- 1Department of Sports Rehabilitation, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, China
- 2Department of General Surgery (Hepatopancreatobiliary surgery), The Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
- 3Academician (Expert) Workstation of Sichuan Province, Metabolic Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Diseases Key Laboratory of Luzhou City, The Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
- 4General Surgery Department, The TCM Hospital of Longquanyi, Chengdu, China
- 5Department of Pathology, Xichong People’s Hospital, Nanchong, China
- 6Department of Anesthesia, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, China
- 7Clinical Medical College, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, China
- 8Department of Oncology, Chongqing General Hospital, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China
Pancreatic cancer (PC) is a very aggressive digestive system tumor, known for its high mortality rate, low cure rate, low survival rate and poor prognosis. In particular, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PADC), which accounts for more than 90% of PC cases, has an overall 5-year survival rate of only 5%, which is an extremely critical situation. Early detection and effective treatment of PC is extremely difficult, which leads many patients to despair. In the current medical context, targeted therapy, as an important strategy for cancer treatment, is expected. However, the problems of immune escape and drug resistance in PC have become two major obstacles that are difficult to be overcome by targeted therapy. How to break through these two difficulties has become a key issue to be solved in the field of PC therapy. In recent years, non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) have continued to heat up in the field of cancer research. NcRNAs play a pivotal role in gene regulation, cell differentiation, development, and disease processes, and their important roles in the genesis, development, and therapeutic response of PC have been gradually revealed. More importantly, ncRNAs have many advantages as therapeutic targets, such as high specificity and low side effects, making them a new favorite in the field of PC therapy. Therefore, the aim of this paper is to provide new ideas and methods for the targeted therapy of PC by reviewing the mechanism of action of four major ncRNAs (circRNAs, lncRNAs, miRNAs, siRNAs) in both immune escape and drug resistance of PC. It is expected that an effective way to overcome immune escape and drug resistance can be found through in-depth study of ncRNA, bringing a ray of hope to PC patients.
1 Introduction
PC is a highly malignant tumor of the digestive system, characterized by high mortality, low cure rates, poor prognosis, and challenges in early detection and treatment (1, 2). Over 90% of PC cases are PADCs, which have an extremely high mortality rate and a 5-year overall survival rate of 5% (3, 4). Other PCs include pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma, cystic tumors, and endocrine pancreatic tumors, which have a lower incidence but may have a relatively better prognosis (5, 6). Approximately 65% of PC tumors are concentrated in the head of the pancreas., followed by those located in the head and tail of the pancreas (7).
Current treatments for PC include surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy (8). Surgery is the preferred treatment for PC, but due to late diagnosis, 80% of patients lose the opportunity for treatment (9, 10). Radiation and chemotherapy can alleviate symptoms and prolong the survival cycle, but have significant side effects and are rarely able to cure patients. Targeted therapy has been a major strategy in cancer treatment research, which has the effect of enhancing therapeutic efficacy and reducing side effects (11). Immunotherapy, like targeted therapy, can specifically target tumor cells, thereby improving therapeutic efficacy and reducing side effects (12). However, both immunotherapy and targeted therapy encounter two significant challenges: immune escape and drug resistance (13).
NcRNAs, i.e. non-coding RNAs, are a class of RNA molecules with no protein-coding function (14). They play an important regulatory role in cells, affecting a variety of life activities in organisms by regulating gene expression, chromatin structure, nuclear translocation, and protein function (15, 16). In recent years, ncRNAs have attracted much attention in the field of cancer research, and are believed to play an important role in the occurrence, development, and therapeutic response of cancer (17). Meanwhile, the targeted therapeutic roles of ncRNAs have also been gradually revealed in PC.
More importantly, ncRNAs have significant advantageous features in serving as therapeutic targets:
1. ncRNAs are highly specific in their expression in tumor tissues, which means that they may become biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and prognosis or novel targets for therapy (18);
2. ncRNAs affect cancer cell proliferation, differentiation, metastasis, and death through the modulation of gene expression processes (19), so that therapies targeting ncRNAs may directly intervene in cancer progression;
3. the regulatory network of ncRNAs is complex and diverse, which provides a wealth of candidate targets for cancer-targeted therapies.
In conclusion, ncRNAs have great potential and prospects in serving as PC therapeutic targets. So in summary, in this paper, we will review the functions and regulatory mechanisms of four major ncRNAs (circRNAs, lncRNAs, miRNAs, siRNAs) in both immune escape and drug resistance to help us better understand the pathogenesis of PC, and at the same time provide new ideas and approaches for PC targeted therapy and immunotherapy.
2 Classification, function of ncRNAs, and their biological mechanisms in diseases
NcRNAs play important roles in gene regulation, cell differentiation, development, and disease processes (20). NcRNAs can be categorized into a number of different types, including miRNAs, circRNAs, lncRNAs, and siRNAs, depending on their length, mode of formation, and function (21).
CircRNAs are abundant, stable RNA molecules with a closed-loop structure that is conserved (22), and usually consist of hundreds of nucleotides (23). They control gene transcription through interactions with RNA-binding proteins, and also regulate signaling pathways through miRNA segregation (24, 25). They have a variety of regulatory roles in the cell, including regulation of gene expression, participation in protein synthesis, etc. (26). CircRNAs can also act as “molecular sponges” for miRNAs, adsorbing and neutralizing miRNAs, thus regulating the inhibitory effects of miRNAs on target genes (27). Through the above mechanisms, CircRNAs continuously regulates the tumor microenvironment (TME) of PC, thereby affecting the occurrence and development of cancer cells.
MiRNAs are endogenous short non-coding RNAs of 19 to 25 nucleotides in size, which are part of the epigenome. MiRNAs regulate gene expression by binding to the mRNA’s 3′-untranslated region (3′-UTR) to either inhibit translation or promote degradation of target genes (28, 29). In the process of immunization against PDAC tumors, miRNAs regulate the recruitment and activation of immune cells to tumors (30, 31). At the same time, miRNAs can also act as oncogenes or oncogenes to participate in the genesis and development of PC (32).
LncRNAs are novel non-coding RNAs over 200 nucleotides in length and are key players in tumorigenesis and immune response (33, 34). They also have multiple regulatory roles in the cell, including regulation of gene expression, participation in cell differentiation, proliferation and apoptosis, etc. (35–37). LncRNAs can bind to proteins to form ribonucleoprotein complexes, thereby regulate the activity, localization and degradation of proteins, etc. (38–40). LncRNAs can also act as oncogenes or oncogenes in PCs to participate in the genesis and development of PCs (41). Like circRNAs, lncRNAs also have the function of sponging miRNAs to inhibit the abundance and activity of miRNAs (42).
SiRNAs are short interfering RNAs, usually consisting of 21-25 nucleotides (43). They are mainly used in cells to interfere with the replication and expression of exogenous viruses or transposons, and thus protect the cells from viral or transposon infection (44). SiRNAs can bind to exogenous mRNAs, induce their degradation, and thus inhibit their translation (45). Meanwhile, siRNAs can also be used to treat PC. By binding siRNAs to liposomes, siRNAs can be introduced into PC cells, which can inhibit the growth and spreading of PC cells (46).
PiRNAs are a unique class of non-coding RNAs, usually 21-35 nucleotides in length, related to the Piwi subfamily of Argonaute proteins in animals, especially in germline cells, used to suppress transposons and maintain genome integrity. Sex (47) (48). Compared to other ncRNAs such as miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs, their functions in cancer, including pancreatic cancer, are unclear. The main function of piRNA is to silence transposable elements through multiple mechanisms (49), including retrotransposons. By forming complexes with Piwi proteins, piRNAs can target transposon transcripts for degradation or translational repression, thereby limiting their proliferation and preventing their deleterious effects on the genome (50). This transposon silencing activity is critical for maintaining germline integrity and preventing genetic instability. In addition to their role in transposon silencing, piRNAs are also involved in other biological processes such as genesis, epigenetic regulation (51). Recent studies have also shown that piR-162725 may regulate the proliferation, migration and invasion phenotype of PADC, and may also regulate the EMT, cell differentiation and metabolism of PADC (52). However, the exact mechanisms and contributions of piRNAs to these processes remain largely unclear and are an active area of research.
In conclusion, ncRNAs play important regulatory roles in organisms; they can regulate gene expression levels, participate in protein synthesis, and regulate cell differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis. An in-depth understanding of the classification and biological mechanisms of ncRNAs can help to better understand their regulatory mechanisms in PC TIME.
3 NcRNAs are involved in the immune response of tumor cells
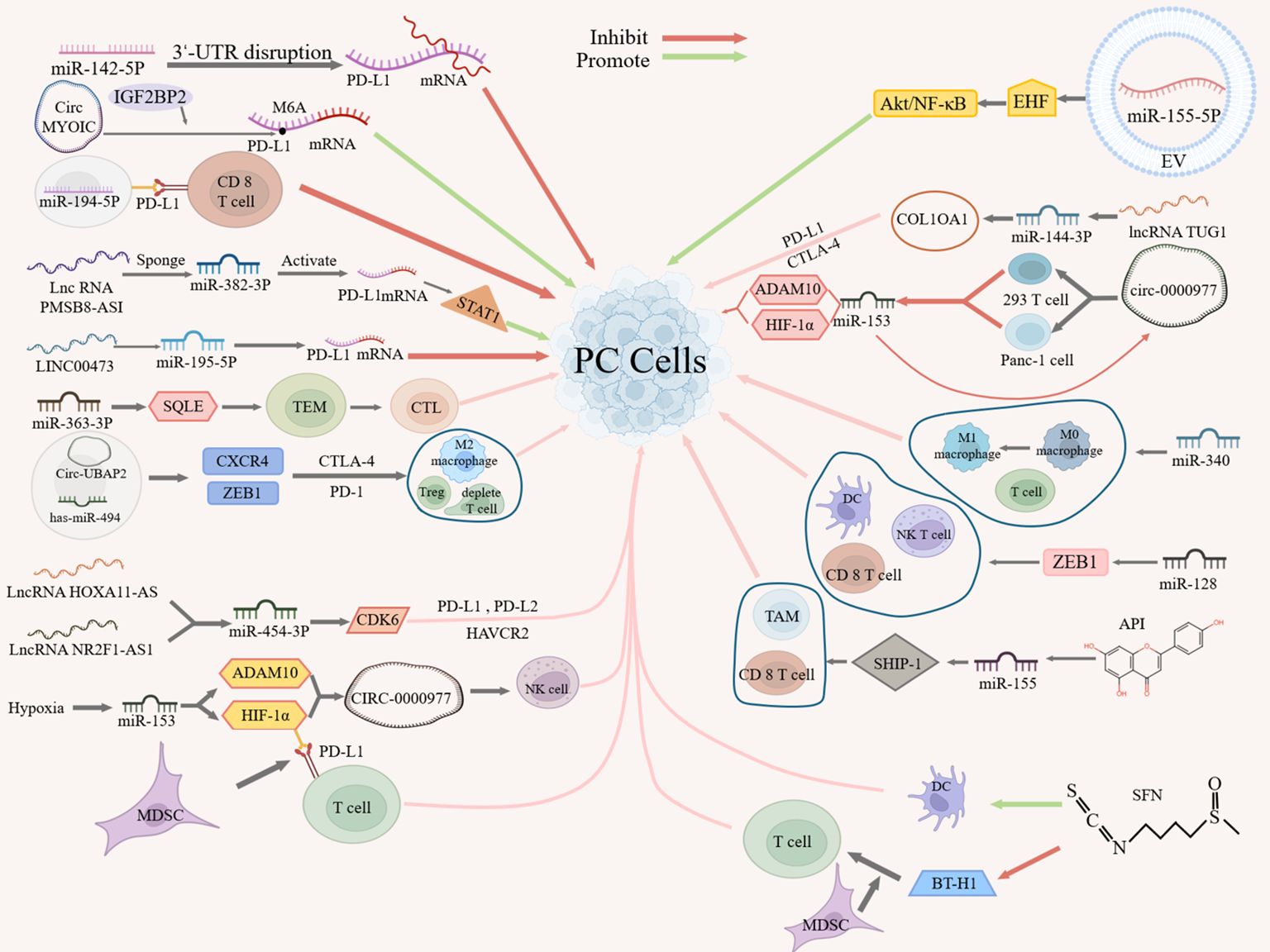
In TIME, tumor cells often evade immune cells, thus affecting the effect of immunotherapy. Understanding the mechanism of ncRNA’s action on immune escape in PC will help us better improve the effect of PC immunotherapy. Studies have shown that ncRNAs can mediate immune response through the following several mechanisms (Figure 1).
On the one hand, ncRNAs can affect the interaction between tumor cells and immune cells by targeting or regulating the expression or signaling of PD-L1, thereby suppressing immune response or inducing immune tolerance. For example, miR-142-5p can regulate PD-L1 expression in PC cells by binding to the 3’UTR of PD-L1 to promote tumor immune response (53). Similarly, circMYO1C can enhance the stability of PD-L1 mRNA by targeting the N6-methyladenosine(M6A) site of PD-L1 mRNA in conjunction with IGF2BP2, thereby accelerating the immune escape of PDAC (54). On the contrary, miR-194-5p enhances the toxic effect of CD8 T cells on PC cells by targeting PD-L1, thereby inhibiting the proliferation, migration and invasion of PC cells, but its specific mechanism of action remains to be investigated (55).In addition, lncRNAs can act as miRNA “molecular sponge” to target PD-L1 expression. For example, lncRNA PMSB8-AS1 acts as a miRNA sponge, which activates PD-L1 expression by interacting with and repressing miR-382-3p to regulate the transcription factor STAT1 to mediate immune escape (56). Similarly, as a miRNA sponge, LINC00473 silencing blocks PC progression by enhancing PD-L1 down-regulation against miR-195-5p (57).
Besides, some studies have shown that ncRNAs associate with immune checkpoints and indirectly influence the expression of other immune checkpoints (e.g., CTLA-4, PD-L2, HAVCR2, etc.), and may in this way mediate immune escape. For example, miR-363-3p can inhibit PANC-1 proliferation by regulating squalene epoxidase (SQLE) expression in PAAD, where SQLE regulates tumor immune cell infiltration, immune checkpoints, and the TME, and high SQLE expression predicts depletion of cytotoxic lymphocytes and loss of antitumor capacity (58). Therefore, miR-363 -3p may regulate immune checkpoints through SQLE and thus inhibit immune escape. A more definitive study has also shown that circ-UBAP2 and has-miR-494 may regulate the expression of CXCR4 and ZEB1, which are positively correlated with the expression of CTLA-4 and PD-1, and thus affect the levels of M2 macrophages, depleted T cells, and T regulatory cells (Tregs) in PAAD tissues (59), suggesting that circ-UBAP2 and has-miR-494 may regulate immune checkpoints through CXCR4 and ZEB1 factors, which in turn inhibit antigen presentation by PCs and promote immune escape. Additionally, lncRNA HOXA11-AS/lncRNA NR2F1-AS1 may regulate cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (CDK6) expression by targeting miR-454-3p, which may have oncogenic roles in PC and is strongly associated with multiple immune cells and cellular infiltration and three immune checkpoints (PD-L1, PD-L2 and HAVCR2) (60), suggesting that lncRNA HOXA11-AS/lncRNA NR2F1-AS1 may regulate immune checkpoints through the miR-454-3p- CDK6 axis, thereby mediating immune escape.
On the other hand, ncRNAs can affect the adaptation and immune escape ability of tumor cells in hypoxic microenvironments by targeting the expression or signaling of hypoxia-inducible factors (e.g., HIF-1α) or tumor suppressors. For example, hypoxia can inhibit immune escape by regulating miR-153 and its two targets, HIF-1α and ADAM10, which in turn promote the expression of CIRC-0000977, as well as by targeting PD-L1 via HIF-1α, which promotes myeloid-derived suppressor cell (MDSC)-involved T cell activation (61). CIRC_0000977 plays a role under hypoxia by regulating related pathways through miR-153, which subsequently affects the killing effect of NK cells on PC cells (61). In addition, PC-derived extracellular vesicle (EV) miR-155-5p can promote tumor immune escape by targeting the tumor suppressor EHF to downregulate, and activate Akt/NF-κB signaling (62).
In addition, ncRNAs can influence interactions in the TME by targeting components or structures of the extracellular matrix or by directly targeting cells, thereby mediating immune infiltration and immune escape. In PAAD, as a structural component of the extracellular matrix, X-type alpha 1 (COL10A1) expression was significantly up-regulated in PC tissues and significantly correlated with immune infiltration, and with immune checkpoints (PD-L1 and CTLA-4), whereas the lncRNA TUG1/miR-144-3p/COL10A1 axis was identified as the most promising upstream ncRNA regulatory pathway, suggesting that lncRNA TUG1/miR-144-3p may influence immune escape by targeting structural components of the extracellular matrix (63). In addition, cicr_0000977, a sponge of miR-153, counteracted the inhibitory effect of miR-153 on HIF-1α and ADAM10 by directly targeting 293T and Panc-1 cells, whereas miR-153 inhibition on HIF1A or cicr_0000977 knockdown on HIF1A-mediated immune escape from PC cells had the opposite effect, i.e. miR-153 inhibition partially attenuated the effect of cicr_0000977 knockdown (61). Similarly, miR-340 and miR-128 can enhance anti-tumor immunity by targeting immune cells. MiR-340 overexpression promotes macrophage(TAM) polarization to an M1-like phenotype in the peripheral and tumor-immune microenvironment, increases the number of T cells, especially CD8 T cells, contributing to the anti-tumor effects of miR-340, thereby counteracting immune escape (64). MiR-128 overexpression, in turn, modulates the percentages of dendritic cells (DCs), CD8 T lymphocytes, and natural killer T cells (NKTs) in tumors and spleens via PDAC zinc-finger E-box-binding homology cassette 1 (ZEB1) thereby enhancing anti-tumor immunity (65).
Moreover, bioflavonoids like apigenin (API) and sulforaphane (SFN) also play a significant role in regulating the immune response through their interaction with miRNAs. For example, API can promote the expression of inositol 5’-phosphatase-1 (SHIP-1) by inhibiting miRNA-155, which leads to the expansion of tumor-killing TAMs and CD8 T cells and promotes the anti-tumor immune response (66). On the other hand, SFN can enhance DC phagocytosis, and can also promote the immune response by decreasing the expression of B7-H1 and MDSC frequency in monocytes exposed to glioma-conditioned medium to reduce immunosuppression and promote T-cell proliferation (67). Among them, the reduction of B7-H1 expression not only relies on the down-regulation of STAT3 phosphorylation by SFN, but also on the up-regulation of miR-194-5p by SFN, but the miR-194-5p signaling pathway of miR-194-5p needs to be further investigated (67).
All in all, NcRNAs play a crucial role in the immune response. They can affect the immune response by influencing the activity, function and proliferation of immune cells in a variety of ways. A deeper understanding of ncRNAs will help us better understand the working mechanism of the immune system and may provide new targets for future immunotherapy and drug development. However, we still have many unanswered questions about the role of ncRNAs in immune cell regulation that require further research and exploration.
4 NcRNA and drug resistance
In the last 3 years, a large number of ncRNAs have been found to be involved in PC drug resistance, promoting or inhibiting the resistance of tumor cells to chemotherapeutic drugs. These findings suggest that ncRNAs may become novel targets for PC immunotherapy (Table 1).
MiRNAs play an important regulatory role in PC drug resistance. For instance, miR-3173-5p, which originates from cancer-associated fibroblast (CAF) exosomes in PADC, mediates gemcitabine (GEM) resistance in PC by targeting ACSL4 (68). Interestingly, miR-3173-5p also can inhibit iron death, resulting in the emergence of GEM resistance in PCs (68). Additionally, it is found that targeting inhibition of miR-378 or glucocorticoid receptor signaling can reduce PDAC glucocorticoid resistance (69).
In addition, lncRNA-miRNA interactions influence PC resistance, e.g., the lncRNA DSCR9, which is significantly down-regulated in PAAD, targets BTG2 by binding to miR-21-5p, which in turn affects PC proliferation, invasion, and GEM resistance (70). Similarly, lncRNA GAS2, significantly down-regulated in GEM-resistant PAN-5 and CaPa-1 cells, may regulate GEM resistance in PC through miR-21; however, its specific mechanism of action remains unclear (71). In addition, lncRNA SH3BP5-AS1, which is up-regulated in GEM-resistant PC cells, activates the expression of CTBP1 in Wnt pathway through competitive binding of ceRNA to miR-139-5p, which promotes GEM-resistant PC cells and tumor invasiveness (72).Moreover, Glycolysis-related LINC 02432 up-regulated in PAAD predicts the activity of PAAD patients against EGFR、MEK and ERK inhibitors by regulating hsa-miR-98-5 p/hexokinase 2 (HK2) axis (73). Besides, up-regulated lncRNA UPK 1A-AS 1 in PC promotes DNA double-strand break repair by regulating the interaction between repair proteins Ku 70 and Ku 80, thus conferring paril-IL 8-dependent oxaliplatin resistance derived from CAF (74). In addition to interacting with miRNAs, LINC00460 also regulates CAF proliferation through the PDAP1/PDGFA/PDGFR signaling pathway, thereby mediating GEM resistance in PADC cells (75).
Ibid, circRNAs also play an important role in PC GEM resistance. CircACTR2 expression is significantly down-regulated in GEM-resistant PC cells, whereas its overexpression can target the PTEN-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway via sponge miR-3-221p to reverse the chemoresistance of PC cells to GEM (76). Similarly, Hsa_circ_0007401, which is down-regulated in PC-resistant cells, acts as a “sponge” of has-miR-6509-3p and thus regulates differential messenger RNA (DEmRNA) (FLI1) to mediate PC GEM resistance (77).
In addition to this, siRNAs are also involved in the regulation of PC drug resistance. SiRNA or lentiviral sh-mediated down-regulation of collagen COL8A1 in PDAC cells inhibited tumor growth, migration, invasion, and GEM resistance (78). It is also found that a ferrous organometallic framework based nanoparticles (FMN) catalyzes the iron-dependent Fenton reaction and inhibits siSLC7A11-mediated upstream glutathione synthesis to carry out intracellular self-amplified iron death, which results in a reduction of DOX-retained P-glycoprotein activity and modulation of Bcl-2/Bax expression to reverse apoptosis-resistant state of tumor cells and promote drug sensitivity (79).
5 Discussion
Above, we revealed the role of four major ncRNAs (circRNAs, lncRNAs, miRNAs, and siRNAs) in the PC immune microenvironment in terms of both immune response and drug resistance, indicating that ncRNAs are expected to be novel potential targets for PC targeting and immunotherapy. And currently, the function and application of ncRNAs are still advancing rapidly. A recent study also synthesized a TME stimulation-responsive poly(beta-amino ester)s (PBAE)-based polymer nano-prodrug (miR-21i@HA-Gem-SS-P12), which can co-deliver miR-21 siRNA and GEM to achieve the combination therapy of miR-21 siRNA and GEM, and shows excellent tumor inhibitory effect in vitro and in vivo in PDAC (80). Therefore, it is just around the corner for ncRNA to become the target of PC immunotherapy.
Nevertheless, there are still many challenges and problems in the practical research and application of ncRNAs. For instance, the stability, selectivity, and specificity of ncRNAs in vivo require further improvement. Additionally, the interactions between ncRNAs and tumor-associated immune cells need to be more clearly understood—such as how miR-194-5p targets PD-L1 to regulate immune cells (55). Further exploration is also needed on the synergistic or antagonistic effects between ncRNAs and other signaling pathways.
Therefore, this paper suggests that future research should be deepened and expanded in the following aspects:
1. Development of Advanced Detection and Analysis Methods: Establish more precise and effective ncRNA detection and analysis techniques to enhance their diagnostic and prognostic value in PC;
2. Elucidation of ncRNA-Immune Cell Interactions: Delve deeper into the mechanisms of ncRNA-tumor-associated immune cell interactions to optimize their synergistic effects in PC immunotherapy;
3. Exploration of ncRNA-Signaling Pathway Crosstalk: Investigate the intricate interplay between ncRNAs and other signaling pathways to refine strategies for comprehensive PC therapy.
By focusing on these key aspects, we can harness the full potential of ncRNAs in the fight against pancreatic cancer.
Author contributions
YG: Writing – original draft. DG: Writing – original draft. SL: Writing – original draft. XG: Writing – original draft. JX: Writing – original draft. JZ: Writing – original draft. LJ: Writing – original draft. JL: Writing – original draft. LZ: Writing – original draft. HL: Writing – original draft. KX: Writing – review & editing. XY: Writing – review & editing. BL: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Key Research and Development Project of the Science & Technology Department of Sichuan Province (Nos.2023YFQ0101), and was supported by Luzhou Key Research and Development Project in Science and Technology (2022-SYF-55).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Hao S, Han W, Ji Y, Sun H, Shi H, Ma J, et al. BANCR positively regulates the HIF-1α/VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 pathway in a hypoxic microenvironment to promote lymphangiogenesis in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol Lett. (2022) 24:422. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13542
2. Miao Y. The effect of comfort care on postoperative quality of life, psychological status, and satisfaction of pancreatic cancer patients. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2022) 2022:9483762. doi: 10.1155/2022/9483762
3. Park HR. Pancastatin A and B have selective cytotoxicity on glucose-deprived PANC-1 human pancreatic cancer cells. J Microbiol Biotechnol. (2020) 30:733–8. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2002.02002
4. Chi H, Su L, Yan Y, Gu X, Su K, Li H, et al. Illuminating the immunological landscape: mitochondrial gene defects in pancreatic cancer through a multiomics lens. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1375143. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1375143
5. Hiyoshi M, Kai K, Hamada T, Yano K, Imamura N, Nanashima A. Curative remnant total pancreatectomy for recurrent pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma: A case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. (2022) 94:107091. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2022.107091
6. Buchsbaum DJ, Croce CM. Will detection of microRNA biomarkers in blood improve the diagnosis and survival of patients with pancreatic cancer? Jama. (2014) 311:363–5. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.284665
7. Nie D, Lan Q, Shi B, Xu F. Survival outcomes of surgical and non-surgical treatment in elderly patients with stage I pancreatic cancer: A population-based analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). (2022) 9:958257. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.958257
8. Moreau M, Ibeh U, Decosmo K, Bih N, Yasmin-Karim S, Toyang N, et al. Flavonoid derivative of cannabis demonstrates therapeutic potential in preclinical models of metastatic pancreatic cancer. Front Oncol. (2019) 9:660. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00660
9. Lee BM, Chung SY, Chang JS, Lee KJ, Seong J. The neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio are prognostic factors in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer treated with chemoradiotherapy. Gut Liver. (2018) 12:342–52. doi: 10.5009/gnl17216
10. Zheng L, Zhang B, He X, Cao G, Li Y, Cai K, et al. A new fusion peptide targeting pancreatic cancer and inhibiting tumor growth. Onco Targets Ther. (2020) 13:7865–75. doi: 10.2147/ott.S246969
11. Liu F, Chen B, Chen W, Chen S, Ma D, Xie M. Preparation of FA-targeted magnetic nanocomposites co-loading TFPI-2 plasmid and cis-platinum and its targeted therapy effects on nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Med Sci. (2021) 18:2355–65. doi: 10.7150/ijms.52643
12. Chiriva-Internati M, Mirandola L, Figueroa JA, Yu Y, Grizzi F, Kim M, et al. Selective expression and immunogenicity of the cancer/testis antigens SP17, AKAP4 and PTTG1 in non-small cell lung cancer: new candidates for active immunotherapy. Chest. (2014). doi: 10.1378/chest.13-0770
13. Yu J, Chen Y, Pan X, Wen W. Relationships of ferroptosis and pyroptosis-related genes with clinical prognosis and tumor immune microenvironment in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:3713929. doi: 10.1155/2022/3713929
14. Chen X, Peng H, Yin Z. Current computational models for prediction of the varied interactions related to noncoding RNAs. BioMed Res Int. (2016) 2016:4183574. doi: 10.1155/2016/4183574
15. Pelia R, Venkateswaran S, Matthews JD, Haberman Y, Cutler DJ, Hyams JS, et al. Profiling non-coding RNA levels with clinical classifiers in pediatric Crohn's disease. BMC Med Genomics. (2021) 14:194. doi: 10.1186/s12920-021-01041-7
16. Enfield KS, Pikor LA, Martinez VD, Lam WL. Mechanistic roles of noncoding RNAs in lung cancer biology and their clinical implications. Genet Res Int. (2012) 2012:737416. doi: 10.1155/2012/737416
17. Liang Y, Song X, Li Y, Ma T, Su P, Guo R, et al. Targeting the circBMPR2/miR-553/USP4 axis as a potent therapeutic approach for breast cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2019) 17:347–61. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.05.005
18. Powrózek T, Ochieng Otieno M. Blood circulating non-coding RNAs for the clinical management of triple-negative breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14:803. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030803
19. Goto K, Roca Suarez AA, Wrensch F, Baumert TF, Lupberger J. Hepatitis C virus and hepatocellular carcinoma: when the host loses its grip. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:3057. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093057
20. Sufianov A, Bessonova M, Begliarzade S, Kudriashov V, Danilov A, Ilyasova T, et al. Studies on the role of non-coding RNAs in controlling the activity of T cells in asthma. Noncoding RNA Res. (2023) 8:211–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2023.02.004
21. Bhogireddy S, Mangrauthia SK, Kumar R, Pandey AK, Singh S, Jain A, et al. Regulatory non-coding RNAs: a new frontier in regulation of plant biology. Funct Integr Genomics. (2021) 21:313–30. doi: 10.1007/s10142-021-00787-8
22. Shi Y, Tian Y, Sun X, Qiu Y, Zhao Y. Silencing circOMA1 Inhibits Osteosarcoma Progression by Sponging miR-1294 to Regulate c-Myc Expression. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:889583. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.889583
23. Sun J, Yin A, Zhang W, Lv J, Liang Y, Li H, et al. CircUBAP2 Inhibits Proliferation and Metastasis of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma via Targeting miR-148a-3p/FOXK2 Pathway. Cell Transplant. (2020) 29:963689720925751. doi: 10.1177/0963689720925751
24. Luo Q, Fu B, Zhang L, Guo Y, Huang Z, Li J. Expression and clinical significance of circular RNA hsa_circ_0079787 in the peripheral blood of patients with axial spondyloarthritis. Mol Med Rep. (2020) 22:4197–206. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11520
25. Zhang S, Cheng J, Quan C, Wen H, Feng Z, Hu Q, et al. circCELSR1 (hsa_circ_0063809) Contributes to Paclitaxel Resistance of Ovarian Cancer Cells by Regulating FOXR2 Expression via miR-1252. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2020) 19:718–30. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.12.005
26. Liang G, Chen S, Xin S, Dong L. Overexpression of hsa_circ_0001445 reverses oxLDL−induced inhibition of HUVEC proliferation via SRSF1. Mol Med Rep. (2021) 24:507. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12146
27. Chen H, Fan X, Zhang W, Ye Y, Cai Z, Zhang K, et al. Deciphering the circRNA-regulated response of western honey bee (Apis mellifera) workers to microsporidian invasion. Biol (Basel). (2022) 11:1285. doi: 10.3390/biology11091285
28. Harder JL, Hodgin JB, Kretzler M. Integrative biology of diabetic kidney disease. Kidney Dis (Basel). (2015) 1:194–203. doi: 10.1159/000439196
29. Ma S, Zhang A, Li X, Zhang S, Liu S, Zhao H, et al. MiR-21-5p regulates extracellular matrix degradation and angiogenesis in TMJOA by targeting Spry1. Arthritis Res Ther. (2020) 22:99. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-2145-y
30. Grzywa TM, Klicka K, Włodarski PK. Regulators at Every Step-How microRNAs Drive Tumor Cell Invasiveness and Metastasis. Cancers (Basel). (2020) 12:3709. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123709
31. Chi H, Chen H, Wang R, Zhang J, Jiang L, Zhang S, et al. Proposing new early detection indicators for pancreatic cancer: Combining machine learning and neural networks for serum miRNA-based diagnostic model. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1244578. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1244578
32. Zhao H, Li M, Li L, Yang X, Lan G, Zhang Y. MiR-133b is down-regulated in human osteosarcoma and inhibits osteosarcoma cells proliferation, migration and invasion, and promotes apoptosis. PLoS One. (2013) 8:e83571. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083571
33. Zhen H, Du P, Yi Q, Tang X, Wang T. LINC00958 promotes bladder cancer carcinogenesis by targeting miR-490-3p and AURKA. BMC Cancer. (2021) 21:1145. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08882-6
34. Park EG, Pyo SJ, Cui Y, Yoon SH, Nam JW. Tumor immune microenvironment lncRNAs. Brief Bioinform. (2022) 23:bbab504. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab504
35. Liu F, Chen N, Gong Y, Xiao R, Wang W, Pan Z. The long non-coding RNA NEAT1 enhances epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and chemoresistance via the miR-34a/c-Met axis in renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:62927–38. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17757
36. Huang X, Chi H, Gou S, Guo X, Li L, Peng G, et al. An aggrephagy-related lncRNA signature for the prognosis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Genes (Basel). (2023) 14:124. doi: 10.3390/genes14010124
37. Chi H, Huang J, Yan Y, Jiang C, Zhang S, Chen H, et al. Unraveling the role of disulfidptosis-related LncRNAs in colon cancer: a prognostic indicator for immunotherapy response, chemotherapy sensitivity, and insights into cell death mechanisms. Front Mol Biosci. (2023) 10:1254232. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1254232
38. Li H, Wang Y, Chen M, Xiao P, Hu C, Zeng Z, et al. Genome-wide long non-coding RNA screening, identification and characterization in a model microorganism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:34109. doi: 10.1038/srep34109
39. Fan T, Sun N, He J. Exosome-derived lncRNAs in lung cancer. Front Oncol. (2020) 10:1728. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01728
40. Huang J, Liu M, Chen H, Zhang J, Xie X, Jiang L, et al. Elucidating the Influence of MPT-driven necrosis-linked LncRNAs on immunotherapy outcomes, sensitivity to chemotherapy, and mechanisms of cell death in clear cell renal carcinoma. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1276715. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1276715
41. Zhuang Z, Huang J, Wang W, Wang C, Yu P, Hu J, et al. Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA TINCR induces cell dedifferentiation and predicts progression in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Front Oncol. (2020) 10:624752. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.624752
42. Alva R, Mirza M, Baiton A, Lazuran L, Samokysh L, Bobinski A, et al. Oxygen toxicity: cellular mechanisms in normobaric hyperoxia. Cell Biol Toxicol. (2023) 39:111–43. doi: 10.1007/s10565-022-09773-7
43. Strahan R, Uppal T, Verma SC. Next-generation sequencing in the understanding of kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) biology. Viruses. (2016) 8:92. doi: 10.3390/v8040092
44. Perez-Mendez M, Zárate-Segura P, Salas-Benito J, Bastida-González F. siRNA design to silence the 3'UTR region of zika virus. BioMed Res Int. (2020) 2020:6759346. doi: 10.1155/2020/6759346
45. Chu G, Shi C, Wang H, Zhang W, Yang H, Li B. Strategies for annulus fibrosus regeneration: from biological therapies to tissue engineering. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2018) 6:90. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2018.00090
46. Yu X, Zhang Y, Chen C, Yao Q, Li M. Targeted drug delivery in pancreatic cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2010) 1805:97–104. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2009.10.001
47. Khanbabaei H, Ebrahimi S, García-Rodríguez JL, Ghasemi Z, Pourghadamyari H, Mohammadi M, et al. Non-coding RNAs and epithelial mesenchymal transition in cancer: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2022) 41:278. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02488-x
48. Della Bella E, Menzel U, Basoli V, Tourbier C, Alini M, Stoddart MJ. Differential Regulation of circRNA, miRNA, and piRNA during Early Osteogenic and Chondrogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Cells. (2020) 9:398. doi: 10.3390/cells9020398
49. Hanusek K, Poletajew S, Kryst P, Piekiełko-Witkowska A, Bogusławska J. piRNAs and PIWI proteins as diagnostic and prognostic markers of genitourinary cancers. Biomolecules. (2022) 12:186. doi: 10.3390/biom12020186
50. Iwasaki YW, Siomi MC, Siomi H. PIWI-interacting RNA: its biogenesis and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. (2015) 84:405–33. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060614-034258
51. Ding X, Li Y, Lü J, Zhao Q, Guo Y, Lu Z, et al. piRNA-823 is involved in cancer stem cell regulation through altering DNA methylation in association with luminal breast cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:641052. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.641052
52. Li W, Gonzalez-Gonzalez M, Sanz-Criado L, Garcia-Carbonero N, Celdran A, Villarejo-Campos P, et al. A novel piRNA enhances CA19-9 sensitivity for pancreatic cancer identification by liquid biopsy. J Clin Med. (2022) 11:7310. doi: 10.3390/jcm11247310
53. Wei L, Sun J, Wang X, Huang Y, Huang L, Han L, et al. Noncoding RNAs: an emerging modulator of drug resistance in pancreatic cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2023) 11:1226639. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1226639
54. Guan H, Tian K, Luo W, Li M. m(6)A-modified circRNA MYO1C participates in the tumor immune surveillance of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma through m(6)A/PD-L1 manner. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:120. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05570-0
55. Wang C, Li X, Zhang L, Chen Y, Dong R, Zhang J, et al. miR-194-5p down-regulates tumor cell PD-L1 expression and promotes anti-tumor immunity in pancreatic cancer. Int Immunopharmacol. (2021) 97:107822. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107822
56. Jiang W, Pan S, Chen X, Wang ZW, Zhu X. The role of lncRNAs and circRNAs in the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in cancer immunotherapy. Mol Cancer. (2021) 20:116. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01406-7
57. Zhou WY, Zhang MM, Liu C, Kang Y, Wang JO, Yang XH. Long noncoding RNA LINC00473 drives the progression of pancreatic cancer via upregulating programmed death-ligand 1 by sponging microRNA-195-5p. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:23176–89. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28884
58. You W, Ke J, Chen Y, Cai Z, Huang ZP, Hu P, et al. SQLE, A key enzyme in cholesterol metabolism, correlates with tumor immune infiltration and immunotherapy outcome of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:864244. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.864244
59. Zhao R, Ni J, Lu S, Jiang S, You L, Liu H, et al. CircUBAP2-mediated competing endogenous RNA network modulates tumorigenesis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Aging (Albany NY). (2019) 11:8484–501. doi: 10.18632/aging.102334
60. Zhao YX, Xu BW, Wang FQ, Jiang FY, Xu JW, Yu DX. nc-RNA-mediated high expression of CDK6 correlates with poor prognosis and immune infiltration in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Med. (2023) 12:5110–23. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5260
61. Ou ZL, Luo Z, Wei W, Liang S, Gao TL, Lu YB. Hypoxia-induced shedding of MICA and HIF1A-mediated immune escape of pancreatic cancer cells from NK cells: role of circ_0000977/miR-153 axis. RNA Biol. (2019) 16:1592–603. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2019.1649585
62. Wang S, Gao Y. Pancreatic cancer cell-derived microRNA-155-5p-containing extracellular vesicles promote immune evasion by triggering EHF-dependent activation of Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. (2021) 100:107990. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107990
63. Liu Q, Zhao H, Guo Y, Zhang K, Shang F, Liu T. Bioinformatics-based analysis: noncoding RNA-mediated COL10A1 is associated with poor prognosis and immune cell infiltration in pancreatic cancer. J Healthc Eng. (2022) 2022:7904982. doi: 10.1155/2022/7904982
64. Xi Q, Zhang J, Yang G, Zhang L, Chen Y, Wang C, et al. Restoration of miR-340 controls pancreatic cancer cell CD47 expression to promote macrophage phagocytosis and enhance antitumor immunity. J Immunother Cancer. (2020) 8:e000253. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2019-000253
65. Xi Q, Chen Y, Yang GZ, Zhang JY, Zhang LJ, Guo XD, et al. miR-128 regulates tumor cell CD47 expression and promotes anti-tumor immunity in pancreatic cancer. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:890. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00890
66. Husain K, Villalobos-Ayala K, Laverde V, Vazquez OA, Miller B, Kazim S, et al. Apigenin targets microRNA-155, enhances SHIP-1 expression, and augments anti-tumor responses in pancreatic cancer. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14:3613. doi: 10.3390/cancers14153613
67. Wang Y, Petrikova E, Gross W, Sticht C, Gretz N, Herr I, et al. Sulforaphane promotes dendritic cell stimulatory capacity through modulation of regulatory molecules, JAK/STAT3- and microRNA-signaling. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:589818. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.589818
68. Qi R, Bai Y, Li K, Liu N, Xu Y, Dal E, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts suppress ferroptosis and induce gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer cells by secreting exosome-derived ACSL4-targeting miRNAs. Drug Resist Update. (2023) 68:100960. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2023.100960
69. Liu L, Han S, Xiao X, An X, Gladkich J, Hinz U, et al. Glucocorticoid-induced microRNA-378 signaling mediates the progression of pancreatic cancer by enhancing autophagy. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:1052. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05503-3
70. Huang H, Li X, Zhang X, Li Z, Han D, Gao W, et al. DSCR9/miR-21-5p axis inhibits pancreatic cancer proliferation and resistance to gemcitabine via BTG2 signaling. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). (2022) 54:1775–88. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2022194
71. Huang K, Yang G. LncRNA GAS5 regulates gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic carcinoma by targeting miRNA-21. Ann Clin Lab Sci. (2023) 53:222–9.
72. Lin C, Wang Y, Dong Y, Lai S, Wang L, Weng S, et al. N6-methyladenosine-mediated SH3BP5-AS1 upregulation promotes GEM chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer by activating the Wnt signaling pathway. Biol Direct. (2022) 17:33. doi: 10.1186/s13062-022-00347-5
73. Tan P, Li M, Liu Z, Li T, Zhao L, Fu W. Glycolysis-related LINC02432/hsa-miR-98-5p/HK2 axis inhibits ferroptosis and predicts immune infiltration, tumor mutation burden, and drug sensitivity in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:937413. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.937413
74. Zhang X, Zheng S, Hu C, Li G, Lin H, Xia R, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast-induced lncRNA UPK1A-AS1 confers platinum resistance in pancreatic cancer via efficient double-strand break repair. Oncogene. (2022) 41:2372–89. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02253-6
75. Zhu XX, Li JH, Ni X, Wu X, Hou X, Li YX, et al. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells regulated the gemcitabine-resistance function of CAFs by LINC00460. Cancer Sci. (2022) 113:3735–50. doi: 10.1111/cas.15547
76. Xu C, Ye Q, Ye C, Liu S. circACTR2 attenuates gemcitabine chemoresiatance in pancreatic cancer through PTEN mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Biol Direct. (2023) 18:14. doi: 10.1186/s13062-023-00368-8
77. Han C, Zheng H, Hu D, Wang M, Wang H, Zhang L. Hsa_circ_0007401 regulates gemcitabine resistance of pancreatic cancer through the hsa-miR-6509-3p/fli1 axis. Med (Baltimore). (2023) 102:e33775. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000033775
78. Yan B, Liu L, Zhao L, Hinz U, Luo Y, An X, et al. Tumor and stroma COL8A1 secretion induces autocrine and paracrine progression signaling in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Matrix Biol. (2022) 114:84–107. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2022.11.002
79. Yang C, Chen Z, Wei M, Hu S, Cai M, Wang N, et al. A self-amplified ferroptosis nanoagent that inhibits the tumor upstream glutathione synthesis to reverse cancer chemoresistance. J Control Release. (2023) 357:20–30. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.03.030
Keywords: tumor-immune interactions, ncRNA, tumor immune microenvironment, targeted therapy, pancreatic cancer
Citation: Gong Y, Gong D, Liu S, Gong X, Xiong J, Zhang J, Jiang L, Liu J, Zhu L, Luo H, Xu K, Yang X and Li B (2024) Deciphering the role of NcRNAs in Pancreatic Cancer immune evasion and drug resistance: a new perspective for targeted therapy. Front. Immunol. 15:1480572. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1480572
Received: 14 August 2024; Accepted: 09 October 2024;
Published: 01 November 2024.
Edited by:
Jiaheng Xie, Central South University, ChinaReviewed by:
Kaige Chen, Wake Forest University, United StatesXin Yu, Baylor College of Medicine, United States
Copyright © 2024 Gong, Gong, Liu, Gong, Xiong, Zhang, Jiang, Liu, Zhu, Luo, Xu, Yang and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ke Xu, Y3FnaHh1a2VAY3F1LmVkdS5jbg==; Xiaoli Yang, eWFuZ3hpYW9saUBzd211LmVkdS5jbg==; Bo Li, bGlib2VyMjAwMkBzd211LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Yu Gong
Yu Gong Desheng Gong
Desheng Gong Sinian Liu5†
Sinian Liu5† Xiangjin Gong
Xiangjin Gong Jingwen Xiong
Jingwen Xiong Jinghan Zhang
Jinghan Zhang Lai Jiang
Lai Jiang Jie Liu
Jie Liu Xiaoli Yang
Xiaoli Yang Bo Li
Bo Li