- 1The Second Clinical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, China
- 2State Key Laboratory of Dampness Syndrome of Chinese Medicine, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine), Guangzhou, China
- 3Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Clinical Research on Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome, Guangzhou, China
- 4Guangdong Provincial Clinical Medicine Research Center for Chinese Medicine Dermatology, Guangzhou, China
- 5Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Joint Lab on Chinese Medicine and Immune Disease Research, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, China
A Corrigendum on
The causal relationship between serum metabolites and the risk of psoriasis: a Mendelian randomization and meta-analysis study
By Yang Y, Zheng X, Lv H, Tang B, Zhong Y, Luo Q, Bi Y, Yang K, Zhong H, Chen H and Lu C (2024) Front. Immunol. 15:1343301. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1343301
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 4 as published. The duplicate Figure 4B was mistakenly uploaded to the position of Figure 4C. The corrected Figure 4 and its caption appear below.
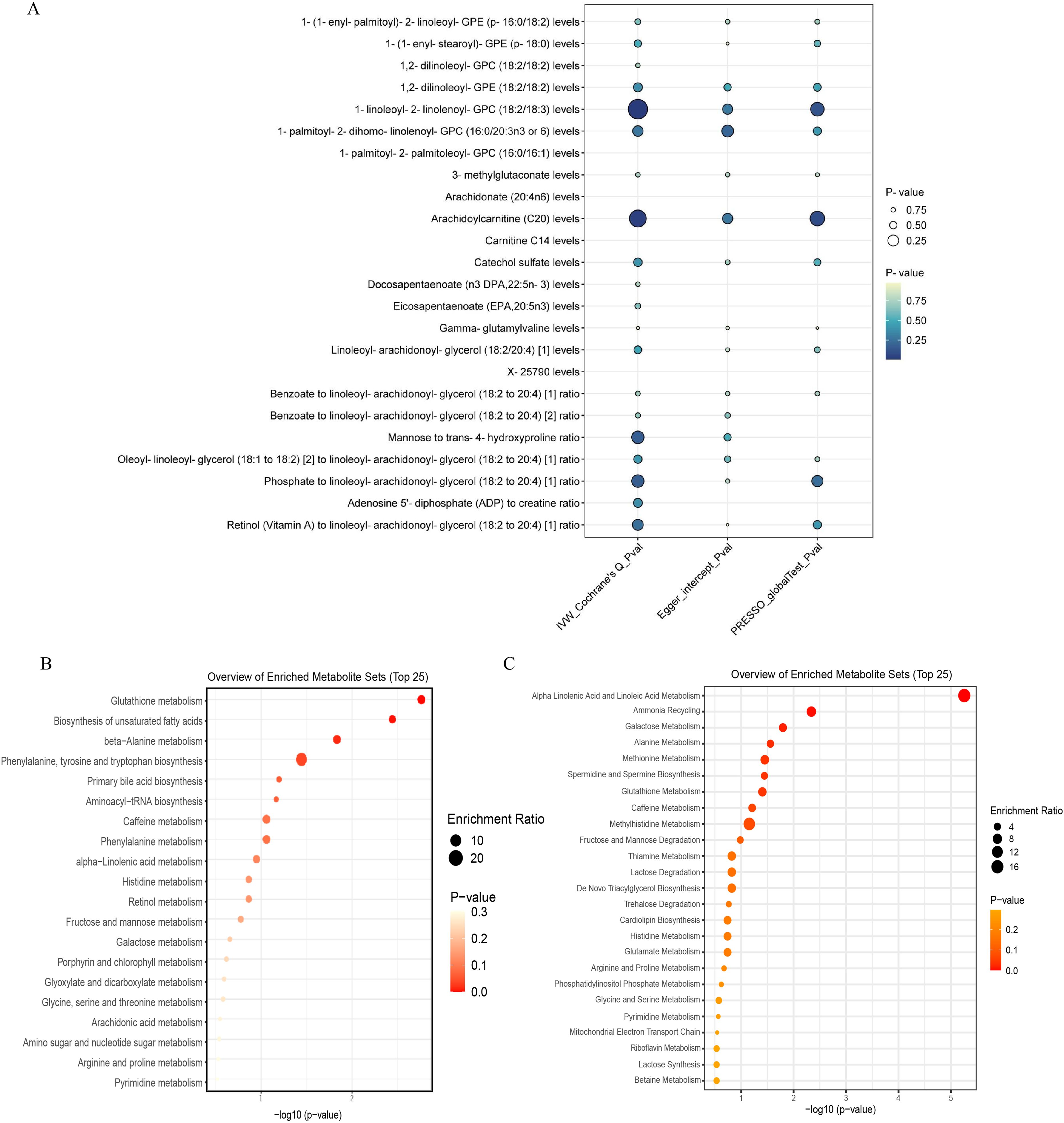
Figure 4. (A) displays the heterogeneity and pleiotropy analysis results of 24 metabolites that have been successfully validated. (B) displays the enrichment pathways of metabolites in KEGG and (C) displays the enrichment pathways of metabolites in SMPDE database.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: psoriasis, Mendelian randomization, metabolites, causal effect, implication
Citation: Yang Y, Zheng X, Lv H, Tang B, Zhong Y, Luo Q, Bi Y, Yang K, Zhong H, Chen H and Lu C (2025) Corrigendum: The causal relationship between serum metabolites and the risk of psoriasis: a Mendelian randomization and meta-analysis study. Front. Immunol. 15:1544371. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1544371
Received: 12 December 2024; Accepted: 16 December 2024;
Published: 06 January 2025.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Yejun Tan, University of Minnesota Health Twin Cities, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Yang, Zheng, Lv, Tang, Zhong, Luo, Bi, Yang, Zhong, Chen and Lu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Haiming Chen, aGVtaW4wNjZAZ3p1Y20uZWR1LmNu; Chuanjian Lu, bGNqQGd6dWNtLmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yujie Yang
Yujie Yang Xuwei Zheng
Xuwei Zheng Haiying Lv1
Haiying Lv1 Bin Tang
Bin Tang Yiyuan Zhong
Yiyuan Zhong Yang Bi
Yang Bi Haiming Chen
Haiming Chen