
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Immunol. , 07 March 2025
Sec. Cancer Immunity and Immunotherapy
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1494708
This article is part of the Research Topic Immunotherapy and Biomarkers for Lung Cancer View all 6 articles
 Dong Zhao1
Dong Zhao1 Minghong Bi2
Minghong Bi2 Xiaofei Cheng3
Xiaofei Cheng3 Shuhong Wang4
Shuhong Wang4 Huaidong Cheng5
Huaidong Cheng5 Xiaoyang Xia6
Xiaoyang Xia6 Huan Chen7
Huan Chen7 Yanbei Zhang8
Yanbei Zhang8 Zhiqiang Hu9
Zhiqiang Hu9 Qisheng Cao10
Qisheng Cao10 Hui Liang11
Hui Liang11 Fan Wang12
Fan Wang12 Xuhong Min13
Xuhong Min13 Ling Xu14
Ling Xu14 Kehai Feng15
Kehai Feng15 Jinhua Zhou16
Jinhua Zhou16 Xinzhong Li17
Xinzhong Li17 Rui Wang18
Rui Wang18 Hua Xie19
Hua Xie19 Xiaosi Chen20
Xiaosi Chen20 Kangsheng Gu21*
Kangsheng Gu21*Objective: Camrelizumab, a programmed death-1 inhibitor, is effective and safe for treating patients with advanced lung cancer according to previous phase 3 trials. However, relevant real-world clinical evidence is required. This study intended to explore the efficacy and safety of camrelizumab-based therapies in patients with advanced lung cancer.
Methods: Patients with advanced lung cancer who received camrelizumab-based therapies as first-line or above treatment were consecutively enrolled in this study. The median follow-up duration was 5 months.
Results: A total of 298 subjects were enrolled. Objective response rate (ORR) and disease control rate (DCR) were 27.2% and 82.2%. Multivariable logistic regression analysis showed that previous pulmonary surgery [odds ratio (OR)=0.440, P=0.024], previous radiotherapy (OR=0.410, P=0.010), and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG PS) score (>1 vs. 0~1) (OR=0.414, P=0.046) were independently and negatively associated with ORR. The median progression-free survival (PFS) [95% confidence interval] was 10.0 (7.8-12.2) months. Median overall survival (OS) was not reached. Multivariable Cox regression analysis suggested that brain metastasis [hazard ratio (HR)=1.548, P=0.036] and liver metastasis (HR=1.733, P=0.035) were independently associated with shorter PFS. Previous chemotherapy (HR=2.376, P=0.022), brain metastasis (HR=2.688, P=0.006), and liver metastasis (HR=2.583, P=0.039) were independently associated with shorter OS. Most adverse events were grade I or II. Grade III and IV adverse events rarely occurred. The occurrence of adverse events was associated with a higher DCR (P=0.003).
Conclusions: Camrelizumab-based therapies may serve as potential treatments for patients with advanced lung cancer. However, further studies with an extended follow-up duration are warranted.
Lung cancer, the most frequently diagnosed cancer, contributes to 2.5 million new cases and 1.8 million cancer-related deaths worldwide in 2022 (1). Lung cancer can be classified into two categories, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC), comprising nearly 85% and 15% of all lung cancer cases, respectively (2, 3). Surgery remains the cornerstone of early-stage lung cancer, but most patients are diagnosed in the advanced stage (3, 4). Despite the advancements in the treatments for advanced lung cancer, the prognosis of these patients is unsatisfactory, with a 5-year relative survival rate of 6% to 33% (5). Therefore, exploring potential treatments is meaningful to improve the prognosis of patients with advanced lung cancer.
The emergence of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), such as programmed death-1 (PD-1) inhibitors, has revolutionized the therapeutic landscape of advanced lung cancer (6, 7). PD-1 inhibitors exert their function by blocking the interaction between PD-1 and its primary ligand, programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), which enables T cells to recognize and attack cancer cells (7, 8). Recently, it has been found that several PD-1 inhibitors, such as nivolumab (9–12), cemiplimab (13, 14), and pembrolizumab (15–18), used alone or combined with chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or radiotherapy, achieve good efficacy with tolerable safety in patients with advanced lung cancer.
Camrelizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody against PD-1, possesses antitumor activity with an acceptable safety profile in multiple advanced cancers (19–23). Regarding advanced lung cancer, previous studies suggested that camrelizumab-based therapies could serve as the first-line treatment for this disease (21, 23). The CameL study reported that first-line camrelizumab plus carboplatin and pemetrexed achieved a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 11.3 months in patients with advanced non-squamous NSCLC (23). The CameL-Sq study observed that the objective response rate (ORR) and disease control rate (DCR) were 64.8% and 88.1% in patients with advanced squamous NSCLC who received first-line camrelizumab plus carboplatin and paclitaxel (21). Nevertheless, most of the existing studies focus on the potential of first-line camrelizumab-based therapies, but their role as a second or subsequent-line treatment for advanced lung cancer deserves to be explored. Also, relevant real-world evidence is required.
Accordingly, this real-world study enrolled patients with advanced lung cancer who received camrelizumab-based therapies as first-line or above treatment, aiming to investigate the efficacy and safety of camrelizumab-based therapies in these patients.
In this prospective, open-label, multicenter, observational study, 298 patients with advanced lung cancer were consecutively enrolled from August 2019 to February 2021. The inclusion criteria were: 1) diagnosed with lung cancer by histological or cytological method; 2) with the IIIB to IV stage of disease; 3) aged more than 18 years old; 4) received camrelizumab as first-line or above treatment; 5) joined this study voluntarily and signed an informed consent form; 6) could benefit from treatment. The exclusion criteria were: 1) with other primary solid cancers or hematological malignancies; 2) with a proven allergy to the experimental drug and/or its excipients; 3) with immunodeficiency diseases; 4) with a history of organ transplantation; 5) pregnant or lactating women. This study received approval from the Ethics Committee. The signed informed consent was collected from each patient. The Clinical Trial Registration number was ChiCTR2000034595.
This study did not interfere with the medication of patients. The regimens were determined according to patients’ own conditions, patients’ own willingness, and doctors’ advice. The types of camrelizumab-based therapies were briefly described as follows: 1) camrelizumab monotherapy, 2) camrelizumab plus chemotherapy, 3) camrelizumab plus targeted therapy, 4) camrelizumab plus chemotherapy and targeted therapy, 5) camrelizumab plus chemotherapy and radiotherapy, 6) camrelizumab plus radiotherapy. The dosage of camrelizumab was 200 mg, which was administered once every 3 weeks via intravenous infusion on the 1st day. During the study period, the administration of medication could be paused, reduced, or discontinued due to the side effects. Treatment was continued until the disease progressed. The targeted therapy, chemotherapy, or radiotherapy administration was based on the actual condition of the patients and the clinical experience of the investigators.
Demographics and disease-related information were collected. The image examination data were also collected, and based on them, the efficacy was evaluated every 2 cycles by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (v.1.1) (RECIST 1.1) (24). The best clinical response was evaluated and documented. Using these responses, the ORR and DCR were computed.
Patients underwent routine follow-ups with a median value of 5 months. PFS was defined as the duration between the start of treatment and disease progression or any-cause mortality. Overall survival (OS) was defined as the duration between the start of treatment and any-cause mortality. Adverse events were also captured, which were evaluated via the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (v.5.0). The primary endpoint was PFS. The secondary endpoints were OS, ORR, DCR, and adverse events.
The data analysis was conducted using SPSS v.26.0 software from IBM, USA. Univariable and forward-stepwise method multivariable logistic regression models were conducted to explore factors associated with ORR. Kaplan-Meier curves were used for survival analyses, and the Log-rank test was used to compare survival between different subgroups. Univariable and forward-stepwise method multivariable Cox regression models were built to explore factors that influenced PFS and OS independently. The forward-stepwise logistic or Cox regression method was used to incorporate all the variables in the univariate analysis into the multivariate model to find the independent influencing factors. Sites of metastases had a very strong association with lymph node metastasis, bone metastasis, brain metastasis, liver metastasis, and pleura metastasis; besides, treatment lines had a very strong association with previous chemotherapy. Therefore, to reduce multicollinearity, sites of metastases and treatment lines are not included in the multivariable analyses. The χ2 test or Fisher’s exact test was applied to compare ORR and DCR between groups. A P value <0.05 (two-sided) indicated significance.
The mean age of patients was 63.7 ± 10.9 years. Sixty-three (21.1%) patients were female and 235 (78.9%) patients were male. There were 248 (83.2%) patients with an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG PS) score of 0~1 and 50 (16.8%) patients with an ECOG PS score of >1. Forty-eight (16.1%), 6 (2.0%), and 244 (81.9%) patients had a tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage of IIIB, IIIC, and IV, respectively. Ninety-three (31.2%) patients received camrelizumab-based therapies as first-line treatment, and the remaining 205 (68.8%) patients received camrelizumab-based therapies as second or subsequent-line treatment. Detailed information of patients is shown in Table 1.
Regarding therapy information, 186 (62.4%) patients received camrelizumab combined with chemotherapy and 71 (23.8%) patients received camrelizumab combined with targeted therapy. The detailed therapy information is exhibited in Table 2.
The rates of complete response (CR), partial response (PR), stable disease (SD), and progressive disease (PD) were 0.7%, 26.5%, 55.0%, and 15.1%, respectively; the clinical response was not evaluated (NE) in 2.7% of patients (Figure 1A). ORR was 27.2% and DCR was 82.2% in patients with advanced lung cancer (Figure 1B). In patients who received first-line camrelizumab-based therapies, ORR and DCR were 36.6% and 86.0%. In patients who received second or subsequent-line camrelizumab-based therapies, ORR and DCR were 22.9% and 80.5%.
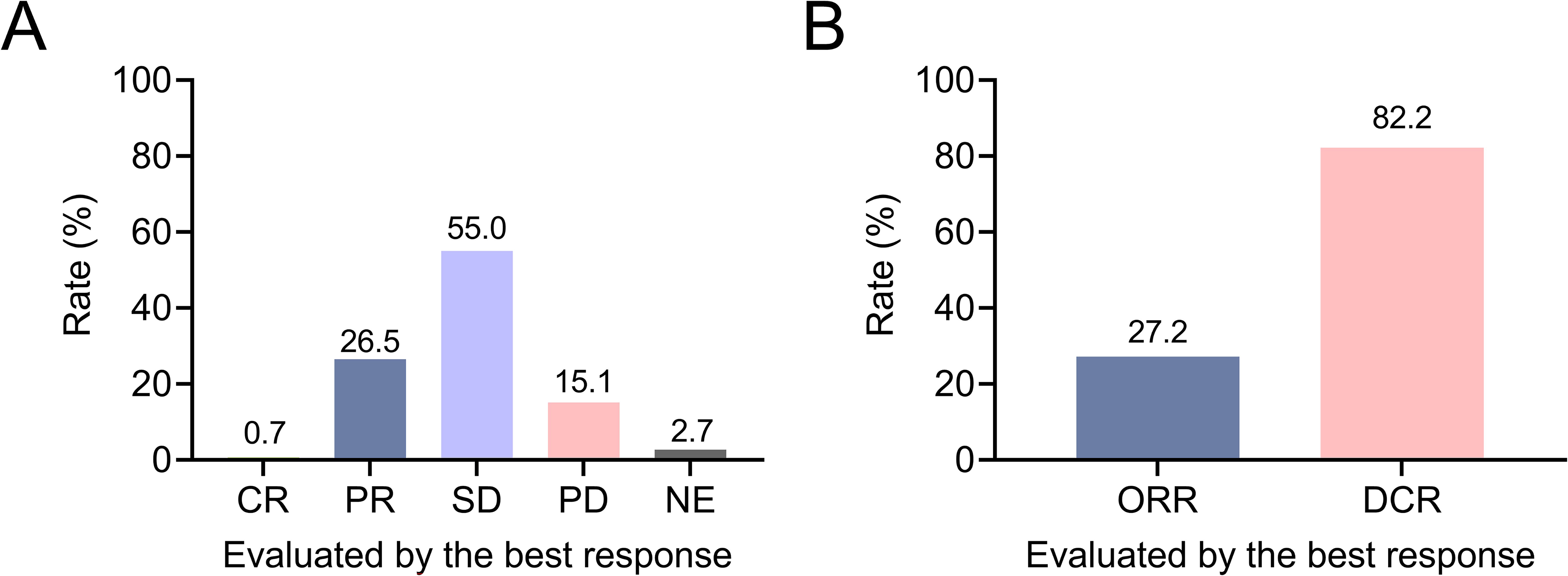
Figure 1. Exhibition of clinical response in patients with advanced lung cancer. Rates of CR, PR, SD, PD, and NE (A); ORR and DCR (B) in patients with advanced lung cancer.
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive, anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive, and Ros proto-oncogene 1 (ROS-1)-positive were not related to ORR or DCR (all P>0.05) (Supplementary Table 1).
Univariable logistic regression analysis showed that age (≥65 years vs. <65 years) was positively associated with ORR [odds ratio (OR)=1.882, P=0.018]. Previous chemotherapy (OR=0.516, P=0.015), previous radiotherapy (OR=0.385, P=0.004), ECOG PS score (>1 vs. 0~1) (OR=0.383, P=0.026), and bone metastasis (OR=0.418, P=0.025) were negatively associated with ORR. According to multivariable logistic regression analysis, previous pulmonary surgery (OR=0.440, P=0.024), previous radiotherapy (OR=0.410, P=0.010), and ECOG PS score (>1 vs. 0~1) (OR=0.414, P=0.046) were independently and negatively associated with ORR (Table 3).
The median PFS [95% confidence interval (CI)] was 10.0 (7.8-12.2) months. The 12-, 24-, 36-, and 48-month accumulating PFS rates were 41.2%, 17.0%, 14.7%, and 14.7%, respectively (Figure 2A). The median OS was not reached. The 12-, 24-, 36-, and 48-month accumulating OS rates were 78.5%, 65.3%, 65.3%, and 65.3%, respectively (Figure 2B).
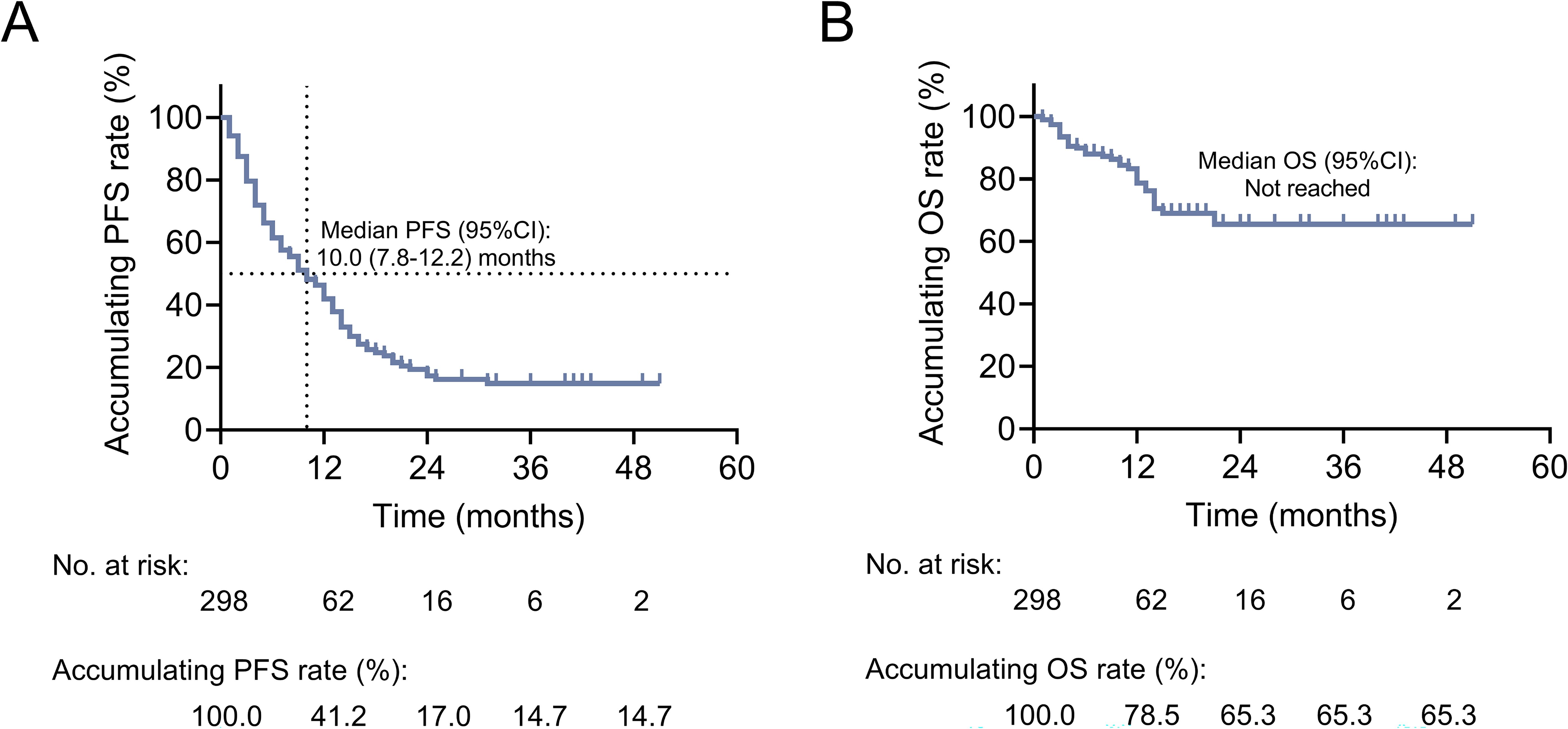
Figure 2. Exhibition of survival profiles in patients with advanced lung cancer. Kaplan-Meier curves of PFS (A) and OS (B) in patients with advanced lung cancer.
PFS and OS were not different between patients who received camrelizumab combined with chemotherapy and those who received camrelizumab without chemotherapy. PFS and OS were also not different between patients who received camrelizumab combined with targeted therapy and those who received camrelizumab without targeted therapy (all P>0.05) (Supplementary Figures 1A–D). Additionally, it was also discovered that PFS (P=0.435) (Supplementary Figure 2A) and OS (P=0.833) (Supplementary Figure 2B) were not different in patients receiving different camrelizumab-based therapies, including camrelizumab monotherapy, camrelizumab plus chemotherapy, camrelizumab plus targeted therapy, camrelizumab plus chemotherapy and targeted therapy, camrelizumab plus chemotherapy and radiotherapy, and camrelizumab plus radiotherapy.
ORR was higher in patients receiving camrelizumab-based therapies as the first-line treatment than those receiving these therapies as the second or above-line treatment (P=0.014). Additionally, OS was prolonged in patients receiving camrelizumab-based therapies as the first-line treatment compared with those receiving these therapies as the second or above-line treatment (P=0.028) (Supplementary Table 2).
Regarding PFS, the univariable Cox regression analysis suggested that brain metastasis [hazard ratio (HR)=1.577, P=0.029] and liver metastasis (HR=1.775, P=0.027) were related to shorter PFS. According to the multivariable Cox regression analysis, brain metastasis (HR=1.548, P=0.036) and liver metastasis (HR=1.733, P=0.035) were independently associated with shorter PFS. The -2 Log Likelihood of the final Cox regression model of PFS was 1626.841, and the Chi-square value was 5.011 with a P value of 0.009, indicating a good fit to the data (Table 4).
Regarding OS, the univariable Cox regression analysis showed that previous chemotherapy (HR=2.215, P=0.034), brain metastasis (HR=2.675, P=0.005), and liver metastasis (HR=2.604, P=0.033) were associated with shorter OS. Squamous cell carcinoma (vs. adenocarcinoma) was associated with prolonged OS (HR=0.344, P=0.009). Multivariable Cox regression analysis disclosed that previous chemotherapy (HR=2.376, P=0.022), brain metastasis (HR=2.688, P=0.006), and liver metastasis (HR=2.583, P=0.039) were independently associated with shorter OS. The -2 Log Likelihood of the final Cox regression model of OS was 415.235, and the Chi-square value was 18.630 with a P value of <0.001, indicating a good fit to the data (Table 4).
The median (range) onset time of adverse events was 1.2 (0.3-16.0) months. Common adverse events of any grade were reactive cutaneous capillary endothelial proliferation (RCCEP) (14.8%), pneumonia (6.0%), fatigue (5.4%), nausea and vomiting (4.4%), and gastrointestinal reaction (4.0%). Most adverse events were of grade I or II. Grade III and IV adverse events rarely occurred. Grade III adverse events included RCCEP (1.7%), myelosuppression (0.7%), gastrointestinal reaction (0.3%), and leukopenia (0.3%). Grade IV adverse events included myelosuppression (0.7%) and hypoalbuminemia (0.3%) (Table 5). Common camrelizumab-related adverse events included RCCEP (14.8%), fatigue (4.0%), pneumonia (2.3%), nausea and vomiting (2.3%), and fever (2.3%). Grade III camrelizumab-related adverse events included RCCEP (1.7%), myelosuppression (0.7%), gastrointestinal reaction (0.3%), and leukopenia (0.3%). No grade IV camrelizumab-related adverse events occurred (Supplementary Table 3). The management of grade I/II adverse events was guided by the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) and the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO) toxicity management guidelines. The management of grade III/IV adverse events involved suspending the treatment and addressing the situation in accordance with the toxicity management guidelines provided by the CSCO.
DCR was different between patients with and without adverse events (P=0.003). In detail, 76.5% of patients without adverse events achieved DCR, and 89.8% of patients with adverse events achieved DCR. ORR, PFS, and OS were not different between patients with and without adverse events (all P>0.05) (Supplementary Table 4).
PFS was longer in male patients than female patients (P=0.041). The median PFS (95% CI) was 11.0 (8.5-13.5) months in male patients; it was 7.0 (3.9-10.1) months in female patients. However, ORR (P=0.216), DCR (P=0.768), and OS (P=0.133) were not different between male and female patients (Supplementary Table 5).
All enrolled patients came from Anhui province. Therefore, the efficacy of camrelizumab-based therapies was compared among patients from Northern, Central, and Southern Anhui. ORR was different among patients from different locations in Anhui Province (P=0.020). ORR was 33.7% in patients from Northern Anhui, 29.5% in patients from Central Anhui, and 15.9% in patients from Southern Anhui. However, DCR (P=0.842), PFS (P=0.420), and OS (P=0.136) were not different among patients from Northern, Central, and Southern Anhui (Supplementary Table 6).
Camrelizumab, alternatively named SHR-1210, effectively inhibits the interaction between PD-1 and PD-L1 and consequently suppresses the immune evasion of tumor cells (25). Several studies have reported that camrelizumab-based therapies achieve favorable treatment responses in patients with advanced lung cancer (21, 26–28). Of note, a real-world study observed that the ORR and DCR of camrelizumab-based therapies were 28.8% and 79.9% in patients with advanced NSCLC (27). Similarly to the previous study (27), we found that camrelizumab-based therapies achieved an ORR and DCR of 27.2% and 82.2%. However, by comparison with some phase 3 trials, although the DCR was similar, the ORR (64.8% (21) and 60.5% (23)) was higher in previous trials than that in our study. Potential reasons would be that (1): camrelizumab-based therapies were in the first-line setting in previous phase 3 trials (21, 23); however, our study did not restrict the treatment lines (2). The combined treatment strategy was camrelizumab plus chemotherapy in the previous phase trials (21, 23), but the combinations were diverse in our study (3). The histological subtype was squamous and non-squamous NSCLC in the previous phase 3 trials (21, 23), while our study included patients with various histological subtypes of lung cancer. These differences between our study and the previous phase 3 trials might contribute to the inconsistent results of ORR. Furthermore, we found that first-line camrelizumab-based therapies yielded a numerically higher ORR (36.6% vs. 22.9%) compared to second or subsequent-line camrelizumab-based therapies. Our findings supported that camrelizumab-based therapies possessed the potential to serve as the first-line treatment for advanced lung cancer.
Driver gene alterations could contribute to the resistance to ICIs, but patients with some specific driver gene alterations could benefit from ICIs (29). As reported by a previous study, patients with advanced NSCLC harboring B-raf proto-oncogene (BRAF) V600E mutation showed a superior benefit from ICIs (30). In our study, we observed that ORR and DCR were not affected by EGFR mutation-positive, ALK-positive, and ROS-1-positive in patients with advanced lung cancer who received camrelizumab-based therapies. However, only 10.4%, 1.3%, and 1.3% of patients carried EGFR mutation-positive, ALK-positive, and ROS-1-positive in this study, which might affect the statistical power. Therefore, our findings should be validated by more studies.
Considering that advanced lung cancer predominantly affects the older, and aging is related to a decline in immune function, it is meaningful to investigate whether the older patients could benefit from camrelizumab-based therapies (31–33). A previous study found that the ORR of camrelizumab-based therapies was not affected by age ≥70 years or <70 years in patients with advanced NSCLC (28). In this research, we applied 65 as the cutoff value and found that age ≥65 years was positively associated with ORR. Our findings provided a reference that camrelizumab-based therapies could be recommended for patients with advanced lung cancer aged more than 65 years.
A previous study found that treatment line, liver metastasis, and treatment duration were strong factors associated with ORR in patients with advanced NSCLC who received camrelizumab-based therapies (28). Our study observed that previous pulmonary surgery, previous radiotherapy, and ECOG PS score >1, were independently and negatively associated with ORR. The potential reasons would be that: (1) previous pulmonary surgery or radiotherapy might affect the tumor microenvironment, which facilitated the immune escape of tumor cells and compromised the efficacy of camrelizumab-based therapies (34–36). (2) An ECOG PS score >1 signified a higher level of impaired physical performance, which could attenuate patients’ ability to tolerate camrelizumab-based therapies, ultimately limiting the therapeutic benefit (37, 38).
Camrelizumab-based therapies achieve satisfactory survival profiles in patients with advanced lung cancer according to previous studies (21, 23, 27, 28). The CameL study reported that camrelizumab plus chemotherapy resulted in the median PFS (95% CI) of 11.0 (8.5-12.5) months and the median OS (95% CI) of 27.1 (21.9-31.5) months in patients with advanced non-squamous NSCLC (26). Consistent with the previous study (26), we found that the median PFS (95% CI) was 10.0 (7.8-12.2) months. However, the median OS was not achieved in our study due to the short follow-up duration. In addition, a previous study reported that the 12-month PFS and OS rates were 50.1% and 73.4% in patients with advanced NSCLC (27). Similarly to the finding of this previous study (27), we found that the 12-month PFS and OS rates were 41.2% and 78.5%. Moreover, we discovered that the 24-, 36-, and 48-month OS rates were 65.3%. However, these data should be interpreted with caution since the median follow-up duration was only 5 months in this study. Further studies with extended follow-up duration were warranted to assess the survival outcomes in patients with advanced lung cancer who received camrelizumab-based therapies.
As reported by previous studies, histological subtype, treatment lines, camrelizumab treatment duration, liver metastasis, and brain metastasis could affect the survival profiles of patients with advanced lung cancer who received ICIs-based therapies (27, 28, 39, 40). Consistent with previous studies (28, 39, 40), we found that brain metastasis and liver metastasis were independently linked with both shorter PFS and OS in patients with advanced lung cancer who received camrelizumab-based therapies. A potential reason would be that brain metastasis and liver metastasis represented an aggressive manifestation of the disease, which might restrain the efficacy of camrelizumab-based therapies and ultimately lead to poor survival (39). In clinical practice, the combinations of camrelizumab-based therapies for the treatment of advanced lung cancer exhibit marked diversity (41, 42), and whether patients could benefit from specific combinations deserves to be explored. According to a previous study, survival profiles were not influenced by combinations in patients with advanced NSCLC who received camrelizumab-based therapies (27). Consistent with the previous study (27), we also found that PFS and OS were not affected by different combinations of camrelizumab-based therapies. Our findings suggested that physicians could consider different treatments in combination with camrelizumab according to patients’ actual conditions. It should be clarified that the classification of the treatment regimen was relatively rough in this study. Therefore, a controlled study with standardized treatment arms was required to reduce the variability and strengthen efficacy assessments for each regimen.
Currently, the findings concerning the impact of gender on the efficacy of immunotherapy are inconsistent (43, 44). In our study, we found that male patients with advanced lung cancer benefited more from camrelizumab-based therapies than female patients in terms of survival. We speculated that some differences between male and female patients, such as sex hormones, genetic factors, and immune response to lung cancer, may contribute to different survival after camrelizumab-based therapies (45, 46). However, the numbers of male and female patients are largely different in our study, which might affect the statistical power. Therefore, the impact of sex on camrelizumab-based therapies in patients with advanced lung cancer should be further validated. Moreover, we also discovered that ORR was different among patients from Northern, Central, and Southern Anhui. Varying levels of medical care in different locations of Anhui might lead to differences in the efficacy of camrelizumab-based therapies in patients with advanced lung cancer.
Safety is one of the major concerns regarding the application of camrelizumab-based therapies for the treatment of advanced lung cancer. Previous studies have reported that common adverse events include decreased white blood cell count, decreased neutrophil count, anemia, and RCCEP in patients with advanced lung cancer who received camrelizumab-based therapies (21, 23, 27). In the current study, we found that the common adverse events at any grade were RCCEP, pneumonia, fatigue, nausea and vomiting, and gastrointestinal reactions in patients with advanced lung cancer who received camrelizumab-based therapies. Overall, most adverse events were mild and manageable, suggesting that camrelizumab-based therapies were safe for advanced lung cancer. Notably, the incidence of RCCEP (14.8%) in our study was relatively lower than that of previous studies (ranging from 18.6% to 78.0%) (21, 23, 27). An explanation was that in this study, some patients received pre-treatment for RCCEP with thalidomide, leading to a relatively low incidence of RCCEP. However, the use of thalidomide to prevent the occurrence of RCCEP was based on the clinical experience in some study centers. Therefore, we did not record the specific number of patients who used thalidomide to prevent the occurrence of RCCEP. To support the clinical practice, future research might be needed to explore the role of preventative thalidomide use in reducing RCCEP. Of note, several previous studies suggested that adverse events were related to the good efficacy of ICIs in patients with advanced lung cancer (47–49). In line with these previous studies, we also observed that adverse events were positively associated with DCR. A potential explanation would be that patients who experienced adverse events might have a more competent immune system, contributing to a higher likelihood of responding to camrelizumab-based therapies (50).
Several limitations should be noted in the current study. (1) Our study shared real-world experience of applying camrelizumab-based therapies to treat patients with advanced lung cancer. Nevertheless, the research region was limited to Anhui province in China, and our findings should be further verified by studies involving diverse geographic and ethnic populations. (2) The single-arm, observational design of this study might induce selection bias and hinder us from drawing a solid conclusion about the superior efficacy of camrelizumab-based therapies versus other treatments in patients with advanced lung cancer. Therefore, further studies could consider designing randomized, controlled trials or comparative observational studies to validate the efficacy and safety of camrelizumab for the treatment of advanced lung cancer. (3) The median follow-up duration was only 5 months, which was relatively short for assessing OS and long-term safety. Considering that the effect of camrelizumab on improving survival required a long period due to delayed immune responses, further studies with long-term follow-up duration were warranted to validate the survival benefits and durability of camrelizumab-based therapies in patients with advanced lung cancer. (4) Although our subgroup analysis found that PFS and OS were not different in patients receiving different camrelizumab-based therapies, the sample size was small in some subgroups, which might affect the statistical power. Therefore, further studies with large sample sizes were required to validate our findings. (5) The number of patients who carried driver gene mutations was small. Therefore, the impact of driver gene mutations on the efficacy of camrelizumab-based therapies should be further verified. (6) Several subgroup analyses based on gender, treatment lines, and geographic locations were conducted. Nevertheless, they might be underpowered due to the small sample size in some subgroups. Therefore, the findings of our subgroup analyses should be further validated by studies with large sample sizes or pooled analyses.
In summary, camrelizumab-based therapies achieve good efficacy with tolerable safety profiles in patients with advanced lung cancer. The efficacy of first-line camrelizumab-based therapies is profound compared with the second or above-line setting in patients with advanced lung cancer. Our findings provide real-world evidence that camrelizumab-based therapies may be a potential first-line treatment for patients with advanced lung cancer.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
DZ: Data curation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. MB: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. XFC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft. SW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft. HDC: Data curation, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. XX: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. HC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft. YZ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Writing – original draft. ZH: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft. QC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. HL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. FW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft. XM: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. LX: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Data curation. KF: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft. JZ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft. XL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. RW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Resources, Writing – review & editing. HX: Data curation, Resources, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. XSC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. KG: Conceptualization, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1494708/full#supplementary-material
1. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
2. Rudin CM, Brambilla E, Faivre-Finn C, Sage J. Small-cell lung cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2021) 7:3. doi: 10.1038/s41572-020-00235-0
3. Thai AA, Solomon BJ, Sequist LV, Gainor JF, Heist RS. Lung cancer. Lancet. (2021) 398:535–54. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00312-3
4. Nooreldeen R, Bach H. Current and future development in lung cancer diagnosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:8661. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168661
5. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. (2022) 72:7–33. doi: 10.3322/caac.21708
6. Tang S, Qin C, Hu H, Liu T, He Y, Guo H, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: progress, challenges, and prospects. Cells. (2022) 11:320. doi: 10.3390/cells11030320
7. Lahiri A, Maji A, Potdar PD, Singh N, Parikh P, Bisht B, et al. Lung cancer immunotherapy: progress, pitfalls, and promises. Mol Cancer. (2023) 22:40. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01740-y
8. Tang Q, Chen Y, Li X, Long S, Shi Y, Yu Y, et al. The role of PD-1/PD-L1 and application of immune-checkpoint inhibitors in human cancers. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:964442. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.964442
9. Sugawara S, Lee JS, Kang JH, Kim HR, Inui N, Hida T, et al. Nivolumab with carboplatin, paclitaxel, and bevacizumab for first-line treatment of advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. (2021) 32:1137–47. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.06.004
10. Borghaei H, de Marinis F, Dumoulin D, Reynolds C, Theelen W, Percent I, et al. SAPPHIRE: phase III study of sitravatinib plus nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. (2024) 35:66–76. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2023.10.004
11. Borghaei H, Gettinger S, Vokes EE, Chow LQM, Burgio MA, de Castro Carpeno J, et al. Five-year outcomes from the randomized, phase III trials checkMate 017 and 057: nivolumab versus docetaxel in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2021) 39:723–33. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.01605
12. Ye H, Pang H, Shi X, Ren P, Huang S, Yu H, et al. Nivolumab and hypofractionated radiotherapy in patients with advanced lung cancer: ABSCOPAL-1 clinical trial. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:657024. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.657024
13. Makharadze T, Gogishvili M, Melkadze T, Baramidze A, Giorgadze D, Penkov K, et al. Cemiplimab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone in advanced NSCLC: 2-year follow-up from the phase 3 EMPOWER-lung 3 part 2 trial. J Thorac Oncol. (2023) 18:755–68. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2023.03.008
14. Sezer A, Kilickap S, Gumus M, Bondarenko I, Ozguroglu M, Gogishvili M, et al. Cemiplimab monotherapy for first-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with PD-L1 of at least 50%: a multicentre, open-label, global, phase 3, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet. (2021) 397:592–604. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00228-2
15. Reck M, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG, Hui R, Csoszi T, Fulop A, et al. Five-year outcomes with pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer with PD-L1 tumor proportion score >/= 50. J Clin Oncol. (2021) 39:2339–49. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.00174
16. Gandhi L, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Gadgeel S, Esteban E, Felip E, De Angelis F, et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:2078–92. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1801005
17. Reckamp KL, Redman MW, Dragnev KH, Minichiello K, Villaruz LC, Faller B, et al. Phase II randomized study of ramucirumab and pembrolizumab versus standard of care in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with immunotherapy-lung-MAP S1800A. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:2295–306. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.00912
18. Jabbour SK, Lee KH, Frost N, Breder V, Kowalski DM, Pollock T, et al. Pembrolizumab plus concurrent chemoradiation therapy in patients with unresectable, locally advanced, stage III non-small cell lung cancer: the phase 2 KEYNOTE-799 nonrandomized trial. JAMA Oncol. (2021) 7:1–9. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.2301
19. Luo H, Lu J, Bai Y, Mao T, Wang J, Fan Q, et al. Effect of camrelizumab vs placebo added to chemotherapy on survival and progression-free survival in patients with advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: the ESCORT-1st randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2021) 326:916–25. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.12836
20. Qin S, Chan SL, Gu S, Bai Y, Ren Z, Lin X, et al. Camrelizumab plus rivoceranib versus sorafenib as first-line therapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (CARES-310): a randomised, open-label, international phase 3 study. Lancet. (2023) 402:1133–46. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00961-3
21. Ren S, Chen J, Xu X, Jiang T, Cheng Y, Chen G, et al. Camrelizumab plus carboplatin and paclitaxel as first-line treatment for advanced squamous NSCLC (CameL-sq): A phase 3 trial. J Thorac Oncol. (2022) 17:544–57. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2021.11.018
22. Yang Y, Qu S, Li J, Hu C, Xu M, Li W, et al. Camrelizumab versus placebo in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin as first-line treatment for recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma (CAPTAIN-1st): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2021) 22:1162–74. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00302-8
23. Zhou C, Chen G, Huang Y, Zhou J, Lin L, Feng J, et al. Camrelizumab plus carboplatin and pemetrexed versus chemotherapy alone in chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (CameL): a randomised, open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir Med. (2021) 9:305–14. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30365-9
24. Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. (2009) 45:228–47. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
25. Reguart N, Reyes R. Spotlight on camrelizumab in advanced squamous lung cancer: another feather in the cap of Chinese checkpoint inhibitors. J Thorac Oncol. (2022) 17:477–80. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2022.01.001
26. Zhou C, Chen G, Huang Y, Zhou J, Lin L, Feng J, et al. Camrelizumab plus carboplatin and pemetrexed as first-line treatment for advanced nonsquamous NSCLC: extended follow-up of cameL phase 3 trial. J Thorac Oncol. (2023) 18:628–39. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2022.12.017
27. Wang R, Shi M, Ji M, Han Z, Chen L, Liu Y, et al. Real world experience with camrelizumab in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a prospective multicenter cohort study (NOAH-LC-101). Transl Lung Cancer Res. (2023) 12:786–96. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-23-121
28. Xu CR, Chen Q, Zhou C, Wu L, Li W, Zhang H, et al. Effectiveness and safety of camrelizumab in inoperable or advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients: a multicenter real-world retrospective observational study (CTONG2004-ADV). Transl Lung Cancer Res. (2023) 12:127–40. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-22-852
29. Otano I, Ucero AC, Zugazagoitia J, Paz-Ares L. At the crossroads of immunotherapy for oncogene-addicted subsets of NSCLC. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2023) 20:143–59. doi: 10.1038/s41571-022-00718-x
30. Negrao MV, Skoulidis F, Montesion M, Schulze K, Bara I, Shen V, et al. Oncogene-specific differences in tumor mutational burden, PD-L1 expression, and outcomes from immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. J Immunother Cancer. (2021) 9:e002891. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002891
31. Ferrara R, Mezquita L, Auclin E, Chaput N, Besse B. Immunosenescence and immunecheckpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer patients: Does age really matter? Cancer Treat Rev. (2017) 60:60–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2017.08.003
32. Tagliamento M, Frelaut M, Baldini C, Naigeon M, Nencioni A, Chaput N, et al. The use of immunotherapy in older patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. (2022) 106:102394. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2022.102394
33. Montrone M, Rosati G, Longo V, Catino A, Massafra R, Nardone A, et al. Immunotherapy in elderly patients affected by non-small cell lung cancer: A narrative review. J Clin Med. (2023) 12:1833. doi: 10.3390/jcm12051833
34. Guo S, Yao Y, Tang Y, Xin Z, Wu D, Ni C, et al. Radiation-induced tumor immune microenvironments and potential targets for combination therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:205. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01462-z
35. Zhang Z, Peng Y, Peng X, Xiao D, Shi Y, Tao Y. Effects of radiation therapy on tumor microenvironment: an updated review. Chin Med J (Engl). (2023) 136:2802–11. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002535
36. Cheng X, Zhang H, Hamad A, Huang H, Tsung A. Surgery-mediated tumor-promoting effects on the immune microenvironment. Semin Cancer Biol. (2022) 86:408–19. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.01.006
37. Friedlaender A, Liu SV, Passaro A, Metro G, Banna G, Addeo A. The role of performance status in small-cell lung cancer in the era of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Clin Lung Cancer. (2020) 21:e539–e43. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2020.04.006
38. Friedlaender A, Banna GL, Buffoni L, Addeo A. Poor-performance status assessment of patients with non-small cell lung cancer remains vague and blurred in the immunotherapy era. Curr Oncol Rep. (2019) 21:107. doi: 10.1007/s11912-019-0852-9
39. Qiao M, Zhou F, Hou L, Li X, Zhao C, Jiang T, et al. Efficacy of immune-checkpoint inhibitors in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with different metastases. Ann Trans Med. (2021) 9:34. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-1471
40. Zhu J, Yu Y, Mei J, Chen S, Li J, Jiang S. Efficacy and safety of camrelizumab combined with albumin-bound paclitaxel as third- or later-line regimen in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1278573. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1278573
41. Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL, Akerley W, Bauman JR, Bharat A, et al. NCCN guidelines insights: non-small cell lung cancer, version 2.2021. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2021) 19:254–66. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2021.0013
42. Ganti AKP, Loo BW, Bassetti M, Blakely C, Chiang A, D’Amico TA, et al. Small cell lung cancer, version 2.2022, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2021) 19:1441–64. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2021.0058
43. Conforti F, Pala L, Bagnardi V, Viale G, De Pas T, Pagan E, et al. Sex-based heterogeneity in response to lung cancer immunotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. (2019) 111:772–81. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djz094
44. Madala S, Rasul R, Singla K, Sison CP, Seetharamu N, Castellanos MR. Gender differences and their effects on survival outcomes in lung cancer patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). (2022) 34:799–809. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2022.03.010
45. May L, Shows K, Nana-Sinkam P, Li H, Landry JW. Sex differences in lung cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15:3111. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123111
46. Vavala T, Catino A, Pizzutilo P, Longo V, Galetta D. Gender differences and immunotherapy outcome in advanced lung cancer. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:11942. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111942
47. Shankar B, Zhang J, Naqash AR, Forde PM, Feliciano JL, Marrone KA, et al. Multisystem immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors for treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol. (2020) 6:1952–6. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.5012
48. Cook S, Samuel V, Meyers DE, Stukalin I, Litt I, Sangha R, et al. Immune-related adverse events and survival among patients with metastatic NSCLC treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. JAMA Netw Open. (2024) 7:e2352302. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.52302
49. Sato K, Akamatsu H, Murakami E, Sasaki S, Kanai K, Hayata A, et al. Correlation between immune-related adverse events and efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer treated with nivolumab. Lung Cancer. (2018) 115:71–4. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.11.019
Keywords: advanced lung cancer, camrelizumab-based therapies, treatment response, survival, adverse events
Citation: Zhao D, Bi M, Cheng X, Wang S, Cheng H, Xia X, Chen H, Zhang Y, Hu Z, Cao Q, Liang H, Wang F, Min X, Xu L, Feng K, Zhou J, Li X, Wang R, Xie H, Chen X and Gu K (2025) Camrelizumab-based therapies for the treatment of advanced lung cancer: a prospective, open-label, multicenter, observational, real-world study. Front. Immunol. 16:1494708. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1494708
Received: 11 September 2024; Accepted: 18 February 2025;
Published: 07 March 2025.
Edited by:
Paul Takam Kamga, Université de Versailles Saint-Quentin-en-Yvelines, FranceReviewed by:
Mohamed Rahouma, NewYork-Presbyterian, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Zhao, Bi, Cheng, Wang, Cheng, Xia, Chen, Zhang, Hu, Cao, Liang, Wang, Min, Xu, Feng, Zhou, Li, Wang, Xie, Chen and Gu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kangsheng Gu, a2FuZ3NoZW5nX2d1QDE2My5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.