
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Immunol. , 22 October 2024
Sec. Cancer Immunity and Immunotherapy
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1491922
This article is part of the Research Topic Formation of Immunological Niches in Tumor Microenvironments: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential View all 22 articles
 Bingchen Wang1†
Bingchen Wang1† Xiao Chen1†
Xiao Chen1† Rongxuan Li1†
Rongxuan Li1† Bolun Ai2†
Bolun Ai2† Feng Ye3
Feng Ye3 Jianjun Zhao1
Jianjun Zhao1 Yefan Zhang1
Yefan Zhang1 Zhen Huang1
Zhen Huang1 Zhiyu Li1
Zhiyu Li1 Xinyu Bi1
Xinyu Bi1 Hong Zhao1
Hong Zhao1 Dayong Cao1*
Dayong Cao1* Jianqiang Cai1*
Jianqiang Cai1* Jianguo Zhou1*
Jianguo Zhou1* Tao Yan4*
Tao Yan4*Background: Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (EHE), is an uncommon, intermediate-grade malignant vascular tumor that can manifest in diverse organs, including the liver, lungs, and bones. Given its unique malignancy profile and rarity, there lacks a consensus on a standardized treatment protocol for EHE, particularly for hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (HEHE). This study aims to elucidate factors influencing the clinical prognosis of EHE by analyzing data from the SEER database, complemented with insights from a departmental cohort of 9 HEHE cases. Through this, we hope to shed light on potential clinical outcomes and therapeutic strategies for HEHE.
Methods: Using SEER data from 22 registries, we analyzed 313 liver cancer patients with ICD-O-3 9130 and 9133 histology. Twelve variables were examined using Cox regression and mlr3 machine learning. Significant variables were identified and compared. Clinical data, imaging characteristics, and treatment methods of nine patients from our cohort were also presented.
Result: In univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses, Age, Sex, Year of diagnosis, Surgery of primary site, Chemotherapy, and Median household income were closely related to survival outcomes. Among the ten survival-related machine learning models, CoxPH, Flexible, Mboost, and Gamboost stood out based on Area Under the Curve(AUC), Decision Curve Analysis(DCA), and Calibration Curve Metrics. In the feature importance analysis of these four selected models, Age and Surgery of primary site were consistently identified as the most critical factors influencing prognosis. Additionally, the clinical data of nine patients from our cohort not only demonstrated unique imaging characteristics of HEHE but also underscored the importance of surgical intervention.
Conclusion: For patients with resectable HEHE, surgical treatment is currently a highly important therapeutic approach.
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (EHE) is a rare vascular tumor, first high-lighted by the seminal studies of Weiss and Enzinger in 1982 (1). This low-grade malignancy is characterized by its unique assembly of predominantly epithelioid endothelial cells. While EHE can be found in various anatomical locations, its presence in the liver, known as hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (HEHE), often navigates the challenging waters of diagnosis, sometimes being mistaken for other hepatic tumors (2, 3). Intriguingly, epidemiological insights suggest a greater inclination toward females, especially those aged 40-55, though its overall incidence is notably low, less than 0.1 per 100,000 (3–9). A defining characteristic of EHE is its absence of vasoformation, distinguishing it from other vascular tumors (10). Delving into its molecular underpinnings, chromosomal rearrangements involving the WWTR1 and CAMTA1 genes emerge as key players, complemented by the noteworthy YAP-THE3 gene fusion (11–13). Diagnostically, EHE’s marked preference for specific endothelial markers is a pivotal feature (14).
Clinical presentations of Hepatic Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma (HEHE) are diverse. While some patients exhibit no symptoms, others may experience a range of manifestations, including right upper quadrant pain, weight loss, jaundice, nausea, anorexia, fatigue, and hepatomegaly (3, 4, 6, 9). In radiographic evaluations, the nodules of HEHE routinely appear to be multiple and peripheral in the image presentation. HEHE distinctly manifests through three primary characteristics: the Capsular Retraction (15, 16), indicative of liver tissue hypertrophy due to tumor-associated fibrotic changes; the Target Sign on T2W imaging, epitomized by a central high-intensity core, flanked by a low-intensity ring and subtly accentuated by an outer high-intensity halo (17); and the Lollipop Sign in enhanced imaging, where the ‘candy’ delineates the evident tumor mass, while the ‘bar’ depicts the occluded vein on T2WI (18). Collectively, these imaging signatures are instrumental in differentiating HEHE from other hepatic metastatic entities.
Due to the rarity of EHE and limited research available, a standardized treatment protocol for HEHE has yet to be established. For 253 diagnosed HEHE patients, survival rates irrespective of the treatment approach were observed to be 83.4% (211 patients) at 1 year, 55.7% (141 patients) at 3 years, and 41.1% (104 patients) at 5 years (9). For HEHE patients, various treatment modalities have been explored in clinical trials and analyses. These include surgical options like hepatectomy and liver transplantation (LT), alternative therapies such as ablation and transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE), as well as systemic treatments encompassing chemotherapy, anti-VEGF therapy, and mTOR inhibitors (19–22). However, one study suggested that the 5-year survival rates across various treatment approaches showed no significant differences, leading to a recommendation for a watchful waiting strategy (23). While the mechanisms and progress in basic research on EHE are continuously advancing, surgical treatments remain the most common and major treatments for patients with EHE at present from a clinical aspect (9).
From the SEER Research data encompassing 22 registries, 313 liver cancer patients diagnosed with histology ICD-O-3 9133 (EHE) and 9130 (HE) were identified for detailed analysis. Key variables such as age, sex, year of diagnosis, race, combined summary stage, surgery of primary site, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, preoperative or postoperative systemic therapy, sequence number, median household income, rural urban continuum code, survival duration, and living status were extracted from their respective fields in the SEER database.
For this study, 9 HEHE patients were selected from our hospital. The inclusion criteria were: 1) patients who underwent liver resection due to hepatic lesions between 2012 and 2022 and were pathologically diagnosed with HEHE post-surgery, and 2) patients aged 18 years or older. Patients were excluded from the study if they met any of the following criteria: 1) Patients who did not undergo surgical resection, and 2) Patients under 18 years of age. Detailed baseline information was compiled, including gender, age, primary diagnosis, tumor ICD, clinical symptoms, underlying conditions, and physical signs. Radiological features covered tumor location, size, multiplicity, peripheral involvement, capsular retraction, target sign, and lollipop sign. Pathological features, including immunohistochemical markers like CD34, CD31, ERG, and Fli1, were documented, with results presented in an embedded pie chart. Laboratory results included markers such as CA199, AFP, CEA, ALT, AST, and additional tests. All clinical and pathological data were obtained through routine hospital procedures. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College. All patients provided informed consent.
Statistical analyses were primarily executed in R Studio. Using the autoReg package, we performed univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses to identify variables related to survival. The dataset was divided into training and validation sets in an 8:2 ratio to prepare for survival-related machine learning and there were no statistically significant differences in baseline characteristics (Supplementary Table 1) or survival information (Supplementary Figure 1) between the training and validation sets. We constructed survival-related machine learning models using the following mlr3 models: “surv.coxph” (a traditional proportional hazards model), “surv.cv_glmnet” (a regularized regression model), “surv.rpart” (a decision tree-based model), “surv.rfsrc” (a random forest model), “surv.gbm” (a gradient boosting model), “surv.flexible” (a flexible parametric spline learner using flexsurv::flexsurvspline()), “surv.blackboost”, “surv.gamboost”, and “surv.glmboost” (all boosting-based models). For each model, we calculated and plotted the AUC (evaluating discriminatory power), calibration curves (assessing prediction accuracy), and DCA (analyzing clinical utility) for both the training and validation sets. Models with an AUC above 0.75, calibration curves fitting the reference line, and beneficial DCA were selected. Feature importance analysis was conducted on the top-performing models to rank variables influencing survival. The important variables identified by traditional Cox regression and machine learning (especially treatment methods) were further analyzed in different subgroups (Figure 1).
The baseline characteristics of 313 patients, stratified by the surgery of the primary site, are presented in Table 1. It can be observed that the choice of surgery of the primary site among the various groups shows statistically significant differences only in the preoperative or postoperative systemic therapy group. In all other groups, the surgery of the primary site (including no surgery or unknown, wedge or segmental resection, lobectomy, hepatectomy, and transplant) does not exhibit statistically significant differences.
Table 2 also presents data for the 313 patients, showing that the mean age at diagnosis is 51 years, with a higher proportion of female patients (53.7%). A portion of the patients (34.5%) were diagnosed at the distant stage. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses identified age (Final HR: 1.03 [1.02-1.04], p<.001), gender (Female vs. Male, Final HR: 0.67 [0.48-0.93], p=.017), year of diagnosis (after 2010 vs. before 2010, Final HR: 0.53 [0.37-0.75], p<.001), surgery of the primary site (wedge or segmental resection or lobectomy vs. no surgery or unknown, Final HR: 0.43 [0.25-0.73], p=.002; hepatectomy and/or transplant vs. no surgery or unknown, Final HR: 0.27 [0.11-0.66], p=.004), chemotherapy (yes vs. no or unknown, Final HR: 1.89 [1.32-2.72], p=.001), and median household income (more than $70,000 vs. below $70,000, Final HR: 0.57 [0.41-0.80], p=.001) as significant variables influencing survival prognosis.
Figure 2A presents the AUC values of 10 different machine learning models at 1, 3, and 5-year specific time points in the training set, while Figure 2B shows the AUC values for these models at the same time points in the validation set. It was observed that the AUC values of the CoxPH model, flexible model, gamboost model, mboost model, and gbm model were all greater than 0.75 (Supplementary Figures 2A–J). However, the DCA curve indicated that the performance of the gbm model was not ideal (Figure 2C), whereas the calibration curves for the CoxPH model, flexible model, gamboost model, and mboost model fit the reference line (Figures 2D–G). Consequently, the CoxPH model, flexible model, gamboost model, and mboost model were selected for subsequent variable importance analysis. Figures 3A–D illustrate the feature importance of relevant variables for the CoxPH model, flexible model, gamboost model, and mboost model at 1, 3, and 5 years, while Figure 3E presents the time-dependent variable importance. It can be clearly seen that, across the different time points, Age and surgery of the primary site consistently emerged as the two most significant factors influencing prognosis. Basic sequencing studies have also found that age is associated with rapid tumor progression, and surgical treatment remains a superior option in the absence of effective chemotherapy and targeted therapy.
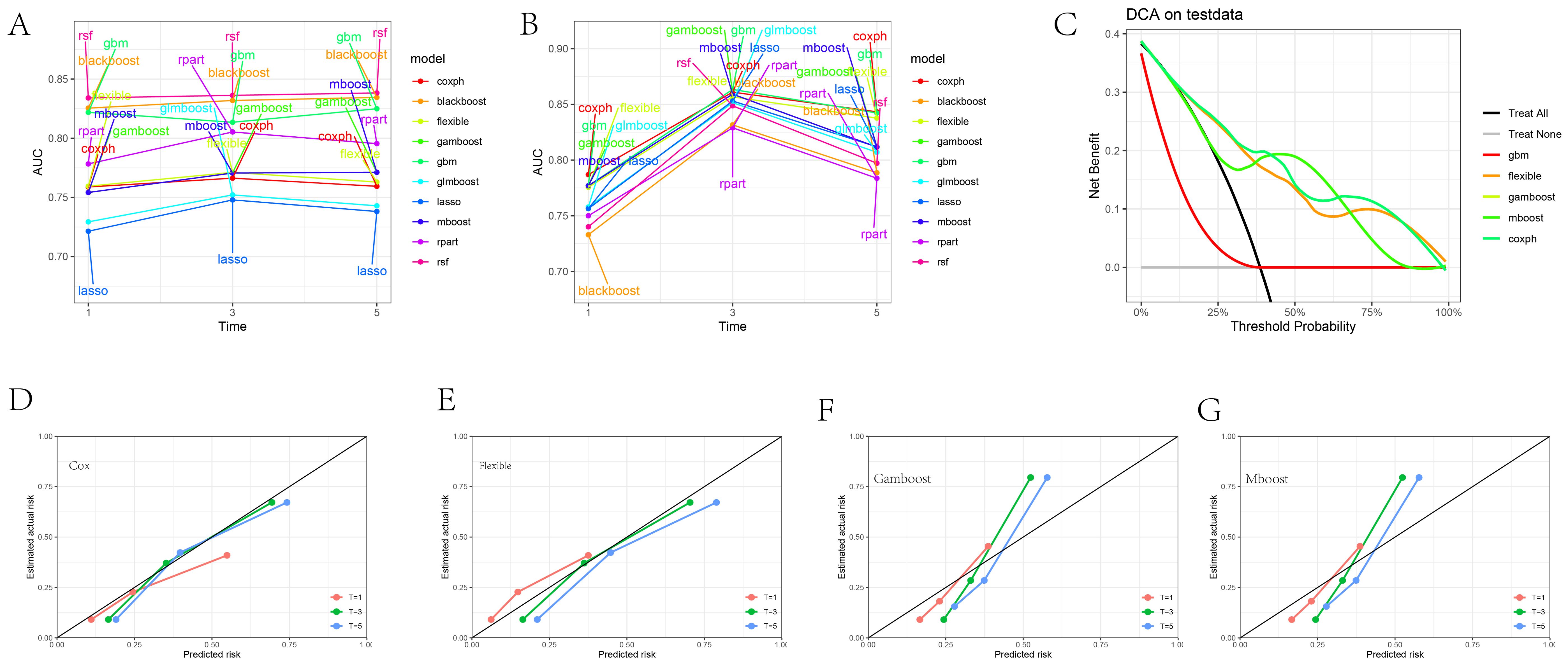
Figure 2. Machine Learning Model Evaluation and Display. (A) AUC values of 10 different machine learning models at 1, 3, and 5-year specific time points in the training set. (B) AUC values of 10 different machine learning models at 1, 3, and 5-year specific time points in the test set. (C) DCA plot of selected machine model. (D–G) Calibration plot of CoxPH, Flexible, Gamboost, mboost machine model.
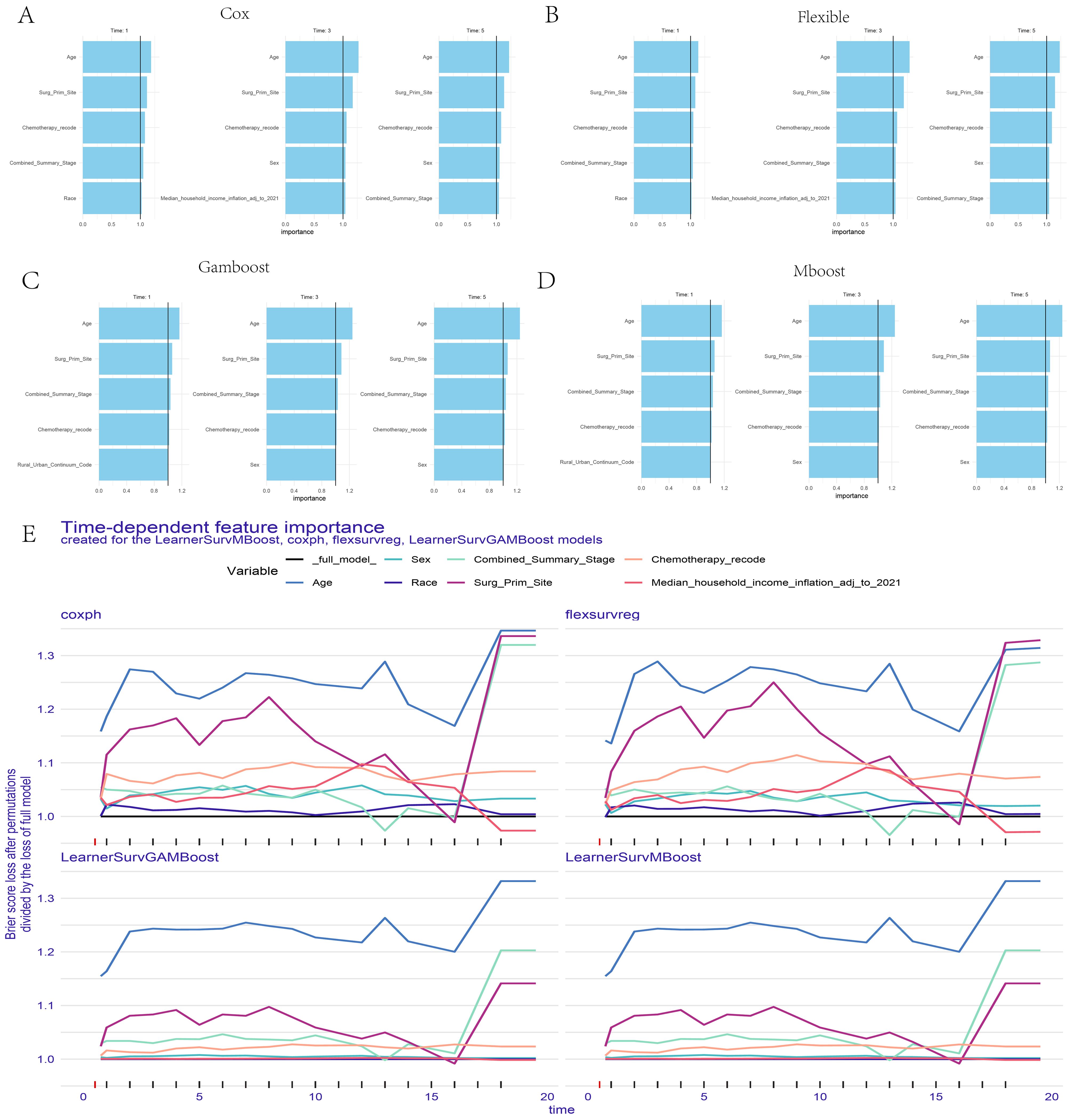
Figure 3. Feature Importance Ranking Display of the Four Selected Models. (A) CoxPH model. (B) Flexible model. (C) Gamboost model (D) Mboost model (E) Time-dependent feature importance of the four models.
At the aim of further exploring the specific therapeutic role of surgery in HEHE tumors, group analyses of surgery’s presence or absence within “Age” group, “Chemotherapy” group, “Stage” group, “Median house income” group, “Race” group, “Radiotherapy” group, “Rural urban continuum” group, “Sequence number” group, “Sex” group, “Systemic therapy and surgery” group and “Year of diagnosis” group, are performed and the forest plot of group analyses is drawn (Figure 4A).
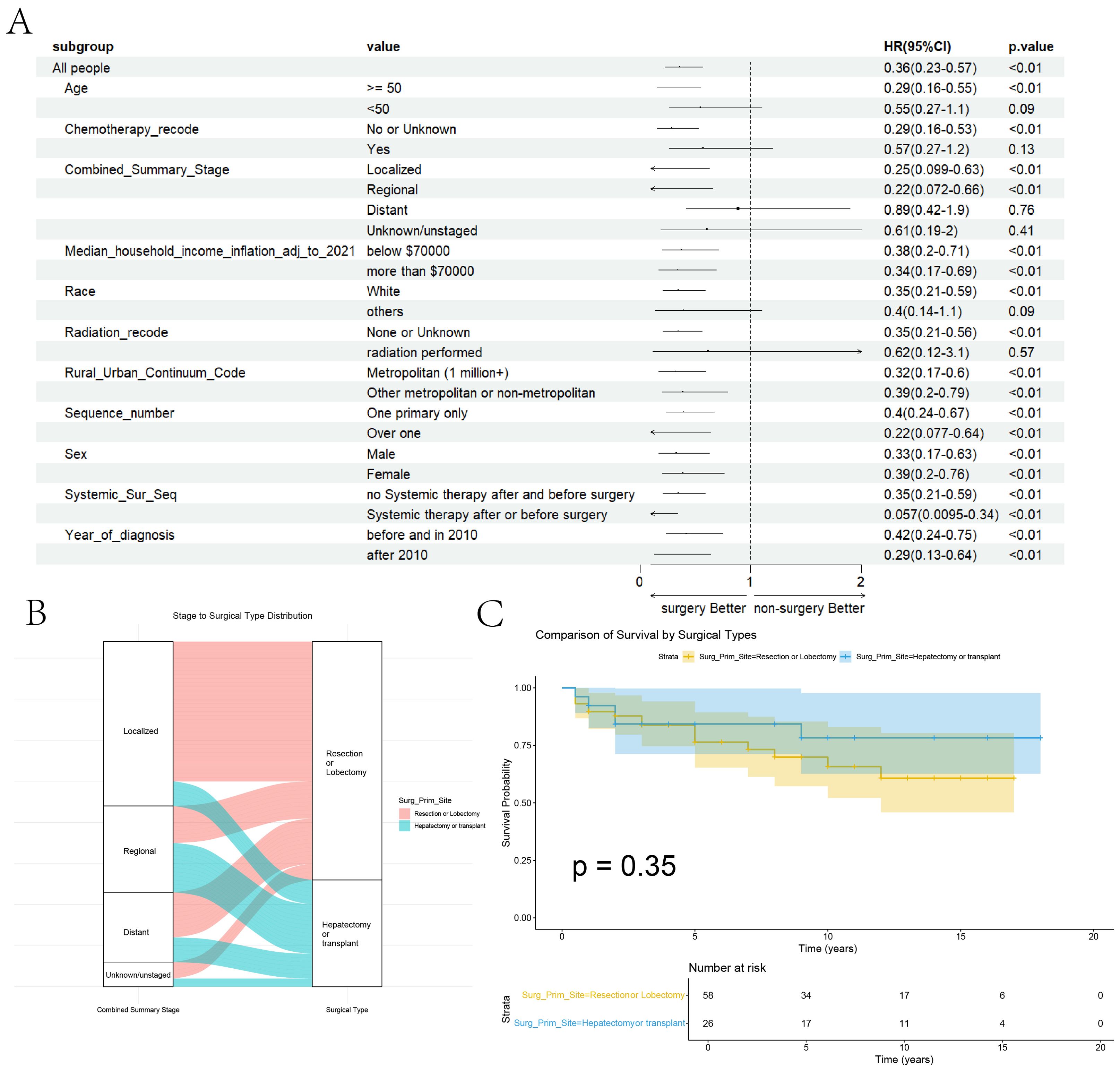
Figure 4. Group Analyses of Surgery and Comparison of Surgery Types. (A) Group Analyses of Surgery within the related variables. (B) The Sankey diagram illustrates the relationship between tumor staging and surgical approaches. (C) Comparison of the Kaplan-Meier curves between the two surgical approaches.
In the forest plot for subgroup analysis, it is evident that surgery has a positive effect across various groups, including the year of diagnosis, presence of preoperative or postoperative adjuvant therapy, gender, sequence number, rural-urban continuum code, and income. Patients with localized or regional stage disease benefit from surgery, whereas those with distant stage disease do not show a significant benefit. Patients undergoing chemotherapy or radiation therapy may not derive a clear benefit from surgery, likely due to their more advanced stage at diagnosis. Interestingly, patients younger than 50 years old do not seem to benefit from surgical treatment, which may be due to the limited sample size leading to the lack of statistical significance for surgical treatment. After performing propensity score matching (PSM) to ensure baseline comparability for surgery performed or not (Supplementary Table 2), surgery remained a significant variable associated with better prognosis in both univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses (Supplementary Table 3). Overall, it can be concluded that patients with limited tumor stages who meet the surgical criteria should undergo further surgical treatment.
In terms of surgical approaches, no significant differences were observed between resection or lobectomy and hepatectomy or transplant across patient-level variables, apart from tumor staging (Supplementary Table 4). The Sankey diagram further highlights a preference for resection or lobectomy in patients with localized tumors, whereas hepatectomy or transplant was more frequently chosen for those with regional or distant disease (Figure 4B). Nonetheless, no statistically significant differences in survival outcomes were detected between the two surgical strategies (Figure 4C).
Inset pie charts are used to visualize baseline information, image feature, pathological features about HEHE patients in our cohort (Figure 5). It’s evident that the majority of patients are in good overall health, with 66.7% having no concurrent illnesses. Similarly, 66.7% of the patients are asymptomatic, and a significant portion of the cohort is female (Figure 5A). When it comes to imaging information for HEHE patients, the majority of tumor lesions are characterized as multiple (66.7%) and peripheral (88.9%). Capsular retraction is observed in 44.4% of cases, while ‘target’ and ‘lollipop’ signs are also significant features, each present in 33.3% of the images (Figures 5B, 6). It can be observed that peripheral ‘target’ signs in T2 MRI (Figures 6A–C, E, F) and capsular retraction (Figure 6A). ‘Lollipop’ signs can be clearly detected in which offer the valuable imaging feature (Figure 6D). The pathological features of HEHE samples from our department can be summarized as follows: HEHE tumors exhibit a range of sizes with some showing no cumulative liver involvement. Histologically, these tumors often present with epithelial-like or spindle-shaped cells, some of which have cellular atypia. Notably, features such as fatty degeneration of surrounding liver tissue, vacuoles in the cytoplasmic membrane, and rare nuclear mitoses can be observed. Furthermore, the presence of multinucleated cells and cells arranged in nests are consistent with epithelioid hemangioendothelioma morphology. When it comes to the pathological immunohistochemical features, the majority of specimens show positive staining for CD31 and CD34 (former), as well as for Ki67, Vimentin, and SMA (latter) at rates of 77.8%, 66.7%, 88.9%, 55.6%, and 44.4%, respectively. The former two markers signify endothelial characteristics, while the latter two indicate cytokeratin and smooth muscle actin markers. Ki67, in particular, implies the proliferative nature of the tumor cells (Figure 5C). A small portion of them also stains positively for MelanA, HMB 45, Flil, ERG in immunohistochemistry while few of them stains positively for CK18, GPC3, Hepatocyte, Desmin (Figures 5D, E). The laboratory parameters (mainly including liver function and tumor markers) of the 9 patients before and after surgery are mostly within the normal range. All nine EHE patients underwent surgery corresponding to the site of tumor growth and their progression-free survival (PFS) was listed (Figure 7). The HEHE recurrence rate is relatively high (4/9),with nearly all recurrence sites located in adjacent liver tissues. Due to the small sample size, it is not sufficient to draw statistically significant conclusions, and further relevant analysis cannot be conducted.
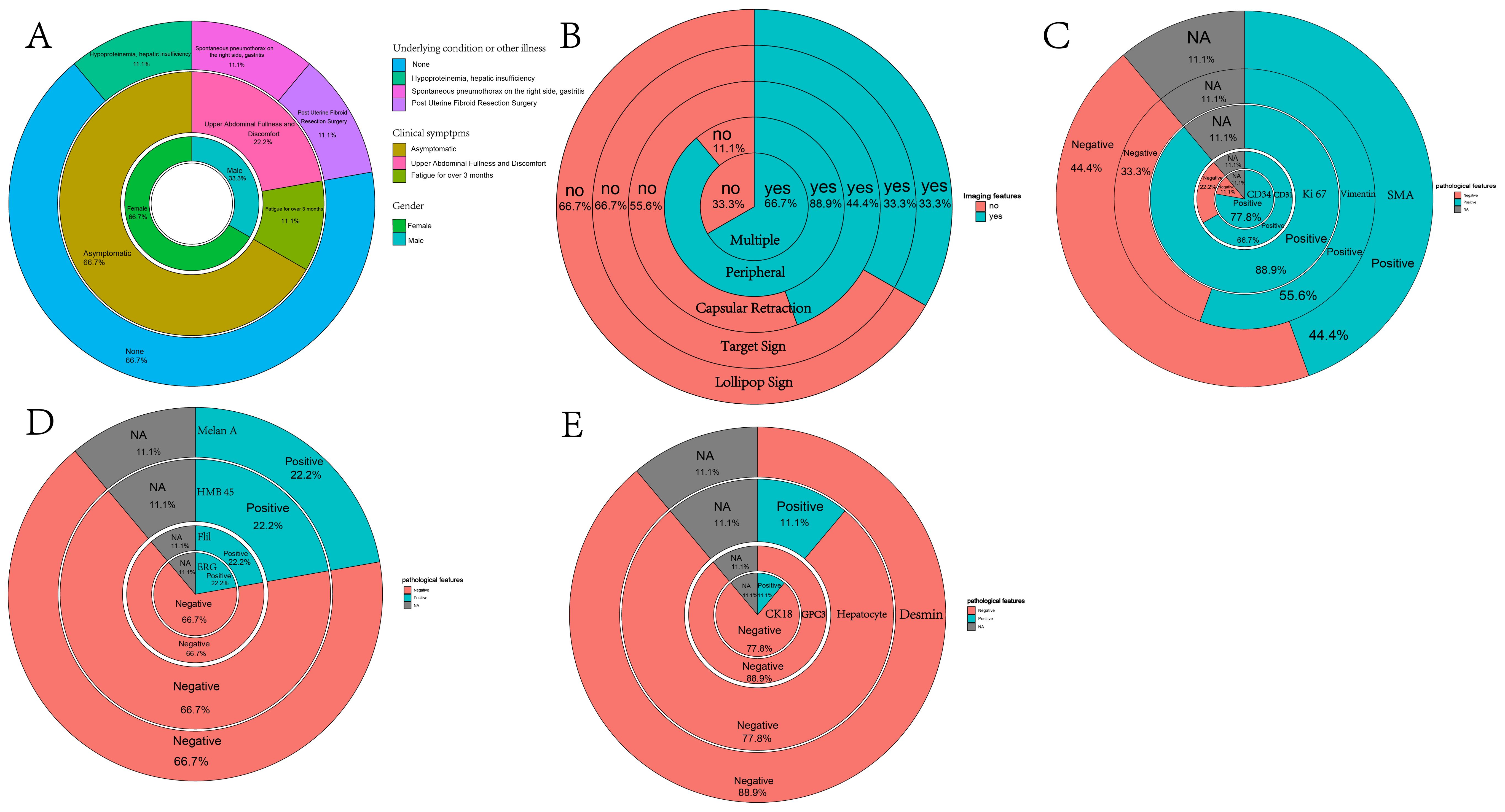
Figure 5. Inset pie charts visualizing various types of information about HEHE patients. (A) Inset pie chart showing the underlying condition or illness, clinical symptoms, and gender of 9 HEHE patients. (B) Inset pie chart showing the imaging features of 9 patients. (C) Inset pie chart showing pathological specimens of 9 patients with immunohistochemical information on CD34, CD31, Ki67, Vimentin, SMA. (D) Inset pie chart showing pathological specimens of 9 patients with immunohistochemical information on ERG, Flil, HMB45, MelanA. (E) Inset pie chart showing pathological specimens of 9 patients with immunohistochemical information on CK18, GPC3, Hepatocyte, Desmin.
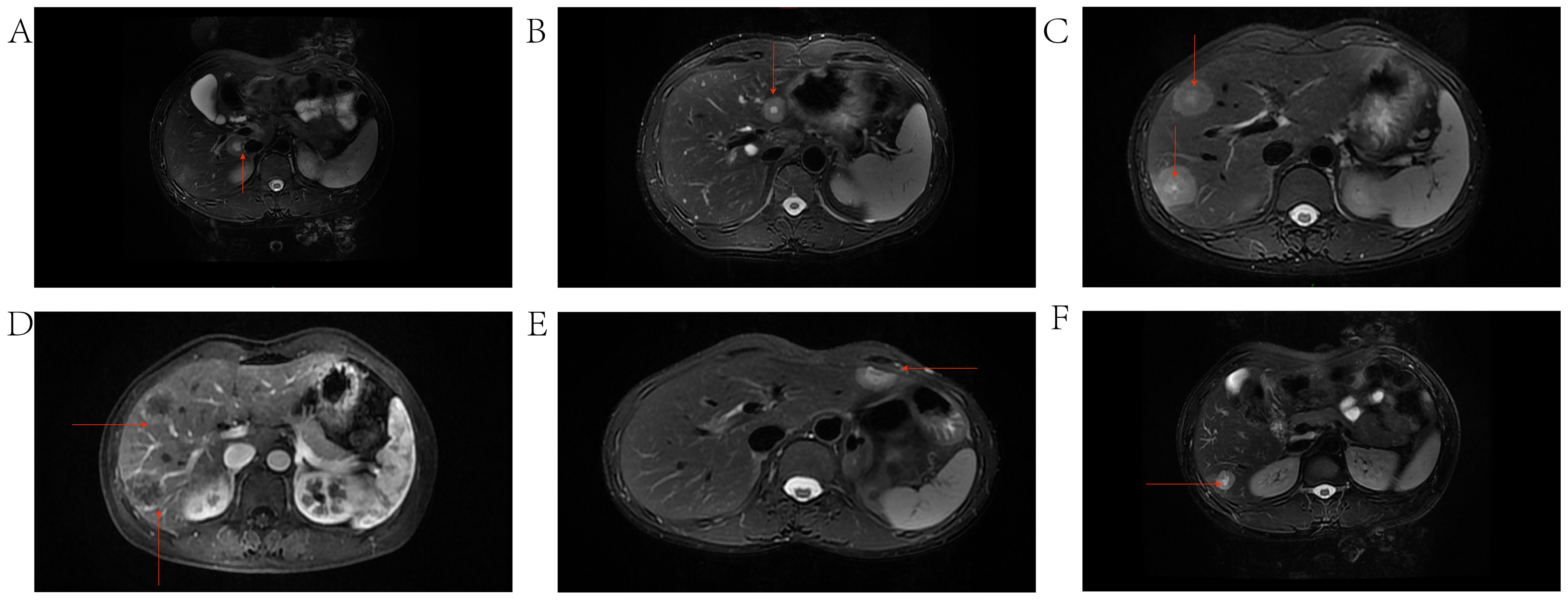
Figure 6. Typical imaging features including capsular retraction, ‘target’ and ‘lollipop’ signs on MRI. (A) HEHE tumor located in the periphery of the caudate lobe of the liver exhibiting the target sign and capsular retraction. (B) HEHE tumor located in the periphery of the left lobe of the liver exhibiting a Target Sign. (C) Multiple HEHE tumors located in the peripheral areas of segment VIII of the liver, exhibiting target signs. (D) EHE tumors exhibiting the Lollipop sign, where the tumor represents the head of the lollipop, and the tortuous, occluded vessels form the stick of the lollipop. (E) HEHE tumor located in the periphery of segment III of the liver, exhibiting a Target Sign. (F) HEHE tumor located in the periphery of the right lobe of the liver, exhibiting the target Sign.
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (EHE) is a unique vascular tumor, initially identified in 1982. When it appears in the liver, it’s termed hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (HEHE) and often poses diagnostic challenges. Though prevalent in females aged 40-55, its incidence is low. Distinctive molecular markers and its absence of vasoformation set it apart from similar tumors. Clinically, HEHE symptoms vary, with some patients being asymptomatic, while others show signs like pain and weight loss. Radiographically, HEHE is characterized by its peripheral distribution and multifocality. Additionally, distinctive imaging features include capsular retraction, ‘target’ sign, and ‘lollipop’ signs. Treatment protocols are diverse and not yet standardized due to its rare occurrence.
Despite the limited dataset in our department, which consists of only 9 cases, the clinical characteristics of HEHE patients exhibit a certain degree of representativeness. Additionally, by combining our departmental data with existing literature, certain clinical features of HEHE can be elucidated. In HEHE patients, a preference for females, non-specific clinical symptoms, and the presence of multiple and peripheral nodular lesions are main manifestations. Capsular retraction, along with the ‘target’ and ‘lollipop’ signs, are prominent radiological hallmarks observed in HEHE imaging. However, right upper quadrant pain is regarded as the most common clinical manifestation of HEHE (5, 6) and some rare cases had rare syndrome such as Budd-Chiari syndrome (24) and Kasabach–Merrit syndrome (25). On contrast-enhanced study, CT and MRI share common features and the character can be described as three patterns. Some tumors display mild homogeneous enhancement in arterial phase without any change in the delayed or portal vein phase. Some masses show ring like enhancement at first in the arterial phase and full enhancement in the delayed and portal phases, which is called “halo sign”. And the last type is the heterogeneous enhancement which progresses in all phases (26, 27). It has been concisely summarized that lesions smaller than 2 cm predominantly exhibit mild homogeneous enhancement; lesions ranging from 2-3cm display ring-like enhancement transitioning to heterogeneous delayed enhancement; lesions exceeding 3 cm predominantly manifest heterogeneous delayed enhancement (28, 29). The imaging characteristics of our cohort of 9 patients, especially those discerned from MRI, largely resonate with the imaging findings delineated in the review literature concerning EHE patients. However, the manifestations of enhancement types in HEHE may seem restricted, given the limited sample size. The immunohistochemical staining characteristics of endothelial cells in the pathology of the 9 patients presented in the department align with the pathological features of EHE: epithelioid cells arranged in cords and nests within the stroma but do not exhibit vasoformation. The pathological finding of poorly formed endothelial cells is the primary criterion for identifying EHE, but It is also proved that immunohistochemistry for CAMTA1 expression of nuclear is a significant method to distinguish EHE from other epithelioid vascular tumors including epithelioid angiosarcoma, epithelioid sarcoma which have the mimic histologic features with the expression of TFE3 by immunohistochemistry being another candidate method (30, 31).
In one study aiming at detecting common secondary genomic variants associated with advanced EHE from 49 participants, more than half patients exhibited pathogenic genomic variants in addition to TAZ-CAMTA1 fusion and 18.4% patients in the study showed potentially targetable genomic variants. Importantly, patients who were older were more likely to have clinically targetable variants and the same condition occurred in patients with III/IV stage (32). The aforementioned literature emphasizes that secondary mutations may be the reason for the transition of EHE from indolent to malignant. It also points out that as age increases and disease stage advances, there may be a higher likelihood of secondary mutations occurring, leading to potentially more uncontrollable disease progression. This is consistent with the impact observed in the analysis of the machine results we examined.
It is unknown why the chemotherapy exhibits opposite effect in our Cox Model. Several reasons might hide behind the above question. First of all, the SEER database lacks comprehensive specific information regarding chemotherapy. It is not clear which chemotherapy agent is used for EHE patients. Secondly, the progress of chemotherapy seemed stagnant before the mechanism of EHE was discovered and the oral drug therapy is limited for the rarity of EHE. Conventional chemotherapy such as anthracyclines regimens、pazopanib、paclitaxel and so on exerted restricted effect on treatment of HEHE (33). Thirdly, the information collected in the SEER database spans a wide range of years, and until recent clinical trials have shown significant efficacy of IFN-a 2b (34), Anti-VEGF chemotherapeutic agents such as bevacizumab, pazopanib, sorafenib thalidomide (35–39) and mTOR inhibitor sirolimus(rapamycin) (20, 40–42) for patients, the effectiveness of chemotherapy in treating EHE patients remained uncertain. By the way, it is hard to explain why the sequence numbers which are all reportable neoplasms over the lifetime of the patient have the positive correlation with survival times.
The use of surgical treatment and surgical types should be considered exhaustively according to the tumors location within the liver、the size of the mass、number of nodules、the status of vascular invasion、condition of extrahepatic diseases (22). Patients who underwent surgical treatments had significantly higher survival than those did nothing, and multivariate analysis revealed surgical therapy was only independent prognostic factor for survival (7). Group analysis can provide a new understanding of the suitability for surgical treatment, specifically identifying when surgery is most beneficial. For example, as mentioned earlier, in cases where the tumor is in a more advanced stage the potential benefits of surgery may be limited. Surgical treatments mainly consist of surgical resection and liver transplantation (LT). There had concluded that over half patients benefited from surgical resection and LT also shows excellent 5-year survival outcome in diverse clinical trials (9, 22, 43–47). some articles summarized that surgical resection had better overall survival rates and higher disease-free-survival than LT (9, 20, 48) while others demonstrated that there was no significantly difference between two modalities (5). To sum up, the choice of surgical resection and liver transplantation should be considered carefully after exact analysis of both benefits and risks and group analysis may offer some valuable insights for surgical decision-making.
There are several limitations in the study. Firstly, in the SEER data, radiation therapy and chemotherapy are all treated as binary variables, and the ‘stage’ variable is categorized as distant, localized, and regional, which may be somewhat generalized and lack specificity. Additionally, as mentioned earlier, the chemotherapy information is limited and outdated, and the study findings may be influenced by a lag in recording research advancements. Furthermore, some of the subgroup analyses lack convincing power due to small sample sizes. Lastly, the dataset from our department is limited in size. While the clinical symptoms, imaging information, and pathological features are somewhat representative, it lacks the generality of larger sample sizes.
Recent advancements in fundamental research and omics analyses are shedding light on EHE’s complexities. One study identified potentially targetable genomic variants in EHE, emphasizing variants like CDKN2A/B, which are notably involved in cell cycle regulation and DNA damage repair (32). Notably, the loss of CDKN2A/B was prevalent in older patients and was linked to more aggressive EHE behavior (49). Investigations also revealed that fusion proteins in EHE can modulate the chromatin environment and hyperactivate a TEAD-based transcriptional program (50). Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) highlighted EHE’s cellular heterogeneity, suggesting potential underlying pathways that merit further exploration (51, 52). While anti-VEGF therapies and mTOR inhibitors have clinical implications, MEK inhibitors and YAP/TAZ-TEAD disruptors have shown promise in reducing EHE cell proliferation, although their clinical efficacy remains to be ascertained (53–56).
Machine learning and Cox regression models have highlighted the significant importance of surgical treatment for HEHE. Given the limited basic research and the lack of further clinical translation for HEHE, surgical treatment remains a worthwhile and preferred option for consideration.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College. All patients provided informed consent. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
BW: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization. XC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft. RL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. BA: Data curation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. FY: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. ZH: Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. XB: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HZ: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. DC: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. JC: Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2023YFC3403800), National Natural Science Foundation of China (82141127), CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (CIFMS) (2021-I2M-C&T-B-057).
We thank everyone who contributed to this study and the staff of the Department of Radiology in our Cancer Hospital for their assistance.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1491922/full#supplementary-material
1. Weiss S. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma a vascular tumor often mistaken for a carcinoma. (1982) 50:970–81. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19820901)50:5<970::AID-CNCR2820500527>3.0.CO;2-Z
2. Weiss S. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma and related lesions. Semin Diagn Pathol. (1986) 3:259–87.
3. Ishak KG, Sesterhenn IA, Goodman MZD, Rabin L, Stromeyer FW. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver: a clinicopathologic and follow-up study of 32 cases. Hum Pathol. (1984) 15:839–52. doi: 10.1016/S0046-8177(84)80145-8
4. Remiszewski P. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver as a rare indication for liver transplantation. WJG. (2014) 20:11333. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i32.11333
5. Ajay PS, Tsagkalidis V, Casabianca A, Burchard PR, Melucci AD, Chacon A, et al. A review of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendotheliomaAnalyzing patient characteristics and treatment strategies. J Surg Oncol. (2022) 126:1423–9. doi: 10.1002/jso.27066
6. Chahrour MA, Khachfe HH, Habib JR, El-Asmar R, Saifi O, Jamali FR. Treatment and prognosis of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: A SEER database analysis. World J Surg. (2021) 45:2886–94. doi: 10.1007/s00268-021-06165-6
7. Noh OK, Kim SS, Yang MJ, Lim SG, Hwang JC, Cho HJ, et al. Treatment and prognosis of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma based on SEER data analysis from 1973 to 2014. Hepatobiliary Pancreatic Dis Int. (2020) 19:29–35. doi: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2019.11.006
8. Sanduzzi-Zamparelli M, Rimola J, Montironi C, Nunes V, Alves VAF, Sapena V, et al. Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: An international multicenter study. Digestive Liver Dis. (2020) 52:1041–6. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2020.05.003
9. Mehrabi A, Kashfi A, Fonouni H, Schemmer P, Schmied BM, Hallscheidt P, et al. Primary Malignant hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: A comprehensive review of the literature with emphasis on the surgical therapy. Cancer. (2006) 107:2108–21. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22225
10. Antonescu C. Malignant vascular tumors—an update. Modern Pathol. (2014) 27:S30–8. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2013.176
11. Errani C. A novel WWTR1-CAMTA1 gene fusion is a consistent abnormality in epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of different anatomic sites. Genes, chromosomes & cancer (2011) 50:644–53. doi: 10.1002/gcc.20886
12. Tanas MR, Sboner A, Oliveira AM, Erickson-Johnson MR, Hespelt J, Hanwright PJ, et al. Identification of a disease-defining gene fusion in epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Sci Transl Med. (2011) 3:98ra82. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002409
13. Antonescu CR, Le Loarer F, Mosquera J-M, Sboner A, Zhang L, Chen C-L, et al. Novel YAP1-TFE3 fusion defines a distinct subset of epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. (2013) 52:775–84. doi: 10.1002/gcc.22073
14. Kuo F-Y, Huang H-Y, Chen C-L, Eng H-L, Huang C-C. TFE3- rearranged hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma-a case report with immunohistochemical and molecular study. APMIS. (2017) 125:849–53. doi: 10.1111/apm.12716
15. Soyer P. Capsular retraction of the liver in Malignant tumor of the biliary tract MRI findings. Clin Imaging. (1994) 18:255–7. doi: 10.1016/0899-7071(94)90003-5
16. Sans N, Fajadet P, Galy-Fourcade D, Trocart J, Jarlaud T, Chiavassa H, et al. Is capsular retraction a specific CT sign of Malignant liver tumor? Eur Radiol. (1999) 9:1543–5. doi: 10.1007/s003300050880
17. Mamone G, Miraglia R. The “Target sign” and the “Lollipop sign” in hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Abdom Radiol. (2019) 44:1617–20. doi: 10.1007/s00261-018-1820-9
18. Alomari AI. The lollipop sign: A new cross-sectional sign of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Eur J Radiol. (2006) 59:460–4. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2006.03.022
19. Weitz J, Klimstra DS, Cymes K, Jarnagin WR, D’Angelica M, La Quaglia MP, et al. Management of primary liver sarcomas. Cancer. (2007) 109:1391–6. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22530
20. Kou K, Chen Y-G, Zhou J-P, Sun X-D, Sun D-W, Li S-X, et al. Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: Update on diagnosis and therapy. WJCC. (2020) 8:3978–87. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i18.3978
21. Cardinal J. Treatment of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: A single-institution experience with 25 cases. Arch Surg. (2009) 144:1035. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.2009.121
22. Stacchiotti S, Miah AB, Frezza AM, Messiou C, Morosi C, Caraceni A, et al. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, an ultra-rare cancer: a consensus paper from the community of experts. ESMO Open. (2021) 6:100170. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100170
23. Thomas RM, Aloia TA, Truty MJ, Tseng WH, Choi EA, Curley SA, et al. Treatment sequencing strategy for hepatic epithelioid haemangioendothelioma. HPB. (2014) 16:677–85. doi: 10.1111/hpb.12202
24. Hayashi Y, Inagaki K, Hirota S, Yoshikawa T, Ikawa H. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma with marked liver deformity and secondary Budd-Chiari syndrome: Pathological and radiological correlation. Pathol Int. (1999) 49:547–52. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1827.1999.00906.x
25. Frider B, Bruno A, Selser J, Vanesa R, Pascual P, Bistoletti R. Kasabach–Merrit syndrome and adult hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma an unusual association. J Hepatol. (2005) 42:282–3. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2004.09.007
26. Studer LL, Selby DM. Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. (2018) 142:263–7. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0171-RS
27. Epelboym Y, Engelkemier DR, Thomas-Chausse F, Alomari AI, Al-Ibraheemi A, Trenor CC, et al. Imaging findings in epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Clin Imaging. (2019) 58:59–65. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2019.06.002
28. Zhou L, Cui M-Y, Xiong J, Dong Z, Luo Y, Xiao H, et al. Spectrum of appearances on CT and MRI of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. BMC Gastroenterol. (2015) 15:69. doi: 10.1186/s12876-015-0299-x
29. Liu X, Yu H, Zhang Z, Si S, Huang J, Tan H, et al. MRI appearances of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a retrospective study of 57 patients. Insights Imaging. (2022) 13:65. doi: 10.1186/s13244-022-01213-8
30. Doyle LA, Fletcher CDM, Hornick JL. Nuclear expression of CAMTA1 distinguishes epithelioid hemangioendothelioma from histologic mimics. Am J Surg Pathol. (2016) 40:94–102. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000511
31. Jung H, Kim H-N, Jang Y, Park C-K, Ha S-Y. CAMTA-1 expression in 24 cases of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma in a single institute: diagnostic utility for differential diagnosis from hepatic angiosarcoma. In Vivo. (2019) 33:2293–7. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11736
32. Seligson ND, Awasthi A, Millis SZ, Turpin BK, Meyer CF, Grand’Maison A, et al. Common secondary genomic variants associated with advanced epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. JAMA Netw Open. (2019) 2:e1912416. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.12416
33. Frezza AM, Ravi V, Lo Vullo S, Vincenzi B, Tolomeo F, Chen TW, et al. Systemic therapies in advanced epithelioid haemangioendothelioma: A retrospective international case series from the World Sarcoma Network and a review of literature. Cancer Med. (2021) 10:2645–59. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3807
34. Liu X, Zhang Z, Huang J, Tan H, Yang Z. Efficacy and safety of interferon-alpha 2b for patients with hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: outcomes of a case-series analysis. CMAR. (2021) 13:8273–9. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S334171
35. Chevreau C, Le Cesne A, Ray-Coquard I, Italiano A, Cioffi A, Isambert N, et al. Sorafenib in patients with progressive epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: A phase 2 study by the French Sarcoma Group (GSF/GETO). Cancer. (2013) 119:2639–44. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28109
36. Agulnik M, Yarber JL, Okuno SH, von Mehren M, Jovanovic BD, Brockstein BE, et al. An open-label, multicenter, phase II study of bevacizumab for the treatment of angiosarcoma and epithelioid hemangioendotheliomas. Ann Oncol. (2013) 24:257–63. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mds237
37. Telli TA, Okten IN, Tuylu TB, Demircan NC, Arikan R, Alan O, et al. VEGF-VEGFR pathway seems to be the best target in hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: A case series with review of the literature. Curr Problems Cancer. (2020) 44:100568. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2020.100568
38. Bally O, Tassy L, Richioud B, Decouvelaere A-V, Blay J-Y, Derbel O. Eight years tumor control with pazopanib for a metastatic resistant epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Clin Sarcoma Res. (2015) 5:12. doi: 10.1186/s13569-014-0018-3
39. Lau A, Malangone S, Green M, Badari A, Clarke K, Elquza E. Combination capecitabine and bevacizumab in the treatment of metastatic hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Ther Adv Med Oncol. (2015) 7:229–36. doi: 10.1177/1758834015582206
40. Stacchiotti S, Simeone N, Lo Vullo S, Baldi GG, Brunello A, Vincenzi B, et al. Activity of sirolimus in patients with progressive epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: A case-series analysis within the Italian Rare Cancer Network. Cancer. (2021) 127:569–76. doi: 10.1002/cncr.33247
41. Fukuhara S, Tahara H, Hirata Y, Ono K, Hamaoka M, Shimizu S, et al. Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma successfully treated with living donor liver transplantation: A case report and literature review. Clin Case Rep. (2020) 8:108–15. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.2558
42. Stacchiotti S, Provenzano S, Dagrada G, Negri T, Brich S, Basso U, et al. Sirolimus in advanced epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: A retrospective case-series analysis from the italian rare cancer network database. Ann Surg Oncol. (2016) 23:2735–44. doi: 10.1245/s10434-016-5331-z
43. Brahmbhatt M, Prenner S, Bittermann T. Liver transplantation for hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma is facilitated by exception points with acceptable long-term outcomes. Transplantation. (2020) 104:1187–92. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002982
44. Lai Q, Feys E, Karam V, Adam R, Klempnauer J, Oliverius M, et al. Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma and adult liver transplantation: proposal for a prognostic score based on the analysis of the ELTR-ELITA registry. Transplantation. (2017) 101:555–64. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001603
45. Konstantinidis IT, Nota C, Jutric Z, Ituarte P, Chow W, Chu P, et al. Primary liver sarcomas in the modern era: Resection or transplantation? J Surg Oncol. (2018) 117:886–91. doi: 10.1002/jso.24979
46. Lerut JP, Orlando G, Adam R, Schiavo M, Klempnauer J, Mirza D, et al. The place of liver transplantation in the treatment of hepatic epitheloid hemangioendothelioma: report of the european liver transplant registry. Ann Surg. (2007) 246:949–57. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31815c2a70
47. Rodriguez JA, Becker NS, O’Mahony CA, Goss JA, Aloia TA. Long-term outcomes following liver transplantation for hepatic hemangioendothelioma: the UNOS experience from 1987 to 2005. J Gastrointest Surg. (2008) 12:110–6. doi: 10.1007/s11605-007-0247-3
48. Grotz TE, Nagorney D, Donohue J, Que F, Kendrick M, Farnell M, et al. Hepatic epithelioid haemangioendothelioma: is transplantation the only treatment option? HPB. (2010) 12:546–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2010.00213.x
49. Seavey CN, Hallett A, Li S, Che K, Pobbati AV, Ma S, et al. Loss of CDKN2A cooperates with WWTR1(TAZ)-CAMTA1 gene fusion to promote tumor progression in epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Clin Cancer Res. (2023) 29:2480–93. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-2497
50. Merritt N, Garcia K, Rajendran D, Lin Z-Y, Zhang X, Mitchell KA, et al. TAZ-CAMTA1 and YAP-TFE3 alter the TAZ/YAP transcriptome by recruiting the ATAC histone acetyltransferase complex. eLife. (2021) 10:e62857. doi: 10.7554/eLife.62857
51. Driskill JH, Zheng Y, Wu B-K, Wang L, Cai J, Rakheja D, et al. WWTR1(TAZ)-CAMTA1 reprograms endothelial cells to drive epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Genes Dev. (2021) 35:495–511. doi: 10.1101/gad.348221.120
52. Seavey CN, Pobbati AV, Hallett A, Ma S, Reynolds JP, Kanai R, et al. WWTR1 (TAZ)- CAMTA1 gene fusion is sufficient to dysregulate YAP/TAZ signaling and drive epithelioid hemangioendothelioma tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. (2021) 35:512–27. doi: 10.1101/gad.348220.120
53. Ma S, Kanai R, Pobbati AV, Li S, Che K, Seavey CN, et al. The TAZ-CAMTA1 fusion protein promotes tumorigenesis via connective tissue growth factor and ras–MAPK signaling in epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Clin Cancer Res. (2022) 28: 3116–26. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-0421
54. Pobbati AV, Rubin BP. Protein-protein interaction disruptors of the YAP/TAZ-TEAD transcriptional complex. Molecules. (2020) 25:6001. doi: 10.3390/molecules25246001
55. Li Q, Sun Y, Jarugumilli GK, Liu S, Dang K, Cotton JL, et al. Lats1/2 sustain intestinal stem cells and wnt activation through TEAD-dependent and independent transcription. Cell Stem Cell. (2020) 26:675–692.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2020.03.002
Keywords: general surgery, hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, SEER, Cox regression analyses, machine learning
Citation: Wang B, Chen X, Li R, Ai B, Ye F, Zhao J, Zhang Y, Huang Z, Li Z, Bi X, Zhao H, Cao D, Cai J, Zhou J and Yan T (2024) Comprehensive evaluation of clinical outcomes in hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma subsets: insights from SEER Database and departmental cohort analysis. Front. Immunol. 15:1491922. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1491922
Received: 05 September 2024; Accepted: 07 October 2024;
Published: 22 October 2024.
Edited by:
Weiling Li, Dalian Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Baifeng Li, The First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Wang, Chen, Li, Ai, Ye, Zhao, Zhang, Huang, Li, Bi, Zhao, Cao, Cai, Zhou and Yan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dayong Cao, Y2FvZGF5b25nZG9jdHR5QDE2My5jb20=; Jianqiang Cai, Y2FpamlhbnFpYW5nZG9jdHR5QDE2My5jb20=; Jianguo Zhou, empndHlkb2N0QDE2My5jb20=; Tao Yan, YmxpenphcmR5dEAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.