- 1Department of Respiratory Diseases, The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou, Henan, China
- 2The First Clinical Medical College of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Henan, China
- 3Collaborative Innovation Center for Chinese Medicine and Respiratory Diseases Co-constructed by Henan Province & Education Ministry of P.R, Zhengzhou, Henan, China
Background: Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) represents the most common extra-articular manifestation of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) and is a major cause of mortality. This study aims to identify and evaluate biomarkers associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (RA-ILD).
Methods: We searched PubMed, Cochrane Library, EMBASE, and Web of Science databases for studies related to biomarkers of RA-ILD up until October 7, 2023. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) and standards recommended by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) were used for quality assessment, and meta-analysis was conducted using Stata18.0 software.
Results: A total of 98 articles were assessed for quality, 48 of which were included in the meta-analysis. 83 studies were of high quality, and 15 were of moderate quality. The meta-analysis showed significant differences in biomarkers such as C-Reactive Protein (CRP), Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR), Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide (anti-CCP) antibody, Rheumatoid Factor (RF), Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6), Surfactant Protein D (SP-D), Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA), Carbohydrate Antigen 19-9 (CA19-9), Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7), C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 10 (CXCL-10), and Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) between RA-ILD patients and RA patients. However, Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio [Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR)], Cancer Antigen 125 [Cancer Antigen 125 (CA-125)], and Cancer Antigen 153 [Cancer Antigen 153 (CA-153)] did not show significant differences between the two groups. KL-6, MMP-7, and Human Epididymis Protein 4 (HE4) are negatively correlated with lung function, and KL-6 is associated with the prognosis of RA-ILD.
Conclusions: Biomarkers hold promising clinical value for prediction, diagnosis, severity assessment, and prognosis evaluation in RA-ILD. However, these findings need to be validated through multicenter, large-sample, prospective cohort studies.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier CRD42023448372.
1 Introduction
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by progressive joint destruction, with a prevalence rate of approximately 0.5% to 1.0% in developed countries (1). Pulmonary involvement is the most common extra-articular manifestation of RA and the leading cause of death among RA patients (2, 3). Currently, the diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (RA-ILD) requires assessment in collaboration with radiology, pathology, rheumatology, and pulmonology experts (4). However, there is a lack of tools for early diagnosis and effective prediction of disease progression. Biomarkers have promising applications in RA-ILD, offering important information about disease activity, progression, and response to treatment. They hold potential value for the management of RA-ILD, yet the diagnostic utility of almost all reported biomarkers, as well as their predictive efficacy for severity and prognosis, has not been well validated (5). No study has comprehensively summarized these biomarkers and quantitatively assessed their relationship with RA-ILD. Therefore, this study aims to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis to screen for biomarkers related to RA-ILD.
2 Manuscript formatting
2.1 Methods
This study was registered on PROSPERO (https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, CRD42023448372) and conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (6).
2.1.1 Search strategy
We searched PubMed, the Cochrane Library, EMBASE, and Web of Science databases for relevant literature published up to October 7, 2023, using the terms “Rheumatoid Arthritis,” “Interstitial Lung Disease,” and “Biomarkers.” We also manually searched the reference lists of eligible studies and related review articles to identify additional reports. The detailed search strategy is provided in Supplementary Data Sheet 1.
2.1.2 Study selection
Two researchers (Guo/Yao) independently screened the titles and abstracts of all retrieved articles to select studies that matched our criteria. Disagreements were resolved through discussion or by a third reviewer (Zhao). Inclusion criteria were: (1) Cohort studies, case-control studies, cross-sectional studies; (2) Patients diagnosed with RA-ILD; (3) Studies reporting on biomarkers for the prediction, diagnosis, severity assessment, and prognosis evaluation of RA-ILD. Exclusion criteria included: (1) for duplicate publications, only the study with the most comprehensive data was selected; (2) incomplete data or missing target indicators; (3) review articles, letters, conference records, editorials, and case reports.
2.1.3 Data extraction and quality assessment
Two researchers (Guo/Yao) independently extracted data from the included studies. Extracted data included the general study characteristics (first author’s name, publication year, study location, study design), information about the studied population (sample size, number of men and women, mean age, diagnostic criteria), and information on the outcomes in the study (biomarker types, measurement methods, etc). If detailed information was not available, we contacted the authors via email to obtain data.Study quality was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for cohort and case-control studies. A score of 0-3 was considered low quality, 4-6 medium quality, and 7-9 high quality. For cross-sectional studies, quality was evaluated according to standards recommended by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), with scores of 0-3 indicating low quality, 4-7 medium quality, and 8-11 high quality. Both researchers collaborated to assess study quality and reached a consensus through discussion.
2.1.4 Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using STATA 18.0 software. When a specific biomarker is represented by more than two independent studies, we conduct a meta-analysis. For the Pearson correlation coefficient, the inverse variance method was used to calculate the pooled correlation coefficients between the biomarkers and RA-ILD, along with their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI). To obtain variance-stabilized correlation coefficients, Pearson’s correlation coefficients were transformed into Fisher’s Z-scores before pooling the estimates (7). For continuous variables, the overall effect size was calculated using mean difference (MD) and CI. Median and interquartile ranges (IQRs) were converted to estimated means and standard deviations (8–10). The adjusted hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were used to assess the prognosis of RA-ILD. Heterogeneity among studies was assessed using the Q test, and the inconsistency index (I2) was expressed as a percentage. A P-value ≤ 0.05 was considered statistically significant (11). A fixed-effect model was generally used to analyze trials with strong homogeneity (I2 ≤ 50%, P > 0.1). In cases of statistical heterogeneity (I2 > 50%, P < 0.1), a random-effects model was applied, followed by sensitivity. Subgroup analysis was conducted based on region and age (according to World Health Organization (WHO) standards, age ≥60 years was classified as elderly, and age <60 years was classified as non-elderly). Meta-regression analysis was also conducted to assess the impact of other potential confounding factors. Publication bias was evaluated using Egger’s test when five or more studies were available for meta-analysis. If publication bias was detected, the trim-and-fill method was used to assess funnel plot asymmetry (12).
2.2 Results
2.2.1 Study selection
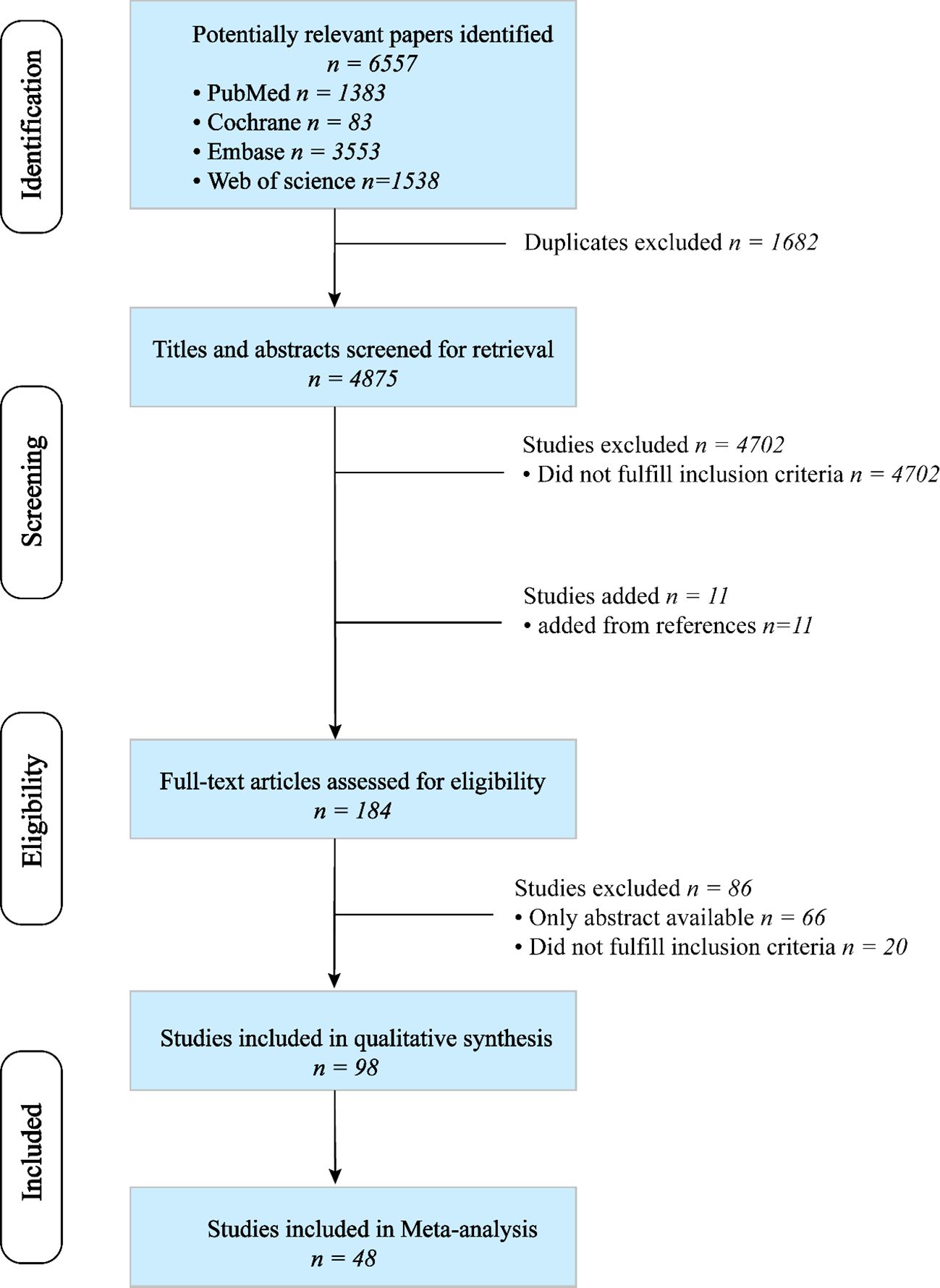
A total of 6,557 articles were retrieved through a search of four databases. After removing duplicates, 4,875 articles were identified. The titles and abstracts were screened, and the reference lists of relevant review articles were reviewed to identify potentially suitable articles. Among 184 articles reviewed, 86 were considered ineligible. Finally, 98 publications met the inclusion criteria (13–110), of which 48 were included in the meta-analysis (13–60). The detailed process of study selection is illustrated in Figure 1.
2.2.2 Study characteristics
The analysis included studies from 13 different countries, primarily employing a case-control study design. The majority of the studies were conducted in China (n=30), followed by Japan (n=18), the United States (n=17), Spain (n=6), South Korea (n=5), Egypt (n=5), Italy (n=4), the United Kingdom (n=2), Turkey (n=2), France (n=2), Mexico (n=2), Sweden (n=1), Germany (n=1), and Saudi Arabia (n=1) with two studies spanning multiple countries. The diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) generally adhered to the 1987 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria or the 2010 ACR/European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) criteria. Most studies assessing Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) utilized High-Resolution Computed Tomography (HRCT), with a few also conducting surgical lung biopsies. The methodological quality of the included studies was evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) or the standards set by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). Among them, 83 studies were of high quality, and 15 were of medium quality. More details on the characteristics of the study subjects can be found in Supplementary Data Sheet 1.
2.2.3 Biomarkers of RA-ILD
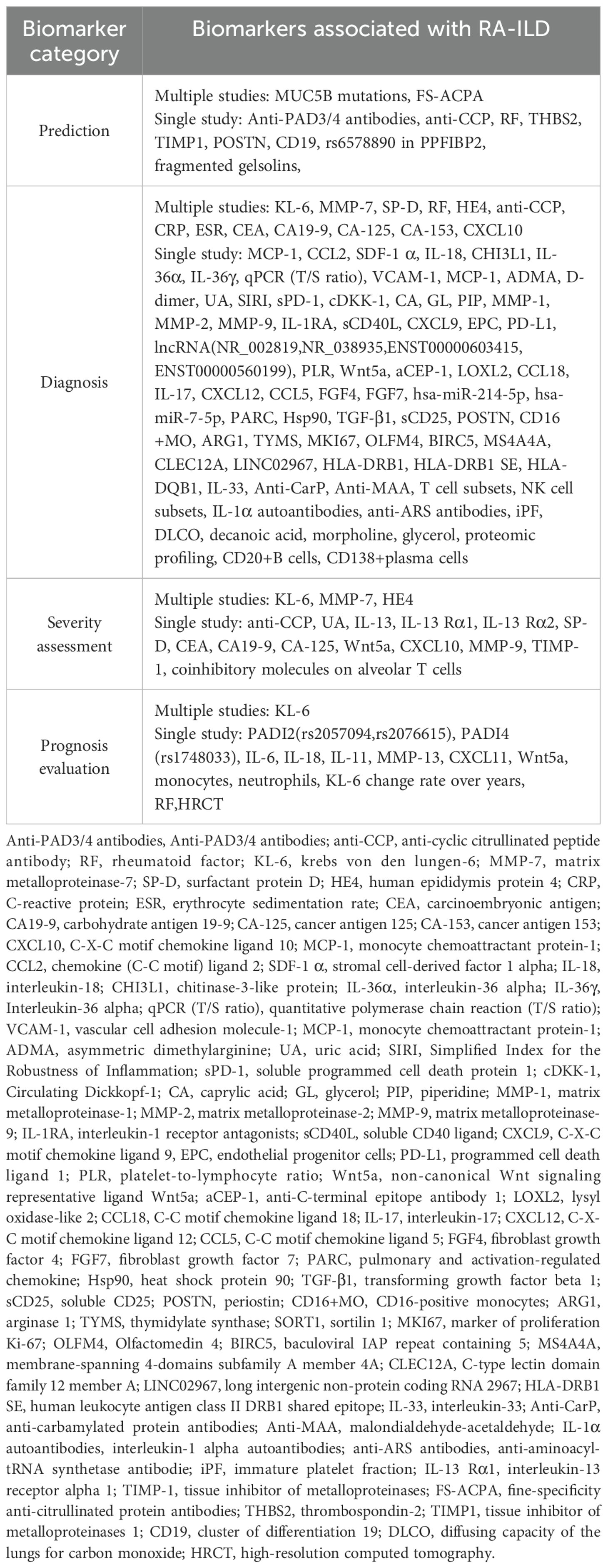
Identified biomarkers were classified into four types: prediction, diagnosis, severity assessment, and prognosis evaluation. There were 11 biomarkers for predicting the occurrence of RA-ILD, 85 for differentiating RA from RA-ILD, 17 for assessing the severity of RA-ILD, and 14 for evaluating prognosis. The specifics are provided in Table 1.
2.2.4 Meta-analysis
2.2.4.1 Biomarkers for the diagnosis of RA-ILD
Biomarkers identified in two or more eligible studies were included in the meta-analysis, including C-Reactive Protein (CRP), Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR), Rheumatoid Factor (RF), Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide (Anti-CCP) antibody, Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6), Surfactant Protein D (SP-D), Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA), Carbohydrate Antigen 19-9 (CA19-9), Cancer Antigen 125 (CA-125), Cancer Antigen 153 (CA-153), Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7), C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 10 (CXCL-10), Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR), and Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR).
2.2.4.1.1 CRP
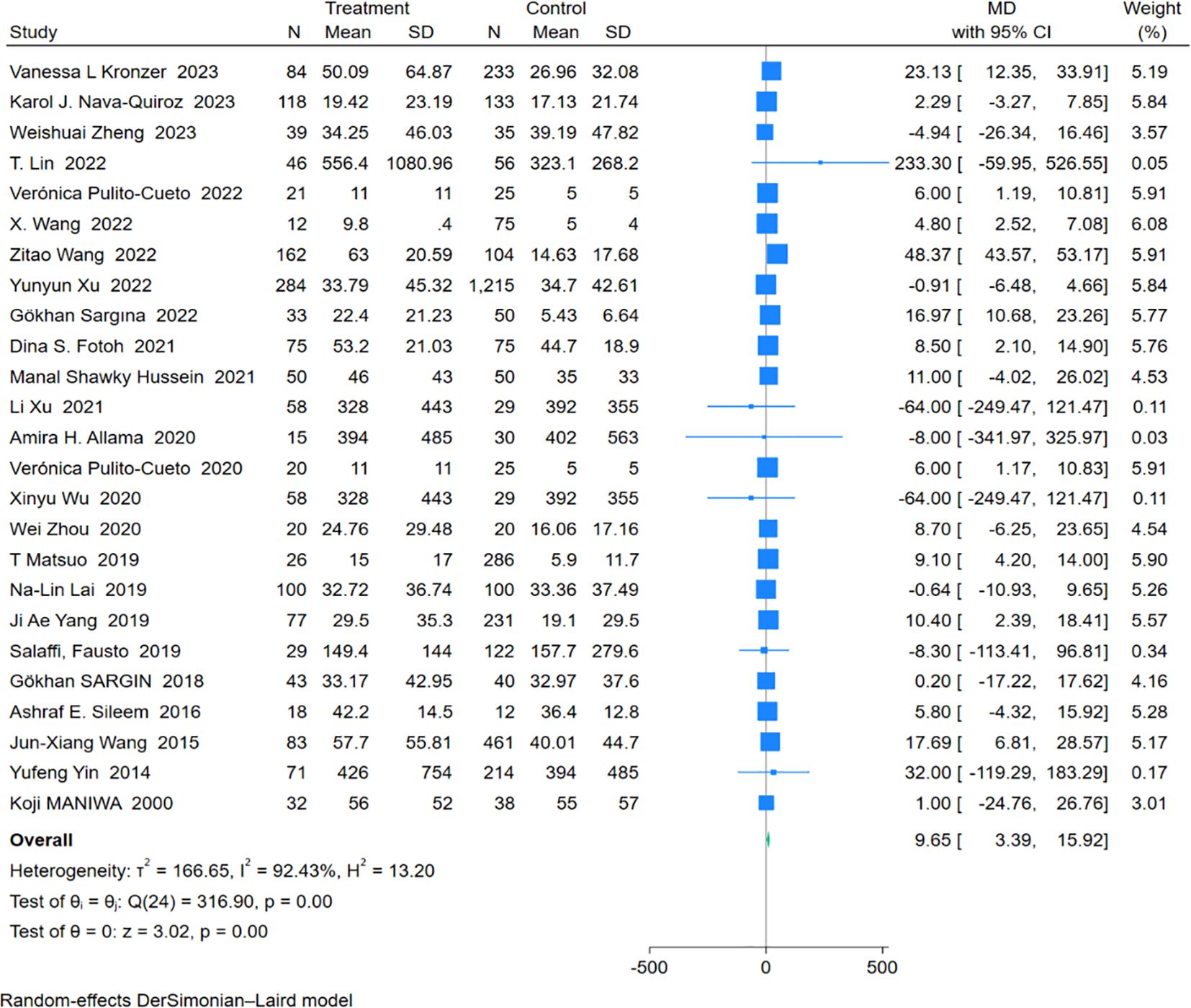
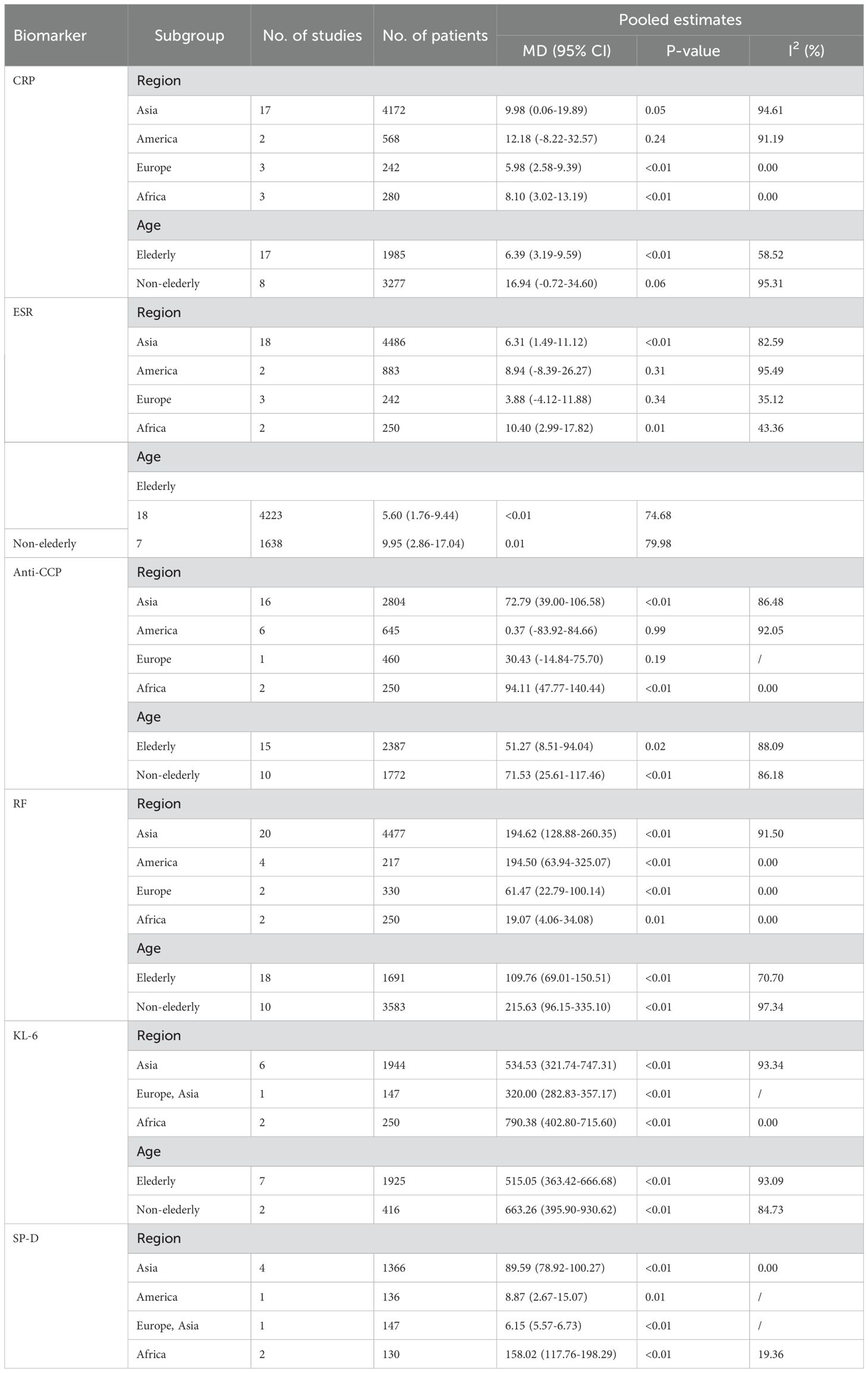
An analysis of 25 studies including 1,574 RA-ILD patients and 3,688 RA patients was conducted to compare CRP levels. The pooled effect size showed significantly higher CRP concentrations in the RA-ILD group compared to the RA group (MD = 9.65; 95% CI: 3.39-15.92; P < 0.001). There was high heterogeneity among the studies (I2 = 92.43%, P < 0.001). The forest plot of the pooled analysis is shown in Figure 2. Subgroup analysis by region showed significant differences in CRP concentrations between RA-ILD and RA groups in Asia (MD = 9.98; 95% CI: 0.06-19.89; P = 0.05), Europe (MD = 5.98; 95% CI: 2.58-9.39; P < 0.001), and Africa (MD = 8.10; 95% CI: 3.02-13.19; P < 0.001), but not in the Americas (MD = 12.18; 95% CI: -8.22-32.57; P = 0.24). Subgroup analysis by age showed significant differences in CRP concentrations between RA-ILD and RA groups among older adults (aged ≥60 years) (MD = 6.39; 95% CI: 3.19-9.59; P < 0.001), but not among younger individuals (aged <60 years) (MD = 16.94; 95% CI: -0.72-34.60; P = 0.06) (Table 2). Meta-regression analysis was conducted to identify sources of heterogeneity, revealing that total sample size (P=0.865) and gender ratio (P=0.192) were not sources of heterogeneity. Specific charts are available in Supplementary Data Sheet 1.
2.2.4.1.2 ESR
Twenty-five studies involving 1,646 patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (RA-ILD) and 4,215 patients with RA were analyzed. The pooled effect size indicated that ESR levels were significantly higher in the RA-ILD group compared to the RA group (Mean Difference (MD) = 6.77; 95% Confidence Interval (CI): 3.02-10.53; P < 0.001). There was substantial heterogeneity among the studies (I2 = 81.75%, P<0.001). The forest plot of the pooled analysis is shown in Figure 3. Subgroup analysis by region revealed that ESR levels were significantly higher in RA-ILD groups in Asia (MD = 6.31; 95% CI: 1.49-11.12; P = 0.01) and Africa (MD = 10.40; 95% CI: 2.99-17.82; P = 0.01), with no significant difference in the Americas (MD = 8.94; 95% CI: -8.39-26.27; P = 0.31) and Europe (MD = 3.88; 95% CI: -4.12-11.88; P = 0.34). Age-based subgroup analysis showed that both older (MD = 5.60; 95% CI: 1.76-9.44; P < 0.001) and younger individuals (MD = 9.95; 95% CI: 2.86-17.04; P < 0.001) in the RA-ILD group had significantly higher ESR levels compared to the RA group. (Table 2) Meta-regression analysis indicated that neither total sample size (P=0.996) nor gender ratio (P=0.538) were sources of heterogeneity. Specific charts are available in Supplementary Data Sheet 1.
2.2.4.1.3 Anti-CCP antibody
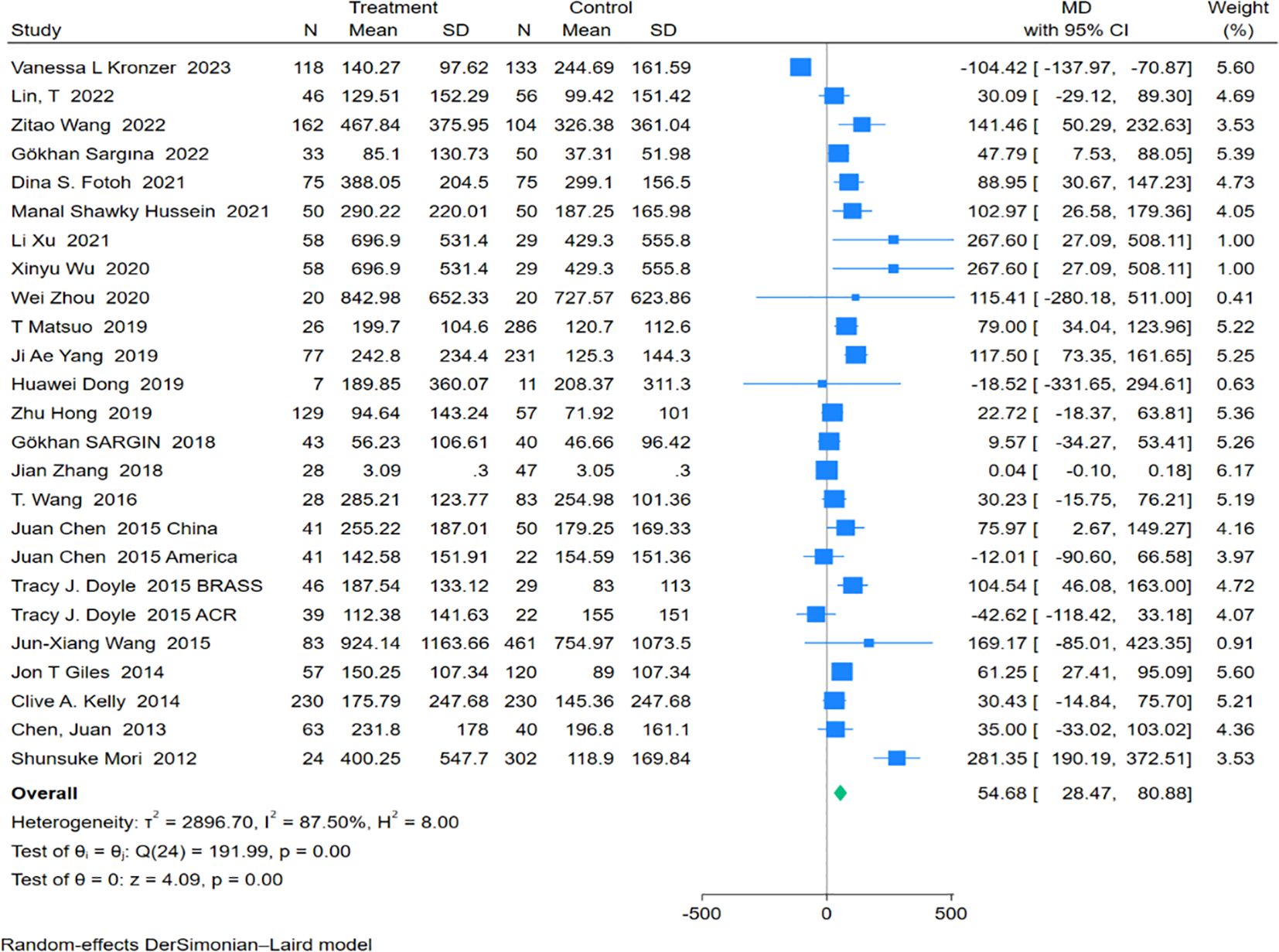
Twenty-five studies encompassing 1,582 RA-ILD patients and 2,577 RA patients were analyzed for anti-CCP antibody levels. The pooled effect size showed significantly higher levels of anti-CCP antibodies in the RA-ILD group compared to the RA group (MD = 54.68; 95% CI: 28.47-80.88; P < 0.001), with substantial heterogeneity observed (I2 = 87.50%, P<0.001). The forest plot of the pooled analysis is illustrated in Figure 4. Subgroup analyses by region indicated significant differences in anti-CCP antibody levels between RA-ILD and RA groups in Asia (MD = 72.79; 95% CI: 39.00-106.58; P < 0.001) and Africa (MD = 94.11; 95% CI: 47.77-140.44; P < 0.001), with no significant differences observed in the Americas (MD = 0.37; 95% CI: -83.92-84.66; P = 0.99) and Europe (MD = 30.43; 95% CI: -14.84-75.70; P = 0.19). Age-based subgroup analysis demonstrated significant differences in both older (MD = 51.27; 95% CI: 8.51-94.04; P =0.02) and younger participants (MD = 71.53; 95% CI: 25.61-117.46; P <0.001) in the RA-ILD group compared to the RA group. (Table 2) Meta-regression analysis showed that neither total sample size (P=0.296) nor gender ratio (P=0.722) were sources of heterogeneity. Detailed charts are included in the Supplementary Data Sheet 1.
2.2.4.1.4 RF
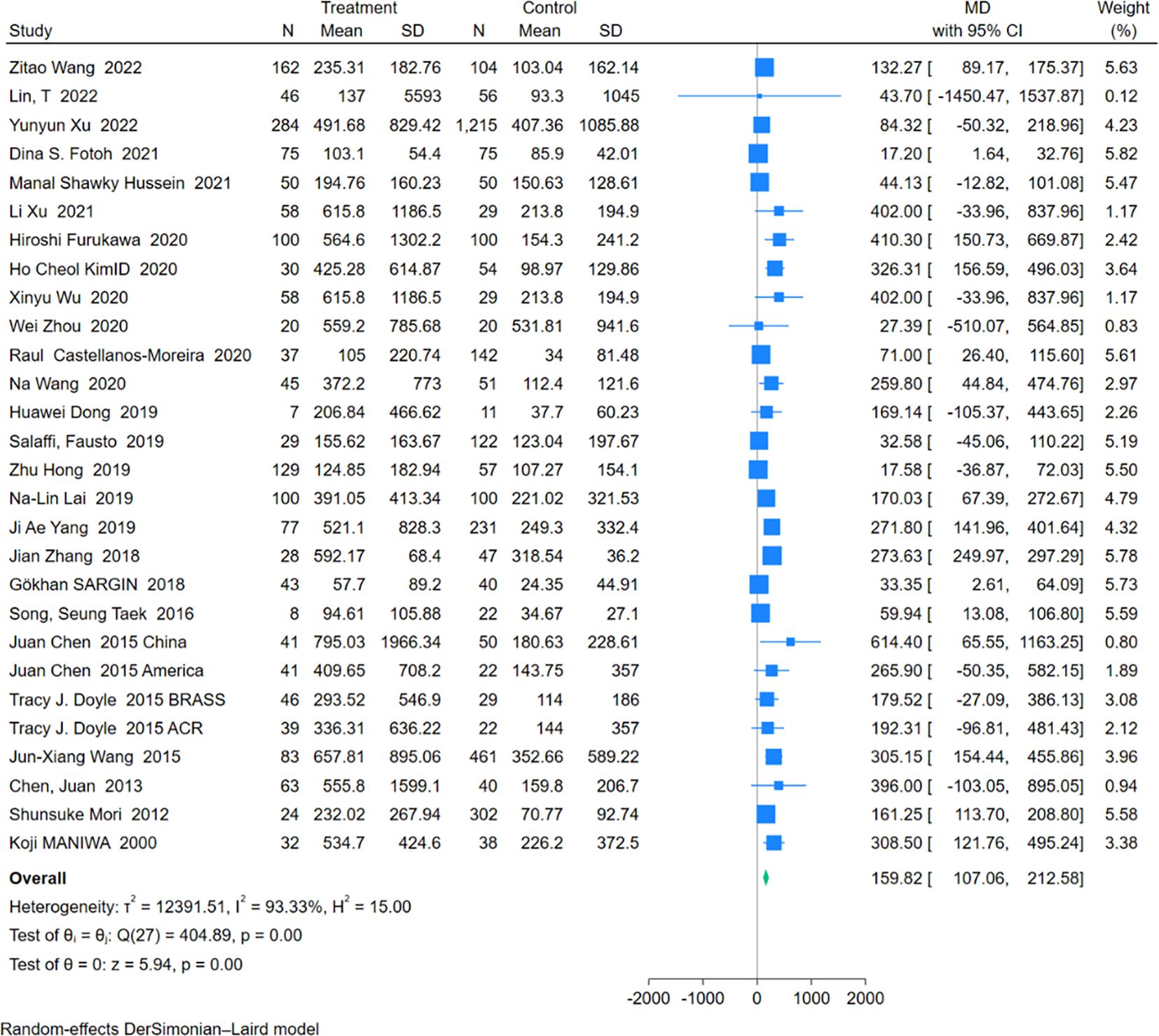
An analysis of 28 studies including 1,755 RA-ILD patients and 3,519 RA patients was conducted to compare RF levels. The pooled effect size indicated significantly higher RF levels in the RA-ILD group compared to the RA group (MD = 159.82; 95% CI: 107.06-212.58; P < 0.001), with high heterogeneity (I2 = 93.33%, P<0.001). The forest plot of the pooled analysis is shown in Figure 5. Subgroup analysis by region showed significant differences in RF levels in Asia (MD = 194.62; 95% CI: 128.88-260.35; P < 0.001), the Americas (MD = 194.50; 95% CI: 63.94-325.07; P < 0.001), Europe (MD = 61.47; 95% CI: 22.79-100.14; P < 0.001), and Africa (MD = 19.07; 95% CI: 4.06-34.08; P =0.01) for the RA-ILD group compared to the RA group. Age-based subgroup analysis demonstrated significant differences in both older (MD = 109.76; 95% CI: 69.01-150.51; P < 0.001) and younger participants (MD = 215.63; 95% CI: 96.15-335.10; P < 0.001) in the RA-ILD group compared to the RA group. (Table 2) Meta-regression analysis showed that neither total sample size (P=0.296) nor gender ratio (P=0.722) were sources of heterogeneity. Detailed charts are included in the Supplementary Data Sheet 1.
2.2.4.1.5 KL-6
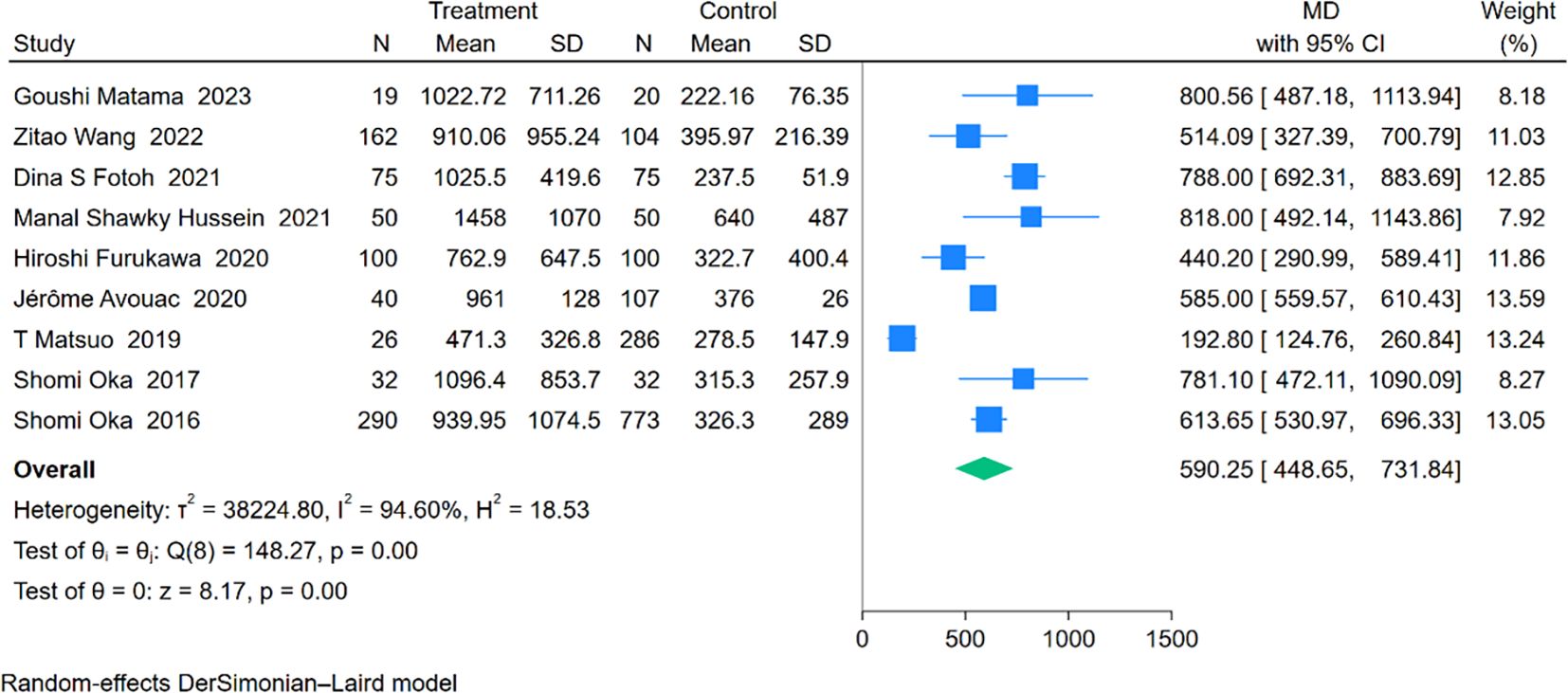
An analysis involving 9 studies compared KL-6 levels between 794 patients with RA-ILD and 1,547 patients with RA. The pooled effect size demonstrated significantly higher KL-6 concentrations in the RA-ILD group compared to the RA group (MD = 590.25; 95% CI: 448.65-731.84; P < 0.001), with substantial heterogeneity observed (I2 = 94.60%, P < 0.001). The forest plot of the pooled analysis is shown in Figure 6. Subgroup analyses by region showed significant differences, with reports from Africa (MD = 790.38; CI: 698.57-882.19; P < 0.001) and Asia (MD = 534.53; CI: 321.74-747.31; P < 0.001), including a study covering both Europe and Asia reporting an MD of 585.00 (CI: 559.57-610.43; P < 0.001). All regions reported significantly higher KL-6 levels in RA-ILD patients compared to RA patients. Age-based subgroup analysis revealed significant differences for both older (MD = 570.00; 95% CI: 401.96-738.03; P < 0.001) and younger individuals (MD = 663.26; 95% CI: 395.90-930.62; P < 0.001). (Table 2) Meta-regression indicates that the proportion of males is the source of heterogeneity(P=0.002). Detailed charts are available in the Supplementary Data Sheet 1.
2.2.4.1.6 SP-D
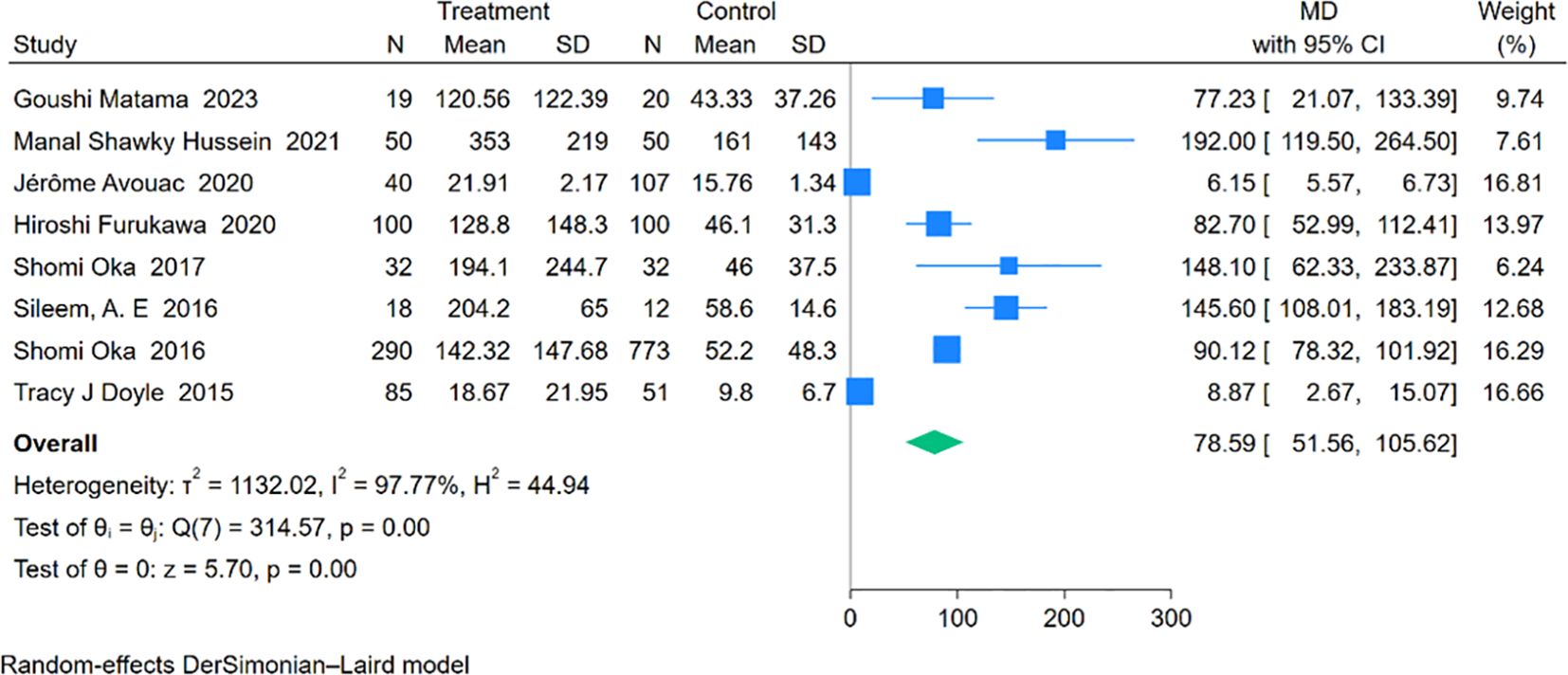
Eight studies involving 634 RA-ILD patients and 1,145 RA patients were analyzed for SP-D concentrations. The pooled effect size indicated significantly higher SP-D levels in the RA-ILD group compared to the RA group (MD = 78.59; 95% CI: 51.56-105.62; P < 0.001), with notable heterogeneity (I2 = 97.77%, P < 0.001). The forest plot of the pooled analysis is shown in Figure 7. Subgroup analysis by region revealed significant differences in SP-D levels in Asia (MD = 89.59; 95% CI: 78.92-100.27; P < 0.001), the Americas (MD = 8.87; 95% CI: 2.67-15.07; P = 0.01), and Africa (MD = 158.02; 95% CI: 117.76-198.29; P < 0.001), with a study covering both Asia and Europe reporting an MD of 6.15 (CI: 5.57-6.73; P < 0.001). (Table 2) Detailed charts are available in the Supplementary Data Sheet 1.
2.2.4.1.7 MMP-7
Three cohort comprising 167 RA-ILD patients and 123 RA patients reported plasma levels of MMP-7. The pooled effect size showed significantly higher MMP-7 concentrations in the RA-ILD group compared to the RA group (MD = 1.00; 95% CI: 0.74-1.25; P < 0.001), with low heterogeneity (I2 = 33.82%, P = 0.22). The forest plot of the pooled analysis is included in the Supplementary Material.
2.2.4.1.8 Tumor markers
Four studies involving 383 patients with RA-ILD and 1,385 patients with RA were analyzed for CEA and CA19-9 concentrations. The pooled effect size demonstrated that CEA (MD = 1.66; 95% CI: 0.28-3.03; P = 0.02) and CA19-9 (MD = 21.92; 95% CI: 10.60-33.24; P < 0.001) levels were significantly higher in the RA-ILD group compared to the RA group, with high heterogeneity observed (CEA: I2 = 94.22%, P < 0.001; CA19-9: I2 = 94.74%, P < 0.001). The forest plot of the pooled analysis is included in the Supplementary Material. Three studies reported serum levels of CA-125 involving 355 RA-ILD patients and 1,338 RA patients. Compared to RA patients, there was no significant difference in CA-125 levels among RA-ILD patients (MD = 15.83; 95% CI: -7.60-39.26; P = 0.19), with high heterogeneity observed (I2 = 97.21%). Three studies reported serum levels of CA-153 involving 99 RA-ILD patients and 170 RA patients. No significant difference was observed in CA-153 levels between RA-ILD and RA patients (MD = 25.83; 95% CI: -4.45-56.11; P = 0.09), with high heterogeneity (I2 = 98.58%). Detailed charts are available in the Supplementary Data Sheet 1.
2.2.4.1.9 Other biomarkers (CXCL-10, PLR, NLR)
Three cohort comprising 167 RA-ILD patients and 123 RA patients reported plasma levels of MMP-7. The pooled effect size showed significantly higher MMP-7 concentrations in the RA-ILD group compared to the RA group (MD = 1.00; 95% CI: 0.74-1.25; P < 0.001), with low heterogeneity (I2 = 33.82%, P = 0.22). The forest plot of the pooled analysis is included in the Supplementary Material. Three cohort reported serum levels of CXCL-10, involving 115 RA-ILD patients and 112 RA patients. A significant difference was observed in CXCL-10 levels between RA-ILD and RA patients (MD = 141.09; 95% CI: 81.24-200.94; P < 0.001), with low heterogeneity (I2 = 0.00%, P = 0.58). Two studies involving 387 RA-ILD patients and 1,413 RA patients analyzed the PLR and NLR. The pooled effect showed a significant difference in NLR between RA-ILD and RA patients (MD = 0.23; 95% CI: 0.12-0.35; P < 0.001), but not for PLR (MD = 0.13; 95% CI: -0.42-0.68; P = 0.64). NLR showed low heterogeneity (I2 = 61.16%, P = 0.11), while PLR showed high heterogeneity (I2 = 93.77%, P < 0.001). The forest plot of the pooled analysis is included in the Supplementary Data Sheet 1.
2.2.4.2 Sensitivity analysis and publication bias
A sensitivity analysis, using a one-study-removed approach, indicated stability in the results for CRP, ESR, anti-CCP antibody, RF, KL-6, SP-D, CA-19-9, MMP-7, CXCL-10, but instability for CEA, CA-125, CA-153. Publication bias assessed using Egger’s test for biomarkers included in five or more studies showed no significant bias for CRP (P=0.71) and ESR (P=0.36); however, potential bias was suggested for anti-CCP antibody (P=0.0116), RF (P=0.0063), KL-6 (P=0.0402), and SP-D (P < 0.001), but trim-and-fill analyses indicated that the adjusted effect sizes remained consistent with the original findings. Detailed charts are available in the Supplementary Data Sheet 1.
2.2.5 Biomarkers for the severity assessment of RA-ILD
Three biomarkers were involved in assessing the severity of RA-ILD, including KL-6, MMP-7, and HE4. Two studies involving a total of 237 RA-ILD patients analyzed the correlation of KL-6 with FVC and DLCO. The pooled effect showed a negative correlation between KL-6 and both FVC and DLCO (FVC: summary r = -0.26, 95% CI = -0.38 – -0.15, P < 0.001; DLCO: summary r = -0.33, 95% CI = -0.43 – -0.21, P < 0.001), with heterogeneity observed for FVC: I2 = 0.00%, P = 0.46, and DLCO: I2 = 76.40%, P = 0.04. Three studies involving a total of 243 RA-ILD patients analyzed the correlation between MMP-7 and DLCO. The pooled effect showed a negative correlation between MMP-7 and DLCO (summary r = -0.40, 95% CI = -0.49 – -0.28, P < 0.001), with low heterogeneity among studies (I2 = 0.00%, P = 0.72). Two studies involving a total of 94 RA-ILD patients analyzed the correlation between HE4 and FVC%. The pooled effect showed a negative correlation between HE4 and FVC% (summary r = -0.26, 95% CI = -0.44 – -0.06, P = 0.001), with low heterogeneity among studies (I2 = 0.00%, P = 0.42). Detailed charts are available in the Supplementary Data Sheet 1.
2.2.6 Biomarkers for the prognostic assessment of RA-ILD
Two studies involving a total of 146 RA-ILD patients were analyzed for the prognosis of KL-6 in RA-ILD. The pooled effect size showed a correlation between KL-6 concentration and the prognosis of RA-ILD (HR = 3.01; 95% CI: 1.57-5.76; P < 0.001), with low heterogeneity among studies (I2 = 0.00%, P=0.98). Detailed charts are available in the Supplementary Data Sheet 1.
2.3 Discussion
This study systematically reviewed potential biomarkers in RA-ILD patients, categorizing them into four types: prediction, diagnosis, severity assessment, and prognosis evaluation. Quantitative research results were then meta-analyzed to explore the relationship between potential biomarkers and RA-ILD.
We have reviewed biomarkers that can be used to predict the occurrence of RA-ILD. However, due to limited relevant studies, we did not conduct a meta-analysis. Among them, mutations in the MUC5B gene have shown promising prospects for predicting the occurrence of RA-ILD. A study by P. A. Juge (45) found that MUC5B promoter variants are strong risk factors for the development of RA-ILD, especially in patients with radiological evidence of UIP pattern. However, the generalizability of these research findings awaits further exploration due to regional and ethnic limitations. Identifying biomarkers that can early detect the occurrence of ILD in RA patients is of great significance for early intervention and improving treatment efficacy in RA-ILD. Therefore, further research on biomarkers predicting the occurrence of RA-ILD is needed.
Our study found that several biomarkers, such as CHI3L1, IL-18, IL-36α, VCAM-1, MCP-1, CCL18, and PLR, showed promising potential in distinguishing RA from RA-ILD. However, due to the limited number of relevant studies, we did not conduct a meta-analysis. The study by Rui Yu et al. (64) demonstrated that serum CHI3L1 levels were elevated in RA-ILD patients, suggesting its potential as a non-invasive biomarker for RA-ILD detection. Interestingly, CHI3L1 also showed promise in differentiating RA-ILD from IPF. In both IPF and RA-ILD patients, MMP-7 and ACPA levels were significantly higher compared to RA patients, and serum CHI3L1 levels could differentiate IPF from RA-ILD (245.8 ± 180.2 ng/mL vs. 116.0 ± 58.3 ng/mL, p<0.001) and predict survival, offering potential value in identifying highly specific biomarkers. Similarly, the study by Verónica Pulito-Cueto et al. (22) found that serum VCAM-1, MCP-1, and ADMA levels were elevated in RA-ILD patients compared to those with RA and IPF, suggesting these biomarkers as useful tools for identifying ILD in RA patients and differentiating RA-ILD from IPF, aiding in the early diagnosis of RA-ILD. Although research on such biomarkers is still limited, they have shown significant value in distinguishing RA from RA-ILD and even RA-ILD from IPF. Their high specificity offers a valuable reference for future large-scale, multicenter clinical studies.
Our meta-analysis results show that in RA-ILD patients, CRP, ESR, anti-CCP antibodies, RF, KL-6, SP-D, CEA, CA19-9, MMP-7, CXCL-10, and NLR are all significantly higher than in RA patients, which indicates promising prospects for distinguishing between RA and RA-ILD patients. However, PLR, CA-125, and CA-153 did not show significant differences in pooled effect sizes between RA-ILD patients and RA patients, indicating the need for further research to explore their relationship with RA-ILD patients.
Previous findings (111, 112) have associated CRP, ESR, anti-CCP antibodies, and RF with RA-ILD. We included more studies and participants, and the pooled results were consistent with previous studies, making the results more reliable. However, our subgroup analysis indicates that biomarker levels vary by region and age among RA-ILD patients. Significant differences in ESR and anti-CCP antibody concentrations were observed between RA-ILD and RA patients in Asia and Africa but not in the Americas and Europe. CRP levels were significantly higher in RA-ILD patients in Asia, Europe, and Africa, but not in the Americas. RF concentrations were significantly higher in RA-ILD patients across all regions, suggesting its potential utility. Nevertheless, the subgroup analysis for the Americas and Europe should be considered cautiously due to the limited number of related studies. These biomarkers’ performance may be influenced by factors such as environmental conditions, genetics, ethnicity, lifestyle, and differences in detection methods across regions. In Asian and African populations, certain genetic variations may exist that affect the immune system’s production of anti-CCP antibodies and regulate inflammatory responses. This genetic polymorphism may lead to significant differences in ESR and anti-CCP antibody levels. Environmental factors are also key contributors—air pollution and the high incidence of infectious diseases in certain regions could impact immune function and inflammatory responses, potentially leading to elevated ESR and changes in anti-CCP antibody levels. Therefore, well-designed studies are needed to further verify the differences between RA-ILD and RA patients in various regions. Additionally, CRP levels were notably higher in the elderly RA-ILD patient group (age ≥60) compared to RA patients, a difference not observed in younger groups, possibly due to physiological changes or reduced immunity in older RA-ILD patients. However, since CRP and ESR are acute-phase reactants, their levels may fluctuate significantly throughout the disease course. Therefore, caution should be exercised when using them as biomarkers for RA-ILD. It is essential to consider the patient’s disease status or combine these markers with other indicators to comprehensively assess pulmonary involvement in RA patients.
Biomarkers related to interstitial lung disease encompass various types related to alveolar epithelial cell damage, fibroproliferation, extracellular matrix remodeling, and immune dysfunction (113), such as SP-D (114), KL-6 (115), and MMP-7 (116). Studie (34, 54) have shown that these biomarkers are elevated in RA-ILD. Our meta-analysis found significant differences in KL-6, SP-D, and MMP-7 between RA-ILD and RA patients. However, meta-regression indicates that the proportion of males is the source of heterogeneity for KL-6, suggesting that there may be differences in KL-6 levels between different genders. However, further exploratory research is still needed to verify this.
New biomarkers are gradually being identified. Tumor markers, mainly produced by malignant cells for screening or monitoring cancer progression, have been found elevated in RA-ILD patients (44, 47), independent of actual cancer presence, drawing widespread attention to their potential role in RA-ILD. Our meta-analysis indicates significant differences in CEA and CA19-9 between RA-ILD and RA patients, whereas no significant differences were observed for CA-125 and CA-153. This provides a reference for selecting precise tumor markers to differentiate between RA and RA-ILD. Blood cell-based indices like Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR) have been reported as biomarkers of systemic inflammatory response, playing a significant role in various cancers, autoimmune rheumatic diseases, and cardiovascular diseases (117–119). Some studies have shown that PLR and NLR are significantly elevated in RA-ILD patients (18, 42). Our meta-analysis reveals a significant difference in NLR between RA-ILD and RA patients, but not for PLR. However, due to the limited number of studies included and the instability of results in sensitivity analysis, the pooled effects of tumor markers and NLR/PLR should be interpreted with caution, and more high-quality research is needed for validation.
Our meta-analysis highlights the differences between individual biomarkers in RA-ILD and RA patients, yet no single marker seems sufficient for diagnosing RA-ILD alone. Studies by Jérôme Avouac et al. (34) suggest that combining KL-6 with SP-D could enhance diagnostic capability for RA-ILD, offering a new approach to selecting suitable biomarkers for RA-ILD. We identified 78 potential biomarkers for distinguishing between RA and RA-ILD and selected 11 with significant differences through meta-analysis, laying the foundation for using multiple biomarkers in combination.
IL-13 is also a fibrogenic cytokine, and IL-13Rα1 and IL-13Rα2 are its two receptors. As transmembrane receptors, IL-13Rα1 can combine with IL-4Rα to form a stable complex (120), which activates the JAK/STAT signaling pathway, inducing TGF-β production and ultimately leading to fibrosis. A study by Manal Shawky Hussein et al. (25) demonstrated that serum IL-13 levels, along with IL-13Rα1 and IL-13Rα2, are positively correlated with HRCT scores (P < 0.001), suggesting that these markers may be used to assess the severity of interstitial lung disease in RA patients, showing high clinical value. However, due to the limited number of related studies, we did not conduct a meta-analysis.
The outcomes of our meta-analysis indicate that MMP-7 is moderately correlated with diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide (DLCO), while KL-6 is weakly correlated with forced vital capacity (FVC) and DLCO, and HE4 is weakly correlated with percentage of predicted forced vital capacity (FVC%). This suggests that MMP-7, KL-6, and HE4 can reflect changes in lung function to some extent. For patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), FVC and DLCO are the most sensitive parameters for evaluating clinical course. Additionally, there is a strong correlation between progressively declining FVC and DLCO values and the clinical severity of ILD (121). ILD-induced deterioration in lung function affects prognosis and increases mortality rates. Early detection, timely treatment, and appropriate intervention are crucial for improving clinical symptoms and survival in RA-ILD patients (84), but lung function tests are costly, have poor repeatability, and low compatibility for critically ill patients. Selecting appropriate biomarkers to assess changes in lung function in patients has significant clinical value. However, the number of studies included in this meta-analysis is limited, and further exploratory research is needed to validate the results and select suitable biomarkers to assess the severity of RA-ILD.
A study by Natalia Mena-Vázquez et al. (25) found that during follow-up, 13 out of 35 RA-ILD patients (37.1%) experienced lung disease progression. Cox regression analysis revealed that the only variable associated with RA-ILD progression was IL-18 (pg/mL) (p= 0.227; p = 0.004). IL-18 is a member of the IL-1 cytokine superfamily, primarily produced by macrophages. Animal studies have shown that IL-18 can induce lung inflammation (122); in humans, elevated IL-18 levels have been observed in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (123), ILD-related inflammatory myopathies (124), and RA-ILD (39). Although further research is needed to determine the exact role of this cytokine in RA-ILD, it may be associated with poorer prognosis in RA-ILD patients and provides a potential direction for future studies.
The findings of our meta-analysis indicate that KL-6 can serve as a prognostic predictor for RA-ILD patients. However, due to the limited number of included studies, the results should be interpreted with caution. Compared to interstitial lung disease associated with other connective tissue diseases, RA-ILD patients have a poorer prognosis (125). Prognostic evaluation at the time of diagnosis is clinically significant. However, there are currently few biomarkers available for RA-ILD prognostic assessment, and there is a lack of accurate, convenient, and cost-effective biomarkers. Further exploratory research is needed to identify and validate suitable biomarkers for assessing RA-ILD prognosis.
Our study has limitations. Firstly, some biomarker meta-analyses results exhibited high heterogeneity, and we could not identify sources of heterogeneity using meta-regression or subgroup analysis, possibly due to differences in environment, genetics, ethnicity, lifestyle, and testing methods. Secondly, although we observed differences in biomarker levels between RA-ILD and RA patients, the studies we included were observational studies and cannot determine cause and effect. Additionally, many studies included are retrospective, single-center, and small-scale, and some biomarkers had few studies, potentially affecting the stability of our results. Thus, more large-scale, multicenter, prospective cohort studies are needed to draw definitive conclusions or reinforce the findings of this study.
2.4 Conclusion
This review comprehensively summarizes biomarkers related to disease prediction, diagnosis, severity assessment, and prognosis evaluation in RA-ILD patients. These biomarkers show promising clinical applications and hold significant importance for early diagnosis, improving treatment efficacy, and enhancing the prognosis of RA-ILD patients. However, large-sample, multicenter, prospective cohort studies are still needed to validate these findings.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
LG: Writing – original draft, Software, Methodology, Data curation. JW: Writing – original draft, Supervision, Methodology, Formal analysis. JL: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Methodology, Funding acquisition. JY: Writing – original draft, Validation, Data curation. HZ: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China's Young Scientists Fund (82105048), National Chinese Medicine Inheritance and Innovation Team Project for the Prevention and Treatment of Respiratory Diseases (ZYYCXTD-C-202206), and Henan Province Special Scientific Research Project on Chinese Medicine (2021JDZY029, 2022ZY1040).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1455346/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Smolen JS, Aletaha D, McInnes IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. (2016) 388:2023–38. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30173-8
2. Hyldgaard C, Hilberg O, Pedersen AB, Ulrichsen SP, Løkke A, Bendstrup E, et al. A population-based cohort study of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: comorbidity and mortality. Ann Rheum Dis. (2017) 76:1700–6. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211138
3. Koduri G, Norton S, Young A, Cox N, Davies P, Devlin J, et al. Interstitial lung disease has a poor prognosis in rheumatoid arthritis: results from an inception cohort. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2010) 49:1483–9. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keq035
4. Kadura S, Raghu G. Rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease: manifestations and current concepts in pathogenesis and management. Eur Respir Rev. (2021) 30(160):210011. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0011-2021
5. Furukawa H, Oka S, Higuchi T, Shimada K, Hashimoto A, Matsui T, et al. Biomarkers for interstitial lung disease and acute-onset diffuse interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. (202) 13:1759720x211022506. doi: 10.1177/1759720x211022506
6. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Bmj. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
7. Zhang Y, Lv S, Li C, Xiong Y, Zhou C, Li X, et al. Smartphone use disorder and future time perspective of college students: the mediating role of depression and moderating role of mindfulness. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. (2020) 14:3. doi: 10.1186/s13034-020-0309-9
8. Shi J, Luo D, Weng H, Zeng XT, Lin L, Chu H, et al. Optimally estimating the sample standard deviation from the five-number summary. Res Synth Methods. (2020) 11:641–54. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.1429
9. Luo D, Wan X, Liu J, Tong T. Optimally estimating the sample mean from the sample size, median, mid-range, and/or mid-quartile range. Stat Methods Med Res. (2018) 27:1785–805. doi: 10.1177/0962280216669183
10. Wan X, Wang W, Liu J, Tong T. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2014) 14:135. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-14-135
11. Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Chandler J, Welch VA, Higgins JP, et al. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2019) 10:Ed000142. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000142
12. Duval S, Tweedie R. Trim and fill: A simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics. (2000) 56:455–63. doi: 10.1111/j.0006-341x.2000.00455.x
13. Makarem YS, Ahmed EA, Makboul M, Farghaly S, Mostafa N, El Zohne RA, et al. CXCL10 as a biomarker of interstitial lung disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Reumatol Clin (Engl Ed). (2024) 20:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.reuma.2023.05.001
14. Zheng W, Hu X, Zou M, Hu N, Song W, Wang R, et al. Plasma IL-36α and IL-36γ as potential biomarkers in interstitial lung disease associated with rheumatoid arthritis: a pilot study in the Chinese population. Inflammation. (2023) 46:285–96. doi: 10.1007/s10753-022-01733-x
15. Nava-Quiroz KJ, Rojas-Serrano J, Pérez-Rubio G, Buendia-Roldan I, Mejía M, Fernández-López JC, et al. Molecular factors in PAD2 (PADI2) and PAD4 (PADI4) are associated with interstitial lung disease susceptibility in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Cells. (2023) 12(18):2235. doi: 10.3390/cells12182235
16. Matama G, Okamoto M, Fujimoto K, Johkoh T, Tominaga M, Mukae H, et al. Periostin is a biomarker of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. J Clin Med. (2023) 12(22):7100. doi: 10.3390/jcm12227100
17. Kronzer VL, Hayashi K, Yoshida K, Davis JM, McDermott GC, Huang W, et al. Autoantibodies against citrullinated and native proteins and prediction of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: a nested case–control study. Lancet Rheumatol. (2023) 5:e77–87. doi: 10.1016/s2665-9913(22)00380-0
18. Xu Y, He H, Zang Y, Yu Z, Hu H, Cui J, et al. Systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) as a novel biomarker in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a multi-center retrospective study. Clin Rheumatol. (2022) 41:1989–2000. doi: 10.1007/s10067-022-06122-1
19. Wang Z, Wang W, Xiang T, Gong B, Xie J. Serum uric acid as a diagnostic biomarker for rheumatoid arthritis–associated interstitial lung disease. Inflammation. (2022) 45:1800–14. doi: 10.1007/s10753-022-01661-w
20. Wang X, Zhu G, Ren Q, Wu J, Gu B, Su D, et al. Increased interleukin-11 associated with disease activity and development of interstitial lung disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2022) 40:135–41. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/mccyj0
21. Sargın G, Yavasoglu I, Senturk T. Immature platelet fraction in rheumatoid arthritis with interstitial lung disease. Reumatol Clin (Engl Ed). (2022) 18:406–9. doi: 10.1016/j.reuma.2021.04.004
22. Pulito-Cueto V, Remuzgo-Martínez S, Genre F, Atienza-Mateo B, Mora-Cuesta VM, Iturbe-Fernández D, et al. Elevated VCAM-1, MCP-1 and ADMA serum levels related to pulmonary fibrosis of interstitial lung disease associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Front Mol Biosci. (2022) 9. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1056121
23. Lin T, Xu S, Wang Y, Nian X, Shan X, Jiang T, et al. Human epididymis protein 4 as a new diagnostic biomarker for rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2022) 40:2167–74. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/zy6hbf
24. Xu L, Jiang L, Nie L, Zhang S, Liu L, Du Y, et al. Soluble programmed death molecule 1 (sPD-1) as a predictor of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Immunol. (2021) 22:69. doi: 10.1186/s12865-021-00460-6
25. Hussein MS, El-Barbary AM, Nada DW, Gaber RA, Elkolaly RM, Aboelhawa MA. Identification of serum interleukin-13 and interleukin-13 receptor subunit expressions: Rheumatoid arthritis–associated interstitial lung disease. Int J Rheum Dis. (2021) 24:591–8. doi: 10.1111/1756-185x.14084
26. Fotoh DS, Helal A, Rizk MS, Esaily HA. Serum Krebs von den Lungen-6 and lung ultrasound B lines as potential diagnostic and prognostic factors for rheumatoid arthritis–associated interstitial lung disease. Clin Rheumatol. (2021) 40:2689–97. doi: 10.1007/s10067-021-05585-y
27. Zhou W, Zheng J, Yuan M, Yuan L, Jia X, Liu H. Differentially expressed lncRNAs in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from middle-aged female patients with rheumatoid arthritis–associated interstitial lung disease. Clin Rheumatol. (2020) 39:2281–9. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-04977-w
28. Wu X, Xu L, Cheng Q, Nie L, Zhang S, Du Y, et al. Increased serum soluble programmed death ligand 1(sPD-L1) is associated with the presence of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: A monocentric cross-sectional study. Respir Med. (2020) 166:105948. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2020.105948
29. Wang N, Zhang Q, Jing X, Guo J, Huang H, Xu Z. The association between MUC5B mutations and clinical outcome in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: A retrospective exploratory study in China. Med Sci Monit. (2020) 26:e920137. doi: 10.12659/msm.920137
30. Pulito-Cueto V, Remuzgo-Martínez S, Genre F, Mora-Cuesta VM, Iturbe-Fernández D, Fernández-Rozas S, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells as a potential biomarker in interstitial lung disease associated with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Med. (2020) 9(12):4098. doi: 10.3390/jcm9124098
31. Kim HC, Choi KH, Jacob J, Song JW. Prognostic role of blood KL-6 in rheumatoid arthritis–associated interstitial lung disease. PloS One. (2020) 15(3):e0229997. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229997
32. Furukawa H, Oka S, Shimada K, Okamoto A, Hashimoto A, Komiya A, et al. Serum metabolomic profiling in rheumatoid arthritis patients with interstitial lung disease: A case–control study. Front Med. (2020) 7. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.599794
33. Castellanos-Moreira R, Rodríguez-García SC, Gomara MJ, Ruiz-Esquide V, Cuervo A, Casafont-Solé I, et al. Anti-carbamylated proteins antibody repertoire in rheumatoid arthritis: evidence of a new autoantibody linked to interstitial lung disease. Ann Rheum Dis. (2020) 79:587–94. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216709
34. Avouac J, Cauvet A, Steelandt A, Shirai Y, Elhai M, Kuwana M, et al. Improving risk-stratification of rheumatoid arthritis patients for interstitial lung disease. PloS One. (2020) 15(5):e0232978. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232978
35. Allam AH, Youssef SMA, Moussa HH, Ezzat Y. Anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies with interstitial lung disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Egypt J chest Dis tubercul. (2020) 69:171–7. doi: 10.4103/ejcdt.ejcdt_102_19
36. Zhu H, Zhao LJ, Zhou Y, Chen Y. Significance of anti-carbamylated protein antibodies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated intersitial lung disease. Beijing da xue xue bao Yi xue ban = J Peking Univ Health Sci. (2019) 51:1003–7. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.06.004
37. Yang JA, Lee JS, Park JK, Lee EB, Song YW, Lee EY. Clinical characteristics associated with occurrence and poor prognosis of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Korean J Intern Med. (2019) 34:434–41. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2016.349
38. Salaffi F, Carotti M, Di Carlo M, Tardella M, Giovagnoni A. High-resolution computed tomography of the lung in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Prevalence of interstitial lung disease involvement and determinants of abnormalities. Med (Baltimore). (2019) 98:e17088. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000017088
39. Matsuo T, Hashimoto M, Ito I, Kubo T, Uozumi R, Furu M, et al. Interleukin-18 is associated with the presence of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: a cross-sectional study. Scand J Rheumatol. (2019) 48:87–94. doi: 10.1080/03009742.2018.1477989
40. Lai NL, Jia W, Wang X, Luo J, Liu GY, Gao C, et al. Risk factors and changes of peripheral NK and T cells in pulmonary interstitial fibrosis of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Can Respir J. (2019) 2019:7262065. doi: 10.1155/2019/7262065
41. Dong H, Julien PJ, Demoruelle MK, Deane KD, Weisman MH. Interstitial lung abnormalities in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: A pilot study evaluating prevalence and progression. Eur J Rheumatol. (2019) 6:193–8. doi: 10.5152/eurjrheum.2019.19044
42. Chen Q, Chen DY, Xu XZ, Liu YY, Yin TT, Li D. Platelet/lymphocyte, lymphocyte/monocyte, and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratios as biomarkers in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Med Sci Monit. (2019) 25:6474–81. doi: 10.12659/msm.916583
43. Zhang J, Li J, Yu X, Xie J. Changes and clinical significance of serum tumor markers in patients with rheumatoid arthritis combined with interstitial lung disease. J Hainan Med Univ (English Edition). (2018) 18):46–9. doi: 10.13210/j.cnki.jhmu.20180903.004
44. Sargin G, Köse R, Şentürk T. Tumor-associated antigens in rheumatoid arthritis interstitial lung disease or Malignancy? Arch Rheumatol. (2018) 33:431–7. doi: 10.5606/ArchRheumatol.2018.6691
45. Juge PA, Lee JS, Ebstein E, Furukawa H, Dobrinskikh E, Gazal S, et al. MUC5B promoter variant and rheumatoid arthritis with interstitial lung disease. N Engl J Med. (2018) 379:2209–19. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1801562
46. Oka S, Furukawa H, Shimada K, Hashimoto A, Komiya A, Fukui N, et al. Plasma miRNA expression profiles in rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2017) 18:21. doi: 10.1186/s12891-017-1389-4
47. Wang T, Zheng XJ, Ji YL, Liang ZA, Liang BM. Tumour markers in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2016) 34:587–91.
48. Song ST, Kim SS, Kim JY, Lee SY, Kim K, Kwon IS, et al. Association of single nucleotide polymorphisms of PADI4 and HLA-DRB1 alleles with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis-related lung diseases. Lung. (2016) 194:745–53. doi: 10.1007/s00408-016-9916-x
49. Sileem AE, Said AM, Alsowey AM, Soliman SA. Clinical significance of serum surfactant protein D in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung diseases. Egypt J Chest Dis Tubercul. (2016) 65:479–84. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcdt.2016.01.003
50. Oka S, Furukawa H, Shimada K, Sugii S, Hashimoto A, Komiya A, et al. Association of human leukocyte antigen alleles with chronic lung diseases in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2016) 55:1301–7. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kew025
51. Wang JX, Du CG. A retrospective study of clinical characteristics of interstitial lung disease associated with rheumatoid arthritis in Chinese patients. Med Sci Monit. (2015) 21:708–15. doi: 10.12659/MSM.890880
52. Restrepo JF, del Rincón I, Battafarano DF, Haas RW, Doria M, Escalante A. Clinical and laboratory factors associated with interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. (2015) 34:1529–36. doi: 10.1007/s10067-015-3025-8
53. Doyle TJ, Patel AS, Hatabu H, Nishino M, Wu G, Osorio JC, et al. Detection of rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease is enhanced by serum biomarkers. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2015) 191:1403–12. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201411-1950oc
54. Chen J, Doyle TJ, Liu Y, Aggarwal R, Wang X, Shi Y, et al. Biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2015) 67:28–38. doi: 10.1002/art.38904
55. Yin Y, Liang D, Zhao L, Li Y, Liu W, Ren Y, et al. Anti-cyclic citrullinated Peptide antibody is associated with interstitial lung disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. PloS One. (2014) 9:e92449. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092449
56. Kelly CA, Saravanan V, Nisar M, Arthanari S, Woodhead FA, Price-Forbes AN, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: associations, prognostic factors and physiological and radiological characteristics–a large multicentre UK study. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2014) 53:1676–82. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keu165
57. Giles JT, Danoff SK, Sokolove J, Wagner CA, Winchester R, Pappas DA, et al. Association of fine specificity and repertoire expansion of anticitrullinated peptide antibodies with rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease. Ann Rheum Dis. (2014) 73:1487–94. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-203160
58. Chen J, Shi Y, Wang X, Huang H, Ascherman D. Asymptomatic preclinical rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Clin Dev Immunol. (2013) 2013:406927. doi: 10.1155/2013/406927
59. Mori S, Koga Y, Sugimoto M. Different risk factors between interstitial lung disease and airway disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Respir Med. (2012) 106:1591–9. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2012.07.006
60. Maniwa K, Ogushi F, Tani K, Ohmoto Y, Muraguchi M, Sone S. Increased incidence of autoantibodies to interleukin-1a in rheumatoid arthritis with interstitial lung disease. Respirology. (2000) 5:315–20. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1843.2000.00269.x
61. Wierczeiko A, Linke M, Friedrich JP, Koch J, Schwarting A, Krause A, et al. A call for gene expression analysis in whole blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) as a biomarker for RA-associated interstitial lung disease. J Rheumatol. (2024) 51:130–3. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.2023-0588
62. Poole JA, Cole KE, Thiele GM, Talmadge JE, England BR, Nelson AJ, et al. Expansion of distinct peripheral blood myeloid cell subpopulations in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 127:111330. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111330
63. Cao S, Liu X, Li Y, Yang Y, Cai X, Cong S, et al. Serum sCD25 is an indicator for rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2024) 42:633–41. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/3iqvk3
64. Yu R, Liu XM, Deng XY, Li ST, Wang YF, Zhang Y, et al. Serum CHI3L1 as a biomarker of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1211790
65. Mena-Vázquez N, Godoy-Navarrete FJ, Lisbona-Montañez JM, Redondo-Rodriguez R, Manrique-Arija S, Rioja J, et al. Inflammatory biomarkers in the diagnosis and prognosis of rheumatoid arthritis–associated interstitial lung disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24(6800). doi: 10.3390/ijms24076800
66. Venerito V, Manfredi A, Lopalco G, Lavista M, Cassone G, Scardapane A, et al. Radiomics to predict the mortality of patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: A proof-of-concept study. Front Med (Lausanne). (2022) 9:1069486. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1069486
67. Qin Y, Wang Y, Meng F, Feng M, Zhao X, Gao C, et al. Identification of biomarkers by machine learning classifiers to assist diagnose rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Res Ther. (2022) 24:115. doi: 10.1186/s13075-022-02800-2
68. Natalini JG, England BR, Baker JF, Chen Q, Singh N, Mahajan TD, et al. Associations between shortened telomeres and rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease among US Veterans. Respir Med. (2022) 201:106943. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2022.106943
69. Matson SM, Deane KD, Peljto AL, Bang TJ, Sachs PB, Walts AD, et al. Prospective identification of subclinical interstitial lung disease in a rheumatoid arthritis cohort is associated with the MUC5B promoter variant. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2022) 205:473–6. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202109-2087le
70. Hayashi S, Matsubara T, Fukuda K, Maeda T, Funahashi K, Hashimoto M, et al. A genome-wide association study identifying single nucleotide polymorphisms in the PPFIBP2 gene was predictive for interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Rheumatol Adv Pract. (2022) 6:rkac088. doi: 10.1093/rap/rkac088
71. Chen N, Diao CY, Gao J, Zhao DB. Risk factors for the progression of rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: Clinical features, biomarkers, and treatment options. Semin Arthritis Rheumatol. (2022) 55:152004. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2022.152004
72. Chen J, Chen Y, Liu D, Lin Y, Zhu L, Song S, et al. Predictors of long-term prognosis in rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:9469. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-13474-w
73. Brink M, Ljung L, Hansson M, Rönnelid J, Holmdahl R, Skriner K, et al. Anti-citrullinated protein antibody specificities and pulmonary fibrosis in relation to genetic loci in early rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2022) 61:4985–90. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keac280
74. Zheng M, Lou A, Zhang H, Zhu S, Yang M, Lai W. Serum KL-6, CA19-9, CA125 and CEA are diagnostic biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease in the Chinese population. Rheumatol Ther. (2021) 8:517–27. doi: 10.1007/s40744-021-00288-x
75. Xue J, Wang YJ, Xia HC, Liang XY, Cui JD, Yu M, et al. Circulating Dickkof-1 as a potential biomarker associated with the prognosis of patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Chin Med J (Engl). (2021) 134:1119–21. doi: 10.1097/cm9.0000000000001267
76. Tyker A, Ventura IB, Lee CT, Strykowski R, Garcia N, Guzy R, et al. High-titer rheumatoid factor seropositivity predicts mediastinal lymphadenopathy and mortality in rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:22821. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02066-9
77. Tanaka N, Nishimura K, Waki D, Kadoba K, Murabe H, Yokota T. Annual variation rate of KL-6 for predicting acute exacerbation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Mod Rheumatol. (2021) 31:1100–6. doi: 10.1080/14397595.2021.1879346
78. Saku A, Fujisawa T, Nishimoto K, Yoshimura K, Hozumi H, Karayama M, et al. Prognostic significance of peripheral blood monocyte and neutrophil counts in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Respir Med. (2021) 182:106420. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2021.106420
79. Natalini JG, Baker JF, Singh N, Mahajan TD, Roul P, Thiele GM, et al. Autoantibody seropositivity and risk for interstitial lung disease in a prospective male-predominant rheumatoid arthritis cohort of U.S. Veterans. Ann Am Thorac Soc. (2021) 18:598–605. doi: 10.1513/annalsats.202006-590oc
80. Nakazawa M, Suzuki K, Takeshita M, Inamo J, Kamata H, Ishii M, et al. Distinct expression of coinhibitory molecules on alveolar T cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated and idiopathic inflammatory myopathy-associated interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2021) 73:576–86. doi: 10.1002/art.41554
81. Mena-Vázquez N, Pérez Albaladejo L, Manrique-Arija S, Romero Barco CM, Gómez Cano C, Ureña Garnica I, et al. Analysis of clinical-analytical characteristics in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and interstitial lung disease: case-control study. Reumatol Clin (Engl Ed). (2021) 17:197–202. doi: 10.1016/j.reumae.2019.06.002
82. Moon J, Lee JS, Yoon YI, Chang SH, Lee YA, Ha YJ, et al. Association of serum biomarkers with pulmonary involvement of rheumatoid arthritis interstitial lung disease: from KORAIL cohort baseline data. J Rheum Dis. (2021) 28:234–41. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2021.28.4.234
83. Liang L, Chen J, Di C, Zhan M, Bao H, Xia C, et al. Serum human epididymis protein 4 as a novel biomarker in identifying patients with interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Med (Lausanne). (2021) 8:755268. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.755268
84. Hammoda RM, Salah-ElDin H, El-Gharbawy NH, Ragab D. Krebs von den Lungen-6, a promising marker in evaluating the severity of interstitial lung disease in Egyptian rheumatoid arthritis patients. Egypt J Immunol. (2021) 28:241–9. doi: 10.55133/eji.280425
85. Kass DJ, Nouraie M, Glassberg MK, Ramreddy N, Fernandez K, Harlow L, et al. Comparative profiling of serum protein biomarkers in rheumatoid arthritis–associated interstitial lung disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2020) 72:409–19. doi: 10.1002/art.41123
86. Del Angel-Pablo AD, Buendía-Roldán I, Mejía M, Pérez-Rubio G, Nava-Quiroz KJ, Rojas-Serrano J, et al. Anti-HLA class II antibodies correlate with C-reactive protein levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis associated with interstitial lung disease. Cells. (2020) 9(3):691. doi: 10.3390/cells9030691
87. Yu M, Guo Y, Zhang P, Xue J, Yang J, Cai Q, et al. Increased circulating Wnt5a protein in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial pneumonia (RA-ILD). Immunobiology. (2019) 224:551–9. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2019.04.006
88. Chen L, Lin H, Qin L, Zhang G, Huang D, Chen P, et al. Identification and validation of mutual hub genes in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and rheumatoid arthritis-associated usual interstitial pneumonia. Heliyon. (2024) 10(7). doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28088
89. England BR, Duryee MJ, Roul P, Mahajan TD, Singh N, Poole JA, et al. Malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde adducts and antibody responses in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2019) 71:1483–93. doi: 10.1002/art.40900
90. Correia CS, Briones MR, Guo R, Ostrowski RA. Elevated anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody titer is associated with increased risk for interstitial lung disease. Clin Rheumatol. (2019) 38:1201–6. doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-04421-0
91. Matsushita M, Tamura N, Ogasawara M, Tada K, Yamaji K, Takasaki Y. The association of anti-aminoacyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase antibodies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and interstitial lung disease. Arch Rheumatol. (2018) 33:26–32. doi: 10.5606/archrheumatol.2018.6401
92. Fu Q, Bai Y, Liu Y, Zhou J, Zheng Y. The serum level and significance of lysyl oxidase-like 2 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Clin Rheumatol. (2018) 37:193–8. doi: 10.1007/s10067-017-3878-0
93. Fadda S, Khairy N, Fayed H, Mousa H, Taha R. Interstitial lung disease in Egyptian patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Frequency, pattern and correlation with clinical manifestations and anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies level. Egypt Rheumatol. (2018) 40:155–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ejr.2017.10.006
94. Alunno A, Bistoni O, Pratesi F, Topini F, Puxeddu I, Valentini V, et al. Association between anti-citrullinated alpha enolase antibodies and clinical features in a cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a pilot study. Reumatismo. (2018) 70:67–71. doi: 10.4081/reumatismo.2018.1028
95. Alunno A, Bistoni O, Pratesi F, La Paglia GMC, Puxeddu I, Migliorini P, et al. Anti-citrullinated alpha enolase antibodies, interstitial lung disease and bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2018) 57:850–5. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex520
96. Suhara K, Miyazaki Y, Okamoto T, Ishizuka M, Tsuchiya K, Inase N. Fragmented gelsolins are increased in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease with usual interstitial pneumonia pattern. Allergol Int. (2016) 65:88–95. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2015.08.002
97. Lee YS, Kim HC, Lee BY, Lee CK, Kim MY, Jang SJ, et al. The value of biomarkers as predictors of outcome in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated usual interstitial pneumonia. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. (2016) 33:216–23.
98. Wang T, Zheng XJ, Liang BM, Liang ZA. Clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Sci Rep. (2015) 5:14897. doi: 10.1038/srep14897
99. Nakashita T, Ando K, Kaneko N, Takahashi K, Motojima S. Potential risk of TNF inhibitors on the progression of interstitial lung disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. BMJ Open. (2014) 4:e005615. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-005615
100. Giles JT, Darrah E, Danoff S, Johnson C, Andrade F, Rosen A, et al. Association of cross-reactive antibodies targeting peptidyl-arginine deiminase 3 and 4 with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. PloS One. (2014) 9:e98794. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098794
101. Harlow L, Rosas IO, Gochuico BR, Mikuls TR, Dellaripa PF, Oddis CV, et al. Identification of citrullinated hsp90 isoforms as novel autoantigens in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2013) 65:869–79. doi: 10.1002/art.37881
102. Xiangyang Z, Lutian Y, Lin Z, Liping X, Hui S, Jing L. Increased levels of interleukin-33 associated with bone erosion and interstitial lung diseases in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine. (2012) 58:6–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2011.12.010
103. Furukawa H, Oka S, Shimada K, Sugii S, Ohashi J, Matsui T, et al. Association of human leukocyte antigen with interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: a protective role for shared epitope. PloS One. (2012) 7:e33133. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033133
104. Ji YX, Huang JA, Zong JP, Lü DF, Xin XF, He J, et al. The serum levels of cytokines in patients with rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease and their clinical significance. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. (2008) 31:264–7.
105. Inui N, Enomoto N, Suda T, Kageyama Y, Watanabe H, Chida K. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies in lung diseases associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Biochem. (2008) 41:1074–7. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2008.06.014
106. Atkins SR, Turesson C, Myers JL, Tazelaar HD, Ryu JH, Matteson EL, et al. Morphologic and quantitative assessment of CD20+ B cell infiltrates in rheumatoid arthritis-associated nonspecific interstitial pneumonia and usual interstitial pneumonia. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2006) 54:635–41. doi: 10.1002/art.21758
107. Turesson C, Matteson EL, Colby TV, Vuk-Pavlovic Z, Vassallo R, Weyand CM, et al. Increased CD4+ T cell infiltrates in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial pneumonitis compared with idiopathic interstitial pneumonitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2005) 52:73–9. doi: 10.1002/art.20765
108. Oyama T, Kohno N, Yokoyama A, Hirasawa Y, Kondo K, Hiwada K, et al. High serum KL-6 levels predict the deterioration of pulmonary function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Japan J Rheumatol. (1999) 9:373–80. doi: 10.1007/bf03041350
109. Oyama T, Kohno N, Yokoyama A, Hirasawa Y, Hiwada K, Oyama H, et al. Detection of interstitial pneumonitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis by measuring circulating levels of KL-6, a human MUC1 mucin. Lung. (1997) 175:379–85. doi: 10.1007/pl00007584
110. Wu X, Jeong Y, Poli de Frías S, Easthausen I, Hoffman K, Oromendia C, et al. Serum proteomic profiling of rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease with a comparison to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax. (2022) 77:1041–4. doi: 10.1136/thorax-2021-217822
111. Zhang M, Yin J, Zhang X. Factors associated with interstitial lung disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PloS One. (2023) 18:e0286191. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286191
112. Xie S, Li S, Chen B, Zhu Q, Xu L, Li F. Serum anti-citrullinated protein antibodies and rheumatoid factor increase the risk of rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: a meta-analysis. Clin Rheumatol. (2021) 40:4533–43. doi: 10.1007/s10067-021-05808-2
113. Jee AS, Sahhar J, Youssef P, Bleasel J, Adelstein S, Nguyen M, et al. Review: Serum biomarkers in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and systemic sclerosis associated interstitial lung disease - frontiers and horizons. Pharmacol Ther. (2019) 202:40–52. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.05.014
114. Beketov VD, Lebedeva MV, Mukhin NA, Serova AG, Ponomarev AB, Popova EN, et al. Clinical significance of the determination of surfactant proteins A and D in assessing the activity of lung sarcoidosis. Ter Arkh. (2018) 90:42–6. doi: 10.26442/terarkh201890342-46
115. Chung C, Kim J, Cho HS, Kim HC. Baseline serum Krebs von den Lungen-6 as a biomarker for the disease progression in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:8564. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12399-8
116. Roque W, Boni A, Martinez-Manzano J, Romero F. A tale of two proteolytic machines: matrix metalloproteinases and the ubiquitin-proteasome system in pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21(11):3878. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113878
117. Zhao G, Liu N, Wang S, Guo J, Song X, Qi Y, et al. Prognostic significance of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with metastatic gastric cancer. Med (Baltimore). (2020) 99:e19405. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000019405
118. Paliogiannis P, Satta R, Deligia G, Farina G, Bassu S, Mangoni AA, et al. Associations between the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios and the presence and severity of psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Exp Med. (2019) 19:37–45. doi: 10.1007/s10238-018-0538-x
119. Yu C, Chen M, Chen Z, Lu G. Predictive and prognostic value of admission neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with CHD. Herz. (2016) 41:605–13. doi: 10.1007/s00059-015-4399-8
120. Weidemann T, Worch R, Kurgonaite K, Hintersteiner M, Bökel C, Schwille P. Single cell analysis of ligand binding and complex formation of interleukin-4 receptor subunits. Biophys J. (2011) 101:2360–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.10.014
121. Zamora-Legoff JA, Krause ML, Crowson CS, Ryu JH, Matteson EL. Progressive decline of lung function in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2017) 69:542–9. doi: 10.1002/art.39971
122. Sawada M, Kawayama T, Imaoka H, Sakazaki Y, Oda H, Takenaka S, et al. IL-18 induces airway hyperresponsiveness and pulmonary inflammation via CD4+ T cell and IL-13. PloS One. (2013) 8:e54623. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054623
123. Kitasato Y, Hoshino T, Okamoto M, Kato S, Koda Y, Nagata N, et al. Enhanced expression of interleukin-18 and its receptor in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2004) 31:619–25. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2003-0306oc
124. Gono T, Sato S, Kawaguchi Y, Kuwana M, Hanaoka M, Katsumata Y, et al. Anti-MDA5 antibody, ferritin and IL-18 are useful for the evaluation of response to treatment in interstitial lung disease with anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2012) 51:1563–70. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kes102
Keywords: rheumatoid arthritis, interstitial lung disease, biomarkers, systematic review, meta-analysis
Citation: Guo L, Wang J, Li J, Yao J and Zhao H (2024) Biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 15:1455346. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1455346
Received: 26 June 2024; Accepted: 07 October 2024;
Published: 29 October 2024.
Edited by:
Raouia Fakhfakh, Centre de Recherche du CHU de Québec, CanadaReviewed by:
Mayra Mejia, INSTITUTO NACIONAL DE ENFERMEDADES RESPIRATORIAS, MexicoRaimon Sanmarti, Hospital Clinic of Barcelona, Spain
Copyright © 2024 Guo, Wang, Li, Yao and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hulei Zhao, aHVsZWk4OTA0MjFAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Luhan Guo
Luhan Guo Jun Wang
Jun Wang Jiansheng Li
Jiansheng Li Jiaheng Yao
Jiaheng Yao Hulei Zhao
Hulei Zhao