- Department of Dermatology, Hunan Key Laboratory of Medical Epigenomics, Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease. The inconsistent prevalence of SLE between monozygotic twins suggests that environmental factors affect the occurrence of this disease. Abnormal epigenetic regulation is strongly associated with the pathogenesis of SLE. Epigenetic mechanisms may be involved in the development of lupus through DNA methylation, histone modification, noncoding RNAs, and other modifications. This review aims to show numerous studies as a treasure map to better understand the effects of aberrant epigenetic modification in the onset and development of SLE, which will benefit the current basic research and provide potential diagnostic biomarkers or therapeutic targets for SLE.
1 Introduction
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by the production of multiple autoantibodies. The produced autoantibodies bind to autoantigens as immune complexes, circulating in the body, depositing in various tissues, and causing chronic inflammation (1). Failure of self-tolerance is considered the main pathogenesis of SLE, causing dysregulation in both the innate and adaptive immune systems. The upstream regulatory mechanisms that determine immune dysfunctions have been extensively documented. Based on genome-wide association studies, many scholars have attributed the pathogenesis of lupus to genetic susceptibility. Through the study of familial SLE, researchers have identified multiple loci of SLE susceptibility (2). However, the consistency of monozygotic twins with lupus is only 24–57% (3). Meanwhile, epidemiological studies of environmental exposure have shown that drugs and ultraviolet light can trigger lupus-like disease (4), suggesting that both environmental factors and genetic predisposition contribute to the development of SLE. For decades, an increasing number of studies have revealed that environmental factors play regulatory roles through epigenetic mechanisms contributing to the development of SLE, indicating that epigenetic regulation is an important contributing factor in SLE (5). This review aims to present recent advances in epigenetic factors involved in the pathogenesis, biomarkers, and therapeutic targets of SLE to facilitate an understanding of the effects of epigenetic abnormalities in SLE pathogenesis.
2 Epigenetic alterations in SLE
Epigenetic changes, including DNA methylation, histone modifications, noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs), and RNA methylation, are thought to be key signaling mediators between the genome and the environment. Richardson et al. reported that CD4+ T cells were observed to increase self-reactivity when they were treated with a DNA methylation inhibitor, 5-azacytidine (6). Since then, a series of studies have identified the function of DNA demethylation in SLE.
2.1 DNA methylation in SLE
DNA methylation is a dynamic process that involves both methylation and demethylation events (7). Methylation acts as a transcriptional repressive modification, which is defined as the addition of a methyl group to the C5 position of cytosine in CpG dinucleotides by DNA methyltransferase (DNMTs). The methyl groups interfere with the binding of transcription factors to DNA, thereby partially causing the silencing of those genes. Abnormal methylation patterns lead to aberrant gene activation, which contributes to SLE development. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) regulates gene transcription, resulting in dysregulation of the immune system in SLE (8). The modification of 5-hmC was found for the first time in the DNA of bacteriophages (9). Hydroxymethylation of 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) produces 5-hmC, which is further oxidized to 5-formylcytosine (5-fC) and 5-carboxycytosine (5-caC) (10). The stepwise oxidation of 5-mC is a demethylation mechanism which activates gene transcription, promotes gene expression and is catalyzed by ten-eleven translocation (TET), a methylcytosine dioxygenase (11) (Figure 1).
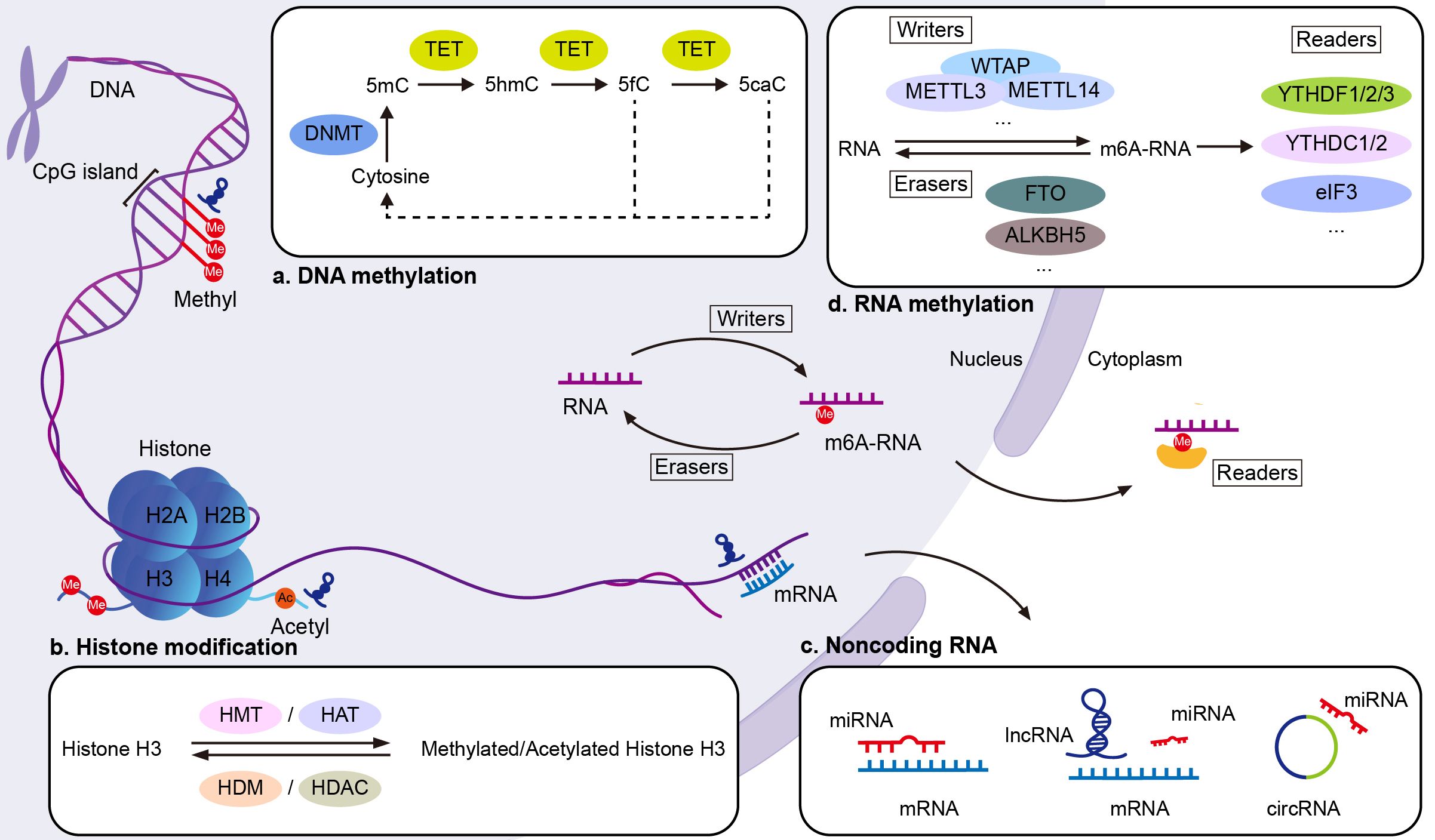
Figure 1. Epigenetic mechanisms in SLE. (A) DNA methylation: DNMTs add methyl groups to the C5 position of cytosine in CpG dinucleotides, forming 5mC. This modification silences genes by interfering with transcription factor binding. TET enzymes reverse this by converting 5mC to 5hmC, the first step in the DNA demethylation process. (B) Histone modifications: Modifications such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, and ubiquitination target specific amino acids in histone tails, altering chromatin structure and gene expression. Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) add acetyl groups to lysine residues, activating transcription, while HDACs remove acetyl groups, repressing transcription. Histone methyltransferases (HMTs) and demethylases (HDMs) respectively add or remove methyl groups on lysine and arginine residues. (C) Noncoding RNAs: MiRNAs regulate gene expression by binding to complementary sequences in the 3′ untranslated region (UTR) of target mRNAs, promoting degradation or inhibiting translation. LncRNAs regulate transcription by interacting with proteins such as transcription factors, and influence translation by binding to mRNA. Both lncRNAs and circRNAs act as miRNA sponges, influencing transcriptional and post-transcriptional gene regulation. (D) RNA methylation: RNA methylation is regulated by three groups of enzymes: “writers” (methyltransferases), “erasers” (demethylases), and “readers” (m6A-binding proteins). This process modifies RNA function post-transcriptionally. Ac, acetyl group; eIF3, eukaryotic initiation factor 3; Me, methyl group; m6RNA, N6-methyladenosine.
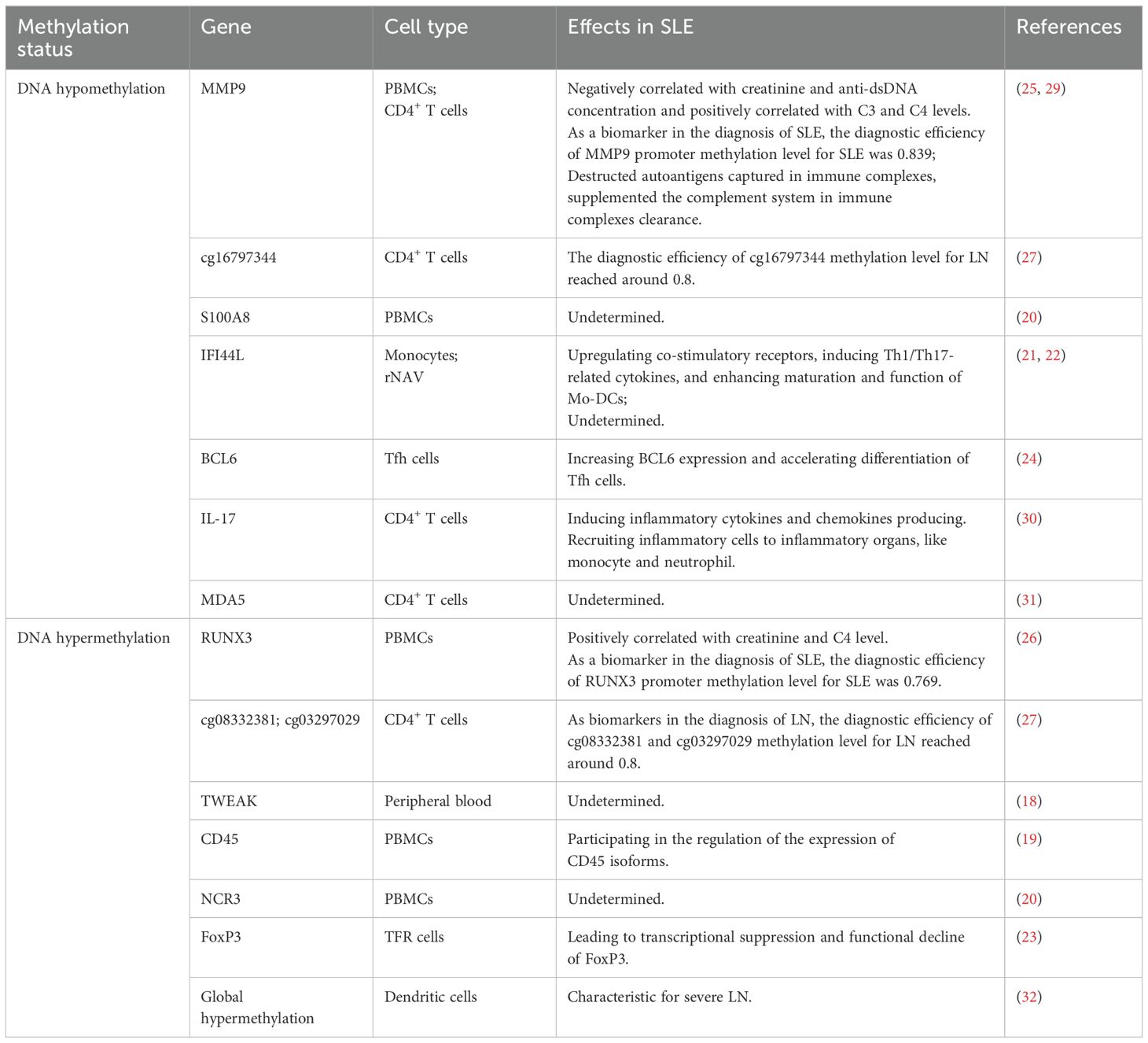
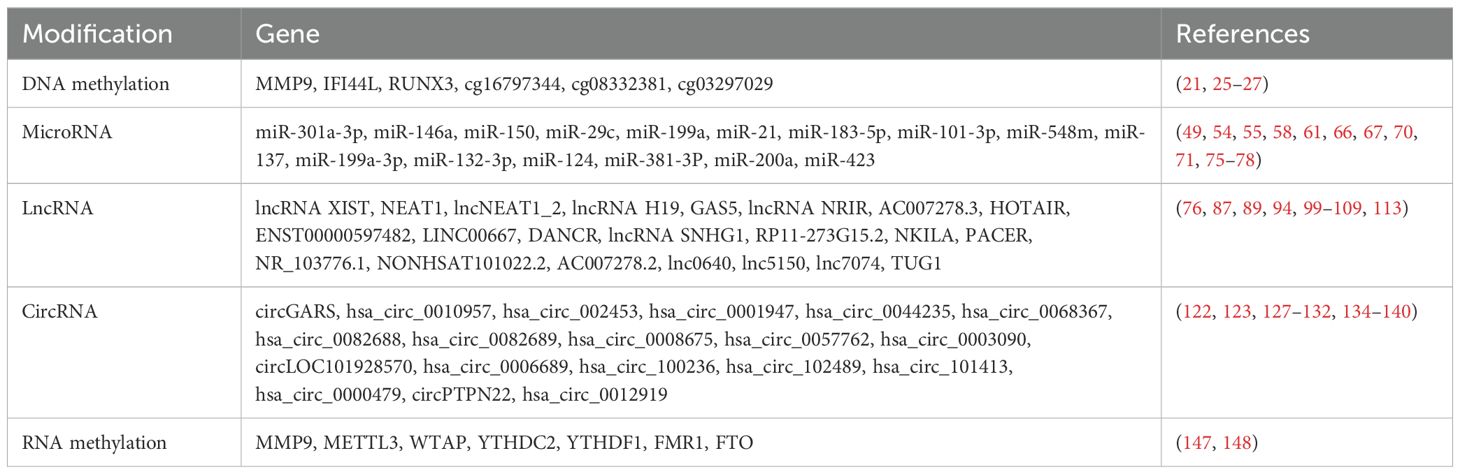
Many signaling pathways, transcription factors, and ncRNAs have been proven to affect DNA methylation patterns in CD4+ T cells, B cells, monocytes, neutrophils, and dendritic cells as well. DNA hypomethylation plays an important role in the pathogenesis of SLE. Studies have revealed that the hypomethylation of global genomic DNA and many immune-related genes in SLE CD4+ T cells result in the overexpression of growth arrest and DNA damage inducible 45 alpha (Gadd45a), CD70, CD11a, CD40L, and perforin, thereby contributing to autoimmunity (12–17). Zhao et al. found that 5-hmC was increased in SLE CD4+ T cells, which indicated that DNA hydroxymethylation was involved in the aberrant regulation of gene transcription in SLE pathogenesis (8). The following are the applications of DNA methylation in SLE reported over the past 2 years. More classical pathogenic mechanisms of DNA methylation in SLE over the past 5 years are listed in Table 1.
Liao et al. found that the decreased mRNA expression and serum concentration of TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) significantly correlated with SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) and renal damage in SLE patients. Increased DNA methylation levels of TWEAK in the peripheral blood of SLE patients suggested that abnormal DNA methylation may participate in SLE pathogenesis by downregulating the expression of TWEAK (18). Local DNA methylation of the CD45 gene was considered to participate in the regulation of CD45 isoform expression in SLE peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) (19). Gao reported that in identifying feature autophagy-related genes (ARGs) in SLE PBMCs, the cg24898863 (S100A8) gene was hypomethylated and upregulated, whereas the cg27490128 (NCR3) gene was hypermethylated and downregulated, prompting the possible mechanism of ARGs involved in the process of SLE (20).
Luo et al. found that the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) interacted with TET2, which induced DNA demethylation of the interferon-inducible 44 like (IFI44L) promoter. Overexpression of IFI44L in monocytes can upregulate co-stimulatory receptors, induce Th1/Th17-related cytokines, and promote maturation of monocyte-derived dendritic cells (21), thus leading to autoimmunity in SLE. Hurtado et al. also reported hypomethylation of the IFI44L gene in resting naive B cells of SLE patients, suggesting that epigenetic alterations are established very early in B-cell ontogeny (22). It has been shown that the conserved noncoding sequence 2 region of forkhead box protein 3 (FoxP3) was hypermethylation in SLE follicular regulatory T cells, leading to transcriptional suppression and functional decline of FoxP3 (23). Liu et al. found that downregulation of ubiquitin-like with PHD and RING finger domains 1 (UHRF1) in the T follicular helper (Tfh) cells of SLE patients, decreased UHRF1 can reduce DNA methylation and H3K27me3 levels in the B cell lymphoma 6 (BCL6) promoter region, which resulted in the increased level of BCL6 and accelerated differentiation of Tfh cells (24). The result revealed the role of UHRF1 in regulating Tfh cell differentiation and provided a potential therapeutic target for SLE.
Recent studies have shown that the matrix metallopeptidase 9 (MMP9) promoter methylation level is significantly reduced while the runt-related transcription factor 3 (RUNX3) promoter methylation level is significantly heightened in SLE PBMCs compared to healthy controls. According to receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis, the diagnostic efficiency of the MMP9 promoter methylation level for SLE was 0.839 while the RUNX3 promoter methylation level for SLE was 0.769, emphasizing the potential utility of MMP9 and RUNX3 methylation levels as biomarkers for SLE diagnosis (25, 26). In the lupus nephritis (LN) group compared to both the SLE group without kidney injury and healthy controls, cg08332381 and cg03297029 were significantly hypermethylated while cg16797344 was significantly hypomethylated. According to ROC curve analysis, the diagnostic efficiency of these sites for LN was approximately 0.8, and the combined efficiency of all three sites exceeded 0.9, which emphasizes the potential use of cg08332381, cg03297029, and cg16797344 methylation levels as biomarkers for LN diagnosis (27).
Methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2) selectively binds to 5-mC residues in CpG dinucleotides to regulate gene expression. Li et al. recently demonstrated that the overexpression of MeCP2 is markedly linked to an elevation in brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), potentially leading to disturbances in normal neuronal function in mice. C57BL/6 transgenic mice with human MeCP2 (B6.Mecp2Tg1) exhibit lupus-like phenotypes and significant central nervous system (CNS) dysfunction, making them a potential model for neuropsychiatric lupus (NPSLE) (28).
2.2 Histone modifications in SLE
Chromatin is composed of nucleosomes, histone octamers, and the surrounding DNA. Various modifications, such as acetylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and methylation, target specific amino acids in histone tails (33), affecting the structure of chromatin and thus regulating post-translational gene expression. H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) results in transcriptional inhibition (34), whereas H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) is associated with transcriptional activation (35) (Figure 1).
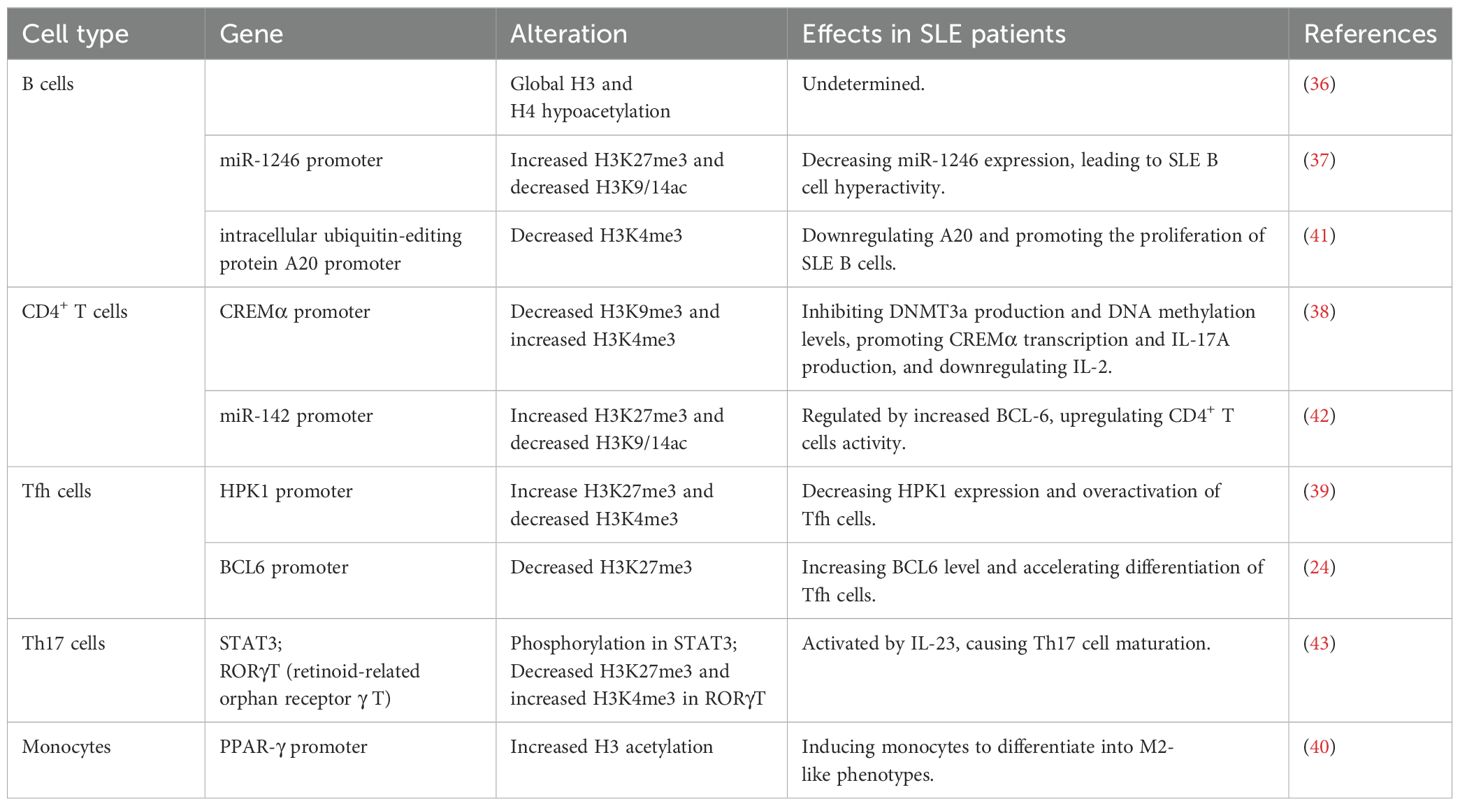
In comparison with healthy controls, B cells have been observed in global histone 3 (H3) and histone 4 (H4) hypoacetylation in SLE patients (36). Zhang et al. found that in the miR-1246 promoter region of SLE B cells, H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) was increased, histone H3 acetylation at Lys9 and Lys14 (H3K9/K14ac) was reduced, and downregulated miR-1246 expression led to B-cell hyperactivity (37).
Luo et al. reported that in CD4+ T cells of SLE, reduced suppressor of variation 3–9 homolog 1 (SUV39H1) in the cAMP-responsive element modulator α (CREMα) promoter region resulted in decreased H3K9me3 levels. The SET domain containing 1 (Set1) expression in the CREMα promoter region was increased. These resulted in decreased DNMT3a and DNA methylation levels and increased H3K4me3 levels, which promoted CREMα transcription and ultimately SLE (38). Studies have found that the reduction of jumonji domain-containing 3 (JMJD3) at the hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 (HPK1) promoter increased H3K27me3, leading to the reduced mixed-lineage leukemia 1 and H3K4me3 abundance in Tfh cells of SLE patients. All of these resulted in HPK1 low expression and Tfh cell overactivation, ultimately inducing the development of SLE (39). Liu et al. reported that elevated M2-like phenotype in SLE monocytes was regulated by elevated acetylation levels of H3 in proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ) promoter. Due to the immunosuppressive function of M2-like monocytes, this study may propose a potential treatment for SLE patients (40).
There is limited research on the impact of histone modifications on the pathogenesis of NPSLE. Recent studies have found that the overexpression of MeCP2 is significantly associated with the upregulation of nuclear receptor corepressor 1 (NCoR1) and histone deacetylases (HDACs). This transcriptional dysregulation may further contribute to the development of lupus-like phenotypes in mice, along with significant central nervous system (CNS) dysfunction (28).
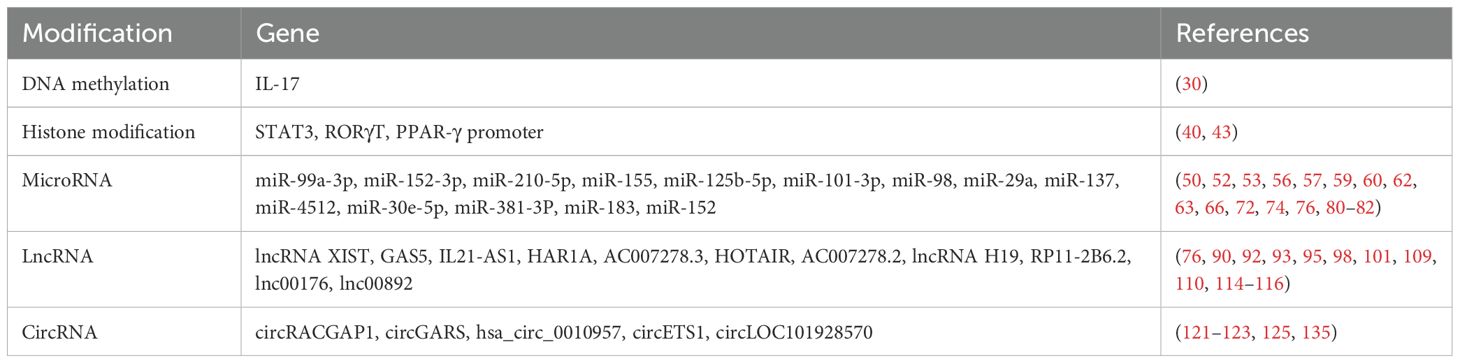
In this study, we present aberrant histone modifications in immune cells from SLE patients during the past 2 years. More classic studies over the past 5 years are listed in Table 2.
2.3 Noncoding RNAs in SLE
The human genome is extensively transcribed, and over 80% of RNA transcripts are ncRNAs, which do not translate into proteins (44). NcRNAs are the most recently discovered epigenetic mechanisms (Figure 1). MicroRNAs (miRNAs), short noncoding RNAs, are single-stranded RNAs of 18–22 nucleotides emerging as key posttranscriptional regulators of target genes by degrading mRNAs and repressing their translation (45). Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have a length of over 200 nucleotides (46). Circular RNA (circRNA) is a type of single-stranded RNA formed as a covalently closed continuous loop. Identifying useful biomarkers for early diagnosis and treatment of SLE is a challenge in current research.
2.3.1 MicroRNAs in SLE
MiRNA binds to target genes at the complementary loci in the 3′ untranslated region to regulate expression by degrading mRNA and inhibiting translation (47). MiRNA regulation plays a pivotal role in many biological processes and diseases, such as cancer and autoimmune diseases, including SLE (48).
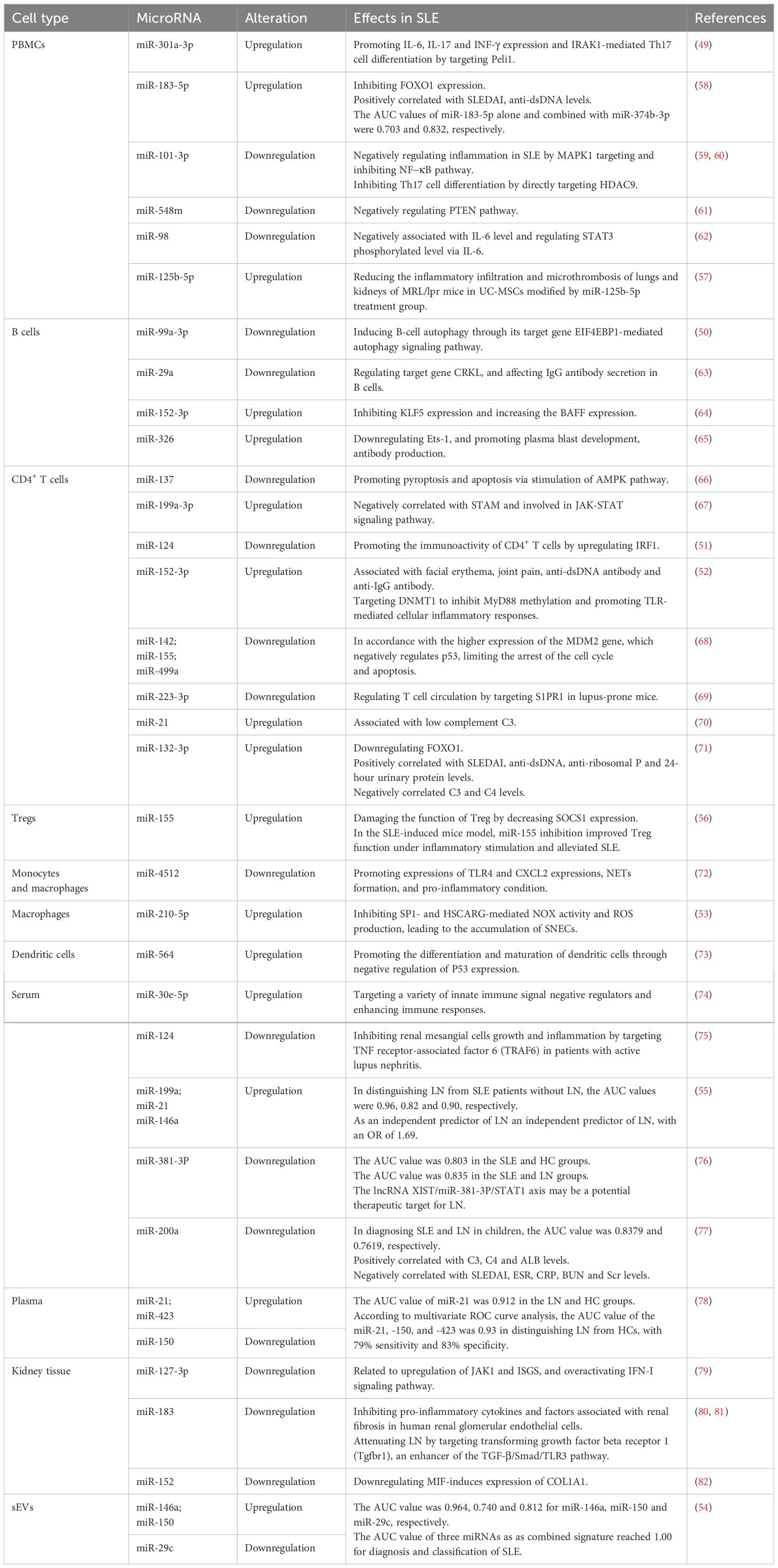
Luo et al. found that the expression of miR-301a-3p is significantly increased in SLE PBMCs, promoting the expression of IL-6, IL-17, and interferon-γ (INF-γ), as well as IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK1)-mediated Th17 cell differentiation by targeting Pellino 1 (Peli1) (49). Downregulated expression of miR-99a-3p can induce B-cell autophagy through its target gene eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 1 (EIF4EBP1)-mediated autophagy signaling pathway in SLE B cells (50). In SLE CD4+ T cells, downregulated miR-124 promotes immunoactivity by upregulating interferon regulatory factor 1 (51). In addition, upregulated miR-152-3p in SLE CD4+ T cells was involved in the development of SLE by targeting DNMT1 to inhibit myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88) methylation and promote toll-like receptor (TLR)-mediated cellular inflammatory responses (52). In terms of innate immunity, upregulation of miR-210-5p in macrophages from SLE patients can inhibit specificity protein 1 (SP1)- and HSCARG-mediated NADPH oxidase (NOX) activity and reactive oxygen species production, leading to the accumulation of secondary necrotic cells, which is involved in the pathogenesis of SLE (53).
Chen et al. constructed a multi-miRNA detection platform based on target-triggered locked hairpin DNA-functionalized Au nanoprobes for the diagnosis and classification of SLE. The results showed that the area under curve (AUC) value for the combined signature of three urinary small extracellular vesicle (sEV) miRNAs (miR-146a, miR-29c, and miR-150) reached 1.00 (54). ElFeky et al. reported that the expression of miR-199a, miR-21, and miR-146a was significantly increased in the serum of LN patients compared to healthy controls (HCs) and SLE patients without LN. According to ROC curve analysis, the AUC values of miR-199a, miR-21, and miR-146a in distinguishing LN from SLE patients without LN were 0.96, 0.82 and 0.90, respectively. Logistic regression analysis showed that miR-199a was an independent predictor of LN with an OR of 1.69 (55).
A recent study reported that miR-155 was upregulated in regulatory T cells (Tregs) from SLE and SLE-induced mice. Inflammation-induced miR-155 impaired Treg function by decreasing suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 (SOCS1) expression. In the SLE-induced mice model, miR-155 inhibition improved Treg function under inflammatory stimulation and alleviated SLE (56). Wu et al. found that the expression of miR-125b-5p was upregulated in SLE PBMCs. After treatment with umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSCs) modified by miR-125b-5p in MRL/lpr mice, the serum levels of IL-4 were elevated while IL-17A levels were reduced, and inflammatory infiltration and microthrombus formation in the lungs and kidneys were decreased (57). Targeting miR-155 and miR-125b-5p offers therapeutic approaches for alleviating SLE.
The above shows the role of miRNAs in SLE during the past 2 years. More classic studies over the past 5 years are listed in Table 3.
2.3.2 Long noncoding RNA in SLE
LncRNAs participate in a variety of biological processes, such as silencing transcription, associating with proteins, activating protein-coding genes, binding to mRNAs, and acting as competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) (83). LncRNAs have been identified to have a pivotal part in several pathogenic disorders (84) and are involved in autoimmune responses.
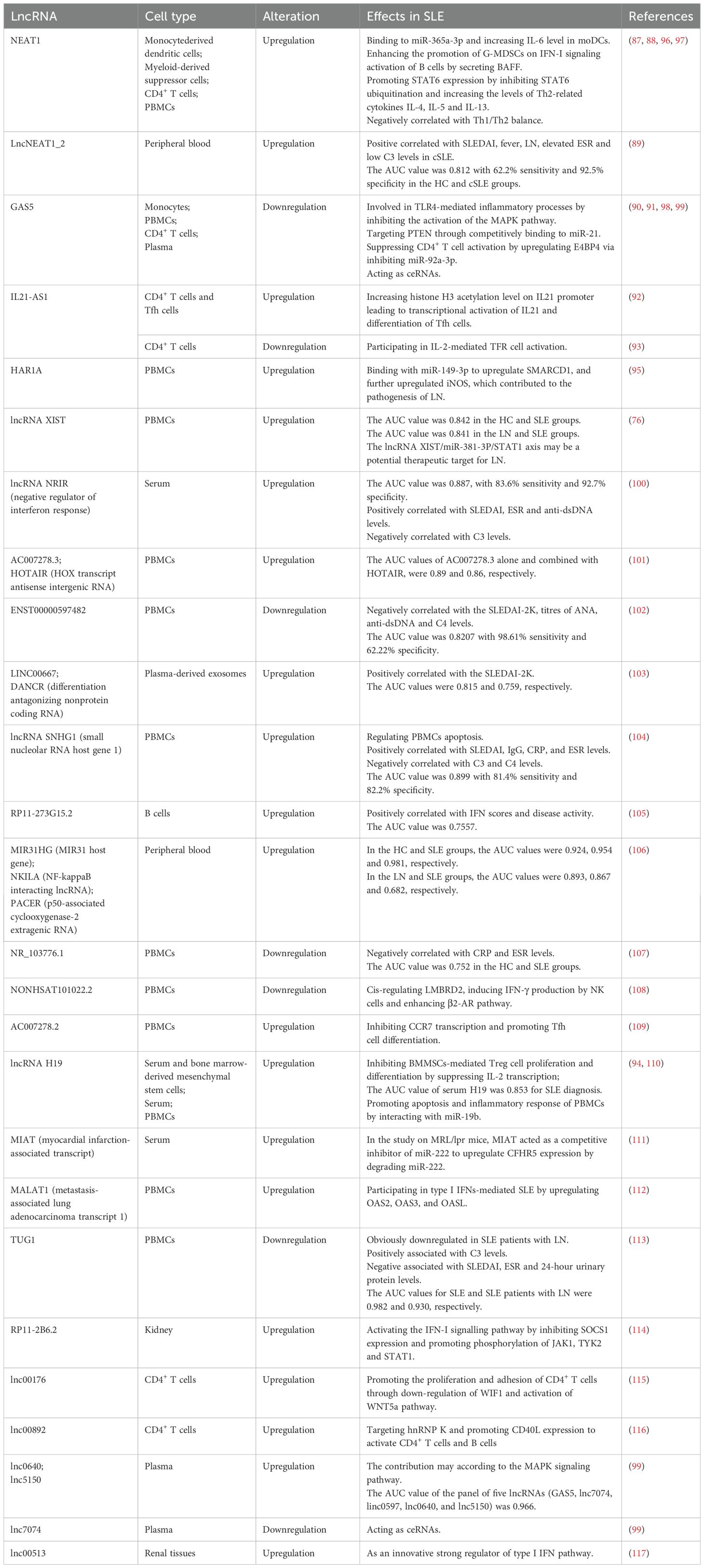
Nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1), the best-characterized lncRNA, is known to play a crucial part in the innate immune response (85, 86). It was found that the upregulation of NEAT1 in monocyte-derived dendritic cells of SLE patients induced the expression of IL-6 and positively correlated with SLEDAI (87). Jiang et al. reported that the increased expression of NEAT1 in SLE PBMCs was negatively correlated with Th1/Th2 balance, which participated in the pathogenesis of SLE (88). LncNEAT1 contained two transcripts, lncNEAT1_1 and lncNEAT1_2, both of which were upregulated in the peripheral blood of childhood-onset SLE (cSLE). The lncNEAT1_2 expression was positively correlated with SLEDAI, fever, renal involvement, elevated ESR, and low C3 levels. According to ROC curve analysis, the AUC value was 0.812, with 62.2% sensitivity and 92.5% specificity (89).
Xiao et al. found that the expression of lncRNA growth arrest-specific transcript 5 (GAS5) was decreased in monocytes of SLE patients and negatively correlated with SLEDAI. GAS5 may be involved in TLR4-mediated inflammatory processes by inhibiting the activation of the mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, thus participating in the pathogenesis of SLE (90). It was also reported that lncRNA GAS5 expression was downregulated in SLE PBMCs and may contribute to SLE by targeting phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) through competitively binding to miR-21 (91).
IL21 anti-sense RNA 1 (IL21-AS1) is a lncRNA located on the antisense strand of the IL21 gene motif. Liu et al. found that IL21-AS1 expression was upregulated in CD4+ T cells and Tfh cells from SLE patients and positively correlated with SLEDAI. Moreover, the increased acetylation levels of histone H3 on the IL21 promoter led to transcriptional activation of IL21 (92). However, a previous study reported that IL21-AS1 expression was downregulated in SLE CD4+ T cells and negatively correlated with SLEDAI, which may influence disease activity by participating in IL-2-mediated follicular regulatory T-cell activation in SLE (93). The different genetic backgrounds and the limited sample size in the previous study may explain the contrasting results of the two studies.
In both the serum and PBMCs of SLE patients, the expression of lncRNA H19 was increased, while that of miR-19b was decreased. Furthermore, according to ROC curve analysis, the AUC value of serum H19 was 0.853 for SLE diagnosis. Upregulation of H19 promoted apoptosis and the inflammatory response of PBMCs by interacting with miR-19b, which may participate in the pathogenesis of SLE (94). A recent study constructed a ceRNA network combined with clinical validation to screen for potential molecular markers of SLE through bioinformatics analysis. The results found that lncRNA X inactive specific transcript (XIST) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) were upregulated, while miR-381-3p was downregulated, in the peripheral blood of SLE. ROC curve analysis suggested that the lncRNA XIST/miR-381-3P/STAT1 axis could serve as a molecular marker for SLE diagnosis and a potential therapeutic target for LN (76). Liu et al. reported that lncRNA highly accelerated region 1 A (HAR1A) was significantly upregulated in PBMCs from LN patients and that it bound to miR-149-3p to upregulate SWItch/sucrose non-fermentable-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily D member 1 (SMARCD1). The HAR1A/miR-149-3p/SMARCD1 pathway upregulated the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), an inflammation inducer. Additionally, their study found that IL-10 secreted by iTreg cells alleviated LN through downregulating lncRNA HAR1A transcription, thereby suppressing SMARCD1-mediated iNOS activation, which might contribute to the identification of new targets for iTreg-based treatment in LN (95).
The above shows the role of lncRNA in SLE during the past 2 years. More information on studies over the past 5 years is provided in Table 4.
2.3.3 Circular RNAs in SLE
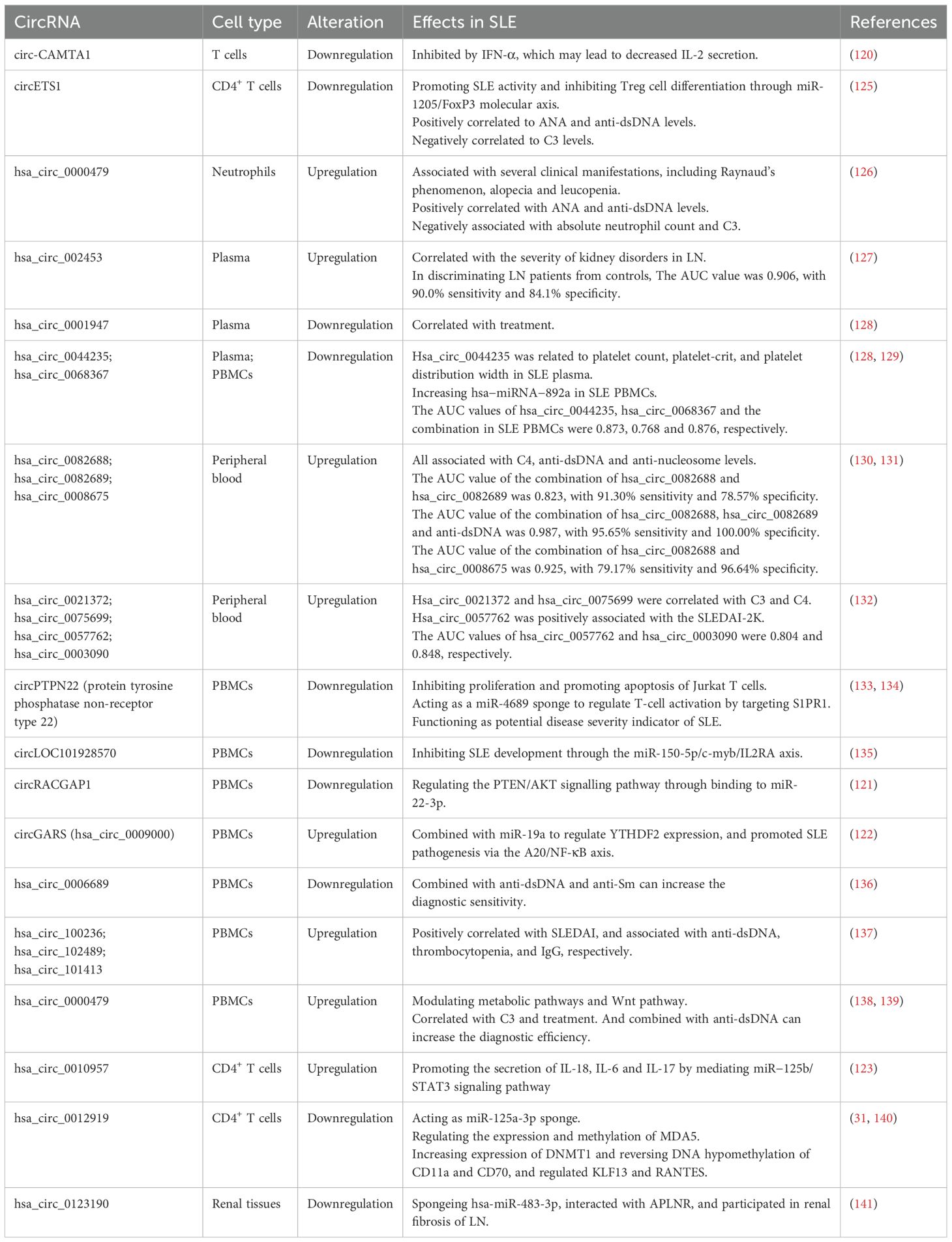
CircRNAs, which form covalently closed RNA circles, regulate gene expression at both transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels. Acting as miRNA sponges, circRNA can competitively bind mRNA, thereby weakening miRNA-mediated gene suppression (118, 119). Compared with miRNA and lncRNA, circRNA is more stable in mammalian cells, suggesting that circRNAs may be ideal biomarkers for human diseases. The role of circRNAs in SLE has garnered much attention in recent years.
Recently, researchers have used co-expression network analysis, bioinformatics analysis, and multilayer integrative analysis to profile the expression of circRNAs in SLE patients. Circ-calmodulin binding transcription activator 1 (CAMTA1) was found significantly decreased in SLE T cells, and was associated with disease activity. In SLE T cells, upregulated IFN-α inhibited circ-CAMTA1 expression, which may influence glucose metabolism and lead to overexpression of miR-181c-5p, thus decreased the secretion of IL-2 (120). The expression of circ-Rac GTPase activating protein 1 (RACGAP1) was downregulated in SLE PBMCs and related to SLEDAI, anti-dsDNA, and C3 levels, which participated in SLE pathogenesis by regulating the PTEN/AKT signaling pathway through binding to miR-22-3p (121). CircGARS (hsa_circ_0009000) was significantly upregulated in SLE PBMCs, which directly combined with miR-19a to regulate the expression of YTH domain-containing family protein 2 (YTHDF2) and promoted the development of SLE via the A20/NF-κB axis (122). It was also reported that increased expression of hsa_circ_0010957 in SLE CD4+ T cells promoted the secretion of IL-18, IL-6, and IL-17 by mediating the miR−125b/STAT3 signaling pathway, contributing to the pathogenesis of SLE (123).
Additionally, Zheng et al. explored the regulatory mechanisms of circRNAs in SLE patients, revealing a potential relationship between the circRNA–microRNA–mRNA regulatory network and pathogenesis of SLE. They dentified that 131 upregulated and 314 downregulated circRNAs in the plasma of SLE patients, with 28 upregulated and 119 downregulated circRNAs overlapping between PBMCs and plasma, which were enriched in ubiquitination, the TNF signaling pathway and the MAPK pathway. Furthermore, they constructed a network including 54 circRNAs, 41 miRNAs, and 2602 mRNAs to understand the regulatory role of circRNAs in SLE pathogenesis, suggesting that circRNAs in this network could serve as a potential diagnostic biomarker of SLE (124). Zou et al. found that circ-ETS Proto-Oncogene 1 (ETS1) was significantly downregulated in SLE CD4+ T cells, and positively correlated to ANA and anti-dsDNA levels while negatively correlated to C3 levels. After transfection of circETS1 overexpression, CD4+T cells differentiated into Treg cells, causing an imbalance in the Th17/Treg ratio. Transfection of miR-1205 mimic and si-FoxP3 reversed the effects of circETS1 overexpression. In addition, inhibition of miR-1205 had therapeutic effects in SLE mice models. Downregulation of circETS1 promoted SLE activity and inhibited Treg cell differentiation through miR-1205/FoxP3 molecular axis, which may be a novel target for SLE treatment (125).
More information on studies on circRNAs in SLE patients over the past 5 years is provided in Table 5.
2.4 RNA methylation in SLE
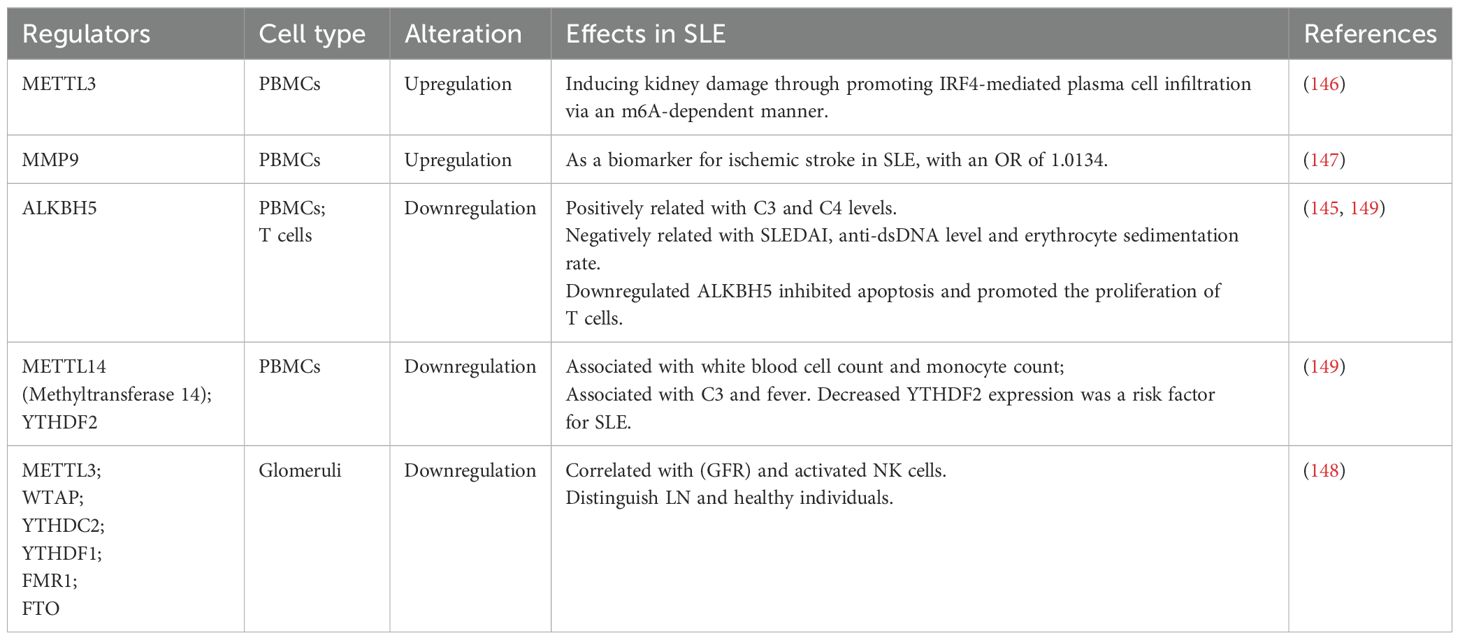
In recent years, methylation modifications have been reported to occur not only in DNA, but also occurs in RNA. RNA modifications are post-transcriptional and can alter RNA function. The most common RNA modification is N6-methyladenosine (m6A), which involves methylation of its adenine. M6A methylation is regulated by methyltransferases and demethyltransferases, and it is recognized by RNA binding proteins (142) (Figure 1). Several studies have reported that abnormal m6A modifications can contribute to the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases by altering the expression of crucial immune factors (143, 144).
Deng et al. found that the expression of AlkB homolog 5 (ALKBH5), a demethyltransferase, was downregulated in both PBMCs and T cells of SLE patients. The expression of ALKBH5 was associated with clinical indicators in SLE, and its downregulation inhibited apoptosis and promoted T cell proliferation, potentially contributing to the development of SLE (145). Liu et al. reported the aberrant m6A methylation in SLE PBMCs. Methyltransferase 3 (METTL3) was upregulated in both SLE and the kidney of MRL/lpr mice, and it promoted the expression of interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4), a gene upregulated by m6A. METTL3 induced kidney damage by promoting IRF4-mediated plasma cell infiltration in an m6A-dependent manner (146). Tian et al. identified a causal relationship between MMP9, an m6A-related gene, and ischemic stroke in SLE. As a biomarker for ischemic stroke in SLE, the odds ratio (OR) was 1.0134 (147). Zhao et al. confirmed that the levels of METTL3, Wilms tumor 1 associated protein (WTAP), YTH domain containing 2 (YTHDC2), YTHDF1, fragile X mental retardation 1 (FMR1), and fat mass and obesity-related protein (FTO) in the glomeruli could effectively distinguish patients with LN from healthy individuals, and that they are correlated with the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and activated natural killer (NK) cells, indicating that they are potential prognostic biomarkers (148).
More classical pathogenic mechanisms of RNA methylation in SLE over the past 5 years are listed in Table 6.
3 Epigenetic factors as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for SLE
As currently available biomarkers of SLE, such as autoantibodies, have limitations in early diagnosis, it is crucial to explore new biomarkers that have high specificity and sensitivity for diagnosing the disease and assessing the severity. Increasing evidence suggests that dysregulated epigenetic modifications in immune cells play a significant role in the pathogenesis of SLE (Figure 2). These epigenetic changes have also been identified as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
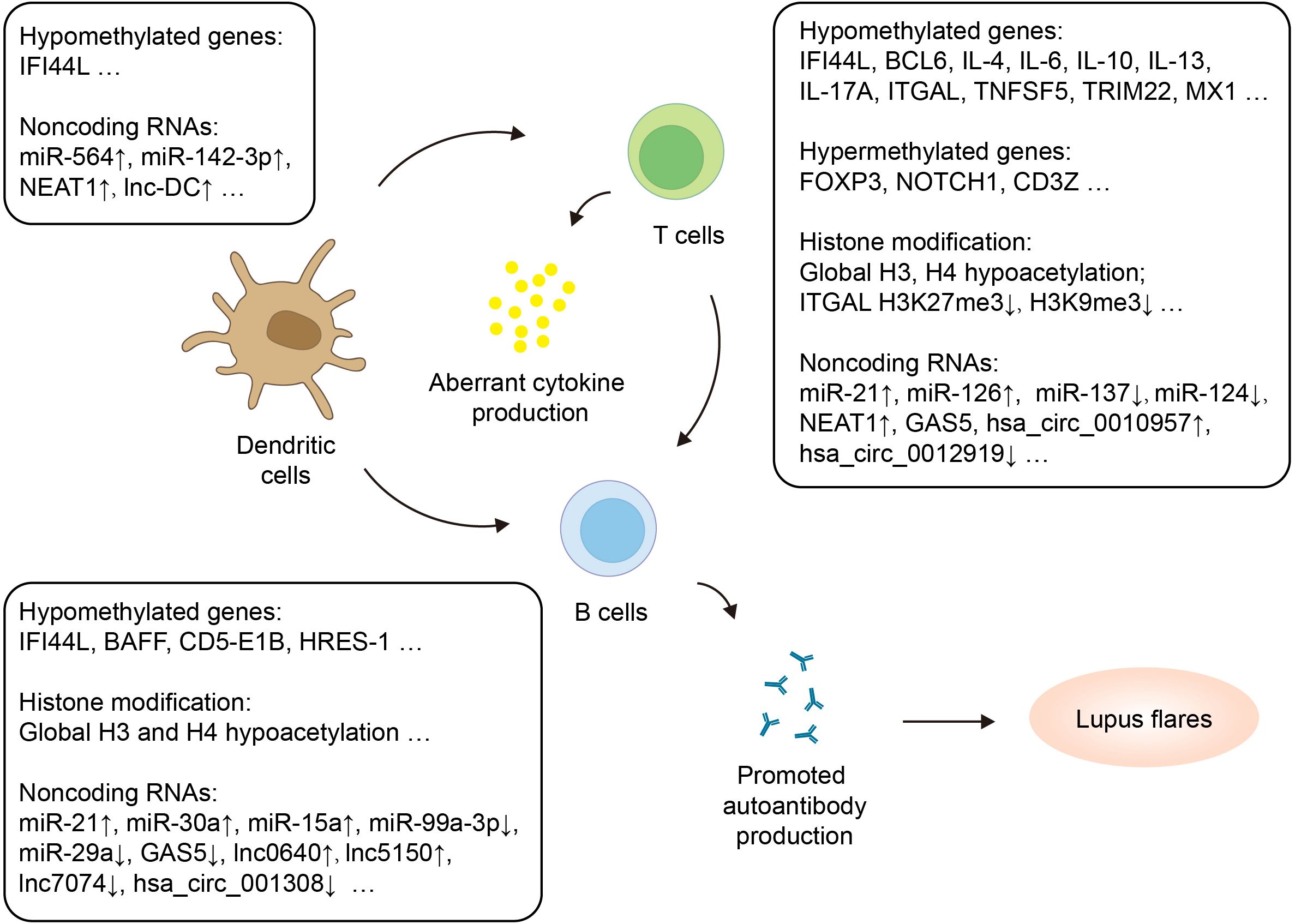
Figure 2. Epigenetic regulation of adaptive immune cells in SLE. Adaptive immune cells with altered epigenetic marks in SLE include dendritic cells, T cells and B cells. The figure highlights hypermethylated and hypomethylated genes, histone modification as well as dysregulated noncoding RNAs. CD5-E1B, CD5 protein and exon 1B; HRSE-1, HTLV-1-related endogenous sequence 1; ITGAL, Integrin Subunit Alpha L; MX1, Myxoma resistance 1; NOTCH1, Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1; TRIM22, Tripartite Motif Containing 22.
DNA methylation is currently the most studied and stable epigenetic modification. The methylation level of the IFI44L promoter has been suggested as a marker that can diagnose in the early stage and potentially predict specific disease manifestations in SLE (150). Zhang et al. published a study on a high-resolution melting-quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay to detect the methylation of the IFI44L promoter for the diagnosis of SLE, which has good consistency with previous pyrosequencing and is simpler and more economical (151). MicroRNAs are smaller than the transcripts of protein-coding genes, which makes microRNAs more resistant to degradation by endogenous RNase enzymes. Moreover, miRNAs have been found in body fluids such as plasma and urine (152), which makes the test samples easier to obtain. Therefore, miRNAs are important biomarkers for the diagnosis, staging, classification, and prognosis of SLE. In addition to the pathogenesis, miRNA dysregulation is related to disease activity, autoantibody production, organ damage, and therapeutic effects. Chen et al. constructed a multi-miRNA detection platform using target-triggered locked hairpin DNA-functionalized Au nanoprobes for the diagnosis and classification of SLE. This platform achieved an AUC value of 1.00 for a combined urinary sEV miRNA signature (miR-146a, miR-29c, and miR-150). It exhibited good practicability in SLE diagnosis, offering advantages such as low cost, rapidity, high sensitivity, and noninvasiveness (54). Compared with miRNAs, lncRNAs are more tissue-specific and biologically complex (46). Therefore, lncRNA is even more advantageous than miRNA as a new biomarker. Many studies have shown that lncRNAs can be used as potential biomarkers for SLE. For instance, upregulation of H19 promoted apoptosis and the inflammatory response of PBMCs by interacting with miR-19b, contributing to the pathogenesis of SLE. And the AUC value of H19 was 0.853 for SLE diagnosis (94). Additionally, lncNEAT1_2 expression was positively correlated with disease activity in cSLE. According to ROC curve analysis, the AUC value was 0.812, with 62.2% sensitivity and 92.5% specificity, suggesting that lncNEAT1_2 may be a potential biomarker for cSLE (89). Chen et al. constructed a ceRNA network combined with clinical validation to screen for potential molecular markers of SLE through bioinformatics analysis. The results confirmed that the lncRNA XIST/miR-381-3P/STAT1 axis could serve as a molecular marker for SLE diagnosis (76). CircRNAs have become a focus of research in many human diseases. Many studies have revealed that circRNAs can manipulate miRNAs and thus have great potential for clinical applications in diseases such as SLE. There have been many studies demonstrating the circRNA expression profile in SLE through various technologies. Through these analyses, researchers have proved that many circRNAs have characteristics for the prediction of disease progression. A circRNA–microRNA–mRNA regulatory network including 54 circRNAs, 41 miRNAs, and 2602 mRNAs was constructed to understand the regulatory role of circRNAs in SLE pathogenesis, which could be potential diagnostic biomarkers of SLE (124).
Epigenetic modifications can be used not only as potential biomarkers, but also as potential therapeutic targets for lupus. In the SLE mouse model, miR-155 inhibition improved Treg function under inflammatory stimulation and alleviated SLE (56). After treatment with UC-MSCs modified by miR-125b-5p in MRL/lpr mice, and inflammatory infiltration and microthrombus formation in the lungs and kidneys were reduced (57). In addition, downregulation of circETS1 promoted SLE activity and inhibited Treg cell differentiation through miR-1205/FoxP3 molecular axis, which may be a novel target for SLE treatment (125).
More potential epigenetic biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets for SLE over the past 5 years are listed in Tables 7 and 8.
4 Conclusions
Discoveries of epigenetic modifications have extended our knowledge of complex regulation in genes and added new insights into understanding the pathogenesis of SLE. There are still challenges in ascertaining the mechanism of epigenetic changes in the occurrence and development of the disease. Epigenetic events have great potential in finding targets for individualized treatment interventions and disease diagnosis biomarkers. With the increasing attention to epigenetic mechanisms, more surprising discoveries will provide new ideas for the treatment of SLE.
Author contributions
XZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Changsha, Hunan, China (NO: kq2208323).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Moulton VR, Suarez-Fueyo A, Meidan E, Li H, Mizui M, Tsokos GC. Pathogenesis of human systemic lupus erythematosus: A cellular perspective. Trends Mol Med. (2017) 23:615–35. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2017.05.006
2. Harley JB, Kelly JA, Kaufman KM. Unraveling the genetics of systemic lupus erythematosus. Springer Semin Immunopathol. (2006) 28:119–30. doi: 10.1007/s00281-006-0040-5
3. Rhodes B, Vyse TJ. The genetics of SLE: an update in the light of genome-wide association studies. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2008) 47:1603–11. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ken247
4. Cooper GS, Parks CG, Treadwell EL, St Clair EW, Gilkeson GS, Dooley MA. Occupational risk factors for the development of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. (2004) 31:1928–33.
5. Aslani S, Mahmoudi M, Karami J, Jamshidi AR, Malekshahi Z, Nicknam MH. Epigenetic alterations underlying autoimmune diseases. Autoimmunity. (2016) 49:69–83. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2015.1134511
6. Richardson B. Effect of an inhibitor of DNA methylation on T cells. II. 5-Azacytidine induces self-reactivity in antigen-specific T4+ cells. Hum Immunol. (1986) 17:456–70. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(86)90304-6
7. Liang P, Song F, Ghosh S, Morien E, Qin M, Mahmood S, et al. Genome-wide survey reveals dynamic widespread tissue-specific changes in DNA methylation during development. BMC Genomics. (2011) 12:231. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-231
8. Zhao M, Wang J, Liao W, Li D, Li M, Wu H, et al. Increased 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in CD4(+) T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun. (2016) 69:64–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2016.03.001
9. WYATT GR, COHEN SS. A new pyrimidine base from bacteriophage nucleic acids. Nature. (1952) 170:1702–1702. doi: 10.1038/1701072a0
10. Liang J, Yang F, Zhao L, Bi C, Cai B. Physiological and pathological implications of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in diseases. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:48813–31. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v7i30
11. Tan Li, Shi. YG. Tet family proteins and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in development and disease. Development. (2012) 139:1895–902. doi: 10.1242/dev.070771
12. Li Y, Zhao M, Yin H, Gao F, Wu X, Luo Y, et al. Overexpression of the growth arrest and DNA damage-induced 45alpha gene contributes to autoimmunity by promoting DNA demethylation in lupus T cells. Arthritis Rheum. (2010) 62:1438–47. doi: 10.1002/art.27363
13. Wu H, Zhao M, Tan L, Lu Q. The key culprit in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus: Aberrant DNA methylation. Autoimmun Rev. (2016) 15:684–9. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2016.03.002
14. Lu Q, Wu A, Richardson BC. Demethylation of the same promoter sequence increases CD70 expression in lupus T cells and T cells treated with lupus-inducing drugs. J Immunol. (2005) 174:6212–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.10.6212
15. Lu Q, Kaplan M, Ray D, Ray D, Zacharek S, Gutsch D, et al. Demethylation of ITGAL (CD11a) regulatory sequences in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. (2002) 46:1282–91. doi: 10.1002/art.10234
16. Lu Q, Wu A, Tesmer L, Ray D, Yousif N, Richardson B. Demethylation of CD40LG on the inactive X in T cells from women with lupus. J Immunol. (2007) 179:6352–8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.9.6352
17. Kaplan MJ, Lu Q, Wu A, Attwood J, Richardson B. Demethylation of promoter regulatory elements contributes to perforin overexpression in CD4+ lupus T cells. J Immunol. (2004) 172:3652–61. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.6.3652
18. Liao L, Li S, Upreti B, Wang X, Yang Y, Lou X, et al. Status of TWEAK DNA methylation and mRNA expression in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. (2023) 32:171–9. doi: 10.1177/09612033221141261
19. Dong Z, Zhang B, Rong J, Yang X, Wang Y, Zhang Q, et al. The aberrant expression of CD45 isoforms and levels of sex hormones in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. (2022) 41:1087–93. doi: 10.1007/s10067-021-05934-x
20. Gao B. Identification of feature autophagy-related genes and DNA methylation profiles in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Med Sci Monit. (2021) 27:e933425. doi: 10.12659/MSM.933425
21. Luo S, Wu R, Li Q, Zhang G. Epigenetic regulation of IFI44L expression in monocytes affects the functions of monocyte-derived dendritic cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol Res. (2022) 2022:4053038. doi: 10.1155/2022/4053038
22. Hurtado C, Rojas-Gualdrón DF, Urrego R, Cashman K, Vásquez-Trespalacios EM, Díaz-Coronado JC, et al. Altered B cell phenotype and CD27+ memory B cells are associated with clinical features and environmental exposure in Colombian systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Front Med (Lausanne). (2022) 9:950452. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.950452
23. Kurata I, Mikami N, Ohyama A, Osada A, Kondo Y, Tsuboi H, et al. Impaired function of PD-1(+) follicular regulatory T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. (2021) 206:28–35. doi: 10.1111/cei.13643
24. Liu L, Hu L, Yang L, Jia S, Du P, Min X, et al. UHRF1 downregulation promotes T follicular helper cell differentiation by increasing BCL6 expression in SLE. Clin Epigenet. (2021) 13:31. doi: 10.1186/s13148-021-01007-7
25. Ehtesham N, Mosallaei M, Zaboli Mahdiabadi M, Kenarangi T, Farhadi A, Heidari MF, et al. Significant hypomethylation of MMP9 gene promoter in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. (2023) 32:1056–65. doi: 10.1177/09612033231185618
26. Ehtesham N, Alesaeidi S, Mohammad Zadeh D, Saghaei M, Fakhri M, Bayati Z, et al. Significant heightened methylation levels of RUNX3 gene promoter in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. (2024) 33:547–54. doi: 10.1177/09612033241241850
27. Liu X, Zhou S, Huang M, Zhao M, Zhang W, Liu Q, et al. DNA methylation and whole-genome transcription analysis in CD4(+) T cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients with or without renal damage. Clin Epigenet. (2024) 16:98. doi: 10.1186/s13148-024-01699-7
28. Li Y, Zhang S, Tang C, Yang B, Atrooz F, Ren Z, et al. Autoimmune and neuropsychiatric phenotypes in a Mecp2 transgenic mouse model on C57BL/6 background. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1370254. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1370254
29. Ugarte-Berzal E, Boon L, Martens E, Rybakin V, Blockmans D, Vandooren J, et al. MMP-9/gelatinase B degrades immune complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:538. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00538
30. Koga T, Ichinose K, Kawakami A, Tsokos GC. The role of IL-17 in systemic lupus erythematosus and its potential as a therapeutic target. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. (2019) 15:629–37. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2019.1593141
31. Zhang C, Zhang C, Ji J, Xiong X, Lu Y. Hsa_circ_0012919 regulates expression of MDA5 by miR-125a-3p in CD4+ T cells of systemic lupus erythematous. Lupus. (2020) 29:727–34. doi: 10.1177/0961203320920706
32. Wardowska A, Komorniczak M, Bułło-Piontecka B, Dȩbska-Ślizień MA, Pikuła M. Transcriptomic and epigenetic alterations in dendritic cells correspond with chronic kidney disease in lupus nephritis. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:2026. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02026
33. Rice JC, Allis CD. Histone methylation versus histone acetylation: new insights into epigenetic regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. (2001) 13:263–73. doi: 10.1016/S0955-0674(00)00208-8
34. Singh SK, Bahal R, Rasmussen TP. Evidence that miR-152-3p is a positive regulator of SETDB1-mediated H3K9 histone methylation and serves as a toggle between histone and DNA methylation. Exp Cell Res. (2020) 395:112216. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.112216
35. Zhang L, Tian S, Zhao M, Yang T, Quan S, Yang Q, et al. SUV39H1-DNMT3A-mediated epigenetic regulation of Tim-3 and galectin-9 in the cervical cancer. Cancer Cell Int. (2020) 20:325. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01380-y
36. Gautam P, Sharma A, Bhatnagar A. Global histone modification analysis reveals hypoacetylated H3 and H4 histones in B Cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Immunol Lett. (2021) 240:41–5. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2021.09.007
37. Zhang Q, Liu Y, Liao J, Wu R, Zhan Y, Zhang P, et al. Deficiency of p53 Causes the Inadequate Expression of miR-1246 in B Cells of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J Immunol. (2022) 209:1492–8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200307
38. Luo S, Zhang H, Xie Y, Huang J, Luo D, Zhang Q. Decreased SUV39H1 at the promoter region leads to increased CREMα and accelerates autoimmune response in CD4(+) T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Epigenet. (2022) 14:181. doi: 10.1186/s13148-022-01411-7
39. Luo S, Xie Y, Huang J, Liu J, Zhang Q. Decreased jumonji domain-containing 3 at the promoter downregulates hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 expression and cytoactivity of T follicular helper cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients. J Immunol Res. (2022) 2022:3690892. doi: 10.1155/2022/3690892
40. Liu Y, Luo S, Zhan Y, Wang J, Zhao R, Li Y, et al. Increased expression of PPAR-γ Modulates monocytes into a M2-like phenotype in SLE patients: an implicative protective mechanism and potential therapeutic strategy of systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:579372. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.579372
41. Fan J, Iwata S, Tanaka Y, Kitanaga Y, Ishii A, Maiko H, et al. Kdm5a promotes B cell activation in systemic lupus erythematosus via downregulation of A20 by histone modification. Pathol Res Pract. (2021) 9:153653. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2021.153653
42. Ding S, Zhang Q, Luo S, Gao L, Huang J, Lu J, et al. BCL-6 suppresses miR-142-3p/5p expression in SLE CD4(+) T cells by modulating histone methylation and acetylation of the miR-142 promoter. Cell Mol Immunol. (2020) 17:474–82. doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0268-3
43. Lee S, Nakayamada S, Kubo S, Yamagata K, Yoshinari H, Tanaka Y. Interleukin-23 drives expansion of Thelper 17 cells through epigenetic regulation by signal transducer and activators of transcription 3 in lupus patients. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2020) 59:3058–69. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa176
44. ENCODE Project Consortium. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature. (2012) 489:57–74. doi: 10.1038/nature11247
45. Eulalio A, Huntzinger E, Izaurralde E. Getting to the root of miRNA-mediated gene silencing. Cell. (2008) 132:9–14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.024
46. Wu GC, Li J, Leng RX, Li XP, Li XM, Wang DG, et al. Identification of long non-coding RNAs GAS5, linc0597 and lnc-DC in plasma as novel biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:23650–63. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15569
47. Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. (2008) 9:102–14. doi: 10.1038/nrg2290
48. Bushati N, Cohen SM. microRNA functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. (2007) 23:175–205. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.23.090506.123406
49. Luo S, Wu R, Li Q, Zhang G. MiR-301a-3p advances IRAK1-mediated differentiation of th17 cells to promote the progression of systemic lupus erythematosus via targeting PELI1. J Healthc Eng. (2021) 2021:2982924. doi: 10.1155/2021/2982924
50. Yang M, Yang B, Deng D. Targeting of EIF4EBP1 by miR-99a-3p affects the functions of B lymphocytes via autophagy and aggravates SLE disease progression. J Cell Mol Med. (2021) 25:10291–305. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.v25.21
51. Chen J, Peng L, Zhao Z, Yang Q, Yin F, Liu M, et al. HDAC1 potentiates CD4 + T cell activation by inhibiting miR-124 and promoting IRF1 in systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell Immunol. (2021) 362:104284. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2021.104284
52. Tao B, Xiang W, Li X, He C, Chen L, Xia X, et al. Regulation of Toll-like receptor-mediated inflammatory response by microRNA-152-3p-mediated demethylation of MyD88 in systemic lupus erythematosus. Inflammation Res. (2021) 70:285–96. doi: 10.1007/s00011-020-01433-y
53. Wu YH, Kuo CF, Hsieh AH, Hsieh HL, Chan YF, Hwang TL. Upregulation of miR-210-5p impairs dead cell clearance by macrophages through the inhibition of Sp1-and HSCARG-dependent NADPH oxidase pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. (2021) 172:441–50. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.06.029
54. Chen X, Xiang Q, Yan S, Wang Y, Su N, Yang X, et al. Simultaneous multi-miRNA detection in urinary small extracellular vesicles using target-triggered locked hairpin DNA-functionalized au nanoprobes for systemic lupus erythematosus diagnosis. Anal Chem. (2024) 96:16370–8. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c03794
55. ElFeky DS, Omar NM, Shaker OG, Abdelrahman W, Gheita TA, Nada MG. Circulatory microRNAs and proinflammatory cytokines as predictors of lupus nephritis. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1449296. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1449296
56. Yu J, Mei J, Zuo D, Zhang M, Yu S, Li F, et al. Inflammatory factor-mediated miR-155/SOCS1 signaling axis leads to Treg impairment in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 141:113013. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113013
57. Wu Z, Hu M, Zhao Q, Lv F, Zhang J, Zhang W, et al. Immunomodulatory mechanism of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells modified by miR-125b-5p in systemic lupus erythematosus. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. (2024) 56:860–7. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.05.017
58. Zhou S, Zhang J, Luan P, Ma Z, Dang J, Zhu H, et al. miR-183-5p is a potential molecular marker of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol Res. (2021) 2021:5547635. doi: 10.1155/2021/5547635
59. Zhao X, Li S, Wang Z, Bai N, Feng Y. miR−101−3p negatively regulates inflammation in systemic lupus erythematosus via MAPK1 targeting and inhibition of the NF−κB pathway. Mol Med Rep. (2021) 23:359. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.11998
60. Sun H, Guo F, Xu L. Downregulation of microRNA-101-3p participates in systemic lupus erythematosus progression via negatively regulating HDAC9. J Cell Biochem. (2020) 121:4310–20. doi: 10.1002/jcb.v121.10
61. Yang X, Shi L, Zheng X, Liu X, Qian J. Modulation of miR-548m encoded by X chromosome on the PTEN pathway in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2022) 40:56–63. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/yjsbqm
62. Yuan S, Tang C, Chen D, Li F, Huang M, Ye J, et al. miR-98 modulates cytokine production from human PBMCs in systemic lupus erythematosus by targeting IL-6 mRNA. J Immunol Res. (2019) 2019:9827574. doi: 10.1155/2019/9827574
63. Shi X, Ye L, Xu S, Guo G, Zuo Z, Ye M, et al. Downregulated miR−29a promotes B cell overactivation by upregulating Crk−like protein in systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol Med Rep. (2020) 22:841–9. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11166
64. Luo S, Ding S, Liao J, Zhang P, Liu Y, Zhao M, et al. Excessive miR-152-3p results in increased BAFF expression in SLE B-cells by inhibiting the KLF5 expression. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:1127. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01127
65. Xia Y, Tao JH, Fang X, Xiang N, Dai XJ, Jin L, et al. MicroRNA-326 upregulates B cell activity and autoantibody production in lupus disease of MRL/lpr mice. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2018) 11:284–91. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.02.010
66. Gong A, Mi L, Wei F, Zhuang Y, Song Y, Pan C, et al. Downregulation of miR-137 Facilitates CD4+ T Cell Pyroptosis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus via Stimulating AMPK Pathway. J Immunol Res. (2023) 2023:1241774. doi: 10.1155/2023/1241774
67. Wang H, Geng G, Zhang D, Han F, Ye S. Analysis of microRNA-199a-3p expression in CD4(+) T cells of systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. (2023) 42:1683–94. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06534-7
68. Latini A, Ciccacci C, Benedittis G, Novelli L, Ceccarelli F, Conti F, et al. Altered expression of miR-142, miR-155, miR-499a and of their putative common target MDM2 in systemic lupus erythematosus. Epigenomics. (2021) 13:5–13. doi: 10.2217/epi-2020-0278
69. Hiramatsu-Asano S, Sunahori-Watanabe K, Zeggar S, Katsuyama E, Mukai T, Morita Y, et al. Deletion of mir223 exacerbates lupus nephritis by targeting S1pr1 in fas(lpr/lpr) mice. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:616141. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.616141
70. Suo QF, Sheng J, Qiang FY, Tang ZS, Yang YY. Association of long non-coding RNA GAS5 and miR-21 levels in CD4(+) T cells with clinical features of systemic lupus erythematosus. Exp Ther Med. (2018) 15:345–50. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5429
71. Qin H, Chen S, Liu X, Liang J, Wu H, Zhu X. miR-132-3p downregulates FOXO1 in CD4(+) T cells and is associated with disease manifestations in patients with lupus. J Int Med Res. (2024) 52:3000605241286762. doi: 10.1177/03000605241286762
72. Yang B, Huang X, Xu S, Li L, Wu W, Dai Y, et al. Decreased miR-4512 levels in monocytes and macrophages of individuals with systemic lupus erythematosus contribute to innate immune activation and neutrsophil NETosis by targeting TLR4 and CXCL2. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:756825. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.756825
73. Teng Z, Lin X, Luan C, Sun Y, Li X. The high expression of miR-564 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus promotes differentiation and maturation of DC cells by negatively regulating TP53 expression in vitro. Lupus. (2021) 30:1469–80. doi: 10.1177/09612033211020367
74. Mishra R, Bhattacharya S, Rawat BS, Kumar A, Kumar A, Niraj K, et al. MicroRNA-30e-5p has an Integrated Role in the Regulation of the Innate Immune Response during Virus Infection and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. iScience. (2020) 23:101322. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101322
75. Zhang L, Zhang X, Si F. MicroRNA-124 represents a novel diagnostic marker in human lupus nephritis and plays an inhibitory effect on the growth and inflammation of renal mesangial cells by targeting TRAF6. Int J Clin And Exp Pathol. (2019) 12:1578–88.
76. Chen J, Li M, Shang S, Cheng L, Tang Z, Huang C. LncRNA XIST/miR-381-3P/STAT1 axis as a potential biomarker for lupus nephritis. Lupus. (2024) 33:1176–91. doi: 10.1177/09612033241273072
77. Zhang H, Zhou X, Li Q, Zheng M. Clinical significance of miR-200a in systemic lupus erythematosus and renal damage in children. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). (2024) 70:94–8. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2024.70.1.13
78. Nakhjavani M, Etemadi J, Pourlak T, Mirhosaini Z, Zununi Vahed S, Abediazar S. Plasma levels of miR-21, miR-150, miR-423 in patients with lupus nephritis. Iran J Kidney Dis. (2019) 13:198–206.
79. Wu L, Han X, Jiang X, Ding H, Qi C, Yin Z, et al. Downregulation of renal hsa-miR-127-3p contributes to the overactivation of type I interferon signaling pathway in the kidney of lupus nephritis. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:747616. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.747616
80. Li X, Luo F, Li J, Luo C. MiR-183 delivery attenuates murine lupus nephritis-related injuries via targeting mTOR. Scandinavian J Immunol. (2019) 90:e12810. doi: 10.1111/sji.12810
81. Qi H, Cao Q, Liu Q. MicroRNA-183 exerts a protective role in lupus nephritis through blunting the activation of TGF-β/Smad/TLR3 pathway via reducing Tgfbr1. Exp Cell Res. (2020) 394:112138. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.112138
82. Zheng J, Guo R, Tang Y, Fu Q, Chen J, Wu L, et al. miR-152 attenuates the severity of lupus nephritis through the downregulation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF)-induced expression of COL1A1. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:158. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00158
83. Zhao CN, Mao YM, Liu LN, Li XM, Wang DG, Pan HF. Emerging role of lncRNAs in systemic lupus erythematosus. Biomedicine Pharmacotherapy. (2018) 106:584–92. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.175
84. Wapinski O, Chang HY. Long noncoding RNAs and human disease. Trends Cell Biol. (2011) 21:354–61. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2011.04.001
85. Zhang Q, Chen CY, Yedavalli VS, Jeang KT. NEAT1 long noncoding RNA and paraspeckle bodies modulate HIV-1 posttranscriptional expression. mBio. (2013) 4:e00596–00512. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00596-12
86. Zhang P, Cao L, Zhou R, Yang X, Wu M. The lncRNA Neat1 promotes activation of inflammasomes in macrophages. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:1495. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09482-6
87. Xiang M, Wang Y, Chen Q, Wang J, Gao Z, Liang J, et al. LncRNA NEAT1 promotes IL-6 secretion in monocyte-derived dendritic cells via sponging miR-365a-3p in systemic lupus erythematosus. Epigenetics. (2023) 18:2226492. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2023.2226492
88. Jiang Y, Zhao Y, Mo X. Expression of lncRNA NEAT1 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and its correlation with Th1/Th2 balance. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. (2021) 14:646–52.
89. Li S, Wang X, Zhao X, Deng J, Kuang W, Zhang J, et al. Long noncoding nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1_2 is a promising biomarker for childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Pediatr Investig. (2024) 8:101–7. doi: 10.1002/ped4.12413
90. Xiao J, Wang D. LncRNA GAS5 as an inflammatory regulator acting through pathway in human lupus. Curr Pharm Des. (2023) 29:1293–9. doi: 10.2174/1381612829666230517102205
91. Liu CH, Lu YL, Huang HT, Wang CF, Luo HC, Wei GJ, et al. Association of LncRNA-GAS5 gene polymorphisms and PBMC LncRNA-GAS5 level with risk of systemic lupus erythematosus in Chinese population. J Cell Mol Med. (2021) 25:3548–59. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16438
92. Liu L, Hu L, Long H, Zheng M, Hu Z, He Y, et al. LncRNA IL21-AS1 interacts with hnRNPU protein to promote IL21 overexpression and aberrant differentiation of Tfh cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Transl Med. (2022) 12:e1117. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.v12.12
93. Hao H, Nakayamada S, Ohkubo N, Yamagata K, Zhang M, Shan Y, et al. Involvement of lncRNA IL21-AS1 in interleukin-2 and T follicular regulatory cell activation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. (2021) 23:302. doi: 10.1186/s13075-021-02682-w
94. Yang H, Wang S, Wang F, Bai X, Ren J. Serum long non-coding Ribonucleic Acid H19 serves as a biomarker for systemic lupus erythematosus and participates in the disease progression. Lupus. (2024) 33:675–84. doi: 10.1177/09612033241243175
95. Liu Y, Li P, Wang L, Jiang L, Li Z, Mei Y, et al. iTreg cells-secreted IL10 alleviates lupus nephritis through inactivating lncRNA HAR1A transcription to suppress SMARCD1-mediated iNOS activation. Autoimmunity. (2024) 57:2423758. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2024.2423758
96. Huang S, Dong D, Zhang Y, Chen Z, Geng J, Zhao Y. Long non-coding RNA nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 promotes activation of T helper 2 cells via inhibiting STAT6 ubiquitination. Hum Cell. (2021) 34:800–7. doi: 10.1007/s13577-021-00496-1
97. Dong G, Yang Y, Li X, Yao X, Zhu Y, Zhang H, et al. Granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells contribute to IFN-I signaling activation of B cells and disease progression through the lncRNA NEAT1-BAFF axis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2020) 1866:165554. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.165554
98. Liu Q, Deng Y, Li C, Xie H, Liu Q, Ming S, et al. LncRNA GAS5 suppresses CD4(+) T cell activation by upregulating E4BP4 via inhibiting miR-92a-3p in systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunol Lett. (2020) 227:41–7. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2020.08.001
99. Wu GC, Hu Y, Guan SY, Ye DQ, Pan HF. Differential plasma expression profiles of long non-coding RNAs reveal potential biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus. Biomolecules. (2019) 9:206. doi: 10.3390/biom9060206
100. Ma Q, Li L, Xing Y. LncRNA NRIR serves as a biomarker for systemic lupus erythematosus and participates in the disease progression. Lupus. (2024) 33(14):1538–46. doi: 10.1177/09612033241294032
101. Rasuli E, Javidi-Aghdam K, Akbarzadeh-Khiavi M, Abdshah A, Gadakchi L, Jafarpour M, et al. Immunoregulatory role of AC007278.3 and HOTAIR long non-coding RNAs in lupus nephritis: potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Mol Biol Rep. (2024) 51:1075. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-10019-4
102. Wang C, Yuan S, Zeng Y, Li W, Ye J, Li F, et al. A novel long noncoding RNA ENST00000597482 serves as a potential biomarker for disease activity and diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. (2024) 33:1089–99. doi: 10.1177/09612033241266988
103. Peng XC, Ma LL, Miao JY, Xu SQ, Shuai ZW. Differential lncRNA profiles of blood plasma-derived exosomes from systemic lupus erythematosus. Gene. (2024) 927:148713. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.148713
104. Jiang L, Qi A, Yang H, Wang S, Wang F, Bai X, et al. LncRNA SNHG1 serves as a biomarker for systemic lupus erythematosus and participates in the disease progression. Apmis. (2024) 132:507–14. doi: 10.1111/apm.v132.7
105. Zhu X, Chen Y, Yin Z, Zhang Y, Shen Y, Dai D, et al. Novel potential lncRNA biomarker in B cells indicates essential pathogenic pathway activation in patients with SLE. Lupus Sci Med. (2024) 11:e001065. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2023-001065
106. Alrefai AA, Abouelenin MAH, Salman MMA, Tawfeek GAE, Abbas MA. Expression profile of long-noncoding RNAs MIR31HG, NKILA, and PACER in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Clin Biochem. (2024) 126:110734. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2024.110734
107. Wang Y, He J, Ma H, Liu J, Du L, Chai C, et al. NR_103776.1 as a novel diagnostic biomarker for systemic lupus erythematosus. Ir J Med Sci. (2024) 193:211–21. doi: 10.1007/s11845-023-03420-8
108. Cheng Q, Chen M, Chen X, Chen X, Jiang H, Wu H, et al. Novel long non-coding RNA expression profile of peripheral blood mononuclear cells reveals potential biomarkers and regulatory mechanisms in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:639321. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.639321
109. You Y, Zhao X, Wu Y, Mao J, Ge L, Guo J, et al. Integrated transcriptome profiling revealed that elevated long non-coding RNA-AC007278.2 expression repressed CCR7 transcription in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:615859. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.615859
110. Chen X, Luo X, Wei Y, Sun H, Dai L, Tangzhou Y, et al. LncRNA H19 induces immune dysregulation of BMMSCs, at least partly, by inhibiting IL-2 production. Mol Med. (2021) 27:61. doi: 10.1186/s10020-021-00326-y
111. Zhang Y, Xie L, Lu W, Lv J, Li Y, Shao Y, et al. LncRNA MIAT enhances systemic lupus erythematosus by upregulating CFHR5 expression via miR-222 degradation. Cent Eur J Immunol. (2021) 46:17–26. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2021.105242
112. Gao F, Tan Y, Luo H. MALAT1 is involved in type I IFNs-mediated systemic lupus erythematosus by up-regulating OAS2, OAS3, and OASL. Braz J Med Biol Res. (2020) 53:e9292. doi: 10.1590/1414-431x20209292
113. Cao HY, Li D, Wang YP, Lu HX, Sun J, Li HB. Clinical significance of reduced expression of lncRNA TUG1 in the peripheral blood of systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Int J Rheum Dis. (2020) 23:428–34. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13786
114. Liao Z, Ye Z, Xue Z, Wu L, Ouyang Y, Yao C, et al. Identification of renal long non-coding RNA RP11-2B6.2 as a positive regulator of type I interferon signaling pathway in lupus nephritis. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:975. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00975
115. Lu C, Shao X, Zhou S, Pan C. LINC00176 facilitates CD4(+)T cell adhesion in systemic lupus erythematosus via the WNT5a signaling pathway by regulating WIF1. Mol Immunol. (2021) 134:202–9. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2021.02.018
116. Liu X, Lin J, Wu H, Wang Y, Xie L, Wu J, et al. A novel long noncoding RNA lincRNA00892 activates CD4(+) T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus by regulating CD40L. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:733902. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.733902
117. Xue Z, Cui C, Liao Z, Xia S, Zhang P, Qin J, et al. Identification of lncRNA linc00513 containing lupus-associated genetic variants as a novel regulator of interferon signaling pathway. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:2967. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02967
118. Gao X, Liu L, Min X, Jia S, Zhao M. Non-coding RNAs in CD4(+) T cells: new insights into the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:568. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00568
119. Li LJ, Huang Q, Pan HF, Ye DQ. Circular RNAs and systemic lupus erythematosus. Exp Cell Res. (2016) 346:248–54. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.07.021
120. Yu HC, Tseng HH, Huang HB, Lu MC. Circ-CAMTA1 regulated by Ca(2+) influx inhibited pyruvate carboxylase activity and modulate T cell function in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. (2024) 26:185. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03422-6
121. Mei HY, Liu J, Shen XP, Wu R. A novel circRNA, circRACGAP1, hampers the progression of systemic lupus erythematosus via miR-22-3p-mediated AKT signalling. Autoimmunity. (2022) 55:360–70. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2022.2073590
122. Zhao X, Dong R, Zhang L, Guo J, Shi Y, Ge L, et al. N6-methyladenosine-dependent modification of circGARS acts as a new player that promotes SLE progression through the NF-κB/A20 axis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2022) 24:37. doi: 10.1186/s13075-022-02732-x
123. He S, Du H, Wang Y, Shi X, Zhou Y. Hsa_circ_0010957 level is increased and sponges microRNA−125b in CD4(+) T cells of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol Med Rep. (2021) 23:469. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12108
124. Zheng F, Tan L, Zhang F, Li S, Lai Z, Xu H, et al. The circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells and the potential associations with the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. (2023) 42:1885–96. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06560-5
125. Zou H, Ma S, Li L, Xia X, Zhou Y, Zhang R. Downregulation of circular RNA ETS1 promotes SLE activity and inhibits Treg cell differentiation through miR-1205/FoxP3 molecular axis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 128:111539. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111539
126. Yao R, Xu L, Cheng G, Wang Z, Liang R, Pei W, et al. Elevated expression of hsa_circ_0000479 in neutrophils correlates with features of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Med. (2024) 56:2309607. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2309607
127. Ouyang Q, Huang Q, Jiang Z, Zhao J, Shi GP, Yang M. Using plasma circRNA_002453 as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of lupus nephritis. Mol Immunol. (2018) 101:531–8. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2018.07.029
128. Luo Q, Ye Y, Zhang L, Gao Y, Rao J, Guo Y, et al. Hsa_circ_0044235 and hsa_circ_0001947 as novel biomarkers in plasma of patients with new-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunotoxicol. (2023) 20:2196453. doi: 10.1080/1547691X.2023.2196453
129. Luo Q, Zhang L, Li X, Fu B, Guo Y, Huang Z, et al. Identification of circular RNAs hsa_circ_0044235 and hsa_circ_0068367 as novel biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Mol Med. (2019) 44:1462–72. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4302
130. Luo Q, Li X, Fu B, Zhang L, Fang L, Qing C, et al. Expression profile and diagnostic value of circRNAs in peripheral blood from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol Med Rep. (2021) 23:1. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11639
131. Luo Q, Zhang L, Xiong L, Fu B, Guo Y, Huang Z, et al. Peripheral blood circular RNA hsa_circ_0082688-hsa_circ_0008675 can be used as a candidate biomarker of systemic lupus erythematosus with renal involvement. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2020) 38:822–33.
132. Li S, Zhang J, Tan X, Deng J, Li Y, Piao Y, et al. Microarray expression profile of circular RNAs and mRNAs in children with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. (2019) 38:1339–50. doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-4392-8
133. Jiang Z, Li S, Jia Y, Wu Q, Chen X, Zhang M, et al. CircPTPN22 modulates T-cell activation by sponging miR-4689 to regulate S1PR1 expression in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. (2023) 25:206. doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03150-3
134. Miao Q, Zhong Z, Jiang Z, Lin Y, Ni B, Yang W, et al. RNA-seq of circular RNAs identified circPTPN22 as a potential new activity indicator in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. (2019) 28:520–8. doi: 10.1177/0961203319830493
135. Zhao X, Dong R, Tang Z, Wang J, Wang C, Song Z, et al. Circular RNA circLOC101928570 suppresses systemic lupus erythematosus progression by targeting the miR-150-5p/c-myb axis. J Transl Med. (2022) 20:547. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03748-2
136. Li W, Fan R, Zhou C, Wei Y, Lin S, Wen S, et al. Circular RNA expression profile of systemic lupus erythematosus and its clinical significance as a potential novel biomarker. Genes Genomics. (2022) 44:1405–14. doi: 10.1007/s13258-022-01315-z
137. Zheng F, Yu X, Tang D, Hong X, Zhang X, Liu D, et al. The identification of circular RNAs from peripheral blood mononuclear cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. BMC Med Genomics. (2021) 14:70. doi: 10.1186/s12920-021-00919-w
138. Guo G, Wang H, Ye L, Shi X, Yan K, Lin K, et al. Hsa_circ_0000479 as a novel diagnostic biomarker of systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:2281. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02281
139. Luo Q, Zhang L, Fang L, Fu B, Guo Y, Huang Z, et al. Circular RNAs hsa_circ_0000479 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells as novel biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmunity. (2020) 53:167–76. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2020.1728529
140. Zhang C, Wang X, Chen Y, Wu Z, Zhang C, Shi W. The down-regulation of hsa_circ_0012919, the sponge for miR-125a-3p, contributes to DNA methylation of CD11a and CD70 in CD4(+) T cells of systemic lupus erythematous. Clin Sci (Lond). (2018) 132:2285–98. doi: 10.1042/CS20180403
141. Zhang C, Gao C, Di X, Cui S, Liang W, Sun W, et al. Hsa_circ_0123190 acts as a competitive endogenous RNA to regulate APLNR expression by sponging hsa-miR-483-3p in lupus nephritis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2021) 23:24. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-02404-8
142. Yang Y, Hsu PJ, Chen YS, Yang YG. Dynamic transcriptomic m(6)A decoration: writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism. Cell Res. (2018) 28:616–24. doi: 10.1038/s41422-018-0040-8
143. Shulman Z, Stern-Ginossar N. The RNA modification N(6)-methyladenosine as a novel regulator of the immune system. Nat Immunol. (2020) 21:501–12. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0650-4
144. Han D, Liu J, Chen C, Dong L, Liu Y, Chang R, et al. Anti-tumour immunity controlled through mRNA m(6)A methylation and YTHDF1 in dendritic cells. Nature. (2019) 566:270–4. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0916-x
145. Deng LJ, Fang XY, Wu J, Li QR, Mao YM, Leng RX, et al. ALKBH5 expression could affect the function of T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus patients: A case-control study. Curr Pharm Des. (2022) 28:2270–8. doi: 10.2174/1381612828666220617154204
146. Liu Y, Wang X, Huang M, Luo A, Liu S, Cai M, et al. METTL3 facilitates kidney injury through promoting IRF4-mediated plasma cell infiltration via an m6A-dependent manner in systemic lupus erythematosus. BMC Med. (2024) 22:511. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03735-y
147. Tian Y, Tao K, Li S, Chen X, Wang R, Zhang M, et al. Identification of m6A-related biomarkers in systemic lupus erythematosus: A bioinformation-based analysis. J Inflammation Res. (2024) 17:507–26. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S439779
148. Zhao H, Pan S, Duan J, Liu F, Li G, Liu D, et al. Integrative analysis of m(6)A regulator-mediated RNA methylation modification patterns and immune characteristics in lupus nephritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:724837. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.724837
149. Luo Q, Rao J, Zhang L, Fu B, Guo Y, Huang Z, et al. The study of METTL14, ALKBH5, and YTHDF2 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol Genet Genomic Med. (2020) 8:e1298. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1298
150. Zhao M, Zhou Y, Zhu B, Wan M, Jiang T, Tan Q, et al. IFI44L promoter methylation as a blood biomarker for systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. (2016) 75:1998–2006. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208410
151. Zhang Bo, Liu L, Zhou T, Shi X, Wu H, Xiang Z, et al. A simple and highly efficient method of IFI44L methylation detection for the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol. (2020) 221:108612. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108612
Keywords: epigenetics, systemic lupus erythematosus, DNA methylation, histone modification, noncoding RNAs, RNA methylation, biomarkers
Citation: Zhou X, Zhou S and Li Y (2025) An updated review on abnormal epigenetic modifications in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 15:1501783. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1501783
Received: 25 September 2024; Accepted: 09 December 2024;
Published: 06 January 2025.
Edited by:
Chris Wincup, King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, United KingdomReviewed by:
Chunshu Yang, The First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, ChinaJun Xue, Fudan University, China
Shangqing Ge, First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhou, Zhou and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yaping Li, bHlwbGlzYUBjc3UuZWR1LmNu
†These authors share first authorship
 Xingyu Zhou
Xingyu Zhou Shengnan Zhou
Shengnan Zhou Yaping Li
Yaping Li