- 1Department of Biomedical Sciences, University of Sassari, Sassari, Italy
- 2Discipline of Clinical Pharmacology, College of Medicine and Public Health, Flinders University, Bedford Park, SA, Australia
- 3Department of Clinical Pharmacology, Flinders Medical Centre, Southern Adelaide Local Health Network, Bedford Park, SA, Australia
Introduction: Systemic sclerosis (SSc), a chronic autoimmune condition, is characterized by microvascular dysfunction, ineffective angiogenesis, and fibrosis. The identification of robust biomarkers reflecting these processes may assist in clinical management and lead to the discovery of new therapies. We sought to address this issue by conducting a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies investigating one such biomarker, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), in SSc patients and healthy controls and in SSc patients with localized or diffuse disease, different video capillaroscopy patterns (early, active, or late), and presence or absence of complications.
Methods: We searched PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science from inception to 15 May 2024. We assessed the risk of bias and the certainty of evidence using the JBI checklist for analytical studies and GRADE, respectively.
Results: In 42 eligible studies, compared to controls, patients with SSc had significantly higher plasma or serum VEGF concentrations (standard mean difference, SMD=0.93, 95% CI 0.71 to 1.15, p<0.001; moderate certainty). In further analyses, VEGF concentrations were significantly higher in SSc patients with diffused disease than those with localized disease (SMD=0.30, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.59, p=0.046; very low certainty), in patients with late vs. active video capillaroscopy pattern (SMD=0.35, 95% CI 0.09 to 0.61, p=0.008; very low certainty), and in patients with pulmonary hypertension than those without (SMD=0.93, 95% CI 0.34 to 1.53, p=0.002; very low certainty). By contrast, no significant differences were observed between SSc patients with and without digital ulcers, interstitial lung disease, and telangiectasias, whereas limited evidence was available for alveolitis. Meta-regression and subgroup analysis of studies investigating VEGF in SSc patients and controls showed no significant associations between the effects size and various patient and study characteristics, including SSc duration and use of corticosteroids, immunosuppressors and vasodilators. By contrast, significant associations were observed with the geographical location where the study was conducted.
Discussion: The results of this systematic review and meta-analysis suggest that VEGF can be useful in the assessment and management of SSc and in the identification of novel therapeutic strategies in this patient group.
Systematic Review Registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero, identifier CRD42024552925.
Introduction
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a chronic and disabling autoimmune condition that is characterized by microvascular dysfunction, ineffective angiogenesis, and localized or diffuse fibrosis (1–4). There is increasing evidence that microvascular damage is a critical pathophysiological step in SSc as it generally occurs before the onset of skin and visceral fibrosis (5, 6). Early clinical manifestations of microvascular damage in SSc primarily involve the Raynaud’s phenomenon, with other manifestations such as telangiectasias, pitting scars, nailfold video capillaroscopy abnormalities, digital ulcers, and pulmonary arterial hypertension occurring during later stages of the disease (7–9). The presence of microvascular offers significant opportunities for the study and the identification of novel SSc biomarkers, an important knowledge gap in this patient population (10, 11). Such biomarkers might facilitate early diagnosis and treatment, critical factors associated with disease progression and clinical outcomes (3, 4, 12). The available evidence suggests that endothelial cell injury secondary to multiple insults, e.g., autoantibodies, viral agents, and excess production of reactive oxygen species, leads to a dysregulation in the production of vasoconstrictive and vasodilating substances, including excess endothelin-1 and reduced nitric oxide (13–17). Alterations in nitric oxide synthesis in SSc patients are also associated with increased concentrations of asymmetric dimethylarginine, an endogenous nitric oxide synthase inhibitor (18, 19). Functional and structural endothelial alterations are also associated with increased expression of cell adhesion molecules and chemokines, which further perpetuates microvascular damage and alterations in vascular tone (20). Overall, these processes lead to a dysregulated increase in pro-angiogenic factors, i.e., vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and endoglin (21, 22), and anti-angiogenic molecules such as pentraxin-3, endostatin, and angiostatin (23, 24). These observations have stimulated a significant body of research to investigate a broad group of potential biomarkers of SSc, including selectins, immunoglobulin-like cell adhesion molecules, VEGF, endoglin, endothelin-1, pentraxin-3, endostatin, angiostatin, angiopoietins, matrix metalloproteinases, neurovascular guidance molecules, sirtuins, cytokines, adipokines, thrombomodulin, soluble CD163, brain natriuretic peptide, von Willebrand factor, and soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (25).
The most studied angiogenic modulator in SSc is VEGF, also known as VEGF-A, the main component of the VEGF family (26). Physiologically, VEGF is a potent pro-angiogenic factor and an essential growth factor for endothelial cells, ensuring the functional and structural integrity of the endothelium and blood vessels through its binding to the target receptors VEGFR-1 and VEFGR-2 as well as non-signaling co-receptors (27). Experimental and clinical studies have reported VEGF activation and increased concentrations in plasma or serum in SSc despite the lack of effective angiogenesis (28–30). Therefore, VEGF activation might further contribute to alterations in blood vessel morphology and tone in SSc (28). This hypothesis is supported by investigations reporting increased VEGF concentrations in SSc patients with systemic fibrosis, specific alterations in nailfold capillary density and patterns (31, 32), and well-established complications, e.g., pulmonary arterial hypertension (31, 33). The significant associations between VEGF elevations, critical pathophysiological processes (microvascular dysfunction, ineffective angiogenesis, and fibrosis) and clinical manifestations suggest that VEGF might represent a useful diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in SSc.
We sought to investigate the potential role of VEGF in SSc by conducting a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies reporting VEGF concentrations in SSc patients and healthy controls and in SSc patients with specific disease types (localized or diffuse), nailfold video capillaroscopy patterns (early, active, or late) (34), and complications. We also investigated associations between the effect size of the differences in VEGF concentrations and specific study and patient characteristics.
Materials and methods
Literature search and study selection
We conducted a systematic search in electronic databases (PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus) from inception to 15 May 2024, using the following terms: “systemic sclerosis” OR “scleroderma” AND “VEGF” OR “vascular endothelial growth factor”. Two investigators independently screened each abstract and, if relevant, the full text articles. Inclusion criteria were: (i) the investigation of VEGF concentrations in patients with SSc diagnosed according accepted guidelines and healthy controls in a case-control study, (ii) evaluation of VEGF concentrations in relation to disease type (localized or diffuse) and/or video capillaroscopy pattern (early, active, or late), (iii) assessment of VEGF concentrations in SSc patients with or without specific complications, (iv) inclusion of adult participants, and (v) availability of the full text of the article in English language. Exclusion criteria were: (i) investigation of VEGF concentrations in immunological conditions other than SSc, (ii) inclusion of participants under 18 years, and (iii) study design other than case-control.
The investigators independently hand-searched the references of the retrieved articles to identify additional studies, and extracted the following variables from each article: year of publication, first author, country and continent where the study was conducted, number of participants, age, male-to-female ratio, mean disease duration, VEGF concentrations, biological matrix assessed (serum or plasma), use of glucocorticoids, immunosuppressors, and vasodilators, fraction of patients affected by diffuse or localized form, early, active, or late video capillaroscopy patterns, digital ulcers, pulmonary hypertension, interstitial lung disease, telangiectasias, and alveolitis.
We assessed the risk of bias using the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) Critical Appraisal Checklist for analytical studies (35), and the certainty of evidence using the Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) Working Group system (36). We fully adhered to the PRISMA 2020 statement (Supplementary Table 1) (37), and registered the study protocol in an international repository (PROSPERO registration number: CRD42024552925).
Statistical analysis
We calculated the standardized mean differences (SMDs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for each study to generate forest plots to investigate differences in VEGF concentrations between SSc patients and healthy controls and between SSc with different disease type, video capillaroscopy pattern, and with or without complications. A p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant. We extracted data from graphs using the Graph Data Extractor software (San Diego, CA, USA) and extrapolated means and standard deviations from medians and interquartile or full ranges as previously reported (38). SMD heterogeneity was assessed using the Q statistic (significance level at p<0.10) and ranked as low (I2 ≤25%), moderate (25%< I2 <75%), or high (I2 ≥75%). We used a random-effects model based on the inverse-variance method in presence of high heterogeneity (39, 40).
We conducted sensitivity analyses to confirm the stability of the results (41), and assessed the presence of publication bias using standard methods (42–44). We also conducted univariate meta-regression and subgroup analyses to investigate possible associations between the effect size and the following parameters: year of publication, study country and continent, number of participants, age, male-to-female ratio, mean disease duration, sample matrix (serum or plasma), disease type, video capillaroscopy pattern, complications, and use of glucocorticoids, immunosuppressors, or vasodilators (45, 46). Statistical analyses were performed using Stata 14 (Stata Corp., College Station, TX, USA).
Results
Systematic search and study selection
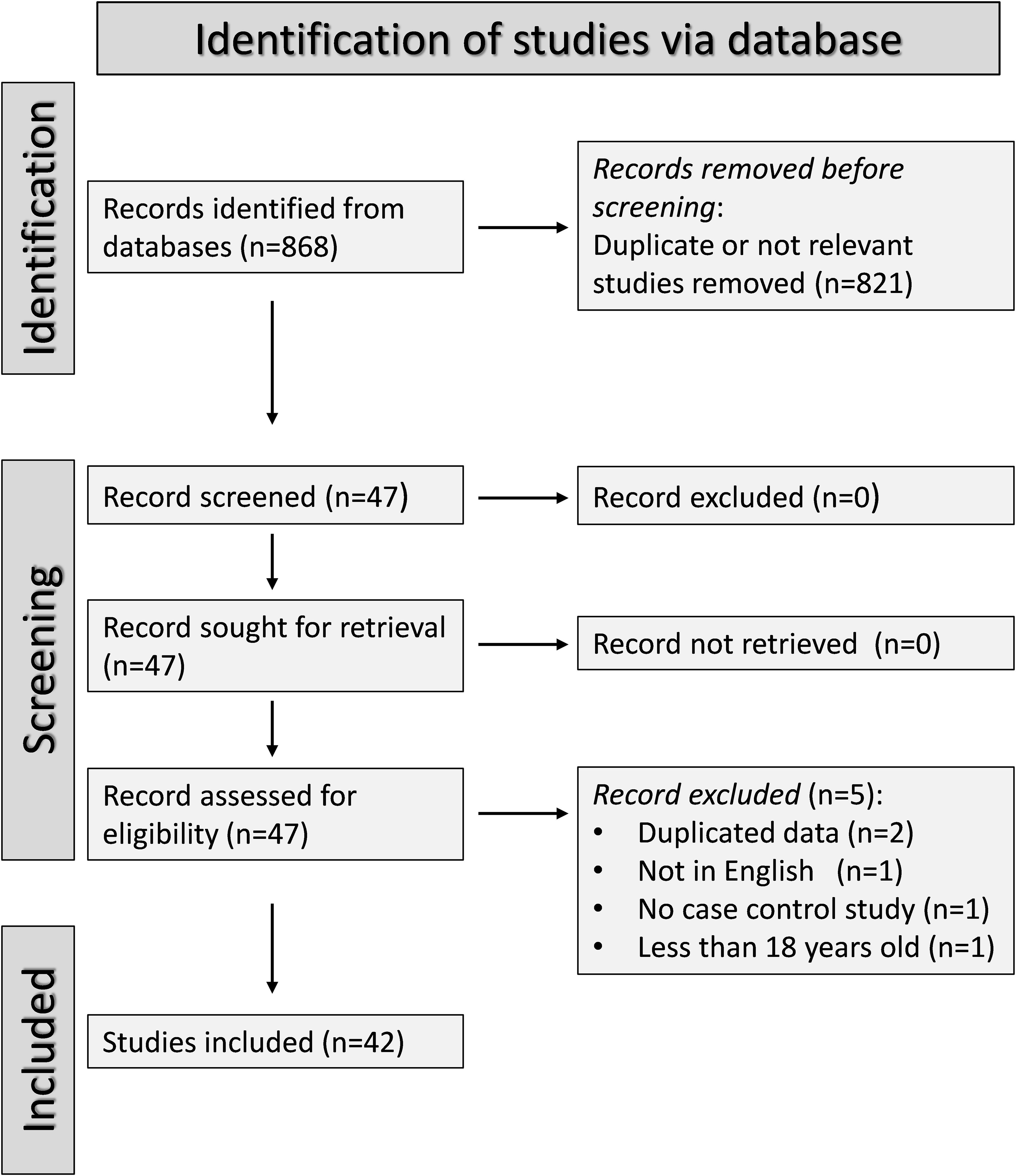
The flow chart of the screening process is illustrated in Figure 1. After initially identifying 568 articles, 521 were excluded because they were either irrelevant (i.e., different biological matrices analysed such as urine or tissues, cellular or molecular studies, animal studies, pharmacological trials outside the scope of our systematic review, longitudinal studies without control groups, and studies without a case-control or cohort design), or presented duplicate data. Full-text review of the remaining 47 articles led to the further exclusion of two studies because they presented duplicate data, one study because it was not case-control, one study written in a non-English language, and one study including participants under 18 years. Therefore, 42 studies were included in the final analysis (22, 28, 31–33, 43, 47–82). The risk of bias was low in 29 studies (28, 32, 47–51, 53–56, 58, 59, 62–65, 68–72, 74–79, 81) and moderate in the remaining 13 (22, 31, 33, 43, 52, 57, 60, 61, 66, 67, 73, 80, 82) (Supplementary Table 2). The initial level of certainty was adjudicated as low (level 2) given the case-control design of the selected studies.
Presence of SSc
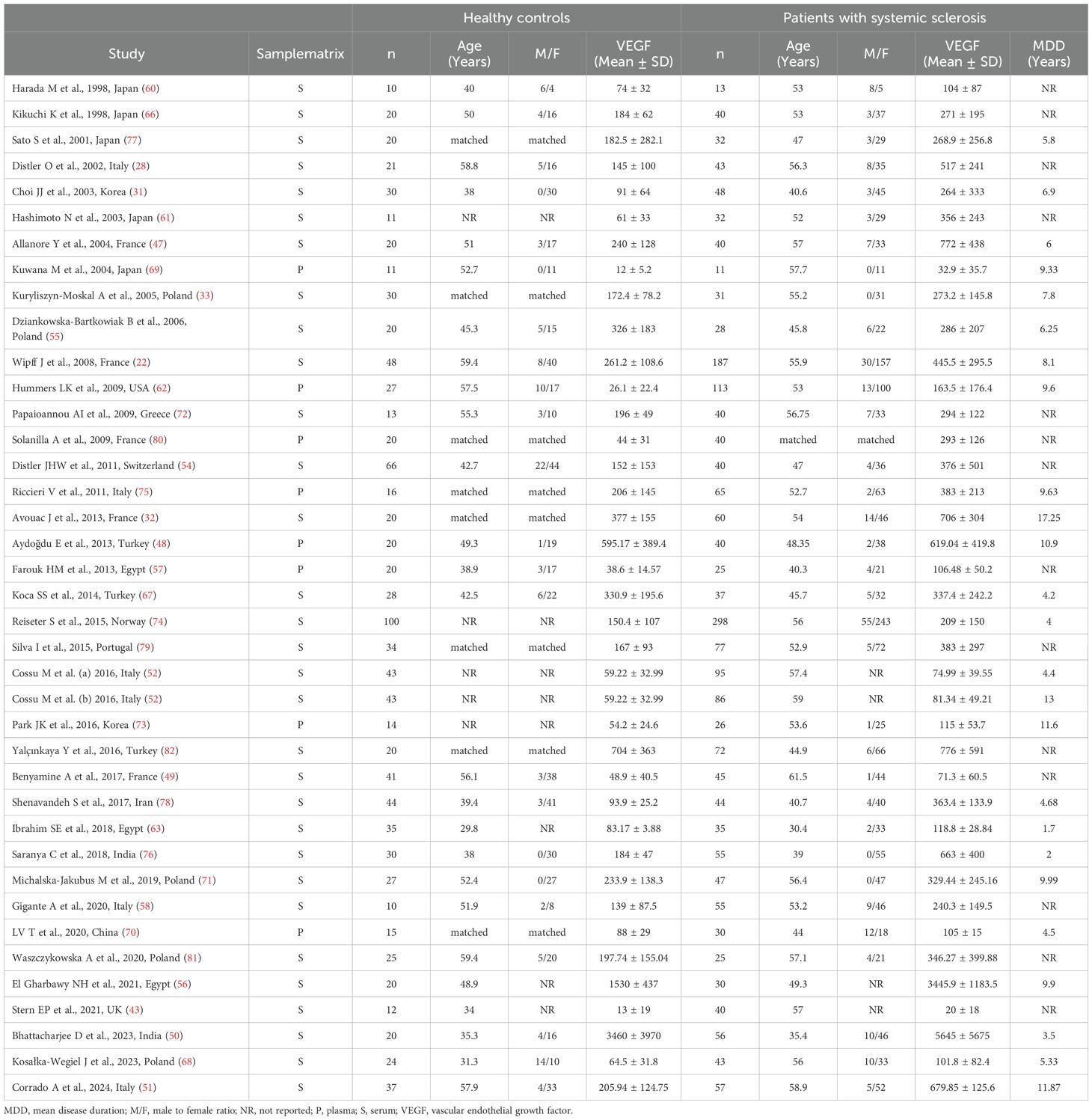
Thirty-eight studies including 39 group comparators assessed VEGF concentrations in 2,181 SSc patients (mean age 52 years, 87% females) and 1,065 healthy controls (mean age 48 years, 82% females) (22, 28, 31–33, 43, 47–52, 54–58, 60–63, 66–82) (Table 1). Twenty studies were conducted in Europe (22, 28, 32, 33, 43, 47, 49, 51, 52, 54, 55, 58, 68, 71, 72, 74, 75, 79–81), 14 in Asia (31, 48, 50, 60, 61, 66, 67, 69, 70, 73, 76–78, 82), three in Africa (56, 57, 63), and one in America (62). VEGF was measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in 32 studies (22, 28, 31–33, 47–51, 54–58, 60–63, 66, 67, 69, 71–74, 76–81) and a platform for multi-analyte profiling in the remaining six (43, 52, 68, 70, 75, 82). Thirty-two studies measured VEGF in serum (22, 28, 31–33, 43, 47, 49–52, 54–56, 58, 60, 61, 63, 66–68, 71, 72, 74, 76–79, 81, 82) and eight in plasma (48, 57, 62, 69, 70, 73, 75, 80). Disease duration was reported in 24 studies and ranged between 1.7 and 17.25 years (22, 31–33, 47, 48, 50–52, 55, 56, 62, 63, 67–71, 73–78).
The risk of bias was considered low in 25 studies (28, 32, 47–51, 54–56, 58, 62, 63, 68–72, 74–79, 81) studies and moderate in the remaining 13 (22, 31, 33, 43, 52, 57, 60, 61, 66, 67, 73, 80, 82) (Supplementary Table 2).
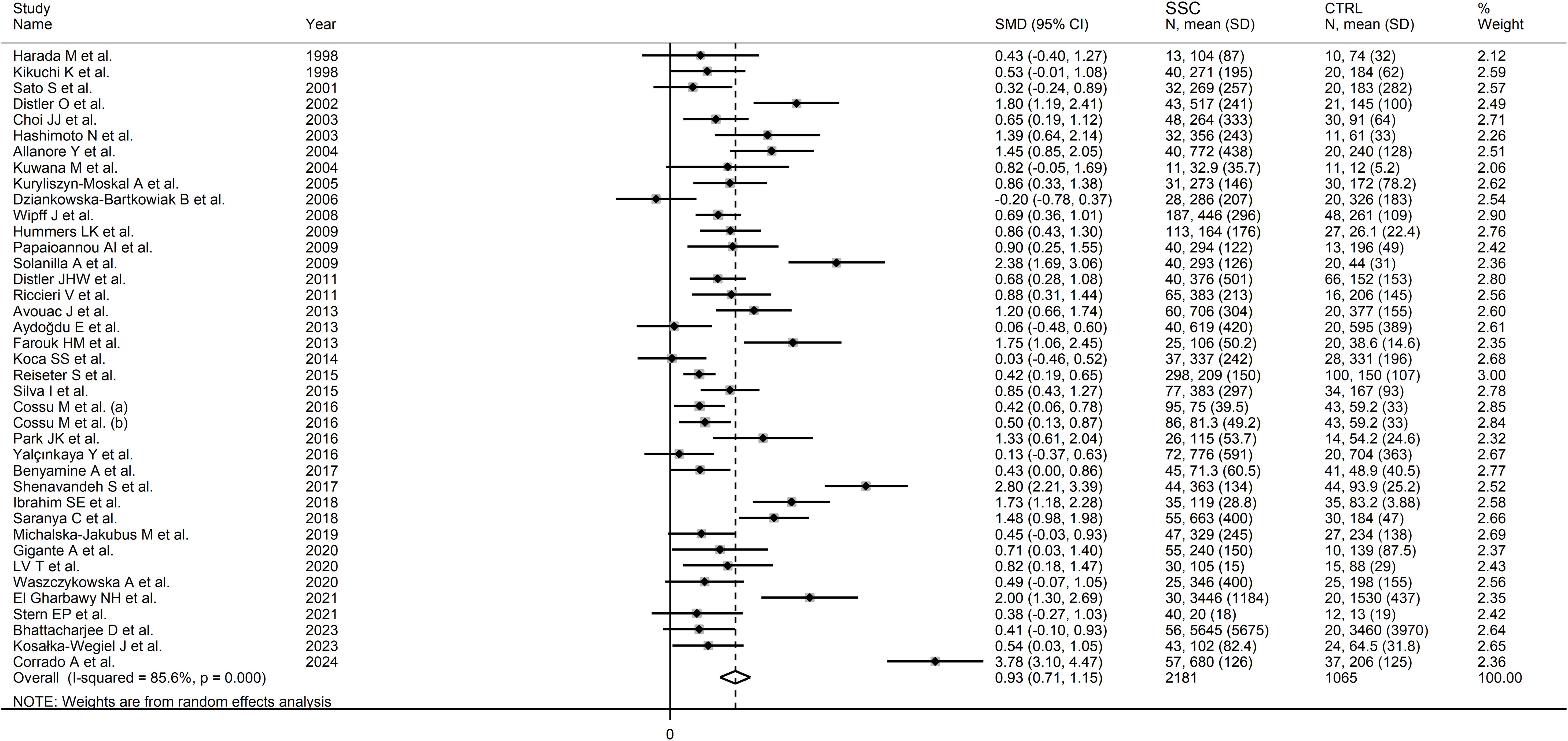
Pooled analyses showed that SSc patients had significantly higher VEGF concentrations than controls (SMD=0.93, 95% CI 0.71 to 1.15, p<0.001; I2 = 85.6%, p<0.001; Figure 2). Sensitivity analysis showed stability of the results, with pooled SMD values ranging between 0.67 and 0.96 (Supplementary Figure 1).
There was significant publication bias (Begg’s test, p=0.003; Egger’s test, p=0.005). The “trim-and-fill” method identified ten missing studies to be added to the left side of the funnel plot to ensure symmetry (Supplementary Figure 2). The resulting effect size was attenuated but still significant (SMD=0.56, 95% CI 0.30 to 0.82, p<0.001).
No significant associations were observed between the effect size and age (t=-1.02, p=0.31), male-to-female ratio (t=1.51, p=0.14), year of publication (t=0.91, p=0.37), number of participants (t=-0.70, p=0.49), mean SSc duration (t=0.60, p=0.55), or use of glucocorticoids (t=-1.85, p=0.08), immunosuppressors (t=-1.05, p=0.32), or vasodilators (t=-0.37, p=0.72) in univariate meta-regression analysis. In sub-group analysis, the pooled SMD of studies conducted in Africa (SMD=1.81, 95% CI 1.44 to 2.18, p<0.001; I2 = 0.0%, p=0.827) was significantly higher (p=0.039) than that of studies conducted in Asia (SMD=0.79, 95% CI 0.39 to 1.19, p<0.001; I2 = 84.8%, p<0.001) but not (p=0.08) Europe (SMD=0.90, 95% CI 0.62 to 1.18, p<0.001; I2 = 86.4%, p<0.001; Figure 3), with a virtually absent heterogeneity in the African subgroup. Non-significant differences (p=0.53) in pooled SMD were observed between studies measuring serum (SMD=0.89, 95% CI 0.65 to 1.13, p<0.001; I2 = 86.8%, p<0.001) and plasma (SMD=1.09, 95% CI 0.61 to 1.91, p=1.57; I2 = 79.1%, p<0.001). Finally, the pooled SMD was non-significantly different (p=0.12) between studies using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (SMD=1.03, 95% CI 0.77 to 1.28, p<0.001; I2 = 87.4%, p<0.001) and a platform for multi-analyte profiling (SMD=0.49, 95% CI 0.31 to 0.67, p<0.001; I2 = 0.0%, p=0.52), with a virtually absent between-study variance in the multi-analyte profiling subgroup.
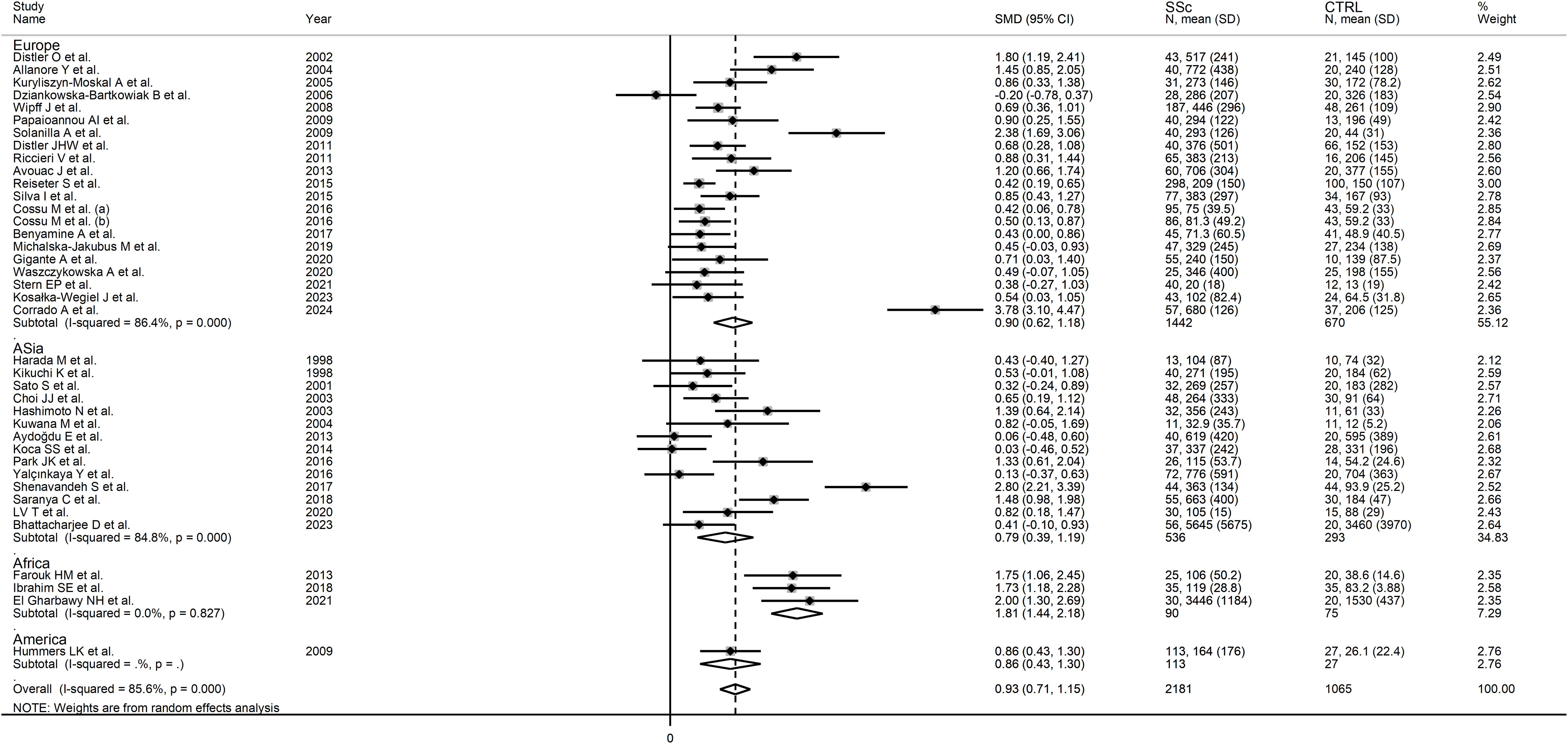
Figure 3. Forest plot of studies investigating VEGF concentrations in SSc patients and controls according to geographical area.
The overall level of certainty was upgraded to moderate (level 3) after considering the low-moderate risk of bias in all studies (no change), the high but partially explainable heterogeneity (no change), the lack of indirectness (no change), the large effect size (SMD=0.93; upgrade one level) (83), and the presence of publication bias which was addressed using the “trim-and-fill” method (no change).
Localized vs. diffuse disease
Eleven studies investigated VEGF concentrations in 228 SSc patients with diffuse form and 279 with localized form (28, 31, 47, 52, 54, 57, 65, 66, 76, 78, 81) (Table 2). Five studies were conducted in Europe (28, 47, 52, 54, 81), five in Asia (31, 65, 66, 76, 78), and one in Africa (57). Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used in all studies except one which used a platform for multi-analyte detection (52). Except for one study (57), measurements were conducted in serum.
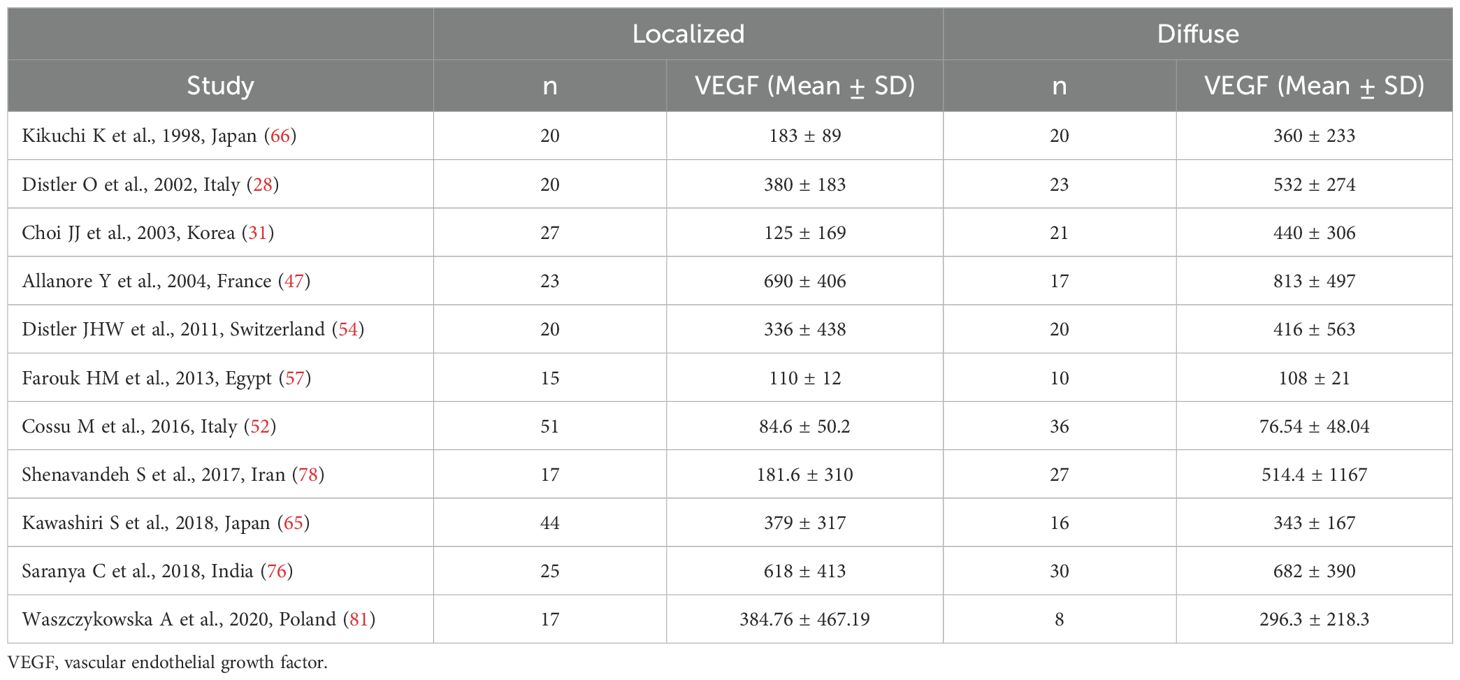
Table 2. Summary of studies reporting VEGF concentrations in SSc patients with localized and diffuse disease.
The risk of bias was considered low in seven studies (28, 47, 54, 65, 76, 78, 81) and moderate in the remaining four (31, 52, 57, 66) (Supplementary Table 2).
The pooled analysis showed that SSc patients with diffuse disease had significantly higher VEGF concentrations than those with localized disease (SMD=0.30, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.59, p=0.046; I2 = 60.3%, p=0.005; Figure 4). The results were stable in sensitivity analysis, with pooled SMD values ranging between 0.19 and 0.36 (Supplementary Figure 3).
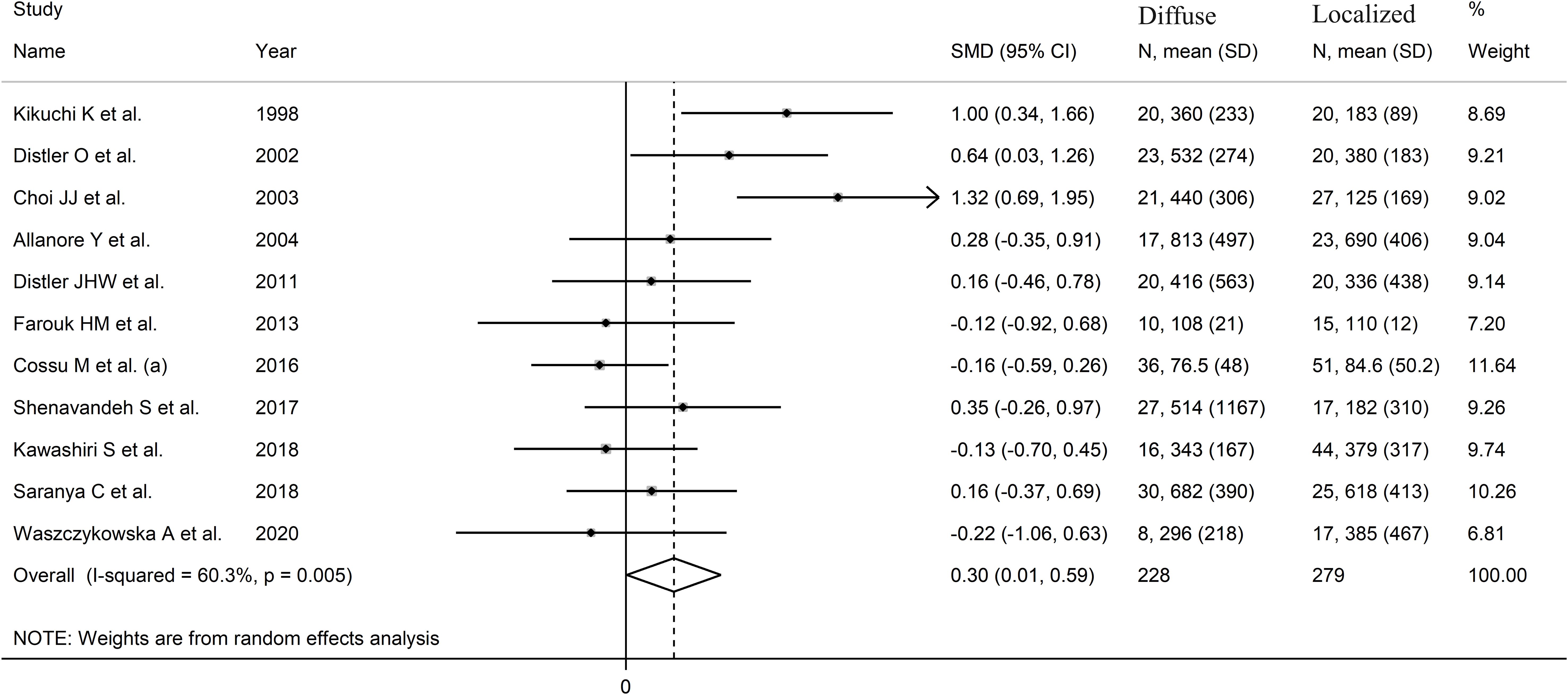
Figure 4. Forest plot of studies investigating VEGF concentrations in SSc patients with diffuse or localized form.
There was no publication bias (Begg’s test, p=0.35; Egger’s test, p=0.46). Accordingly, the “trim-and-fill” method did not identify any missing study to be added to the funnel plot to ensure symmetry (Supplementary Figure 4). The resulting effect size was increased and still significant (SMD=0.51, 95% CI 0.08 to 0.94; p=0.021).
A limited number of meta-regression and subgroup analyses could be performed due to the limited number of studies. No significant associations were found between the effect size and sample size (t=-0.65, p=0.53). By contrast, there was a significant correlation with the year of publication (t=-3.95, p=0.003; Supplementary Figure 5A), as also confirmed by cumulative analysis performed using the metacum command (Supplementary Figure 5B). In sub-group analysis, the pooled SMD was significantly different in studies conducted in Asia (SMD=0.53, 95% CI 0.01 to 1.05, p=0.048; I2 = 73.5%, p=0.004) but not Europe (SMD=0.13, 95% CI -0.18 to 0.44, p=0.41; I2 = 24.9%, p=0.25; Figure 5), with a substantial reduction in heterogeneity in the European subgroup.
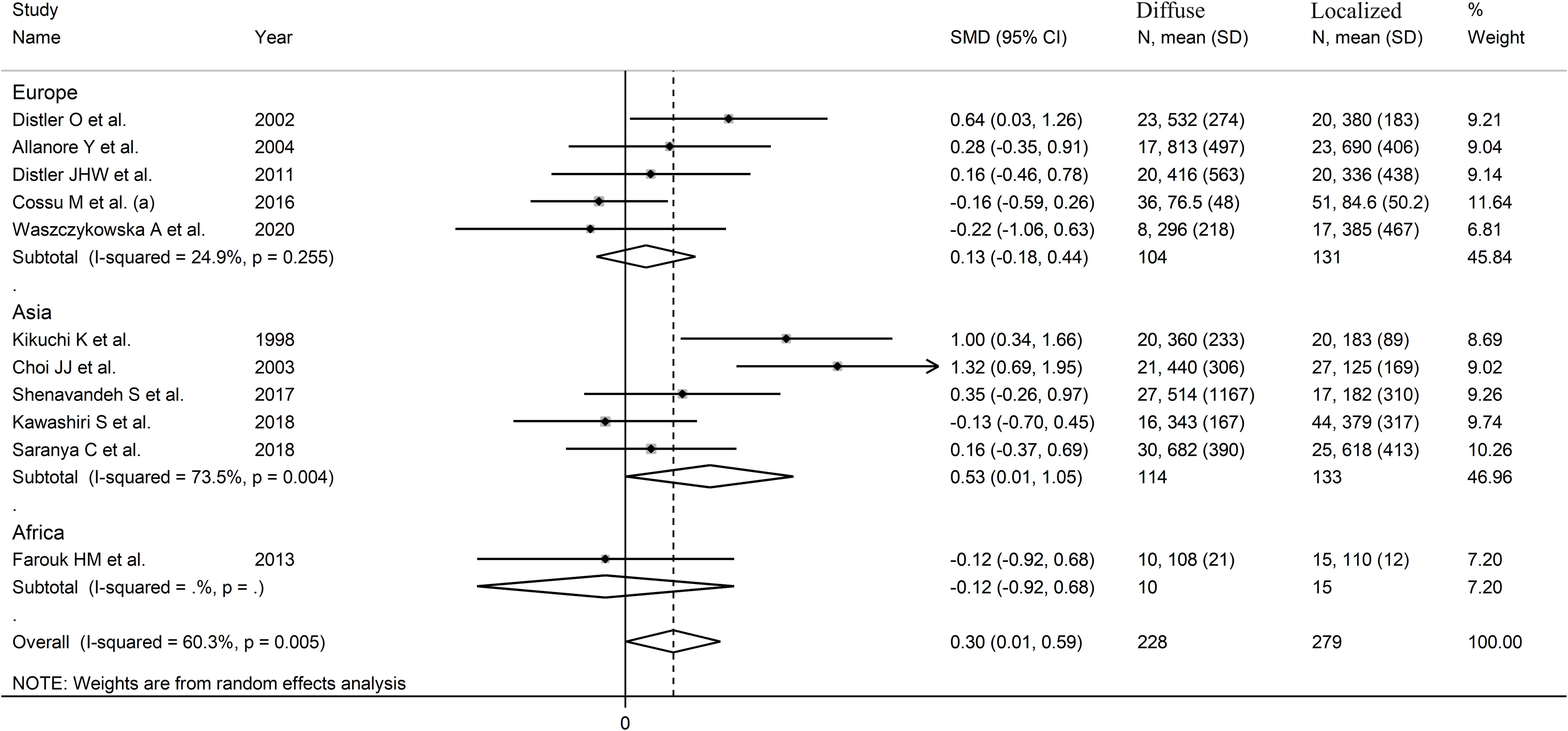
Figure 5. Forest plot of studies investigating VEGF concentrations in SSc patients with localized or diffuse form according to geographical area where the study was conducted.
The overall level of certainty remained low (level 2) after considering the low-moderate risk of bias in all studies (no change), the high but partially explainable heterogeneity (no change), the lack of indirectness (no change), the small effect size (SMD=0.30; no change) (83), and the lack of publication bias (no change).
Capillaroscopy pattern
Five studies reported serum VEGF concentrations in SSc patients stratified according to the capillaroscopy pattern (28, 32, 59, 71, 82) (Table 3). Four studies were conducted in Europe (28, 32, 59, 71) and one in Asia (82). All studies used an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay except one, which used used a platform for multi-analyte detection (82).
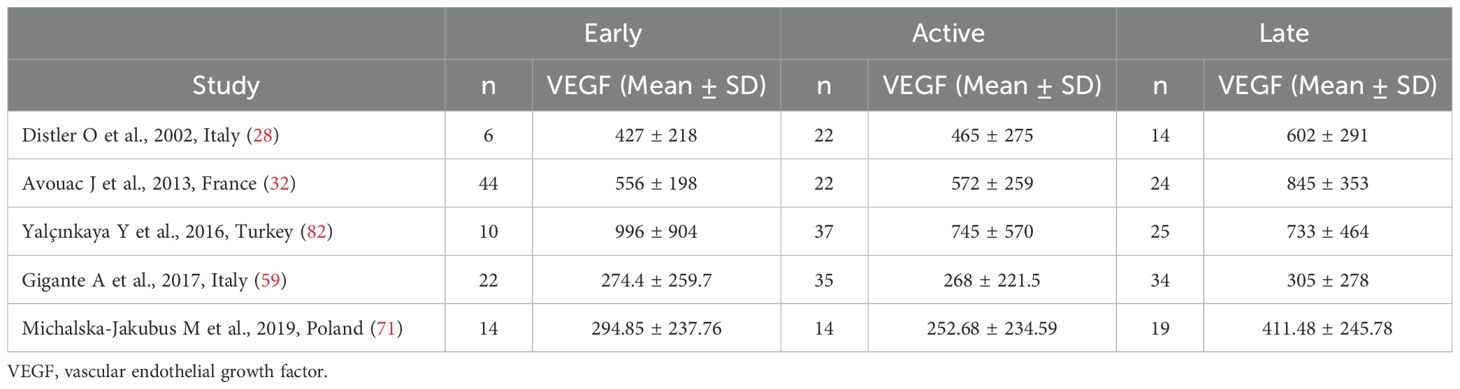
Table 3. Summary of studies reporting VEGF concentrations in SSc patients according to capillaroscopy pattern.
Pooled analysis showed non-significant differences in VEGF concentrations between early and active SSc patients (SMD=-0.06, 95% CI -0.34 to 0.22, p=0.68; I2 = 0.0%, p=0.85; Figure 6). Sensitivity analysis confirmed the stability of the results, with pooled SMD values ranging between -0.12 and 0.00 (Supplementary Figure 6). Assessment of publication bias, meta-regression and sub-group analyses could not be performed because of the small number of studies.
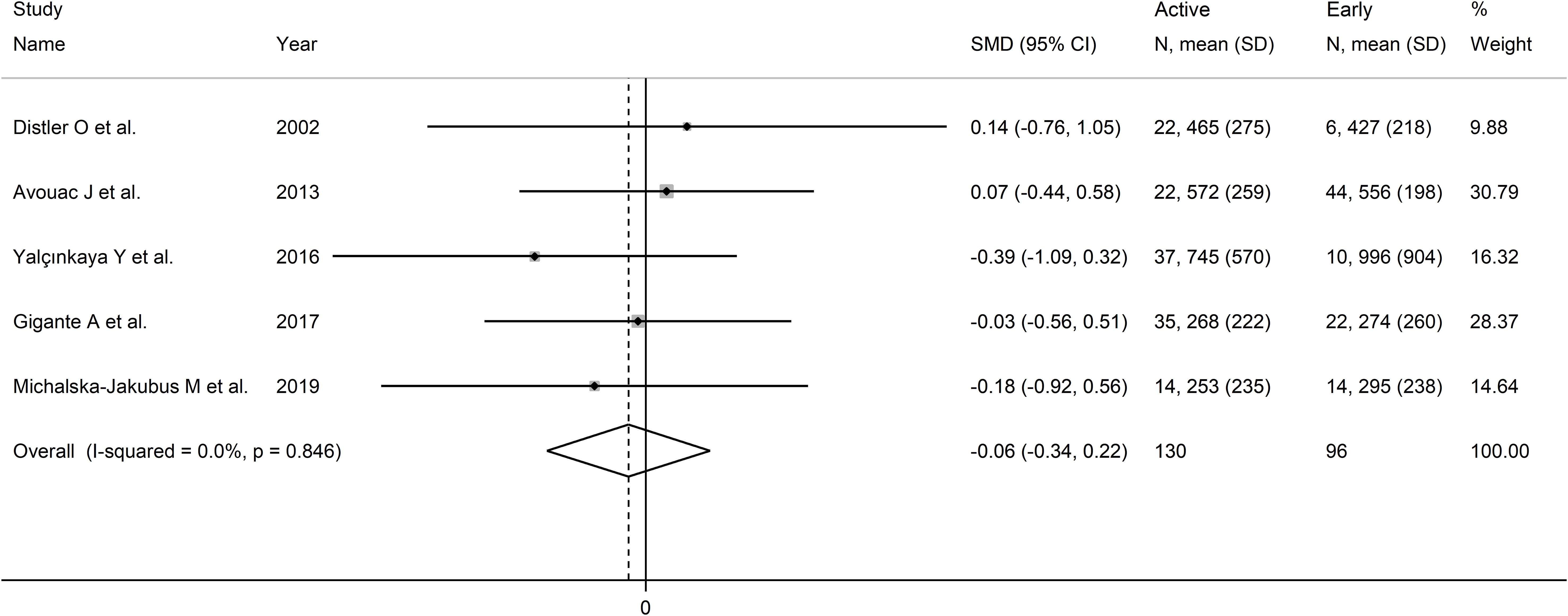
Figure 6. Forest plot of studies investigating VEGF concentrations in SSc patients according to capillaroscopy pattern (early vs. active).
Pooled analysis showed that VEGF concentrations was higher in late than active SSc patients (SMD=0.35, 95% CI 0.09 to 0.61, p=0.008; I2 = 38.9%, p=0.16; Figure 7). Sensitivity analysis confirmed stability of the results, with pooled SMD values ranging between 0.23 and 0.49 (Supplementary Figure 7). Assessment of publication bias, meta-regression and sub-group analyses could not be performed because of the small number of studies.
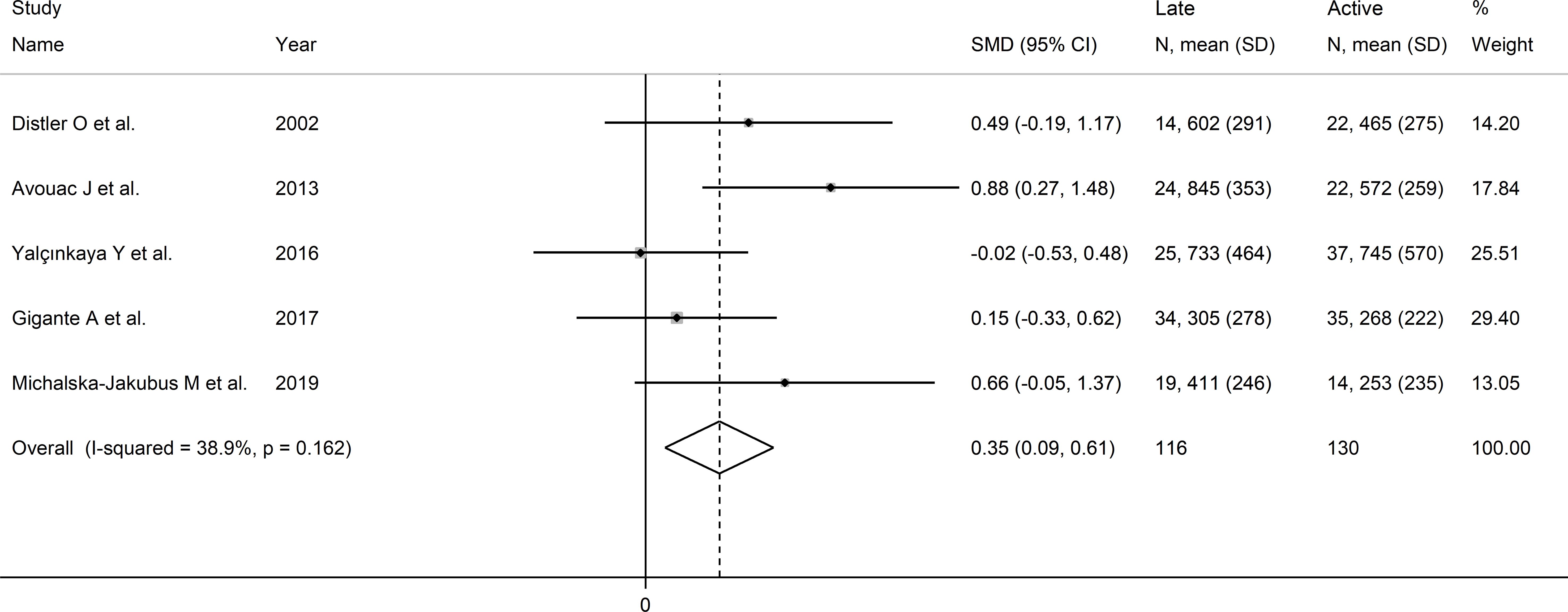
Figure 7. Forest plot of studies investigating VEGF concentrations according to capillaroscopy pattern (active vs. late).
Pooled results showed that VEGF concentrations were non-significantly different between late and early SSc patients (SMD=0.40, 95% CI -0.13 to 0.93, p=0.14; I2 = 67.3%, p=0.016; Figure 8). The results were stable in sensitivity analysis (pooled SMD values ranged between 0.17 and 0.58; Supplementary Figure 8). Assessment of publication bias, meta-regression and sub-group analyses could not be performed because of the small number of studies.
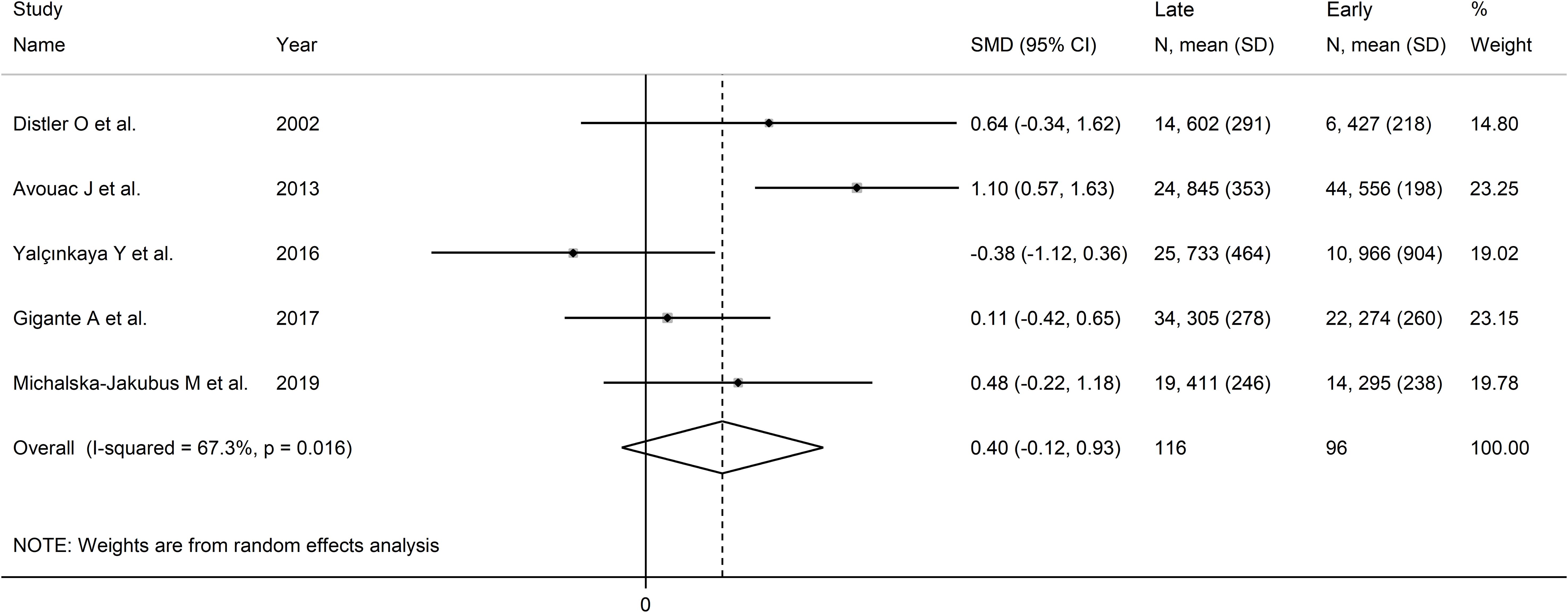
Figure 8. Forest plot of studies investigating VEGF concentrations according to capillaroscopy pattern (early vs. late).
The overall level of certainty was downgraded to very low (level 1) because of the lack of assessment of publication bias.
Digital ulcers
Seven studies investigated serum VEGF concentrations in 562 SSc patients, 265 without and 297 with digital ulcers (28, 52, 58, 59, 65, 79) (Table 4). All studies were conducted in Europe except one which was conducted in Asia (65). All studies used an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay except one, which used used a platform for multi-analyte detection (52).
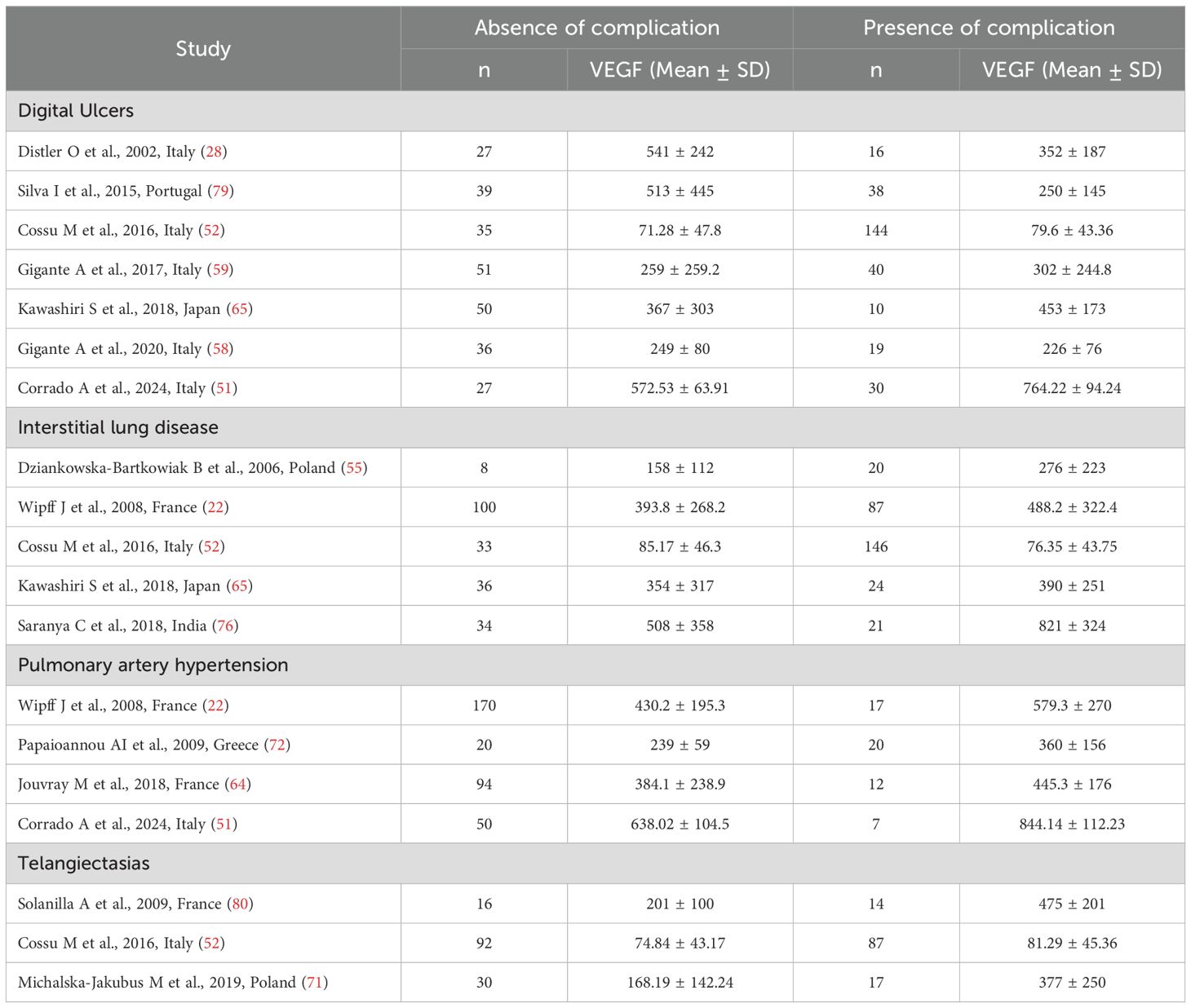
Table 4. Summary of studies reporting VEGF concentrations in SSc patients with and without complications.
Pooled results showed non-significant between-group differences in VEGF concentrations (SMD=0.14, 95% CI -0.51 to 0.79, p=0.67; I2 = 91.0%, p<0.001; Figure 9). Sensitivity analysis showed stability of the results, with an effect size ranging between -0.20 and 0.30 (Supplementary Figure 9).
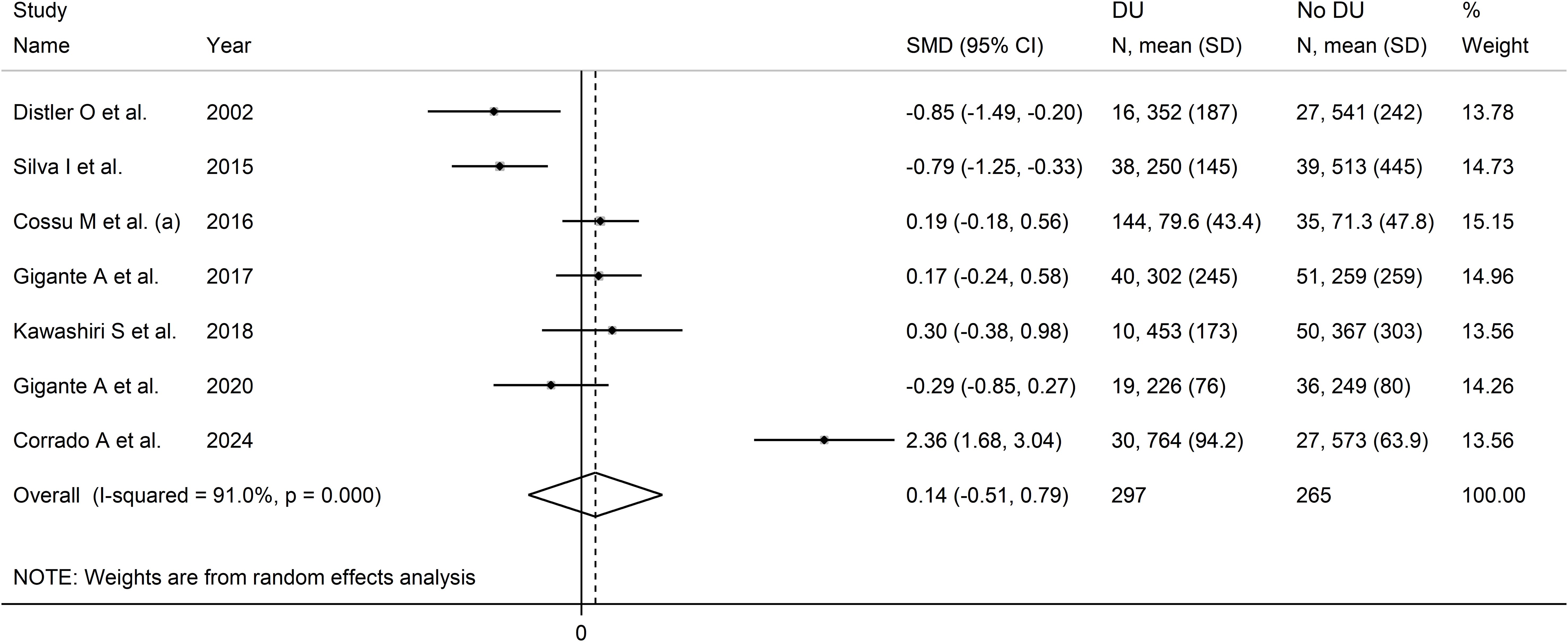
Figure 9. Forest plot of studies investigating VEGF concentrations in SSc patients with or without digital ulcers.
Assessment of publication bias, meta-regression and sub-group analyses could not be performed because of the small number of studies. Consequently, the overall certainty of evidence was downgraded to very low (level 1).
Interstitial lung disease
Five studies investigated serum VEGF concentrations in 509 SSc patients, 211 without and 298 with interstitial lung disease (22, 52, 55, 65, 76) (Table 4). Three studies were performed in Europe (22, 52, 55) and two in Asia (65, 76). All studies used an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay except one, which used used a platform for multi-analyte detection (52).
Pooled results showed that SSc patients with interstitial lung disease had non-significantly higher VEGF concentrations than SSc patients without (SMD=0.29, 95% CI -0.06 to 0.65, p=0.11; I2 = 65.5%, p=0.021; Figure 10). Sensitivity analysis showed that the pooled SMD value become significant after removing the study by Cossu et al. (52) (SMD=0.43, 95% CI 0.12 to 0.74, p=0.001, I2 = 34.9%, p=0.23), with a concomitant reduction in between-study variance (Supplementary Figure 10).
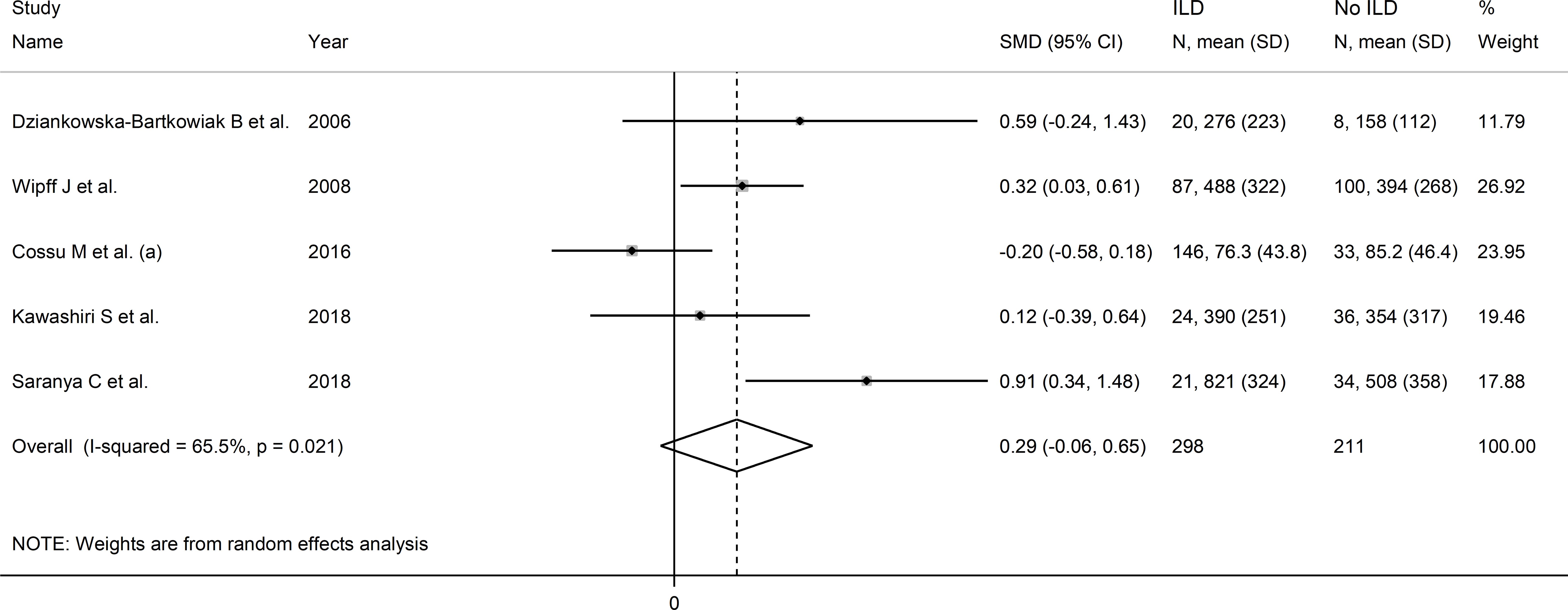
Figure 10. Forest plot of studies investigating VEGF concentrations in SSc patients with or without interstitial lung disease.
Assessment of publication bias, meta-regression and sub-group analyses could not be performed because of the small number of studies. Consequently, the overall certainty of evidence was downgraded to very low (level 1).
Pulmonary hypertension
Four studies investigated serum VEGF concentrations in 390 SSc patients, 334 without and 56 with pulmonary hypertension (22, 51, 64, 72). All studies were conducted in Europe and used an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Pooled results showed that SSc patients with pulmonary hypertension had significantly higher VEGF concentrations than SSc patients without (SMD=0.93, 95% CI 0.34 to 1.53, p=0.002; I2 = 70.9%, p=0.016; Figure 11).
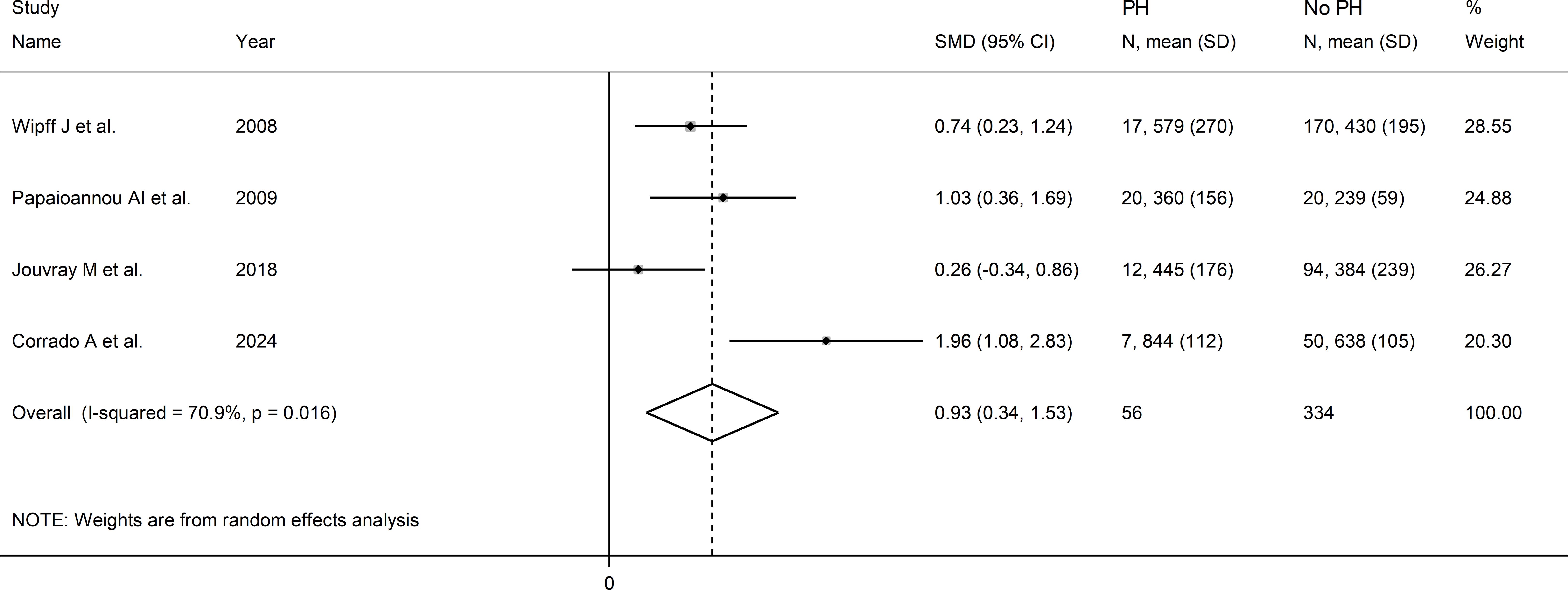
Figure 11. Forest plot of studies investigating VEGF concentrations in SSc patients with and without pulmonary hypertension.
Assessment of sensitivity, publication bias, meta-regression and sub-group analyses could not be performed because of the small number of studies. Consequently, the overall certainty of evidence was downgraded to very low (level 1).
Telangiectasias
Three studies investigated VEGF concentrations in 256 SSc patients, 138 without and 118 with telangiectasias (52, 71, 80). All studies were conducted in Europe and used an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Two studies measured serum (52, 71) and the remaining one plasma (80).
Pooled results showed a non-significant trend toward higher VEGF concentrations in patients with telangiectasias (SMD=0.94, 95% CI -0.03 to 1.91, p=0.058, I2 = 88.4%, p<0.001; Figure 12).
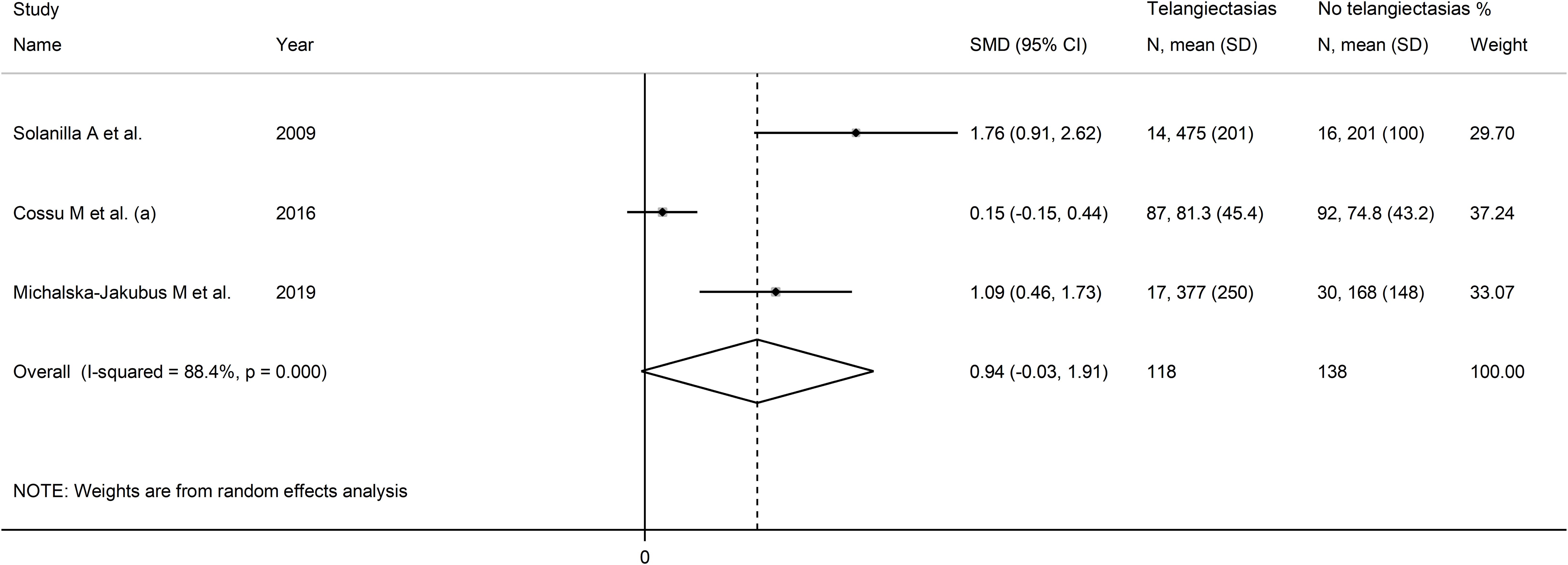
Figure 12. Forest plot of studies investigating VEGF concentrations in SSc patients with and without telangiectasias.
Assessment of sensitivity, publication bias, meta-regression and sub-group analyses could not be performed because of the small number of studies. Consequently, the overall certainty of evidence was downgraded to very low (level 1).
Alveolitis
One study performed in Italy reported VEGF concentrations in 55 SSc patients, 27 without and 28 with alveolitis (53). Patients with alveolitis had non-significantly higher VEGF concentrations compared to those without (median: 53.9 pg/mL, IQR 5.5–184.3 pg/mL vs. 31.8 pg/mL, IQR 5.5–321.8 pg/mL, p>0.05).
Discussion
This systematic review and meta-analysis has highlighted the presence of significant elevations in plasma or serum VEGF concentrations in patients with SSc when compared to healthy controls. In further analyses specifically in SSc patients, higher VEGF concentrations were significantly associated with diffuse disease, late vs. active video capillaroscopy pattern, and pulmonary hypertension. The alterations in VEGF concentrations associated with microvascular (video capillaroscopy pattern) and macrovascular (pulmonary hypertension) complications are also likely to reflect a state of nitric oxide dysregulation and endothelial dysfunction (84–87). By contrast, there were no significant associations with other complications such as digital ulcers, interstitial lung disease, or telangiectasias, whereas only one study reported non-significant differences in VEGF concentrations between SSc patients with and without alveolitis.
Meta-regression and subgroup analysis of studies investigating VEGF concentrations in SSc patients and controls showed non-significant associations between the effect size of the reported differences and various patient and study characteristics, particularly mean SSc duration and use of established, e.g., immunosuppressors and vasodilators (88), and less common, e.g. corticosteroids (89), treatments. By contrast, significant associations were observed with the geographical location where the study was conducted with a significantly higher effect size in African than Asian, but not European, studies. Meta-regression and subgroup analyses of studies investigating VEGF in SSc patients with localized and diffuse disease showed a significant and inverse association between the effect size and publication year and the lack of significant differences in European studies when compared to studies conducted in Asia which reported significant differences. The lack of significant associations between the effect size of between-group differences in VEGF concentrations and mean disease duration suggests that VEGF concentrations are already increased during the early stages of SSc compared to the general population. However, such concentrations can further increase in SSc patients with more advanced disease, as suggested by the higher VEGF concentrations observed in SSc patients with late compared to active videocapillaroscopy pattern. Taken together, the results of this systematic review and meta-analysis suggest that measuring VEGF concentrations can be useful in assessing and managing patients with SSc during different stages of the disease. However, the role of VEGF in different clinical manifestations of SSc requires confirmation in further studies. Furthermore, prospective studies are warranted to determine whether VEGF may be useful not only as a diagnostic but also as a prognostic biomarker in SSc.
Studies conducted in experimental models of SSc using VEGF transgenic mice have shown that VEGF exerts dose-dependent pro-fibrotic effects (21). Notably, these effects were accompanied by ineffective angiogenesis and vasculopathy, a common feature in SSc patients (29). Therefore, alterations in VEGF are likely to reflect a common pathway involved in the development of vasculopathy, inefficient angiogenesis, and fibrosis in SSc (30). Notably, VEGF pre-mRNA can lead to the synthesis of two heterodimers exerting opposite effects on angiogenesis, VEGF165 (pro-angiogenic) and VEGF165b (anti-angiogenic) (90, 91). The relative overexpression of VEGF165b in SSc has been shown to be associated with increased expression of transforming growth factor-β1 and serine/arginine protein 55 splicing factor, exerting pro-fibrotic effects, in endothelial cells, keratinocytes, and fibroblasts as well as significant capillary morphological alterations (92). In our analyses, increased VEGF concentrations were particularly evident in SSc patients with diffuse disease, pulmonary hypertension, and late vs. active capillaroscopy pattern. Future studies should investigate whether VEGF165 and VEGF165b play a pathophysiological role in these subgroups as well as the therapeutic role of VEGF modulators (93, 94). Clearly, the identification of possible interventions targeting VEGF requires additional research to determine the most promising target(s), i.e., VEGF, VEGF165, or VEGF165b. Additional research should also investigate the possible influence of ethnicity and genetic factors in the complex interplay between VEGF and SSc, as also suggested in our subgroup analyses (95).
Our study has several strengths, include the assessment of VEGF concentrations in a wide range of SSc subtypes (extent of fibrosis, video capillaroscopy patterns, and key clinical complications), the evaluation of the certainty of evidence for each endpoint, and the evaluation of specific study and patient characteristics associated with the effect size. One important limitation is the high heterogeneity observed. However, this could be partially explained in our sub-group analyses (presence of SSc: study location and analytical method used; disease type: study location). Another limitation is represented by the limited number of studies providing details regarding the presence of disease states and/or risk factors associated per se with alterations in circulating VEGF concentrations (96–98).
In conclusion, our study has shown significant elevations in VEGF concentrations in SSc and, particularly, diffuse disease, specific video capillaroscopy patterns, and pulmonary hypertension. Pending further prospective studies investigating a wide range of SSc subtypes in different geographical locations, measuring VEGF concentrations might assist in assessing and managing patients with this chronic and disabling autoimmune disorder.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
AZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AM: Data curation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1442913/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Trojanowska M. Cellular and molecular aspects of vascular dysfunction in systemic sclerosis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2010) 6:453–60. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2010.102
2. Ren H, Liu L, Xiao Y, Shi Y, Zeng Z, Ding Y, et al. Further insight into systemic sclerosis from the vasculopathy perspective. BioMed Pharmacother. (2023) 166:115282. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115282
3. Allanore Y, Simms R, Distler O, Trojanowska M, Pope J, Denton CP, et al. Systemic sclerosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2015) 1:15002. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2015.2
4. Volkmann ER, Andreasson K, Smith V. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet. (2023) 401:304–18. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01692-0
5. Matucci-Cerinic M, Kahaleh B, Wigley FM. Review: evidence that systemic sclerosis is a vascular disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2013) 65:1953–62. doi: 10.1002/art.37988
6. Romano E, Rosa I, Fioretto BS, Matucci-Cerinic M, Manetti M. New insights into profibrotic myofibroblast formation in systemic sclerosis: when the vascular wall becomes the enemy. Life (Basel). (2021) 11:610. doi: 10.3390/life11070610
7. Saygin D, Highland KB, Tonelli AR. Microvascular involvement in systemic sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Microcirculation. (2019) 26:e12440. doi: 10.1111/micc.12440
8. Cutolo M, Soldano S, Smith V. Pathophysiology of systemic sclerosis: current understanding and new insights. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. (2019) 15:753–64. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2019.1614915
9. Lemmers JMJ, Velauthapillai A, van Herwaarden N, Vonk MC. Change of the microvascularization in systemic sclerosis, a matter of air. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. (2021) 35:101683. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2021.101683
10. Lescoat A, Cavalin C, Ehrlich R, Cazalets C, Ballerie A, Belhomme N, et al. The nosology of systemic sclerosis: how lessons from the past offer new challenges in reframing an idiopathic rheumatological disorder. Lancet Rheumatol. (2019) 1:e257–e64. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(19)30038-4
11. Lescoat A. Very Early Diagnosis of Systemic Sclerosis: Deciphering the heterogeneity of systemic sclerosis in the very early stages of the disease. J Scleroderma Relat Disord. (2023) 8:3–6. doi: 10.1177/23971983221129211
12. Distler O, Allanore Y, Denton CP, Matucci-Cerinic M, Pope JE, Hinzmann B, et al. Factors influencing early referral, early diagnosis and management in patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2018) 57:813–7. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex504
13. Ihn H, Sato S, Fujimoto M, Igarashi A, Yazawa N, Kubo M, et al. Characterization of autoantibodies to endothelial cells in systemic sclerosis (SSc): association with pulmonary fibrosis. Clin Exp Immunol. (2000) 119:203–9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01115.x
14. Kahaleh B. The microvascular endothelium in scleroderma. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2008) 47 Suppl 5:v14–5. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ken279
15. Farina A, Rosato E, York M, Gewurz BE, Trojanowska M, Farina GA. Innate immune modulation induced by EBV lytic infection promotes endothelial cell inflammation and vascular injury in scleroderma. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:651013. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.651013
16. Neidhart M, Kuchen S, Distler O, Bruhlmann P, Michel BA, Gay RE, et al. Increased serum levels of antibodies against human cytomegalovirus and prevalence of autoantibodies in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (1999) 42:389–92. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199902)42:2<389::AID-ANR23>3.0.CO;2-P
17. Maehara T, Kaneko N, Perugino CA, Mattoo H, Kers J, Allard-Chamard H, et al. Cytotoxic CD4+ T lymphocytes may induce endothelial cell apoptosis in systemic sclerosis. J Clin Invest. (2020) 130:2451–64. doi: 10.1172/JCI131700
18. Dooley A, Gao B, Bradley N, Abraham DJ, Black CM, Jacobs M, et al. Abnormal nitric oxide metabolism in systemic sclerosis: increased levels of nitrated proteins and asymmetric dimethylarginine. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2006) 45:676–84. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kei276
19. Pagkopoulou E, Soulaidopoulos S, Katsiki N, Malliari A, Loutradis C, Karagiannis A, et al. The role of asymmetric dimethylarginine in endothelial dysfunction and abnormal nitric oxide metabolism in systemic sclerosis: results from a pilot study. Clin Rheumatol. (2023) 42:1077–85. doi: 10.1007/s10067-022-06472-w
20. Sato S. Abnormalities of adhesion molecules and chemokines in scleroderma. Curr Opin Rheumatol. (1999) 11:503–7. doi: 10.1097/00002281-199911000-00010
21. Maurer B, Distler A, Suliman YA, Gay RE, Michel BA, Gay S, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor aggravates fibrosis and vasculopathy in experimental models of systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2014) 73:1880–7. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203535
22. Wipff J, Avouac J, Borderie D, Zerkak D, Lemarechal H, Kahan A, et al. Disturbed angiogenesis in systemic sclerosis: high levels of soluble endoglin. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2008) 47:972–5. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ken100
23. Shirai Y, Okazaki Y, Inoue Y, Tamura Y, Yasuoka H, Takeuchi T, et al. Elevated levels of pentraxin 3 in systemic sclerosis: associations with vascular manifestations and defective vasculogenesis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2015) 67:498–507. doi: 10.1002/art.38953
24. Almeida I, Oliveira Gomes A, Lima M, Silva I, Vasconcelos C. Different contributions of angiostatin and endostatin in angiogenesis impairment in systemic sclerosis: a cohort study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2016) 34 Suppl 100:37–42.
25. Fioretto BS, Rosa I, Matucci-Cerinic M, Romano E, Manetti M. Current trends in vascular biomarkers for systemic sclerosis: A narrative review. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:4097. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044097
26. Holmes DI, Zachary I. The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family: angiogenic factors in health and disease. Genome Biol. (2005) 6:209. doi: 10.1186/gb-2005-6-2-209
27. Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. (2003) 9:669–76. doi: 10.1038/nm0603-669
28. Distler O, del Rosso A, Giacomelli R, Cipriani P, Conforti ML, Guiducci S, et al. Angiogenic and angiostatic factors in systemic sclerosis: increased levels of vascular endothelial growth factor are a feature of the earliest disease stages and are associated with the absence of fingertip ulcers. Arthritis Res Ther. (2002) 4:R11. doi: 10.1186/ar596
29. Distler O, Distler JH, Scheid A, Acker T, Hirth A, Rethage J, et al. Uncontrolled expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors leads to insufficient skin angiogenesis in patients with systemic sclerosis. Circ Res. (2004) 95:109–16. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000134644.89917.96
30. Flower VA, Barratt SL, Ward S, Pauling JD. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in systemic sclerosis. Curr Rheumatol Rev. (2019) 15:99–109. doi: 10.2174/1573397114666180809121005
31. Choi JJ, Min DJ, Cho ML, Min SY, Kim SJ, Lee SS, et al. Elevated vascular endothelial growth factor in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol. (2003) 30:1529–33.
32. Avouac J, Vallucci M, Smith V, Senet P, Ruiz B, Sulli A, et al. Correlations between angiogenic factors and capillaroscopic patterns in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2013) 15:R55. doi: 10.1186/ar4217
33. Kuryliszyn-Moskal A, Klimiuk PA, Sierakowski S. Soluble adhesion molecules (sVCAM-1, sE-selectin), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and endothelin-1 in patients with systemic sclerosis: relationship to organ systemic involvement. Clin Rheumatol. (2005) 24:111–6. doi: 10.1007/s10067-004-0987-3
34. Cutolo M, Pizzorni C, Tuccio M, Burroni A, Craviotto C, Basso M, et al. Nailfold videocapillaroscopic patterns and serum autoantibodies in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatol (Oxford). (2004) 43:719–26. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keh156
35. Moola S, Munn Z, Tufanaru C, Aromataris E, Sears K, Sfetcu R, et al. Systematic reviews of etiology and risk. In: Aromataris E, Munn Z, editors. Joanna briggs institute reviewer’s manual. Johanna Briggs Institute, Adelaide, Australia (2017).
36. Balshem H, Helfand M, Schunemann HJ, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. J Clin Epidemiol. (2011) 64:401–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.07.015
37. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
38. Wan X, Wang W, Liu J, Tong T. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2014) 14:135. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-14-135
39. Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. (2002) 21:1539–58. doi: 10.1002/sim.1186
40. Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. (2003) 327:557–60. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
41. Tobias A. Assessing the influence of a single study in the meta-analysis estimate. Stata Tech Bull. (1999) 47:15–7.
42. Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics. (1994) 50:1088–101. doi: 10.2307/2533446
43. Stern EP, Unwin R, Burns A, Ong VH, Denton CP. Exploring molecular pathology of chronic kidney disease in systemic sclerosis by analysis of urinary and serum proteins. Rheumatol Adv Pract. (2021) 5:rkaa083. doi: 10.1093/rap/rkaa083
44. Duval S, Tweedie R. Trim and fill: A simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics. (2000) 56:455–63. doi: 10.1111/j.0006-341x.2000.00455.x
45. Borenstein M, Higgins JP. Meta-analysis and subgroups. Prev Sci. (2013) 14:134–43. doi: 10.1007/s11121-013-0377-7
46. Mathur MB, VanderWeele TJ. Meta-regression methods to characterize evidence strength using meaningful-effect percentages conditional on study characteristics. Res Synth Methods. (2021) 12:731–49. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.1504
47. Allanore Y, Borderie D, Lemarechal H, Ekindjian OG, Kahan A. Nifedipine decreases sVCAM-1 concentrations and oxidative stress in systemic sclerosis but does not affect the concentrations of vascular endothelial growth factor or its soluble receptor 1. Arthritis Res Ther. (2004) 6:R309–14. doi: 10.1186/ar1183
48. Aydoğdu E, Pamuk ÖN, Dönmez S, Pamuk GE. Decreased interleukin-20 level in patients with systemic sclerosis: are they related with angiogenesis? Clin Rheumatol. (2013) 32:1599–603. doi: 10.1007/s10067-013-2317-0
49. Benyamine A, Magalon J, Cointe S, Lacroix R, Arnaud L, Bardin N, et al. Increased serum levels of fractalkine and mobilisation of CD34+CD45– endothelial progenitor cells in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2017) 19:60. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1271-7
50. Bhattacharjee D, Mondal S, Saha A, Misra S, Chatterjee S, Rao A, et al. Effect of vasodilator and immunosuppressive therapy on the endothelial dysfunction in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Med. (2022) 23:905–15. doi: 10.1007/s10238-022-00845-w
51. Corrado A, Mansueto N, Correale M, Rella V, Tricarico L, Altomare A, et al. Flow Mediated Dilation in Systemic Sclerosis: Association with clinical findings, capillaroscopic patterns and endothelial circulating markers. Vasc Pharmacol. (2024) 154:107252. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2023.107252
52. Cossu M, Andracco R, Santaniello A, Marchini M, Severino A, Caronni M, et al. Serum levels of vascular dysfunction markers reflect disease severity and stage in systemic sclerosis patients. Rheumatology. (2016) 55:1112–6. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kew017
53. De Santis M, Bosello SL, Capoluongo E, Inzitari R, Peluso G, Lulli P, et al. A vascular endothelial growth factor deficiency characterises scleroderma lung disease. Ann Rheum Dis. (2012) 71:1461–5. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200657
54. Distler JHW, Strapatsas T, Huscher D, Dees C, Akhmetshina A, Kiener HP, et al. Dysbalance of angiogenic and angiostatic mediators in patients with mixed connective tissue disease. Ann Rheum Dis. (2011) 70:1197–202. doi: 10.1136/ard.2010.140657
55. Dziankowska-Bartkowiak B, Waszczykowska E, Dziankowska-Zaboroszczyk E, de Graft-Johnson JE, Zalewska A, Luczynska M, et al. Decreased ratio of circulatory vascular endothelial growth factor to endostatin in patients with systemic sclerosis–association with pulmonary involvement. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2006) 24:508–13.
56. El Gharbawy NH, Sheha DS, Bawady SA, El Leithy SA. Vascular endothelial growth factor profile and Vitamin D level in Systemic Sclerosis Egyptian patients. Egypt J Immunol. (2021) 28:168–75. doi: 10.55133/eji.280117
57. Farouk HM, Hamza SH, El Bakry SA, Youssef SS, Aly IM, Moustafa AA, et al. Dysregulation of angiogenic homeostasis in systemic sclerosis. Int J Rheum Dis. (2013) 16:448–54. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12130
58. Gigante A, Gasperini ML, Rosato E, Navarini L, Margiotta D, Afeltra A, et al. Phase angle could be a marker of microvascular damage in systemic sclerosis. Nutrition. (2020) 73:110730. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2020.110730
59. Gigante A, Navarini L, Margiotta D, Amoroso A, Barbano B, Cianci R, et al. Angiogenic and angiostatic factors in renal scleroderma-associated vasculopathy. Microvascular Res. (2017) 114:41–5. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2017.06.003
60. Harada M, Mitsuyama K, Yoshida H, Sakisaka S, Taniguchi E, Kawaguchi T, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. (1998) 27:377–80. doi: 10.1080/03009749850154429
61. Hashimoto N, Iwasaki T, Kitano M, Ogata A, Hamano T. Levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and hepatocyte growth factor in sera of patients with rheumatic diseases. Modern Rheumatol. (2003) 13:129–34. doi: 10.3109/s10165-002-0211-8
62. Hummers LK, Hall AMY, Wigley FM, Simons M. Abnormalities in the regulators of angiogenesis in patients with scleroderma. J Rheumatol. (2009) 36:576–82. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.080516
63. Ibrahim SE, Morad CS, Farouk N, Louis A. Platelet indices as markers of inflammation in systemic sclerosis patients: Relation to vascular endothelial growth factor and flow mediated dilatation. Egyptian Rheumatol. (2018) 40:239–42. doi: 10.1016/j.ejr.2017.12.001
64. Jouvray M, Launay D, Dubucquoi S, Sobanski V, Podevin C, Lambert M, et al. Whole-body distribution and clinical association of telangiectases in systemic sclerosis. JAMA Dermatol. (2018) 154:796–805. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.0916
65. Kawashiri SY, Nishino A, Igawa T, Takatani A, Shimizu T, Umeda M, et al. Prediction of organ involvement in systemic sclerosis by serum biomarkers and peripheral endothelial function. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2018) 36 Suppl 113:102–8.
66. Kikuchi K, Kubo M, Kadono T, Yazawa N, Ihn H, Tamaki K. Serum concentrations of vascular endothelial growth factor in collagen diseases. Br J Dermatol. (1998) 139:1049–51. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.1998.02563.x
67. Koca SS, Akbas F, Ozgen M, Yolbas S, Ilhan N, Gundogdu B, et al. Serum galectin-3 level in systemic sclerosis. Clin Rheumatol. (2013) 33:215–20. doi: 10.1007/s10067-013-2346-8
68. Kosałka-Węgiel J, Lichołai S, Dziedzina S, Milewski M, Kuszmiersz P, Korona A, et al. Association between clinical features and course of systemic sclerosis and serum interleukin-8, vascular endothelial growth factor, basic fibroblast growth factor, and interferon alpha. Adv Clin Exp Med. (2023) 33:369–77. doi: 10.17219/acem/168724
69. Kuwana M, Okazaki Y, Yasuoka H, Kawakami Y, Ikeda Y. Defective vasculogenesis in systemic sclerosis. Lancet. (2004) 364:603–10. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(04)16853-0
70. Lv T, Yang F, Zhang K, Lv M, Zhang Y, Zhu P. The risk of circulating angiogenic T cells and subsets in patients with systemic sclerosis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2020) 81:106282. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106282
71. Michalska-Jakubus M, Cutolo M, Smith V, Krasowska D. Imbalanced serum levels of Ang1, Ang2 and VEGF in systemic sclerosis: Integrated effects on microvascular reactivity. Microvascular Res. (2019) 125:103881. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2019.103881
72. Papaioannou AI, Zakynthinos E, Kostikas K, Kiropoulos T, Koutsokera A, Ziogas A, et al. Serum VEGF levels are related to the presence of pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic sclerosis. BMC Pulmonary Med. (2009) 9:18. doi: 10.1186/1471-2466-9-18
73. Park JK, Fava A, Carrino J, Del Grande F, Rosen A, Boin F. Association of acroosteolysis with enhanced osteoclastogenesis and higher blood levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2016) 68:201–9. doi: 10.1002/art.39424
74. Reiseter S, Molberg Ø, Gunnarsson R, Lund MB, Aalokken TM, Aukrust P, et al. Associations between circulating endostatin levels and vascular organ damage in systemic sclerosis and mixed connective tissue disease: an observational study. Arthritis Res Ther. (2015) 17. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0756-5
75. Riccieri V, Stefanantoni K, Vasile M, Macri V, Sciarra I, Iannace N, et al. Abnormal plasma levels of different angiogenic molecules are associated with different clinical manifestations in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2011) 29:S46–52.
76. Saranya C, Ramesh R, Bhuvanesh M, Balaji C, Balameena S, Rajeswari S. Serum vascular endothelial growth factor levels as a marker of skin thickening, digital ischemia, and interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis. Indian J Rheumatol. (2018) 13:182–5. doi: 10.4103/injr.injr_132_17
77. Sato S, Hasegawa M, Takehara K. Serum levels of interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 correlate with total skin thickness score in patients with systemic sclerosis. J Dermatol Sci. (2001) 27:140–6. doi: 10.1016/s0923-1811(01)00128-1
78. Shenavandeh S, Tarakemeh T, Sarvestani EK, Nazarinia MA. Serum vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), soluble VEGF receptor-1 (sVEGFR-1) and sVEGFR-2 in systemic sclerosis patients: Relation to clinical manifestations and capillaroscopy findings. Egyptian Rheumatol. (2017) 39:19–24. doi: 10.1016/j.ejr.2016.03.004
79. Silva I, Teixeira A, Oliveira J, Almeida I, Almeida R, Vasconcelos C. Predictive value of vascular disease biomarkers for digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2015) 33:S127–30.
80. Solanilla A, Villeneuve J, Auguste P, Hugues M, Alioum A, Lepreux S, et al. The transport of high amounts of vascular endothelial growth factor by blood platelets underlines their potential contribution in systemic sclerosis angiogenesis. Rheumatology. (2009) 48:1036–44. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kep154
81. Waszczykowska A, Goś R, Waszczykowska E, Dziankowska-Bartkowiak B, Podgórski M, Jurowski P. The role of angiogenesis factors in the formation of vascular changes in scleroderma by assessment of the concentrations of VEGF and sVEGFR2 in blood serum and tear fluid. Mediators Inflamm. (2020) 2020:1–8. doi: 10.1155/2020/7649480
82. Yalçınkaya Y, Adın- Çınar S, Artim-Esen B, Kamalı S, Pehlivan Ö, Öcal L, et al. Capillaroscopic findings and vascular biomarkers in systemic sclerosis: Association of low CD40L levels with late scleroderma pattern. Microvascular Res. (2016) 108:17–21. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2016.07.002
83. Cohen J. Statistical power analysis. Curr Dir Psychol Sci. (1992) 1:98–101. doi: 10.1111/1467-8721.ep10768783
84. Patnaik E, Lyons M, Tran K, Pattanaik D. Endothelial dysfunction in systemic sclerosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:14385. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814385
85. Dimitroulas T, Giannakoulas G, Papadopoulou K, Sfetsios T, Karvounis H, Dimitroula H, et al. Left atrial volume and N-terminal pro-B type natriuretic peptide are associated with elevated pulmonary artery pressure in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Rheumatol. (2010) 29:957–64. doi: 10.1007/s10067-010-1494-3
86. Lammi MR, Kolstad KD, Saketkoo LA, Khatri A, Utz PJ, Steen VD, et al. Endothelial biomarkers of systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary hypertension. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). (2023). doi: 10.1002/acr.25180
87. Minopoulou I, Theodorakopoulou M, Boutou A, Arvanitaki A, Pitsiou G, Doumas M, et al. Nailfold capillaroscopy in systemic sclerosis patients with and without pulmonary arterial hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Med. (2021) 10:1528. doi: 10.3390/jcm10071528
88. Pope JE, Denton CP, Johnson SR, Fernandez-Codina A, Hudson M, Nevskaya T. State-of-the-art evidence in the treatment of systemic sclerosis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2023) 19:212–26. doi: 10.1038/s41584-023-00909-5
89. Blagojevic J, Legendre P, Matucci-Cerinic M, Mouthon L. Is there today a place for corticosteroids in the treatment of scleroderma? Autoimmun Rev. (2019) 18:102403. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2019.102403
90. Houck KA, Ferrara N, Winer J, Cachianes G, Li B, Leung DW. The vascular endothelial growth factor family: identification of a fourth molecular species and characterization of alternative splicing of RNA. Mol Endocrinol. (1991) 5:1806–14. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-12-1806
91. Woolard J, Wang WY, Bevan HS, Qiu Y, Morbidelli L, Pritchard-Jones RO, et al. VEGF165b, an inhibitory vascular endothelial growth factor splice variant: mechanism of action, in vivo effect on angiogenesis and endogenous protein expression. Cancer Res. (2004) 64:7822–35. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0934
92. Manetti M, Guiducci S, Romano E, Ceccarelli C, Bellando-Randone S, Conforti ML, et al. Overexpression of VEGF165b, an inhibitory splice variant of vascular endothelial growth factor, leads to insufficient angiogenesis in patients with systemic sclerosis. Circ Res. (2011) 109:e14–26. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.242057
93. Distler O, Highland KB, Gahlemann M, Azuma A, Fischer A, Mayes MD, et al. Nintedanib for systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. N Engl J Med. (2019) 380:2518–28. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1903076
94. Ebata S, Yoshizaki-Ogawa A, Sato S, Yoshizaki A. New era in systemic sclerosis treatment: recently approved therapeutics. J Clin Med. (2022) 11:4631. doi: 10.3390/jcm11154631
95. Wei N, Chen Z, Xue Z, Zhu Y. Polymorphism of VEGF gene in susceptibility to chronic immune-mediated inflammatory diseases: a meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int. (2015) 35:1351–60. doi: 10.1007/s00296-015-3279-0
96. Kimura K, Hashiguchi T, Deguchi T, Horinouchi S, Uto T, Oku H, et al. Serum VEGF–as a prognostic factor of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. (2007) 194:182–8. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2006.07.025
97. Ugur MG, Kutlu R, Kilinc I. The effects of smoking on vascular endothelial growth factor and inflammation markers: A case-control study. Clin Respir J. (2018) 12:1912–8. doi: 10.1111/crj.12755
Keywords: vascular endothelial growth factor, systemic sclerosis, biomarkers, vascular dysfunction, fibrosis, complications
Citation: Zinellu A and Mangoni AA (2024) Vascular endothelial growth factor as a potential biomarker in systemic sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 15:1442913. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1442913
Received: 03 June 2024; Accepted: 12 November 2024;
Published: 28 November 2024.
Edited by:
Katarzyna Romanowska-Próchnicka, National Institute of Geriatrics, Rheumatology and Rehabilitation, PolandReviewed by:
Theodoros Dimitroulas, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, GreeceJelena Colic, University of Belgrade, Serbia
Copyright © 2024 Zinellu and Mangoni. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Arduino A. Mangoni, YXJkdWluby5tYW5nb25pQGZsaW5kZXJzLmVkdS5hdQ==
 Angelo Zinellu
Angelo Zinellu Arduino A. Mangoni
Arduino A. Mangoni