- 1Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL, United States
- 2Center for Clinical and Translational Science, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, United States
- 3Mayo Clinic Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, United States
- 4Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, United States
- 5Department of Cancer Biology, Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL, United States
- 6Center for Systems Biology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, United States
- 7Department of Molecular Pharmacology & Experimental Therapeutics, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, United States
- 8Department of Vascular Surgery, Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL, United States
- 9School of Chemical Engineering, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, QLD, Australia
- 10Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, QLD, Australia
- 11Van Cleve Cardiac Regenerative Medicine Program, Mayo Clinic Center for Regenerative Medicine, Rochester, MN, United States
- 12Department of Clinical Genomics, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, United States
- 13Department of Immunology, Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL, United States
Introduction: Extracellular vesicles (EVs) can potently inhibit inflammation yet there is a lack of understanding about the impact of donor characteristics on the efficacy of EVs. The goal of this study was to determine whether the sex and age of donor platelet-derived EVs (PEV) affected their ability to inhibit viral myocarditis.
Methods: PEV, isolated from men and women of all ages, was compared to PEV obtained from women under 50 years of age, which we termed premenopausal PEV (pmPEV). Because of the protective effect of estrogen against myocardial inflammation, we hypothesized that pmPEV would be more effective than PEV at inhibiting myocarditis. We injected PEV, pmPEV, or vehicle control in a mouse model of viral myocarditis and examined histology, gene expression, protein profiles, and performed proteome and microRNA (miR) sequencing of EVs.
Results: We found that both PEV and pmPEV significantly inhibited myocarditis; however, PEV was more effective, which was confirmed by a greater reduction of inflammatory cells and proinflammatory and profibrotic markers determined using gene expression and immunohistochemistry. Proteome and miR sequencing of EVs revealed that PEV miRs specifically targeted antiviral, Toll-like receptor (TLR)4, and inflammasome pathways known to contribute to myocarditis while pmPEV contained general immunoregulatory miRs.
Discussion: These differences in EV content corresponded to the differing anti-inflammatory effects of the two types of EVs on viral myocarditis.
1 Introduction
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are biological nanoparticles that can be used therapeutically because of their ability to act as biocompatible disease modulators. EVs function as important systems for cellular communication in the body, encapsulating autocrine, paracrine, and endocrine messages that regulate local and systemic responses (1, 2). The umbrella term ‘EV’ refers to lipid bilayer encapsulated, functional nanoparticles from two main biogenesis categories: either an invagination of the plasma membrane and intracellular processing into vesicles (exosomes), or an outward budding of the plasma membrane during specific cell responses, including apoptosis (ectosomes or microvesicles) (3, 4). However, these categories are distinct in name and biogenesis only, as functional differences cannot yet be ascertained (4). There are currently no accepted exosome or microvesicle-specific markers, and thus EVs are characterized as bulk, heterogenous products (3, 5). The notorious heterogeneity of EVs has created significant limitations to their use as therapies. EVs contain an unlimited variety of functional contents including DNA, mRNA, microRNA (miRs), glycans, and proteins (5, 6). Depending on the state of the parent cell at the time the EV is formed, they may also contain cellular organelles or portions of organelles like mitochondria (3, 7). EV heterogeneity is further induced by differing isolation procedures, storage temperatures, and processing times, all of which can alter the composition of EVs and complicate batch-to-batch consistency of therapeutic products (3, 5).
Another understudied source of heterogeneity is donor origin. The importance of identifying an ‘ideal donor’ is not a new topic, as the regenerative medicine field has documented concerns regarding this issue for many years (8, 9). However, poor understanding regarding the impact of donor selection on EV characteristics remains a significant gap in knowledge. The body of literature surrounding preclinical EV therapies is growing; however, donor selection criteria other than age is a largely unexplored topic (10, 11). Regardless of whether EVs are derived from cell culture or extracted directly from patient fluids or tissues, identification of ideal donors or ideal donor subsets that confer maximum therapeutic potency is essential.
We recently reported that platelet-derived EVs were able to reduce myocardial inflammation and fibrosis and improve cardiac function in a translational model of viral myocarditis (12). Myocarditis is defined as inflammation of the heart and is commonly associated with viral infections such as SARS-CoV-2 and coxsackie B virus (CVB) infections (13–15). Our group uses an autoimmune CVB3 model of myocarditis, where a mild viral infection with a human derived-CVB3 strain acts as an adjuvant to induce myocarditis (16). The model is highly translational, matching the time-course, clinical features, pathogenesis of disease, and biomarkers of human lymphocytic myocarditis, including progression to dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) and heart failure in susceptible strains of mice (14, 17–19). Clinical myocarditis has been reported to have a sex ratio of around 3.5:1 male to female (14, 19). Our animal model of CVB3 myocarditis also displays a clear sex difference where the immune response by sex has been well characterized [reviewed in (13, 14)]. We, and others, have shown previously that testosterone increases CVB3 myocarditis while estrogen/17β1-estradiol is cardioprotective (14, 19–21). Key pathways that increase CVB3 myocarditis in males include Toll-like receptor (TLR)4 signaling on cardiac mast cells and macrophages, and inflammasome activation, which lead to elevated interleukin (IL)-1β levels that increase inflammation and remodeling/fibrosis, resulting in acute myocarditis and progression to DCM in white background mice (i.e., BALB/c, A/J) (14, 22, 23). Because of the strongly protective role of estrogen in myocarditis, here we investigated whether specific donor demographics (sex and age) would alter the ability of EVs to reduce myocarditis. We tested whether platelets obtained from women under the age of 50 would be more effective at reducing myocarditis than EVs obtained from the platelets of men and women of all ages.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Ethics statement
Mice were maintained under pathogen-free conditions in the animal facility at Mayo Clinic Florida, with approval from the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) at Mayo Clinic Florida for all procedures (IACUC A00002398). Mice were used and humanely euthanized according to the standards of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institutes of Health and in accordance with practices of the Mayo Clinic Florida IACUC.
2.2 Platelet-derived EV products
Human EVs were obtained from pooled apheresis platelets from two groups of United States donors to make two analogous, but separate products. A batch of platelet-derived EVs (PEV) was created from 10 male and female donors of all ages, as previously described (24, 25). Similarly, a batch of EVs was created from 10 women under the age of 50 years, which we termed premenopausal PEV (pmPEV). Both PEV and pmPEV were processed in the same manner. Briefly, a clinical grade manufacturing protocol was used to pool conditioned medium from apheresis platelets and isolate exosomes according to US patent 20160324A1 (24, 25). Serial filtration and lyophilization processes yielded a bioactive extracellular vesicle cake in sterile vials, which was confirmed to be pyrogen free, without preservatives, and room temperature stable up to 24 months. The presence of platelet-derived EVs was confirmed using EV markers CD63 and CD9, and platelet marker CD41, as previously (24, 25). PEV is manufactured by Rion, Inc. (Rochester, Minnesota, USA) and is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use as an investigational new drug in human clinical trials for wound healing (NCT04664738) and has received FDA approval for Phase 1 clinical trials in ischemic heart disease. pmPEV was produced specifically for use in this project. PEV and pmPEV were reconstituted in 1x sterile phosphate buffered saline (PBS) at 11.2 mg dry weight for PEV/mL and 8.0 mg dry weight for pmPEV/mL to achieve a final concentration of 1x10 12 particles/mL for both products (24, 25).
2.3 Extracellular vesicle characterization
2.3.1 Nanoparticle tracking analysis
Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) was used to determine the size distribution and particle concentration of reconstituted PEV and pmPEV using a Nanosight NS300 V3.3.4 (Malvern Panalytical, Malvern, United Kingdom) for three replicates with measurement time at 60 s, flow rate 40 µL/min, camera level 11, and detection threshold 4, as previously (12).
2.3.2 Tunable resistive pulse sensing
Tunable resistive pulse sensing (TRPS) was used as an orthogonal method for size and concentration measures and to analyze zeta potential using an Exoid (catalog# EX1, Izon Science, Boston, Massachusetts, USA) and a 200 nm nanopore (catalog#NP200, Izon Science, Boston, Massachusetts, USA). Briefly, samples were run through a nanopore which detects resistive pulses caused by single nanoparticles passing through the charged and pressurized system. Calibration using beads (catalog#CPC200, Izon Science, Boston, Massachusetts, USA) was performed prior to sample data acquisition according to manufacturer specification and software prompts. Samples were diluted in 1xPBS with the following measurement specifications and quality control reporting: PEV (stretch: 45.49 mm, pressure: 700 Pa, voltage: 700 mV, bandwidth filter: not applied, particle rate: 474.6 particles/min, average current: 140.08 nA, and average RMS noise: 16.82 pA), pmPEV (stretch: 45.49, pressure: 1000, voltage: 600, bandwidth filter: not applied, particle rate: 212.0, average current: 126.01, and average RMS noise: 19.25). Analysis of calibration and sample data was performed using Izon data suite software version 1.0.2.32.
2.3.3 EV multiplex panel
The ProcartaPlex Human Exosome Characterization Panel 6-PlexEV multiplex assay (catalog#EPXX060-15845-901, Invitrogen, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA) was used to determine six markers: EV tetraspanins CD81, CD63, and CD9; cytosolic markers syntenin-1 and cytochrome c; and immune receptor very late antigen (VLA)-4. To make replicable comparisons, protein amounts of these markers in reconstituted PEV and pmPEV were calculated relative to amounts in a standardized EV reference control from the HCT116 human colorectal cell line (E1, catalog# 00000861, Oxford Nanopore, Oxford, Oxfordshire, United Kingdom). Plate measurements were made using a FLEXMAP 3D Luminex 200 (catalog#FLEXMAP-3D-RUO, R&D Systems, Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA) analyzed on The ProcartaPlex Analysis App on the ThermoFisher Connect cloud-based platform: https://apps.thermofisher.com/apps/procartaplex.
2.3.4 Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) were used to determine protein levels of lipoproteins apolipoprotein (Apo)A1 (catalog#DAPA10, R&D Systems, Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA) and ApoB (catalog#DAPB00, R&D Systems, Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA) in reconstituted PEV, pmPEV, and standardized control (E1, catalog# 00000861, Oxford Nanopore, Oxford, Oxfordshire, United Kingdom) samples, following kit specifications. Final protein concentrations were read at 450 nm by an 800 TS Microplate Reader (cat # 800TS-SN, BioTeK, Winooski, Vermont, USA). Protein concentrations were normalized to total amount of protein per sample in duplicate, calculated from a Bradford assay.
2.3.5 Size-exclusion chromatography
Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) was performed on PEV and pmPEV prior to visualization techniques (microscopy imaging) during characterization using an Automated Fraction Collector V1 (Izon Science, Boston, Massachusetts, USA) with a qEVoriginal column (70nm Legacy Column, cat# SP1, Izon Science, Boston, Massachusetts, USA). Briefly, following the machine default prompts for this column, 0.5 mL of reconstituted PEV or pmPEV were loaded to the top of the column and eluted into thirteen 0.5 mL fractions using a cryoprotective 5% sucrose buffer (26). Fractions 7-11, which contained enriched EVs were pooled and used for microscopy.
2.3.6 Transmission electron microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) imaging was conducted at the Mayo Clinic Microscopy and Cell Analysis Core (Rochester, Minnesota, USA) to visualize reconstituted PEV and pmPEV. Briefly, 3 µL of each reconstituted product was placed on a carbon-coated polymer film, mounted on a 200-mesh copper TEM grid, and allowed to thin and dry. 3 µL of negative stain (1% phosphotungstic acid) was added to the sample on the grid and allowed to thin and dry. Grids were loaded into a JEOL 1400 (JEOL USA, Inc., Peabody, Massachusetts, USA) transmission electron microscope operating at 80 KeV. Representative images were captured using a Gatan 832 Orius digital camera (Gatan, Pleasanton, California, USA).
2.3.7 Western blot
After reconstitution, PEV and pmPEV were lysed in 1x radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer (RIPA; catalog#89900, Pierce, Thermo-Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA) and 100X Halt™ Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (catalog#1862495, Pierce, Thermo-Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA), per manufacturer instructions. A bicinchoninic acid assay (BCA) (Pierce BCA Reagents A (catalog#23228) and B (catalog#1859078), Thermo-Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA) was used to determine lysate concentration. A total of 10.3 µg protein was loaded per lane in NuPAGE™ 4-12%, Bis-Tris, 1.0–1.5 mm, Mini Protein Gels (catalog# NP0322BOX, Thermo-Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA) and run at 165 volts in 1X NuPAGE™ 4-morpholinepropanesulfonic acid (MOPS) sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) Running Buffer (catalog#NP000102, Thermo-Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA) for 45 minutes. A Trans-Blot Turbo Transfer System was used to transfer protein to Nitrocellulose membranes using the with Mini 0.2 µm Nitrocellulose Transfer Packs (catalog#1704158, BioRad, Hercules, California, USA). Blots were blocked in 5% bovine serum albumin (BSA) in Tris-buffered saline with Tween 20 (TBST) before incubation in primary antibody solution (Supplementary Table 1). The blot was then incubated in secondary antibody solution Peroxidase AffiniPure Goat Anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) (catalog#115-035-003, 1:7500) or Peroxidase AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) (catalog#111-035-003, 1:7500) (Jackson ImmunoResearch, West Grove, Pennsylvania, USA) in 10 mL of 5% milk in TBST and imaged using a XOMAT film imager (Carestream Health, Rochester, New York, USA).
2.3.8 Tri-color direct stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy
The ONI Profiler Kit for tetraspanin profiling of EVs (catalog# 00000861, Oxford Nanopore, Oxford, Oxfordshire, United Kingdom) was used to visualize the provided standard control and SEC fractions 7-11 of PEV and pmPEV. Staining for tetraspanins CD9, CD63, and CD81 was performed according to manufacturer instructions and direct stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (dSTORM) images of all samples were acquired on an Oxford NanoImager (ONI) Microscope (Oxford, Oxfordshire, United Kingdom) in total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) microscopy mode to provide a resolution of 20-30 nm. Images were acquired using the 488 and 647 lasers and laser power was increased until visible photoswitching of fluorophores was apparent while samples were covered in buffer (GLOX beta-mercapto-ethanol with Pyranose Oxidase as previously (27). A total of 4,000 images were acquired for each channel, and localizations were determined in CODI (Oxford Nanoimaging/ONI), with localizations filtered by frame index and p value, as previously described (12). Subsequent positivity analyses were performed on all samples to determine tetraspanin profiles.
2.4 In vivo treatments
Mice were obtained from the Jackson Laboratory (8-week-old adult male BALB/cJ strain #000651, Bar Harbor, Maine, USA) and were maintained under pathogen-free conditions in the Mayo Clinic Florida animal facility. Ten mice per group (control, PEV, pmPEV) were infected intraperitoneally (ip) with 103 plaque forming units (PFU) of heart-passaged stock of coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3) on day 0, and myocarditis examined at day 10 post infection (pi). CVB3 (Nancy strain) was obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) (catalog#VR-30, ATCC, Manassas, Virginia, USA) and grown in Vero cells (catalog# CCL-81, ATCC, Manassas, Virginia, USA) to create a virus stock (16). 100 μL of tissue culture-passaged virus stock (103 PFU) was injected ip into 4-week-old female BALB/c mice (strain #000651, Jackson Laboratory, Bar Harbor, Maine, USA) and virus was obtained from hearts at day 3 pi by homogenization in Gibco Minimum Essential Media (cat#11095-080, Thermo-Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA) supplemented with 2% heat inactivated fetal bovine serum (16). Heart homogenate was centrifuged at 4°C for 20 minutes at 795 g (16). Supernatant, which contains infectious virus and damaged heart proteins (termed heart-passaged virus) was stored at -80°C until used to induce myocarditis (16). 0.25 mL of PEV, pmPEV, or 1x PBS vehicle control was administered ip to mice on days -1, 0, 1 with 103 PFU of heart-passaged virus injected ip on day 0 and myocarditis examined at day 10 pi.
2.5 Histology
Mouse hearts were cut in half longitudinally, fixed in 10% phosphate-buffered formalin for 48 hours, and embedded in paraffin, as previously reported (28). 5 µm sections were used for all histological staining. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain was used to assess myocarditis and pericarditis, or the percentage of the heart with myocardial or pericardial inflammation, respectively, normalized to the overall size of the heart section, as previously described (28–30). Masson’s trichrome was used to assess fibrosis, or collagen deposition, normalized to the total size of the heart section. CD45 (Biolegend, San Diego, CA, 103102, 1:200, rat), CD11b (Abcam, Cambridge, United Kingdom, ab133357, 1:3000, rabbit), CD3 (Abcam, ab16669, 1:200, rabbit), F4/80 (BioRad, Hercules, CA, MCA497G, 1:250, rat), TLR4 (Novus Biologicals, Littleton, CO, NB100-56580-0.1mg, 1:400, rabbit), TLR2 (Abcam, Cambridge United Kingdom, ab209216, 1:200, rabbit), or C3aR (R&D, Minneapolis, MN, MAB10417-100, 1:200, rat) with secondary antibodies (anti-rabbit: cat#K4003, Envision+ anti-rabbit labeled polymer, Agilent (Dako), Santa Clara, CA or cat#RT517 rat-on-rodent kit, Biocare, Pacheco, California, USA) were used to assess specific immune cell populations in the heart. Stained slides were scanned using an Aperio AT2 slide scanner to select representative images (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany). To analyze immunohistochemistry slides, the ventricles of each sample were manually selected by a lab member blinded to study groups. The default “positive pixel” algorithm from Aperio eSlide Manager (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany) was modified for each stain by adjusting the Color Saturation Threshold so that the program’s selection of positive and negative pixel counts accurately reflected each stain with hue set at 0.1 or brown (CD45: 0.03, CD11b: 0.14, CD3: 0.03, F4/80: n/a, TLR4: 0.10, TLR2: 0.03, C3aR: n/a), as previously described (12). The percentage of positive pixels within each annotation was determined with a positivity parameter as a surrogate for stain positivity: positivity = number of positive pixels/(total number of pixels, both positive and negative, in the annotation layer), as previously described (31).
2.6 Quantitative real-time PCR
RNA isolation was performed on heart tissue, which was first homogenized using a Tissuelyser (Qiagen, Germantown, Maryland, USA), with 7 mm stainless steel beads in RNeasy Lysis Buffer (RLT) with 0.5% DX buffer to reduce foam, as previously (32). A QIAcube instrument (catalog#9001292, Qiagen, Germantown, Maryland, USA) was used to automatically isolate and purify RNA, with reagents for RNase easy fibrous mini kit including a DNase and proteinase K step (catalog#74704, Qiagen, Germantown, Maryland, USA). RNA quantification was determined in µg/µL using NanoDrop (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA), as previously described (29, 32, 33). RNA was converted to complementary DNA (cDNA) using high-capacity cDNA reverse transcriptase kit (catalog#4368813, Applied Biosystems, Foster City, California, USA), as previously described (29, 32, 33). Gene expression from mouse hearts was assessed by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) using assay-on-demand primers and probe sets and the ABI 7000 Taqman system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, California, USA). Probe sets listed in Supplementary Table 2 were purchased from Thermo-Scientific (Waltham, Massachusetts, USA). Probe sets to detect CVB3 viral protein 1 (VP1) were obtained from Integrated DNA Technologies (Coralville, Iowa, USA) (34). Gene expression was analyzed by assessing comparative quantification, which is then used to calculate relative gene expression (RGE) using the formula: RGE = 2 − (ΔCt − ΔCt(max)), as previously.
2.7 Protein sequencing and analysis
Trypsin digestion and column fractionation were performed on reconstituted samples prior to tandem liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry, as detailed below. The Mayo Clinic Proteomic Analysis CORE completed primary and secondary analyses.
2.7.1 Tandem mass tag labeling of peptides
100μg of peptide from each sample was solubilized in 100μL of 100mM triethylammonium bicarbonate (TEAB), pH 8.5, and mixed with 100μg of a unique TMT 6plex reagent solubilized in 10μL of acetonitrile. After incubation for 1h at room temperature the reactions were quenched with 5μL of 5% hydroxylamine and a 2μL aliquot from each sample was pooled and analyzed by tandem mass spectrometry to ensure the labeling efficiency was greater than 98%. The samples were then pooled to match the reporter ion intensities from each channel and the mix was acidified. Excess TMT reagents were removed using solid phase extraction with a Waters Sep Pak Plus C18 cartridge and the eluted TMT labeled peptides lyophilized.
2.7.2 Basic pH HPLC fractionation
To reduce the sample complexity, the dried peptide mixture was solubilized in 500μL 10mM ammonium formate, pH 8.5 and separated into 96 fractions using a Dionex Ultimate 3000 RS HPLC system with a Waters XBridge BEH C18 4.6mm x 250mm column. The system was set up with 10mM ammonium formate; pH 8.5 in water for the A solvent and 10mM ammonium formate; pH 8.5/90% acetonitrile for the B solvent. The separation gradient was 5%B to 60%B over 60 minutes followed by a 2-min jump to 80%B while maintaining a constant flow rate of 0.5ml/minute. The 96 fractions were concatenated to 24 fractions and lyophilized.
2.7.3 NanoLC-tandem mass spectrometry data acquisition
The peptide fractions were analyzed by nanoLC-tandem mass spectrometry using a Thermo Scientific Exploris 480 Orbitrap mass spectrometer coupled to a Thermo Ulimate 3000 RSLCnano HLPC system with 0.1% formic acid in 98% water/2% acetonitrile for the A solvent and 0.1% formic acid in 80% acetonitrile/10% isopropanol/10% water for the B solvent. Each fraction was solubilized in 0.1% formic acid and pumped onto a Halo C18 2.7µm EXP stem trap (Optimize Technologies, Oregon City, OR) with 0.1% formic acid/0.05% TFA at a flow rate of 8mL/minute. The trap was placed in line with a 50cm x 75um EasySpray C18 column and the peptides separated with a gradient of 3%B to 35%B over 90minutes at a flow rate of 300nL/minute. The mass spectrometer was set for data dependent acquisition with a 3 sec cycle time. The MS1 survey scan range was from 350-1600 m/z at resolution 120,000 (at 200m/z) and the AGC set for a maximum of 1E6 ions and a 50ms ion injection time. Ions in the scan range of 350-1600 m/z with positive charge states from 2-4 were sequentially selected for high energy collisional dissociation (HCD) fragmentation MS/MS scans at resolution 45,000 with a NCE setting of 39 and the isolation width set to 0.7 m/z. The MS2 AGC setting was 200% (2E5 ions) and the max ion injection time was set to 105ms. The dynamic exclusion feature was used to prevent ions selected for MS2 and any ions within an m/z of 7ppm from being selected for fragmentation for 30 seconds.
2.7.4 Protein identification and TMT quantitation
The mass spectrometry raw data files were analyzed using Proteome Discoverer 2.5 (Thermo Scientific), setup for MS2 reporter ion quantification with TMT 6plex isobaric labels. The fractions were searched against a Swissprot human (2020_01) database using Sequest HT with parameters set for full trypsin specificity with oxidized Met and N-term protein acetylation allowed as variable modifications and carbamidomethyl cysteine, TMT lysine and TMT peptide n-terminus as fixed modifications. Mass tolerances were set at 10 ppm for precursor ions and.02 Dalton for MS2 fragment ions. Protein identifications with a 1 peptide minimum were filtered at 1% FDR using the Percolator node. Reporter ion channel correction factors were applied to PSMs and filtered to exclude peptides exceeding the threshold maximum of 50% isolation interference. Sample groups missing values were removed for comparisons with no imputation applied.
2.8 Proteomic pathway enrichment visualization
We performed pathway enrichment analysis to create multiple visualizations of our data using minor modifications to the protocol presented by Reimand et al. (35).
To visualize the differentially expressed proteins between PEV and pmPEV, we performed enrichment analysis on all transcripts with nominal p-value < 0.01. Gprofiler (36) was used to run an ordered query on this list, which was ordered from most to least significant p value beneath this cut off. Duplicates or transcripts without a known Ensembl ID were excluded to clean this list and the ordered query was rerun on the cleaned data, with the term size limited to 5-350, as per recommendation (35). Cytoscape V8.0.0 was used to visualize enriched pathways of this dataset with the output files from gProfiler and the Enrichment Map application within this software. Node cutoff was set to FDR(Q) value < 0.01 and default edge cutoff was used. Nodes were colored based on log fold change value and manually arranged to allow easy visualization of differences between the products.
We were also interested in displaying the distinctly enriched proteomes of both the PEV and pmPEV products and used the same methods to display these data for transcripts with p values < 0.01 of positive log2-fold change (PEV) or negative log2-fold change (pmPEV). After gProfiler analysis and Enrichment Map visualization, the nodes were further ‘super’ clustered based on their shared genes and the AutoAnnotate function within Cytoscape/Enrichment Map was used to identify clusters of nodes with shortened pathway names.
Finally, we wanted to display overlapping pathway involvement of 10 proteins shared by our 2 products and 3 similar plasma/platelet EV products from the literature (37–39). We used Gprofiler to run a non-ordered query on this list, with the same term size limits as above, and then used Cytoscape to visualize shared pathways of these proteins. AutoAnnotate was again used to label superclusters of proteins.
2.9 MicroRNA sequencing and analysis
Next-generation sequencing for miRs was performed by the Mayo Clinic Molecular Biology Core. Three samples of each product (PEV and pmPEV) were resuspended and analyzed. Qubit fluorometry (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA) and an Agilent BioAnalyzer (Santa Clara, California, USA) were used to determine total RNA concentration and quality. RNA libraries were prepared from 1 ng total RNA according to Qiagen’s guidelines for the QIAseq miRNA Library Kit (Qiagen, Germantown, Maryland, USA). Briefly, adaptors were ligated to the 3’ and 5’ ends of miRs, then a complementary primer was annealed to 3’ adaptor sequences followed by reverse transcription to generate a cDNA library of small RNAs. cDNA libraries were purified and then enriched, where a unique index was added to each sample. A final purification step was performed prior to the quantitation of completed libraries. Libraries were sequenced at approximately 30 million read pairs per sample, following Illumina’s standard protocol using the Illumina cBot (catalog#SY-301-2002, San Diego, California, USA) and HiSeq 3000/4000 PE Cluster Kit (catalog#PE-410-1001, Illumina, San Diego, California, USA). The flow cell was sequenced as 50 X 2 paired end reads on an Illumina HiSeq 4000 using HiSeq 3000/4000 sequencing kit and HD 3.4.0.38 collection software. Base-calling was performed using Illumina’s RTA version 2.7.7.
2.10 Sequencing visualization
R analysis was used to visualize sequencing results in heat maps and principal component analysis (PCA) plots. Heatmaps were created using Pheatmap version 1.0.12 within R 4.3.1 using row-wise scaling to ensure data normalization, followed by the application of unbiased hierarchical clustering for both rows and columns. This allowed identification of inherent patterns, groupings, and outliers within the data, facilitating comprehensive data exploration. PCA plots were created using the ‘stats’ package in R 4.3.1. This allowed calculation of the explained variance and the contribution of each principal component to the overall variance. Subsequently, ‘dplyr’ version 1.1.2 and ‘plotly’ version 4.10.2 were used to visualize PCA results in a three-dimensional plot. PC1 was represented on the X-axis, PC2 on the Y-axis, and PC3 on the Z-axis, offering a comprehensive view of the data’s underlying structure.
2.11 Statistical analysis
Normally distributed data comparing three groups were analyzed using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Dunnett’s test for multiple comparisons, unless otherwise specified. Statistical outliers were identified in Prism and removed prior to analysis. The data were expressed as scatter plot and mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM), unless otherwise noted. A value of p < 0.05 was considered significant. Precise p values for comparisons are listed in the text while graphs display *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 and ****, p < 0.0001. Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 9.5.1.
3 Results
3.1 PEV and pmPEV display classic EV characteristics
PEV and pmPEV were reconstituted from a lyophilized powder with PBS prior to characterization, as previously described (12, 24, 25). Size distribution using nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) showed that the mean diameter of PEV was 208.2 ± 13.3 nm and pmPEV was 155.1 ± 3.5 nm, with two modal peaks at 100-200 nm and 200-300 nm for PEV versus one modal peak at 90-160 nm for pmPEV (Figure 1A). These findings were confirmed using the orthogonal technique tunable resistive pulse sensing (TRPS), showing a mild secondary peak for PEV and only one model peak for pmPEV at similar approximate sizes to the NTA analysis (Supplementary Figures 1C–E). TRPS also revealed an expected negative zeta potential charge for both products (Figure 1B) (40, 41). Western blot identified the presence of classic EV markers including cytosolic heat shock cognate protein 70 (HSC70) and the membrane tetraspanin CD9; however, the presence of negative EV markers calnexin and Golgi matrix protein 130 (GM-130) were also detected in both products (Figure 1C) confirming the presence of both EVs and intracellular nanoparticles in these heterogenous blood platelet products. Full images of the western blots are found in Supplementary Figures 1A, B. ELISAs of ApoA1 and ApoB showed that PEV had higher ApoB content than pmPEV while PEV and pmPEV contained similar amounts of ApoA1 (Figure 1D) indicating the presence of Apo in both products. A reference EV control from HCT116, a human cancer colorectal cell line, was also included to allow comparison of these products to a commercially available, standardized EV product. The control also contained ApoA1 and ApoB demonstrating that even ‘purified’ controls contain similar co-isolating, non-EV contaminants (Figure 1D). A multiplex EV assay for five markers of EVs quantitated abundance of tetraspanins CD9, CD63, and CD81, and cytosolic proteins cytochrome C and syntenin-1 in each product compared to the EV control (Figure 1E).
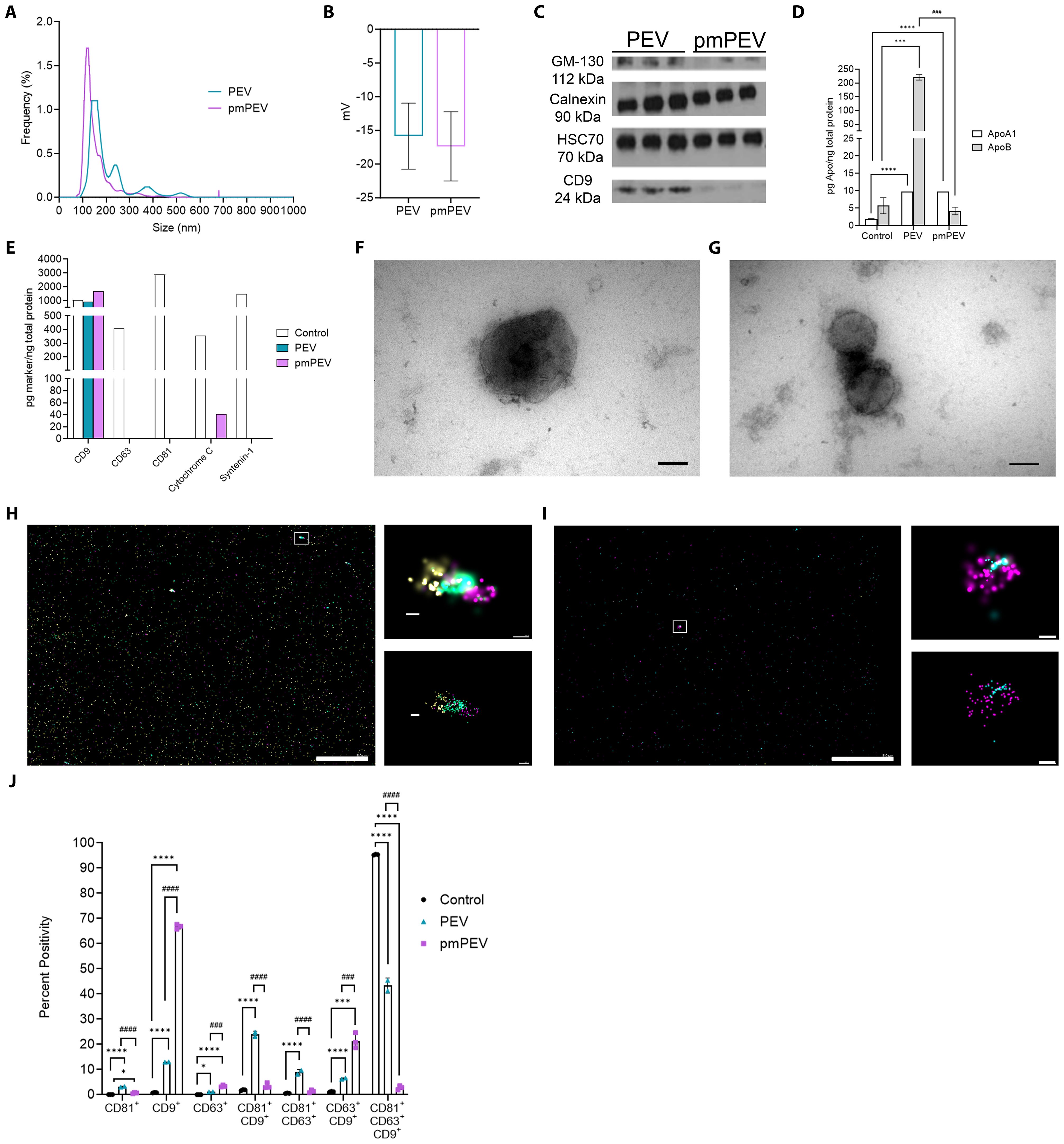
Figure 1. Characterization revealed platelet-derived EVs (PEV) and premenopausal (pm)PEV display typical extracellular vesicle (EV) profiles. PEV and pmPEV were reconstituted at 11.2 mg/mL or 8.0 mg/mL, respectively, as per manufacturer instructions. For characterization, size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) was performed on samples to provide a smaller noise to particle ratio. Fractions 7-11 from SEC were analyzed for size distribution using (A) nanoparticle tracking analysis, which was also measured by tunable resistive pulse sensing (TRPS) in Supplementary Figures 1C–E. TRPS was also used to measure (B) zeta potential, shown as mean ± SD. (C) Western blot analysis was performed to test for positive and negative EV markers, full blots found in Supplementary Figures 1A, B. (D) ELISAs and (E) EV multiplex assays were performed on samples in duplicate after reconstitution and without SEC to appropriately estimate relative abundance of positive and negative markers of EVs. (F, G) PEV and pmPEV samples were visualized with transmission electron microscopy for morphology (magnification 150,000X, Scale bars: 100 nm); widefield images found in Supplementary Figures 1F–I. Visualization was also conducted with directed stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (dSTORM) for tetraspanin profiling; CD9 (yellow), CD81 (teal), CD63 (magenta). (H, I) Large left image and right top image show raw depictions and right bottom image shows precision depictions of dSTORM; Scale bars: left image 5.0 µm; top and bottom images 100 nm. (J) Quantification of tetraspanin profiling using percent positivity was measured for each marker (single, double, or triple positive EVs) and for each sample. (J) Data show mean ± SD quantified from 3 independent pictures for each sample. Statistical analysis performed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s multiple comparison test; *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001 compared to control. ###, p < 0.001; ####, p < 0.0001 compared to PEV.
Using an EV marker multiplex assay kit the standardized control showed the presence of all EV markers, while PEV contained only CD9 and pmPEV contained CD9 and cytochrome c (Figure 1E). Cytochrome c is associated with mitochondria and can be found in both the cytoplasm and in EVs, although this marker is not specific to EVs and may be found in intracellular vesicles as well, perhaps demonstrating either pathological processes in the cell concerning mitochondria or contamination of the EV control and pmPEV product with intracellular particles (3). Transmission electron microscopy revealed a heterogenous mixture of membrane-bound particles with internal electron densities and spherical morphology consistent with the expected shape of EVs as well as background debris and clumping of particles, suggesting the presence of lipoproteins and other non-EV components (Figures 1F, G and Supplementary Figures 1F–I). Direct stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (dSTORM), a super resolution microscopy capable of localizing single molecules at a resolution of 20 nanometers, was used to visualize individual EVs in 3D space as well as visualizing tricolor antibody staining of the tetraspanins CD81, CD9, and CD63 (Figures 1H, I). Although CD63 and CD81 were not detected in bulk multiplex assay analysis, the highly sensitive dSTORM technique allowed detection of all three tetraspanins in PEV and pmPEV products as well as in the EV control (Figure 1E versus Figures 1H, I). Quantification of dSTORM revealed that PEV had relatively more CD81+/CD9+/CD63+ triple positive EVs, while pmPEV had more CD9+ single positive EVs (Figure 1J). Additionally, PEV had more CD81+/CD9+ and CD81+/CD63+ double positive EVs while pmPEV had more CD63+/CD9+ double positive EVs (Figure 1J). This heterogeneity is typical for EVs and the significance of the observed tetraspanin distributions is currently unclear. Overall, these findings indicate that PEV and pmPEV share typical EV characteristics and are heterogenous products that also contain non-vesicular nanoparticles.
3.2 PEV and pmPEV treatments decreased acute myocarditis, but PEV was more effective
We recently published that innate treatment of male BALB/c mice with PEV significantly decreased myocardial inflammation and fibrosis and improved cardiac function (12). In this study we wanted to determine whether donor factors of sex and age altered the efficacy of two different EV products. We hypothesized that pmPEV from young females would be more effective than PEV from males and females of all ages in preventing myocarditis. This rationale was based on the known protective effect of estrogen in reducing cardiovascular disease in women, the lower incidence of myocarditis in women, and preclinical research showing that estrogen reduces myocardial inflammation in female mice with CVB3 myocarditis (14, 19, 42).
In this study we treated male BALB/c mice with 250 μL of PEV or pmPEV or PBS vehicle control injected intraperitoneally (ip) on days -1, 0, and +1 post infection (pi), while CVB3 with heart proteins was also injected ip on day 0 and we assessed endpoints during peak acute myocarditis at day 10 pi, as previously (12). Clinically myocarditis often presents as perimyocarditis (43), which is also found in our model of CVB3 viral myocarditis (12, 33, 44, 45). For that reason, we assessed the effects of PEV or pmPEV treatments on myocarditis (that is, perimyocarditis) and pericarditis (that is, pericardial inflammation alone) using H&E staining (Figures 2A–D). We found that neither PEV nor pmPEV significantly altered pericarditis compared to PBS treated controls (p = 0.64, p = 0.78, respectively) (Figures 2A, B; Supplementary Table 3). However, both PEV (p = 0.0002) and pmPEV (p = 0.0036) significantly reduced myocarditis (Figures 2C, D; Supplementary Table 3). There were no significant differences comparing PEV to pmPEV for myocarditis (p = 0.52) or pericarditis (p = 0.97) (Figures 2B, D; Supplementary Table 3). During acute myocarditis, fibrosis may be observed at this early stage of the pathogenesis of disease primarily around vessels with very little, if any, myocardial fibrosis (44, 46). Quantifying scans of slides stained with trichrome blue to detect collagen deposition revealed that PEV significantly reduced fibrosis/perivascular fibrosis compared to PBS treated controls (p = 0.0079) at this acute myocarditis timepoint, which was not observed for mice treated with pmPEV compared to controls (p = 0.0601) (Figures 2E, F; Supplementary Table 3). In our prior work, we saw that decreased fibrosis at day 10 pi corresponded with prevention of cardiac dysfunction later during chronic myocarditis (12), suggesting that PEV may have greater potential than pmPEV to prevent progression to chronic myocarditis/DCM.
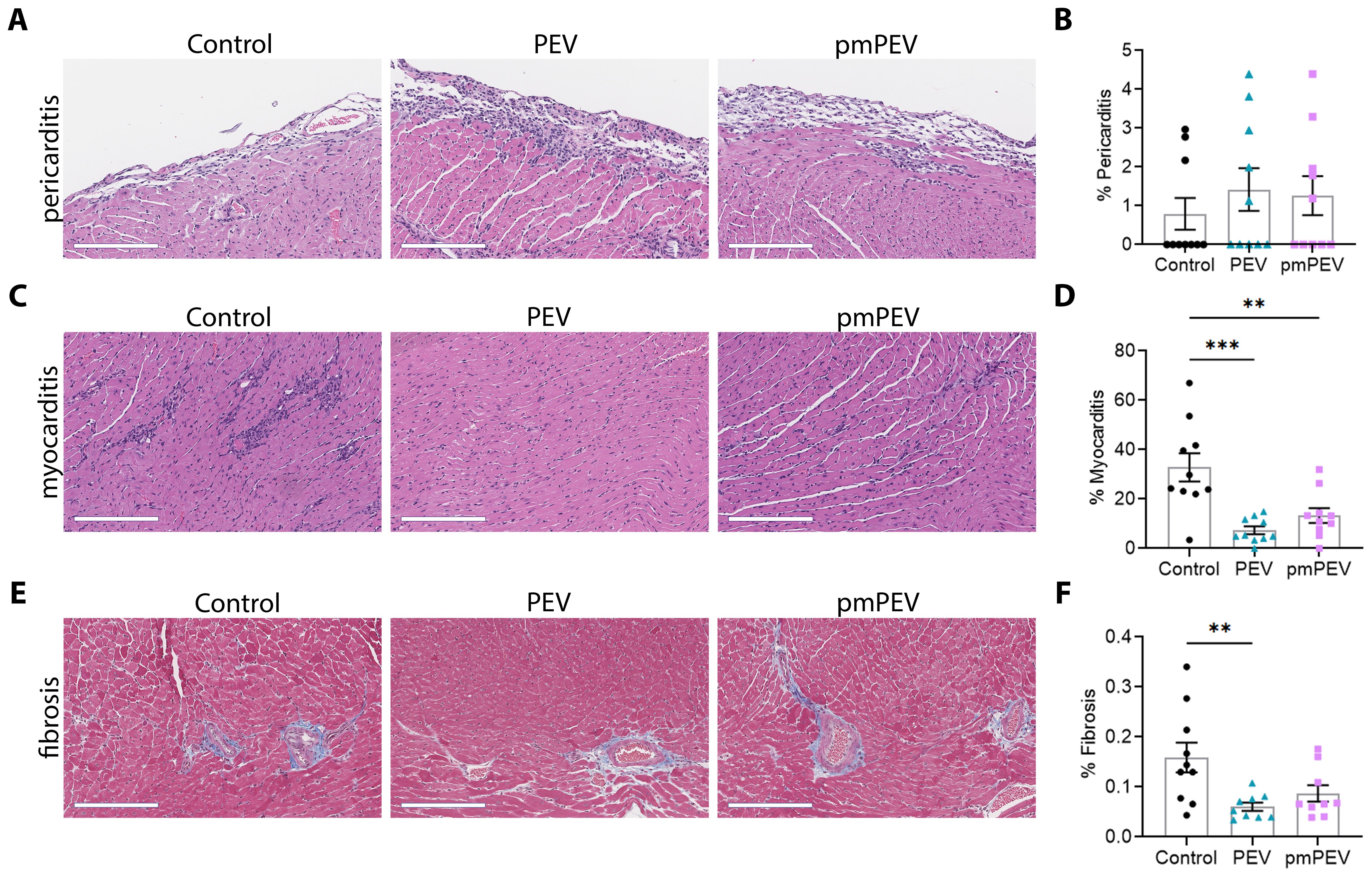
Figure 2. Treatment with PEV or pmPEV decreased myocardial inflammation and fibrosis. EVs from healthy men and women (PEV), or from healthy premenopausal women (pmPEV) (0.25 mL of 1010 EVs/mL), or control (0.25 mL of 1X PBS) were given ip to male BALB/c 8-week-old mice on days -1, 0, 1 pi with 103 PFU of CVB3 given ip on day 0. Representative photos of (A) pericarditis, (C) myocarditis, (E) fibrosis at day 10 pi; Scale bars: 200 µm. Quantification of inflammation (B, D) or fibrosis (E) was performed on individual hearts. Data show mean ± SEM for 10 mice/group, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison, *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 (see Supplementary Table 3).
To further confirm these findings, we conducted immunohistochemistry (IHC) to verify protein levels of key immune cell and signaling markers (Supplementary Figure 2; Supplementary Table 4). Heart sections were stained individually for four key markers of immune cells including CD45 (all lymphocytes), CD11b (activated macrophages, mast cells, neutrophils, and some dendritic cells), CD3 (all T cells), and F4/80 (macrophages), TLR4, TLR2, and one marker of the complement cascade C3aR (Supplementary Figure 2). We found that PEV reduced most of these markers during myocarditis, including CD45 (p = 0.0187), as well as CD11b (p = 0.0305), CD3 (p = 0.0087), F4/80 (p = 0.0177), and C3aR (p = 0.0007) compared to the PBS-treated control, while pmPEV only reduced C3aR (p = 0.0157) (Supplementary Figure 2; Supplementary Table 4). While neither treatment significantly reduced TLR4 or TLR2 compared to control, PEV reduced TLR2 more than pmPEV (p = 0.0489) (Supplementary Figure 2; Supplementary Table 4). These IHC data reinforce a pattern of PEV eliciting stronger immune regulation effects than pmPEV.
3.3 Global immune gene downregulation occurred with PEV and pmPEV treatment during myocarditis, but was more comprehensive for PEV
As mentioned earlier, the immune profile that increases CVB3 myocarditis in male mice at day 10 pi has been extensively studied and is known to involve several key pathways including activation of both mast cells and macrophages by complement, TLR2, TLR4/IL-1 receptor, and inflammasome pathways that lead to elevated IL-1β levels and increased remodeling/fibrosis. We examined these primary immune cells and signaling pathways using quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) to compare the treatment groups to controls (Figure 3). Results shown in the gene matrices in Figure 3 are displayed individually by gene in Supplementary Figure 3 and individual ANOVA and pairwise comparisons for each gene are shown in Supplementary Table 5. Importantly, qRT-PCR revealed that treatment with PEV (p = 0.12) or pmPEV (p = 0.74) did not alter CVB3 viral protein levels in the heart compared to PBS treated mice during myocarditis (1-way ANOVA p = 0.14) (Figures 3A, B). We found that both PEV and pmPEV significantly decreased most of the immune genes that we examined, confirming histology findings. However, more genes were decreased by PEV treatment that were not decreased by pmPEV treatment, including CD11b (p = 0.0018), C-X-C motif chemokine ligand (Cxcl)-9 (p = 0.0047), Cxcl10 (p = 0.0009), caspase-1 (Casp1, p = 0.0018), nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich-containing family, pyrin domain-containing-3 (Nlrp3) (p = 0.0075), interleukin (IL)-1 receptor 2/ST2 (p = 0.0076), and complement component 3 antagonist receptor 1 (C3aR1) (p = 0.0029) (Figures 3A, B; Supplementary Figure 3; Supplementary Table 5). Additionally, PEV reduced fibrosis markers, which in contrast remained unchanged after pmPEV treatment, including matrix metalloprotease (Mmp)3 (p = 0.0032), Mmp9 (p = 0.0391), tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 (TIMP1) (p = 0.0134) and collagen 1A1 (Col1a1, p = 0.0415) (Figures 3C, D; Supplementary Figure 3; Supplementary Table 5). Overall, analysis of genes known to be important in contributing to CVB3 myocarditis in males showed more global reduction using PEV treatment compared to pmPEV treatment, which was the opposite of our original hypothesis.
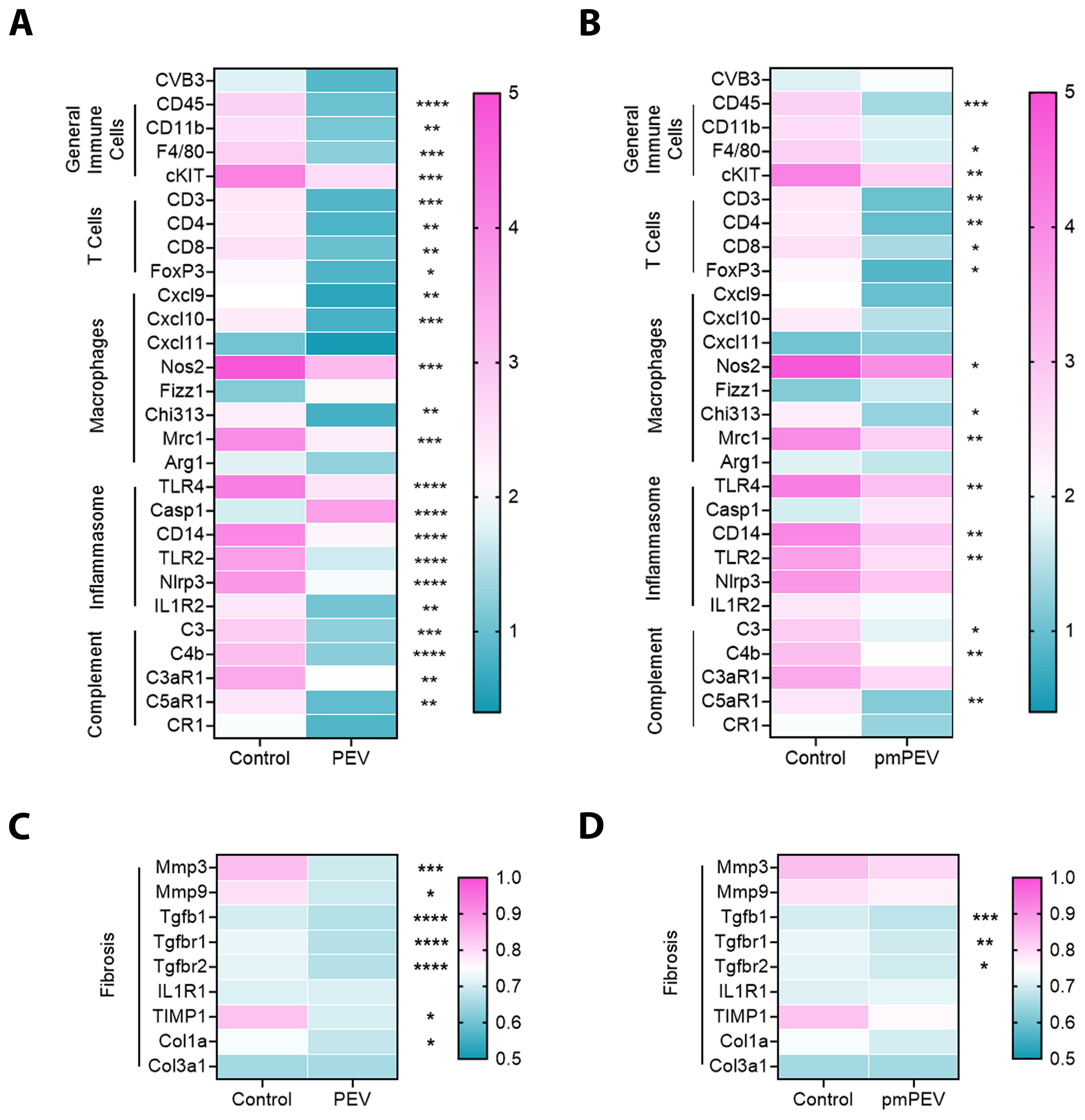
Figure 3. PEV and pmPEV globally downregulate immune and fibrosis markers, but more changes occur with PEV. EVs from healthy men and women (PEV), or from healthy premenopausal women (pmPEV) (0.25 mL of 1010 NPs/mL) or control (0.25 mL of 1X PBS) were given to male BALB/c 8-week-old mice ip on days -1, 0, 1 pi with 103 PFU of CVB3 given ip on day 0. Relative gene expression (RGE) from whole hearts by qRT-PCR at day 10 pi was used to assess (A, B) acute myocarditis immune markers and (C, D) fibrosis markers indicated on the left axis of each matrix in individual experiments compared to the housekeeping gene Hprt (see Supplementary Figure 3 for individual data). Data show mean RGE for 10 mice/group, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison were conducted for each marker but are depicted separately as PEV or pmPEV vs. control; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001 (see Supplementary Figure 3, Supplementary Table 5).
3.4 PEV and pmPEV display distinct proteomic profiles
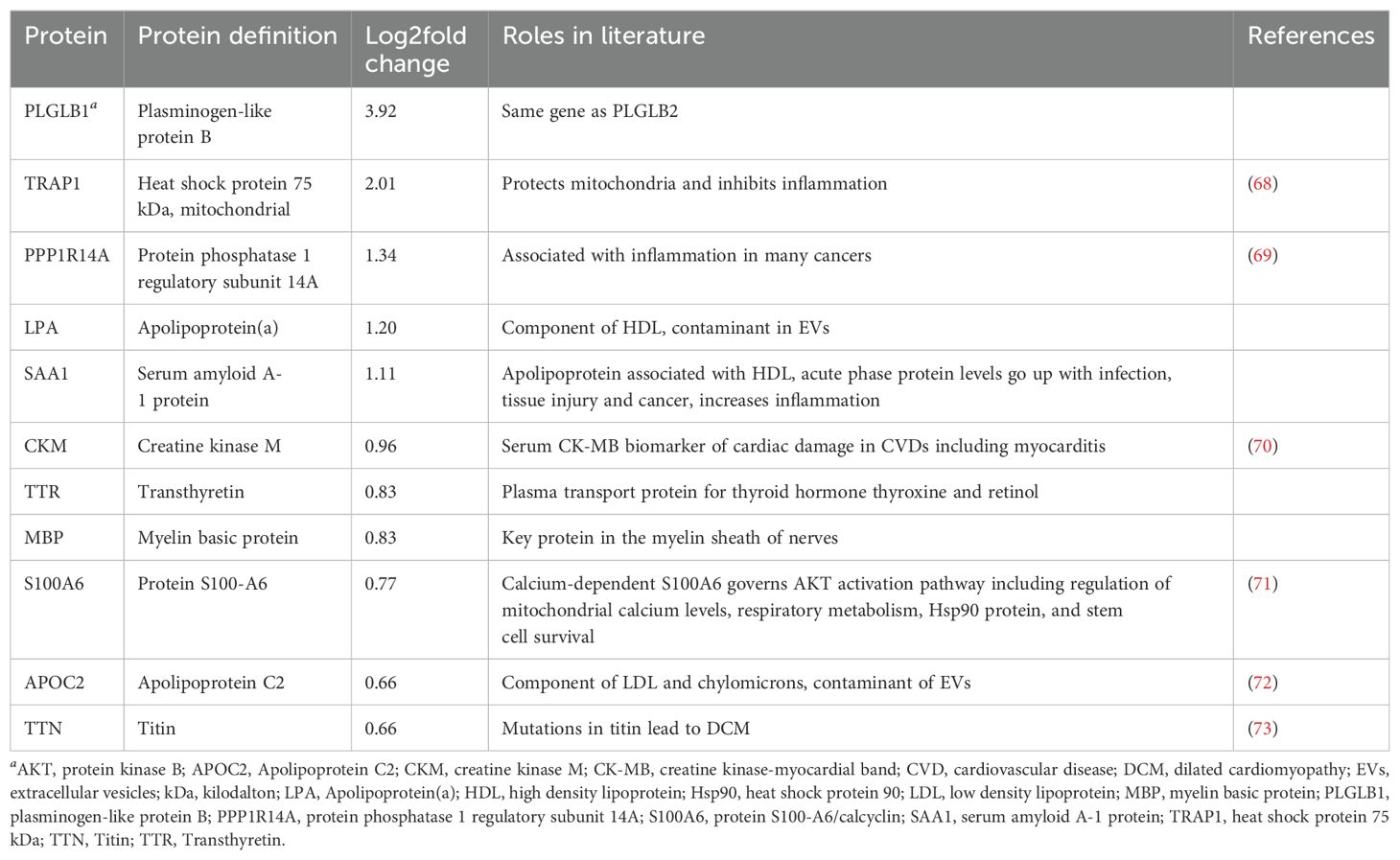
To better understand the contents of PEV and pmPEV, we performed proteomic analysis of each product. Principal component analysis of these proteomes revealed that PEV and pmPEV displayed distinct protein profiles with product replicates grouping together (Figure 4A). Non-biased hierarchal clustering further confirmed that the EV products grouped tightly within their own replicates, yet PEV and pmPEV were clearly distinct products (Figure 4B). A volcano plot of comparisons of individual protein expression in PEV versus pmPEV showed a large, shared proteome (p > 0.05), but also many proteins that were significantly different between PEV and pmPEV (Figure 4C). The most differently expressed proteins (p < 0.001) in PEV were pregnancy zone protein (PZP) (α2-macroglobulin protease inhibiter associated with pregnancy (47)], cytochrome b5 reductase 1 (CBR1) [a NADPH-dependent oxidoreductase important in ATP production found to decrease oxidative stress and inflammation (48, 49)], endophilin-β2 (SH3GLB2) [elevated after viral infection, associated with autophagy (50, 51)], and immunoglobulins (Ig) V2-14 and V3-9 (Figure 4C). In contrast, the most differentially expressed protein in pmPEV (p < 0.001) was lysl-oxidase L3 (LOXL3) [important in crosslinking collagen and elastin increasing T cell-associated fibrosis and cardiomyopathy (52–54)] (Figure 4C).
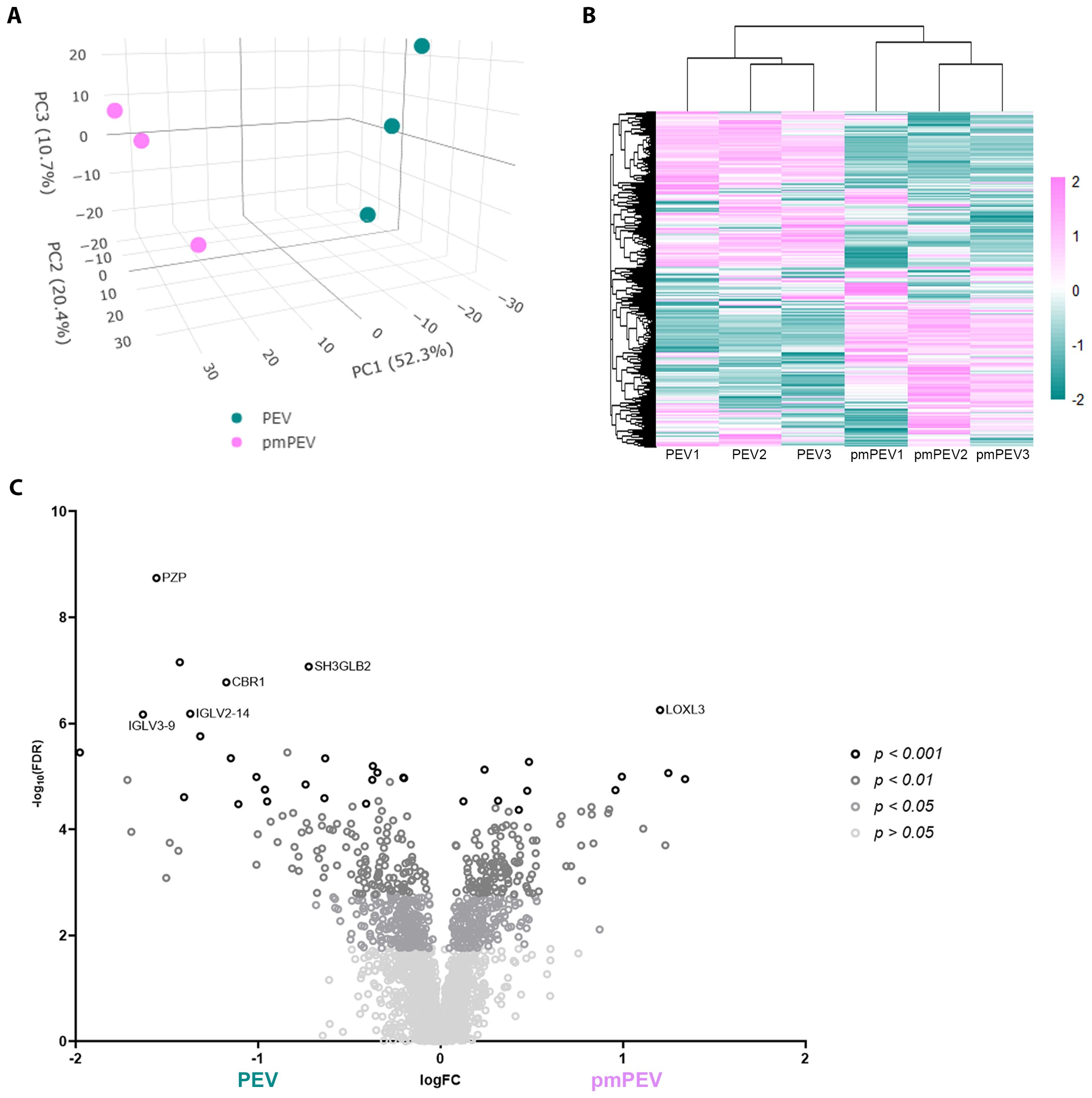
Figure 4. Initial assessment of PEV versus pmPEV proteome. (A) Principal component analysis. (B) Hierarchal clustering. (C) Volcano plot of significantly different proteins.
3.5 Proteomic analysis reveals immune-specific enrichment in PEV and pmPEV
To better understand the proteins that were differentially expressed in PEV versus pmPEV, we applied a pathway enrichment pipeline to the proteome data which identified that, in general, more immune pathways were enriched in PEV while pmPEV was mainly enriched for general EV or biogenic nanoparticle pathways (Figure 5A). However, both products were enriched for various proteins associated with EVs or non-vesicular particles, and proteins involved in increasing inflammation (Figures 5B, C).
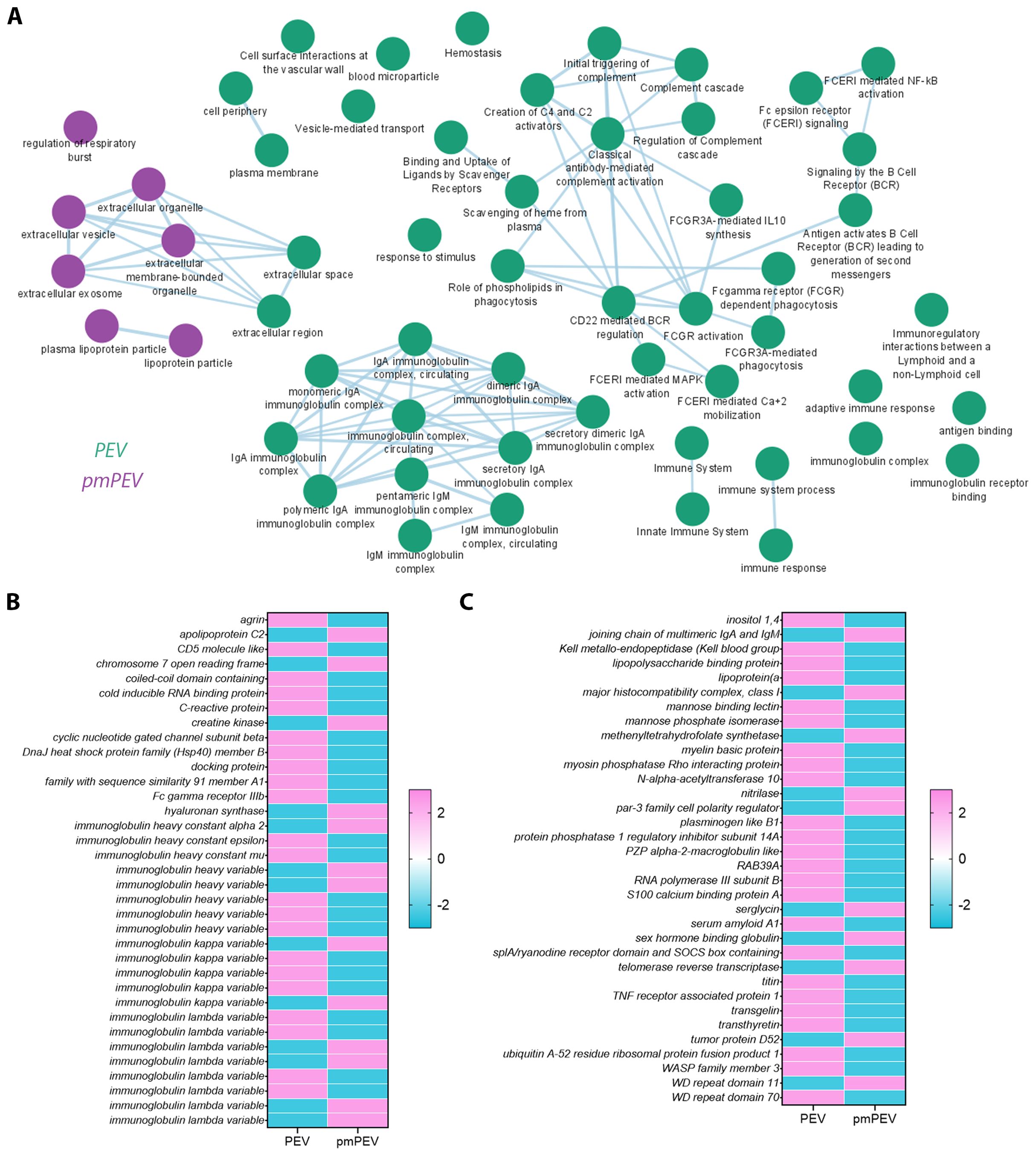
Figure 5. Proteomic analysis of PEV versus pmPEV reveal immune-specific enrichment in PEV and pmPEV. (A) Cytoscape pathway shows super-clusters of proteins in PEV (green) versus pmPEV (purple). Differentially enriched proteins between (B) PEV and (C) pmPEV with adjusted p value < 0.01.
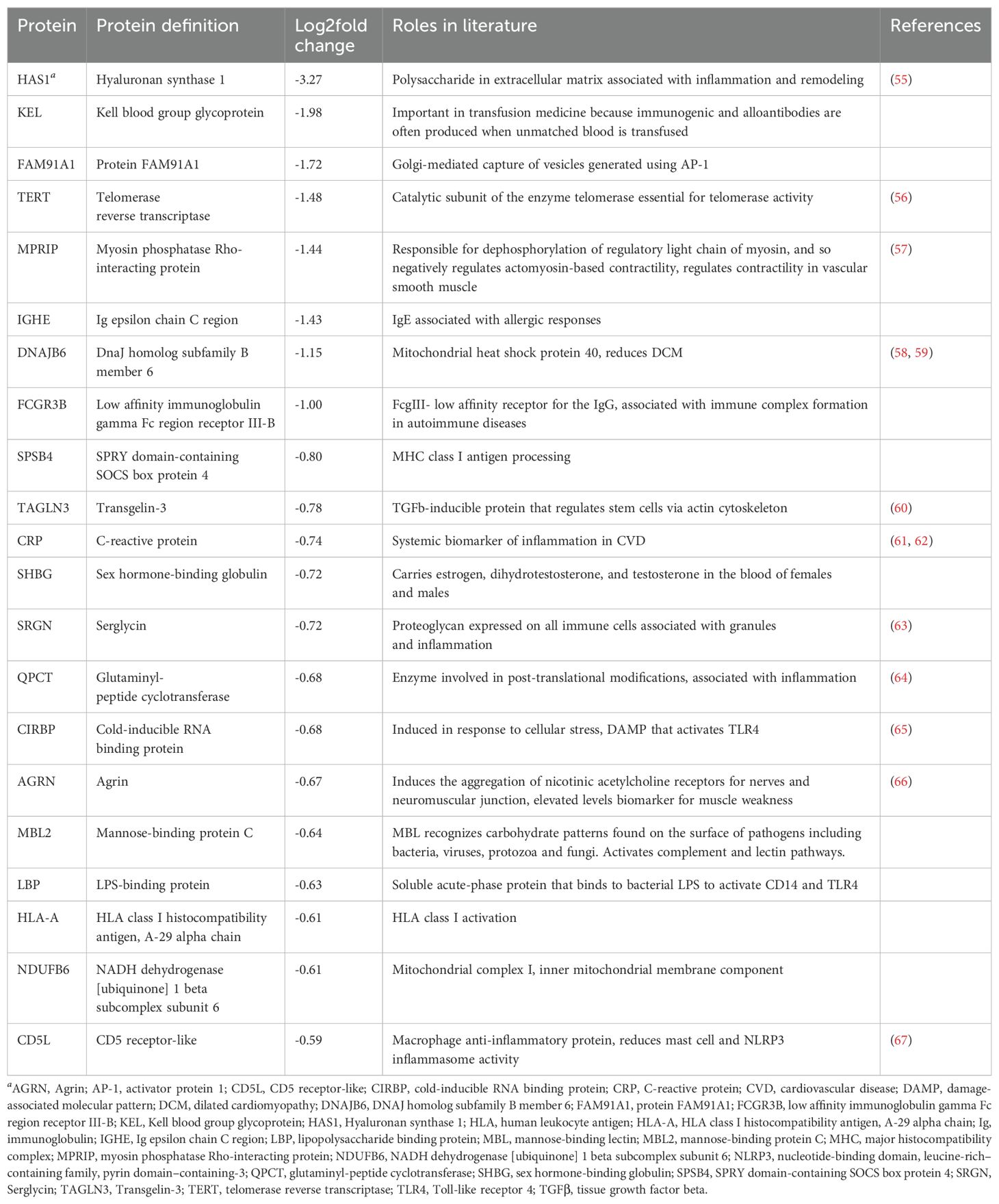
Although some proteins in each product were reported to be immunoregulatory in the literature, the majority of the proteins differentially expressed in PEV or pmPEV were associated with promoting inflammation (Tables 1, 2, respectively). Many immunoglobulins/immunoglobulin (Ig) components were increased in PEV and pmPEV including IgE and IgG, which may have activated/maintained activation of pericardial mast cells providing at least one possible explanation for why PEV and pmPEV treatment did not reduce pericardial inflammation which is associated with mast cell degranulation (74–76). Although PEV and pmPEV had many distinct proteins (Tables 1, 2), the overall functions of most of these proteins from both products was similar in that they may promote inflammation, based on the literature.
3.6 PEV and pmPEV share similar proteome to other reported platelet/plasma EVs
Because we found significant differences in the proteomes of PEV versus pmPEV, we wanted to examine whether our platelet-derived EV products were similar or different from other published proteomes of platelet/plasma EV products isolated using a similar extraction method (i.e., ultracentrifugation). Using a comparison method presented by Palviainen et al., we compared the shared proteome of PEV and pmPEV to the shared proteome of 3 other platelet/plasma EV products from the literature (37–39). A comparison of all shared or distinct proteins between the studies are depicted in a modified 4-way Venn diagram in Figure 6A. All 5 products shared 10 proteins including complement components C3, C1qc and C1s as well as the contaminants ApoA1 and ApoE. Other proteins shared between the 5 products included α2-macroglobulin (A2M) [anti-protease in blood, inhibits coagulation, stimulates immune response, and acts as carrier by binding many cytokines in the blood such as IL-1β and TGFβ (77)], fibrinogen A (FGA) (coagulation protein), histidine-containing phosphocarrier protein (HPr) (a small cytoplasmic protein that is a component of the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sugar phosphotransferase system/PTS), galectin-3 binding protein (LGALS3BP) [increased after viral infection leading to increased interferons/IFNs (78)], and transferrin (TF) (protein that binds iron in blood serum). We illustrate the shared protein pathway superclusters of these 10 proteins in Figure 6B using Cytoscape. Overall, these findings indicate that the shared proteome of PEV and pmPEV is similar to other platelet or plasma-derived products isolated using ultracentrifugation, and that complement components and contamination with apolipoproteins may be a common characteristic of these products. Importantly, both PEV and pmPEV significantly reduced myocarditis in our translational animal model despite this potentially proinflammatory protein content.
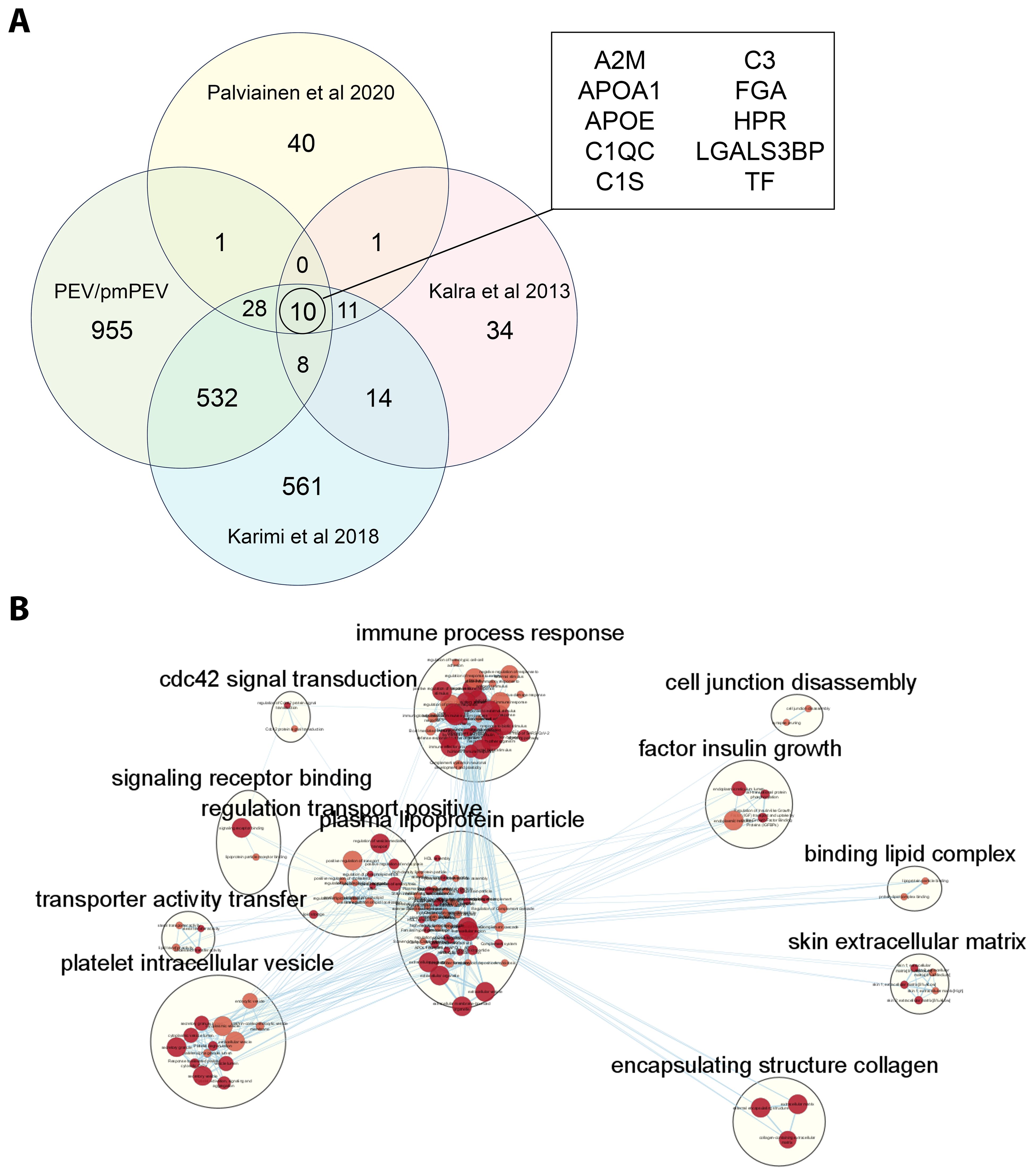
Figure 6. PEV and pmPEV share a proteome with other platelet/plasma EV products. (A) 4-way Venn diagram shows shared proteome of PEV and pmPEV compared to 3 other platelet EV products reported in the literature. (B) Cytoscape pathway visualization depicts super-clusters of pathways from the shared proteome of all five of these platelet/plasma EV products. The 12 superclusters visualized include: cdc42 signal transduction, immune process response, cell junction disassembly, factor insulin growth, signalling receptor binding, regulation transport positive, plasma lipoprotein particle, binding lipid complex, transporter activity transfer, platelet intracellular vesicle, skin extracellular matrix, and encapsulating structure collagen.
3.7 miR sequencing reveals enriched anti-inflammatory miR content in PEV and pmPEV, but some proinflammatory content in pmPEV
We also conducted miRNA (miR) sequencing on PEV and pmPEV products to better understand the effect of miR content on their ability to inhibit myocarditis (Figure 7). PCA (Figure 7A) and heatmap (Figure 7B) showed that PEV and pmPEV samples were different than each other and were similar, but with some variation, within their own groups. We identified 31 miRs that were differentially expressed between PEV and pmPEV (Figure 7C).
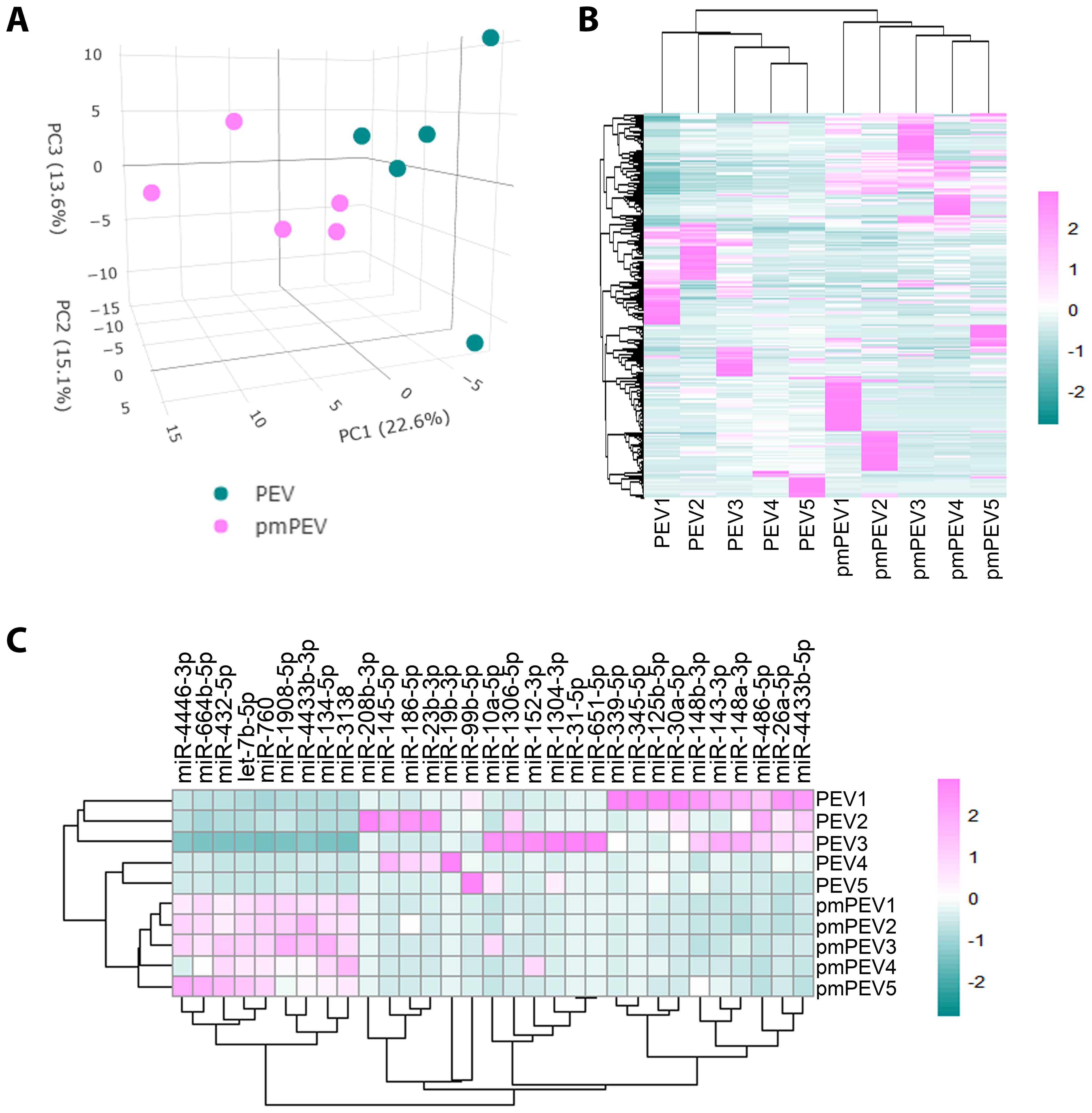
Figure 7. PEV and pmPEV enriched for anti-inflammatory miRs, but pmPEV had a more proinflammatory signature. (A) Principal component analysis. (B) Hierarchical clustering of miRs. (C) Hierarchal clustering of differentially expressed miRs.
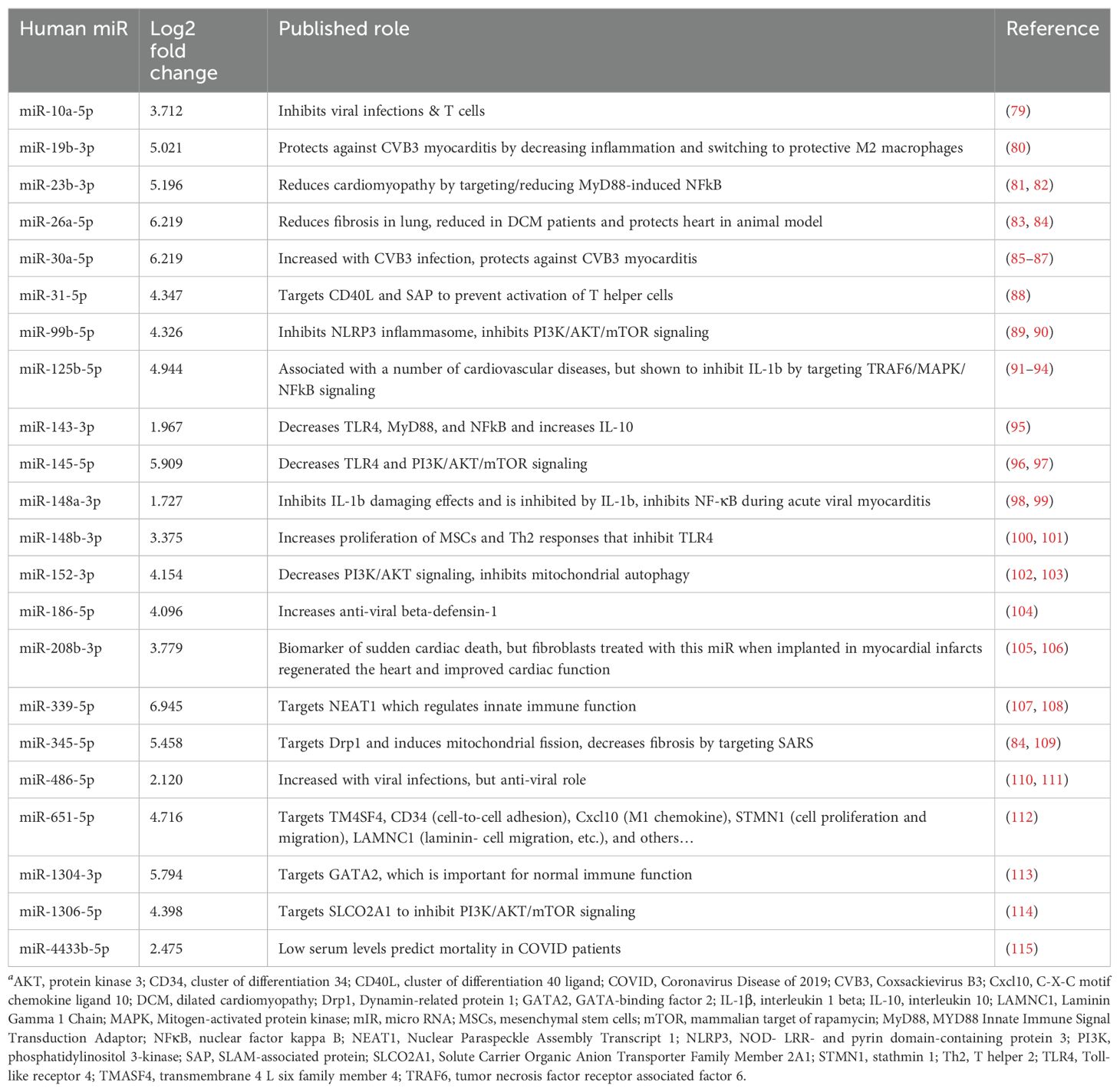
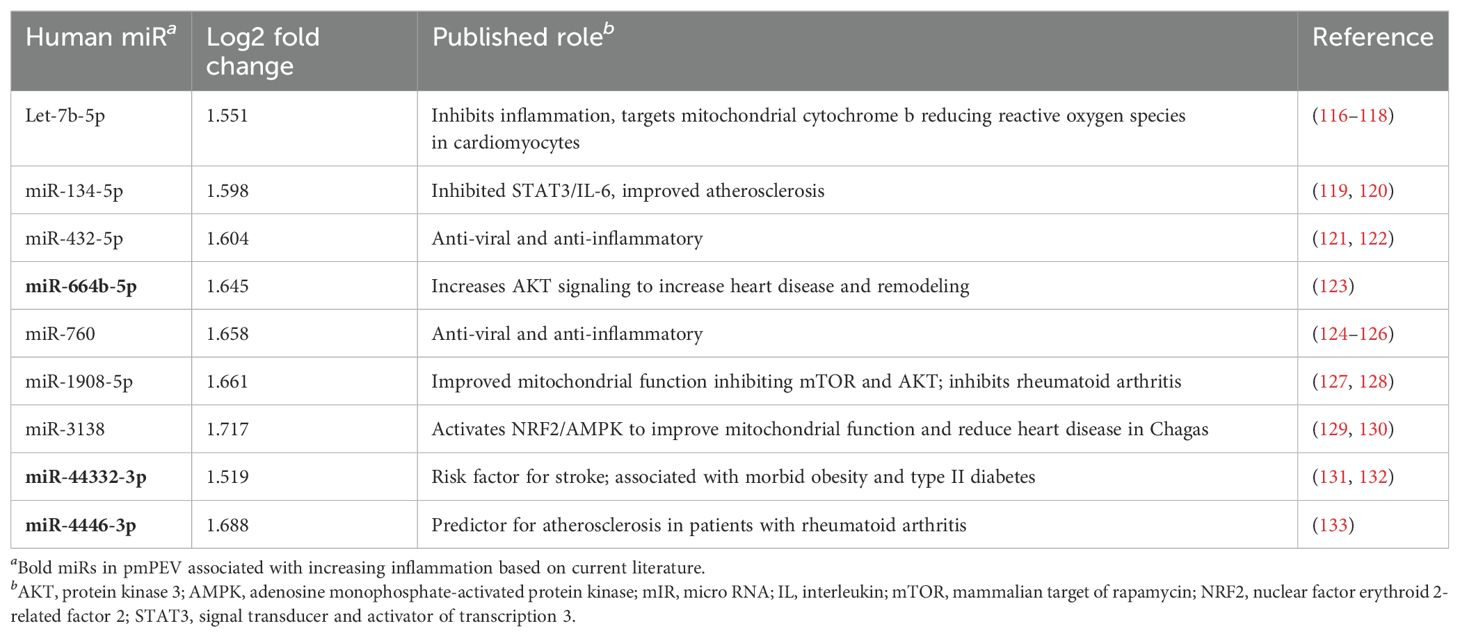
A literature review was conducted for the 31 miRs to better understand how they could modulate the primary gene pathways. The findings from the literature search are shown in Tables 3, 4 and illustrated in Figure 8. Both PEV and pmPEV contained miRs that inhibited key pathways of the pathogenesis of myocarditis like the TLR4/inflammasome pathway. Remarkably, all the miRs in PEV were reported in the literature to be anti-viral, anti-inflammatory, to inhibit the TLR4/inflammasome pathway, or had been shown to decrease CVB3 myocarditis in an animal model (80, 85–87) (Table 3), which correlates to the global shut-down of myocardial inflammation observed for PEV. In contrast, pmPEV had three miRs that were proinflammatory out of 9 distinct miRs (33%) with the remaining 6 having generally inhibitory roles according to the literature (Table 4). Overall, the miR content of PEV and pmPEV were consistent with the histologic, qRT-PCR, and IHC data showing that PEV more effectively regulated the immune response during myocarditis than pmPEV.
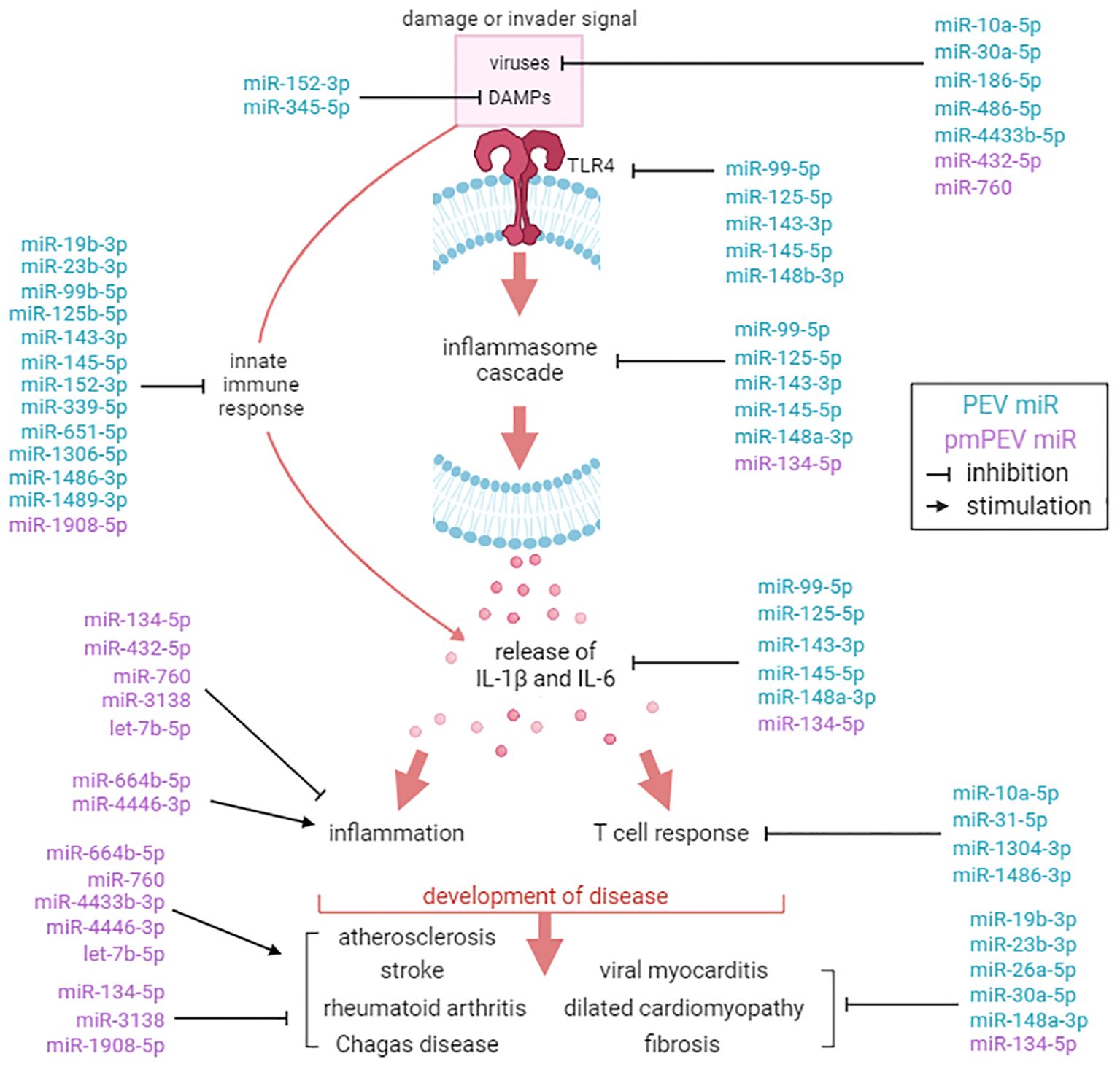
Figure 8. Comparison of miR targets between PEV and pmPEV. Mechanistic effects of miRs reported in the literature identified in PEV (blue) versus pmPEV (purple) that influence key pathways in the pathogenesis of viral myocarditis. References and descriptions of miRs found in Tables 3, 4. This figure was created using BioRender.com.
4 Discussion
EVs obtained from patients are typically extracted from healthy volunteers, yet little specific information about the donors is obtained/reported. In this study, we aimed to better understand the effect of donor sex and age on the effectiveness of EVs as a therapy for viral myocarditis. We hypothesized that EVs derived from platelets from healthy female volunteers under the age of 50, which we termed premenopausal PEV or pmPEV, would be more effective at inhibiting myocarditis than PEV obtained from healthy male and female volunteers of all ages. However, we found that PEV was more effective than pmPEV at inhibiting myocarditis, although both products were anti-inflammatory and significantly reduced myocarditis. Additionally, miR content most closely aligned with the effectiveness of each product to reduce myocarditis. All of the miRs enriched in PEV had reported roles in the literature that inhibited specific pathways known to be involved in the pathogenesis of viral myocarditis including reducing viral replication, TLR4 signaling, inflammasome/NLRP3, and IL-1β (Table 3). Incredibly, several of the miRs enriched in PEV have already been tested in CVB3 infection, CVB3 myocarditis models, and/or cardiomyopathy/DCM models, where they were found to decrease disease (81, 83–85, 87, 98). In contrast, although most miRs in pmPEV were anti-inflammatory, three miRs were reported to have proinflammatory effects (Table 4). Additionally, the anti-inflammatory miRs enriched in pmPEV were less specific for pathways known to drive myocarditis and were generally anti-inflammatory (Table 4). Importantly, even though PEV and pmPEV had distinct proteomes and transcriptomes, both products were able to significantly decrease myocarditis. This finding indicates that even though batches of EV products obtained from different healthy donors differ in proteomic and miR content, their overall potential for therapeutic effectiveness is high. Additionally, by examining proteomics, we showed that the miR profile of these products was more important than their proteomic profile at determining the effectiveness of treatment.
Our data also suggest that regenerative therapy strategies that pool miRs that specifically and simultaneously target multiple stages of the known pathogenesis of disease may be highly effective at preventing inflammation. In this study we identified 31 miRs that very effectively reduced viral myocarditis in a highly translational animal model. Importantly, many of these miRs should also reduce remodeling, and thus have the potential to reduce progression to chronic inflammatory cardiomyopathy/DCM in addition to decreasing acute myocarditis. We did not observe miRs that have been reported in the literature to inhibit mast cell activation/degranulation in either product. If the products had also contained this miR content, they may have more effectively reduced pericarditis/perimyocarditis. Additionally, the proteomic content of both of the tested products contained several factors including IgE and IgG and/or their components that could have activated mast cells, thereby counteracting the anti-inflammatory actions of the miR content. We also did not observe other miRs that may reduce myocarditis such as miR-122, which has been found to inhibit tripartite motif-containing protein 29 (TRIM29) where low levels of TRIM29 reduce viral replication and inflammation in a fulminant model of viral myocarditis (134–136).
Myocarditis patients lack disease-specific therapies due to the broad innate and adaptive immune mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of disease, and so this disease presents an ideal model for testing a heterogeneous product that may be able to globally reduce a number of specific pathways- an approach that specific targeted therapy cannot accomplish. EV-based products offer promising potential as ‘global’ therapies, as they carry a variety of functional DNA, RNA, miR, and protein cargo that can provide the broad, yet targeted, messaging needed to effectively control viral infection, inflammation and remodeling that drives the pathogenesis of myocarditis.
5 Limitations
It remains unclear whether the age and sex of the donor products affected the miR and protein content of the EVs. One possibility is that higher estrogen levels in younger women under age 50 resulted in a more robust proinflammatory profile as estrogen at high levels/doses is known to exert proinflammatory effects but at low levels/doses to be anti-inflammatory (137, 138). Another possibility is that men develop more robust immune responses to CVB infection, as we observe when we examine sex differences in viral myocarditis (14), that generates more protective miRs in their EVs. CVB3 is a common infection worldwide with individuals in the population being reinfected with different serotypes of enteroviruses each year, similar to colds and the flu (139), and so it is not surprising to find miRs that target CVB in our donor EVs. A different experimental approach is needed in the future to identify the effect of sex and age donor parameters on the EV protein and miR content, likely using individually based products instead of pooling, so that specific donor contributions can be identified, or testing several independent batches of products with donor pools that match more specifically according to sex and age. Additionally, we injected the EVs during the innate immune response to viral infection, which is the optimal time to test the effect of the product on myocarditis, as we showed previously (12, 33); however, this is not a clinically relevant timepoint. We showed previously that PEV given during acute myocarditis at days 7, 8, and 9 pi was able to significantly reduce myocarditis and improve cardiac function (12), suggesting these products can also be used effectively at clinically relevant time points. Future studies should also examine the effect of PEV/pmPEV and/or miRs given intravenously or by intracardiac injection, which are more clinically relevant routes of administration. While EVs are known to contain the functional contents that we tested, this study could not confirm the source of the proteins and miRs identified from these bulk, heterogenous products. For example, the miRs we identified could be present within the EVs in PEV and pmPEV, associated with the external EV protein corona as has been shown elsewhere (140), or present in the bulk products as extracellular miRs, which are stable in plasma (141). The focus of the study was to primarily characterize the differences of the products; a clearer understanding of the roles played by components in immunoregulation during myocarditis would require functional testing of candidate proteins and the miRs we identified. Research has shown common contaminants, including some lipoproteins like high density lipoprotein, can also have anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective effects (142), and it is not clear from this work to what extent those lipoproteins participated in the anti-inflammatory effects we observed by PEV and pmPEV. Future research should determine the ability of each miR to effectively inhibit viral myocarditis during a clinically relevant timepoint, although likely the aggregate effect of these miRs heavily contributed to the broad reduction of myocarditis without immunosuppression during viral infection.
6 Conclusions
We found that PEV and pmPEV products significantly decreased myocardial inflammation in a highly translational mouse model of viral myocarditis. We identified 31 miRs that specifically targeted key pathways in the pathogenesis of myocarditis according to the literature that are candidates for future miR-related therapies for viral myocarditis.
Data availability statement
The miRNA sequencing data presented in the study are deposited in the NCBI GEO repository, accession number GSE283563. The proteomic data are deposited in the PRIDE Proteomics repository, accession number PXD058698.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Mayo Clinic Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
DB: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PG: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. DD: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. JF: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. EM: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. MW: Writing – review & editing, Data curation. VX: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. MA: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. KB: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. EW: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. SK: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. BE: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. SW: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. LM: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. KK: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. AJ: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. AM-L: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. IC: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. AH: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. HF: Resources, Writing – review & editing. JW: Methodology, Resources, Writing – review & editing. AB: Conceptualization, Resources, Writing – review & editing. PS: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. AT: Resources, Writing – review & editing. LC: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing. DF: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work is partially supported by the Mayo Clinic Center for Regenerative Medicine in Florida (DF, JW), the Mayo Clinic Center for Biomedical Discovery (JW), National Institutes of Health (NIH) TL1 TR002380 (DB, DD, MW, EW, AJ, DF), National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases under award numbers R21 AI152318 (DF, JW), R21 AI145356 (DF), R21 AI154927 (DF), R21 AI163302 (KB), National Heart Lung and Blood Institute under award number R01 HL164520 (DF), the American Heart Association under award number 20TPA35490415 (DF), the American Heart Association under award number 23SCEFIA1153413 (KB), and The University of Queensland (JW). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the funding agencies.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Dennis Dickson Histology Group for their work embedding and staining slides for this project. This group includes Dennis W. Dickson, Linda Rousseau, Virginia Phillips, Ariston Libraro, and Monica Castanedes. We thank the Mayo Microscopy and Cell Analysis Core, the Mayo Clinic Genome Analysis Core, and the Mayo Clinic Proteomic Analysis Core facilities for their experimental and technical support.
Conflict of interest
AB, PS, and AT, along with Mayo Clinic have ownership interest in Rion, Inc.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1468969/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Salomon C, Das S, Erdbrügger U, Kalluri R, Kiang Lim S, Olefsky JM, et al. Extracellular vesicles and their emerging roles as cellular messengers in endocrinology: An Endocrine Society scientific statement. Endocr Rev. (2022) 43:441–68. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnac009
2. Beetler DJ, Di Florio DN, Bruno KA, Ikezu T, March KL, Cooper LT Jr, et al. Extracellular vesicles as personalized medicine. Mol Aspects Med. (2023) 91:101155. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2022.101155
3. Thery C, Witwer KW, Aikawa E, Alcaraz MJ, Anderson JD, Andriantsitohaina R, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. (2018) 7:1535750. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2018.1535750
4. Colombo M, Raposo G, Thery C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. (2014) 30:255–89. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-101512-122326
5. Lotvall J, Hill AF, Hochberg F, Buzás EI, Di Vizio D, Gardiner C, et al. Minimal experimental requirements for definition of extracellular vesicles and their functions: A position statement from the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. (2014) 3:26913. doi: 10.3402/jev.v3.26913
6. Walker SA, Aguilar Díaz De León JS, Busatto S, Wurtz GA, et al. Glycan node analysis of plasma-derived extracellular vesicles. Cells. (2020) 9:1946. doi: 10.3390/cells9091946
7. Marcoux G, Magron A, Sut C, Laroche A, Laradi S, Hamzeh-Cognasse H, et al. Platelet-derived extracellular vesicles convey mitochondrial DAMPs in platelet concentrates and their levels are associated with adverse reactions. Transfusion. (2019) 59:2403–14. doi: 10.1111/trf.15300
8. Costa LA, Eiro N, Fraile M, Gonzalez LO, Saá J, Garcia-Portabella P, et al. Functional heterogeneity of mesenchymal stem cells from natural niches to culture conditions: Implications for further clinical uses. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2021) 78:447–67. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03600-0
9. Bertolino GM, Maumus M, Jorgensen C, Noel D. Recent advances in extracellular vesicle-based therapies using induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Biomedicines. (2022) 10:2281. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092281
10. Abbasi Sourki P, Pourfathollah AA, Kaviani S, Soufi Zomorrod M, Ajami M, Wollenberg B, et al. The profile of circulating extracellular vesicles depending on the age of the donor potentially drives the rejuvenation or senescence fate of hematopoietic stem cells. Exp Gerontol. (2023) 175:112142. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2023.112142
11. Wang W, Wang L, Ruan L, Oh J, Dong X, Zhuge Q, et al. Extracellular vesicles extracted from young donor serum attenuate inflammaging via partially rejuvenating aged T-cell immunotolerance. FASEB J. (2018) 32:fj201800059R. doi: 10.1096/fj.201800059R
12. Beetler DJ, Bruno KA, Watkins MM, Xu V, Chekuri I, Giresi P, et al. Reconstituted extracellular vesicles from human platelets decrease viral myocarditis in mice. Small. (2023) 19:e2303317. doi: 10.1002/smll.202303317
13. Fairweather D, Cooper LT Jr., Blauwet LA. Sex and gender differences in myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy. Curr Probl Cardiol. (2013) 38:7–46. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2012.07.003
14. Fairweather D, Beetler DJ, Musigk N, Heidecker B, Lyle MA, Cooper LT Jr, et al. Sex and gender differences in myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy: An update. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2023) 10:1129348. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1129348
15. Tschope C, Ammirati E, Bozkurt B, Caforio ALP, Cooper LT, Felix SB, et al. Myocarditis and inflammatory cardiomyopathy: Current evidence and future directions. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2021) 18:169–93. doi: 10.1038/s41569-020-00435-x
16. Myers JM, Fairweather D, Huber SA, Cunningham MW. Autoimmune myocarditis, valvulitis, and cardiomyopathy. Curr Protoc Immunol. (2013) 14:11–51. doi: 10.1002/0471142735.im1514s101
17. Kottwitz J, Bruno KA, Berg J, Salomon GR, Fairweather D, Elhassan M, et al. Myoglobin for detection of high-risk patients with acute myocarditis. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. (2020) 13:853–63. doi: 10.1007/s12265-020-09957-8
18. Blanco-Dominguez R, Sánchez-Díaz R, de la Fuente H, Jiménez-Borreguero LJ, Matesanz-Marín A, Relaño M, et al. A novel circulating microRNA for the detection of acute myocarditis. N Engl J Med. (2021) 384:2014–27. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2003608
19. Coronado MJ, Bruno KA, Blauwet LA, Tschöpe C, Cunningham MW, Pankuweit S, et al. Elevated sera sST2 is associated with heart failure in men ≤50 years old with myocarditis. J Am Heart Assoc. (2019) 8:e008968. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.008968
20. Huber S. ERbeta and ERalpha differentially regulate NKT and Vgamma4(+) T-cell activation and T-regulatory cell response in coxsackievirus B3 infected mice. J Clin Cell Immunol. (2015) 6:1–9. doi: 10.4172/2155-9899.1000372
21. Koenig A, Buskiewicz I, Huber SA. Age-associated changes in estrogen receptor ratios correlate with increased female susceptibility to coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis. Front Immunol. (2017) 8:1585. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01585
22. Roberts BJ, Moussawi M, Huber SA. Sex differences in TLR2 and TLR4 expression and their effect on coxsackievirus-induced autoimmune myocarditis. Exp Mol Pathol. (2013) 94:58–64. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2012.06.005
23. Frisancho-Kiss S, Davis SE, Nyland JF, Frisancho JA, Cihakova D, Barrett MA, et al. Cutting Edge: Cross-regulation by TLR4 and T cell Ig mucin-3 determines sex differences in inflammatory heart disease. J Immunol. (2007) 178:6710–4. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.11.6710
24. Rolland TJ, Peterson TE, Singh RD, Rizzo SA, Boroumand S, Shi A, et al. Exosome biopotentiated hydrogel restores damaged skeletal muscle in a porcine model of stress urinary incontinence. NPJ Regener Med. (2022) 7:58. doi: 10.1038/s41536-022-00240-9
25. Shi G, Long Z, De la Vega RE, Behfar A, Moran SL, Evans C, et al. Purified exosome product enhances chondrocyte survival and regeneration by modulating inflammation and promoting chondrogenesis. Regener Med. (2023) 18:55–71. doi: 10.2217/rme-2022-0132
26. Walker SA, Davidovich I, Yang Y, Lai A, Goncalves JP, Deliwala V, et al. Sucrose-based cryoprotective storage of extracellular vesicles. Extracellular Vesicle. (2022) 1:100016. doi: 10.1016/j.vesic.2022.100016
27. Arsic A, Stajkovic N, Spiegel R, Nikic-Spiegel I. Effect of Vectashield-induced fluorescence quenching on conventional and super-resolution microscopy. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:6441. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63418-5
28. Fairweather D, Yusung S, Frisancho S, Barrett M, Gatewood S, Steele R, et al. IL-12 receptor beta 1 and Toll-like receptor 4 increase IL-1 beta- and IL-18-associated myocarditis and coxsackievirus replication. J Immunol. (2003) 170:4731–7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.9.4731
29. Coronado MJ, Brandt JE, Kim E, Bucek A, Bedja D, Abston ED, et al. Testosterone and interleukin-1beta increase cardiac remodeling during coxsackievirus B3 myocarditis via serpin A 3n. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2012) 302:H1726–1736. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00783.2011
30. Frisancho-Kiss S, Coronado MJ, Frisancho JA, Lau VM, Rose NR, Klein SL, et al. Gonadectomy of male BALB/c mice increases Tim-3(+) alternatively activated M2 macrophages, Tim-3(+) T cells, Th2 cells and Treg in the heart during acute coxsackievirus-induced myocarditis. Brain Behav Immun. (2009) 23:649–57. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2008.12.002
31. Bruno KA, Macomb LP, Morales-Lara AC, Mathews JE, Frisancho JA, Yang AL, et al. Sex-specific effects of plastic caging in murine viral myocarditis. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:8834. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168834
32. Onyimba JA, Coronado MJ, Garton AE, Kim JB, Bucek A, Bedja D, et al. The innate immune response to coxsackievirus B3 predicts progression to cardiovascular disease and heart failure in male mice. Biol Sex Differ. (2011) 2:2. doi: 10.1186/2042-6410-2-2
33. Abston ED, Barin JG, Cihakova D, Bucek A, Coronado MJ, Brandt JE, et al. IL-33 independently induces eosinophilic pericarditis and cardiac dilation: ST2 improves cardiac function. Circ Heart Fail. (2012) 5:366–75. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.111.963769
34. Antoniak S, Owens AP 3rd, Baunacke M, Williams JC, Lee RD, Weithäuser A, et al. PAR-1 contributes to the innate immune response during viral infection. J Clin Invest. (2013) 123:1310–22. doi: 10.1172/JCI66125
35. Reimand J, Isserlin R, Voisin V, Kucera M, Tannus-Lopes C, Rostamianfar A, et al. Pathway enrichment analysis and visualization of omics data using g:Profiler, GSEA, Cytoscape and EnrichmentMap. Nat Protoc. (2019) 14:482–517. doi: 10.1038/s41596-018-0103-9
36. Kolberg L, Raudvere U, Kuzmin I, Adler P, Vilo J, Peterson H. g:Profiler-interoperable web service for functional enrichment analysis and gene identifier mapping (2023 update). Nucleic Acids Res. (2023) 51:W207–12. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad347
37. Palviainen M, Saraswat M, Varga Z, Kitka D, Neuvonen M, Puhka M, et al. Extracellular vesicles from human plasma and serum are carriers of extravesicular cargo-Implications for biomarker discovery. PLoS One. (2020) 15:e0236439. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236439
38. Kalra H, Adda CG, Liem M, Ang CS, Mechler A, Simpson RJ, et al. Comparative proteomics evaluation of plasma exosome isolation techniques and assessment of the stability of exosomes in normal human blood plasma. Proteomics. (2013) 13:3354–64. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201300282
39. Karimi N, Cvjetkovic A, Jang SC, Crescitelli R, Hosseinpour Feizi MA, Nieuwland R, et al. Detailed analysis of the plasma extracellular vesicle proteome after separation from lipoproteins. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2018) 75:2873–86. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2773-4
40. Akagi T, Ichiki T. Cell electrophoresis on a chip: What can we know from the changes in electrophoretic mobility? Anal Bioanal Chem. (2008) 391:2433–41. doi: 10.1007/s00216-008-2203-9
41. Frohlich E. The role of surface charge in cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of medical nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine. (2012) 7:5577–91. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S36111
42. Bairey Merz CN, Ramineni T, Leong D. Sex-specific risk factors for cardiovascular disease in women-making cardiovascular disease real. Curr Opin Cardiol. (2018) 33:500–5. doi: 10.1097/HCO.0000000000000543
43. Fairweather D, Beetler DJ, Di Florio DN, Musigk N, Heidecker B, Cooper LT Jr. COVID-19, myocarditis and pericarditis. Circ Res. (2023) 132:1302–19. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.321878
44. Fairweather D, Frisancho-Kiss S, Yusung SA, Barrett MA, Davis SE, Gatewood SJ, et al. Interferon-gamma protects against chronic viral myocarditis by reducing mast cell degranulation, fibrosis, and the profibrotic cytokines transforming growth factor-beta 1, interleukin-1 beta, and interleukin-4 in the heart. Am J Pathol. (2004) 165:1883–94. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)63241-5
45. Fairweather D, Frisancho-Kiss S, Njoku DB, Nyland JF, Kaya Z, Yusung SA, et al. Complement receptor 1 and 2 deficiency increases coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis, dilated cardiomyopathy, and heart failure by increasing macrophages, IL-1beta, and immune complex deposition in the heart. J Immunol. (2006) 176:3516–24. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.6.3516
46. Bruno KA, Mathews JE, Yang AL, Frisancho JA, Scott AJ, Greyner HD, et al. BPA alters estrogen receptor expression in the heart after viral infection activating cardiac mast cells and T cells leading to perimyocarditis and fibrosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2019) 10:598. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00598
47. Kashiwagi H, Ishimoto H, Izumi SI, Seki T, Kinami R, Otomo A, et al. Human PZP and common marmoset A2ML1 as pregnancy related proteins. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:5088. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61714-8
48. Mao L, Wang K, Zhang P, Ren S, Sun J, Yang M, et al. Carbonyl reductase 1 attenuates ischemic brain injury by reducing oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. Transl Stroke Res. (2021) 12:711–24. doi: 10.1007/s12975-021-00912-6
49. Xiao R, Youngjun O, Zhang X, Thi NN, Lu H, Hwang I. Osmotic stress-induced localisation switch of CBR1 from mitochondria to the endoplasmic reticulum triggers ATP production via beta-oxidation to respond to osmotic shock. Plant Cell Environ. (2023) 46:3420–32. doi: 10.1111/pce.14671
50. Ji X, Huang C, Mao H, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Yue B, et al. Identification of immune- and autophagy-related genes and effective diagnostic biomarkers in endometriosis: A bioinformatics analysis. Ann Transl Med. (2022) 10:1397. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-5979
51. Fino KK, Yang L, Silveyra P, Hu S, Umstead TM, DiAngelo S, et al. SH3GLB2/endophilin B2 regulates lung homeostasis and recovery from severe influenza A virus infection. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:7262. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07724-5
52. Yu Q, Horak K, Larson DF. Role of T lymphocytes in hypertension-induced cardiac extracellular matrix remodeling. Hypertension. (2006) 48:98–104. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000227247.27111.b2
53. Yu Q, Vazquez R, Zabadi S, Watson RR, Larson DF. T-lymphocytes mediate left ventricular fibrillar collagen cross-linking and diastolic dysfunction in mice. Matrix Biol. (2010) 29:511–8. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2010.06.003
54. Wang N, Zhou X, Tang F, Wang X, Zhu X. Identification of LOXL3-associating immune infiltration landscape and prognostic value in hepatocellular carcinoma. Virchows Arch. (2021) 479:1153–65. doi: 10.1007/s00428-021-03193-4
55. Parnigoni A, Viola M, Karousou E, Rovera S, Giaroni C, Passi A, et al. Hyaluronan in pathophysiology of vascular diseases: Specific roles in smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, and macrophages. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2022) 323:C505–19. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00061.2022
56. McKelvey BA, Umbricht CB, Zeiger MA. Telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) regulation in thyroid cancer: A review. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2020) 11:485. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00485
57. Surks HK, Richards CT, Mendelsohn ME. Myosin phosphatase-Rho interacting protein. A new member of the myosin phosphatase complex that directly binds RhoA. J Biol Chem. (2003) 278:51484–93. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305622200
58. Qiu XB, Shao YM, Miao S, Wang L. The diversity of the DnaJ/Hsp40 family, the crucial partners for Hsp70 chaperones. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2006) 63:2560–70. doi: 10.1007/s00018-006-6192-6
59. Hayashi M, Imanaka-Yoshida K, Yoshida T, Wood M, Fearns C, Tatake RJ, et al. A crucial role of mitochondrial Hsp40 in preventing dilated cardiomyopathy. Nat Med. (2006) 12:128–32. doi: 10.1038/nm1327
60. Elsafadi M, Manikandan M, Dawud RA, Alajez NM, Hamam R, Alfayez M, et al. Transgelin is a TGFbeta-inducible gene that regulates osteoblastic and adipogenic differentiation of human skeletal stem cells through actin cytoskeleston organization. Cell Death Dis. (2016) 7:e2321. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.196
61. Amezcua-Castillo E, González-Pacheco H, Sáenz-San Martín A, Méndez-Ocampo P, Gutierrez-Moctezuma I, Massó F, et al. C-reactive protein: The quintessential marker of systemic inflammation in coronary artery disease-advancing toward precision medicine. Biomedicines. (2023) 11:2444. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092444
62. Liu Y, Guan S, Xu H, Zhang N, Huang M, Liu Z. Inflammation biomarkers are associated with the incidence of cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2023) 10:1175174. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1175174
63. Korpetinou A, Skandalis SS, Labropoulou VT, Smirlaki G, Noulas A, Karamanos NK, et al. Serglycin: At the crossroad of inflammation and malignancy. Front Oncol. (2014) 3:327. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2013.00327
64. Coimbra JRM, Moreira PI, Santos AE, Salvador JAR. Therapeutic potential of glutaminyl cyclases: Current status and emerging trends. Drug Discovery Today. (2023) 28:103644. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2023.103644
65. Lujan DA, Ochoa JL, Hartley RS. Cold-inducible RNA binding protein in cancer and inflammation. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. (2018) 9:10. doi: 10.1002/wrna.2018.9.issue-2
66. Monti E, Sarto F, Sartori R, Zanchettin G, Löfler S, Kern H, et al. C-terminal agrin fragment as a biomarker of muscle wasting and weakness: A narrative review. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2023) 14:730–44. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13189
67. Weng D, Gao S, Shen H, Yao S, Huang Q, Zhang Y, et al. CD5L attenuates allergic airway inflammation by expanding CD11c(high) alveolar macrophages and inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation via HDAC2. Immunology. (2022) 167:384–97. doi: 10.1111/imm.13543
68. Amoroso MR, Matassa DS, Sisinni L, Lettini G, Landriscina M, Esposito F. TRAP1 revisited: Novel localizations and functions of a ‘next-generation’ biomarker. Int J Oncol. (2014) 45:969–77. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2530
69. Wang Z, Huang R, Wang H, Peng Y, Fan Y, Feng Z, et al. Prognostic and immunological role of PPP1R14A as a pan-cancer analysis candidate. Front Genet. (2022) 13:842975. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.842975
70. Hu Y, Ren J, Dong X, Zhang D, Qu Y, Yang C, et al. Fulminant giant cell myocarditis vs. lymphocytic myocarditis: A comparison of their clinical characteristics, treatments, and outcomes. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2021) 8:770549. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.770549
71. Grahn THM, Niroula A, Végvári Á, Oburoglu L, Pertesi M, Warsi S, et al. S100A6 is a critical regulator of hematopoietic stem cells. Leukemia. (2020) 34:3323–37. doi: 10.1038/s41375-020-0901-2
72. Papafilippou L, Nicolaou A, Kendall AC, Camacho-Munoz D, Hadjidemetriou M. The lipidomic profile of the nanoparticle-biomolecule corona reflects the diversity of plasma lipids. Nanoscale. (2023) 15:11038–51. doi: 10.1039/d2nr05982g
73. Eldemire R, Tharp CA, Taylor MRG, Sbaizero O, Mestroni L. The sarcomeric spring protein titin: Biophysical properties, molecular mechanisms, and genetic mutations associated with heart failure and cardiomyopathy. Curr Cardiol Rep. (2021) 23:121. doi: 10.1007/s11886-021-01550-y
74. Jin J, Jiang Y, Chakrabarti S, Su Z. Cardiac mast cells: A two-head regulator in cardiac homeostasis and pathogenesis following injury. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:963444. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.963444
75. Levick SP, Meléndez GC, Plante E, McLarty JL, Brower GL, Janicki JS. Cardiac mast cells: The centrepiece in adverse myocardial remodelling. Cardiovasc Res. (2011) 89:12–9. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq272
76. Janicki JS, Brower GL, Levick SP. The emerging prominence of the cardiac mast cell as a potent mediator of adverse myocardial remodeling. Methods Mol Biol. (2015) 1220:121–39. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-1568-2_8
77. Vandooren J, Itoh Y. Alpha-2-macroglobulin in inflammation, immunity and infections. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:803244. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.803244
78. Xu G, Xia Z, Deng F, Liu L, Wang Q, Yu Y, et al. Inducible LGALS3BP/90K activates antiviral innate immune responses by targeting TRAF6 and TRAF3 complex. PloS Pathog. (2019) 15:e1008002. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008002
79. Zhou Z, Luo G, Li C, Zhang P, Chen W, Li X, et al. Metformin induces M2 polarization via AMPK/PGC-1alpha/PPAR-gamma pathway to improve peripheral nerve regeneration. Am J Transl Res. (2023) 15:3778–92.
80. Jiahui C, Jiadai Z, Nan Z, Rui Z, Lipin H, Jian H, et al. miR-19b-3p/PKNOX1 regulates viral myocarditis by regulating macrophage polarization. Front Genet. (2022) 13:902453. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.902453
81. Cao C, Zhang Y, Chai Y, Wang L, Yin C, Shou S, et al. Attenuation of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by regulation of microRNA-23b is mediated through targeting of MyD88-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Inflammation. (2019) 42:973–86. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-00958-7
82. Luo Q, Ma H, Guo E, Yu L, Jia L, Zhang B, et al. MicroRNAs promote the progression of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy and neurovascular dysfunction through upregulation of NF-kappaB signaling pathway-associated HDAC7/ACTN4. Front Neurol. (2022) 13:909828. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.909828
83. Cheng X, Jian D, Xing J, Liu C, Liu Y, Cui C, et al. Circulating cardiac microRNAs safeguard against dilated cardiomyopathy. Clin Transl Med. (2023) 13:e1258. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1258
84. Zhao J, Jian D, Xing J, Liu C, Liu Y, Cui C, et al. MiR-26a-5p from HucMSC-derived extracellular vesicles inhibits epithelial mesenchymal transition by targeting Adam17 in silica-induced lung fibrosis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2023) 257:114950. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.114950
85. Fan KL, Li MF, Cui F, Feng F, Kong L, Zhang FH, et al. Altered exosomal miR-181d and miR-30a related to the pathogenesis of CVB3 induced myocarditis by targeting SOCS3. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2019) 23:2208–15. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201903_17268
86. Li J, Xie Y, Li L, Li X, Shen L, Gong J, et al. MicroRNA-30a modulates type I interferon responses to facilitate coxsackievirus B3 replication via targeting tripartite motif protein 25. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:603437. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.603437
87. Zhang Y, Cai S, Ding X, Lu C, Wu R, Wu H, et al. MicroRNA-30a-5p silencing polarizes macrophages toward M2 phenotype to alleviate cardiac injury following viral myocarditis by targeting SOCS1. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2021) 320:H1348–60. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00431.2020
88. Ripamonti A, Provasi E, Lorenzo M, De Simone M, Ranzani V, Vangelisti S, et al. Repression of miR-31 by BCL6 stabilizes the helper function of human follicular helper T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2017) 114:12797–802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1705364114
89. Zeng WY, Gu WY, Xyu L, Zhang Y, Han C. miR-99b-5p inhibits the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome to alleviate the neurotoxicity induced by paclitaxel chemotherapy. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. (2022) 38:438–42. doi: 10.12047/j.cjap.6289.2022.082
90. Li YJ, Wang Y, Wang YY. MicroRNA-99b suppresses human cervical cancer cell activity by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:9577–91. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27645
91. Rasheed Z, Rasheed N, Abdulmonem WA, Khan MI. MicroRNA-125b-5p regulates IL-1beta induced inflammatory genes via targeting TRAF6-mediated MAPKs and NF-kappaB signaling in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:6882. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42601-3
92. Jie J, Xu X, Li W, Wang G. Regulation of apoptosis and inflammatory response in interleukin-1beta-induced nucleus pulposus cells by miR-125b-5p via targeting TRIAP1. Biochem Genet. (2021) 59:475–90. doi: 10.1007/s10528-020-10009-8
93. Ben-Zvi I, Volinsky N, Grosman-Rimon L, Haviv I, Rozen G, Andria N, et al. Cardiac-peripheral transvenous gradients of microRNA expression in systolic heart failure patients. ESC Heart Fail. (2020) 7:835–43. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12597
94. Tiedt S, Prestel M, Malik R, Schieferdecker N, Duering M, Kautzky V, et al. RNA-Seq identifies circulating miR-125a-5p, miR-125b-5p, and miR-143-3p as potential biomarkers for acute ischemic stroke. Circ Res. (2017) 121:970–80. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311572
95. Wang Y, Li H, Shi Y, Wang S, Xu Y, Li H, et al. miR-143-3p impacts on pulmonary inflammatory factors and cell apoptosis in mice with mycoplasmal pneumonia by regulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB pathway. Biosci Rep. (2020) 40:BSR20193419. doi: 10.1042/BSR20193419
96. Jara D, et al. Type I interferon dependent hsa-miR-145-5p downregulation modulates MUC1 and TLR4 overexpression in salivary glands from Sjögren’s syndrome patients. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:685837. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.685837
97. Moradi F, Mohajerani F, Sadeghizadeh M. CCAT2 knockdown inhibits cell growth, and migration and promotes apoptosis through regulating the hsa-mir-145-5p/AKT3/mTOR axis in tamoxifen-resistant MCF7 cells. Life Sci. (2022) 311:121183. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.121183
98. Bao JL, Lin L. MiR-155 and miR-148a reduce cardiac injury by inhibiting NF-kappaB pathway during acute viral myocarditis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2014) 18:2349–56.
99. Lai H, Fan J, Zhang Y, Pan B, Pan W, Fang J, et al. Overexpression of miR-148a-3p inhibits extracellular matrix degradation and alleviates IL-1beta-induced intervertebral disc degeneration. Iran J Basic Med Sci. (2023) 26:157–63. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2022.64645.14228
100. Mollazadeh S, Fazly Bazzaz BS, Neshati V, de Vries AAF, Naderi-Meshkin H, Mojarad M, et al. Overexpression of microRNA-148b-3p stimulates osteogenesis of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: The role of microRNA-148b-3p in osteogenesis. BMC Med Genet. (2019) 20:117. doi: 10.1186/s12881-019-0854-3
101. Gil-Martinez M, Lorente-Sorolla C, Rodrigo-Muñoz JM, Lendínez MÁ, Núñez-Moreno G, de la Fuente L, et al. Analysis of differentially expressed microRNAs in serum and lung tissues from individuals with severe asthma treated with oral glucocorticoids. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:1611. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021611
102. Ge S, Wang D, Kong Q, Gao W, Sun J. Function of miR-152 as a tumor suppressor in human breast cancer by targeting PIK3CA. Oncol Res. (2017) 25:1363–71. doi: 10.3727/096504017X14878536973557
103. Deng Z, Yao J, Xiao N, Han Y, Wu X, Ci C, et al. DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) suppresses mitophagy and aggravates heart failure via the microRNA-152-3p/ETS1/RhoH axis. Lab Invest. (2022) 102:782–93. doi: 10.1038/s41374-022-00740-8
104. Othumpangat S, Noti JD. Beta-defensin-1 regulates influenza virus infection in human bronchial epithelial cells through the STAT3 signaling pathway. Pathogens. (2023) 12:123. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12010123
105. Huang S, Zhang J, Wan H, Wang K, Wu J, Cao Y, et al. Plasma extracellular vesicles microRNA-208b-3p and microRNA-143-3p as novel biomarkers for sudden cardiac death prediction in acute coronary syndrome. Mol Omics. (2023) 19:262–73. doi: 10.1039/d2mo00257d
106. Cho J, Kim S, Lee H, Rah W, Cho HC, Kim NK, et al. Regeneration of infarcted mouse hearts by cardiovascular tissue formed via the direct reprogramming of mouse fibroblasts. Nat BioMed Eng. (2021) 5:880–96. doi: 10.1038/s41551-021-00783-0
107. Gast M, Nageswaran V, Kuss AW, Tzvetkova A, Wang X, Mochmann LH, et al. tRNA-like transcripts from the NEAT1-MALAT1 genomic region critically influence human innate immunity and macrophage functions. Cells. (2022) 11:3970. doi: 10.3390/cells11243970
108. Reichelt-Wurm S, Pregler M, Wirtz T, Kretz M, Holler K, Banas B, et al. The interplay of NEAT1 and miR-339-5p influences on mesangial gene expression and function in various diabetic-associated injury models. Noncoding RNA. (2022) 8:52. doi: 10.3390/ncrna8040052
109. Wang P, Fang Y, Qiu J, Zhou Y, Wang Z, Jiang C. miR-345-5p curbs hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis progression by suppressing hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression. Toxicol Lett. (2022) 370:42–52. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2022.09.008
110. Hao QQ, Wang QH, Xia W, Qian HZ. Circulating miRNA expression profile and bioinformatics analysis in patients with occult hepatitis B virus infection. J Med Virol. (2020) 92:191–200. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25594
111. Peng S, Wang J, Wei S, Li C, Zhou K, Hu J, et al. Endogenous cellular microRNAs mediate antiviral defense against influenza A virus. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2018) 10:361–75. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2017.12.016
112. Mou Y, Ding X. LncRNA ST8SIA6-AS1 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression by governing miR-651-5p/TM4SF4 axis. Anticancer Drugs. (2022) 33:741–51. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001326
113. Zhao D, Wu K, Sharma S, Xing F, Wu SY, Tyagi A, et al. Exosomal miR-1304-3p promotes breast cancer progression in African Americans by activating cancer-associated adipocytes. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:7734. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35305-2
114. Wang W, Zhang J, Fan Y, Zhang L. MiR-1306-5p predicts favorable prognosis and inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of colorectal cancer cells via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Cell Cycle. (2022) 21:1491–501. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2054245
115. Giannella A, Riccetti S, Sinigaglia A, Piubelli C, Razzaboni E, Di Battista P, et al. Circulating microRNA signatures associated with disease severity and outcome in COVID-19 patients. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:968991. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.968991
116. Gong L, Xiao J, Yi J, Xiao J, Lu F, Liu X. Immunomodulatory effect of serum exosomes from Crohn disease on macrophages via Let-7b-5p/TLR4 signaling. Inflammation Bowel Dis. (2022) 28:96–108. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izab132
117. Nematian SE, Mamillapalli R, Kadakia TS, Majidi Zolbin M, Moustafa S, et al. Systemic inflammation induced by microRNAs: Endometriosis-derived alterations in circulating microRNA 125b-5p and Let-7b-5p regulate macrophage cytokine production. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2018) 103:64–74. doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-01199
118. Li H, Dai B, Fan J, Chen C, Nie X, Yin Z, et al. The different roles of miRNA-92a-2-5p and let-7b-5p in mitochondrial translation in db/db mice. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2019) 17:424–35. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.06.013
119. Xiong Y, Huang H, Chen F, Tang Y. CircDLGAP4 induces autophagy and improves endothelial cell dysfunction in atherosclerosis by targeting PTPN4 with miR-134-5p. Environ Toxicol. (2023) 38:2952–66. doi: 10.1002/tox.23930
120. Liu D, Liu Y, Hu Y, Ming Y, Meng X, Tan H, et al. MiR-134-5p/Stat3 axis modulates proliferation and migration of MSCs co-cultured with glioma C6 cells by regulating Pvt1 expression. Life (Basel). (2022) 12:1648. doi: 10.3390/life12101648
121. Banaganapalli B, Al-Rayes N, Awan ZA, Alsulaimany FA, Alamri AS, Elango R, et al. Multilevel systems biology analysis of lung transcriptomics data identifies key miRNAs and potential miRNA target genes for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Comput Biol Med. (2021) 135:104570. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104570
122. Mohammadinasr M, Montazersaheb S, Molavi O, Kahroba H, Talebi M, Ayromlou H, et al. Multiplex analysis of cerebrospinal fluid and serum exosomes microRNAs of untreated relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) and proposing noninvasive diagnostic biomarkers. Neuromolecular Med. (2023) 25:402–14. doi: 10.1007/s12017-023-08744-3
123. Walkowski B, Kleibert M, Majka M, Wojciechowska M. Insight into the role of the PI3K/Akt pathway in ischemic injury and post-infarct left ventricular remodeling in normal and diabetic heart. Cells. (2022) 11:1553. doi: 10.3390/cells11091553
124. Xu L, Zhao Q, Li D, Luo J, Ma W, Jin Y, et al. MicroRNA-760 resists ambient PM(2.5)-induced apoptosis in human bronchial epithelial cells through elevating heme-oxygenase 1 expression. Environ pollut. (2021) 284:117213. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117213
125. Frye CJ, Cunningham CL, Mihailescu MR. Host microRNA interactions with the SARS-CoV-2 viral genome 3’-untranslated region. bioRxiv. (2023), 2023.05.18.541401. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.18.541401
126. Cui X, Li Y, Bao J, Wang K, Wu X. Downregulation of miR-760 causes human intervertebral disc degeneration by targeting the MyD88/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2022) 10:813070. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.813070
127. Soubeyrand S, Lau P, Beehler K, McShane K, McPherson R. miR1908-5p regulates energy homeostasis in hepatocyte models. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:23748. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-03156-4
128. Yao X, Wang Q, Zeng P, Hou L, Yang Y, Lu D, et al. LncRNA HOTTIP from synovial fibroblast-derived exosomes: A novel molecular target for rheumatoid arthritis through the miR-1908-5p/STAT3 axis. Exp Cell Res. (2021) 409:112943. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112943
129. Chen Y, Lin D, Shi C, Guo L, Liu L, Chen L, et al. MiR-3138 deteriorates the insulin resistance of HUVECs via KSR2/AMPK/GLUT4 signaling pathway. Cell Cycle. (2021) 20:353–68. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1870335
130. Nunes JPS, Andrieux P, Brochet P, Almeida RR, Kitano E, Honda AK, et al. Co-exposure of cardiomyocytes to IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha induces mitochondrial dysfunction and nitro-oxidative stress: Implications for the pathogenesis of chronic Chagas disease cardiomyopathy. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:755862. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.755862
131. Sonoda T, Matsuzaki J, Yamamoto Y, Sakurai T, Aoki Y, Takizawa S, et al. Serum microRNA-based risk prediction for stroke. Stroke. (2019) 50:1510–8. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.023648
132. Aas V, Øvstebø R, Brusletto BS, Aspelin T, Trøseid AS, Qureshi S, et al. Distinct microRNA and protein profiles of extracellular vesicles secreted from myotubes from morbidly obese donors with type 2 diabetes in response to electrical pulse stimulation. Front Physiol. (2023) 14:1143966. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1143966
133. Ormseth MJ, Solus JF, Sheng Q, Chen SC, Ye F, Wu Q, et al. Plasma miRNAs improve the prediction of coronary atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. (2021) 40:2211–9. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05573-8
134. Wang J, Lu W, Zhang J, Du Y, Fang M, Zhang A, et al. Loss of TRIM29 mitigates viral myocarditis by attenuating PERK-driven ER stress response in male mice. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:3481. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44745-x
135. Yang Y, Li Q, Guo L. MicroRNA−122 acts as tumor suppressor by targeting TRIM29 and blocking the activity of PI3K/AKT signaling in nasopharyngeal carcinoma in vitro. Mol Med Rep. (2018) 17:8244–52. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8894
136. Fang M, Zhang A, Du Y, Lu W, Wang J, Minze LJ, et al. TRIM18 is a critical regulator of viral myocarditis and organ inflammation. J Biomed Sci. (2022) 29:55. doi: 10.1186/s12929-022-00840-z
137. Straub RH. The complex role of estrogens in inflammation. Endocr Rev. (2007) 28:521–74. doi: 10.1210/er.2007-0001
138. Cutolo M, Gotelli E. Complex role of oestrogens in the risk and severity of rheumatoid arthritis in menopause. RMD Open. (2023) 9:e003176. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-003176
139. Huang J, Liao Q, Ooi MH, Cowling BJ, Chang Z, Wu P, et al. Epidemiology of recurrent hand, foot and mouth disease, China, 2008-2015. Emerg Infect Dis. (2018) 24:432–42. doi: 10.3201/eid2403.171303
140. Vidaurre-Agut C, Rivero-Buceta EM, Landry CC, Botella P. Isolation and quantification of miRNA from the biomolecular corona on mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Nanomaterials (Basel). (2021) 11:1196. doi: 10.3390/nano11051196
141. Geekiyanage H, Rayatpisheh S, Wohlschlegel JA, Brown R Jr., Ambros V. Extracellular microRNAs in human circulation are associated with miRISC complexes that are accessible to anti-AGO2 antibody and can bind target mimic oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U. S. A. (2020) 117:24213–23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2008323117
Keywords: coxsackievirus B3, innate immunity, complement, TLR4, sex differences, microRNA
Citation: Beetler DJ, Giresi P, Di Florio DN, Fliess JJ, McCabe EJ, Watkins MM, Xu V, Auda ME, Bruno KA, Whelan ER, Kocsis SPC, Edenfield BH, Walker S A, Macomb LP, Keegan KC, Jain A, Morales-Lara AC, Chekuri I, Hill AR, Farres H, Wolfram J, Behfar A, Stalboerger PG, Terzic A, Cooper L T Jr and Fairweather D (2025) Therapeutic effects of platelet-derived extracellular vesicles on viral myocarditis correlate with biomolecular content. Front. Immunol. 15:1468969. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1468969
Received: 22 July 2024; Accepted: 18 October 2024;
Published: 06 January 2025.
Edited by:
Enrico Brunetta, Humanitas Research Hospital, ItalyReviewed by:
Junji Xing, Houston Methodist Research Institute, United StatesGiorgio Mangino, Sapienza University of Rome, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Beetler, Giresi, Di Florio, Fliess, McCabe, Watkins, Xu, Auda, Bruno, Whelan, Kocsis, Edenfield, Walker, Macomb, Keegan, Jain, Morales-Lara, Chekuri, Hill, Farres, Wolfram, Behfar, Stalboerger, Terzic, Cooper and Fairweather. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: DeLisa Fairweather, RmFpcndlYXRoZXIuRGVMaXNhQG1heW8uZWR1
†These authors share senior authorship
 Danielle J. Beetler1,2,3
Danielle J. Beetler1,2,3 Damian N. Di Florio
Damian N. Di Florio Matthew E. Auda
Matthew E. Auda Katelyn A. Bruno
Katelyn A. Bruno Emily R. Whelan
Emily R. Whelan Stephen P. C. Kocsis
Stephen P. C. Kocsis Andrea C. Morales-Lara
Andrea C. Morales-Lara Anneliese R. Hill
Anneliese R. Hill Atta Behfar
Atta Behfar Andre Terzic
Andre Terzic Leslie T. Cooper Jr
Leslie T. Cooper Jr DeLisa Fairweather
DeLisa Fairweather