- 1Heart Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou, China
- 2First Clinical Medical College, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou, China
- 3Second Clinical Medical College, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou, China
- 4College of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou, China
- 5Henan Evidence-Based Medicine Center of Chinese Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou, China
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by persistent inflammatory responses throughout all stages of its progression. Modulating these inflammatory responses is a promising avenue for the development of cardiovascular disease therapies. Splicing events modulate gene expression and diversify protein functionality, exerting pivotal roles in the inflammatory mechanisms underlying atherosclerosis. These insights may provide novel opportunities for developing anti-inflammatory therapies for this disease. This article systematically discusses the diverse splice variants and how splicing events impact the inflammatory response in atherosclerosis via endothelial cells, macrophages, and vascular smooth muscle cells, highlighting their underlying molecular mechanisms and implications. Furthermore, this study summarizes clinical evidence supporting splicing-related molecules as diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets in atherosclerosis. Lastly, we outline the current challenges and future research directions concerning splicing events and inflammatory responses in atherosclerosis. This offers a novel perspective and evidence for formulating new therapeutic strategies aimed at lowering the risk of atherosclerosis.
1 Introduction
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease that serves as both a leading cause and the pathological basis of cardiovascular diseases (1). Approximately 500 million people worldwide currently suffer from cardiovascular diseases, which account for about one-third of total global deaths (2, 3). Despite significant reductions in cardiovascular mortality achieved through existing atherosclerosis treatment strategies (4), the persistently high incidence underscores the necessity for novel preventive and management approaches, marking a critical focus for future research (5). The pathological characteristics of atherosclerosis include vascular endothelial damage, lipid accumulation, and the formation of oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) (6). Endothelial cells (ECs), monocytes/macrophages, vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), dendritic cells, B cells, and T cells all participate in the atherosclerotic process (7, 8). Inflammatory responses act as key drivers of atherosclerosis progression, exacerbating the risk of residual cardiovascular complications. Anti-inflammatory strategies targeting atherosclerosis hold significant potential for future therapeutic development (9, 10).
RNA splicing is an essential mechanism for the formation of both coding mRNA and certain non-coding RNAs (11). Splicing events encompass constitutive splicing, alternative splicing, and trans-splicing, with approximately 95% of human genes linked to alternative splicing (12). The accuracy of RNA splicing is critical for maintaining normal gene function and cellular homeostasis (13). Recent research has indicated that splicing events play a broad role in asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and chronic inflammatory diseases such as atherosclerosis (14, 15). Specifically, in atherosclerosis, alternative splicing regulates the activation, adhesion, and subsequent differentiation of monocytes into macrophages (16). Additionally, abnormal splicing events are closely associated with the inflammatory responses involving endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells, contributing significantly to the progression of atherosclerosis. Inflammatory responses are interwoven throughout the pathological process of atherosclerosis, emerging evidence underscores the pivotal role of splicing-mediated inflammation in driving disease progression (Table 1) (17, 18). Investigating the molecular mechanisms underlying splicing events in atherosclerosis-related inflammatory responses is highly significant. We systematically analyzed the relationship between splicing events and inflammatory responses in atherosclerosis, aiming to highlight their potential as novel diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
2 Pathological mechanisms and inflammatory responses in atherosclerosis
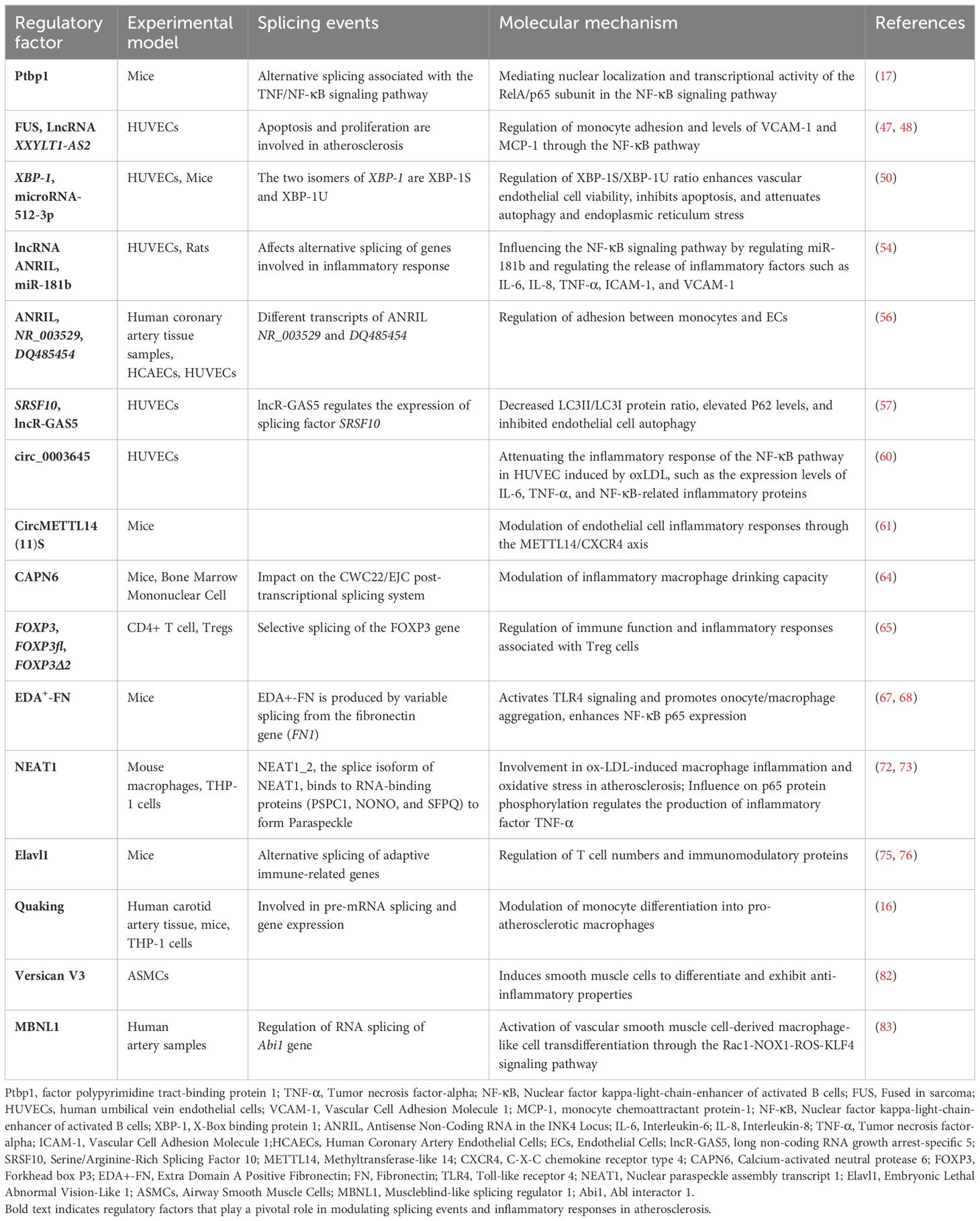
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory cardiovascular disease driven by multiple factors (19). The primary pathological mechanisms include ECs injury, dysregulated lipid metabolism and accumulation, macrophage recruitment, and proliferation and migration of VSMCs (Figure 1) (20). ECs injury and dysfunction are recognized as the initial stages of atherosclerosis (21). Atherosclerosis risk factors, including hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and hyperglycemia, contribute to endothelial damage. Following endothelial dysfunction, LDL infiltrates and accumulates within the vascular intima, where it undergoes oxidation by reactive oxygen species to form pro-inflammatory ox-LDL (22). The interaction between ox-LDL and proteoglycans exacerbates endothelial dysfunction, further promoting monocyte adhesion, accumulation, and differentiation into macrophages (23, 24). Macrophages engulf ox-LDL, resulting in the formation of foam cells. Activated immune inflammatory cells, such as T lymphocytes, neutrophils, and monocytes, persistently infiltrate atherosclerotic plaques. They release pro-inflammatory cytokines, including Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), Interleukin-1β(IL-1β), and Interleukin-6(IL-6) (25). Ultimately, the accumulation of foam cells impairs macrophage efferocytosis and triggers cell death (via apoptosis or necrosis), leading to the formation of a necrotic lipid core (26).
Figure 1. Mechanisms of atherosclerosis and the inflammatory response. The intricate interplay between diverse cellular populations and cytokines within the vascular microenvironment orchestrates the progression of atherosclerosis. The primary pathological mechanisms include Endothelial Cells (ECs) injury, dysregulated lipid metabolism and accumulation, macrophage recruitment, and proliferation and migration of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells (VSMCs). Upon endothelial cell injury, the inflammatory response is activated, allowing low-density lipoprotein (LDL) to infiltrate the vascular intima where it accumulates and undergoes oxidation by reactive oxygen species (ROS), forming pro-inflammatory oxidized low-density lipoproteins (ox-LDL). Concurrently, immune-inflammatory cells, including T-lymphocytes, neutrophils, and monocytes, are continuously recruited and infiltrate emerging atheromatous plaques. Macrophages engulf ox-LDL, transforming into foam cells that contribute to the formation of a necrotic lipid core.
During the progression of atherosclerosis, endothelial cell injury and dysfunction, leukocyte recruitment, and foam cell formation activate inflammatory signaling pathways and release inflammatory factors, thereby promoting the formation and development of atherosclerotic plaques and increasing plaque instability (27). Endothelial dysfunction and inflammatory responses are tightly interconnected in atherosclerosis, where injured endothelial cells promote tissue repair by expressing inflammatory factors such as monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), Interleukin-8(IL-8), selectins, chemokines, and adhesion molecules such as Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule 1 (VCAM-1) and Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 (ICAM-1). Meanwhile, macrophages, VSMCs, and lymphocytes participate in the inflammatory response associated with atherosclerosis (28, 29). Foam cells predominantly originate from the differentiation of M2 macrophages (8), and VSMCs can transdifferentiate into macrophage-like cells (30), exacerbating endothelial injury. In addition, lymphocytes, encompassing both B cells and T cells, play intricate roles in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis (31). Subsets of B cells exhibit dual functions, being both protective and pathogenic during the progression of atherosclerotic disease (27). Meanwhile, autoreactive effector T cells are capable of recognizing self-antigens such as oxLDL (30), thereby triggering inflammatory responses. Overall, chronic inflammation and immune dysregulation significantly influence the progression of atherosclerosis. Elucidating the underlying pathological mechanisms will deepen our understanding of this disease and foster the development of novel therapeutic strategies.
3 Concise of the splicing events
Splicing events are critical post-transcriptional processes essential for the formation of mature mRNA, encompassing constitutive splicing, alternative splicing, and trans-splicing (11). The process of removing introns from pre-mRNA and retaining exons, thereby connecting them to form mature mRNA, is known as constitutive splicing and is regulated by spliceosomes (32). Constitutive splicing is essential for sustaining fundamental cellular functions. Alternative splicing regulates the selective removal of introns from mRNA precursors while retaining specific exons (33), serving as a crucial factor in gene expression and protein functional diversity in multicellular eukaryotes (34, 35). Additionally, alternative splicing can interact with non-coding RNAs, including long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), circular RNAs (circRNAs), and microRNAs (miRNAs). While non-coding RNAs do not directly encode proteins, they influence gene transcription by regulating splicing events (36, 37). Recent research has shown that various splicing events and non-coding RNAs can mediate inflammatory responses in atherosclerosis by regulating RNA splicing (38–40). Considering the significant role of splicing events in the inflammatory response in atherosclerosis, we further investigated the interplay between splicing events, non-coding RNAs, and inflammation in this condition.
4 splicing events in atherosclerosis-related inflammatory responses
4.1 Regulation of inflammatory responses by splicing events in ECs
ECs, as critical regulators of immune cell aggregation and local inflammation, represent promising therapeutic targets for managing inflammatory responses (41). Risk factors for atherosclerosis, including hypertension and hyperglycemia, stimulate endothelial cells (42), activating the IκB kinase (IKK) complex, resulting in the phosphorylation and degradation of IκB, thereby releasing Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) into the nucleus,subsequently triggering the expression of pro-inflammatory molecules such as ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and MCP-1, which exacerbates endothelial cell injury (43, 44). Emerging evidence indicates that splicing events play a role in the inflammatory response associated with endothelial dysfunction by regulating the NF-κB signaling pathway (45). Under conditions of low and disturbed blood flow, the splicing factor polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1(Ptbp1) is crucial for ECs activation and influences several alternative splicing events related to the TNF/NF-κB signaling pathway (46), mediating the nuclear localization and transcriptional activity of the RelA/p65 subunit in the NF-κB pathway, thus affecting the expression of inflammatory factors (17). Fused in sarcoma (FUS), an RNA-binding protein, is implicated in alternative splicing related to apoptosis and proliferation in atherosclerosis (47). Additionally, LncRNA XXYLT1-AS2 can upregulate FUS expression, inhibiting the proliferation and adhesion of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), and regulating monocyte adhesion as well as the levels of VCAM-1 and MCP-1 via the NF-κB pathway (48). Furthermore, X-Box binding protein 1 (XBP1), as a transcription factor, plays a crucial role in atherosclerosis by regulating the inflammatory response (49). Recent studies have indicated that downregulation of microRNA-512-3p modulates the ratio of XBP-1S/XBP-1U by targeting XBP-1, enhancing vascular EC viability, inhibiting apoptosis, and alleviating autophagy and endoplasmic reticulum stress (50), thereby mitigating inflammation and slowing the progression of atherosclerosis.
Various non-coding RNAs also play a key role in the inflammatory response associated with atherosclerosis. The Antisense Non-Coding RNA in the INK4 Locus (ANRIL) is a multifunctional lncRNA that is closely associated with the inflammatory response (51–53). Further studies suggest that ANRIL modulates the NF-κB signaling pathway via miR-181b, subsequently affecting the release of inflammatory factors such as IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α, ICAM-1, and VCAM-1 (54). Inhibition of circANRIL expression can mitigate vascular endothelial injury and inflammatory responses in atherosclerotic rats models (55). Interestingly, alternative splicing generates distinct ANRIL transcripts, NR_003529 and DQ485454, which exhibit opposing effects in coronary artery disease (CAD). Upregulation of NR_003529 enhances the adhesion between monocytes and ECs, while downregulation of DQ485454 has a comparable effect (56). Enhanced expression of long non-coding RNA growth arrest-specific 5 (lncR-GAS5) can reduce the LC3II/LC3I protein ratio and increase P62 levels, thereby inhibiting autophagic processes. This function of lncR-GAS5 is associated with the splicing factor Serine/Arginine-Rich Splicing Factor 10 (SRSF10) (57). Moreover, circRNAs participate in inflammatory responses related to endothelial cells (58, 59), circ_0003645 is another circRNA associated with atherosclerosis. Inhibition of circ_0003645 expression can reduce the inflammatory response in the NF-κB pathway induced by oxLDL in HUVECs, including the expression levels of IL-6, TNF-α, and NF-κB-related inflammatory proteins (60). Concurrently, CircMETTL14 (11) S exacerbates inflammation in ECs and promote the progression of atherosclerosis through the Methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14)/C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) axis (61). In summary, endothelial cell injury plays a critical regulatory role in the inflammation associated with atherosclerosis. Splicing events and various non-coding RNAs participate in the progression of atherosclerotic disease by influencing endothelial cell function and inflammation (Figure 2). However, there seems to be a lack of extensive clinical studies to validate these observations. Conversely, the relationships between splicing events associated with the inflammatory response in atherosclerosis continue to pose challenges for our future research.
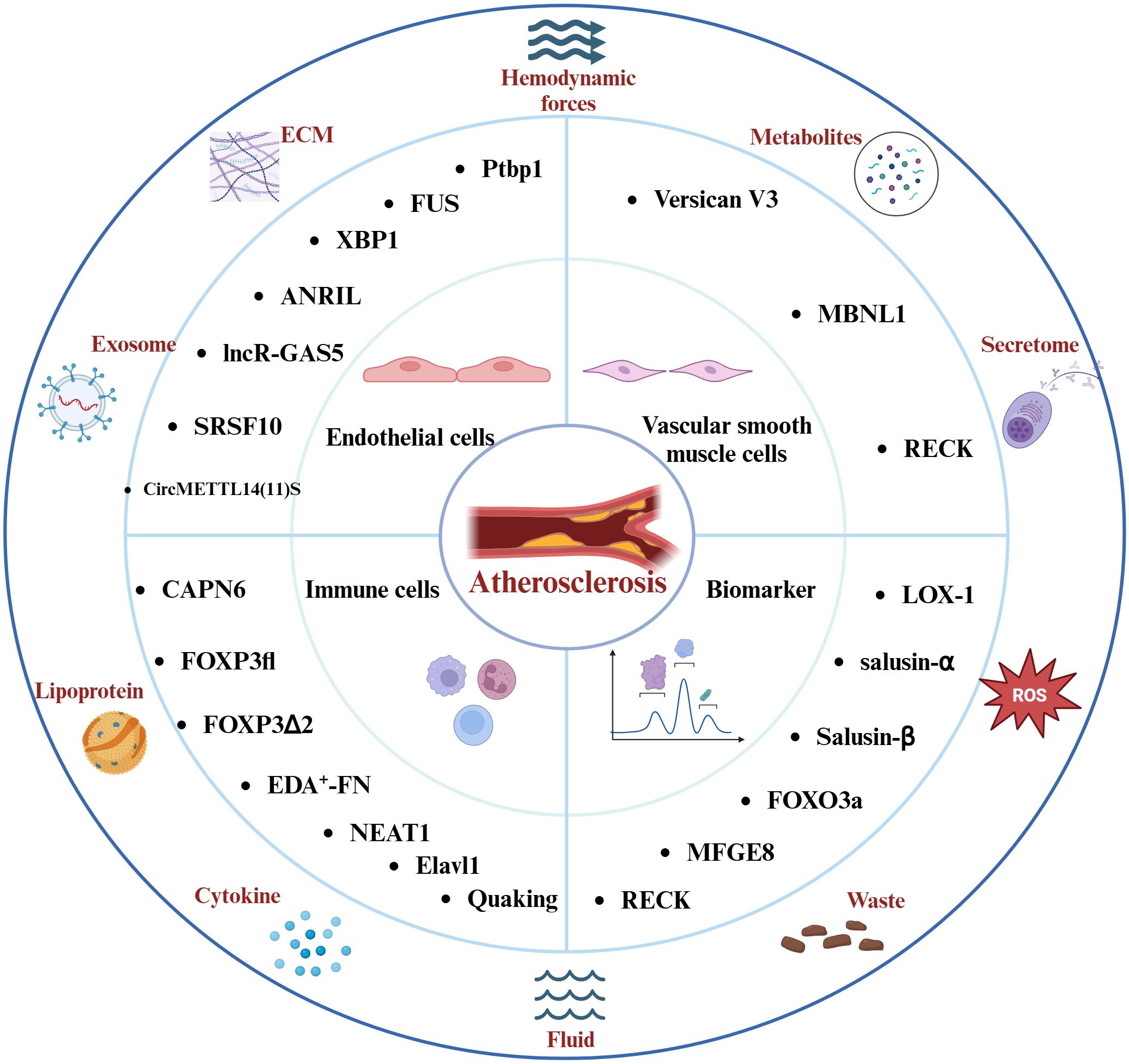
Figure 2. Factors Affecting the Atherosclerotic Inflammatory Response and the Molecules of Splicing Events Associated with the Atherosclerotic Inflammatory Response. Hemodynamics, lipoproteins, reactive oxygen species, and other elements play pivotal roles in the progression of this disease. The intricate interplay among endothelial cells, immune cells, vascular smooth muscle cells, and the inflammatory response constitutes the core pathological mechanism underlying atherosclerosis. Molecules involved in distinct splicing events modulate the inflammatory response in atherosclerosis and hold promise as potential diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets for the disease.
4.2 Regulation of inflammatory responses by splicing events in immune cells
Macrophages contribute to plaque formation in atherosclerosis by inducing chronic inflammation (62). Recent research has shown that specific splicing events influence the functions of macrophages and T cells, thereby modulating inflammatory response. Calcium-activated neutral protease 6 (CAPN6) is an atypical calpain enzyme (63). In atherosclerotic disease, CAPN6 is specifically expressed in inflammatory macrophages. Notably, recent research has indicated that CAPN6 protein is induced in inflammatory conditions, resulting in dysregulation of the CWC22/EJC post-transcriptional splicing system, which further affects the phagocytic ability of inflammatory macrophages (64). Consequently, targeting CAPN6 or the associated CWC22/EJC system could represent an effective therapeutic strategy for atherosclerosis. Selective splicing of the Forkhead box P3 (FOXP3) gene mediates the effector functions of regulatory T cells and influences the stability of atherosclerotic plaques. FOXP3fl and FOXP3Δ2 are distinct splice variants of FOXP3; FOXP3Δ2 can influence Treg cell function, with low levels of FOXP3Δ2 associated with plaque instability. This may be connected to the role of FOXP3Δ2 in Treg cell immune functions and inflammatory responses by regulating Glycoprotein A Repetitions Predominant (GARP) expression and its interaction with Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-β) (65). In conclusion, selective splicing of FOXP3 regulates the effector functions of regulatory T cells and is linked to the stability of atherosclerotic plaques. Fibronectin (FN) is a crucial extracellular matrix protein (18). Extra Domain A Positive Fibronectin (EDA+-FN) is a variant of FN generated by alternative splicing of FN1 (66). EDA+-FN promotes the recruitment of monocytes/macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques through Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling activation (67). Notably, EDA+-FN can further aggravate the inflammatory response in atherosclerosis by engaging integrin α5β1 and increasing NF-κB p65 expression (68).
Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1) is a lncRNA involved in multiple pathological mechanisms in atherosclerosis, such as apoptosis, foam cell formation, and inflammation (69–71). NEAT1 interacts with miR-128 and is involved in ox-LDL-induced inflammation and oxidative stress response in macrophages during atherosclerosis (72). Notably, recent research has revealed that the splice isoform NEAT1_2 binds to RNA-binding proteins (PSPC1, NONO, and SFPQ) to form paraspeckles, which subsequently affect the phosphorylation of the p65 protein and regulate the production of the inflammatory factor TNF-α (73). The endothelial RNA-binding protein Elavl1 (HuR) modulates genes related to migration, inflammation, and adhesion, facilitating the recruitment and proliferation of T cells (74, 75). Additionally, HuR modulates pre-mRNA splicing and translation in endothelial cells (ECs), enhancing the expression of immune regulatory proteins, such as C1q and CD27, while reducing the population of CD8+ T cells (76). Moreover, the lncRNA SUGCT-AS1 expression is significantly elevated in M1 macrophages, and it regulates the nuclear-cytoplasmic translocation of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein U (hnRNPU) by binding, thereby influencing the alternative splicing of Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma Translocation Gene 1 (MALT1). This process significantly impacts the NF-κB signaling pathway, as well as the expression and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines (77). Importantly, the RNA-binding protein Quaking plays a vital role in pre-mRNA splicing and gene expression, and it is regarded as a crucial transcriptional regulator in the differentiation of monocytes into pro-atherosclerotic macrophages (16). Extensive research has demonstrated that splicing events, along with related long non-coding RNAs and RBPs, play crucial roles in atherosclerosis (Figure 2). Future studies should focus on the regulation of genes responsible for the differentiation of monocytes into anti-inflammatory macrophages, offering a promising therapeutic approach to mitigating inflammation-driven atherosclerosis progression.
4.3 Regulation of inflammatory responses by splicing events in vsmcs
The phenotypic plasticity of VSMCs enables them to undergo transitions in response to pathological stimuli, such as pro-inflammatory factors and mechanical stretching (78), which is essential for the stability of atherosclerotic plaques (79). Versican, a multifunctional proteoglycan, is a significant high-molecular-weight glycoprotein that belongs to the glycosaminoglycan family (80). Among its splice variants, V3 is particularly notable for its ability to regulate adhesion plaque signaling pathways, modulating cell-extracellular matrix interactions (81). By influencing the expression of genes related to the complement system, chemokines, chemokine receptors, and transcription factors involved in inflammation, V3 promotes the differentiation of VSMCs and exerts anti-inflammatory effects (82). It is widely recognized that VSMCs can convert into macrophage-like cells during the process of atherosclerosis. Earlier research has shown that the dysregulation of Muscleblind-like splicing regulator 1 (MBNL1) can induce splicing events in the Abi1 gene, leading to the production of a specific variant, Abi1-Δe10. This variant activates the transdifferentiation of VSMCs into macrophage-like cells by enhancing the Rac1-NOX1-ROS-KLF4 signaling pathway (83), potentially representing one of the mechanisms affecting inflammation in atherosclerosis.
Reversion-Inducing-Cysteine-Rich Protein with Kazal Motifs (RECK) is a membrane-anchored glycoprotein that modulates matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and is closely linked to inflammatory responses in cardiovascular diseases (84). Recent research indicates that OxLDL can enhance the proliferation and migration of VSMCs by inhibiting RECK expression via the NF-κB pathway (85). Conversely, overexpression of RECK suppresses IL-17A and MMP-13 expression, thereby diminishing SMC migration (86). Additionally, another study revealed that overexpression of RECK reduced the proliferation and migration of VSMCs induced by hypoxia and mediated by miR-195-5p, while inhibiting the protein expression of MMP-3, -9, and -13, as well as inflammatory responses (87). Notably, specific splice variants of RECK could act as potential biomarkers for coronary atherosclerotic disease (88). Furthermore, in a mouse model of atherosclerosis, circular RNA circEsyt2 interacts with PCBP1 to regulate its intracellular localization. Silencing circEsyt2 significantly enhances the interaction between the RNA splicing factor PCBP1 and U2AF65, leading to increased β-splicing of p53, which alters the expression of p53 target genes and inhibits VSMC proliferation (89). These findings underscore the intricate relationship between inflammatory responses and the regulation of VSMC proliferation, migration, and differentiation, which collectively influence plaque stability. Regulating splicing events to modulate the interactions between VSMCs and inflammatory responses seems to be a crucial strategy for maintaining plaque stability in AS moving forward (Figure 2).
5 The potential of splicing event-related molecules as biomarkers for the diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerosis
The risk for patients with atherosclerosis remains high, even with standardized treatment strategies, due to the crucial role of splicing events in the inflammatory response mechanisms of atherosclerosis, investigating splicing-related molecules as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis and therapeutic targets for atherosclerosis holds great promise (90). Lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (LOX-1) is closely related to atherosclerosis and is present in immune cells such as ECs, macrophages, and lymphocytes (91, 92). LOX-1 can activate inflammatory signaling pathways and molecules related to inflammation, including NF-κB and NLRP3 (93). Furthermore, it can upregulate cell adhesion molecules and MCP-1 via activation of the MAPK pathway, thereby facilitating the adhesion and infiltration of monocytes. Studies have shown that overexpression of the LOX-1 splicing variant Lectin-like Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-1 Inhibitor (LOXIN) reduces ox-LDL-induced apoptosis, providing a protective effect (94, 95). In a 20-year prospective study, circulating LOX-1 was linked to the inflammatory marker High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (Hs-CRP), which elevated the risk of myocardial infarction, and this association remained significant even after adjusting for related risk factors (96). Numerous studies have identified LOX-1 as having distinct diagnostic and prognostic value in atherosclerosis (97–99).
Salusin-α and Salusin-β are bioactive peptides derived from the C-terminal alternative splicing of the torsin family member 2A (TOR2A) protein, exhibiting opposing roles in atherosclerosis (100). Previous research has demonstrated that salusin-β mediates the NF-κB signaling pathway and is involved in the inflammatory response of endothelial cells (101), enhancing the expression of inflammatory factors including VCAM-1, MCP-1, IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β, and NADPH oxidase 2 (102). Notably, a clinical trial revealed a significant difference in salusin-β levels between CAD patients and the control group, highlighting its potential as a biomarker for atherosclerosis (103). Recent research has further shown that Salusin-β outperforms salusin-α as a biomarker for atherosclerosis (104). Serum Salusin-β levels are significantly associated with the incidence and severity of CAD (105), suggesting that Salusin-β in serum may serve as a potential biomarker for diagnosing and reflecting the progression of CAD. It is noteworthy that coronary artery ectasia (CAE) is a condition closely associated with atherosclerosis, and Salusin-β predicts CAE with a sensitivity of 78.9% and specificity of 75.0% (106). ANRIL and circANRIL are known to be closely linked to endothelial injury and inflammatory responses associated with atherosclerosis (55). Recent studies indicate that a clinical diagnostic model incorporating ANRIL and conventional risk factors has a sensitivity of 84% and specificity of 96%, which can be utilized for the early diagnosis and treatment of CAD (107). FOXO3a is involved in regulating the inflammatory response and apoptosis in endothelial cells by modulating alternative splicing and gene expression (108). Interestingly, studies have identified an association between the risk of CAD and the rs12196996 polymorphism located in the flanking intron of circFOXO3 (109).
Milk Fat Globule-EGF Factor 8 (MFGE8) is a protein that encodes epidermal growth factor 8, mediating the inflammatory response in atherosclerosis linked to risk factors such as hypertension and hyperglycemia (110). It plays a critical role in the calcification and senescence of VSMCs induced by high-glucose human umbilical vein endothelial cell exosomes, closely associated with inflammatory responses mediated by IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 (111). Another study shows that MFGE8 participates in the Angiotensin II-mediated inflammatory response associated with the NF-κB signaling pathway, and its knockout reduces levels of MCP-1, TNF-α, ICAM-1, and VCAM-1 produced as a result of NF-κB activation (112). Notably, recent research has identified that the intronic insertion rs534125149 and splice site variants (splicing receptor variant rs201988637) in MFGE8 are linked to the prevention of coronary artery atherosclerosis (40). Moreover, MFG-E8 levels correlate with the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) risk score (113). The aforementioned RECK plays a role in the inflammatory response in atherosclerosis, and its various splice variants can act as biomarkers for CAD. Long RECK and short RECK exhibit differential expression in patients with stable and unstable angina pectoris, with short RECK being expressed at lower levels in acute myocardial infarction, potentially linked to RECK’s function as an MMP inhibitor and its anti-inflammatory effects (88). Recent research has additionally shown that empagliflozin can inhibit the proliferation and migration of VSMCs by increasing RECK expression (85). Serine-arginine protein kinase (SRPK) modulates the function of Serine/Arginine-rich (SR) proteins through phosphorylation, thereby altering the balance of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) splice variants (114).Research indicates that the SRPK1 inhibitor DBS1 effectively disrupts the binding of SRPK to its substrates (115), resulting in a shift in VEGF splicing from pro-angiogenic to anti-angiogenic forms, highlighting its significant potential in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. These findings suggest the potential of splice event-related molecules as targets for the diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerosis (Figure 2). However, further research on splice events associated with AS inflammatory responses is still lacking. Continued investigation into RNA splicing mechanisms and the development of new intervention strategies will facilitate advancements in AS diagnosis and treatment.
6 Perspectives and challenges
The inflammatory response is a key driver of atherosclerosis and will likely become one of the primary approaches for treating cardiovascular diseases in the future. Our study elucidates the molecular mechanisms linking abnormal splice events to the inflammatory response in atherosclerosis, offering a novel perspective on the role of splice events in this condition. Specifically, various splice events mediate endothelial cell injury, macrophage differentiation, and the proliferation and migration of VSMCs in atherosclerosis through the inflammatory response. Their interrelated interactions contribute to the progression of atherosclerosis, further underscoring the significance of splice events in the inflammatory response associated with atherosclerosis. Nonetheless, several unresolved questions persist. While molecules associated with splice events are implicated in the inflammatory response in atherosclerosis, their specific mechanisms of action and the ways in which they influence the functions of other cells remain unclear. Further research is needed to understand how modulating splice events affects other cell types, presenting a significant challenge for future studies. Additionally, we observed a correlation between splice molecules and the risk of atherosclerosis, which supports their potential as diagnostic biomarkers for atherosclerosis. However, future validation through large-scale studies will be necessary. Despite the significant therapeutic potential of targeting splice events in the future, several challenges exist in their clinical application. The effective delivery of splice-targeted therapies remains a primary obstacle, highlighting the need for new carrier systems to improve the delivery and efficiency of these treatments. Splicing factors generally engage in the splicing of multiple genes, meaning that targeting these factors could simultaneously influence various splice events and other biological processes, which raises important considerations regarding treatment specificity. Additionally, prolonged interventions could induce immune responses and impact cellular functions, necessitating further research into the safety of long-term applications. In summary, future research needs to tackle these challenges to ensure the efficacy, specificity, and safety of splice-targeted interventions in atherosclerosis.
7 Conclusion
Overall, our research elucidates the molecular mechanisms through which abnormal splicing events mediate inflammation and immune responses in atherosclerosis from multiple perspectives. Furthermore, it investigates the potential of splice factors as diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets for atherosclerosis. offering a fresh outlook that could provide valuable insights for future treatments. While existing clinical and basic research has validated the crucial role of splicing events in the inflammatory response associated with atherosclerosis, the specific mechanisms of action still necessitate additional foundational and clinical studies for confirmation. Conversely, we need to further explore the relationship between splice event-mediated inflammatory responses and other pathological mechanisms in atherosclerosis to provide new therapeutic strategies that can enhance treatment outcomes.
Author contributions
AW: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CW: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BX: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YS: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. BL: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. QZ: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. RY: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. XW: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. MZ: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. JW: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.82030120, No.82074226), Henan Provincial Key Research and Development Project (Grant No.231111310200), Henan Province medical science and technology research Project (Grant No. LHGJ20220572).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
oxLDL, oxidized low-density lipoprotein; ECs, Endothelial cells; VSMCs, vascular smooth muscle cells; TNF-α, Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; IL-6, Interleukin-6; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; IL-8, Interleukin-8; VCAM-1, Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule 1; ICAM-1, Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule 1; lncRNAs, long non-coding RNAs; circRNAs, circular RNAs; miRNAs, microRNAs; IKK, IκB kinase; NF-κB, Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; Ptbp1, polypyrimidine tract-binding protein; FUS, Fused in sarcoma; XBP1, X-Box binding protein 1; ANRIL, Antisense Non-Coding RNA in the INK4 Locus; HUVECs, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; CAD, coronary artery disease; lncR-GAS5, long non-coding RNA growth arrest-specific 5; SRSF10, Serine/Arginine-Rich Splicing Factor 10; METTL14, Methyltransferase-like 14; CXCR4, C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; CAPN6, Calcium-activated neutral protease 6; FOXP3, Forkhead box P3; GARP, Glycoprotein A Repetitions Predominant; TGF-β, Transforming Growth Factor-beta; FN, Fibronectin; EDA+-FN, Extra Domain A Positive Fibronectin; TLR4, Toll-like receptor 4; NEAT1, Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1; Elavl1, Embryonic Lethal Abnormal Vision-Like 1; MBNL1, Muscleblind-like splicing regulator 1; RECK, Reversion-Inducing-Cysteine-Rich Protein with Kazal Motifs; MMPs, metalloproteinases; LOX-1, Lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1; LOXIN, Lectin-like Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-1 Inhibitor; Hs-CRP; High-sensitivity C-reactive protein; AS, atherosclerosis; CAE, coronary artery ectasia; MFGE8, Milk Fat Globule-EGF Factor 8; TIMI, The Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction; SR, Serine/Arginine-rich; SRPK, Serine-arginine protein kinase; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
References
1. Gan J, Guo L, Zhang X, Yu Q, Yang Q, Zhang Y, et al. Anti-inflammatory therapy of atherosclerosis: focusing on IKKβ. J Inflammation (Lond). (2023) 20:8. doi: 10.1186/s12950-023-00330-5
2. Roth GA, Mensah GA, Johnson CO, Addolorato G, Ammirati E, Baddour LM, et al. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors, 1990-2019: update from the GBD 2019 study. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2020) 76:2982–3021. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010
3. Amini M, Zayeri F, Salehi M. Trend analysis of cardiovascular disease mortality, incidence, and mortality-to-incidence ratio: results from global burden of disease study 2017. BMC Public Health. (2021) 21:401. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-10429-0
4. Chou R, Cantor A, Dana T, Wagner J, Ahmed AY, Fu R, et al. Statin use for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in adults: updated evidence report and systematic review for the US preventive services task force. JAMA. (2022) 328:754–71. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.12138
5. Xing Y, Lin X. Challenges and advances in the management of inflammation in atherosclerosis. J Adv Res. (2024), S2090–1232(24)00253-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.06.016
6. Jiang H, Zhou Y, Nabavi SM, Sahebkar A, Little PJ, Xu S, et al. Mechanisms of oxidized LDL-mediated endothelial dysfunction and its consequences for the development of atherosclerosis. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:925923. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.925923
7. Gui Y, Zheng H, Cao RY. Foam cells in atherosclerosis: novel insights into its origins, consequences, and molecular mechanisms. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:845942. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.845942
8. Mehu M, Narasimhulu CA, Singla DK. Inflammatory cells in atherosclerosis. Antioxidants (Basel). (2022) 11:233. doi: 10.3390/antiox11020233
9. Weber C, Habenicht AJR, von Hundelshausen P. Novel mechanisms and therapeutic targets in atherosclerosis: inflammation and beyond. Eur Heart J. (2023) 44:2672–81. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad304
10. Abbate A, Toldo S, Marchetti C, Kron J, Van Tassell BW, Dinarello CA. Interleukin-1 and the inflammasome as therapeutic targets in cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. (2020) 126:1260–80. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.315937
11. van den Hoogenhof MM, Pinto YM, Creemers EE. RNA splicing: regulation and dysregulation in the heart. Circ Res. (2016) 118:454–68. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.307872
12. Jiang J, Wu H, Ji Y, Han K, Tang JM, Hu S, et al. Development and disease-specific regulation of RNA splicing in cardiovascular system. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2024) 12:1423553. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1423553
13. Cao J, Wei Z, Nie Y, Chen HZ. Therapeutic potential of alternative splicing in cardiovascular diseases. EBioMedicine. (2024) 101:104995. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.104995
14. Tian X, Zhou G, Li H, Zhang X, Zhao L, Zhang K, et al. RBM25 binds to and regulates alternative splicing levels of Slc38a9, Csf1, and Coro6 to affect immune and inflammatory processes in H9c2 cells. PeerJ. (2023) 11:e16312. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16312
15. Vierbuchen T, Agarwal S, Johnson JL, Galia L, Lei X, Stein K, et al. The lncRNA LUCAT1 is elevated in inflammatory disease and restrains inflammation by regulating the splicing and stability of NR4A2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2023) 120:e2213715120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2213715120
16. de Bruin RG, Shiue L, Prins J, de Boer HC, Singh A, Fagg WS, et al. Quaking promotes monocyte differentiation into pro-atherogenic macrophages by controlling pre-mRNA splicing and gene expression. Nat Commun. (2016) 7:10846. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10846
17. Hensel JA, Nicholas SE, Kimble AL, Nagpal AS, Omar OMF, Tyburski JD, et al. Splice factor polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1 (Ptbp1) primes endothelial inflammation in atherogenic disturbed flow conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2022) 119:e2122227119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2122227119
18. Murphy PA, Jailkhani N, Nicholas SA, Del Rosario AM, Balsbaugh JL, Begum S, et al. Alternative splicing of FN (Fibronectin) regulates the composition of the arterial wall under low flow. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2021) 41:e18–32. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314013
19. Doran AC. Inflammation resolution: implications for atherosclerosis. Circ Res. (2022) 130:130–48. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.319822
20. Wang T, Butany J. Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Diagn histopathology. (2017) 23:473–8. doi: 10.1016/j.mpdhp.2017.11.009
21. Jebari-Benslaiman S, Galicia-García U, Larrea-Sebal A, Olaetxea JR, Alloza I, Vandenbroeck K, et al. Pathophysiology of atherosclerosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:3346. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063346
22. Jing L, Shu-Xu D, Yong-Xin R. A review: Pathological and molecular biological study on atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. (2022) 531:217–22. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2022.04.012
23. Malekmohammad K, Bezsonov EE, Rafieian-Kopaei M. Role of lipid accumulation and inflammation in atherosclerosis: focus on molecular and cellular mechanisms. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2021) 8:707529. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.707529
24. Björkegren JLM, Lusis AJ. Atherosclerosis: recent developments. Cell. (2022) 185:1630–45. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.04.004
25. Arnold N, Lechner K, Waldeyer C, Shapiro MD, Koenig W. Inflammation and cardiovascular disease: the future. Eur Cardiol. (2021) 16:e20. doi: 10.15420/ecr.2020.50
26. Kojima Y, Weissman IL, Leeper NJ. The role of efferocytosis in atherosclerosis. Circulation. (2017) 135:476–89. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.025684
27. Kong P, Cui ZY, Huang XF, Zhang DD, Guo RJ, Han M. Inflammation and atherosclerosis: signaling pathways and therapeutic intervention. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2022) 7:131. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-00955-7
28. Shao C, Wang J, Tian J, Tang YD. Coronary artery disease: from mechanism to clinical practice. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2020) 1177:1–36. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-2517-9_1
29. Zhu Y, Xian X, Wang Z, Bi Y, Chen Q, Han X, et al. Research progress on the relationship between atherosclerosis and inflammation. Biomolecules. (2018) 8:80. doi: 10.3390/biom8030080
30. Hou P, Fang J, Liu Z, Shi Y, Agostini M, Bernassola F, et al. Macrophage polarization and metabolism in atherosclerosis. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:691. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06206-z
31. Engelen SE, Robinson AJB, Zurke YX, Monaco C. Therapeutic strategies targeting inflammation and immunity in atherosclerosis: how to proceed? Nat Rev Cardiol. (2022) 19:522–42. doi: 10.1038/s41569-021-00668-4
32. Ding F, Elowitz MB. Constitutive splicing and economies of scale in gene expression. Nat Struct Mol Biol. (2019) 26:424–32. doi: 10.1038/s41594-019-0226-x
33. Liu Y, Liu X, Lin C, Jia X, Zhu H, Song J, et al. Noncoding RNAs regulate alternative splicing in Cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 40:11. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01798-2
34. Rogalska ME, Vivori C, Valcárcel J. Regulation of pre-mRNA splicing: roles in physiology and disease, and therapeutic prospects. Nat Rev Genet. (2023) 24:251–69. doi: 10.1038/s41576-022-00556-8
35. Marasco LE, Kornblihtt AR. The physiology of alternative splicing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2023) 24:242–54. doi: 10.1038/s41580-022-00545-z
36. Gareev I, Kudriashov V, Sufianov A, Begliarzade S, Ilyasova T, Liang Y, et al. The role of long non-coding RNA ANRIL in the development of atherosclerosis. Noncoding RNA Res. (2022) 7:212–16. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2022.09.002
37. Holdt LM, Kohlmaier A, Teupser D. Long noncoding RNAs of the arterial wall as therapeutic agents and targets in atherosclerosis. Thromb Haemost. (2019) 119:1222–36. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1692680
38. Aryal B, Suárez Y. Non-coding RNA regulation of endothelial and macrophage functions during atherosclerosis. Vascul Pharmacol. (2019) 114:64–75. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2018.03.001
39. Hussain MS, Afzal O, Gupta G, Altamimi ASA, Almalki WH, Alzarea SI, et al. Probing the links: Long non-coding RNAs and NF-κB signalling in atherosclerosis. Pathol Res Pract. (2023) 249:154773. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154773
40. Ruotsalainen SE, Surakka I, Mars N, Karjalainen J, Kurki M, Kanai M, et al. Inframe insertion and splice site variants in MFGE8 associate with protection against coronary atherosclerosis. Commun Biol. (2022) 5:802. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03552-0
41. Murphy PA, Butty VL, Boutz PL, Begum S, Kimble AL, Sharp PA, et al. Alternative RNA splicing in the endothelium mediated in part by Rbfox2 regulates the arterial response to low flow. Elife. (2018) 7:e29494. doi: 10.7554/eLife.29494
42. Chang TT, Yang HY, Chen C, Chen JW. CCL4 inhibition in atherosclerosis: effects on plaque stability, endothelial cell adhesiveness, and macrophages activation. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:6567. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186567
43. Karunakaran D, Nguyen MA, Geoffrion M, Vreeken D, Lister Z, Cheng HS, et al. RIPK1 expression associates with inflammation in early atherosclerosis in humans and can be therapeutically silenced to reduce NF-κB activation and atherogenesis in mice. Circulation. (2021) 143:163–77. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.038379
44. Yu H, Lin L, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Hu H. Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2020) 5:209. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00312-6
45. Huang HS, Huang XY, Yu HZ, Xue Y, Zhu PL. Circular RNA circ-RELL1 regulates inflammatory response by miR-6873-3p/MyD88/NF-κB axis in endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2020) 525:512–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.02.109
46. Wufuer A, Luohemanjiang X, Du L, Lei J, Shabier M, Han DF, et al. ANRIL overexpression globally induces expression and alternative splicing of genes involved in inflammation in HUVECs. Mol Med Rep. (2023) 27:27. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12915
47. Hou J, Yang S, Guo Y, Yan N, Jia S. FUS regulates the alternative splicing of cell proliferation genes related to atherosclerosis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). (2023) 248:1459–68. doi: 10.1177/15353702231187642
48. Wang Q, Yang Y, Fu X, Wang Z, Liu Y, Li M, et al. Long noncoding RNA XXYLT1-AS2 regulates proliferation and adhesion by targeting the RNA binding protein FUS in HUVEC. Atherosclerosis. (2020) 298:58–69. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2020.02.018
49. Wang T, Zhou J, Zhang X, Wu Y, Jin K, Wang Y, et al. X-box binding protein 1: an adaptor in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Aging Dis. (2023) 14:350–69. doi: 10.14336/AD.2022.0824
50. Ge P, Gao M, Du J, Yu J, Zhang L. Downregulation of microRNA-512-3p enhances the viability and suppresses the apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells, alleviates autophagy and endoplasmic reticulum stress as well as represses atherosclerotic lesions in atherosclerosis by adjusting spliced/unspliced ratio of X-box binding protein 1 (XBP-1S/XBP-1U). Bioengineered. (2021) 12:12469–81. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2006862
51. Razeghian-Jahromi I, Karimi Akhormeh A, Zibaeenezhad MJ. The role of ANRIL in atherosclerosis. Dis Markers. (2022) 2022:8859677. doi: 10.1155/2022/8859677
52. Deng L, Guo Y, Liu J, Chen S, Wang X, Zhao H, et al. Long noncoding RNA ANRIL knockdown attenuates neuroinflammation following ischemic stroke via suppressing the expression of NF-κB in vitro and in vivo. Neurol Res. (2021) 43:767–77. doi: 10.1080/01616412.2021.1934317
53. Ebadi N, Ghafouri-Fard S, Taheri M, Arsang-Jang S, Omrani MD. Expression analysis of inflammatory response-associated genes in coronary artery disease. Arch Physiol Biochem. (2022) 128:601–7. doi: 10.1080/13813455.2019.1708953
54. Guo F, Tang C, Li Y, Liu Y, Lv P, Wang W, et al. The interplay of LncRNA ANRIL and miR-181b on the inflammation-relevant coronary artery disease through mediating NF-κB signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. (2018) 22:5062–75. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13790
55. Shi P, Ji H, Zhang H, Yang J, Guo R, Wang J. circANRIL reduces vascular endothelial injury, oxidative stress and inflammation in rats with coronary atherosclerosis. Exp Ther Med. (2020) 20:2245–51. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8956
56. Cho H, Li Y, Archacki S, Wang F, Yu G, Chakrabarti S, et al. Splice variants of lncRNA RNA ANRIL exert opposing effects on endothelial cell activities associated with coronary artery disease. RNA Biol. (2020) 17:1391–401. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1771519
57. Fan Y, Zhang Y, Zhao H, Liu W, Xu W, Jiang L, et al. lncR-GAS5 upregulates the splicing factor SRSF10 to impair endothelial autophagy, leading to atherogenesis. Front Med. (2023) 17:317–29. doi: 10.1007/s11684-022-0931-4
58. Wang T, Li C, Shi M, Zhou S, Chen J, Wang F. Circular RNA circZNF532 facilitates angiogenesis and inflammation in diabetic retinopathy via regulating miR-1243/CARM1 axis. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2022) 14:14. doi: 10.1186/s13098-022-00787-z
59. Tao G, Zhong C, Zhang L, Zhong X, Li X, Wang Z, et al. Circ_0005699 participates in ox-LDL-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury via targeting the miR-636/TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Biochem Eng J. (2022) 186:108579. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2022.108579
60. Qin M, Wang W, Zhou H, Wang X, Wang F, Wang H. Circular RNA circ_0003645 silencing alleviates inflammation and apoptosis via the NF-κB pathway in endothelial cells induced by oxLDL. Gene. (2020) 755:144900. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020
61. Kang P, Dong P. CircMETTL14(11)S upregulated METTL14 and induced CXCR4 to aggravate endothelial inflammation and atherosclerosis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 126:110979. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110979
62. Yang S, Yuan HQ, Hao YM, Ren Z, Qu SL, Liu LS, et al. Macrophage polarization in atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. (2020) 501:142–6. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.10.034
63. Miyazaki T. Calpain and cardiometabolic diseases. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:16782. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316782
64. Miyazaki T, Tonami K, Hata S, Aiuchi T, Ohnishi K, Lei XF, et al. Calpain-6 confers atherogenicity to macrophages by dysregulating pre-mRNA splicing. J Clin Invest. (2016) 126:3417–32. doi: 10.1172/JCI85880
65. Joly AL, Seitz C, Liu S, Kuznetsov NV, Gertow K, Westerberg LS, et al. Alternative splicing of FOXP3 controls regulatory T cell effector functions and is associated with human atherosclerotic plaque stability. Circ Res. (2018) 122:1385–94. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.312340
66. Huang P, Wen F, Tuerhong N, Yang Y, Li Q. Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy: focusing on alternative splicing. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1437774. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1437774
67. Doddapattar P, Gandhi C, Prakash P, Dhanesha N, Grumbach IM, Dailey ME, et al. Fibronectin splicing variants containing extra domain A promote atherosclerosis in mice through toll-like receptor 4. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2015) 35:2391–400. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.306474
68. Doddapattar P, Dev R, Jain M, Dhanesha N, Chauhan AK. Differential roles of endothelial cell-derived and smooth muscle cell-derived fibronectin containing extra domain A in early and late atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2020) 40:1738–47. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314459
69. Zhang X, Guan MX, Jiang QH, Li S, Zhang HY, Wu ZG, et al. NEAT1 knockdown suppresses endothelial cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by regulating miR-638/AKT/mTOR signaling in atherosclerosis. Oncol Rep. (2020) 44:115–25. doi: 10.3892/or.2020.7605
70. Huang H, Peng B, Chen Q, Wang Y, Li R. Long non-coding RNA nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) facilitates foam cell formation and atherosclerosis progression through the miR-17-5p/itchy E3 ubiquitin protein ligase (ITCH)/liver kinase B1 (LKB1) axis. Circ J. (2024) 88:1697–708. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-23-0769
71. Jiang X, Zhang M. The roles of long noncoding RNA NEAT1 in cardiovascular diseases. Hypertens Res. (2024) 47:735–46. doi: 10.1038/s41440-023-01551-0
72. Chen DD, Hui LL, Zhang XC, Chang Q. NEAT1 contributes to ox-LDL-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in macrophages through inhibiting miR-128. J Cell Biochem. (2019) 120:2493–501. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27541
73. Huang-Fu N, Cheng JS, Wang Y, Li ZW, Wang SH. Neat1 regulates oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced inflammation and lipid uptake in macrophages via paraspeckle formation. Mol Med Rep. (2018) 17:3092–98. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.8211
74. Fu X, Zhang J, Sun K, Zhang M, Wang S, Yuan M, et al. Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 promotes HuR/ELAVL1 cytoplasmic localization and inflammatory gene expression by regulating p38 MAPK activity. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2024) 81:253. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05292-2
75. Sachse M, Tual-Chalot S, Ciliberti G, Amponsah-Offeh M, Stamatelopoulos K, Gatsiou A, et al. RNA-binding proteins in vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. (2023) 374:55–73. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2023.01.008
76. Nicholas SE, Helming SR, Ménoret A, Pathoulas C, Xu MM, Hensel J, et al. Endothelial immunosuppression in atherosclerosis: translational control by elavl1/huR. bioRxiv. (2024), 2024.08.02.605922. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.02.605922
77. Lim YH, Yoon G, Ryu Y, Jeong D, Song J, Kim YS, et al. Human lncRNA SUGCT-AS1 regulates the proinflammatory response of macrophage. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:13315. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713315
78. Basatemur GL, Jørgensen HF, Clarke MCH, Bennett MR, Mallat Z. Vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2019) 6:727–44. doi: 10.1038/s41569-019-0227-9
79. Aherrahrou R, Guo L, Nagraj VP, Aguhob A, Hinkle J, Chen L, et al. Genetic regulation of atherosclerosis-relevant phenotypes in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. (2020) 127:1552–65. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317415
80. Wight TN, Kang I, Evanko SP, Harten IA, Chang MY, Pearce OMT, et al. Versican-A critical extracellular matrix regulator of immunity and inflammation. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:512. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00512
81. Islam S, Watanabe H. Versican: A dynamic regulator of the extracellular matrix. J Histochem Cytochem. (2020) 68:763–75. doi: 10.1369/0022155420953922
82. Kang I, Barth JL, Sproul EP, Yoon DW, Workman GA, Braun KR, et al. Expression of V3 versican by rat arterial smooth muscle cells promotes differentiated and anti-inflammatory phenotypes. J Biol Chem. (2015) 290:21629–41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.657486
83. Li Y, Guo X, Xue G, Wang H, Wang Y, Wang W, et al. RNA Splicing of the Abi1 Gene by MBNL1 contributes to macrophage-like phenotype modulation of vascular smooth muscle cell during atherogenesis. Cell Prolif. (2021) 54:e13023. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13023
84. Russell JJ, Grisanti LA, Brown SM, Bailey CA, Bender SB, Chandrasekar B. Reversion inducing cysteine rich protein with Kazal motifs and cardiovascular diseases: The RECKlessness of adverse remodeling. Cell Signal. (2021) 83:109993. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.109993
85. Chandrasekar B, Mummidi S, DeMarco VG, Higashi Y. Empagliflozin reverses oxidized LDL-induced RECK suppression, cardiotrophin-1 expression, MMP activation, and human aortic smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Mediators Inflamm. (2023) 2023:6112301. doi: 10.1155/2023/6112301
86. Mummidi S, Das NA, Carpenter AJ, Yoshida T, Yariswamy M, Mostany R, et al. RECK suppresses interleukin-17/TRAF3IP2-mediated MMP-13 activation and human aortic smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:22242–59. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28792
87. Xu D, Dai R, Chi H, Ge W, Rong J. Long non-coding RNA MEG8 suppresses hypoxia-induced excessive proliferation, migration and inflammation of vascular smooth muscle cells by regulation of the miR-195-5p/RECK axis. Front Mol Biosci. (2021) 8:697273. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.697273
88. Vancheri C, Morini E, Prandi FR, Alkhoury E, Celotto R, Romeo F, et al. Two RECK splice variants (Long and short) are differentially expressed in patients with stable and unstable coronary artery disease: A pilot study. Genes (Basel). (2021) 12:939. doi: 10.3390/genes12060939
89. Gong X, Tian M, Cao N, Yang P, Xu Z, Zheng S, et al. Circular RNA circEsyt2 regulates vascular smooth muscle cell remodeling via splicing regulation. J Clin Invest. (2021) 131:e147031. doi: 10.1172/JCI147031
90. Gu Y, Ma X, Li J, Ma Y, Zhang Y. Identification of candidate targets for the diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerosis by bioinformatics analysis. Am J Transl Res. (2021) 13:4137–51.
91. Akhmedov A, Sawamura T, Chen CH, Kraler S, Vdovenko D, Lüscher TF. Lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (LOX-1): a crucial driver of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J. (2021) 42:1797–807. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa770
92. Tam J, Thankam F, Agrawal DK, Radwan MM. Critical role of LOX-1-PCSK9 axis in the pathogenesis of atheroma formation and its instability. Heart Lung Circ. (2021) 30:1456–66. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2021.05.085
93. Barreto J, Karathanasis SK, Remaley A, Sposito AC. Role of LOX-1 (Lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor 1) as a cardiovascular risk predictor: mechanistic insight and potential clinical use. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2021) 41:153–66. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.315421
94. Veas C, Jara C, Willis ND, Pérez-Contreras K, Gutierrez N, Toledo J, et al. Overexpression of LOXIN protects endothelial progenitor cells from apoptosis induced by oxidized low density lipoprotein. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. (2016) 67:326–35. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000358
95. Lubrano V, Balzan S, Papa A. LOX-1 variants modulate the severity of cardiovascular disease: state of the art and future directions. Mol Cell Biochem. (2024) 479:2245–54. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04859-0
96. Schiopu A, Björkbacka H, Narasimhan G, Loong BJ, Engström G, Melander O, et al. Elevated soluble LOX-1 predicts risk of first-time myocardial infarction. Ann Med. (2023) 55:2296552. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2296552
97. Pyrpyris N, Dimitriadis K, Beneki E, Iliakis P, Soulaidopoulos S, Tsioufis P, et al. LOX-1 receptor: A diagnostic tool and therapeutic target in atherogenesis. Curr Probl Cardiol. (2024) 49:102117. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2023.102117
98. Sheikh MSA. Circulatory soluble LOX-1 is a novel predictor for coronary artery disease patients. Cardiovasc J Afr. (2023) 34:104–8. doi: 10.5830/CVJA-2022-038
99. Kott KA, Genetzakis E, Gray MP, Hansen P, McGuire HM, Yang JY, et al. Serum soluble lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (sLOX-1) is associated with atherosclerosis severity in coronary artery disease. Biomolecules. (2023) 13:1187. doi: 10.3390/biom13081187
100. Xu A, Wang L, Luo M, Zhang H, Ning M, Pan J, et al. Overexpression of salusin-β downregulates adipoR1 expression to prevent fatty acid oxidation in HepG2 cells. Mol Med Rep. (2024) 29:18. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2023.13141
101. Koya T, Miyazaki T, Watanabe T, Shichiri M, Atsumi T, Kim-Kaneyama JR, et al. Salusin-β accelerates inflammatory responses in vascular endothelial cells via NF-κB signaling in LDL receptor-deficient mice in vivo and HUVECs in vitro. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2012) 303:H96–105. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00009.2012
102. Esfahani M, Saidijam M, Najafi R, Goodarzi MT, Movahedian A. The effect of salusin-β on expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). ARYA Atheroscler. (2018) 14:1–10. doi: 10.22122/arya.v14i1.1602
103. Arkan A, Atukeren P, Ikitimur B, Simsek G, Koksal S, Gelisgen R, et al. The importance of circulating levels of salusin-α, salusin-β, and heregulin-β1 in atherosclerotic coronary arterial disease. Clin Biochem. (2021) 87:19–25. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2020.10.003
104. Wang Y, Wang S, Zhang J, Zhang M, Zhang H, Gong G, et al. Salusin-β is superior to salusin-α as a marker for evaluating coronary atherosclerosis. J Int Med Res. (2020) 48:300060520903868. doi: 10.1177/0300060520903868
105. Liu J, Ren YG, Zhang LH, Tong YW, Kang L. Serum salusin-β levels are associated with the presence and severity of coronary artery disease. J Investig Med. (2015) 63:632–5. doi: 10.1097/JIM.0000000000000184
106. Yildirim A, Kucukosmanoglu M. Relationship between serum salusin beta levels and coronary artery ectasia. Acta Cardiol Sin. (2021) 37:130–7. doi: 10.6515/ACS.202103_37(2).20200910A
107. Akan G, Nyawawa E, Nyangasa B, Turkcan MK, Mbugi E, Janabi M, et al. Severity of coronary artery disease is associated with diminished circANRIL expression: A possible blood based transcriptional biomarker in East Africa. J Cell Mol Med. (2024) 28:e18093. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18093
108. Abudureyimu S, He C, Xie W, Chen Z, Airikenjiang H, Abulaiti D, et al. FOXO3a functions as a transcriptional and co-transcriptional splicing regulator in vascular endothelial cell lines. Gene. (2024) 904:148221. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.148221
109. Zhou YL, Wu WP, Cheng J, Liang LL, Cen JM, Chen C, et al. CircFOXO3 rs12196996, a polymorphism at the gene flanking intron, is associated with circFOXO3 levels and the risk of coronary artery disease. Aging (Albany NY). (2020) 12:13076–89. doi: 10.18632/aging.103398
110. Rout M, Malone-Perez MW, Park G, Lerner M, Kimble Frazer J, Apple B, et al. Contribution of circulating Mfge8 to human T2DM and cardiovascular disease. Gene. (2024) 927:148712. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.148712
111. Ni YQ, Li S, Lin X, Wang YJ, He JY, Song WL, et al. Exosomal MFGE8 from high glucose induced endothelial cells is involved in calcification/senescence of vascular smooth muscle cells. bioRxiv. (2021), 2021–09. doi: 10.1101/2021.09.10.459867
112. Ni L, Liu L, Zhu W, Telljohann R, Zhang J, Monticone RE, et al. Inflammatory role of milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor VIII in age-associated arterial remodeling. J Am Heart Assoc. (2022) 11:e022574. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.022574
113. Karayiğit O, Nurkoç SG, Başyığıt F. Association between serum MFG-E8 levels and coronary severity index in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Turkish J Clinics Laboratory. (2022) 13:463–9. doi: 10.18663/tjcl.1065496
114. Oltean S, Gammons M, Hulse R, Hamdollah-Zadeh M, Mavrou A, Donaldson L, et al. SRPK1 inhibition in vivo: modulation of VEGF splicing and potential treatment for multiple diseases. Biochem Soc Trans. (2012) 40:831–5. doi: 10.1042/BST20120051
Keywords: atherosclerosis, splicing events, inflammatory response, molecular mechanisms, biomarker
Citation: Wang A, Wang C, Xuan B, Sun Y, Li B, Zhao Q, Yu R, Wang X, Zhu M and Wei J (2024) The role of splicing events in the inflammatory response of atherosclerosis: molecular mechanisms and modulation. Front. Immunol. 15:1507420. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1507420
Received: 07 October 2024; Accepted: 02 December 2024;
Published: 17 December 2024.
Edited by:
Jianan Zhao, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, ChinaReviewed by:
Meng Wanting, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, ChinaYangYi Gu, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Wang, Xuan, Sun, Li, Zhao, Yu, Wang, Zhu and Wei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jingjing Wei, MTM3ODM2Njk2MDJAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Mingjun Zhu, emh1bWluZ2p1bjMxN0AxNjMuY29t; Xinlu Wang, d2FuZ3hpbmx1MTEwQDEyNi5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Aolong Wang
Aolong Wang Chengzhi Wang3†
Chengzhi Wang3† Qifei Zhao
Qifei Zhao Xinlu Wang
Xinlu Wang Mingjun Zhu
Mingjun Zhu Jingjing Wei
Jingjing Wei