
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Immunol. , 13 November 2024
Sec. Vaccines and Molecular Therapeutics
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1448408
This article is part of the Research Topic SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines Beyond the Pandemic Era View all 24 articles
Objective: Pakistan has been seriously affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, with numerous waves of infection. Using different vaccine and booster doses was a key component to control and combat this pandemic. This study aims to monitor the heterologous and homologous booster vaccination doses that generate immune responses in healthy adults after 9 months of vaccination.
Methods: In this cross-sectional, observational study a total of 173 samples were collected. Participants from both genders (Male and Female) between the ages of 18 to 25 years were enrolled for the study. Participants who had booster shots of homologous Sinopharm BBIBP CorV and heterologous Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines were included only, with the use of a Roche Cobas-e601 analyzer, the antibody titers in the blood serum were quantified by the ECLIA method. IBM SPSS 22 was utilized for descriptive statistical analysis and P< 0.05 was considered significant.
Results: In this study the IgG antibody levels were measured against the full length of receptor binding domain (RBD) of the spike (S) protein. The mean antibody titer in the Pfizer group was 9764 ± 10976 U/mL and 5762 ± 4302 U/mL in the Sinopharm group. The Mean IgG antibody levels of the Pfizer-vaccinated group were significantly higher than the Sinopharm-vaccinated group (P=0.000, each). Comparing the Sinopharm BBIBP CorV booster dosage to the Pfizer booster, Pfizer BNT162b2demonstrated a stronger immune response. However, there were no immunological gender-specific significant differences. The administration of a third dosage of Pfizer BNT162b2 after two doses of BBIBP CorV
Conclusion: The administration of a third dosage of Pfizer BNT162b2 after two doses of BBIBP-CorV is recommended to boost the humoral immune response in the general population while there was no gender-specific difference observed. More effectiveness can be attained by administering additional doses due to the antibody decay.
The Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) has emerged as one of the greatest challenges to humanity since World War II. The economies of various countries have been severely affected due to this pandemic, significantly the economy of Developing countries like Pakistan (1). Pakistan faced six waves of the COVID-19 pandemic from June 2020 to April 2023. According to the published reports more than 1,580,327 infected cases and 30,654 deaths have been confirmed in Pakistan due to the COVID-19 pandemic till April 16, 2023 (2).
In the absence of targeted therapeutics and drugs, innate and acquired immunity were the primary defenders against SARS-CoV-2. The entry of the foreign elements (Viruses) triggers the initiation of an immune response with the establishment of immune memory. The neutralizing antibodies present in the serum that persist for an extended duration offer long-lasting protection (3). Hence induction and reinforcement of the humoral response through vaccination is considered as the fundamental strategy for effectively controlling and managing COVID-19 infection. Within the humoral response, the production of antibodies ensures the elimination of viruses and the relative prevention of infection (4).
The government of Pakistan launched a massive immunization campaign by establishing various vaccine deployment centers in all districts of the country. A wide range of vaccines were deployed, offering diverse mechanisms of action comprising mRNA vaccines, namely Moderna mRNA-1273 and Pfizer BNT162b2; inactivated vaccines, including Sinopharm and CoronaVac Sinovac; and non-replicating viral vector-based vaccines, such as AstraZeneca, CanSino/PakVac, and Sputnik V (1).
Despite the initial stages of vaccination, the risk of the pandemic persisted. Several factors contributed to reinfection, including vaccine hesitancy, the mutation of the spike protein, and the decay of COVID-19 neutralizing antibodies. In light of these factors, researchers advised the administration of booster shots to enhance protection against the deadly virus. The booster shots for the COVID-19 vaccine were also deployed by the Government of Pakistan, however only 48.04 million vaccinees received the third booster dose (5).
A booster dose refers to an extra administration of the vaccine. This booster dose may consist of the same product used in the initial series (homologous) or a different product (heterologous) (6).
The Pfizer BioNTech (BNT162b2) is an mRNA-based vaccine that has been modified to encode a complete spike protein. In phase I and II clinical trials, the analysis of immune responses revealed the induction of Th1-skewed activity in the majority of participants. Elevated amounts of T-cell growth factor (IL-2), lymphokine-12 (IL-12), and type II interferon (IFN) were found in the assays, which provided proof of this. Th1-skewed activity refers to a preferential activation and dominance of Th1 cells, which are a specific subset of CD4+ T cells. It is worth noting that T-cell immune responses have a longer duration and contribute to the establishment of long-term immunity. The phase III clinical trials demonstrated a vaccine efficacy of 95%, particularly among the older and more vulnerable population. Importantly, no instances of serious toxicity were observed during these trials (7). A non-significant difference between vaccinated females and males were observed, when anti-S1 and anti-RBD antibody levels were analyzed in the subjects who were injected with mRNA vaccine for SARS-CoV-2 (8). Inoculation of supplementary or booster doses of mRNA vaccines may present a viable approach for substantially augmenting the immunogenicity elicited by standalone inactivated virus vaccines. Consequently, this strategy holds the potential to confer protection against both established and emerging variants, thus bolstering overall efficacy (9, 10).
Beijing Bio-institute of Biological Products (BBIBP)/Sinopharm tested beta-propiolactone inactivated whole virus as a COVID-19 vaccine candidate with an alum adjuvant. Clinical trials carried out during the initial stage of COVID-19 demonstrated that BBIBP-CorV exhibited sufficient effectiveness in minimizing new infections and COVID-19-associated deaths caused by SARS-CoV-2. The expected protective effectiveness was 78.89% (95% CI 65.79%, 86.97%), while vaccine effectiveness, considering person-years of follow-up, was 78.07% (95% CI 64.82%, 86.33%). Notably, there were no significant differences in vaccine efficacy between males and females, with point estimates of 78.4% and 75.6%, respectively. These findings support the safety and effectiveness of BBIBP-CorV in a real-world deployment (11).
The Sinovac vaccine is believed to operate using a similar approach as Sinopharm, but mRNA vaccines are considered better surrogates according to studies. For those who received the classical vaccines Sinopharm/Sinovac or those facing challenges with their immunity, a booster dose is recommended (12, 13). The heterologous regimen of mRNA vaccine with initial two doses of inactivated vaccine was found more effective against SARS CoV-2 new variants (14). The deployment of heterologous booster shots for protection against Coronavirus, enhances immune response by increasing both the functionality and quantity of T follicular helper (Tfh) cells. This promotes B-cell activation and antibody production. The mechanism of presenting varied antigens, activates innate immune pathway and enhances CD4 T-cell responses. This mechanism results in higher number of antibody producing cells and enhanced cross protection against different variants of virus, leading to more robust and strong immune response (15).
This prospective observational study aims to monitor heterologous and homologous vaccine booster doses induced IgG antibody response of two different vaccines BBIBP CorV Sinopharm and Pfizer BNT162b2 in healthy adults and to estimate gender-specific immune response differences. The antibody IgG levels were measured after 9 months of administration of a booster dose to monitor antibody decay. Monitoring post-vaccination immune response and antibody production among vaccinees after valuable outcomes will aid in the selection of the most efficacious vaccine in the future and a more targeted approach can be implemented to control pandemics.
This observational study was conducted at the University of the Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan, between February 2022 and March 2023. The research was approved by ethical review committees of the University of the Punjab, Lahore, the University of Lahore, Combined Military Hospital, Lahore, and CMH Lahore Medical College, Lahore Pakistan (File no. 2265-TRG).
The study included participants of both genders (male and female) aged between 18 and 25 years. The participants underwent a full vaccination regimen, nine months prior to onset of this study, i.e. received first two doses of an inactivated whole virus vaccine (either Sinopharm or Sinovac) and also received booster doses of Pfizer and Sinopharm, respectively. A total of 173 samples (of which 95 females and 78 males) of both genders were collected from four places: the University of Punjab, the University of Lahore, CMH Lahore Medical College, and the Combined Military Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan. The ratio of male to female was 54.9% (females) and 45.1% (males) respectively. Using vaccination cards provided by Pakistan’s National Database and Registration Authority (NADRA), the participants’ age and immunization status were confirmed. Informed written and verbal consent was obtained from all participants or their legal guardians. The confidentiality of the data was assured to the respondents.
Participants with a history of active or previous infection with COVID-19, recent or incomplete vaccination, or any documented medical condition were excluded from the study, after taking a detailed medical history of last three years. Additionally, individuals with comorbidity or undergoing treatment with antibiotics, corticosteroids, or immunosuppressants were also excluded from the study population.
Informed consent, both verbal and written, was obtained from all participants, with a strong emphasis on maintaining the confidentiality of their data. 3 ml of venous blood was collected from each participant, which was carefully collected using aseptic procedures by trained lab staff and added to serum collection tubes. The cellular residue was separated from the serum, and the resulting serum was stored in capped vials at a temperature of -80°C until further analysis. Approximately 1.5 ml aliquots were utilized for the analysis.
To analyze the immune response of anti-SARS-CoV-2 RBD antibodies, the Roche Diagnostics test kit entitled (Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2) was employed. The measurement and quantitative analysis of immunoglobulin G (IgG) were carried out using the electrochemiluminescence immunoassay (ECLIA) double antigen sandwich method on a fully automated Hitachi Cobas e601 analyzer. The assay kit’s measuring range spanned from 0.40 to 250 U/ml, with a concentration threshold of >0.80 U/ml. In case exceeding the kit’s range, dilutions of 1:10, 1:100, or 1:400 were applied using the manufacturer-provided diluents (Roche diluents universal 2 for Elecsys Cobas e-analyzers).
Before sample analysis, the Roche Cobas e601 analyzer underwent calibration and quality control procedures to ensure optimal performance. Each test kit had a capacity of 200 samples. The Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S kit (Roche Diagnostics) exhibited a manufacturer’s claimed level of precision of 99.98% and sensitivity of 98.8% (16).
Version 22 of IBM SPSS was used for the descriptive statistical study. Categorical variables were presented as frequencies and percentages. Numerical variables were presented as standard deviations. Independent t-test was employed to assess the difference in antibody levels between male and female participants, of both vaccines. Univariate regression analysis was applied to evaluate the impact of gender and vaccine type on mean antibody titer levels. A significance level of p<0.05 was considered statistically significant for this study.
The mean age of the participants was 22 years. Of the 173 participants, 79 received booster doses of Pfizer-BNT162b2, while 94 received a booster of Sinopharm BBIBP-CorV, as shown in Table 1.
The Pfizer-BNT162b2 group had a mean antibody level of 9764 ± 10976 U/ml, while the Sinopharm BBIBP-CoV group had a mean antibody level of 5762 ± 4302 U/ml, as illustrated in Figure 1. With a p-value of 0.001, the difference between the two groups was found to be statistically significant.
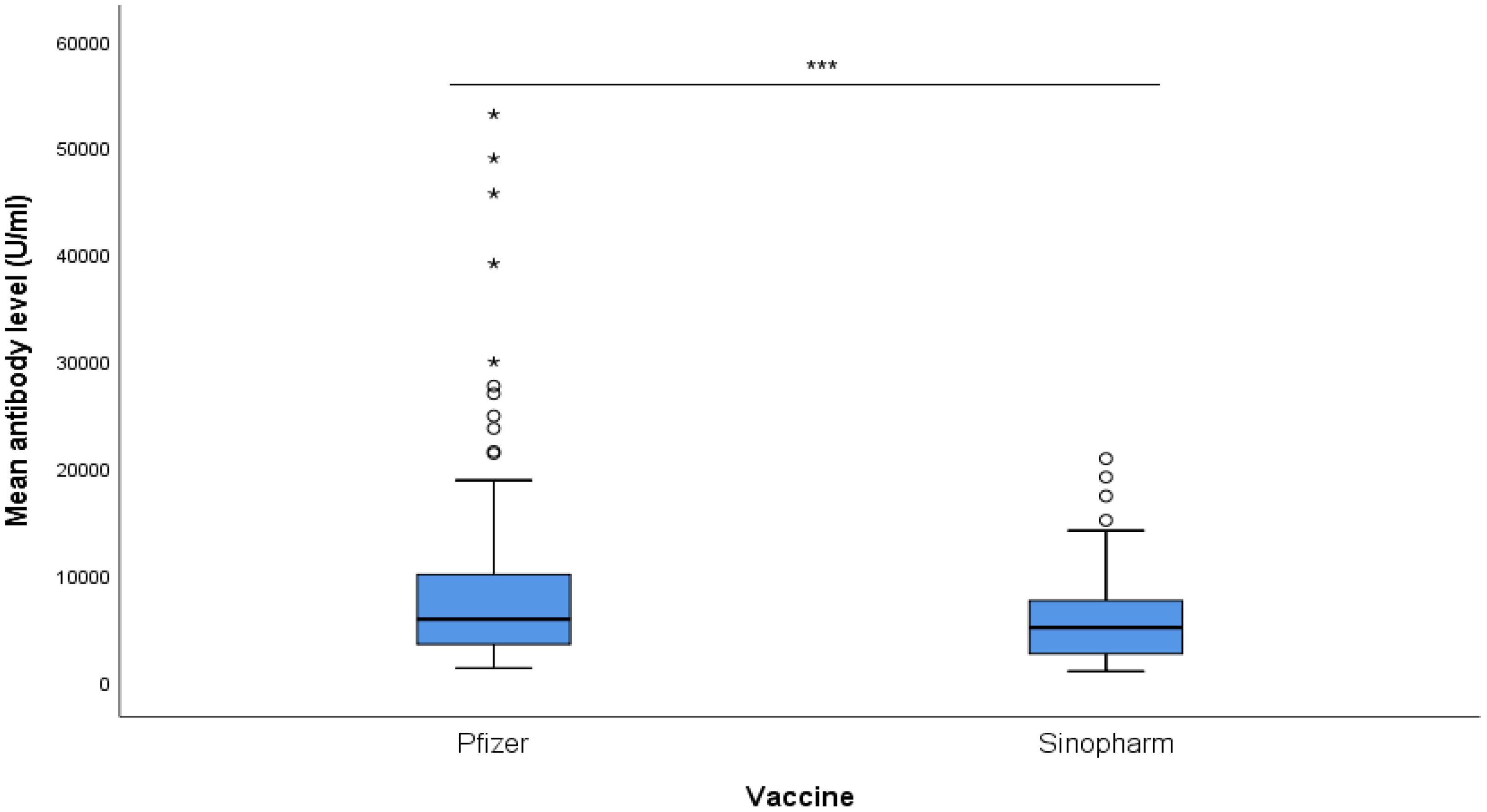
Figure 1. Mean antibody level (U/ml) of Pfizer and Sinopharm vaccine groups, illustrated in Box plot (n=173). *** - p<0.001. No statistically significant difference was observed between the mean antibody levels of males and females, receiving either Pfizer or Sinopharm booster dose. Gender-wise comparisons of mean antibody levels in Pfizer and Sinopharm groups are visualized in Table 2 and Figure 2. "asterisk" these symbols indicates levels of significant differences, greater the number of asterisks greater will be the significant differences.
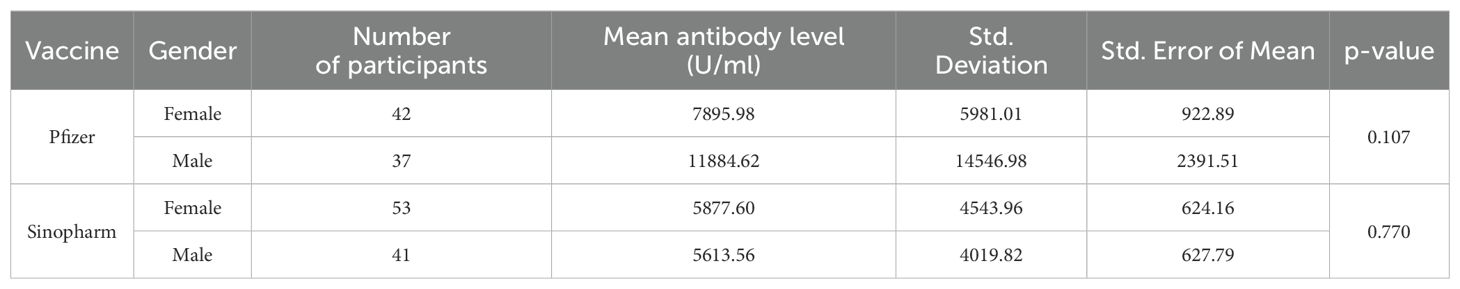
Table 2. Gender-wise comparison of mean antibody level (U/ml) in Pfizer and Sinopharm vaccine group (n=173).
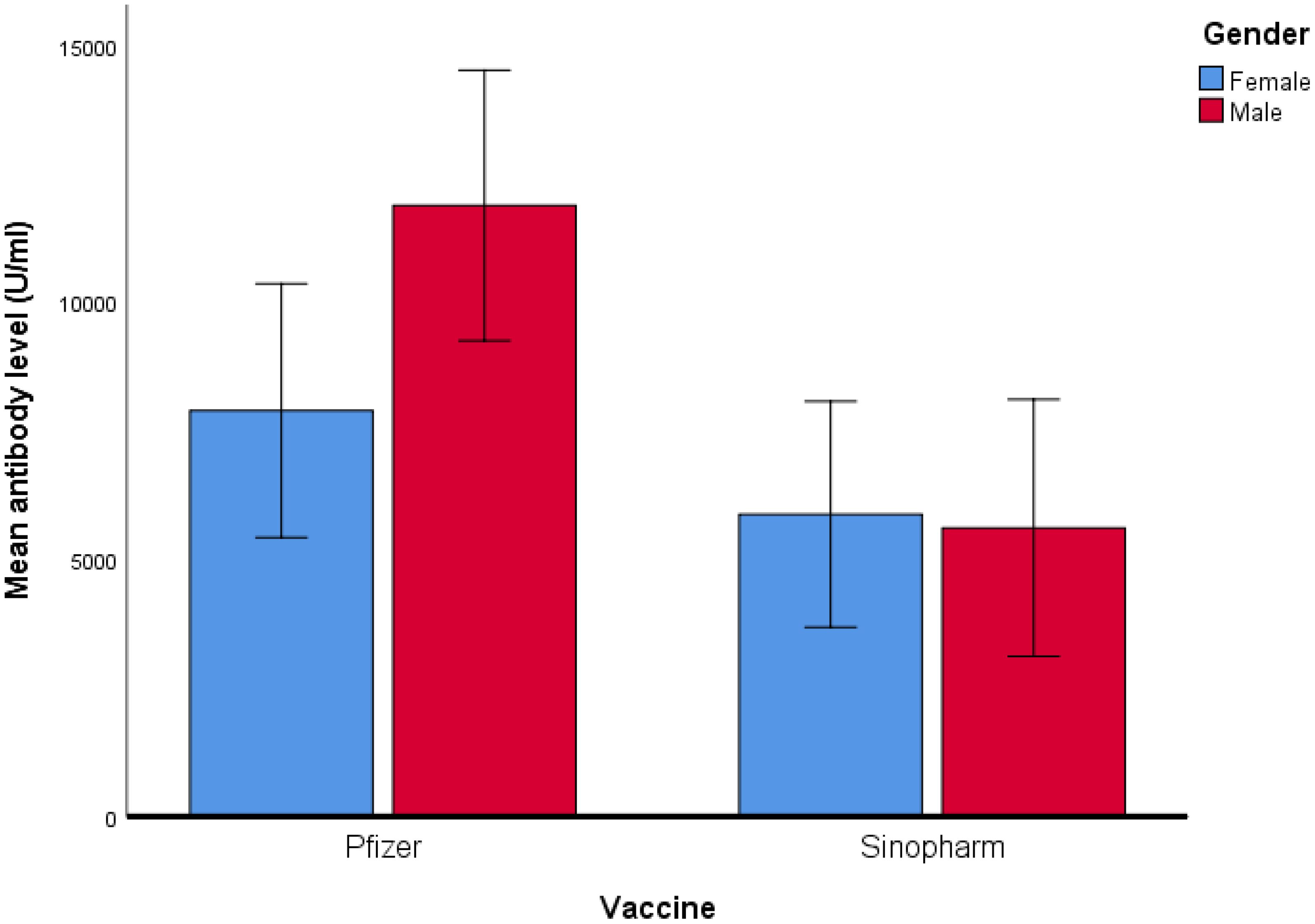
Figure 2. Comparison of mean antibody level (U/ml) in Pfizer and Sinopharm vaccine group (n=173). Log10 algorithm was applied to transform the data, followed by univariate linear regression to observe the impact of gender and different types of vaccines on mean antibody level. Table 3A reveals a significantly higher mean antibody level in the Pfizer group, as compared to the Sinopharm group. However, the difference in mean antibody levels between males and females was not statistically significant, as detailed in Table 3B.
This observational study was undertaken to compare heterologous Pfizer and homologous Sinopharm (booster doses) of the COVID-19 vaccinations, when Omicron variant of SARS-COV-2 was predominant in Pakistan (17). The samples of both genders (Male & Female) for antibody IgG analysis were collected after 9 months post-Covid-booster dosage. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first study conducted in Pakistan on the effectiveness and comparison of booster doses of COVID-19 vaccination. Our findings demonstrate that both heterologous and homologous vaccine booster doses generated anti-SARS-CoV-2 RBD antibodies, which play a crucial role in mitigating COVID-19. However, antibody responses were different. It was observed in other findings that receiving a third dose of the vaccine during both the Delta- and Omicron-predominant periods was found to be extremely effective at reducing the number of COVID-19-related hospitalizations. Reduction in severe COVID-19-related cases is associated to a timely administration of the booster doses (18).
As the production of antibodies ensures the elimination of viruses and prevents infection. This investigation determines that deployment of a heterologous vaccine regimen consisting of Pfizer BNT162b2 with two initial doses of Sinopharm induces a more effective antibody response when compared to a homologous vaccination comprising Sinopharm. These findings emphasize the advantage of combining different vaccine formulations to enhance immunogenicity. In previous studies, it was observed that a BNT162b2 booster elicited a greater immune response after two ChAdOx1 priming doses than after three doses of ChAdOx1. BNT162b2 was recommended by Keskin et al. as a booster following two CoronaVac priming doses (19). It was also noticed in a national study conducted on subjects aged 60 and above that those who received a third dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine had a much lower incidence of confirmed COVID-19 and severe disease (20). The delivery of the third dose mRNA vaccine was also supported by various clinical trials. Our results are in line with the studies showing an increase in antibody levels following a third dose of the COVID-19 vaccine BNT162b2 (21, 22).
However, in our previous published study (23), the immunity developed in same age group by two doses of Pfizer BNT162b2 remained superior (Male mean: 15,899.71& Female mean: 9401.01) to immune response produced by heterologous administration of Pfizer BNT162b2 booster dose after an initial two doses of inactivated virus vaccine regimen (Male mean: 11884.62& Female mean: 7895.98) measured in this study. The performance of Pfizer BNT162b2 as a third dose demonstrated its effectiveness greater when compared with a homologous regimen of inactivated booster doses (Table 2). While the comparison between the mean of antibody levels of just two doses of inactivated vaccine measured in our previous study (Male mean: 5301.054& Female mean: 5024.72) and those measured in this study with inactivated booster dose have minimal differences which indicates least effectiveness of inactivated whole virus vaccine as booster dose than mRNA i.e. Pfizer BNT162b2 vaccine. The homologous vaccination regimen of Pfizer BNT 162b2 (three doses of mRNA vaccine) could be a better option than heterologous regimen in order to develop more durable and stronger immune response. It was observed that when serum-neutralizing antibodies were analyzed after the administration of the initial two doses (findings of our previous study) and after the administration of a third inactivated vaccine dose (findings of our current study) the IgG antibodies demonstrated minimum variance. A possible factor of the least efficacy of inactivated whole virus vaccines might be due to the decline of antibodies with time. To investigate the factors contributing to decline of the immune response elicited by inactivated virus vaccines requires rigorous and extensive research endeavors. However, when comparing inactivated vaccine with mRNA vaccines in recent studies it was reported that inactivated vaccines as a booster resulted notably lower frequency of adverse effects when compared to mRNA vaccines. There is limited data available in which adverse effects of inactivated vaccine booster dosage are reported (9, 24, 25).
While monitoring neutralizing activities of vaccines, Sinopharm BBIBP-CorV showed least neutralization activity against both Delta and Omicron variants. A homologous booster dose improved neutralizing response, but in some cases it still lose its activity against Omicron variant, demonstrating low immunogenicity when compared to mRNA vaccine doses. While Sinopharm vaccine resulted in significant escape from vaccine-induced immune response by Omicron sub-variant (26), studies using mouse models suggested that mRNA vaccines, specially the Wuhan strain (WT) receptor binding domain, produce efficient neutralizing antibodies against other various sub-variants, however, their efficacy against Omicron is minimal. Interestingly, an mRNA vaccine for Omicron variant generates high concentration of antibodies but it is least effective for other variants. In contrast, hybrid vaccines provide greater protection against all COVID-19 sub-variants and highlights its importance for booster strategies in enhancing immune responses and managing variant escape (27).
In studies, it was reported that females generally display strong innate and acquired immunogenecity than males. Which leads to produce higher antibody response. Key hormones such as estrogen and testosterone are linked with higher concentration of antibodies in females and lower concentration in males respectively. Moreover genetic factors play crucial role: as female X chromosomes harbor additional immune related genes when compared with Y chromosomes in males. The sex related immunogenecity is also dependant on age. The older female demonstrated better efficacy than males although adverse reactions don’t necessarily reduce with age (28). However, in this study antibodies generated by mRNA booster doses in males were found significantly greater than females while in Sinopharm group there was a non-significant difference observed in male and female induced antibodies after administration of boosters. This pattern was also observed in our previous published study on same age group sample (23).
Many previous studies demonstrated that BNT162b2 is highly effective in preventing severe SARS-CoV-2 infection and mortality, particularly in those with declining immunity after primary immunization, and that booster doses of vaccination are probably required to limit SARS-CoV-2 transmission. The outcome of this study is consistent with the findings of various previous studies (29, 30) as antibody levels produced by Pfizer BNT162b2 as a booster dose demonstrated favorable outcomes while evaluation. To address the concern of wanning of immunity, a fourth vaccine dose is recommended, this strategy is already implemented in countries such as Israel, the United Kingdom, and the United States of America. The fourth dose was found to be more effective than the third dose (25).
One limitation of this study is its small sample size, while another concern is the absence of analysis for cellular immune response induced by the vaccines as this observation is entirely based on antibody response. Therefore, future research campaigns must address the important factors responsible for antibody decay. It is crucial to conduct large-scale population-based research to ensure perfect outcomes, with the surveillance of cellular immune responses.
The Pfizer BNT162b2 booster dose immunization generated a significantly stronger immune response when compared to the booster dose of inactivated whole virus vaccine booster i.e. Sinopharm BBIBP-CorV. Hence, the Pfizer BNT162b2 booster dosage significantly raised antibody levels, indicating a vaccination approach that would offer superior defense against different SARS-COV-2 subtypes. Gender-Specific differences were non-significant, indicating that gender had no impact on vaccine effectiveness. These findings support the advice of Pfizer BNT162b2 (mRNA vaccine) booster dose administration since it provides promising protection. An additional booster dose of vaccines can develop a more durable immune response due to the decay of antibodies.
This study will be helpful for several health authorities for the deployment of COVID-19 vaccines and their booster doses which provide higher immune response, in the future. The study will facilitate subjects who have vaccine-induced lower immune response to select suitable booster doses. Future studies may focus on finding the reason for the decline of antibodies even after the administration of booster doses.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
The studies involving humans were approved by ethical review committee of University of the Punjab, Lahore, Combined Military Hospital Lahore (CMH) and CMH Lahore Medical College, Lahore, Pakistan (File no.2265-TRG). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
NR: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MB: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. MR: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Resources, Writing – review & editing. SZ: Investigation, Resources, Software, Writing – review & editing. HF: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. For this study, all types of funding were provided by the Centre for Clinical and Nutritional Chemistry, School of Chemistry University of the Punjab, Lahore. Technical and instrumental support for this study was provided by the Department of Pathology, Combined Military Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan.
We are thankful to CMH Lahore and Roche Diagnostics Pakistan for helping us in this study by collecting samples and providing kits for analysis respectively. We are also grateful to the University of Lahore and CMH Lahore Medical College for allowing us for Data Collection. We highly appreciate the passion of the participants who took part in this study actively.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Mustafa ZU, Maqbool F, Wahid M, Salman M, Haroon S, Khan YH, et al. Short-term adverse effects of COVID-19 vaccines after the first, second, and booster doses: a cross-sectional survey from Punjab, Pakistan, and the implications. SciELO Brasil. (2023) 56:e0044–2023. doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0044-2023
2. Amjad Z, Maryam I, Munir M, Salman M, Baraka MA, Mustafa ZU, et al. Covid-19 vaccines status, acceptance and hesitancy among maintenance hemodialysis patients: a cross-sectional study and the implications for Pakistan and beyond. MDPI Vaccines. (2023) 11:904. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11050904
3. Chowdhury MA, Hossain N, Kashem MA, Shahid MA, Alam A. Immune response in COVID-19: A review. J Infection Public Health. (2020) 13:1619–29. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.001
4. Melenotte C, Silvin A, Goubet AG, Lahmar I, Dubuisson A, Zumla A, et al. Immune responses during COVID-19 infection. OncoImmunology. (2020) 9:1807836. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2020.1807836
5. Ahmad M, Sattar A, Aroosa S, Majeed A, Rasheed MA, Ahmad W, et al. Attitude and acceptance towards COVID-19 booster doses among literacy advantaged population in Pakistan: A cross-sectional study. MDPI Vaccines. (2023) 11:1238. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11071238
6. Hause AM. Safety monitoring of COVID-19 vaccine booster doses among adults—United States, September 22, 2021–February 6, 2022. Morbidity Mortality Weekly Rep (MMWR. (2022) 71:249. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/71/wr/pdfs/mm7107e1-H.pdf. CDC.
7. Walsh EE, Frenck RW Jr, Falsey AR, Kitchin N, Absalon J, Gurtman A, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of two RNA-based Covid-19 vaccine candidates. New Engl J Med. (2020) 383:2439–50. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa202790
8. Wheeler SE, Shurin GV, Yost M, Anderson A, Pinto L, Wells A, et al. Differential antibody response to mRNA COVID-19 vaccines in healthy subjects. Microbiol Spectr. (2021) 9:e0034121. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00341-21
9. Yavuz E, Günal Ö, Başbulut E, Şen A. SARS-CoV-2 specific antibody responses in healthcare workers after a third booster dose of CoronaVac or BNT162b2 vaccine. J Med Virol. (2022) 94:3768–75. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27794
10. Galvan V, Quarleri JJG. Comparison of antibody and T cell responses elicited by BBIBP-CorV (Sinopharm) and BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 in healthy adult humans. Geroscience. (2022) 44:57–61. doi: 10.1007/s11357-021-00501-3
11. Wang C, Chen LY, Lu QB, Cui F. Vaccination with the inactivated vaccine (Sinopharm BBIBP-corV) ensures protection against SARS-coV-2 related disease. MDPI Vaccines. (2022) 10:920. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10060920
12. Bayram A, Demirbakan H, Günel Karadeniz P, Erdoğan M, Koçer I. Quantitation of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein after two doses of CoronaVac in healthcare workers. J Med Virol. (2021) 93:5560–7. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27098
13. Alqassieh R, Suleiman A, Abu-Halaweh S, Santarisi A, Shatnawi O, Shdaifat L, et al. Pfizer-BioNTech and Sinopharm: a comparative study on post-vaccination antibody titers. MDPI Vaccines. (2021) 9:1223. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9111223
14. Lau CS, Oh MLH, Phua SK, Liang YL, Li Y, Huo J, et al. Kinetics of the Neutralizing and Spike SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies following the Sinovac Inactivated Virus Vaccine Compared to the Pfizer mRNA Vaccine in Singapore. MDPI Antibodies. (2022) 11:38. doi: 10.3390/antib11020038
15. Song Y, Wang J, Yang Z, He Q, Bao C, Xie Y, et al. Heterologous booster vaccination enhances antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 by improving Tfh function and increasing B-cell clonotype SHM frequency. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1406138. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1406138
16. Poljak M, Valenčak AO, Štamol T, Seme K. Head-to-head comparison of two rapid high-throughput automated electrochemiluminescence immunoassays targeting total antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 nucleoprotein and spike protein receptor binding domain. J Clin Virol. (2021) 137:104784. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2021.104784
17. Bukhari AR, Ashraf J, Kanji A, Rahman YA, Trovão NS, Thielen PM, et al. Sequential viral introductions and spread of BA. 1 across Pakistan provinces during the Omicron wave. BMC Genomics. (2023) 24:432. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09539-3
18. Thompson MG, et al. Effectiveness of a third dose of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19–associated emergency department and urgent care encounters and hospitalizations among adults during periods of Delta and Omicron variant predominance—VISION Network, 10 States, August 2021–January 2022. Morbidity Mortality Weekly Rep (MMWR). (2022) 71(4):139–45. Available online at: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/71/wr/mm7104e3.htm?s%5C_cid=mm7104e3%5C_x (Accessed January 28, 2022).
19. Keskin AU, Bolukcu S, Ciragil P, Topkaya AE. SARS-CoV-2 specific antibody responses after third CoronaVac or BNT162b2 vaccine following two-dose CoronaVac vaccine regimen. J Med Virol. (2022) 94:39–41. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27350
20. Bar-On YM, Goldberg Y, Mandel M, Bodenheimer O, Freedman L, Kalkstein N, et al. BNT162b2 vaccine booster dose protection: A nationwide study from Israel. New Engl J Med. (2021). doi: 10.1101/2021.08.27.21262679
21. Barda N, Dagan N, Cohen C, Hernán MA, Lipsitch M, Kohane IS, et al. Effectiveness of a third dose of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine for preventing severe outcomes in Israel: an observational study. Lancet. (2021) 398:2093–100. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02249-2
22. Saciuk Y, Kertes J, Shamir Stein N, Ekka Zohar A. Effectiveness of a third dose of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine. J Infect Dis. (2022) 225:30–3. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiab556
23. Rizvi NB, Farooq H, Khan QA, Rana MZ, Zaffar S, Shahid M, et al. Comparative analysis of igG antibody titers induced by three different SARS-COV-2 vaccines in healthy adults of Pakistan. Curr Microbiol. (2023) 80:373. doi: 10.1007/s00284-023-03485-9
24. Yue L, Xie T, Yang T, Zhou J, Chen H, Zhu H, et al. A third booster dose may be necessary to mitigate neutralizing antibody fading after inoculation with two doses of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. J Med Virol. (2022) 94:35. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27334
25. Çağlayan D, Süner AF, Şiyve N, Güzel I, Irmak Ç, Işik E, et al. An analysis of antibody response following the second dose of CoronaVac and humoral response after booster dose with BNT162b2 or CoronaVac among healthcare workers in Turkey. J Med Virol. (2022) 94:2212–21. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27620
26. Wang X-J, Yao L, Zhang HY, Zhu KL, Zhao J, Zhan BD, et al. Neutralization sensitivity, fusogenicity, and infectivity of Omicron subvariants. Genome Med. (2022) 14:146. doi: 10.1186/s13073-022-01151-6
27. Lee I-J, Sun CP, Wu PY, Lan YH, Wang IH, Liu WC, et al. A booster dose of Delta× Omicron hybrid mRNA vaccine produced broadly neutralizing antibody against Omicron and other SARS-CoV-2 variants. J Biomed Sci. (2022) 29:49. doi: 10.1186/s12929-022-00830-1
28. Jensen A, Stromme M, Moyassari S, Chadha AS, Tartaglia MC, Szoeke C, et al. COVID-19 vaccines: Considering sex differences in efficacy and safety. Contemp Clin Trials. (2022) 115:106700. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2022.106700
29. Arbel R, Hammerman A, Sergienko R, Friger M, Peretz A, Netzer D, et al. BNT162b2 vaccine booster and mortality due to Covid-19. New Engl J Med. (2021) 385:2413–20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2115624
Keywords: COVID-19, virus, vaccine, booster, homologous model
Citation: Rizvi NB, Bibi M, Rana MZ, Zaffar S and Farooq H (2024) Comparison of antibody responses of heterologous and homologous Covid-19 booster vaccination: an observational study. Front. Immunol. 15:1448408. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1448408
Received: 13 June 2024; Accepted: 04 October 2024;
Published: 13 November 2024.
Edited by:
Shisan (bob) Bao, The University of Sydney, AustraliaReviewed by:
Akihiko Sakamoto, Yamaguchi University, JapanCopyright © 2024 Rizvi, Bibi, Rana, Zaffar and Farooq. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Nayab Batool Rizvi, bmF5YWJiYXRvb2wuY2hlbUBwdS5lZHUucGs=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.