- 1Department of Immunotherapy and Leishmania Vaccine Research, Pasteur Institute of Iran, Tehran, Iran
- 2Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Research Center, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran
- 3Autoimmune Bullous Disease Research Center, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- 4School of Medicine, Razi Hospital, Tehran, Iran
- 5Noor Eye Hospital, Tehran, Iran
- 6Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Institute of Biomedicine, Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden
Background: The JAK-STAT signaling pathway is a central cascade of signal transduction for the myriad of cytokines in which dysregulation has been implicated in progression of inflammatory and infectious diseases. However, the involvement of this pathway in human cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) due to Leishmania (L.) tropica warrants further investigation.
Methods: This study sought to investigate differential gene expression of several cytokines and their associated jak-stat genes in the lesions of L. tropica-infected patients byquantitative Real-Time PCR. Further, the expression of five inhibitory immune checkpoint genes was evaluated.
Results: Results showed that the gene expression levelsof both Th1 (ifng, il12, il23) and Th2 (il4, il10) types cytokines were increased in the lesion of studied patients. Further, elevated expression levels of il35, il21, il27 and il24 genes were detected in the lesions of CL patients. Notably, the expression of the majority of genes involved in JAK/STAT signaling pathway as well as checkpoint genes including pdl1, ctla4 and their corresponding receptors was increased.
Conclusion: Our finding revealed dysregulation of cytokines and related jak-stat genes in the lesion of CL patients. These results highlight the need for further exploration of the functional importance of these genes in the pathogenesis of, and immunity to, CL.
1 Introduction
Cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) is a complex skin infection caused by over 20 different Leishmania species that are transmitted through the bite of infected sandflies. CL is endemic in more than 90 countries, with most infections occurring in South and Central America, the Mediterranean Basin, and regions ranging from the Middle East to Central Asia (1). In the Old World, the etiologic agents of CL include Leishmania (L.) major, L. tropica, and L. aethiopica, and also less commonly in the Mediterranean Basin, L. infantum and L. donovani (2). In terms of clinical manifestations, there are two main types of CL: zoonotic CL (ZCL) caused by L. major (rural or wet type lesion) and anthroponotic CL (ACL) caused by L. tropica (urban or dry type lesion) (3). The L. tropica that causes ACL is restricted to humans and has shown drug resistance, so treating CL patients successfully is challenging. Further, unresponsive chronic patients such as recurrence cases (recidivans) serve as a reservoir of infection for other individuals since a human is an isolated reservoir host (4, 5). Nevertheless, only a limited number of human research have concentrated on understanding immune response mechanisms involved in L. tropica infection (6–8).
Several studies have evaluated the expression of key cytokines related to intralesional and systemic immune response during the acute and chronic stages of CL infection caused by L. tropica (8–10). Cytokine gene expression study in CL lesions has revealed higher levels of ifng, il10, tnfα, il1β, il8, il4, mcp1, and inos, indicating CL is caused by an exaggerated and inadequately controlled T helper 1 (Th1) immune response (8). Furthermore, in chronic ACL patients, high levels of IFN-γ, IL-5, and IL-13 imply a mixed Th1/Th2 response, whereas, in acute patients, high levels of IFN-γ and low levels of IL-5 and IL-13 suggested a predominantly Th1 response (9). The differentiation of Th cells is regulated by transcription factors such as Tbet and GATA3, which can, in turn, convert naïve CD4+ T cells into Th1 and Th2 subsets (11). The biological effect of most Th1/Th2 associated cytokines is mediated by Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) signaling pathway, which is reported to have an important function in promoting the host immune response against various diseases (12).
The human JAKs family known as non-receptor tyrosine protein kinases contains four members, JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TY2, which transmit regulatory signals of cytokine and recruit one or more STAT proteins. The human STATs family, as transcription factors, contains six STATs, STAT1-6, activated by tyrosine phosphorylation by the JAKs family (13). They are essential for modulating signaling that occurs downstream of cytokine receptors (13, 14). Despite the progress on cytokines’ critical roles in shaping the host immune response to Leishmania infection, the role of the JAK/STAT pathway in mediating biological activities of cytokines is rather understudied in human CL, particularly in CL due to L. tropica (12). Additionally, in infectious diseases such as CL, immune checkpoints have been demonstrated to have a significant impact on disease outcomes by regulating T cell effector activity (15). Inhibitory immune checkpoint molecules, or inhibitory receptors, are expressed in numerous immune cells, leading to exhausted T-cells and promoting pathogenesis (16). Our recent study on the transcriptome of ulcerative (UCL) and non-ulcerative (NUCL) patients infected with L. tropica highlighted the enrichment of “IFNs signaling”, “TCR complex” and “FcγR-dependent phagocytosis pathways (17).
The present study aimed to shed light on jak/stat-related gene expression patterns in skin biopsy samples collected from CL patients infected with L. tropica by quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR). Further, differential gene expression of Th1 and Th2-related cytokines, transcription factors, and inhibitory checkpoints were investigated. Our results pinpoint the intralesional profile between jak/stat-related genes and related inflammatory cytokines that are involved in the pathogenicity of L. tropica-infected patients.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Ethics approval and informed consent
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Pasteur Institute of Iran (IR.PII.REC.1400.022), and study protocols were performed in compliance with the relevant ethical regulations. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants, including CL patients and healthy volunteers enrolled in the study.
2.2 Data and sample collection
The samples were collected from patients referred to the Dermatology Clinic at Mashhad Medical School in Mashhad, and Razi Dermatology Hospital in Tehran IRAN, with suspected CL lesions from January to October 2023. Inclusion criteria for CL patients enrolled in this study were as follows: No history of receiving anti-leishmanial treatment, having an active lesion for a maximum of 1 year, and a characteristic skin lesion-positive PCR for L. tropica. The control samples were collected from healthy volunteers undergoing esthetical surgery at Noor Eye Hospital (Tehran). The included volunteers in this study had no history of leishmaniasis or other skin problems.
2.3 PCR diagnostics of CL patients
To identify Leishmania species, the skin lesion samples, which were collected with a non-invasive and tape disc-based method as described by Taslimi et al. (16), were analyzed with polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay, targeting internal transcribed spacer 1(ITS1). Then, RFLP analysis using 1U HaeIII enzyme (Roche) was performed on the PCR products.
2.4 Skin biopsies from CL patients and healthy volunteers
A total of 19 CL patients and 10 healthy individuals were included in our study. Demographic characteristics of patients, including age and gender, as well as characteristics of lesions, such as size, number, and duration, were recorded using a patient information sheet. Two-millimeter punch skin biopsies were taken from each included participant. In the CL group, skin biopsies were taken from the border of the lesion. The biopsies were immediately transferred to RNA later solution (Qiagen GmbH, Hilden, Germany) and stored at -20°C for subsequent processing.
2.5 RNA extraction, cDNA synthesis, and quantitative real-time PCR
Total RNA of skin biopsy samples was extracted using a total RNA extraction kit (Pars tous, Iran) following the manufacturer’s protocol. RNA quantity was measured using a Nanodrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, USA), and RNA integrity (RIN) was evaluated on an Agilent Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies, USA). Two patient samples were excluded from the study because of low RIN values.
Genomic DNA was removed from the extracted RNA by DNase I (Ambion, USA). After that, cDNA was synthesized using High Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kits (Applied Biosystems, USA) as per the manufacturer’s protocol. qRT-PCR assay was performed in ABI Real-time PCR Detection System (Applied Biosystems, CA, USA) in a reaction volume of 10 μL containing 2X QuantiFast SYBR Green PCR Kit (Qiagen, GmbH, Hilden, Germany) and a specific primer (5pmol). The thermal cycle was as follows: 95°C for 5 min, 40 cycles at 95°C for 20 sec, and 60°C for 30 min.
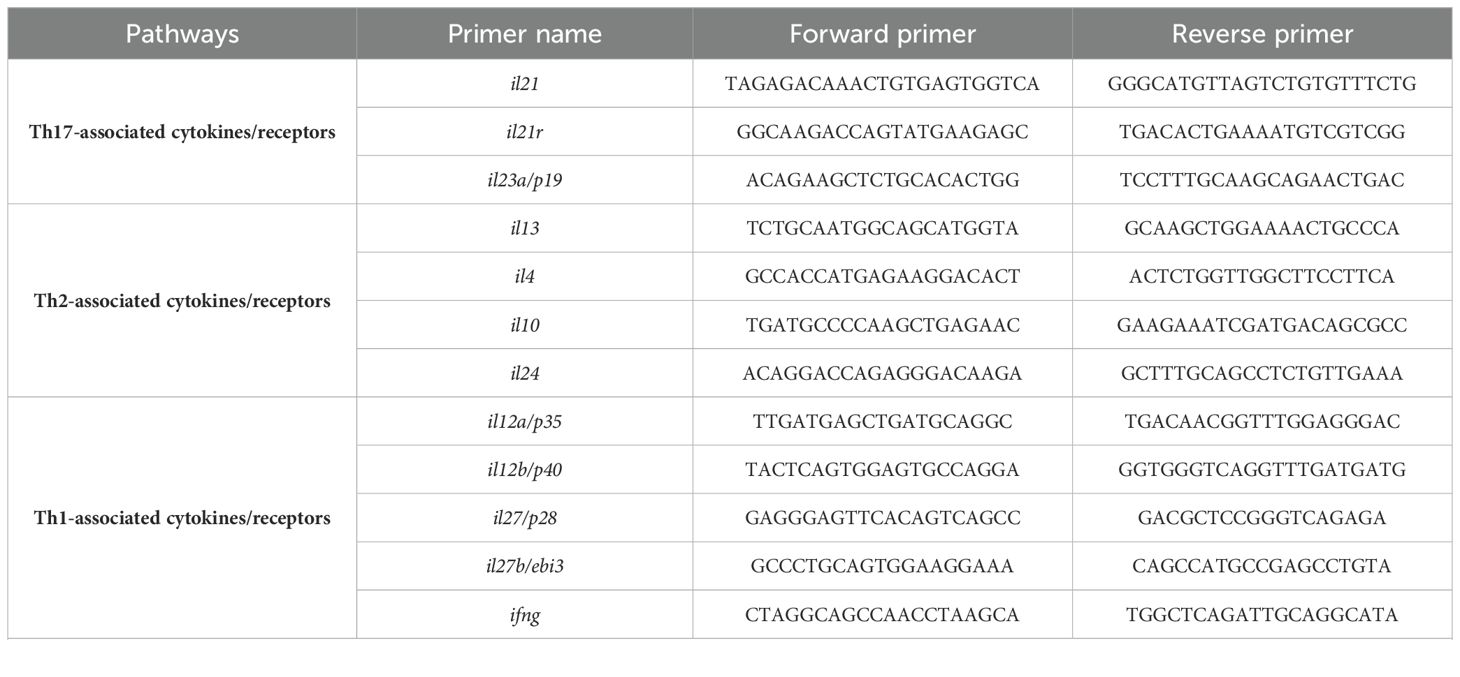
Additionally, RT-qPCR was performed to evaluate parasite load in each clinical sample using 7SLRNA gene (18). All assays were done in duplicate. The list of primers used in this study is presented in Table 1.
2.6 Statistical analysis
The relative gene expression analysis was performed using the 2-ΔΔCT method. Human GAPDH was used as an internal control in this analysis. The expression level of the studied genes between CL and control groups was compared by the Mann–Whitney U test and a p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. The comparison of differential gene expression was carried out based on the criteria of log2|fold change (FC) |> 1. The absolute quantification was performed by standard curves which were constructed by serial dilution of cDNA products of 1.5 × 106 L. tropica. GraphPad Prism 8.0 (GraphPad Software Inc., CA, USA) software was used for statistical analyses and drawing scatter plots. The volcano plot was created using ggplot2 (v 3.3.5) and ggrepel (v 0.9.1) packages in R (4.1.2, https://www.r-project.org/) (19). Principal component analysis (PCA) plot was generated using tidyverse package. Pearson correlation test with the R corrplot package (v 4.4.0) was applied to identify correlations between the studied genes. Absolute correlation values ≥ 0.8 were considered strong correlation. The correlation matrix was visualized with the R corrplot package (v 0.92).
3 Results
3.1 Clinical characteristics and parasite load in CL lesions
This study included 17 L. tropica-infected CL patients with an average age of 42.88 ± 4.5 years old, including 12 (70.6%) female and 5 (29.4%) male. Ten healthy individuals, including 7 (70%) females and 3 (30%) males with an average age of 50.7± 2.97 years old, were also involved in this study. Eight patients (41.2%) had a single lesion and the rest of them were found with more than two skin lesions at the time of enrollment. The average duration and surface area of lesions in the patients were 26.15± 7.9 (cm2) and 4.15± 0.63 (month), respectively. The present study investigated the parasite load in lesions of patients infected with L. tropica. The average load of parasites found in the lesions was 7700 ± 3700 parasites/cells, with a range from 1400 to 17100 parasites/cells. Further, the analysis revealed no significant correlation between the characteristics of the lesions and the parasite load in each patient. The results of the parasite load and lesion characteristics are shown in Supplementary Figure 1.
3.2 Differential gene expression analysis
To determine the differentially expressed genes, the magnitude of fold changes among 38 immune-related genes in the skin lesions of L. tropica-infected patients to healthy group were compared, and up-and down-regulated genes were determined. As depicted in Figure 1A, principal component analysis (PCA) on gene expression of the studied genes separated patients from healthy controls across the PC-1 of 65.92%.
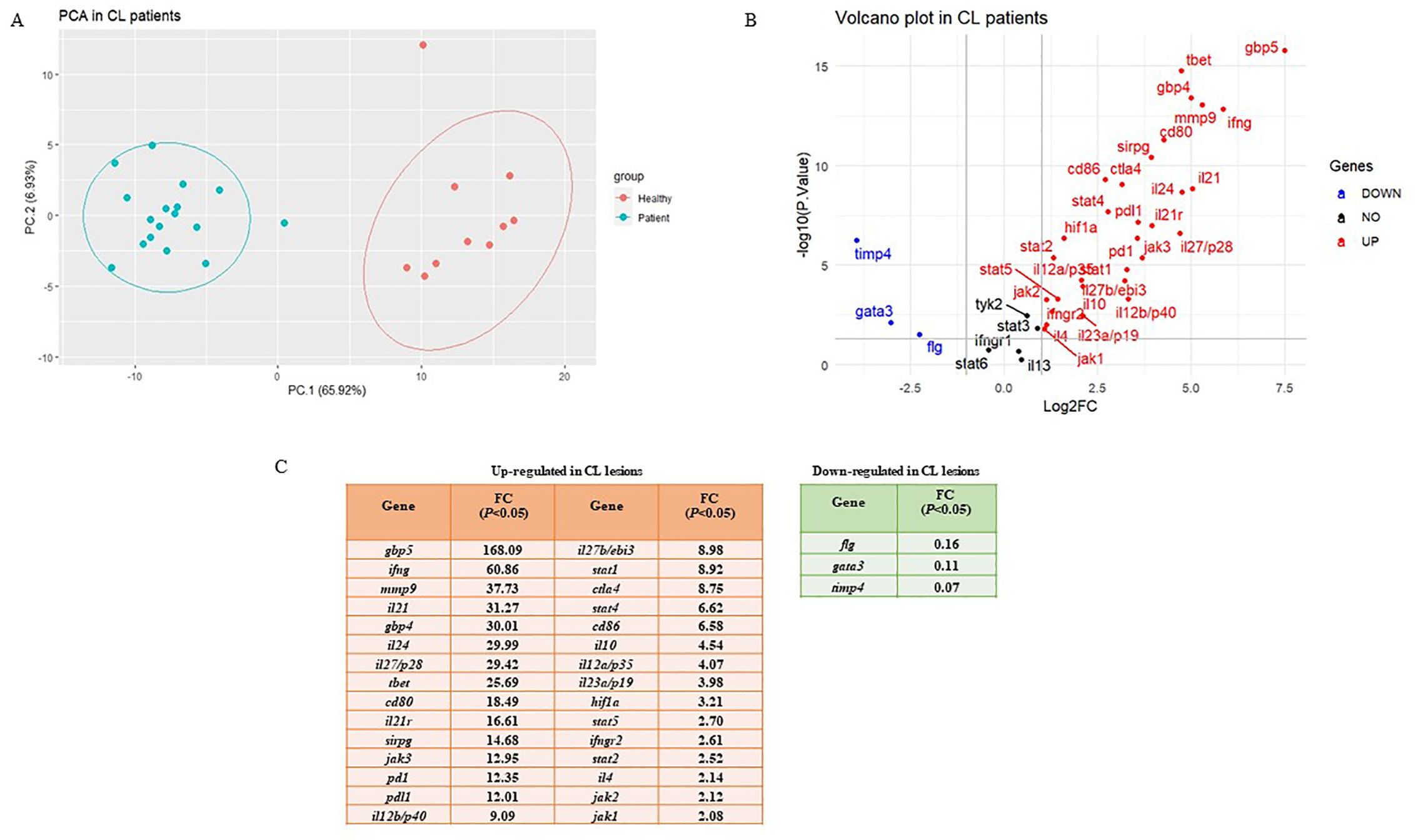
Figure 1. Differential expression gene analysis. (A) Principal Component Analysis (PCA) for skin lesions of CL patients (blue circles, n = 17) compared to the healthy group (red circles, n = 10). (B) Volcano plots of the tested genes in CL patients when compared to a healthy group. (C) Statistically significant up-and down-regulated genes in CL lesions compared to healthy skin. CL, cutaneous leishmaniasis; FC, fold change.
The list of genes included in the study is as follows: 11 Th1/Th2/Th17- associated cytokines (ifng, il12a/p35, il12b/p40, il27b/ebi3, il27/p28, il23a/p19, il4, il13, il10, il24, and il21), three cytokine receptors (il21r, ifngr1, and ifngr2), five immune checkpoints (pd1, pdl1, ctla4, cd80, and cd86), 10 Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK-STAT; stat1, stat2, stat3, stat4, stat5, stat6, jak1, jak2, jak3 and tyk2), two extracellular matrix related genes (mmp9 and timp4), two guanylate-binding protein (gbp4 and gbp5), three transcription factors (TFs; tbet, gata3, and hif1a), one immunoglobulin-like cell surface receptor (sirpg), and one epidermal barrier function associated gene (flg). Further, a volcano plot of Log2 fold changes versus the P values (-Log10) of the studied genes depicted the identified statistically significant up-and-down-regulated genes in CL patients compared to the control (Figure 1B). The fold change values are also presented in Figure 1C.
3.3 Intralesional expression level of Th1/Th2/Th17-associated cytokines and their receptors in L. tropica-infected patients
We evaluated the expression of several Th1/Th2/Th17-associated cytokines and corresponding receptors by the qRT-PCR method. Compared to the healthy group, expression levels of il12a/p35, il12b/p40, il27b/ebi3, il27/p28, and il23a/p19, as members of il12 family cytokines showed increased expression levels in L. tropica-infected patients (Figures 2A–E). All up-regulated genes were statistically significant (P<0.05). In addition to il12a and il12b, the expression of other Th1-related cytokines/cytokine receptors, including ifng, ifngr1, and ifngr2, were also evaluated, and ifng and ifngr2 found as statistically significantly over-expressed genes, while the expression of ifngr1 was decreased (P>0.05), in L. tropica-infected patients (Figures 2F–H). Further, assessing the expression of Th2-associated cytokines/cytokine receptors, including il4, il13, il10, and il24, showed statistically significant up-regulation in patients versus the healthy group (Figures 2I–L). il21 and its corresponding receptor, il21r, were a pair of genes upregulated as members of the Th17 cell subset. Besides, we found the expression magnitude of Th1-associated cytokines was higher than Th2-associated cytokines.
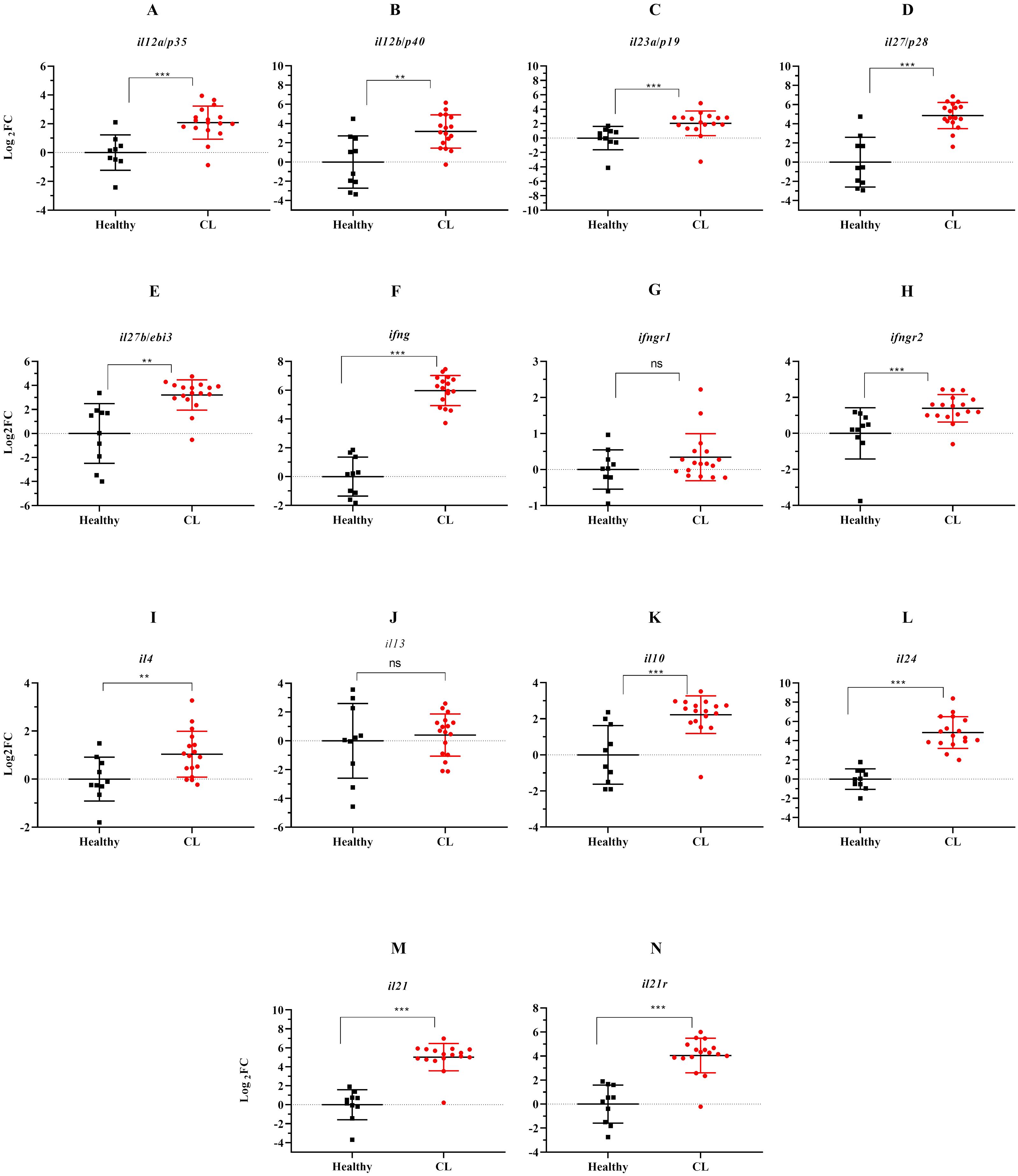
Figure 2. The effect of L. tropica infection on mRNA expression of 11 cytokine genes in the skin lesion of CL patients. Relative mRNA expression of (A) il12a/p35, (B) il12b/p40, (C) il23a/p19, (D) il27b/p28, (E) il27b/ebi3, (F) ifng, (G) ifngr1, (H) ifngr2, (I) il4, (J) il13, (K) il10, (L) il24, (M) il21, and (N) il21r. Data are normalized using gapdh as the control gene. **P < 0.01, and ***P< 0.001. The results were shown as the mean +/- SD of duplicate measurements. CL, Cutaneous leishmaniasis. ns, non-significant.
3.4 Expression levels of jak-stat genes and other Th1/Th2-related transcription factors during L. tropica infection
Next, we assessed expression levels of jak-stat genes and other Th1/Th2-related transcription factors in the lesion of L. tropica patients. The relative expression analysis of six stat genes, namely stat1, stat2, stat3, stat4, stat5, and stat6, in L. tropica-infected patients, revealed all stat genes except for stat6 were upregulated (Figures 3A–E). However, we observed down-regulation in stat6 expression level; albeit not statistically significant (Figure 3F). Among jak family genes, jak1-3 genes were found to be statistically significantly over-expressed (P<0.001) (Figures 3G–I), while no change was observed in the expression of the tyk2 gene (Figure 3J). Additionally, the expression of tbet and gata3, as key TFs linked to Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation, was significantly upregulated (Figures 3K, L).
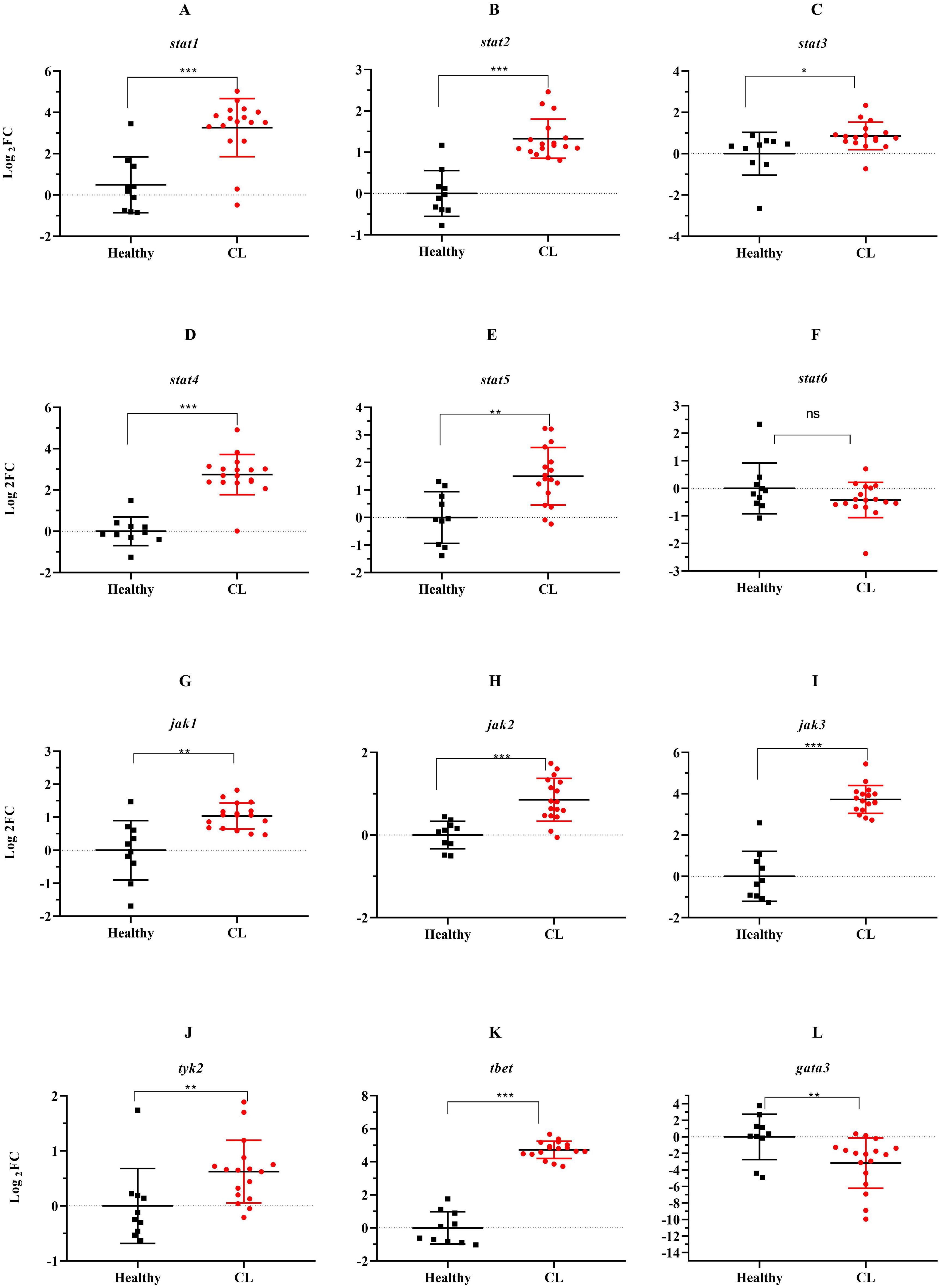
Figure 3. The expression levels of 10 jak-stats genes and two Th1/2 related-TF between L. tropica infected patients and healthy group. (A) stat1, (B) stat2, (C) stat3, (D) stat4, (E) stat5, (F) stat6, (G) jak1, (H) jak2, (I) jak3, (J) tyk2, (K) tbet, and (L) gata3. Data are normalized using gapdh as the control gene. *P<0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P< 0.001. The results were shown as the mean +/- SD of duplicate measurements. CL, Cutaneous leishmaniasis.
3.5 Differential expression of the immune checkpoints and other genes in the lesions of L. tropica infected patients
During the course of an immune response, various immune checkpoint pathways undergo activation or deactivation. Inhibitory immune checkpoint molecules, including CTLA4/CD80/CD86 and PD1/PDL1, are known to suppress T-cell activation. Our results herein showed that the expression level of inhibitory immune checkpoint molecules, including ctla4/cd80/cd86 and pd1/pdl1 genes was heightened in the lesions of L. tropica-infected patients compared to the skin of healthy individuals (Figures 4A–E). The expression level of seven other genes, which functions as transcription factor (hif1a), extracellular matrix (mmp9, timp4), interferon-inducible GTPases (gbp4, gbp5), T-cell adhesion (sirpg), and epidermal barrier (flg) was also assessed by qRT-PCR. As depicted in Figure 5, expression of gbp4, gbp5, hif1a, mmp9, and sirpg was increased in the patients compared to the healthy group (P< 0.001). Whereas expression of timp4 and flg genes was found to be downregulated (P< 0.001).
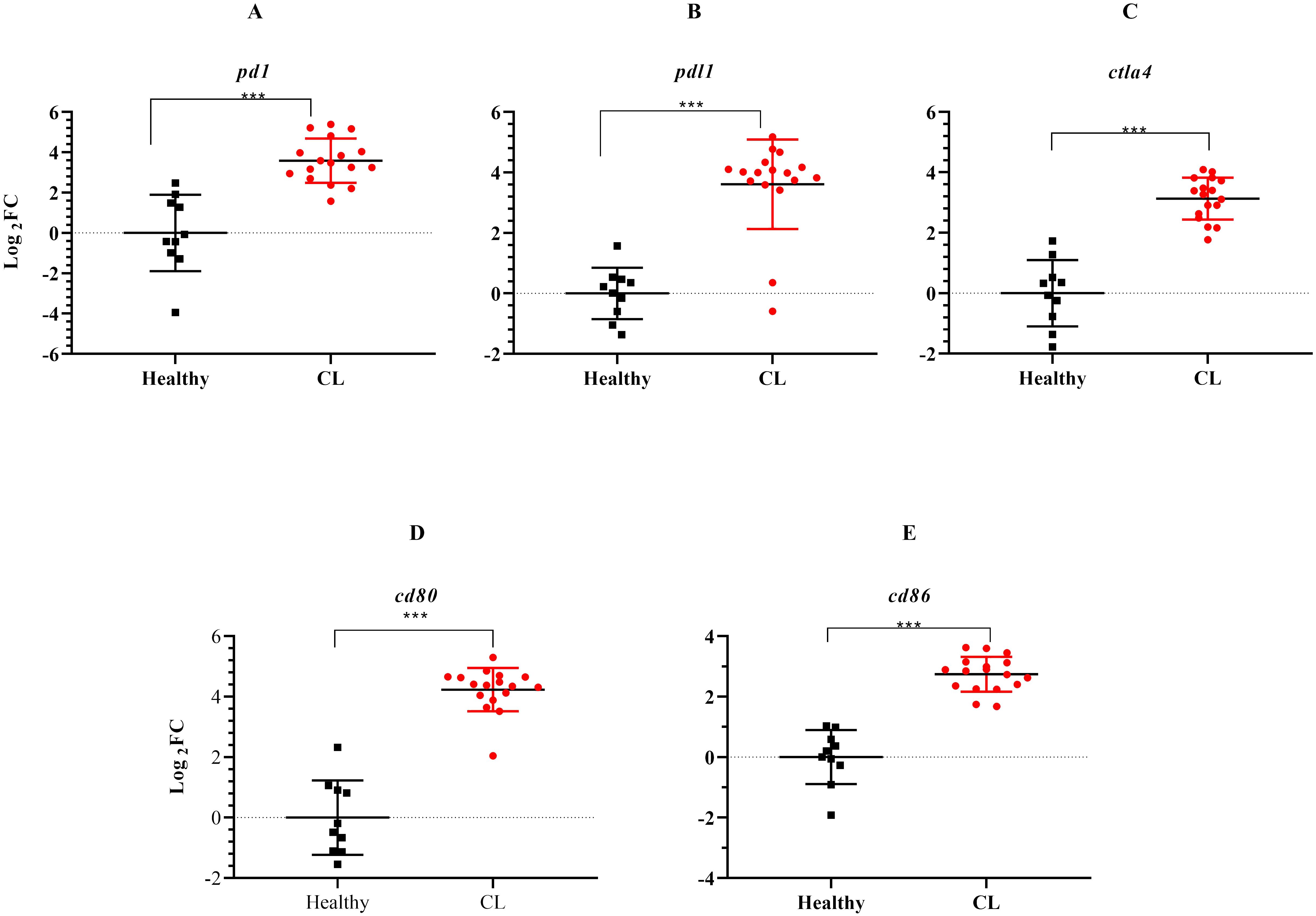
Figure 4. The expression levels of immune checkpoint genes between L. tropica infected patients and healthy group. (A) pd1, (B) pdl1, (C) ctla4, (D) cd80, (E) cd86. Data are normalized using gapdh as the control gene. ***P< 0.001. The results were shown as the mean +/- SD of duplicate measurements. CL, Cutaneous leishmaniasis.
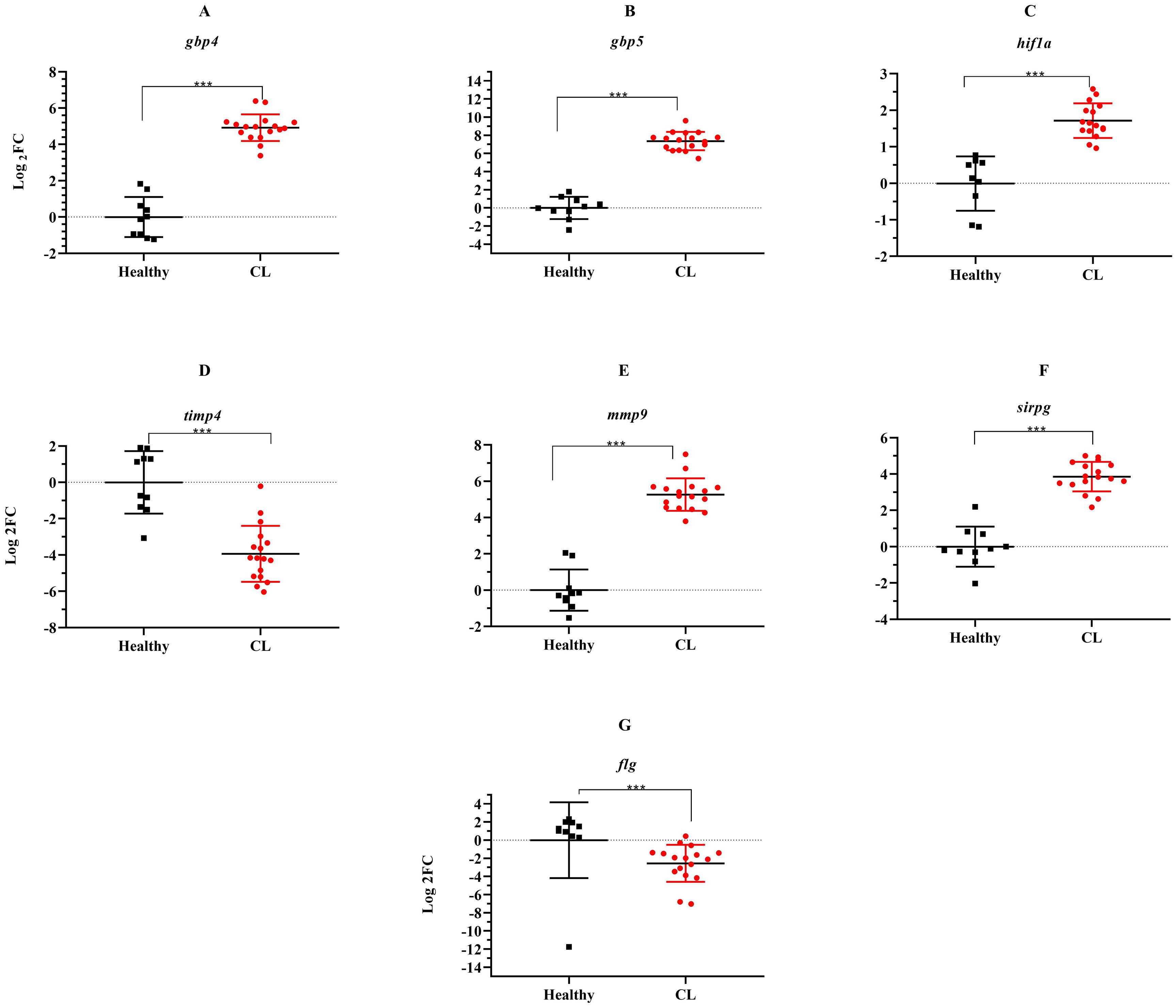
Figure 5. The relative expression of several genes induced during L. tropica infection. (A) gbp4, (B) gbp5, (C) hif1a, (D) timp4, (E) mmp9, (F) sirpg, and (G) flg. Data are normalized using gapdh as the control gene. ***P< 0.001. The results were shown as the mean +/- SD of duplicate measurements CL, Cutaneous leishmaniasis.
3.6 Correlation analysis
The correlation analyses demonstrate a significant positive correlation between the expression of cytokine and jak-stat genes. Specifically, the expression of ifng, il12(p35), and il35(ebi3) showed a positive correlation with stat1 and stat4 expression (r2>0.5, P<0.05). Moreover, within jak genes, the expression of jak1 was associated with ifng, and il23(p19), while jak2 was linked to il10, il35(ebi3), and il21 (r2>0.6, P<0.05). Furthermore, the jak3 gene expression exhibits a correlation with ifng, il10, and il21 (r2>0.5, P<0.05), as depicted in Figure 6. Additionally, our analysis highlighted a positive correlation between cd80 and stat1 (r2>0.6, P<0.05), as well as between cd86 and stat4 (r2>0.5, P<0.05) among immune checkpoint genes. Notably, the correlation values for the other selected genes are shown in Figure 6.
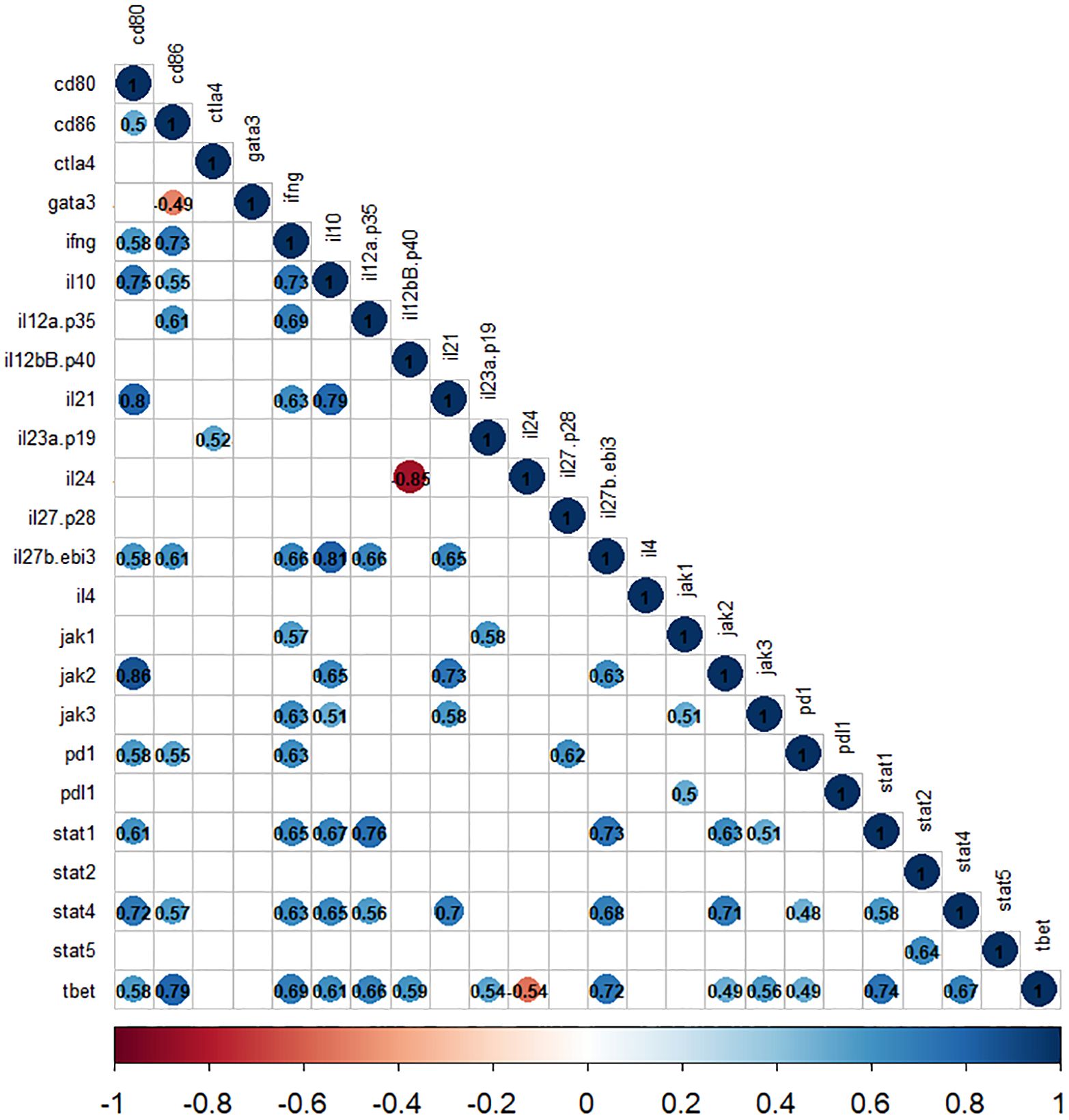
Figure 6. The correlation matrix shows the relationships between cytokines and jak-stat genes in L. tropica-infected patients. The correlation values are displayed in matrices and color-coded: blue for positive correlations and red for negative correlations. Any correlation values that are not statistically significant (P>0.05) are represented by blank white spaces.
4 Discussion
Previous studies have shown the critical role played by cytokine expression status in determining the ultimate fate of leishmaniasis, favoring either the host or the parasite (20, 21). The aberrant activation of JAK-STATs signaling pathway is recognized as the main factor behind regulation mediated by these cellular mediators in various inflammatory and infectious diseases (22). However, signaling pathways are complex and interconnected, the central regulatory role of the pathway holds promise for potential interventional implications in a multitude of diseases (14, 23). Herein, we investigated the intralesional expression of 24 cytokine/jak/stat genes in the skin lesions of L. tropica-infected patients. We have also evaluated the expression of 5 inhibitory immune checkpoint genes along with nine genes related to transcription factors, extracellular matrix, interferon-inducible GTPases, T-cell adhesion, and epidermal barrier function in the lesions of L. tropica-infected patients.
We observed that the expression of several pro-inflammatory cytokines/cytokine receptors, including il12 family, ifng, and ifngr2, were increased in the skin lesion of L. tropica-infected patients. IL-12 is considered a crucial host-protective cytokine in CL by driving the development of IFN-γ -producing T cells (24, 25). The regulatory effect of IL-12 on T-cells is achieved through the transduction of JAK2/TYK2 and STAT4 pathways (26). The biological effect of IFN-γ, as another crucial pro-inflammatory cytokine in CL (27), is mediated by the activation of JAK1/JAK2 and STAT1 in T cells. The signaling of IL-12 and IFN-γ through STAT4 and STAT1 also stimulated the expression of Th1 master regulator gene, Tbet, and induced further IFN-γ production (28). Our data showed that in addition to il12 (p35 and p40) and ifng, the expression of jak1, jak2, stat1, stat4, and tbet was also increased in the skin lesion of L. tropica patients. The results may reflect the effective recruitment of immune cells characterized by increased pro-inflammatory cytokines and activated downstream genes. In agreement with our result, skin samples of CL patients infected with L. braziliensis showed upregulation of ifng and stat1. The study also revealed that high levels of ifng expression in the lesions were associated with the activation of cytolytic pathways (29). In other studies, blood (26) and skin samples (manuscript in preparation) of patients with CL due to L. tropica demonstrated overexpression of stat1 and IFN-responsive genes. Nonetheless, downregulation of several immune-related genes, including stat1, nfκb, ifngr2, and il12rb2 were reported in the blood of the severe clinical form of CL, diffuse CL caused by L. mexicana (30). Further, gbp genes, which induced in response to IFN, reported to play a role in conferring cell-autonomous immunity against various pathogens (29, 31, 32). However, the role of these genes in CL is not well established. Previous reports on overexpression of different isoforms of the GBPs family in CL patients suggested a possible role for these large GTPases in protection against Leishmania infection (33–35). For instance, an overexpressed level of gbp5 was reported in L. braziliensis and L. tropica CL biopsy samples, with involvement in inflammation (33, 35). Similarly, we herein found overexpression of gbp4 and gbp5 in L. tropica lesions. This expression pattern may show the predominant transcriptional alternation linked to ifng in CL due to L. tropica.
We could also show the upregulation of il23 (p19/p40) and il27 (p28/ebi3) as other members of the il12 family cytokine. The increased level of IL-23 is described to have an association with the maintenance of Th17 cells, which may contribute to the persistence of inflammation or promote the chronicity of CL infection caused by L. amazonensis and L. braziliensis (36). By contrast, the correlation of il23 expression with healed L. major CL lesions and reducing disease immunopathology has been documented (37). IL-23 exerts its function mainly via activation of JAK2/TYK2 and STAT3 (38). Notably, STAT3 and TYK2 are described as a crucial component for Th17 cell development and the key isoform of the JAK family in the IL-23 signaling cascade, respectively (39). However, in our study, the il23-dependent effects were not significantly changed in the lesion of L. tropica-infected patients. On the other hand, IL-27 (P28/Ebi3), is acknowledged to have a dual function in inducing the immuno-pathology of Leishmaniasis (40–42). The dubious role of IL-27, on one side, favors the host by induction of protective immune response in L. major infection (40), an effiect mainly mediated inhibition of Th2 cell response and, on the other side, contributes to enhancing disease during L. amazonensis and L. braziliensis infection through IL-10 induction (41, 43). The specific effects of IL-27 in immune cell subsets occurred after activation of JAK1/JAK2 and mainly three isoforms of STAT, namely, STAT1, STAT3, and STAT5. In a STAT1-dependent manner, the signaling molecule can positively affect the expression of T-bet and IFN-γ as well as induce downregulation of the GATA3 and the Th2-associated cytokines (44, 45). Based on the observed expression pattern in our study, we speculated that the induction of il27 in L. tropica CL lesions may have an immunostimulatory effect, presumably favoring the host immunity through downregulation of Th2 type genes. Besides, IL-27 as well as IFN-γ is reported to have the potential to stimulate overexpression of co-inhibitory checkpoints and their key cytokine, IL-10, on T cells in a STAT1-dependent manner, which mitigates tissue damage (46, 47). In the present study, evaluating the expression of two inhibitory receptors (pd1, ctla4) and their corresponding ligands (pdl1, cd80, cd86) as well as il10 showed overexpression in the lesion tissue of CL patients. Aligned with our result, a recent study highlighted an increase in the expression of pdl1 in skin lesions of CL patients infected by L. donovani (48). However, the exact role of immune checkpoints during CL infection is still inconclusive. In our study, these genes seem to have a role in maintaining immune homeostasis which prevents overwhelming inflammation. Besides, we found expression of downstream genes regulated by il10 namely, tyk2, jak1, and stat3 remained unchanged except for jak1 in the CL skin lesions. IL-10 has been reported to counteract an exacerbated immunopathology induced by a high magnitude of Th1 immune response and accelerate the wound healing process, at the same time, playing a role in the progression of the infection and parasite persistence in CL (49–51). Further research is needed to fully elucidate the mechanisms by which IL-10 affects the course of the disease and to determine the optimal dosage and timing of IL-10 administration in CL patients.
Alongside IL-10, IL-35 (EBI3/p35), as regulatory T and B cell-derived cytokine (52, 53), also has immunosuppressive activity. A recent study reported a significant increase in IL-35 production in PBMC infected by L. infantum and L. donovani, whereas no change in IL-35 concentrations was identified in response to L. major and L. tropica infection (54). We could also herein identify the overexpression of ebi3 and p35 in the lesion of L. tropica-infected patients. Additionally, evaluating jak/stat genes transduced by IL-35 showed the overexpression of jak1, jak2, stat1, and stat4. This pattern indicates that the simultaneous expression of immunosuppressive cytokine genes like il10 and il35 in L. tropica-infected tissues possibly resulted in the persistence of the lesions despite the presence of a high magnitude of inflammatory cytokine. However, further investigation is warranted to elucidate the extent of involvement of these cytokines in the immune response against CL caused by L. tropica.
IL-24 is a multifunctional cytokine produced by both immune and non-immune cells, such as keratinocytes (55) and its biological activity is mediated via the JAK1/STAT3 pathway. Upregulation of IL-24 is reported to be involved in wound repair and pathogenesis of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases such as psoriasis (56–58). However, the protective role of IL-24 has been described in animal studies of several diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease (59). In the context of leishmaniasis, the biological role and expression pattern of IL-24 is poorly studied, with one preprint report showing elevated levels of IL-24 in CD274+ and IDO1+ myeloid cells in human CL skin lesions (60). Overall, based on the role of il24 in wound healing, we tend to speculate a protective role against L. tropica infection by modulating immunopathology following increased production of inflammatory response. However, further studies need to ascertain the exact role of this cytokine in CL.
We could also document the upregulation of il21/il21r and its downstream jak1/jak3 and stat1 genes. The activation of STAT1 by IL-21 is noted to intensify Th1 immune response and IFN-γ production (61, 62). Therefore, the high level of il21/il21r expression in our study can be considered another possible factor for the significantly elevated level of ifng and its downstream genes in L. tropica CL lesion. IL-21 plays an important role in the disease pathology of various diseases by increasing the T-cell effector responses (63). However, studies related to the role played by this cytokine in the context of leishmaniasis are limited (43, 55, 64–66), the current evidence suggests a potential disease-enhancing role for this mediator.
The effect of GATA3 expression change on FLG, which encodes the epidermal barrier protein filaggrin, in keratinocytes was pointed out in human inflammatory skin diseases (67). Our data showed that the expression of both genes was downregulated in the lesion of L. tropica infection. It can be reasonable to speculate that the downregulation of flg was influenced by the downregulation of gata3 and this downregulation affected the epidermal integrity of the skin and skin microbiome composition in L.tropica CL lesions. Along with this gene, we found the overexpression level of mmp9 and the downregulation of its natural regulator, timp4, in the CL lesions. An imbalanced production of MMPs and TIMPs is reported in the occurrence of tissue damage in various diseases (68–70). Our findings suggest that downregulated timp4 may augment mmp9 activity and the imbalanced level of mmp9 and timp4 could affect the resolution of the L. tropica CL lesion formation. Notably, the overall findings of this study are summarized in Figure 7, illustrating the conceptual framework of cytokine-receptor engagement activating the JAK-STAT pathway in the inflammatory and immune response activation observed in the lesions.
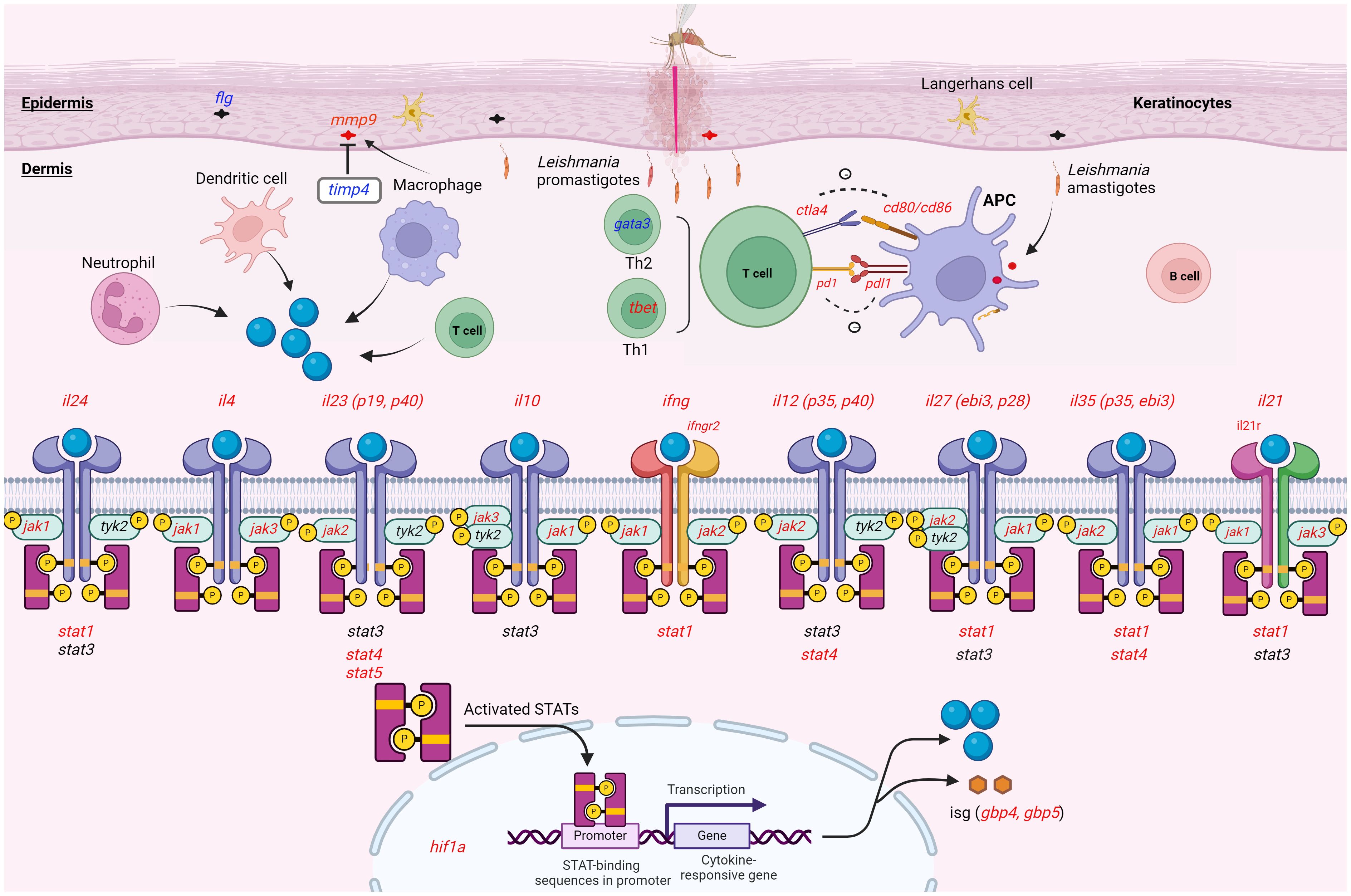
Figure 7. Schematic representation illustrating the expression pattern of the genes analyzed within the lesion of CL patients infected with L. tropica. This figure provides a whole overview of the signaling cascade without linking the effect of the cytokines to a specific immune cell. Upon Leishmania entry into the dermis, different innate cells such as neutrophils, macrophages, and dendritic cells infiltrate the site of infection. The cell produces effector molecules like cytokine resulting in either a permissive or hostile environment for the parasite. The effector function of the immune cell also instructs T helper (e.g., tbet/gata3) cell differentiation. In skin resident cells as well as migratory immune cells, the Janus kinase (JAK)-signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway can be induced by a myriad of cytokines present during skin inflammation. Cytokines (il24, il4, il10, ifng, il12, il27, il35 and il21) interact with the corresponding receptors (ifngr2, and il21r), which phosphorylate JAKs (jak1, jak2, jak3 and tyk2) and activates stat genes (stat1-6). Activated STAT forms a dimer. The dimerized STAT translocate to the nucleus and mediates the transcriptional regulation of target genes like interferon-stimulated gene (ISG; gbp4, and gbp5), and inflammatory molecules. During an immune response, different stimulatory and inhibitory immune checkpoints (pd1/pdl1, ctl4/cd80/cd86) pathways can also induce or suppress. This interaction mainly occurs between a T cell and a macrophage, and DC as antigen-presenting cells (APCs). Up- and down-regulated genes were presented in red and blue colors, respectively. Gene with an unchanged expression was also shown in black. CL, cutaneous leishmaniasis. This image was created with BioRender.com.
One of the limitations of our study is sole focus on transcriptome of the studied genes. Analysis of protein expression of the studied genes and integration of transcript and protein data in a larger cohort would further strengthen these findings, and may significantly enhance our understanding of signaling pathways involved in L. tropica infection.
In summary, our study herein suggests the dysregulation of 11 pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines and their associated jak-stat genes in the skin lesion of CL patients infected by L. tropica. We also highlighted the expression of il21, il24 and il35 genes, which are rather understudied in human CL (Figure 7). A significant positive correlation between stat1 and stat4 expression and the expression of various cytokines and immune checkpoint genes was observed in patients infected with L. tropica, indicating potential interconnections between these factors in the context of the infection. Furthermore, we detected elevated levels of Th1 and Th2 response in the lesions of patients infected with L. tropica. This suggests the balance of cytokines is a crucial factor in determining the clinical outcome, rather than the quantity of cytokines. Our findings warrant further exploration of the regulatory impact and the functional significance of the cytokines and their downstream genes on the pathogenesis of CL on larger cohorts. Such an investigation is likely to yield valuable insights into their biological functions, potentially paving the way for the identification of novel therapeutic options to counter CL.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Research Ethics Committee of the Pasteur Institute of Iran -IR.PII.REC.1400.022. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
SH: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Software, Methodology, Formal Analysis. NM: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Software, Methodology, Formal Analysis. HH: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Methodology. VMG: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Resources. MK: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Resources. MD: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Resources. AS: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Resources. NT: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Resources. RES: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Resources. SR: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Supervision, Project administration, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization. AMH: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Supervision, Project administration, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the European Union’s H2020 LeiSHield MATI RISE (Research and Innovation Staff Exchange), under the Marie SkłodowskaCurie grant agreement No 778298. It has also received funding from research Pasteur Institute of Iran under grant No. 1232.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the studies’ volunteers for their participation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1436029/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Ghatee MA, Taylor WR, Karamian M. The geographical distribution of cutaneous leishmaniasis causative agents in Iran and its neighboring countries, a review. Front Public Health. (2020) 8:11. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00011
2. Bhargava P, Singh R. Developments in diagnosis and antileishmanial drugs. Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis. (2012) 2012:626838. doi: 10.1155/2012/626838
3. Rasti S, Delavari M, Arani TST, Mousavi SGA. Epidemiological and clinical study on the cutaneous leishmaniasis in Aran and Bidgol, center of Iran. Int Arch Health Sci. (2018) 5:72–5. doi: 10.4103/iahs.iahs_26_18
4. Sharifi I, Khosravi A, Aflatoonian MR, Salarkia E, Bamorovat M, Karamoozian A, et al. Cutaneous leishmaniasis situation analysis in the Islamic Republic of Iran in preparation for an elimination plan. Front Public Health. (2023) 11:1091709. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1091709
5. Bamorovat M, Sharifi I, Agha Kuchak Afshari S, Ghasemi Nejad Almani P. Mutual role of patients and the healthcare system in the control of cutaneous leishmaniasis. Transboundary Emerging Dis. (2023) 2023:7814940. doi: 10.1155/2023/7814940
6. Khosravi A, Sharifi I, Fekri A, Kermanizadeh A, Bamorovat M, Mostafavi M, et al. Clinical features of anthroponotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in a major focus, Southeastern Iran, 1994–2014. Iranian J parasitology. (2017) 12:544.
7. Kumar R, Bumb RA, Salotra P. Correlation of parasitic load with interleukin-4 response in patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania tropica. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. (2009) 57:239–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2009.00607.x
8. Kumar R, Bumb RA, Salotra P. Evaluation of localized and systemic immune responses in cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania tropica: interleukin-8, monocyte chemotactic protein-1 and nitric oxide are major regulatory factors. Immunology. (2010) 130:193–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03223.x
9. Ajdary S, Riazi-Rad F, Alimohammadian M-H, Pakzad S-R. Immune response to Leishmania antigen in anthroponotic cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Infection. (2009) 59:139–43. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2009.05.010
10. Serarslan G, Atik E. Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in human cutaneous leishmaniasis. Mol Cell Biochem. (2005) 280:147–9. doi: 10.1007/s11010-005-8542-3
11. Jenner RG, Townsend MJ, Jackson I, Sun K, Bouwman RD, Young RA, et al. The transcription factors T-bet and GATA-3 control alternative pathways of T-cell differentiation through a shared set of target genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2009) 106:17876–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909357106
12. Seif F, Khoshmirsafa M, Aazami H, Mohsenzadegan M, Sedighi G, Bahar M. The role of JAK-STAT signaling pathway and its regulators in the fate of T helper cells. Cell communication Signaling. (2017) 15:1–13. doi: 10.1186/s12964-017-0177-y
13. Morris R, Kershaw NJ, Babon JJ. The molecular details of cytokine signaling via the JAK/STAT pathway. Protein Science. (2018) 27:1984–2009. doi: 10.1002/pro.3519
14. Hu Q, Bian Q, Rong D, Wang L, Song J, Huang H-S, et al. JAK/STAT pathway: Extracellular signals, diseases, immunity, and therapeutic regimens. Front Bioengineering Biotechnol. (2023) 11:1110765. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1110765
15. Masoudzadeh N, Östensson M, Persson J, Mashayekhi Goyonlo V, Agbajogu C, Taslimi Y, et al. Molecular signatures of anthroponotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in the lesions of patients infected with Leishmania tropica. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:16198. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72671-7
16. Taslimi Y, Sadeghipour P, Habibzadeh S, Mashayekhi V, Mortazavi H, Müller I, et al. A novel non-invasive diagnostic sampling technique for cutaneous leishmaniasis. PloS Negl Trop Diseases. (2017) 11:e0005750. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005750
17. Masoudzadeh N, Östensson M, Persson J, Goyonlo VM, Agbajogu C, Taslimi Y, et al. Molecular signatures of anthroponotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in the lesions of patients infected with Leishmania tropica. Sci Rep. (2020) 10(1):1–15. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72671-7
18. Romero I, Téllez J, Suárez Y, Cardona M, Figueroa R, Zelazny A, et al. Viability and burden of Leishmania in extralesional sites during human dermal leishmaniasis. PloS Negl Trop Dis. (2010) 4:e819. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000819
19. R Core Team. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. R-project org (2018).
20. Dayakar A, Chandrasekaran S, Kuchipudi SV, Kalangi SK. Cytokines: key determinants of resistance or disease progression in visceral leishmaniasis: opportunities for novel diagnostics and immunotherapy. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:670. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00670
21. Scott P, Artis D, Uzonna J, Zaph C. The development of effector and memory T cells in cutaneous leishmaniasis: the implications for vaccine development. Immunol Rev. (2004) 201:318–38. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.00198.x
22. Sarapultsev A, Gusev E, Komelkova M, Utepova I, Luo S, Hu D. JAK-STAT signaling in inflammation and stress-related diseases: implications for therapeutic interventions. Mol Biomed. (2023) 4:40. doi: 10.1186/s43556-023-00151-1
23. Liu J, Wang F, Luo F. The role of JAK/STAT pathway in fibrotic diseases: molecular and cellular mechanisms. Biomolecules. (2023) 13:119. doi: 10.3390/biom13010119
24. Trinchieri G. Interleukin-12 and the regulation of innate resistance and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. (2003) 3:133–46. doi: 10.1038/nri1001
25. Güler ML, Gorham JD, Hsieh CS, Mackey AJ, Steen RG, Dietrich WF, et al. Genetic susceptibility to Leishmania: IL-12 responsiveness in TH1 cell development. Science. (1996) 271:984–7. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5251.984
26. Bahrami F, Masoudzadeh N, Van Veen S, Persson J, Lari A, Sarvnaz H, et al. Blood transcriptional profiles distinguish different clinical stages of cutaneous leishmaniasis in humans. Mol Immunol. (2022) 149:165–73. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2022.07.008
27. Kima P, Soong L. Interferon gamma in leishmaniasis. Front Immunol. (2013) 4. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00156
28. Lawless VA, Zhang S, Ozes ON, Bruns HA, Oldham I, Hoey T, et al. Stat4 regulates multiple components of IFN-γ-inducing signaling pathways1. J Immunol. (2000) 165:6803–8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.12.6803
29. Tretina K, Park ES, Maminska A, MacMicking JD. Interferon-induced guanylate-binding proteins: Guardians of host defense in health and disease. J Exp Med. (2019) 216:482–500. doi: 10.1084/jem.20182031
30. Fernández-Figueroa EA, Imaz-Rosshandler I, Castillo-Fernández JE, Miranda-Ortíz H, Fernández-López JC, Becker I, et al. Down-regulation of TLR and JAK/STAT pathway genes is associated with diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis: A gene expression analysis in NK cells from patients infected with leishmania mexicana. PloS Negl Trop Dis. (2016) 10:e0004570. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004570
31. Kresse A, Konermann C, Degrandi D, Beuter-Gunia C, Wuerthner J, Pfeffer K, et al. Analyses of murine GBP homology clusters based on in silico, in vitro and in vivo studies. BMC Genomics. (2008) 9:1–12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-158
32. Schoggins JW. Interferon-stimulated genes: what do they all do? Annu Rev Virol. (2019) 6:567–84. doi: 10.1146/annurev-virology-092818-015756
33. Novais FO, Carvalho LP, Passos S, Roos DS, Carvalho EM, Scott P, et al. Genomic profiling of human Leishmania Braziliensis lesions identifies transcriptional modules associated with cutaneous immunopathology. J Invest Dermatol. (2015) 135:94–101. doi: 10.1038/jid.2014.305
34. Farias Amorim C, ON F, Nguyen BT, Nascimento MT, Lago J, Lago AS, et al. Localized skin inflammation during cutaneous leishmaniasis drives a chronic, systemic IFN-γ signature. PloS Negl Trop Dis. (2021) 15:e0009321. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009321
35. Masoudzadeh N, Mizbani A, Taslimi Y, Mashayekhi V, Mortazavi H, Sadeghipour P, et al. Leishmania tropica infected human lesions: Whole genome transcription profiling. Acta Trop. (2017) 176:236–41. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2017.08.016
36. Rodrigues GF, Alcântara LS, Barros JPB, de Lima ACS, Campos MB, Moraes C, et al. In situ expression of Th17 immunologic mediators in American cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania (V.) Braziliensis and Leishmania (L.) amazonensis in the Brazilian Amazon. Front Trop Dis. (2023) 4. doi: 10.3389/fitd.2023.1067595
37. Tolouei S, Ghaedi K, Khamesipour A, Akbari M, Baghaei M, Hasheminia SJ, et al. IL-23 and IL-27 levels in macrophages collected from peripheral blood of patients with healing vs non-healing form of cutaneous leishmaniasis. Iranian J Parasitol. (1970) 7:18–25.
38. Parham C, Chirica M, Timans J, Vaisberg E, Travis M, Cheung J, et al. A receptor for the heterodimeric cytokine IL-23 is composed of IL-12Rβ1 and a novel cytokine receptor subunit, IL-23R. J Immunol. (2002) 168:5699–708. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.11.5699
39. Park H, Li Z, Yang XO, Chang SH, Nurieva R, Wang Y-H, et al. A distinct lineage of CD4 T cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing interleukin 17. Nat Immunol. (2005) 6:1133–41. doi: 10.1038/ni1261
40. Anderson CF, Stumhofer JS, Hunter CA, Sacks D. IL-27 regulates IL-10 and IL-17 from CD4+ cells in nonhealing Leishmania major infection. J Immunol. (2009) 183:4619–27. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0804024
41. Barreto-de-Souza V, Ferreira PL, Vivarini Ade C, Calegari-Silva T, Soares DC, Regis EG, et al. IL-27 enhances Leishmania amazonensis infection via ds-RNA dependent kinase (PKR) and IL-10 signaling. Immunobiology. (2015) 220:437–44. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2014.11.006
42. Batten M, Li J, Yi S, Kljavin NM, Danilenko DM, Lucas S, et al. Interleukin 27 limits autoimmune encephalomyelitis by suppressing the development of interleukin 17-producing T cells. Nat Immunol. (2006) 7:929–36. doi: 10.1038/ni1375
43. Costa DL, Cardoso TM, Queiroz A, Milanezi CM, Bacellar O, Carvalho EM, et al. Tr-1-like CD4+CD25-CD127-/lowFOXP3- cells are the main source of interleukin 10 in patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania Braziliensis. J Infect Dis. (2015) 211:708–18. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu406
44. Yoshimoto T, Yoshimoto T, Yasuda K, Mizuguchi J, Nakanishi K. IL-27 suppresses Th2 cell development and Th2 cytokines production from polarized Th2 cells: a novel therapeutic way for Th2-mediated allergic inflammation. J Immunol. (2007) 179:4415–23. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.7.4415
45. Takeda A, Hamano S, Yamanaka A, Hanada T, Ishibashi T, Mak TW, et al. Cutting edge: role of IL-27/WSX-1 signaling for induction of T-bet through activation of STAT1 during initial Th1 commitment. J Immunol. (2003) 170:4886–90. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.10.4886
46. Chihara N, Madi A, Kondo T, Zhang H, Acharya N, Singer M, et al. Induction and transcriptional regulation of the co-inhibitory gene module in T cells. Nature. (2018) 558:454–9. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0206-z
47. de Freitas ESR, Gálvez RI, Pereira VRA, de Brito MEF, Choy SL, Lotter H, et al. Programmed cell death ligand (PD-L)-1 contributes to the regulation of CD4(+) T effector and regulatory T cells in cutaneous leishmaniasis. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:574491. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.574491
48. Dey NS, Senaratne S, Somaratne V, Madarasinghe NP, Seneviratne B, Forrester S, et al. Early reduction in PD-L1 expression predicts faster treatment response in human cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Clin Invest. (2021) 131:e142765. doi: 10.1172/JCI142765
49. Belkaid Y, Piccirillo CA, Mendez S, Shevach EM, Sacks DL. CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells control Leishmania major persistence and immunity. Nature. (2002) 420:502–7. doi: 10.1038/nature01152
50. Castellano LR, Argiro L, Dessein H, Dessein A, da Silva MV, Correia D, et al. Potential use of interleukin-10 blockade as a therapeutic strategy in human cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Immunol Res. (2015) 2015:152741. doi: 10.1155/2015/152741
51. Anderson CF, Oukka M, Kuchroo VJ, Sacks D. CD4(+)CD25(-)Foxp3(-) Th1 cells are the source of IL-10-mediated immune suppression in chronic cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Exp Med. (2007) 204:285–97. doi: 10.1084/jem.20061886
52. Wang RX, Yu CR, Dambuza IM, Mahdi RM, Dolinska MB, Sergeev YV, et al. Interleukin-35 induces regulatory B cells that suppress autoimmune disease. Nat Med. (2014) 20:633–41. doi: 10.1038/nm.3554
53. Ye C, Yano H, Workman CJ, Vignali DAA. Interleukin-35: structure, function and its impact on immune-related diseases. J Interferon Cytokine Res. (2021) 41:391–406. doi: 10.1089/jir.2021.0147
54. Divenuto F, Marascio N, Quirino A, Giancotti A, Filice S, Gigliotti S, et al. Cellular mediators in human leishmaniasis: Critical determinants in parasite killing or disease progression. Acta Tropica. (2023) 248:107037. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2023.107037
55. Khatonier R, Khan AM, Sarmah P, Ahmed GU. Role of IL-21 in host pathogenesis in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. J Parasit Dis. (2018) 42:500–4. doi: 10.1007/s12639-018-1025-8
56. Liu S, Hur YH, Cai X, Cong Q, Yang Y, Xu C, et al. A tissue injury sensing and repair pathway distinct from host pathogen defense. Cell. (2023) 186:2127–43.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.03.031
57. Sa SM, Valdez PA, Wu J, Jung K, Zhong F, Hall L, et al. The effects of IL-20 subfamily cytokines on reconstituted human epidermis suggest potential roles in cutaneous innate defense and pathogenic adaptive immunity in psoriasis. J Immunol. (2007) 178:2229–40. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.4.2229
58. Mitamura Y, Nunomura S, Furue M, Izuhara K. IL-24: A new player in the pathogenesis of pro-inflammatory and allergic skin diseases. Allergol Int. (2020) 69:405–11. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2019.12.003
59. Zhong Y, Zhang X, Chong W. Interleukin-24 immunobiology and its roles in inflammatory diseases. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:627. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020627
60. Dey NS, Dey S, Brown N, Senarathne S, Reis LC, Sengupta R, et al. IL-32 producing CD8+ memory T cells and Tregs define the IDO1/PD-L1 niche in human cutaneous leishmaniasis skin lesions. medRxiv. (2024). doi: 10.1101/2024.01.02.23300281
61. Wan C-K, Andraski AB, Spolski R, Li P, Kazemian M, Oh J, et al. Opposing roles of STAT1 and STAT3 in IL-21 function in CD4+ T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2015) 112:9394–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1511711112
62. Strengell M, Sareneva T, Foster D, Julkunen I, Matikainen S. IL-21 up-regulates the expression of genes associated with innate immunity and Th1 response. J Immunol. (2002) 169:3600–5. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.7.3600
63. Monteleone G, Pallone F, MacDonald TT. Interleukin-21: a critical regulator of the balance between effector and regulatory T-cell responses. Trends Immunol. (2008) 29:290–4. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2008.02.008
64. Bollig N, Brüstle A, Kellner K, Ackermann W, Abass E, Raifer H, et al. Transcription factor IRF4 determines germinal center formation through follicular T-helper cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2012) 109:8664–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1205834109
65. Espitia CM, Zhao W, Saldarriaga O, Osorio Y, Harrison LM, Cappello M, et al. Duplex real-time reverse transcriptase PCR to determine cytokine mRNA expression in a hamster model of New World cutaneous leishmaniasis. BMC Immunol. (2010) 11:31. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-11-31
66. Kong F, Saldarriaga OA, Spratt H, Osorio EY, Travi BL, Luxon BA, et al. Transcriptional profiling in experimental visceral leishmaniasis reveals a broad splenic inflammatory environment that conditions macrophages toward a disease-promoting phenotype. PloS Pathog. (2017) 13:e1006165. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006165
67. Zeitvogel J, Jokmin N, Rieker S, Klug I, Brandenberger C, Werfel T. GATA3 regulates FLG and FLG2 expression in human primary keratinocytes. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:11847. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10252-x
68. Teles RM, Teles RB, Amadeu TP, Moura DF, Mendonça-Lima L, Ferreira H, et al. High matrix metalloproteinase production correlates with immune activation and leukocyte migration in leprosy reactional lesions. Infect Immun. (2010) 78:1012–21. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00896-09
69. Brunner S, Kim J-O, Methe H. Relation of matrix metalloproteinase-9/tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 ratio in peripheral circulating CD14+ monocytes to progression of coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. (2010) 105:429–34. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2009.10.013
Keywords: Leishmania tropica, cutaneous leishmaniasis, JAK-STAT signaling pathway, cytokines, immune checkpoints
Citation: Hadifar S, Masoudzadeh N, Heydari H, Mashayekhi Goyonlo V, Kerachian M, Daneshpazhooh M, Sadeghnia A, Tootoonchi N, Erfanian Salim R, Rafati S and Harandi AM (2024) Intralesional gene expression profile of JAK-STAT signaling pathway and associated cytokines in Leishmania tropica-infected patients. Front. Immunol. 15:1436029. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1436029
Received: 21 May 2024; Accepted: 02 September 2024;
Published: 19 September 2024.
Edited by:
Antonio Osuna, University of Granada, SpainReviewed by:
André Alves Dias, Oswaldo Cruz Foundation (Fiocruz), BrazilJuan Diego Maya, University of Chile, Chile
Copyright © 2024 Hadifar, Masoudzadeh, Heydari, Mashayekhi Goyonlo, Kerachian, Daneshpazhooh, Sadeghnia, Tootoonchi, Erfanian Salim, Rafati and Harandi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sima Rafati, c19yYWZhdGlAeWFob28uY29t; , c2ltYS1yYWZhdGlzeUBwYXN0ZXVyLmFjLmly; Ali M. Harandi, YWxpLmhhcmFuZGlAbWljcm9iaW8uZ3Uuc2U=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Shima Hadifar
Shima Hadifar Nasrin Masoudzadeh1†
Nasrin Masoudzadeh1† Maryam Daneshpazhooh
Maryam Daneshpazhooh Sima Rafati
Sima Rafati Ali M. Harandi
Ali M. Harandi