- 1Clinical Medical College, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
- 2Dermatology Department, National Center for Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing, China
Introduction: Generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) is a rare and potentially life-threatening auto-inflammatory disease. Currently, there are no consensus-based guidelines or universally accepted treatments. Biologics represent a potential therapeutic option. This study systematically assessed the efficacy and safety of biologics in GPP.
Methods: Relevant studies from three databases were systematically searched until June 28, 2024. Statistical information, including the single-arm proportion rate of the outcomes and 95% confidence intervals (CIs), was analyzed to determine treatment effects. Heterogeneity was assessed using I² values, and subgroup analyses were performed based on drug targets and treatment durations. Data were quantitatively synthesized using a random-effects meta-analysis. Analyses were performed using R statistical software version 4.4.0.
Results: A total of 329 patients from 16 studies were included. The proportion of responders treated with IL-36 inhibitors and IL-17 inhibitors is higher than those treated with TNF-α inhibitors and IL-23 inhibitors. IL-36 inhibitors appear to achieve the highest response rates between 4 and 8 weeks, while IL-17 inhibitors, TNF-alpha inhibitors, and IL-23 inhibitors show a gradual increase in response rates up to 12 weeks. IL-36 inhibitors achieve a 40% (95% CI: 27%-54%) GPPASI75 response rate and a 55% (95% CI: 41%-68%) GPPGA (0,1) response rate within 2 weeks, significantly outperforming other biologics. The recurrence rates of GPP within 52 weeks, ranked from highest to lowest, are: IL-36 inhibitors (21% [95% CI: 9%-28%]), TNF-alpha inhibitors (20% [95% CI: 2%-46%]), IL-17 inhibitors (15% [95% CI: 1%-37%]), and IL-23 inhibitors (5% [95% CI: 0%-29%]). Additionally, 6% (95% CI: 1%-11%) of patients experienced severe adverse events.
Discussion: This meta-analysis highlights the efficacy and safety of biologics in patients with GPP, offering valuable evidence to guide future clinical practice. IL-36 inhibitors show a faster and more substantial clinical response in GPP compared to other biologics. Further research is necessary to assess their role in specific subpopulations and to evaluate their potential long-term effects on flare prevention.
1 Introduction
Generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) is a rare and potentially life-threatening auto-inflammatory disease, characterized by recurrent, sudden flares of widespread painful erythema covered with sterile pustules that may coalesce to form lakes of pus (1–3). Reported mortality rates, ranging from 4% to 24%, underscore the severity of this condition (2, 4, 5).
Conventional treatments such as retinoids, cyclosporine, and methotrexate may be effective in certain cases of GPP, but they often come with significant side effects and may be inadequate for more severe cases (6, 7). With the advent of new biologic therapies, there are now more suitable treatment options available. The joint guidelines from the American Academy of Dermatology and National Psoriasis Foundation recommend infliximab, adalimumab, ustekinumab, secukinumab, ixekizumab, and brodalumab as effective monotherapies for treating GPP in adults (8, 9). Additionally, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved spesolimab in September 2022 for treating GPP flares in adults, based on data from two trials (10, 11). However, there are currently no consensus-based guidelines or universally accepted treatments available.
To date, there have been no meta-analyses on the use of biologics for GPP, and the available randomized controlled trials (RCTs) (11, 12) are insufficient for such an analysis. The low prevalence and relapsing-remitting nature of GPP make obtaining high-quality evidence on the efficacy and safety of treatments challenging. Additionally, the potential severity of acute flares poses significant challenges for conducting randomized placebo-controlled trials in this population (13). Therefore, we conducted a single-arm meta-analysis to assess the efficacy and safety of biologics in treating GPP.
2 Methods
This systematic review and meta-analysis adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (14). The protocol was registered with PROSPERO (CRD42024564157).
2.1 Data source and search strategy
Two authors (B.L.C and Q.W.L) conducted an online search on PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) from inception to June 28, 2024. The search keywords included combinations of terms related to biologics, generalized pustular psoriasis, and clinical trials. The complete search strategy is detailed in Supplementary Table S1. Additionally, a manual search of the reference lists of screened articles was performed. No language restrictions were applied.
2.2 Eligibility criteria and study selection
Eligibility criteria were: (1) RCTs, single-arm trials and observational studies involving patients with GPP; (2) studies involving biologics for GPP; (3) studies reporting Generalized Pustular Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (GPPASI), Generalized Pustular Psoriasis Physician Global Assessment (GPPGA), the GPP flare during maintenance, or adverse events (15–17). Titles and abstracts of potential studies were independently screened by two authors (B.L.C and Q.W.L). Irrelevant studies were excluded based on the following criteria: (1) duplicate studies from the same trials; (2) reviews and case reports. Full texts were assessed for eligibility when abstracts provided insufficient information. Discrepancies were resolved through discussion with the senior author (Y.P.B).
2.3 Data extraction and evaluation of the risk of bias
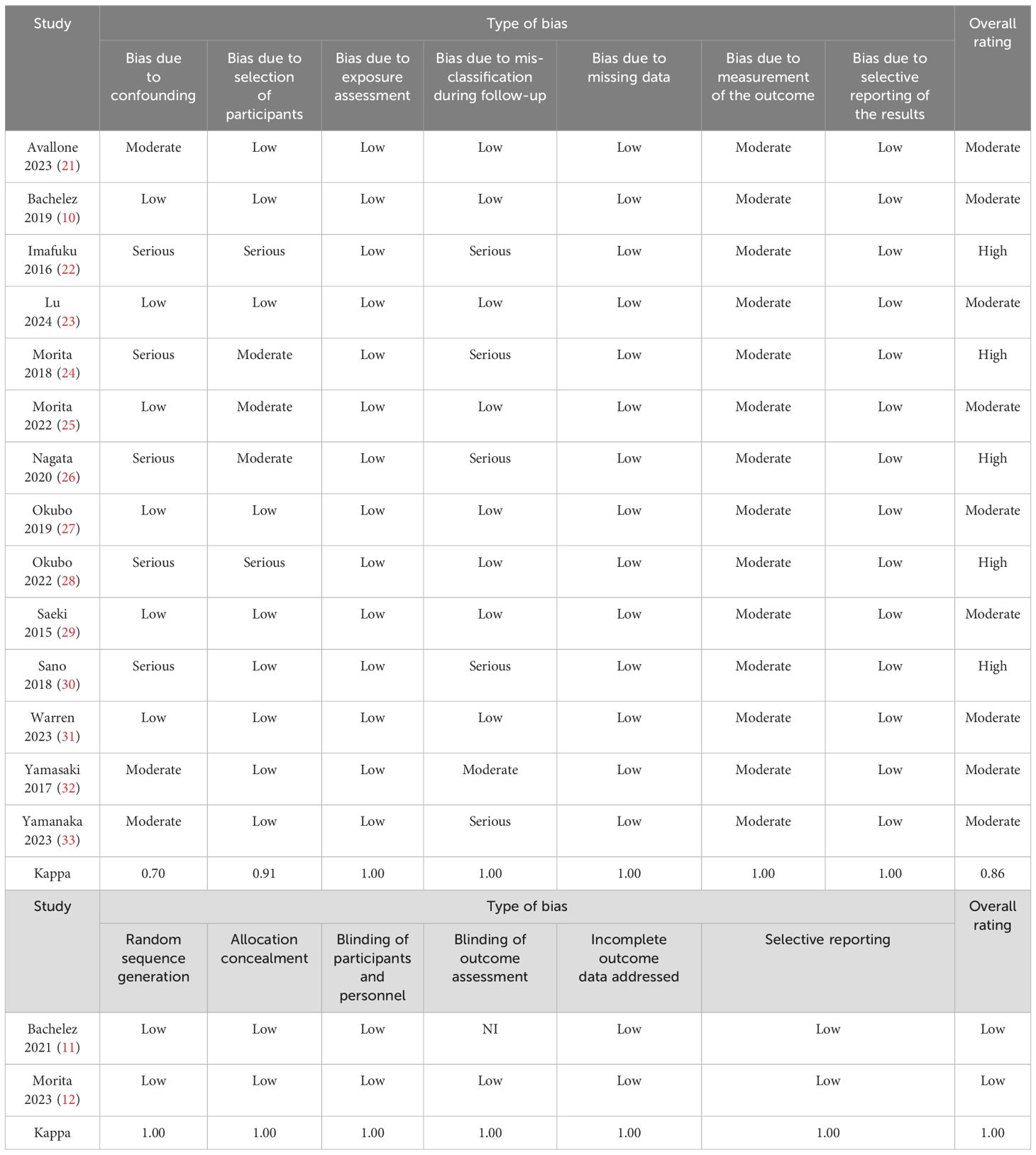
The characteristics of included studies were extracted, including authors, registration number, study period, funding sources, race of participants, region, sample size, age, sex, treatment regimens, and outcomes such as the proportion of GPPASI 75/90/100, GPPGA (0, 1), GPP flare during maintenance, and adverse events (15–17). Two authors (B.L.C and Q.W.L) independently assessed the quality using the Risk Of Bias In Non-randomized Studies - of Interventions (ROBINS-I) tool (18), the Cochrane Collaboration risk of bias tool (19), and the GRADE assessment (20). Consistency was assessed using the kappa coefficient, as shown in Table 1. Any disagreements were resolved through consensus with the senior author (Y.P.B).
2.4 Data synthesis and statistical analysis
Statistical information, including the single-arm proportion rate of the outcomes and 95% confidence intervals (CIs), was analyzed to determine treatment effects. Heterogeneity was assessed using I² values, and subgroup analyses were performed based on drug targets and treatment durations. Data were quantitatively synthesized using a random-effects meta-analysis. All tests were two-sided, and a p-value < 0.05 was considered significant. Funnel plots and the Egger test were used to evaluate publication bias in the included studies. Sensitivity analyses were conducted to assess the robustness and reliability of the combined results. Analyses were performed using R statistical software version 4.4.0.
3 Results
3.1 Study characteristics
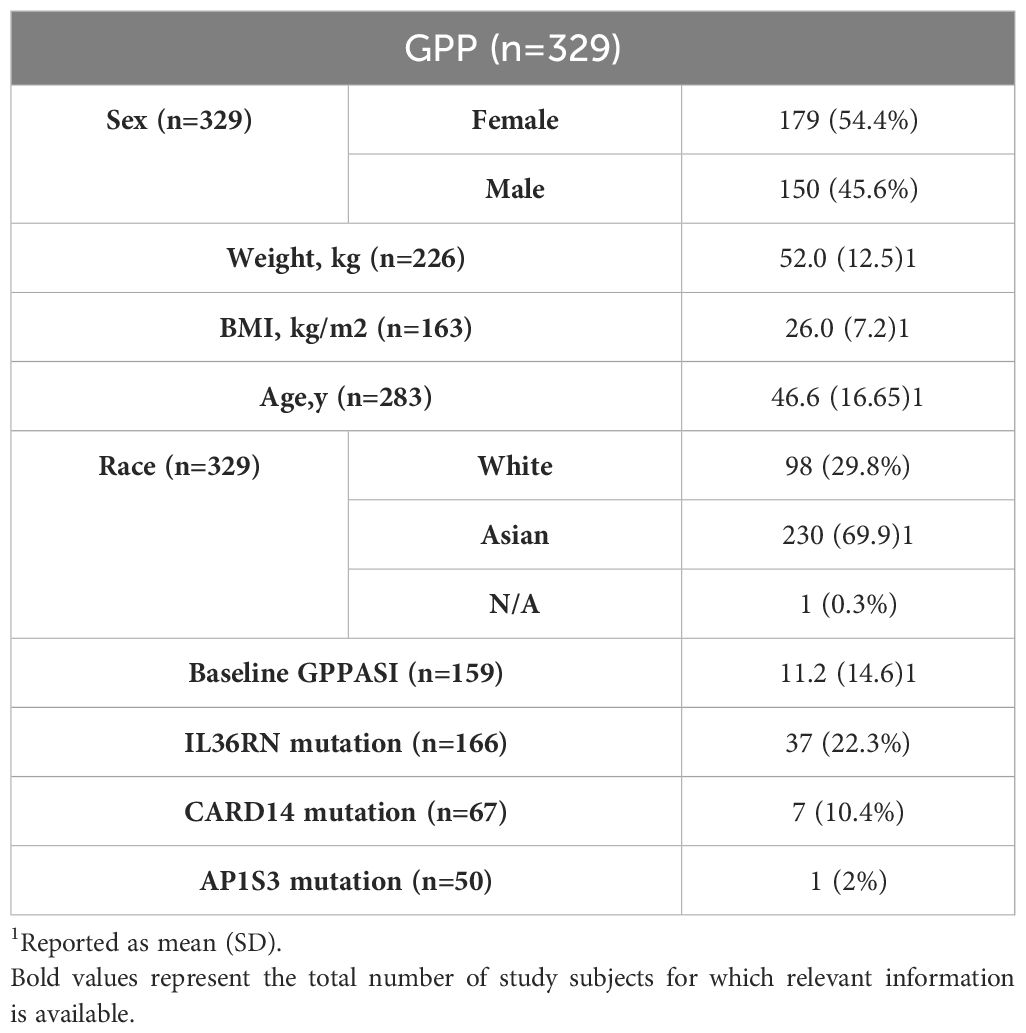
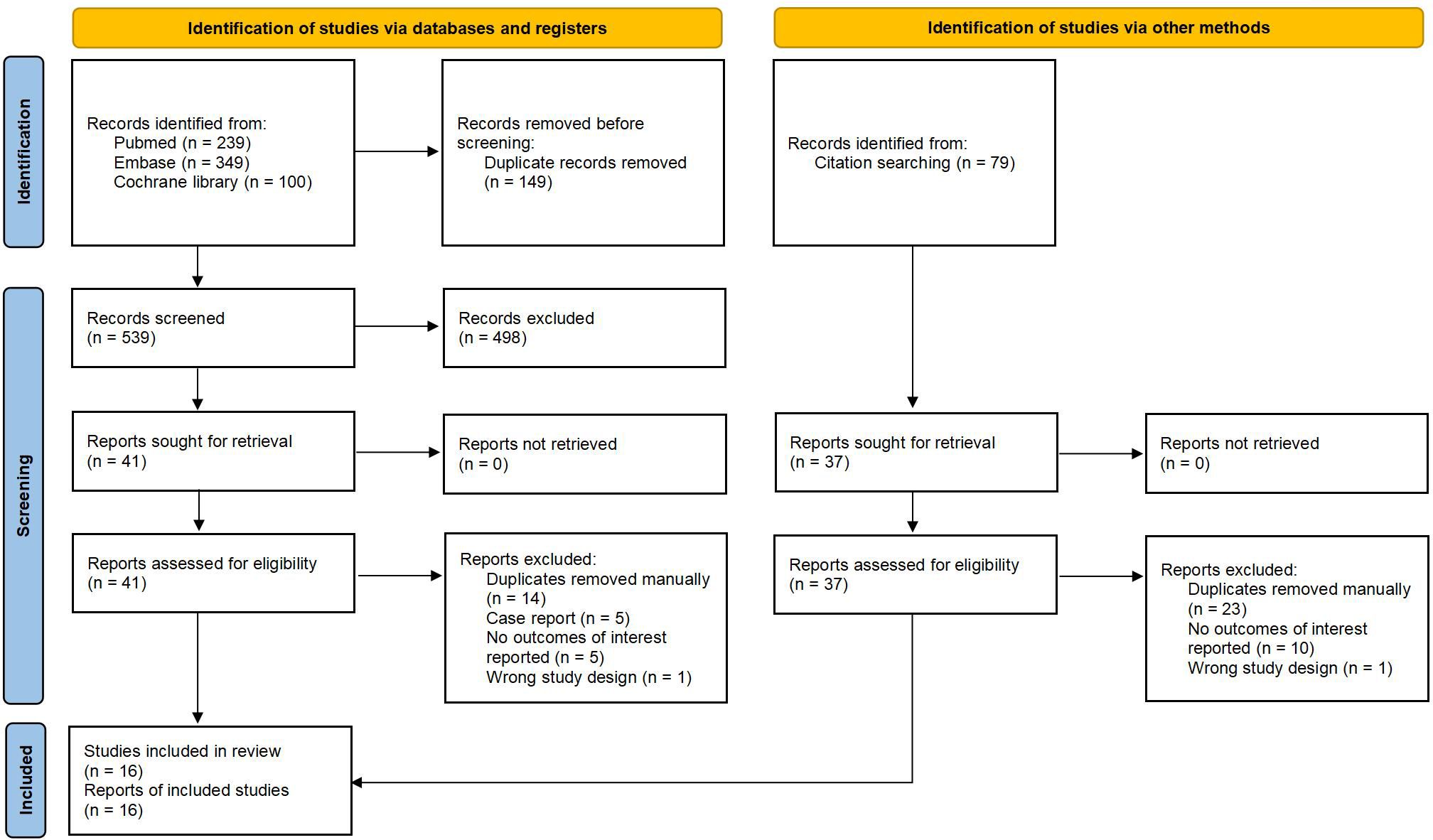
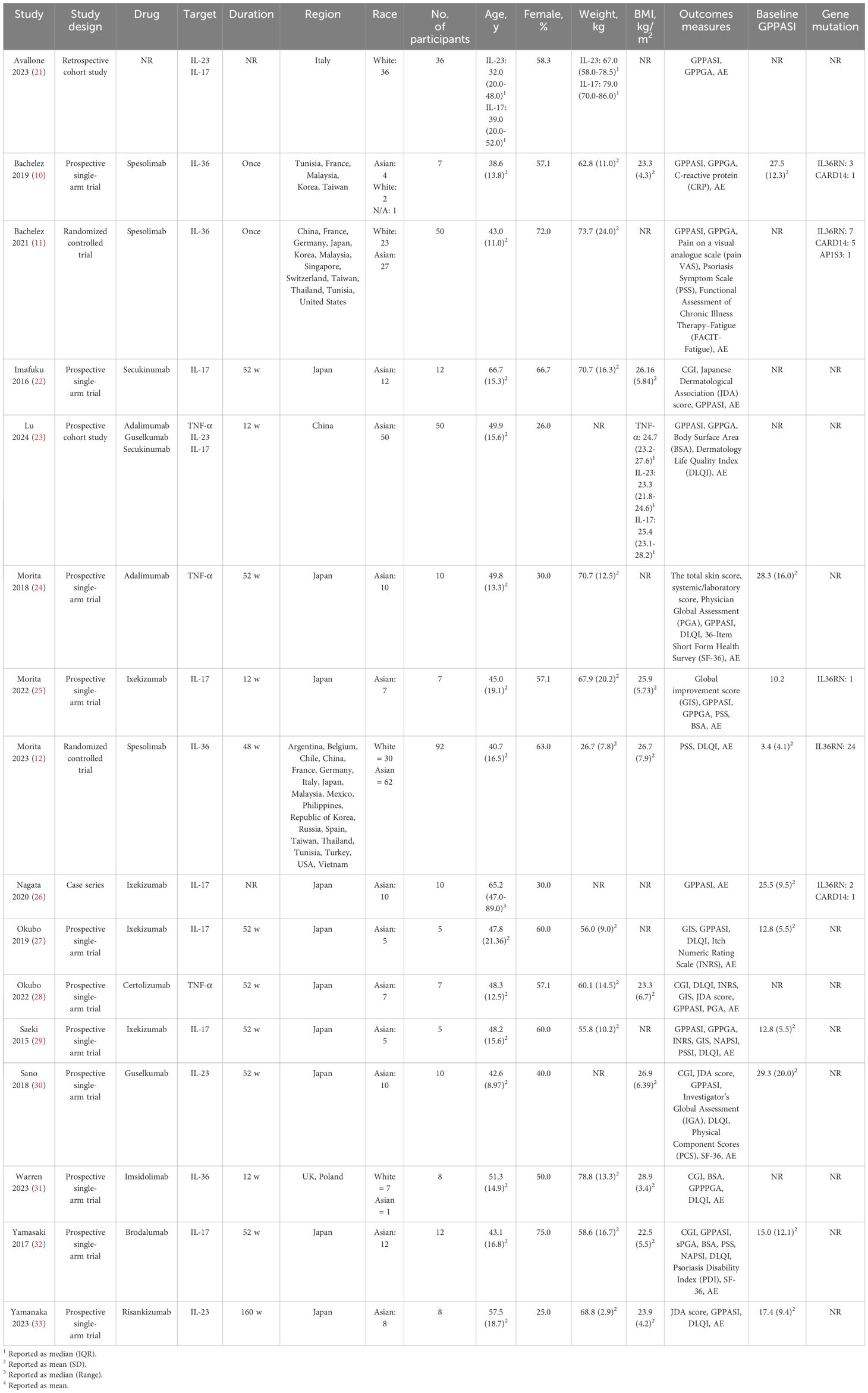
Out of the 767 articles identified, 16 trials met the inclusion criteria (Figure 1). The demographic data and characteristics of the included studies are summarized in Table 1, 2 (10–12, 21–33). The excluded trials are listed in Supplementary Table S3. One trial was funded by a not-for-profit foundation (23). One trial was with no funding support (21). And the remaining trials received funding from the pharmaceutical industry (10–12, 22, 24–33). Four trials were conducted in multiple countries (10–12, 31), while the rest were conducted in Italy (21), China (23) or Japan (22, 24–30, 32, 33). The total sample size consisted of 329 patients: 157 patients received IL-36 targeted biologics (spesolimab, imsidolimab); 97 patients received IL-17 targeted biologics (brodalumab, ixekizumab, secukinumab); 43 patients received IL-23 targeted biologics (guselkumab, risankizumab); 32 patients received TNF-α targeted biologics (adalimumab, certolizumab).
3.2 Risk of bias assessment
ROBINS-I is a new tool used for evaluating the risk of bias in observational studies (18). Cochrane Collaboration risk of bias tool (19) was utilized for assessing the risk of bias in randomized controlled trials. Detailed information can be found in Table 3.
3.3 GPPASI
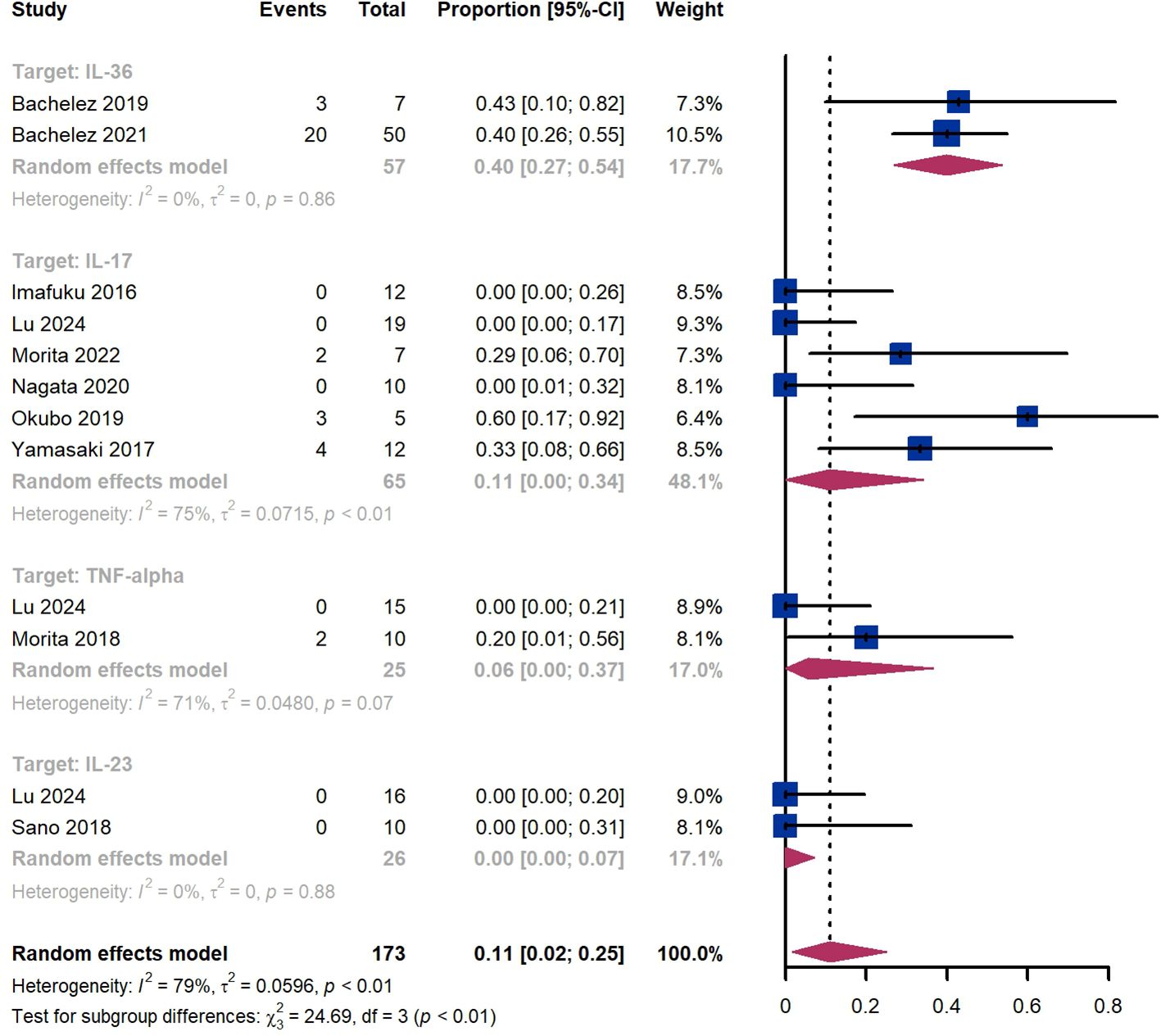
Within 2 weeks, we observed a GPPASI 75 responder proportion of 11% (95% CI 2%-25%) among 173 patients, including 40% (95% CI 27%-54%) for patients treated by IL-36 targeted biologics, 11% (95% CI 0%-34%) for those treated by IL-17 targeted biologics, 6% (95% CI 0%-37%) for those treated by TNF-α targeted biologics, 0% (95% CI 0%-7%) for those treated by IL-23 targeted biologics (Figure 2). The Egger test for publication bias indicated evidence of bias (P = 0.52).
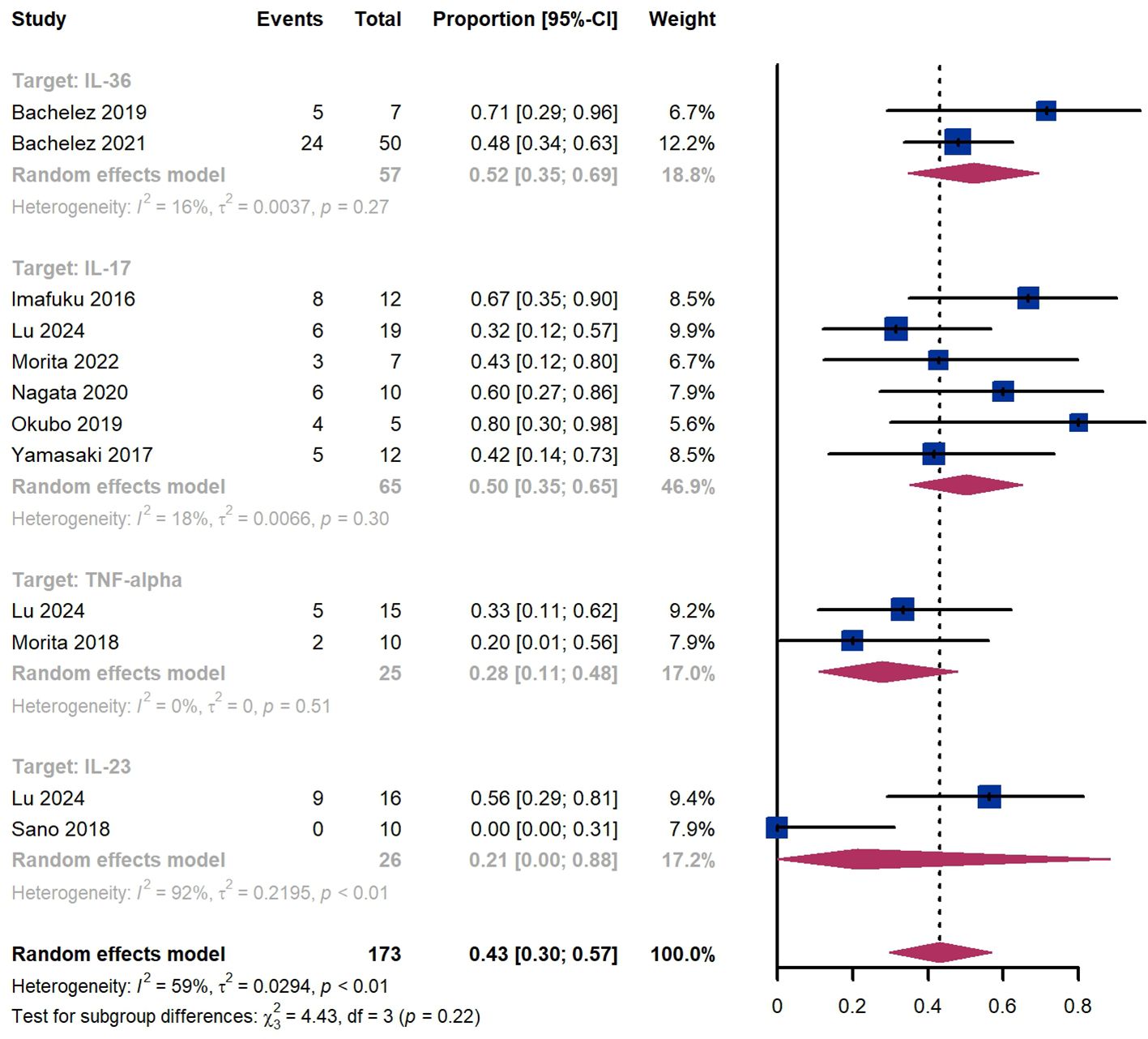
Within 4 weeks, we observed a GPPASI 75 responder proportion of 43% (95% CI 30%-57%) among 173 patients, including 52% (95% CI 35%-69%) for patients treated by IL-36 targeted biologics, 50% (95% CI 35%-65%) for those treated by IL-17 targeted biologics, 28% (95% CI 11%-48%) for those treated by TNF-α targeted biologics (Figure 3). The Egger test for publication bias indicated evidence of bias (P = 0.97).
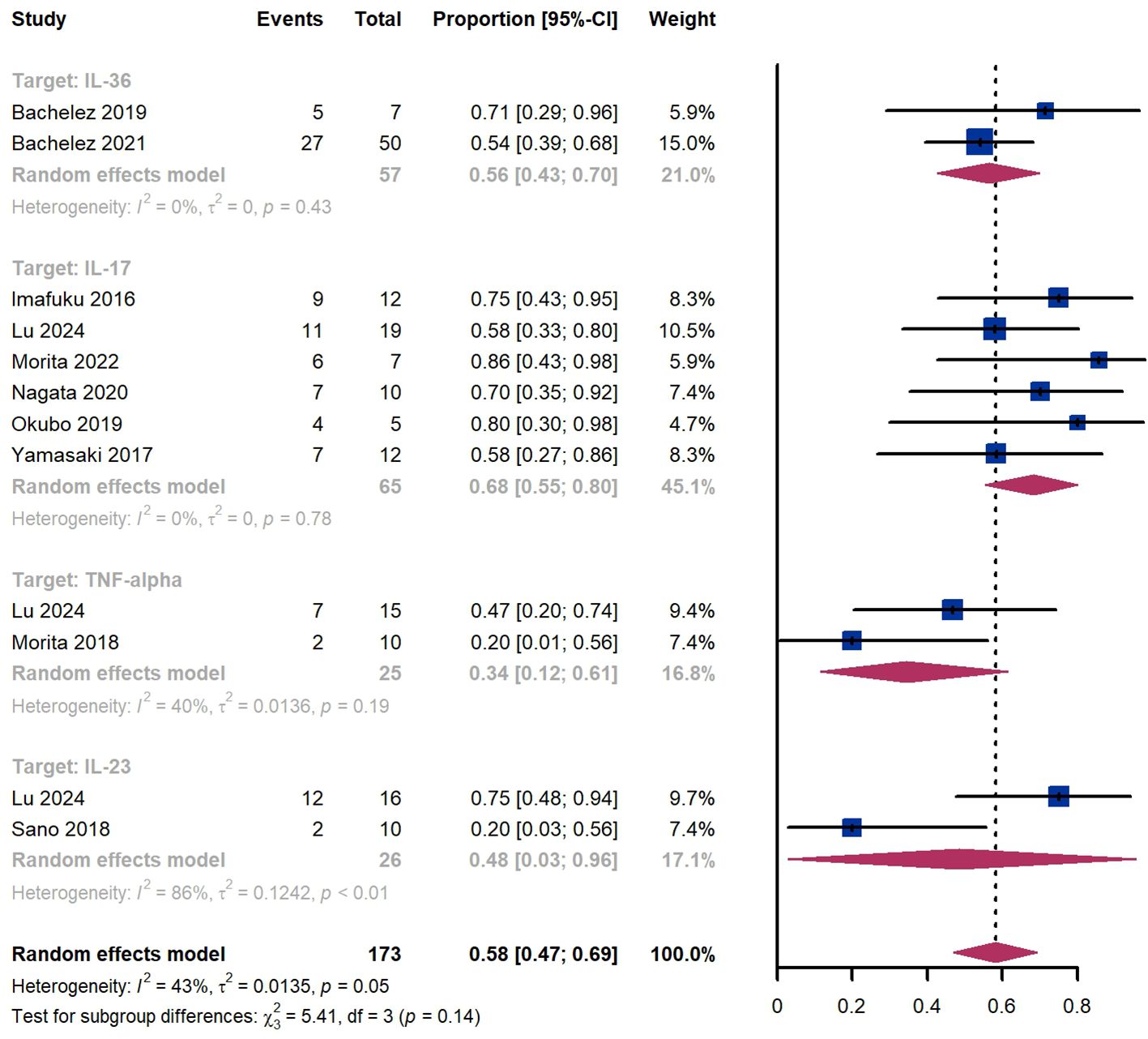
Within 8 weeks, we observed a GPPASI 75 responder proportion of 58% (95% CI 47%-69%) among 173 patients, including 56% (95% CI 43%-70%) for patients treated by IL-36 targeted biologics, 68% (95% CI 55%-80%) for those treated by IL-17 targeted biologics, 34% (95% CI 12%-61%) for those treated by TNF-α targeted biologics (Figure 4). The Egger test for publication bias indicated evidence of bias (P = 0.61).
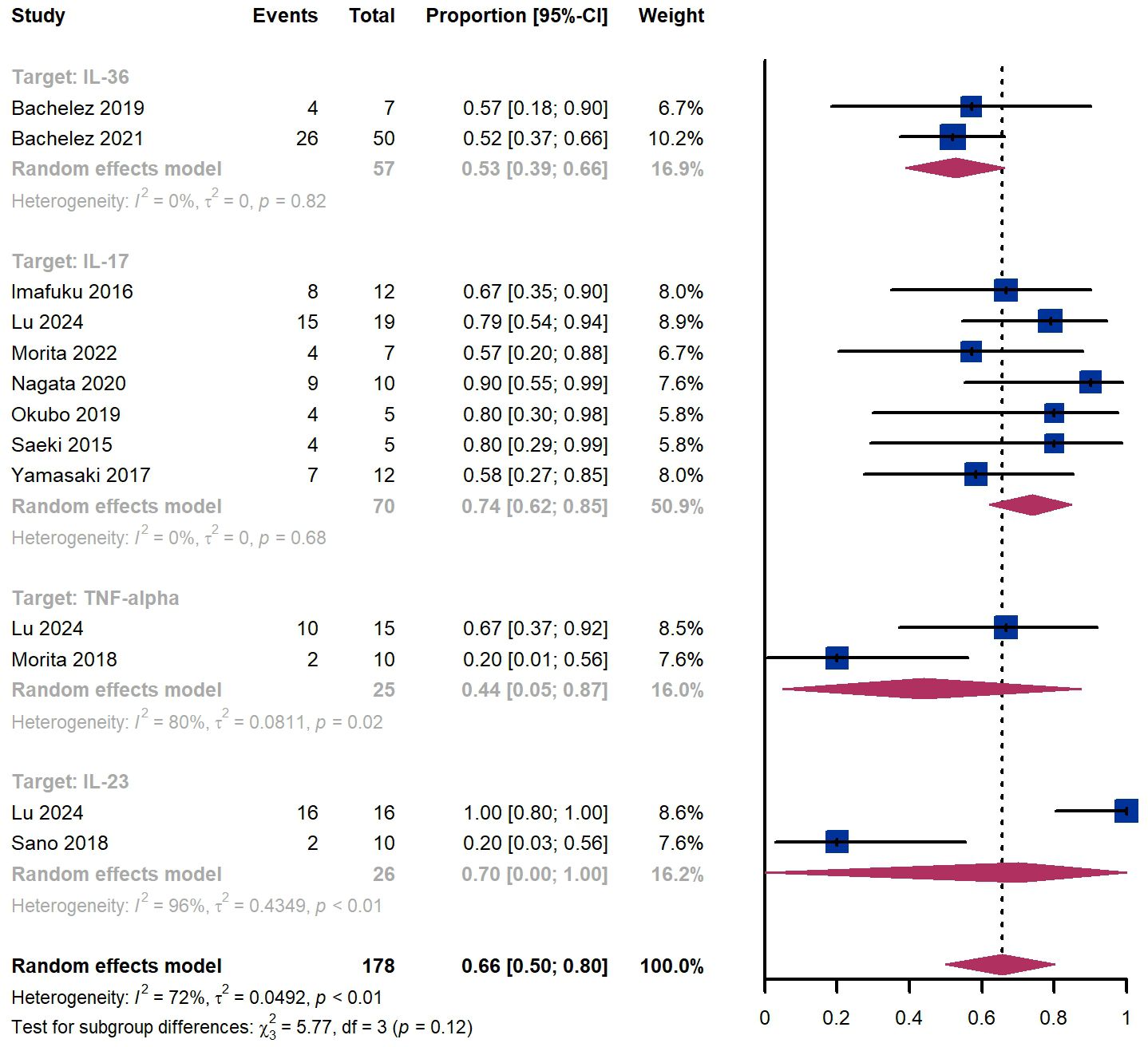
Within 12 weeks, we observed a GPPASI 75 responder proportion of 66% (95% CI 50%-80%) among 178 patients, including 53% (95% CI 39%-66%) for patients treated by IL-36 targeted biologics, 74% (95% CI 62%-85%) for those treated by IL-17 targeted biologics (Figure 5). The Egger test for publication bias indicated no evidence of bias (P = 0.79).
And we observed a GPPASI 90 responder proportion of 1% (95% CI 0%-4%) among 123 patients within 2 weeks, 16% (95% CI 7%-28%) among 123 patients within 4 weeks, 36% (95% CI 23%-50%) among 123 patients within 8 weeks, 50% (95% CI 34%-67%) among 172 patients within 12 weeks. As for GPPASI 100, we observed a responder proportion of 0% (95% CI 0%-2%) among 123 patients within 2 weeks, 1% (95% CI 0%-5%) among 123 patients within 4 weeks, 4% (95% CI 0%-12%) among 123 patients within 8 weeks, 9% (95% CI 1%-20%) among 164 patients within 12 weeks.
3.4 GPPGA (0, 1)
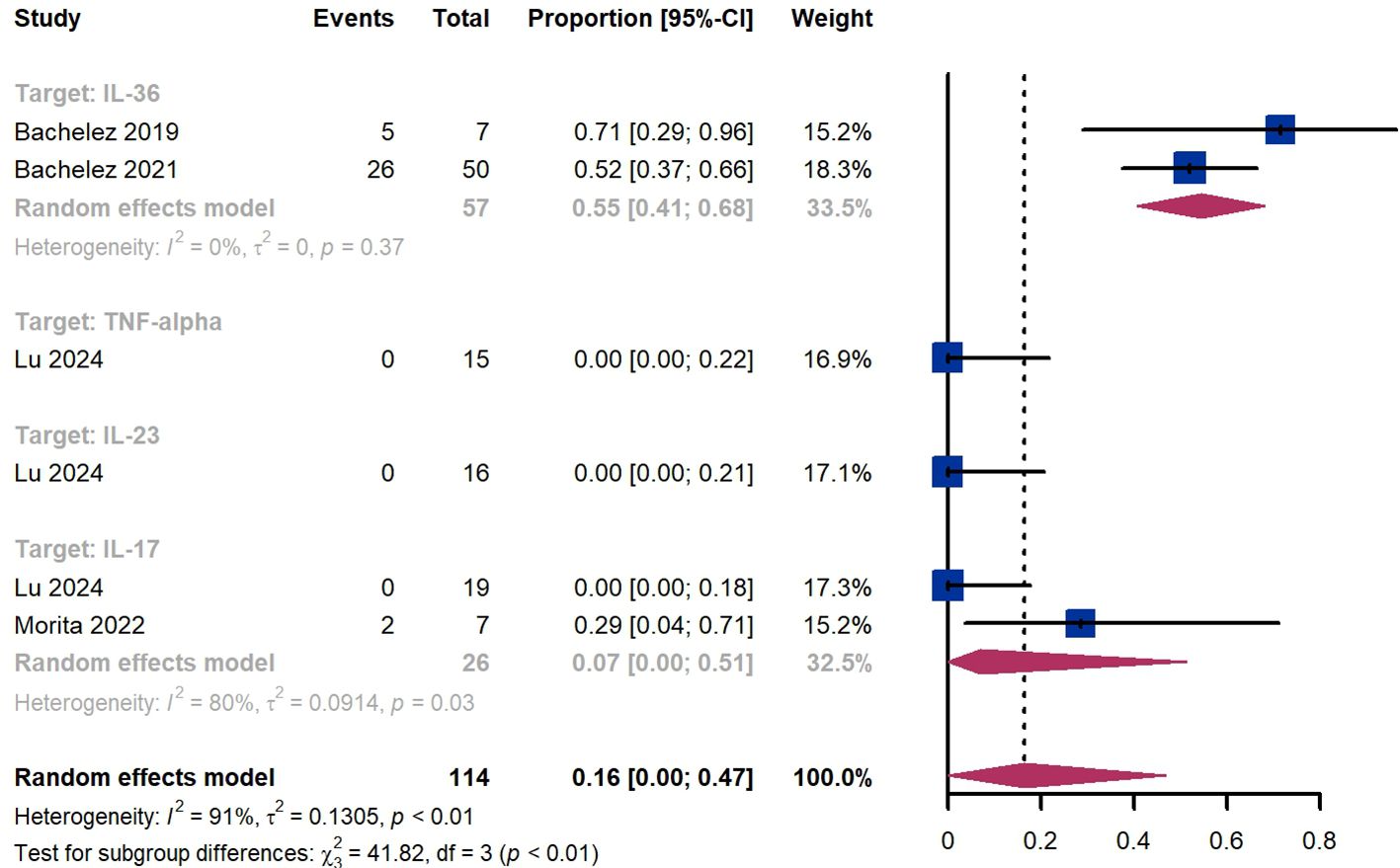
Treatment success was defined as achieving a GPPGA score of 0 or 1. Within 2 weeks, we observed a responder proportion of 16% (95% CI 0%-47%) among 114 patients, including 55% (95% CI 41%-68%) for patients treated by IL-36 targeted biologics, 0% (95% CI 0%-22%) for those treated by TNF-α targeted biologics, 0% (95% CI 0%-21%) for those treated by IL-23 targeted biologics, 7% (95% CI 0-51%) for those treated by IL-17 targeted biologics (Figure 6). The Egger test for publication bias indicated no evidence of bias (P = 0.52).
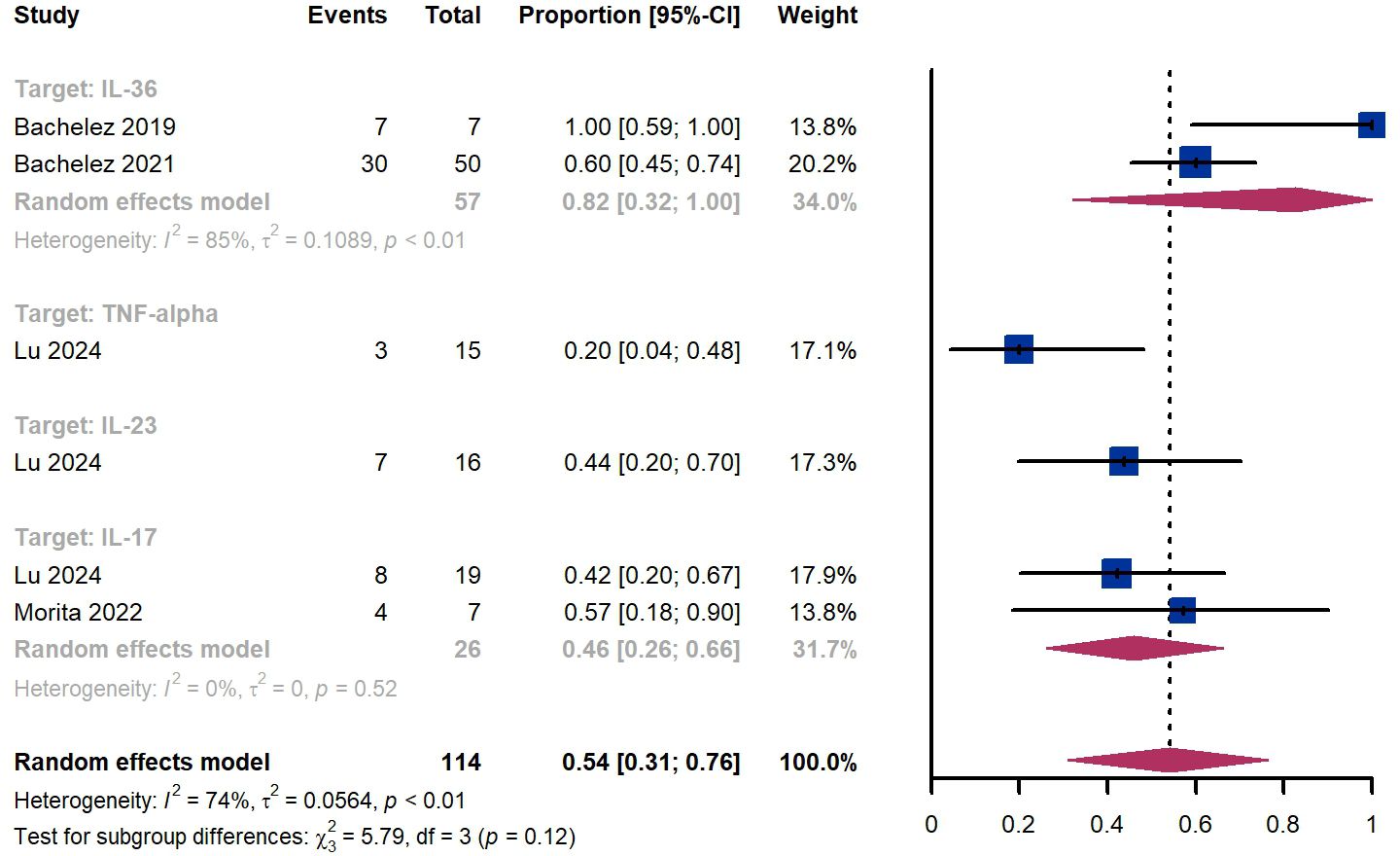
Within 4 weeks, we observed a responder proportion of 54% (95% CI 31%-76%) among 114 patients, including 82% (95% CI 32%-100%) for patients treated by IL-36 targeted biologics, 20% (95% CI 4%-48%) for patients treated by TNF-α targeted biologics, 44% (95% CI 20%-70%) for those treated by IL-23 targeted biologics, 46% (95% CI 26-66%) for those treated by IL-17 targeted biologics (Figure 7). The Egger test for publication bias indicated no evidence of bias (P = 0.87).
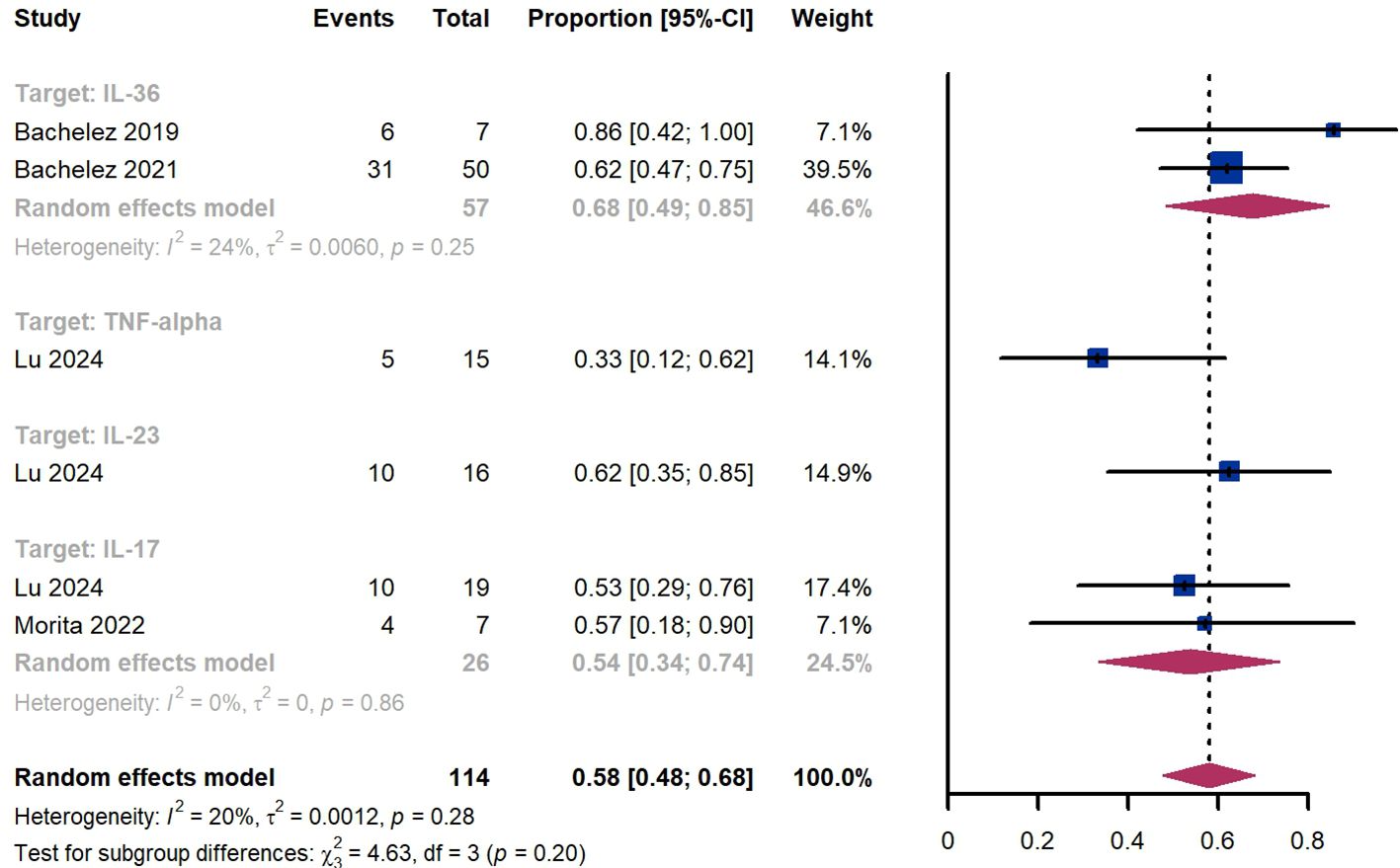
Within 8 weeks, we observed a responder proportion of 58% (95% CI 48%-68%) among 114 patients, including 68% (95% CI 49%-85%) for patients treated by IL-36 targeted biologics, 33% (95% CI 12%-62%) for patients treated by TNF-α targeted biologics, 62% (95% CI 35%-85%) for those treated by IL-23 targeted biologics, 54% (95% CI 34-74%) for those treated by IL-17 targeted biologics (Figure 8). The Egger test for publication bias indicated no evidence of bias (P = 0.99).
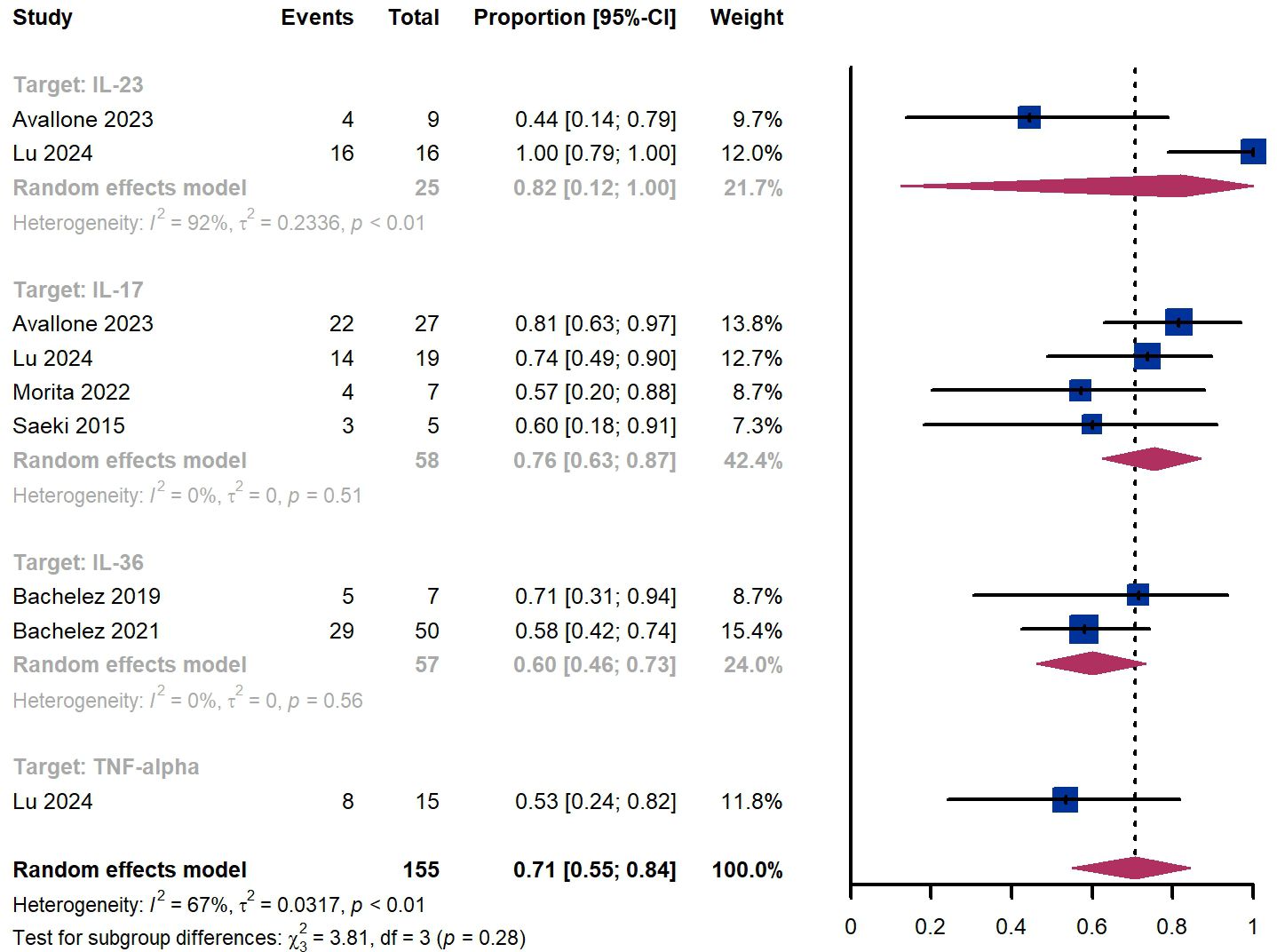
Within 12 weeks, we observed a responder proportion of 71% (95% CI 55%-84%) among 155 patients, including 76% (95% CI 63-87%) for those treated by IL-17 targeted biologics, 60% (95% CI 46%-73%) for patients treated by IL-36 targeted biologics, 53% (95% CI 24%-82%) for those treated by TNF-α targeted biologics, (Figure 9). The Egger test for publication bias indicated no evidence of bias (P = 0.97).
3.5 GPP flare
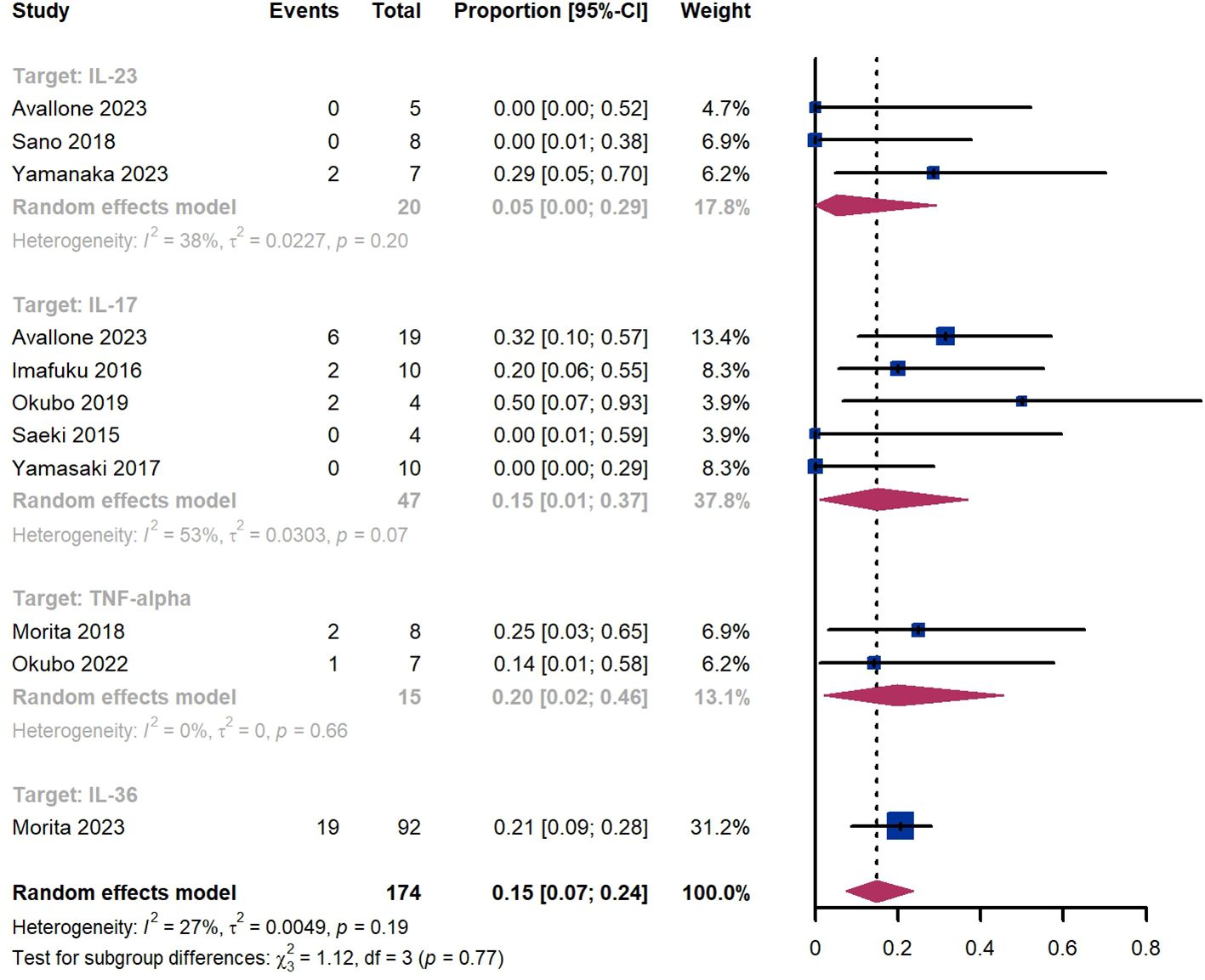
Within 52 weeks, we observed a GPP flare proportion of 15% (95% CI 7%-24%) among 174 patients, including 5% (95% CI 0%-29%) for those treated by IL-23 targeted biologics, 15% (95% CI 1-37%) for those treated by IL-17 targeted biologics, 20% (95% CI 2%-46%) for those treated by TNF-α targeted biologics, 21% (95% CI 9%-28%) for patients treated by IL-36 targeted biologics (Figure 10). The Egger test for publication bias indicated no evidence of bias (P = 0.52).
Within 52 weeks, we observed a GPP flare proportion of 15% (95% CI 7%-24%) among 174 patients, including 5% (95% CI 0%-29%) for those treated by IL-23 targeted biologics, 15% (95% CI 1-37%) for those treated by IL-17 targeted biologics, 20% (95% CI 2%-46%) for those treated by TNF-α targeted biologics, 21% (95% CI 9%-28%) for patients treated by IL-36 targeted biologics (Figure 10). The Egger test for publication bias indicated no evidence of bias (P = 0.52).
3.6 Adverse events
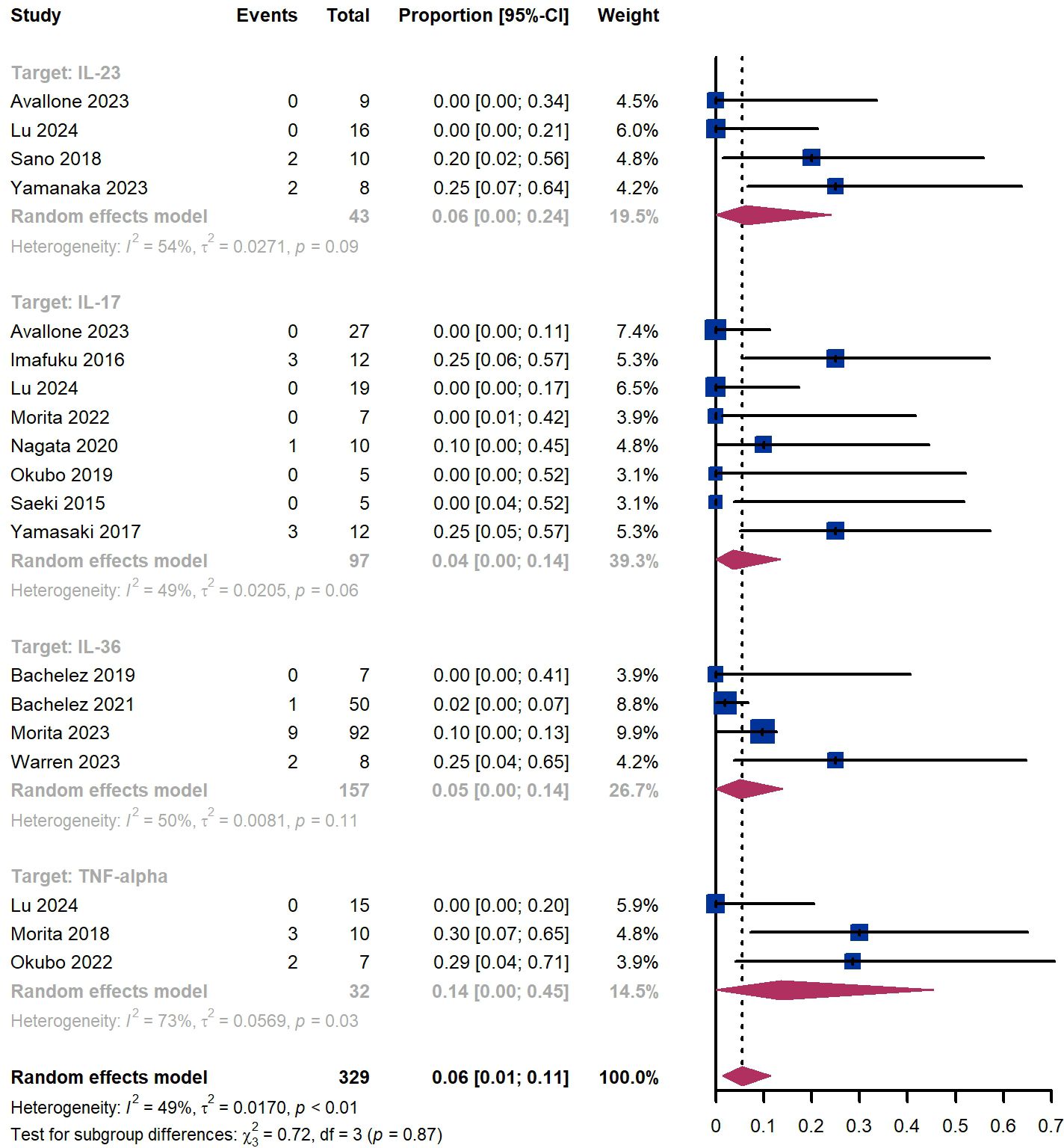
Out of 329 patients, 249 experienced adverse events, resulting in an incidence rate of 75.7%. The most common side effects included infection (20.4%), skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders (16.1%), injection site reaction (12.5%), and dry mucosa (12.2%) (Supplementary Table S4). Additionally, we observed that 6% (95% CI 1%-11%) of patients experienced severe adverse events, including 6% (95% CI 0%-24%) for those treated by IL-23 targeted biologics, 4% (95% CI 0-14%) for those treated by IL-17 targeted biologics, 5% (95% CI 0-14%) for patients treated by IL-36 targeted biologics, 14% (95% CI 0%-45%) for those treated by TNF-α targeted biologics (Figure 11). The Egger test for publication bias indicated no evidence of bias (P = 0.29). A funnel plot is provided in Supplementary Figure S1.
3.7 Sensitivity analysis
We evaluated the impact of each study on the pooled results for the proportion of all outcomes to demonstrate stability and sensitivity (Supplementary Figures S2). With the exception of minor adjustments in CIs, the overall incidences obtained through the combined analysis remained consistent across all included studies. This suggests that our estimated proportion of responders is relatively robust and conservative.
4 Discussion
This systematic review examines the effectiveness and safety of biologics in treating GPP. Dysregulation of the IL-36 inflammatory pathway appears to be the main driver of GPP pathogenesis (34). IL-23 regulates the synthesis of IL-17, which in turn stimulates the production of pro-inflammatory IL-36R agonists, further over-activating the IL-36 pathway (35). TNF-α is associated with increased production of IL-36R agonists, which stimulate the IL-36 pathway and induce more TNF-α production in a continuous inflammatory loop. TNF-α inhibitors indirectly suppress the expression of IL-36γ, thereby reducing activation of the pro-inflammatory IL-36 pathway (36, 37).
This study indicates that the proportion of responders achieving GPPASI 75 and GPPGA (0, 1) tends to increase over the course of 12 weeks. Subgroup analysis by targets shows that responders treated with IL-36 and IL-17 inhibitors have higher rates than those treated with TNF-α and IL-23 inhibitors. IL-36 inhibitors demonstrates better efficacy than IL-17 inhibitors at 2 and 4 weeks, whereas IL-17 inhibitors surpass the efficacy of IL-36 inhibitors at 8 and 12 weeks. IL-36 inhibitors seem to reach the highest response rates between 4 and 8 weeks, while IL-17, TNF-alpha, and IL-23 inhibitors show a gradual increase in response rates up to 12 weeks.
GPP is characterized by recurrent, sudden flares of widespread painful erythema covered with sterile pustules, which may coalesce into lakes of pus (1–3). Studies suggest that GPP flares can be potentially life-threatening due to complications such as sepsis and multisystem organ failure (5, 38, 39). The higher mortality rates associated with GPP compared to other forms of psoriasis underscore the urgent need for treatments that can rapidly control the disease. This study demonstrates that IL-36 inhibitors can achieve a 40% (95% CI 27%-54%) GPPASI75 response rate and a 55% (95% CI 41%-68%) GPPGA (0,1) response rate within 2 weeks, significantly outperforming other biologics.
Additionally, this study reveals that the recurrence rates of GPP within 52 weeks, from highest to lowest, are: IL-36 inhibitors (21% [95% CI 9%-28%]), TNF-alpha inhibitors (20% [95% CI 2%-46%]), IL-17 inhibitors (15% [95% CI 1%-37%]), and IL-23 inhibitors (5% [95% CI 0%-29%]). This suggests that IL-17 inhibitors may offer better long-term flare prevention than IL-36 inhibitors. However, analysis of the long-term preventive effects of IL-36 inhibitors should be interpreted with caution due to the small sample sizes.
In summary, these data demonstrate the significant effectiveness of IL-36 inhibitors in treating GPP, providing rapid control and improvement. Further research is needed to explore the long-term effects on flare prevention.
Furthermore, we observed that 6% (95% CI 1%-11%) of patients experienced severe adverse events, with rates varying among biologics: IL-17 inhibitors (4% [95% CI 0%-14%]), IL-36 inhibitors (5% [95% CI 0%-14%]), IL-23 inhibitors (6% [95% CI 0%-24%]), and TNF-α inhibitors (14% [95% CI 0%-45%]). This suggests that biologics generally have a strong safety profile for the treatment of GPP. IL-36 inhibitors and IL-17 inhibitors demonstrate higher efficacy and better safety profiles compared to IL-23 inhibitors and TNF-α inhibitors in GPP.
This study should be interpreted with several limitations. Moderate heterogeneity and publication bias in the included studies may affect the reliability of the results. The rarity of GPP and the lack of large-scale clinical trials present challenges for deriving evidence-based therapeutic options. Most clinical trials originate from Japan, possibly due to the variation in prevalence across ethnicities, being more common in Asian populations and less so in Caucasian populations (1, 6). Additionally, while GPP primarily affects adults, with a median diagnosis age around 50, it can also occur in children (40). GPP is linked to IL36RN gene mutations (1), which are more frequent in children/adolescents (93.8%) compared to adults (27.5%) (41). Limited data on efficacy and safety in children reduces generalizability to younger populations. Some subgroups include very few studies, decreasing the power of our analysis and the ability to detect effects of certain biologics and long-term flare prevention. These limitations highlight the need for future studies to better address these issues.
Conclusion
This meta-analysis highlights the efficacy and safety of biologics in patients with GPP, offering evidence for their future clinical application. IL-36 inhibitors deliver a faster and more substantial clinical response compared to other biologics. Further research is needed to assess their role in specific subpopulations and to evaluate their potential in the long-term prevention of flares.
Author contributions
BC: Writing – original draft, Visualization, Software, Methodology, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization. QL: Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization. XD: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Conceptualization. YB: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 82074445).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Y-PB, for her generous support during the preparation of this manuscript. The authors thank the reviewers for helpful comments on the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1462158/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Gooderham MJ, Van Voorhees AS, Lebwohl MG. An update on generalized pustular psoriasis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. (2019) 15:907–19. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2019.1648209
2. Choon SE, Lai NM, Mohammad NA, Nanu NM, Tey KE, Chew SF. Clinical profile, morbidity, and outcome of adult-onset generalized pustular psoriasis: analysis of 102 cases seen in a tertiary hospital in Johor, Malaysia. Int J Dermatol. (2014) 53:676–84. doi: 10.1111/ijd.2014.53.issue-6
3. Choon SE, Navarini AA, Pinter A. Clinical course and characteristics of generalized pustular psoriasis. Am J Clin Dermatol. (2022) 23:21–9. doi: 10.1007/s40257-021-00654-z
4. Kharawala S, Golembesky AK, Bohn RL, Esser D. The clinical, humanistic, and economic burden of generalized pustular psoriasis: a structured review. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. (2020) 16:239–52. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2019.1708193
5. Miyachi H, Konishi T, Kumazawa R, Matsui H, Shimizu S, Fushimi K, et al. Treatments and outcomes of generalized pustular psoriasis: A cohort of 1516 patients in a nationwide inpatient database in Japan. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2022) 86:1266–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2021.06.008
6. Boehner A, Navarini AA, Eyerich K. Generalized pustular psoriasis - a model disease for specific targeted immunotherapy, systematic review. Exp Dermatol. (2018) 27:1067–77. doi: 10.1111/exd.2018.27.issue-10
7. Hoegler KM, John AM, Handler MZ, Schwartz RA. Generalized pustular psoriasis: a review and update on treatment. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2018) 32:1645–51. doi: 10.1111/jdv.2018.32.issue-10
8. Menter A, Strober BE, Kaplan DH, Kivelevitch D, Prater EF, Stoff B, et al. Joint AAD-NPF guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2019) 80:1029–72. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.057
9. Wang WM, Jin HZ. Biologics in the treatment of pustular psoriasis. Expert Opin Drug Saf. (2020) 19:969–80. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2020.1785427
10. Bachelez H, Choon SE, Marrakchi S, Burden AD, Tsai TF, Morita A, et al. Inhibition of the interleukin-36 pathway for the treatment of generalized pustular psoriasis. N Engl J Med. (2019) 380:981–3. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1811317
11. Bachelez H, Choon SE, Marrakchi S, Burden AD, Tsai TF, Morita A, et al. Trial of spesolimab for generalized pustular psoriasis. N Engl J Med. (2021) 385:2431–40. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2111563
12. Morita A, Strober B, Burden AD, Choon SE, Anadkat MJ, Marrakchi S, et al. Efficacy and safety of subcutaneous spesolimab for the prevention of generalised pustular psoriasis flares (Effisayil 2): an international, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet (london england). (2023) 402:1541–51. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01378-8
13. Gwillim EC, Nichols AJ. Spesolimab for generalized pustular psoriasis: a review of two key clinical trials supporting initial US regulatory approval. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1359481. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1359481
14. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Bmj. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
15. Association JD. Japanese dermatological guidelines for general pustular psoriasis. (2015). Available at: https://www.dermatol.or.jp/uploads/uploads/files/guideline/1372913421_3.pdf.
16. Terui T, Akiyama M, Ikeda S. Practice guidelines 2014 for generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP). Jpn J Dermatol. (2015) 125:2211–57. Available at: https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1370579811649399680.
17. Iwatsuki K. Practice guidelines 2010 for generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP): treatment guidelines incorporating TNF-α inhibitor. Jpn J Dermatol. (2010) 120:815. Available from URL: https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1370579811649399680.
18. Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC, Savović J, Berkman ND, Viswanathan M, et al. ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. Bmj. (2016) 355:i4919. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i4919
19. Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Bmj. (2011) 343:d5928. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d5928
20. Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Chandler J, Welch VA, Higgins JP, et al. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2019) 10:Ed000142. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000142
21. Avallone G, Maronese CA, Murgia G, Carrera CG, Mastorino L, Roccuzzo G, et al. Interleukin-17 vs. Interleukin-23 inhibitors in pustular and erythrodermic psoriasis: A retrospective, multicentre cohort study. J Clin Med. (2023) 12:1662. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041662
22. Imafuku S, Honma M, Okubo Y, Komine M, Ohtsuki M, Morita A, et al. Efficacy and safety of secukinumab in patients with generalized pustular psoriasis: a 52-week analysis from phase III open-label multicenter Japanese study. J Dermatol. (2016) 43:1011–7. doi: 10.1111/jde.2016.43.issue-9
23. Lu J, Huang D, Yang N, Qin H, Yu Y, Zhong X, et al. Better efficacy, lower recurrence rate and decreased CD8(+)T(RM) with guselkumab treatment for generalized pustular psoriasis: A prospective cohort study from China. Clin Immunol. (2024) 259:109899. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2024.109899
24. Morita A, Yamazaki F, Matsuyama T, Takahashi K, Arai S, Asahina A, et al. Adalimumab treatment in Japanese patients with generalized pustular psoriasis: Results of an open-label phase 3 study. J Dermatol. (2018) 45:1371–80. doi: 10.1111/jde.2018.45.issue-12
25. Morita A, Okubo Y, Morisaki Y, Torisu-Itakura H, Umezawa Y. Ixekizumab 80 mg every 2 weeks treatment beyond week 12 for Japanese patients with generalized pustular psoriasis and erythrodermic psoriasis. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). (2022) 12:481–94. doi: 10.1007/s13555-021-00666-x
26. Nagata M, Kamata M, Fukaya S, Hayashi K, Fukuyasu A, Tanaka T, et al. Real-world single-center experience with 10 cases of generalized pustular psoriasis successfully treated with ixekizumab. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2020) 82:758–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2019.09.040
27. Okubo Y, Mabuchi T, Iwatsuki K, Elmaraghy H, Torisu-Itakura H, Morisaki Y, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of ixekizumab in Japanese patients with erythrodermic or generalized pustular psoriasis: subgroup analyses of an open-label, phase 3 study (UNCOVER-J). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2019) 33:325–32. doi: 10.1111/jdv.2019.33.issue-2
28. Okubo Y, Umezawa Y, Sakurai S, Hoshii N, Nakagawa H. Efficacy and safety of certolizumab pegol in Japanese patients with generalized pustular psoriasis and erythrodermic psoriasis: 52-week results. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). (2022) 12:1397–415. doi: 10.1007/s13555-022-00741-x
29. Saeki H, Nakagawa H, Ishii T, Morisaki Y, Aoki T, Berclaz PY, et al. Efficacy and safety of open-label ixekizumab treatment in Japanese patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis, erythrodermic psoriasis and generalized pustular psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2015) 29:1148–55. doi: 10.1111/jdv.2015.29.issue-6
30. Sano S, Kubo H, Morishima H, Goto R, Zheng R, Nakagawa H. Guselkumab, a human interleukin-23 monoclonal antibody in Japanese patients with generalized pustular psoriasis and erythrodermic psoriasis: Efficacy and safety analyses of a 52-week, phase 3, multicenter, open-label study. J Dermatol. (2018) 45:529–39. doi: 10.1111/jde.2018.45.issue-5
31. Warren RB, Reich A, Kaszuba A, Placek W, Griffiths CEM, Zhou J, et al. Imsidolimab, an anti-interleukin-36 receptor monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of generalized pustular psoriasis: results from the phase II GALLOP trial. Br J Dermatol. (2023) 189:161–9. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljad083
32. Yamasaki K, Nakagawa H, Kubo Y, Ootaki K. Efficacy and safety of brodalumab in patients with generalized pustular psoriasis and psoriatic erythroderma: results from a 52-week, open-label study. Br J Dermatol. (2017) 176:741–51. doi: 10.1111/bjd.14702
33. Yamanaka K, Okubo Y, Yasuda I, Saito N, Messina I, Morita A. Efficacy and safety of risankizumab in Japanese patients with generalized pustular psoriasis or erythrodermic psoriasis: Primary analysis and 180-week follow-up results from the phase 3, multicenter IMMspire study. J Dermatol. (2023) 50:195–202. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.16667
34. Marrakchi S, Puig L. Pathophysiology of generalized pustular psoriasis. Am J Clin Dermatol. (2022) 23:13–9. doi: 10.1007/s40257-021-00655-y
35. Zhou J, Luo Q, Cheng Y, Wen X, Liu J. An update on genetic basis of generalized pustular psoriasis (Review). Int J Mol Med. (2021) 47:118. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.4951
36. Mercurio L, Failla CM, Capriotti L, Scarponi C, Facchiano F, Morelli M, et al. Interleukin (IL)-17/IL-36 axis participates to the crosstalk between endothelial cells and keratinocytes during inflammatory skin responses. PloS One. (2020) 15:e0222969. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222969
37. Chen WJ, Yu X, Yuan XR, Chen BJ, Cai N, Zeng S, et al. The role of IL-36 in the pathophysiological processes of autoimmune diseases. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:727956. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.727956
38. Hanna ML, Singer D, Bender SD, Valdecantos WC, Wu JJ. Characteristics of hospitalizations and emergency department visits due to generalized pustular psoriasis in the United States. Curr Med Res Opin. (2021) 37:1697–703. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2021.1951192
39. Viguier M, Allez M, Zagdanski AM, Bertheau P, de Kerviler E, Rybojad M, et al. High frequency of cholestasis in generalized pustular psoriasis: Evidence for neutrophilic involvement of the biliary tract. Hepatology. (2004) 40:452–8. doi: 10.1002/hep.20305
40. Rivera-Díaz R, Daudén E, Carrascosa JM, Cueva P, Puig L. Generalized pustular psoriasis: A review on clinical characteristics, diagnosis, and treatment. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). (2023) 13:673–88. doi: 10.1007/s13555-022-00881-0
Keywords: generalized pustular psoriasis, biologics, systematic review, meta-analysis, single-arm
Citation: Chen B-l, Liu Q-w, Dong X-w and Bai Y-p (2024) Biologics for generalized pustular psoriasis: a systematic review and single-arm meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 15:1462158. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1462158
Received: 09 July 2024; Accepted: 27 September 2024;
Published: 14 October 2024.
Edited by:
Michael A. Firer, Ariel University, IsraelReviewed by:
Marc Henri De Longueville, UCB Pharma, BelgiumManuelle Viguier, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Reims, France
Copyright © 2024 Chen, Liu, Dong and Bai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yan-ping Bai, emhpQHRzaW5naHVhLmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors share first authorship
 Bai-lin Chen
Bai-lin Chen Qian-wei Liu
Qian-wei Liu Xiao-wan Dong1,2
Xiao-wan Dong1,2