
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Immunol. , 05 September 2024
Sec. Primary Immunodeficiencies
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1467807
This article is a correction to:
Abnormalities of Thymic Stroma may Contribute to Immune Dysregulation in Murine Models of Leaky Severe Combined Immunodeficiency
 Francesca Rucci1
Francesca Rucci1 Pietro Luigi Poliani2
Pietro Luigi Poliani2 Stefano Caraffi1
Stefano Caraffi1 Tiziana Paganini3
Tiziana Paganini3 Elena Fontana2
Elena Fontana2 Silvia Giliani3
Silvia Giliani3 Frederick W. Alt4
Frederick W. Alt4 Luigi Daniele Notarangelo1*
Luigi Daniele Notarangelo1*A Corrigendum on
Abnormalities of thymic stroma may contribute to immune dysregulation in murine models of leaky severe combined immunodeficiency
By Rucci F, Poliani PL, Caraffi S, Paganini T, Fontana E, Giliani S, Alt FW and Notarangelo LD (2011). Front. Immun. 2:15. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2011.00015
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 5 as published.
“The insets within the right upper and middle panels showing a higher magnification of the AIRE immunostaining have been corrected. In the original panels, there was a mistake in placing the original insets from a higher magnification image.”
The corrected Figure 5 and its caption appear below.
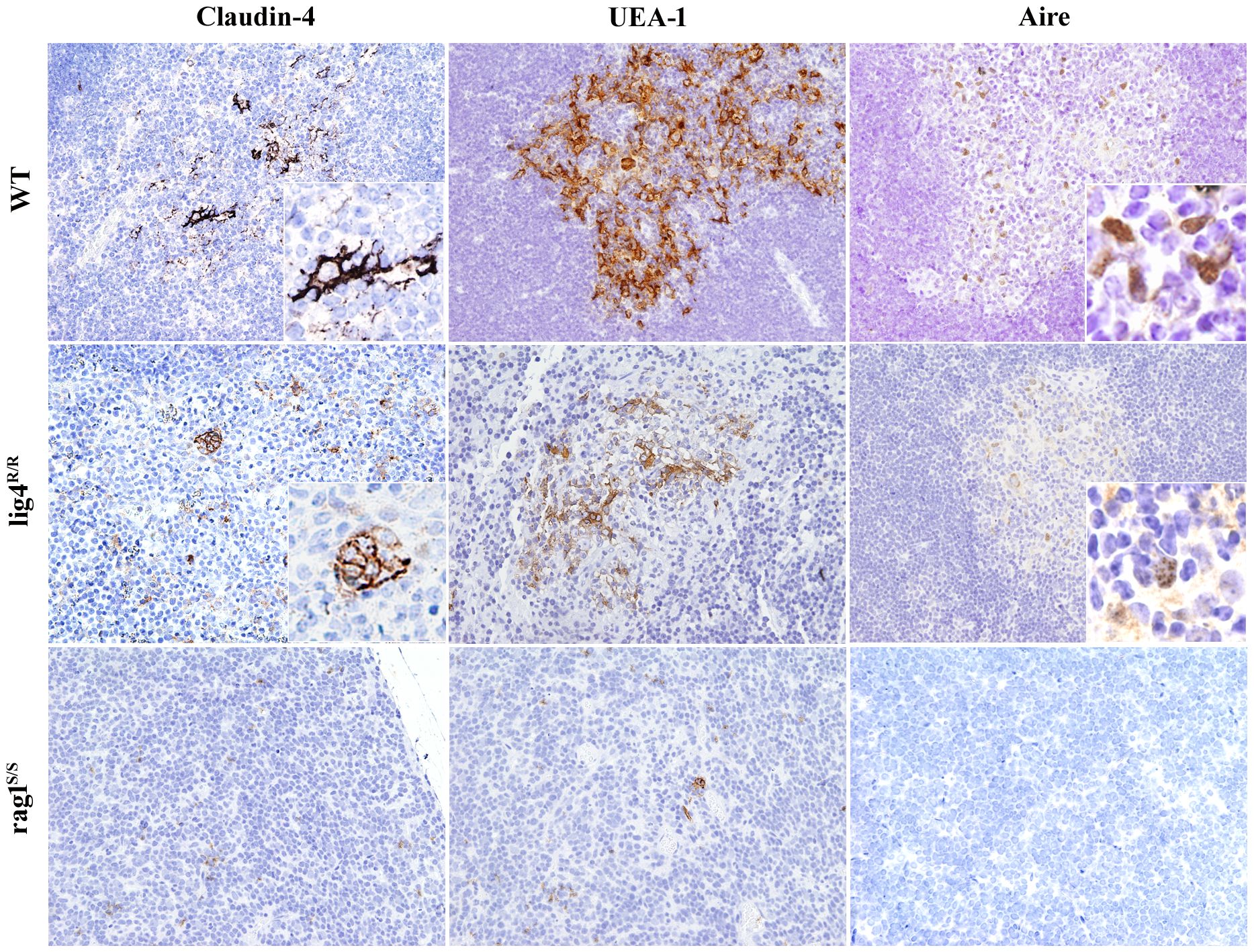
Figure 5. Maturation of medullary thymic epithelial cells (mTECs) in wild-type (WT), Lig4R/R, and Rag1S/S mice. Mature mTECs from WT mice express claudin-4 (Cld4), Ulex europaeus agglutinin 1 (UEA-1) and Aire (upper panels). Insets highlight fully mature mTECs showing immunoreactivity (IR) for Cld4 and the characteristic granular dot-like Aire positivity in the nuclei. Thymuses from Lig4R/R mice show residual presence of mTECs that reach full maturation with positivity for UEA-1, Cld4, and Aire expression (middle panels). Loss of corticomedullary demarcation (CMD) with impaired maturation of mTECs was observed in the thymuses from the Rag1S/S mice in which only rare UEA-1 IR cells but no mature Cld4+ and Aire+ cells were found (lower panels). IR staining: brown. All panels are from 20× original magnification; insets are from 40× original magnification. One representative example of five mice analyzed per each strain.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: severe combined immunodeficiency, recombination-activating gene 1, DNA ligase 4, thymic epithelial cells, thymus, dendritic cells, Aire, regulatory T cells
Citation: Rucci F, Poliani PL, Caraffi S, Paganini T, Fontana E, Giliani S, Alt FW and Notarangelo LD (2024) Corrigendum: Abnormalities of thymic stroma may contribute to immune dysregulation in murine models of leaky severe combined immunodeficiency. Front. Immunol. 15:1467807. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1467807
Received: 20 July 2024; Accepted: 09 August 2024;
Published: 05 September 2024.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Menno C. van Zelm, Monash University, AustraliaCopyright © 2024 Rucci, Poliani, Caraffi, Paganini, Fontana, Giliani, Alt and Notarangelo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Luigi Daniele Notarangelo, bHVpZ2kubm90YXJhbmdlbG9AY2hpbGRyZW5zLmhhcnZhcmQuZWR1
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.