- 1Chongqing Key Laboratory of Translational Research for Cancer Metastasis and Individualized Treatment, Chongqing University Cancer Hospital, Chongqing, China
- 2Chongqing Cancer Multi-omics Big Data Application Engineering Research Center, Chongqing University Cancer Hospital, Chongqing, China
- 3Department of Health Statistics, School of Public Health, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
Objective: In China, lung cancer ranks first in both incidence and mortality among all malignant tumors. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) constitutes the vast majority of cases, accounting for 80% to 85% of cases. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), either as monotherapies or combined with other treatments, have become the standard first-line therapy for NSCLC patients. This study aimed to establish a nomogram model for NSCLC patients receiving immunotherapy incorporating demographic information, clinical characteristics, and laboratory indicators.
Methods: From January 1, 2019, to December 31, 2022, a prospective longitudinal cohort study involving 1321 patients with NSCLC undergoing immunotherapy was conducted at Chongqing University Cancer Hospital. Clinical and pathological characteristics, as well as follow-up data, were collected and analyzed. To explore prognostic factors affecting overall survival (OS), a Cox regression model was used to test the significance of various variables. Independent prognostic indicators were identified through multivariate analysis and then used to construct a nomogram prediction model. To validate the accuracy and practicality of this model, the concordance index (C-index), area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), calibration curve, and decision curve analysis (DCA) were used to assess the predictive performance of the nomogram.
Result: In the final model, 11 variables from the training cohort were identified as independent risk factors for patients with NSCLC: age, KPS score, BMI, diabetes, targeted therapy, Hb, WBC, LDH, CRP, PLR, and LMR. The C-index for OS in the training cohort was 0.717 (95% CI, 0.689–0.745) and 0.704 (95% CI, 0.660–0.750) in the validation cohort. Calibration curves for survival probability showed good concordance between the nomogram predictions and actual observations. The AUCs for 1-year, 2-year, and 3-year OS in the training cohort were 0.724, 0.764, and 0.79, respectively, and 0.725, 0.736, and 0.818 in the validation cohort. DCA demonstrated that the nomogram model had a greater overall net benefit.
Conclusion: A prognostic model for OS in NSCLC patients receiving immunotherapy was established, providing a simple and reliable tool for predicting patient survival (https://icisnsclc.shinyapps.io/DynNomapp/). This model offers valuable guidance for clinicians in making treatment decisions and recommendations.
Introduction
The global cancer statistics for 2022 reveal that lung cancer (1), following other cancers, has become the second most common cancer worldwide and is also the malignancy with the highest mortality rate. Lung cancer accounts for 21% of all cancer-related deaths (2), making it the leading cause of cancer mortality globally. Approximately 340 people die from lung cancer each day, with a 5-year relative survival rate of 25% (3, 4). In China, lung cancer ranks highest in both incidence and mortality among all malignant tumors (5). The incidence and mortality rates of lung cancer continue to rise worldwide. Lung cancer is categorized into small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) on the basis of histological characteristics, with NSCLC accounting for 80% to 85% of cases (6, 7).
Precision treatment technologies for lung cancer are advancing rapidly, with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) emerging as a focal point of research and significantly improving survival outcomes for some lung cancer patients. Particularly for patients with advanced NSCLC who lack driver gene mutations, ICIs used alone or in combination with other therapies have become a first-line standard treatment (8–10). Cancer immunotherapy combats cancer by enhancing the body’s immune system. In recent years, immunotherapy has rapidly developed and is now used alongside surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and endocrine therapy to fight cancer. Immunotherapy employs two main strategies: the first is to stimulate the immune system through vaccine therapy to recognize and attack cancer cells (active immunotherapy), and the second is to use checkpoint inhibitors to increase the inhibitory state of the immune system, thereby restoring its ability to eliminate cancer cells (passive immunotherapy) (11). Monoclonal antibodies targeting immune checkpoints, including programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) and its ligand PD-L1, have shown response rates of up to 40% in monotherapy (12).
Given the complex fluid dynamics of tumors and the immunogenic variations within the tumor microenvironment (TME), relying solely on a single biomarker to accurately predict the efficacy of ICIs remains an unstable approach (13, 14). Numerous studies have established a prognostic evaluation framework for NSCLC patients treated with ICIs, integrating multidimensional information from clinical practice, pathological histology, genomics, and radiomics to provide a more comprehensive understanding of treatment prospects (15, 16). Therefore, this study aimed to develop a comprehensive overall survival risk prediction model for patients with NSCLC receiving immunotherapy that incorporates demographic information, clinical characteristics, and laboratory indicators.
Materials and methods
Data sources and patient screening
In a prospective cohort study, data were collected from 1478 NSCLC patients recorded in the Chongqing University Cancer Hospital tumor database between January 1, 2019, and December 31, 2022. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) aged ≥18 years; (2) histopathologically confirmed NSCLC; (3) receiving at least two cycles of ICI treatment; and (4) complete clinical data. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) death within 48 hours of admission; (2) poor treatment compliance; (3) severe underlying diseases (e.g., severe cardiovascular disease, liver or renal failure, or stroke with severe sequelae); and (4) incomplete follow-up records. This study was conducted following the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Chongqing University Cancer Hospital. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. The flowchart of this study is shown below.
Clinical factor
In this study, we collected data on demographic characteristics, including age, sex (female and male), body mass index (BMI), and marital status (married and others). Clinical characteristics, including the Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS) score; hypertension, diabetes, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD); and clinical information regarding surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy, were also recorded. Additionally, we collected laboratory variables from patients before and during treatment (every 6 weeks), including hemoglobin (Hb), white blood cell count (WBC), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), C-reactive protein (CRP), T lymphocytes (T cells), B lymphocytes (B cells), natural killer (NK) cells, the albumin/globulin ratio (ALB/GLB), β2-microglobulin, the CD4/CD8 ratio, the platelet−lymphocyte ratio (PLR), the neutrophil−lymphocyte ratio (NLR), and the lymphocyte−monocyte ratio (LMR).
Outcomes and follow-up
The primary outcomes were the probabilities of 1-year, 2-year, and 3-year OS. OS was defined as the time from the initial diagnosis to death, loss to follow-up, or the last follow-up. All the subjects were followed up every 6 weeks until the endpoint of follow-up. The last follow-up date was May 31, 2024. The median survival time of patients in this study, along with the 95% confidence interval, was 25.13 (24.9, 25.37) months. We used a combination of active (data collection via phone calls) and passive (information matched through the hospital information system) follow-up methods to obtain and evaluate patient survival outcomes comprehensively.
Construction of the nomogram
The patient cohort was randomly divided into two groups at a 7:3 ratio: the training cohort with 925 subjects and the validation cohort with 396 subjects. Data from the training cohort were used to develop the nomogram model. To assess the role of each covariate as a prognostic factor for OS, an initial Cox stepwise regression analysis was performed to identify the optimal model. These variables were then included in a multivariate Cox regression model to analyse their independent associations with OS further, thereby identifying key independent risk factors influencing OS. Nomogram construction was based on the stepwise process’s Cox proportional hazards regression model.
Model performance and validation
The predictive accuracy of the model was measured via the concordance index (C-index), while the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) was used to evaluate the predictive performance of the nomogram comprehensively. Additionally, calibration curves were employed for visual assessment, illustrating the consistency between the model’s predicted results and actual observations. Decision curve analysis (DCA) was utilized to further quantify the model’s clinical utility. This method compares the clinical “net benefit” of using the nomogram to guide decisions against two extreme strategies, “treat all” and “treat none,” thereby providing a comprehensive evaluation of the model’s practical application value.
Statistical analysis
Data analysis was performed via R version 4.3.1. The development and evaluation of the model were conducted with the R packages “survival” (version 3.5–7), “foreign” (version 0.8–84), “rms” (version 6.7–0), “timeROC” (version 0.4), and “ggDCA” (version 1.1). Additionally, a web server for the NSCLC nomogram was developed via the R packages “rsconnect” (version 1.0.2) and “DynNom” (version 5.0.2) (access link):. Missing data were handled via the multiple imputation method from the “mice” package (version 3.16.0). Categorical variables in the baseline data are expressed as frequencies and percentages [N(%)], and continuous variables are expressed as the means (SDs) or medians (IQRs). Differences in demographic and clinical characteristics between the training and validation cohorts were compared via Pearson’s chi-square test for categorical variables and one-way ANOVA for continuous variables. Significant feature variables were identified via stepwise Cox regression and multivariate Cox regression models. All the statistical tests were two-tailed, with the significance level at P < 0.05.
Results
Baseline characteristics of immunotherapy patients
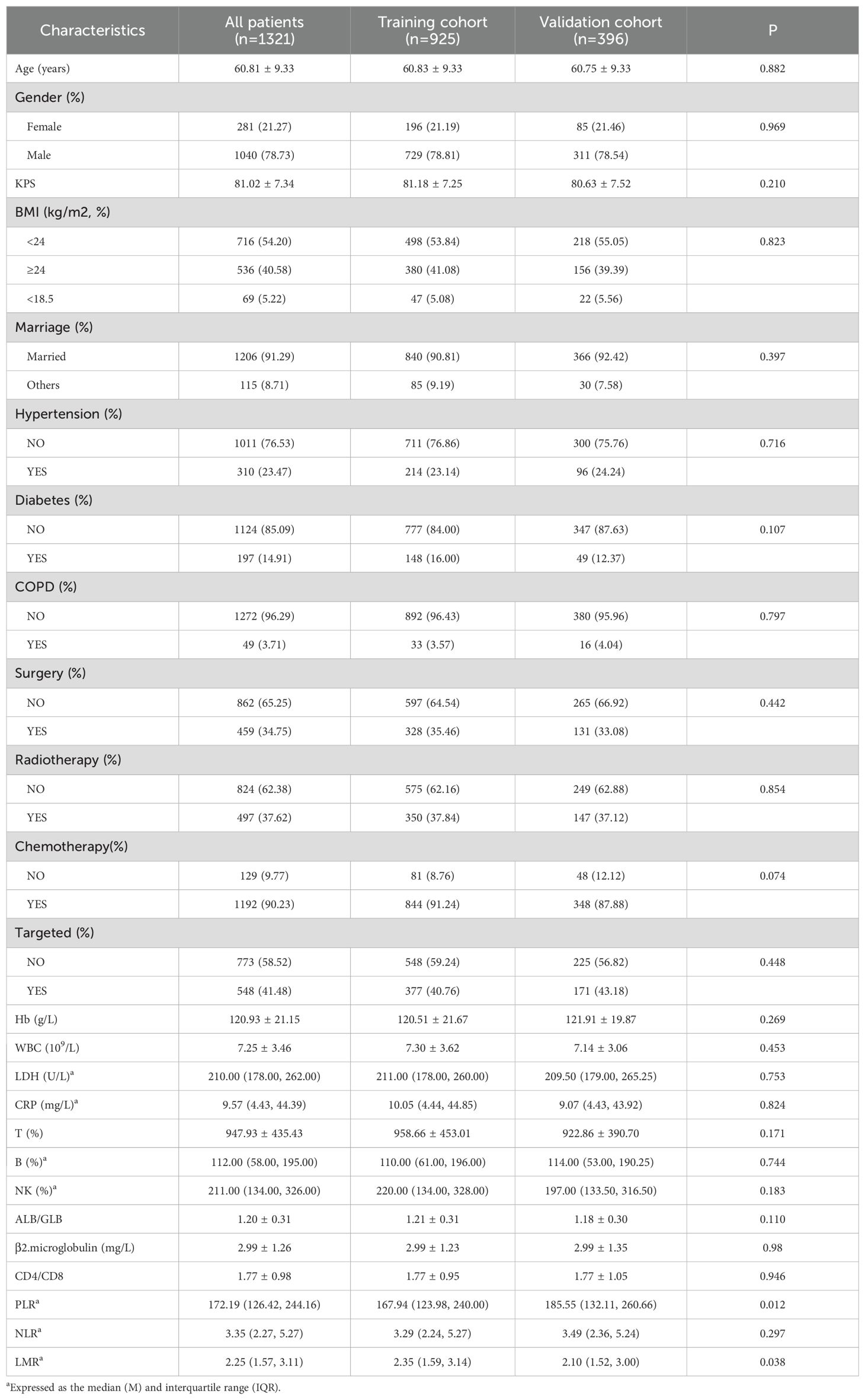
A total of 1,321 patients with complete information were included in the study and randomly divided into training (n = 925) and validation (n = 396) cohorts at a 7:3 ratio. The median survival time and 95% confidence interval for the entire cohort were 25.13 (24.9, 25.37) months, those for the training cohort were 25.10 (24.8, 25.33) months, and those for the validation cohort were 25.47 (24.5, 29.43) months. During the follow-up period, 838 patients (63.44%) survived, whereas 483 patients (36.56%) died. There were 1,040 males (78.73%) and 281 females (21.27%), with a mean age of 60.81 ± 9.33 years. Among the patients, 91.29% were married. The majority of patients chose chemotherapy (90.23%). Targeted therapy was chosen by 41.48% of the patients. The proportions of patients who chose surgery and radiotherapy were similar, at 34.75% and 37.62%, respectively. The demographics, clinical characteristics, and laboratory indicators of the total cohort, training cohort, and validation cohort are shown in Table 1, and there were no statistically significant differences between the training and validation cohorts.
Independent prognostic factors in the training cohort
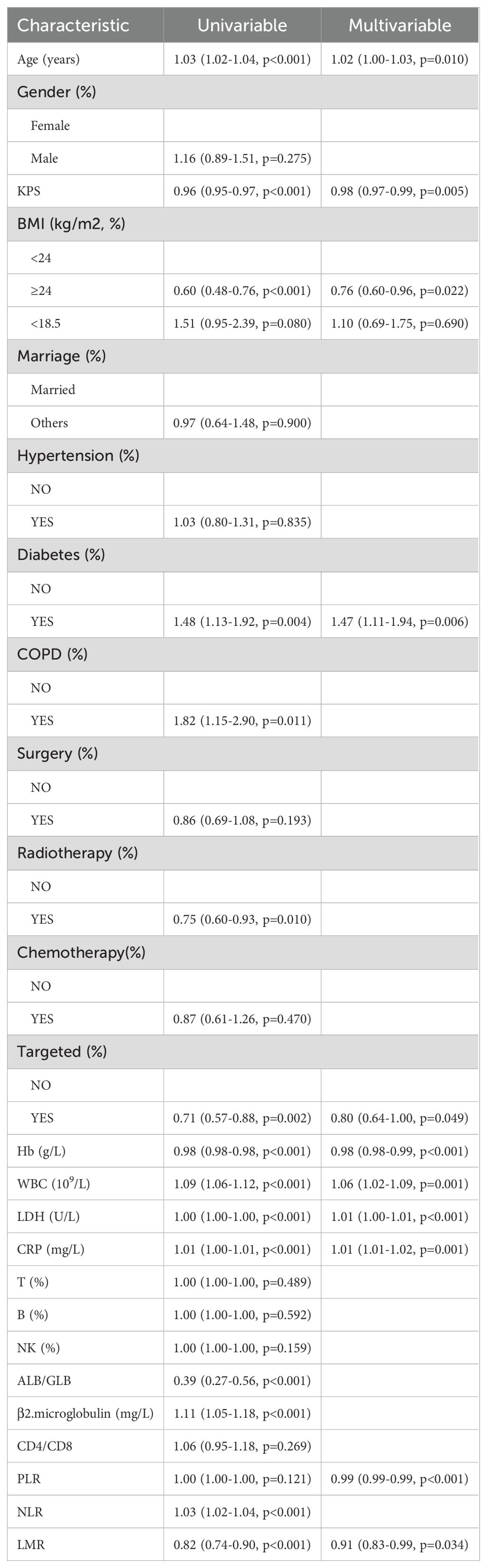
In the training cohort (n = 925), independent prognostic factors were analysed via the Cox proportional hazards model, and the modelling results are shown in Table 2. In the univariate analysis, the following variables were found to be significant predictors of OS: age; Karnofsky Performance Scale (KPS) score; BMI; diabetes status; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD); radiotherapy; targeted therapy; Hb, white blood cell (WBC) count; lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), C-reactive protein (CRP), serum albumin (ALB)/globulin (GLB), β2-microglobulin, the NLR, and the LMR (all p < 0.05). In the multivariate analysis, the independent prognostic factors were age (hazard ratio [HR]: 1.03; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.02–1.03), KPS (HR: 0.98; CI: 0.97–0.99), BMI (HR: 0.76; CI: 0.60–0.96), diabetes (HR: 1.47; CI: 1.11–1.94), targeted therapy (HR: 0.80; CI: 0.64–1.00), Hb (HR: 0.98; CI: 0.98–0.99), WBC (HR: 1.06; CI: 1.02–1.09), LDH (HR: 1.00; CI: 1.00–1.00), CRP (HR: 1.00; CI: 1.00–1.01), PLR (HR: 1.00; CI: 1.00–1.00), and LMR (HR: 0.91; CI: 0.83–0.99).
Development of the prognostic nomogram model
To construct predictive models for 1-year, 2-year, and 3-year OS in NSCLC patients, we selected independent prognostic factors identified through multivariate analysis and subsequently developed a nomogram, as shown in Figure 1. We converted each selected variable into corresponding scores on the basis of the coefficients estimated from the Cox regression model. These scores were then summed, and the total score was used to estimate the patient’s OS probability from a reference table. We developed an accessible web server for the NSCLC nomogram model (https://icisnsclc.shinyapps.io/DynNomapp/). Users can display the patient’s survival plot and probability by selecting the appropriate indicators and survival time on the left side of the web server interface (Figure 2). For example, a patient who is 61 years old with a KPS score of 81, BMI < 24, no diabetes, no targeted therapy, Hb = 121, WBC = 7, LDH = 243, CRP = 34, PLR = 197, and LMR = 3 has 1-year, 2-year, and 3-year survival probabilities of 0.90, 0.62, and 0.32, respectively.
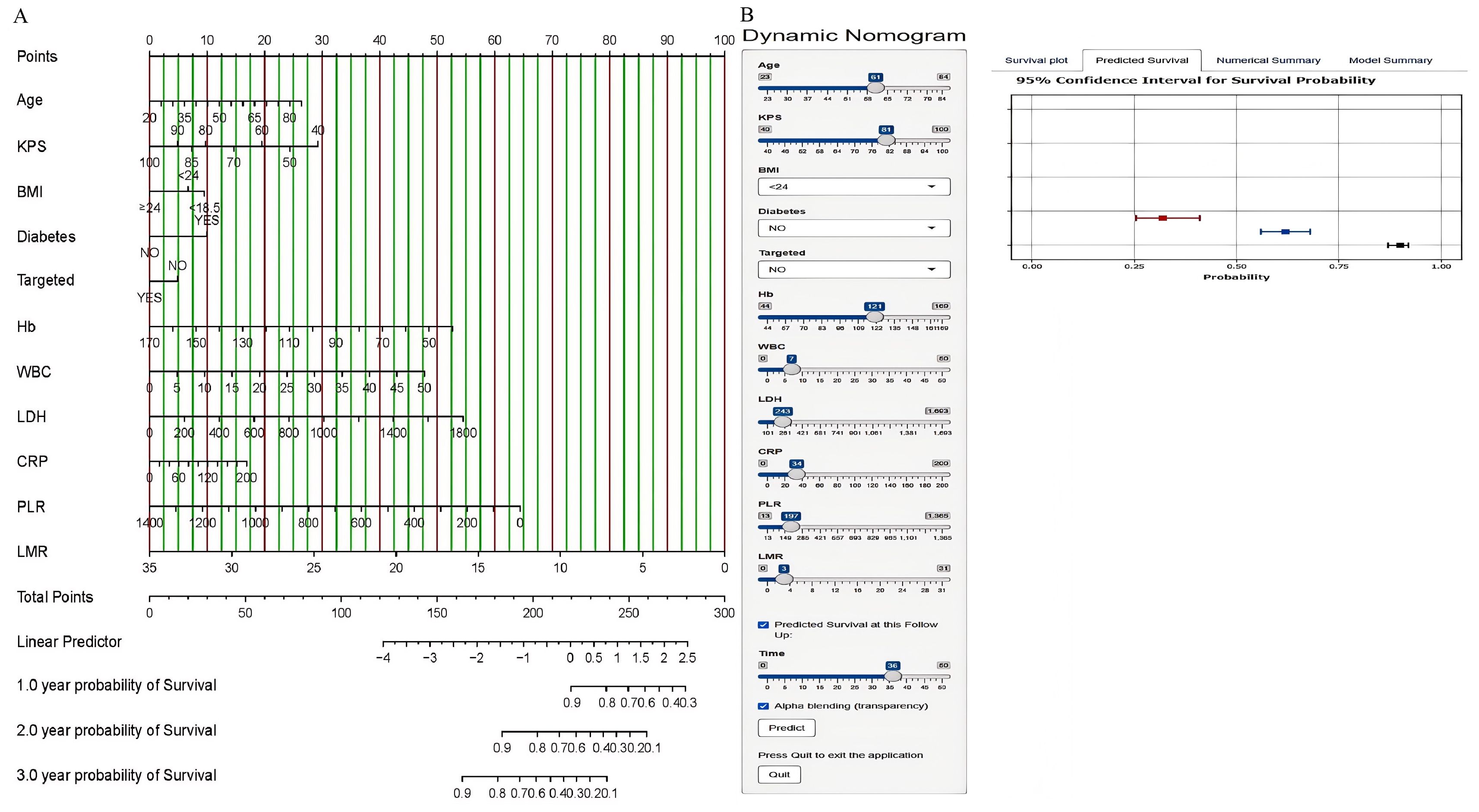
Figure 2. Nomogram for predicting the 1-year, 2-year, and 3-year OS of NSCLC patients in the training cohort (A) and the online nomogram tool (B).
Model performance and validation of the nomogram
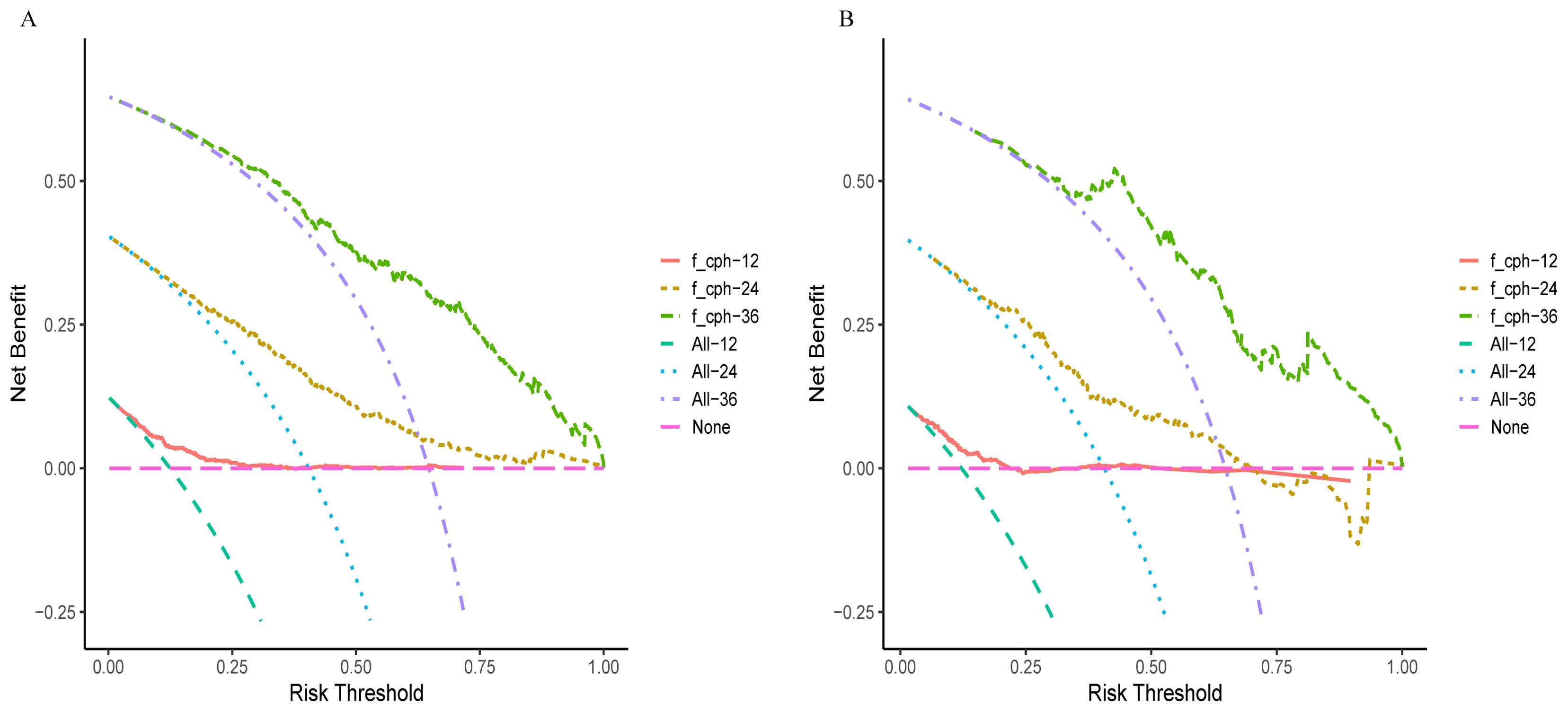
In the training and validation cohorts, the C-indexes were 0.717 (95% CI, 0.689–0.745) and 0.704 (95% CI, 0.660–0.750), respectively. The area under the curve (AUC) values for predicting 1-year, 2-year, and 3-year OS in the training cohort were 0.724, 0.764, and 0.797, respectively (Figure 3A), and those in the validation cohort were 0.725, 0.736, and 0.818, respectively (Figure 3B). Moreover, the calibration curves for 1-year, 2-year, and 3-year survival demonstrated good performance, indicating strong agreement between the predicted probabilities and the observed outcomes (Figures 3C, D). Additionally, DCA was utilized to evaluate the predictive power of the nomogram. The DCA results for the validation cohort indicated that, except when the predicted probability threshold exceeded 75%, the nomogram provided greater net benefits and more accurate clinical outcome predictions than the prediction that all patients would die or survive (Figure 4).
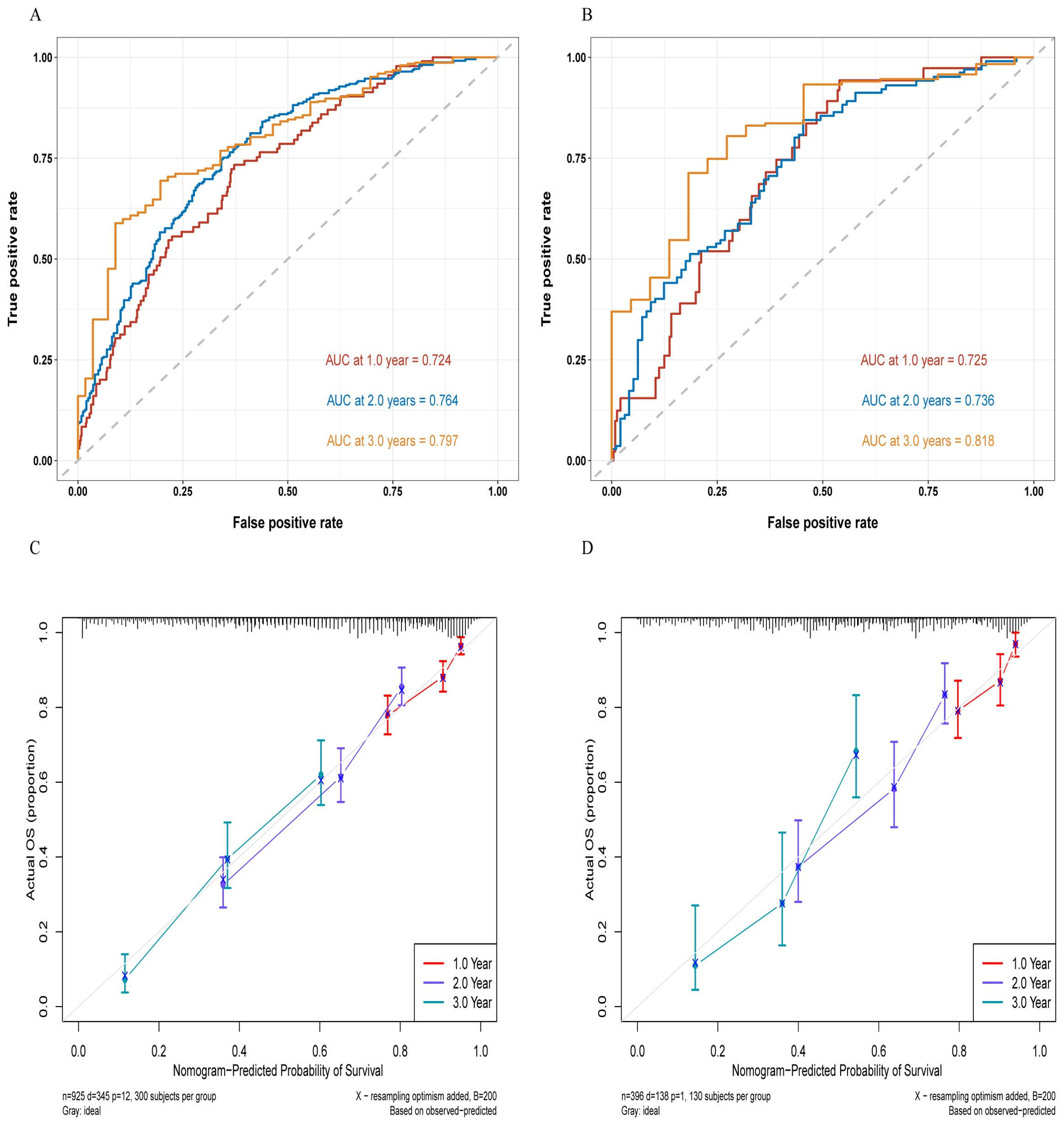
Figure 3. ROC curves for the training cohort (A) and the validation cohort (B), as well as the calibration curves for the training cohort (C) and the validation cohort (D).
The risk stratification ability of the nomogram
Using the nomogram model to predict risk scores, a threshold of 0.473 was set via the `surv_cutpoint` function to categorize patients into low-risk (scores below the threshold) and high-risk groups (scores above the threshold). K−M survival analysis of the training and validation cohorts revealed highly significant differences between these two groups (p < 0.0001), as shown in Figure 5. In the training cohort, the median survival time for the high-risk group was 15 months (95% CI, 13.53–20.43), whereas that for the low-risk group was 37.17 months (95% CI, 35.87–NA). In the validation cohort, the median survival time for the high-risk group was 13.53 months (95% CI, 13.33–21.93), and for the low-risk group, it was 37.03 months (95% CI, 33.17–NA).
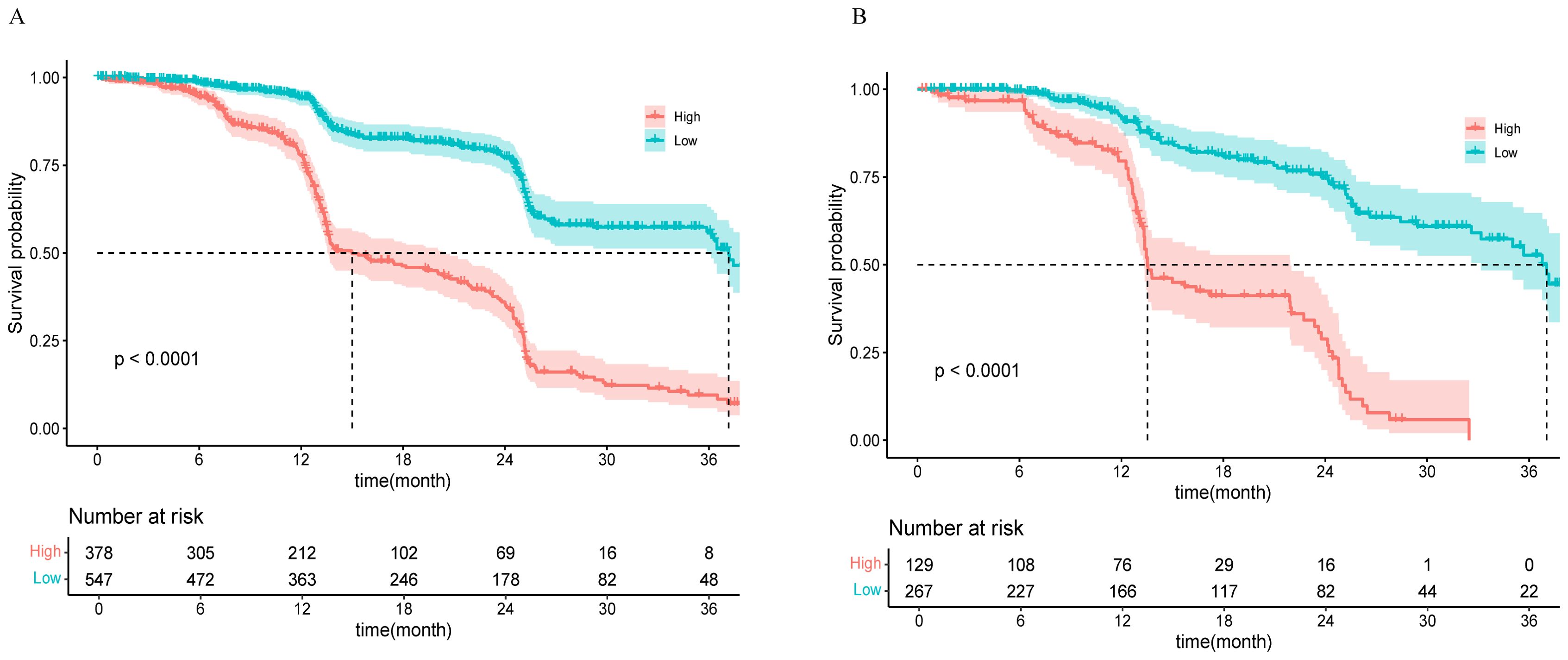
Figure 5. K−M curves for the high-risk and low-risk groups in the training cohort (A) and the validation cohort (B).
Discussion
This study aimed to develop an OS risk prediction model for NSCLC patients undergoing immunotherapy incorporating demographic information, clinical characteristics, and laboratory indicators. A nomogram was constructed based on age, KPS, BMI, diabetes status, targeted therapy, Hb, WBC, LDH, CRP, PLR, and LMR. The model demonstrated good predictive ability and was developed as an online NSCLC prediction tool.
Previous studies on predicting OS in NSCLC patients are numerous. Mezquita et al. found that the pre-treatment Lung Immune Prognostic Index (LIPI) was closely associated with poor efficacy of ICIs in patients with NSCLC. LIPI consists of two key indicators: the derived neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (dNLR) and LDH levels, where a dNLR greater than 3 and LDH exceeding the upper limit of normal (ULN) are independent predictors of poor prognosis (17, 18). In patients with advanced NSCLC (aNSCLC), continuing immunotherapy after disease progression was associated with prolonged OS and PFS (19). A prognostic risk model for NSCLC based on seven smoking-related genes demonstrated stable predictive ability, with FCGBP having the highest mutation frequency (20). Additionally, studies have shown that in Asian patients with advanced NSCLC receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors, obesity (BMI) is associated with better OS (18). Cheng Lu et al. reported that CellDiv features (computer-extracted tumor cell diversity features) strongly predict 5-year OS in early-stage NSCLC patients and are related to apoptotic signalling and cell differentiation pathways (21). In 2020, the Mazzaschi team prospectively collected baseline peripheral blood from 109 NSCLC patients receiving continuous ICI treatment to construct the immune effect score (IeffS) based on a tumor−host interaction model. IeffS revealed that elevated PD-L1, reduced CD8+PD-1+ cells, and the absence of NK cells were risk factors for reduced ICI efficacy (P<0.01). In combination with LIPI, it significantly impacted PFS (HR=4.61), OS (HR=4.03), and ICI response rates (P<0.001) (22). A phase III trial in stage I-III NSCLC patients reported a median PFS of 20.8 months for the standard chemotherapy group compared with 31.6 months for the nivolumab group, with 24% of patients achieving pathological complete response (23). However, some previous studies have been limited in their choice of predictive factors, focusing on single dimensions (24–26). In contrast, this study enhances predictive performance and comprehensiveness by incorporating a comprehensive set of predictive factors from three domains.
The nomogram model has been widely adopted tumor prognosis risk assessment, demonstrating excellent predictive accuracy (27). In 2021, Zeng et al. conducted a retrospective analysis of immunotherapy plus chemotherapy data from 130 stage IIIA-IVB NSCLC patients and developed a PFS prediction nomogram based on bone metastasis, the dNLR, smoking status, and PD-L1 expression. The low-risk group had a significantly longer median PFS (P<0.001). The model demonstrated good predictive performance, with C-indexes of 0.725 and 0.688 in the training and validation sets, respectively (28). In 2020, the Hopkins team developed and validated a prognostic tool based on clinical trials to identify advanced NSCLC patients who would benefit from atezolizumab treatment. This tool includes factors such as PD-L1 expression levels, dNLR values, CRP concentrations, LDH activity, albumin (ALB) levels, patient performance status, the period since self-diagnosed metastasis, and the number of metastatic sites. The low-risk group benefited the most, and this study was the first to identify CRP as an OS predictor, with CRP reduction associated with prolonged OS (P<0.001, c=0.66) (29). Other studies have constructed nomogram models based on patients’ general characteristics, histological features, pathological and immunohistochemical results, inflammation, and nutritional indicators to effectively predict OS and PFS in NSCLC patients after surgery (30). Mengmeng Song et al. identified the ALI, LCR, and NLR as the top three inflammation/nutrition indicators for predicting the prognosis of lung cancer patients (31). A study on local tumor response and survival outcomes following combined treatment of stereotactic radiosurgery and immunotherapy in NSCLC with brain metastases revealed that a KPS score of < 80 (p = 0.001) and a lung-specific molecular marker graded prognostic assessment (lung-mol GPA) score of < 1.5 (p = 0.02) were predictive of poorer survival outcomes (32). The variables included in this study are broadly consistent with previous studies, and Hb and WBC count have been newly identified as independent prognostic factors for NSCLC patients. This finding provides a new perspective and an essential basis for evaluating disease prognosis.
The biological complexity and heterogeneity of NSCLC underscore the necessity of personalized treatment. Molecular targeted therapies based on driver gene mutations, such as EGFR, ALK, and ROS1, have achieved significant advances in the treatment of advanced NSCLC. However, various resistance mechanisms, such as secondary mutations and bypass activation, limit the long-term efficacy of targeted therapies. The limitations of single-agent therapies suggest that combination treatments may improve outcomes. ICIs, in combination with chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or radiotherapy, have shown promising results in clinical studies (33). Traditionally, radiotherapy has been thought to kill tumor cells mainly by damaging DNA. However, radiotherapy can also control metastatic lesions outside the irradiated field through the “abscopal effect.” This mechanism involves radiotherapy-induced tumor cell death, releasing tumor-associated antigens, which activate a systemic immune response to control tumor proliferation (34). For patients with unresectable stage III NSCLC and wild-type driver genes, combining radiotherapy and immunotherapy in initial treatment is crucial for significantly improving efficacy (35). The PACIFIC trial was a landmark study that demonstrated durvalumab, an ICI, significantly prolonged PFS and OS in patients after concurrent chemoradiotherapy. The real-world effectiveness and safety of durvalumab are consistent with the results of the PACIFIC trial, further supporting its use as the standard treatment for patients with unresectable stage III NSCLC (36).
The limitations of this study primarily lie in the lack of a multicenter research design and external validation. Although the sample size was relatively large, the findings need to be confirmed in larger-scale prospective cohorts. This limitation may introduce selection bias, thereby restricting the generalizability and representativeness of the results. Future research should aim to establish a multicenter collaborative framework to enhance the comprehensiveness and reliability of the data. Moreover, personalized prediction has become possible with advancements in genomics, translational medicine, and precision medicine technologies. The study found that AI models can accurately predict tumor response and PFS of ICIs in advanced NSCLC by assessing PD-L1 tumor proportion score (TPS). In the future, it may be feasible to offer more efficient and convenient personalized risk assessment strategies by integrating advanced gene testing techniques and the assistance of artificial intelligence (37, 38).
Conclusion
In this study, we developed an OS risk prediction model for patients undergoing immunotherapy for NSCLC that incorporates demographic information, clinical characteristics, and laboratory indicators. The model demonstrated good predictive ability and was developed as an online NSCLC prediction tool. This tool facilitates convenient and efficient individualized risk assessment, providing real-time prognostic prediction services for healthcare providers and patients.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Chongqing University Cancer Hospital’s Ethics Committee. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
HML: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. YY: Data curation, Resources, Writing – original draft. QX: Data curation, Formal analysis, Supervision, Writing – original draft. GL: Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. ZH: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. XL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. WZ: Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing. HKL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing Municipality (CSTB2024NSCQ-MSX0229).
Acknowledgments
We thank all the participants, as no meaningful research could have been conducted without them.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Ca-A Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
2. Ni S, Liang Q, Jiang X, Ge Y, Jiang Y, Liu L. Prognostic models for immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer: A comprehensive review. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e29840. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29840
3. Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:12–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21820
4. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. (2023) 73:17–48. doi: 10.3322/caac.21763
5. Xia C, Dong X, Li H, Cao M, Sun D, He S, et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: profiles, trends, and determinants. Chin Med J. (2022) 135:584–90. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002108
6. Duma N, Santana-Davila R, Molina JR. Non-small cell lung cancer: epidemiology, screening, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. (2019) 94:1623–40. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2019.01.013
7. Liu X, Cho WC. Precision medicine in immune checkpoint blockade therapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Trans Med. (2017) 6:7. doi: 10.1186/s40169-017-0136-7
8. Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL, Akerley W, Bauman JR, Bharat A, et al. NCCN guidelines(R) insights: non-small cell lung cancer, version 2.2023. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2023) 21:340–50. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2023.0020
9. Mountzios G, Remon J, Hendriks LEL, Garcia-Campelo R, Rolfo C, Van Schil P, et al. Immune-checkpoint inhibition for resectable non-small-cell lung cancer - opportunities and challenges. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2023) 20:664–77. doi: 10.1038/s41571-023-00794-7
10. Reck M, Remon J, Hellmann MD. First-line immunotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:586–97. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.01497
11. Chen R, Manochakian R, James L, Azzouqa AG, Shi H, Zhang Y, et al. Emerging therapeutic agents for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol. (2020) 13:58. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00881-7
12. Mok TSK, Wu YL, Kudaba I, Kowalski DM, Cho BC, Turna HZ, et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for previously untreated, PD-L1-expressing, locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-042): a randomised, open-label, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. (2019) 393:1819–30. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32409-7
13. Brueckl WM, Ficker JH, Zeitler G. Clinically relevant prognostic and predictive markers for immune-checkpoint-inhibitor (ICI) therapy in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). BMC Cancer. (2020) 20:1185. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07690-8
14. Zheng Y, Tang L, Liu Z. Multi-omics analysis of an immune-based prognostic predictor in non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer. (2021) 21:1322. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-09044-4
15. Rakaee M, Adib E, Ricciuti B, Sholl LM, Shi W, Alessi JV, et al. Association of machine learning-based assessment of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes on standard histologic images with outcomes of immunotherapy in patients with NSCLC. JAMA Oncol. (2023) 9:51–60. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.4933
16. She Y, Jin Z, Wu J, Deng J, Zhang L, Su H, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning model for non-small cell lung cancer survival. JAMA Netw Open. (2020) 3:e205842. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.5842
17. Lahiri A, Maji A, Potdar PD, Singh N, Parikh P, Bisht B, et al. Lung cancer immunotherapy: progress, pitfalls, and promises. Mol Cancer. (2023) 22:40. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01740-y
18. Mezquita L, Auclin E, Ferrara R, Charrier M, Remon J, Planchard D, et al. Association of the lung immune prognostic index with immune checkpoint inhibitor outcomes in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol. (2018) 4:351–7. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.4771
19. Ge X, Zhang Z, Zhang S, Yuan F, Zhang F, Yan X, et al. Immunotherapy beyond progression in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res. (2020) 9:2391–400. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-1252
20. Li Q, Wang T, Tang Y, Zou X, Shen Z, Tang Z, et al. A novel prognostic signature based on smoking-associated genes for predicting prognosis and immune microenvironment in NSCLC smokers. Cancer Cell Int. (2024) 24:171. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03347-9
21. Lu C, Bera K, Wang X, Prasanna P, Xu J, Janowczyk A, et al. A prognostic model for overall survival of patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: a multicentre, retrospective study. Lancet Digital Health. (2020) 2:E594–606. doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30225-9
22. Mazzaschi G, Minari R, Zecca A, Cavazzoni A, Ferri V, Mori C, et al. Soluble PD-L1 and circulating CD8+PD-1+ and NK cells enclose a prognostic and predictive immune effector score in immunotherapy treated NSCLC patients. Lung Cancer. (2020) 148:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.07.028
23. Forde PM, Spicer J, Lu S, Provencio M, Mitsudomi T, Awad MM, et al. Neoadjuvant nivolumab plus chemotherapy in resectable lung cancer. N Engl J Med. (2022) 386:1973–85. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2202170
24. Jiang Q, Yue X, Lei H, Mao W, Li Y, Chen X. Comparison of survival outcomes between clinical trial participants and non-participants of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective cohort study. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e22660. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22660
25. Ma S, Li Z, Wang L. The advanced lung cancer inflammation index (ALI) predicted the postoperative survival rate of patients with non-small cell lung cancer and the construction of a nomogram model. World J Surg Oncol. (2024) 22:158. doi: 10.1186/s12957-024-03432-3
26. Reckamp KL, Redman MW, Dragnev KH, Minichiello K, Villaruz LC, Faller B, et al. Phase II randomized study of ramucirumab and pembrolizumab versus standard of care in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with immunotherapy-lung-MAP S1800A. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:2295–306. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.00912
27. Fan L, Yang Z, Chang M, Chen Z, Wen Q. CT-based delta-radiomics nomogram to predict pathological complete response after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. J Transl Med. (2024) 22:579. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05392-4
28. Zeng H, Huang WW, Liu YJ, Huang Q, Zhao SM, Li YL, et al. Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting prognosis to immune checkpoint inhibitors plus chemotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:685047. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.685047
29. Hopkins AM, Kichenadasse G, Garrett-Mayer E, Karapetis CS, Rowland A, Sorich MJ. Development and validation of a prognostic model for patients with advanced lung cancer treated with the immune checkpoint inhibitor atezolizumab. Clin Cancer Res. (2020) 26:3280–6. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-2968
30. Ma S, Wang L. Prognostic factors and predictive model construction in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a retrospective study. Front Oncol. (2024) 14:1378135. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1378135
31. Song M, Zhang Q, Song C, Liu T, Zhang X, Ruan G, et al. The advanced lung cancer inflammation index is the optimal inflammatory biomarker of overall survival in patients with lung cancer. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2022) 13:2504–14. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13032
32. Singh C, Qian JM, Yu JB, Chiang VL. Local tumor response and survival outcomes after combined stereotactic radiosurgery and immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastases. J Neurosurg. (2020) 132:512–7. doi: 10.3171/2018.10.JNS181371
33. Wang M, Herbst RS, Boshoff C. Toward personalized treatment approaches for non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat Med. (2021) 27:1345–56. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01450-2
34. Shang S, Liu J, Verma V, Wu M, Welsh J, Yu J, et al. Combined treatment of non-small cell lung cancer using radiotherapy and immunotherapy: challenges and updates. Cancer Commun (Lond). (2021) 41:1086–99. doi: 10.1002/cac2.v41.11
35. Zhao L, Zhao Z, Yan X, Wu F, Sun N, Guo R, et al. Comparison of efficacy and safety of first-line treatment options for unresectable stage III non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective analysis. Int J Clin Pract. (2024) 2024:8585035. doi: 10.1155/2024/8585035
36. O’Leary C, Naidoo J. PACIFIC in the real world. J Thorac Oncol. (2023) 18:133–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2022.11.015
37. Kim H, Kim S, Choi S, Park C, Park S, Pereira S, et al. Clinical validation of artificial intelligence-powered PD-L1 tumor proportion score interpretation for immune checkpoint inhibitor response prediction in non-small cell lung cancer. JCO Precis Oncol. (2024) 8:e2300556. doi: 10.1200/PO.23.00556
38. Qiu Q, Xing L, Wang Y, Feng A, Wen Q. Development and validation of a radiomics nomogram using computed tomography for differentiating immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis from radiation pneumonitis for patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Front Immunol. (2022) 13. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.870842
Keywords: NSCLC, PD-1/PD-L1, ICIS, nomogram, prognosis
Citation: Li H, Yuan Y, Xu Q, Liang G, Hu Z, Li X, Zhang W and Lei H (2024) A comprehensive nomogram for assessing the prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving immunotherapy: a prospective cohort study in China. Front. Immunol. 15:1487078. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1487078
Received: 27 August 2024; Accepted: 31 October 2024;
Published: 20 November 2024.
Edited by:
Yun Chen, Nanjing Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Leonidas Papastavrou, Athens Medical Center, GreeceJelena Stojsic, University of Belgrade, Serbia
Qiang Wen, Stanford University, United States
Copyright © 2024 Li, Yuan, Xu, Liang, Hu, Li, Zhang and Lei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Haike Lei, dG9oYWlrZUAxNjMuY29t; Wei Zhang, Y3FjaHpoYW5nd2VpQDE2My5jb20=; Xiaosheng Li, dG94aWFvc2hlbmdAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Hongmei Li
Hongmei Li Yuliang Yuan1†
Yuliang Yuan1† Qianjie Xu
Qianjie Xu Haike Lei
Haike Lei