- Department of Biophysics and Cell Biology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Debrecen, Debrecen, Hungary
The human voltage-gated proton channel (HV1) provides an efficient proton extrusion pathway from the cytoplasm contributing to the intracellular pH regulation and the oxidative burst. Although its pharmacological inhibition was previously shown to induce cell death in various cell types, no such effects have been examined in polarized macrophages albeit HV1 was suggested to play important roles in these cells. This study highlights that 5-chloro-2-guanidinobenzimidazole (ClGBI), the most widely applied HV1 inhibitor, reduces the viability of human THP-1-derived polarized macrophages at biologically relevant doses with M1 macrophages being the most, and M2 cells the least sensitive to this compound. ClGBI may exert this effect principally by blocking HV1 since the sensitivity of polarized macrophages correlates well with their HV1 expression levels; inhibitors of other macrophage ion channels that may be susceptible for off-target ClGBI effects cause no viability reductions; and Zn2+, another non-specific HV1 blocker, exerts similar effects. As a potential mechanism behind the ClGBI-induced cell death, we identify a complex pH dysregulation involving acidification of the cytoplasm and alkalinization of the lysosomes, which eventually result in membrane ceramide accumulation. Furthermore, ClGBI effects are alleviated by ARC39, a selective acid sphingomyelinase inhibitor supporting the unequivocal significance of ceramide accumulation in the process. Altogether, our results suggest that HV1 inhibition leads to cellular toxicity in polarized macrophages in a polarization-dependent manner, which occurs due to a pH dysregulation and concomitant ceramide overproduction mainly depending on the activity of acid sphingomyelinase. The reduced macrophage viability and plausible concomitant changes in homeostatic M1-M2 balance could contribute to both the therapeutic and potential side effects of HV1 inhibitors that show great promise in the treatment of neuroinflammation and malignant diseases.
1 Introduction
The human voltage-gated proton channel (HV1) is built up by four transmembrane helical segments that act as a voltage-sensor domain and a physiologically outwardly directed proton-conductive pathway in the cell membrane. HV1 is regulated by the membrane potential and pH, activating at depolarizing voltages and during cytosolic acidification (1, 2). While other voltage-gated channels are composed of four voltage-sensor domains controlling one central permeation pore domain, HV1 has a unique dimer structure lacking a conventional pore with each subunit having its own proton permeation pathway localized in the voltage-sensor domain and one gate controlled by one voltage sensor (3). HV1 is expressed in a wide variety of human cell types in which the channel is mainly involved in two major cellular functions. First, a HV1-mediated proton extrusion from the cytoplasm provides a charge compensation for the transmembrane electron transfer occurring due to the activity of the NADPH oxidase and is thus required for a sustained production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). This counterbalancing activity has been linked to the respiratory burst and bacterial clearance of neutrophil granulocytes (4–6), antibody production of B lymphocytes (7), transport-mediated CO2 disposal in the heart (8), immunosuppressive activity of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (9) and various effector functions of T lymphocytes (10). While such regulation is essential for these physiological functions, a HV1-enabled ROS overproduction can also contribute to activation and proinflammatory cytokine production of microglia in neuroinflammation (11). Second, the proton efflux mediated by HV1 efficiently modulates intracellular pH for appropriate sperm activation, motility and capacitation (6, 12, 13) or migration and mineral matrix production of chorion-derived mesenchymal stem cells (14). However, HV1 can also relieve extensive metabolic acidosis that frequently arises during the rapid proliferation of tumor cells and, therefore, its overexpression frequently observed in malignant neoplasms facilitates tumor growth (9).
Although various peptide and small-molecule compounds have been described thus far to inhibit the conductive function of HV1 (6, 15–19), guanidine-containing compounds, particularly 5-chloro-2-guanidinobenzimidazole (ClGBI), are still the most widely applied for this purpose (8, 9, 13, 14, 20–25). Due to the mitigation of ROS overproduction, an inhibition of HV1 was proposed to show great promise in acute lung injury (26), ischemic stroke (27, 28), multiple sclerosis (29, 30), brain and spinal cord injury (31–33), and peripheral neuropathic and inflammatory pain (18, 34). Furthermore, by eliminating the protection from proliferation-associated metabolic acidosis, a HV1 block was proposed to favorably reduce the growth rate of various malignant tumors such as breast cancer (25, 35, 36), colorectal carcinoma (37), glioblastoma multiforme (38) or leukemia (15, 39). The pH dysregulation associated with blocking HV1 conductivity can lead to cell death by triggering apoptotic processes, which may thus contribute to both the intended and adverse effects of the compounds. Consistently, a pharmacological HV1 inhibition was previously shown to compromise the viability of various cell types including Jurkat T lymphocytes (20), chorion-derived mesenchymal stem cells (14), activated mouse microglia (23), myeloid-derived suppressor cells (9), breast cancer (25) and glioblastoma multiforme cell lines (38).
Macrophages, essential cellular components of the innate immune system, are plastic and heterogeneous cells whose differentiation and activation are distinctively elicited by a large variety of stimuli. In general, macrophages are classified into M1, or classically activated, and M2, or alternatively activated subsets. M1 macrophages activated by Th1 cytokines, such as interferon-γ, and Toll-like receptor ligands, e.g., bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS), produce proinflammatory cytokines and mediators, and participate in defense mechanisms against pathogens and tumors, while M2 macrophages induced by Th2 or anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-4 (IL-4), interleukin-13 (IL-13) or interleukin-10 (IL-10), are rather involved in the resolution of inflammation, scavenging apoptotic cells and debris, tissue remodeling and immune regulation (40, 41). Although this dichotomous classification is convenient, it is largely oversimplified since M2 macrophages can be further divided into distinct functional subpopulations. Therefore, M1 and M2 phenotypes rather represent extremes of a continuum of functional states, and these phenotypes are dynamically interconvertible through reprogramming depending on microenvironmental signals (42–44). Nevertheless, the M1-M2 classification is still an operationally useful framework for didactic reasons and because dysregulated macrophage polarization is often associated with the occurrence and progression of various diseases. An imbalance in macrophage polarization with proinflammatory M1 dominance was linked to a consequently enhanced inflammation in atherosclerosis, obesity and metabolic disorder, and autoimmune diseases such as Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis or autoimmune hepatitis. On the contrary, an M2 preponderance can contribute to allergic airway inflammation and asthma, and a shift from tumor-infiltrating M1 macrophages to a predominantly M2-like tumor-associated macrophage phenotype is associated with immune evasion of malignant tumors. Hence, altering the balance of macrophage polarization is considered as a potential therapeutic target in these disorders and, therefore, understanding the factors regulating polarization and the role of certain proteins in differentially activated macrophages carries substantial biomedical relevance (43, 45). HV1 expression was previously described in murine and human, including THP-1-derived macrophages as well (46, 47). In these cells, the proton efflux mediated by HV1 was subsequently shown to play important roles in the sustained ROS production (48), proper phagosomal acidification and pH oscillations (49, 50), and protection from intracellular fungal pathogens (51). However, the potential effects of blocking the HV1 channel on the viability of polarized macrophages have not been thoroughly tested yet in spite of the fact that a reduced viability and plausible changes in homeostatic M1-M2 balance could largely alter both macrophage-related physiological and pathophysiological processes.
As mentioned above, intracellular pH dysregulation caused by HV1 inhibition is often associated with triggering cell death processes (9, 20, 23, 25, 38). However, the molecular details of this connection have not been elucidated yet. Membrane ceramides comprise a special class of sphingolipids, which are characterized by unique membrane biophysical properties due to their extreme hydrophobicity and compactness resulting from a very small hydrophilic headgroup (52–54). While ceramides are generally present normally at minuscule levels in the cell membrane, various stress stimuli including tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), ionizing radiation and chemotherapeutic drugs result in their accumulation, which in turn activates different forms of cell death such as necrosis or apoptosis. Accordingly, the level of membrane ceramides is strictly regulated by a highly complex interconnected network of enzymes involved in their production and degradation. Ceramides typically accumulate through de novo synthesis, which mainly depends on the activity of the rate-limiting enzyme, serine palmitoyltransferase, or degradation of the ubiquitous sphingomyelin by neutral or acidic sphingomyelinase (55–57). Given that activities of these enzymes strongly depend on pH (58–60), it is tempting to speculate that complex pH alterations associated with HV1 inhibition may lead to cell death through ceramide overproduction.
In this study, we show that ClGBI, the most widely applied inhibitor of HV1, dose-dependently reduces the viability of human THP-1-derived polarized macrophages at biologically relevant doses and the sensitivity of the distinctly polarized macrophages differ with M1 cells being the most prone, and M2 macrophages the least sensitive to the compound. Through obtaining similar results with Zn2+, another HV1 blocker, and demonstrating the lack of notable effects of blockers of other ion channels that are relevant in macrophages and possible subjects of off-target ClGBI inhibition, we also provide experimental evidence for this ClGBI-induced effect indeed being mediated predominantly through HV1 inhibition. In addition, we show that the compromised viability occurs due to a complex pH dysregulation involving both the cytoplasmic and lysosomal compartments, and it is accompanied by elevations in membrane ceramide levels. Furthermore, supporting the intrinsic role of ceramide in the HV1 block-induced compromised viability of macrophages, we demonstrate that the effects of ClGBI can be alleviated by ARC39, a compound that selectively inhibits acid sphingomyelinase-mediated ceramide production.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Cell culture, differentiation and polarization of macrophages
The human acute monocytic leukemia-derived cell line THP-1 was obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA) and cultivated according to its specifications. THP-1 cells were differentiated into macrophages for 24 h by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) at a final concentration of 10 ng/ml to achieve sufficient differentiation and minimize unspecific gene expression changes (61, 62), which was followed by a resting period of 24 h in the absence of PMA to ensure the M0 phenotype of the produced macrophages (61, 63). The differentiated M0 macrophages were subsequently polarized for 24-48 h into classical M1 macrophages with 100 ng/ml lipopolysaccharide (LPS; E. coli O111:B4 ultrapure, Sigma-Aldrich) plus 20 ng/ml interferon-γ (IFN-γ; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA), or M2 macrophages using 20 ng/ml interleukin-4 (IL-4; Thermo Fisher Scientific) plus 20 ng/ml interleukin-13 (IL-13; Thermo Fisher Scientific), according to a widely applied protocol (64–67). All treatments were carried out at 37°C.
2.2 Analysis of plasma membrane expression of CD markers in polarized macrophages
Differentiated and polarized THP-1-derived macrophages grown in 6-well plates were washed and treated with accutase (Sigma-Aldrich) at room temperature for 5 min to gently detach adherent cells without compromising cell viability (68). After stopping the reaction with cell culture medium and washing, Fc receptors of cells were blocked for 20 min with human FcR blocking reagent (Miltenyi Biotec, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany) applied at 10 µg/ml. Subsequently, cells were labeled with one of the following antibodies: FITC-conjugated anti-CD64 (at a concentration of 4 µg/ml), Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated anti-CD71 (4 µg/ml), FITC-conjugated anti-CD80 (4 µg/ml), PE-Cy5-conjugated CD86 (1 µg/ml), PE-conjugated CD206 (0.5 µg/ml). All antibodies were obtained from Thermo Fisher and applied for 20 min at room temperature. After washing, the fluorescence intensity of individual cells was measured using a NovoCyte 3000RYB flow cytometer (ACEA Biosciences, San Diego, CA) with the following excitation wavelengths and emission filters, respectively: FITC – 488 nm and 530/30 nm; Alexa Fluor 647 – 640 nm and 660/20 nm; PE-Cy5 – 561 nm and 660/20 nm; PE – 561 nm and 586/20 nm. During data analysis carried out in FCS Express (De Novo Software, Los Angeles, CA), the average fluorescence intensity of at least 10,000 cells of normal morphology on FSC-SSC dot plots was calculated for each sample. The low extent of nonspecific binding of antibodies was supported by data obtained with isotope control antibodies FITC-conjugated Mouse IgG1 kappa Isotype Control, PE-Cy5-conjugated Mouse IgG1 kappa Isotype Control, PE-conjugated Mouse IgG1 kappa Isotype Control and Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated Mouse IgG2b kappa Isotype Control (all from Thermo Fisher) applied at identical experimental conditions (Supplementary Figure 1).
2.3 Examination of effects of ion channel inhibitors on the viability of polarized macrophages
THP-1 cells seeded into 24-well plates were differentiated into macrophages and polarized as above, and treated subsequently for 24 h with ion channel inhibitors supplemented into the culture media of cells. In the case of ClGBI (5-chloro-2-guanidinobenzimidazole; Sigma-Aldrich), a dilution series with concentrations ranging between 16 and 256 µM was used, while in other experiments cells were treated with 20 pM Vm24 scorpion toxin (Alomone Labs, Jerusalem, Israel), 20 nM TTX (tetrodotoxin; Alomone Labs), 1 mM TEA+ (tetraethylammonium; Sigma-Aldrich), or 1 mM (nominal) ZnCl2 (Sigma-Aldrich). For the investigation of potential protective effects of pretreatments with ceramide production inhibitors against ClGBI-induced toxicity, 1 µM myriocin (Sigma-Aldrich), 2 µM GW4869 (Sigma-Aldrich) or 5 µM ARC39 (Cayman Chemical, Ann Arbor, MI) was given to polarized M0, M1 and M2 macrophages 30 min before the application of ClGBI. For the determination of the fraction of viable cells calculated as viable fraction = number of double negative cells/number of all cells, as described previously (53, 69, 70), we collected the supernatant containing cells detached from the surface of the well, and pooled them with the adherent cells, which were detached by accutase. This cell suspension was labeled with Sytox Green Dead Cell Stain (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated annexin V (Thermo Fisher Scientific) at dilutions of 1:1000 and 1:20, respectively, in annexin binding buffer for 15 minutes at room temperature. Fluorescence intensities of at least 10,000 individual cells per sample were subsequently measured using a NovoCyte 3000RYB flow cytometer. Sytox Green and Alexa Fluor 647 fluorophores were excited at 488 and 640 nm, respectively, and emitted intensities were measured using 530/30 and 660/20 emission filters, respectively. During data analysis, the fraction of Sytox Green and annexin V negative viable cells was calculated for each sample using FCS Express.
2.4 Determination of HV1 expression in polarized macrophages
Differentiated and polarized THP-1-derived macrophages grown in 12-well plates were washed and detached with accutase, which was followed by fixation in ice-cold methanol (Sigma-Aldrich) for 20 minutes. After permeabilization in 0.1% Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich), cells were blocked with human FcR blocking reagent and 5% BSA for 30 minutes at room temperature. Subsequently, cells were labeled with anti-HV1 antibodies (PA5-24964, Thermo Fisher Scientific) for 60 minutes at room temperature at 5 µg/ml and, after washing, with Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG antibodies (Thermo Fisher Scientific) for 30 minutes at room temperature at a dilution of 1:500 (25). All steps were carried out in a solution containing 1% BSA and 0.1% Triton X-100. The fluorescence intensity of individual cells was measured with NovoCyte 3000RYB using excitation at 640 nm and a 660/20 emission band pass filter and average fluorescence intensities of at least 10,000 cells with a normal morphology gated on FSC-SSC plots were calculated in each sample in FCS Express. The low extent of nonspecific binding of the primary antibody was supported by data obtained with the isotope control antibody Rabbit IgG Isotype Control (Thermo Fisher) applied at identical experimental conditions (Supplementary Figure 2).
2.5 Investigation of time-dependent effects of ClGBI on the cytoplasmic pH of polarized macrophages
THP-1 cells seeded into 24-well plates were differentiated into macrophages and polarized as above, and treated subsequently for 1, 4 or 18 h with 50 or 100 µM ClGBI supplemented into the culture media of cells. In the last 30 min of incubation at 37°C, 5 µM pHrodo Red AM Intracellular pH Indicator (Thermo Fisher) was further added to cells (71). After washing and detachment of cells with accutase, the fluorescence intensity of individual cells was measured with NovoCyte 3000RYB using excitation at 561 nm and a 586/20 emission band pass filter and average fluorescence intensities of at least 10,000 cells with a normal morphology gated on FSC-SSC plots were calculated in each sample in FCS Express. For calibration samples, cells were further incubated for 5 min at 37°C in the presence of 10 µM valinomycin and 10 µM nigericin dissolved into cellular calibration pH buffers according to the instruction of the manufacturer, which was followed by measurement as above. Corresponding pH values were interpolated from the calibration curve.
2.6 Examination of time-dependent effects of ClGBI on the lysosomal pH of polarized macrophages
THP-1 cells seeded into 8-well chambered coverglass were differentiated into macrophages and polarized as above, and treated subsequently for 1, 4 or 18 h with 50 or 100 µM ClGBI supplemented into the culture media of cells. 3 hours before the measurement time, 70,000 MW, anionic dextrane conjugated to pH-sensitive fluorescein and pH-insensitive tetramethylrhodamine (TAMRA) (Thermo Fisher) was added to cells for 1 h at 37°C, which was followed by washing and a chase of 2 h at 37°C to ensure the exclusive lysosomal accumulation of the indicator (72). Live cell imaging was carried out in medium buffered with 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, and images were taken at the midplane of cells using an LSM880 confocal laser-scanning microscope (Carl Zeiss AG, Jena, Germany). Fluorescein and TAMRA were excited at 488 nm and 543 nm, respectively, and their emission was detected in the wavelength ranges of 493-559 nm and 559-685 nm, respectively. During image analysis in Matlab (Mathworks, Natick, MA), after manual selection of pixels corresponding to an individual cell based on the transmission image, a threshold value of the TAMRA fluorescence intensity was determined and pixels having larger TAMRA intensity than the threshold were identified as lysosomal pixels. Subsequently, the average fluorescein/TAMRA fluorescence intensity ratio positively correlating with the value of lysosomal pH was calculated for each cell using data of lysosomal pixels exclusively. For calibration samples, cells were incubated for 15 min at 37°C in the presence of 10 µM valinomycin, 10 µM nigericin and 0.1 µM bafilomycin dissolved into cellular calibration pH buffers according to the instruction of the manufacturer, which was followed by measurement as above. Corresponding pH values for each ratio were interpolated from the calibration curve.
2.7 Analysis of time-dependent effects of ClGBI on the plasma membrane ceramide levels of polarized macrophages
THP-1 cells seeded into 24-well plates were differentiated into macrophages and polarized as above, and treated subsequently for 1, 4 or 18 h with 50 or 100 µM ClGBI supplemented into the culture media of cells. After washing, detachment with accutase and FcR blocking as above, treated and control M0, M1 and M2 cells were labeled with anti-ceramide antibodies clone 15B4 (Sigma-Aldrich) at 4 µg/ml for 60 min at room temperature, which was followed by washing and a 20-min staining with Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgM antibody (Thermo Fisher Scientific) at 4 µg/ml at room temperature. The fluorescence intensity of individual cells was measured with NovoCyte 3000RYB using excitation at 640 nm and a 660/20 emission band pass filter and average fluorescence intensities of at least 10,000 cells with a normal morphology gated on FSC-SSC plots were calculated in each sample in FCS Express. The low extent of nonspecific binding of the primary antibody was supported by data obtained with the isotope control antibody Mouse IgM Isotype Control (Thermo Fisher) applied at identical experimental conditions (Supplementary Figure 5).
2.8 Statistical analysis
Measured data are represented as mean ± SEM obtained from n biological replicates for flow cytometry or n individual cells from five independent experiments for confocal microscopy, as indicated in figure legends. In measurements carried out with a flow cytometer, at least 10,000 cells per sample were analyzed in each independent experiment. The p values were calculated by Tukey’s HSD test carried out after significant differences were obtained for between-group effects in ANOVA. Differences were considered significant when p < 0.05 (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001).
3 Results
3.1 Establishment and validation of a THP-1-derived polarized macrophage model
In order to generate a simple, efficient and reproducible experimental model of human polarized macrophages, we differentiated acute monocytic leukemia-derived THP-1 cells into macrophages using a low, 10 ng/ml concentration of PMA for 24 h, which, similar to what we observed in our previous studies (73, 74), resulted in attachment of the cells to the bottom of the culture dish, and substantial changes in cellular morphology typical for macrophages with reduced nucleocytoplasmic ratio. After resting PMA-differentiated macrophages for additional 24 h in medium lacking PMA or other activators to ensure M0 phenotype, the cells were polarized according to the classical M1 activation route via LPS and IFN-γ, or on the alternative M2 pathway using IL-4 and IL-13 (64–67). To validate our experimental model, the success of polarization was subsequently tested after 24 and 48 h of polarization by examining the cell surface expression pattern of CD markers characteristic for the different macrophages using flow cytometry. In agreement with literature data, THP-1-derived macrophages treated with LPS and IFN-γ for 24 or 48 h showed distinctive properties of M1 activation manifested in significantly elevated levels of CD64, CD80 and CD86, which were accompanied by no changes in CD206 expression and reduced CD71 levels (Figure 1; Supplementary Figure 1). In contrast, cells treated with IL-4 and IL-13 for 24 or 48 h displayed an M2-like CD marker expression profile with significantly increased amounts of cell surface CD71 and CD86 in the absence of changes in CD64 or CD80 expression. In addition, significantly higher expression of the M2-specific CD206 was found in IL-4 and IL-13-treated cells, however, that appeared only after 48 h. Furthermore, CD expression patterns were strongly similar after 24-h and 48-h polarization, which altogether imply that our generated M1 and M2 cells exhibit cell surface CD expression profiles characteristic for classically and alternatively activated macrophages (75, 76), respectively, already after 24 h polarization, which are retained at least for 48 h. Therefore, experiments described in the next sections and performed between 24 and 48 h of polarization were carried out in stably polarized macrophages.
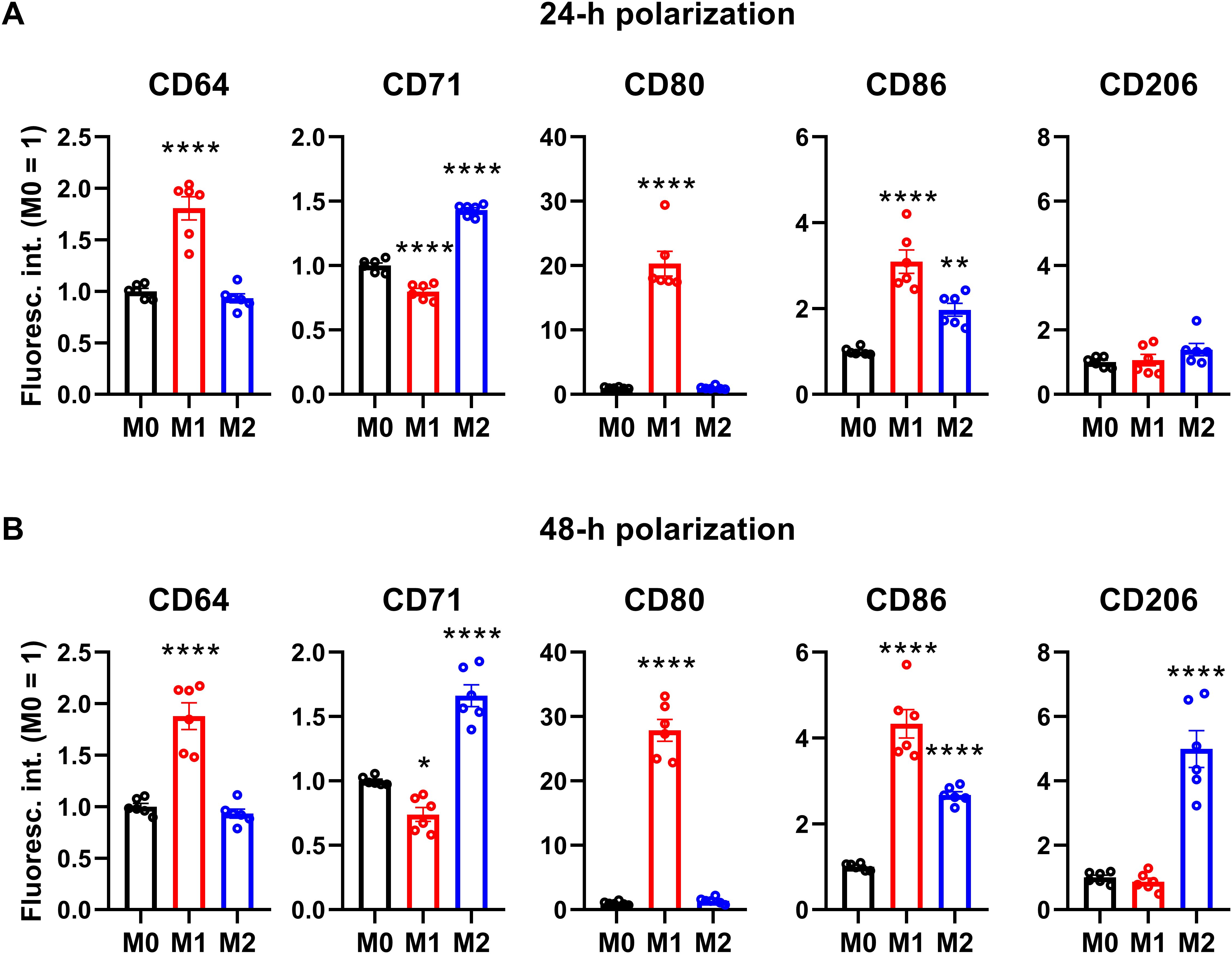
Figure 1. Cell surface CD marker expression profiles of M0, M1 and M2 THP-1-derived macrophages. THP-1 cells were differentiated into macrophages for 24 h by 10 ng/ml PMA, which was followed by a 24-h resting period in the absence of PMA. The differentiated M0 macrophages were subsequently polarized for 24 h (A) or 48 h (B) into classical M1 macrophages with 100 ng/ml LPS plus 20 ng/ml IFN-γ, or M2 macrophages using 20 ng/ml IL-4 plus 20 ng/ml IL-13. After accutase-mediated detachment and Fc receptor blocking, the cell surface expression of CD markers of differentiated and polarized macrophages was quantified using fluorophore-conjugated antibodies and flow cytometry. The average fluorescence intensity of at least 10,000 individual cells of normal morphology per sample was determined and subsequently normalized to the mean value of M0 samples. The normalized fluorescence intensity values obtained in n = 6 biological replicates, and their average values (± SEM) are plotted in both panels. Asterisks indicate significant differences compared to M0 samples (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001, ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD test).
3.2 The HV1 inhibitor ClGBI dose- and polarization-dependently reduces the viability of polarized macrophages
To test whether HV1 inhibition compromises the viability of polarized macrophages similarly to that described in various cell types (9, 14, 20, 23, 25, 38), we treated THP-1-derived macrophages polarized as above with a concentration series of ClGBI, a widely applied inhibitor of the channel (8, 9, 13, 14, 20–25). For this, ClGBI-treated and control cells were gently detached with accutase, which was previously shown not to affect cell viability (68), and subsequently labeled with Sytox Green and Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated annexin V to identify necrotic and apoptotic cells, respectively, and determine the fraction of double negative viable cells using flow cytometry (53, 69, 70). In all three examined THP-1-derived macrophage populations, ClGBI significantly and dose-dependently reduced the fraction of living cells (Figure 2). Notably, ClGBI resulted in dramatically lower cell viability at 128 and 256 µM, i.e. concentrations widely applied in cellular studies examining the functions of HV1 (8, 13, 14, 21, 22). Furthermore, the sensitivity of cells varied among the different macrophages as, at most examined concentrations, the effect induced in M1 cells was significantly higher, while that of M2 macrophages significantly lower than in the case of resting M0 macrophages.
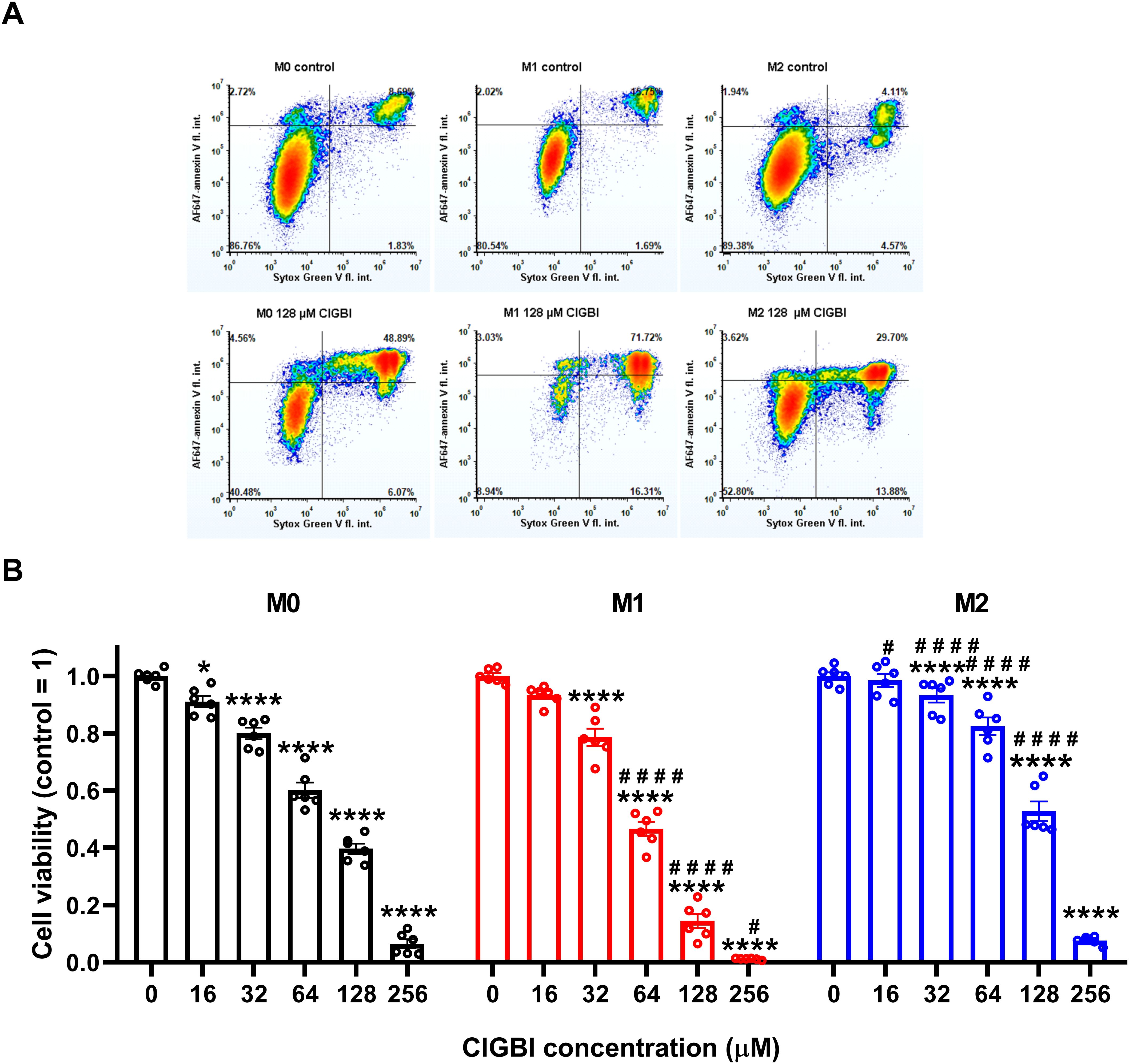
Figure 2. The HV1 inhibitor ClGBI dose-dependently compromises the viability of polarized macrophages most effectively in M1 cells. THP-1 cells were differentiated into macrophages for 24 h by 10 ng/ml PMA, which was followed by a 24-h resting period in the absence of PMA. The differentiated M0 macrophages were subsequently polarized for 24 h into classical M1 macrophages with 100 ng/ml LPS plus 20 ng/ml IFN-γ, or M2 macrophages using 20 ng/ml IL-4 plus 20 ng/ml IL-13. Cells were subsequently treated for 24 h with ClGBI at concentrations ranging between 16 and 256 µM. After collecting cells in suspension and those detached by accutase, the macrophages were labeled with Sytox Green and Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated annexin V to identify necrotic and apoptotic cells, respectively. Fluorescence intensities of individual cells were measured using flow cytometry and the relative fraction of double negative viable cells was determined in each sample containing at least 10,000 cells, and normalized to the mean value determined in control untreated samples. (A) Representative density plots demonstrate the effect of 128 µM ClGBI on the viability of M0, M1 and M2 macrophages. (B) The normalized viable ratios obtained in n = 6 biological replicates, and their average values (± SEM) are plotted in the figure. Asterisks indicate significant differences compared to control samples (*p < 0.05, ****p < 0.0001), while hashes show that compared to M0 at the given applied ClGBI concentration (#p < 0.05, ####p < 0.0001), which were determined by Tukey’s HSD test carried out after significant differences were obtained for between-group effects in ANOVA.
3.3 The ClGBI-induced decrease in viability of polarized macrophages is mediated through HV1 inhibition
To corroborate that ClGBI-induced reductions in cell viability are induced by HV1 inhibition and not the off-target effects of the compound on other macrophage-resident ion channels (77), we examined the impact of other relevant ion channel blockers on the viability of M0, M1 and M2 THP-1-derived macrophages by applying Vm24 scorpion toxin, a specific blocker of KV1.3 (78), tetrodotoxin, a specific inhibitor of voltage-gated sodium channels (79), TEA+, a wide-spectrum potassium channel blocker (80), and Zn2+, a well-known non-specific inhibitor of HV1 (1). Vm24, tetrodotoxin, TEA+ and Zn2+ were applied at concentrations most commonly utilized in in vitro functional assays and cellular studies. In these experiments, TTX failed to affect cell viability, and the potassium channel inhibitors Vm24 or TEA+ resulted in only mild effects mainly in M1 cells. On the contrary, the HV1 inhibitor Zn2+ remarkably reduced the viability of macrophages, particularly in M1 cells in accordance with ClGBI effects (Figure 3). While the effect induced by Zn2+ on M1 macrophages was significantly larger than that on M0 cells, the difference between M1 and M2 was on the verge of statistical significance (p=0.0678). Although the significant difference between the effect of ClGBI on the viability of M1 and M2 macrophages would suggest a similar correlation for the effect of Zn2+, the lack of a smaller effect of Zn2+ on the viability of M2 macrophages can potentially be attributed to the importance of Zn-sensitive proteins in the function of M2 macrophages and consequent potential off-target effects or the lower potency of Zn2+ compared to ClGBI (81).
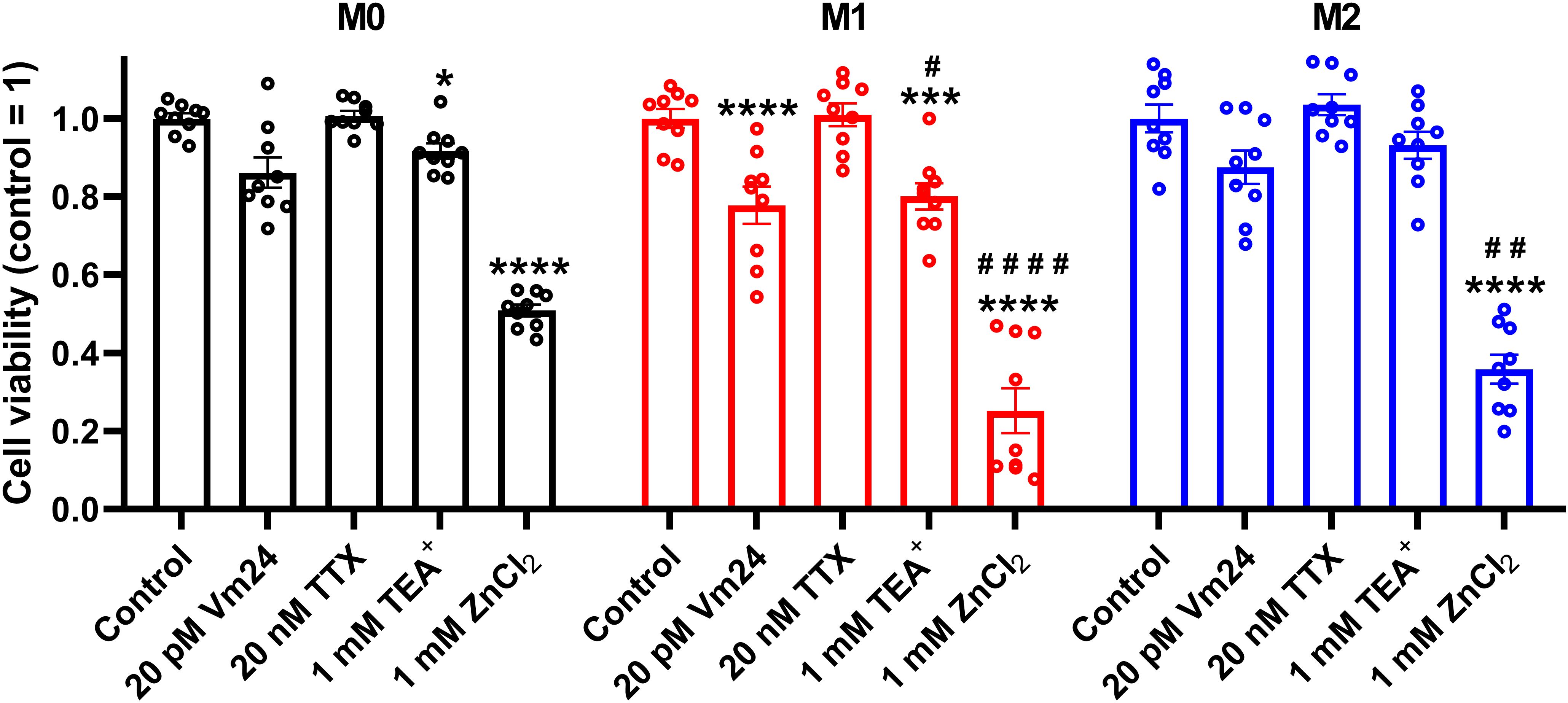
Figure 3. Effects of ion channel blockers on the viability of polarized macrophages. THP-1 cells were differentiated into macrophages for 24 h by 10 ng/ml PMA, which was followed by a 24-h resting period in the absence of PMA. The differentiated M0 macrophages were subsequently polarized for 24 h into classical M1 macrophages with 100 ng/ml LPS plus 20 ng/ml IFN-γ, or M2 macrophages using 20 ng/ml IL-4 plus 20 ng/ml IL-13. Cells were subsequently treated for 24 h with 20 pM Vm24 scorpion toxin, 20 nM TTX, 1 mM TEA+ or 1 mM (nominal) ZnCl2. After collecting cells in suspension and those detached by accutase, the macrophages were labeled with Sytox Green and Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated annexin V to identify necrotic and apoptotic cells, respectively. Fluorescence intensities of individual cells were measured using flow cytometry and the relative fraction of double negative viable cells was determined in each sample containing at least 10,000 cells, and normalized to the mean value determined in control untreated samples. The normalized viable ratios obtained in n = 9 biological replicates, and their average values (± SEM) are plotted in the figure. Asterisks indicate significant differences compared to control samples (*p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001), while hashes show that compared to M0 at the given applied inhibitor concentration (#p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ####p < 0.0001), which were determined by Tukey’s HSD test carried out after significant differences were obtained for between-group effects in ANOVA.
Since both of the examined HV1 blockers, ClGBI and Zn2+, compromised the viability of M1 macrophages to a larger extent than in M0 or M2 cells (Figures 2, 3), we next investigated the HV1 expression in these cells using flow cytometry. Consistent with the larger effects of HV1 blockers, M1 cells exhibited significantly higher HV1 expression than M0 cells, while the abundance of HV1 was the lowest in M2 cells (Figure 4A; Supplementary Figure 2). Furthermore, an excellent correlation was found between the extents of reductions in the viability of M0, M1 and M2 macrophages and the levels of HV1 expression (Figure 4B). Altogether, the results obtained with other relevant ion channel inhibitors and the correlation between HV1 expression and the extent of HV1 inhibition-induced reductions in cell viability convincingly support that the effects elicited by ClGBI may in fact be caused by its inhibitory actions on HV1.
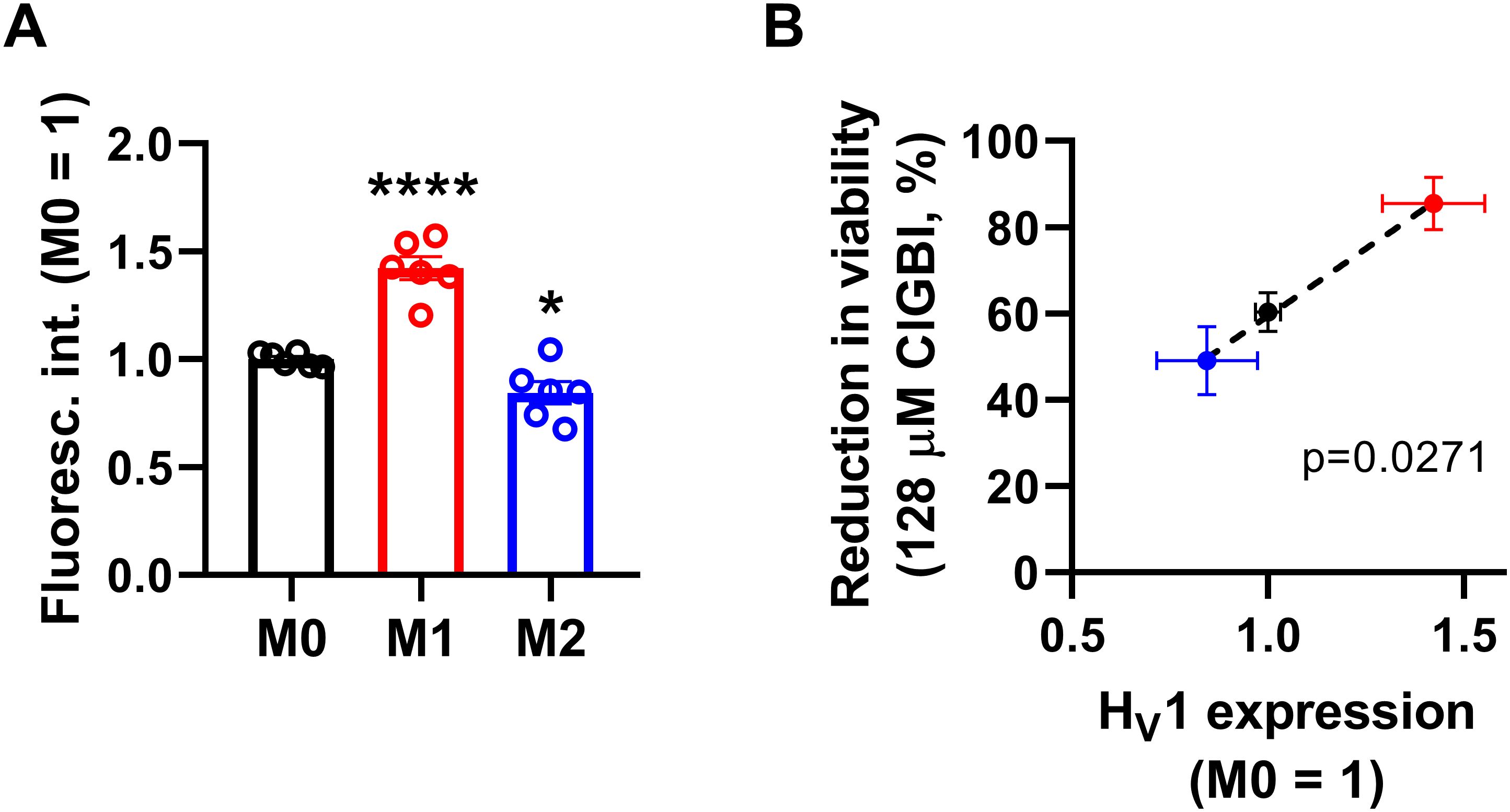
Figure 4. The HV1 expression of polarized macrophages correlates with the ClGBI-induced reduction in cell viability. (A) THP-1 cells were differentiated into macrophages for 24 h by 10 ng/ml PMA, which was followed by a 24-h resting period in the absence of PMA. The differentiated M0 macrophages were subsequently polarized for 24 h into classical M1 macrophages with 100 ng/ml LPS plus 20 ng/ml IFN-γ, or M2 macrophages using 20 ng/ml IL-4 plus 20 ng/ml IL-13. After accutase-mediated detachment, fixation, permeabilization and Fc receptor blocking, the HV1 expression of differentiated and polarized macrophages was quantified using indirect immunofluorescence labeling and flow cytometry. The average fluorescence intensity of at least 10,000 individual cells of normal morphology per sample was determined and subsequently normalized to the mean value of M0 samples. The normalized fluorescence intensity values obtained in n = 6 biological replicates, and their average values (± SEM) are plotted in the figure. Asterisks indicate significant differences compared to M0 samples (*p < 0.05, ****p < 0.0001, ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD test). (B) Average values (± SEM) of reduction in the viability of M0, M1 and M2 macrophages induced by 128 µM ClGBI as a function of HV1 expression normalized to M0 cells. The p value determined with Deming regression analysis is shown in the panel, which revealed significant correlation between the extent of compromised cell viability and HV1 expression.
3.4 ClGBI-induced alterations in cytoplasmic and lysosomal pH of polarized macrophages
Since an HV1 deficiency or inhibition was previously shown to affect pH regulation by inducing cytoplasmic acidification in different cell types (8, 10, 13, 18, 20, 23, 28, 36, 82), we next investigated changes in the pH of the cytoplasm of polarized macrophages by using flow cytometry and pHrodo Red AM, an intracellular pH-sensitive fluorescence indicator that traverses the cell membrane and remains within the intracellular space upon cleavage by nonspecific esterases (71). In these measurements, we applied ClGBI for various durations at concentrations roughly corresponding to the dose eliciting 50% decreases in cell viability, i.e. 100 µM for M0 and M2 cells and 50 µM for M1 cells. Furthermore, to ensure comparability of sensitivities, we carried out experiments by adding 100 µM to M1 cells as well. Given that cell death is generally associated with losing adherence, in these experiments and those described later when examining the mechanism of ClGBI action, we analyzed only the cells that remained adherent to the cell culture dish after the treatment to investigate molecular events leading to cell death and not solely appearing as a consequence of it. We observed time-dependent increases in the fluorescence intensity of the dye in all macrophage populations referring to a pH reduction. To quantify these alterations, we performed calibration with samples incubated in the presence of a combination of valinomycin and nigericin dissolved into cellular calibration buffers of known pH. When interpolating pH values of samples from the calibration curve, we found significant time-dependent pH decreases in all macrophage subtypes in response to ClGBI (Figure 5; Supplementary Figure 3). Notably, the magnitudes of changes were the largest in M1 cells, particularly at 100 µM concentration of the compound, in accordance with the higher HV1 expression of these cells.
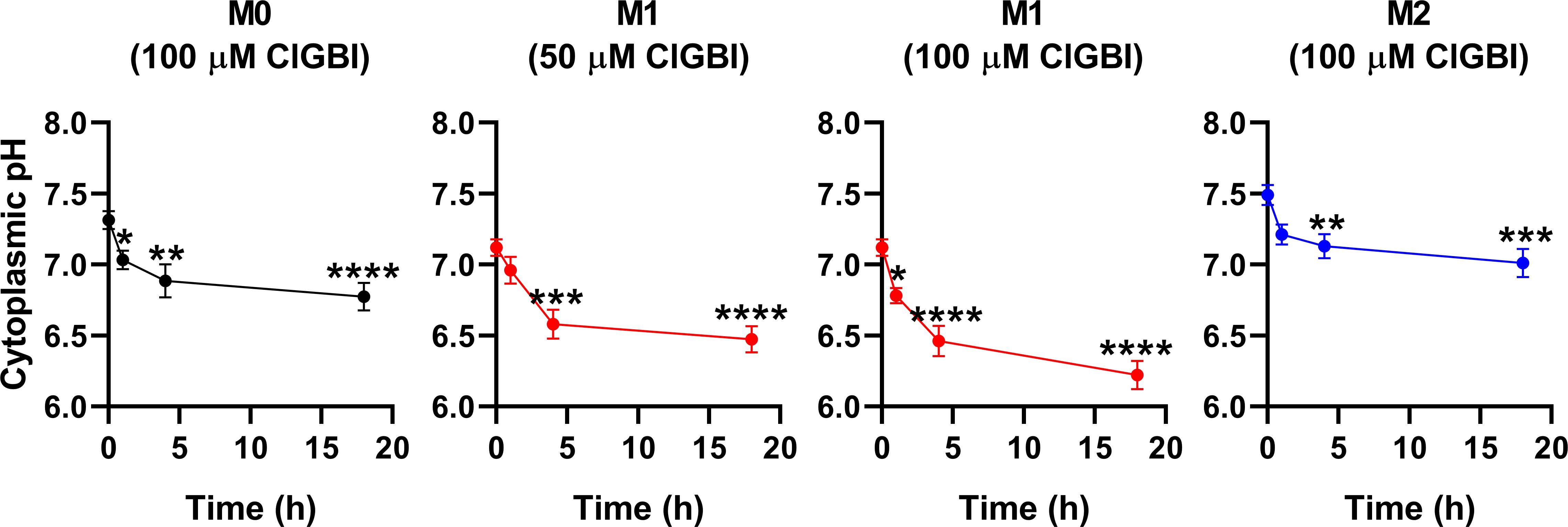
Figure 5. ClGBI time-dependently acidifies the cytoplasm of polarized macrophages most efficiently in M1 cells. THP-1 cells were differentiated into macrophages for 24 h by 10 ng/ml PMA, which was followed by a 24-h resting period in the absence of PMA. The differentiated M0 macrophages were subsequently polarized for 24 h into classical M1 macrophages with 100 ng/ml LPS plus 20 ng/ml IFN-γ, or M2 macrophages using 20 ng/ml IL-4 plus 20 ng/ml IL-13. Cells were subsequently treated for 1, 4 or 18 h with 50 or 100 µM ClGBI. In the last 30 min of incubation, the cytoplasmic pH indicator pHrodo Red AM was further added to cells. After accutase-mediated detachment, the fluorescence intensity of individual cells was measured using flow cytometry and the average fluorescence intensity of at least 10,000 cells of normal morphology per sample was determined. Corresponding pH values of individual cells were subsequently interpolated from the calibration curve determined based on calibration samples incubated with valinomycin and nigericin dissolved into cellular calibration pH buffers. The average pH values obtained from n = 12 biological replicates (± SEM) are plotted in the figure. Asterisks indicate significant differences compared to untreated control samples (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD test).
While lysosomal pH alterations in response to HV1 inhibition and their potential link to compromised viability have not been examined previously in any cell types, based on the facts that a deficiency or a block of the channel modifies phagosomal pH acidification (49, 50) and reduced lysosomal acidity is often associated with cell death (82, 83), it is reasonable to assume that such lysosomal pH changes may occur due to reduced HV1 conductance, which could contribute to cellular toxicity. To confirm this hypothesis, we evaluated ClGBI-induced effects on lysosomal pH. For this, polarized macrophages were treated with ClGBI as described above, and also incubated for 1 h in the presence of 70,000 MW, anionic dextrane conjugated to a pH-sensitive and a pH-insensitive fluorophore, fluorescein and tetramethylrhodamine, respectively, which was followed by a chase period in the absence of the dextrane for 2 h. This protocol ensured that the indicator is exclusively accumulated into the lysosomes (72). Hence, fluorescence microscopic determination of the Fluorescein/TAMRA ratio quantifies the lysosomal pH of cells. Fluorescein/TAMRA ratios can be directly translated into lysosomal pH values by applying calibration samples with valinomycin, nigericin and bafilomycin dissolved into cellular calibration buffers of known pH. By using this method, we observed significant time-dependent alkalinization of the lysosomes of M0, M1 and M2 macrophages as well in response to blocking HV1 channels with ClGBI (Figure 6; Supplementary Figure 4). Again, the largest effects were found in M1 macrophages at 100 µM ClGBI. Altogether, our results suggest a profound pH dysregulation throughout the cell in response to HV1 inhibition, which involves both the cytoplasmic and lysosomal compartments.
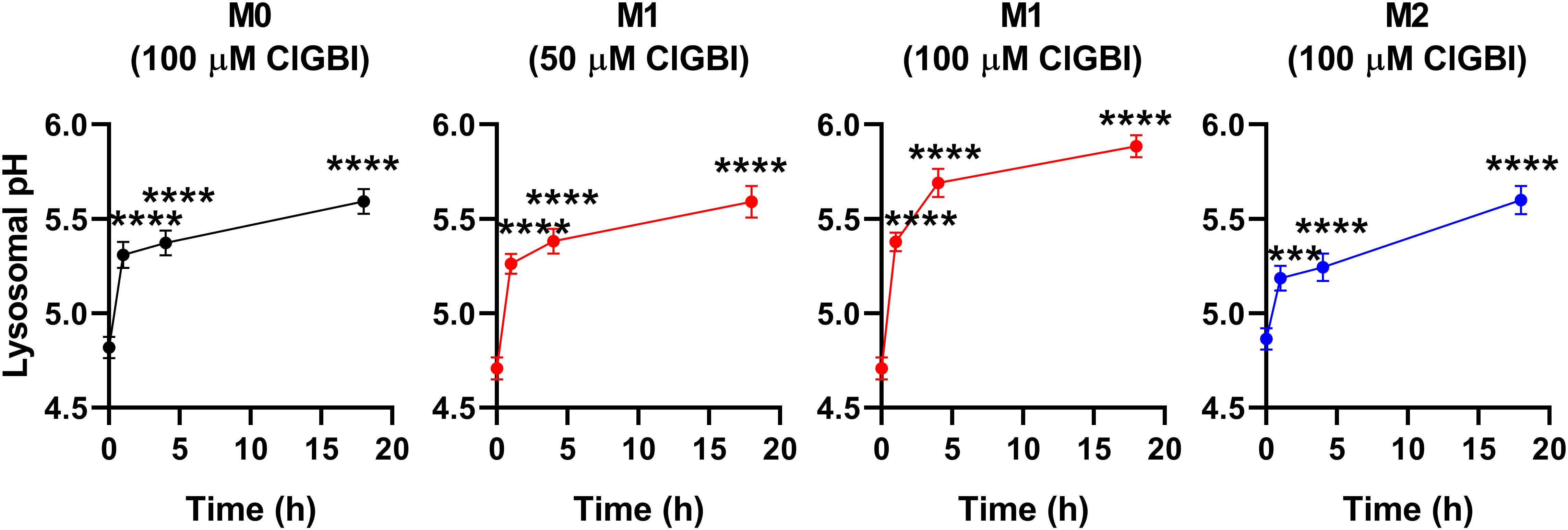
Figure 6. ClGBI time-dependently alkalizes the lyosomes of polarized macrophages most efficiently in M1 cells. THP-1 cells were differentiated into macrophages for 24 h by 10 ng/ml PMA, which was followed by a 24-h resting period in the absence of PMA. The differentiated M0 macrophages were subsequently polarized for 24 h into classical M1 macrophages with 100 ng/ml LPS plus 20 ng/ml IFN-γ, or M2 macrophages using 20 ng/ml IL-4 plus 20 ng/ml IL-13. Cells were subsequently treated for 1, 4 or 18 h with 50 or 100 µM ClGBI. 3 hours before the measurement time, 70,000 MW, anionic dextrane conjugated to pH-sensitive fluorescein and pH-insensitive tetramethylrhodamine (TAMRA) was added to cells for 1 h, which was followed by a chase of 2 h. Then, images were taken at the midplane of cells using a confocal microscope and the average fluorescein/TAMRA fluorescence intensity ratio positively correlating with the value of lysosomal pH was calculated for each individual cell using data of pixels corresponding to lysosomes. pH values were subsequently interpolated from the calibration curve determined based on calibration samples incubated with valinomycin, nigericin and bafilomycin dissolved into cellular calibration pH buffers. The average pH values obtained from n = 60-80 individual cells obtained from five independent experiments (± SEM) are plotted in the figure. Asterisks indicate significant differences compared to untreated control samples (***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD test).
3.5 ClGBI-induced reductions in cell viability are associated with parallel time-dependent elevations of plasma membrane ceramide levels
While experiments outlined in the previous section demonstrated pH alterations, they did not provide information about the possible molecular mechanisms connecting the reduced HV1 conductance, complex pH dysregulation and cell death. Considering the substantial link between increased ceramide levels and various forms of cell death (55, 57) and the fact that ceramide is synthetized by pH-sensitive enzymes (58–60), we hypothesized that an elevation in membrane ceramide levels contributes to the effects of HV1 inhibitors on cell viability. To confirm this assumption, first we quantified time-dependent changes in the membrane abundance of ceramide using flow cytometry and anti-ceramide antibodies as previously (53). First, we compared membrane ceramide levels of untreated samples and found that the membrane abundance of ceramide was significantly higher in M1 cells than in M0 or M2 macrophages (Figure 7A; Supplementary Figure 5). Furthermore, in these measurements, ClGBI resulted in significant time-dependent increases in membrane ceramide levels in M0, M1 and M2 macrophages as well, and the largest elevation was seen in M1 cells in response to 100 µM ClGBI (Figure 7B; Supplementary Figure 5). These experiments convincingly showed that a HV1 inhibition was accompanied by increased ceramide levels, however, they did not provide any details about the exact molecules involved in the plausible causative relationship between the two.
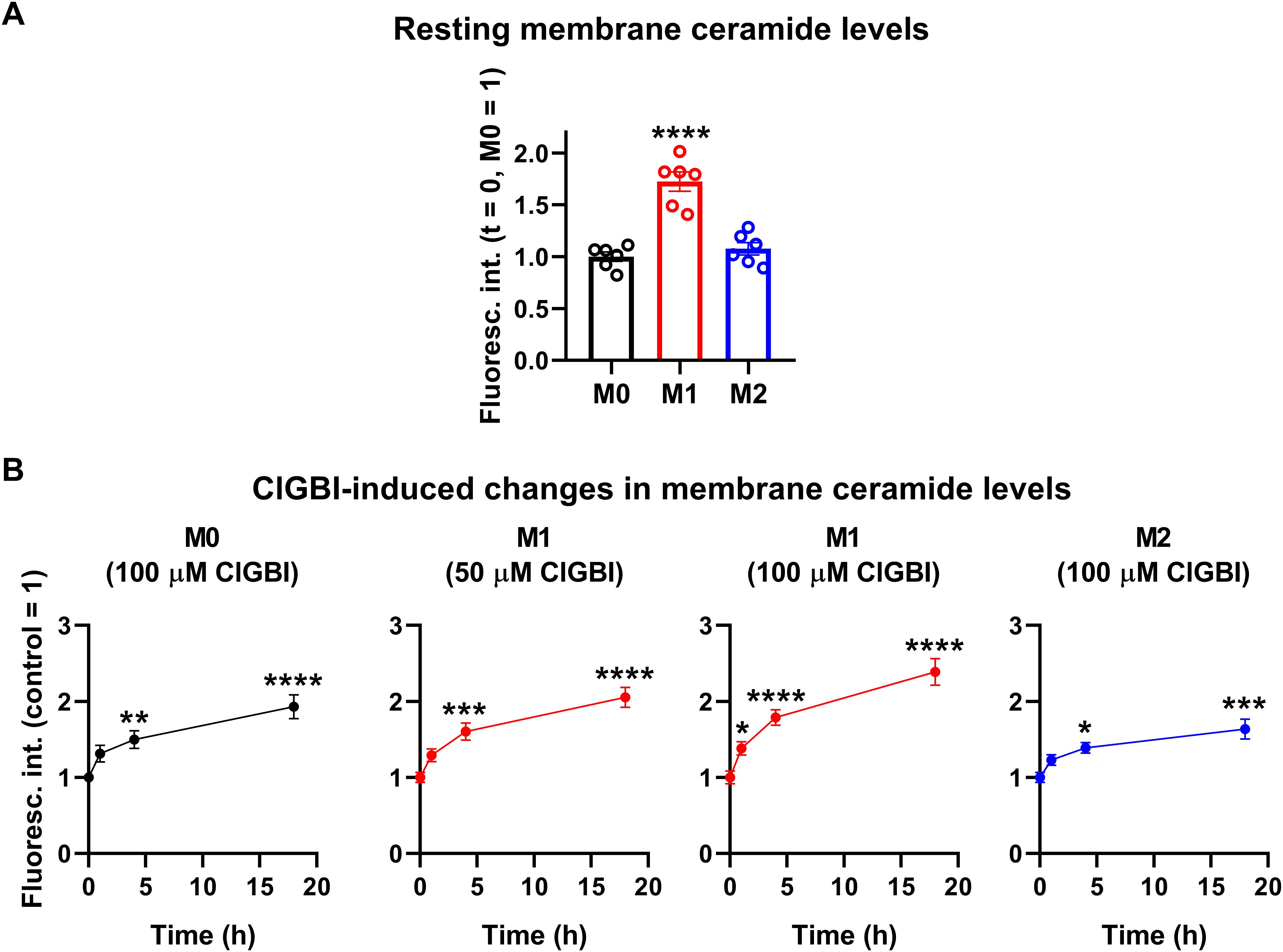
Figure 7. ClGBI induces a time-dependent elevation in membrane ceramide levels of polarized macrophages most effectively in M1 cells. THP-1 cells were differentiated into macrophages for 24 h by 10 ng/ml PMA, which was followed by a 24-h resting period in the absence of PMA. The differentiated M0 macrophages were subsequently polarized for 24 h into classical M1 macrophages with 100 ng/ml LPS plus 20 ng/ml IFN-γ, or M2 macrophages using 20 ng/ml IL-4 plus 20 ng/ml IL-13. Cells were subsequently treated for 1, 4 or 18 h with 50 or 100 µM ClGBI. After accutase-mediated detachment and Fc receptor blocking, cells were labeled with anti-ceramide antibodies followed by AlexaFluor647-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgM antibodies. Fluorescence intensities of individual cells were subsequently measured using flow cytometry and the average fluorescence intensity of at least 10,000 cells of normal morphology per sample was determined. (A) Average fluorescence intensities of each untreated sample were subsequently normalized to the mean value determined in the untreated M0 macrophages and the normalized fluorescence intensity values obtained in n = 6 biological replicates, and their average values (± SEM) are plotted in the panel. Asterisks indicate significant differences compared to M0 samples (****p < 0.0001, ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD test). (B) Alternatively, for each cell type, average fluorescence intensities of each sample were normalized to the mean value determined in the untreated, control sample. The average values (± SEM) of normalized fluorescence intensities obtained from n = 6 biological replicates are plotted in the figure. Asterisks indicate significant differences compared to untreated control samples (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD test).
3.6 ClGBI-induced reductions in cell viability are alleviated by an inhibitor of acid sphingomyelinase
If elevated membrane ceramide levels indeed contributed to the compromised cell viability induced by an HV1 block, such an effect should be alleviated by an inhibition of ceramide synthesis. Since ceramide production mainly occurs through de novo synthesis, or activation of neutral and acid sphingomyelinases (55–57), we examined the potential protective effects of inhibitors of these pathways. Namely, we inhibited serine palmitoyltransferase with myriocin (84), neutral sphingomyelinase with GW4869 (85), and acid sphingomyelinase with ARC39 (86). In these experiments THP-1-derived macrophages were pre-treated with these inhibitors, which was followed by an incubation in the presence of ClGBI, 100 µM in the case of M0 and M2 cells while 50 µM in M1 macrophages, and determination of the fraction of viable cells as above (Figure 2). In accordance with our previous experiments, ClGBI largely reduced viability in M0, M1 and M2 cells as well (Figure 8A). However, inhibitors of ceramide production provided partial protection against ClGBI. While such effects induced by the serine palmitoyltransferase inhibitor myriocin and the neutral sphingomyelinase blocker GW4869 were rather negligible, ARC39, that specifically inhibits acid sphingomyelinase, largely alleviated ClGBI-induced compromised viabilities in all cell types, but particularly in M1 macrophages. Furthermore, ClGBI-elicited increases in plasma membrane ceramide levels were attenuated by ARC39 in all macrophage subtypes (Figure 8B). Altogether, these results confirmed that blocking HV1 results in cellular toxicity, which is mediated by an overproduction of ceramide, mainly through acid sphingomyelinase activity.
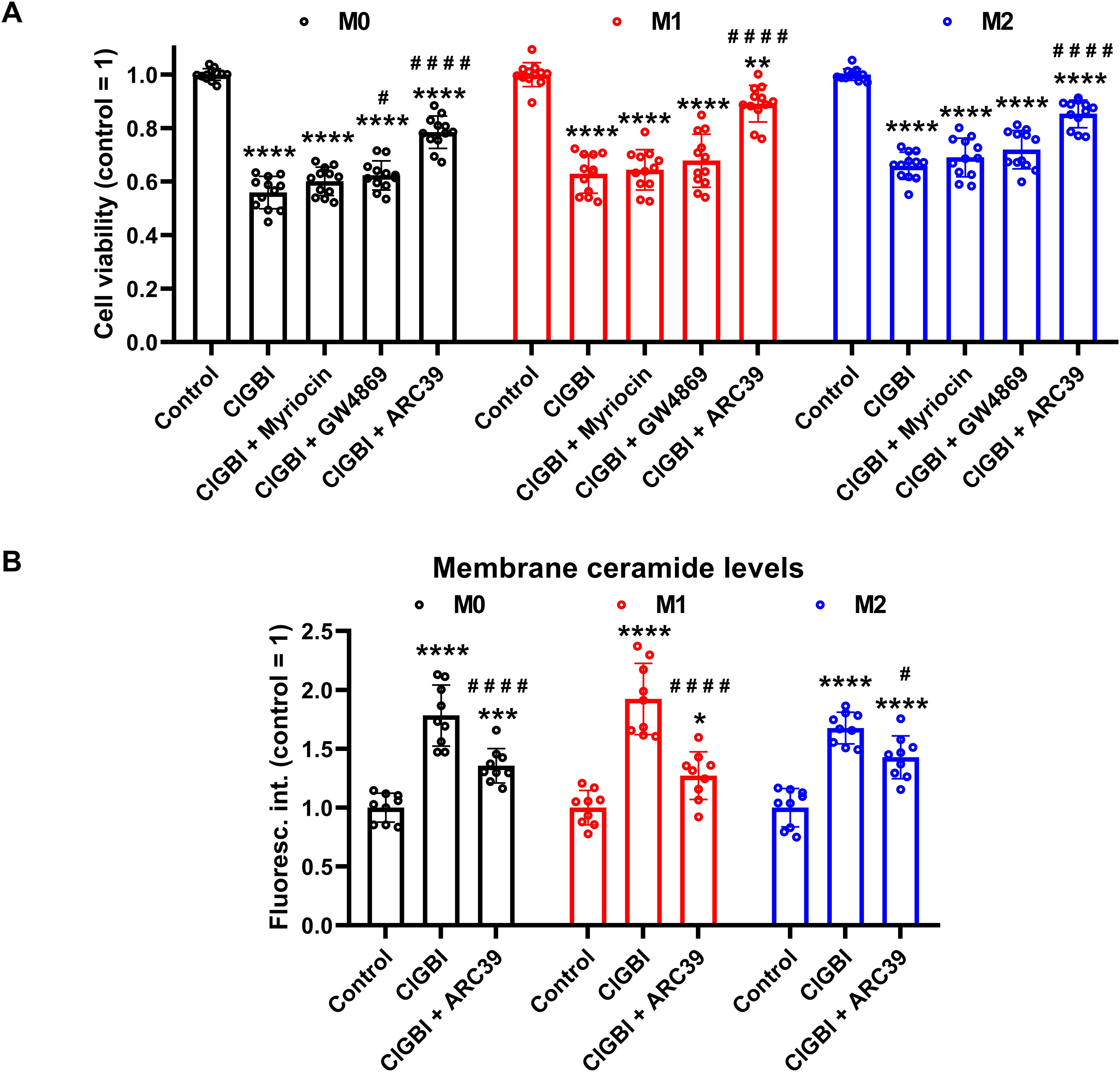
Figure 8. Protective effects of ceramide production inhibitors against the ClGBI-induced toxicity in polarized macrophages. (A) THP-1 cells were differentiated into macrophages for 24 h by 10 ng/ml PMA, which was followed by a 24-h resting period in the absence of PMA. The differentiated M0 macrophages were subsequently polarized for 24 h into classical M1 macrophages with 100 ng/ml LPS plus 20 ng/ml IFN-γ, or M2 macrophages using 20 ng/ml IL-4 plus 20 ng/ml IL-13. Cells were then pre-treated with 1 µM of the serine palmitoyltransferase inhibitor myriocin, 2 µM of the neutral sphingomyelinase blocker GW4869 or 5 µM of the acidic sphingomyelinase inhibitor ARC39 for 30 min, which was followed by a 24-h application of 100 µM ClGBI in M0 and M2 cells, or 50 µM ClGBI in M1 macrophages. After collecting cells in suspension and those detached by accutase, the macrophages were labeled with Sytox Green and Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated annexin V to identify necrotic and apoptotic cells, respectively. Fluorescence intensities of individual cells were measured using flow cytometry and the relative fraction of double negative viable cells was determined in each sample containing at least 10,000 cells, and normalized to the mean value determined in control untreated samples. The normalized live fractions obtained in n = 12 biological replicates, and their average values (± SEM) are plotted in the figure. Asterisks indicate significant differences compared to untreated, control samples (**p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001), while hashes show that compared to cells treated only with ClGBI (#p < 0.05, ####p < 0.0001), which were determined by Tukey’s HSD test carried out after significant differences were obtained for between-group effects in ANOVA. (B) THP-1 cells differentiated, rested and polarized as above were pre-treated with 5 µM ARC39 for 30 min, which was followed by a 24-h application of 100 µM ClGBI in M0 and M2 cells, or 50 µM ClGBI in M1 macrophages. After accutase-mediated detachment and Fc receptor blocking, cells were labeled with anti-ceramide antibodies followed by AlexaFluor647-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgM antibodies. Fluorescence intensities of individual cells were subsequently measured using flow cytometry and the average fluorescence intensity of at least 10,000 cells of normal morphology per sample was determined. For each cell type, average fluorescence intensities of each sample were normalized to the mean value determined in the untreated, control sample. The normalized fluorescence intensity values obtained in n = 9 biological replicates, and their average values (± SEM) are plotted in the panel. Asterisks indicate significant differences compared to untreated, control samples (*p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001), while hashes show that compared to cells treated only with ClGBI (#p < 0.05, ####p < 0.0001), which were determined by Tukey’s HSD test carried out after significant differences were obtained for between-group effects in ANOVA.
4 Discussion
Considering that HV1 inhibitors show great therapeutic promise in various human pathological conditions such as neuroinflammation and malignant diseases, understanding the effects of channel blockers exerted on the viability of macrophages with different polarization is of crucial importance regarding both the therapeutic effects and the potential side effects of these blockers. This study highlights that ClGBI, the most widely used inhibitor of HV1, compromises the viability of THP-1-derived polarized macrophages at concentrations typically applied in in vitro functional tests, and M1 macrophages show superior sensitivity to this compound when compared to M0 and, in particular, M2 cells. Our results indicate that ClGBI indeed elicits this action primarily by blocking HV1 since i) the ClGBI sensitivity of M0, M1 and M2 macrophages shows strong correlation with their HV1 expression levels, i.e. M1 macrophages with the highest HV1 abundance are the most susceptible; ii) inhibitors of other ion channels that are relevant in macrophage functions and potentially also blocked by ClGBI cause no notable reductions in viability; and iii) Zn2+, another non-specific HV1 blocker, shows a similar tendency to reduce cell viability as ClGBI. In our experiments, ClGBI concomitantly induced a complex cellular pH dysregulation manifested in acidification of the cytoplasm and alkalinization of the lysosomes, which eventually resulted in the accumulation of membrane ceramides. Highlighting the fundamental role of the ceramide level elevation in the process, the compromised cell viability in response to ClGBI in M0, M1 and M2 macrophages was effectively alleviated by a pre-treatment with ARC39, a specific inhibitor of the pH-sensitive acid sphingomyelinase. Altogether, our data suggest that HV1 inhibition leads to cellular toxicity in polarized macrophages in a polarization-dependent manner, which occurs due to a pH dysregulation and concomitant ceramide overproduction mainly depending on the activity of the pH-sensitive acid sphingomyelinase (Figure 9).
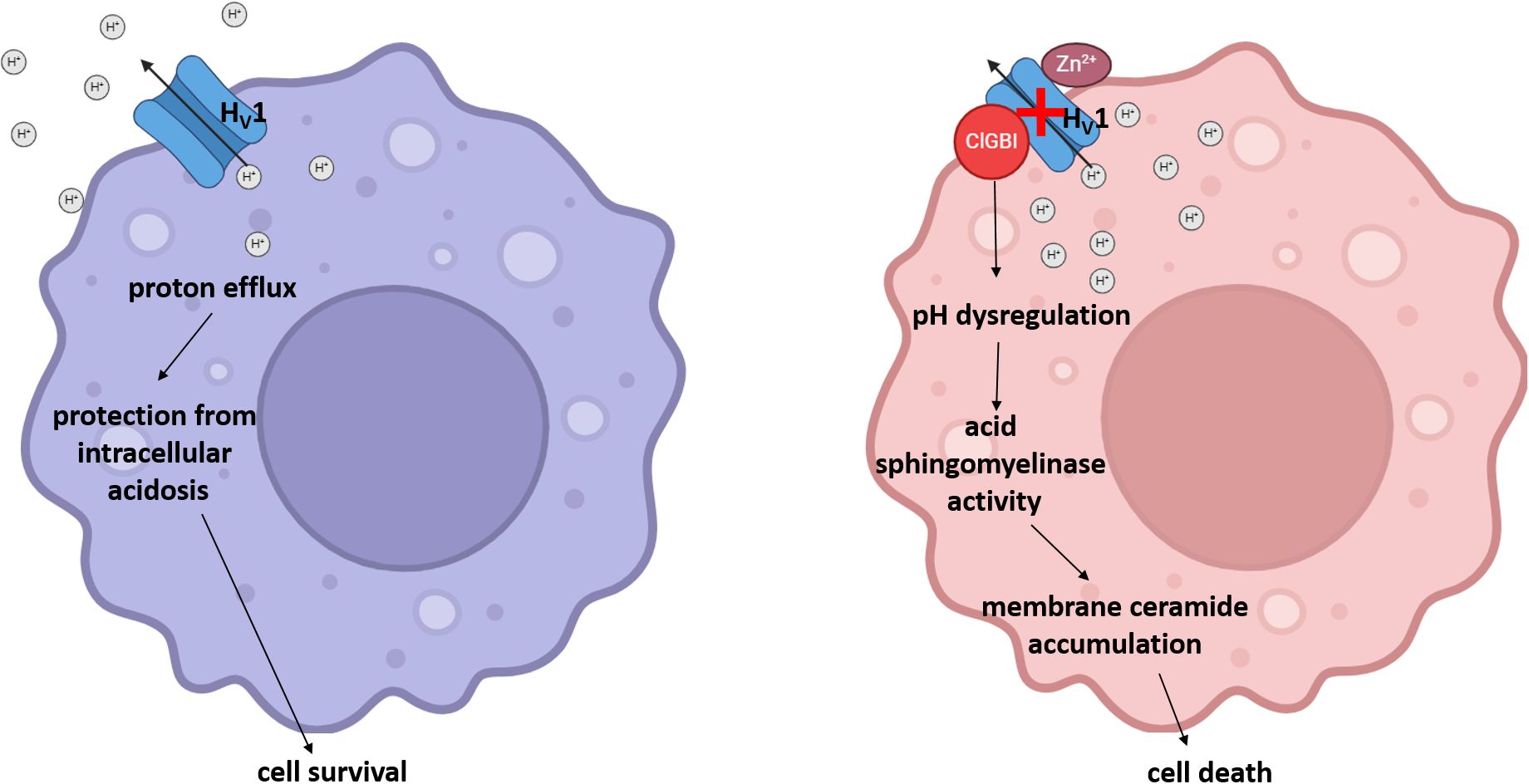
Figure 9. The potential molecular mechanism of the HV1 inhibition-induced compromised viability of polarized macrophages. Under normal circumstances, the HV1-mediated proton extrusion from the cytoplasm protects cells from intracellular acidosis and consequent cell death. However, a pharmacological HV1 inhibition leads to a complex pH dysregulation throughout the cell involving cytoplasmic and lysosomal compartments, which results in ceramide overproduction mainly through the activity of acid sphingomyelinase in polarized macrophages, and eventually the compromised viability of cells.
In our study, we utilized a model system of polarized M1 and M2 macrophages based on macrophages differentiated from human THP-1 moncytoid cells. THP-1-derived macrophages are frequently applied for a large variety of purposes in medical research (87, 88). In our experimental setup, we first differentiated THP-1 cells into macrophages using 10 ng/ml PMA, an activator of protein kinase C, just as in our previous studies (73, 74). Given that higher concentrations of PMA can result in an undesirable induction of gene expression during macrophage differentiation leading to an M1-like phenotype, we applied such a low PMA concentration to maintain the responsiveness of macrophages to secondary stimuli (61, 62). Moreover, after differentiation, the resulting macrophages were rested for 24 h in medium lacking PMA to ensure their M0 phenotype more closely resembling that of primary human monocyte-derived macrophages and retain their plasticity to stimulus-directed polarization (61, 63). The differentiated M0 macrophages were subsequently polarized into classical M1 macrophages with LPS and IFN-γ, or M2 macrophages using IL-4 and IL-13. While concerns were raised previously regarding translational limitations of results obtained with THP-1-derived macrophages mainly in cases of alternative polarization pathways (89–91), THP-1-derived macrophages remain widely applied and generally accepted as simplified, suitable and reliable biologically relevant model systems. This is justified by their easy and safe use, storage and recovery, purity, good polarizability, homogenous genetic background minimizing the degree of variability in the cell phenotype, their human origin that avoids problems regarding the translatability of results obtained with mouse models resulting from major differences between the human and mouse immune system, and their ability to mimic functional activities of both M1 and M2 macrophages after an appropriate polarization (87, 88). Accordingly, our treatments, similarly to those described by other studies applying similar polarization protocols in THP-1-derived macrophages as well (64–67), resulted in CD expression profiles characteristic of M1 and M2 macrophages (75, 76), respectively. In particular, LPS plus IFN-γ-induced polarization caused upregulation of M1 markers such as CD64, CD80 and CD86, while IL-4 and IL-13 treated cells exhibited higher levels of M2 markers such as CD71 and CD86 (Figure 1). Furthermore, the latter were characterized by increased abundance of CD206, a traditional M2 marker, however, only at later time points. While the delayed appearance of CD206 might suggest inappropriateness of our M2 model at first glance, that could rather be attributed to the application accutase to detach cells for flow cytometry analysis. Namely, accutase was previously shown to artificially reduce levels of certain cell surface markers such as CD163 or CD206 while leaving the expression of antigen presentation markers such as CD80 or CD86, and FcγR markers such as CD64 unaffected (92), which could explain the lack of notable increases of CD206 in our experiments in M2 cells in the case of a 24-h polarization (Figure 1). In spite of this disadvantage, we utilized accutase to detach macrophages throughout our study, particularly in viability experiments, since it does not induce substantial changes in polarization and cell surface protein levels like trypsinization, and does not lead to reduced viability as EDTA-mediated detachment or cell scraping (68). While the expression of CD206 was found rather modest in our IL-4- and IL-13-polarized cells, considering its previously published delayed appearance in THP-1-derived M2 macrophages (65) and the potential reduction of its membrane expression due to accutase treatment, even such a moderate elevation demonstrates the success of our polarization protocol. Results of our CD marker analysis imply that polarized phenotypes are established already after 24 h and retained at least for 48 h, i.e. stable during the duration of our viability experiments. Altogether, while keeping in mind its potential limitations, our experimental model based on human THP-1-derived macrophages is appropriate to examine the functional importance of HV1 in polarized macrophages.
The fundamental roles of HV1 are widely documented in human macrophages. The presence of an effective proton-conducting extrusion pathway regulated by membrane potential and pH has long been described in mouse peritoneal macrophages, which was suggested to contribute to alkalinization of the cytoplasm thereby providing protection against intracellular acidification associated with activation and microbicidal mechanisms of these cells (93). Similar HV1 currents were also found in PMA-differentiated THP-1-derived non-polarized macrophages (46). In accordance with the suggested role of HV1 in the compensatory charge movement during the oxidative burst process, in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages, a sustained ROS production induced by PMA and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) was reduced in response to its inhibition by Zn2+ (48), while the genetic deficiency of the channel resulted in delayed acidification and lower ROS production of phagosomes (50). Furthermore, HV1-silenced or HV1-/- mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages showed attenuated ROS production and compromised protection from infection with the intracellular fungal pathogen Histoplasma capsulatum (51). Additionally, HV1 inhibition by Zn2+ modified phagosomal pH acidification in human peripheral blood monocyte-derived macrophages and the channel was suggested to contribute to the different phagosomal pH regulation and ROS production ability of macrophages polarized along the M1 and M2 pathways (49). While the expression of HV1 is relatively well-documented in macrophages, the effects of its inhibition on the viability of polarized cells have not been explicitly tested before in spite of the fact that blocking HV1 resulted in compromised viability in various cell types including Jurkat T lymphocytes (20), chorion-derived mesenchymal stem cells (14), activated mouse microglia (23), myeloid-derived suppressor cells (9), breast cancer (25) and glioblastoma multiforme cell lines (38).
Here, we evaluated the effects of HV1 inhibition by ClGBI, a guanidinium-containing compound, on the viability of polarized macrophages. Guanidinium-based HV1 blockers were described based on a seminal study demonstrating that substituting an arginine for the native asparagine at a residue localized at the narrowest part of the channel exerts deleterious effects on proton conduction. An identical blocking mechanism was found when applying soluble guanidinium ions intracellularly (3). When analyzing potential guanidine derivative inhibitors with different chemical modifications, ClGBI emerged as a compound capable of reaching its intracellular binding site from the extracellular side of the membrane and inhibiting the channel with relatively high affinity (24). Subsequently, ClGBI has been the most extensively used for inhibiting HV1 and investigate its function and biological relevance (8, 9, 13, 14, 20–23, 25). Here, we found that the HV1 inhibitor ClGBI dose-dependently reduced the viability of THP-1-derived macrophages with M0, M1 and M2 phenotypes as well (Figure 2), leading to death of most cells at concentrations widely applied in cellular studies examining the biological functions of the channel (8, 9, 13, 14, 21). However, a recent study examining the selectivity of ClGBI found that this compound also affects the function of various voltage-gated potassium and sodium channels such as KV1.1, KV1.3, KV1.4, KV1.5, KV10.1, KV11.1, NaV1.4 and NaV1.5 (77). This raises the question whether an HV1 inhibition indeed mediates ClGBI effects on macrophage viability, particularly, since these channels play important roles in the regulation of phagocytosis, migration and inflammatory cytokine release in macrophages (94, 95). Several lines of evidence support the HV1-mediated ClGBI effects and argue against its non-specific actions. i) First, blockers of relevant ion channels expressed in macrophages did not notably modify cell viabilities in our experiments at concentrations typically used in functional assays (Figure 3). ii) Second, Zn2+, another HV1 inhibitor (1), similarly compromised the viability of polarized macrophages (Figure 3). iii) Third, the extent of ClGBI effects correlated well with the expression level of HV1. Namely, M1 macrophages characterized by the highest HV1 abundance were the most sensitive to ClGBI, while M2 cells having lower expression displayed the lowest sensitivity (Figures 2, 4). The higher abundance and importance of HV1 in M1 macrophages is consistent with previous studies. For example, it has been shown previously that a 24-h or 48-h treatment with the M1 cytokine TNF-α significantly increased the expression of proton currents in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages (48). GM-CSF, another M1 cytokine, also enhanced HV1 expression in a STAT3- and STAT5-dependent manner in these cells (51). In accordance, LPS and IFN-γ activate NADPH oxidase (96, 97), which may in turn make the cell physiology more dependent on proton flux that is mainly provided by HV1 presumably leading to an increased expression of the channel in M1 cells and their augmented ClGBI sensitivity. Furthermore, in human peripheral blood monocyte-derived macrophages, HV1 inhibition by Zn2+ eliminated pH oscillations and led to sustained alkalinization of phagosomes of M1 macrophages, while in M2 cells it only exerted little effect on the fast development of phagosomal acidification (49). In keeping with the weaker ClGBI effects found in our study, IL-4 was recently shown to modulate Zn2+ homeostasis by triggering metallothionein- and Zn exporter-dependent increases in the labile Zn2+ pool, and presumably lower resulting HV1 conductance, in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages (81). iv) Fourth, ClGBI-induced and HV1 inhibition-mediated toxicity was accompanied by an extensive pH dysregulation in the cells as discussed below.
Maintaining intracellular pH within the physiological range is essential for practically all cellular functions. HV1 is crucial in this aspect by providing a fast and efficient proton efflux during processes acutely acidifying the cytoplasm such as respiratory burst of immune cells or the Warburg effect of malignant cells (98). Accordingly, the deficiency or inhibition of the channel was previously shown to induce acidification in Jurkat T lymphocytes (20), isolated resting and activated mouse T lymphocytes (10), human sperm (13), canine ventricular myocytes (8), mouse dorsal root ganglion neurons (18), mouse and human microglial cells (23), breast cancer (25, 35, 36), colorectal carcinoma (37) and glioblastoma multiforme cells (38). The abnormal acidification induced by blocking HV1 was associated with compromised cell viability in most cases. However, such a connection has not been examined previously in macrophages. Here, we observed that the ClGBI-induced compromised viability was associated with significant acidification of the cytoplasm (Figure 5) in all examined macrophage classes with the largest effects observed in M1 cells that were already more acidic even in the absence of treatment when compared to M0 and M2 cells. In response to 100 µM ClGBI, the acidic pH shift, which was approximately 0.90, 0.54 and 0.48 pH units in M1, M0 and M2 cells, respectively, after 18 h treatment, can be considered large enough to substantially change cellular processes eventually culminating in cell death. Furthermore, such cytoplasmic alterations are expected to influence pH regulation of cellular compartments as well. While sporadic studies already proposed the expression and physiological roles of HV1 in phagosomes of macrophages (49, 50), the effects of channel inhibition have not been tested yet on lysosomes that represent important components of various cell death pathways (82, 83). In our measurements, we found large-scale time-dependent significant alkalinization of the lysosomes in response to a HV1 block, which reached a pH shift of 1.18, 0.78 and 0.73 in M1, M0 and M2 macrophages, respectively, in response to an 18-h application of 100 µM ClGBI (Figure 6), which is in accordance with previous reports on apoptosis-related alterations of the lysosomal pH in other cell types. The molecular mechanisms relating cytoplasmic and lysosomal pH alterations are very complex and incompletely understood (82, 99), and their elucidation is beyond the scope of the current manuscript. Nevertheless, HV1 channels are expected to provide a contribution and our findings altogether point at large-scale pH alterations throughout the cells in response to ClGBI-mediated HV1 inhibition.
Elevations in membrane ceramide levels can represent the link between pH dysregulation and cell death induced by blocking HV1 channels. Under resting conditions, ceramides are scarcely found in the cell membrane and constitute only <1% of total membrane lipids. However, stress stimuli substantially increase their abundance resulting in the formation of ceramide-enriched membrane platforms that facilitate signaling pathways participating in cell death processes including apoptosis, necroptosis, autophagy and ER stress and cell cycle arrest. Such mechanisms were shown to mediate cytotoxic effects of TNFα, ionizing radiation and various chemotherapeutic agents such as etoposide, cisplatin, daunorubicin, or gemcitabine plus doxorubicin combination. Ceramide overproduction occurs due to an imbalance of ceramide production and degradation mainly resulting from the activation of de novo ceramide synthesis involving serine palmitoyltransferase, or the degradation of sphingomyelin by neutral or acid sphingomyelinase (55–57). Since the activities of these enzymes are strongly pH-dependent (58–60), we hypothesized that ceramide overproduction resulting from the pH dysregulation-induced enzyme activity imbalance is an important factor leading to cell death in response to an HV1 block. Supporting this assumption, we observed time-dependent elevations in membrane ceramide levels in response to ClGBI (Figure 7). Interestingly, we also found already higher ceramide levels in M1 macrophages when compared to M0 and M2 cells even in the absence of a ClGBI treatment, which can result from an overexpression and activation of neutral and, in particular, acidic sphingomyelinase that are typical features of classical M1 polarization (100–102). The increased ceramide abundance can in turn elevate the propensity of M1 macrophages for ceramide overproduction and thus contribute to the higher sensitivity of these cells to the HV1 block-induced reduced viability. In addition, to unequivocally demonstrate the role of the ceramide level elevation, we tested the potential contribution of the ceramide producing enzymes using specific inhibitors, myriocin to reduce the activity serine palmitoyltransferase (84), GW4869 to block neutral sphingomyelinase (85), and ARC39 to inhibit acid sphingomyelinase (86). From among the tested inhibitors, ARC39 was able to impressively alleviate ClGBI-induced cell death, decreasing the effect of the HV1 blocker by 50-70% (Figure 8). Furthermore, ARC39 significantly attenuated elevations in plasma membrane ceramide levels in response to ClGBI, mainly in M1 cells. Altogether, our results imply that an HV1 inhibition compromises cell viability in a polarization-dependent manner, which results from a complex cellular pH dysregulation and ceramide accumulation that solidly depends on the activity of acid sphingomyelinase.
In summary, our study demonstrates for the first time that an inhibition of HV1 channels and the consequent complex cellular pH dysregulation compromises the viability of human polarized macrophages, most efficiently that of M1 cells, which is casually linked to ceramide overproduction that mainly depends on the activity of acid sphingomyelinase (Figure 9). Given that pH dysregulation and the resulting ceramide accumulation are expected to be general responses to HV1 inhibition, the reduced cell viability has to be taken into account when interpreting results of in vitro functional assays utilizing HV1 blockers. The medical relevance of our findings stems from the fact that HV1 inhibitors show great promise in various pathological conditions linked to ROS overproduction and associated inflammatory immune activation, and abnormal proliferation. In microglia of the nervous system, the HV1-mediated proton efflux is essential to counterbalance the acidosis arising from the charge transfer activity of NADPH oxidase producing ROS. Hence, a sustained ROS production is enabled by HV1 conductance, which plays crucial roles in neuroinflammation and consequent neuronal loss (11). Accordingly, in mouse disease models, genetic HV1 deficiency prevented neuronal death, brain damage and motor deficits in ischemic stroke (27, 28), carotid artery stenosis-induced white matter injury (103), demyelination in cuprizone- or lysophosphatidylcholine-induced multiple sclerosis models (29, 30), and neuronal apoptosis and pyroptosis, functional loss and pain hypersensitivity in traumatic brain and spinal cord injury models (31–34). Furthermore, a pharmacological inhibition of peripheral sensory neurons in dorsal root ganglia attenuated inflammatory pain and morphine-induced analgesic tolerance and hyperalgesia (18). These studies imply the beneficial applicability of HV1 inhibitors in neuroinflammation-associated pathological conditions. Considering the functional similarities between microglia and macrophages, the molecular mechanism of HV1 block-induced compromised viability outlined in this manuscript can contribute to the intended effects in these examples. However, potential off-target adverse effects involving impaired macrophage functions should be taken into account when applying HV1 blockers in these indications in the future. Malignant diseases comprise another group of disorders for the potential utilization of HV1 inhibitors. Rapidly proliferating neoplastic tumor cells are generally slightly depolarized and acidic due to a characteristic metabolic shift often referred to as the Warburg effect. Moreover, these cells typically overexpress the HV1 channel, which results in a highly beneficial efficient proton extrusion pathway. This provides a protective mechanism against intracellular acidosis and creates an acidic extracellular microenvironment that favors the degradation of the extracellular matrix facilitating invasion and contributes to an evasion from the immune surveillance (98). Consistently, HV1 overexpression is associated with disease severity and poor prognosis in breast cancer (36) and colorectal carcinoma (37). Furthermore, an siRNA-induced downregulation of HV1 inhibited proliferation, migration and invasion of both breast cancer, colorectal carcinoma and myeloid sarcoma cell lines, and a genetic HV1 deficiency delayed their growths in mouse tumor xenografts (15, 35–37). The pharmacological inhibition of the channel also seems promising as Zn2+ treatment reduced survival and migration of human glioblastoma multiforme cells (38) and ClGBI decreased cell viability in both monolayer and three-dimensional multicellular spheroid cultures of breast cancer cells (25). On the other hand, according to our results, an HV1 inhibition may also reduce the viability of polarized macrophages, mainly that of M1 cells with typical anti-tumor activities, and thereby favoring the predominant intratumoral appearance of M2-like tumor-associated macrophages, culminating in an M1-M2 imbalance, which may contribute to the immune evasion of neoplastic cells. These potential effects should be tested in the future, and may point to the need for a tailored selective tumor cell targeting approach for the application of HV1 blockers. Altogether, our findings imply that HV1 inhibitors can compromise the viability of polarized macrophages, which has to be taken into account both for their intended and adverse effects.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
TK: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BCS: Formal analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. RCK: Investigation, Writing – original draft. VS: Investigation, Writing – original draft. PN: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. ZV: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. GP: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. FZ: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Hungarian National Research, Development and Innovation Office (OTKA FK146740, EKÖP-24-4-II-DE-74, FZ; OTKA FK143400, TK; EKÖP-24-2-DE-298, RCK; OTKA K138075 and ANN133421, PN; OTKA K132906, ZV; and OTKA K143071, GP). This work was supported by the ÚNKP-23-4-II-DE-169 (FZ) and ÚNKP-23-5-DE-488 (TK) New National Excellence Program of the Ministry for Culture and Innovation from the source of the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund. The project was supported by the János Bolyai Research Scholarship of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences (BO/00392/23, TK; and BO/00676/24, FZ). This research work was conducted with the support of the National Academy of Scientist Education Program of the National Biomedical Foundation under the sponsorship of the Hungarian Ministry of Culture and Innovation (RCK). Supported by the University of Debrecen Program for Scientific Publication.
Acknowledgments
We thank the expert technical assistance of Rita Utasi-Szabo.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1487578/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Ramsey IS, Moran MM, Chong JA, Clapham DE. A voltage-gated proton-selective channel lacking the pore domain. Nature. (2006) 440:1213–6. doi: 10.1038/nature04700
2. Sasaki M, Takagi M, Okamura Y. A voltage sensor-domain protein is a voltage-gated proton channel. Science. (2006) 312:589–92. doi: 10.1126/science.1122352
3. Tombola F, Ulbrich MH, Isacoff EY. The voltage-gated proton channel Hv1 has two pores, each controlled by one voltage sensor. Neuron. (2008) 58:546–56. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.03.026
4. El Chemaly A, Okochi Y, Sasaki M, Arnaudeau S, Okamura Y, Demaurex N. VSOP/Hv1 proton channels sustain calcium entry, neutrophil migration, and superoxide production by limiting cell depolarization and acidification. J Exp Med. (2010) 207:129–39. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091837
5. Ramsey IS, Ruchti E, Kaczmarek JS, Clapham DE. Hv1 proton channels are required for high-level NADPH oxidase-dependent superoxide production during the phagocyte respiratory burst. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2009) 106:7642–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0902761106
6. Zhao R, Kennedy K, De Blas GA, Orta G, Pavarotti MA, Arias RJ, et al. Role of human Hv1 channels in sperm capacitation and white blood cell respiratory burst established by a designed peptide inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2018) 115:E11847–E56. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1816189115
7. Capasso M, Bhamrah MK, Henley T, Boyd RS, Langlais C, Cain K, et al. HVCN1 modulates BCR signal strength via regulation of BCR-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species. Nat Immunol. (2010) 11:265–72. doi: 10.1038/ni.1843
8. Ma J, Gao X, Li Y, DeCoursey TE, Shull GE, Wang HS. The HVCN1 voltage-gated proton channel contributes to pH regulation in canine ventricular myocytes. J Physiol. (2022) 600:2089–103. doi: 10.1113/JP282126
9. Alvear-Arias JJ, Carrillo C, Villar JP, Garcia-Betancourt R, Pena-Pichicoi A, Fernandez A, et al. Expression of H(v)1 proton channels in myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) and its potential role in T cell regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2022) 119:e2104453119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2104453119
10. Coe D, Poobalasingam T, Fu H, Bonacina F, Wang G, Morales V, et al. Loss of voltage-gated hydrogen channel 1 expression reveals heterogeneous metabolic adaptation to intracellular acidification by T cells. JCI Insight. (2022) 7. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.147814
11. Shen Y, Luo Y, Liao P, Zuo Y, Jiang R. Role of the voltage-gated proton channel Hv1 in nervous systems. Neurosci Bull. (2023) 39:1157–72. doi: 10.1007/s12264-023-01053-6
12. Lishko PV, Botchkina IL, Fedorenko A, Kirichok Y. Acid extrusion from human spermatozoa is mediated by flagellar voltage-gated proton channel. Cell. (2010) 140:327–37. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.12.053
13. Matamoros-Volante A, Trevino CL. Capacitation-associated alkalization in human sperm is differentially controlled at the subcellular level. J Cell Sci. (2020) 133. doi: 10.1242/jcs.238816
14. Meszaros B, Papp F, Mocsar G, Kokai E, Kovacs K, Tajti G, et al. The voltage-gated proton channel hHv1 is functionally expressed in human chorion-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:7100. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63517-3
15. El Chemaly A, Jaquet V, Cambet Y, Caillon A, Cherpin O, Balafa A, et al. Discovery and validation of new Hv1 proton channel inhibitors with onco-therapeutic potential. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. (2023) 1870:119415. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2022.119415
16. Piga M, Varga Z, Feher A, Papp F, Korpos E, Bangera KC, et al. Identification of a novel structural class of H(V)1 inhibitors by structure-based virtual screening. J Chem Inf Model. (2024) 64:4850–62. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.4c00240
17. Tang D, Yang Y, Xiao Z, Xu J, Yang Q, Dai H, et al. Scorpion toxin inhibits the voltage-gated proton channel using a Zn(2+) -like long-range conformational coupling mechanism. Br J Pharmacol. (2020) 177:2351–64. doi: 10.1111/bph.14984
18. Zhang Q, Ren Y, Mo Y, Guo P, Liao P, Luo Y, et al. Inhibiting Hv1 channel in peripheral sensory neurons attenuates chronic inflammatory pain and opioid side effects. Cell Res. (2022) 32:461–76. doi: 10.1038/s41422-022-00616-y
19. Zhao C, Hong L, Galpin JD, Riahi S, Lim VT, Webster PD, et al. HIFs: New arginine mimic inhibitors of the Hv1 channel with improved VSD-ligand interactions. J Gen Physiol. (2021) 153. doi: 10.1085/jgp.202012832
20. Asuaje A, Smaldini P, Martin P, Enrique N, Orlowski A, Aiello EA, et al. The inhibition of voltage-gated H(+) channel (HVCN1) induces acidification of leukemic Jurkat T cells promoting cell death by apoptosis. Pflugers Arch. (2017) 469:251–61. doi: 10.1007/s00424-016-1928-0
21. Cozzolino M, Gyongyosi A, Korpos E, Gogolak P, Naseem MU, Kallai J, et al. The voltage-gated Hv1 H(+) channel is expressed in tumor-infiltrating myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076216
22. Gattas MV, Jaffe A, Barahona J, Conner GE. Proton channel blockers inhibit Duox activity independent of Hv1 effects. Redox Biol. (2020) 28:101346. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101346
23. Hernandez-Espinosa DR, Gale JR, Scrabis MG, Aizenman E. Microglial reprogramming by Hv1 antagonism protects neurons from inflammatory and glutamate toxicity. J Neurochem. (2023) 165:29–54. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15760
24. Hong L, Kim IH, Tombola F. Molecular determinants of Hv1 proton channel inhibition by guanidine derivatives. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2014) 111:9971–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1324012111
25. Ventura C, Leon IE, Asuaje A, Martin P, Enrique N, Nunez M, et al. Differential expression of the long and truncated Hv1 isoforms in breast-cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. (2020) 235:8757–67. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29719
26. Zhao R, Lopez B, Schwingshackl A, Goldstein SAN. Protection from acute lung injury by a peptide designed to inhibit the voltage-gated proton channel. iScience. (2023) 26:105901. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105901
27. Tian DS, Li CY, Qin C, Murugan M, Wu LJ, Liu JL. Deficiency in the voltage-gated proton channel Hv1 increases M2 polarization of microglia and attenuates brain damage from photothrombotic ischemic stroke. J Neurochem. (2016) 139:96–105. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13751
28. Wu LJ, Wu G, Akhavan Sharif MR, Baker A, Jia Y, Fahey FH, et al. The voltage-gated proton channel Hv1 enhances brain damage from ischemic stroke. Nat Neurosci. (2012) 15:565–73. doi: 10.1038/nn.3059
29. Chen M, Yang LL, Hu ZW, Qin C, Zhou LQ, Duan YL, et al. Deficiency of microglial Hv1 channel is associated with activation of autophagic pathway and ROS production in LPC-induced demyelination mouse model. J Neuroinflamm. (2020) 17:333. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-02020-y
30. Liu J, Tian D, Murugan M, Eyo UB, Dreyfus CF, Wang W, et al. Microglial Hv1 proton channel promotes cuprizone-induced demyelination through oxidative damage. J Neurochem. (2015) 135:347–56. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13242
31. Li X, Yu Z, Zong W, Chen P, Li J, Wang M, et al. Deficiency of the microglial Hv1 proton channel attenuates neuronal pyroptosis and inhibits inflammatory reaction after spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflamm. (2020) 17:263. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01942-x
32. Li Y, Ritzel RM, He J, Cao T, Sabirzhanov B, Li H, et al. The voltage-gated proton channel Hv1 plays a detrimental role in contusion spinal cord injury via extracellular acidosis-mediated neuroinflammation. Brain Behav Immun. (2021) 91:267–83. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.10.005
33. Ritzel RM, He J, Li Y, Cao T, Khan N, Shim B, et al. Proton extrusion during oxidative burst in microglia exacerbates pathological acidosis following traumatic brain injury. Glia. (2021) 69:746–64. doi: 10.1002/glia.23926
34. Peng J, Yi MH, Jeong H, McEwan PP, Zheng J, Wu G, et al. The voltage-gated proton channel Hv1 promotes microglia-astrocyte communication and neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve injury. Mol Brain. (2021) 14:99. doi: 10.1186/s13041-021-00812-8
35. Wang Y, Li SJ, Pan J, Che Y, Yin J, Zhao Q. Specific expression of the human voltage-gated proton channel Hv1 in highly metastatic breast cancer cells, promotes tumor progression and metastasis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2011) 412:353–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.07.102
36. Wang Y, Li SJ, Wu X, Che Y, Li Q. Clinicopathological and biological significance of human voltage-gated proton channel Hv1 protein overexpression in breast cancer. J Biol Chem. (2012) 287:13877–88. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.345280
37. Wang Y, Wu X, Li Q, Zhang S, Li SJ. Human voltage-gated proton channel hv1: a new potential biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer. PloS One. (2013) 8:e70550. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070550
38. Ribeiro-Silva L, Queiroz FO, da Silva AM, Hirata AE, Arcisio-Miranda M. Voltage-gated proton channel in human glioblastoma multiforme cells. ACS Chem Neurosci. (2016) 7:864–9. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.6b00083
39. Hondares E, Brown MA, Musset B, Morgan D, Cherny VV, Taubert C, et al. Enhanced activation of an amino-terminally truncated isoform of the voltage-gated proton channel HVCN1 enriched in Malignant B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2014) 111:18078–83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1411390111
40. Gordon S. Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol. (2003) 3:23–35. doi: 10.1038/nri978
41. Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Locati M, Allavena P, Sica A. Macrophage polarization: tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends Immunol. (2002) 23:549–55. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4906(02)02302-5
42. Lawrence T, Natoli G. Transcriptional regulation of macrophage polarization: enabling diversity with identity. Nat Rev Immunol. (2011) 11:750–61. doi: 10.1038/nri3088
43. Locati M, Curtale G, Mantovani A. Diversity, mechanisms, and significance of macrophage plasticity. Annu Rev Pathol. (2020) 15:123–47. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-012418-012718
44. Mosser DM, Edwards JP. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. (2008) 8:958–69. doi: 10.1038/nri2448
45. Murray PJ, Wynn TA. Protective and pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat Rev Immunol. (2011) 11:723–37. doi: 10.1038/nri3073
46. DeCoursey TE, Cherny VV. Voltage-activated proton currents in human THP-1 monocytes. J Membr Biol. (1996) 152:131–40. doi: 10.1007/s002329900092
47. Kapus A, Romanek R, Grinstein S. Arachidonic acid stimulates the plasma membrane H+ conductance of macrophages. J Biol Chem. (1994) 269:4736–45. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(17)37606-8
48. Thomas MP, Chartrand K, Reynolds A, Vitvitsky V, Banerjee R, Gendelman HE. Ion channel blockade attenuates aggregated alpha synuclein induction of microglial reactive oxygen species: relevance for the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem. (2007) 100:503–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04315.x
49. Canton J, Khezri R, Glogauer M, Grinstein S. Contrasting phagosome pH regulation and maturation in human M1 and M2 macrophages. Mol Biol Cell. (2014) 25:3330–41. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-05-0967
50. El Chemaly A, Nunes P, Jimaja W, Castelbou C, Demaurex N. Hv1 proton channels differentially regulate the pH of neutrophil and macrophage phagosomes by sustaining the production of phagosomal ROS that inhibit the delivery of vacuolar ATPases. J Leukoc Biol. (2014) 95:827–39. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0513251
51. Subramanian Vignesh K, Landero Figueroa JA, Porollo A, Caruso JA, Deepe GS Jr. Granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor induced Zn sequestration enhances macrophage superoxide and limits intracellular pathogen survival. Immunity. (2013) 39:697–710. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.09.006
52. Alonso A, Goni FM. The physical properties of ceramides in membranes. Annu Rev Biophys. (2018) 47:633–54. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-070317-033309
53. Szabo BC, Szabo M, Nagy P, Varga Z, Panyi G, Kovacs T, et al. Novel insights into the modulation of the voltage-gated potassium channel K(V)1.3 activation gating by membrane ceramides. J Lipid Res. (2024) 65(8):100596. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2024.100596
54. Zakany F, Mandity IM, Varga Z, Panyi G, Nagy P, Kovacs T. Effect of the lipid landscape on the efficacy of cell-penetrating peptides. Cells. (2023) 12. doi: 10.3390/cells12131700
55. Hannun YA, Obeid LM. Sphingolipids and their metabolism in physiology and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2018) 19:175–91. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2017.107
56. Kovacs T, Zakany F, Nagy P. It takes more than two to tango: complex, hierarchal, and membrane-modulated interactions in the regulation of receptor tyrosine kinases. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14. doi: 10.3390/cancers14040944
57. Ogretmen B. Sphingolipid metabolism in cancer signalling and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. (2018) 18:33–50. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2017.96
58. Hanada K, Hara T, Nishijima M. Purification of the serine palmitoyltransferase complex responsible for sphingoid base synthesis by using affinity peptide chromatography techniques. J Biol Chem. (2000) 275:8409–15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.12.8409
59. Muhle C, Kornhuber J. Characterization of a neutral Sphingomyelinase activity in human serum and plasma. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032467
60. Teichgraber V, Ulrich M, Endlich N, Riethmuller J, Wilker B, De Oliveira-Munding CC, et al. Ceramide accumulation mediates inflammation, cell death and infection susceptibility in cystic fibrosis. Nat Med. (2008) 14:382–91. doi: 10.1038/nm1748
61. Lund ME, To J, O'Brien BA, Donnelly S. The choice of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate differentiation protocol influences the response of THP-1 macrophages to a pro-inflammatory stimulus. J Immunol Methods. (2016) 430:64–70. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2016.01.012
62. Park EK, Jung HS, Yang HI, Yoo MC, Kim C, Kim KS. Optimized THP-1 differentiation is required for the detection of responses to weak stimuli. Inflammation Res. (2007) 56:45–50. doi: 10.1007/s00011-007-6115-5
63. Daigneault M, Preston JA, Marriott HM, Whyte MK, Dockrell DH. The identification of markers of macrophage differentiation in PMA-stimulated THP-1 cells and monocyte-derived macrophages. PloS One. (2010) 5:e8668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008668
64. Chen Y, Lu J, Xie Z, Tang J, Lian X, Li X. The mechanism of Alisol B23 acetate inhibiting lung cancer: targeted regulation of CD11b/CD18 to influence macrophage polarization. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2022) 16:3677–89. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S375073
65. Genin M, Clement F, Fattaccioli A, Raes M, Michiels C. M1 and M2 macrophages derived from THP-1 cells differentially modulate the response of cancer cells to etoposide. BMC Cancer. (2015) 15:577. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1546-9
66. Yang L, Han P, Cui T, Miao Y, Zhao T, Cui Z, et al. M2 macrophage inhibits the antitumor effects of Lenvatinib on intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1251648. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1251648
67. Zhang M, Liu K, Zhang Q, Xu J, Liu J, Lin H, et al. Alpha fetoprotein promotes polarization of macrophages towards M2-like phenotype and inhibits macrophages to phagocytize hepatoma cells. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1081572. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1081572
68. Song Q, Zhang Y, Zhou M, Xu Y, Zhang Q, Wu L, et al. The culture dish surface influences the phenotype and dissociation strategy in distinct mouse macrophage populations. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:920232. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.920232
69. Kovacs T, Kurtan K, Varga Z, Nagy P, Panyi G, Zakany F. Veklury(R) (remdesivir) formulations inhibit initial membrane-coupled events of SARS-CoV-2 infection due to their sulfobutylether-beta-cyclodextrin content. Br J Pharmacol. (2023) 180:2064–84. doi: 10.1111/bph.16063
70. Zakany F, Szabo M, Batta G, Karpati L, Mandity IM, Fulop P, et al. An omega-3, but Not an omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Decreases Membrane Dipole Potential and Stimulates Endo-Lysosomal Escape of Penetratin. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:647300. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.647300
71. Yurdagul A Jr., Subramanian M, Wang X, Crown SB, Ilkayeva OR, Darville L, et al. Macrophage metabolism of apoptotic cell-derived arginine promotes continual efferocytosis and resolution of injury. Cell Metab. (2020) 31:518–33 e10. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.001
72. Deriy LV, Gomez EA, Zhang G, Beacham DW, Hopson JA, Gallan AJ, et al. Disease-causing mutations in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator determine the functional responses of alveolar macrophages. J Biol Chem. (2009) 284:35926–38. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.057372
73. Batta G, Soltesz L, Kovacs T, Bozo T, Meszar Z, Kellermayer M, et al. Alterations in the properties of the cell membrane due to glycosphingolipid accumulation in a model of Gaucher disease. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:157. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18405-8
74. Kovacs T, Batta G, Zakany F, Szollosi J, Nagy P. The dipole potential correlates with lipid raft markers in the plasma membrane of living cells. J Lipid Res. (2017) 58:1681–91. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M077339
75. Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, Allavena P, Vecchi A, Locati M. The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. (2004) 25:677–86. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2004.09.015
76. Orecchioni M, Ghosheh Y, Pramod AB, Ley K. Macrophage Polarization: Different Gene Signatures in M1(LPS+) vs. Classically and M2(LPS-) vs. Alternatively Activated Macrophages. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:1084. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01084
77. Szanto TG, Feher A, Korpos E, Gyongyosi A, Kallai J, Meszaros B, et al. 5-Chloro-2-guanidinobenzimidazole (ClGBI) is a non-selective inhibitor of the human H(V)1 channel. Pharm (Basel). (2023) 16. doi: 10.3390/ph16050656
78. Varga Z, Gurrola-Briones G, Papp F, Rodriguez de la Vega RC, Pedraza-Alva G, Tajhya RB, et al. Vm24, a natural immunosuppressive peptide, potently and selectively blocks Kv1.3 potassium channels of human T cells. Mol Pharmacol. (2012) 82:372–82. doi: 10.1124/mol.112.078006
79. Duran-Riveroll LM, Cembella AD. Guanidinium toxins and their interactions with voltage-gated sodium ion channels. Mar Drugs. (2017) 15. doi: 10.3390/md15100303
80. Varga Z, Juhasz T, Matta C, Fodor J, Katona E, Bartok A, et al. Switch of voltage-gated K+ channel expression in the plasma membrane of chondrogenic cells affects cytosolic Ca2+-oscillations and cartilage formation. PLoS One. (2011) 6:e27957. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027957
81. Subramanian Vignesh K, Landero Figueroa JA, Porollo A, Divanovic S, Caruso JA, Deepe GS Jr. IL-4 induces metallothionein 3- and SLC30A4-dependent increase in intracellular Zn(2+) that promotes pathogen persistence in macrophages. Cell Rep. (2016) 16:3232–46. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.08.057
82. Zhang W, Bai J, Hang K, Xu J, Zhou C, Li L, et al. Role of lysosomal acidification dysfunction in mesenchymal stem cell senescence. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2022) 10:817877. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.817877
83. Li SS, Zhang M, Wang JH, Yang F, Kang B, Xu JJ, et al. Monitoring the Changes of pH in Lysosomes during Autophagy and Apoptosis by Plasmon Enhanced Raman Imaging. Anal Chem. (2019) 91:8398–405. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b01250
84. Monasterio BG, Jimenez-Rojo N, Garcia-Arribas AB, Riezman H, Goni FM, Alonso A. Plasma membrane effects of sphingolipid-synthesis inhibition by myriocin in CHO cells: a biophysical and lipidomic study. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:955. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-04648-z
85. Zietzer A, Jahnel AL, Bulic M, Gutbrod K, Dusing P, Hosen MR, et al. Activation of neutral sphingomyelinase 2 through hyperglycemia contributes to endothelial apoptosis via vesicle-bound intercellular transfer of ceramides. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2021) 79:48. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-04049-5
86. Naser E, Kadow S, Schumacher F, Mohamed ZH, Kappe C, Hessler G, et al. Characterization of the small molecule ARC39, a direct and specific inhibitor of acid sphingomyelinase. vitro J Lipid Res. (2020) 61:896–910. doi: 10.1194/jlr.RA120000682
87. Chanput W, Mes JJ, Wichers HJ. THP-1 cell line: an in vitro cell model for immune modulation approach. Int Immunopharmacol. (2014) 23:37–45. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.08.002
88. Mohd Yasin ZN, Mohd Idrus FN, Hoe CH, Yvonne-Tee GB. Macrophage polarization in THP-1 cell line and primary monocytes: A systematic review. Differentiation. (2022) 128:67–82. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2022.10.001
89. Rynikova M, Adamkova P, Hradicka P, Stofilova J, Harvanova D, Matejova J, et al. Transcriptomic analysis of macrophage polarization protocols: vitamin D(3) or IL-4 and IL-13 do not polarize THP-1 monocytes into reliable M2 macrophages. Biomedicines. (2023) 11. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020608
90. Shiratori H, Feinweber C, Luckhardt S, Linke B, Resch E, Geisslinger G, et al. THP-1 and human peripheral blood mononuclear cell-derived macrophages differ in their capacity to polarize in vitro. Mol Immunol. (2017) 88:58–68. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2017.05.027
91. Tedesco S, De Majo F, Kim J, Trenti A, Trevisi L, Fadini GP, et al. Convenience versus biological significance: are PMA-differentiated THP-1 cells a reliable substitute for blood-derived macrophages when studying in vitro polarization? Front Pharmacol. (2018) 9:71. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00071
92. Chen S, So EC, Strome SE, Zhang X. Impact of detachment methods on M2 macrophage phenotype and function. J Immunol Methods. (2015) 426:56–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2015.08.001
93. Kapus A, Romanek R, Qu AY, Rotstein OD, Grinstein S. A pH-sensitive and voltage-dependent proton conductance in the plasma membrane of macrophages. J Gen Physiol. (1993) 102:729–60. doi: 10.1085/jgp.102.4.729
94. Feske S, Wulff H, Skolnik EY. Ion channels in innate and adaptive immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. (2015) 33:291–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032414-112212
95. Selezneva A, Gibb AJ, Willis D. The contribution of ion channels to shaping macrophage behaviour. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:970234. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.970234
96. Greenlee-Wacker MC, Nauseef WM. IFN-gamma targets macrophage-mediated immune responses toward Staphylococcus aureus. J Leukoc Biol. (2017) 101:751–8. doi: 10.1189/jlb.4A1215-565RR
97. Mills EL, Kelly B, Logan A, Costa ASH, Varma M, Bryant CE, et al. Succinate dehydrogenase supports metabolic repurposing of mitochondria to drive inflammatory macrophages. Cell. (2016) 167:457–70.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.08.064
98. Alvear-Arias JJ, Pena-Pichicoi A, Carrillo C, Fernandez M, Gonzalez T, Garate JA, et al. Role of voltage-gated proton channel (Hv1) in cancer biology. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1175702. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1175702
99. Mindell JA. Lysosomal acidification mechanisms. Annu Rev Physiol. (2012) 74:69–86. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-012110-142317
100. Jiang J, Shi Y, Cao J, Lu Y, Sun G, Yang J. Role of ASM/Cer/TXNIP signaling module in the NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Lipids Health Dis. (2021) 20:19. doi: 10.1186/s12944-021-01446-4
101. Lu Z, Li Y, Syn WK, Wang Z, Lopes-Virella MF, Lyons TJ, et al. Amitriptyline inhibits nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and atherosclerosis induced by high-fat diet and LPS through modulation of sphingolipid metabolism. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2020) 318:E131–E44. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00181.2019
102. Wang J, Keshava S, Das K, Kolesnick R, Jiang XC, Pendurthi UR, et al. Alterations to sphingomyelin metabolism affect hemostasis and thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2023) 43:64–78. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.122.318443
Keywords: HV1, cell viability, M1 macrophages, M2 macrophages, polarization, ceramide, pH regulation, acid sphingomyelinase
Citation: Kovacs T, Cs. Szabo B, Kothalawala RC, Szekelyhidi V, Nagy P, Varga Z, Panyi G and Zakany F (2024) Inhibition of the HV1 voltage-gated proton channel compromises the viability of human polarized macrophages in a polarization- and ceramide-dependent manner. Front. Immunol. 15:1487578. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1487578
Received: 28 August 2024; Accepted: 02 December 2024;
Published: 17 December 2024.
Edited by:
Krzysztof Guzik, Jagiellonian University, PolandReviewed by:
Malgorzata Bzowska, Jagiellonian University, PolandMichael J. Surace, AstraZeneca (United States), United States
Copyright © 2024 Kovacs, Cs. Szabo, Kothalawala, Szekelyhidi, Nagy, Varga, Panyi and Zakany. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Florina Zakany, ZmxvcmluYS56YWthbnlAbWVkLnVuaWRlYi5odQ==
 Tamas Kovacs
Tamas Kovacs Bence Cs. Szabo
Bence Cs. Szabo Peter Nagy
Peter Nagy Zoltan Varga
Zoltan Varga Gyorgy Panyi
Gyorgy Panyi Florina Zakany
Florina Zakany