- 1Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, China
- 2Department of General Surgery, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 3Department of Anesthesiology, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Background: Glucose-to-lymphocyte ratio (GLR) plays an important role in the prognosis of various tumors. The aim of this study was to comprehensively evaluate the prognostic value of GLR in solid tumors through the meta-analysis.
Methods: A comprehensive search of eligible studies was performed by scrutinizing the Pubmed, Embase and Web of science databases until May 30, 2024. The pooled hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated to evaluate overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS) and recurrence free survival (RFS).
Results: A total of 22 studies from 14 articles involving 9472 patients were included in the study. The pooled analysis showed that cancer patients with high GLR was significantly associated with unfavorable OS (HR:1.48,95% CI:1.34-1.63) and DFS/RFS (HR:2.20,95% CI:1.66-2.92). Subgroup analysis further showed that high GLR had better predictive value in liver cancer (HR:2.66, 95%CI:1.80-3.93), breast cancer (HR:2.13, 95%CI:1.10-4.13) and pancreatic cancer (HR:1.92, 95%CI:1.30-2.84).
Conclusions: GLR can be used as an effective prognostic marker in patients with solid tumors.
Introduction
According to the World Health Organization, cancers have become the leading cause of human death (1). In China, colorectal, stomach, esophagus and liver cancers are also commonly diagnosed as the leading causes of cancer deaths (2). Despite tremendous progress in the prevention and treatment of cancer, the incidence and mortality of cancers continue to rise (3). Many cancer patients are diagnosed at advanced stages and miss the best time for treatment. Many effective prognostic markers have been used for cancers, but their clinical application is not satisfactory. Therefore, there is an urgent need to identify new and more effective prognostic markers for cancers.
Inflammatory, immune and nutritional status influence tumor biological behavior (4–6). Multiple immunoinflammatory or nutritional indicators have been used to assess the prognosis of patients with tumors (7–9). However, these indicators only reflect inflammation, immune and nutritional status, and do not embody the body’s metabolic status. Tumor prognosis is not only related to inflammation, immunity and nutritional status, but also closely associated with glucose metabolism (10). Therefore, a new prognostic marker that can indicate both inflammatory immune status and metabolic status is needed.
Glucose-to-lymphocyte ratio(GLR) composed of glucose and lymphocyte as a new prognostic marker, is believed that it can effectively reflect the body’s glucose metabolism and inflammatory immune status (11). GLR was found to play an important role in tumor prognosis. Navarro et al. suggested that preoperative GLR was an independent predictor of overall survival(OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) in gallbladder cancer (12). Yang et al. showed that GLR can independently predict the prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer (13). Yılmaz et al. found that GLR was a new prognostic biomarker in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (14). Hannarici et al. revealed that GLR was found to be independently prognostic factor for both recurrence free survival (RFS) and OS in metastatic gastric cancer (15). Park et al. reported that elevated preoperative GLR was associated with aggressive tumor characteristics and was an independent predictor of poor OS in patients with pancreatic cancer (16). Ni et al. displayed that high GLR represented adverse prognosis in renal cell carcinoma patients (17). Yang et al. disclosed that GLR was independent prognostic factors for patients with non-small cell lung cancer (18). Zhang et al. proved that GLR had predictive value for the survival of patients with breast cancer (19). Liu et al. demonstrated that elevated preoperative GLR was remarkably associated with poorer prognosis in patients with esophageal cancer and melanoma (20). However, due to the limited number of patients in a single study, the reliability of the conclusions was insufficient. Therefore, we conducted a meta-analysis to synthesize and clarify the applicability of GLR as a prognostic marker in solid tumors.
Material and methods
Search strategy
Articles in electronic databases (Pubmed, Embase and Web of science) were retrieved until May 30, 2024. We used the following keywords: “glucose to lymphocyte ratio” OR “glucose-to-lymphocyte ratio”. Language restriction was not set. The titles, abstracts, full texts, and the possible references were screened to identify qualified studies.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Three researchers independently conducted the literature search. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) investigated the relationship between GLR and survival outcomes in solid tumors. (2) provided sufficient data to calculate the hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) insufficient data to calculate the 95% CIs and HRs; (2) abstracts, case reports, reviews and letters.
Data extraction and quality assessment
The relevant information was extracted, such as the name of the first author, year of publication, country, cancer type, sample size, treatment methods, analysis types and survival outcomes. We assessed the quality of each study according to the Newcastle–Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale (NOS) (21). The multivariate analysis was preferred because it considered the confounding factors.
Statistical analysis
All data analysis was performed using the STATA version 12.0 software (Stata Corporation, College Station, TX, USA). HRs and their corresponding 95% CIs were used to analyze the pooled data. A fixed effects model was used when I (2) was <50%. A random effects model was used when I (2) was >50% (22). The subgroup analysis was performed to further explore the prognostic value of GLR in solid tumors. Meta-regression was used to explore the sources of heterogeneity. Sensitivity analysis was used to test the stability of the results. Begg’s test, Egger’s test and trim-and-fill method were used to assess publication bias (23, 24). P<0.05 denoted statistical significance.
Results
Search results
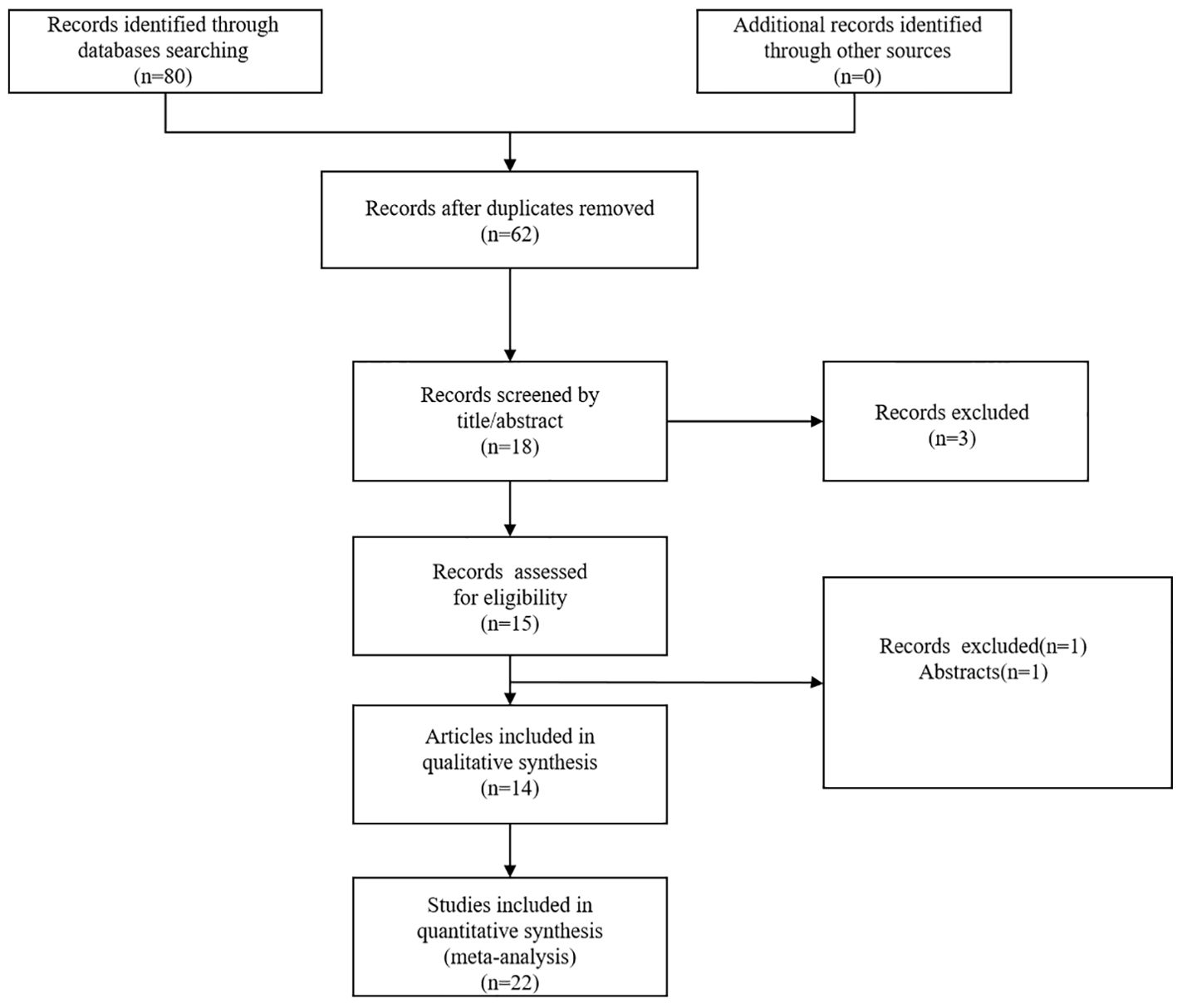
Through a systematic literature search, we primarily identified a total of 80 articles. After removal of 62 duplicate publications, 18 articles remained. We further excluded 4 articles by browsing the titles and abstracts. Finally, we identified 22 studies from 14 articles published between 2019 and 2024 (9, 12–20, 25–28). The flow diagram of the literature search was shown in Figure 1.
Study characteristics
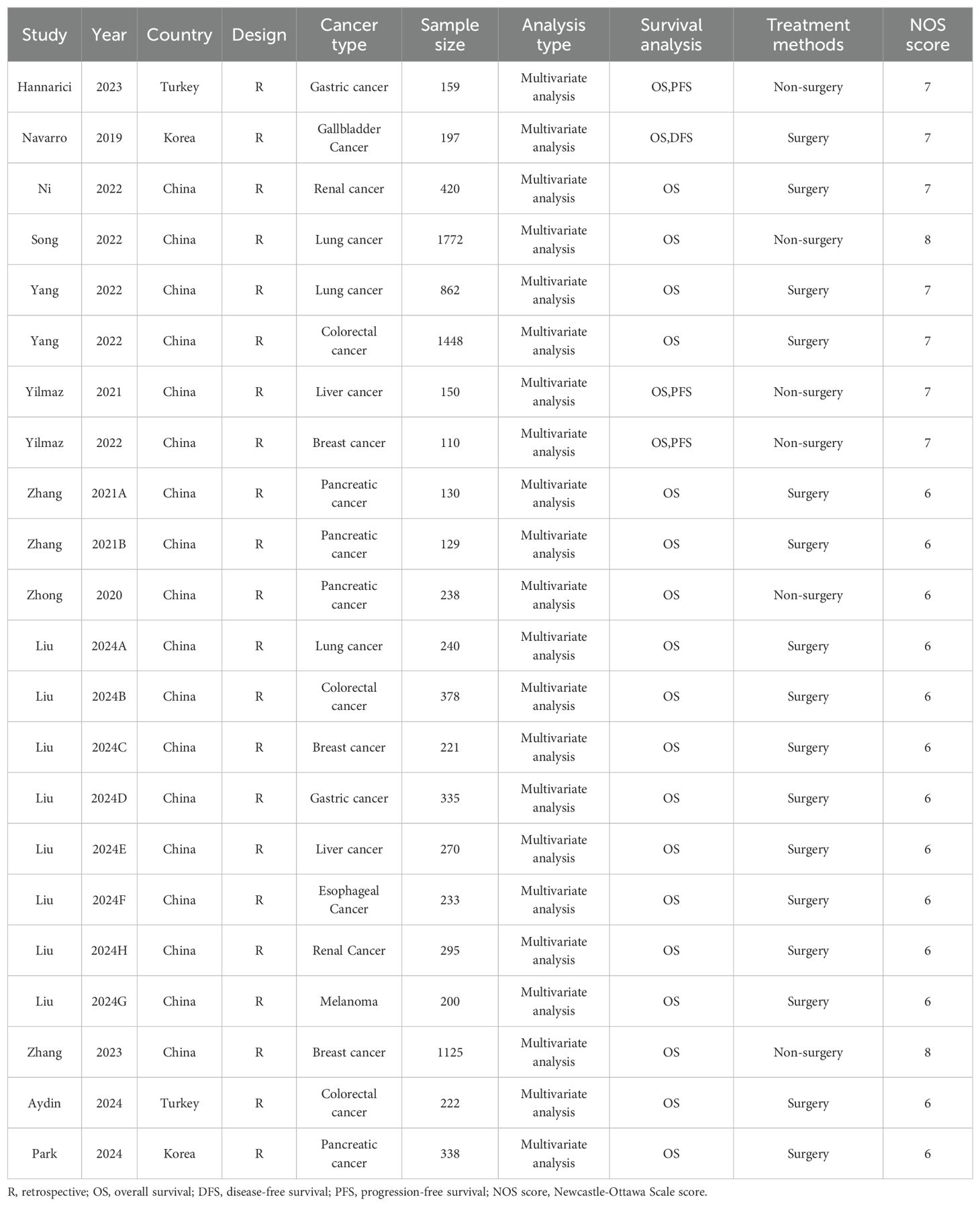
The total number of patients in the included articles was 9472 (range: 110–1772 patients).18 studies were produced in China, 2 study were conducted in Korea and 2 study were from Turkey. 22 studies reported overall survival data, 1 study displayed disease-free survival data, and 3 studies covered recurrence free survival data. 10 different tumors were included, such as gastric cancer, gallbladder cancer, renal cancer, lung cancer, colorectal cancer, liver cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, esophageal cancer and melanoma. The NOS scores of the included studies ranged from 6 to 8 (mean: 6.5). The basic information was shown in (Table 1).
Association between high GLR and OS
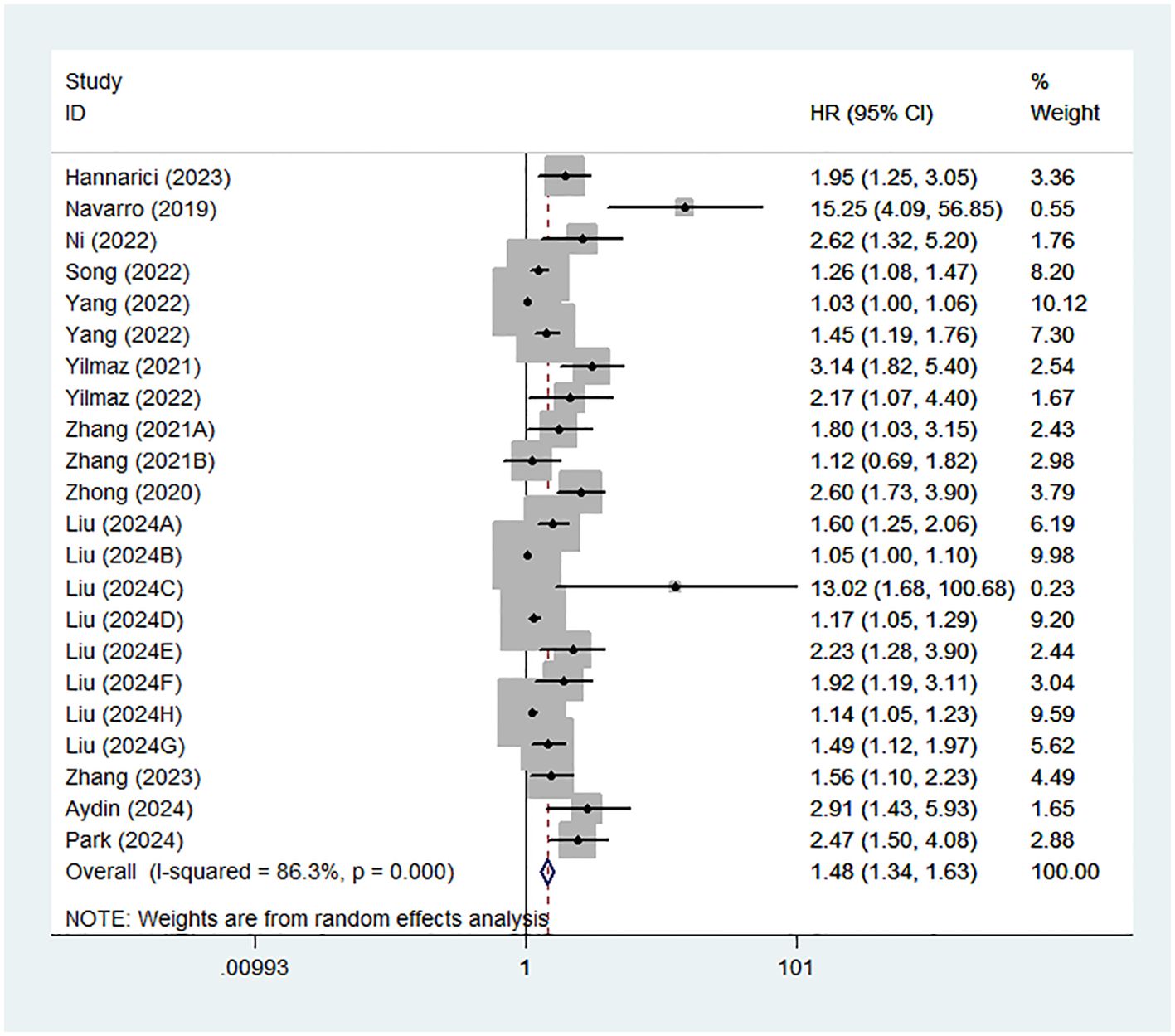
22 studies from 14 articles explored the association between GLR and prognosis using OS. We used a random effects model to calculate the pooled HRs due to moderate heterogeneity (I2 = 86.3%). The results of the meta-analysis revealed that high GLR was significantly related to poor OS (HR:1.48,95% CI:1.34-1.63) (Figure 2).
Subgroup analysis and meta-regression for OS
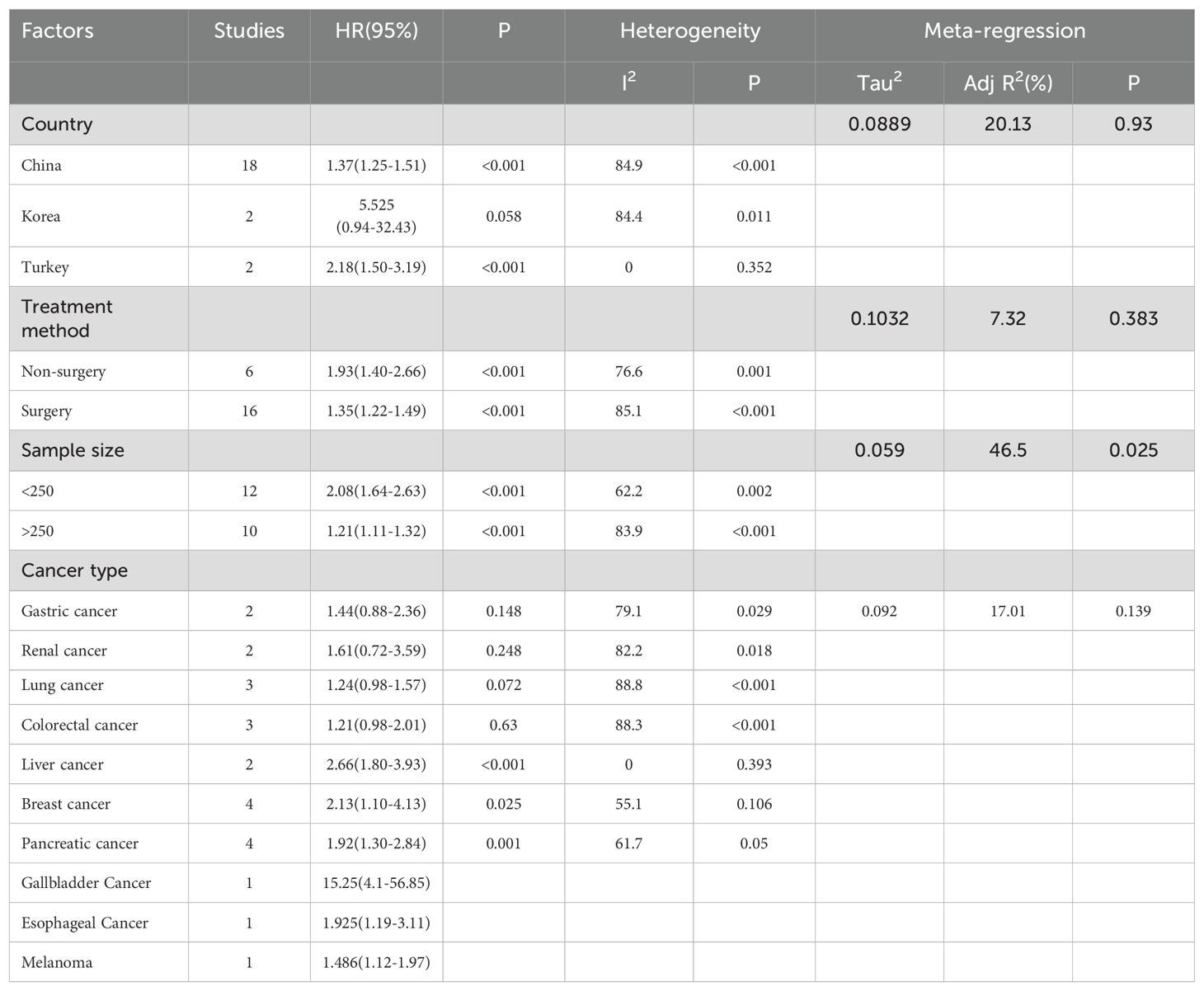
We further conducted subgroup analysis based on cancer type, sample size, treatment method and country. The results were shown in (Table 2). We found that high GLR was an unfavorable prognostic marker in liver cancer (HR:2.66, 95%CI:1.80-3.93), breast cancer (HR:2.13, 95%CI:1.10-4.13) and pancreatic cancer (HR:1.92, 95%CI:1.30-2.84). Moreover, we also found that high GLR was associated with poor OS for the China group (HR: 1.37; 95% CI:1.25–1.51) and Turkey group (HR:2.18; 95% CI: 1.50–3.19). Regardless of the surgical or non-surgical group, high GLR indicated adverse prognosis. Meta-regression showed that sample size was the main source of heterogeneity.
Association between high GLR and DFS/PFS
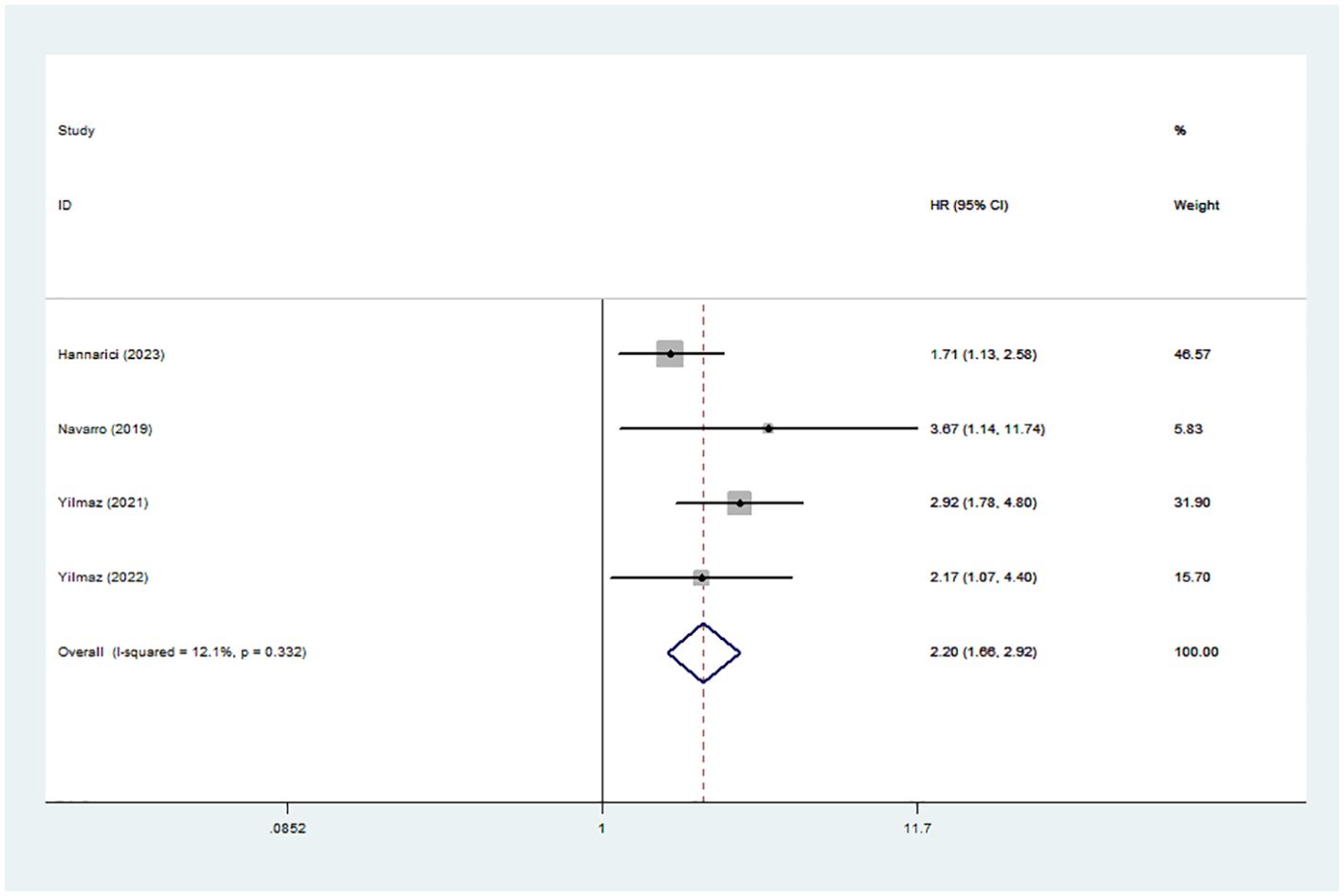
4 studies involving 616 patients documented the association between high GLR and prognosis using DFS/PFS. A fixed-effect model was used because of the obvious heterogeneity (I2 = 12.1%). The results showed that high GLR was correlated with adverse DFS/PFS (HR:2.20,95% CI:1.66-2.92) (Figure 3).
Sensitivity analysis
Sensitivity analysis was implemented by removing one study. The results were consistent with the comprehensive analysis, confirming that the outcomes of the combined OS and DFS/PFS were stable (Figures 4A, B).
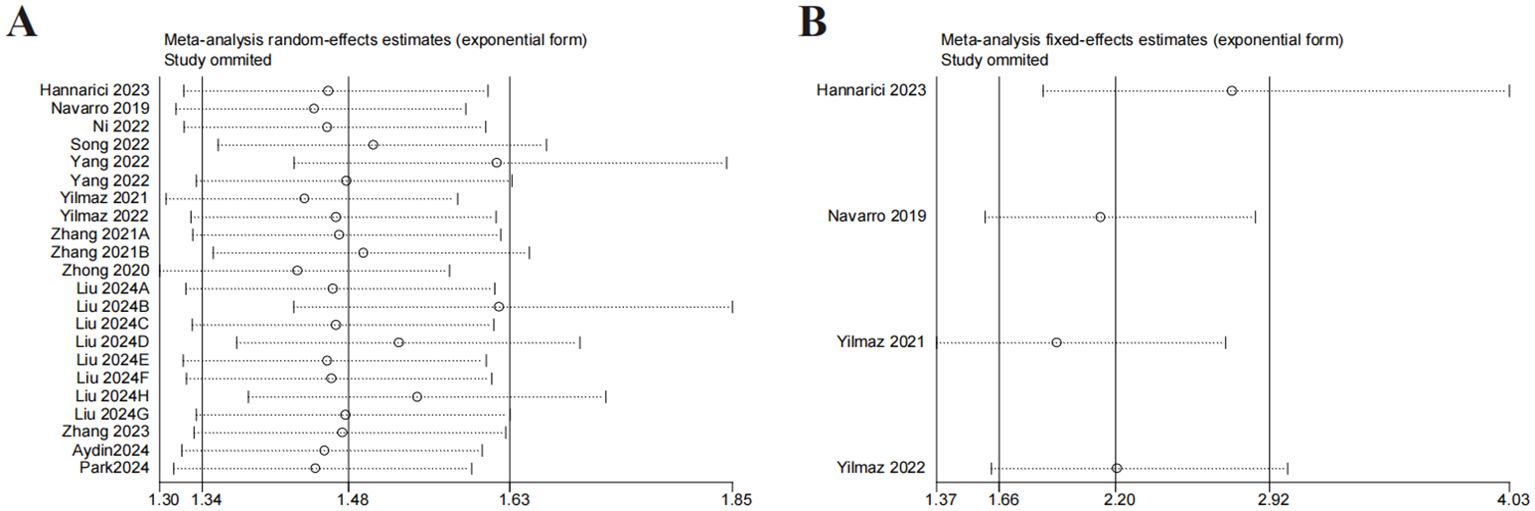
Figure 4. Sensitivity analysis. (A) sensitivity analysis for OS. (B) sensitivity analysis for DFS/PFS.
Publication bias
Begg’s test and Egger’s test were used to evaluate the publication bias. P value of Begg’s test and Egger’s test for OS was 0.028 and 0.01 (Figure 5A), respectively. There was a degree of publication bias. However, we found that the comprehensive results were not affected through the trim-and-fill method (HR:1.258,95%CI:1.140-1.388) (Figure 5B). P values of Begg’s and Egger’s tests for DFS/PFS were 0.734 and 0.411, respectively (Figure 5C). P was more than 0.05 and no significant bias was observed.
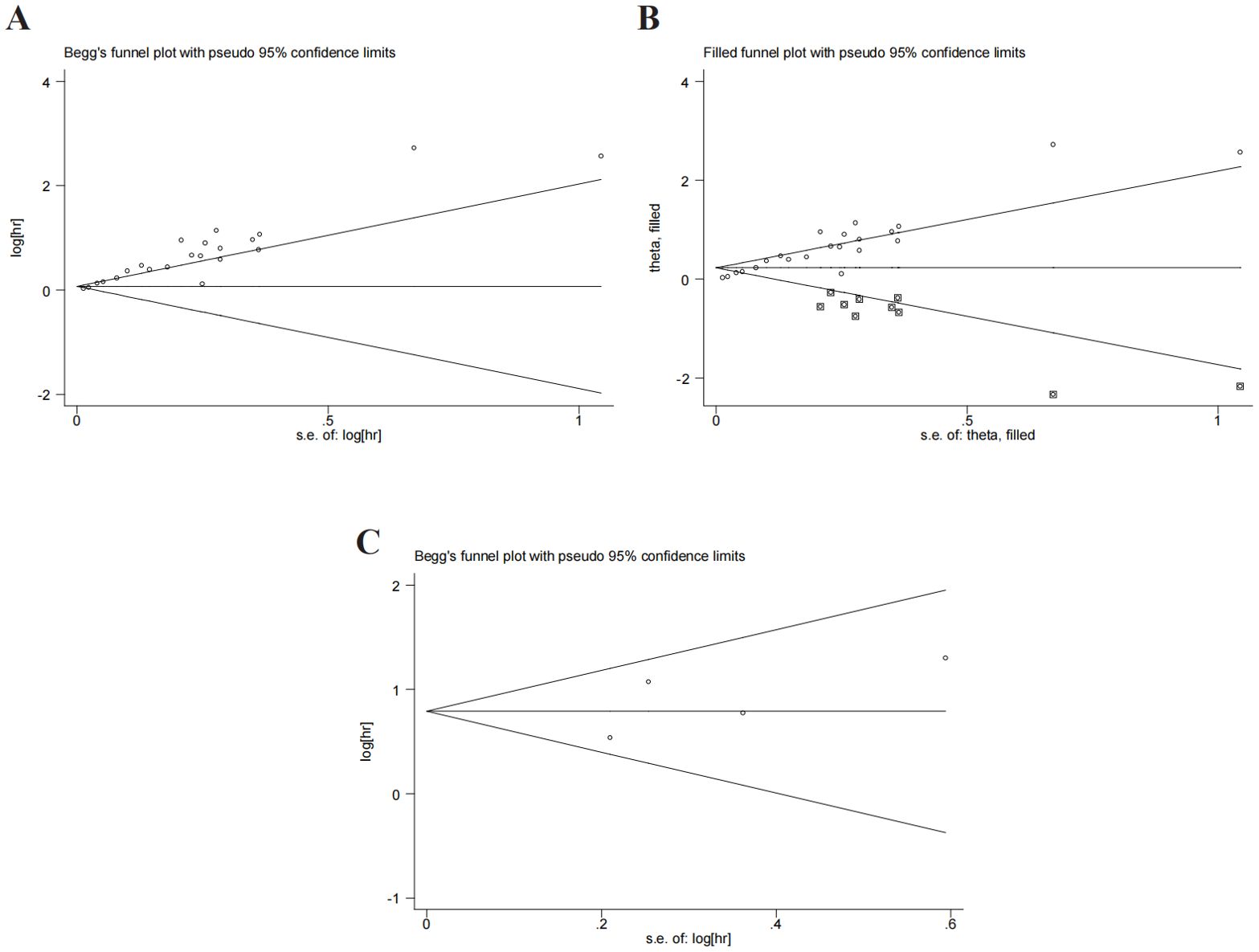
Figure 5. Publication bias. (A) publication bias for OS. (B) trim-and-fill method for OS. (C) publication bias for DFS/PFS.
Discussion
To our knowledge, this study was the first meta-analysis to comprehensively assess the prognostic value of GLR in solid tumors. Our results suggested that high GLR was significantly associated with unfavorable OS and DFS/PFS in solid tumors. Subgroup analysis further showed that high GLR had better predictive value in liver cancer, breast cancer and pancreatic cancer.
GLR was firstly established as an effective prognostic indicator for gallbladder cancer (12). Subsequently, its prognostic value was confirmed in other cancers. In non-neoplastic diseases such as acute pancreatitis, myocardial infarction and acute respiratory distress syndrome, GLR also was shown to play an important role (29–31). Blood glucose was thought to be involved in the development of inflammation (32). The disturbance of glucose metabolism or hyperglycemia was found to promote the proliferation of tumor cells and increase the risk of death in patients (33). As one of immune cells, lymphocyte played a vital role in anti-tumor immune defense. Lymphocytopenia in tumor patients predicted poor prognosis (34). By combining blood glucose level and lymphocytes, GLR overcame the limitations of using blood glucose level or lymphocytes alone, and can more effectively reflect the metabolic, inflammatory and immune status of tumor patients.
GLR had significant advantages in predicting the prognosis of tumor patients by evaluating the metabolic, inflammatory and immune status of tumor patients. However, the specific mechanism that GLR affected the prognosis of tumor patients remained unclear. We tried to explain the phenomenon by the composition of GLR.
Blood glucose is an important component of human plasma, and is a good indicator of the body’s metabolic and endocrine functions. The survival of cancer cells is dependent on glucose. Hyperglycemia can promote the proliferation, invasion and migration of tumor cells, and enhance drug resistance of tumor cells (35). Hyperglycemia is conducive to the metabolic adaptation of tumor microenvironment and the maintenance of local immunosuppression (36). Hyperglycemia accelerates cancer progression by increasing reactive oxygen species levels (37). Elevated blood glucose levels produce many free radicals, leading to inflammation and metabolic disorders (38). Inflammation can accelerate cancer progression and lead to adverse survival (39). Evidence suggests that high blood glucose levels are associated with poor survival outcomes in a variety of tumors (40).
Lymphocyte as the important part of immune system plays an indispensable role in anti-tumor immune defense. Lymphocytes can inhibit tumor progression by directly inhibiting tumor cell proliferation (41). In addition, lymphocytes can activate cell-mediated immune responses and stimulate cytokines to promote tumor lysis (42). The data shows that T cells are more effective in suppressing anti-tumor immune response under hypoglycemic conditions (43). Accumulating evidences suggest that lymphocytes can reflect the nutritional status of patients (44). Studies have shown that high lymphocyte levels in the blood benefit the prognosis of patients with tumors, while lymphocytopenia may predict poorer survival outcomes (45, 46).
A high GLR indicated high glucose levels and a low lymphocyte count. The high GLR reflected more obvious the inflammation of tumor patients and the worse immune function of tumor patients. Therefore, it was not difficult to understand that high GLR was associated with a poor prognosis in patients with solid tumors.
There were some limitations in the study. Firstly, all articles had small sample sizes. Secondly, the included articles were retrospective studies. Thirdly, all studies included in the meta-analysis were conducted in Asia. More studies from other regions were warranted. Fourthly, publication bias for OS existed in the study. Finally, due to the lack of data, we were unable to assess the relationship between GLR and some pathological features.
Although there were some defects, the study also had some strengths. Firstly, we firstly demonstrated the prognostic value of GLR in solid tumors by meta-analysis. Secondly, the combined results were stable through sensitivity analysis. Thirdly, the trim-and-fill method found that the results for OS were unaffected by the publication bias. Finally, as a convenient serum marker, GLR can dynamically monitor the prognosis and therapeutic effect of patients with solid tumors.
In conclusions, we demonstrated that high GLR was associated with unfavorable survival outcome in solid tumors. GLR can serve as an effective prognostic indicator for patients with solid tumors, especially for liver, breast and pancreatic cancers. It can help doctors better identify high-risk patients so they can treat them more effectively. However, due to the shortcomings, more prospective studies were needed to confirm our findings.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
RL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. YS: Data curation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft. JC: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. WM: Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft. JW: Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft. CC: Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. WW: Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1454393/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
2. Maomao C, He L, Dianqin S, Siyi H, Xinxin Y, Fan Y, et al. Current cancer burden in China: epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Cancer Biol Med. (2022) 19:1121–38. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2022.0231
3. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:229–63. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
4. Greten FR, Grivennikov SI. Inflammation and cancer: triggers, mechanisms, and consequences. Immunity. (2019) 51:27–41. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.06.025
5. Mellman I, Chen DS, Powles T, Turley SJ. The cancer-immunity cycle: Indication, genotype, and immunotype. Immunity. (2023) 56:2188–205. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.09.011
6. Schab M, Skoczen S. Nutritional status, body composition and diet quality in children with cancer. Front Oncol. (2024) 14:1389657. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1389657
7. Peng P, Chen L, Shen Q, Xu Z, Ding X. Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) and Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) score for predicting outcomes of breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pak J Med Sci. (2023) 39:1535–41. doi: 10.12669/pjms.39.5.7781
8. Guven DC, Sahin TK, Erul E, Kilickap S, Gambichler T, Aksoy S. The association between the pan-immune-inflammation value and cancer prognosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14:2675. doi: 10.3390/cancers14112675
9. Song M, Zhang Q, Song C, Liu T, Zhang X, Ruan G, et al. The advanced lung cancer inflammation index is the optimal inflammatory biomarker of overall survival in patients with lung cancer. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2022) 13:2504–14. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13032
10. Bose S, Le A. Glucose metabolism in cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2018) 1063:3–12. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-77736-8_1
11. Li L, Zou G, Liu J. Preoperative glucose-to-lymphocyte ratio is an independent predictor for acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery in patients in intensive care unit. Int J Gen Med. (2021) 14:6529–37. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S335896
12. Navarro J, Kang I, Hwang HK, Yoon DS, Lee WJ, Kang CM. Glucose to lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic marker in patients with resected pT2 gallbladder cancer. J Surg Res. (2019) 240:17–29. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2019.02.043
13. Yang M, Zhang Q, Ge Y, Tang M, Zhang X, Song M, et al. Glucose to lymphocyte ratio predicts prognoses in patients with colorectal cancer. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. (2023) 19:542–8. doi: 10.1111/ajco.13904
14. Yılmaz A, Şimşek M, Hannarici Z, Büyükbayram ME, Bilici M, Tekin SB. The importance of the glucose-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib. Future Oncol. (2021) 17:4545–59. doi: 10.2217/fon-2021-0457
15. Hannarici Z, Yılmaz A, Buyukbayram ME, Turhan A, Çağlar AA, Bilici M, et al. The value of pretreatment glucose-to-lymphocyte ratio for predicting survival of metastatic gastric cancer. Future Oncol. (2023) 19:315–25. doi: 10.2217/fon-2022-0579
16. Park SH, Kang IC, Hong SS, Kim HY, Hwang HK, Kang CM. Glucose-to-lymphocyte ratio (GLR) as an independent prognostic factor in patients with resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma-cohort study. Cancers (Basel). (2024) 16:1844. doi: 10.3390/cancers16101844
17. Ni J, Li Z, Song W, Zhang H, Wang Y, Zhang Y, et al. Prognostic value of glucose to lymphocyte ratio for patients with renal cell carcinoma undergoing laparoscopic nephrectomy: A multi-institutional, propensity score matching cohort study. Front Surg. (2022) 9:911411. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.911411
18. Yang M, Zhang Q, Ge YZ, Tang M, Hu CL, Wang ZW, et al. Prognostic roles of glucose to lymphocyte ratio and modified glasgow prognosis score in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:871301. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.871301
19. Zhang XW, Ge YZ, Song MM, Ruan GT, Xie HL, Hu CL, et al. Prognostic power of nutrition-inflammation indicators in patients with breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. (2023) 23:e312–21. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2023.04.009
20. Liu L, Zhang BB, Li YZ, Huang WJ, Niu Y, Jia QC, et al. Preoperative glucose-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts survival in cancer. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1284152. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1284152
21. Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. (2010) 25:603–5. doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z
22. Huedo-Medina TB, Sánchez-Meca J, Marín-Martínez F, Botella J. Assessing heterogeneity in meta-analysis: Q statistic or I2 index? Psychol Methods. (2006) 11:193–206. doi: 10.1037/1082-989X.11.2.193
23. Zeng YF, Wei XY, Guo QH, Chen SY, Deng S, Liu ZZ, et al. The efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 in treatment of glioma: a single-arm meta-analysis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1168244. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1168244
24. Duval S, Tweedie R. Trim and fill: A simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometric. (2000) 56:455–63. doi: 10.1111/j.0006-341X.2000.00455.x
25. Aydin İC, Subasi IE, Sunar AO, Ademoglu S, Gulmez S, Dincer M, et al. GLR in colorectal cancers: an easily accessible prognostic marker. Int J Gen Med. (2024) 17:2361–9. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S463769
26. Yilmaz H, Nigdelioglu B, Aytac A, Turan M, Oktay E, Yersal O, et al. The prognostic importance of glucose-to-lymphocyte ratio and uric acid in metastatic breast cancer patients treated with Cdk 4/6 inhibitors. Future Oncol. (2022) 18:3043–53. doi: 10.2217/fon-2022-0464
27. Zhang Y, Xu Y, Wang D, Kuang T, Wu W, Xu X, et al. Prognostic value of preoperative glucose to lymphocyte ratio in patients with resected pancreatic cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. (2021) 26:135–44. doi: 10.1007/s10147-020-01782-y
28. Zhong A, Cheng CS, Kai J, Lu R, Guo L. Clinical significance of glucose to lymphocyte ratio (GLR) as a prognostic marker for patients with pancreatic cancer. Front Oncol. (2020) 10:520330. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.520330
29. Liu J, Hu X. Association between glucose-to-lymphocyte ratio and in-hospital mortality in acute myocardial infarction patients. PloS One. (2023) 18:e0295602. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295602
30. Zhang Y, Zhang S. Prognostic value of glucose-to-lymphocyte ratio in critically ill patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: A retrospective cohort study. J Clin Lab Anal. (2022) 36:e24397. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24397
31. Chen Y, Tang S, Wang Y. Prognostic value of glucose-to-lymphocyte ratio in critically ill patients with acute pancreatitis. Int J Gen Med. (2021) 14:5449–60. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S327123
32. Hotamisligil GS. Inflammation, metaflammation and immunometabolic disorders. Nature. (2017) 542:177–85. doi: 10.1038/nature21363
33. Hirakawa Y, Ninomiya T, Mukai N, Doi Y, Hata J, Fukuhara M, et al. Association between glucose tolerance level and cancer death in a general Japanese population: the Hisayama Study. Am J Epidemiol. (2012) 176:856–64. doi: 10.1093/aje/kws178
34. Wild AT, Ye X, Ellsworth SG, Smith JA, Narang AK, Garg T, et al. The association between chemoradiation-related lymphopenia and clinical outcomes in patients with locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Am J Clin Oncol. (2015) 38:259–65. doi: 10.1097/COC.0b013e3182940ff9
35. Li W, Zhang X, Sang H, Zhou Y, Shang C, Wang Y, et al. Effects of hyperglycemia on the progression of tumor diseases. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. (2019) 38:327. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1309-6
36. Rice CM, Davies LC, Subleski JJ, Maio N, Gonzalez-Cotto M, Andrews C, et al. Tumour-elicited neutrophils engage mitochondrial metabolism to circumvent nutrient limitations and maintain immune suppression. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:5099. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07505-2
37. Li W, Liu H, Qian W, Cheng L, Yan B, Han L, et al. Hyperglycemia aggravates microenvironment hypoxia and promotes the metastatic ability of pancreatic cancer. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. (2018) 16:479–87. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2018.10.006
38. Wang B, Smyl C, Chen CY, Li XY, Huang W, Zhang HM, et al. Suppression of postprandial blood glucose fluctuations by a low-carbohydrate, high-protein, and high-omega-3 diet via inhibition of gluconeogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:1823. doi: 10.3390/ijms19071823
39. Coussens LM, Werb Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature. (2002) 420:860–7. doi: 10.1038/nature01322
40. Zhao H, Wu K. Effect of hyperglycemia on the occurrence and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Am J Transl Res. (2024) 16:2070–81. doi: 10.62347/NYHH3132
41. Zou Z, Li J, Ji X, Wang T, Chen Q, Liu Z, et al. Naples prognostic score as an independent predictor of survival outcomes for resected locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients after neoadjuvant treatment. J Inflammation Res. (2023) 16:793–807. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S401446
42. Koliaraki V, Prados A, Armaka M, Kollias G. The mesenchymal context in inflammation, immunity and cancer. Nat Immunol. (2020) 21:974–82. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0741-2
43. Kishton RJ, Sukumar M, Restifo NP. Metabolic regulation of T cell longevity and function in tumor immunotherapy. Cell Metab. (2017) 26:94–109. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.06.016
44. McMillan DC. Systemic inflammation, nutritional status and survival in patients with cancer. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. (2009) 12:223–6. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e32832a7902
45. Clark EJ, Connor S, Taylor MA, Madhavan KK, Garden OJ, Parks RW. Preoperative lymphocyte count as a prognostic factor in resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. HPB (Oxford). (2007) 9:456–60. doi: 10.1080/13651820701774891
Keywords: glucose-to-lymphocyte ratio, tumor, prognosis, meta-analysis, survival
Citation: Liu R, Shen Y, Cui J, Ma W, Wang J, Chen C and Wang W (2024) Association between glucose to lymphocyte ratio and prognosis in patients with solid tumors. Front. Immunol. 15:1454393. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1454393
Received: 03 September 2024; Accepted: 22 November 2024;
Published: 06 December 2024.
Edited by:
Giuseppe Bronte, University of Ferrara, ItalyReviewed by:
Mansoor-Ali Vaali-Mohammed, King Saud University, Saudi ArabiaHester Doyle, Yale University, United States
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Shen, Cui, Ma, Wang, Chen and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Weixing Wang, d2FuZ3d4QHdodS5lZHUuY24=; Chen Chen, YXBwcmVjaWF0aW9uQHdodS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Rongqiang Liu
Rongqiang Liu Yankun Shen
Yankun Shen Jiahui Cui
Jiahui Cui Wangbin Ma
Wangbin Ma Jianguo Wang1
Jianguo Wang1 Chen Chen
Chen Chen Weixing Wang
Weixing Wang