
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Immunol. , 09 December 2024
Sec. Cancer Immunity and Immunotherapy
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1469918
This article is part of the Research Topic Non-coding RNAs in disease development and progression View all 4 articles
 Chenbo Yang1,2†
Chenbo Yang1,2† Jiao Shu1,2†
Jiao Shu1,2† Yiwei Li1,2,3†
Yiwei Li1,2,3† Na Zhao1,2
Na Zhao1,2 Xiaonan Liu1,2
Xiaonan Liu1,2 Xiangyu Tian1,2
Xiangyu Tian1,2 Zexin Sun1,2,3
Zexin Sun1,2,3 Muhammad Saud Tabish1,2
Muhammad Saud Tabish1,2 Yichen Hong1,2,3
Yichen Hong1,2,3 Kuisheng Chen1,2*
Kuisheng Chen1,2* Miaomiao Sun1,2*
Miaomiao Sun1,2*The proliferation of tumors is not merely self-regulated by the cancer cells but is also intrinsically connected to the tumor microenvironment (TME). Within this complex TME, cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are pivotal in the modulation of tumor onset and progression. Rich signaling interactions exist between CAFs and tumor cells, which are crucial for tumor regulation. Long non-coding RNAs (LncRNAs) emerge from cellular transcription as a class of functionally diverse RNA molecules. Recent studies have revealed that LncRNAs are integral to the crosstalk between CAFs and tumor cells, with the capacity to modify cellular transcriptional activity and secretion profiles, thus facilitating CAFs activation, tumor proliferation, metastasis, drug resistance, and other related functionalities. This comprehensive review revisits the latest research on LncRNA-mediated interactions between CAFs and tumor cells, encapsulates the biological roles of LncRNAs, and delves into the molecular pathways from a broader perspective, aspiring to offer novel perspectives for a deeper comprehension of the etiology of tumors and the enhancement of therapeutic approaches.
According to the latest estimates by the International Agency for Research on Cancer, about one in five men or women will develop cancer in their lifetime, and approximately one in nine men and one in twelve women will die from it. Cancer remains a significant threat to human life and health (1). Over the years, clinicians and researchers have focused on the “pathological state caused by genetic changes in the tumor (Somatic Mutation Theory, SMT)” and have designed cancer treatment methods based on this theory. However, the individual differences in treatment effects compel us to consider the potential functions of the tumor stroma (2). The progression of cancer is not a single growth process of tumor cells, but an interaction based on the tumor microenvironment (TME) and tumor cells. Even if some cells have a high tumor mutation burden, there are no obvious pathological changes, indicating that the external TME can manipulate tumor cells to present different fates (3, 4). In colorectal cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer, and esophageal cancer, high stromal tumors often indicate a low survival rate, and the proportion of tumor stroma is related to prognosis (5). Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs) are the most prominent components of the tumor stroma and have a profound impact on the process of tumor occurrence and development. They play a key regulatory role in tumor cell proliferation, metabolic reprogramming, migration and invasion, stemness, as well as the remodeling of the tumor extracellular matrix (ECM), angiogenesis, metastasis, immune suppression, and resistance to therapy (6, 7).
Although the SMT cannot fully explain the disease of cancer, cancer is still considered a “genetic disease” where extensive genetic changes within cells disrupt tissue homeostasis and promote the development of cancer. With the advancement of gene sequencing technology, the results of genetic research have increased exponentially. Approximately 75% of the human genome is transcribed, but only 2% of the transcribed genes are mRNAs that encode proteins, with the rest initially considered “transcriptional waste” (8). After further deepening the molecular understanding of cancer, it has been found that non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are involved in the occurrence, progression, and metastasis of cancer. In particular, long non-coding RNAs (LncRNAs), which are transcripts longer than 200 nucleotides, differ from mRNAs and miRNAs and form a rich and complex network of tumor LncRNAs due to their various mechanisms of action (9).
This article links CAFs and LncRNA in the TME, reviews recent relevant research, and focuses on LncRNA as an important participant between CAFs and tumors, its impact on tumors and related molecular networks. It explores the occurrence and development of tumors from multiple perspectives of “tumor stroma” and “genes”, which helps to deepen the understanding of cancer diseases and innovate cancer treatment models.
Normal fibroblasts are quiescent cells derived from mesenchymal cells that maintain tissue homeostasis and structural integrity. When fibroblasts are activated by injury or inflammatory factors, the deposition of the ECM is enhanced, and the contractile force is increased, which promotes wound healing. After the healing and remodeling are completed, fibroblasts undergo apoptosis and disappear or return to a quiescent state (10). However, if inflammation persists, such as in the case of tumors, it can lead to the emergence of a subgroup of over-activated fibroblasts. These fibroblasts, which are over-activated and maintain their functions within the tumor tissue stroma, are referred to as CAFs (11). Cytokines, reactive oxygen species (ROS), hypoxia, and ncRNAs are all key regulatory factors for fibroblast activation. A major source of CAFs is the recruitment and activation of normal fibroblasts within the local tissue (12). Stem cells retain the ability to differentiate; whether they are mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow (13), hematopoietic stem cells (14), adipose-derived stem cells (15), or cancer stem cells (16), they can all differentiate into CAFs through signal transduction. CAFs can also originate from mature differentiated cells, such as epithelial cells that can transdifferentiate into CAFs through epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and endothelial cells that can transdifferentiate into CAFs through endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EndMT) (17, 18). Additionally, pericytes and stellate cells can also transform into CAFs (19, 20) (Figure 1).
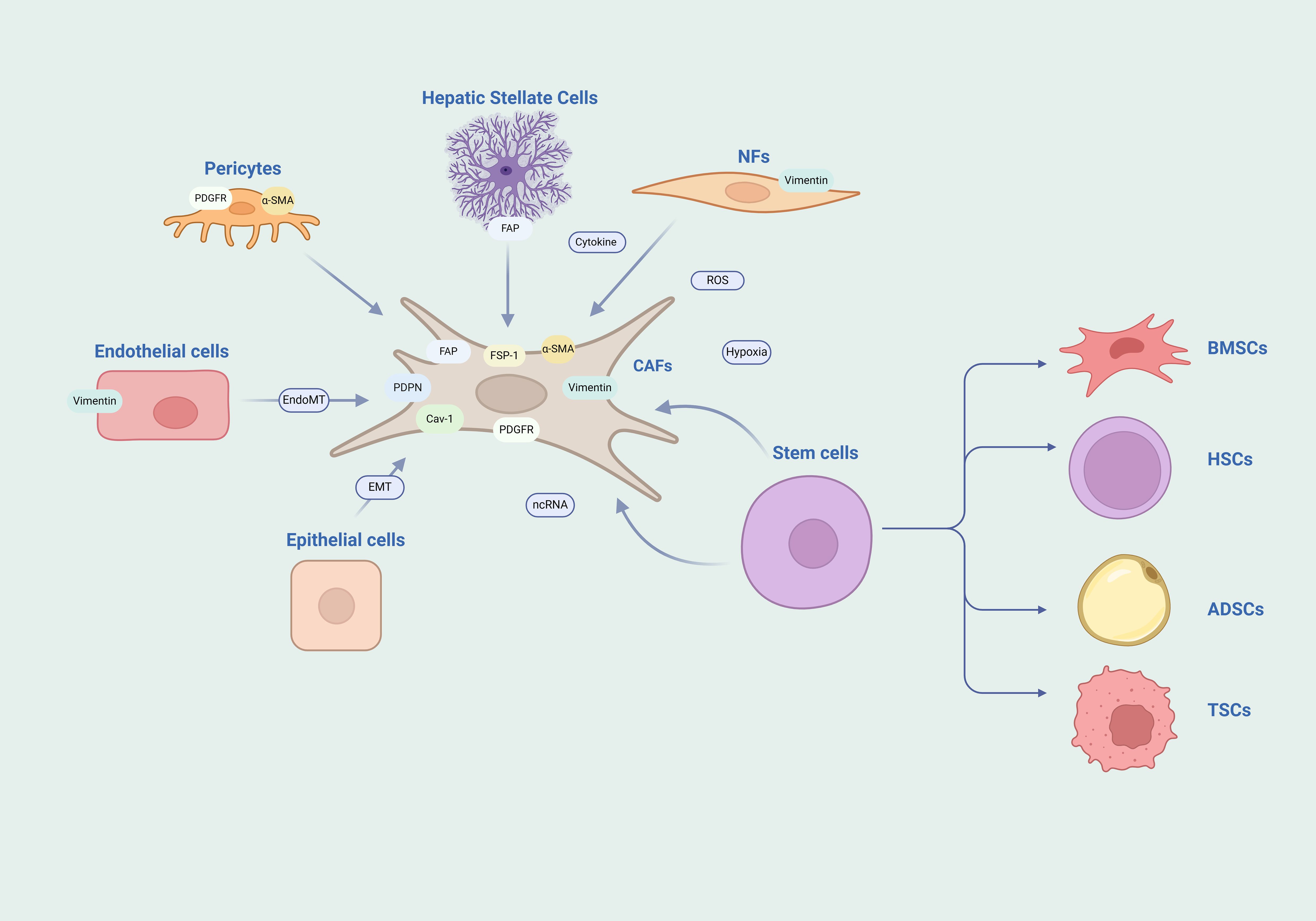
Figure 1. Heterogeneity of CAFs. The diversity of origins and the complexity of markers for CAFs are notable features. The heterogeneity of CAFs is highlighted by their diverse origins and the intricate array of their markers. They may arise from a spectrum of cell sources such as NFs, endothelial cells, epithelial cells, stem cells, pericytes, and stellate cells. Moreover, the markers typically associated with CAFs are not exclusive and can be found expressed in other cell types as well. NFs, normal fibroblasts; BMSCs, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; HSCs, hematopoietic stem cells; ADSCs, adipose derived stem cells; TSCs, tumor stem cells.
Pathological diagnosis remains the foundation of cancer research, and cellular origins and subtypes can be clearly identified through immunohistochemical staining and molecular analysis. However, due to the diversity of sources of CAFs, there are still no specific markers for CAFs to date. The more common markers currently used for CAFs include Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP), Fibroblast-Specific Protein 1 (FSP1), Alpha-Smooth Muscle Actin (α-SMA), Vimentin, Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor (PDGFR), Caveolin-1, and Podoplanin. However, these proteins have limitations as they are also expressed in other cells and are not specifically expressed in CAFs (21, 22). FAP is expressed in immune cells and stellate cells (23, 24); FSP1 is expressed in macrophages (25); α-SMA is expressed in pericytes and smooth muscle cells (26, 27); Vimentin is expressed in endothelial cells (28); PDGFR is expressed in pericytes (26). Therefore, the identification of CAFs is based on the strength of the expression of marker proteins, rather than the presence or absence of the protein expression, and usually a combination of multiple markers is used to determine CAFs.
CAFs have a crucial impact on the occurrence and progression of tumors. Studies have found that most CAFs promote tumor growth, but there are also some CAFs that have anti-cancer effects. It is precisely because of the various sources and different activation mechanisms of CAFs that they exhibit a high degree of heterogeneity and have different functional effects on tumors (29). Based on biomarkers, functions, and locations, CAFs are usually divided into restraining CAFs (rCAFs), myofibroblast CAFs (myCAFs), inflammatory CAFs (iCAFs), and antigen-presenting CAFs (apCAFs) (30, 31). MyCAFs are related to the ECM and can synthesize collagen to mediate ECM remodeling; iCAFs mainly secrete various cytokines, growth factors, and chemokines to regulate tumor immune suppression; apCAFs induce naive CD4 T cells to differentiate into regulatory T cells (Tregs) in an antigen-specific manner; rCAFs are the most special and play a role in inhibiting tumor growth. MyCAFs, iCAFs, and apCAFs promote tumor cell proliferation, migration, invasion, metabolic reprogramming, therapeutic resistance, etc., through a variety of mechanisms (32, 33). Different subtypes of CAFs are not unchangeable; different subtypes of CAFs will transform into each other, indicating that multiple subtypes of CAFs will appear in the tumor tissue at the same time, and using single-cell technology, researchers have found multiple cellular phenotypic subtypes of CAFs.
LncRNAs lack efficient open reading frames, and only a minority can encode proteins. However, this does not imply that LncRNAs are “noise in the transcription process” (34). An increasing body of research has confirmed that LncRNAs play a crucial role in the development and progression of cancer, affecting cellular proliferation, growth, differentiation, and apoptosis, ultimately exerting either oncogenic or tumor-suppressive effects. Extensive reviews have already summarized the genomic localization, classification, functions, mechanisms of action, and tumor expression of LncRNAs (8, 35). This article will only briefly summarize their molecular functions to facilitate an understanding of how LncRNAs act as “communication mediators” between CAFs and tumor cells. LncRNAs are distributed in the nucleus, cytoplasm, and mitochondria, which endows them with the ability to interact with DNA, RNA, and proteins at multiple levels of transcriptional regulation, post-transcriptional regulation, and epigenetic regulation, exhibiting a variety of functional roles (36, 37): (1) Signal Transduction: LncRNAs are associated with specific signal transduction pathways, acting as “molecular signals” in the process of signal regulation; (2) Decoys: LncRNAs, similar to transcription factors or repressors, affect the function of regulatory factors, including enzymes, transcription factors, and miRNAs, by binding to decoy sites, thereby promoting gene activation or silencing. The competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network formed by LncRNA-miRNA-mRNA is a typical representative; (3) Guiding: After binding with protein complexes, LncRNAs guide them to downstream target gene promoters or genomic sites; (4) Scaffolding: LncRNAs can act as “molecular scaffolds,” linking various proteins to form complexes and directing them to specific genomic locations or target gene promoters, participating in gene activation, gene repression, and chromatin modification.
The concept of tumor cells and the TME is often metaphorically described as “seeds and soil,” highlighting the interdependence where the “seeds” cannot thrive without the nourishment and signals provided by the “soil.” This symbiotic relationship underscores the critical role of communication between the TME and tumor cells. CAFs, integral constituents of the TME, engage in diverse modes of communication with tumor cells, thereby modulating their growth. With a spotlight on LncRNAs, this review delves into the intricate pathways of interaction between CAFs and tumor cells (Figure 2, Table 1).
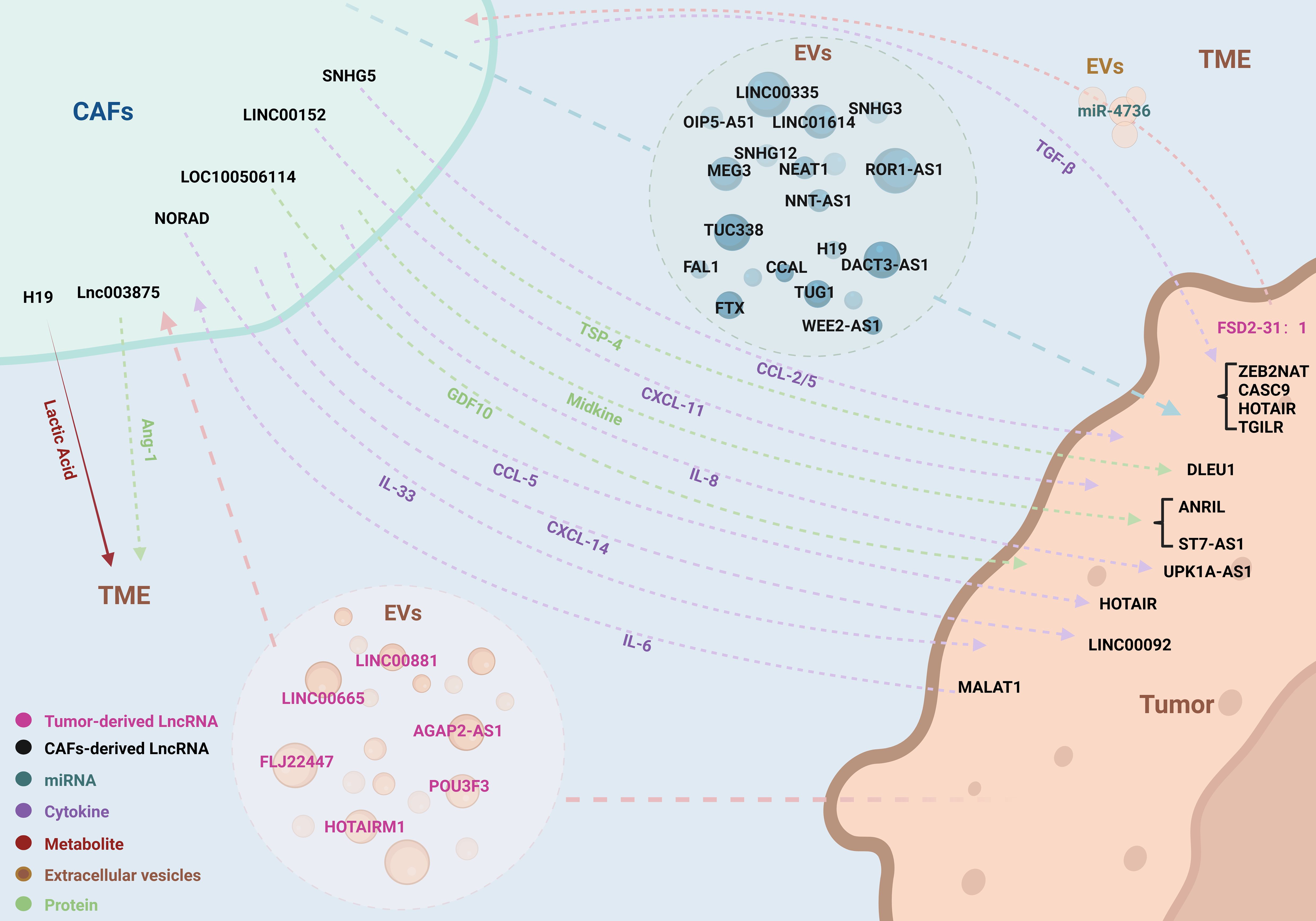
Figure 2. LncRNAs coordinate the complex bidirectional interactions between CAFs and tumor cells. LncRNAs orchestrate a variety of interactive pathways between CAFs and tumor cells, encompassing EVs, cytokines, secretory proteins, metabolites, and miRNAs. This communication paradigm operates in a bidirectional manner, facilitating a complex and dynamic interplay that influences tumor progression and microenvironmental modulation.
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are enriched with bioactive cargo, which includes proteins, lipids, metabolites, RNA, and DNA. This cargo can be transferred to recipient cells, thereby influencing their function and facilitating intercellular communication (38). In the TME, EVs are involved in the exchange of information among various cell types, including tumor cells, epithelial cells, CAFs, endothelial cells, and immune cells, playing a crucial role in both promoting and suppressing tumor progression (39). The transfer of EVs between cancer cells and stromal cells has been identified as a mechanism for reprogramming tissues and altering environmental homeostasis. EVs derived from cancer cells, once taken up by stromal cells, can reshape the TME into a pro-tumorigenic environment; conversely, EVs derived from stromal cells can be internalized by cancer cells, further influencing tumor progression. RNA is unstable within the TME, prone to degradation by enzymes or destruction by pH changes, thus requiring the protective lipid bilayer of EVs for intercellular communication involving RNA. EVs exhibit a broad size range due to the heterogeneity in cell types and formation processes, primarily consisting of two subpopulations: exosomes, which are small membrane vesicles with a diameter of 30-150 nm, and microvesicles, which are larger membrane vesicles with a diameter of 150-1000 nm. In addition to these common subpopulations, there are also EVs with even larger diameters (40). The reciprocal exchange of EVs between CAFs and cancer cells involves the storage of LncRNA within EVs, participating in the regulation of tumorigenesis through this pathway.
Cytokines are pivotal in establishing the communication link between CAFs and tumor cells. These biological messengers carry intrinsic information, activating signaling cascades or binding to receptor proteins to engage in a variety of biological processes. The cytokine family includes growth factors, chemokines, interleukins, interferons, tumor necrosis factors, and colony-stimulating factors—glycoproteins that do not necessitate exosomal encapsulation (41). Through paracrine release, CAFs and tumor cells disseminate cytokines to transmit biological messages, modulating the expression of LncRNAs within recipient cells, thereby influencing the levels of downstream proteins and the overall trajectory of tumor progression. LncRNAs may also function upstream of cytokines, with their differential expression in CAFs and tumor cells potentially altering cytokine secretion and impacting cellular functions. Transforming growth factor β(TGF-β) is a crucial trigger for the activation and formation of CAFs and is also a participant in the malignant biological behaviors of tumor cells; this bidirectional effect is an important pathway mediated by LncRNAs for mutual communication between CAFs and tumor cells (42, 43). Furthermore, chemoattractant cytokine ligands (CCL), C-X-C motif chemokine ligands (CXCL), and interleukins (IL) have been implicated in LncRNA-mediated communication between CAFs and tumor cells via similar pathways (44). Secreted proteins, akin to cytokines, may participate in the regulatory network either upstream or downstream of LncRNAs, adding another layer of complexity to the intricate interplay between these cellular actors.
Tumors are characterized by the distinctive metabolic process of aerobic glycolysis, and CAFs play a crucial role in the intricate metabolic activities within tumors. Tumor cells induce metabolic reprogramming in CAFs, leading to an increase in glucose uptake and lactate production, which in turn supplies a carbon source for the tumor cells (45). The byproducts of energy metabolism also serve as a conduit for LncRNA-mediated communication between CAFs and tumor cells. The upregulation of LncRNAs within CAFs modifies the expression of glycolysis-related proteins downstream, enhancing lactate generation and its release into the TME, which subsequently regulates the functionality of tumor cells (46). This metabolic interplay underscores the intricate dialogue facilitated by LncRNAs, highlighting the pivotal role of CAFs in the metabolic landscape of cancer.
Uncontrolled proliferation of tumor cells is a defining characteristic of tumor growth. The elevated expression of LncRNAs within EVs from CAFs significantly boosts the tumor cells’ proliferative abilities upon EVs internalization. This phenomenon is exemplified in various cancers: WEE2-AS1 and SNHG3 in colorectal cancer (47, 48); NEAT1 in endometrial cancer (49); LINC00355 in bladder cancer (50); SNHG3 in breast cancer (51); TUC338 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (52); FTX in oral squamous cell carcinoma (53); and NNT-AS1 in pancreatic cancer (54). The co-culture of CAFs with colorectal cells triggers an elevation in the levels of UCA1 within the tumor cells, which in turn significantly boosts their proliferative capacity (55). Within CAFs, elevated expression of NORAD augments the release of IL-33 to gastric cancer cells, thereby stimulating their proliferative activity (56). A parallel can be drawn with oral squamous cell carcinoma, where high expression levels of LOC100506114 intensify the secretion of the GDF10 protein into tumor cells (57). In liver cancer, the overexpression of LINC00152 enhances the secretion of CXCL-11 (58). Furthermore, the secretion of TGF-β by CAFs upregulates the TGILR levels within gastric cancer cells, exacerbating their proliferative capacity (59).
Tumor metastasis epitomizes the terminal outcome of a complex series of cellular behaviors in the invasive cascade, encompassing the spread of tumor cells to distant tissues and their adaptation to novel environments, including migration, invasion, and EMT (60). Elevated levels of LncRNAs within EVs from CAFs, once internalized by tumor cells, significantly augment their metastatic capabilities. This is exemplified in various cancers: TUG1 in liver cancer (61); MEG3 and HOTAIRM1 in lung cancer (62, 63); LINC00355 in bladder cancer (50); TUC338 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (52); FTX in oral squamous cell carcinoma (53); and NNT-AS1 in pancreatic cancer (54). Co-culture with colorectal cells leads to heightened UCA1 expression, enhancing the metastatic potential (55). The secretion of TGF-β by CAFs upregulates the expression of specific LncRNAs—HOTAIR in breast cancer (64), ZEB2NAT in bladder cancer (65), TGILR in gastric cancer (59), and CASC9 in cervical cancer (66)—thus facilitating the metastatic spread of tumor cells. Furthermore, CAFs secrete a variety of cytokines and proteins that upregulate LncRNAs within tumor cells, further promoting metastasis. For instance, CXCL-14 secreted by CAFs upregulates LINC00092 in ovarian cancer (67), and Midkine upregulates ST7-AS1 in gastric cancer (68). The differential expression of LncRNAs within CAFs themselves, through the secretion of cytokines, can also foster the metastatic behavior of tumor cells. Examples include the high expression of LOC100506114 enhancing GDF10 secretion to promote oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis (57), LINC00152 enhancing CXCL-11 secretion to promote liver cancer metastasis (58), and NORAD enhancing IL-33 secretion to promote gastric cancer metastasis (56).
Therapy resistance stands as a formidable barrier in oncology, with a range of factors—including genetic mutations, immune suppression, physical barriers, TME, and growth dynamics—propelling the development of this resistance (69). The diverse capabilities of CAFs, such as their ECM remodeling, cytokine secretion, and metabolic reprogramming, indicate an intrinsic connection to the phenomenon of therapeutic resistance. LncRNAs like H19, FAL1, and CCAL, encapsulated in CAF-derived EVs, can induce oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer cells upon internalization (70–72). The internalization of CAF-origin EVs by lung cancer cells results in elevated MEG3 and SNHG12 levels, conferring cisplatin resistance (62, 73). LINC00355, transported by CAF-derived exosomes, fosters cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer cells (74), while H19 induces paclitaxel resistance in breast cancer cells through the same exosomal pathway (75). The deficiency of DACT3-AS1 in CAF-derived exosomes has been associated with oxaliplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells (76). Co-culture with CAFs leads to an increase in DNM3OS levels in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells, endowing them with radioresistance (77). Furthermore, cytokines secreted by CAFs, such as IL-8, which upregulates UPK1A-AS1 in pancreatic cancer, can induce oxaliplatin resistance (78). CCL-5 upregulates HOTAIR in lung cancer, causing cisplatin resistance (79). Midkine, another cytokine, upregulates ANRIL in oral squamous cell carcinoma, leading to cisplatin resistance (80), and it similarly promotes ST7-AS1 in gastric cancer, enhancing cisplatin resistance (68).
Altered energy metabolism is a defining characteristic of cancer, where tumor cells undergo metabolic reprogramming to thrive and persist in inhospitable conditions, encompassing the metabolism of glucose, proteins, and lipids (81). Tumor cells exhibit a high rate of glycolysis and lactate production irrespective of oxygen availability, a metabolic pathway that is modulated by CAFs through the action of LncRNAs. For instance, TUG1 within CAF-derived EVs boosts glycolysis in liver cancer (61), while SNHG3 enhances this process in breast cancer (51), and NNT-AS1 does so in pancreatic cancer (54). The secretion of CXCL-14 by CAFs upregulates LINC00092 in ovarian cancer, thereby promoting its glycolytic activity (67). Paralleling glycolysis, the predilection for glutamine is a hallmark of tumor cells; lung cancer cells that internalize exosomes released by CAFs witness a marked elevation in LINC01614 levels, correlating with increased glutamine uptake and ATP synthesis (82). Furthermore, heightened expression of H19 in CAFs escalates lactate secretion, fostering a highly acidic tumor microenvironment that is propitious for tumorigenesis (46).
Tumor cells bypass the regulatory mechanisms of the normal cell cycle, allowing for unchecked proliferation and sustaining a state of diminished apoptosis (83). CAFs secrete exosomes that introduce OIP5-AS1 into lung cancer cells, which in turn upregulates Programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1), attenuating the incidence of apoptosis (84). Ferroptosis represents an iron-dependent form of regulated cell death, triggered by the suppression of amino acid transporters and resulting in heightened lipid peroxidation that leads to cell demise (85). Studies have revealed that CAFs modulate the susceptibility of tumor cells to ferroptosis through the action of LncRNAs. For example, FTX within exosomes derived from CAFs suppresses ferroptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma (53), while ROR1-AS1 curbs this form of cell death in lung cancer cells (86). Additionally, the TSP-4 protein secreted by CAFs, upon internalization by glioma cells, upregulates DLEU1 expression, thereby inhibiting ferroptosis (87).
Angiogenesis is an essential condition for the formation and growth of tumors, providing vital oxygen, nutrients, and growth factors to tumor cells that fuel their swift progression. It is a well-established fact that without angiogenesis, solid tumors are unlikely to expand beyond a mere 3 millimeters (88). Within breast cancer tissues, CAFs exhibit heightened levels of SNHG5, which stimulates the secretion of CCL-2 and CCL-5 into vascular endothelial cells, thus promoting both angiogenesis and the permeability of blood vessels (89). In placental site trophoblastic tumors, CAFs demonstrate elevated expression of lnc003875, resulting in an increased release of Ang-1, a key driver of angiogenesis (90).
The interaction between tumor cells and CAFs is a two-way street. It is crucial to recognize that while CAFs can drive the biology of tumors, tumor cells can also exert influence in the opposite direction, impacting the CAF phenotype through the release of EVs, cytokines, or metabolic products. This reciprocal modulation can lead to a further reshaping of TME, ultimately fostering tumor growth. For instance, oral squamous cell carcinoma cells release exosomes rich in FLJ22447, which, upon elevating its levels in fibroblasts, activate CAFs and stimulate tumor proliferation (91). Lung cancer cells utilize exosomes to shuttle AGAP2-AS1 to fibroblasts, thereby activating CAFs and enhancing tumor growth (92). Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells transfer POU3F3 to fibroblasts through exosomes, activating CAFs and promoting both tumor metastasis and resistance to cisplatin (93). Osteosarcoma cells deliver LINC00881 to lung fibroblasts via exosomes, facilitating their metamorphosis into CAFs that support lung metastasis (94). Bladder cancer cells dispatch exosomes containing LINC00665 to CAFs, stimulating their activation and secretion of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which promotes lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis (95). Pancreatic cancer cells, with diminished FSD2-31:1 expression, transport miR-4736 to fibroblasts via EVs, enhancing autophagy and curbing their activation, which in turn inhibits tumor advancement (96). An increase in MALAT1 expression in gastric cancer cells diminishes autophagy and quickens the secretion of IL-6, an activator of CAFs. Once activated, these CAFs secrete more IL-6, establishing a positive feedback loop that accelerates gastric cancer progression (97). Glioma tumor stem cells, with high expression of HOTAIRM1, upregulate TGF-β expression, driving the transformation of stem cells into CAFs and promoting tumor growth (98).
Owing to the multifaceted roles of LncRNAs, they exert intricate control over downstream signaling cascades or target proteins through a spectrum of molecular mechanisms. This mediation of information exchange between CAFs and tumor cells endows LncRNAs with significant tumor regulatory capabilities. In this article, we systematically classify the associated signaling pathways and construct a molecular network map with the aspiration of pinpointing pivotal pathways. Such an approach is expected to deepen our comprehension of how LncRNAs function within the complex interplay of CAFs and tumor cells, potentially unveiling novel therapeutic targets in cancer biology (Figure 3).

Figure 3. The molecular mechanism network of LncRNAs involved in the crosstalk between CAFs and tumor cells. A comprehensive network diagram was created, depicting the molecular mechanisms involving LncRNAs associated with CAFs, providing a detailed visual representation of the complex interactions and pathways in the tumor microenvironment.
The TGF-β signaling pathway exerts a multifaceted influence within TME, with its overexpression implicated in processes such as EMT, ECM deposition, the activation of CAFs, and modulation of immune responses (99). The SMAD pathway stands as a quintessential signaling cascade initiated by the intracellular kinase domain of TGF-β. Originating from CAFs, TGF-β prompts the assembly of SMAD2/3/4 onto the HOTAIR promoter, enhancing HOTAIR transcription in breast cancer cells. This triggers H3K27 trimethylation on the promoters of CDK5RAP1 and EGR-1, activating CDK5 expression and establishing the TGF-β/SMAD/HOTAIR/CDK5 axis (64). SMAD3, phosphorylated by TGF-β, translocates to the nucleus, binding to the TGILR promoter and promoting its transcription; TGILR sustains TARBP2 protein stability, hastening TARBP2-mediated degradation of miR-1306 and miR-33a, and upregulating TCF4, thereby advancing gastric cancer progression (59). LncRNAs are capable of modulating TGF-β secretion by CAFs, thereby igniting the SMAD signaling. Within CAFs, the interaction of LOC100506114 with the transcription factor RUNX2 escalates GDF10 expression. GDF10, akin to a TGF-β component, incites SMAD3 and downstream ERK protein expression, forging the LOC100506114/RUNX2/GDF10/SMAD3/ERK signaling route (57). TGF-β can also set in motion a plethora of downstream proteins via mechanisms such as phosphorylation, ubiquitination, acetylation, and protein interactions, collectively termed the non-SMAD signaling pathways (100). TGF-β from CAFs boosts ZEB2NAT transcription in bladder cancer cells, intensifying ZEB2 expression (65). In glioma stem cells, HOTAIRM1, through a ceRNA mechanism, forms the HOTAIRM1/miR-133b-3p/TGF-β regulatory loop, upregulating TGF-β to facilitate the metamorphosis of stem cells into CAFs (98). SNHG5 within CAFs catalyzes the recruitment of IGF2BP2, assembling an SNHG5-IGF2BP2-ZNF281 trimeric complex that amplifies ZNF281 and downstream CCL-2/5 expression. Subsequently, CCL-2/5 stimulates the P38/MAPK pathway associated with TGF-β in endothelial cells, thereby fostering angiogenesis (89).
The NF-κB signaling pathway is frequently activated in cancer and is largely attributed to the activation of inflammatory cytokines or upstream proteins within TME (101). The LINC01614, derived from CAFs, triggers P65 phosphorylation in lung cancer cells via ANXA2, thereby activating the NF-κB signaling cascade and enhancing the transcription of the glutamine transporters SLC38A2 and SLC7A5. Additionally, the secretion of IL-6 and CXCL-10 by lung cancer cells creates a positive feedback loop by further increasing LINC01614 levels in CAFs (82). IL-8 originating from CAFs initiates the NF-κB signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer cells, with P65 binding to the promoter region to boost the transcription of UPK1A-AS1, which acts as a molecular scaffold for Ku70 and Ku80, thereby augmenting the cell’s DNA repair capabilities (78). AGAP2-AS1 fosters the stabilization of its own RNA through the RNA stability protein EIF4A3 and positively modulates MyD88 and the subsequent NF-κB signaling pathway, establishing the AGAP2-AS1/EIF4A3/MyD88/NF-κB axis to stimulate CAF activation (92). LINC00881 in lung fibroblasts competitively interacts with miR-29c-3p to bind MMP2, increasing MMP2 expression and NF-κB signaling activity, thus promoting their differentiation into CAFs (94).
The AKT signaling pathway, omnipresent in cellular mechanisms, boasts an extensive array of upstream regulatory elements and a plethora of downstream signaling junctions. It plays a pivotal role in cellular processes such as survival, metabolism, and movement (102). CAFs secrete Midkine, which elevates the expression of ST7-AS1 in gastric cancer cells. ST7-AS1 facilitates the phosphorylation of PI3K and AKT, igniting the PI3K/AKT cascade and engendering drug resistance in tumor cells (68). Within the context of endometrial cancer, CAF-derived NEAT1 operates as a “ceRNA” for miR-26a/b-5p, leading to the overexpression of target genes STAT3 and YKL-40, and thus modulating tumor behavior (49). Co-culturing CAFs with colorectal cancer cells results in the joint repression of miR-143 expression by UCA1 and mTOR, causing an increase in the downstream KRAS protein levels. This interplay fosters tumor proliferation and metastatic potential (55).
The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, when dysregulated, is intimately linked to a spectrum of diseases. Activation of the Wnt pathway prompts the translocation of β-catenin to the nucleus, thereby stimulating the transcription of genes pivotal for cell proliferation, survival, and migration (103). CAFs facilitate the transfer of CCAL into colorectal cancer cells, which in turn fosters the interaction between Hu antigen R (HuR) and β-catenin, thereby igniting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling cascade (72). In the context of colorectal cancer, CAF-derived H19 also engages in a competitive binding mechanism with β-catenin to miR-141, leading to the upregulation of β-catenin and the subsequent activation of the pathway (70). Moreover, the lncRNA LINC00355, originating from CAFs, acts as a “molecular sponge,” forming the LINC00355/miR-15a-5p/HMGA2 axis and enhancing the expression of the β-catenin downstream effector HMGA2 (50).
The Warburg effect, a quintessential characteristic of cancer, is closely linked to the activation of pathways that foster tumor metastasis and the reconfiguration of the TME (104). The augmentation of glycolysis is orchestrated through the upregulation of glycolytic enzymes and transport proteins, such as Pyruvate kinase (PK), Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), Hexokinase (HK), Phosphofructokinase (PFK), and Glucose transporters (GLUT). SNHG3, originating from CAFs, functions as a “molecular sponge,” sequestering miR-330 and thereby enhancing the glycolytic activity in breast cancer cells by interacting with PKM (51). In a parallel mechanism, TUG1, derived from CAFs, enters liver cancer cells and engages in the TUG1/miR-524-5p/SIX1 pathway, facilitating SIX1-driven glycolysis through the “ceRNA” mechanism (61). The secretion of CXCL-14 by CAFs elevates the expression of LINC00092 in ovarian cancer cells, which in turn stabilizes PFKFB2 expression, propelling tumor glycolysis (67). The surge in glycolytic activity is predominantly governed by the modulation of Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) and c-myc, with HIF-1α stimulating the expression of glycolytic enzymes like HK2 and LDHA, and transporters including MCT4 and GLUT1, thus escalating intracellular glycolysis (105). CAFs can channel NNT-AS1 into pancreatic cancer cells, establishing the NNT-AS1/miR-889-3p/HIF-1 axis that amplifies glycolytic activity and bolsters tumor progression (54). Within the TME, CAFs predominantly adopt a catabolic role, supplying lactate to tumor cells. An upregulation of H19 in CAFs diminishes the miR-675-5p-mediated degradation of the target protein PFKFB3, thereby activating PFKFB3-driven glycolysis. The heightened secretion of lactate by CAFs, in turn, accelerates the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma (46).
The growth of a tumor signifies a perturbed equilibrium between cellular proliferation and cellular injury, yielding an array of signals within the microenvironment during cellular demise (106). For example, CAFs secrete CCL5, which elevates HOTAIR expression in lung cancer cells. HOTAIR diminishes the expression of the apoptotic initiator caspase-3 while enhancing the expression of the anti-apoptotic protein BCL-2 (79). In the context of oral squamous cell carcinoma, Midkine from CAFs boosts ANRIL expression, reduces caspase-3 levels, and stimulates the expression of MRP1 and ABCC2, thereby influencing the apoptotic landscape (80). Beyond the traditional apoptosis pathways, CAFs are instrumental in orchestrating ferroptosis, a form of regulated cell death associated with iron metabolism. CAF-derived FTX interacts with TET2, leading to the demethylation of the FEN1 promoter and an increase in FEN1 expression. FEN1, in turn, suppresses ACSL4 expression by binding to its promoter, curbing ferroptosis in tumor cells (53). ROR1-AS1, by engaging with IGF2BP1, preserves the stability of SLC7A11 mRNA, thereby inhibiting ferroptosis in lung cancer cells (86). The release of TSP-4 by CAFs instigates HSF1 activation in glioblastoma, which in turn promotes DLEU1 expression. DLEU1, through its interaction with ZFP36, facilitates the degradation of the ferroptosis transcription factor ATF3, upregulates SLC7A11 expression, and ultimately suppresses ferroptosis in tumor cells (87). DACT3-AS1, functioning as a tumor suppressor and exhibiting low expression in CAFs, fosters ferroptosis and enhances tumor cell sensitivity to oxaliplatin via the DACT3-AS1/miR-181a-5p/SIRT1 pathway (76).
Autophagy serves as a cellular survival mechanism, essential for the degradation of damaged cellular components and misfolded proteins, thereby nourishing cell growth. Initially, autophagy acts as a suppressor in early-stage tumorigenesis, yet it assumes a promotional role in the later stages of tumor development (107). The upregulation of the tumor-originated FLJ22447 in fibroblasts can impede the p62-driven autophagy-lysosome degradation pathway, sustaining the stability of the IL-33 protein and activating IRAK3. This sequence of events propels the metamorphosis of fibroblasts into CAFs (91). The LncRNA MALAT1, translocated from tumor cells to fibroblasts, complexes with ELAVL1, causing PTEN mRNA destabilization and the subsequent suppression of PTEN at the transcriptional tier. This cascade activates the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, diminishes autophagic flux, and induces the overexpression of SQSTM1, which in turn activates NF-κB. These events collectively promote the activation of CAFs and the secretion of IL-6 (97). The LncRNA FAL1, emanating from CAFs, functions as a “molecular scaffold” for Beclin1 and TRIM3 within colorectal cancer cells, augmenting the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of Beclin1 by TRIM3 and consequently repressing autophagy (71). FSD2-31:1 exhibits tumor-suppressive effects and is underexpressed in pancreatic cancer cells. It mediates the transfer of downstream miR-4736 to fibroblasts via EVs. miR-4736 inhibits ATG7, thereby reducing autophagy levels and promoting the activation of CAFs (96).
HuR, a ubiquitous RNA-binding protein, plays a crucial role in the post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. It is capable of responding to a multitude of stimuli, thereby facilitating the translation of specific mRNAs (108). CAFs produce SNHG3, which mitigates the degradative effect of miR-34b-5p on HuR, enhancing the stability of HOXC6 mRNA and thus fueling the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells (48). Furthermore, SNHG12 is transported to lung cancer cells from CAFs through EVs. Once bound to HuR, SNHG12 promotes the mRNA stability and expression of XIAP, contributing to the malignant progression of the disease (73).
Beyond the well-documented signaling pathways like TGF-β, NF-κB, Wnt, and AKT, as previously outlined, LncRNAs also orchestrate a variety of other signaling routes between CAFs and tumor cells. In esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, for example, the PDGFβ/PDGFRβ/FOXO1/DNM3OS signaling axis (77) and the POU3F3/IL-6 pathway (93) play significant roles. The LncRNA WEE2-AS1, when transferred from CAFs to colorectal cancer cells, functions as a “molecular scaffold” for the proteins MOB1A and the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase praja2. This interaction facilitates the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of MOB1A, thereby dampening the Hippo signaling cascade and allowing YAP to translocate to the nucleus and initiate gene transcription (47). Furthermore, the LncRNA LINC00665, secreted by breast cancer cells, can directly interact with hnRNPL, enhancing the transcription of RAB27B. This interaction stimulates the secretion of HGF by CAFs, which in turn promotes the development of tumor lymphatic vessels (95).
In the context of lung cancer, the “ceRNA” molecular mechanism is instrumental in establishing critical pathways, including OIP5-AS1/miR-142-5p/PD-L1 (84), MEG3/miR-15a-5p/CCNE1 (62), and HOTAIRM1/miR-328-5p/SPON2 (63). Comparable “ceRNA” mechanisms have been identified in other cancers: the LINC00152/miR-205-5p/CXCL-11 pathway in liver cancer (58); the NORAD/miR-496/IL-33 pathway in gastric cancer (56); the LINC00355/miR-34b-5p/ABCB1 pathway in bladder cancer (74); the CASC9/miR-215/TWIST2 pathway in cervical cancer (66); the TUC338/miR-8485/CBX2 pathway in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (52); and the lnc003875/miR-363/EGR1/Ang-1 pathway in placental site trophoblastic tumor (90). Beyond their role as “ceRNA,” LncRNAs also exert epigenetic control over miRNAs. For example, H19, upon transfer from CAFs to lung cancer cells, recruits the DNMT1 enzyme, leading to increased methylation and subsequent suppression of miR-497 expression, a strategy that enhances the tumor cells’ drug resistance (75).
Early detection of cancer is essential for precise therapeutic strategies and prognostic evaluation, but existing diagnostic approaches do not fully meet the expectations. Hence, the quest for biomarkers that exhibit both specificity and sensitivity is imperative. The dysregulation of LncRNAs is linked to the genesis, progression, metastasis, and prognostic outcomes of cancer, positioning them as promising candidates for biomarkers (109, 110). Upon reviewing the communication medium LncRNAs between CAFs and tumor cells, it has been observed that most LncRNAs are highly expressed in tumors and are associated with pathological indicators such as tumor volume, degree of differentiation, and tumor staging. Furthermore, they correlate with patient prognosis indicators, such as overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS), and progression-free survival (PFS), suggesting that CAFs-associated LncRNAs may serve as potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for cancer (Table 2). However, the current evidence is insufficient to support the use of LncRNAs as established biomarkers in clinical diagnostics. There is a need to expand sample sizes and validate these findings in large-scale, multi-population, multi-center studies. Additionally, further analysis is required to determine whether LncRNAs are independent risk factors for cancer and independent prognostic markers.
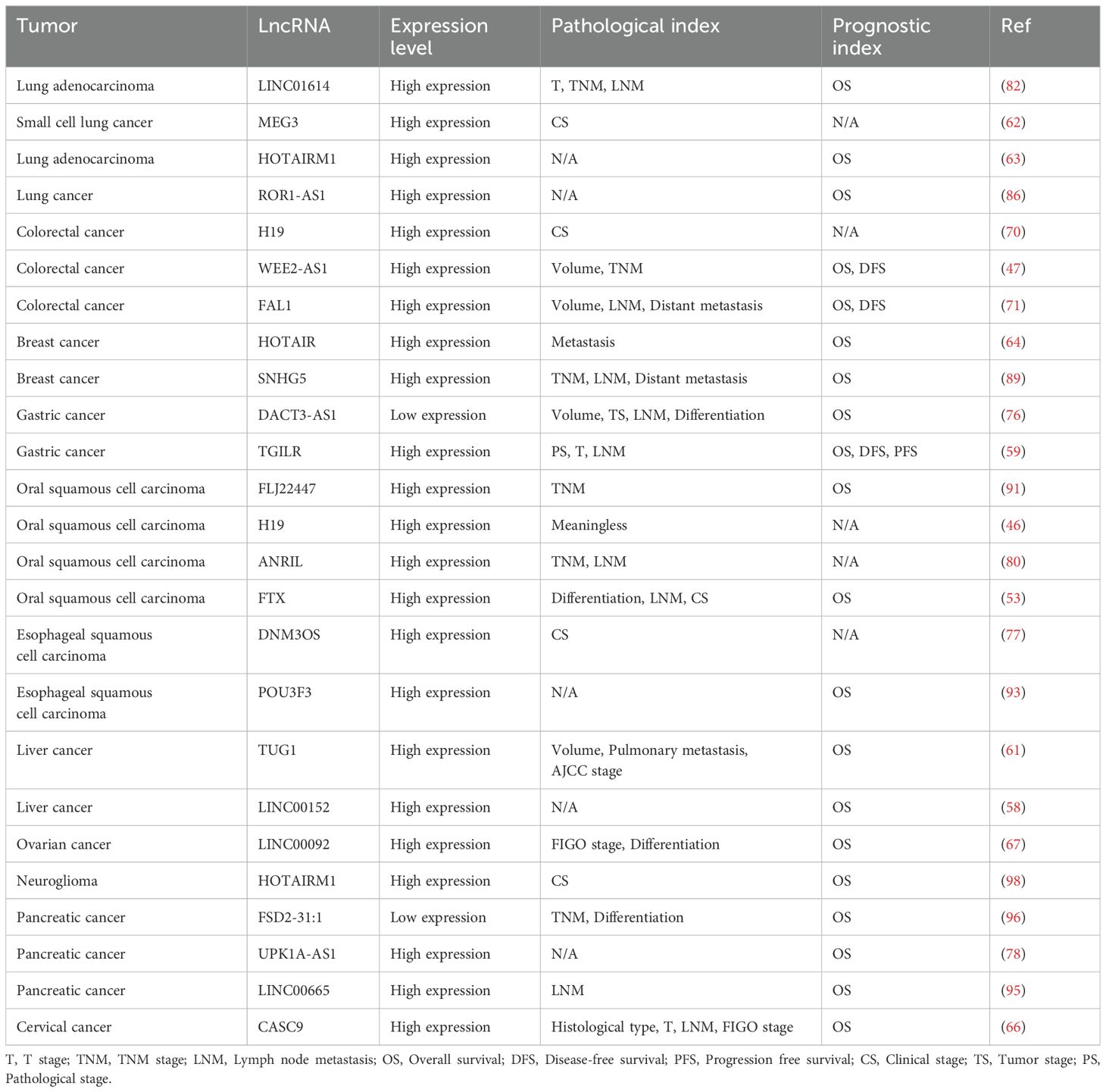
Table 2. The relationship between CAFs-related LncRNAs and tumor pathological indicators and prognosis.
Liquid biopsy, as an emerging technique for tumor detection, offers several advantages, including non-invasiveness, low risk, and the ability to perform dynamic monitoring. Subsequent research is recommended to explore the potential application of CAFs-associated LncRNAs in the field of tumor liquid biopsy.
With an ever-increasing comprehension of cancer, the research spotlight has transcended the confines of the cancer cells themselves, delving into the complex functionalities of the TME, which are paramount in tumor growth, metastasis, resistance to therapy, and relapse. CAFs occupy a significant role within the TME, engaging in reciprocal communication with cancer cells to foster a nurturing environment for tumorigenesis. LncRNAs, as novel molecular couriers, have captured the interest of researchers for their multifaceted roles in the genesis and evolution of cancer.
The aberrant modulation of specific signaling cascades within tumors is a pivotal determinant of their development. CAFs or cancer cells initiate upstream signals via paracrine signaling, intercellular interactions, and exosome release, modulating the activation or suppression of particular pathways, thus influencing the malignancy of the tumor’s biological behavior. Our focus has been on the interplay between CAFs and cancer cells, encapsulating the patterns of their crosstalk and examining the signaling pathways and biological functions mediated by LncRNAs in their communication, while mapping out a molecular network based on these regulatory pathways.
Grasping the intricacies of these pathways and the modulatory influence of CAFs on tumor advancement is crucial for refining current oncological therapeutics. For example, targeting the EVs or proteins secreted by CAFs could sever the link between cancer cells and CAFs; inhibiting CAFs’ activation and reprogramming them into a dormant state of fibroblasts; or homing in on LncRNAs of CAF origin within cancer cells to impede their downstream signaling cascades. Although this review encompasses a vast array of LncRNA-mediated communication mechanisms between CAFs and cancer cells, there remains a dearth of research into the intricate regulatory networks within the TME. This gap could result in an oversight of other unknown factors or the activation of latent compensatory signals when obstructing the signaling pathways of the tumor stroma. Consequently, within the broader context of cancer treatment, it is imperative to consider the intercommunication between cancer cells and CAFs from a holistic perspective.
CY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft. YL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft. NZ: Investigation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. XL: Investigation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. XT: Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing. ZS: Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing. MT: Writing – review & editing. YH: Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing. KC: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. MS: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The present study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 82070222 and 82370208) and the Training Program for Young and Middle−aged Health Science and Technology Innovation Leaders in Henan Province (grant no. YXKC2022015).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
SMT, Somatic Mutation Theory; TME, tumor microenvironment; CAFs, cancer-associated fibroblasts; ECM, extracellular matrix; ncRNAs, non-coding RNAs; LncRNAs, long non-coding RNAs; ROS, reactive oxygen species; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; EndMT, endothelial-mesenchymal transition; FAP, fibroblast activation protein; FSP1, fibroblast-specific protein 1; α-SMA, alpha-smooth muscle actin; PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor; rCAFs, restraining CAFs; myCAFs, myofibroblast CAFs; iCAFs, inflammatory CAFs; apCAFs, antigen-presenting CAFs; Tregs, regulatory T cells; EVs, extracellular vesicles; ceRNA, competing endogenous RNA; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β; CCL, chemoattractant cytokine ligands; CXCL, C-X-C motif chemokine ligands; IL, interleukins; PD-L1, programmed death ligand 1; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; PK, pyruvate kinase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; HK, hexokinase; PFK, phosphofructokinase; GLUT, glucose transporters; HuR, Hu antigen R; HIF-1, Hypoxia-inducible factor 1; TNM, TNM stage; LNM, Lymph node metastasis; OS, Overall survival; DFS, Disease-free survival; PFS, Progression free survival; CS, Clinical stage; TS, Tumor stage; PS, Pathological stage.
1. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
2. Monti N, Verna R, Piombarolo A, Querqui A, Bizzarri M, Fedeli V. Paradoxical behavior of oncogenes undermines the somatic mutation theory. Biomolecules. (2022) 12:662. doi: 10.3390/biom12050662
3. Shiu J, Lander AD. When oncogenes do not cause cancer. Elife. (2021) 10:e74912. doi: 10.7554/eLife.74912
4. Quail DF, Joyce JA. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med. (2013) 19(11):1423–37. doi: 10.1038/nm.3394
5. Dunbar KJ, Wong KK, Rustgi AK. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in esophageal cancer. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2024) 17:687–95. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2024.01.008
6. Chen X, Song E. Turning foes to friends: targeting cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. (2019) 18:99–115. doi: 10.1038/s41573-018-0004-1
7. Hu D, Li Z, Zheng B, Lin X, Pan Y, Gong P, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in breast cancer: Challenges and opportunities. Cancer Commun (Lond). (2022) 42:401–34. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12291
8. Herman AB, Tsitsipatis D, Gorospe M. Integrated lncRNA function upon genomic and epigenomic regulation. Mol Cell. (2022) 82:2252–66. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.05.027
9. Ali T, Grote P. Beyond the RNA-dependent function of LncRNA genes. Elife. (2020) 9:e60583. doi: 10.7554/eLife.60583
10. Rimal R, Desai P, Daware R, Hosseinnejad A, Prakash J, Lammers T, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: Origin, function, imaging, and therapeutic targeting. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. (2022) 189:114504. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114504
11. Foster DS, Jones RE, Ransom RC, Longaker MT, Norton JA. The evolving relationship of wound healing and tumor stroma. JCI Insight. (2018) 3:e99911. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.99911
12. Arina A, Idel C, Hyjek EM, Alegre ML, Wang Y, Bindokas VP, et al. Tumor-associated fibroblasts predominantly come from local and not circulating precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2016) 113:7551–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1600363113
13. Quante M, Tu SP, Tomita H, Gonda T, Wang SS, Takashi S, et al. Bone marrow-derived myofibroblasts contribute to the mesenchymal stem cell niche and promote tumor growth. Cancer Cell. (2011) 19:257–72. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.01.020
14. Larue AC, Masuya M, Ebihara Y, Fleming PA, Visconti RP, Minamiguchi H, et al. Hematopoietic origins of fibroblasts: I. In vivo studies of fibroblasts associated with solid tumors. Exp Hematol. (2006) 34:208–18. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2005.10.009
15. Jotzu C, Alt E, Welte G, Li J, Hennessy BT, Devarajan , et al. Adipose tissue derived stem cells differentiate into carcinoma-associated fibroblast-like cells under the influence of tumor derived factors. Cell Oncol (Dordr). (2011) 34:55–67. doi: 10.1007/s13402-011-0012-1
16. Liao Z, Tan ZW, Zhu P, Tan NS. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in tumor microenvironment - Accomplices in tumor Malignancy. Cell Immunol. (2019) 343:103729. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2017.12.003
17. Kalluri R, Weinberg RA. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. (2009) 119:1420–8. doi: 10.1172/JCI39104
18. Potenta S, Zeisberg E, Kalluri R. The role of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer progression. Br J Cancer. (2008) 99:1375–9. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604662
19. Hosaka K, Yang Y, Seki T, Fischer C, Dubey O, Fredlund E, et al. Pericyte-fibroblast transition promotes tumor growth and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2016) 113:E5618–5627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1608384113
20. Yin C, Evason KJ, Asahina K, Stainier DY. Hepatic stellate cells in liver development, regeneration, and cancer [J. J Clin Invest. (2013) 123:1902–10. doi: 10.1172/JCI66369
21. Qin Q, Yu R, Eriksson JE, Tsai HI, Zhu H. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma therapy: Challenges and opportunities. Cancer Lett. (2024) 591:216859. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.216859
22. Sun H, Wang X, Wang X, Xu M, Sheng W. The role of cancer-associated fibroblasts in tumorigenesis of gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:874. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05320-8
23. Arnold JN, Magiera L, Kraman M, Fearon DT. Tumoral immune suppression by macrophages expressing fibroblast activation protein-α and heme oxygenase-1. Cancer Immunol Res. (2014) 2:121–6. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-13-0150
24. Qi M, Fan S, Huang M, Pan J, Li Y, Miao Q, et al. Targeting FAPα-expressing hepatic stellate cells overcomes resistance to antiangiogenics in colorectal cancer liver metastasis models. J Clin Invest. (2022) 132:e157399. doi: 10.1172/JCI157399
25. Österreicher CH, Penz-Österreicher M, Grivennikov SI, Grivennikov SI, Guma M, Koltsova EK, Datz C, et al. Fibroblast-specific protein 1 identifies an inflammatory subpopulation of macrophages in the liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2011) 108:308–13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1017547108
26. Giurdanella G, Montalbano G, Gennuso F, Brancati S, Lo Furno D, Augello A, et al. Isolation, cultivation, and characterization of primary bovine cochlear pericytes: A new in vitro model of stria vascularis. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:1978–86. doi: 10.1002/jcp.v234.3
27. Fang L, Zhang M, Li J, Zhou L, Tamm M, Roth M. Airway smooth muscle cell mitochondria damage and mitophagy in COPD via ERK1/2 MAPK. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213987
28. Glaser-Gabay L, Raiter A, Battler A, Hardy B. Endothelial cell surface vimentin binding peptide induces angiogenesis under hypoxic/ischemic conditions. Microvasc Res. (2011) 82:221–6. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2011.07.006
29. Pereira BA, Vennin C, Papanicolaou M, Chambers CR, Herrmann D, Morton JP, et al. CAF subpopulations: A new reservoir of stromal targets in pancreatic cancer. Trends Cancer. (2019) 5:724–41. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2019.09.010
30. Biffi G, Tuveson DA. Diversity and biology of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Physiol Rev. (2021) 101:147–76. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00048.2019
31. Öhlund D, Handly-Santana A, Biffi G, Elyada E, Almeida AS, Ponz-Sarvise M, et al. Distinct populations of inflammatory fibroblasts and myofibroblasts in pancreatic cancer. J Exp Med. (2017) 214:579–96. doi: 10.1084/jem.20162024
32. Elyada E, Bolisetty M, Laise P, Flynn WF, Courtois ET, Burkhart RA, et al. Cross-species single-cell analysis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma reveals antigen-presenting cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cancer Discovery. (2019) 9:1102–23. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0094
33. Hosein AN, Brekken RA, Maitra A. Pancreatic cancer stroma: an update on therapeutic targeting strategies. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2020) 17:487–505. doi: 10.1038/s41575-020-0300-1
34. Slack FJ, Chinnaiyan AM. The role of non-coding RNAs in oncology. Cell. (2019) 179:1033–55. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.10.017
35. Kopp F, Mendell JT. Functional classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. (2018) 172:393–407. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.01.011
36. Bhan A, Soleimani M, Mandal SS. Long noncoding RNA and cancer: A new paradigm. Cancer Res. (2017) 77:3965–81. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2634
37. Yao ZT, Yang YM, Sun MM, He Y, Liao L, Chen KS, et al. New insights into the interplay between long non-coding RNAs and RNA-binding proteins in cancer. Cancer Commun (Lond). (2022) 42:117–40. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12254
38. Kalluri R, Lebleu VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. (2020) 367:eaau6977. doi: 10.1126/science.aau6977
39. Kalluri R, Mcandrews KM. The role of extracellular vesicles in cancer. Cell. (2023) 186:1610–26. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.03.010
40. Maacha S, Bhat AA, Jimenez L, Raza A, Haris M, Uddin S, et al. Extracellular vesicles-mediated intercellular communication: roles in the tumor microenvironment and anti-cancer drug resistance. Mol Cancer. (2019) 18:55. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-0965-7
41. Propper DJ, Balkwill FR. Harnessing cytokines and chemokines for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2022) 19:237–53. doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00588-9
42. Dauer P, Zhao X, Gupta VK, Sharma N, Kesh K, Gnamlin P, et al. Inactivation of cancer-associated-fibroblasts disrupts oncogenic signaling in pancreatic cancer cells and promotes its regression. Cancer Res. (2018) 78:1321–33. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-2320
43. Cruz-Bermúdez A, Laza-Briviesca R, Vicente-Blanco RJ, García-Grande A, Coronado MJ, Laine-Menéndez S, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts modify lung cancer metabolism involving ROS and TGF-β signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. (2019) 130:163–73. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.10.450
44. Oya Y, Hayakawa Y, Koike K. Tumor microenvironment in gastric cancers. Cancer Sci. (2020) 111:2696–707. doi: 10.1111/cas.v111.8
45. Li Z, Sun C, Qin Z. Metabolic reprogramming of cancer-associated fibroblasts and its effect on cancer cell reprogramming. Theranostics. (2021) 11:8322–36. doi: 10.7150/thno.62378
46. Yang J, Shi X, Yang M, Luo J, Gao Q, Wang X, et al. Glycolysis reprogramming in cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes the growth of oral cancer through the lncRNA H19/miR-675-5p/PFKFB3 signaling pathway. Int J Oral Sci. (2021) 13:12. doi: 10.1038/s41368-021-00115-7
47. Yang P, Zhang D, Wang T, Ji J, Jin C, Peng C, et al. CAF-derived exosomal WEE2-AS1 facilitates colorectal cancer progression via promoting degradation of MOB1A to inhibit the Hippo pathway. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:796. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05240-7
48. Zhao J, Lin H, Huang K, Li S. Cancer-associated fibroblasts-derived extracellular vesicles carrying lncRNA SNHG3 facilitate colorectal cancer cell proliferation via the miR-34b-5p/HuR/HOXC6 axis. Cell Death Discovery. (2022) 8:346. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01116-z
49. Fan JT, Zhou ZY, Luo YL, Luo Q, Chen SB, Zhao JC, et al. Exosomal lncRNA NEAT1 from cancer-associated fibroblasts facilitates endometrial cancer progression via miR-26a/b-5p-mediated STAT3/YKL-40 signaling pathway. Neoplasia. (2021) 23:692–703. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2021.05.004
50. Zhang Y, Luo G, You S, Zhang L, Liang C, Chen X. Exosomal LINC00355 derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes bladder cancer cell proliferation and invasion by regulating miR-15a-5p/HMGA2 axis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). (2021) 53:673–82. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmab041
51. Li Y, Zhao Z, Liu W, Li X. SNHG3 functions as miRNA sponge to promote breast cancer cells growth through the metabolic reprogramming. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. (2020) 191:1084–99. doi: 10.1007/s12010-020-03244-7
52. Li T, Tian L, Cao J, Liu M. Cancer-associated fibroblasts secret extracellular vesicles to support cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cell Probes. (2023) 72:101934. doi: 10.1016/j.mcp.2023.101934
53. Li Y, Ma Z, Li W, Xu X, Shen P, Zhang SE, et al. PDPN(+) CAFs facilitate the motility of OSCC cells by inhibiting ferroptosis via transferring exosomal lncRNA FTX. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:759. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06280-3
54. Zhang P, Wang Q, Lu W, Zhang F, Wu D, Sun J. NNT-AS1 in CAFs-derived exosomes promotes progression and glucose metabolism through miR-889-3p/HIF-1α in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:6979. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57769-6
55. Jahangiri B, Khalaj-Kondori M, Asadollahi E, Sadeghizadeh M. Cancer-associated fibroblasts enhance cell proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer SW480 cells by provoking long noncoding RNA UCA1. J Cell Commun Signal. (2019) 13:53–64. doi: 10.1007/s12079-018-0471-5
56. Huang C, Liu J, He L, et al. The long noncoding RNA noncoding RNA activated by DNA damage (NORAD)-microRNA-496-Interleukin-33 axis affects carcinoma-associated fibroblasts-mediated gastric cancer development. Bioengineered. (2021) 12:11738–55. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2009412
57. Zhang D, Song Y, Li D, Liu X, Pan Y, Ding L, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote tumor progression by lncRNA-mediated RUNX2/GDF10 signaling in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Oncol. (2022) 16:780–94. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12935
58. Liu G, Yang ZF, Sun J, Sun BY, Zhou PY, Zhou C, et al. The LINC00152/miR-205-5p/CXCL11 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma cancer-associated fibroblasts affects cancer cell phenotypes and tumor growth. Cell Oncol (Dordr). (2022) 45:1435–49. doi: 10.1007/s13402-022-00730-4
59. Qin S, Guo Q, Liu Y, Zhang X, Huang P, Yu H, et al. A novel TGFbeta/TGILR axis mediates crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and tumor cells to drive gastric cancer progression. Cell Death Dis. (2024) 15:368. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06744-0
60. Valastyan S, Weinberg RA. Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell. (2011) 147:275–92. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.024
61. Lu L, Huang J, Mo J, Da X, Li Q, Fan M, et al. Exosomal lncRNA TUG1 from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes liver cancer cell migration, invasion, and glycolysis by regulating the miR-524-5p/SIX1 axis. Cell Mol Biol Lett. (2022) 27:17. doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00309-9
62. Sun Y, Hao G, Zhuang M, Lv H, Liu C, Su K. MEG3 lncRNA from exosomes released from cancer-associated fibroblasts enhances cisplatin chemoresistance in SCLC via a miR-15a-5p/CCNE1 axis. Yonsei Med J. (2022) 63:229–40. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2022.63.3.229
63. Chen Z, Bian C, Huang J, Li X, Chen L, Xie X, et al. Tumor-derived exosomal HOTAIRM1 regulates SPON2 in CAFs to promote progression of lung adenocarcinoma. Discovery Oncol. (2022) 13:92. doi: 10.1007/s12672-022-00553-7
64. Ren Y, Jia HH, Xu YQ, Zhou X, Zhao XH, Wang YF, et al. Paracrine and epigenetic control of CAF-induced metastasis: the role of HOTAIR stimulated by TGF-ß1 secretion. Mol Cancer. (2018) 17:5. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0758-4
65. Zhuang J, Lu Q, Shen B, Huang X, Shen L, Zheng X, et al. TGFβ1 secreted by cancer-associated fibroblasts induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition of bladder cancer cells through lncRNA-ZEB2NAT. Sci Rep. (2015) 5:11924. doi: 10.1038/srep11924
66. Zhang J, Wang Q, Quan Z. Long non-coding RNA CASC9 enhances breast cancer progression by promoting metastasis through the meditation of miR-215/TWIST2 signaling associated with TGF-β expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2019) 515:644–50. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.05.080
67. Zhao L, Ji G, Le X, Wang C, Xu L, Feng M, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00092 acts in cancer-associated fibroblasts to drive glycolysis and progression of ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. (2017) 77:1369–82. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-1615
68. Yang KD, Wang Y, Zhang F, Li QL, Luo BH, Feng DY, et al. CAF-derived midkine promotes EMT and cisplatin resistance by upregulating lncRNA ST7-AS1 in gastric cancer. Mol Cell Biochem. (2022) 477:2493–505. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04436-x
69. Sharma M, Bakshi AK, Mittapelly N, Gautam S, Marwaha D, Rai N, et al. Recent updates on innovative approaches to overcome drug resistance for better outcomes in cancer. J Control Release. (2022) 346:43–70. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.04.007
70. Ren J, Ding L, Zhang D, Shi G, Xu Q, Shen S, et al. Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts promote the stemness and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer by transferring exosomal lncRNA H19. Theranostics. (2018) 8:3932–48. doi: 10.7150/thno.25541
71. Zhu S, Mao J, Zhang X, Wang P, Zhou Y, Tong J, et al. CAF-derived exosomal lncRNA FAL1 promotes chemoresistance to oxaliplatin by regulating autophagy in colorectal cancer. Dig Liver Dis. (2024) 56:330–42. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2023.06.010
72. Deng X, Ruan H, Zhang X, Xu X, Zhu Y, Peng H, et al. Long noncoding RNA CCAL transferred from fibroblasts by exosomes promotes chemoresistance of colorectal cancer cells. Int J Cancer. (2020) 146:1700–16. doi: 10.1002/ijc.v146.6
73. Tan D, Li G, Zhang P, Peng C, He B. LncRNA SNHG12 in extracellular vesicles derived from carcinoma-associated fibroblasts promotes cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Bioengineered. (2022) 13:1838–57. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2018099
74. Luo G, Zhang Y, Wu Z, Zhang L, Liang C, Chen X. Exosomal LINC00355 derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes bladder cancer cell resistance to cisplatin by regulating miR-34b-5p/ABCB1 axis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). (2021) 53:558–66. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmab023
75. Tao S, Wang J, Li F, Shi B, Ren Q, Zhuang Y, et al. Extracellular vesicles released by hypoxia-induced tumor-associated fibroblasts impart chemoresistance to breast cancer cells via long noncoding RNA H19 delivery. FASEB J. (2024) 38:e23165. doi: 10.1096/fj.202300203R
76. Qu X, Liu B, Wang L, Liu L, Zhao W, Liu C, et al. Loss of cancer-associated fibroblast-derived exosomal DACT3-AS1 promotes Malignant transformation and ferroptosis-mediated oxaliplatin resistance in gastric cancer. Drug Resist Update. (2023) 68:100936. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2023.100936
77. Zhang H, Hua Y, Jiang Z, Yue J, Shi M, Zhen X, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast-promoted lncRNA DNM3OS confers radioresistance by regulating DNA damage response in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 25:1989–2000. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-0773
78. Zhang X, Zheng S, Hu C, Li G, Lin H, Xia R, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast-induced lncRNA UPK1A-AS1 confers platinum resistance in pancreatic cancer via efficient double-strand break repair. Oncogene. (2022) 41:2372–89. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02253-6
79. Sun X, Chen Z. Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived CCL5 contributes to cisplatin resistance in A549 NSCLC cells partially through upregulation of lncRNA HOTAIR expression. Oncol Lett. (2021) 22:696. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12957
80. Zhang D, Ding L, Li Y, Ren J, Shi G, Wang Y, et al. Midkine derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes cisplatin-resistance via up-regulation of the expression of lncRNA ANRIL in tumour cells. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:16231. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13431-y
81. Faubert B, Solmonson A, Deberardinis RJ. Metabolic reprogramming and cancer progression. Science. (2020) 368:eaaw5473. doi: 10.1126/science.aaw5473
82. Liu T, Han C, Fang P, Ma Z, Wang X, Chen H, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast-specific lncRNA LINC01614 enhances glutamine uptake in lung adenocarcinoma. J Hematol Oncol. (2022) 15:141. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01359-4
83. Tong X, Tang R, Xiao M, Xu J, Wang W, Zhang B, et al. Targeting cell death pathways for cancer therapy: recent developments in necroptosis, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and cuproptosis research. J Hematol Oncol. (2022) 15:174. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01392-3
84. Jiang Y, Wang K, Lu X, Wang Y, Chen J. Cancer-associated fibroblasts-derived exosomes promote lung cancer progression by OIP5-AS1/miR-142-5p/PD-L1 axis. Mol Immunol. (2021) 140:47–58. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2021.10.002
85. Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. (2012) 149:1060–72. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
86. Yao F, Zhao Y, Wang G, Zhao M, Hong X, Ye Z, et al. Exosomal lncRNA ROR1-AS1 from cancer-associated fibroblasts inhibits ferroptosis of lung cancer cells through the IGF2BP1/SLC7A11 signal axis. Cell Signal. (2024) 120:111221. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111221
87. Zhao J, Yang S, Lv C, Liu Y. Cancer-associated fibroblasts suppressed ferroptosis in glioblastoma via upregulating lncRNA DLEU1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2023) 324:C1039–c1052. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00454.2022
88. Song X, Guo Y, Song P, Duan D, Guo W. Non-coding RNAs in regulating tumor angiogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:751578. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.751578
89. Zeng H, Hou Y, Zhou X, Lang L, Luo H, Sun Y, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts facilitate premetastatic niche formation through lncRNA SNHG5-mediated angiogenesis and vascular permeability in breast cancer. Theranostics. (2022) 12:7351–70. doi: 10.7150/thno.74753
90. Zhang S, Tao X, Cao Q, Feng X, Wu J, Yu H, et al. lnc003875/miR-363/EGR1 regulatory network in the carcinoma -associated fibroblasts controls the angiogenesis of human placental site trophoblastic tumor (PSTT). Exp Cell Res. (2020) 387:111783. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.111783
91. Ding L, Ren J, Zhang D, Li Y, Huang X, Hu Q, et al. A novel stromal lncRNA signature reprograms fibroblasts to promote the growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma via LncRNA-CAF/interleukin-33. Carcinogenesis. (2018) 39:397–406. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgy006
92. Xu Q, Zhao T, Han H, Fan J, Xie W. EIF4A3 stabilizes the expression of lncRNA AGAP2-AS1 to activate cancer-associated fibroblasts via MyD88/NF-κb signaling. Thorac Cancer. (2023) 14:450–61. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14762
93. Tong Y, Yang L, Yu C, Zhu W, Zhou X, Xiong Y, et al. Tumor-Secreted Exosomal lncRNA POU3F3 Promotes Cisplatin Resistance in ESCC by Inducing Fibroblast Differentiation into CAFs. Mol Ther Oncolytics. (2020) 18:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.05.014
94. Chang X, Tan Q, Xu J, Wu X, Wang Y, Zhang Y, et al. Tumor-derived exosomal linc00881 induces lung fibroblast activation and promotes osteosarcoma lung migration. Cancer Cell Int. (2023) 23:287. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03121-3
95. Li Y, Zheng H, Luo Y, Lin Y, An M, Kong Y, et al. An HGF-dependent positive feedback loop between bladder cancer cells and fibroblasts mediates lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis. Cancer Commun (Lond). (2023) 43:1289–311. doi: 10.1002/cac2.v43.12
96. Geng X, Li L, Luo Y, Yang W, Hu J, Zhao Z, et al. Tumor cell derived lnc-FSD2-31:1 contributes to cancer-associated fibroblasts activation in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression through extracellular vesicles cargo miR-4736. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2023) 10:e2203324. doi: 10.1002/advs.202203324
97. Wang Z, Wang X, Zhang T, Su L, Liu B, Zhu Z, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 promotes gastric cancer progression via inhibiting autophagic flux and inducing fibroblast activation. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:368. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03645-4
98. Wang H, Li H, Jiang Q, Dong X, Li S, Cheng S, et al. HOTAIRM1 Promotes Malignant Progression of Transformed Fibroblasts in Glioma Stem-Like Cells Remodeled Microenvironment via Regulating miR-133b-3p/TGFβ Axis. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:603128. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.603128
99. Peng D, Fu M, Wang M, Wei Y, Wei X. Targeting TGF-β signal transduction for fibrosis and cancer therapy. Mol Cancer. (2022) 21:104. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01569-x
100. Moustakas A, Heldin CH. Non-smad TGF-beta signals. J Cell Sci. (2005) 118:3573–84. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02554
101. Didonato JA, Mercurio F, Karin M. NF-κB and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol Rev. (2012) 246:379–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01099.x
102. Manning BD, Toker A. AKT/PKB signaling: navigating the network. Cell. (2017) 169:381–405. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.04.001
103. Liu J, Xiao Q, Xiao J, Niu C, Li Y, Zhang X, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signalling: function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2022) 7:3. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00762-6
104. Zhong X, He X, Wang Y, Hu Z, Huang H, Zhao S, et al. Warburg effect in colorectal cancer: the emerging roles in tumor microenvironment and therapeutic implications. J Hematol Oncol. (2022) 15:160. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01358-5
105. Reinfeld BI, Rathmell WK, Kim TK, Rathmell JC. The therapeutic implications of immunosuppressive tumor aerobic glycolysis. Cell Mol Immunol. (2022) 19:46–58. doi: 10.1038/s41423-021-00727-3
106. Gregory CD. Hijacking homeostasis: Regulation of the tumor microenvironment by apoptosis. Immunol Rev. (2023) 319:100–27. doi: 10.1111/imr.v319.1
107. Camuzard O, Santucci-Darmanin S, Carle GF, Pierrefite-Carle V. Autophagy in the crosstalk between tumor and microenvironment. Cancer Lett. (2020) 490:143–53. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.06.015
108. Wu X, Xu L. The RNA-binding protein HuR in human cancer: A friend or foe? Adv Drug Delivery Rev. (2022) 184:114179. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114179
109. Schmitt AM, Chang HY. Long noncoding RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell. (2016) 29:452–63. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.03.010
Keywords: long non-coding RNAs, cancer-associated fibroblasts, tumor microenvironment, signaling pathway, tumor growth
Citation: Yang C, Shu J, Li Y, Zhao N, Liu X, Tian X, Sun Z, Tabish MS, Hong Y, Chen K and Sun M (2024) Long non-coding RNAs are involved in the crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and tumor cells. Front. Immunol. 15:1469918. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1469918
Received: 24 July 2024; Accepted: 22 November 2024;
Published: 09 December 2024.
Edited by:
Chandrasekhar Kanduri, University of Gothenburg, SwedenReviewed by:
Ranran Zhang, University of Alberta, CanadaCopyright © 2024 Yang, Shu, Li, Zhao, Liu, Tian, Sun, Tabish, Hong, Chen and Sun. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kuisheng Chen, Y2hlbmtzaDIwMDJAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Miaomiao Sun, c3VubWlhb21pYW9oZEAxNjMuY29t
†These authors share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.