- 1Department of Neurology, Shandong Provincial Third Hospital, Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan, China
- 2Shandong Provincial Third Hospital, Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan, China
- 3Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, China
- 4Department of General Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, China
Background: The efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with CTLA-4 inhibitors in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer is controversial. This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with CTLA-4 inhibitors for advanced colorectal cancer.
Methods: PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, and Web of Science databases were systematically searched for relevant studies. Outcomes including median progression-free survival (mPFS), median overall survival (mOS), overall response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) and ≥grade 3 TRAEs were extracted for further analysis. The risk of bias was assessed by subgroup analysis.
Results: 12 articles with 566 patients were identified and subjected to meta-analysis. With regard to survival analysis, the pooled mOS and mPFS were 6.66 months (95%CI 4.85-9.16) and 2.92 months (95%CI 2.23-3.83), respectively. In terms of tumor response, the pooled ORR and DCR were 21% (95%CI 6%-41%) and 49% (95%CI 27%-71%), respectively. The pooled AEs rate and ≥ grade 3 AEs rate were 94% (95%CI 86%-99%) and 44% (95%CI 30%-58%).
Conclusion: PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with CTLA-4 inhibitors have shown promising clinical responses in the treatment of colorectal cancer (CRC). Although the incidence of adverse reactions is high, they are generally tolerable.
Systematic review registration: https://inplasy.com/, identifier INPLASY202480030.
1 Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most commonly diagnosed malignancy worldwide and the fourth leading cause of cancer-related death (1, 2). Its global incidence is expected to rise to 2.5 million new cases by 2035 (3, 4). CRC development results from a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors, including a sedentary lifestyle, age, obesity, and dietary habits (4–8). Due to its insidious onset, approximately 20% of cases are diagnosed as metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) (9), and about 40% of patients with localized disease experience recurrence after prior treatment (10).The high mortality rate in advanced colorectal cancer (aCRC) is largely due to tumor progression and metastasis. Despite advances in treatment, the prognosis for aCRC patients remains poor, with a median overall survival (mOS) of 30 months (11, 12) and a 5-year survival rate of less than 14% (13, 14). Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy remain the primary therapeutic interventions for CRC, often used in combination depending on disease localization and progression (15–18). Surgery is the cornerstone of curative treatment for localized CRC (stage I–III) (19), and in mCRC with limited metastasis, surgery and chemotherapy may achieve curative outcomes in some cases (14, 19, 20). However, complete cancer cell removal is often unattainable, leading to disease recurrence in many patients (21). Although significant progress has been made in systemic and local therapies for aCRC, it remains rarely curable. Resistance to conventional treatments, systemic toxicity, and low selectivity highlight the need for more effective alternatives (13, 21, 22).
Immunotherapy has emerged as a promising approach, aiming to reverse tumor-induced immune suppression and activate antitumor responses (23). Immune checkpoints, such as programmed cell death 1 (PD-1), its ligand (PD-L1), and cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4), have been extensively studied because of their overexpression in many solid tumors and hematological malignancies (24, 25). Blocking the interaction between PD-1/PD-L1 or CTLA-4 and their ligands activates T cells, promoting tumor infiltration and cancer cell death (26, 27). In response, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) for patients with microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) or mismatch repair-deficient (dMMR) CRC. These cancers exhibit high mutation rates and a strong neoantigen burden, triggering robust T cell-mediated tumor immune responses (28–30). A recent study showed that 100% of 12 patients with advanced dMMR rectal cancer achieved a complete clinical and pathological response after six months of treatment with dostarlimab (31). However, ICIs have limited efficacy in proficient mismatch repair (pMMR), microsatellite-stable (MSS), or microsatellite instability-low (MSI-L) CRC, which account for 85% of cases (32, 33). Given the biological complexity of the tumor microenvironment (TME) in most solid tumors, a multi-checkpoint inhibition strategy seems logical (34). Since CTLA-4 and PD-1 target non-redundant pathways, combining inhibitors for both may provide additive or synergistic effects. Some clinical trials have reported improved outcomes with combined PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 blockade compared to monotherapy (35). However, other studies suggest that combining these inhibitors has shown limited success in treating CRC (36). Moreover, combined ICI therapy is associated with a higher incidence of adverse events compared to single-agent treatment (37). To address these uncertainties, we conducted a systematic meta-analysis of the existing literature to evaluate the efficacy and safety of combining PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors in CRC treatment.
2 Methods
2.1 Article searching
This meta-analysis was conducted in strict accordance with the guidelines outlined in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) checklist (38), which ensures comprehensive, transparent, and methodologically sound reporting of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. The study protocol has been registered with the International Platform of Registered Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Protocols (INPLASY) under Registration ID: INPLASY202480030.We performed a thorough search of online databases, including the Cochrane Library, Embase, and PubMed, for relevant clinical trials published up until April 13, 2024. The search terms included “anti-PD-1,” “anti-PD-L1,” “anti-CTLA-4,” “immune checkpoint inhibitors,” “colorectal cancer,” “CRC,” “mCRC,” and “aCRC.” Both free-text terms and Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) were used to search within titles and abstracts. Additionally, the reference lists of selected articles were screened to ensure comprehensive coverage. In cases of duplicate publications, the most comprehensive studies were selected for inclusion in the meta-analysis. Two authors independently extracted all relevant data, and any discrepancies were resolved through discussion and consensus.
2.2 Study selection
Obtained records were exported to EndNote software (Clarivate Analytics, Philadelphia, PA, USA).After removing the duplicate publications, two review authors independently reviewed the title/abstract of the articles according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Afterward, the same two authors screened the full-texts of the selected records, independently. Discrepancies were resolved by consulting a third author.
2.3 Eligibility criteria
Trials were included if the following criteria were met (1):patients with aCRC aged 18 years or older were enrolled; (2):a PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors with or without other standard treatments was given to one of the study arms; and (3):outcomes of interest in terms of efficacy (i.e. median overall survival [mOS], median progression-free survival [mPFS], objective response rate [ORR], disease control rate [DCR]),and safety (i.e.AEs and ≥ grade 3 AEs)were reported.
The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Non-advanced CRC included early, middle and locally advanced CRC; (2) animal experiments, cell research, reviews, meta-analyses,duplicates, case reports, or letters were not taken into consideration; and (3) studies with patient number less than 10 were excluded. Two investigators independently identified potential eligible articles through inclusion and exclusion criteria. Any disagreement regarding study inclusion was resolved between these two or with a third investigator.
2.4 Data extraction and quality assessment
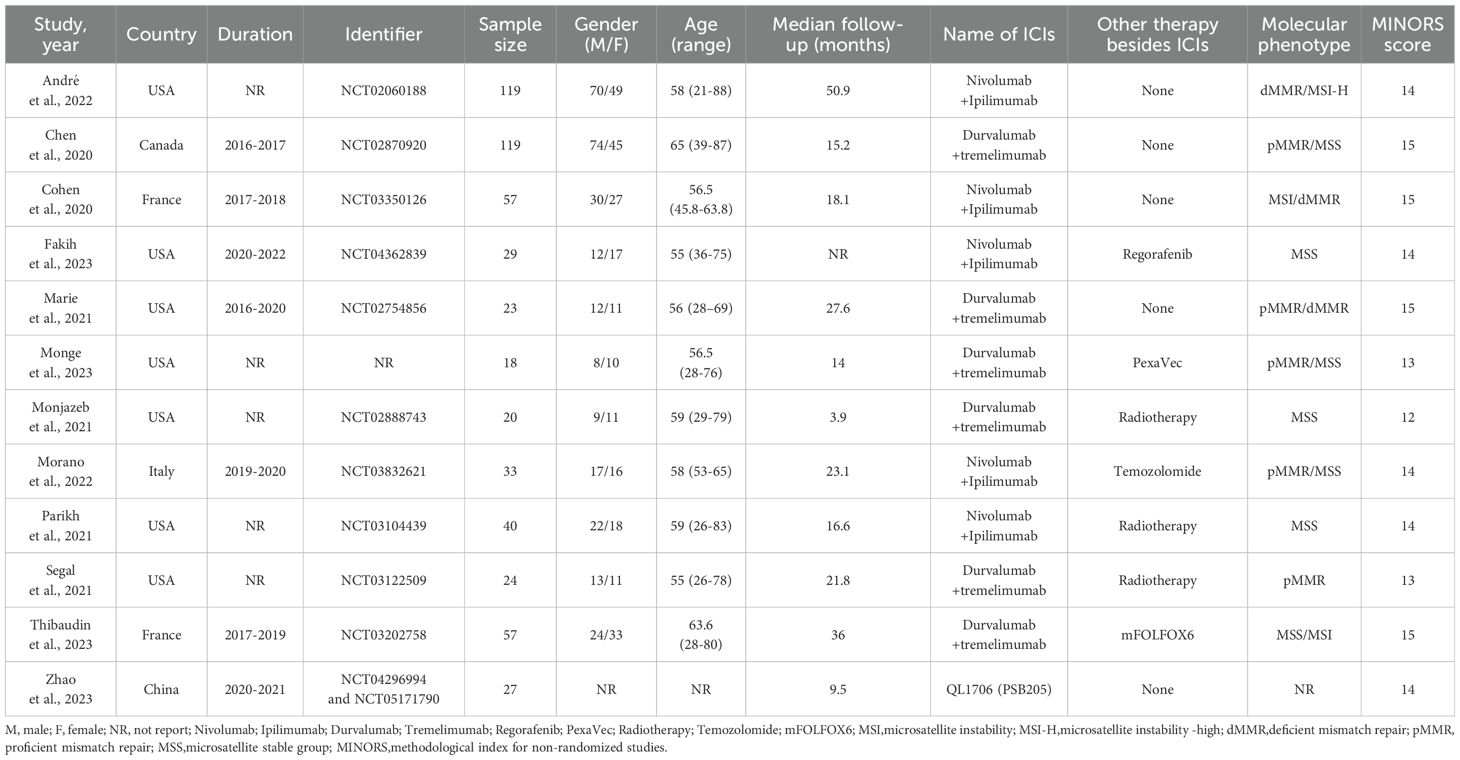
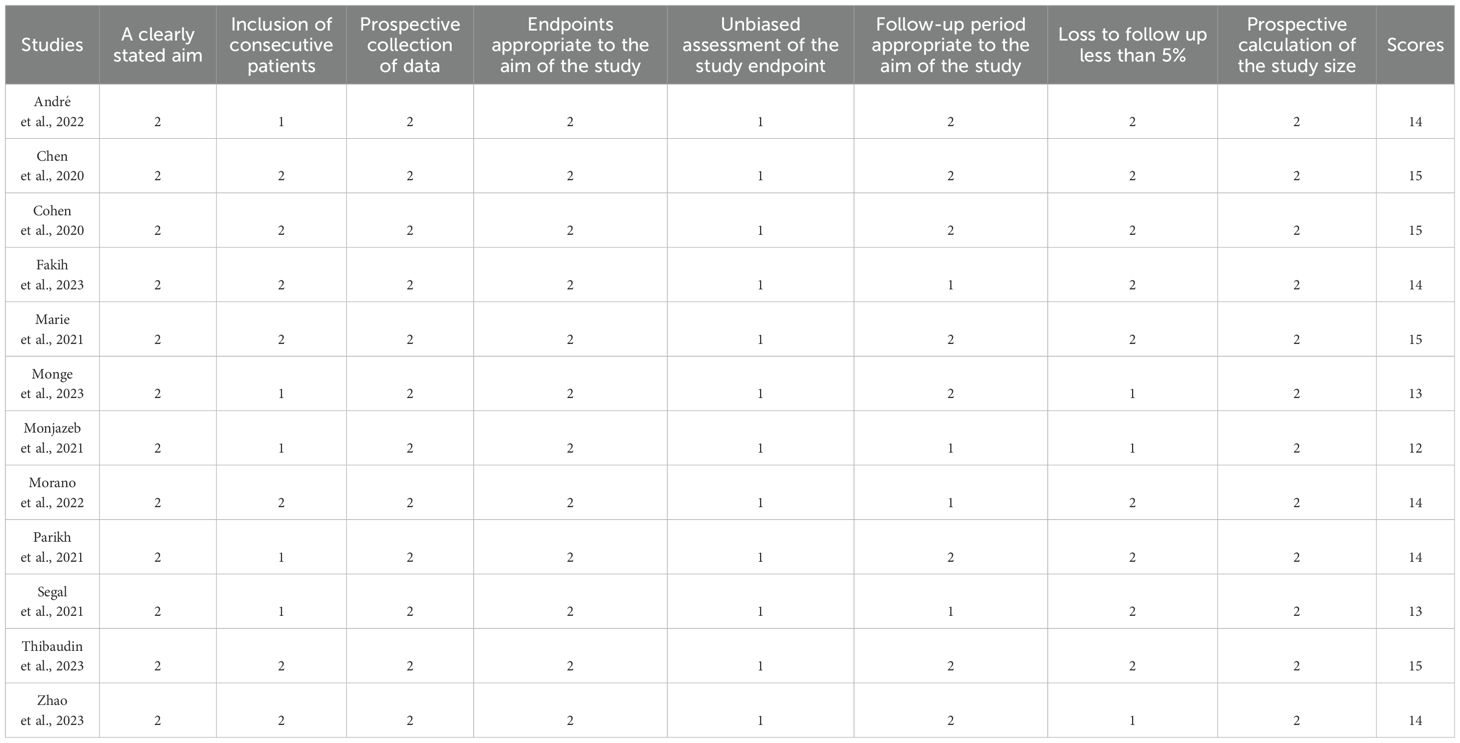
Two researchers conducted independent literature searches, following predetermined criteria and specified strategies. This approach ensures a thorough and unbiased exploration of available literature, utilizing a systematic and structured methodology. Meticulous data extraction was performed, encompassing essential details such as authors, publication year, country, trial duration, Identifier, sample size, gender, age, median follow-up, name of ICIs, Other therapy besides ICIs,molecular phenotype and survival analyses, including mOS, mPFS, DCR, ORR, AEs、≥ grade 3 AEs. All included studies were treated as non-randomized trials. The quality of each study was meticulously evaluated using the methodological index for non-randomized studies (MINORS) (39). Studies scoring above 12 points were considered high-quality indicators. This stringent evaluation ensures that only studies meeting robust methodological standards contribute to the overall analysis.
2.5 Data synthesis
The primary efficacy endpoint was to estimate the mOS and mPFS after receiving PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with CTLA-4 inhibitors treatment regimens and the secondary efficacy endpoint was to estimate the pooled rate of ORR and DCR. The safety outcome was the pooled rate of AEs and ≥ grade 3 AEs, We used Cochrane’s Q statistic to assess between-study heterogeneity and calculated the Isquare statistic. A random-effect model was applied if obvious heterogeneity was present (I2 >50%), otherwise, a fixed-effect model was chosen (40). The subgroup analysis was conducted according to country(USA, Other), sample(≥40, <40),other therapy(None,Yes), ICIs types (Nivolumab+Ipilimumab, Durvalumab+tremelimumab, QL1706 (PSB205)) and molecular phenotype (dMMR/MSI-H, pMMR/MSS, NR). Differences between groups were tested by the chi-square test. We used STATA version 18.0 (41) to calculate the pooled rates with metaprop command, which requires a nominator and a denominator (which is the total sample size) and some other options like random or fixed effects model. This command was built on the existing Stata command metan, which is routinely used to pool ratios and differences of means (42). A p-value less than 0.05 were treated as statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Study selection and characteristics of the included studies
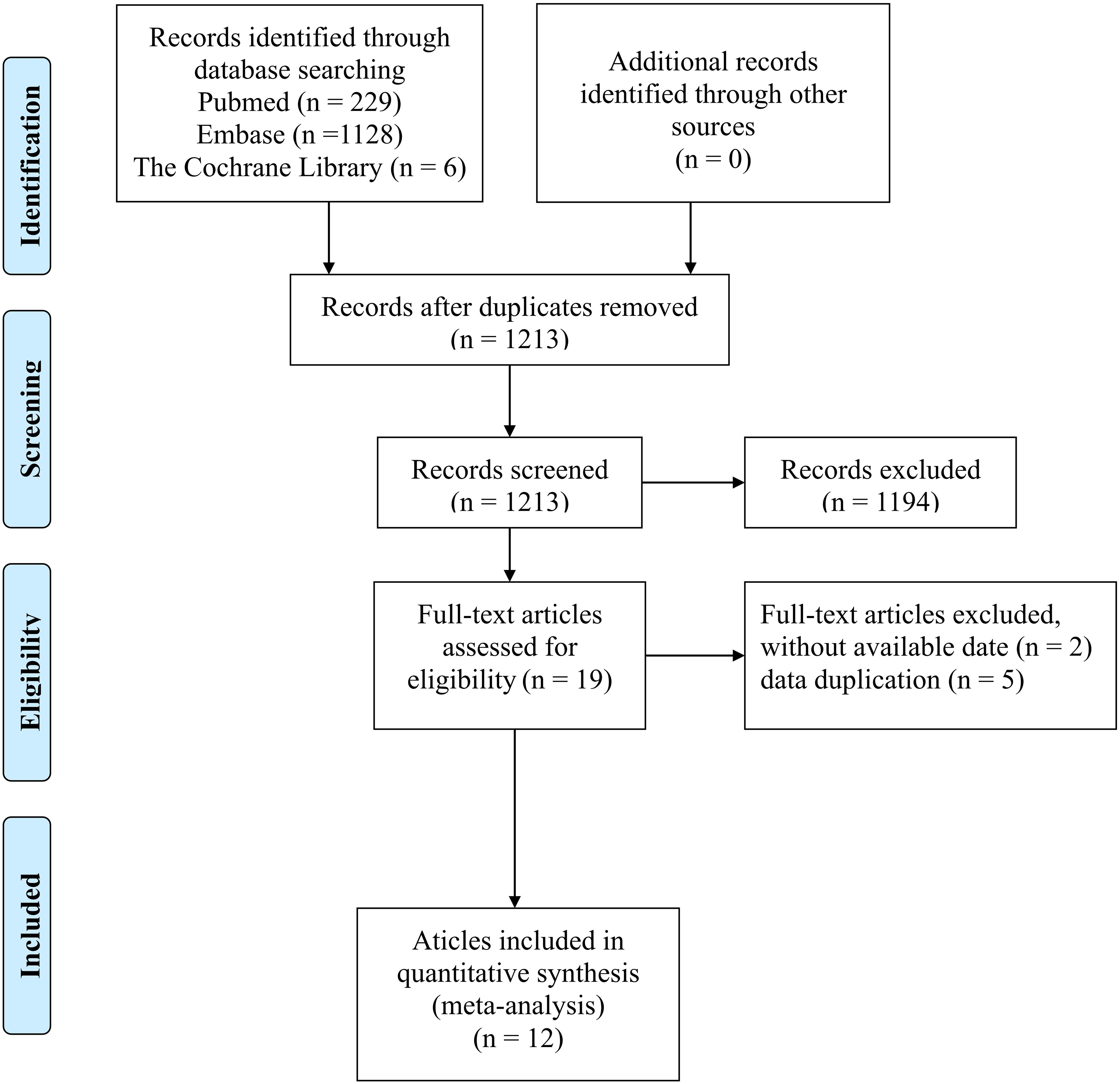
There were 1363 documents searched from the databases. Of these, 150 replicated studies were deleted. After reading the title and abstract of each article, 19 articles were screened out. The full texts of these articles were then assessed comprehensively. 12 articles (35, 36, 43–52)that meet the criteria were selected with a total of 566 patients. Figure 1 summarizes the detailed information about article selection. The 12 and 11 included studies were eligible for ORR and DCR, respectively. The 8 included studies were eligible for mPFS and adverse reaction data analysis, and of those, 6 were eligible for mOS data analysis. Table 1 lists the characteristics of the 12 trials. The extracted characteristics were summarized as follows: authors, publication year, country, trial duration, Identifier, sample size, gender, age, median follow-up, name of ICIs, Other therapy besides ICIs and molecular phenotype.
3.2 Quality assessment
12 non-randomized studies were assessed using the methodological index for non-randomized studies (MINORS), which categorized studies into three dimensions based on eight items, including stated aim, population election, endpoints, and prospective calculation. The quality assessment details are shown in Table 2.
3.3 Efficacy
3.3.1 Survival
5 studies with a total of 221 patients were included to determine the OS of patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor and CTLA-4 inhibitor. As shown in Figure 2A, the random-effect model meta-analysis illuminated that the pooled mOS was 6.66 months (95%CI: 4.85-9.16, I2 = 79.9%, P=0.001), suggesting that PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 immune checkpoint inhibitors achieved good mOS in the treatment of aCRC. We also analyzed the mPFS of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor and CTLA-4 inhibitor in advanced CRC. As shown in Figure 2B, the pooled mPFS of 340 patients in 8 studies was 2.92 months (95%CI: 2.23-3.83, I2 = 98.3%, P<0.0001). The result suggests that PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors and CTLA-4 inhibitors performed well in terms of mPFS in the treatment of aCRC. These results all indicate a PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors and CTLA-4 inhibitors are to the benefit of aCRC patients’ survival, as supported by the meta-analysis outcomes.
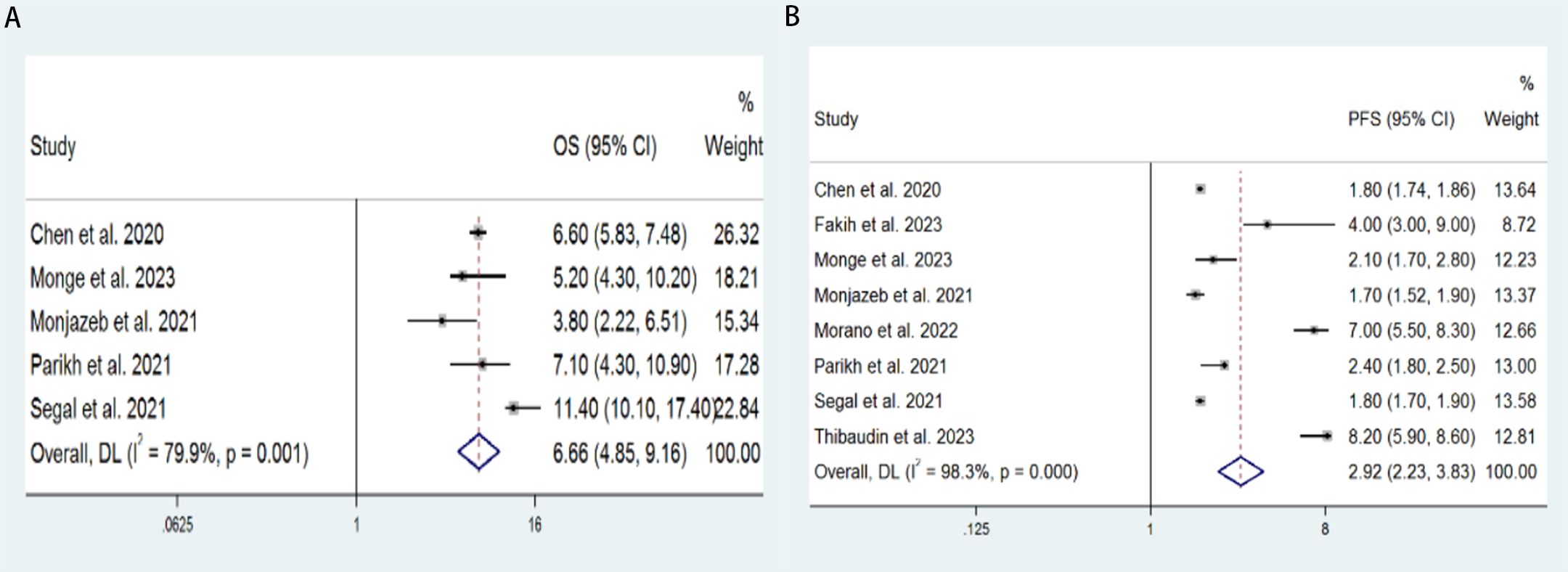
Figure 2. Forest plot for the (A) median overall survival (mOS) and (B) median progression-free survival (mPFS) in aCRC patients receiving PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with CTLA-4 inhibitors.
3.3.2 Response rates
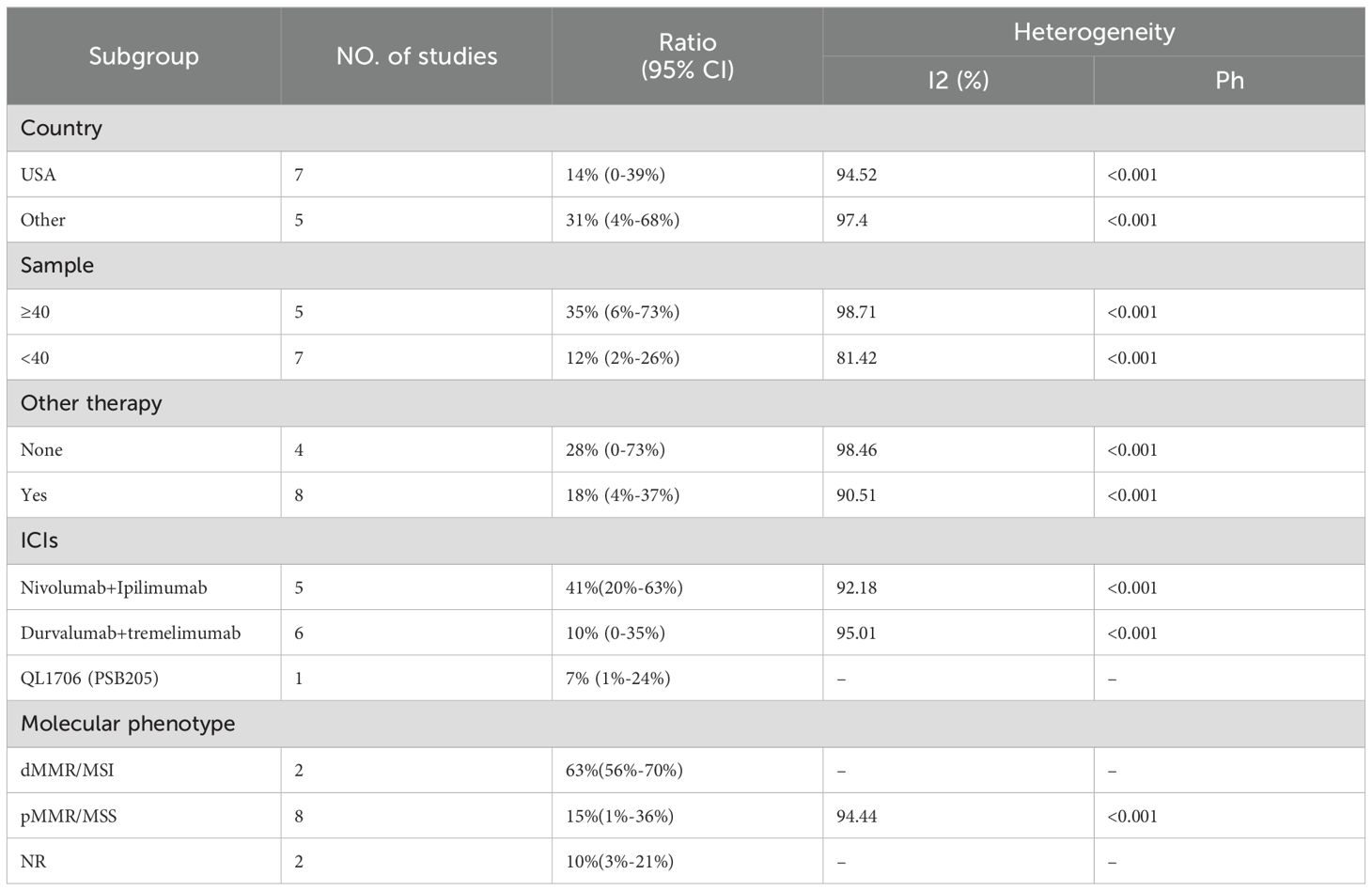
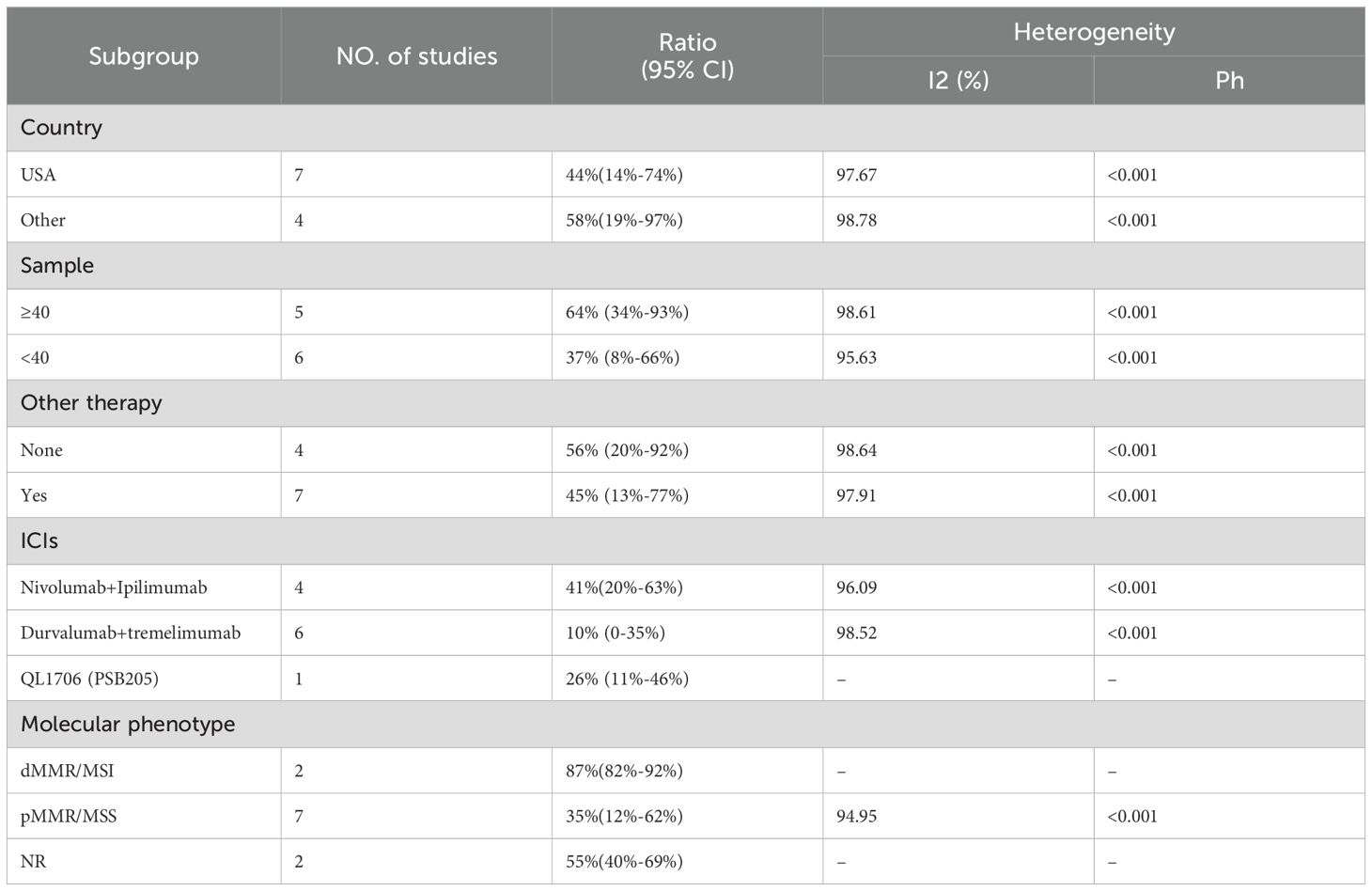
We included 12 studies with a total of 566 patients to assess the objective response rate (ORR). The pooled ORR was 21% (95% CI: 6%–41%, I² = 95.92%, P < 0.001, Figure 3A). For disease control rate (DCR), we pooled data from 11 studies involving 563 patients, resulting in a DCR of 49% (95% CI: 27%–71%, I² = 98.05%, P < 0.001, Figure 3B). Subgroup analyses were conducted based on country (USA vs. Other), sample size (≥40 vs. <40), additional therapy (None vs. Yes), type of immune checkpoint inhibitors (Nivolumab+Ipilimumab, Durvalumab+Tremelimumab, QL1706 [PSB205]), and molecular phenotype (dMMR/MSI-H vs. pMMR/MSS vs. NR) to further explore the efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors. As shown in Table 3, the ORR for patients treated in the USA was significantly lower compared to patients from other countries. Additionally, studies with sample sizes ≥40 reported better ORR than those with <40 samples. The subgroup of patients who did not receive additional therapies showed higher ORR compared to those who did. Furthermore, the combination of Nivolumab and Ipilimumab demonstrated a higher ORR than both Durvalumab+Tremelimumab and QL1706 (PSB205). The ORR for patients with dMMR/MSI-H was also higher than for those with pMMR/MSS. Similarly, the DCR followed the same pattern. More favorable outcomes were observed in patients from non-USA countries, in studies with sample sizes ≥40, in those not receiving other therapies, in patients treated with Nivolumab+Ipilimumab, and in those with dMMR/MSI-H (Table 4). These subgroup differences may be key sources of heterogeneity.
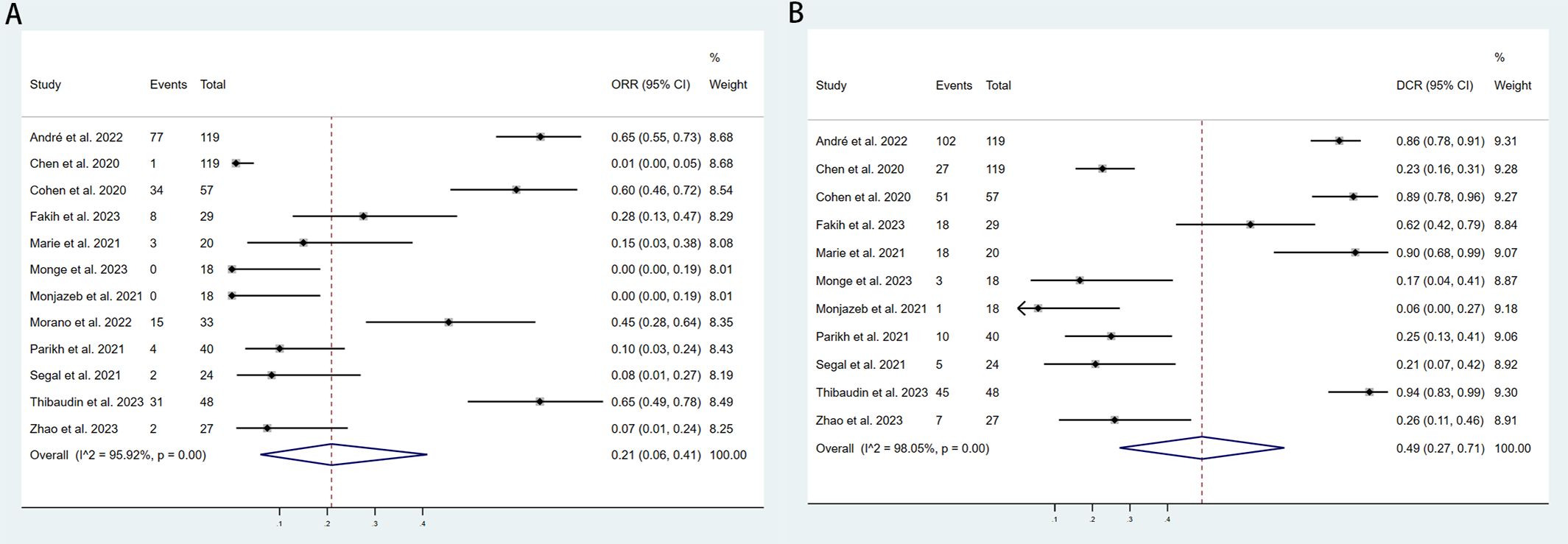
Figure 3. Forest plot for the (A) Objective response rate (ORR) and (B) Disease control rate (DCR) in aCRC patients receiving PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with CTLA-4 inhibitors.
3.4 Safety
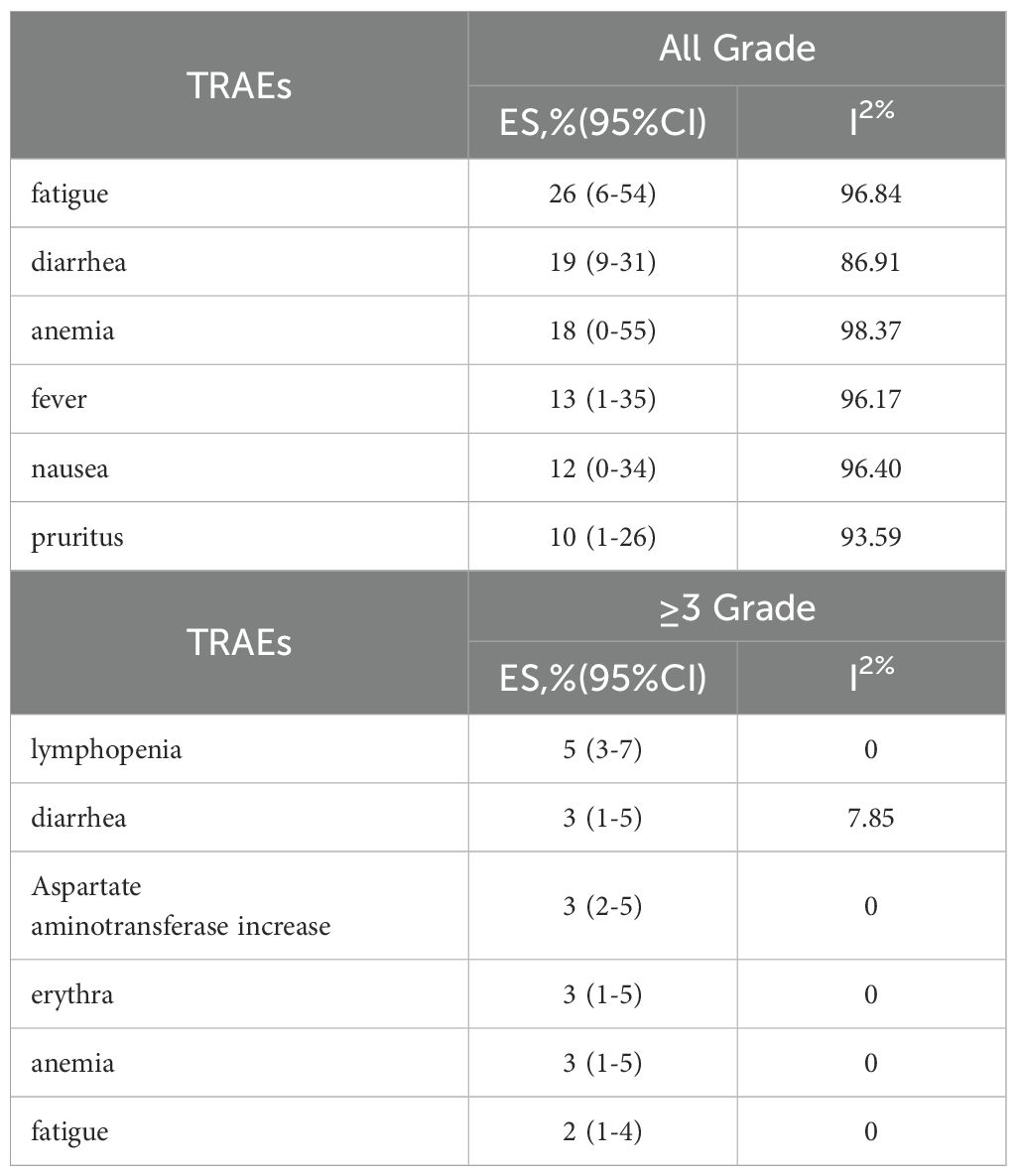
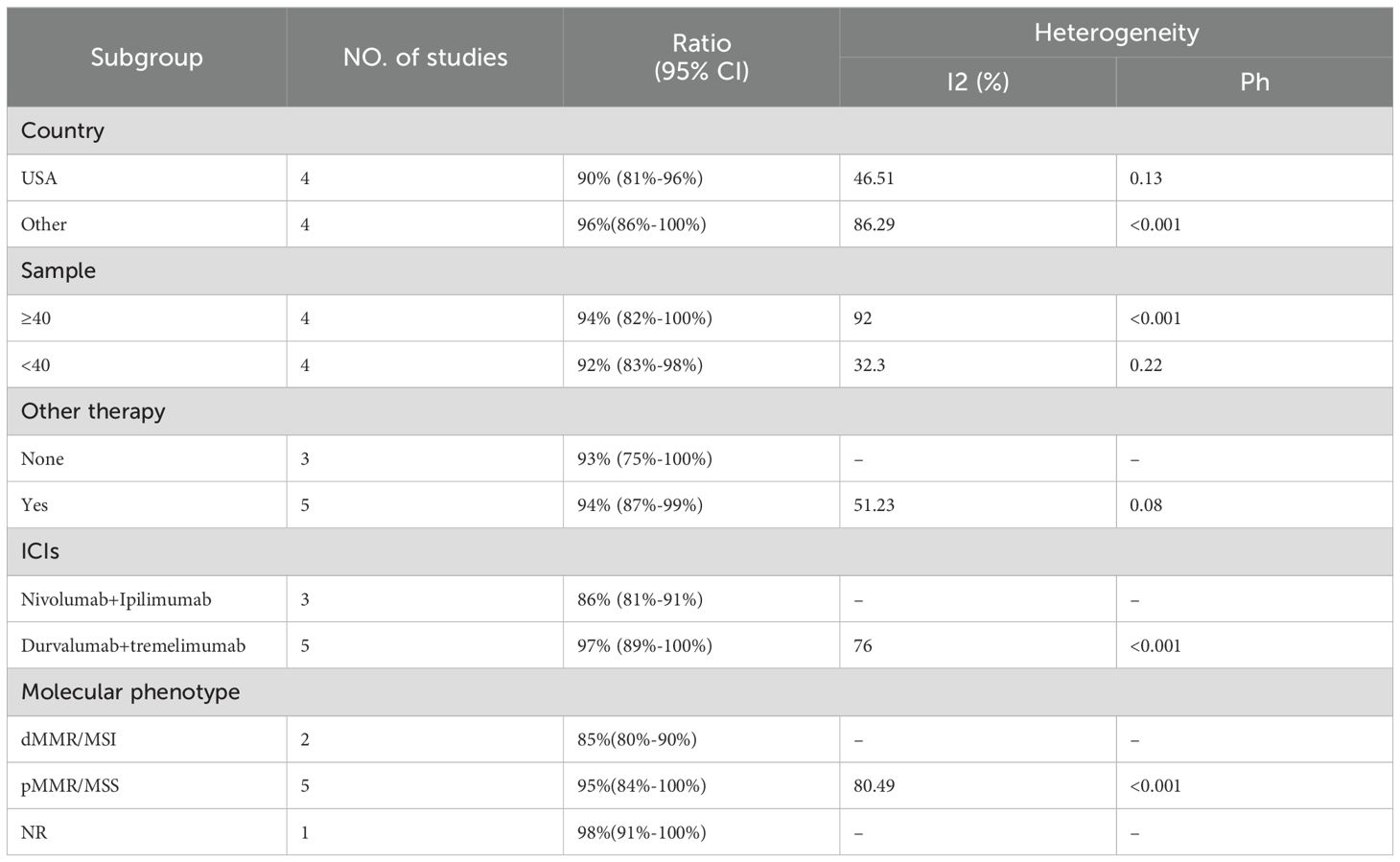
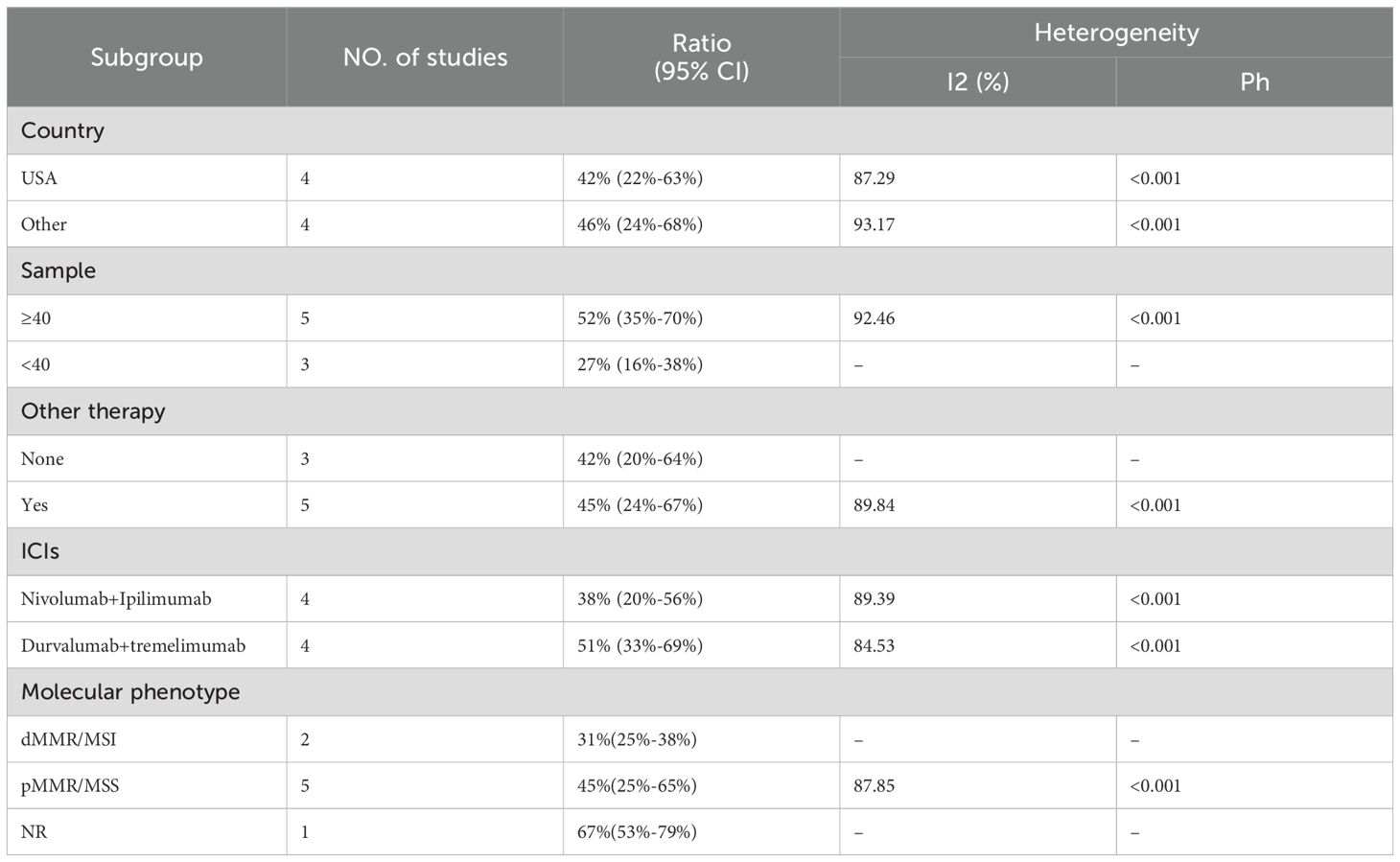
The adverse events (AEs) associated with the combination of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 and anti-CTLA-4 in treating aCRC were analyzed, including both all-grade AEs and ≥ grade 3 AEs. Most patients experienced grade 1–2 AEs, which were generally well tolerated. Data from 8 studies reported on the rates of any-grade AEs and ≥ grade 3 AEs. As shown in Figure 4, the pooled rate of all-grade AEs was 94% (95% CI: 86%–99%, I² = 84.02%, P < 0.001, Figure 4A), while the pooled rate of ≥ grade 3 AEs was 44% (95% CI: 30%–59%, I² = 90.47%, P < 0.001, Figure 4B). Table 5 and Supplementary Figures S1, S2 indicate that the three most commonly reported AEs were fatigue (26%, 95% CI: 6%–54%), diarrhea (19%, 95% CI: 9%–31%), and anemia (18%, 95% CI: 0%–55%). The most frequent ≥ grade 3 AEs were lymphopenia (5%, 95% CI: 3%–7%), diarrhea (3%, 95% CI: 1%–5%), and increased aspartate aminotransferase (3%, 95% CI: 2%–5%).Subgroup analyses of AEs and ≥ grade 3 AEs were conducted, as shown in Tables 6 and 7. The results suggested that country, sample size, additional therapies, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), and molecular phenotype were potential sources of heterogeneity. Patients in the USA had a lower incidence of both all-grade AEs (90% vs. 96%) and ≥ grade 3 AEs (42% vs. 46%) compared to those from other countries, with lower heterogeneity. Studies with sample sizes ≥ 40 reported higher rates of all-grade AEs (94% vs. 92%) and ≥ grade 3 AEs (52% vs. 27%) than those with sample sizes < 40. Additionally, patients receiving other therapies in combination with PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors had slightly higher rates of both all-grade AEs (94% vs. 93%) and ≥ grade 3 AEs (45% vs. 42%). The type of ICIs used also influenced AE rates: Nivolumab+Ipilimumab had a lower rate of all-grade AEs (86% vs. 97%) compared to Durvalumab+Tremelimumab, with similar trends observed for ≥ grade 3 AEs (38% vs. 51%). Finally, the pMMR/MSS molecular phenotype was associated with a higher incidence of all-grade AEs (95% vs. 85%) and a greater occurrence of ≥ grade 3 AEs (45% vs. 31%).
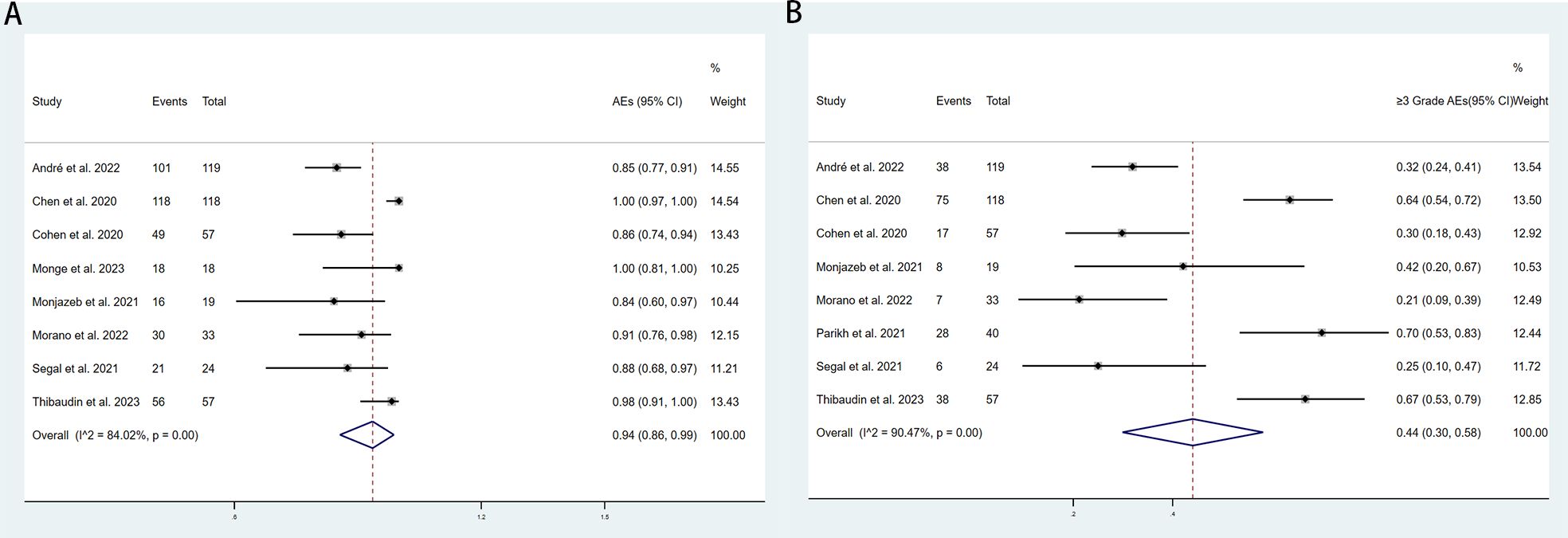
Figure 4. Forest plot for the (A) adverse events(AEs) rate and (B) and ≥grade 3 AEs rate in aCRC patients receiving PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with CTLA-4 inhibitors.
4 Discussion
Chemotherapy, cytotoxic drugs, and molecular targeted therapies have commonly been used in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer (aCRC), but their efficacy has plateaued (14, 53). Recently, numerous clinical trials related to immunotherapy have confirmed that it is an encouraging new treatment strategy for colorectal cancer (54–57). The two most widely studied immune checkpoints are PD-1 and CTLA-4. PD-1 is a cell surface receptor commonly found on T cells, B cells, and NK cells. When the PD-1 receptor binds to its ligand, it inhibits cell proliferation, cytokine secretion, and the cytotoxic capabilities of immune cells, thus weakening the immune response (58). CTLA-4 receptors, expressed on activated or regulatory T cells, bind to B7 ligands on antigen-presenting cells with a higher affinity and lower surface density. This binding prevents CD28 receptors from interacting with B7 ligands, leading to a net downregulation of T cell activation (59). A previous meta-analysis indicated that PD-1 inhibitors and combination immunotherapy demonstrate promising clinical responses and overall survival (OS) rates, alongside manageable adverse events (AEs) in the treatment of dMMR colorectal cancer (60). Although single-agent immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) perform well, one study noted that ICI therapy resistance has been observed in up to 50% of patients with microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) CRC. Furthermore, single-agent ICIs show minimal efficacy in patients with proficient mismatch repair (pMMR) or microsatellite stable (MSS) metastatic CRC (61, 62). To address tumor escape mechanisms, substantial efforts have been made to enhance the clinical efficacy of ICIs in colorectal cancer through combination therapies. Specifically, the combination of CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 blockade increases T cell activation and treatment efficacy, resulting in better antitumor outcomes (56, 63). Preclinical studies have shown that combined immunotherapy is superior to monotherapy. The dual blockade of PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 can increase the number of T cells regulated by multiple mechanisms and enhance their effector function (64). Currently, extensive research is being conducted to extend the indications for dual immune checkpoint blockade with PD-1 and CTLA-4 to various solid tumors (64, 65). However, the efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 immune checkpoint inhibitors in the treatment of aCRC remain largely unconfirmed. Twelve clinical trials involving 566 patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) have reported results for these agents. Therefore, we conducted a meta-analysis to provide valid and reliable conclusions. We compared the effectiveness and AEs of several therapy regimens involving PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 immune checkpoint inhibitors for potential clinical application. The pooled objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), and overall AE rate were 50%, 33%, 94%, and 44%, respectively. The pooled median overall survival (mOS) and median progression-free survival (mPFS) were 8.81 months and 2.57 months.
In order to further analyze the efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 immune checkpoint inhibitors, we performed subgroup analyses based on country (USA, Other), sample size (≥40, <40), other therapies (None, Yes), types of ICIs (Nivolumab+Ipilimumab, Durvalumab+tremelimumab, QL1706 (PSB205)), and molecular phenotypes (dMMR/MSI-H, pMMR/MSS, NR). In terms of country, the USA exhibited lower ORR and DCR, as well as fewer AEs and grade ≥3 AEs compared to other countries. Regarding sample size, when the sample size is ≥40, this may indicate higher ORR, DCR, and an increased incidence of AEs and grade ≥3 AEs. Concerning ICIs types, Nivolumab+Ipilimumab is considered to have higher efficacy and safety than Durvalumab+tremelimumab and QL1706 (PSB205). From the molecular phenotype perspective, the efficacy of dual ICIs in pMMR/MSS aCRC patients is lower than that in dMMR/MSI-H aCRC patients, while the incidence of adverse events may be higher. This discrepancy arises because MSI-H tumors typically have a high tumor mutation burden (TMB) and a high tumor neoantigen burden (TNB), which can activate the immune system more effectively. In contrast, MSS tumors have a lower mutation burden and generate relatively fewer neoantigens, reducing the likelihood of T cells recognizing and attacking tumor cells (4, 61). Notably, the combination of different treatment modalities is often believed to enhance therapeutic effects. However, our analysis yielded opposite results. When PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 immune checkpoint inhibitors are combined with other treatments (such as chemotherapy, radiotherapy, etc.), the ORR and DCR are significantly lower, and the risk of adverse effects is higher. This may be due to the limited number of studies that we did not categorize by different treatment regimens. However, a careful review of the literature reveals that the efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 immune checkpoint inhibitors combined with chemotherapy is better than the pooled results. Past studies have demonstrated that cytotoxic chemotherapy could reduce immunosuppressive T-regulatory cells, induce cell surface death receptor density to promote immune killing, and enhance the release of neoantigens in the microenvironment (66–68). In the Thibaudin study, a median PFS of 8.2 months and an objective response rate of 63% were reported for the treatment plan involving durvalumab and tremelimumab combined with mFOLFOX6, which compares favorably with FOLFOX monotherapy (44). This study supports the notion that chemo-immunotherapy could promote immune responses against shared tumor antigens and neoantigens in MSS metastatic CRC, with this immune response associated with therapeutic efficacy. In another study, temozolomide in combination with ipilimumab and nivolumab in patients with microsatellite stabilization achieved encouraging results, with median PFS and mOS of 7.0 and 18.4 months, respectively, and an overall response rate of 45% (47). This provides evidence of the role of temozolomide as an immune-sensitizing agent for MSS and immune-cold aCRCs. However, the combination of radiotherapy with CTLA-4 and PD-1 blockers for the treatment of aCRC was less than satisfactory. Although preclinical data suggest that radiation can induce tumor-specific immune responses (69), increase T-cell infiltration (70), and promote immune-mediated tumor cell death (71), clinical trials to date have not met their intended goals. In a study involving 40 aCRC patients receiving nivolumab and ipilimumab in combination with radiation therapy, Parikh observed a DCR of 25% and an ORR of 10% (48), significantly lower than those reported in previous studies that did not involve radiation therapy. Two other similar clinical trials combining PD-L1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors with radiation therapy in aCRC patients also failed to meet their predefined endpoints, although they noted that this treatment can enhance the immunogenicity of the local and systemic immune microenvironment (36, 49). In the future, more clinical trials are warranted to investigate the timing factors associated with radiation in immunotherapy and to identify appropriate radiation dosages (72, 73).
The results of this meta-analysis demonstrate that the combination of PD-1 inhibitors and CTLA-4 inhibitors has shown promising and profound clinical responses in clinical studies. The synergistic effect of combining PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors surpasses the sum of their individual contributions as monotherapies (74, 75). Thibaudin reported that the median progression-free survival (mPFS) for metastatic colorectal cancer treated with durvalumab and tremelimumab in combination with FOLFOX was 8.2 months, significantly higher than the mPFS of 5-6 months for FOLFOX alone and comparable to the mPFS of 8 months for the bevacizumab-combined chemotherapy regimen (44, 76). A previous meta-analysis of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in the treatment of aCRC suggested that the objective response rate (ORR) for dMMR/MSI-H aCRC was 37%, while that for pMMR/MSS aCRC was 11% (77). In our molecular phenotype subgroup analysis, the ORR for PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors combined with CTLA-4 inhibitors in dMMR/MSI-H aCRC was 63%, whereas in pMMR/MSS aCRC it was 18%, both significantly higher than the 37% and 11% observed for PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors alone, respectively. Treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) are associated with overactivation of the immune system, leading to damage to one or more organs. As expected, we observed that the incidence of TRAEs in patients receiving the combination of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 and anti-CTLA-4 therapy was higher compared to those receiving anti-PD-1/PD-L1 monotherapy (94% vs. 85%) (36, 77). Among the included studies, the highest incidence of grade ≥3 TRAEs was reported by Parikh (48). Notably, despite a high incidence of grade ≥3 TRAEs in this study, only a few patients discontinued treatment due to clinically relevant toxicity. Similar results were observed in other studies. Moreover, we found that grade ≥3 TRAEs often occurred in the early stages of treatment, and most TRAEs could be controlled and resolved with a short interruption of treatment and a brief course of oral steroid therapy (61, 78). Currently, the incidence of TRAEs is common in anti-PD-1/PD-L1 + anti-CTLA-4 combination therapy, although the pathogenesis is poorly understood (79). We believe that the occurrence of grade ≥3 TRAEs may be associated with drug dosage, treatment cycles, and the patients’ physical conditions. In anti-PD-1/PD-L1 + anti-CTLA-4 combination therapy, it is crucial to enhance monitoring of immunotherapy during treatment, pay attention to severe TRAEs, and manage them according to relevant guidelines.
5 Limitations
There are several limitations in the current meta-analysis. First, most studies had small sample sizes. Additionally, there is currently limited data on the combination therapy of PD-1 inhibitors and CTLA-4 inhibitors, and few studies are randomized or blinded. Second, we relied on published trial data but did not have access to raw patient data, which may introduce biases in our analysis. Therefore, more large-scale clinical trials are needed to further validate the efficacy and safety of the combination therapy of PD-1 inhibitors and CTLA-4 inhibitors. Third, it is crucial to identify the predominant factors influencing immunosuppressive therapy. Due to the limited experimental data, this study did not analyze the associations between gender, age, tumor mutation burden (TMB), tumor neoantigen burden (TNB), and the site of metastasis with treatment efficacy and safety.
6 Conclusion
In summary, our meta-analysis demonstrates the efficacy and safety of combination therapy with PD-1 inhibitors and CTLA-4 inhibitors in patients with aCRC, supporting its potential for future clinical application. However, due to the limited clinical data available, further large-scale, multicenter randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are necessary to confirm these findings.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
DS: Data curation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft. SH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. NM: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft. BY: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. JG: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by Servier. The funders had no role or input in the study itself.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1485303/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Buckowitz A, Knaebel HP, Benner A, Blaker H, Gebert J, Kienle P, et al. Microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer is associated with local lymphocyte infiltration and low frequency of distant metastases. Br J Cancer. (2005) 92:1746–53. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602534
2. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2018) 68:394–424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492
3. Arnold M, Sierra MS, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut. (2017) 66:683–91. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310912
4. Dekker E, Tanis PJ, Vleugels JLA, Kasi PM, Wallace MB. Colorectal cancer. Lancet. (2019) 394:1467–80. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32319-0
5. Baidoun F, Elshiwy K, Elkeraie Y, Merjaneh Z, Khoudari G, Sarmini MT, et al. Colorectal cancer epidemiology: recent trends and impact on outcomes. Curr Drug Targets. (2020) 22:998–1009. doi: 10.2174/1389450121999201117115717
6. Ionescu VA, Gheorghe G, Bacalbasa N, Chiotoroiu AL, Diaconu C. Colorectal cancer: from risk factors to oncogenesis. Medicina (Kaunas). (2023) 59(9):1646. doi: 10.3390/medicina59091646
7. Murphy CC, Zaki TA. Changing epidemiology of colorectal cancer - birth cohort effects and emerging risk factors. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2024) 21:25–34. doi: 10.1038/s41575-023-00841-9
8. Ranasinghe R, Mathai M, Zulli A. A synopsis of modern - day colorectal cancer: where we stand. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. (2022) 1877:188699. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2022.188699
9. Cronin KA, Scott S, Firth AU, Sung H, Henley SJ, Sherman RL, et al. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, part 1: national cancer statistics. Cancer. (2022) 128:4251–84. doi: 10.1002/cncr.34479
10. Kahi CJ, Boland CR, Dominitz JA, Giardiello FM, Johnson DA, Kaltenbach T, et al. Colonoscopy surveillance after colorectal cancer resection: recommendations of the us multi-society task force on colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. (2016) 150:758–68 e11. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.01.001
11. Venook AP, Niedzwiecki D, Lenz HJ, Innocenti F, Fruth B, Meyerhardt JA, et al. Effect of first-line chemotherapy combined with cetuximab or bevacizumab on overall survival in patients with kras wild-type advanced or metastatic colorectal cancer: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2017) 317:2392–401. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.7105
12. Stintzing S, Modest DP, Rossius L, Lerch MM, von Weikersthal LF, Decker T, et al. Folfiri plus cetuximab versus folfiri plus bevacizumab for metastatic colorectal cancer (Fire-3): A post-hoc analysis of tumour dynamics in the final ras wild-type subgroup of this randomised open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2016) 17:1426–34. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30269-8
13. Shin AE, Giancotti FG, Rustgi AK. Metastatic colorectal cancer: mechanisms and emerging therapeutics. Trends Pharmacol Sci. (2023) 44:222–36. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2023.01.003
14. Biller LH, Schrag D. Diagnosis and treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: A review. JAMA. (2021) 325:669–85. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.0106
15. Schmoll HJ, Van Cutsem E, Stein A, Valentini V, Glimelius B, Haustermans K, et al. Esmo consensus guidelines for management of patients with colon and rectal cancer. A personalized approach to clinical decision making. Ann Oncol. (2012) 23:2479–516. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mds236
16. Van Cutsem E, Cervantes A, Nordlinger B, Arnold D, Group EGW. Metastatic colorectal cancer: esmo clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. (2014) 25 Suppl 3:iii1–9. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu260
17. Yoshino T, Arnold D, Taniguchi H, Pentheroudakis G, Yamazaki K, Xu R-H, et al. Pan-Asian adapted esmo consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: A jsmo-esmo initiative endorsed by csco, kaco, mos, sso and tos. Ann Oncol. (2018) 29:44–70. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx738/4634047
18. Van Cutsem E, Cervantes A, Adam R, Sobrero A, Van Krieken JH, Aderka D, et al. Esmo consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. (2016) 27:1386–422. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw235
19. Vogel JD, Eskicioglu C, Weiser MR, Feingold DL, Steele SR. The American society of colon and rectal surgeons clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of colon cancer. Dis Colon Rectum. (2017) 60:999–1017. doi: 10.1097/DCR.0000000000000926
20. Cremolini C, Schirripa M, Antoniotti C, Moretto R, Salvatore L, Masi G, et al. First-line chemotherapy for mcrc-a review and evidence-based algorithm. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2015) 12:607–19. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2015.129
21. Ogura A, Konishi T, Cunningham C, Garcia-Aguilar J, Iversen H, Toda S, et al. Neoadjuvant (Chemo)Radiotherapy with total mesorectal excision only is not sufficient to prevent lateral local recurrence in enlarged nodes: results of the multicenter lateral node study of patients with low ct3/4 rectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2019) 37:33–43. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.00032
22. Gonzalez-Perera I, Gutierrez-Nicolas F, Nazco-Casariego GJ, Ramos-Diaz R, Hernandez-San Gil R, Perez-Perez JA, et al. 5-fluorouracil toxicity in the treatment of colon cancer associated with the genetic polymorphism 2846 a>G (Rs67376798). J Oncol Pharm Pract. (2017) 23:396–8. doi: 10.1177/1078155216647202
23. Yan Y, Zhang L, Zuo Y, Qian H, Liu C. Immune checkpoint blockade in cancer immunotherapy: mechanisms, clinical outcomes, and safety profiles of pd-1/pd-L1 inhibitors. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). (2020) 68:36. doi: 10.1007/s00005-020-00601-6
24. Seidel JA, Otsuka A, Kabashima K. Anti-pd-1 and anti-ctla-4 therapies in cancer: mechanisms of action, efficacy, and limitations. Front Oncol. (2018) 8:86. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00086
25. Robert C. A decade of immune-checkpoint inhibitors in cancer therapy. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:3801. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17670-y
26. Haanen JB, Robert C. Immune checkpoint inhibitors. Prog Tumor Res. (2015) 42:55–66. doi: 10.1159/000437178
27. Assunta Sgambato FC, Sacco PC, Palazzolo G, Maione P, Rossi A. Anti pd-1 and pdl-1 immunotherapy in the treatment of advanced non small cell lung cancer (Nsclc): A review on toxicity profile and its management. Curr Drug Saf. (2016) 11:62–8. doi: 10.2174/1574886311207040289
28. Cancer Genome Atlas N. Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature. (2012) 487:330–7. doi: 10.1038/nature11252
29. Maby P, Tougeron D, Hamieh M, Mlecnik B, Kora H, Bindea G, et al. Correlation between density of cd8+ T-cell infiltrate in microsatellite unstable colorectal cancers and frameshift mutations: A rationale for personalized immunotherapy. Cancer Res. (2015) 75:3446–55. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-3051
30. Stadler ZK, Battaglin F, Middha S, Hechtman JF, Tran C, Cercek A, et al. Reliable detection of mismatch repair deficiency in colorectal cancers using mutational load in next-generation sequencing panels. J Clin Oncol. (2016) 34:2141–7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.65.1067
31. Cercek A, Lumish M, Sinopoli J, Weiss J, Shia J, Lamendola-Essel M, et al. Pd-1 blockade in mismatch repair-deficient, locally advanced rectal cancer. N Engl J Med. (2022) 386:2363–76. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2201445
32. Kalyan A, Kircher S, Shah H, Mulcahy M, Benson A. Updates on immunotherapy for colorectal cancer. J Gastrointest Oncol. (2018) 9:160–9. doi: 10.21037/jgo.2018.01.17
33. Boland CR, Thibodeau SN, Hamilton SR, Sidransky D, Eshelman JR, Burt RW, et al. A national cancer institute workshop on microsatellite instability for cancer detection and familial predisposition: development of international criteria for the determination of microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. (1999) 59:249–56. doi: 10.1134/1.1601761
34. Guha P, Heatherton KR, O’Connell KP, Alexander IS, Katz SC. Assessing the future of solid tumor immunotherapy. Biomedicines. (2022) 10(3):655. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10030655
35. Chen EX, Jonker DJ, Loree JM, Kennecke HF, Berry SR, Couture F, et al. Effect of combined immune checkpoint inhibition vs best supportive care alone in patients with advanced colorectal cancer: the Canadian cancer trials group co.26 study. JAMA Oncol. (2020) 6:831–8. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.0910
36. Monjazeb AM, Giobbie-Hurder A, Lako A, Thrash EM, Brennick RC, Kao KZ, et al. A randomized trial of combined pd-L1 and ctla-4 inhibition with targeted low-dose or hypofractionated radiation for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27:2470–80. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-4632
37. Simmet V, Eberst L, Marabelle A, Cassier PA. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-based combinations: is dose escalation mandatory for phase I trials? Ann Oncol. (2019) 30:1751–9. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz286
38. Moher D LA, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the prisma statement. Open Med. (2009) 3:123–30. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000100
39. Karem Slim EN, Forestier D, Kwiatkowski F, panis Y, Chipponi J. Methodological index for non-randomized studies (Minors): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J Surg. (2003) 73:712–6. doi: 10.1046/j.1445-2197.2003.02748.x
40. Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Chandler J, Welch VA, Higgins JP, et al. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: A new edition of the cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2019) 10:ED000142. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000142
42. Nyaga VN, MarcArbyn, Aerts M. Metaprop: A stata commandtoperform meta-analysis of binomial data. Arch OF Public Health. (2014) 72(1):39. doi: 10.1186/2049-3258-72-39
43. Andre T, Lonardi S, Wong KYM, Lenz HJ, Gelsomino F, Aglietta M, et al. Nivolumab plus low-dose ipilimumab in previously treated patients with microsatellite instability-high/mismatch repair-deficient metastatic colorectal cancer: 4-year follow-up from checkmate 142. Ann Oncol. (2022) 33:1052–60. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.06.008
44. Thibaudin M, Fumet JD, Chibaudel B, Bennouna J, Borg C, Martin-Babau J, et al. First-line durvalumab and tremelimumab with chemotherapy in ras-mutated metastatic colorectal cancer: A phase 1b/2 trial. Nat Med. (2023) 29:2087–98. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02497-z
45. Fakih M, Sandhu J, Lim D, Li X, Li S, Wang C. Regorafenib, ipilimumab, and nivolumab for patients with microsatellite stable colorectal cancer and disease progression with prior chemotherapy: A phase 1 nonrandomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. (2023) 9:627–34. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.7845
46. Monge C, Xie C, Myojin Y, Coffman K, Hrones DM, Wang S, et al. Phase I/ii study of pexavec in combination with immune checkpoint inhibition in refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. J Immunother Cancer. (2023) 11(2):e005640. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-005640
47. Morano F, Raimondi A, Pagani F, Lonardi S, Salvatore L, Cremolini C. Temozolomide followed by combination with low-dose ipilimumab and nivolumab in patients with microsatellite-stable,O6-methylguanine–DNA methyltransferase–silenced metastatic colorectal cancer: the maya trial. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:1562–73. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.02583
48. Parikh AR, Szabolcs A, Allen JN, Clark JW, Wo JY, Raabe M, et al. Radiation therapy enhances immunotherapy response in microsatellite stable colorectal and pancreatic adenocarcinoma in a phase ii trial. Nat Cancer. (2021) 2:1124–35. doi: 10.1038/s43018-021-00269-7
49. Segal NH, Cercek A, Ku G, Wu AJ, Rimner A, Khalil DN, et al. Phase ii single-arm study of durvalumab and tremelimumab with concurrent radiotherapy in patients with mismatch repair-proficient metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27:2200–8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2474
50. Zhao Y, Ma Y, Zang A, Cheng Y, Zhang Y, Wang X, et al. First-in-human phase I/ib study of ql1706 (Psb205), a bifunctional pd1/ctla4 dual blocker, in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Hematol Oncol. (2023) 16:50. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01445-1
51. Cohen R, Bennouna J, Meurisse A, Tournigand C, de la Fouchardiere C, Tougeron D, et al. Recist and irecist criteria for the evaluation of nivolumab plus ipilimumab in patients with microsatellite instability-high/mismatch repair-deficient metastatic colorectal cancer: the gercor nipicol phase ii study. J Immunother Cancer. (2020) 8(2):e001499. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001499
52. Kanikarla Marie P, Haymaker C, Parra ER, Kim YU, Lazcano R, Gite S, et al. Pilot clinical trial of perioperative durvalumab and tremelimumab in the treatment of resectable colorectal cancer liver metastases. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27:3039–49. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0163
53. Weng J, Li S, Zhu Z, Liu Q, Zhang R, Yang Y, et al. Exploring immunotherapy in colorectal cancer. J Hematol Oncol. (2022) 15:95. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01294-4
54. Le DT, Durham JN, Smith KN, Wang H, Bartlett BR, Aulakh LK. Mismatch-repair deficiency predicts response of solid tumors to pd-1 blockade. Science. (2017) 357:409–13. doi: 10.1126/science.aan6733
55. Diaz LA Jr., Shiu KK, Kim TW, Jensen BV, Jensen LH, Punt C, et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for microsatellite instability-high or mismatch repair-deficient metastatic colorectal cancer (Keynote-177): final analysis of a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. (2022) 23:659–70. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00197-8
56. Overman MJ, Lonardi S, Wong KYM, Lenz HJ, Gelsomino F, Aglietta M, et al. Durable clinical benefit with nivolumab plus ipilimumab in DNA mismatch repair–deficient/microsatellite instability–high metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2018) 36:773–9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.76.9901
57. Heinz-Josef Lenz EVC, Limon ML, Wong KaYM, Hendlisz A, Aglietta M. First-line nivolumab plus low-dose ipilimumab for microsatellite instability-high/mismatch repair-deficient metastatic colorectal cancer: the phase ii checkmate 142 study. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:161–70. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.01015
58. Beatriz M, Carreno FB, Thu A, Chau V, Ling DL, Jussif J, et al. Ctla-4 (Cd152) can inhibit T cell activation by twoDifferent mechanisms depending on its level of cell surface expression1. J Immunol. (2000) 165:1352–6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.3.1352
59. Zou C, Qiu H, Tang W, Wang Y, Lan B, Chen Y. Ctla4 tagging polymorphisms and risk of colorectal cancer: A case-control study involving 2,306 subjects. Onco Targets Ther. (2018) 11:4609–19. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S173421
60. Chunhui Jin XZ, Huang X, Gong T, Wei Z, You J. Efficacy and safety of pd-1/pd-L1 and ctla-4 immune checkpoint inhibitors in colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. J Comp Eff Res. (2022) 11:203–12. doi: 10.2217/cer-2021-0134
61. Le DT, Uram JN, Wang H, Bartlett BR, Kemberling H, Eyring AD, et al. Pd-1 blockade in tumors with mismatch-repair deficiency. N Engl J Med. (2015) 372:2509–20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1500596
62. Refae S, Gal J, Ebran N, Otto J, Borchiellini D, Peyrade F, et al. Germinal immunogenetics predict treatment outcome for pd-1/pd-L1 checkpoint inhibitors. Invest New Drugs. (2020) 38:160–71. doi: 10.1007/s10637-019-00845-w
63. Chalabi M, Fanchi LF, Dijkstra KK, Van den Berg JG, Aalbers AG, Sikorska K, et al. Neoadjuvant immunotherapy leads to pathological responses in mmr-proficient and mmr-deficient early-stage colon cancers. Nat Med. (2020) 26:566–76. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0805-8
64. Chae YK, Arya A, Iams W, Cruz MR, Chandra S, Choi J, et al. Current landscape and future of dual anti-ctla4 and pd-1/pd-L1 blockade immunotherapy in cancer; lessons learned from clinical trials with melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer (Nsclc). J Immunother Cancer. (2018) 6:39. doi: 10.1186/s40425-018-0349-3
65. Gengwei Huo WL, Zhang S, Chen P. Efficacy of pd-1/pd-L1 plus ctla-4 inhibitors in solid tumors based on clinical characteristics: A meta-analysis. Immunotherapy. (2023) 15:189–207. doi: 10.2217/imt-2022-0140
66. Vanneman M, Dranoff G. Combining immunotherapy and targeted therapies in cancer treatment. Nat Rev Cancer. (2012) 12:237–51. doi: 10.1038/nrc3237
67. Zitvogel L, Kepp O, Kroemer G. Immune parameters affecting the efficacy of chemotherapeutic regimens. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2011) 8:151–60. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2010.223
68. Suzuki E, Kapoor V, Jassar AS, Kaiser LR, Albelda SM. Gemcitabine selectively eliminates splenic gr-1+/cd11b+ Myeloid suppressor cells in tumor-bearing animals and enhances antitumor immune activity. Clin Cancer Res. (2005) 11:6713–21. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0883
69. Sharabi AB, Nirschl CJ, Kochel CM, Nirschl TR, Francica BJ, Velarde E, et al. Stereotactic radiation therapy augments antigen-specific pd-1-mediated antitumor immune responses via cross-presentation of tumor antigen. Cancer Immunol Res. (2015) 3:345–55. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-14-0196
70. Klug F, Prakash H, Huber PE, Seibel T, Bender N, Halama N, et al. Low-dose irradiation programs macrophage differentiation to an inos(+)/M1 phenotype that orchestrates effective T cell immunotherapy. Cancer Cell. (2013) 24:589–602. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.09.014
71. Golden EB, Frances D, Pellicciotta I, Demaria S, Helen Barcellos-Hoff M, Formenti SC. Radiation fosters dose-dependent and chemotherapy-induced immunogenic cell death. Oncoimmunology. (2014) 3:e28518. doi: 10.4161/onci.28518
72. Monjazeb AM, Schoenfeld JD. Radiation dose and checkpoint blockade immunotherapy: unanswered questions. Lancet Oncol. (2016) 17:e3–4. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00541-0
73. Michael B, Foote GA, Rousseau B, Segal NH. Facts and hopes in colorectal cancer immunotherapy. Colorectal Cancer Immunother. (2023) 29:4032–9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-2176
74. Wei SC, Levine JH, Cogdill AP, Zhao Y, Anang NAS, Andrews MC, et al. Distinct cellular mechanisms underlie anti-ctla-4 and anti-pd-1 checkpoint blockade. Cell. (2017) 170:1120–33 e17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.024
75. Wei SC, Anang NAS, Sharma R, Andrews MC, Reuben A, Levine JH, et al. Combination anti-ctla-4 plus anti-pd-1 checkpoint blockade utilizes cellular mechanisms partially distinct from monotherapies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2019) 116:22699–709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1821218116
76. Loupakis F, Cremolini C, Masi G, Lonardi S, Zagonel V, Salvatore L, et al. Initial therapy with folfoxiri and bevacizumab for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. (2014) 371:1609–18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1403108
77. Li Y, Du Y, Xue C, Wu P, Du N, Zhu G, et al. Efficacy and safety of anti-pd-1/pd-L1 therapy in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. (2022) 22:431. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02511-7
78. Grimm MO, Oppel-Heuchel H, Foller S. Treatment with pd-1/pd-L1 and ctla-4 immune checkpoint inhibitors: immune-mediated side effects. Urol A. (2018) 57:543–51. doi: 10.1007/s00120-018-0635-1
Keywords: immune checkpoint inhibitors, colorectal cancer, immunotherapy, PD-1, PD-L1, CTLA-4
Citation: Song D, Hou S, Ma N, Yan B and Gao J (2024) Efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 immune checkpoint inhibitors in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 15:1485303. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1485303
Received: 23 August 2024; Accepted: 15 October 2024;
Published: 01 November 2024.
Edited by:
Guendalina Froechlich, University of Naples Federico II, ItalyCopyright © 2024 Song, Hou, Ma, Yan and Gao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jing Gao, MTU4NjY3Mjc3NzFAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Dandan Song
Dandan Song Shufu Hou
Shufu Hou Ning Ma
Ning Ma Bing Yan3
Bing Yan3