- 1Zhongshan City People’s Hospital, Zhongshan, Guangdong, China
- 2The Second Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu Medicial College, China National Nuclear Corporation 416 Hospital, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 3Guangdong Medical University, Zhangjiang, Guangdong, China
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the diagnostic value of 7-tumor associated autoantibodies (7-TAAB) and to evaluate the relationship between 7-TAAB and clinical features in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), which can be used to guide clinical diagnosis and treatment and achieve its clinical value.
Methods: (1) Blood specimens were collected from patients with ESCC who had not previously received antitumor therapy (ESCC group) and those who had normal medical check-ups in the hospital during the same period (control group). The concentrations of 7-TAAB (P53, PGP9.5, SOX2, GAGE7, GBU4-5, MAGE A1, and CAGE) in serum were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The concentrations of 7-TAAB were compared between the ESCC and control groups, and the positive rate of 7-TAAB was calculated to determine the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of 7-TAAB. The diagnostic value of 7-TAAB was analyzed using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. (2) The clinical data of patients with ESCC were collected and the correlation between the rate of 7-TAAB and clinical features was analyzed.
Results: (1) The serum levels and positivity rates of five antibodies (PGP9.5, SOX2, GBU4-5, MAGE-A1, and CAGE) were higher in the ESCC group than in the control group (P < 0.05) and the positive expression rate of the combined serum 7-TAAB in the ESCC group was significantly higher than that in the control group (P < 0.05). (2) The sensitivity of single antibody detection was 4.20%–17.65%, with a specificity of 96.49%–100%, and accuracy of 51.07%–57.94%. The sensitivity of 7-TAAB combined detection was 49.58%, the specificity was 92.98%, and the accuracy was 70.81%. (3) The ROC curve showed that the 7-TAAB combined test had a certain diagnostic value for ESCC and that its diagnostic efficacy was significantly higher than that of the single autoantibody tests. The diagnostic efficacy of the combined test with the remaining five antibodies (PGP9.5, SOX2, GBU4-5, MAGE-A1, and CAGE) was similar to that of the 7-TAAB combined test after eliminating the two antibodies with low expression rates. (4) Univariate analysis revealed significant differences in the positive expression rates of the 7-TAAB combination test in terms of age, hemoglobin level, albumin level, tumor location, tumor length, lymph node stage, and tumor clinical stage (P < 0.05), and multivariate analysis revealed that age and lymph node stage were independent factors affecting antibody expression.
Conclusion: The multi-tumor-associated autoantibody combination test not only has a good auxiliary diagnostic value but also closely correlates with the clinical features of ESCC.
1 Introduction
According to the global oncology data released by the International Agency for Research on Cancer in 2022, esophageal cancer ranks 11th and 7th in terms of new cases and deaths, respectively. China is a particularly high-risk area for esophageal cancer, of which 95.5% of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), making it a major country for ESCC worldwide (1, 2). In recent years, studies have shown that in the early stages of tumor development, abnormally expressed tumor proteins can be recognized by the body’s immune system, which then stimulates autoimmune responses to produce numerous autoantibodies, which are referred to as tumor-associated autoantibodies (TAAB) (3). The 7-TAAB, which consist of the P53, PGP9.5, SOX2, GAGE7, GBU4-5, MAGE A1, and CAGE antibodies, represent an antibody spectrum. As a new serum marker, the 7-TAAB detection method, which has been applied in clinical tumor research (4, 5), has several advantages, including that it is convenient, inflicts less trauma on patients than other methods, and is easy to obtain specimens for. P53 is one of the earliest discovered oncogenes that participates in the development of tumors through DNA repair and apoptosis-inducing cells (6). PGP9.5, a ubiquitin hydroxyl-terminal hydrolase, plays a key role in tumor development by increasing the deubiquitination of cell cycle proteins (7). SOX2 is an important transcription factor that regulates cell development and is closely associated with various tumors (8). GBU4-5, an RNA-conjugating enzyme that regulates processes such as cell growth and division by encoding the DEAD-box protein to achieve oncogenesis. GAGE7, MAGE A1, and CAGE, as members of the tumor-testis antigen family, accelerate tumor formation, delay tumor cell apoptosis, and promote tumor cell metastasis (9–11). At present, the 7-TAAB detection method has not been applied in esophageal cancer research. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the diagnostic value of 7-TAAB and evaluate the relationship between 7-TAAB and clinical features in ESCC, which can be used to guide clinical diagnosis and treatment and achieve good clinical value.
2 Patients and methods
2.1 Patients
One hundred and nineteen patients with ESCC confirmed by histopathology who visited our hospital between April 2022 and November 2023 were selected as the ESCC group, and 114 healthy people with a normal physical examination in the same period were selected as the control group. Tumor staging was based on the 8th edition of the International TNM staging criteria for esophageal and gastric junction cancer (AJCC/UICC). This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Zhongshan City People’s Hospital (Zhongshan, China) under approval number 2024-074. This study was also conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All participants provided their written informed consent prior to their inclusion in the study.
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) all patients in the experimental group were diagnosed with ESCC by pathology and were not treated with any antitumor therapy before admission; (2) all patients had normal liver and kidney functions; and (3) all patients had complete data.
The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) previous or current malignant tumors in other parts of the body; (2) esophageal metastases from other malignant tumors; and (3) combined autoimmune diseases such as type I diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis, or diseases that affect immune function (e.g., HIV).
2.2 Methods
In both groups, 5 ml of peripheral venous blood samples were collected in the early morning fasting state, and the serum was separated by centrifugation at a radius of 10 cm and a rotational speed of 4000 rpm for 10 min, before being subjected to enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The 7-TAAB were detected using an ELISA kit produced by Hangzhou Kaipaul Bio-technology Co., with the following positive reference values: P53 ≥ 13.1 U/mL, PGP9.5 ≥ 11.1 U/mL, SOX2 ≥ 10.3 U/mL, GAGE7 ≥ 14.4 U/mL, GBU4.5 ≥ 7.0 U/mL, MAGE A1 ≥ 11.9 U/mL, and CAGE ≥ 7.2 U/mL. Interpretation of the results: If the concentration of any of the antibodies is higher than the positive value, the test is considered “positive”.
2.3 Statistical analysis
All data were analyzed using the SPSS software(version 26.0). For measures that conformed to a normal distribution, the mean ± standard deviation (x ± s) was expressed using the independent samples t-test for measures that did not conform to a normal distribution, the median (lower quartile, upper quartile) [M(P25, P75)] was expressed, and the two groups were compared using the Mann–Whitney U test. Count data were expressed as cases or percentages (%), and comparisons between the two groups were made using the chi-squared or Fisher’s exact probability method on a four-compartment scale. Comparisons between multiple groups were made using the chi-square test on the RxC list or Fisher’s exact probability method on the RxC list. Diagnostic efficacy was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC curve). For multivariate analysis, binary logistic regression analysis was used (P ≤ 0.05 was considered a statistically significant difference).
3 Results
3.1 Baseline characteristics of patients
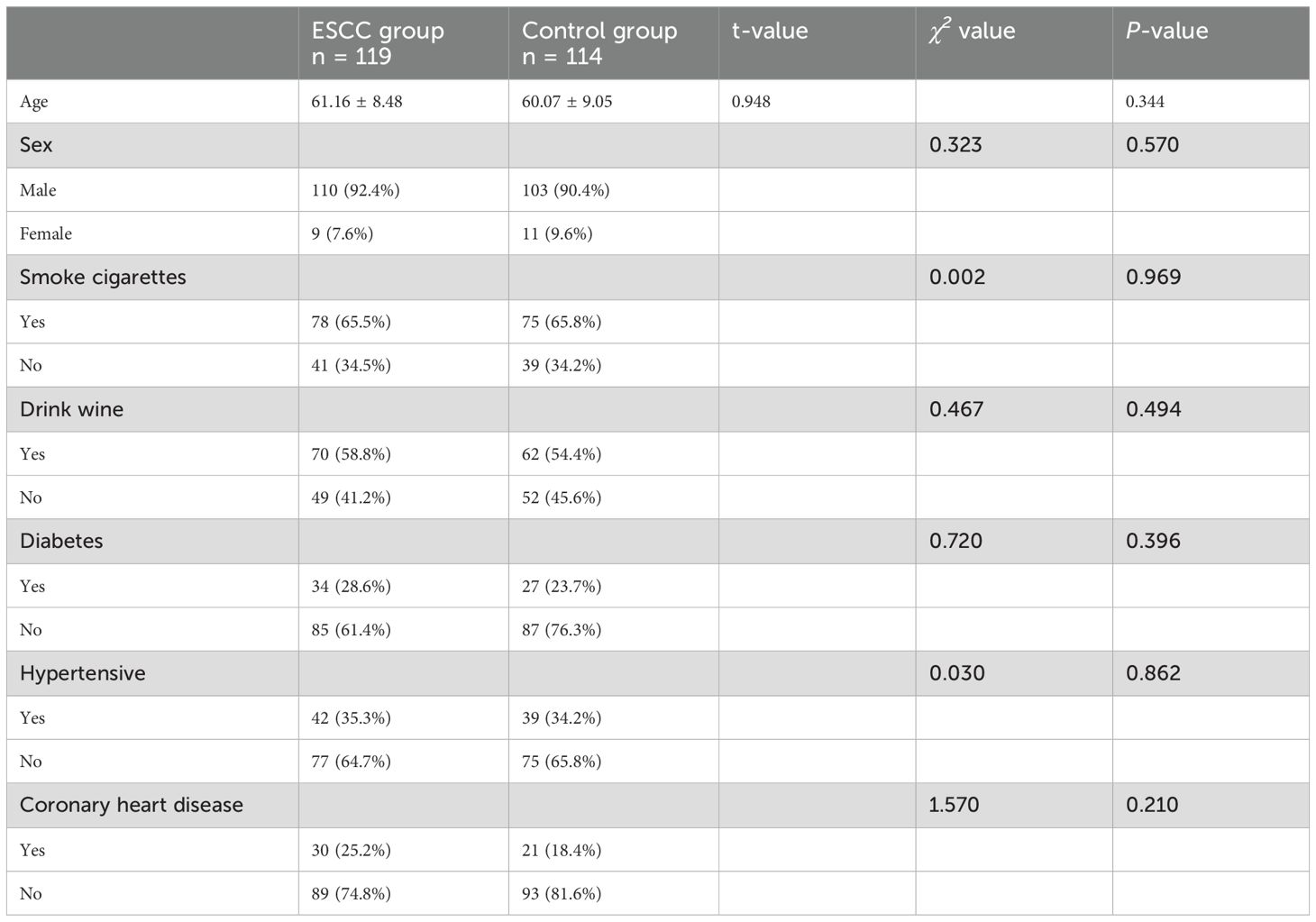
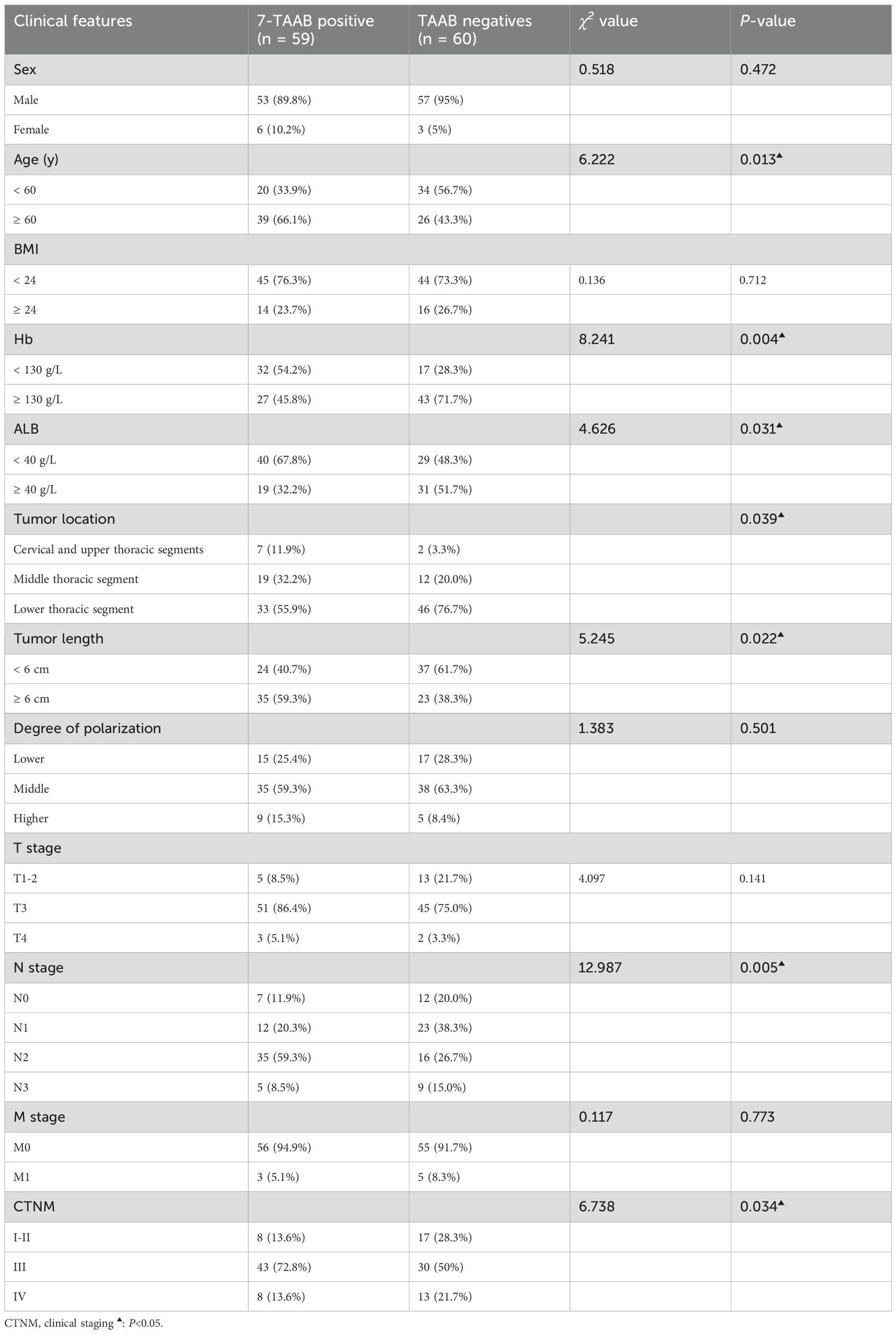
A total of 233 study subjects were included, comprising 119 patients in the ESCC group and 114 patients in the control group, with no significant difference in sex, age, or history of tobacco and alcohol addiction between the two groups (P > 0.05) (see Table 1 for details).
3.2 Comparison of serum 7-TAAB levels and positive expression rates between the two groups
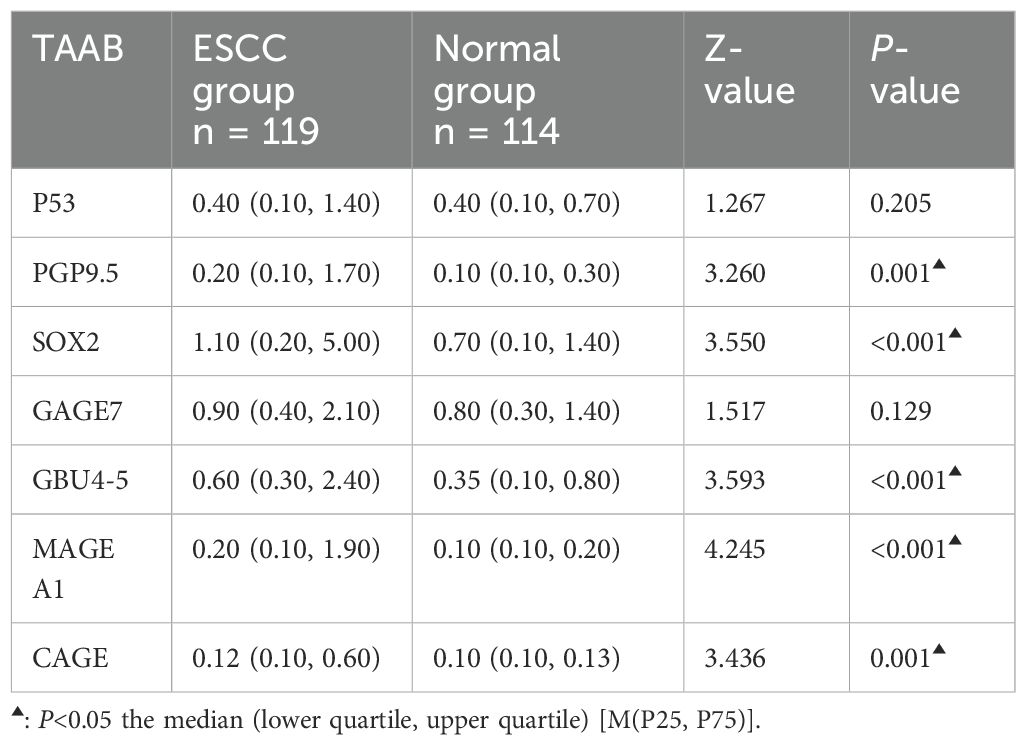
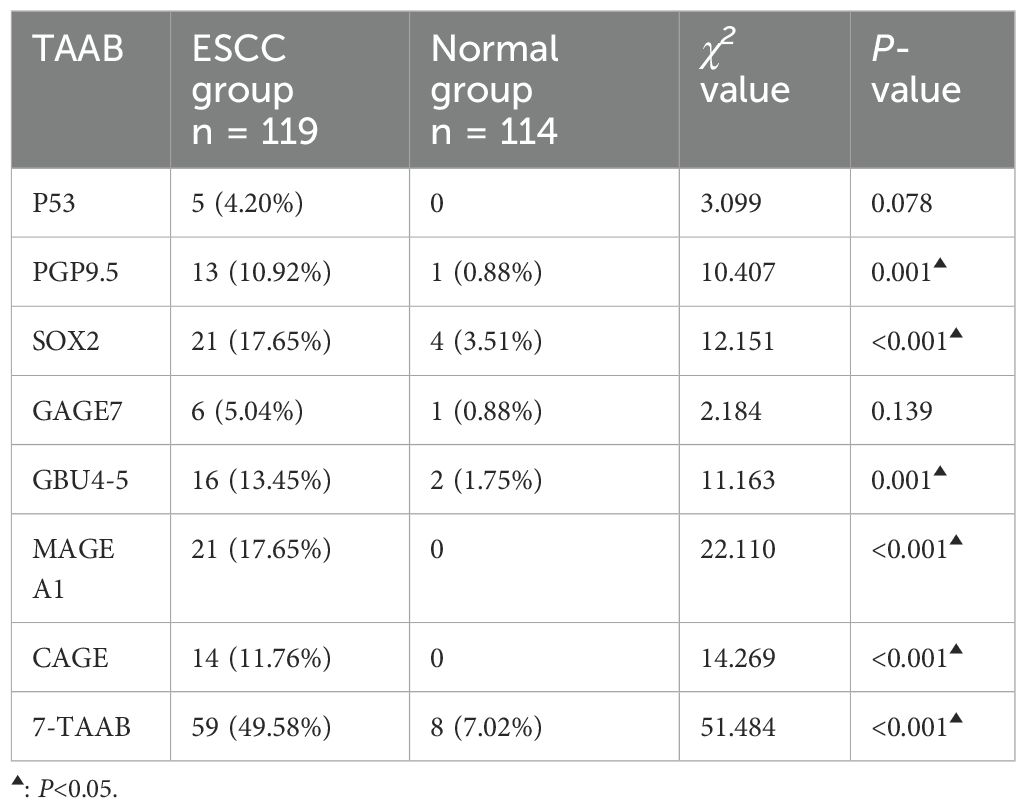
The antibody levels and positive expression rates of PGP9.5, SOX2, GBU4-5, MAGE A1, and CAGE were significantly higher in the ESCC group than in the control group (P < 0.05). The positive expression rate of the serum 7-TAAB combination test in patients in the ESCC group was significantly higher than that in the control group (P < 0.05) (for details, see Tables 2, 3; Figure 1).
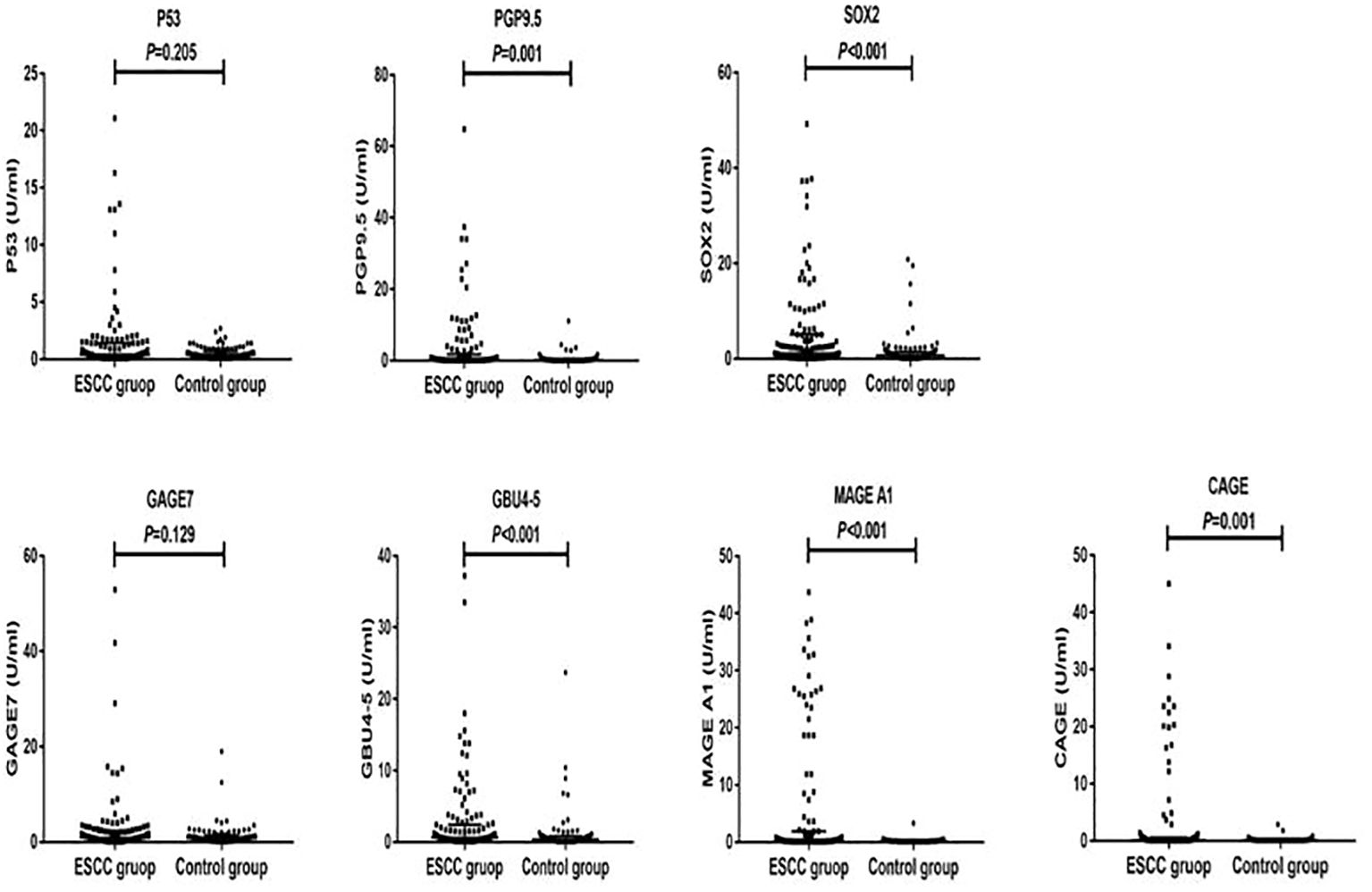
Figure 1. Distribution of serum expression levels of 7-TAAB in the two groups. Figure 1 shows the distribution of P53, PGP9.5, SOX2, GAGE7, GBU4-5, MAGE A1, and CAGE serum levels in the ESCC and control groups.
3.3 Diagnostic value of 7-TAAB single and combined tests for ESCC
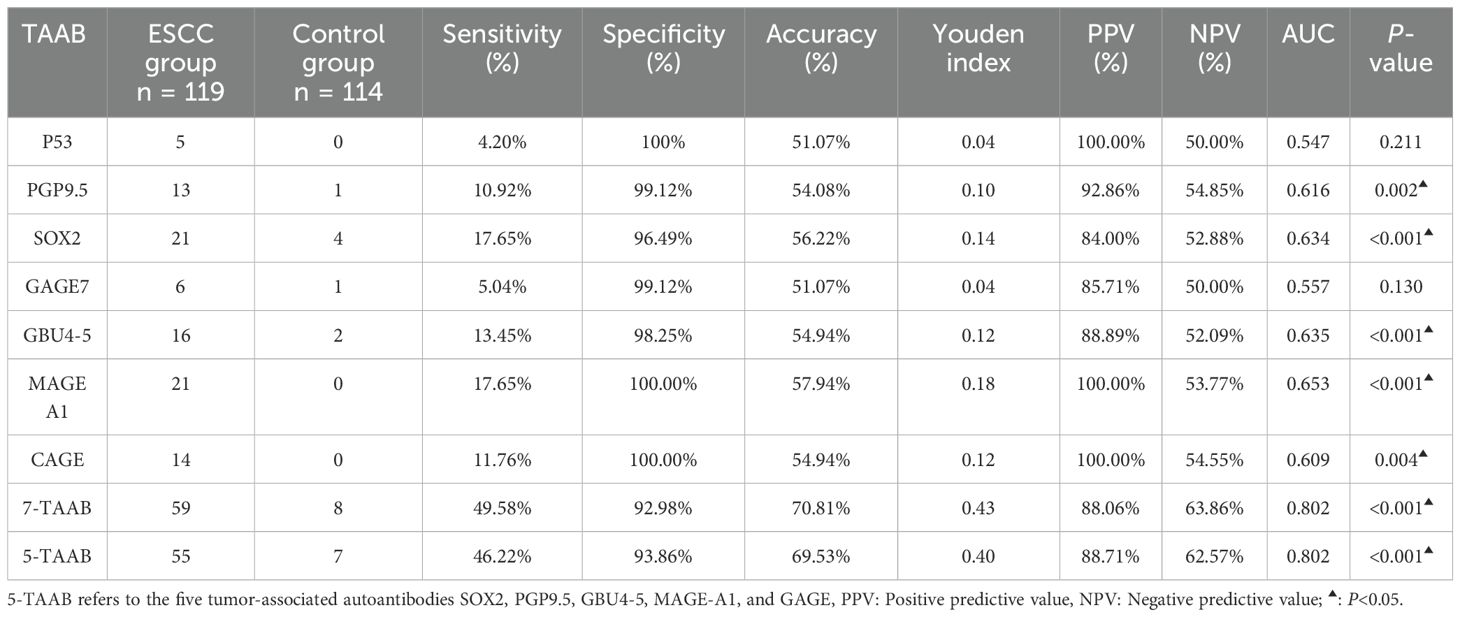
The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of the single antibody test were 4.20%–17.65%, 96.49%–100%, and 51.07%–57.94% respectively. The ROC curve showed that except for P53 (AUC = 0.547, P = 0.211) and GAGE7 (AUC = 0.557, P = 0.130), the remaining five antibodies played a role in the diagnosis of ESCC, and the diagnostic value of MAGE A1 was the highest (AUC = 0.653, P < 0.001). The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of the 7-TAAB combination test were 49.58%, 92.98%, and 70.81% respectively, and the AUC value of the 7-TAAB combination test was 0.802 (P < 0.001). Therefore, the 7-TAAB combination test not only has diagnostic value for ESCC, but it is also significantly better than the individual antibody tests. By eliminating the P53 and GAGE7 antibodies, the composition of the 5-TAAB combination test and the diagnostic value of the 5-TAAB combined test and the 7-TAAB combined test were the same (for details, see Table 4; Figures 2, 3).
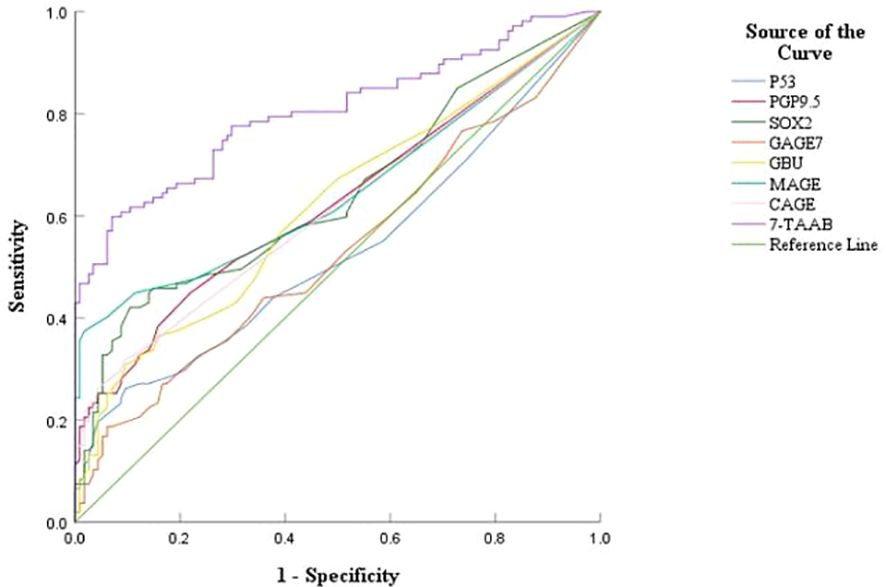
Figure 2. ROC curves of 7-TAAB single and combined tests for the diagnosis of ESCC. Figure 2 compares the ROC curves for the combined P53, PGP9.5, SOX2, GAGE7, GBU4-5, MAGE A1, CAGE, and 7-TAAB assays.
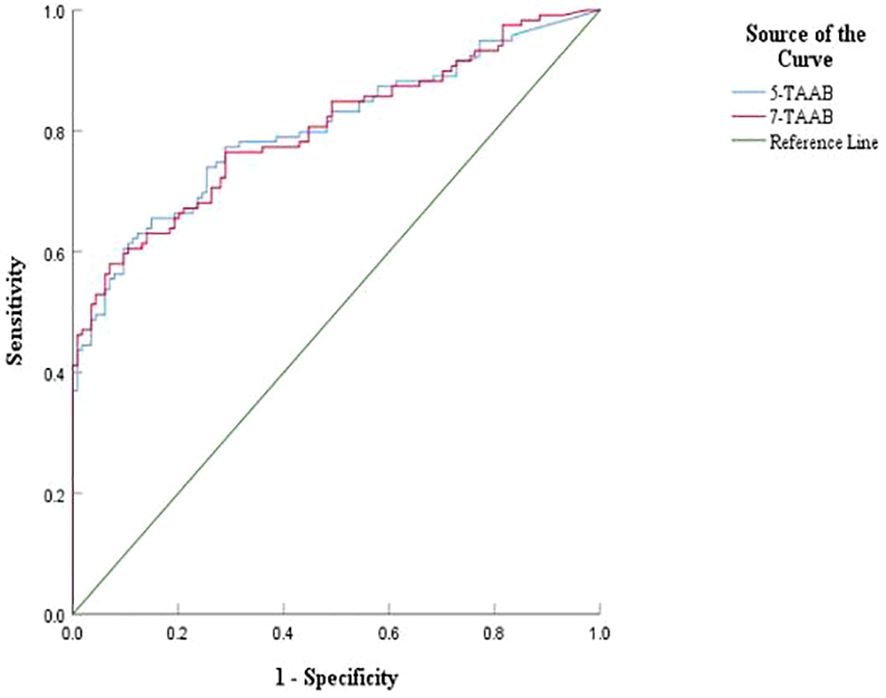
Figure 3. Comparison of ROC curves between 5-TAAB and 7-TAAB co-tests for ESCC diagnosis. 5-TAAB refers to the five tumor-associated autoantibodies SOX2, PGP9.5, GBU4-5, MAGE-A1, and GAGE.
3.4 Relationship between the clinical features of ESCC and the positive expression of 7-TAAB
The expression of 7-TAAB was significant with regard to age, hemoglobin level, albumin level, tumor location, tumor length, lymph node stage, and tumor clinical stage, whereas there was no significant difference between sex, body mass index, degree of differentiation, depth of infiltration, history of smoking and drinking, and distant metastasis (P > 0.05). Age and N stage were found to be independent factors influencing 7-TAAB expression in ESCC by multifactorial analysis (P > 0.05) (for details, see Tables 5, 6).
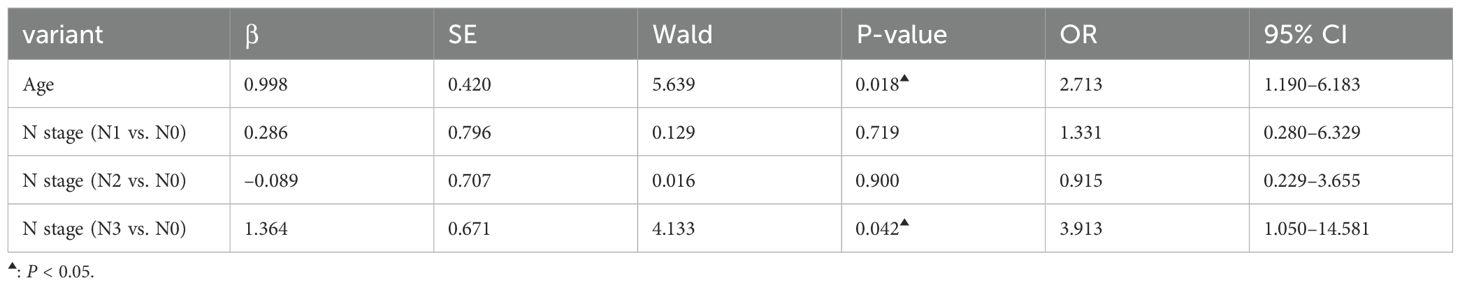
Table 6. Multifactorial analysis of clinical characteristics of patients with ESCC with positive expression of the combined 7-TAAB assay.
4 Discussion
Currently, there are no effective tumor markers for esophageal cancer. Although tumor-associated autoantibodies(TAAB) have been used in the study of esophageal squamous carcinoma, several studies have shown that their sensitivity is low at about 10%-30% and their accuracy is not high, so it is particularly important to find new antibody markers (12, 13). The 7-TAAB antibody spectrum has been approved by the China Food and Drug Administration in China. It has been widely used in the early diagnosis of lung cancer, with a sensitivity as high as 47%–65% and specificity as high as 51–81% (14–16), and its diagnostic accuracy has been increasingly recognized worldwide.
No studies have been found on the application of 7-TAAB to esophageal cancer, and only individual P53, GAGE7, and CAGE antibodies have been used in the clinical diagnosis of esophageal cancer (17–20). Our results revealed that the antibody levels and positive expression rates of PGP9.5, SOX2, GBU4-5, MAGE-A1, and CAGE were higher than those in the control group, whereas no statistical difference was found in the levels or positive expression rates of P53 and GAGE7, a finding that was contrary to that of Wang and Kunizaki (19, 21). The P53 and GAGE7 antibodies are the most common tumor antibodies, with several studies (19, 21, 22) showing a significant difference in expression between patients with esophageal cancer and healthy controls; however, the low expression levels of P53 and GAGE7 in the present study may be related to the interception of the reference values of antibody levels, individual differences between patients and the accuracy of different manufacturers of detection reagents. Therefore, we need to expand the sample size and adjust the reference values for antibody levels for further in-depth study.
The diagnostic efficacy of the 7-TAAB test for ESCC was evaluated by analyzing the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy indices. Although the specificity of the single antibody test was 96.49%–100%, the accuracy was only 50%–60%, which was of low diagnostic value; the reason for this is that the sensitivities were all low, ranging from 4.20% to 17.65%, indicating that the single antibody does not yet meet the clinical requirements. By unifying the seven antibodies, we found that the accuracy reached 70.81%, the sensitivity was increased to 49.53%, and the specificity (92.98%) was also high, which was consistent with the conclusions of Sun and Zhang (17, 18), who used multiple antibodies to diagnose esophageal cancer and suggested that the combined detection of 7-TAAB has a certain clinical diagnostic value and can be used to distinguish ESCC in the population. Although the sensitivity of the 7-TAAB combination test is low, and it is clearly insufficient for early screening of ESCC, its specificity is high, and it can be used for auxiliary diagnosis of ESCC.
The results of Xiao et al. (20), showed that the sensitivity and accuracy of the combined detection of multiple TAABs were higher (83.03% and 78.33%), respectively, which was significantly better than the results of the present study, which might be mainly related to the higher number and different types of selected antibodies in Xiao et al.’s study. The results were reanalyzed with the remaining five antibodies by eliminating the two antibodies with low positive expression rates, P53 and GAGE7, and it was found that their sensitivity was 46.22%, specificity was 93.86%, and accuracy was 69.53%, which was comparable to that of the 7-TAAB combination assay. Therefore, a new set of antibody profiles specifically for ESCC should be developed in the future; this would not only reduce the cost of detection, but would also improve diagnostic efficacy.
Several studies (23–27) have shown that TAAB is correlated with the clinical features of some tumors, including lung cancer, endometrial cancer, thymic tumors, and ESCC, which reflect the biological characteristics of these tumors to some extent. By analyzing the expression of the seven antibodies and their clinical characteristics, we found that antibody expression was significantly correlated with some clinical characteristics of tumors. Moreover, through multivariate analysis, we found that lymph node staging and age were independent factors influencing the positive expression of ESCC antibodies, indicating that antibody expression tends to occur in patients with poor lymph node staging and advanced age. First, poor lymph node staging is often indicative of tumor progression, and second, lymph nodes themselves are immune sites; therefore, these patients may be more susceptible to immune stimulation and tend to produce antibodies more easily. Currently, there are no studies on the occurrence of TAAB in elderly patients. We speculate that this may be due to the different body conditions of patients of different ages, or perhaps the slow metabolism of elderly patients leads to the deposition of more antibodies that are easily detected, although the specific mechanism of production remains unclear. However, antibody detection is often necessary in elderly patients. We conclude that 7-TAAB expression is correlated with the clinical features of ESCC, suggesting that tumor antibody expression may be linked to the development of ESCC, which may provide a guiding basis for the assessment of ESCC in the future.
Therefore, 7-TAAB is valuable in the auxiliary diagnosis and clinical assessment of ESCC and is worthy of further study. It is hoped that more clinical studies can be conducted in the future to identify a set of new antibody profiles with higher sensitivity and specificity for ESCC and to improve the diagnostic and therapeutic dilemmas and prognosis of ESCC in China.
5 Conclusion
The multi-tumor-associated autoantibody combination test not only has a good auxiliary diagnostic value, but is also closely correlated with the clinical features of ESCC.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of Zhongshan City People’s Hospital (Zhongshan, China) under approval number 2024-074. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
SZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. KL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. YY: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CY: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. YLiu: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. YLiang: Data curation, Investigation, Project administration, Software, Writing – original draft. WL: Investigation, Project administration, Validation, Writing – original draft. JZ: Data curation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. HY: Conceptualization, Investigation, Resources, Writing – original draft. SG: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YW: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Zhongshan Municipal Science and Technology Bureau (No. 2023B1035 and No. 2021SYF01).
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank LetPub (www.letpub.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript, Zhongshan People’s Hospital for providing technical support, and all participating investigators.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
7-TAAB, 7-tumor associated autoantibodies; TAAB, tumor-associated autoantibodies; ESCC, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; ROC, receiver operating characteristic; PPV, Positive predictive value; NPV, Negative predictive value.
References
1. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
2. Qiu M, Lin J, Li X, Luo R, Liu B, Lin J. Current state of esophageal cancer surgery in China: a national database analysis. BMC Cancer. (2019) 19:1064. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6191-2
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
3. Tomer Y, Sherer Y, Shoenfeld Y. Autoantibodies, autoimmunity and cancer (review). Oncol Rep. (1998) 5:753–61. doi: 10.3892/or.5.3.753
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
4. Chen P, Lu W, Chen T. Seven tumor-associated autoantibodies as a serum biomarker for primary screening of early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. J Clin Lab Anal. (2021) 35:e24020. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24020
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
5. Mu Y, Li J, Xie F, Xu L, Xu G. Efficacy of autoantibodies combined with tumor markers in the detection of lung cancer. J Clin Lab Anal. (2022) 36:e24504. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24504
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
6. de Oliveira GAP, Petronilho EC, Pedrote MM, Marques MA, Vieira TCRG, Cino EA, et al. The status of p53 oligomeric and aggregation states in cancer. Biomolecules. (2020) 10:548. doi: 10.3390/biom10040548
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
7. Spataro V, Norbury C, Harris AL. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in cancer. Br J Cancer. (1998) 77:448–55. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1998.71
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
8. Wuebben EL, Rizzino A. The dark side of SOX2: cancer - a comprehensive overview. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:44917–43. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16570
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
9. Cilensek ZM, Yehiely F, Kular RK, Deiss LP. A member of the GAGE family of tumor antigens is an anti-apoptotic gene that confers resistance to Fas/CD95/APO-1, interferon-g, taxol and g-irradiation. Cancer Biol Ther. (2002) 1:379–86. doi: 10.4161/cbt.1.4.11
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
10. Yue J, Diao L, Li B, Zou Z, Xiao J, Chen D, et al. Relationship of MAGE-A1 expression with Ki-67 and tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte response in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer. (2004) 23:219–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-467X.2004.02.025
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
11. Cho B, Lim Y, Lee D-Y, Park S-Y, Lee H, Kim WH, et al. Identification and characterization of a novel cancer/testis antigen gene CAGE. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2002) 292:715–26. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2002.6701
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
12. Wang H, Yang X, Sun G, Yang Q, Cui C, Wang X, et al. Identification and evaluation of autoantibody to a novel tumor-associated antigen GNA11 as a biomarker in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:661043. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.661043
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
13. Chen WX, Hong XB, Hong CQ, Liu M, Li L, Huang LS, et al. Tumor-associated autoantibodies against Fascin as a novel diagnostic biomarker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. (2017) 41:327–32. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2016.10.011
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
14. Ren S, Zhang S, Jiang T, He Y, Ma Z, Cai H, et al. Early detection of lung cancer by using an autoantibody panel in Chinese population. Oncoimmunology. (2017) 7:e1384108. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1384108
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
15. Zhang R, Ma L, Li W, Zhou S, Xu S. Diagnostic value of multiple tumor-associated autoantibodies in lung cancer. Onco Targets Ther. (2019) 12:457–69. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S187734
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
16. Huang H, Luo W, Ni Y, Sun S, Wang C, Zhang L. The diagnostic efficiency of seven autoantibodies in lung cancer. Eur J Cancer Prev. (2020) 29:315–20. doi: 10.1097/cej.0000000000000559
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
17. Sun G, Ye H, Wang X, Li T, Jiang D, Qiu C, et al. Autoantibodies against tumor-associated antigens combined with microRNAs in detecting esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. (2020) 9:1173–82. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2792
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
18. Zhang H, Qin J, Ren P, Shi J, Xia J, Ye H, et al. A panel of autoantibodies against multiple tumor-associated antigens in the immunodiagnosis of esophageal squamous cell cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2016) 65:1233–42. doi: 10.1007/s00262-016-1886-6
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
19. Wang H, Zhong L, Xu J, Zhang X, Wang J. Detection of serum autoantibody against GAGE-7 in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World Chin J Digestol. (2010) 18:998. doi: 10.11569/wcjd.v18.i10.998
20. Xiao K, Ma X, Wang Y, Zhu C, Guo L, Lu R. Diagnostic value of serum tumor-associated autoantibodies in esophageal cancer. biomark Med. (2021) 15:1333–43. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2021-0351
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
21. Kunizaki M, Hamasaki K, Wakata K, Tobinaga S, Sumida Y, Hidaka S, et al. Clinical value of serum p53 antibody in the diagnosis and prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. (2018) 38:1807–13. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.12419
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
22. Chai Y, Peng B, Dai L, Qian W, Zhang Y, Zhang JY. Autoantibodies response to MDM2 and p53 in the immunodiagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Scand J Immunol. (2014) 80:362–8. doi: 10.1111/sji.12202
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
23. Takashi S, Satoshi Y, Akihiko O, Naoya Y, Yusuke T, Kentaro M, et al. Clinical impact of preoperative serum p53 antibody titers in 1487 patients with surgically treated esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a multi-institutional study. Esophagus. (2021) 18:65–71. doi: 10.1007/s10388-020-00761-6
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
24. Wang Y, Jiao Y, Ding C, Sun W. The role of autoantibody detection in the diagnosis and staging of lung cancer. Ann Transl Med. (2021) 9:1673. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-5357
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
25. Atakan S, Bayiz H, Sak S, Poyraz A, Vural B, Yildirim AS, et al. Autologous anti-SOX2 antibody responses reflect intensity but not frequency of antigen expression in small cell lung cancer. BMC Clin Pathol. (2014) 14:24. doi: 10.1186/1472-6890-14-24
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
26. Srdelić S, Kuzmić-Prusac I, Spagnoli GC, Juretić A, Čapkun V. MAGE-A4 and MAGE-A1 immunohistochemical expression in high-grade endometrial cancer. Int J Gynecol Pathol. (2019) 38:59–65. doi: 10.1097/pgp.0000000000000470
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
27. Sakane T, Murase T, Okuda K, Masaki A, Nakanishi R, Inagaki H. Expression of cancer testis antigens in thymic epithelial tumors. Pathol Int. (2021) 71:471–9. doi: 10.1111/pin.13103
PubMed Abstract | PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
Keywords: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, 7-tumor associated autoantibodies, combination test, diagnostic value, clinical features
Citation: Zhou S, Liu K, Yang Y, Yuan C, Liu Y, Liang Y, Li W, Zhang J, Ye H, Gong S, Wu Y and Huang W (2024) Diagnostic value of multi-tumor-associated autoantibody expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and correlation of clinical features. Front. Immunol. 15:1518431. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1518431
Received: 28 October 2024; Accepted: 25 November 2024;
Published: 18 December 2024.
Edited by:
Tiezheng Hou, University College London, United KingdomReviewed by:
Wei Wang, Southern Medical University, ChinaMingran Xie, University of Science and Technology of China, China
Bin Qi, Affiliated Cancer Hospital & Institute of Guangzhou Medical University, China
Kongjia Luo, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center (SYSUCC), China
Copyright © 2024 Zhou, Liu, Yang, Yuan, Liu, Liang, Li, Zhang, Ye, Gong, Wu and Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Weizhao Huang, Z2FybWluZzk3QDEyNi5jb20=; Yingmeng Wu, cm93dW1lbmdAaG90bWFpbC5jb20=; Sheng Gong, cHV0YW90YW5nc2h1aUBxcS5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Sihao Zhou
Sihao Zhou Kejun Liu1,3†
Kejun Liu1,3† Jingjing Zhang
Jingjing Zhang Weizhao Huang
Weizhao Huang