
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CASE REPORT article
Front. Immunol. , 23 December 2024
Sec. Cancer Immunity and Immunotherapy
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1510069
 Xin Fei1
Xin Fei1 Zhong Zheng2
Zhong Zheng2 Zhen-ya Zhao3
Zhen-ya Zhao3 Da-wei Ren3
Da-wei Ren3 Su-ying Wang4
Su-ying Wang4 Shi-jie Ye1
Shi-jie Ye1 Lin-chun Liang5*
Lin-chun Liang5* Da Li6,7*
Da Li6,7* Xiao-long Jia2*
Xiao-long Jia2* Qi Ma7,8*†
Qi Ma7,8*†Primary small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate is extremely rare, highly aggressive, and has a very poor prognosis, with an overall survival typically not exceeding one year. Standard treatment is generally based on the regimen for small cell lung cancer (SCLC), with guidelines recommending etoposide combined with cisplatin (EP regimen) as the first-line treatment. However, their therapeutic effects are limited. For primary small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate that has failed the EP regimen treatment, there is currently a lack of relevant treatment methods. Here, we report a case of small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate with multiple metastases, whose disease rapidly progressed despite receiving EP and second-line systemic chemotherapy. The patient was then administered a combination of anlotinib and tislelizumab. After treatment, the patient’s symptoms were controlled, tumor marker levels decreased, and imaging showed significant improvement. The patient had a progression-free survival time of more than 22 months and continued to receive treatment. This is the first report of the use of anlotinib combined with tislelizumab for the treatment of primary small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate, providing a new therapeutic option for patients with this disease.
Neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC) is characterized by low or absence of androgen receptor (AR) expression and an increased neuroendocrine phenotype, with an overall survival typically not exceeding one year. Clinically, NEPC can be classified into primary (de novo NEPC or dn-NEPC) and treatment-induced (t-NEPC) types. The former refers to neuroendocrine tumors present at the initial diagnosis, accounting for only 2% of all cases (1), and is usually more aggressive than t-NEPC. The latter refers to neuroendocrine tumors induced by androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), with an incidence of up to 17% in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) (1), making it a highly aggressive histological subtype of CRPC (2). Primary NEPC can be divided into several histological types including common prostate cancer with neuroendocrine differentiation, adenocarcinoma with Paneth cell neuroendocrine differentiation, and carcinoid, small cell, and large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (3) (Table 1). Among them, pure small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma is the most aggressive type of NEPC, with the worst prognosis, and the overall survival (OS) is generally within one year (4–6).
There is no standard treatment for primary NEPC, and treatment is often referred to as the small cell lung cancer (SCLC) protocol. Here, we report an elderly patient with primary small cell NEPC who experienced disease remission and achieved radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS) over 22 months after failure of platinum-based therapy and subsequently received anlotinib combined with tislelizumab immunotherapy. This is the first case reported in the literature of anlotinib combined with tislelizumab for the treatment of primary small cell NEPC. To our knowledge, this patient has the longest rPFS reported in the literature.
The elderly patient presented with a history of urinary frequency and urgency for over 10 years, which had worsened over the past half month. Transrectal ultrasound in December 2021 indicated a prostate volume of 53 ml, with PSA levels of 1.71 ng/ml. A pelvic MRI [Figures 1(1A–C)] performed in January 2022 suggested the following: (1) malignant prostate lesion invading the bladder, seminal vesicles, and rectum; and (2) multiple enlarged pelvic lymph nodes.
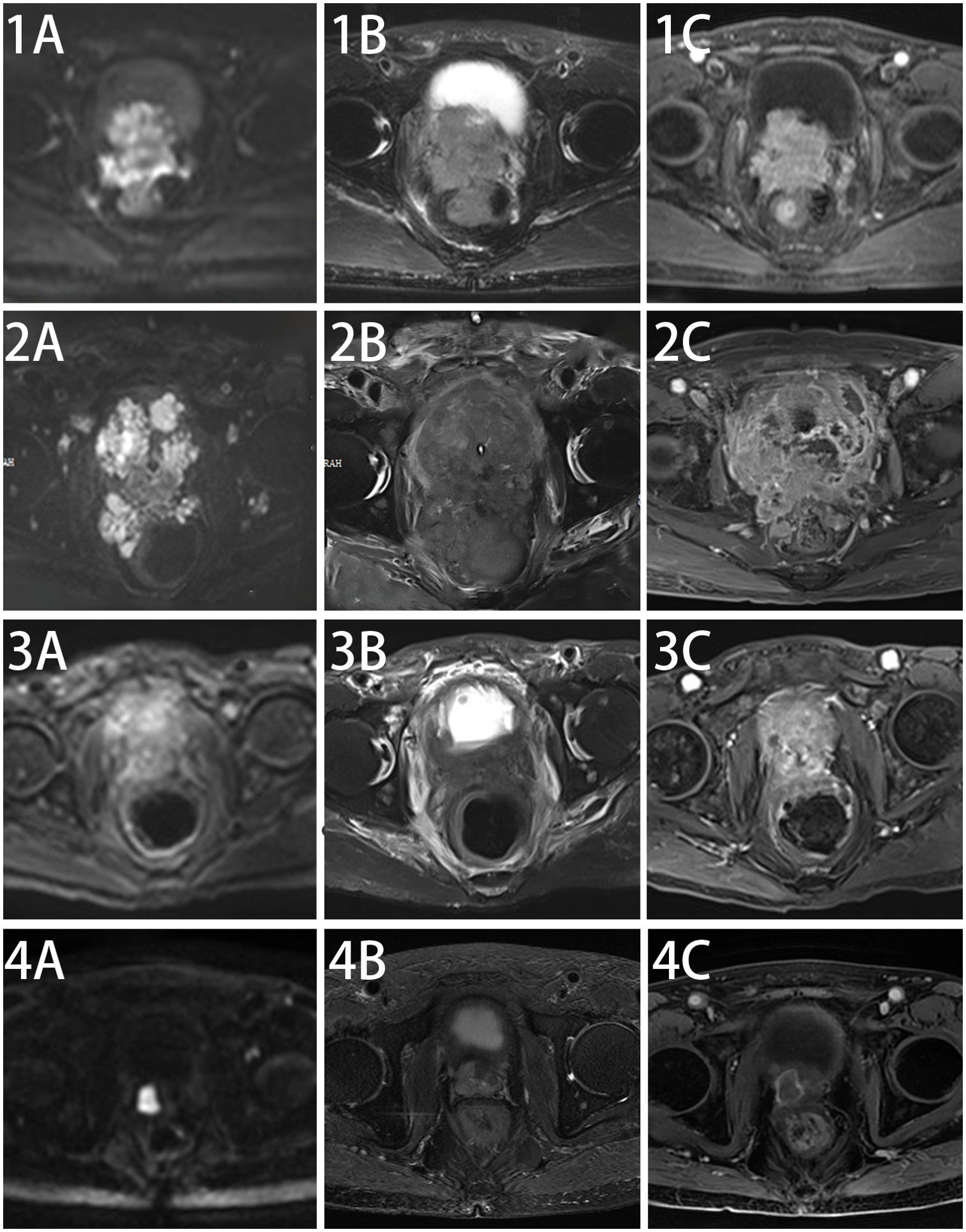
Figure 1. Changes in pelvic MRI images before and after treatment in this patient. Pelvic MRI Scan at diagnosis of this disease (1A–C), after chemotherapy (2A–C), after five cycles of anlotinib + tislelizumab treatment (3A–C) and maintenance treatment of anlotinib + tislelizumab (4A–C).
A prostate biopsy in January 2022, revealed “poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma (small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma).” Biopsy samples from various prostate regions revealed small round cells with nest-like, cord-like, and diffuse growth patterns. The immunohistochemical staining results were consistent with poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma (small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma). The results showed: PSA (−), PSAP (−), NKX3.1 (weakly in individual cells), Ki-67 (+ 90%), Syn (+++), CgA (+ scattered), CD56 (++), 34βE12 (+), P504S (±), AR (−) (Figure 2), PD-L1 (−) (Supplementary Figure 1).
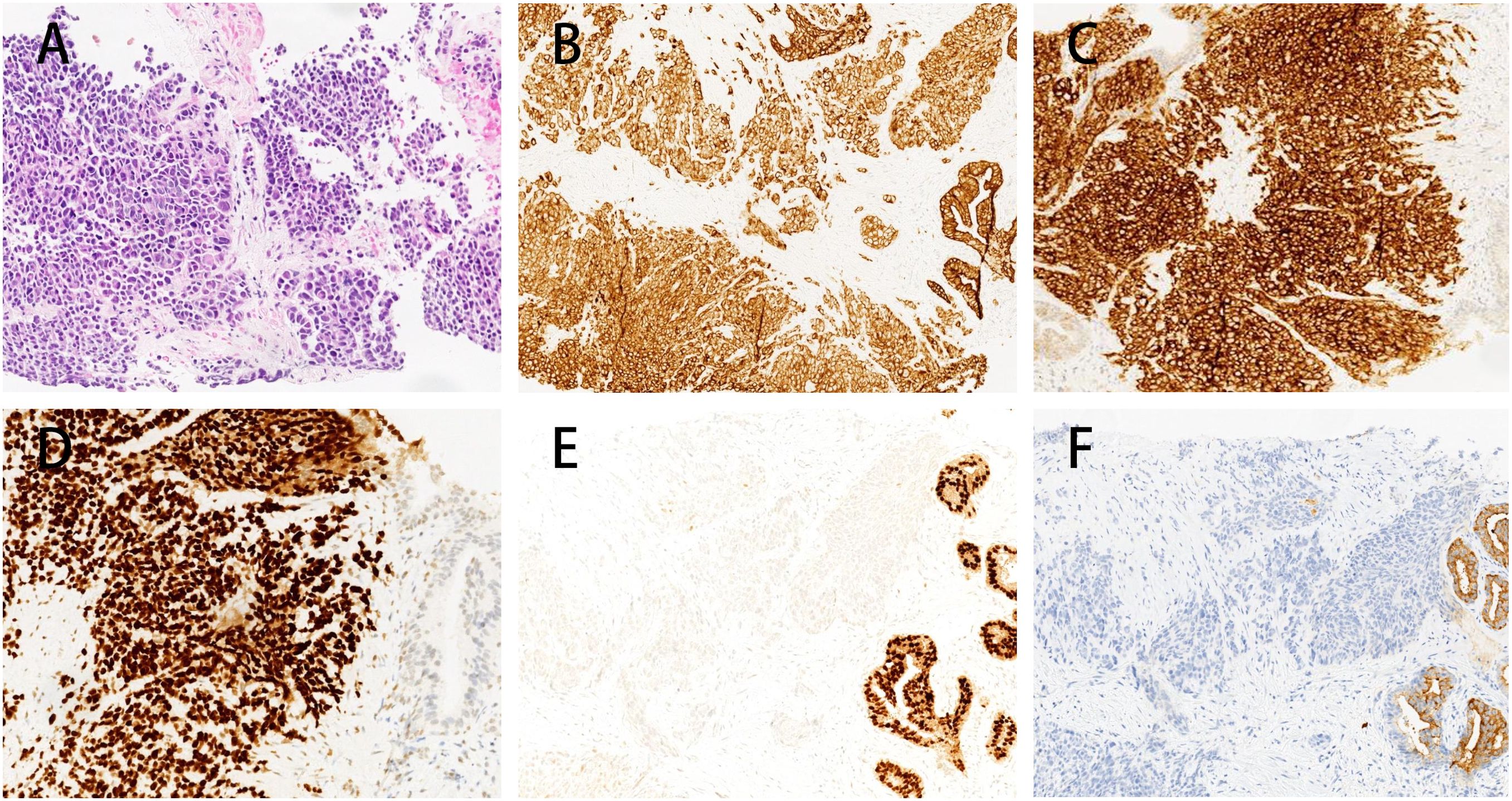
Figure 2. Immunohistochemistry of prostate biopsy specimens in this patient. Immunohistochemical analysis of the prostate biopsy specimen showing microscopic features of nests, cords, and diffuse growth of small round cells. The tumor cells exhibit a profile consistent with poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma (small cell carcinoma) (A), characterized by positive pan-cytokeratin (CK) staining (B), strong staining for Synaptophysin (+++) (C), strong TTF-1 expression (+++) (D), focal weak NKX3.1 staining (E) and PSA-negative expression in the tumor area and a small area with PSA positive expression in the normal prostate tissue (F).
The patient’s creatinine clearance rate was 46.65 ml/min, and PSA levels were low (Figure 3), while NSE and other tumor markers were elevated significantly (Figure 3), consistent with the pathological diagnosis. Based on pathology and imaging, he was diagnosed as “primary small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate.” The patient had an ECOG score of 0, indicating good general condition.
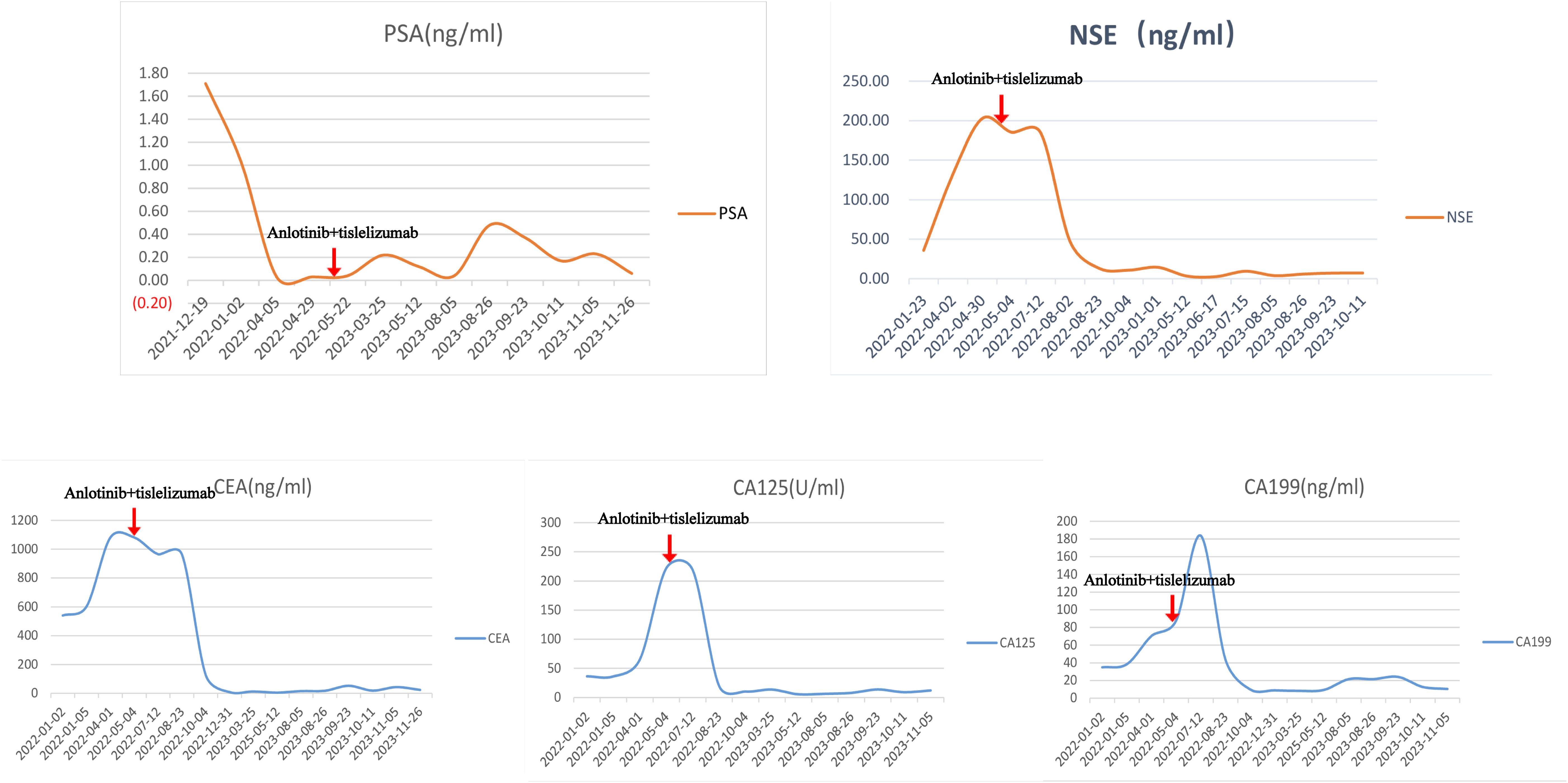
Figure 3. Patient’s PSA, NSE, and related tumor markers of this patient. The changes in PSA (prostate-specific antigen), NSE (neuron-specific enolase), and related tumor markers (CEA, CA125, CA199) before and after anlotinib and tislelizumab treatment in this patient.
To determine metastasis, a 18F-FDG PET-CT scan in January 2022, showed “prostate malignancy involving bilateral seminal vesicles, posterior bladder wall; multiple lymph node metastases around the prostate and along bilateral iliac vessels; liver metastasis in segment S3; bone metastasis in T10 and S1 vertebral body,” indicating multiple metastases including lymph nodes, liver, and bone of this highly aggressive tumor.
Currently, the NCCN Guidelines for the treatment of primary small cell NEPC are referred to as the NCCN Guidelines for SCLC. Considering the patient’s age and low creatinine clearance rate, chemotherapy with a decreased dose of the EP regimen (etoposide 300 mg + cisplatin 60 mg) was administered in February 2022 and March 2022. Despite two rounds of chemotherapy, NSE and related tumor markers continued to increase (Figure 3), and imaging indicated further progression. During treatment, the patient’s renal function quickly deteriorated. Abdominal CT scans showed hydronephrosis in both kidneys, and the tumor has invaded the bilateral ureteral orifices (Supplementary Figure 2. The details are provided in Supplementary Videos 1, 2). Thus, bilateral percutaneous nephrostomy was performed to rapidly relieve obstruction and improve renal function. The patient also experienced severe gastrointestinal side effects during EP chemotherapy. Given the tumor markers, imaging progression, symptomatic progression, and treatment side effects, first-line EP chemotherapy was deemed to fail. The patient’s ECOG score was 2.
After a multidisciplinary team (MDT) discussion and reference to the NCCN guidelines, the patient received second-line chemotherapy with “irinotecan 100 mg + carboplatin 140 mg” in April 2022. Following chemotherapy, NSE and related tumor markers continued to increase (Figure 3), and imaging indicated further progression [Figures 1(2A–C)]. The patient also experienced significant bone marrow suppression and fatigue during the chemotherapy. Given the elevation of tumor markers, imaging progression, symptomatic progression, and treatment side effects, second-line treatment was also deemed to fail. The patient’s ECOG score was 3.
Since there is no standard treatment for primary small cell NEPC, and the tumor is rapidly progressing, another MDT discussion was held to provide a new treatment strategy for this patient. After thorough discussion and informed consent from the patient and his family, innovative therapy was administered to this patient. In May 2022, the patient received combined targeted immunotherapy with “anlotinib 8 mg/day for 14 days + tislelizumab 200 mg/day per 21 days,” administered every three weeks. After the 5th cycle of combined targeted and immunotherapy, on August 2022, pelvic MRI [Figures 1(3A–C)] and tumor markers, including NSE (Figure 3), showed tumor shrinkage and a significant decline in tumor markers, proving the therapy’s effectiveness.
A follow-up 18F-FDG PET-CT on November 2022, indicated: “Compared to January 2022 PET-CT: the prostate is significantly smaller, FDG metabolism significantly reduced; Scattered small lymph nodes around the prostate and bilateral iliac vessels, no increased FDG metabolism; liver metastasis in segment S3, no abnormal increase in FDG metabolism; Low metabolic osteoblastic metastases in T10 and S1 vertebral body.” The patient’s ECOG score improved to 1.
However, in November and December 2022, the patient experienced two episodes of severe COVID-19 pneumonia. He had to pause the anti-tumor treatment. After recovering from COVID-19, owing to the cessation of anti-tumor therapy, the patient developed severe back pain, particularly at night and after carrying heavy loads. Upon re-evaluation in March 2023, MDT discussions led to the resumption of “anlotinib + tislelizumab” treatment in March 2023.
Unfortunately, in November 2023, the patient experienced stroke. MDT discussions considered that the possibility of the combined treatment of anlotinib and tislelizumab was low. After recovery from stroke, he continued anti-tumor treatment, although his ECOG score was 3.
The patient survived for over two years, receiving 25 cycles of treatment, maintaining good general condition, and no significant side effects were observed during treatment. On 16 March 2024, pelvic MRI showed no significant progression [Figures 1(4A–C)].
Considering the patient’s age and the impact of two bouts of COVID-19 infection and stroke during anti-tumor therapy, the overall survival may be affected. However, after the diagnosis of primary small cell NEPC with multiple lymph node, liver, and bone metastases, the patient has survived for more than two years, which is, to our knowledge, the longest survival reported in the literature to date.
Primary small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate is a poorly differentiated neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC) that is extremely rare (<1%), highly aggressive, and has a very poor prognosis, with an overall survival typically not exceeding one year (4, 5). It often presents with symptoms related to local infiltration or metastatic disease, including bowel or bladder invasion; hydronephrosis; metastatic disease to visceral organs such as the liver, lungs, and central nervous system; and primarily osteolytic bone metastases (7). Currently, the treatment of NEPC often references the treatment strategy for small cell lung cancer (SCLC). According to the 2022 NCCN SCLC guidelines, the first choice is chemotherapy with a platinum-based drug combined with etoposide (EP regimen) is recommended for patients with limited-stage disease (8). For patients with extensive-stage disease, the preferred treatment is a platinum-based drug combined with etoposide and PD-L1 inhibitors, such as atezolizumab or durvalumab (9). However, even with the EP regimen combined with PD-L1 inhibitors, primary NEPC still exhibits extremely low survival rates and poor prognoses. Wee et al. analyzed seven NEPC patients who received a combination treatment of carboplatin, etoposide, and atezolizumab (two of whom had newly diagnosed small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate) and found that the median follow-up time was 6.5 months (range: 1.5–15.1), with a median progression-free survival (mPFS) of 3.4 months and a median overall survival (mOS) of only 8.4 months (with the longest patient OS being 15.1 months) (5). Therefore, the treatment of primary NEPC faces challenges of both rarity and poor efficacy.
Here, we report an innovative treatment approach for primary small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate in an elderly patient. The patient, with advanced age, had a low creatinine clearance rate and an ECOG performance status score of 0. After the pathological diagnosis of primary small cell NEPC, imaging revealed multiple lymph node, liver, and bone metastases. According to the 2022 NCCN SCLC guidelines, platinum-based drugs should be combined with etoposide and PD-L1 inhibitors such as atezolizumab or durvalumab. Since atezolizumab/durvalumab was not yet approved in China for this indication in 2022, the patient received an EP regimen as the first-line treatment. After two cycles of EP chemotherapy, the patient’s creatinine levels continued to rise, and gastrointestinal side effects were significant. The patient’s symptoms, tumor markers, and imaging findings also improved. The ECOG performance status score increased from 0 to 2. All these parameters indicated treatment failure of the first-line EP chemotherapy. After a multidisciplinary team (MDT) discussion and considering the patient’s condition, second-line chemotherapy with irinotecan combined with carboplatin was administered according to the 2022 NCCN guidelines. However, after second-line chemotherapy, re-evaluation showed that NSE and related tumor markers were still elevated, imaging suggested further progression, and the patient experienced significant side effects during chemotherapy, indicating failure of second-line irinotecan combined with carboplatin chemotherapy.
There is no standard third-line therapy for NEPC, and the patient’s tumor continues to progress rapidly. We performed a literature review and found that tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), such as anlotinib, combined with PD-1 inhibitors, have shown good therapeutic effects and safety in SCLC in recent years. Zhang et al. retrospectively analyzed patients with recurrent SCLC who received anlotinib combined with a PD-1 inhibitor as ≥ second-line treatment and found that the progression-free survival (PFS) of patients receiving combination therapy was significantly longer than that of patients receiving PD-1 inhibitors alone (n = 14, 5.0 months vs. 3.0 months; P = 0.005), suggesting that anlotinib combined with PD-1 inhibitors may have good efficacy and manageable toxicity in SCLC (10). Zhang et al. described a patient aged >70 years with extensive-stage SCLC who achieved good survival (median overall survival of 13 months) and safety with third-line pembrolizumab combined with anlotinib therapy after the failure of standard treatment (11). Hao et al. retrospectively analyzed 36 SCLC patients who had received at least one systemic chemotherapy regimen and found that the objective response rate (ORR) was 27.8% (95% CI: 14.2%–45.2%) and the disease control rate (DCR) was 80.6% (95% CI: 64.0%–91.8%), indicating that anlotinib combined with a PD-1 inhibitor has significant efficacy and safety for previously treated SCLC patients (12).
Therefore, after MDT discussion and after thorough discussion and informed consent from the patient, we decided to treat the patient with a combination of anlotinib and tislelizumab as an innovative attempt. Subsequently, the patient received treatment every three weeks for a cycle, showing good tolerance and without significant side effects. NSE and related tumor markers dramatically decreased, tumor reduction was significant on imaging, and the treatment efficacy was remarkable. The ECOG performance status score recovered to 1, and the patient’s physical condition improved. The patient has survived for more than two years, having received over 25 treatment cycles.
Anlotinib is a multi-target tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI). It can inhibit various targets including vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFR), platelet-derived growth factor receptors (PDGFR), fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFR), and c-Kit (13). It inhibits tumor cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis and reduces tumor blood supply by inhibiting tumor angiogenesis and growth factor signaling pathways. Compared with other TKIs, anlotinib has better anti-angiogenic activity and higher selectivity, with a significantly lower incidence of grade 3 or higher adverse effects (14, 15).
Tislelizumab (BGB-A317) is a novel anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody that blocks the PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway, relieves the immune suppression of T cells, and enhances the anti-tumor immune response. Compared to traditional anti-PD-1 antibodies, its Fc region has been structurally optimized, resulting in stronger antitumor activity compared to nivolumab and pembrolizumab. In the 2023 WCLC, tislelizumab combined with chemotherapy demonstrated significant survival benefits in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC) (RATIONALE 312, NCT04005716), with OS extending to 15.5 months (versus 13.5 months in the control group, HR: 0.75, 95% CI: 0.61–0.92, P = 0.0035), and the 1-year PFS rate was four times that of the control group (20.7% vs. 4.5%) (16).
Studies on the efficacy of immunotherapy for NEPC are limited. Although prostate cancer is typically considered a “cold tumor,” the immune microenvironment of primary NEPC remains largely unknown. Theoretically, anti-angiogenic agents can inhibit tumor growth and metastasis by disrupting the tumor blood supply, resulting in a lack of oxygen and nutrients. However, after anti-angiogenesis therapy, a complex local balance exists between pro-angiogenic factors, anti-angiogenic factors, and vascular normalization (17). During tumor vascular normalization, the function of immunosuppressive cells such as regulatory T cells (Tregs), tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) may be weakened, thereby improving the immune microenvironment of the tumor (17, 18). Furthermore, these suppressive cells not only affect tumor immune responses through immune suppression but also stimulate tumor angiogenesis by increasing the expression of pro-angiogenic factors in the extracellular matrix. There seems to be a reciprocal regulation between the immune response and vascular normalization (19). The combination of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and anti-angiogenic agents may have potential synergistic anti-tumor effects.
Du et al. conducted a retrospective real-world study on 25 patients with mCRPC who received PD-1 inhibitors combined with anlotinib after progression to standard treatment. The study found that six patients (24.0%) exhibited a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) response and 11 patients (44.0%) experienced a decrease in PSA levels (20). Additionally, the study found that mCRPC patients with DNA damage repair (DDR) and homologous recombination repair (HRR) defects had relatively longer PSA progression-free survival (PSA-PFS; 2.5 months vs. 1.2 months, P = 0.027; 3.3 months vs. 1.2 months, P = 0.017) (20). However, Du’s report did not include cases of NEPC, and our case suggests that patients with NEPC may also benefit from anlotinib combined with PD-1 inhibitor treatment.
Unfortunately, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the patient was hospitalized twice for severe COVID-19 infection, leading to interruption of anlotinib combined with tislelizumab treatment. After recovering from COVID-19, the MDT discussion decided to continue the anlotinib and tislelizumab treatment cycles. In November 2023, the patient experienced a stroke, which led to another interruption in treatment. The MDT assessed that stroke was less likely to be related to anlotinib and tislelizumab treatment. After recovering from stroke, the patient resumed anlotinib and tislelizumab treatment again. The patient is currently undergoing treatment, but these attacks have impeded the patient’s physical condition. Currently his ECOG performance status score is 3. These concomitant diseases may significantly reduce a patient’s expected OS.
In brief, this elderly patient was diagnosed with metastatic primary small cell NEPC. After treatment failure of the first- and second-line chemotherapy according to the guidelines, the patient was treated with anlotinib and tislelizumab. This combination led to a significant reduction in NSE and other related tumor markers, and imaging revealed notable tumor shrinkage. Progression-free survival (rPFS) exceeded 22 months. Although overall survival (OS) data are not yet available, the patient survived for more than two years after diagnosis. This case provides valuable insights into the future management of similar patients.
To our knowledge, this is the first report of the use of anlotinib combined with tislelizumab for the treatment of primary small cell NEPC, achieving good efficacy and safety in this patient. This case suggests that for patients with primary small cell NEPC, anlotinib-targeted therapy combined with PD-1 inhibitor immunotherapy may bring significant benefits. This case indicates that in NEPC patients, after the failure of standard treatments, anlotinib combined with tislelizumab can be considered as a preferred treatment option. Additionally, we recommend exploring anlotinib combined with tislelizumab as a first-line treatment choice in patients with NEPC. More clinical trials and real-world data are needed to support the application of anlotinib in combination with PD-1 inhibitors in primary NEPC.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Ningbo University, Approval No. 2024 Research 186RS. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
XF: Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZZ: Writing – review & editing. Z-yZ: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. D-wR: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. S-yW: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. S-jY: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. L-cL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. DL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. X-lJ: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. QM: Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Ningbo Clinical Research Center for Urological Disease, No.2019A21001.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1510069/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | expression of PD-L1 in this patient. Results of PD-L1 immunohistochemistry (IHC) in this patient. (A) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining; (B) PD-L1 negative control; (C) PD-L1 positive control; (D) PD-L1 IHC result of the patient, showing negativity (-).
Supplementary Figure 2 | Non-contrast CT scan of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder (March 2022). showed tumor invaded to both the ureteral orifice.
Supplementary Video 1 | Non-contrast CT scan of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder of this patient (March 2022).
Supplementary Video 2 | Non-contrast CT scan of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder of this patient (April 2022).
1. Aggarwal R, Huang J, Alumkal JJ, Zhang L, Feng FY, Thomas GV, et al. Clinical and genomic characterization of treatment-emergent small-cell neuroendocrine prostate cancer: A multi-institutional prospective study. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. (2018) 36:2492–503. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.77.6880
2. Lee AR, Gan Y, Xie N, Ramnarine VR, Lovnicki JM, Dong X. Alternative RNA splicing of the GIT1 gene is associated with neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Cancer Sci. (2019) 110:245–55. doi: 10.1111/cas.13869
3. Aggarwal R, Zhang T, Small EJ, Armstrong AJ. Neuroendocrine prostate cancer: subtypes, biology, and clinical outcomes. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2014) 12:719–26. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2014.0073
4. Zhang Y, Ouyang W, Sun G, Ding B, Yan L, Wang Z, et al. Pure small cell carcinoma of prostate: A report of 8 cases. Urol Int. (2018) 101:263–8. doi: 10.1159/000493160
5. Wee CE, Costello BA, Orme JJ, Quevedo JF, Pagliaro LC. Chemotherapy with atezolizumab for small cell or neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate: A single institution experience. Prostate. (2021) 81:938–43. doi: 10.1002/pros.24189
6. Deorah S, Rao MB, Raman R, Gaitonde K, Donovan JF. Survival of patients with small cell carcinoma of the prostate during 1973-2003: a population-based study. BJU Int. (2012) 109:824–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10523.x
7. Marcus DM, Goodman M, Jani AB, Osunkoya AO, Rossi PJ. A comprehensive review of incidence and survival in patients with rare histological variants of prostate cancer in the United States from 1973 to 2008. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. (2012) 15:283–8. doi: 10.1038/pcan.2012.4
8. Faivre-Finn C, Snee M, Ashcroft L, Appel W, Barlesi F, Bhatnagar A, et al. Concurrent once-daily versus twice-daily chemoradiotherapy in patients with limited-stage small-cell lung cancer (CONVERT): an open-label, phase 3, randomised, superiority trial. Lancet Oncol. (2017) 18:1116–25. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30318-2
9. Goldman JW, Dvorkin M, Chen Y, Reinmuth N, Hotta K, Trukhin D, et al. Durvalumab, with or without tremelimumab, plus platinum-etoposide versus platinum-etoposide alone in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): updated results from a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2021) 22:51–65. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30539-8
10. Zhang X, Zeng L, Li Y, Xu Q, Yang H, Lizaso A, et al. Anlotinib combined with PD-1 blockade for the treatment of lung cancer: a real-world retrospective study in China. Cancer Immunol Immunother CII. (2021) 70:2517–28. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-02869-9
11. Zhang Z, Li Y, Dong Y, Li J, Zhang B, Zhang C, et al. Successful treatment of a patient with multiple-line relapsed extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer receiving penpulimab combined with anlotinib: A case report. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:846597. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.846597
12. Hao YY, Qiao YP, Cheng JD. Clinical activity and safety of anlotinib combined with PD-1 blockades for patients with previously treated small cell lung cancer. Int J Gen Med. (2021) 14:10483–93. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S337316
13. Shen G, Zheng F, Ren D, Du F, Dong Q, Wang Z, et al. Anlotinib: a novel multi-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor in clinical development. J Hematol OncolJ Hematol Oncol. (2018) 11:120. doi: 10.1186/s13045-018-0664-7
14. Xie C, Wan X, Quan H, Zheng M, Fu L, Li Y, et al. Preclinical characterization of anlotinib, a highly potent and selective vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 inhibitor. Cancer Sci. (2018) 109:1207–19. doi: 10.1111/cas.13536
15. Cao JZ, Wu W, Pan JF, Wang HW, Jiang JH, Ma Q. Case report: anlotinib combined with sintilimab as third-line treatment in a metastatic urothelial bladder carcinoma patient with FGFR3 mutation. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:643413. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.643413
16. Cheng Y, Fan Y, Zhao Y, Huang D, Li X, Zhang P, et al. OA01.06 first-line chemotherapy with or without tislelizumab for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: RATIONALE-312 phase 3 study. J Thorac Oncol. (2023) 18:S46. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2023.09.027
17. Kazerounian S, Lawler J. Integration of pro- and anti-angiogenic signals by endothelial cells. J Cell Commun Signal. (2018) 12:171–9. doi: 10.1007/s12079-017-0433-3
18. Tian L, Goldstein A, Wang H, Ching Lo H, Sun Kim I, Welte T, et al. Mutual regulation of tumour vessel normalization and immunostimulatory reprogramming. Nature. (2017) 544:250–4. doi: 10.1038/nature21724
19. Fukumura D, Kloepper J, Amoozgar Z, Duda DG, Jain RK. Enhancing cancer immunotherapy using antiangiogenics: opportunities and challenges. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2018) 15:325–40. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2018.29
Keywords: small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma, NEPC, case report, anlotinib, tislelizumab, prostate cancer
Citation: Fei X, Zheng Z, Zhao Z-y, Ren D-w, Wang S-y, Ye S-j, Liang L-c, Li D, Jia X-l and Ma Q (2024) Anlotinib combined with tislelizumab in the treatment of primary small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate: a case report and literature review. Front. Immunol. 15:1510069. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1510069
Received: 12 October 2024; Accepted: 02 December 2024;
Published: 23 December 2024.
Edited by:
Sheng Liu, Indiana University Bloomington, United StatesReviewed by:
Qiong Wang, Southern Medical University, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Fei, Zheng, Zhao, Ren, Wang, Ye, Liang, Li, Jia and Ma. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lin-chun Liang, bGlhbmdsaW5jaHVuMzNAMTI2LmNvbQ==; Da Li, bGlkYW9uY29uZXdAemp1LmVkdS5jbg==; Xiao-long Jia, Znl5amlheGlhb2xvbmdAbmJ1LmVkdS5jbg==; Qi Ma, Znl5bWFxaUBuYnUuZWR1LmNu
†ORCID: Qi Ma, orcid.org/0000-0002-5350-0362
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.