
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Immunol., 24 June 2024
Sec. Inflammation
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1429862
This article is a correction to:
Material basis and molecular mechanisms of Chaihuang Qingyi Huoxue Granule in the treatment of acute pancreatitis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking-based strategy
 Jia Yang1†
Jia Yang1† Yu-Hong Jiang2†
Yu-Hong Jiang2† Xin Zhou3,4
Xin Zhou3,4 Jia-Qi Yao2
Jia-Qi Yao2 Yang-Yang Wang1
Yang-Yang Wang1 Jian-Qin Liu3,4
Jian-Qin Liu3,4 Peng-Cheng Zhang2
Peng-Cheng Zhang2 Wen-Fu Tang2*
Wen-Fu Tang2* Zhi Li3,4*
Zhi Li3,4*by Yang J, Jiang Y-H, Zhou X, Yao J-Q, Wang Y-Y, Liu J-Q, Zhang P-C, Tang W-F and Li Z (2024). Front. Immunol. 15:1353695. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1353695
Error in Figure/Table Legend
In the published article, there was an error in the legend for Figure 8E as published. The correct graph should display BCL-2/b-actin data, but due to an oversight, it currently shows the same data as Figure 8D (BAX/b-actin). We apologize for any confusion this may have caused and are committed to rectifying this issue promptly. The corrected figure appears below.
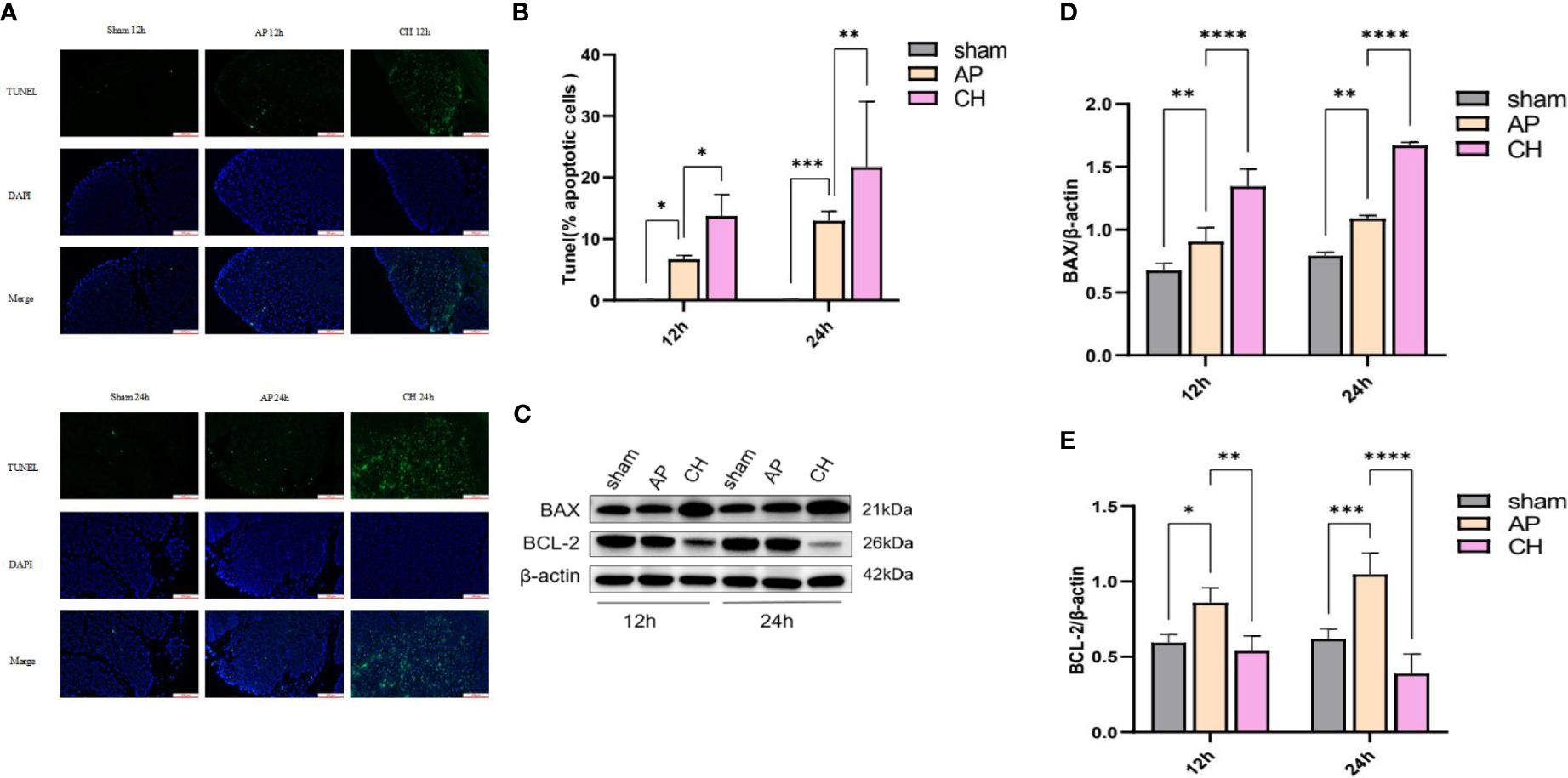
Figure 8 Administration of CH increases the apoptosis of pancreatic acinar cell in rats with AP. (A) Images from the TUNEL assay of pancreatic tissue, 100 μm scale bar. (n = 6). (B) Statistical results on the proportion of pancreatic acinar cells undergoing apoptosis in each group. Mean ± SD (n = 6) data were reported for each group, and statistical significance was observed. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 in comparison to the AP group. (C) Expression levels of BAX, BCL–2, and β–actin in various animal model groups. (n = 3). (D) Corresponding ratios of BAX/β–actin. Mean ± SD data were reported for each group, and statistical significance was observed (n = 3). **P < 0.01 and ****P < 0.0001 in comparison to the AP group. (E) Corresponding ratios of BCL–2/β–actin. Mean ± SD data were reported for each group, and statistical significance was observed (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 in comparison to the AP group.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: acute pancreatitis, Chaihuang Qingyi Huoxue Granule, network pharmacology, molecular docking, pancreatic acinar cells, Traditional Chinese
Citation: Yang J, Jiang Y-H, Zhou X, Yao J-Q, Wang Y-Y, Liu J-Q, Zhang P-C, Tang W-F and Li Z (2024) Corrigendum: Material basis and molecular mechanisms of Chaihuang Qingyi Huoxue Granule in the treatment of acute pancreatitis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking-based strategy. Front. Immunol. 15:1429862. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1429862
Received: 08 May 2024; Accepted: 12 June 2024;
Published: 24 June 2024.
Edited by:
Ravi Kumar Sharma, Chandigarh University, IndiaReviewed by:
Vikas Kumar, Chandigarh University, IndiaCopyright © 2024 Yang, Jiang, Zhou, Yao, Wang, Liu, Zhang, Tang and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhi Li, bGl6aGktc3dtdUAxMjYuY29t; Wen-Fu Tang, dGFuZ3dmQHNjdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.