- 1Department of Pediatrics, Xiangyang Central Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Arts and Science, Xiangyang, Hubei, China
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Children’s Digital Health and Data Center, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, China
PIM1, the proviral integration site for Moloney murine leukemia virus, is a member of the serine/threonine protein kinase family. It is involved in many biological events, such as cell survival, cell cycle progression, cell proliferation, and cell migration, and has been widely studied in malignant diseases. However, recent studies have shown that PIM1 plays a prominent role in immunoinflammatory diseases, including autoimmune uveitis, inflammatory bowel disease, asthma, and rheumatoid arthritis. PIM1 can function in inflammatory signal transduction by phosphorylating multiple inflammatory protein substrates and mediating macrophage activation and T lymphocyte cell specification, thus participating in the development of multiple immunoinflammatory diseases. Moreover, the inhibition of PIM1 has been demonstrated to ameliorate certain immunoinflammatory disorders. Based on these studies, we suggest PIM1 as a potential therapeutic target for immunoinflammatory diseases and a valid candidate for future research. Herein, for the first time, we provide a detailed review that focuses on the roles of PIM1 in the pathogenesis of immunoinflammatory diseases.
1 Introduction
The proviral integration site for Moloney murine leukemia virus (PIM) is a family of serine/threonine protein kinases that include PIM1, PIM2, and PIM3. They are abnormally expressed in many oncologic diseases and have become an important therapeutic target for cancer (1). Among them, PIM1 was the first member to be discovered and has been studied the most. It is involved in various biological processes, such as cell survival, the cell cycle, cell proliferation and migration (2–4). Although PIM1 has been established to have a role in cancer progression, there is increasing evidence for wider pathological roles of PIM1 within the context of immunoinflammatory diseases, including Lupus nephritis (LN) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (5–7).
The PIM gene is a proto-oncogene encoding a serine/threonine protein kinase. The oncogene PIM1, which has an open reading frame and encodes a protein of 313 amino acids, is frequently activated by provirus insertion in murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomas. The structure prediction of PIM1 is shown in Figure 1. It spans six exons and is preceded and followed in all reading frames by stop codons (8). The murine PIM1 gene encodes a 44 kDa protein (PIM1L) and a 34 kDa protein (PIM1S) (9). PIM1L is synthesized via alternate translation starting at an upstream CUG codon and is the amino-terminal extension of PIM1S (10). The nucleotide AUG at positions 431–433 is the start codon for PIM1S, and the nucleotide CUG at sites 158–160 is the start codon for PIM1L (11). The expression of PIM1, irrespective of patient age or sex, is widespread and ranges from the haematopoietic and lymphoid system to the synovium and kidney (7, 9, 12).
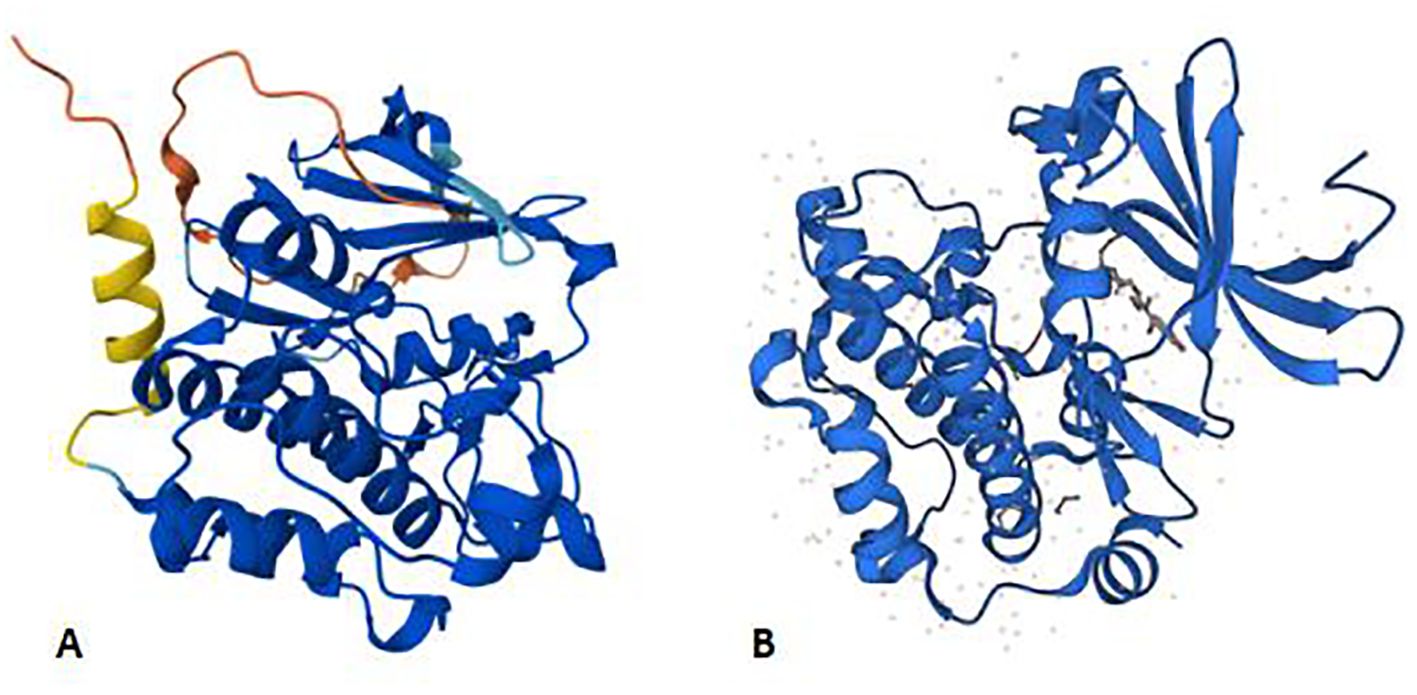
Figure 1. Panels (A, B) shows the AlphaFold structure prediction of murine PIM1 and human PIM1, respectively. Both of them consist of 313 amino acids. AlphaFold produces a per-residue model confidence score (pLDDT) between 0 and 100 to represent the model confidence. Very high (pLDDT > 90) High (90 > pLDDT > 70) Low (70 > pLDDT > 50) Very low (pLDDT < 50).
Protein kinases can catalyse phosphorylation, which is one of the most significant posttranslational modifications of proteins and has been demonstrated to be a basic regulatory mechanism of cellular processes, including signal transduction, autophagy, and cell fate determination (4). Targeting the specific kinases that regulate the production of inflammatory mediators is one of the main treatment methods used to alleviate dysregulated inflammation in immunoinflammatory diseases (13). As a member of the serine/threonine protein kinase family, PIM1 plays a key role in inflammatory signal transduction through the phosphorylation of various inflammatory protein substrates, such as protein kinase B (AKT) and nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB), thereby mediating macrophage activation and T lymphocyte cell differentiation, which contributes to the occurrence and development of immunoinflammatory diseases (12, 14, 15). As expected, recent studies have shown the treatment effect of PIM1 inhibitors on multiple immunoinflammatory diseases. This review mainly analyses the key roles of PIM1 in the pathogenesis of immunoinflammatory diseases and reveals PIM1 as an emerging target for treating inflammatory disorders of the immune system.
2 Regulatory mechanism of PIM1
2.1 JAK/STAT signaling pathway
A variety of ligands, such as cytokines and growth factors, and their receptors activate the Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducers of activated transcription (STAT) pathway (16). The four JAK proteins and the seven STAT proteins mediate intracellular signal transduction downstream of cytokine receptors, which participate in the pathology of allergic, autoimmune, and inflammatory diseases (17). Furthermore, abundant evidence has emerged in recent years that the overproduction of cytokines, especially interleukin-6 (IL-6), may cause the pathogenesis of some immunoinflammatory disorders (18). Therefore, the JAK/STAT signaling pathway and IL-6 have become attractive therapeutic targets for numerous immunoinflammatory diseases (19, 20).
Substantial evidence has shown that the JAK2/STAT3 pathway is one of the upstream regulatory pathways of PIM1 (21–23). Further study revealed that IL-6, a proinflammatory cytokine, can bind to its receptor and activate the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway, thus upregulating the expression of PIM1 (24, 25). Notably, PIM1 inhibitors can suppress the phosphorylation of IκB kinase, which contributes to the decreased NF-κB activity (26). Moreover, PIM1 has been demonstrated to phosphorylate p65/RelA, thereby increasing NF-κB activity and IL-6 production, which in turn enhances PIM1 expression and creates a positive feedback loop (27). In addition, transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1)-binding protein 3 (TAB3) regulates PIM1 expression by promoting STAT3 phosphorylation and activation through the formation of the TAB3–TAK1–STAT3 complex (28). In addition, PIM1 has already been revealed as one of the first known target genes of STAT5 (29, 30), and limited evidence indicates that STAT4 and STAT6 also regulate PIM1 expression (31). In contrast to the PIM1–NF-κB–IL-6 axis, PIM1 can modulate the JAK2/STAT3/5 signaling pathway by interacting with suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1) and SOCS3, resulting in a negative feedback loop in the JAK2-STAT3/5-PIM1 axis (Figure 2) (22, 32, 33). Overall, PIM1 plays an essential role in the crosstalk between the JAK2-STAT3/5 pathway and the NF-κB–IL-6 pathway, which are attractive targets for treating immunoinflammatory diseases.
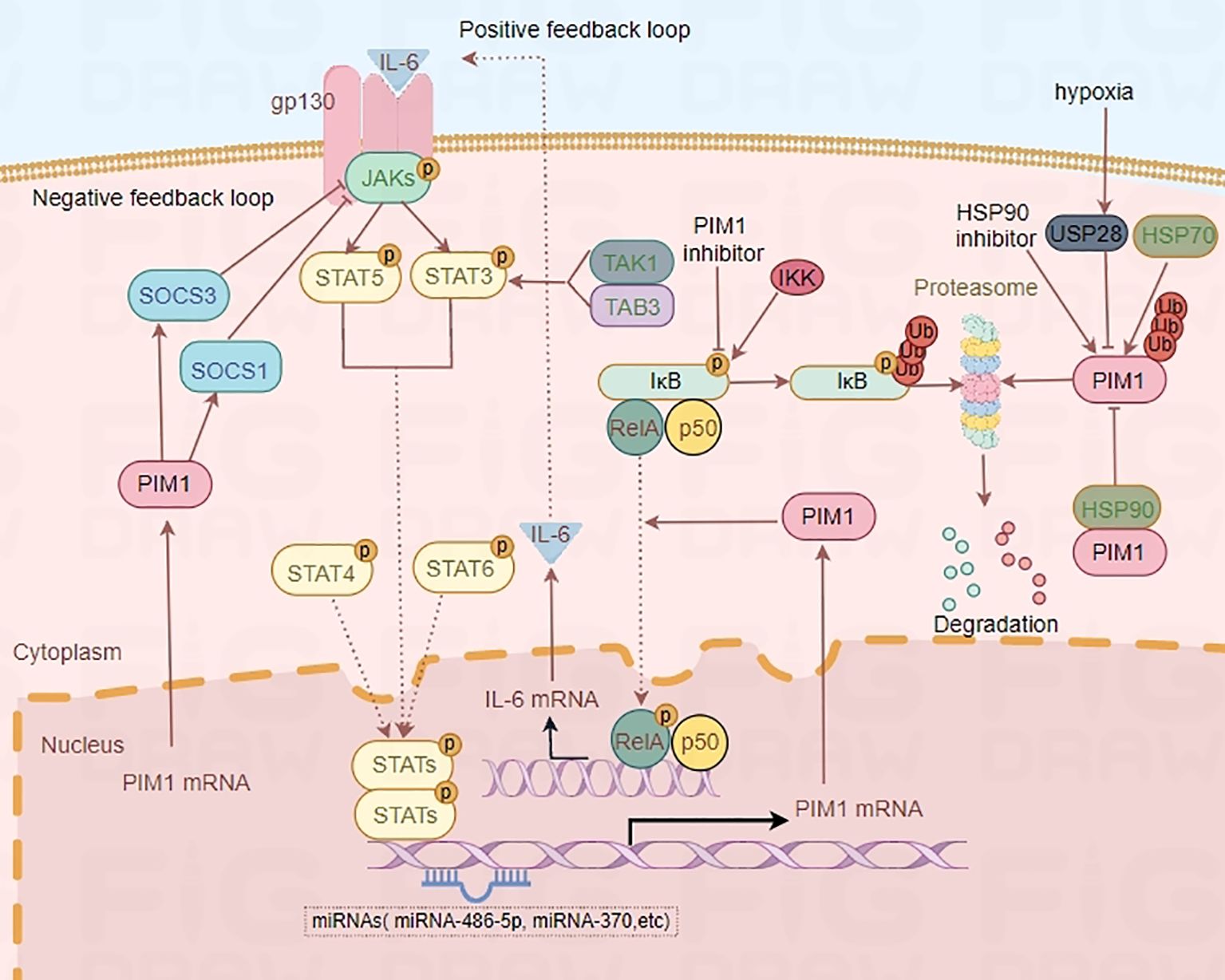
Figure 2. Regulatory mechanism of PIM1. IL-6-STAT3/5-PIM1 axis increases NF-κB activity and IL-6 production, which in turn enhances PIM1 expression and creates a positive feedback loop. However, PIM1 kinase can also modulate the JAKs/STAT3/5 signaling pathway by interacting with SOCS1 and SOCS3, and result in a negative feedback loop in JAKs-STAT3/5-PIM1 axis. Moreover, HSP90 and hypoxia-induced overexpression of USP28 can protect PIM1 from proteasomal degradation while HSP70 is associated with the degradation of PIM1 by ubiquitin.
2.2 MicroRNAs
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), which are single-strand endogenous and noncoding RNA molecules with a length of approximately 22 nucleotides, have emerged as a principal group of gene expression regulators related to a wide spectrum of biological processes through the modulation of the translation and stability of their target mRNAs (34). MiRNAs, which are crucial for the progression of immunoinflammatory diseases (35, 36), play a vital role in B- and T-lymphocyte development, megakaryocytopoiesis, monocytopoiesis, and granulopoiesis, as demonstrated in mice with deficient or overexpressed copies of particular miRNAs (37). In a preclinical study, miRNA-486-5p expression was found to be significantly correlated with the expression of IL-6, IL-8, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interferon-γ (IFN-γ). Further cell experiments revealed that miRNA-486-5p could target histone acetyltransferase 1 (HAT1) to regulate the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-triggered inflammatory response of alveolar macrophages (38). In addition, exosomal miRNA-486-5p derived from rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes (RA-FLSs) induces osteoblast differentiation through the Tob1/BMP/Smad pathway, contributing to the pathogenesis of RA (35). Accordingly, it can be inferred that upregulated miRNA-486-5p is involved in the inflammatory response and immunoinflammatory diseases. Many lines of evidence suggest that the proinflammatory factor PIM1 is a target gene of miRNA-486-5p, which can negatively regulate the expression of PIM1 through binding to the PIM1 mRNA 3’-UTR and mediate cellular oxidative stress, cell proliferation, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition (39–41). Therefore, we deduced that the miRNA-486-5p/PIM1 axis may play a role in the immunoinflammatory response. miRNA-370 was also found to act as a tumor suppressor that targets PIM1 gene expression, thus regulating glycolysis in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines (42, 43). In addition to miRNA-486-5p and miRNA-370, other miRNAs, such as miRNA-33a, miRNA-328-3p, and miRNA-1294, have also been revealed to target the PIM1 gene directly (42–46). However, most of the miRNA/PIM1 axes have been studied in malignant conditions, and further studies are needed to determine the role of miRNAs/PIM1 in immunoinflammatory diseases.
2.3 HSP90 and the ubiquitin−proteasome pathway
Heat shock proteins (HSPs) are molecular chaperones that participate in the refolding of misfolded proteins, thus contributing to the maintenance of cellular homeostasis (47). These proteins can be classified into several families, such as HSP70, HSP90, HSP110, and chaperonin. HSP90 is involved in many cellular processes, such as apoptosis, autophagy, and the immune response, since it has abundant protein substrates (48, 49). The ubiquitin−proteasome pathway plays key roles in almost all cellular processes, in which proteins tagged with certain types of polyubiquitin chains are specifically recognized and removed by the proteasome (50). A study revealed that overexpressed deubiquitinase ubiquitin-specific protease 28 (USP28) in hypoxia condition regulated the stability of PIM1 by reducing its ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation (51). In addition, it has been reported that HSP90 and the ubiquitin−proteasome pathway jointly participate in regulating the stability of PIM1 (52). In that study, HSP90 was found to protect PIM1 from proteasomal degradation, while HSP70 was associated with the degradation of PIM1 by ubiquitin (52). Specifically, PIM1 physically interacts with HSP90α and HSP90β and is rapidly degraded upon exposure to the HSP90-specific inhibitor geldanamycin (53). Moreover, similar to PIM1, HSP90α expression is controlled by a signal from the cytokine receptor gp130. These findings suggest that HSP90 is coregulated with PIM1 and contributes to PIM1 stabilization and functionality (53).
3 The role of PIM1 in classical macrophage activation
Macrophages are heterogeneous cells that play a vital role in inflammatory and tissue reparative responses. Their activation or deactivation by different signals in the contexts of microorganisms, the tissue microenvironment, and cytokine signals partially imprints this diversity (54). There are two main polarization states of macrophages: classically activated macrophages (M1) and alternatively activated macrophages (M2), which display pro- and anti-inflammatory phenotypes, respectively. The polarization state of macrophages is dependent on molecules in the microenvironment, including several cytokines and chemokines (55). Numerous studies have shown that M1 macrophages can be activated by lipopolysaccharides (LPS) or T helper 1 (Th1) cell cytokines such as IFN-γ (56, 57). M1 macrophages can also produce proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-6, IL-23 and TNF-α, which are involved in Th1 and Th17 cell differentiation (58, 59), while disruption of this intricate crosstalk by blocking IL-6 or IL-23 function alters these conditions (60). In addition, classically activated macrophage-derived exosomes are also reported to aggravate immune-mediated disorders by boosting Th1 and Th17 responses (61). It follows that classical macrophage activation plays a key role in Th1 and Th17 differentiation, promoting chronic inflammation and the occurrence of immunoinflammatory disease.
PIM1 expression was found to be significantly induced in RAW264.7 cells activated by LPS (62), which may be attributed to the overproduction of IL-6 by activated macrophages. Many lines of evidence suggest that activation of the NF-κB pathway and the Nod-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome promotes macrophage activation, while inhibition of these pathways can downregulate the M1 phenotype of macrophages and ameliorate inflammatory diseases (58, 63). PIM1, a downstream effector of many cytokine signaling pathways, plays a proinflammatory role in immunoinflammatory disease. It has been shown to activate NF-κB signaling by phosphorylating RelA/p65 Ser276 to defend against ubiquitin-mediated degradation and recruit RelA/p65 to kappa B-elements after TNF-α stimulation, while PIM1 knockdown weakens IL-6 production by interfering with RelA/p65 activation (64). Many studies have shown that PIM1 inhibitors such as SMI-4a and KMU-470 can also suppress macrophage inflammatory responses by inhibiting the upregulation of a major component of the inflammasome complex, NLRP3, and the phosphorylation of IκB kinase and NF-κB (26, 65). A recent study indicated that suppression of PIM1 by SMI-4a specifically blocks the oligomerization of apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD (ASC) in the assembly stage and rapidly inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in mouse and human macrophages (66). Taken together, these findings indicate that PIM1 plays a vital role in activating inflammatory signaling, which contributes to classical macrophage activation, and PIM1 inhibitors are potential anti-inflammatory agents for treating immunoinflammatory diseases.
4 The role of PIM1 in CD4+ T-cell differentiation
T-cell differentiation is a highly regulated, multistep process that is essential for the immunological response. Once activated, naïve CD4+ T cells differentiate into distinct cytokine-producing Th subsets. By producing lineage-specific cytokines, effector Th subsets play significant roles in regulating immune responses and are involved in the pathogenesis of many immunoinflammatory diseases, including autoimmunity, allergies, and asthma (67).
Accumulating evidence has shown that inhibiting PIM1 reduces the proportion of Th17 cells and increases the proportion of regulatory T cells (Tregs) in patients with immunoinflammatory diseases (15, 62), likely due to the regulatory effects of PIM1 on the AKT/Forkhead box O1 (FOXO1) signaling pathway and Forkhead box protein 3 (FOXP3) phosphorylation (Figure 3) (14, 15). Moreover, as we mentioned before, PIM1 plays a vital role in classical macrophage activation, which also contributes to Th1 and Th17 differentiation. However, Buchacher et al. demonstrated that PIM kinases inhibit early Th17 cell differentiation and control the Th1/Th17 axis in healthy individuals, potentially via STAT1 and STAT3 (68). This contradiction may be attributed to the different stages of Th differentiation and the different health conditions of individuals.
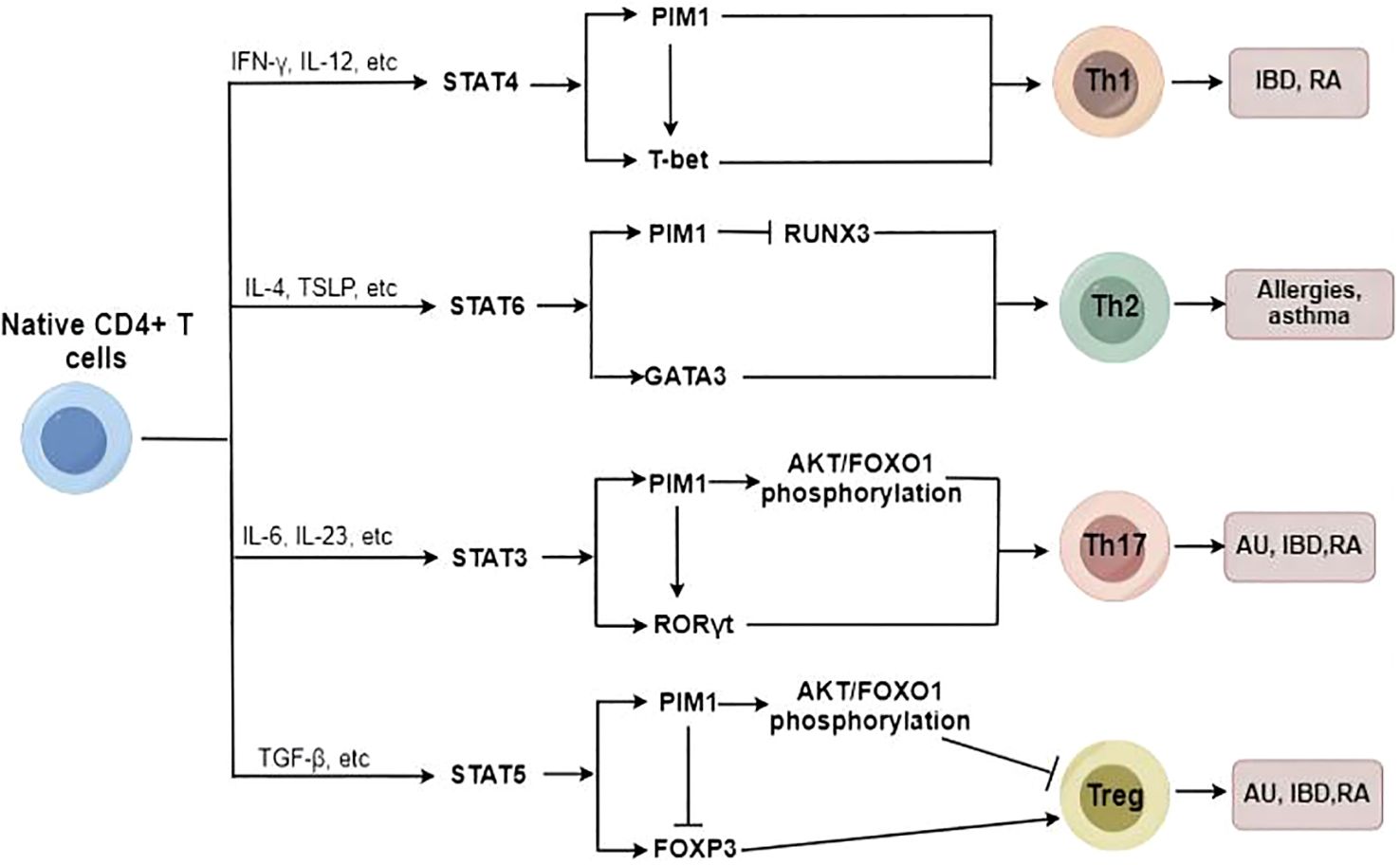
Figure 3. The potential role of PIM1 in Native CD4+ T cell differentiation. PIM1 plays an essential role in promoting Th17/Th1/Th2 cell differentiation and inhibiting Treg cell differentiation under abnormal immunoinflammatory conditions.
In addition, PIM1 plays a critical role in regulating Th2 cell differentiation, and inhibition of PIM1 suppresses Th2 cell differentiation by enhancing Runt-related transcription factor 3 (RUNX3) expression (69). In addition to regulating Th2/Th17/Treg cell differentiation, PIM1 also acts as a potent promoter of Th1 cell differentiation. The PIM1 protein levels can be strongly upregulated by Th1-specific cytokines such as IL-12 and IFN-α in immunocytes (70), and PIM1 accordingly is involved in regulating IL-12/STAT4 signaling, which is a critical pathway in Th1 cell differentiation (31). Therefore, PIM1 inhibition has been identified as a protective measure to reduce the proinflammatory immune response through the downregulation of excessive Th1-type immune responses (62).
Overall, PIM1 plays an essential role in promoting Th17/Th1/Th2 cell differentiation to varying degrees and inhibiting Treg cell differentiation under abnormal immunoinflammatory conditions; thus, targeting PIM1 has the potential to attenuate the imbalance of T-cell subsets and ameliorate immunoinflammatory diseases.
5 The relationship between PIM1 and immunoinflammatory diseases
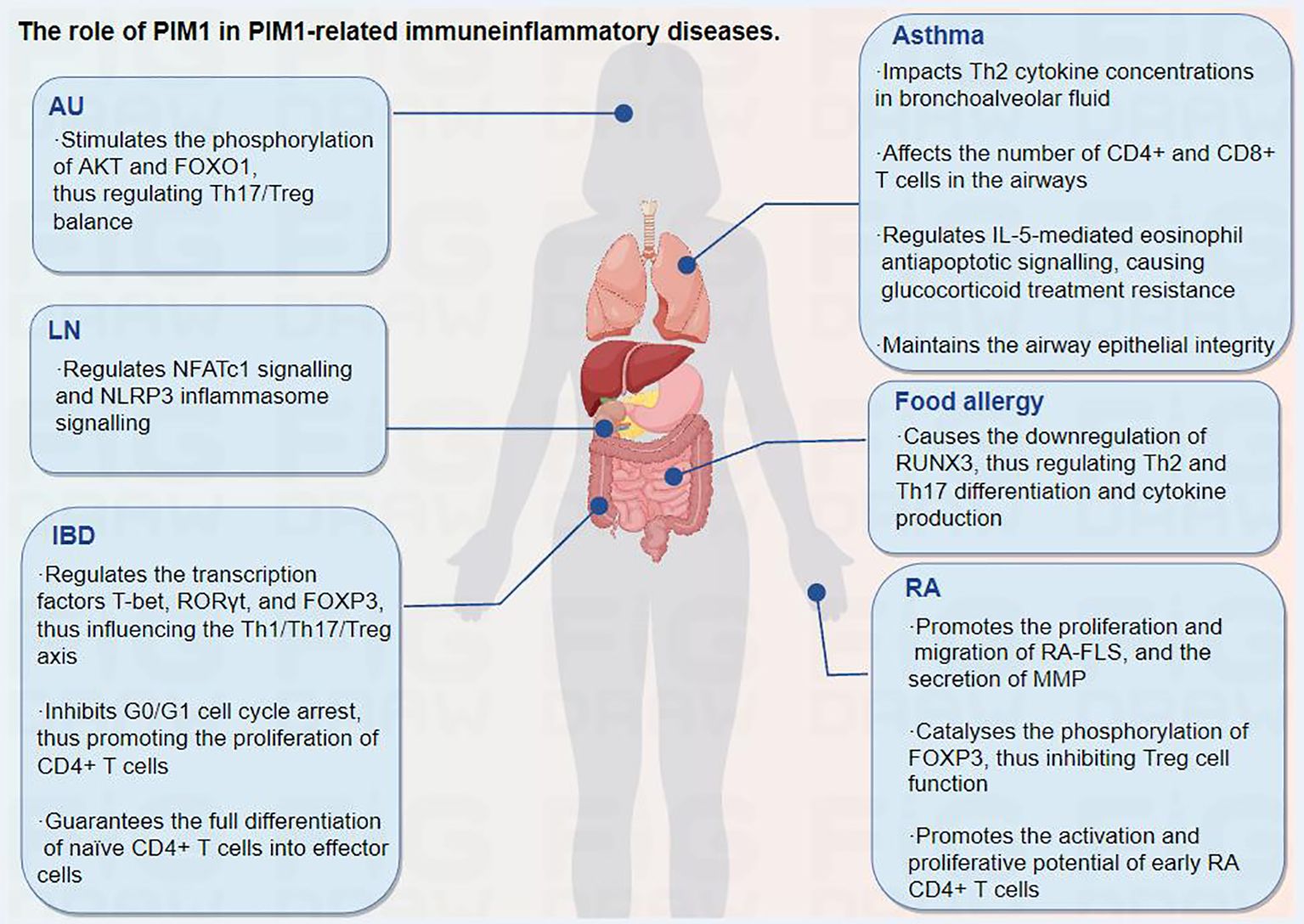
5.1 PIM1 and AU
Autoimmune uveitis (AU), a sight-threatening disease affecting ocular tissues such as the ciliary body, vitreous body, choroid and retina, is initiated by the aberrant activation of CD4+ T cells and subsequent recruitment of inflammatory cells (granulocytes, monocytes/macrophages) to the eyes, which ultimately causes tissue impairment and potentially leads to blindness (71, 72). Strikingly, enhanced pathogenicity of Th17 cells and an imbalance of the Th17/Treg axis have been identified as key reasons for the pathogenesis of AU (73–75). In addition, an imbalanced Th1/Th2 ratio, caused by activation of the Notch signaling pathway, also contributes to the occurrence of AU (75). Thus, modulating CD4+ T-cell homeostasis may serve as a measure to prevent abnormal immunoinflammatory responses and improve the pathological condition of AU. Accumulating evidence suggests that the phosphoinositide 3 kinase (PI3K)/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathway plays an important role in regulating Th17/Treg homeostasis in autoimmune diseases (76–78). Specifically, AKT can regulate T-cell differentiation through the negative regulation of FOXO1. When FOXO1 is located in the nucleus, it enhances the function of Treg cells by maintaining the expression of FOXP3 but inhibits the differentiation of Th17 cells by inhibiting the expression of retinoid-related orphan receptor gamma t (RORγt) (79–81). However, phosphorylated AKT can directly phosphorylate FOXO1, thereby inducing FOXO1 to leave the nucleus. It becomes sequestrated in the cytosol and loses its regulatory function in Th17 cells and Treg cells (81, 82). Therefore, it is plausible that restoring proper regulation of the AKT/FOXO1 pathway may serve as a potential measure to facilitate Th17/Treg homeostasis in AU.
Recent studies have revealed the upregulation of PIM1 in T-cell subsets in animal models of experimental AU (15, 83). In addition, human uveitis, Vogt−Koyanagi−Harada disease (VKH), is characterized by the overexpression of PIM1 in CD4+ T cells and plasma cells, and PIM1 inhibition decreases the expansion of CD4+ T and B cells (15). Rac1 and the inhibitor of differentiation (ID2)/PIM1 axis were found to potentiate the pathogenicity of Th17 cells during EAU (74). Kurarinone, a major component of the traditional Chinese medicine Sophorae Flavescentis Radix, can regulate the Th17/Treg balance and ameliorate AU via Rac1 and ID2/PIM1 axis inhibition (74). In another recent study, progesterone was also found to improve the Th17/Treg imbalance by reversing the ID2/PIM1 axis, thereby alleviating the pathogenicity of Th17 cells in AU (84).
Moreover, the immunosuppressor mycophenolate mofetil can improve abnormal immune cell activation in AU by reducing the expression of several pathogenic factors, including PIM1 (83). In addition, a recent multicellular immunokinetic study reported that PIM1 can promote an imbalance of Th17 and Treg cells, while inhibition of PIM1 activity reduces the ratio of Th17 cells and increases the ratio of Treg cells, thereby restoring the Th17/Treg cell balance in AU (15). Further study revealed that PIM1 can stimulate the phosphorylation of AKT and FOXO1 in total CD4+ T cells, resulting in an abnormal AKT/FOXO1 pathway and contributing to the Th17/Treg cell imbalance in AU, which can be ameliorated by PIM1 inhibition (Figure 4) (15). Overall, PIM1, which is aberrantly expressed in AU, is involved in mediating the Th17/Treg imbalance, and targeting PIM1 may be a promising therapeutic approach for AU.
5.2 PIM1 and IBD
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, refers to a group of refractory and chronic inflammatory disorders of the gastrointestinal tract that are primarily diagnosed during adolescence and young adulthood, with an increasing incidence in pediatric populations (85). Therefore, IBD has been increasingly recognized as a serious, worldwide health-care problem. IBD is thought to be caused by an aberrant and continuing mucosal immune response to the intestinal microflora, strongly affected by a genetic predisposition of the individual (85, 86). Numerous studies have shown that IBD development is accompanied by an enhanced immune response and decreased immune tolerance, which results from immune activation of Th17 and Th1 cells and a reduction in the number of Treg cells (87–89). Dysregulation of this balance between effector T-cell subsets, especially the Th17/Treg axis, leads to chronic inflammation and autoimmunity in IBD (89).
It has been revealed that PIM1 expression is positively correlated with the degree of intestinal inflammation in experimental murine IBD models, suggesting that PIM1 signaling participates in the intestinal inflammatory response (90). Further studies revealed that inhibition of PIM1 reduces the mRNA and protein expression of transcription factors, including T-box expressed in T cells (T-bet) and RORγt, which are important for Th1 and Th17 differentiation from naïve T cells, respectively, and increases the mRNA and protein levels of the specific expression factor FOXP3 in Treg cells, thus improving the imbalance of T-cell subsets and attenuating mucosal inflammatory damage (62, 91, 92).
Moreover, classically activated macrophages play pivotal roles in IBD, and PIM1 inhibitors can reduce the proinflammatory response in IBD by inhibiting the hyperactivation of macrophages (62). In addition, the inhibition of PIM1 results in G0/G1 cell cycle arrest, which inhibits the proliferation of CD4+ T cells without compromising their ability to survive (93). Naïve CD4+ T cells are unable to fully differentiate into effector cells in vitro and in vivo in the absence of PIM1 kinase activity. Thus, PIM1 kinase activity may contribute to sustained disease severity, as evidenced by the successful use of a PIM1 inhibitor as a therapeutic measure in an IBD model mediated by CD4+ T cells (93). In general, PIM1 plays an important role in CD4+ T-cell proliferation and differentiation, and inhibition of PIM1 kinase activity may provide therapeutic benefit in IBD.
5.3 PIM1 and RA
RA is a chronic, autoimmune inflammatory disease that mainly impacts the joints and periarticular soft tissues, leading to joint inflammation, destruction, and even disability (94). To date, there is no cure for RA, and the treatment effect varies across patients, indicating an undetermined pathogenic diversity (95). Nonetheless, early and accurate diagnosis is still crucial for optimal therapeutic success in RA, especially for patients with high risk factors for a poor prognosis. The immune response composition of RA synovial tissue includes congenital (e.g., monocytes, dendritic cells, innate lymphocytes) and adaptive (e.g., Th1, Th17, B cells, and plasma cells) immune responses, as well as strong tissue inflammatory responses that aggravate joint destruction (95, 96).
Excessive STAT3 activation and dysregulated STAT3 signaling in CD4+ T cells have been proposed as early pathophysiologies in the clinical phase of RA (97). A clinical study demonstrated that the STAT3 target genes PIM1, B-cell leukemia-3 (BCL3), and SOCS3 in peripheral blood CD4+ T cells from treatment-naïve RA patients show the strongest differential regulation, with each gene’s expression highly associated with paired intracellular phospho-STAT3 (5). Furthermore, in a meta-analysis of 279 patients, the majority of the signature’s capacity to distinguish between RA patients was mediated via the same three genes, independent of age, joint involvement, or acute phase response (5). It follows that the dysregulation of PIM1, SOCS3 and BCL3 in circulating CD4+ T cells, which is mediated by aberrant STAT3 activation, is a distinguishing feature of early RA that occurs independently of the acute phase response. As such, PIM1 is also upregulated in the RA synovium, T cells, macrophages and RA-FLSs (12).
Moreover, significant suppression of RA-FLS proliferation, migration, and matrix metalloprotease (MMP) secretion from stimulated RA-FLSs was found upon PIM1 knockdown or AZD1208 administration. The phosphorylation levels of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) response element binding protein and extracellular signal-regulated kinase in RA-FLSs were notably affected by PIM1 knockdown (12). These results suggest that PIM1 can serve as a novel regulator of the invasive and aggressive behavior of RA-FLSs, which indicates its potential as a target for RA treatment.
PIM1 has been implicated in the cytokine-dependent proliferation and survival of T lymphocytes (31). In addition, PIM1 can specifically catalyse the phosphorylation of the FOXP3 Ser422 site, thus negatively regulating the transcriptional activity of FOXP3 and inhibiting Treg cell function (14). A recent clinical study showed that PIM1 levels are upregulated in synovial CD4+ T cells from patients with early RA. Further ex vivo research indicated that the activation and proliferative potential of early RA CD4+ T cells stimulated by the overproduction of proinflammatory cytokines such as IFN-γ and IL-17 and the reduced proportion of FOXP3+ Treg cells are reversed by exposure to PIM1 kinase inhibitors, thus effectively alleviating arthritis progression and cartilage destruction (98). In addition, a dual IL-1 receptor-associated kinase-4 (IRAK4)/PIM1 inhibitor has also been found to function by blocking TLR/myeloid differentiation factor-88 (MYD88)-mediated crosstalk of NF-κB activation, inhibiting the JAK/STAT pathway and PIM1 expression, thus improving RA conditions (6). Taken together, PIM1 plays a critical role in regulating the invasive and aggressive behavior of RA-FLSs and diagnosing RA in the early phase, which indicates its great potential as a target for RA treatment.
5.4 PIM1 and allergic diseases
Allergic diseases, which include eczema, atopic dermatitis, allergic asthma, and food allergy, are systemic disorders resulting from an impaired immune system. The constantly rising incidence rates of these disorders, along with their high recurrence rates, are creating a significant medical and socioeconomic burden and drawing increasing amounts of attention. Many factors, including the living environment, the maternal-foetal environment, genetics, epigenetics, and the immune system, play complex roles in the pathogenesis of allergic illnesses (99).
Asthma, one of the most common chronic, noncommunicable diseases in children and adults, is characterized by variable restriction of airflow and leads to variable respiratory symptoms (100). The development of allergic asthma is influenced mostly by allergen-specific Th2 cells and pulmonary Th2 cell responses (101), and glucocorticoid administration is an effective treatment for steroid-sensitive asthma (102). It has been revealed that pulmonary PIM1 concentrations are increased in mouse models of asthma after ovalbumin sensitization and challenge (103). Moreover, inhibition of PIM1 kinase activity prevents the development of goblet cell metaplasia, eosinophilic airway inflammation, and airway hyperresponsiveness and increases Th2 cytokine concentrations in bronchoalveolar fluid in a dose-dependent manner, revealing the key role of PIM1 in the full development of allergen-induced airway responses. In addition, a significant reduction in the number of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and in the concentrations of cytokines have also been found in the airways (103).
CD4+ and CD8+ effector T cells are involved in the development of allergic inflammation, and PIM1 has been found to enhance the activity of nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFATc) and the production of IL-2, promoting the proliferation and survival of IL-2-dependent T lymphocytes (103, 104). Moreover, inhibition of PIM1 kinase activity alleviates the immune response by limiting the activation and proliferation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (98, 103, 104). PIM1 also plays a major role in IL-5-mediated eosinophil antiapoptotic signaling, causing glucocorticoid treatment resistance, while blocking PIM1 signaling restores glucocorticoid receptor-mediated apoptosis in IL-5-activated eosinophils, thereby ameliorating glucocorticoid resistance in eosinophil asthma (105). However, it has also been reported that PIM1 kinase activity can help maintain airway epithelial integrity and prevent airway epithelial inflammatory activation to exert a beneficial effect in a house dust mite-driven model (HDM) of allergic asthma (106). Overall, the inhibition of PIM1 seems to be more beneficial than harmful in treating asthma. Targeting PIM1 may be effective in preventing the development of airway hyperresponsiveness, airway inflammation, and cytokine production in patients with asthma.
Food allergy refers to adverse food reactions mediated by immunological mechanisms, namely, abnormal or excessive immune reactions caused by food proteins, which can be mediated by IgE or non-IgE. Among them, peanuts are important food allergens that cause severe allergic reactions. Furthermore, unlike many other food allergies, peanut allergies typically persist into adulthood (107). Th2 cell differentiation and the release of IL-4 and IL-13 drive IgE-mediated activation of mast cells, which are involved in food allergic reactions (108). The activation of PIM1 plays an essential role in the development of peanut-induced intestinal anaphylaxis (69, 108). Specifically, PIM1 kinases can phosphorylate RUNX family members, enhance their activity, and regulate their expression (69, 109). Among the RUNX family members, RUNX3 is a known silencer of the IL-4 gene locus, which inhibits IL-4 production in T cells and regulates T-cell differentiation via a physical interaction with NFAT (110). The activation of PIM1 leads to the downregulation of RUNX3, while the inhibition of PIM1 can reduce Th2 and Th17 differentiation and cytokine production through the upregulation of RUNX3, thus attenuating intestinal allergic inflammation (69, 108). Collectively, this evidence suggests that targeting the PIM1/RUNX3 axis may be a novel potential measure for the control of food-induced allergic reactions through the regulation of Th2 and Th17 differentiation.
5.5 PIM1 and LN
LN is one of the most serious and common complications of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), which is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by multiple organ involvement and a large number of complications. Long-term inflammation may cause irreversible damage to the kidney and may lead to chronic renal disease that can progress to end-stage renal disease. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome plays an important role in the pathogenesis of LN, while inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome provides a new strategy for LN treatment (111).
A clinical study revealed that PIM1 expression is upregulated in peripheral blood monocytes from patients with SLE and in renal biopsy tissue from patients with LN (7). Further in vitro and in vivo studies suggested that PIM1 can regulate the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by regulating intracellular Ca2+, while PIM1 inhibition suppresses NFATc1 signaling and NLRP3 inflammasome signaling in mouse and human podocytes, thus improving the clinical symptoms and pathological damage of LN (7). In addition, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta (CEBPβ), a basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor involved in innate immunity, regulates NLRP3 inflammasome activation and participates in the pathogenesis of SLE (112). CEBPβ can bind to the PIM1 promoter and promote the transcriptional activity of PIM1, while CEBPβ knockdown downregulates PIM1 expression, inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cell pyroptosis, and reduces the secretion of the inflammatory factors IL-1β and IL-6. Correspondingly, the overexpression of PIM1 reversed all of these effects (112). Therefore, targeting the PIM1/NLRP3 pathway may have therapeutic potential for LN.
6 Discussion
PIM1 has been a research hotspot for neoplastic diseases in the past. However, recent studies have shown that PIM1 also plays a vital role in the occurrence and development of immunoinflammatory diseases. Immunoinflammatory diseases such as AU, IBD and RA are characterized by abnormal PIM1 expression, which can affect the development of inflammatory diseases by mediating inflammatory signaling pathways, classical macrophage activation, and imbalances between effector T cells. Research on PIM1 in immunoinflammatory diseases provides novel ideas for exploring the pathogenesis and therapeutic use of PIM1 in clinical immunoinflammatory diseases. Numerous studies have shown that targeting PIM1 may be an effective treatment for immunoinflammatory diseases. Targeting PIM kinases also presents a compelling approach since knock-down of PIM leads to non-fatal phenotypes in vivo (113) and pan-PIM inhibition appears to be generally tolerated in Phase I/II studies (114, 115). In addition, PIM1 has been shown to be a potential biomarker for evaluating the status of certain immunoinflammatory diseases, such as RA (5, 12). Despite much progress in discovering the role of PIM1 in the pathogenesis of immunoinflammatory diseases, the molecular mechanisms underlying its effects and signaling pathways are still poorly understood. The function of PIM1 in immunoinflammatory diseases must be fully elucidated. Moreover, most of the studies were conducted in pathological animal models. The expression of PIM1 is not clear in patients with some immunoinflammatory diseases, such as IBD and asthma. Therefore, there is a pressing need to conduct additional clinical studies to further validate the roles of PIM1 as well as the safety and effects of PIM1 kinase inhibitors in immunoinflammatory diseases.
Author contributions
XY: Writing – original draft. CL: Writing – original draft. YXL: Writing – original draft. ZL: Writing – original draft. BZ: Writing – review & editing. DZ: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all participants in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Glossary
AKT: Protein kinase B
ASC: Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD
AU: Autoimmune uveitis
BCL3: B cell leukemia-3
bZip: Basic leucine zipper
cAMP: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
CEBPβ: CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta
FOXO1: Forkhead box O1
FOXP3: Forkhead box protein 3
HAT1: Histone acetyltransferase 1
HDM: House dust mite-driven model
HSPs: Heat shock proteins
IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease
ID2: Inhibitor of differentiation
IFN-γ: Interferon-γ
IL-6: Interleukin-6
IRAK4: IL-1 receptor associated kinase-4
JAK: Janus kinase
LN: Lupus nephritis
LPS: Lipopolysaccharides
M1: Classically activated macrophages
M2: Alternatively activated macrophages
MiRNAs: MicroRNAs
MMP: Matrix metalloprotease
MYD88: Myeloid differentiation factor-88
NFATc: Nuclear factor of activated T cells
NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
NLRP3: Nod-like receptor protein 3
PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3 kinase
PIM: Proviral integration site for Moloney murine leukemic virus
RA: Rheumatoid arthritis
RA-FLSs: RA fibroblast-like synoviocytes
RORγt: Retinoid-related orphan receptor gamma t
RUNX3: Runt-related transcription factor
SLE: Systemic lupus erythematosus
SOCS1: Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1
STAT: Signal transducers of activated transcription
TAK1: Transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase 1
TAB3: TAK1-binding protein 3
T-bet: T-box expressed in T cells
Th1: T helper 1 cell
TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4
TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α
Tregs: Regulatory T cells
USP28: ubiquitin-specific protease 28
VKH: Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease
References
1. Panchal NK, Sabina EP. A serine/threonine protein PIM kinase as a biomarker of cancer and a target for anti-tumor therapy. Life Sci. (2020) 255:117866. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117866
2. Ebeid DE, Firouzi F, Esquer CY, Navarrete JM, Wang BJ, Gude NA, et al. PIM1 promotes survival of cardiomyocytes by upregulating c-kit protein expression. Cells. (2020) 9:2001. doi: 10.3390/cells9092001
3. Yin F, Zhao R, Gorja DR, Fu X, Lu N, Huang H, et al. Novel dual inhibitor for targeting PIM1 and FGFR1 kinases inhibits colorectal cancer growth in vitro and patient-derived xenografts in vivo. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2022) 12:4122–37. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.07.005
4. Yuan Y, Wang C, Zhuang X, Lin S, Luo M, Deng W, et al. PIM1 promotes hepatic conversion by suppressing reprogramming-induced ferroptosis and cell cycle arrest. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:5237. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32976-9
5. Anderson AE, Maney NJ, Nair N, Lendrem DW, Skelton AJ, Diboll J, et al. Expression of STAT3-regulated genes in circulating CD4+ T cells discriminates rheumatoid arthritis independently of clinical parameters in early arthritis. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2019) 58:1250–8. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez003
6. Yoon SB, Hong H, Lim HJ, Choi JH, Choi YP, Seo SW, et al. A novel IRAK4/PIM1 inhibitor ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis and lymphoid Malignancy by blocking the TLR/MYD88-mediated NF-κB pathway. Acta Pharm Sin B. (2023) 13:1093–109. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.12.001
7. Fu R, Xia Y, Li M, Mao R, Guo C, Zhou M, et al. Pim-1 as a therapeutic target in Lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2019) 71:1308–18. doi: 10.1002/art.40863
8. Selten G, Cuypers HT, Boelens W, Robanus-Maandag E, Verbeek J, Domen J, et al. The primary structure of the putative oncogene pim-1 shows extensive homology with protein kinases. Cell. (1986) 46:603–11. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90886-x
9. Bachmann M, Möröy T. The serine/threonine kinase Pim-1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2005) 37:726–30. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2004.11.005
10. Saris CJ, Domen J, Berns A. The pim-1 oncogene encodes two related protein-serine/threonine kinases by alternative initiation at AUG and CUG. EMBO J. (1991) 10:655–64. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07994.x
11. Egli N, Zajonz A, Burger MT, Schweighoffer T. Human CD180 transmits signals via the PIM-1L kinase. PloS One. (2015) 10:e0142741. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142741
12. Ha YJ, Choi YS, Han DW, Kang EH, Yoo IS, Kim JH, et al. PIM-1 kinase is a novel regulator of proinflammatory cytokine-mediated responses in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2019) 58:154–64. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key261
13. Zarrin AA, Bao K, Lupardus P, Vucic D. Kinase inhibition in autoimmunity and inflammation. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2021) 20:39–63. doi: 10.1038/s41573-020-0082-8
14. Lin F, Luo X, Tsun A, Li Z, Li D, Li B. Kaempferol enhances the suppressive function of Treg cells by inhibiting FOXP3 phosphorylation. Int Immunopharmacol. (2015) 28:859–65. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.03.044
15. Li H, Xie L, Zhu L, Li Z, Wang R, Liu X, et al. Multicellular immune dynamics implicate PIM1 as a potential therapeutic target for uveitis. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:5866. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33502-7
16. Xin P, Xu X, Deng C, Liu S, Wang Y, Zhou X, et al. The role of JAK/STAT signaling pathway and its inhibitors in diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. (2020) 80:106210. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106210
17. Benucci M, Bernardini P, Coccia C, De Luca R, Levani J, Economou A, et al. JAK inhibitors and autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Autoimmun Rev. (2023) 22:103276. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2023.103276
18. Hofer MJ, Campbell IL. Immunoinflammatory diseases of the central nervous system - the tale of two cytokines. Br J Pharmacol. (2016) 173:716–28. doi: 10.1111/bph.13175
19. Gao Q, Liang X, Shaikh AS, Zang J, Xu W, Zhang Y. JAK/STAT signal transduction: promising attractive targets for immune, inflammatory and hematopoietic diseases. Curr Drug Targets. (2018) 19:487–500. doi: 10.2174/1389450117666161207163054
20. Jones SA, Jenkins BJ. Recent insights into targeting the IL-6 cytokine family in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. (2018) 18:773–89. doi: 10.1038/s41577-018-0066-7
21. Liu Q, Li A, Wang L, He W, Zhao L, Wu C, et al. Stomatin-like protein 2 promotes tumor cell survival by activating the JAK2-STAT3-PIM1 pathway, suggesting a novel therapy in CRC. Mol Ther Oncolytics. (2020) 17:169–79. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.03.010
22. Liu Z, Han M, Ding K, Fu R. The role of Pim kinase in immunomodulation. Am J Cancer Res. (2020) 10:4085–97.
23. Park JH, Lee NK, Lim HJ, Ji ST, Kim YJ, Jang WB, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of mTOR attenuates replicative cell senescence and improves cellular function via regulating the STAT3-PIM1 axis in human cardiac progenitor cells [published correction appears in Exp Mol Med. 2023 Nov;55(11):2473] Exp Mol Med. (2020) 52:615–28. doi: 10.1038/s12276-020-0374-4
24. Gao X, Liu X, Lu Y, Wang Y, Cao W, Liu X, et al. PIM1 is responsible for IL-6-induced breast cancer cell EMT and stemness via c-myc activation. Breast Cancer. (2019) 26:663–71. doi: 10.1007/s12282-019-00966-3
25. Jin B, Wang Y, Wu CL, Liu KY, Chen H, Mao ZB. PIM-1 modulates cellular senescence and links IL-6 signaling to heterochromatin formation. Aging Cell. (2014) 13:879–89. doi: 10.1111/acel.12249
26. Baek HS, Min HJ, Hong VS, Kwon TK, Park JW, Lee J, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of the novel PIM kinase inhibitor KMU-470 in RAW 264.7 cells through the TLR4-NF-κB-NLRP3 pathway. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:5138. doi: 10.3390/ijms21145138
27. Gao AY, Diaz Espinosa AM, Gianì F, Pham TX, Carver CM, Aravamudhan A, et al. Pim-1 kinase is a positive feedback regulator of the senescent lung fibroblast inflammatory secretome. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. (2022) 323:L685–97. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00023.2022
28. Li Q, Chen L, Luo C, Chen Y, Ge J, Zhu Z, et al. TAB3 upregulates PIM1 expression by directly activating the TAK1-STAT3 complex to promote colorectal cancer growth. Exp Cell Res. (2020) 391:111975. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.111975
29. Lacronique V, Boureux A, Monni R, Dumon S, Mauchauffé M, Mayeux P, et al. Transforming properties of chimeric TEL-JAK proteins in Ba/F3 cells. Blood. (2000) 95:2076–83. doi: 10.1182/blood.V95.6.2076
30. Cao T, Jiang N, Liao H, Shuai X, Su J, Zheng Q. The FLT3-ITD mutation and the expression of its downstream signaling intermediates STAT5 and Pim-1 are positively correlated with CXCR4 expression in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:12209. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48687-z
31. Tahvanainen J, Kyläniemi MK, Kanduri K, Gupta B, Lähteenmäki H, Kallonen T, et al. Proviral integration site for Moloney murine leukemia virus (PIM) kinases promote human T helper 1 cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. (2013) 288:3048–58. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.361709
32. Peltola KJ, Paukku K, Aho TL, Ruuska M, Silvennoinen O, Koskinen PJ. Pim-1 kinase inhibits STAT5-dependent transcription via its interactions with SOCS1 and SOCS3. Blood. (2004) 103:3744–50. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-09-3126
33. Yoshimura A, Ito M, Chikuma S, Akanuma T, Nakatsukasa H. Negative regulation of cytokine signaling in immunity. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. (2018) 10:a028571. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a028571
34. Mortazavi-Jahromi SS, Aslani M, Mirshafiey A. A comprehensive review on miR-146a molecular mechanisms in a wide spectrum of immune and non-immune inflammatory diseases. Immunol Lett. (2020) 227:8–27. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2020.07.008
35. Chen J, Liu M, Luo X, Peng L, Zhao Z, He C, et al. Exosomal miRNA-486-5p derived from rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes induces osteoblast differentiation through the Tob1/BMP/Smad pathway. Biomater Sci. (2020) 8:3430–42. doi: 10.1039/c9bm01761e
36. Singh RP, Massachi I, Manickavel S, Singh S, Rao NP, Hasan S, et al. The role of miRNA in inflammation and autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. (2013) 12:1160–5. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2013.07.003
37. Wang LS, Li L, Li L, Chu S, Shiang KD, Li M, et al. MicroRNA-486 regulates normal erythropoiesis and enhances growth and modulates drug response in CML progenitors. Blood. (2015) 125:1302–13. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-06-581926
38. Zhang J, Xu Z, Kong L, Gao H, Zhang Y, Zheng Y, et al. miRNA-486-5p promotes COPD progression by targeting HAT1 to regulate the TLR4-triggered inflammatory response of alveolar macrophages. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2020) 15:2991–3001. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S280614
39. Pinelli S, Alinovi R, Poli D, Corradi M, Pelosi G, Tiseo M, et al. Overexpression of microRNA-486 affects the proliferation and chemosensitivity of mesothelioma cell lines by targeting PIM1. Int J Mol Med. (2021) 47:117. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.4950
40. Ma N, Li S, Lin C, Cheng X, Meng Z. Mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium attenuates oxidative stress injury in hepatocytes partly by regulating the miR-486-5p/PIM1 axis and the TGF-β/Smad pathway. Bioengineered. (2021) 12:6434–47. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1972196
41. Liu Y, Zhang J, Xing C, Wei S, Guo N, Wang Y. miR-486 inhibited osteosarcoma cells invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting PIM1. Cancer biomark. (2018) 23:269–77. doi: 10.3233/CBM-181527
42. Pan XP, Jiya BR, Wang F, Lan Z. Physcion increases the sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib through miRNA-370/PIM1 axis-regulated glycolysis. World J Gastrointest Oncol. (2023) 15:1400–11. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i8.1400
43. Pan XP, Wang HX, Tong DM, Li Y, Huang LH, Wang C. miRNA-370 acts as a tumor suppressor via the downregulation of PIM1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2017) 21:1254–63.
44. Letson CT, Balasis ME, Newman H, Binder M, Vedder A, Kinose F, et al. Targeting BET proteins downregulates miR-33a to promote synergy with PIM inhibitors in CMML. Clin Cancer Res. (2023) 29:2919–32. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-3929
45. Karatas OF. Antiproliferative potential of miR-33a in laryngeal cancer Hep-2 cells via targeting PIM1. Head Neck. (2018) 40:2455–61. doi: 10.1002/hed.25361
46. Li M, Zhang M, Chen M, Xiao J, Mu X, Peng J, et al. KLF2-induced circZKSCAN1 potentiates the tumorigenic properties of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by targeting the miR-1294/PIM1 axis. Cell Cycle. (2022) 21:1376–90. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2051293
47. Shan Q, Ma F, Wei J, Li H, Ma H, Sun P. Physiological functions of heat shock proteins. Curr Protein Pept Sci. (2020) 21:751–60. doi: 10.2174/1389203720666191111113726
48. Peng C, Zhao F, Li H, Li L, Yang Y, Liu F. HSP90 mediates the connection of multiple programmed cell death in diseases. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:929. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05373-9
49. Schopf FH, Biebl MM, Buchner J. The HSP90 chaperone machinery. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2017) 18:345–60. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2017.20
50. Chen RH, Chen YH, Huang TY. Ubiquitin-mediated regulation of autophagy. J BioMed Sci. (2019) 26:80. doi: 10.1186/s12929-019-0569-y
51. Toth RK, Solomon R, Warfel NA. Stabilization of PIM kinases in hypoxia is mediated by the deubiquitinase USP28. Cells. (2022) 11:1006. doi: 10.3390/cells11061006
52. Shay KP, Wang Z, Xing PX, McKenzie IF, Magnuson NS. Pim-1 kinase stability is regulated by heat shock proteins and the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Mol Cancer Res. (2005) 3:170–81. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-04-0192
53. Mizuno K, Shirogane T, Shinohara A, Iwamatsu A, Hibi M, Hirano T. Regulation of pim-1 by hsp90. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2001) 281:663–9. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.4405
54. Locati M, Curtale G, Mantovani A. Diversity, mechanisms, and significance of macrophage plasticity. Annu Rev Pathol. (2020) 15:123–47. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-012418-012718
55. Kadomoto S, Izumi K, Mizokami A. Macrophage polarity and disease control. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 23:144. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010144
56. Huang Y, Tian C, Li Q, Xu Q. TET1 Knockdown Inhibits Porphyromonas gingivalis LPS/IFN-γ-Induced M1 Macrophage Polarization through the NF-κB Pathway in THP-1 Cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:2023. doi: 10.3390/ijms20082023
57. Liu L, Guo H, Song A, Huang J, Zhang Y, Jin S, et al. Progranulin inhibits LPS-induced macrophage M1 polarization via NF-кB and MAPK pathways. BMC Immunol. (2020) 21:32. doi: 10.1186/s12865-020-00355-y
58. Wu K, Yuan Y, Yu H, Dai X, Wang S, Sun Z, et al. The gut microbial metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide aggravates GVHD by inducing M1 macrophage polarization in mice. Blood. (2020) 136:501–15. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019003990
59. Mangalam AK, Rattan R, Suhail H, Singh J, Hoda MN, Deshpande M, et al. AMP-activated protein kinase suppresses autoimmune central nervous system disease by regulating M1-type macrophage-Th17 axis. J Immunol. (2016) 197:747–60. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501549
60. Van Raemdonck K, Umar S, Palasiewicz K, Volkov S, Volin MV, Arami S, et al. CCL21/CCR7 signaling in macrophages promotes joint inflammation and Th17-mediated osteoclast formation in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2020) 77:1387–99. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03235-w
61. Du T, Yang CL, Ge MR, Liu Y, Zhang P, Li H, et al. M1 macrophage derived exosomes aggravate experimental autoimmune neuritis via modulating Th1 response. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1603. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01603
62. Shen YM, Zhao Y, Zeng Y, Yan L, Chen BL, Leng AM, et al. Inhibition of Pim-1 kinase ameliorates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice. Dig Dis Sci. (2012) 57:1822–31. doi: 10.1007/s10620-012-2106-7
63. Ge G, Bai J, Wang Q, Liang X, Tao H, Chen H, et al. Punicalagin ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis by downregulating M1 macrophage and pyroptosis via NF-κB signaling pathway. Sci China Life Sci. (2022) 65:588–603. doi: 10.1007/s11427-020-1939-1
64. Nihira K, Ando Y, Yamaguchi T, Kagami Y, Miki Y, Yoshida K. Pim-1 controls NF-kappaB signalling by stabilizing RelA/p65. Cell Death Differ. (2010) 17:689–98. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2009.174
65. Wang J, Cao Y, Liu Y, Zhang X, Ji F, Li J, et al. PIM1 inhibitor SMI-4a attenuated lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through suppressing macrophage inflammatory responses via modulating p65 phosphorylation. Int Immunopharmacol. (2019) 73:568–74. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.05.040
66. Zhang Z, Xie S, Qian J, Gao F, Jin W, Wang L, et al. Targeting macrophagic PIM-1 alleviates osteoarthritis by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation via suppressing mitochondrial ROS/Cl- efflux signaling pathway. J Transl Med. (2023) 21:452. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04313-1
67. Zhu J. T helper cell differentiation, heterogeneity, and plasticity. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. (2018) 10:a030338. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a030338
68. Buchacher T, Shetty A, Koskela SA, Smolander J, Kaukonen R, Sousa AGG, et al. PIM kinases regulate early human Th17 cell differentiation. Cell Rep. (2023) 42:113469. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113469
69. Wang M, Okamoto M, Domenico J, Han J, Ashino S, Shin YS, et al. Inhibition of Pim1 kinase prevents peanut allergy by enhancing Runx3 expression and suppressing T(H)2 and T(H)17 T-cell differentiation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2012) 130:932–44.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.07.032
70. Aho TL, Lund RJ, Ylikoski EK, Matikainen S, Lahesmaa R, Koskinen PJ. Expression of human pim family genes is selectively up-regulated by cytokines promoting T helper type 1, but not T helper type 2, cell differentiation. Immunology. (2005) 116:82–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02201.x
71. Wildner G, Diedrichs-Möhring M. Resolution of uveitis. Semin Immunopathol. (2019) 41:727–36. doi: 10.1007/s00281-019-00758-z
72. Zhang M, Zhang X. T cells in ocular autoimmune uveitis: Pathways and therapeutic approaches. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 114:109565. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109565
73. Chong WP, Mattapallil MJ, Raychaudhuri K, Bing SJ, Wu S, Zhong Y, et al. The cytokine IL-17A limits Th17 pathogenicity via a negative feedback loop driven by autocrine induction of IL-24. Immunity. (2020) 53:384–397.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.06.022
74. Gu C, Liu Y, Lv J, Zhang C, Huang Z, Jiang Q, et al. Kurarinone regulates Th17/Treg balance and ameliorates autoimmune uveitis via Rac1 inhibition. J Adv Res. (2024). doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.03.013
75. Zhou M, Qu R, Yin X, Qiu Y, Peng Y, Liu B, et al. Prednisone acetate modulates Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg cell homeostasis in experimental autoimmune uveitis via orchestrating the Notch signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 116:109809. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.109809
76. Chen Y, Li Z, Li H, Su W, Xie Y, Pan Y, et al. Apremilast regulates the Teff/Treg balance to ameliorate uveitis via PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 signaling pathway. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:581673. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.581673
77. Xu Q, Zhang X, Li T, Shao S. Exenatide regulates Th17/Treg balance via PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 pathway in db/db mice. Mol Med. (2022) 28:144. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00574-6
78. Samarpita S, Rasool M. Majoon chobchini reinstates PDL-1 expression and blocks dendritic cell -T helper 17 pathogenic axis in rheumatoid arthritis animal model. Cytokine. (2023) 163:156136. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2023.156136
79. Ouyang W, Liao W, Luo CT, Yin N, Huse M, Kim MV, et al. Novel Foxo1-dependent transcriptional programs control T(reg) cell function. Nature. (2012) 491:554–9. doi: 10.1038/nature11581
80. Lainé A, Martin B, Luka M, Mir L, Auffray C, Lucas B, et al. Foxo1 is a T cell-intrinsic inhibitor of the RORγt-Th17 program. J Immunol. (2015) 195:1791–803. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500849
81. Hedrick SM, Hess Michelini R, Doedens AL, Goldrath AW, Stone EL. FOXO transcription factors throughout T cell biology. Nat Rev Immunol. (2012) 12:649–61. doi: 10.1038/nri3278
82. Huang H, Tindall DJ. Dynamic FoxO transcription factors. J Cell Sci. (2007) 120:2479–87. doi: 10.1242/jcs.001222
83. Wang R, Zhu L, Li H, Peng X, Zhao S, Su W. Single-Cell transcriptomes of immune cells provide insights into the therapeutic effects of mycophenolate mofetil on autoimmune uveitis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 119:110223. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110223
84. Liu X, Gu C, Lv J, Jiang Q, Ding W, Huang Z, et al. Progesterone attenuates Th17-cell pathogenicity in autoimmune uveitis via Id2/Pim1 axis. J Neuroinflamm. (2023) 20:144. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02829-3
85. Rosen MJ, Dhawan A, Saeed SA. Inflammatory bowel disease in children and adolescents. JAMA Pediatr. (2015) 169:1053–60. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2015.1982
86. Rudbaek JJ, Agrawal M, Torres J, Mehandru S, Colombel JF, Jess T. Deciphering the different phases of preclinical inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2024) 21:86–100. doi: 10.1038/s41575-023-00854-4
87. Li M, Gan C, Zhang R, Wang J, Wang Y, Zhu W, et al. TRAF5 regulates intestinal mucosal Th1/Th17 cell immune responses via Runx1 in colitis mice. Immunology. (2023) 170:495–509. doi: 10.1111/imm.13685
88. Cao H, Diao J, Liu H, Liu S, Liu J, Yuan J, et al. The pathogenicity and synergistic action of Th1 and Th17 cells in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm Bowel Dis. (2023) 29:818–29. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izac199
89. Zhang S, Zhong R, Tang S, Chen L, Zhang H. Metabolic regulation of the Th17/Treg balance in inflammatory bowel disease. Pharmacol Res. (2024) 203:107184. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107184
90. Shen YM, Zeng Y, Liu T. Expression of Pim-1 kinases in mice colitis model induced with dextran sulfate sodium. Prog Modern Biomed. (2012) 12:6838–41.
91. Shen Y, Xie Y, Zhao Y, Long Y, Li L, Zeng Y. Pim-1 inhibitor attenuates trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid induced colitis in the mice. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. (2018) 42:382–6. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2018.01.002
92. Ou R, Shen Y, Zeng Y, Zou L, Jiang N, Xu M. Effects of Pim-1 inhibitor on mouse model of inflammatory bowel disease induced by TNBS. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. (2018) 43:481–9. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2018.05.004
93. Jackson LJ, Pheneger JA, Pheneger TJ, Davis G, Wright AD, Robinson JE, et al. The role of PIM kinases in human and mouse CD4+ T cell activation and inflammatory bowel disease. Cell Immunol. (2012) 272:200–13. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2011.10.011
94. Di Matteo A, Bathon JM, Emery P. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. (2023) 402:2019–33. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01525-8
95. Zhang F, Jonsson AH, Nathan A, Millard N, Curtis M, Xiao Q, et al. Deconstruction of rheumatoid arthritis synovium defines inflammatory subtypes. Nature. (2023) 623:616–24. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06708-y
96. Smolen JS, Aletaha D, McInnes IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. (2016) 388:2023–38. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30173-8
97. Anderson AE, Pratt AG, Sedhom MA, Doran JP, Routledge C, Hargreaves B, et al. IL-6-driven STAT signalling in circulating CD4+ lymphocytes is a marker for early anticitrullinated peptide antibody-negative rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2016) 75:466–73. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205850
98. Maney NJ, Lemos H, Barron-Millar B, Carey C, Herron I, Anderson AE, et al. Pim kinases as therapeutic targets in early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2021) 73:1820–30. doi: 10.1002/art.41744
99. Wang J, Zhou Y, Zhang H, Hu L, Liu J, Wang L, et al. Pathogenesis of allergic diseases and implications for therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:138. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01344-4
100. Porsbjerg C, Melén E, Lehtimäki L, Shaw D. Asthma. Lancet. (2023) 401:858–73. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02125-0
101. León B, Ballesteros-Tato A. Modulating Th2 cell immunity for the treatment of asthma. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:637948. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.637948
102. Boulet LP, Gupta S, FitzGerald JM. Inhaled glucocorticoids in asthma. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:2050–1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1804801
103. Shin YS, Takeda K, Shiraishi Y, Jia Y, Wang M, Jackson L, et al. Inhibition of Pim1 kinase activation attenuates allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2012) 46:488–97. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2011-0190OC
104. Rainio EM, Sandholm J, Koskinen PJ. Cutting edge: Transcriptional activity of NFATc1 is enhanced by the Pim-1 kinase. J Immunol. (2002) 168:1524–7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.4.1524
105. Pazdrak K, Moon Y, Straub C, Stafford S, Kurosky A. Eosinophil resistance to glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis is mediated by the transcription factor NFIL3. Apoptosis. (2016) 21:421–31. doi: 10.1007/s10495-016-1226-5
106. de Vries M, Hesse L, Jonker MR, van den Berge M, van Oosterhout AJ, Heijink IH, et al. Pim1 kinase activity preserves airway epithelial integrity upon house dust mite exposure. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. (2015) 309:L1344–53. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00043.2015
107. Lee T, Edwards-Salmon S, Vickery BP. Current and future treatments for peanut allergy. Clin Exp Allergy. (2023) 53:10–24. doi: 10.1111/cea.14244
108. Wang M, Gelfand EW. Targeting Pim1 kinase in the treatment of peanut allergy. Expert Opin Ther Targets. (2014) 18:177–83. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2014.855721
109. Aho TL, Sandholm J, Peltola KJ, Ito Y, Koskinen PJ. Pim-1 kinase phosphorylates RUNX family transcription factors and enhances their activity. BMC Cell Biol. (2006) 7:21. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-7-21
110. Lee SH, Jeong HM, Choi JM, Cho YC, Kim TS, Lee KY, et al. Runx3 inhibits IL-4 production in T cells via physical interaction with NFAT. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2009) 381:214–7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.02.026
111. Oliveira CB, Lima CAD, Vajgel G, Sandrin-Garcia P. The role of NLRP3 inflammasome in lupus nephritis. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:12476. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212476
112. Wang X, Cheng W, Chen X, Gong Y, Wang G, Zhang X, et al. Inhibition of CEBPB attenuates lupus nephritis via regulating Pim-1 signaling. Mediators Inflamm. (2022) 2022:2298865. doi: 10.1155/2022/2298865
113. Bellon M, Nicot C. Targeting Pim kinases in hematological cancers: molecular and clinical review. Mol Cancer. (2023) 22:18. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01721-1
114. Cortes J, Tamura K, DeAngelo DJ, de Bono J, Lorente D, Minden M, et al. Phase I studies of AZD1208, a proviral integration Moloney virus kinase inhibitor in solid and haematological cancers. Br J Cancer. (2018) 118:1425–33. doi: 10.1038/s41416-018-0082-1
115. Patel MR, Donnellan W, Byrne M, Asch AS, Zeidan AM, Baer MR, et al. Phase 1/2 study of the pan-PIM kinase inhibitor INCB053914 alone or in combination with standard-of-care agents in patients with advanced hematologic Malignancies. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. (2023) 23:674–86. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2023.05.002
Keywords: PIM1, serine/threonine protein kinase, immunoinflammatory disease, inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis
Citation: Yang X, Liu C, Lei Y, Liu Z, Zhu B and Zhao D (2024) PIM1 signaling in immunoinflammatory diseases: an emerging therapeutic target. Front. Immunol. 15:1443784. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1443784
Received: 04 June 2024; Accepted: 02 September 2024;
Published: 20 September 2024.
Edited by:
Runze Qiu, Nanjing Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Hans David Brightbill, Amgen, United StatesDongping Yuan, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, China
Copyright © 2024 Yang, Liu, Lei, Liu, Zhu and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bin Zhu, emh1YmluMjBzY2lAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Dongchi Zhao, emhhb193aDIwMDRAaG90bWFpbC5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Xue Yang
Xue Yang Chunming Liu2†
Chunming Liu2† Bin Zhu
Bin Zhu Dongchi Zhao
Dongchi Zhao