- 1School of Medicine, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- 2Department of Exercise Physiology and Corrective Exercises, Faculty of Sport Sciences, Urmia University, Urmia, Iran
- 3Department of Immunology, School of Public Health, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- 4Department of Biochemistry, School of Medicine, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- 5Student Research Committee, Birjand University of Medical Sciences, Birjand, Iran
- 6Cellular and Molecular Research Center, Birjand University of Medical Sciences, Birjand, Iran
- 7Department of Biology, University of Sistan and Baluchestan, Zahedan, Iran
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes joint inflammation and gradual tissue destruction. New research has shown how important noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) are for changing immune and inflammatory pathways, such as the WNT signaling pathway, which is important for activating synovial fibroblasts and osteoblasts to work. This article examines the current understanding of several ncRNAs, such as miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs, that influence NF-κB signaling in the pathogenesis of RA. We investigate how these ncRNAs impact NF-κB signaling components, altering cell proliferation, differentiation, and death in joint tissues. The paper also looks at how ncRNAs can be used as potential early detection markers and therapeutic targets in RA because they can change important pathogenic pathways. This study highlights the therapeutic potential of targeting ncRNAs in RA therapy techniques, with the goal of reducing inflammation and stopping disease progression. This thorough analysis opens up new possibilities for understanding the molecular foundations of RA and designing novel ncRNA-based treatments.
Background
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation that progresses. Permanent synovitis triggers the disease, resulting in irreversible joint damage. Individuals with RA frequently suffer bilateral joint soreness, edema, and stiffness. Damage to extra-articular organs and systems may occur as RA worsens. The risk of incidence of cardiovascular illness, a significant and potentially deadly comorbidity, closely correlates with RA disease activity (1). A worldwide health concern, RA affects around 240 out of every 100,000 people. Moreover, the prevalence of RA is rising globally in line with the fast-growing aging population (2). The pathophysiology and etiology of RA are extremely complex and unknown. They involve inheritance, triggers from the environment, and epigenetic alterations (3). The four main characteristics of RA pathology are usually acknowledged to be synovial hyperplasia, ongoing inflammation, articular cartilage deterioration, and bone erosion (4). Recent developments in RA pathophysiology have produced novel biologic and small-molecule inhibitors over the last 20 years. However, due to inadequate therapy, many RA patients continue to suffer from severe disability and a lower quality of life. Thus, to enhance therapeutic results, more understanding of the cellular and molecular pathways behind tissue damage, persistent inflammation, and synovial hyperplasia is required (5).
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are essential for controlling gene expression and biological processes, as demonstrated by recent developments in molecular biology (6). While not encoding proteins like coding RNAs, non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are nonetheless active in several aspects of gene expression during and after transcription (7). NcRNAs are classified into three groups, each having its own mechanism, including microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs) (8, 9).
MicroRNAs are short RNA molecules, measuring approximately 22 nucleotides in length. When miRNAs bind to the 3’ untranslated regions (UTRs) of target mRNAs, they stop translation or destroy the mRNA (Fabian, Sonenberg et al., 2010). Phenotypic scaffolds, guides, or decoys, long non-coding RNAs (>200 nucleotides), influence the dynamics of chromatin and the expression of genes (10). Circular RNAs function as miRNA sponges, trapping miRNAs and avoiding them from attaching to target mRNAs due to their covalently closed loop topologies (11).
Extensive research has demonstrated how important dysregulated NF-κB activation is for the emergence of several autoimmune disorders, such as RA (12, 13). The NF-κB family of inducible transcription factors regulates several genes involved in immunological and inflammatory responses (14). Abnormalities caused by aberrant NF-κB activation in RA lead to long-term inflammation and joint destruction (14).
The aim of this study is to recognize and characterize ncRNAs associated with the NF-κB signaling pathway in RA. Finding out how different ncRNAs, like miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs, control this pathway is important because NF-κB is a key player in the progress of RA. By investigating these ncRNAs, we hope to gain insights into their specific contributions and interactions within the NF-κB signaling network. This study aims to reveal novel molecular targets for developing more effective RA therapies.
The complex pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis
The presence or absence of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs) divides RA into two main subgroups: ACPA-positive RA and ACPA-negative RA (15). Generally, ACPA-positive rheumatoid arthritis is associated with a more severe disease trajectory, elevated rates of joint erosion, and greater disability compared to ACPA-negative rheumatoid arthritis (16). The two subtypes also differ in terms of their fundamental genetic risk factors and environmental impacts. Environmental variables, including smoking, predispose a genotype to ACPA-positive rheumatoid arthritis (17). Peptidyl arginine deiminases (PADs) mediate a process known as citrullination, which facilitates the transformation of the amino acid arginine into citrulline (18). Certain bacterial pathogens, such as Porphyromonas gingivalis (associated with periodontal disease) and Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, can also induce this alteration and contribute to the exacerbation of rheumatoid arthritis progression (19). Citrullinated proteins transform into neoantigens upon formation and present themselves to CD4+ T lymphocytes through major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules, particularly HLA-DRB1 alleles, which significantly correlate with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility (Figure 1A) (20, 21). When T cells are activated and present these modified peptides, they trigger B cells to produce autoantibodies such as ACPAs and RF (Figure 1B) (22). These autoantibodies can be identified years before the onset of clinical symptoms, signifying an initial phase of immunological activation.
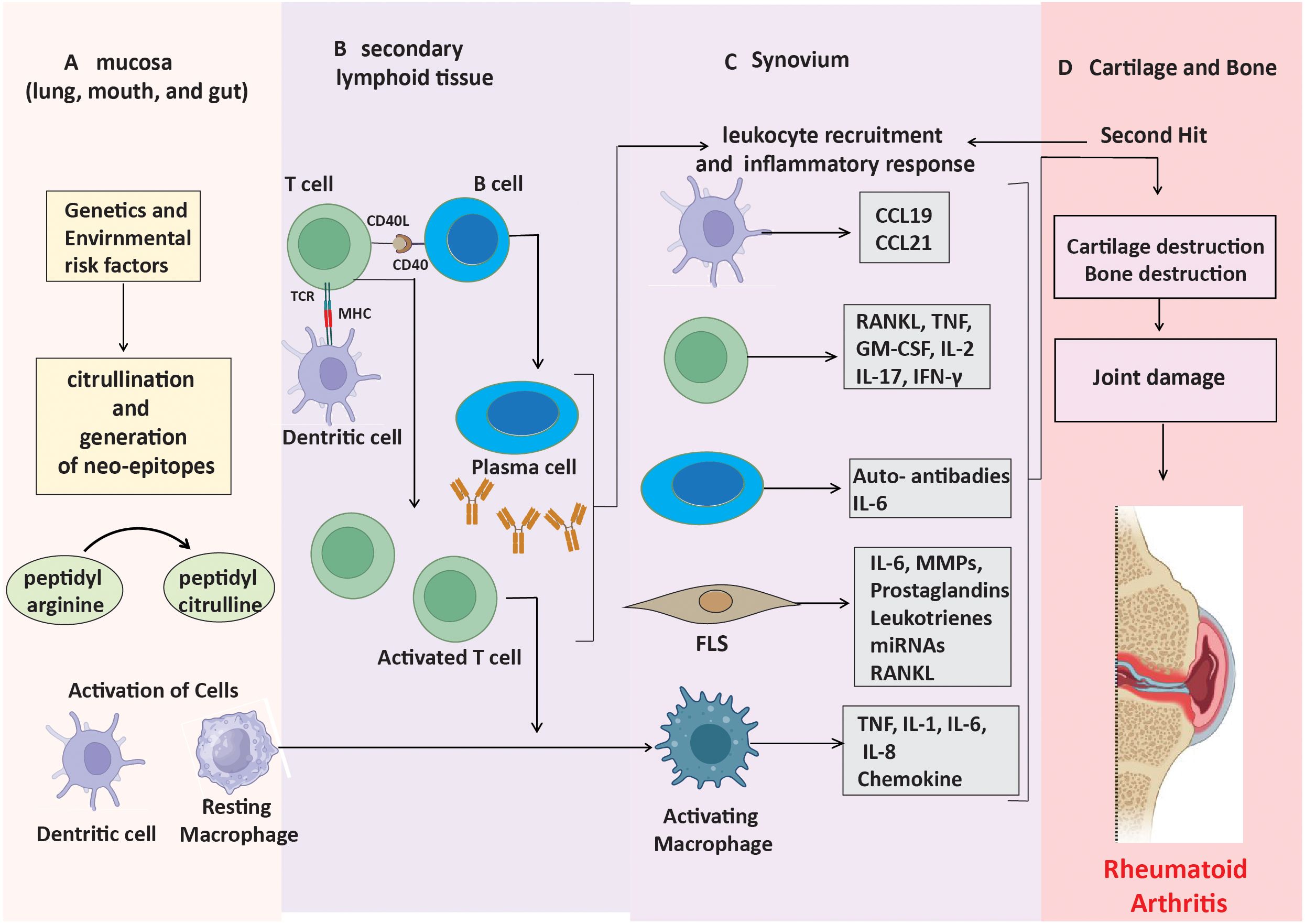
Figure 1. Mechanisms leading to ACPA-positive RA progression. (A) Neo-epitopes form in mucosa through post-translational modifications. (B) APCs present these peptides, triggering autoantibody production. (C) Stromal cells, APCs, and macrophages produce inflammatory factors, driving synovial inflammation. (D) Cytokines and immune responses contribute to cartilage and bone destruction.
In the early stages of ACPA-positive rheumatoid arthritis, a lot of CD4+ T cells and macrophages enter the synovium (23). This causes the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6. This leads to the activation of synovial fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) and an increased production of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), which decompose the extracellular matrix (Figure 1C) (24). The paracrine and autocrine functions of cytokines, along with ongoing adaptive immune responses, contribute to disease progression by promoting FLS to adopt an invasive phenotype, which facilitates cartilage degradation and bone erosion (Figure 1D). These altered FLS can also move between joints, sustaining inflammation in several joint regions (25).
Even though ACPA-negative rheumatoid arthritis is similar to other types in terms of joint involvement and inflammation, it has its own immune system and molecular features. In contrast to ACPA-positive RA, ACPA-negative RA does not depend on citrullination or the existence of anti-citrullinated antibodies for its pathogenesis. The pathogenesis is instead governed by stromal cells, particularly fibroblast-like synoviocytes, which are crucial in mediating inflammation and advancing disease progression. In healthy synovial tissue, FLS play a crucial role in sustaining the synovial lining and synthesizing proteins essential for joint lubrication (26). On the other hand, in RA, they transform into aggressive pathogenic cells. They learn to express Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and work as antigen-presenting cells (APCs) (27, 28). These stromal cells express antigens via histocompatibility complex (MHC) II receptors and release cytokines and chemokines. Thus, these stromal cells are part of the innate immune system (29). In ACPA-negative RA, cytokines activate endothelial cells, resulting in the recruitment of more immune cells, including Th17 cells and macrophages, into the synovial compartment, thereby intensifying the inflammatory response. Furthermore, infiltrating cells, including fibroblasts, macrophages, T cells, B cells, and plasma cells, stimulated by blood-activated fibroblasts and macrophages, contribute to the pathophysiology of ACPA-negative rheumatoid arthritis (30). These cells create a proinflammatory milieu within the synovium, wherein stromal cells, especially FLS, are crucial in maintaining inflammation and facilitating disease advancement. Activated cells release proinflammatory cytokines, including IL-1, IL-6, IL-17, TNF-α, and MMPs, resulting in the eventual degradation of cartilage and bone (31, 32). Furthermore, activated B cells, with the aid of antigen-presenting cells and Th cells, ultimately undergo differentiation into plasma cells for the purpose of synthesizing and producing diverse immunoglobulins. There is evidence that the release of Th1 cytokines in RA leads to more Th17 cells entering the synovial tissues and the production of IL-17 (33, 34).
As the disease progresses, activated fibroblast-like synoviocytes form direct interactions with dendritic cells, macrophages, and pre-osteoclasts. RANK-RANKL signaling facilitates interactions that enhance osteoclast development and bone resorption, leading to bone erosion in regions where the synovium, bone, and cartilage converge (35). Furthermore, innate immune cells play a significant role in ACPA-negative rheumatoid arthritis, since stromal cells and macrophages collaborate to promote osteoclast development via the RANKL/RANK pathway (36). This connection facilitates bone erosion at the junction of the synovium and periosteal membrane, leading to joint destruction that differs from the antibody-mediated mechanisms observed in ACPA-positive rheumatoid arthritis (37). Cytokine and chemokine signaling pathways are essential for sustaining the inflammatory milieu in the synovium. Depending on the cytokine environment, activated T cells divide into different subsets, such as Th1, Th17, and regulatory T cells (Treg) (38). The immune cells, in conjunction with FLS, perpetuate chronic synovial inflammation and exacerbate the damaging characteristics of ACPA-negative RA (Figure 2).
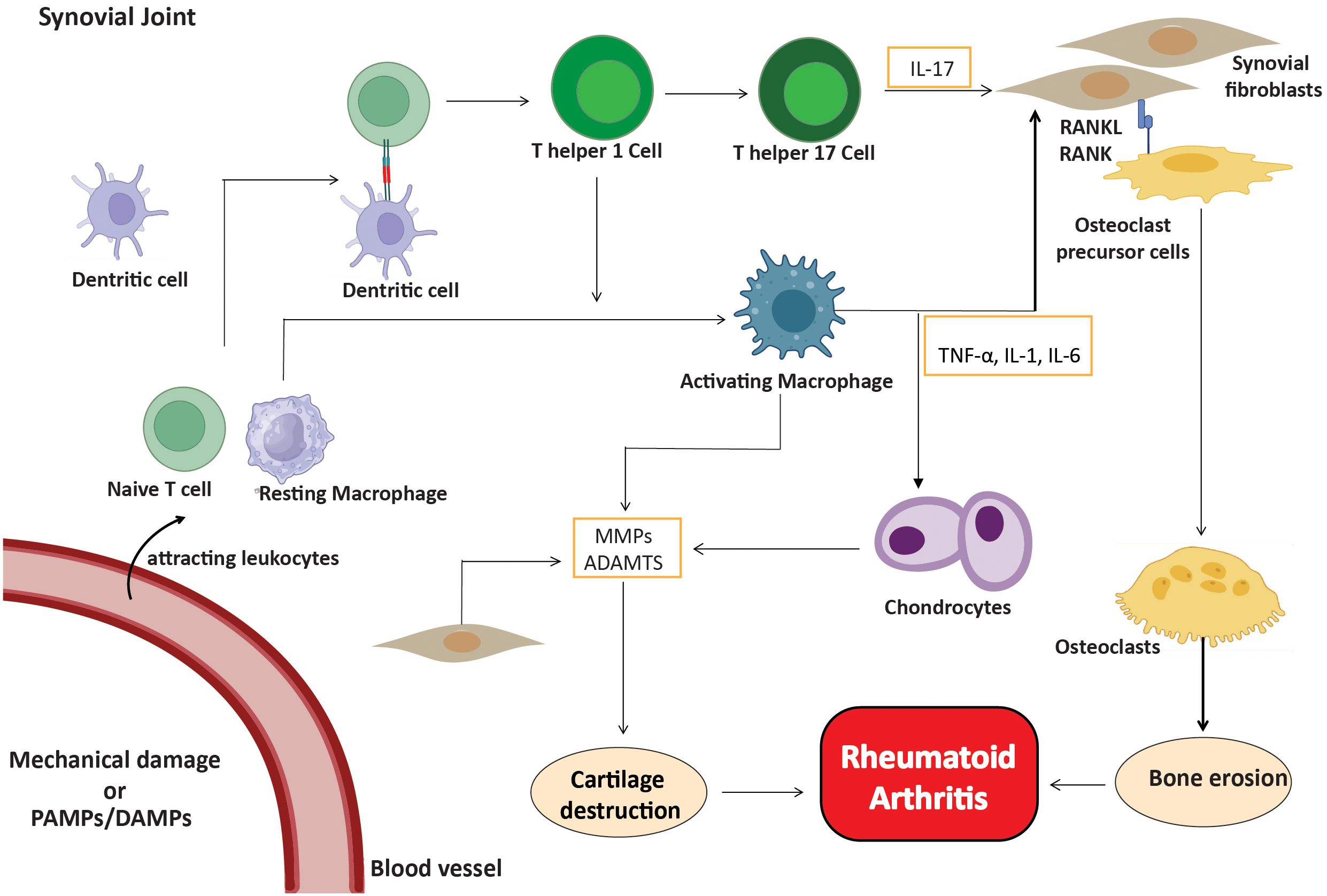
Figure 2. Inflammatory cells in ACPA-negative RA. Fibroblasts, macrophages, T cells, B cells, and plasma cells create a proinflammatory environment, with FLS being crucial. Activated cells release cytokines (IL-1, IL-6, IL-17, TNF-α) and MMPs, leading to cartilage and bone degradation.
An overview of NF-κB signaling pathway in RA
Researchers have linked NF-κB to the development of numerous inflammatory disorders, including RA (39, 40). Two distinct pathways can trigger this mechanism: the classical or canonical pathway and the alternative or non-canonical pathway (41). NF-κB subunits first bind to p100 or p105 precursors in the noncanonical pathway. The process then converts these precursors into p50 and p52 subunits, respectively (42). The C-terminal regions of these precursors contain IB-like domains, which impede nuclear localization until they undergo cleavage. The IKK complex activates NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK), regulating its processing (43). The NF-κB pathway is stimulated in a different way by signals from TNFR superfamily members like BAFFR, CD40, and lymphotoxin receptors (44, 45). There is a key regulatory mechanism that frees NF-κB dimers from IκB. It is made up of IKKα, IKKβ, and the scaffold protein IKKγ/Nemo (46, 47). Subsequently, the liberated IκB molecules undergo degradation by proteasomes (48). The NF-κB dimers move into the nucleus and attach to κB sites on certain genes (43). This alters the expression of those genes and initiates the transcription of genes implicated in immune and inflammatory responses (Figure 3A) (48).
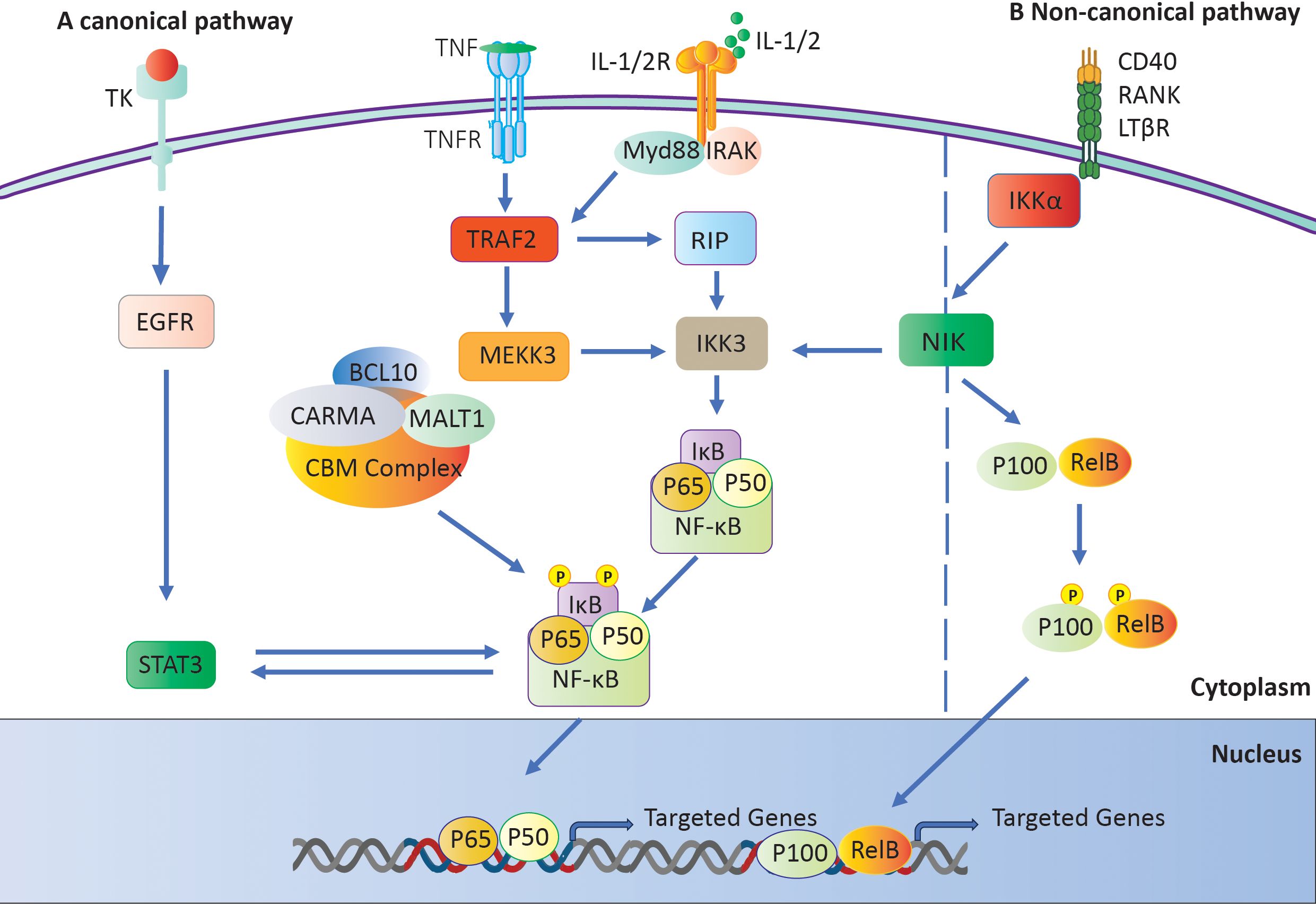
Figure 3. The NF-κB signaling pathway. (A) The IKK complex activates the canonical pathway by phosphorylating and degrading IκB, which results in the activation of NF-κB. (B) Activation of a Not canonical Pathway: The NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK) initiates the activation of IKKα, which in turn generates and transports p52 and phosphorylates p100.
The noncanonical pathway primarily involves the IκB family members p100 and p105. When receptors like CD40 and lymphotoxin receptor (LTR) are activated, NIK phosphorylates p100 (49). This causes p100 to go through ubiquitination, which creates p52. Once paired, p52 and RelB move to the nucleus, attaching to B sites to control the expression of genes they are interested in (Figure 3B) (50).
NF-κB initiates the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1, TNF-α, and IL-6, in monocytes and macrophages (51). Cytokines have the ability to stimulate NF-κB in both the innate immune system and fibroblast cells. This activation leads to the production of additional cytokines and chemokines, which in turn promote inflammation (51). These compounds then attract other inflammatory cells, contributing to inflammation’s propagation. In RA, the two different canonical and noncanonical NF-κB pathways promote the conversion of monocytes and macrophages into osteoclasts, resulting in bone resorption and inflammatory bone loss (52). NF-κB indirectly enhances Th17 cell formation by inducing IL-1, IL-6, and IL-23 secretion in cells involved in innate immunity. It directly regulates Th17 lineage transcription factor activity in T cells (53, 54). NF-κB activation that isn’t working right also makes it easier for B cells to attack the body’s own tissues and for antibodies to be made that attack the body itself. Both of these things play a part in the development of RA (55, 56). Studies show that people with RA who have high levels of a B-cell activating factor from the TNF family have abnormal, noncanonical NF-κB activation (43, 45, 57, 58). Therefore, NF-κB has an important function in the development of rheumatoid arthritis by influencing multiple cell types (57).
Non-coding RNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: modulating NF-κB signaling
The expression patterns of ncRNAs vary greatly between immune-mediated diseases and across different cell types and organs. Furthermore, specific ncRNAs frequently exhibit abnormal regulation in various inflammatory and autoimmune disorders (59). Research has consistently shown that certain types of non-coding RNAs, like miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs, are dysregulated in people with RA (60–62). Additionally, a growing body of evidence has revealed a unique profile of non-coding RNAs that exhibit differential expression in RA, underscoring their potential as dependable biomarkers for diagnosis and therapeutic approaches (59). However, we still don’t fully understand the precise roles and molecular mechanisms of these ncRNAs in the development of RA.
In this summary, we focus on the roles of ncRNAs in RA, with a particular emphasis on miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs, as documented in the available research. It is very important to understand how these dysregulated ncRNAs affect inflammation and autoimmunity in order to figure out how RA starts. It is crucial to discover the specific genes that are affected by these abnormally produced non-coding RNAs in RA in order to develop reliable indicators and efficient therapies.
MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: influencing the NF-κB pathway
MicroRNAs are short RNA molecules, usually 18 to 25 nucleotides long, that regulate gene expression after transcription. miRNAs either accelerate the breakdown of mRNA or inhibit its translation into proteins to achieve this regulation (63). Multiple studies have emphasized the crucial significance of miRNAs in several autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and Sjögren’s syndrome. Nevertheless, the levels of expression and function of miRNAs may vary among distinct disorders (63, 64). miRNAs have a crucial role in a wide range of important biological functions and disease processes. These include controlling the cell cycle, sustaining stem cell populations, facilitating organ development, stimulating angiogenesis, and impacting carcinogenesis (65).
Dysregulation of inflammatory pathways is a key driver of RA, which is defined by chronic inflammation and joint deterioration. In particular, NF-κB signaling stimulation is a key mechanism by which many miRNAs promote these inflammatory processes (promoting inflammation) (Table 1) (66). MiR-203 significantly enhances synovial inflammation by boosting the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and MMP-1 (67). miR-128-3p enhances NF-κB signaling, which in turn causes heightened inflammatory responses, by downregulating TNFAIP3, a crucial inhibitor of NF-κB (68). Likewise, miR-19b amplifies inflammation in the synovium by increasing NF-κB activity through blocking its negative regulators (69). miR-221-3p increases the production of IL-6 and IL-8 by telling macrophages to change into the pro-inflammatory M1 type (70). In addition, miR-138 enhances the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines via stimulating NF-κB (71). Importantly, miR-16 plays a role in promoting methotrexate resistance in RA by enhancing cell survival and reducing apoptosis, leading to decreased drug sensitivity. This miRNA contributes to the persistence of inflammation and limits the effectiveness of methotrexate, thus promoting disease progression in RA (72). Research indicates that mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can mitigate rheumatoid arthritis by lowering miR-548e levels and suppressing IκB translation, which in turn diminishes NF-κB signaling activity and alleviates inflammation (73).
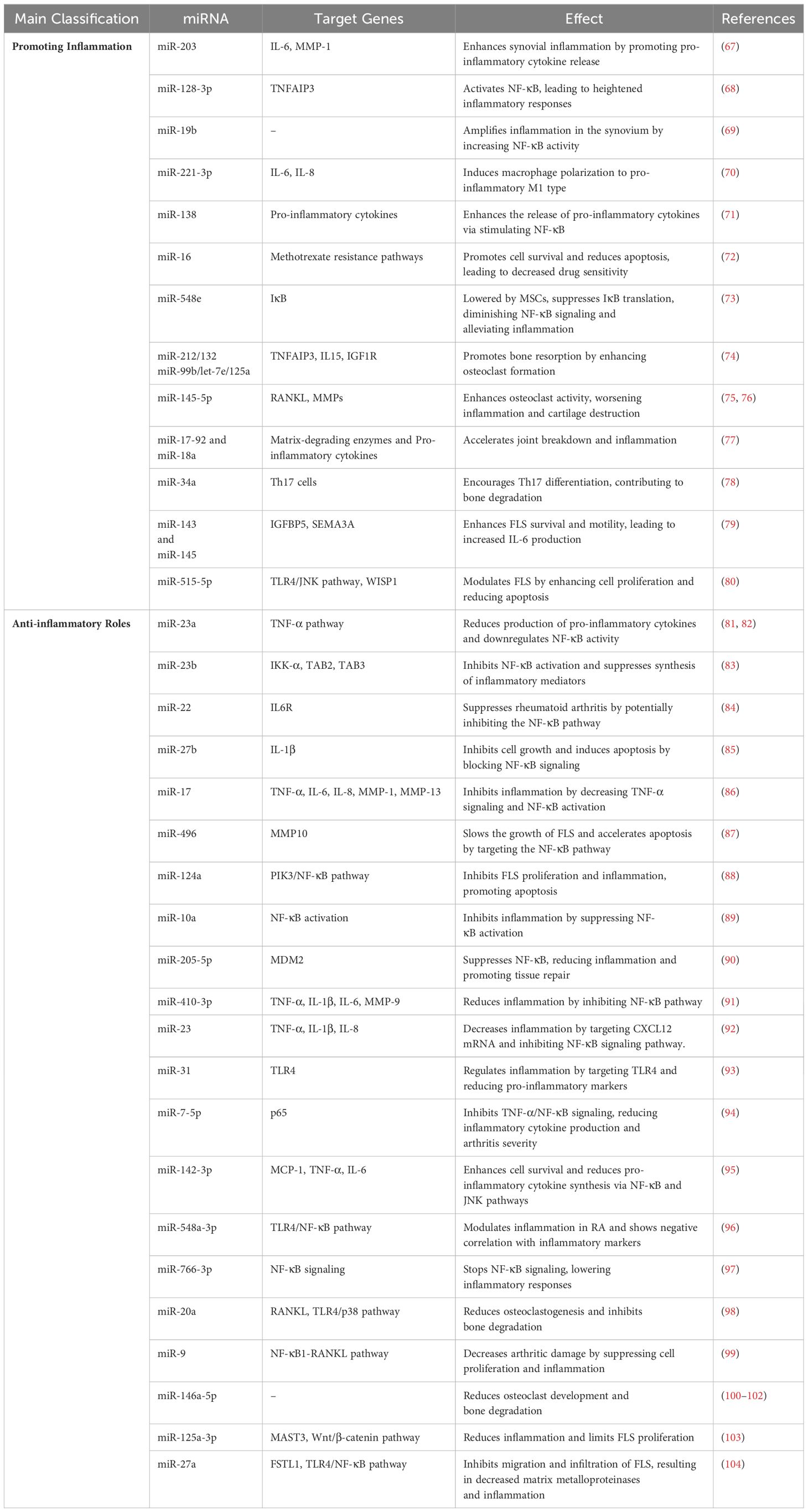
Table 1. MicroRNAs implicated in the pathogenesis of RA and their association with the NF-κB signaling pathway.
In RA, osteoclastogenesis is a crucial mechanism facilitating bone resorption and joint deterioration. Multiple miRNAs facilitate this process by enhancing the formation and function of osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone resorption. These miRNAs frequently function by activating inflammatory pathways such as NF-κB or by enhancing the production of molecules that facilitate bone disintegration.
The microRNAs miR-212/132 and miR-99b/let-7e/125a promote bone resorption by increasing osteoclast development and targeting important regulators such as TNFAIP3, IL15, and IGF1R, which are crucial for regulating inflammation and metabolism in bones (74). This is analogous to the function of miR-145-5p, which enhances osteoclast activity and bone degradation. miR-145-5p increases RANKL and MMP levels through NF-κB activation. Its upregulation worsens inflammation and cartilage destruction, making it a potential target for RA treatment (75, 76). By raising the levels of matrix-degrading enzymes and pro-inflammatory cytokines, the miR-17-92 cluster, and miR-18a in particular, makes joints break down faster and cause more inflammation (77). Moreover, miR-34a encourages Th17 cell differentiation, which indirectly causes bone degradation and osteoclast development (78).
In addition, elevated inflammation in RA results in hyperactivation of FLS, which are the main contributors to synovial inflammation and joint deterioration. These cells undergo excessive proliferation due to persistent inflammation, leading to synovial hyperplasia and joint deterioration.
Numerous miRNAs modulate the proliferation, survival, and apoptosis of FLS, thereby affecting the degree of inflammation. Key microRNAs such as miR-143 and miR-145 are upregulated in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes, targeting IGFBP5 and SEMA3A, resulting in elevated IL-6 production, NF-κB activation, and improved fibroblast-like synoviocyte survival and motility (79). miR-515-5p modulates fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis by enhancing cell proliferation and diminishing apoptosis via the TLR4/JNK pathway and the WISP1 gene. The inhibition of miR-515-5p mitigates these effects, indicating its involvement in regulating inflammation and fibroblast-like synoviocyte activity in rheumatoid arthritis (80).
While certain microRNAs have negative impacts on RA, others act as protective agents by lowering cytokine production and downregulating inflammatory pathways, especially NF-κB (anti-inflammatory roles) (Table 1). MiR-23a exhibits anti-inflammatory properties in RA by inhibiting TNF-α signaling and reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6 and IL-8. By targeting the NF-κB pathway (81, 82). Similarly, miR-23b inhibits NF-κB activation and suppresses the synthesis of inflammatory mediators via inhibiting IKK-α, TAB2, and TAB3 (83). Moreover, miR-22 suppresses rheumatoid arthritis by targeting IL6R and potentially inhibiting the NF-κB pathway (84). Furthermore, overexpression of miR-27b stopped cells from growing, sped up cell death, and blocked the NF-κB signaling pathway by focusing on IL-1β (85).
In addition, miR-17 stops inflammation by decreasing TNF-α signaling. This lowers the activation of NF-κB, STAT3, and c-Jun, which in turn lowers the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-6, IL-8, MMP-1, and MMP-13 (86). Importantly, miR-496 slowed the growth of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes and sped up apoptosis by targeting MMP10 and changing the NF-κB pathway (87). MiR-124a inhibits FLS proliferation and inflammation in RA by targeting the PIK3/NF-κB pathway, reducing cytokine levels, and promoting FLS apoptosis, making it a potential therapeutic target (88). Similarly, miR-10a regulates inflammation by inhibiting NF-κB activation; its suppression leads to increased FLS proliferation and cytokine production, suggesting its role as a target for RA management (89).
Exosome-delivered miR-205-5p targets MDM2 and suppresses NF-κB, which in turn reduces inflammation in the joints and promotes tissue repair (90). Likewise, miR-410-3p reduces inflammation in RA by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway, leading to decreased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and MMP-9 (91). Overexpression of miR-23 also decreased inflammation by lowering levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-8. This was done by targeting CXCL12 mRNA and stopping the NF-κB signaling pathway (92). Interestingly, miR-31 regulates inflammation in RA by targeting TLR4 and reducing pro-inflammatory markers like TNF-α and IL-1, while promoting apoptosis in synovial cells, positioning it as a potential therapeutic target for RA (93). Moreover, miR-7-5p inhibits the TNF-α/NF-κB signaling pathway by binding to the 3’-UTR of p65, resulting in diminished production of inflammatory cytokines and alleviating arthritis severity (94).
miR-142-3p enhances cell survival and diminishes the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines (MCP-1, TNF-α, IL-6) via the NF-κB and JNK pathways. Inhibition of miR-142-3p negates these protective effects (95). In addition, miR-548a-3p is markedly downregulated in rheumatoid arthritis patients and modulates inflammation through the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway (96). It exhibits a negative correlation with inflammation markers (CRP, RF, ESR) and contributes to the attenuation of cellular activity and immunological responses. miR-766-3p stops NF-κB signaling, which lowers inflammatory responses in RA (97).
Specific miRNAs reduce inflammation and bone degradation associated with RA by blocking critical inflammatory pathways, therefore safeguarding joint tissues and averting bone loss. These miRNAs function by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis, diminishing the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and facilitating the resolution of inflammation. miR-20a reduces osteoclastogenesis and inhibits bone degradation by modulating RANKL via the TLR4/p38 signaling pathway. The injection of agomiR-20a suppresses osteoclast growth and bone erosion, underscoring its potential as a therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis to avert bone loss (98). Lee et al. discovered that miR-9 decreases arthritic damage by suppressing the NF-κB1-RANKL pathway, hence decreasing cell proliferation and inflammation (99). Bogunia-Kubik et al. found that the NFkB1 ins/ins genotype is linked to a lower response to TNF-α inhibitor therapy in people with rheumatoid arthritis, as shown by lower levels of miR-146a-5p before treatment. Following therapy, the protective rs2910164-C allele was correlated with elevated miR-146a-5p levels. Furthermore, miR-146a administration to Ly6Chigh monocytes reduced osteoclast development and bone degradation, indicating its potential as a therapeutic target in arthritis (100–102).
Certain microRNAs in RA are essential for modulating inflammation and proliferation of fibroblast-like synovial cells, which are significant contributors to joint destruction in RA. miR-125a-3p reduces inflammation and restricts the proliferation of fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting MAST3 and regulating the Wnt/β-catenin and NF-κB signaling pathways (103). miR-27a, which is downregulated in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis, inhibits the migration and infiltration of FLS via targeting follistatin-like protein 1 (FSTL1). This action results in diminished amounts of matrix metalloproteinases and Rho family proteins, while also inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB pathway (104).
Long non-coding RNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: key players in NF-κB signaling
LncRNAs are a recently discovered group of non-coding RNAs that are widely expressed in different human organs and typically consist of more than 200 nucleotides (105). LncRNAs can be categorized into five distinct categories according to their structure and function: sense, antisense, bidirectional, intronic, and intergenic (106). Within the field of oncology, specific lncRNAs exhibit oncogenic characteristics, while others impede the growth and advancement of tumors. These lncRNAs display varied expression patterns and exert distinct biological effects within tumor cells (107). Recent studies have shown that different lncRNAs are expressed at different levels in immune cells in diverse autoimmune illnesses, such as rheumatoid arthritis (63, 108, 109). These results show that distinct lncRNA expression profiles, which may also manifest uniquely in different cells and tissues, distinguish various autoimmune diseases.
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of RA patients upregulated the long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) HIX003209, which was associated with TLR2 and TLR4. HIX003209 promotes inflammation by sponging miR-6089, thus enhancing TLR4/NF-κB signaling in macrophages. This lncRNA increased macrophage proliferation and activation, contributing to RA pathogenesis. Therefore, targeting lncRNA HIX003209 could be a potential therapeutic strategy for reducing inflammation in RA (110). Furthermore, RA patients significantly increased LINC00305 expression, which correlates with disease activity markers such as DAS28, C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, rheumatoid factor, and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody. The rs2850711 polymorphism in LINC00305 was associated with higher RA susceptibility, especially in individuals with AT and TT genotypes. High levels of LINC00305, NF-κB, and MMP-3 were found in these genotypes. This suggested that LINC00305 and its genetic variant played important roles in diagnosing RA, managing it, and making it worse (111).
Yang et al. discovered that the long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) H19 makes the inflammatory damage caused by TNF-α worse in MH7A cells, which are used to study RA. The levels of H19 went up because of TNF-α. This made TAK1 phosphorylated, which turned on the NF-κB and JNK/p38 MAPK pathways. Silencing H19 reduced inflammatory cytokines (IL-8, IL-1β, and IL-6), while H19 overexpression reversed this effect, indicating that H19 enhances inflammation through the TAK1 pathway in RA (112). Moreover, overexpression of LINC01197 in a mouse RA model reduced disease severity, inhibited fibroblast-like synoviocyte (RA-FLS) proliferation and inflammation, and promoted apoptosis. By sponging miR-150, LINC01197 functioned by increasing THBS2 expression and inactivating the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway, thereby reducing inflammation and suggesting LINC01197 as a potential therapeutic target for RA (113). Overexpressing OIP5-AS1 also decreased the severity of RA symptoms and levels of inflammatory factors (IL-1β, IL-10, IL-6, and TNF-α) in a rat model. OIP5-AS1 connects to miR-448 and raises the expression of paraoxonase 1 (PON1). This stops the growth and inflammation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes (RA-FLS). Activation of TLR3 promoted RA progression, while OIP5-AS1 inactivated the TLR3-NF-κB signaling pathway. Therefore, OIP5-AS1 mitigates RA progression through the miR-448-PON1 axis and the TLR3-NF-κB pathway, offering potential for molecularly based RA treatments (114).
Tang et al. found that RA-affected synovial tissues increase the expression of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) PVT1, while miR-145-5p expression decreases. PVT1 interacts with miR-145-5p and exerts a negative regulatory effect. More PVT1 and less miR-145-5p were found in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA-FLSs) when TNF-α was present. It was possible to silence PVT1 by targeting the NF-κB pathway through miR-145-5p. This decreased TNF-α-induced cell proliferation, increased apoptosis, and decreased the production of inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β and IL-6). These findings indicate that PVT1 has a significant impact on rheumatoid arthritis by regulating cell growth and inflammation via miR-145-5p (115).
Furthermore, the delivery of LncRNA-GAS5 siRNA caused a decrease in joint swelling and a reduction in the quantity of arthritis-related biochemicals, oxidative stress markers, and cytokines in the serum of RA patients. Some other things that were lowered were miR-103, MMP-13, Akt, NF-κB, FGF21, PI3K, and p38 in cartilage. Histopathological analysis showed that LncRNA-GAS5 siRNA ameliorated cartilage pathological changes, suggesting that it prevents cartilage destruction through decreasing miR-103 expression and associated inflammatory pathways (116).
Xiao et al. investigated the function of NEAT1 in RA and discovered its upregulation in RA-FLSs. NEAT1 promotes RA-FLS proliferation and inflammatory cytokine production, while inhibiting apoptosis through miR-204-5p targeting by the NF-κB pathway. Silencing NEAT1 reduced cellular proliferation and inflammation while increasing apoptosis in TNF-α-treated RA-FLSs. These findings suggest that NEAT1 could be a possible therapeutic target for RA by modulating miR-204-5p and the NF-κB pathway (117).
In a different study, it was shown that the exosomal lncRNAHAND2-AS1 stops the activation of RA-FLS. By blocking miR-143-3p and raising TNFAIP3 expression, HAND2-AS1 lowers RA-FLS growth, migration, and inflammation and speeds up cell death through the NF-κB pathway. This suggests that MSC-derived exosomal HAND2-AS1 could be a potential therapeutic approach for RA (118). Furthermore, linc00152 was upregulated in RA-FLS and stimulated by TNF-α/IL-1β through the NF-κB pathway. Linc00152 caused inflammation by blocking miR-103a, which increased TAK1 expression and turned on the NF-κB pathway that is controlled by TAK1. Additionally, NF-κB enhanced linc00152 expression via the transcription factor YY1. This linc00152/NF-κB feedback loop exacerbated RA-FLS inflammation, suggesting that linc00152 could be a potential diagnostic and therapeutic target for RA (119).
Liu et al. investigated the role of lncRNA XIST in RA and found it to be significantly upregulated in RA synovial tissues and cells. By sponging miR-126-3p, XIST promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in RA-FLS. Lowering XIST levels raised miR-126-3p levels, which blocked the NF-κB pathway by lowering p-p65 and p-IκBα expression. This caused RA-FLS cells to multiply less and die more. This study suggests that targeting the XIST/miR-126-3p/NF-κB axis could be a potential therapeutic approach for RA (120).
Another study showed that linc00324 increased the number of CD4+ T cells and the release of MIP-1α by turning on the NF-κB pathway. This was achieved by targeting and sponging miR-10a-5p, which normally inhibits CD4+ T cell proliferation and NF-κB activation. It’s possible that linc00324 makes RA inflammation worse through the miR-10a-5p/NF-κB axis because overexpressing miR-10a-5p reversed its pro-inflammatory effects. This identified LINC00324 as a potential therapeutic target for RA (121). However, RA-FLSs and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from RA patients downregulate the lncRNA MAPKAPK5-AS1 (MK5-AS1). By connecting to miR-146a-3p and controlling SIRT1 expression, MK5-AS1 overexpression in RA-FLSs reduced inflammation and boosted apoptosis. This was done by affecting the NF-κB pathway. These effects were reversed by SIRT1 knockdown or miR-146a-3p overexpression. The study also revealed that WTAP downregulation promoted MK5-AS1 RNA stability. This research suggests that MK5-AS1, via the miR-146a-3p/SIRT1/NF-κB axis, could be a potential therapeutic target for RA (122).
Sun et al. discovered that the long non-coding RNA AL928768.3 encourages the growth, invasion, and inflammation of RA-FLS and stops cell death by turning on the LTB-mediated NF-κB pathway. Overexpression of AL928768.3 increased IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and LTB levels, as well as NF-κB signaling proteins, while knockdown had the opposite effect, which could be reversed by LTB overexpression. This highlights AL928768.3 as a potential therapeutic target for RA (Table 2) (123).
Circular RNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: controlling NF-κB signaling
The unique covalently closed loop structure of circRNA makes it stand out from other non-coding RNAs. It doesn’t have any 5′ end caps or 3′ polyadenylate tails (124). Circular RNA molecules often possess a circular structure, which provides them with stability and often results in a half-time of more than 48 hours (125). CircRNAs are categorized into three primary types: exonic circRNAs (ecircRNAs), circular intronic RNAs (ciRNAs), and exon-intron circRNAs (EIciRNAs) (126). Their synthesis in cells usually occurs due to exon skipping and subsequent circularization, which can be assisted by intron pairing or the activity of RNA-binding proteins (126). C CircRNAs have been detected not just in mammals but also in fungi, plants, and protists. These molecules are predominantly expressed in a tissue-specific way and can be identified in peripheral blood, exosomes, and different organs (Figure 4) (127, 128).
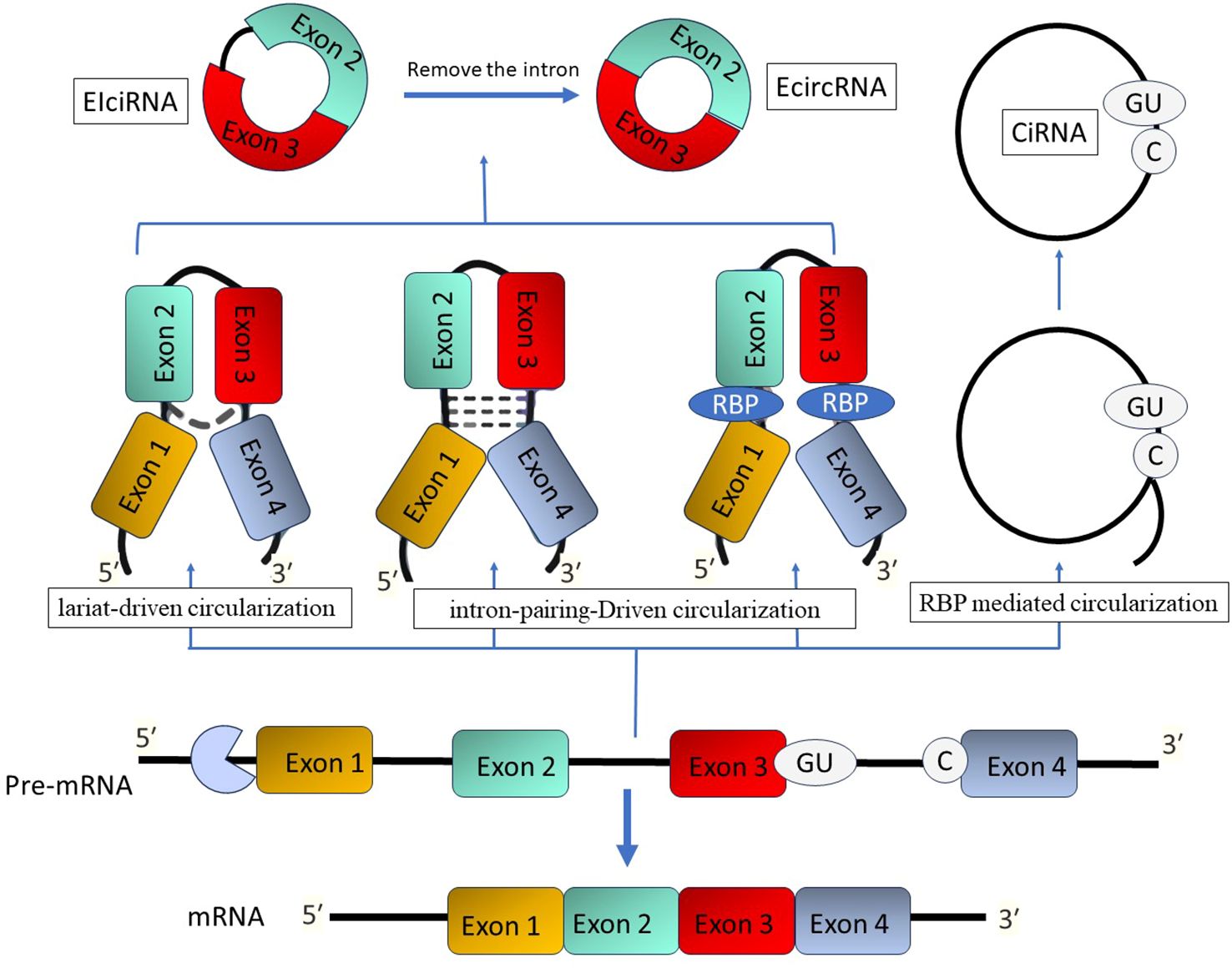
Figure 4. The process of circular RNA formation. There are three methods that give rise to circular RNAs: lariat-driven, intron-pairing-driven, and RBP-mediated circularization. Endogenous inverted repeat-derived circular RNAs (EIciRNAs) are composed of conserved exons and introns. Splicing generates circular intronic RNAs (ciRNAs) that possess a 7-nucleotide GU-rich region adjacent to the 5′ splice site and an 11-nucleotide C-rich motif at the branch point.
CircRNAs have the ability to behave as miRNA decoys, sequestering miRNAs and inhibiting their interaction with their endogenous mRNA targets, similar to lncRNAs (129). The interaction mainly takes place in the cytoplasm, where ecircRNAs might have important functions in several pathological and physiological processes through the competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) mechanism (130). In contrast, ciRNAs and EIciRNAs primarily influence gene expression within the nucleus. CircRNAs have a role in regulating the expression of target messenger RNAs (mRNAs) by absorbing miRNAs. This contact, known as ceRNA interaction, has an impact on several processes such as autoimmune and inflammation (126, 129). Nevertheless, the intricate mechanisms underlying the ceRNA actions of circRNA in RA have not been well investigated.
Circular RNAs play a role in the control of several immune-related illnesses by acting as miRNA sponges or reservoirs (126). Studies have emphasized the substantial impact of circRNAs in a wide range of diseases, such as cancer, disorders of the nervous system, and cardiovascular diseases (131, 132). Their crucial role in antiviral immunity has been firmly established, offering possible therapeutic possibilities by focusing on circRNAs for immunologic treatments (133, 134).
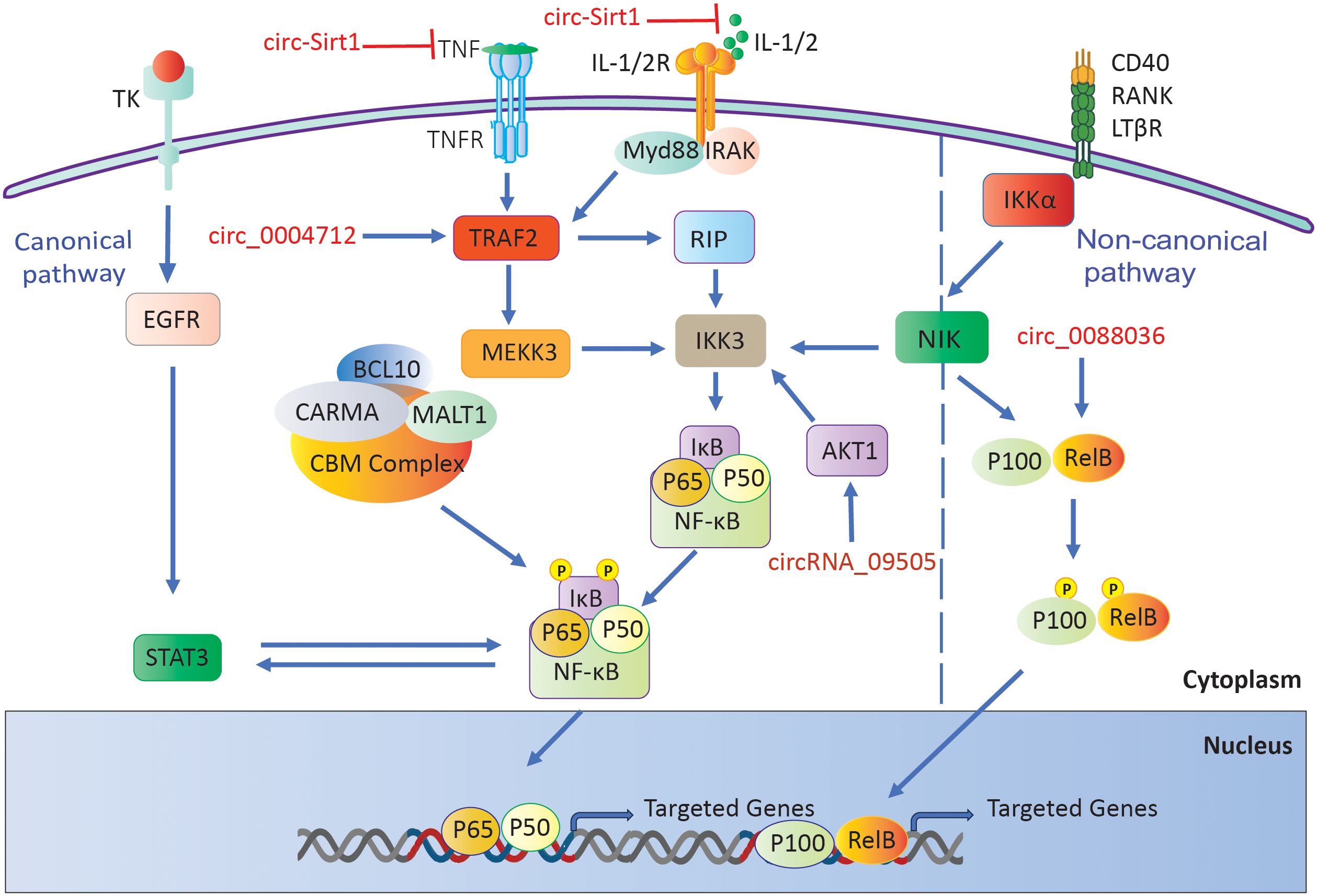
Yang et al. discovered a notable increase in the expression of circRNA_09505 in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of individuals with RA. This circular RNA enhances macrophage growth and secretion of cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-12) by acting as a miR-6089 inhibitor, resulting in the stimulation of the AKT1/NF-κB signaling pathway. In mice with collagen-induced arthritis (CIA), CircRNA_09505 knockdown reduced arthritic symptoms and inflammation, indicating its contribution to the worsening of rheumatoid arthritis (135).
Furthermore, overexpressing circ-Sirt1 inhibited proliferation and induced apoptosis in RA-FLS. This circRNA lowered the amounts of inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α) and matrix metalloproteinases (MMP1 and 3) while raising the levels of Sirt1 and Nrf2. This decreased oxidative stress and inflammation. The protective effects were mediated through miR-132, which enhanced the Sirt1 pathway, highlighting Circ-Sirt1’s potential therapeutic role in RA (136).
Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that circ_0088036 is elevated in both the sera and RA-FLS cells of individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. This upregulation of circ_0088036 contributes to the stimulation of cell proliferation, advancement of the cell cycle, and activation of inflammatory responses by acting as a sponge for miR-1263. This interaction resulted in the overexpression of REL, a constituent of the NF-κB pathway, hence augmenting NF-κB signaling. The specific suppression of circ_0088036 hindered the growth of RA-FLS cells and triggered programmed cell death, indicating its involvement in the development of rheumatoid arthritis through the miR-1263/REL/NF-κB pathway (137).
A separate investigation revealed that circ_0004712 exhibited increased expression in both RA synovial tissues and RA-FLS. Researchers found that the upregulation of circ_0004712 stimulates cell proliferation, migration, and inflammation while simultaneously suppressing apoptosis. This circular RNA acts as a sponge for miR-633, resulting in an increase in TRAF6 expression, which in turn activates the NF-κB signaling pathway. Knocking down circ_0004712 led to a decrease in aggressive behaviors in RA-FLS, suggesting its involvement in RA progression through the miR-633/TRAF6/NF-κB pathway (Figure 5) (138).
NcRNA-based therapies for RA: new biomarkers and treatment approaches
In recent years, there has been a significant rise in the investigation of the potential of ncRNAs as biomarkers in RA (139). Nevertheless, the development of ncRNA-based therapeutics for RA is still in the beginning stages. miRNA-based therapies, which include antagonists that lower miRNA expression, promote RA, and mimics that restore the activity of miRNAs that suppress RA, are some of the most promising approaches (140). For instance, studies have shown that methotrexate increases the levels of miR-877-3p, leading to a decrease in GM-CSF and CCL3, thereby restricting the growth and migration of synoviocytes (141). Similarly, Resolvin D1 raises CTGF by increasing miR-146a-5p‐85, and berberine, a chemical found in plants, stops FLS growth and bone loss by targeting Wnt/β-catenin and RANKL-mediated pathways (142).
Another strategy is to modify miRNAs’ upstream regulators in the ceRNA network. In this complex structure, circRNAs and lncRNAs function as molecular sponges. By manipulating these substrates, it is possible to alter the activity of miRNAs and the results of RA (140). As an example, astragaloside lowers the lncRNA LOC100912373, which then activates miR-17-5p’s blocking of PDK1 and limits the growth of FLS (143). Paeoniflorin regulates the circ-FAM120A/miR-671-5p axis, inhibiting inflammation, cell cycle progression, and synoviocyte proliferation (144).
The ceRNA network is also a mechanism through which certain miRNA antagonists’ function. As an example, the triptolide-controlled hsa-circ-0003353/miR-31-5p/CDK1 axis and tocilizumab’s impact on lncRNA MIR31HG/miR-214/PTEN/AKT improve miRNA sponges, which leads to less inflammation, cell cycle arrest, and cellular proliferation (145, 146). Recognized mechanisms enhance the respective miRNA sponges and alleviate the suppression of miRNAs on their target genes. This leads to diminished cell cycle arrest, cellular proliferation, and reduced production of inflammatory mediators.
Furthermore, using plant-derived miRNAs as dietary interventions is a promising approach to RA therapy (147). Despite the potential for safety and convenience, this method faces obstacles in terms of the optimal plant miRNA types, their stability in the body, and the interval of treatment (147).
Advances in miRNA delivery through tissue engineering technologies have made new therapeutic options possible. Exosomes are particularly promising due to their biocompatibility and targeted delivery capabilities, while synthetic nanoparticles and cationic liposomes are extensively utilized to improve miRNA uptake and stability (148). Exosomes encapsulate miRNAs, protecting them from degradation in the extracellular environment. A thorough screening of plasma exosomes from RA patients discovered 14 dysregulated miRNAs. Among them, miR-204-5p was significantly downregulated and inversely linked with important clinical markers like ESR, RF, and CRP. FLS proliferation is inhibited by exosomes derived from T cells that contain miR-204-5p, suggesting a potential therapeutic function (148).
Exosomes derived from MSCs also exhibit substantial therapeutic potential. For example, bone marrow MSC exosomes (BM-MSC-EVs) containing miR-34a activate the p53 signaling pathway, thereby inducing apoptosis and suppressing FLS proliferation (149). In the same vein, BM-MSC-EVs deliver miR-223 to the NLRP3 inflammasome, thereby reducing inflammation. The therapeutic strategy is attractive due to the reduced risk of rejection associated with the use of autologous MSC-derived exosomes (150).
Furthermore, miRNA profiling has the potential to revolutionize RA treatment through precision medicine, providing new opportunities for personalized therapies and enhanced patient outcomes. This is particularly true for drug validation and early diagnosis. Continued research into miRNA-based therapeutics will provide innovative, highly targeted treatment options in the future, revolutionizing RA management (151).
Understanding the hub’s function in normal regulation is just as important as identifying it to target critical pathways in the miRNA network for treatment. For instance, both miR-20a and miR-26b can target the NF-κB signaling pathway (152). Nevertheless, NF-κB also serves physiological purposes by facilitating the typical immune response (153). Normal immune response will be compromised if the inflammatory process and immune cells are completely inhibited. Consequently, it is imperative to resolve the critical issue of achieving equilibrium or shifting the balance in favor of RA treatment. Furthermore, studies have shown that the genes targeted by miR-223 have opposing effects on FLS cells. Some of its effects include reducing inflammation and inducing apoptosis in FLS cells by targeting NLRP3 (154), and increasing FLS proliferation and arthritis by targeting FOXO1 (155). It is possible that the non-standardization of research circumstances and baseline variables is responsible for these contradictory results. The miRNA panel may help shed light on the molecular processes of RA in different cell types and make RA diagnoses easier. Through the use of miRNAs in cancer to trigger cell death and prevent blood vessel formation, or FLS hyperplasia, it may also provide new information and ideas for future studies. As our comprehension of the subject expands, conducting a more thorough investigation of the miRNAs in RA patients may provide additional insights into diagnosis and treatment (140). Furthermore, miRNA profiling has the potential to transform RA treatment through precision medicine, thereby enabling the development of personalized therapies and improved patient outcomes. This is especially true in the context of drug validation and early diagnosis. In the future, innovative, highly targeted treatment options will be provided by ongoing research into miRNA-based therapeutics, which will revolutionize RA management (156).
Conclusions
Non-coding RNAs play a key role in controlling the NF-κB signaling pathway, and this study looked into how they affect the progression of rheumatoid arthritis. Non-coding RNAs, such as microRNAs, long non-coding RNAs, and circular RNAs, profoundly affect inflammatory and immunological responses essential for the therapy of RA. Our work has contributed to the comprehension of the functional dynamics of these ncRNAs, emphasizing their potential as biomarkers and therapeutic targets. NcRNAs’ complex control of the NF-κB pathway facilitates novel therapeutic techniques that may improve RA treatment’s precision and efficacy. The increasing interest in ncRNA-based therapies presents opportunities for novel treatment approaches. However, we must resolve obstacles related to efficient gene regulation and delivery to fully realize their therapeutic advantages.
Author contributions
ZR: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DS: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. NE: Data curation, Writing – original draft. MH: Validation, Writing – original draft. YM: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. FS: Project administration, Visualization, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Crowson CS, Rollefstad S, Ikdahl E, Kitas GD, Van Riel PL, Gabriel SE, et al. Impact of risk factors associated with cardiovascular outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann rheumatic Dis. (2018) 77:48–54. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211735
2. Safiri S, Kolahi AA, Hoy D, Smith E, Bettampadi D, Mansournia MA, et al. Global, regional and national burden of rheumatoid arthritis 1990–2017: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease study 2017. Ann rheumatic Dis. (2019) 78:1463–71. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215920
3. Fu J, Nogueira SV, Drongelen VV, Coit P, Ling S, Rosloniec EF, et al. Shared epitope–aryl hydrocarbon receptor crosstalk underlies the mechanism of gene–environment interaction in autoimmune arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2018) 115:4755–60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1722124115
4. McInnes IB, Schett G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. New Engl J Med. (2011) 365:2205–19. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1004965
5. McInnes IB, Schett G. Pathogenetic insights from the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. (2017) 389:2328–37. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31472-1
6. Fu X-D. Non-coding RNA: a new frontier in regulatory biology. Natl Sci Rev. (2014) 1:190–204. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwu008
7. Dykes IM, Emanueli C. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional gene regulation by long non-coding RNA. Genomics Proteomics Bioinf. (2017) 15:177–86. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2016.12.005
8. Rezaei Z, Sadri F. MicroRNAs involved in inflammatory breast cancer: oncogene and tumor suppressors with possible targets. DNA Cell Biol. (2021) 40:499–512. doi: 10.1089/dna.2020.6320
9. Chamani E, Sargolzaei J, Tavakoli T, Rezaei Z. microRNAs: novel markers in diagnostics and therapeutics of celiac disease. DNA Cell Biol. (2019) 38:708–17. doi: 10.1089/dna.2018.4561
10. Mishra K, Kanduri C. Understanding long noncoding RNA and chromatin interactions: what we know so far. Non-coding RNA. (2019) 5:54. doi: 10.3390/ncrna5040054
11. He AT, Liu J, Li F, Yang BB. Targeting circular RNAs as a therapeutic approach: current strategies and challenges. Signal transduction targeted Ther. (2021) 6:185. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00569-5
12. Bhatt D, Ghosh S. Regulation of the NF-κB-mediated transcription of inflammatory genes. Front Immunol. (2014) 5:82482. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00071
13. Makarov SS. NF-kappa B in rheumatoid arthritis: a pivotal regulator of inflammation, hyperplasia, and tissue destruction. Arthritis Res. (2001) 3:200–6. doi: 10.1186/ar300
14. Peng X, Wang Q, Li W, Ge G, Peng J, Xu Y, et al. Comprehensive overview of microRNA function in rheumatoid arthritis. Bone Res. (2023) 11:8. doi: 10.1038/s41413-023-00244-1
15. Seegobin SD, Ma MH, Dahanayake C, Cope AP, Scott DL, Lewis CM, et al. ACPA-positive and ACPA-negative rheumatoid arthritis differ in their requirements for combination DMARDs and corticosteroids: secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Res Ther. (2014) 16:R13. doi: 10.1186/ar4439
16. Grosse J, Allado E, Roux C, Pierreisnard A, Couderc M, Clerc-Urmes I, et al. ACPA-positive versus ACPA-negative rheumatoid arthritis: two distinct erosive disease entities on radiography and ultrasonography. Rheumatol Int. (2020) 40:615–24. doi: 10.1007/s00296-019-04492-5
17. Meng W, Zhu Z, Jiang X, Too CL, Uebe S, Jagodic M, et al. DNA methylation mediates genotype and smoking interaction in the development of anti-citrullinated peptide antibody-positive rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2017) 19:71. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1276-2
18. Dreyton CJ, Knuckley B, Jones JE, Lewallen DM, Thompson PR. Mechanistic studies of protein arginine deiminase 2: evidence for a substrate-assisted mechanism. Biochemistry. (2014) 53:4426–33. doi: 10.1021/bi500554b
19. Cheng Z, Meade J, Mankia K, Emery P, Devine DA. Periodontal disease and periodontal bacteria as triggers for rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. (2017) 31:19–30. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2017.08.001
20. Symonds P, Marcu A, Cook KW, Metheringham RL, Durrant LG, Brentville VA. Citrullinated epitopes identified on tumour MHC class II by peptide elution stimulate both regulatory and Th1 responses and require careful selection for optimal anti-tumour responses. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:764462. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.764462
21. Hill JA, Bell DA, Brintnell W, Yue D, Wehrli B, Jevnikar AM, et al. Arthritis induced by posttranslationally modified (citrullinated) fibrinogen in DR4-IE transgenic mice. J Exp Med. (2008) 205:967–79. doi: 10.1084/jem.20072051
22. Krishnamurthy A, Joshua V, Haj Hensvold A, Jin T, Sun M, Vivar N, et al. Identification of a novel chemokine-dependent molecular mechanism underlying rheumatoid arthritis-associated autoantibody-mediated bone loss. Ann Rheum Dis. (2016) 75:721–9. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208093
23. Tuncel J, Holmberg J, Haag S, Hopkins MH, Wester-Rosenlöf L, Carlsen S, et al. Self-reactive T cells induce and perpetuate chronic relapsing arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2020) 22:95. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-2104-7
24. Mousavi MJ, Karami J, Aslani S, Tahmasebi MN, Vaziri AS, Jamshidi A, et al. Transformation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis; from a friend to foe. Autoimmun Highlights. (2021) 12:3. doi: 10.1186/s13317-020-00145-x
25. Zou Y, Zeng S, Huang M, Qiu Q, Xiao Y, Shi M, et al. Inhibition of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase suppresses fibroblast-like synoviocytes-mediated synovial inflammation and joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Pharmacol. (2017) 174:893–908. doi: 10.1111/bph.v174.9
26. Mor A, Abramson SB, Pillinger MH. The fibroblast-like synovial cell in rheumatoid arthritis: a key player in inflammation and joint destruction. Clin Immunol. (2005) 115:118–28. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2004.12.009
27. Crowley T. Innate immune memory in fibroblasts. Birmingham, UK: University of Birmingham (2018).
28. Kim KW, Cho ML, Lee SH, Oh HJ, Kang CM, Ju JH, et al. Human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts promote osteoclastogenic activity by activating RANKL via TLR-2 and TLR-4 activation. Immunol Lett. (2007) 110:54–64. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2007.03.004
29. Ospelt C, Brentano F, Rengel Y, Stanczyk J, Kolling C, Tak PP, et al. Overexpression of toll-like receptors 3 and 4 in synovial tissue from patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: toll-like receptor expression in early and longstanding arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatism: Off J Am Coll Rheumatol. (2008) 58:3684–92. doi: 10.1002/art.v58:12
30. Su X, Ye J, Hsueh EC, Zhang Y, Hoft DF, Peng G. Tumor microenvironments direct the recruitment and expansion of human Th17 cells. J Immunol. (2009) 184:1630–41. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902813
31. Pandolfi F, Franza L, Carusi V, Altamura S, Andriollo G, Nucera E. Interleukin-6 in rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:5238. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155238
32. Xu Y, Hunt NH, Bao S. The role of granulocyte macrophage-colony-stimulating factor in acute intestinal inflammation. Cell Res. (2008) 18:1220–9. doi: 10.1038/cr.2008.310
33. Kosmaczewska A, Świerkot J, Ciszak L, Wiland P. The role of Th1, Th17, and Treg cells in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis including anti-inflammatory action of Th1 cytokines. Adv Hygiene Exp Med. (2011) 65:397–403. doi: 10.5604/17322693.948971
34. Arroyo-Villa I, Bautista-Caro MB, Balsa A, Aguado-Acín P, Nuño L, Bonilla-Hernán MG, et al. Frequency of Th17 CD4+ T cells in early rheumatoid arthritis: a marker of anti-CCP seropositivity. PloS One. (2012) 7:e42189. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042189
35. Funaki Y, Hasegawa Y, Okazaki R, Yamasaki A, Sueda Y, Yamamoto A, et al. Resolvin E1 inhibits osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption by suppressing IL-17-induced RANKL expression in osteoblasts and RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation. Yonago Acta Med. (2018) 61:008–18. doi: 10.33160/yam.2018.03.002
36. Dougall WC, Glaccum M, Charrier K, Rohrbach K, Brasel K, De Smedt T, et al. RANK is essential for osteoclast and lymph node development. Genes Dev. (1999) 13:2412–24. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.18.2412
37. Hayer S, Bauer G, Willburger M, Sinn K, Alasti F, Plasenzotti R, et al. Cartilage damage and bone erosion are more prominent determinants of functional impairment in longstanding experimental arthritis than synovial inflammation. Dis Models Mech. (2016) 9:1329–38. doi: 10.1242/dmm.025460
38. Bergström B, Lundqvist C, Vasileiadis GK, Carlsten H, Ekwall O, Ekwall A-KH. The rheumatoid arthritis risk gene AIRE is induced by cytokines in fibroblast-like synoviocytes and augments the pro-inflammatory response. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:1384. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01384
39. Barrow M. An Overview of the NF-kB mechanism of pathophysiology in rheumatoid arthritis, investigation of the NF-kB ligand RANKL and related nutritional interventions. Autoimmun Rev. (2021) 20:102741. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102741
40. Sabir JS, El Omri A, Banaganapalli B, Al-Shaeri MA, Alkenani NA, Sabir MJ, et al. Dissecting the role of NF-κb protein family and its regulators in rheumatoid arthritis using weighted gene co-expression network. Front Genet. (2019) 10:1163. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.01163
41. Mazewski C, Perez RE, Fish EN, Platanias LC. Type I interferon (IFN)-regulated activation of canonical and non-canonical signaling pathways. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:606456. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.606456
42. Ghosh G, Wang VY-F. Origin of the functional distinctiveness of NF-κB/p52. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:764164. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.764164
43. Yu H, Lin L, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Hu H. Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: mechanism and clinical study. Signal transduction targeted Ther. (2020) 5:209. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00312-6
44. Zhang T, Ma C, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Hu H. NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. MedComm. (2021) 2:618–53. doi: 10.1002/mco2.v2.4
45. Wang H, Mei D, Liang F-Q, Xue Z-Y, Wang P, Liu R-J, et al. BAFF promotes FLS activation through BAFFR-mediated non-canonical NF-κB pathway and the effects of CP-25. Inflammation. (2023) 46:861–75. doi: 10.1007/s10753-022-01774-2
46. Zhang J, Zhang R, Li W, Ma X-C, Qiu F, Sun C-P. IκB kinase β (IKKβ): Structure, transduction mechanism, biological function, and discovery of its inhibitors. Int J Biol Sci. (2023) 19:4181. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.85158
47. Adli M, Merkhofer E, Cogswell P, Baldwin AS. IKKα and IKKβ Each function to regulate NF-κB activation in the TNF-induced/canonical pathway. PloS One. (2010) 5:e9428. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009428
48. Williams LM, Gilmore TD. Looking down on NF-κB. Mol Cell Biol. (2020) 40:e00104-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00104-20
49. Morgan D, Garg M, Tergaonkar V, Tan SY, Sethi G. Pharmacological significance of the non-canonical NF-κB pathway in tumorigenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Reviews Cancer. (2020) 1874:188449. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188449
50. Rodriguez BN, Huang H, Chia JJ, Hoffmann A. The noncanonical NFκB pathway: Regulatory mechanisms in health and disease. WIREs Mech Dis. (2024) e1646. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1646
51. Chojnacka K, Lewandowska U. Inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion by polyphenol-rich extracts in macrophages via NF-κB pathway. Food Rev Int. (2023) 39:5459–78. doi: 10.1080/87559129.2022.2071936
52. Berardi S, Corrado A, Maruotti N, Cici D, Cantatore F. Osteoblast role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Biol Rep. (2021) 48:2843–52. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06288-y
53. Chong WP, Mattapallil MJ, Raychaudhuri K, Bing SJ, Wu S, Zhong Y, et al. The cytokine IL-17A limits Th17 pathogenicity via a negative feedback loop driven by autocrine induction of IL-24. Immunity. (2020) 53:384–97.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.06.022
54. Harbour SN, DiToro DF, Witte SJ, Zindl CL, Gao M, Schoeb TR, et al. TH17 cells require ongoing classic IL-6 receptor signaling to retain transcriptional and functional identity. Sci Immunol. (2020) 5:eaaw2262. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aaw2262
55. Nandakumar KS, Fang Q, Wingbro Ågren I, Bejmo ZF. Aberrant activation of immune and non-immune cells contributes to joint inflammation and bone degradation in rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:15883. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115883
56. Morales-Núñez JJ, Muñoz-Valle JF, García-Chagollán M, Cerpa-Cruz S, Martínez-Bonilla GE, Medina-Rosales VM, et al. Aberrant B-cell activation and B-cell subpopulations in rheumatoid arthritis: analysis by clinical activity, autoantibody seropositivity, and treatment. Clin Exp Immunol. (2023) 214:314–27. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxad076
57. Manou-Stathopoulou S, Lewis MJ. Diversity of NF-κB signalling and inflammatory heterogeneity in Rheumatic Autoimmune Disease. Semin Immunol. (2021) 58:101649. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2022.101649
58. Barnabei L, Laplantine E, Mbongo W, Rieux-Laucat F, Weil R. NF-κB: at the borders of autoimmunity and inflammation. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:716469. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.716469
59. Wang J, Yan S, Yang J, Lu H, Xu D, Wang Z. Non-coding RNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: from bench to bedside. Front Immunol. (2020) 10:3129. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03129
60. Tavasolian F, Abdollahi E, Rezaei R, Momtazi-borojeni AA, Henrotin Y, Sahebkar A. Altered expression of microRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis. J Cell Biochem. (2018) 119:478–87. doi: 10.1002/jcb.v119.1
61. Cai X, Wang X, Cao C, Gao Y, Zhang S, Yang Z, et al. HBXIP-elevated methyltransferase METTL3 promotes the progression of breast cancer via inhibiting tumor suppressor let-7g. Cancer Lett. (2018) 415:11–9. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.11.018
62. Zheng F, Yu X, Huang J, Dai Y. Circular RNA expression profiles of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in rheumatoid arthritis patients, based on microarray chip technology. Mol Med Rep. (2017) 16:8029–36. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7638
63. Wang J, Yan S, Yang J, Lu H, Xu D, Wang Z. Non-coding RNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: from bench to bedside. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:3129. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03129
64. Chen J-Q, Papp G, Szodoray P, Zeher M. The role of microRNAs in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev. (2016) 15:1171–80. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2016.09.003
65. Yang N, Zhu S, Lv X, Qiao Y, Liu Y-J, Chen J. MicroRNAs: pleiotropic regulators in the tumor microenvironment. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:2491. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02491
66. Chen X-M, Huang Q-C, Yang S-L, Chu Y-L, Yan Y-H, Han L, et al. Role of micro RNAs in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: novel perspectives based on review of the literature. Medicine. (2015) 94:e1326. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001326
67. Stanczyk J, Ospelt C, Karouzakis E, Filer A, Raza K, Kolling C, et al. Altered expression of microRNA-203 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts and its role in fibroblast activation. Arthritis rheumatism. (2011) 63:373–81. doi: 10.1002/art.30115
68. Xia Z, Meng F, Liu Y, Fang Y, Wu X, Zhang C, et al. Decreased MiR-128-3p alleviates the progression of rheumatoid arthritis by up-regulating the expression of TNFAIP3. Bioscience Rep. (2018) 38. doi: 10.1042/BSR20180540
69. Gantier MP, Stunden HJ, McCoy CE, Behlke MA, Wang D, Kaparakis-Liaskos M, et al. A miR-19 regulon that controls NF-κB signaling. Nucleic Acids Res. (2012) 40:8048–58. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks521
70. Quero L, Tiaden AN, Hanser E, Roux J, Laski A, Hall J, et al. miR-221-3p drives the shift of M2-macrophages to a pro-inflammatory function by suppressing JAK3/STAT3 activation. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:3087. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03087
71. Shao L, Hou C. miR-138 activates NF-κB signaling and PGRN to promote rheumatoid arthritis via regulating HDAC4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2019) 519:166–71. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.08.092
72. Wang J, Mao N, Liu Y, Xie X, Tian J, Li F, et al. Inhibition of miR-16 enhances the sensitivity of fibroblast-like synovial cells to methotrexate by restraining MDR1/P-gp expression via NF-κB pathway. RSC Adv. (2019) 9:26619–27. doi: 10.1039/C9RA04991F
73. Yan X, Cen Y, Wang Q. Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate experimental rheumatoid arthritis through microRNA-regulated IκB expression. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:28915. doi: 10.1038/srep28915
74. de la Rica L, García-Gómez A, Comet NR, Rodríguez-Ubreva J, Ciudad L, Vento-Tormo R, et al. NF-κB-direct activation of microRNAs with repressive effects on monocyte-specific genes is critical for osteoclast differentiation. Genome Biol. (2015) 16:2. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0561-5
75. Chen Y, Wang X, Yang M, Ruan W, Wei W, Gu D, et al. miR-145-5p increases osteoclast numbers in vitro and aggravates bone erosion in collagen-induced arthritis by targeting osteoprotegerin. Med Sci monitor: Int Med J Exp Clin Res. (2018) 24:5292–300. doi: 10.12659/MSM.908219
76. Wang X, Tang K, Wang Y, Chen Y, Yang M, Gu C, et al. Elevated microRNA−145−5p increases matrix metalloproteinase−9 by activating the nuclear factor−κB pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Med Rep. (2019) 20:2703–11. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10499
77. Trenkmann M, Brock M, Gay RE, Michel BA, Gay S, Huber LC. Tumor necrosis factor α-induced microRNA-18a activates rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts through a feedback loop in NF-κB signaling. Arthritis rheumatism. (2013) 65:916–27. doi: 10.1002/art.37834
78. Xie M, Wang J, Gong W, Xu H, Pan X, Chen Y, et al. NF-κB-driven miR-34a impairs Treg/Th17 balance via targeting Foxp3. J Autoimmun. (2019) 102:96–113. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2019.04.018
79. Hong BK, You S, Yoo SA, Park D, Hwang D, Cho CS, et al. MicroRNA-143 and -145 modulate the phenotype of synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis. Exp Mol Med. (2017) 49:e363. doi: 10.1038/emm.2017.108
80. Cai D, Hong S, Yang J, San P. The effects of microRNA-515-5p on the toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/JNK signaling pathway and WNT1-inducible-signaling pathway protein 1 (WISP-1) expression in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synovial (RAFLS) cells following treatment with receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa-B ligand (RANKL). Med Sci monitor: Int Med J Exp Clin Res. (2020) 26:e920611. doi: 10.12659/MSM.920611
81. Hu J, Zhai C, Hu J, Li Z, Fei H, Wang Z, et al. MiR-23a inhibited IL-17-mediated proinflammatory mediators expression via targeting IKKα in articular chondrocytes. Int Immunopharmacol. (2017) 43:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.11.031
82. Bao X, Ma L, He C. MicroRNA-23a-5p regulates cell proliferation, migration and inflammation of TNF-α-stimulated human fibroblast-like MH7A synoviocytes by targeting TLR4 in rheumatoid arthritis. Exp Ther Med. (2021) 21:479. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.9910
83. Zhu S, Pan W, Song X, Liu Y, Shao X, Tang Y, et al. The microRNA miR-23b suppresses IL-17-associated autoimmune inflammation by targeting TAB2, TAB3 and IKK-α. Nat Med. (2012) 18:1077–86. doi: 10.1038/nm.2815
84. Yang QY, Yang KP, Li ZZ. MiR-22 restrains proliferation of rheumatoid arthritis by targeting IL6R and may be concerned with the suppression of NF-κB pathway. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. (2020) 36:20–6. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12124
85. Lei S, Chen G, Deng L, He J. Upregulation of miR-27b facilitates apoptosis of TNF-α-stimulated fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Yonsei Med J. (2019) 60:585–91. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.6.585
86. Akhtar N, Singh AK, Ahmed S. MicroRNA-17 suppresses TNF-α Signaling by interfering with TRAF2 and cIAP2 association in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. J Immunol. (2016) 197:2219–28. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600360
87. Xing XW, Shi HY, Liu S, Feng SX, Feng SQ, Gong BQ. miR-496/MMP10 is involved in the proliferation of IL-1β-induced fibroblast-like synoviocytes via mediating the NF-κB signaling pathway. Inflammation. (2021) 44:1359–69. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01421-2
88. Yang B, Ge Y, Zhou Y, Wang J, Xie X, Li S, et al. miR-124a inhibits the proliferation and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes via targeting PIK3/NF-κB pathway. Cell Biochem Funct. (2019) 37:208–15. doi: 10.1002/cbf.v37.4
89. Mu N, Gu J, Huang T, Zhang C, Shu Z, Li M, et al. A novel NF-κB/YY1/microRNA-10a regulatory circuit in fibroblast-like synoviocytes regulates inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:20059. doi: 10.1038/srep20059
90. Ma W, Tang F, Xiao L, Han S, Yao X, Zhang Q, et al. miR-205-5p in exosomes divided from chondrogenic mesenchymal stem cells alleviated rheumatoid arthritis via regulating MDM2 in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. J musculoskeletal neuronal Interact. (2022) 22:132–41.
91. Wang Y, Xu N, Zhao S, Jiao T, Fu W, Yang L, et al. miR-410-3p suppresses cytokine release from fibroblast-like synoviocytes by regulating NF-κB signaling in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammation. (2019) 42:331–41. doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0896-2
92. Gao B, Sun G, Wang Y, Geng Y, Zhou L, Chen X. microRNA-23 inhibits inflammation to alleviate rheumatoid arthritis via regulating CXCL12. Exp Ther Med. (2021) 21:459. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.9890
93. Luo C, Liang JS, Gong J, Zhang HL, Feng ZJ, Yang HT, et al. miRNA-31 over-expression improve synovial cells apoptosis induced by RA. Bratislavske lekarske listy. (2018) 119:355–60. doi: 10.4149/BLL_2018_066
94. Wen X, Chen X, Liang X, Zhao H, Li Y, Sun X, et al. The small molecule NSM00191 specifically represses the TNF-α/NF-кB axis in foot and ankle rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Biol Sci. (2018) 14:1732–44. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.24232
95. Meng D, Li J, Li H, Wang K. Salvianolic acid B remits LPS-induced injury by up-regulating miR-142-3p in MH7A cells. Biomedicine pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine pharmacotherapie. (2019) 115:108876. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108876
96. Wang Y, Zheng F, Gao G, Yan S, Zhang L, Wang L, et al. MiR-548a-3p regulates inflammatory response via TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. J Cell Biochem. (2019) 120:1133–40. doi: 10.1002/jcb.v120.2
97. Hayakawa K, Kawasaki M, Hirai T, Yoshida Y, Tsushima H, Fujishiro M, et al. MicroRNA-766-3p contributes to anti-inflammatory responses through the indirect inhibition of NF-κB signaling. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:809. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040809
98. Kong XH, Shi SF, Hu HJ, Wang JX. MicroRNA-20a suppresses RANKL-modulated osteoclastogenesis and prevents bone erosion in mice with rheumatoid arthritis through the TLR4/p38 pathway. J Biol regulators homeostatic Agents. (2021) 35:921–31. doi: 10.23812/20-604-A
99. Lee WS, Yasuda S, Kono M, Kudo Y, Shimamura S, Kono M, et al. MicroRNA-9 ameliorates destructive arthritis through down-regulation of NF-κB1-RANKL pathway in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Clin Immunol (Orlando Fla). (2020) 212:108348. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108348
100. Bogunia-Kubik K, Wysoczańska B, Piątek D, Iwaszko M, Ciechomska M, Świerkot J. Significance of polymorphism and expression of miR-146a and NFkB1 genetic variants in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Archivum immunologiae therapiae experimentalis. (2016) 64:131–6. doi: 10.1007/s00005-016-0443-5
101. Hassine HB, Boumiza A, Sghiri R, Baccouche K, Boussaid I, Atig A, et al. Micro RNA-146a but not IRAK1 is associated with rheumatoid arthritis in the Tunisian population. Genet testing Mol Biomarkers. (2017) 21:92–6. doi: 10.1089/gtmb.2016.0270
102. Ammari M, Presumey J, Ponsolles C, Roussignol G, Roubert C, Escriou V, et al. Delivery of miR-146a to ly6C(high) monocytes inhibits pathogenic bone erosion in inflammatory arthritis. Theranostics. (2018) 8:5972–85. doi: 10.7150/thno.29313
103. Wang Y, Yin Z, Zhang N, Song H, Zhang Q, Hao X, et al. MiR-125a-3p inhibits cell proliferation and inflammation responses in fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis by mediating the Wnt/β-catenin and NF-κB pathways via targeting MAST3. J musculoskeletal neuronal Interact. (2021) 21:560–7.
104. Shi DL, Shi GR, Xie J, Du XZ, Yang H. MicroRNA-27a inhibits cell migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes by targeting follistatin-like protein 1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Molecules Cells. (2016) 39:611–8. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2016.0103
105. Xu D, Jiang Y, Yang L, Hou X, Wang J, Gu W, et al. Long noncoding RNAs expression profile and functional networks in rheumatoid arthritis. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:95280. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20036
106. Xu G, Chen J, Pan Q, Huang K, Pan J, Zhang W, et al. Long noncoding RNA expression profiles of lung adenocarcinoma ascertained by microarray analysis. PloS One. (2014) 9:e104044. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104044
107. Jin Y, Wu P, Zhao W, Wang X, Yang J, Huo X, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00165-induced by STAT3 exerts oncogenic properties via interaction with Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 to promote EMT in gastric cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2018) 507:223–30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.11.012
108. Scaria V. Joining the long shots: emerging evidence on the role of long noncoding RNAs in rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Rheum Dis. (2014) 17:831–3. doi: 10.1111/apl.2015.17.issue-8
109. Hur K, Kim S-H, Kim J-M. Potential implications of long noncoding RNAs in autoimmune diseases. Immune network. (2019) 19:e4. doi: 10.4110/in.2019.19.e4
110. Yan S, Wang P, Wang J, Yang J, Lu H, Jin C, et al. Long Non-coding RNA HIX003209 Promotes Inflammation by Sponging miR-6089 via TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:2218. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02218
111. Wahba AS, Ibrahim ME, Mesbah NM, Saleh SM, Abo-Elmatty DM, Mehanna ET. Serum LINC00305 expression and its genetic variant rs2850711 are associated with clinical and laboratory features of rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Biomed Sci. (2020) 77:142–7. doi: 10.1080/09674845.2020.1744942
112. Yang J, Li Y, Wang L, Zhang Z, Li Z, Jia Q. LncRNA H19 aggravates TNF-α-induced inflammatory injury via TAK1 pathway in MH7A cells. BioFactors (Oxford England). (2020) 46:813–20. doi: 10.1002/biof.v46.5
113. Zhao F, Dong J, Guo J, Bi L. Inhibiting role of long non-coding RNA LINC01197 in inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis through the microRNA-150/THBS2 axis. Exp Cell Res. (2020) 394:112136. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.112136
114. Qing P, Liu Y. Inhibitory role of long non-coding RNA OIP5-AS1 in rheumatoid arthritis progression through the microRNA-448-paraoxonase 1-toll-like receptor 3-nuclear factor κB axis. Exp Physiol. (2020) 105:1708–19. doi: 10.1113/eph.v105.10
115. Tang J, Yi S, Liu Y. Long non-coding RNA PVT1 can regulate the proliferation and inflammatory responses of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by targeting microRNA-145-5p. Hum Cell. (2020) 33:1081–90. doi: 10.1007/s13577-020-00419-6
116. Chen H, He C, Liu Y, Li X, Zhang C, Qin Q, et al. LncRNA-GAS5 inhibits expression of miR 103 and ameliorates the articular cartilage in adjuvant-induced arthritis in obese mice. Dose-response: Publ Int Hormesis Soc. (2020) 18:1559325820942718. doi: 10.1177/1559325820942718
117. Xiao J, Wang R, Zhou W, Cai X, Ye Z. LncRNA NEAT1 regulates the proliferation and production of the inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by targeting miR-204-5p. Hum Cell. (2021) 34:372–82. doi: 10.1007/s13577-020-00461-4
118. Su Y, Liu Y, Ma C, Guan C, Ma X, Meng S. Mesenchymal stem cell-originated exosomal lncRNA HAND2-AS1 impairs rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte activation through miR-143-3p/TNFAIP3/NF-κB pathway. J orthopaedic Surg Res. (2021) 16:116. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02248-1
119. Zhang J, Gao FF, Xie J. LncRNA linc00152/NF-κB feedback loop promotes fibroblast-like synovial cells inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis via regulating miR-103a/TAK1 axis and YY1 expression. Immunity Inflammation Dis. (2021) 9:681–93. doi: 10.1002/iid3.v9.3
120. Liu W, Song J, Feng X, Yang H, Zhong W. LncRNA XIST is involved in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by sponging miR-126-3p via the NF-κB pathway. Autoimmunity. (2021) 54:326–35. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2021.1937608
121. Xie B, Lin F, Bao W, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Li X, et al. Long noncoding RNA00324 is involved in the inflammation of rheumatoid arthritis by targeting miR-10a-5p via the NF-κB pathway. Immunity Inflammation Dis. (2023) 11:e906. doi: 10.1002/iid3.v11.6
122. Wen J, Liu J, Wan L, Jiang H, Xin L, Sun Y, et al. m(6)A-mediated lncRNA MAPKAPK5-AS1 induces apoptosis and suppresses inflammation via regulating miR-146a-3p/SIRT1/NF-κB axis in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Cycle. (2023) 22:2602–21. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2024.2302281
123. Sun L, Hu L, Chen P, Li Y, Tu J, Chen J. Long non-coding RNA AL928768.3 promotes rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes proliferation, invasion and inflammation, while inhibits apoptosis via activating lymphotoxin beta mediated NF-κB signaling pathway. Inflammation. (2024) 47:543–56. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01927-x
124. Salzman J. Circular RNA expression: its potential regulation and function. Trends Genet. (2016) 32:309–16. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2016.03.002
125. Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, Slevin MK, Burd CE, Liu J, et al. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. Rna. (2013) 19:141–57. doi: 10.1261/rna.035667.112
126. Yang L, Fu J, Zhou Y. Circular RNAs and their emerging roles in immune regulation. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:2977. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02977
127. Barrett SP, Wang PL, Salzman J. Circular RNA biogenesis can proceed through an exon-containing lariat precursor. elife. (2015) 4:e07540. doi: 10.7554/eLife.07540
128. Wang PL, Bao Y, Yee M-C, Barrett SP, Hogan GJ, Olsen MN, et al. Circular RNA is expressed across the eukaryotic tree of life. PloS One. (2014) 9:e90859. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090859
129. Chen X, Yang T, Wang W, Xi W, Zhang T, Li Q, et al. Circular RNAs in immune responses and immune diseases. Theranostics. (2019) 9:588. doi: 10.7150/thno.29678
130. Qian L, Yu S, Chen Z, Meng Z, Huang S, Wang P. The emerging role of circRNAs and their clinical significance in human cancers. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Reviews Cancer. (2018) 1870:247–60. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2018.06.002
131. Huang Y, Zhang C, Xiong J, Ren H. Emerging important roles of circRNAs in human cancer and other diseases. Genes Dis. (2021) 8:412–23. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2020.07.012
132. Sun J-Y, Shi Y, Cai X-Y, Liu J. Potential diagnostic and therapeutic value of circular RNAs in cardiovascular diseases. Cell Signalling. (2020) 71:109604. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109604
133. Awan FM, Yang BB, Naz A, Hanif A, Ikram A, Obaid A, et al. The emerging role and significance of circular RNAs in viral infections and antiviral immune responses: possible implication as theranostic agents. RNA Biol. (2021) 18:1–15. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1790198
134. Fang Z, Jiang C, Li S. The potential regulatory roles of circular RNAs in tumor immunology and immunotherapy. Front Immunol. (2021) 11:617583. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.617583
135. Yang J, Cheng M, Gu B, Wang J, Yan S, Xu D. CircRNA_09505 aggravates inflammation and joint damage in collagen-induced arthritis mice via miR-6089/AKT1/NF-κB axis. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11:833. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03038-z
136. Zhang S, Zhao J, Ma W. Circ-Sirt1 inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, and ameliorates inflammation in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Autoimmunity. (2021) 54:514–25. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2021.1969550
137. Wang X, Liu D, Cui G, Shen H. Circ_0088036 mediated progression and inflammation in fibroblast-like synoviocytes of rheumatoid arthritis by miR-1263/REL-activated NF-κB pathway. Transplant Immunol. (2022) 73:101604. doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2022.101604
138. Zhang S, Shen Z, Chao G, Du X, Zhang W, Jin D, et al. Circ_0004712 silencing suppresses the aggressive changes of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by targeting miR-633/TRAF6 axis. Biochem Genet. (2023) 61:521–37. doi: 10.1007/s10528-022-10265-w
139. Liu J, Song S, Zhao R, Zhang H-Y, Zhang S-X. The functions and networks of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomedicine Pharmacotherapy. (2023) 163:114707. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114707
140. Zhang Y, Yang M, Xie H, Hong F, Yang S. Role of miRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Cells. (2023) 12:1749. doi: 10.3390/cells12131749
141. Iwamoto N, Furukawa K, Endo Y, Shimizu T, Sumiyoshi R, Umeda M, et al. Methotrexate alters the expression of microRNA in fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:11561. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111561
142. Sun W, Ma J, Zhao H, Xiao C, Zhong H, Ling H, et al. Resolvin D1 suppresses pannus formation via decreasing connective tissue growth factor caused by upregulation of miRNA-146a-5p in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2020) 22:1–14. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-2133-2
143. Jiang H, Fan C, Lu Y, Cui X, Liu J. Astragaloside regulates lncRNA LOC100912373 and the miR−17−5p/PDK1 axis to inhibit the proliferation of fibroblast−like synoviocytes in rats with rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Mol Med. (2021) 48:1–10. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.4963
144. Ma J, Meng Q, Zhan J, Wang H, Fan W, Wang Y, et al. Paeoniflorin suppresses rheumatoid arthritis development via modulating the circ-FAM120A/miR-671-5p/MDM4 axis. Inflammation. (2021) 44:2309–22. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01504-0
145. Wen J-T, Liu J, Wan L, Xin L, Guo J-C, Sun Y-Q, et al. Triptolide inhibits cell growth and inflammatory response of fibroblast-like synoviocytes by modulating hsa-circ-0003353/microRNA-31-5p/CDK1 axis in rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2022) 106:108616. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108616
146. Cao L, Jiang H, Yang J, Mao J, Wei G, Meng X, et al. LncRNA MIR31HG is induced by tocilizumab and ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte-mediated inflammation via miR-214-PTEN-AKT signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY). (2021) 13:24071. doi: 10.18632/aging.203644
147. Saquib M, Agnihotri P, Monu X, Biswas S. Exogenous miRNA: a perspective role as therapeutic in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. (2021) 23:43. doi: 10.1007/s11926-021-01009-7
148. Wu L-F, Zhang Q, Mo X-B, Lin J, Wu Y-L, Lu X, et al. Identification of novel rheumatoid arthritis-associated MiRNA-204-5p from plasma exosomes. Exp Mol Med. (2022) 54:334–45. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00751-x
149. Wu H, Zhou X, Wang X, Cheng W, Hu X, Wang Y, et al. miR-34a in extracellular vesicles from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells reduces rheumatoid arthritis inflammation via the cyclin I/ATM/ATR/p53 axis. J Cell Mol Med. (2021) 25:1896–910. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15857
150. Huang Y, Lu D, Ma W, Liu J, Ning Q, Tang F, et al. miR-223 in exosomes from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis via downregulation of NLRP3 expression in macrophages. Mol Immunol. (2022) 143:68–76. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2022.01.002
151. Evangelatos G, Fragoulis GE, Koulouri V, Lambrou GI. MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: From pathogenesis to clinical impact. Autoimmun Rev. (2019) 18:102391. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2019.102391
152. Ibrahim SSA, Kandil LS, Ragab GM, El-Sayyad SM. Micro RNAs 26b, 20a inversely correlate with GSK-3 β/NF-κB/NLRP-3 pathway to highlight the additive promising effects of atorvastatin and quercetin in experimental induced arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2021) 99:108042. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108042
153. Kok FO, Wang H, Riedlova P, Goodyear CS, Carmody RJ. Defining the structure of the NF-ĸB pathway in human immune cells using quantitative proteomic data. Cell Signal. (2021) 88:110154. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.110154
154. Wu ZM, Luo J, Shi XD, Zhang SX, Zhu XB, Guo J. Icariin alleviates rheumatoid arthritis via regulating miR-223-3p/NLRP3 signalling axis. Autoimmunity. (2020) 53:450–8. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2020.1836488
155. Dudics S, Venkatesha SH, Moudgil KD. The micro-RNA expression profiles of autoimmune arthritis reveal novel biomarkers of the disease and therapeutic response. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:2293. doi: 10.3390/ijms19082293
Keywords: noncoding RNAs, NF-κB signaling pathway, rheumatoid arthritis, therapeutic targets, synovial fibroblasts
Citation: Seyedi D, Espandar N, Hojatizadeh M, Mohammadi Y, Sadri F and Rezaei Z (2024) Noncoding RNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: modulators of the NF-κB signaling pathway and therapeutic implications. Front. Immunol. 15:1486476. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1486476
Received: 26 August 2024; Accepted: 11 October 2024;
Published: 28 October 2024.
Edited by:
Philippe Saas, Etablissement Français du Sang AuRA, FranceReviewed by:
Avijit Goswami, Aten Porus Lifesciences Pvt. Ltd., IndiaZhengping Huang, Guangdong Second Provincial General Hospital, China
Copyright © 2024 Seyedi, Espandar, Hojatizadeh, Mohammadi, Sadri and Rezaei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zohreh Rezaei, ei5yZXphZWkyMjJAcGdzLnVzYi5hYy5pcg==; Farzad Sadri, Ri5zYWRyaTg3QHlhaG9vLmNvbQ==
 Dina Seyedi1
Dina Seyedi1 Farzad Sadri
Farzad Sadri Zohreh Rezaei
Zohreh Rezaei