- 1Department of Liver Surgery, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, China
- 2Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, China
- 3Guangdong Provincial Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, China
Background: Systemic chemotherapy (SC) stands the only first-line treatment for advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA) for the past few decades. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have been proved to provide additional benefit in disease control. However, oncological outcome of iCCA remains poor and awaits further improvement with new treatment modalities. Promising results have been observed in lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab (Len-P) as a second-line therapy in iCCA. This study aimed to explore the safety and efficacy of Len-P as a first-line therapy for iCCA patients in real-world clinical practice.
Methods: We retrospectively enrolled 133 patients with advanced iCCA who received Len-P or SC between May 2019 and May 2023. Overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), and adverse events (AEs) were compared between the two groups.
Results: There were 72 patients and 61 patients in the Len-P and SC groups, respectively. The median OS for the Len-P and SC groups was 16.3 and 17.8 months, respectively. The median PFS for the Len-P and SC groups was 8.9 and 11.4 months, respectively. There was no significant difference in ORR and DCR between the Len-P and SC groups (ORR: 22.2% vs. 23%; P=0.92; DCR: 69.4% vs. 77%; P=0.58). Additionally, the overall incidence of AEs was lower in the Len-P group than SC group. Low inflammation-based scores were indicative of favorable outcomes in patients undergoing Len-P therapy.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that Len-P is promising for the treatment of advanced ICC, with highly improved safety. It emerges as a viable treatment alternative for advanced iCCA. Inflammation-based scores show potential utility in identifying individuals likely to benefit from Len-P therapy.
Introduction
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA), the second most common primary liver cancer, is characterized by surreptitious presentation, aggressive progression, and unfavorable prognosis (1–3). Recent data indicates a concerning rise in the annual incidence rate of iCCA in China, with an average annual increase of 11.1% (4). Complete surgical resection is currently the only potential curative treatment for iCCA, however, approximately 70-80% of patients are deemed tumor unresectable due to an advanced stage at diagnosis (5). Thus, there is a critical need for effective systemic treatments.
Currently, the first-line chemotherapy regimen for patients with advanced biliary tract cancers (BTCs) is gemcitabine with cisplatin (GEMCIS), which has a modest median overall survival (OS) of 11.7 months and median progression-free survival (PFS) of 8.0 months (6). Similarly, gemcitabine with oxaliplatin (GEMOX) manifests comparable efficacy for the treatment of BTCs (7, 8). However, gemcitabine-based chemotherapy is associated with a high incidence of adverse events, especially hematological toxicities, significantly hampering patient tolerance (9).
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), targeting programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) and programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) has shifted the treatment paradigm for hepatobiliary malignancies. Combining ICIs with standard chemotherapy has emerged as a promising strategy, enhancing clinical outcomes in patients with advanced BTCs. For instance, in the TOPAZ-1 phase 3 trial, patients who received GEMCIS along with durvalumab, a PD-L1 inhibitor, exhibited a statistically significant improvement in OS compared to those treated with GEMCIS and placebo (10). This finding established the combination of GEMCIS with durvalumab as the standard-of-care first-line treatment for advanced BTCs (1, 11). Meanwhile, various real-world studies demonstrated that immunotherapy enhanced the outcomes in patients with iCCA (12–14). Moreover, another phase 3 trial, KEYNOTE-966, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study, examined the combination therapy of pembrolizumab, a PD-1 inhibitor, with systemic chemotherapy. The combination of GEMCIS with pembrolizumab significantly improved the median OS of patients compared to the GEMCIS with the placebo group, with median OS values of 12.7 months vs. 10.9 months, demonstrating its clinical impact in improving patient outcomes (15). Despite these advances, the tolerability and effectiveness of combination therapies are often limited by chemotherapy-related adverse events (AEs), highlighting the need for alternative first-line treatments for advanced iCCA.
Lenvatinib, a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor, interferes with multiple oncogenic signaling pathways including vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) 1-3 and fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) 1-4 (16) and has demonstrated its ability to improve therapeutic outcomes across various solid tumors (17). In iCCA preclinical studies, lenvatinib has been proven to exert antitumor effects through cancer cell signaling pathways and the tumor microenvironment (18, 19). A recent phase 2 trial demonstrated that toripalimab plus lenvatinib and GEMOX are promising first-line regimens for the treatment of advanced iCCA. The median OS and PFS were 22.5 and 10.2 months, respectively (20). Preclinical studies have also suggested that lenvatinib may enhance the antitumor effects of PD-1 inhibitor immunotherapy (21, 22). This combination strategy has attracted interest due to its potential to balance efficacy with a more manageable safety profile. However, there is a lack of real-world evidence to support this combination treatment.
Given the therapeutic potential of this treatment, and the need to better understand patient subgroups that would benefit, our study focuses on evaluating the safety and efficacy of Len-P vs. standard systemic chemotherapy (GEMCIS and GEMOX, SC) in patients with iCCA. We aim to identify potential biomarkers for predicting the efficacy of this combination therapy, based on preliminary evidence suggesting that inflammatory markers such as the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), lymphocyte-to-C-reactive protein ratio (LCR), lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR), systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), and prognostic nutritional index (PNI) may serve as predictive indicators for Len-P treatment response (23).
Materials and methods
Patients
This retrospective study included a cohort of 133 patients diagnosed with iCCA, who underwent initial treatment with Len-P or first-line SC at Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, China, from May 2019 to May 2023. Patients meeting the following criteria were eligible for inclusion: aged 18 years or older; histopathological confirmation of iCCA; initial treatment with Len-P or first-line SC; and an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS) score of 2 or lower. Patients were excluded based on the following exclusion criteria: prior or existing malignancies; unassessable lesions before treatment; absence of monitoring; Child-Pugh class C before treatment; less than two cycles of Len-P; missing medical records; alternative systemic chemotherapy; receiving other therapies, and treated as second-line or later. These criteria are shown in Figure 1. The retrospective analysis received approval from the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of our cancer center.
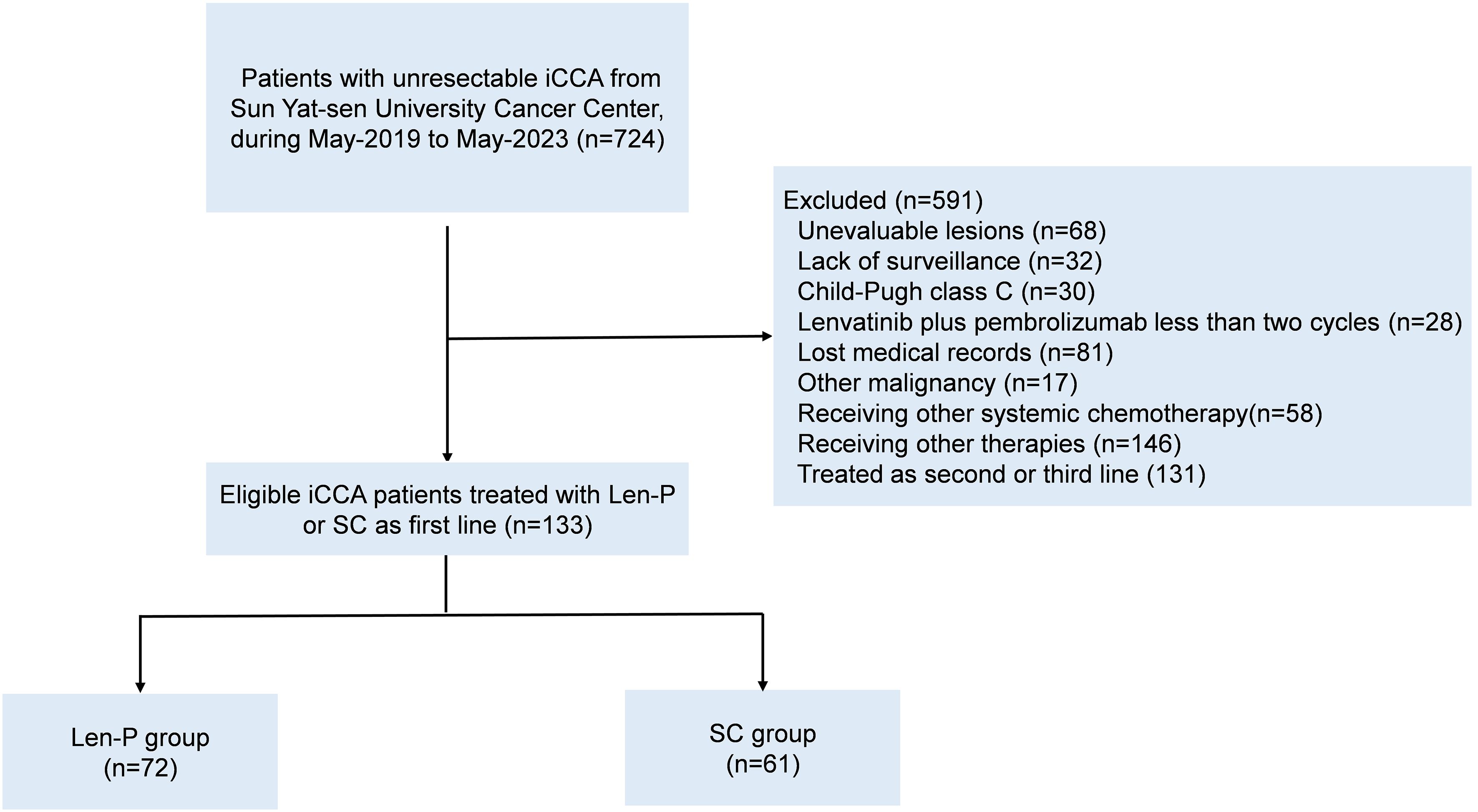
Figure 1. Flowchart for patient inclusion. Abbreviations: iCCA, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; Len-P, lenvatinib-pembrolizumab; SC, systemic chemotherapy.
Treatment procedures
Patients were administered a combination regimen of pembrolizumab and lenvatinib. Those with a body weight less than 60 kg received a daily dose of 8 mg of lenvatinib, whereas those weighing 60 kg or more received a daily dose of 12 mg. Pembrolizumab was administered intravenously at a dosage of 200 mg once every three weeks. GEMCIS and GEMOX were used as first-line chemotherapy regimens. In the GEMCIS cohort, each treatment cycle consisted of cisplatin (25 mg per square meter of body surface area (BSA)) followed by gemcitabine (1000 mg per square meter of BSA), administered on days 1 and 8 every three weeks. In the GEMOX cohort, each cycle included oxaliplatin (85 per square meter of BSA) on day 1 and gemcitabine (1000 per square meter of BSA) on days 1 and 8 every three weeks. Treatment with systemic chemotherapy was discontinued at 24 weeks or in the case of disease progression, intolerable adverse effects, or patient preference. The administration and potential cessation due to adverse effects was directed by the drug manufacturer’s prescribing instructions.
Data collection
All data were sourced from the medical archives of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center. Demographic and clinical parameters included: age, gender, ECOG PS, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine transaminase (ALT), albumin (ALB), total bilirubin (TBIL), carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9), carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), white blood cell count (WBC), platelet count (PLT), hemoglobin (HGB), largest tumor size, tumor number, macroscopic vascular invasion, lymph node metastasis, extra-hepatic metastasis, tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) staging, NLR, LCR, LMR, SII, and PNI. The hematological assessments and tumor burdens were determined within 5 days before initial treatment. The NLR, LCR, LMR, SII, and PNI were computed per the methods outlined in Supplementary Table S1. Radiographic response was assessed via magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) conducted at baseline and, after treatment initiation, every 6 weeks. The Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) 1.1, including complete response (CR), partial response (PR), stable disease (SD), and progressive disease (PD), was used to evaluate tumor response (24).
The primary endpoints in this study were overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS). OS was defined as the duration spanning from the initiation of treatment to cancer-related death. PFS was characterized as the time from initial treatment to disease advancement, iCCA recurrence, the event of death attributable to iCCA, or the most recent follow-up date. The secondary endpoints encompassed the objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), and incidence of treatment-related adverse events (AEs). ORR was specified as the proportion of patients achieving either CR or PR, with a requisite minimum duration of 4 weeks from the initial radiographic verification. DCR was defined as the combination of ORR and the ratio of patients exhibiting SD. Adverse events were evaluated as per CTCAE version 5.0.
Statistical analysis
Non-normally distributed data were represented asmedians and ranges. Continuous parametric variables were analyzed with the unpaired Student’s t-test, while continuous non-parametric variables were analyzed using the Mann–Whitney U test. Categorical data were evaluated using Pearson’s correlation coefficient chi-square test with continuity correction or Fisher’s exact probability method. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses based on the Forward LR method were executed to identify independent predictive variables. To ensure consistency in the cutoff values of prognostic scores within the cohort, the optimal cutoff point for single value indicators such as NLR, LCR, LMR, SII, and PNI was determined utilizing R version 4.0.1 (Supplementary Figures S1A–E). OS and PFS were presented through Kaplan-Meier curves, and inter-group disparities were assessed using the log-rank test results. Statistical significance was at a P value < 0.05. All statistical analyses were carried out using SPSS 25.0 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL) and R version 4.0.1.
Results
Patient characteristics
During the period spanning from May 2019 to May 2023, a total of 133 patients with iCCA underwent initial treatment with Len-P or first-line SC were retrospectively enrolled at Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center in China. Among them, 72 patients were enrolled in the Len-P group, while 61 patients comprised in the SC group, as depicted in Figure 1. Detailed demographic characteristics of each group are presented in Table 1. There were no significant baseline characteristics observed between the Len-P and SC groups. In the Len-P group, the average age was 55.9 years, with 40 male patients. The mean size of the largest tumor was 7 cm. Most patients presented with multiple tumors (77.8%), 26 individuals (36.1%) exhibited macrovascular invasion, 58 patients (80.6%) had lymph node metastasis, and 30 patients (41.7%) had extra-hepatic metastasis. In the SC group, the mean age was 56.1 years old and 33 patients were male. The mean largest tumor size was 6.9 cm, most patients had multiple tumors (68.9%), 17 patients (27.9%) had macrovascular invasion, 42 patients (68.9%) had lymph node metastasis, and 22 patients (36.1%) had extra-hepatic metastasis. Based on tumor characteristics, the majority of patients in this study presented with a substantial tumor burden and had advanced iCCA. Several systemic inflammatory markers, including NLR, LCR, LMR, SII, and PNI were analyzed. There were no significant differences between the two groups.
Univariate and multivariable Cox regression analyses
Prognostic factors of all clinical variables were subjected to univariate analysis. The univariate analyses found that ECOG PS, CA19-9, CEA, NLR, LCR, LMR, PNI, macrovascular invasion, and extra-hepatic metastasis were significant risk determinants for OS across all patients. PFS analysis identified ECOG PS, CEA, LCR, macrovascular invasion, and extra-hepatic metastasis as noteworthy risk factors. Further details are outlined in Table 2. Subsequent multivariate Cox proportional analysis underscored the significance of CEA (P=0.014), LCR (P<0.001), macrovascular invasion (P=0.001), and extra-hepatic metastasis (P=0.003) as autonomous prognostic indicators of OS (Table 2). The multivariate Cox proportional analysis also identified ECOG PS (P=0.001) and CEA (P=0.009) as significant and autonomous prognostic elements for PFS (Table 2).
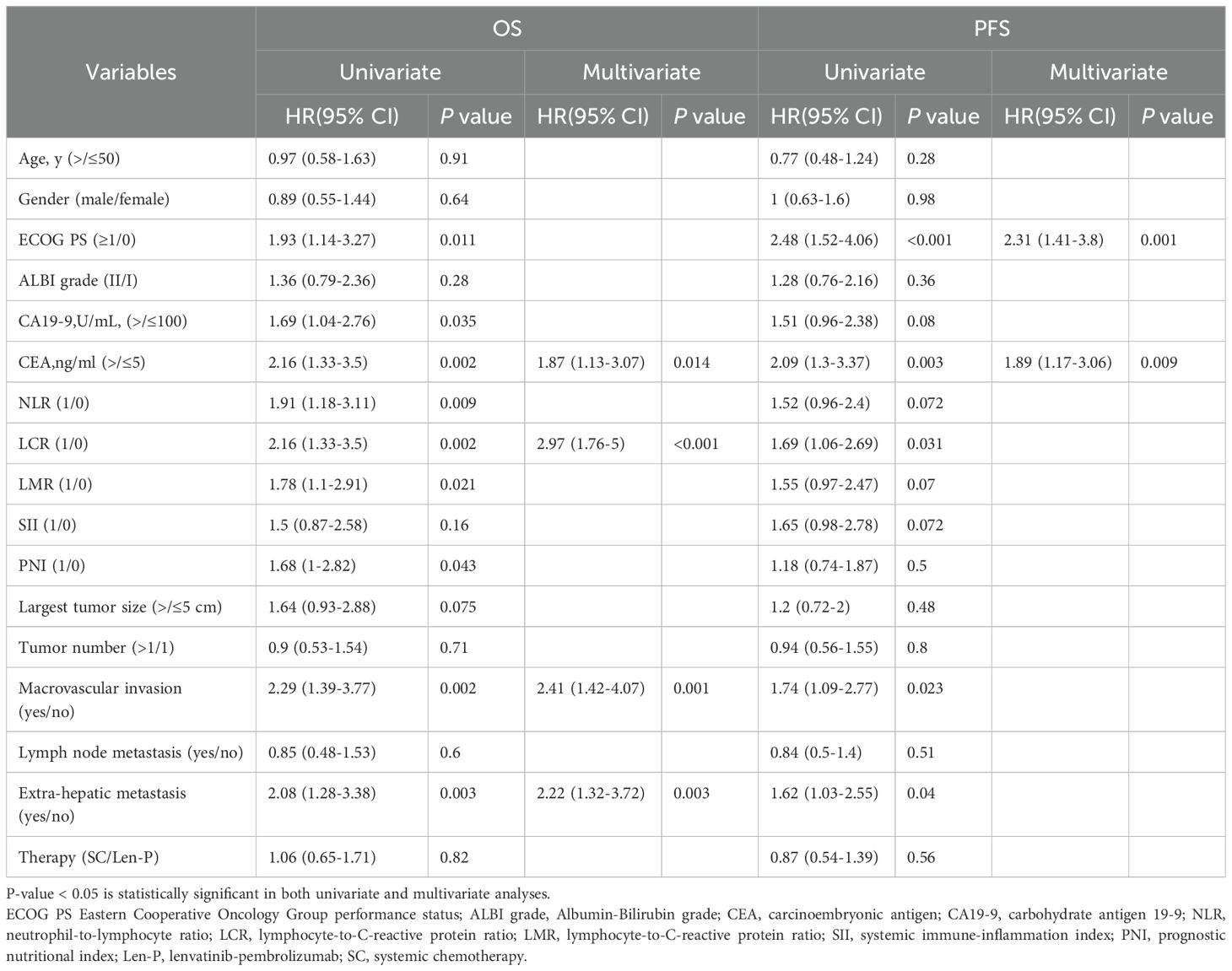
Table 2. Univariate and multivariate cox regression analyses of risk factors for overall survival and progression free survival in all patients.
Patient survival and tumor response
The median OS for the Len-P and SC groups was 16.3 and 17.8 months, respectively. The median PFS for the Len-P and SC groups was 8.9 and 11.4 months, respectively. Noteworthy improvements in OS were seen in patients with positive tumor response (CR and PR) in contrast to non-responders (SD and PD) (P = 0.0014; Figure 2A). Furthermore, responders (CR and PR) had a prolonged PFS compared to non-responders (SD and PD) (P < 0.0001; Figure 2B). No significant differences were observed between the Len-P and SC groups concerning OS (P=0.83; Figure 2C) and PFS (P=0.57; Figure 2D). The median follow-up duration for the Len-P group and SC group was 22.6 months and 19.7 months, respectively. Patients in the SC group were stratified into two subgroups (GEMCIS and GEMOX). Comparative analyses of GEMCIS and GEMOX against Len-P were conducted in regard to OS and PFS (Supplementary Figure S2).
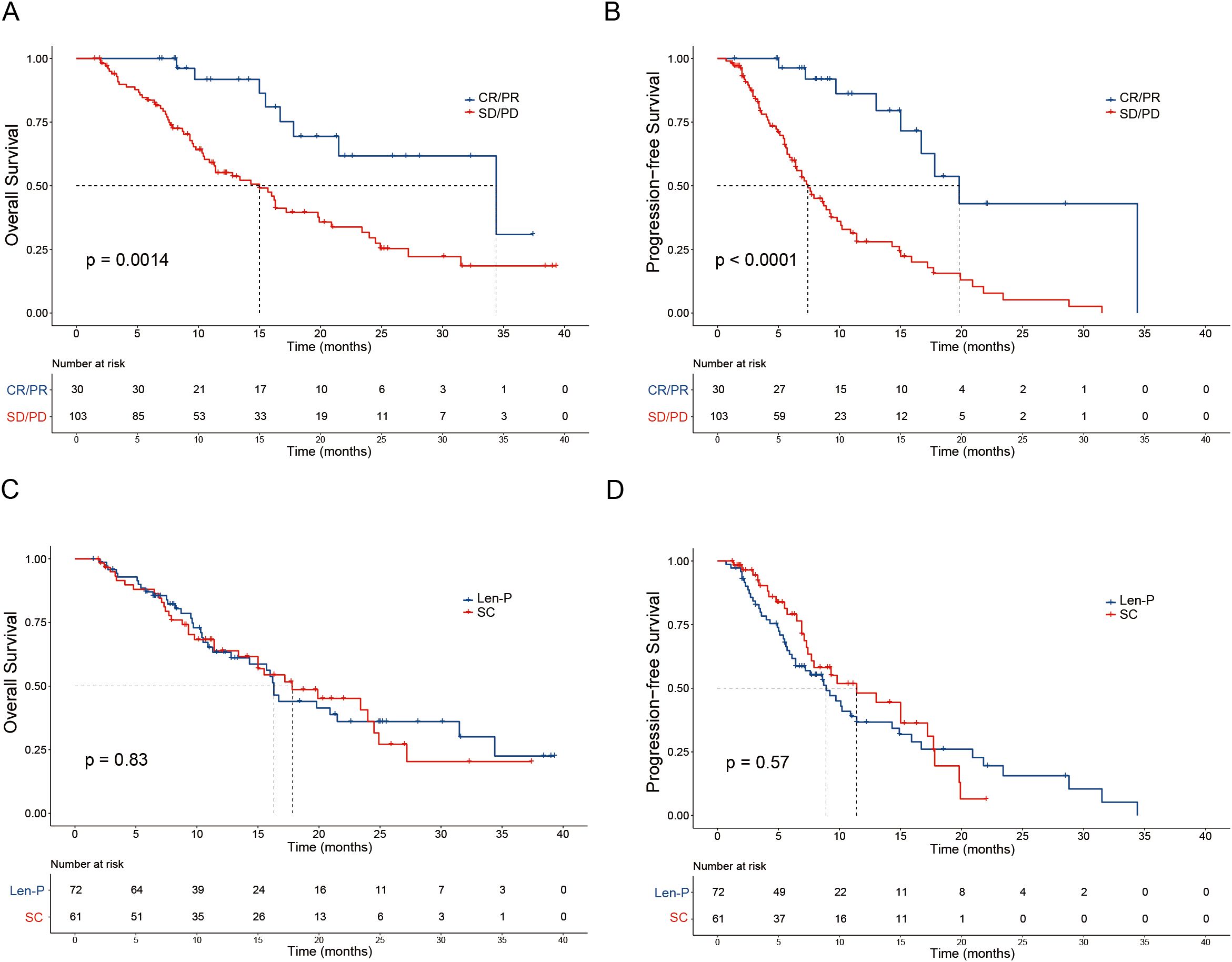
Figure 2. Patient survival was shown by the Kaplan–Meier curves. The overall survival (A) and progression-free survival (B) in patients with tumor response (CR/PR vs SD/PD) according to RECIST1.1 criteria. The overall survival (C) and progression-free survival (D) in patients treated with Len-P versus SC. p values were assessed using the log-rank test. RECIST1.1, Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors 1.1; CR, complete response; PR, partial response; SD, stable disease; PD, progressive disease; Len-P, lenvatinib-pembrolizumab; SC, systemic chemotherapy.
The subgroup analyses for OS and PFS are presented in Figures 3A, B. Len-P conferred comparable clinical benefit in terms of both OS and PFS across the various subgroups when compared to SC. The tumor responses of the patients are detailed in Table 3. According to RECIST 1.1 criteria, there was no significant difference in ORR and DCR between the Len-P and SC group (ORR: 22.2% vs 23%; P=0.92; DCR: 69.4% vs 77%; P=0.58). The optimal response for intra-hepatic target lesions by RECIST1.1 criteria is illustrated in the waterfall plot in Figure 4.
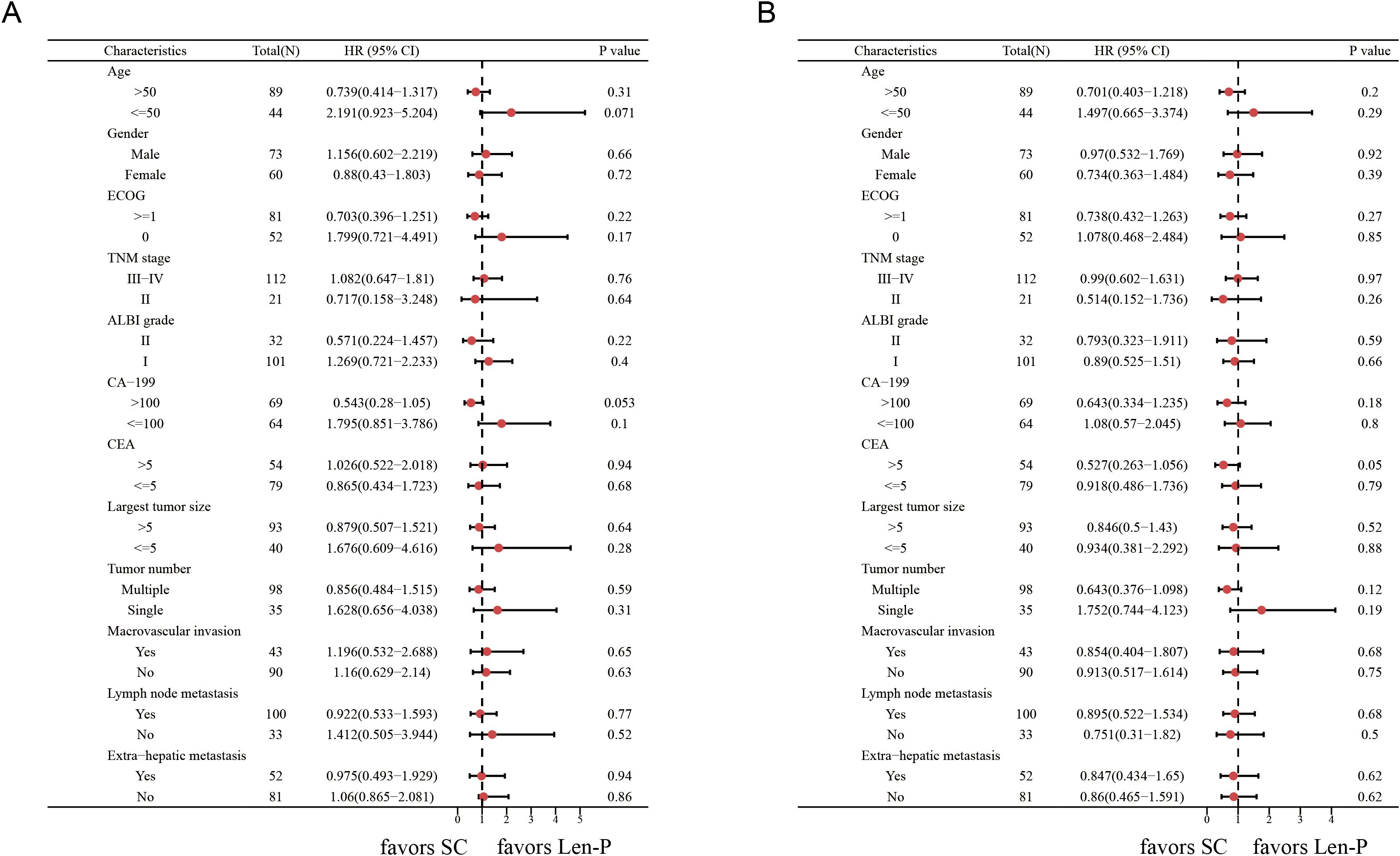
Figure 3. Forest plots of (A) overall survival and (B) progression-free survival in different patient subgroups. p values were assessed using the log-rank test. HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; ECOG, hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy; TNM, tumor-node-metastasis; ALBI grade, Albumin-Bilirubin grade; CA19-9, carbohydrate antigen 19-9; CEA, carcinoembryonic antigen. Len-P, lenvatinib-pembrolizumab; SC, systemic chemotherapy.
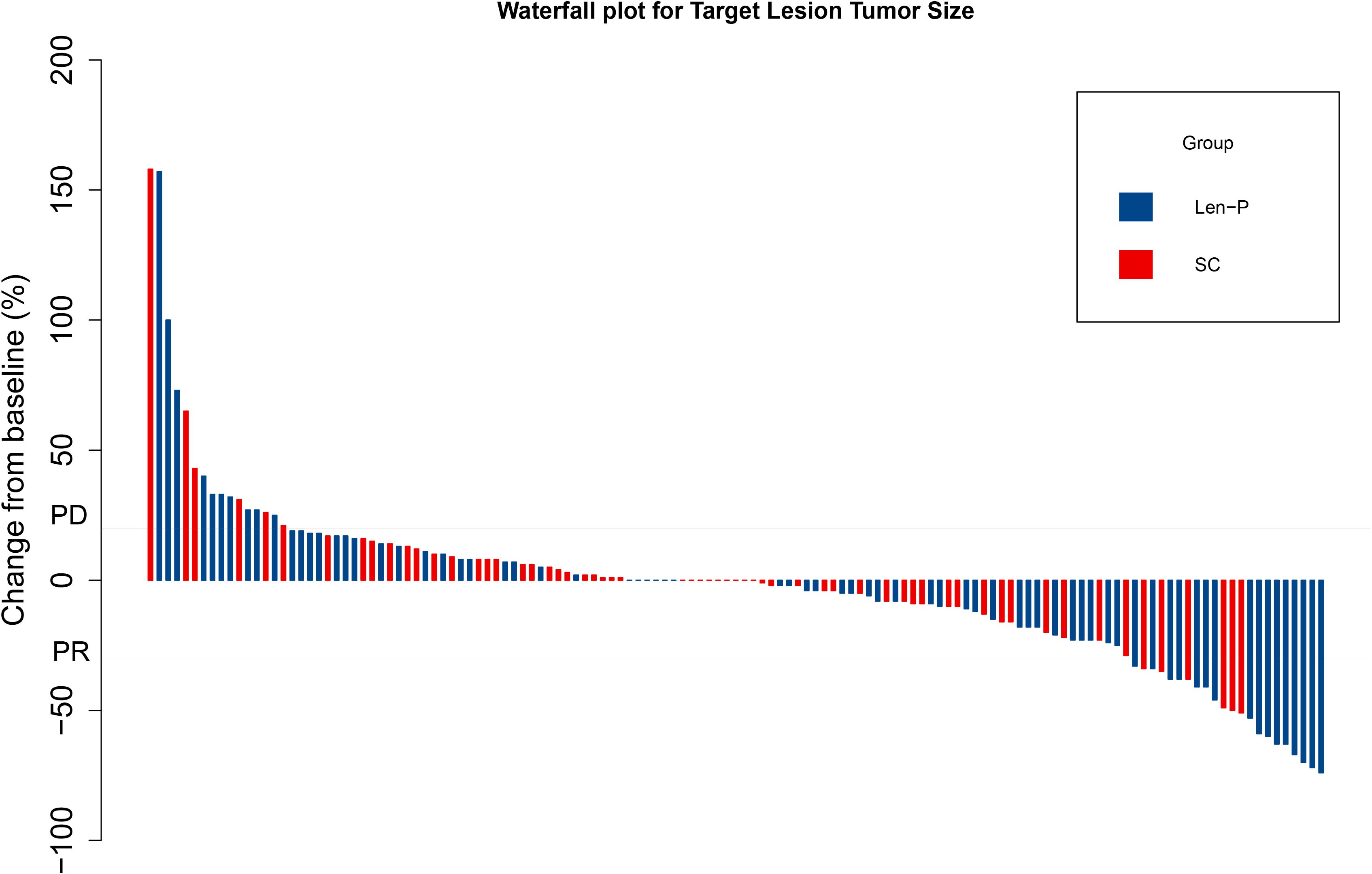
Figure 4. Waterfall plot for tumor size changes of intra-hepatic target lesions. PD, progressive disease; PR, partial response. Len-P, lenvatinib-pembrolizumab; SC, systemic chemotherapy.
Safety
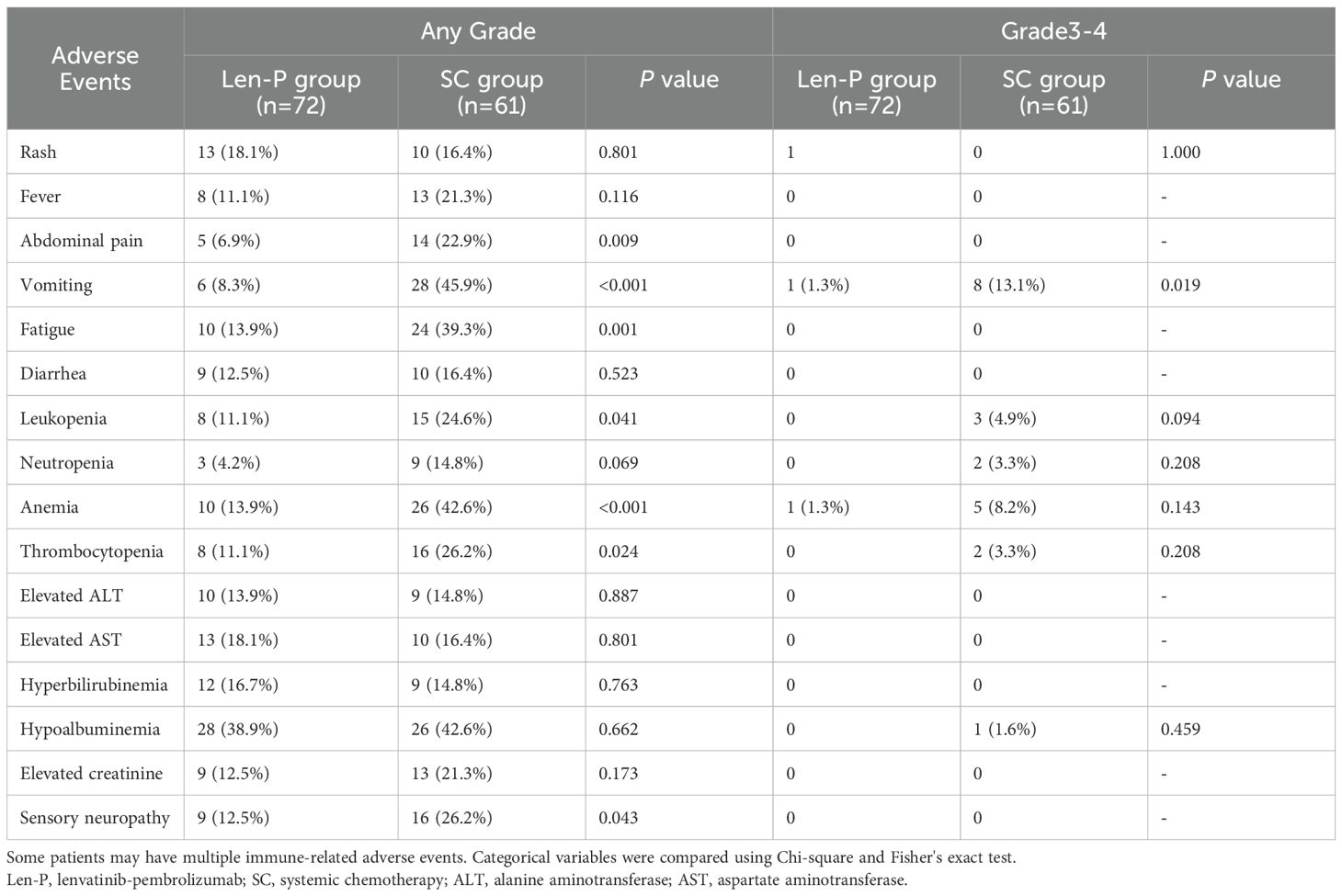
SC led to a higher frequency of AEs in comparison to Len-P, as shown in Table 4. The following AEs exhibited lower prevalence in the Len-P compared to SC group: abdominal pain (5 (6.9%) vs. 14 (22.9%); P=0.009), vomiting (6 (8.3%) vs. 28 (45.9%); P<0.001), fatigue (10 (13.9%) vs. 24 (39.3%); P=0.001), leukopenia (8 (11.1%) vs. 15 (24.6%); P=0.041), anemia (10 (13.9%) vs. 26 (42.6%); P<0.001), thrombocytopenia (8 (11.1%) vs. 16 (26.2%); P=0.024), and sensory neuropathy (9 (12.5%) vs. 16 (26.2%); P=0.043). A notable difference was found in the overall occurrence of severe AEs, which was higher in the SC group than in the Len-P group. In the Len-P cohort, treatment discontinuation due to adverse events occurred in 4 patients (5.6%), while in the SC cohort, this number was 8 patients (13.1%). All adverse events were effectively managed, and no mortality attributable to treatment toxicity was reported in the follow-up period.
Inflammation-based scores analysis for Len-P group
In the Len-P group, the univariate analyses revealed that inflammation-based scores, including NLR, LCR, LMR, SII, and PNI emerged as significant risk factors impacting OS. The multivariate Cox proportional analysis particularly emphasized the roles of NLR (P=0.045) and LMR (P=0.011) as independent and significant prognostic determinants for OS (Supplementary Table S2). All inflammation-based scores were associated with OS outcomes of patients undergoing Len-P treatment. Specifically, low NLR (P=0.0021), LCR (P=0.00018), LMR (P=0.00026), SII (P=0.006), and PNI (P=0.028) scores were indicative of favorable prognoses (Supplementary Figures S3A–E).
Discussion
The application of pembrolizumab in conjunction with lenvatinib for iCCA has not been thoroughly evaluated within a real-world context previously. In this study, we scrutinized the application of this therapeutic modality in a retrospective real-world cohort, with a specific emphasis on efficacy and safety relative to first-line SC, and identifying patients who may experience an enhanced benefit. We validated the efficacy and safety of the combined therapy as a viable option for patients with advanced iCCA. The strengths of this current study lie in (1) the incorporation of an expanded real-world study cohort in China comprising a total of 133 patients (Len-P vs. SC: 72 vs 61), (2) the implementation of comprehensive outcome subgroup analyses to identify subpopulations that may benefit from screening, and (3) the documentation of long- and short-term treatment outcomes for patients with advanced iCCA undergoing either Len-P or standard chemotherapy.
iCCA is a gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma characterized by a high degree of malignancy and a poor prognosis. Most iCCA patients are ineligible for surgical intervention due to the advanced stage of the disease, leading to the administration of SC to manage tumor progression. In recent years, GEMCIS and GEMOX have emerged as the established first-line chemotherapy regimens (6, 25, 26). Nevertheless, the presence of adverse events presents a challenge for the use of SC. There is a need for a treatment regimen that reduces the occurrence of adverse events while attaining similar survival outcomes.
In the current study of 133 patients, we compared Len-P with first-line SC (GEMCIS and GEMOX) and found that the median OS for the Len-P and SC groups was 16.3 and 17.8 months, respectively (P=0.83), and the median PFS was 8.9 and 11.4 months, respectively (P=0.57). According to RECIST 1.1 criteria, there was no significant difference in ORR and DCR between the Len-P and SC group (ORR: 22.2% vs. 23%; P=0.92; DCR: 69.4% vs. 77%; P=0.58). These findings indicate that Len-P exhibited comparable clinical efficacy to SC in patient outcomes.
Our efficacy data aligns with previous research. In a phase II study of toripalimab combined with lenvatinib as first-line therapy for 31 patients with advanced iCCA, the median OS and PFS were recorded at 22.5 months and 10.2 months, respectively (20). KEYNOTE-966 investigated pembrolizumab in combination with GEMCIS for BTC patients, and found a median OS of 12.7 months (95% CI 11.5–13.6) in the pembrolizumab cohort (15). Furthermore, the phase II LEAP-005 trial evaluated lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab as a second-line regimen for 31 advanced BTC patients, and found a median PFS of 6.1 months, median OS of 8.6 months, ORR of 10%, and DCR of 68% (27). Together, these results provide robust backing for the effectiveness of Len-P in treating advanced iCCA. Len-P is a viable first-line treatment option, especially for patients who cannot tolerate or refuse chemotherapy. To further support our conclusions, prospective randomized controlled clinical trials are needed.
Safety serves as a crucial benchmark in assessing a treatment regimen beyond therapeutic efficacy. Generally, there was a lower incidence of AEs in the Len-P cohort compared to the SC cohort. Abdominal pain, vomiting, fatigue, leukopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and sensory neuropathy were less frequent in the Len-P cohort. Likewise, the prevalence of grade 3–4 adverse events was diminished in the Len-P cohort. In SC cohort, to achieve the desired effect of tumor eradication, the concentration of the drug may reach a level that induces damage to body systems, resulting in AEs. These AEs are typically severe and effective management is challenging. Thus, Len-P emerges as a potentially safe and efficacious therapeutic regimen for patients with advanced iCCA.
To identify the population of patients with the greatest benefit from Len-P, we conducted univariate and multivariable Cox regression analyses. Our study revealed that inflammation-based scores were reliable indicators for predicting the effectiveness of Len-P in patients with iCCA. The etiology of iCCA overlaps with that of primary sclerosing cholangitis, primary biliary cirrhosis, and other conditions characterized by biliary tract inflammation and fibrosis (28). Inflammation plays a pivotal role in the initiation and progression of iCCA (29). Mounting evidence indicates a correlation between the inflammatory environment and response to PD-1 inhibitors in advanced malignancies, including iCCA (23, 30–35). Inflammatory markers could have utility in identifying individuals who are likely to respond better to Len-P therapy.
This study has some limitations. Firstly, the retrospective approach exposes the study to potential selection biases. Its retrospective nature limits us to performing statistical analyses to compare for statistical differences (i.e., P < 0.05), and ultimately, we still need to interpret the significance in conjunction with the clinical context. Therefore, a prospective, multicenter, randomized controlled trial is essential to corroborate our findings. Secondly, the retrospective methodology may have led to an incomplete evaluation of adverse occurrences, despite our thorough examination of the clinical records. Thirdly, the execution of multiple subgroup analyses may have led to a reduction in the sample size and reduce statistical power, necessitating cautious interpretation of the conclusions. Finally, further laboratory studies are warranted to elucidate the fundamental mechanisms underpinning the efficacy of Len-P in patients with iCCA.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that Len-P is a promising and safe therapeutic modality for patients with advanced iCCA. It is a viable treatment alternative to SC for advanced iCCA. Inflammatory-based scores have potential utility in identifying individuals more likely to respond well to Len-P therapy.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Institutional Review Board of the Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
ZY: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. WW: Writing – original draft. ZWH: Writing – original draft. YF: Writing – original draft. ZLH: Writing – original draft. YP: Writing – original draft. JW: Writing – original draft. JC: Writing – original draft. ZZ: Writing – review & editing. YZ: Writing – review & editing. MC: Writing – review & editing. DH: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No: 82103566), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2022A1515110961 to JW), Guangzhou Science and Technology Plan Project (2023A04J2125 to JW), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No: 2023M744018 to YF), the Postdoctoral Fellowship Program of CPSF (No. GZC20233219 to YF).
Acknowledgments
Authors thank Bullet Edits Limited for the linguistic editing and proofreading of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1494520/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | Schematic of the method used to determine the optimal cutoff points of NLR, LCR, LMR, SII, and PNI using R version for survival prediction. NLR, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; LCR, lymphocyte-to-C-reactive protein ratio; LMR, lymphocyte-to-C-reactive protein ratio; SII, systemic immune-inflammation index; PNI, prognostic nutritional index.
Supplementary Figure 2 | The overall survival and progression-free survival of the two groups of patients. Kaplan-Meier curves of (A) overall survival and (B) progression-free survival for patients in the Len-P, GEMCIS and GEMOX groups. p values were assessed using the log-rank test. Len-P, lenvatinib-pembrolizumab; GEMCIS, gemcitabine plus cisplatin; GEMOX, oxaliplatin plus gemcitabine.
Supplementary Figure 3 | Kaplan–Meier curves of the overall survival of iCCA patients after Len-P therapy. (A) NLR (B) LCR, (C) LMR, (D) SII, and (E) PNI. p values were assessed using the log-rank test. iCCA, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; NLR, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; LCR, lymphocyte-to-C-reactive protein ratio; LMR, lymphocyte-to-C-reactive protein ratio; SII, systemic immune-inflammation index; PNI, prognostic nutritional index.
References
1. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL-ILCA Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatol. (2023) 79:181–208. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.03.010
2. Moris D, Palta M, Kim C, Allen PJ, Morse MA, Lidsky ME. Advances in the treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: An overview of the current and future therapeutic landscape for clinicians. CA Cancer J Clin. (2023) 73:198–222. doi: 10.3322/caac.21759
3. Sirica AE, Gores GJ, Groopman JD, Selaru FM, Strazzabosco M, Wei Wang X, et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: continuing challenges and translational advances. Hepatology. (2019) 69:1803–15. doi: 10.1002/hep.30289
4. Florio AA, Ferlay J, Znaor A, Ruggieri D, Alvarez CS, Laversanne M, et al. Global trends in intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma incidence from 1993 to 2012. Cancer. (2020) 126:2666–78. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32803
5. Endo I, Gonen M, Yopp AC, Dalal KM, Zhou Q, Klimstra D, et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: rising frequency, improved survival, and determinants of outcome after resection. Ann Surg. (2008) 248:84–96. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e318176c4d3
6. Valle J, Wasan H, Palmer DH, Cunningham D, Anthoney A, Maraveyas A, et al. Cisplatin plus gemcitabine versus gemcitabine for biliary tract cancer. N Engl J Med. (2010) 362:1273–81. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0908721
7. Lee J, Park SH, Chang HM, Kim JS, Choi HJ, Lee MA, et al. Gemcitabine and oxaliplatin with or without erlotinib in advanced biliary-tract cancer: a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. (2012) 13:181–8. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70301-1
8. Kim ST, Kang JH, Lee J, Lee HW, Oh SY, Jang JS, et al. Capecitabine plus oxaliplatin versus gemcitabine plus oxaliplatin as first-line therapy for advanced biliary tract cancers: a multicenter, open-label, randomized, phase III, noninferiority trial. Ann Oncol. (2019) 30:788–95. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz058
9. Abdel-Rahman O, Elsayed Z, Elhalawani H. Gemcitabine-based chemotherapy for advanced biliary tract carcinomas. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2018) 4:Cd011746. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011746.pub2
10. Oh DY, Ruth He A, Qin S, Chen LT, Okusaka T, Vogel A, et al. Durvalumab plus gemcitabine and cisplatin in advanced biliary tract cancer. NEJM Evid. (2022) 1:EVIDoa2200015. doi: 10.1056/EVIDoa2200015
11. Rushbrook SM, Kendall TJ, Zen Y, Albazaz R, Manoharan P, Pereira SP, et al. British Society of Gastroenterology guidelines for the diagnosis and management of cholangiocarcinoma. Gut. (2023) 73:16–46. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-330029
12. Zhao R, Zhou J, Miao Z, Xiong X, Wei W, Li S, et al. Efficacy and safety of lenvatinib plus durvalumab combined with hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1397827. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1397827
13. Mitzlaff K, Kirstein MM, Müller C, Venerito M, Olkus A, Dill MT, et al. Efficacy, safety and differential outcomes of immune-chemotherapy with gemcitabine, cisplatin and durvalumab in patients with biliary tract cancers: A multicenter real world cohort. United Eur Gastroenterol J. (2024). doi: 10.1002/ueg2.12656
14. Rimini M, Masi G, Lonardi S, Nichetti F, Pressiani T, Lavacchi D, et al. Durvalumab plus gemcitabine and cisplatin versus gemcitabine and cisplatin in biliary tract cancer: a real-world retrospective, multicenter study. Targeted Oncol. (2024) 19:359–70. doi: 10.1007/s11523-024-01060-1
15. Kelley RK, Ueno M, Yoo C, Finn RS, Furuse J, Ren Z, et al. Pembrolizumab in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin compared with gemcitabine and cisplatin alone for patients with advanced biliary tract cancer (KEYNOTE-966): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. (2023) 401:1853–65. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00727-4
16. Al-Salama ZT, Syed YY, Scott LJ. Lenvatinib: A review in hepatocellular carcinoma. Drugs. (2019) 79:665–74. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-01116-x
17. Motzer RJ, Taylor MH, Evans TRJ, Okusaka T, Glen H, Lubiniecki GM, et al. Lenvatinib dose, efficacy, and safety in the treatment of multiple Malignancies. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. (2022) 22:383–400. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2022.2039123
18. Deng L, Bao W, Zhang B, Zhang S, Chen Z, Zhu X, et al. AZGP1 activation by lenvatinib suppresses intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:590. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06092-5
19. Lu JC, Wu LL, Sun YN, Huang XY, Gao C, Guo XJ, et al. Macro CD5L(+) deteriorates CD8(+)T cells exhaustion and impairs combination of Gemcitabine-Oxaliplatin-Lenvatinib-anti-PD1 therapy in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:621. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44795-1
20. Shi GM, Huang XY, Wu D, Sun HC, Liang F, Ji Y, et al. Toripalimab combined with lenvatinib and GEMOX is a promising regimen as first-line treatment for advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a single-center, single-arm, phase 2 study. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:106. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01317-7
21. Yi C, Chen L, Lin Z, Liu L, Shao W, Zhang R, et al. Lenvatinib targets FGF receptor 4 to enhance antitumor immune response of anti-programmed cell death-1 in HCC. Hepatology. (2021) 74:2544–60. doi: 10.1002/hep.31921
22. Adachi Y, Kamiyama H, Ichikawa K, Fukushima S, Ozawa Y, Yamaguchi S, et al. Inhibition of FGFR reactivates IFNγ Signaling in tumor cells to enhance the combined antitumor activity of lenvatinib with anti-PD-1 antibodies. Cancer Res. (2022) 82:292–306. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-2426
23. Yang Z, Zhang D, Zeng H, Fu Y, Hu Z, Pan Y, et al. Inflammation-based scores predict responses to PD-1 inhibitor treatment in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Inflammation Res. (2022) 15:5721–31. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S385921
24. Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. (2009) 45:228–47. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
25. Okusaka T, Nakachi K, Fukutomi A, Mizuno N, Ohkawa S, Funakoshi A, et al. Gemcitabine alone or in combination with cisplatin in patients with biliary tract cancer: a comparative multicentre study in Japan. Br J Cancer. (2010) 103:469–74. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605779
26. Fiteni F, Nguyen T, Vernerey D, Paillard MJ, Kim S, Demarchi M, et al. Cisplatin/gemcitabine or oxaliplatin/gemcitabine in the treatment of advanced biliary tract cancer: a systematic review. Cancer Med. (2014) 3:1502–11. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2014.3.issue-6
27. Gomez-Roca C, Yanez E, Im S-A, Alvarez EC, Senellart H, Doherty M, et al. LEAP-005: A phase II multicohort study of lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab in patients with previously treated selected solid tumors—Results from the colorectal cancer cohort. J Clin Oncol. (2021) 39:94. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2021.39.3_suppl.94
28. Razumilava N, Gores GJ. Cholangiocarcinoma. Lancet. (2014) 383:2168–79. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61903-0
29. Crusz SM, Balkwill FR. Inflammation and cancer: advances and new agents. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2015) 12:584–96. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2015.105
30. Klümper N, Saal J, Berner F, Lichtensteiger C, Wyss N, Heine A, et al. C reactive protein flare predicts response to checkpoint inhibitor treatment in non-small cell lung cancer. J Immunother Cancer. (2022) 10(3):e004024. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-004024
31. Zhang Y, Lu L, He Z, Xu Z, Xiang Z, Nie RC, et al. C-reactive protein levels predict responses to PD-1 inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:808101. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.808101
32. Tan D, Fu Y, Tong W, Li F. Prognostic significance of lymphocyte to monocyte ratio in colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Int J Surg. (2018) 55:128–38. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.05.030
33. Ma JY, Liu Q. Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of lymphocyte to monocyte ratio in patients with gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Int J Surg. (2018) 50:67–71. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.01.002
34. Zhang K, Hua YQ, Wang D, Chen LY, Wu CJ, Chen Z, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. J Transl Med. (2019) 17:30. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-1782-x
Keywords: intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, lenvatinib, pembrolizumab, systemic chemotherapy, survival, adverse events
Citation: Yang Z, Wu W, Hu Z, Fu Y, Hu Z, Pan Y, Wang J, Chen J, Zhou Z, Zhang Y, Chen M and Hu D (2024) Comparison of lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab versus first-line systemic chemotherapy for advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a real-world retrospective study. Front. Immunol. 15:1494520. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1494520
Received: 11 September 2024; Accepted: 14 November 2024;
Published: 29 November 2024.
Edited by:
Lorenzo Fornaro, Pisana University Hospital, ItalyReviewed by:
Andrea Casadei Gardini, Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, ItalyFrancesco Crea, The Open University (United Kingdom), United Kingdom
Copyright © 2024 Yang, Wu, Hu, Fu, Hu, Pan, Wang, Chen, Zhou, Zhang, Chen and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dandan Hu, aHVkZEBzeXN1Y2Mub3JnLmNu; Minshan Chen, Y2hlbm1zaEBzeXN1Y2Mub3JnLmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Zhenyun Yang
Zhenyun Yang Weijie Wu
Weijie Wu Zhiwen Hu1,2,3†
Zhiwen Hu1,2,3† Yizhen Fu
Yizhen Fu Zili Hu
Zili Hu Yangxun Pan
Yangxun Pan Zhongguo Zhou
Zhongguo Zhou Yaojun Zhang
Yaojun Zhang Dandan Hu
Dandan Hu