying subunit (GCLM) (52). Experiments in GCLM knockout mice demonstrated that during cancer initiation, cancer cell proliferation and metabolic activity increase, leading to intracellular accumulation of ROS, and that GSH protects cancer cells from oxidative damage by neutralizing reactive oxidants and promoting tumor progression (53). Since Cys is one of the components of GSH, increased production of GSH may deplete the endogenous source of Cys (54). Subsequently, to survive and proliferate, cancer cells accelerate the uptake of extracellular cystine via the CSSC/Glu reverse transporter (xCT transporter) (54, 55). Cysteine enzymes reduce the serum levels of Cys and deplete extracellular Cys. Cysteine enzymes include cysteine proteases, synthetases, and hydrolases and their regulation may be beneficial in controlling cancer progression (56).
Cysteine protease inhibitor (CST1) expression is upregulated in both primary and metastatic GC, suggesting a poor prognosis (Figure 2). CST1 can increase the stability of GPX4, a phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase, through two pathways. These include: 1. CST1 interacts directly with GPX4 to increase the stability of GPX4 protein via the proteasome pathway. 2. CST1 also recruits the deubiquitinating enzyme OTUB1 to inhibit GPX4 ubiquitination, which improves the stability of GPX4 and inhibits the expression of ferritin in GC cells. CST1 reduces the intracellular level of ROS by increasing the stability of GPX4, thus inhibiting ferroptosis and promoting EMT and metastasis in GC cells (57). The overall efficacy of chemotherapy for metastatic GC is poor; therefore, targeting CST1 may be a promising strategy for the treatment of metastatic GC.
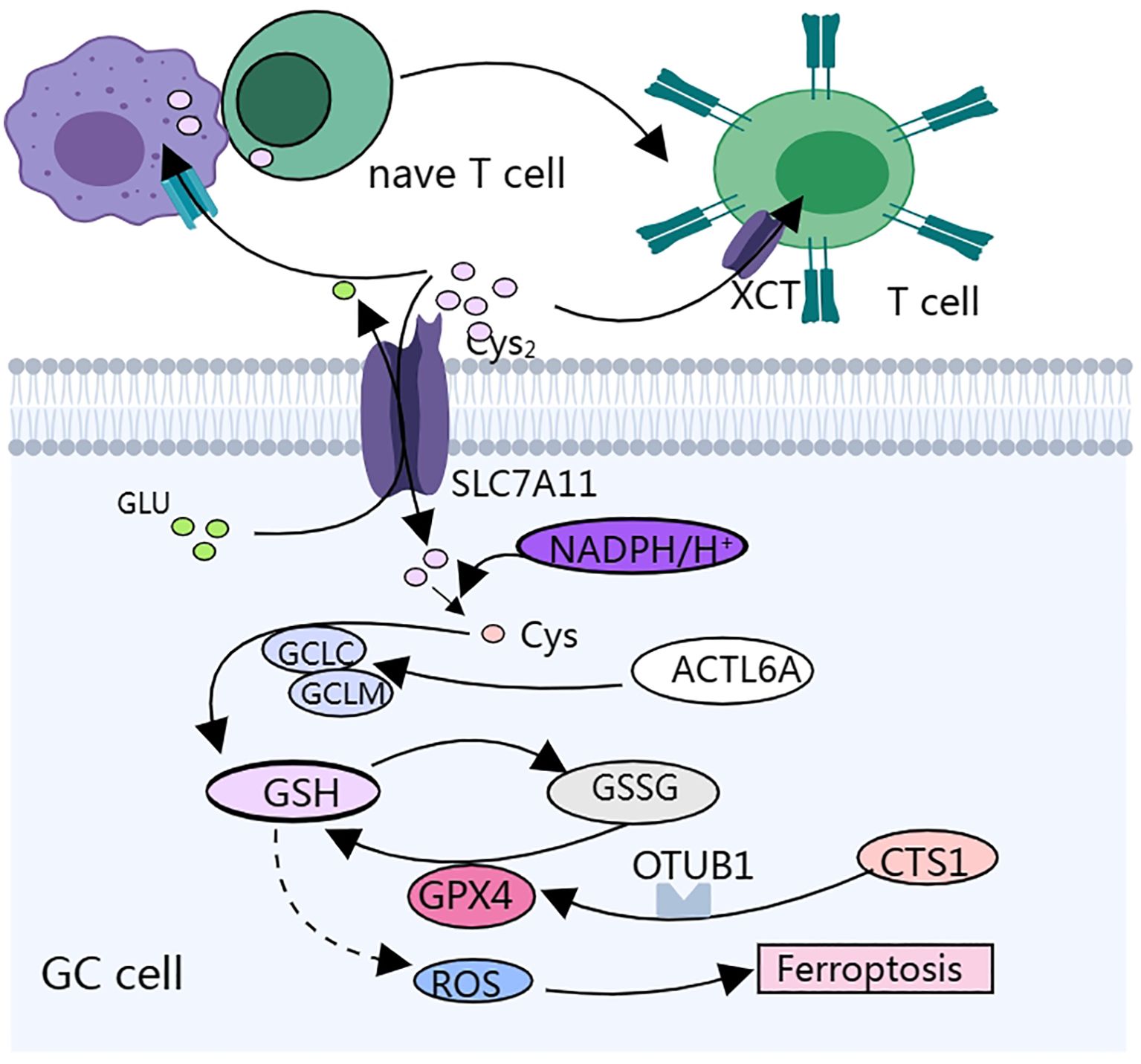
Figure 2. Cysteine metabolism affects gastric cancer progression and the biological function of immune cells mainly by regulating cellular redox status.
Cystine/glutamate reverse transporter SLC7A11 is a membrane channel transporter protein that can increase the synthesis of L-glutathione (GSH) in GC cells, help cancer cells resist ferroptosis-induced reactive oxygen species(ROS)and iron accumulation, enable GC cells to survive under hypoxic conditions, and promote peritoneal metastasis (PM) of GC (58, 59) (Figure 2). SLC7A11-mediated cystine uptake promotes GPX4 protein synthesis without affecting GPX4 mRNA or protein degradation (60). Cysteine and methionine deprivation was found to synergize with the GPX4 (glutathione peroxidase 4) inhibitor RSL3 to increase the number of iron-dead cells and lipid peroxidation in mouse and human glioma lines, and a reduced cysteine- and methionine-restricted diet improved the response of mice to RSL3 treatment and prolonged survival (61). GC cells highly express actin-like protein 6A (ACTL6A), which upregulates the expression of the catalytic subunit of γ-L-glutamyl-L-cysteine ligase (GCLC), thereby decreasing the reactive oxygen species (ROS) level and inhibiting ferroptosis, and inhibition of ACTL6A and GCLC may be a potential therapeutic strategy for GCs (62).
T lymphocytes are key components of the human immune system and are mainly responsible for regulating the immune response and directly killing infected or tumor cells. Most effector T cells die through apoptosis after performing their immediate effector function, whereas a small proportion of effector T cells differentiate into memory T cells, which provide a durable protective response to the body (63, 64). T cells in the TME are deprived of amino acids and accumulate metabolites that directly affect their metabolic and immune functions.
Tumor cells overexpressing SLC7A11 compete for cystine uptake, leaving the TME cystine-depleted. Cystine deprivation results in ferroptosis and the terminal depletion of CD8+ T cells, resulting in increased cell death and increased PD-1 expression. Knockdown of SLC7A11 in tumor cells, overexpression of SLC7A11 in T cells, overexpression of GCLC in T cells, and cystine supplementation enhanced the anti-tumor ability of CD8+ T cells (65).
Researchers have constructed cysteine gamma-cleaving enzyme (CTH)-overexpressing T cells and used a mouse model of melanoma to perform a metastasis assay of pericytes, a key enzyme in the transsulfuration pathway. CTH-overexpressing T cells have been found to better control tumor growth in mice. The mechanism does not increase cysteine autonomy in T cells but inhibits tumor growth by altering amino acid availability in the tumor microenvironment (66).
Initial T cells lack the cystine/glutamate exchange transporter system, Xct, and therefore rely on neighboring macrophages and dendritic cells (DCs) for cysteine, which is acquired via the alanine-serine-cysteine transporter during the early stages of activation (67, 68). Notably, depleted T cells within the TME typically contain fragmented mitochondria and excess ROS; therefore, the removal of accumulated ROS from the TME is a promising strategy for preventing T cell dysfunction and depletion (69). The antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (N-AC) is a precursor of GSH biosynthesis. In a mouse model, N-AC treatment significantly enhanced the therapeutic effect of over-transferred T cells, which could partially reverse T cell dysfunction by limiting oxidative stress (69).
The TME consists of stromal progenitor cells and tumor-associated mesenchymal stem cells (TC-MSCs). TC-MSCs can play an immunosuppressive role by inhibiting the proliferation of T cells (70), and maturation of dendritic cells (DCs) (71). Cystathionase is a key enzyme for cysteine synthesis. MSCs inhibit cysteine production by suppressing the expression of the cystathionase gene on DCs, which results in T cells lacking cysteine and attenuating T cell immune function (72). Neem Leaf Glycoprotein (NLGP) is a natural glycoprotein extracted from the leaves of neem tree (Neem tree, Azadirachta indica) and is an immunomodulator. IL-10 phosphorylates STAT3 by binding to the receptor on the surface of DCs, and the phosphorylated STAT3 can bind to the promoter region of the cystathionase gene and inhibit its expression. NLGP treatment of TC-MSCs significantly attenuated the expression of IL-10, restored the expression of the cystathionase gene, and promoted the proliferation of T cells and the recovery of their functions (73). However, there have been no studies on the use of NLGP for the treatment of GC.
A subgroup of patients with GC with high expression of human cysteine protease gene (CTSL) and low expression of CD4 lineage transcription factor gene (ZBTB7B) had higher immune infiltration and lower tumor purity, however, this group of patients had the shortest survival and the worst prognosis, and further studies found that this subgroup showed higher levels of immune checkpoints and more abundant cancer-related signaling pathways, including the TGF-β signaling pathway, targeting which may enhance the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in these patients, and that this subgroup may be able to benefit from the use of TGF-β signaling pathway. This subgroup shows higher levels of immune checkpoints and a richer array of cancer-related signaling pathways, including the TGF-β signaling pathway, and targeting this pathway may enhance the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in these patients (74). However, this has not yet been experimentally verified.
Glutamic acid is a non-essential amino acid that is interconvertible with glutamine, an important metabolic substrate and energy source critical for the growth and survival of many tumor cells (75, 76). Differences in microbial composition and metabolites in proximal and distal GCs were found using RNA sequencing, which may reveal different mechanisms of gastric carcinogenesis and progression; glutamate and glutamine, as microbial metabolites, may be associated with gastric carcinogenesis (77). Analysis of water-soluble metabolites in gastric tissues of a gastric rat model using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)-based metabolomics revealed that the metabolic profiles of GC tissues were significantly different from those of normal tissues, which may be related to changes in glutamate metabolism (78). The glutamate metabolic pathway is associated with the immune microenvironment and metabolic remodeling in GC (79).
Cancer cells take up glutamine through glutamine transporter protein (ASCT2), and the glutamine taken up is broken down into glutamate by glutaminase in the cell, which is involved in the synthesis of proteins and nucleotides (76, 80). A proportion of 77% of human GC tissues highly expresses the glutamine transporter protein ASCT2, and 12% highly express glutamine synthetase GS. In vitro and in vivo experiments have demonstrated that the combined inhibition of ASCT2 and GS can effectively block the glutamine pathway in cancer cells, providing a new potential target for the treatment of gastric cancer (81). Topoisomerase inhibitors such as topotecan (TPT) were found to inhibit glutamine uptake through the downregulation of ASCT2, cause oxidative stress, and induce apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway in cellular experiments, animal experiments, and sequencing techniques (82).
GDH, a key enzyme in glutamine catabolism, is expressed in the cytoplasmic membrane of gastric cancer cells and inhibits tumor growth through the Notch signaling pathway (83). Glutamate metabolism affects 5-FU resistance in gastric cancer, researchers have constructed 5-FU-resistant cell lines, and metabolic analysis has shown that proline dehydrogenase (PRODH) mRNA expression, which catalyzes the conversion of proline to glutamate and the production of superoxide (84).
Glutamate can also act as a neurotransmitter to influence tumor development and it plays a role in regulating intracellular calcium ion concentration through glutamate receptors (85). Aberrant DNA methylation is one of the major mechanisms by which tumor suppressor genes are silenced in GC, and the glutamate receptor GRIK2 has been identified as a novel epigenetic target (86).
GC is highly heterogeneous and characterized by high levels of autophagy, metabolic disorders, and hypoxia (87, 88). Oncogenic signaling-induced metabolic alterations are critical for cancer development. Activated mTOR regulates cell growth and metabolism. m TOR signaling regulates the three major metabolisms and inhibits catabolic processes such as autophagy (89–91). When nutrients are deficient or subjected to other self-induced signals, mTOR activity is inhibited, and autophagy is initiated (91).
Autophagy interacts with amino acid metabolism to provide energy to the cancer cells (Figure 3). mTORC1 regulates glutamine metabolism, and SIRT4 is a mitochondria-localized member of the sirtuin family, which is a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD)-dependent enzyme. sirtuin 4 inhibits the activity of glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) through ADP-ribosylation, and mTORC1 promotes SIRT4 (92). mTORC2 may promote glutamine catabolism by inhibiting the expression of GS expression (93). Prolonged mTOR inhibition also induces an adaptive increase in glutamine catabolism, allowing tumor cells to avoid the loss of glycolysis and thus mediate resistance to mTOR inhibition (94). Glutamine activates mTORC1 and induces glutamine-dependent cell death (glutamine apoptosis) via two parallel metabolic pathways (95). One: Glutamine is metabolized to α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) via glutaminase (GLS) and glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH), which ultimately activates mTORC1 via proline hydroxylases (PHDs) by facilitating GTP loading of RAGB12 (96). Second, glutamine can indirectly activate mTORC1 by inhibiting AMPK through asparagine synthetase (ASNS) and GABA bypass metabolism to produce ATP.
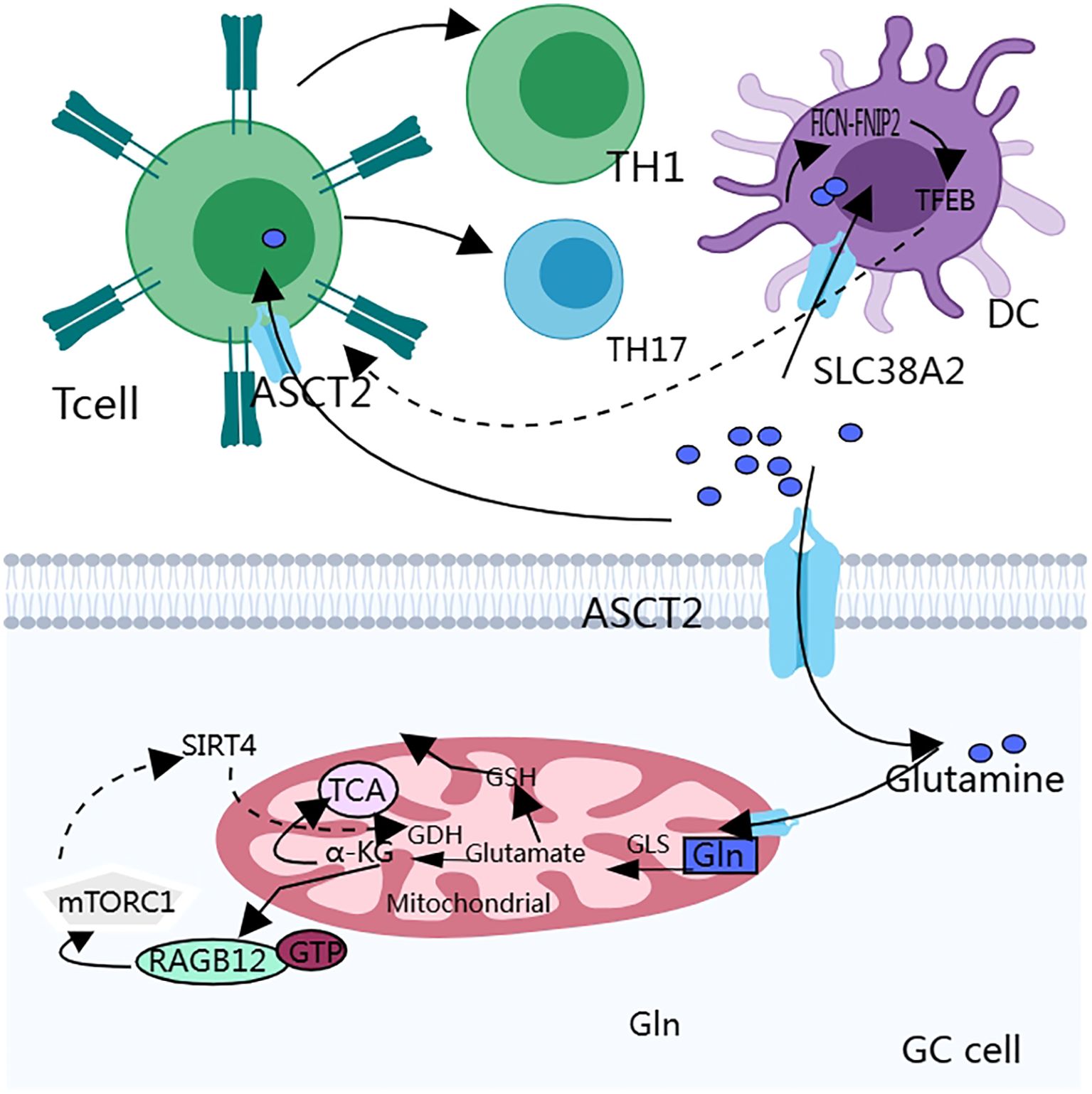
Figure 3. Glutamine metabolism interacts with the autophagy process of cancer cells, which in turn affects the biological behavior of cancer cells. In addition, the anti-tumor immune function of T cells is easily disturbed because they lack glutamine transporters and have a weaker uptake capacity for glutamine than cancer cells.
Our experiments demonstrated that the simultaneous inhibition of ASNS and GLS effectively inhibits mTORC1 (95). Glutamine-mediated apoptosis can be used in combination with existing cancer treatments (e.g., chemotherapy and radiotherapy) to enhance therapeutic effects. For example, drugs that inhibit mTORC1 can be used in combination with nutrient deprivation therapy to effectively kill cancer cells. Some mTORC1 inhibitors such as everolimus and temsirolimus have been approved for clinical use. A variety of glutaminolytic inhibitors are currently in clinical trials, such as the GLS inhibitors BPTES (97) and CB-839 (98).
The influence of glutamate metabolism on GC immunity is multifaceted and involves multiple dimensions of the TME, immune cell activation, and antitumor effects (Figure 3).
mTORC1 is also a central metabolic regulator that coordinates environmental and intracellular signals for T cell activation (99). ASCT2 plays an important role in T cell receptor signaling. ASCT2 deficiency leads to reduced TH1 and TH17 cell production and affects inflammatory T cell responses. ASCT2 activates mTORC1 by promoting glutamine uptake, and the activation of mTORC1 also affects TH1 and TH17 cell differentiation (100).
In the TME, immune cells compete with cancer cells for glutamine; initial T cells lack the cystine/glutamate exchange transporter system (67, 68), and depleted T cells have dysregulated metabolic activities, including glutamine catabolism and ROS accumulation (101). Most tumor cells preferentially rely on glutamine metabolism for proliferation, leading to glutamine deficiency in T cells (102), When cancer cells become addicted to glutamine, the function of dendritic cells, which have an antigen-presenting role, is suppressed, and the anti-tumor immune function is dramatically reduced (103).
Folliculin (FICN) is a tumor suppressor protein that plays an important role in a variety of cell types, particularly in the regulation of cell growth, proliferation, and metabolism (104, 105). Transcription Factor EB (TFEB) is a transcription factor that regulates lysosomal biogenesis and functional activity and affects the antigen-presenting capacity of dendritic cells (DCs) (106). DCs compete with cancer cells for glutamine uptake via SLC38A2 Glutamine availability affects the formation of the FICN-FNIP2 complex, which in turn regulates TFEB activity and affects the antigen-presenting function of DCs, which in turn affects CD8+ T cell activation (103, 107). These studies suggest that SLC38A2 and FICN could be used as drug targets to enhance the efficacy of immunotherapy.
In a mouse model of colorectal cancer, high levels of ammonia in the TME inhibited T cell function, leading to T cell depletion and resistance to immunotherapy, and L-ornithine stimulated the urea cycle and glutamine synthesis to achieve ammonia detoxification and reactivate the immune response, resulting in a reduction in tumor growth and prolonged survival in a mouse model of the tumor (108). T cell-based cancer immunotherapy can be improved by modulating ammonia detoxification mechanisms. For example, by upregulating the expression of CPS1, a key enzyme in the urea cycle, ammonia levels can be reduced, and the survival and anti-tumor effects of CD8+ memory T cells can be improved (109).
Glutamine metabolism can modulate antitumor immunity, but these experiments were not studied simultaneously in the presence of GC. Future studies could be conducted in a mouse model of GC, which could allow observation of the overall impact of the relevant therapeutic agents.
CagA-positive Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori CagA) plays a key role in gastric carcinogenesis, and Hippo pathway dysregulation occurs frequently in GC and is involved in H. pylori-induced gastric carcinogenesis (110, 111) (Figure 4). The Hippo pathway is a serine-threonine kinase cascade reaction that typically consists of two parts. First, a series of serine-threonine kinases are core components of the pathway, such as MST1/2 and LAST1/2. The second is a transcriptional cofactor, Yes-associated protein (YAP), with a transcriptional co-activator and PDZ-binding motif (TAZ) (112, 113). The activation of MST1/2 can activate LAST1/2 by phosphorylation and activated LAST1/2 can phosphorylate and inhibit the activity of YAP and TAZ, thereby inhibiting cell growth and value addition. Dysregulation of this pathway is associated with invasion (114), metastasis (115), chemoresistance (116), and maintenance/expansion of tumor stem cell (CSCs) compartments in malignant tumors (117). CagA invades gastric epithelial cells to form the Cag A/PAR1b complex, which can inhibit polarity-regulated kinase PAR1b-mediated phosphorylation of BRCA1, thereby affecting nuclear translocation of BRCA1, and the lack of nuclear BRCA1 leads to BRCAness, a cellular state that promotes DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), and the Cag A/PAR1b interaction can also stimulate the Hippo signaling pathway, which promotes the translocation of YAP from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, allowing it to form a complex with the TEAD family, thus exerting an anti-apoptotic effect and giving the cell time to repair DSBs through error-prone mechanisms (110). A study on hepatocellular carcinoma found that the small-molecule inhibitor XMU-MP-1 promoted liver regeneration by inhibiting MST1/2 activation (113).
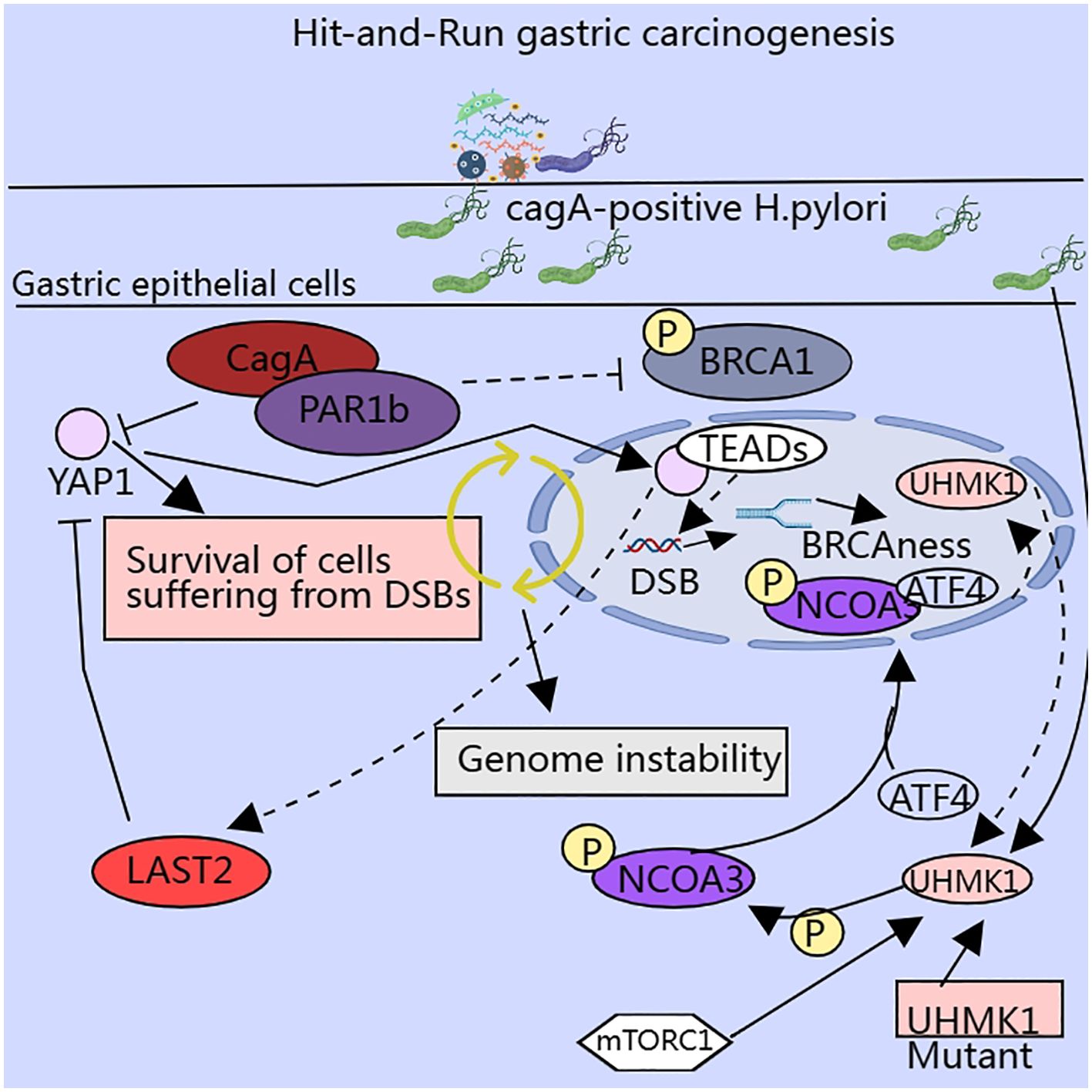
Figure 4. Enzymes involved in serine metabolism influence the malignant potential of cancer cells via multiple pathways.
However, there are not enough studies to show that serine metabolism can directly act on the Hippo pathway. Serine can promote cell growth and proliferation by activating mTORC1, and the activation of YAP/TAZ can promote the transcription of SLC7A5, which promotes the activation of the mTORC1 pathway, thereby exerting a pro-tumorigenic effect (118, 119). This suggests that serine metabolism indirectly regulates the Hippo signaling pathway through the mTOR signaling pathway.
SEM-type gastric carcinomas exhibit marked resistance to chemotherapy, and it was found that these carcinomas highly express the glutaminase GLS, but they are resistant to glutamine catabolism inhibition. Serine availability can affect the catalytic activity of PHGDH and the overall efficiency of the serine synthesis pathway. Under glutamine starvation, SEM-type GC cells maintain cell survival by upregulating the mitochondrial folate cycle pathway driven by 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase (PHGDH), which produces nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) to scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) (120). The therapeutic modality of combined inhibition of GLS and PHGDH has potential clinical applications (120, 121).
SHMT2 plays a key role in serine metabolism, especially in the one-carbon metabolic pathway in mitochondria, affecting methylation and nucleotide synthesis (122). SHMT2 is highly expressed in GC and is associated with poor prognosis (123, 124). In vitro and in vivo experiments verified that SHMT2 knockdown promotes GC progression through various pathways such as regulating the stability of HIF1α, affecting the downstream VEGF and STAT3 pathways, and maintaining redox homeostasis in GC cells under hypoxic conditions (124).
Tumor metastasis requires adaptation to new environments. The lack of serine and glycine in the brain may inhibit tumor cell growth. However, the occurrence of brain metastases suggests that tumor cells can overcome this metabolic limitation. Using proteomics, metabolomics, and multiple brain metastasis models, researchers have demonstrated that PHGDH is a major determinant of brain metastasis in various human cancer types and preclinical models. Enhanced serine synthesis is important for nucleotide production and proliferation of highly aggressive metastatic brain cells. Furthermore, the copy number of the oncogene MYC is high in patients with lung cancer brain metastases, and MYC upregulates the expression of pyridoxal phosphate-binding protein SHMT2, which catalyzes the synthesis of serine, glycine, and nucleotides. The use of PHGDH and SHMT1/2 inhibitors may be beneficial for treating brain metastases (125–127). The incidence of brain metastasis from GC is relatively low. Patients with meningeal metastases from GC have increased MYC copy numbers in their cerebrospinal fluid. This suggests that brain metastases from GC may overcome metabolic limitations via this mechanism (128). Therefore, targeting metabolism is not an effective strategy for cancer treatment. However, it has been demonstrated that inhibiting metabolism can sometimes inhibit the growth of normal cells while inhibiting the growth of cancer cells. Therefore, it is essential to implement a reasonable treatment plan considering specific circumstances.
UHMK1, a serine and threonine kinase, is highly expressed in GC tissues and promotes GC progression by enhancing the synthesis of slave purines. It was found that UHMK1 enhances the expression of purine metabolism-related genes by phosphorylating Recombinant nuclear receptor co-activator 3 (NCOA3), which strengthens the binding ability of NCOA3 and ATF4. ATF4 has a role independent of the UHMK1-NCOA3-ATF4 axis, and silencing ATF4 also inhibited serine metabolism and glycolysis. H. pylori infection induced NCOA3 - S1062/T1067 phosphorylation and enhanced the promoter activity of UHMK1 via ATF4. The above results suggest that UHMK1 may be an attractive therapeutic target for GC (129). A study of human fibroblasts demonstrated that TGF-β1 also stimulates ATF4 expression, contingent on the TGF-β1–mTORC1–ATF4 axis, which facilitates serine–glycine synthesis to ensure sufficient amino acids for cell growth and metabolism. Targeting the TGF-β1–mTORC1–ATF4 axis may represent a novel therapeutic strategy (130). Moreover, the transcription factor ATF4 stimulates the transcription of the cell cycle protein Cyclin A1 and accelerates S-phase progression through the formation of a transcriptional complex with PICH and PoI II, thereby contributing to 5-FU chemoresistance (131).
During T cell activation, mitochondrial proteins undergo significant remodeling, and ultimately the mitochondria undergo metabolic reprogramming and enhancement of one-carbon metabolic pathways. If SHMT2 is inhibited in naïve T cells, this ultimately leads to a decrease in both T cell viability and the abundance of antigen-specific T cells in vivo, which closely resembles the metabolic characteristics of many cancer cells (132). Regulatory T cells are important in the maintenance of immune homeostasis; serine promotes glutathione production, and glutathione levels affect serine uptake and synthesis. If the integrity of this feedback loop is critical to ensure the normal function of regulatory T cells, disruption of this loop leads to severe autoimmunity with an enhanced anti-tumor response. For example, specific knockdown of glutamate cysteine ligase (Gclc) in mice leads to increased Treg cell serine metabolism, mTOR activation and proliferation, and decreased Treg cell immune suppression. Cysteine ligase (Gclc) knockdown in mice leads to increased serine metabolism in Tregs, increased mTOR activation and proliferation, and decreased the immunosuppressive capacity of Tregs cells (133). GSH is highly abundant in Tregs. GSH limits mTOR activation by regulating serine uptake and synthesis and maintains the normal expression of forkhead box P3 (FoxP3) to maintain the immune function of Tregs. FoxP3 is a transcription factor that is mainly expressed in regulatory T cells (Tregs). Differentiation, development, and maintenance of function (134).
Serine metabolism is critical for the regulation of macrophage polarization, and serine metabolism reduces IGF1 expression by increasing the promoter abundance of S-adenosylmethionine-dependent lysine trimethylation at position 27 of histone H3, which is regulated through the p38-JAK-STAT1 signaling axis, and by restricting the uptake of exogenous serine or by inhibiting the key enzyme of serine metabolism, phosphoglycerol dehydrogenase PHGDH promotes macrophage polarization to a pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype and enhances anti-tumor immunity (135).
Serine plays an important role in the metabolic pathways of GC and may indirectly influence the anti-tumor immune response in gastric cancer by affecting the functional and metabolic status of immune cells. However, further studies are required to clarify the specific mechanisms underlying serine metabolism in GC development and immunotherapy.
BCAT1 and BCAT2 are common branched-chain amino acid aminotransferases that convert branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) to branched-chain alpha keto acid and catalyze the conversion of alpha-ketoglutarate to glutamate. Mutations in the codon responsible for encoding BCAT1 have been identified in clinical GC samples, and these mutations result in higher enzymatic activity of BCAT1, which promotes BCAA catabolism and accelerates cell growth motility and tumor development. Rho protein, a Ras-related guanosine triphosphatase, is involved in the formation of stress fibers and focal adhesions and plays a key role in the reorganization of the cytoskeleton. This mutation results in increased Rhoc activity (136). High BCAA levels can upregulate the expression of the glucose transporter molecule Glut1 on the surface of CD8+ T cells via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase–AKT–mTORC1–FoxO1 signaling pathway. This results in altered glucose uptake and the downstream metabolic profile of CD8+ T cells. Furthermore, BCAA supplementation enhances the anti-tumor effects of immunotherapy (137).
Taurine is a semi-essential sulfur-containing β-amino acid that is widely distributed in mammalian tissues and organs, typically in free form. It is not involved in protein synthesis; however, it can be synthesized endogenously or obtained from food. For example, taurine is synthesized from methionine and cysteine in the human liver. Other organs can also uptake taurine from the bloodstream. Cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase is the rate-limiting enzyme in taurine synthesis. Taurine is formed via the metabolism of methionine and cysteine in hepatocytes. Other cells can also uptake taurine from the bloodstream. Cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase has a low activity in the human body, making it susceptible to taurine deficiency. Taurine is also present in the TME and may affect the metabolism of tumor and immune cells (138–141). GC cells upregulate taurine transporter SLC6A6, competing for taurine in the microenvironment and triggering endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in CD8+ T cells to upregulate ATF4. The specific mechanism is that taurine deficiency induces eIF2α phosphorylation, which subsequently promotes the transcription of ATF4 through PERK–JAK1–STAT3 pathway activation and ultimately leads to the upregulation of immune checkpoint expression and the depletion of CD8+ T cell function. Taurine supplementation improves this state (142). Resistance to chemotherapy is frequently associated with poor therapeutic efficacy. Chemotherapy resistance leads to an increase in the expression of SP1 and thus SLC6A6 in GC cells, which results in a lower level of taurine in the microenvironment. These findings suggest that chemotherapy-induced immunotherapeutic resistance can be improved by targeting the SP1–SLC6A6 axis (142).
GC is the fifth most common malignant tumor worldwide and has an extremely high mortality rate. The reprogramming of amino acid metabolism in GC provides a favorable environment for its growth and survival and can affect the biological functions of both cancer cells and immune cells by participating in multiple signaling pathways through the TME. Therefore, therapeutic strategies targeting amino acid metabolism may provide new options to enhance the effects of chemotherapy and immunotherapy in GC. However, amino acid metabolism is complex, and different amino acid metabolic processes interact to regulate pathway activation. Targeting amino acid metabolism can help regulate anti-tumor immunity and inhibit the progression of GC, but the number of drugs that have entered clinical trials is limited to animal experiments. The reasons for the limitations of drug application in clinics are as follows: 1. Amino acids are not only nutrients for cancer cells but also for many normal cells, and the human body is an organic whole; therefore, how to specifically target specific pathways needs further consideration. 2. Therapeutic resistance. Metabolic pathways interact with each other, and after the application of drugs that target amino acid metabolism for some time, cancer cells may develop resistance to specific amino acid pathways. 3. Most experiments remain at the stage of mouse animal testing, and the short research cycle of hormonal mice may not be able to highlight the efficacy of long-term treatments. 4. Amino acid metabolism in mice may differ from that in humans.
It is often difficult to achieve the desired therapeutic effects with a single treatment. Therefore, drugs targeting amino acid metabolism need to be used in combination with other therapeutic approaches (e.g., chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and immunotherapy) to enhance their therapeutic effect. However, designing an effective combination therapy strategy is complex. Although drugs targeting amino acid metabolism are rarely used clinically, studies have shown that this strategy is a promising therapeutic tool.
YJ: Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QT: Conceptualization, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. XQ: Writing – review & editing. YY: Writing – review & editing. CP: Writing – review & editing. MH: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. KD: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. WZha: Writing – review & editing. MX: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. DW: Writing – review & editing. WZhu: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. XL: Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by The Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20231252), Key Medical Research Projects of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission (K2023026), Science and Technology Planning Social Development Project of Zhenjiang City (SH2022047), and the Medical Education Collaborative Innovation Fund of Jiangsu University (JDY2022003).
We would like to acknowledge all participants of this study and the technical support provided by the Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University. We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for the English language editing.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
2. Bagheri M, Akrami H. Studying the non-coding RNA expression and its role in drug resistance mechanisms of gastric cancer. Pathology Res Practice. (2025) 265. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155742
3. Wang Y, Hong Z, Song J, Zhong P, Lin L. METTL3 promotes drug resistance to oxaliplatin in gastric cancer cells through DNA repair pathway. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1257410. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1257410
4. Zang WJ, Hu YL, Qian CY, Feng Y, Liu JZ, Yang JL, et al. HDAC4 promotes the growth and metastasis of gastric cancer via autophagic degradation of MEKK3. Br J Cancer. (2022) 127. doi: 10.1038/s41416-022-01805-7
5. Sanati M, Ghafouri-Fard S. The role of circRNAs in resistance to doxorubicin. Cell Communication Signaling : CCS. (2024) 22. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01952-9
6. Liu Y, Ao X, Wang Y, Li X, Wang J. Long non-coding RNA in gastric cancer: Mechanisms and clinical implications for drug resistance. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:841411. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.841411
7. Chen D, Lin X, Zhang C, Liu Z, Chen Z, Li Z, et al. Dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor BEZ235 as a promising therapeutic strategy against paclitaxel-resistant gastric cancer via targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Cell Death Disease. (2018) 9. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0132-2
8. Hirashita Y, Tsukamoto Y, Yanagihara K, Fumoto S, Hijiya N, Nakada C, et al. Reduced phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 is associated with sensitivity to MEK inhibition in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Science. (2016) 107. doi: 10.1111/cas.13094
9. Huang Y, Liang L, Zhao YX, Yao BH, Zhang RM, Song L, et al. RUNX2 reverses p53-induced chemotherapy resistance in gastric cancer. Pharmacogenomics Personalized Med. (2023) 16. doi: 10.2147/PGPM.S394393
10. Rao X, Zhang C, Luo H, Zhang J, Zhuang Z, Liang Z, et al. Targeting gastric cancer stem cells to enhance treatment response. Cells. (2022) 11. doi: 10.3390/cells11182828
11. Walcher L, Kistenmacher AK, Suo H, Kitte R, Dluczek S, Strauß A, et al. Cancer stem cells-origins and biomarkers: Perspectives for targeted personalized therapies. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1280. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01280
12. Smyth EC, Nilsson M, Grabsch HI, van Grieken NC, Lordick F. Gastric cancer. Lancet (London England). (2020) 396. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31288-5
13. Kim ST, Cristescu R, Bass AJ, Kim K-M, Odegaard JI, Kim K, et al. Comprehensive molecular characterization of clinical responses to PD-1 inhibition in metastatic gastric cancer. Nat Med. (2018) 24:1449–58. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0101-z
14. . Nagtegaal ID, Odze RD, Klimstra D, Paradis V, Rugge M, Schirmacher P, et al. The 2019 WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. Histopathology. (2020) 76. doi: 10.1111/his.13975
15. Saldanha OL, Muti HS, Grabsch HI, Langer R, Dislich B, Kohlruss M, et al. Direct prediction of genetic aberrations from pathology images in gastric cancer with swarm learning. Gastric Cancer Off J Int Gastric Cancer Assoc Jpn Gastric Cancer Assoc. (2023) 26. doi: 10.1007/s10120-022-01347-0
16. Bruni D, Angell HK, Galon J. The immune contexture and immunoscore in cancer prognosis and therapeutic efficacy. Nat Rev Cancer. (2020) 20. doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-0285-7
17. Wang MM, Coupland SE, Aittokallio T, Figueiredo CR. Resistance to immune checkpoint therapies by tumour-induced T-cell desertification and exclusion: key mechanisms, prognostication and new therapeutic opportunities. Br J Cancer. (2023) 129. doi: 10.1038/s41416-023-02361-4
18. Wainberg ZA, Fuchs CS, Tabernero J, Shitara K, Muro K, Van Cutsem E, et al. Efficacy of pembrolizumab monotherapy for advanced Gastric/Gastroesophageal junction cancer with programmed death ligand 1 combined positive score ≥10. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. (2021) 27. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2980
19. Yamashita K, Iwatsuki M, Harada K, Eto K, Hiyoshi Y, Ishimoto T, et al. Prognostic impacts of the combined positive score and the tumor proportion score for programmed death ligand-1 expression by double immunohistochemical staining in patients with advanced gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer Off J Int Gastric Cancer Assoc Jpn Gastric Cancer Assoc. (2020) 23. doi: 10.1007/s10120-019-00999-9
20. André T, Shiu KK, Kim TW, Jensen BV, Jensen LH, Punt C, et al. Pembrolizumab in microsatellite-Instability-High advanced colorectal cancer. New Engl J Med. (2020) 383. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2017699
21. Samstein RM, Lee CH, Shoushtari AN, Hellmann MD, Shen R, Janjigian YY, et al. Tumor mutational load predicts survival after immunotherapy across multiple cancer types. Nat Genet. (2019) 51. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0312-8
22. Wang Z, Zhang Q, Qi C, Bai Y, Zhao F, Chen H, et al. Combination of AKT1 and CDH1 mutations predicts primary resistance to immunotherapy in dMMR/MSI-h gastrointestinal cancer. J Immunotherapy Cancer. (2022) 10. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-004703
23. Lin Y, Pan X, Zhao L, Yang C, Zhang Z, Wang B, et al. Immune cell infiltration signatures identified molecular subtypes and underlying mechanisms in gastric cancer. NPJ Genomic Med. (2021) 6. doi: 10.1038/s41525-021-00249-x
24. Zhou Z, Li M. Evaluation of BRCA1 and BRCA2 as indicators of response to immune checkpoint inhibitors. JAMA Network Open. (2021) 4. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.7728
25. Galli F, Aguilera JV, Palermo B, Markovic SN, Nisticò P, Signore A. Relevance of immune cell and tumor microenvironment imaging in the new era of immunotherapy. J Exp Clin Cancer Research : CR. (2020) 39. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01586-y
26. Wu F, Fan J, He Y, Xiong A, Yu J, Li Y, et al. Single-cell profiling of tumor heterogeneity and the microenvironment in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Nat Commun. (2021) 12. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22801-0
27. Gonzalez H, Hagerling C, Werb Z. Roles of the immune system in cancer: from tumor initiation to metastatic progression. Genes Dev. (2018) 32. doi: 10.1101/gad.314617.118
28. Sahai E, Astsaturov I, Cukierman E, DeNardo DG, Egeblad M, Evans RM, et al. A framework for advancing our understanding of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Rev Cancer. (2020) 20. doi: 10.1038/s41568-019-0238-1
29. Kang B, Camps J, Fan B, Jiang H, Ibrahim MM, Hu X, et al. Parallel single-cell and bulk transcriptome analyses reveal key features of the gastric tumor microenvironment. Genome Biol. (2022) 23. doi: 10.1186/s13059-022-02828-2
30. Rose WC, Oesterling MJ, Womack M. Comparative growth on diets containing ten and 19 amino acids, with further observations upon the role of glutamic and aspartic acids. J Biol Chem. (1948) 176.
31. Vander Heiden MG, DeBerardinis RJ. Understanding the intersections between metabolism and cancer biology. Cell. (2017) 168. doi: 10.1016/j.Cell.2016.12.039
32. Lemberg KM, Gori SS, Tsukamoto T, Rais R, Slusher BS, et al. Clinical development of metabolic inhibitors for oncology. J Clin Invest. (2022) 132. doi: 10.1172/JCI148550
33. Hussain A, Xie L, Deng G, Kang X. Common alterations in plasma free amino acid profiles and gut microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolites of five types of cancer patients. Amino Acids. (2023) 55. doi: 10.1007/s00726-023-03308-y
34. Liu Z, Wang A, Pu Y, Li Z, Xue R, Zhang C, et al. Genomic and transcriptomic profiling of hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the stomach. Oncogene. (2021) 40:5705–17. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01976-2
35. Wang Z, Yip LY, Lee JHJ, Wu Z, Chew HY, Chong PKW, et al. Methionine is a metabolic dependency of tumor-initiating cells. Nat Med. (2019) 25:825–37. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0423-5
36. Chen C, Zhao X, Wang H, Xu L, Fu Y, Huang G, et al. NNMT enriches for AQP5 + cancer stem cells to drive malignant progression in early gastric cardia adenocarcinoma. Gut. (2024) 73:63–77. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2022-328408
37. Jiang Y, Wang Y, Chen G, Sun F, Wu Q, Huang Q, et al. Nicotinamide metabolism face-off between macrophages and fibroblasts manipulates the microenvironment in gastric cancer. Cell Metab. (2024) S155041312400189X. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.05.013
38. Xue J, Sv S, Sander J, Draffehn A, Krebs W, Quester I, et al. Transcriptome-based network analysis reveals a spectrum model of human macrophage activation. Immunity. (2014) 40. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.01.006
39. Mantovani A, Marchesi F, Malesci A, Laghi L, Allavena P. Tumour-associated macrophages as treatment targets in oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2017) 14. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.217
40. Zhu Y, Yang J, Xu D, Xm G, Zhang Z, Jl H, et al. Disruption of tumour-associated macrophage trafficking by the osteopontin-induced colony-stimulating factor-1 signalling sensitises hepatoCellular carcinoma to anti-PD-L1 blockade. Gut. (2019) 68. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318419
41. Li J, Sun J, Zeng Z, Liu Z, Ma M, Zheng Z, et al. Tumour-associated macrophages in gastric cancer: From function and mechanism to application. Clin Trans Med. (2023) 13. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1386
42. Hu X, Ma Z, Xu B, Li S, Yao Z, Liang B, et al. Glutamine metabolic microenvironment drives M2 macrophage polarization to mediate trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive gastric cancer. Cancer Commun (London England). (2023) 43. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12459
43. Zhang Y, Yang H, Zhao J, Wan P, Hu Y, Lv K, et al. Activation of MAT2A-RIP1 signaling axis reprograms monocytes in gastric cancer. J Immunotherapy Cancer. (2021) 9. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001364
44. Li M, Konteatis Z, Nagaraja N, Chen Y, Zhou S, Ma G, et al. Leveraging structure-based drug design to identify next-generation MAT2A inhibitors, including brain-penetrant and peripherally efficacious leads. J Medicinal Chem. (2022) 65. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01595
45. Konteatis Z, Travins J, Gross S, Marjon K, Barnett A, Mandley E, et al. Discovery of AG-270, a first-in-Class oral MAT2A inhibitor for the treatment of tumors with homozygous MTAP deletion. J Medicinal Chem. (2021) 64. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01895
46. Li T, Yt T, Yx C, Xj Z, Wang W, Liao K, et al. Methionine deficiency facilitates antitumour immunity by altering m6A methylation of immune checkpoint transcripts. Gut. (2023) 72. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2022-326928
47. You Q, Wang F, Du R, Pi J, Wang H, Huo Y, et al. m6 a reader YTHDF1-targeting engineered small ExtraCellular vesicles for gastric cancer therapy via epigenetic and immune regulation. Advanced Materials (Deerfield Beach Fla.). (2023) 35. doi: 10.1002/adma.202204910
48. Liu S, Cai X, Wu J, Cong Q, Chen X, Li T, et al. Phosphorylation of innate immune adaptor proteins MAVS, STING, and TRIF induces IRF3 activation. Sci (New York N.Y.). (2015) 347. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa2630
49. Fang L, Hao Y, Yu H, Gu X, Peng Q, Zhuo H, et al. Methionine restriction promotes cGAS activation and chromatin untethering through demethylation to enhance antitumor immunity. Cancer Cell. (2023) 41. doi: 10.1016/j.cCell.2023.05.005
50. Miao L, Qi J, Zhao Q, Wu Q-N, Wei D-L, Wei X-L, et al. Targeting the STING pathway in tumor-associated macrophages regulates innate immune sensing of gastric cancer cells. Theranostics. (2020) 10:498–515. doi: 10.7150/thno.37745
51. Trachootham D, Alexandre J, Huang P. Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: a radical therapeutic approach? nature reviews. Drug Discovery. (2009) 8. doi: 10.1038/nrd2803
52. Dalton TP, Dieter MZ, Yang Y, Shertzer HG, Nebert DW. Knockout of the mouse glutamate cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (Gclc) gene: embryonic lethal when homozygous, and proposed model for moderate glutathione deficiency when heterozygous. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2000) 279. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2000.3930
53. Harris IS, Treloar AE, Inoue S, Sasaki M, Gorrini C, Lee KC, et al. Glutathione and thioredoxin antioxidant pathways synergize to drive cancer initiation and progression. Cancer Cell. (2015) 27. doi: 10.1016/j.cCell.2014.11.019
54. Zhang W, Trachootham D, Liu J, Chen G, Pelicano H, Garcia-Prieto C, et al. Stromal control of cystine metabolism promotes cancer cell survival in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat Cell Biol. (2012) 14. doi: 10.1038/ncb2432
55. Timmerman LA, Holton T, Yuneva M, Louie RJ, Padró M, Daemen A, et al. Glutamine sensitivity analysis identifies the xCT antiporter as a common triple-negative breast tumor therapeutic target. Cancer Cell. (2013) 24. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.08.020
56. Mungai PT, Waypa GB, Jairaman A, Prakriya M, Dokic D, Ball MK, et al. Hypoxia triggers AMPK activation through reactive oxygen species-mediated activation of calcium release-activated calcium channels. Mol Cell Biol. (2011) 31. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05124-11
57. Li D, Wang Y, Dong C, Chen T, Dong A, Ren J, et al. CST1 inhibits ferroptosis and promotes gastric cancer metastasis by regulating GPX4 protein stability via OTUB1. Oncogene. (2023) 42. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02537-x
58. Lei G, Zhang Y, Koppula P, et al. The role of ferroptosis in ionizing radiation-induced cell death and tumor suppression. Cell Res. (2020) 30. doi: 10.1038/s41422-019-0263-3
59. Lin Z, Song J, Gao Y, Huang S, Dou R, Zhong P, et al. Hypoxia-induced HIF-1α/lncRNA-PMAN inhibits ferroptosis by promoting the cytoplasmic translocation of ELAVL1 in peritoneal dissemination from gastric cancer. Redox Biol. (2022) 52. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102312
60. Zhang Y, Rv S, Nie L, Liu X, Wang C, Lee H, et al. mTORC1 couples cyst(e)ine availability with GPX4 protein synthesis and ferroptosis regulation. Nat Commun. (2021) 12. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21841-w
61. Upadhyayula PS, Higgins DM, Mela A, Banu M, Dovas A, Zandkarimi F, et al. Dietary restriction of cysteine and methionine sensitizes gliomas to ferroptosis and induces alterations in energetic metabolism. Nat Commun. (2023) 14. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36630-w
62. Yang Z, Zou S, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Zhang P, Xiao L, et al. ACTL6A protects gastric cancer cells against ferroptosis through induction of glutathione synthesis. Nat Commun. (2023) 14. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39901-8
63. Raud B, McGuire PJ, Jones RG, Sparwasser T, Berod L. Fatty acid metabolism in CD8+ T cell memory: Challenging current concepts. Immunol Rev. (2018) 283. doi: 10.1111/imr.12655
64. Buck MD, O’Sullivan D, Klein Geltink RI, Curtis JD, Chang CH, Sanin DE, et al. Mitochondrial dynamics controls T cell fate through metabolic programming. Cell. (2016) 166. doi: 10.1016/j.Cell.2016.05.035
65. Han C, Ge M, Xing P, Xia T, Zhang C, Ma K, et al. Cystine deprivation triggers CD36-mediated ferroptosis and dysfunction of tumor infiltrating CD8+ t cells. Cell Death Disease. (2024) 15. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06503-1
66. Lancien M, Gueno L, Salle S, Merieau E, Beriou G, Th N, et al. Cystathionine-gamma-lyase overexpression in t cells enhances antitumor effect independently of cysteine autonomy. Cancer Science. (2021) 112. doi: 10.1111/cas.14862
67. Garg SK, Yan Z, Vitvitsky V, et al. Differential dependence on cysteine from transsulfuration versus transport during T cell activation. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2011) 15. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3496
68. Angelini G, Gardella S, Ardy M, Ciriolo MR, Filomeni G, Di Trapani G, et al. Antigen-presenting dendritic cells provide the reducing extraCellular microenvironment required for t lymphocyte activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2002) 99. doi: 10.1073/pnas.022630299
69. Vardhana SA, Hwee MA, Berisa M, Dk W, Yost KE, King B, et al. Impaired mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation limits the self-renewal of t cells exposed to persistent antigen. Nat Immunol. (2020) 21. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0725-2
70. Rasmusson I, Ringdén O, Sundberg B, Le Blanc K. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit lymphocyte proliferation by mitogens and alloantigens by different mechanisms. Exp Cell Res. (2005) 305. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.12.013
71. Beyth S, Borovsky Z, Mevorach D, Liebergall M, Gazit Z, Aslan H, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells alter antigen-presenting cell maturation and induce T-cell unresponsiveness. Blood. (2005) 105. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-07-2921
72. Ghosh T, Barik S, Bhuniya A, Dhar J, Dasgupta S, Ghosh S, et al. Tumor-associated mesenchymal stem cells inhibit naïve T cell expansion by blocking cysteine export from dendritic cells. Int J Cancer. (2016) 139. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30265
73. Ghosh T, Nandi P, Ganguly N, Guha I, Bhuniya A, Ghosh S, et al. NLGP counterbalances the immunosuppressive effect of tumor-associated mesenchymal stem cells to restore effector T cell functions. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2019) 10. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1349-z
74. Cui K, Yao S, Liu B, Sun S, Gong L, Li Q, et al. A novel high-risk subpopulation identified by CTSL and ZBTB7B in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. (2022) 127. doi: 10.1038/s41416-022-01936-x
75. Dang CV. Rethinking the warburg effect with myc micromanaging glutamine metabolism. Cancer Res. (2010) 70. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3556
76. Wise DR, Thompson CB. Glutamine addiction: a new therapeutic target in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci. (2010) 35. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2010.05.003
77. Yang Y, Dai D, Jin W, Huang Y, Zhang Y, Chen Y, et al. Microbiota and metabolites alterations in proximal and distal gastric cancer patients. J Trans Med. (2022) 20. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03650-x
78. Gu J, Huang C, Hu X, Xia J, Shao W, Lin D. Nuclear magnetic resonance-based tissue metabolomic analysis clarifies molecular mechanisms of gastric carcinogenesis. Cancer Science. (2020) 111. doi: 10.1111/cas.14443
79. Yuan Q, Deng D, Pan C, Ren J, Wei T, Wu Z, et al. Integration of transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics data to reveal HER2-associated metabolic heterogeneity in gastric cancer with response to immunotherapy and neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:951137. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.951137
80. McGivan JD, Bungard CI. The transport of glutamine into mammalian cells. Front Biosci J Virtual Libr. (2007) 12. doi: 10.2741/2109
81. Ye J, Huang Q, Xu J, Huang J, Wang J, Zhong W, et al. Targeting of glutamine transporter ASCT2 and glutamine synthetase suppresses gastric cancer cell growth. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2018) 144. doi: 10.1007/s00432-018-2605-9
82. Wang L, Liu Y, Zhao TL, Li ZZ, He JY, Zhang BJ, et al. Topotecan induces apoptosis via ASCT2 mediated oxidative stress in gastric cancer. Phytomedicine Int J Phytother Phytopharm. (2019) 57. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.12.011
83. Wu YJ, Hu ZL, Hu SD, Li YX, Xing XW, Yang Y, et al. Glutamate dehydrogenase inhibits tumor growth in gastric cancer through the notch signaling pathway. Cancer biomark Sect Dis Markers. (2019) 26. doi: 10.3233/CBM-190022
84. Sasada S, Miyata Y, Tsutani Y, Tsuyama N, Masujima T, Hihara J, et al. Metabolomic analysis of dynamic response and drug resistance of gastric cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil. Oncol Rep. (2013) 29. doi: 10.3892/or.2012.2182
85. Liu B, Sun Y, Wang W, Ren J, Wang D. BHLHE40-mediated transcriptional activation of GRIN2D in gastric cancer is involved in metabolic reprogramming. Funct Integr Genomics. (2024) 24. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01495-9
86. Wu CS, Lu YJ, Li HP, Hsueh C, Lu CY, Leu YW, et al. Glutamate receptor, ionotropic, kainate 2 silencing by DNA hypermethylation possesses tumor suppressor function in gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. (2010) 126. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24958
87. Zhou H, Yuan M, Yu Q, Zhou X, Min W, Gao D. Autophagy regulation and its role in gastric cancer and colorectal cancer. Cancer biomark Sect Dis Markers. (2016) 17. doi: 10.3233/CBM-160613
88. Chen M, Wang G, Xu Z, Sun J, Liu B, Chang L, et al. Loss of RACK1 promotes glutamine addiction via activating AKT/mTOR/ASCT2 axis to facilitate tumor growth in gastric cancer. Cell Oncol (Dordrecht Netherlands). (2024) 47. doi: 10.1007/s13402-023-00854-1
89. Zhang Y, Kwok-Shing Ng P, Kucherlapati M, Chen F, Liu Y, Tsang YH, et al. A pan-cancer proteogenomic atlas of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway alterations. Cancer Cell. (2017) 31. doi: 10.1016/j.cCell.2017.04.013
90. Saxton RA, Sabatini DM. mTOR signaling in growth, metabolism, and disease. Cell. (2017) 169. doi: 10.1016/j.Cell.2017.03.035
91. Dibble CC, Manning BD. Signal integration by mTORC1 coordinates nutrient input with biosynthetic output. Nat Cell Biol. (2013) 15. doi: 10.1038/ncb2763
92. Csibi A, Fendt SM, Li C, Poulogiannis G, Choo AY, Chapski DJ, et al. The mTORC1 pathway stimulates glutamine metabolism and cell proliferation by repressing SIRT4. Cell. (2021) 184. doi: 10.1016/j.Cell.2021.03.059
93. van der Vos KE, Eliasson P, Proikas-Cezanne T, Vervoort SJ, van Boxtel R, Putker M, et al. Modulation of glutamine metabolism by the PI(3)K-PKB-FOXO network regulates autophagy. Nat Cell Biol. (2012) 14. doi: 10.1038/ncb2536
94. Momcilovic M, Bailey ST, Lee JT, Fishbein MC, Braas D, Go J, et al. The GSK3 signaling axis regulates adaptive glutamine metabolism in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell. (2018) 33. doi: 10.1016/j.cCell.2018.04.002
95. Bodineau C, Tomé M, Courtois S, Costa ASH, Sciacovelli M, Rousseau B, et al. Two parallel pathways connect glutamine metabolism and mTORC1 activity to regulate glutamoptosis. Nat Commun. (2021) 12. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25079-4
96. Durán RV, Oppliger W, Robitaille AM, Heiserich L, Skendaj R, Gottlieb E, et al. Glutaminolysis activates rag-mTORC1 signaling. Mol Cell. (2012) 47. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.05.043
97. Hensley CT, Wasti AT, DeBerardinis RJ. Glutamine and cancer: Cell biology, physiology, and clinical opportunities. J Clin Invest. (2013) 123. doi: 10.1172/JCI69600
98. Zhao Y, Feng X, Chen Y, Selfridge JE, Gorityala S, Du Z, et al. 5-fluorouracil enhances the antitumor activity of the glutaminase inhibitor CB-839 against PIK3CA-mutant colorectal cancers. Cancer Res. (2020) 80. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-0600
99. Huang H, Long L, Zhou P, Chapman NM, Chi H. mTOR signaling at the crossroads of environmental signals and T-cell fate decisions. Immunol Rev. (2020) 295. doi: 10.1111/imr.12845
100. Nakaya M, Xiao Y, Zhou X, Chang JH, Chang M, Cheng X, et al. Inflammatory T cell responses rely on amino acid transporter ASCT2 facilitation of glutamine uptake and mTORC1 kinase activation. Immunity. (2014) 40. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.04.007
101. Zhao Y, Shao Q, Peng G. Exhaustion and senescence: two crucial dysfunctional states of t cells in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Mol Immunol. (2020) 17. doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0344-8
102. Reinfeld BI, Madden MZ, Wolf MM, et al. Cell-programmed nutrient partitioning in the tumour microenvironment. Nature. (2021) 593. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03442-1
103. Guo C, You Z, Shi H, Sun Y, Du X, Palacios G, et al. SLC38A2 and glutamine signalling in cDC1s dictate anti-tumour immunity. Nature. (2023). doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06299-8
104. Settembre C, Zoncu R, Medina DL, Vetrini F, Erdin S, Huynh T, et al. A lysosome-to-nucleus signalling mechanism senses and regulates the lysosome via mTOR and TFEB. EMBO J. (2012) 31. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.32
105. Baba M, Furihata M, Hong SB, Tessarollo L, Haines DC, Southon E, et al. Kidney-targeted birt-Hogg-Dube gene inactivation in a mouse model: Erk1/2 and akt-mTOR activation, cell hyperproliferation, and polycystic kidneys. J Natl Cancer Institute. (2008) 100. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djm288
106. Samie M, Cresswell P. The transcription factor TFEB acts as a molecular switch that regulates exogenous antigen-presentation pathways. Nat Immunol. (2015) 16. doi: 10.1038/ni.3196
107. Xu K, Shyu A, Li MO. A tug-of-war over methionine. Cell Metab. (2020) 32. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.10.016
108. Bell HN, Huber AK, Singhal R, Korimerla N, Rebernick RJ, Kumar R, et al. Microenvironmental ammonia enhances T cell exhaustion in colorectal cancer. Cell Metab. (2023) 35. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.11.013
109. Tang K, Zhang H, Deng J, Wang D, Liu S, Lu S, et al. Ammonia detoxification promotes CD8+ T cell memory development by urea and citrulline cycles. Nat Immunol. (2023) 24. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01365-1
110. Imai S, Ooki T, Murata-Kamiya N, Komura D, Tahmina K, Wu W, et al. Helicobacter pylori CagA elicits BRCAness to induce genome instability that may underlie bacterial gastric carcinogenesis. Cell Host Microbe. (2021) 29:941–958.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2021.04.006
111. Molina-Castro SE, Tiffon C, Giraud J, Boeuf H, Sifre E, Giese A, et al. The hippo kinase LATS2 controls helicobacter pylori-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and intestinal metaplasia in gastric mucosa. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatology. (2020) 9. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2019.10.007
112. Messina B, Sardo FL, Scalera S, Memeo L, Colarossi C, Mare M, et al. Hippo pathway dysregulation in gastric cancer: from helicobacter pylori infection to tumor promotion and progression. Cell Death Disease. (2023) 14. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05568-8
113. Driskill JH, Pan D. The hippo pathway in liver homeostasis and pathophysiology. Annu Rev Pathology. (2021) 16. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-030420-105050
114. Wang Y, Liu J, Ying X, Lin PC, Zhou BP. Twist-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition promotes breast tumor cell invasion via inhibition of hippo pathway. Sci Rep. (2016) 6. doi: 10.1038/srep24606
115. Zhang X, Yang L, Szeto P, Gk A, Zhang Y, Kulkarni A, et al. The hippo pathway oncoprotein YAP promotes melanoma cell invasion and spontaneous metastasis. Oncogene. (2020) 39. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-1362-9
116. Zeng R, Dong J. The hippo signaling pathway in drug resistance in cancer. Cancers. (2021) 13. doi: 10.3390/cancers13020318
117. Li J, Li Z, Wu Y, et al. The Hippo effector TAZ promotes cancer stemness by transcriptional activation of SOX2 in head neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. (2019) 10. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1838-0
118. Ong YT, Andrade J, Armbruster M, Shi C, Castro M, Costa ASH, et al. A YAP/TAZ-TEAD signalling module links endothelial nutrient acquisition to angiogenic growth. Nat Metab. (2022) 4. doi: 10.1038/s42255-022-00584-y
119. Hansen CG, Ng YL, Lam WL, Plouffe SW, Guan KL. The Hippo pathway effectors YAP and TAZ promote cell growth by modulating amino acid signaling to mTORC1. Cell Res. (2015) 25. doi: 10.1038/cr.2015.140
120. Yoon BK, Kim H, Tae Gyu OH, Se Kyu OH, Sugyeong JO, Kim M, et al. PHGDH preserves one-carbon cycle to confer metabolic plasticity in chemoresistant gastric cancer during nutrient stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2023) 120:e2217826120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2217826120
121. Sadiqa A, Rasul A, Hassan M, Sultana S, Jabeen F. Identification of novel natural inhibitors to human 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase (PHGDH) for cancer treatment. Molecules (Basel Switzerland). (2022) 27. doi: 10.3390/molecules27186108
122. Fan J, Ye J, Kamphorst JJ, Shlomi T, Thompson CB, Rabinowitz JD. Quantitative flux analysis reveals folate-dependent NADPH production. Nature. (2014) 510. doi: 10.1038/nature13236
123. Shan Y, Liu D, Li Y, Wu C, Ye Y. The expression and clinical significance of serine hydroxymethyltransferase2 in gastric cancer. PeerJ. (2024) 12. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16594
124. Wang W, Wang M, Du T, Hou Z, You S, Zhang S, et al. SHMT2 promotes gastric cancer development through regulation of HIF1α/VEGF/STAT3 signaling. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087150
125. Ducker GS, Ghergurovich JM, Mainolfi N, Suri V, Jeong SK, Hsin-Jung Li S, et al. Human SHMT inhibitors reveal defective glycine import as a targetable metabolic vulnerability of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2017) 114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1706617114
126. Sun L, Song L, Wan Q, Wu G, Li X, Wang Y, et al. cMyc-mediated activation of serine biosynthesis pathway is critical for cancer progression under nutrient deprivation conditions. Cell Res. (2015) 25. doi: 10.1038/cr.2015.33
127. Ngo B, Kim E, Osorio-Vasquez V, Doll S, Bustraan S, Rj L, et al. Limited environmental serine and glycine confer brain metastasis sensitivity to PHGDH inhibition. Cancer Discovery. (2020) 10. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-1228
128. Chen X, Bai K, Zhang Y, Xu Y, Huo Y, Wang S, et al. Genomic alterations of cerebrospinal fluid cell-free DNA in leptomeningeal metastases of gastric cancer. J Trans Med. (2023) 21. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04077-8
129. Feng X, Ma D, Zhao J, Song Y, Zhu Y, Zhou Q, et al. UHMK1 promotes gastric cancer progression through reprogramming nucleotide metabolism. EMBO J. (2020) 39:e102541. doi: 10.15252/embj.2019102541
130. Selvarajah B, Azuelos I, Platé M, Guillotin D, Forty EJ, Contento G, et al. mTORC1 amplifies the ATF4-dependent de novo serine-glycine pathway to supply glycine during TGF-β1-induced collagen biosynthesis. Sci Signaling. (2019) 12. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aav3048
131. Ye H, Shi W, Yang J, Wang L, Jiang X, Zhao H, et al. PICH activates cyclin A1 transcription to drive S-phase progression and chemoresistance in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. (2023) 83. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-1331
132. Ron-Harel N, Santos D, Ghergurovich JM, Sage PT, Reddy A, Lovitch SB, et al. Mitochondrial biogenesis and proteome remodeling promote one-carbon metabolism for T cell activation. Cell Metab. (2016) 24. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.06.007
133. Kurniawan H, Franchina DG, Guerra L, Bonetti L, Baguet LS, Grusdat M, et al. Glutathione restricts serine metabolism to preserve regulatory T cell function. Cell Metab. (2020) 31. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.03.004
134. Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY. Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory t cells. Nat Immunol. (2003) 4. doi: 10.1038/ni904
135. Shan X, Hu P, Ni L, Shen L, Zhang Y, Ji Z, et al. Serine metabolism orchestrates macrophage polarization by regulating the IGF1-p38 axis. Cell Mol Immunol. (2022) 19. doi: 10.1038/s41423-022-00925-7
136. Qian L, Li N, Lu XC, Xu M, Liu Y, Li K, et al. Enhanced BCAT1 activity and BCAA metabolism promotes RhoC activity in cancer progression. Nat Metab. (2023) 5. doi: 10.1038/s42255-023-00818-7
137. Yao CC, Sun RM, Yang Y, Zhou HY, Meng ZW, Chi R, et al. Accumulation of branched-chain amino acids reprograms glucose metabolism in CD8+ t cells with enhanced effector function and anti-tumor response. Cell Rep. (2023) 42. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112186
138. Ping Y, Shan J, Liu Y, Liu F, Wang L, Liu Z, et al. Taurine enhances the antitumor efficacy of PD-1 antibody by boosting CD8+ T cell function. Cancer Immunology Immunotherapy: CII. (2023) 72. doi: 10.1007/s00262-022-03308-z
139. Bouckenooghe T, Remacle C, Reusens B. Is taurine a functional nutrient? Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. (2006) 9. doi: 10.1097/01.mco.0000247469.26414.55
140. Marcinkiewicz J, Kontny E. Taurine and inflammatory diseases. Amino Acids. (2014) 46:7–20. doi: 10.1007/s00726-012-1361-4
141. Bhat MA, Ahmad K, Khan MSA, Bhat MA, Almatroudi A, Rahman S, et al. Expedition into taurine biology: Structural insights and therapeutic perspective of taurine in neurodegenerative diseases. Biomolecules. (2020) 10. doi: 10.3390/biom10060863
Keywords: amino acid metabolism, immunotherapy, chemotherapy resistance, tumor microenvironment, methylation
Citation: Jiang Y, Tao Q, Qiao X, Yang Y, Peng C, Han M, Dong K, Zhang W, Xu M, Wang D, Zhu W and Li X (2025) Targeting amino acid metabolism to inhibit gastric cancer progression and promote anti-tumor immunity: a review. Front. Immunol. 16:1508730. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1508730
Received: 09 October 2024; Accepted: 24 January 2025;
Published: 13 February 2025.
Edited by:
Fabrizio Fontana, University of Milan, ItalyReviewed by:
Bjørn Steen Skålhegg, University of Oslo, NorwayCopyright © 2025 Jiang, Tao, Qiao, Yang, Peng, Han, Dong, Zhang, Xu, Wang, Zhu and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaoqin Li, MTAwMDAxMDMwNEB1anMuZWR1LmNu; Wen Zhu, Njc2ODgyMzhAcXEuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.