- 1Department of Epidemiology, Public Health Faculty, Institute of Health, University of Gondar, Gondar, Ethiopia
- 2Department of Epidemiology, Public Health Faculty, Institute of Health, Jimma University, Jimma, Ethiopia
- 3Department of Anatomy, School of Biomedical Sciences, Jimma University, Jimma, Ethiopia
- 4Department of Biomedical Sciences, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Wollo University, Dessie, Ethiopia
- 5School of Nursing, Faculty of Health Sciences, Jimma University, Jimma, Ethiopia
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Bahir Dar University, Bahir Dar, Ethiopia
- 7Department of Surgery, Faculty of Health Sciences, Institute of Health, Jimma University, Jimma, Ethiopia
- 8Department of Biochemistry, School of Biomedical Sciences, Jimma University, Jimma, Ethiopia
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a highly infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Nasopharyngeal swabs (NP swabs) were used for patients with COVID-19 who demonstrated serious clinical symptoms and disturbances in biochemical parameters. The biochemical profiles of these patients remain ambiguous and differ from wave to wave of COVID-19 infections. Herein, we conducted a multicenter retrospective cohort study with 538 patients with COVID-19 at six COVID-19 treatment centers in Ethiopia. Professional data collectors collected the data. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize the data, and independent t-tests and chi-square tests were used to assess the relationships between the continuous and categorical variables across waves, respectively. In total, 240 and 298 patients were included from the first and second waves, respectively. Men and individuals aged 53–69 years were more likely to be infected in each wave. The mean alkaline phosphatase (p < 0.001) and sodium levels (p = 0.035) significantly differed between patients across the two waves of COVID-19; the significant difference in the alkaline phosphatase levels of patients between the two waves was −45.425. All the symptoms of COVID-19 were significantly (p < 0.05) associated with the waves of the pandemic. Patients in both waves had no chronic disease comorbidities. This study showed that the mean alkaline phosphatase and sodium levels differed significantly across the first two waves of the pandemic at six COVID-19 treatment centers in Ethiopia while all clinical symptoms of COVID-19 were associated with the first two waves of the pandemic.
1 Introduction
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), is a member of a large family of enveloped-positive single-stranded RNA (ribonucleic acid) viruses of medical importance (1). The virus particle exhibits a characteristic “corona” (crown) of spike proteins around the lipid envelope, which is the basis of these viruses being referred to as coronaviruses (2). Coronaviruses are a large family of viruses that cause ailments ranging from asymptomatic illness to illnesses with high morbidity and mortality, including Middle East respiratory syndrome and severe acute respiratory syndrome (3).
The 2019 novel coronavirus produced a new illness that was first recognized in human beings in Wuhan, China in December 2019 and swiftly spread to become a pandemic (4). The World Health Organization (WHO) declared a public health emergency on 30 January 2020 (5). On 11 March 2020, the WHO declared the disease a pandemic (6). According to a worldwide report on 18 November 2021, the virus had spread to >222 countries and territories. Altogether, 255,772,102 laboratory-confirmed infections and 5,139,858 confirmed deaths have been reported worldwide (5). In 2024, COVID-19 remains a monitored global health issue, though prevalence rates and variant distributions vary by region. WHO reports show that in recent months, global COVID-19 cases have decreased in most areas, with slight increases in others, particularly in countries in the Western Pacific and some parts of Africa (7).
The disease is highly infectious, and patients with COVID-19 demonstrate serious clinical symptoms, including increased body temperature, dry cough, diarrhea, headaches, myalgia, fever, fatigue, dyspnea, vomiting, anorexia, and multiple organ dysfunction (4, 8). The clinical manifestations of COVID-19 vary from asymptomatic to acute respiratory distress, depending on the viral route of entry, viral load, host immunity, age, and comorbidities such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, chronic respiratory disease, and cancer (8). The severe stage of the disease can be characterized by acute respiratory distress syndrome, treatment-resistant septic shock, metabolic acidosis, and bleeding and coagulation dysfunction (9, 10).
The current reporting on laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 cases reports changes in the biochemical parameters of patients (i.e., levels of ferritin, CRP, IL-6, LDH, AST, ALT, PT, D-dimer, procalcitonin, PLT dimer, and APTT) (11). Therefore, these biochemical parameters can be used as predictive markers. Many studies have proven that comorbidities, age, and abnormalities together with numerous scientific biomarkers may be essential for understanding illness severity (12). Although the clinical characteristics of COVID-19 have been widely reported, a summary of the changes in the common biochemical variables observed in patients infected during different waves of COVID-19 remains poorly investigated. Published laboratory findings of COVID-19 infections have been collected from hospital-admitted patients at single time points, which limits our understanding of the dynamic biochemical changes during the course of the disease and how clinical symptoms and disease severity differ across waves (13). Thus, the consistency and differences in the biochemical parameters of patients with COVID-19 across waves remain largely unknown. Therefore, this study assessed the biochemical profiles of patients with COVID-19 during the first and second waves of the pandemic in Ethiopia.
2 Methods
2.1 Study design, setting and population
A multicenter retrospective cohort study was conducted at six COVID-19 treatment centers in Ethiopia [Jimma University Medical Center (JUMC), St. Peter’s Specialized Hospital, EKA Kotebe General Hospital, Bethzatha General Hospital, Hallelujah General Hospital, and Bahir Dar University Tibebe Ghion Specialized Hospital] to assess the biochemical profiles of patients with COVID-19. A total of 538 study participants (COVID-19 PCR- and RDT-positive) were recruited from the selected COVID-19 treatment centers in Ethiopia and the WHO Structured Laboratory Testing and Reporting Checklist was used.
2.2 Data collection tool and procedure
Data were collected using a structured checklist. The checklist was adapted from the WHO tool for data extraction and developed after an extensive review of the literature and similar study tools (14, 15). Professional and experienced data collectors and supervisors were selected and trained by the principal and co-investigator for data collection. They practiced using the data collection tool with the principal investigator for 2 days before starting official data extraction. Data were then gathered from both electronic and paper medical records of suspected and confirmed COVID-19 cases. Information collected included demographic details (age, sex, educational status, ethnicity, nationality, and marital status), medical history (comorbidities), clinical signs and symptoms, physical examination results, COVID-19 status, and hospital stay details. Additionally, laboratory data, patient demographic information, medical histories, and biochemical profiles [direct bilirubin, urea, blood urea nitrogen, total bilirubin, blood glucose, cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL), Serum Glutamate Pyruvate Transaminase / Alanine Aminotransferase (measured in units per liter) (SGPT/ALT U/L), Serum Glutamate Oxaloacetate Transaminase / Aspartate Aminotransferase (measured in units per liter) (SGOT/AST U/L), gamma-glutamic, transpeptidase, alkaline phosphatase, sodium (NA+), potassium (K+), chloride (Cl-), phosphorus, magnesium, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and calcium (Ca+)] were extracted from these records.
2.2.1 Data quality control and statistical analysis
The selected data collectors were trained to collect data from medical records. Facilitators and supervisors were assigned to control and guide data collection, thereby increasing consistency in data collection. Collected data were checked for completeness and consistency before entry and double data entry into EpiData 4.6. Double data entry is a data management method used to improve data accuracy and reduce entry errors. In this process, two independent data entry operators enter the same dataset separately, creating two versions. These entries are then compared, and any discrepancies between the two are reviewed and resolved. After checking the data, it was exported to SPSS version 25. Descriptive statistics were used to determine frequencies with percentages and means. Graphs, charts, and tables were used to summarize the data. Independent t-tests were used to compare the mean biochemical and hematological profiles of the patients with COVID-19, and chi-square tests were conducted to identify associations between categorical variables across the waves.
2.3 Ethical considerations
Ethical clearance and approval for this research were obtained from the Institutional Review Board of Jimma University (Ref. No. JUIRB43/22). The directors of the selected COVID-19 treatment centers were contacted via a formal letter by the director’s office of the Institute of Health, Research, and Innovation at Jimma University. Supporting letters were secured from each treatment center. All participants were informed of the objectives of the study, and written informed consent was obtained before starting data collection.
3 Results
3.1 Sociodemographic characteristics of participants
A total of 538 patients with COVID-19 were included in the analysis: 240 (44.6%) from the first wave and 298 (55.4%) from the second wave. The mean age in the first wave was 56 ± 2 years, and ranged from 1 to 97; the mean age in the second wave was 56 ± 1 years, and ranged from 16 to 95. An unequal sex distribution was observed in both sets of patients; furthermore, the education and marital status significantly differed between both waves (p < 0.05). Increased age was evident during the first wave but not during the second wave. During the first wave of COVID-19, of the 240 patients, 93 (38.75%) had hypertension, 83 (34.58%) had diabetes mellitus, 44 (18.33%) had chronic liver disease, and 31 (12.92%) had a history of ischemic heart disease. During the second COVID-19 wave, of the 298 patients, 116 (38.93%) had hypertension, 98 (32.89%) had diabetes mellitus, and 37 (12.41%) had a medical history of ischemic heart disease (Table 1).
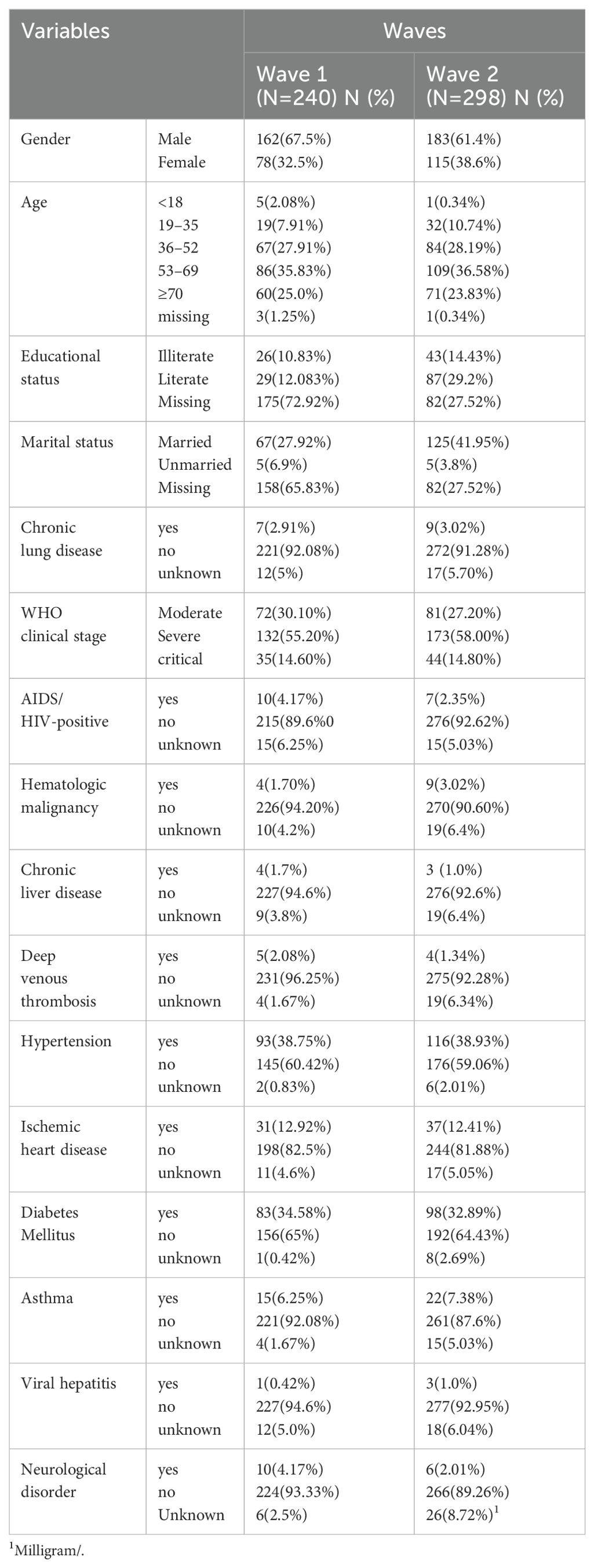
Table 1. The distribution and association socio-demographic characteristics and medical history of COVID-19 patients across Waves in Ethiopia.
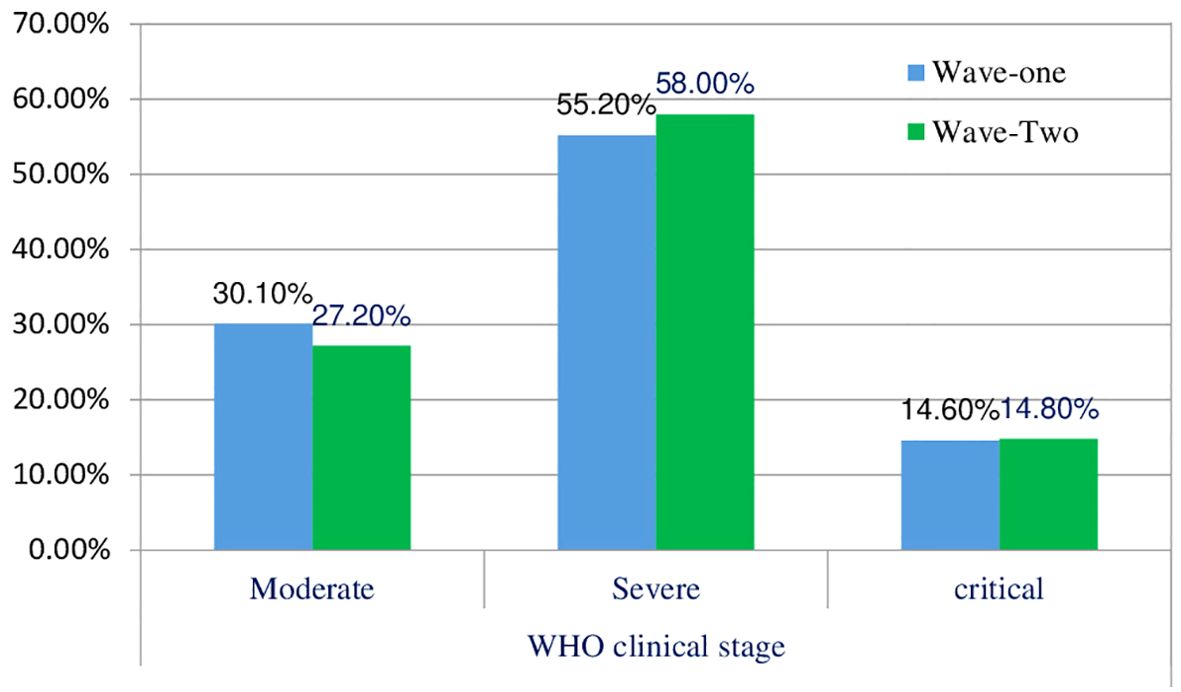
3.2 The clinical stage of patients with COVID-19 across waves
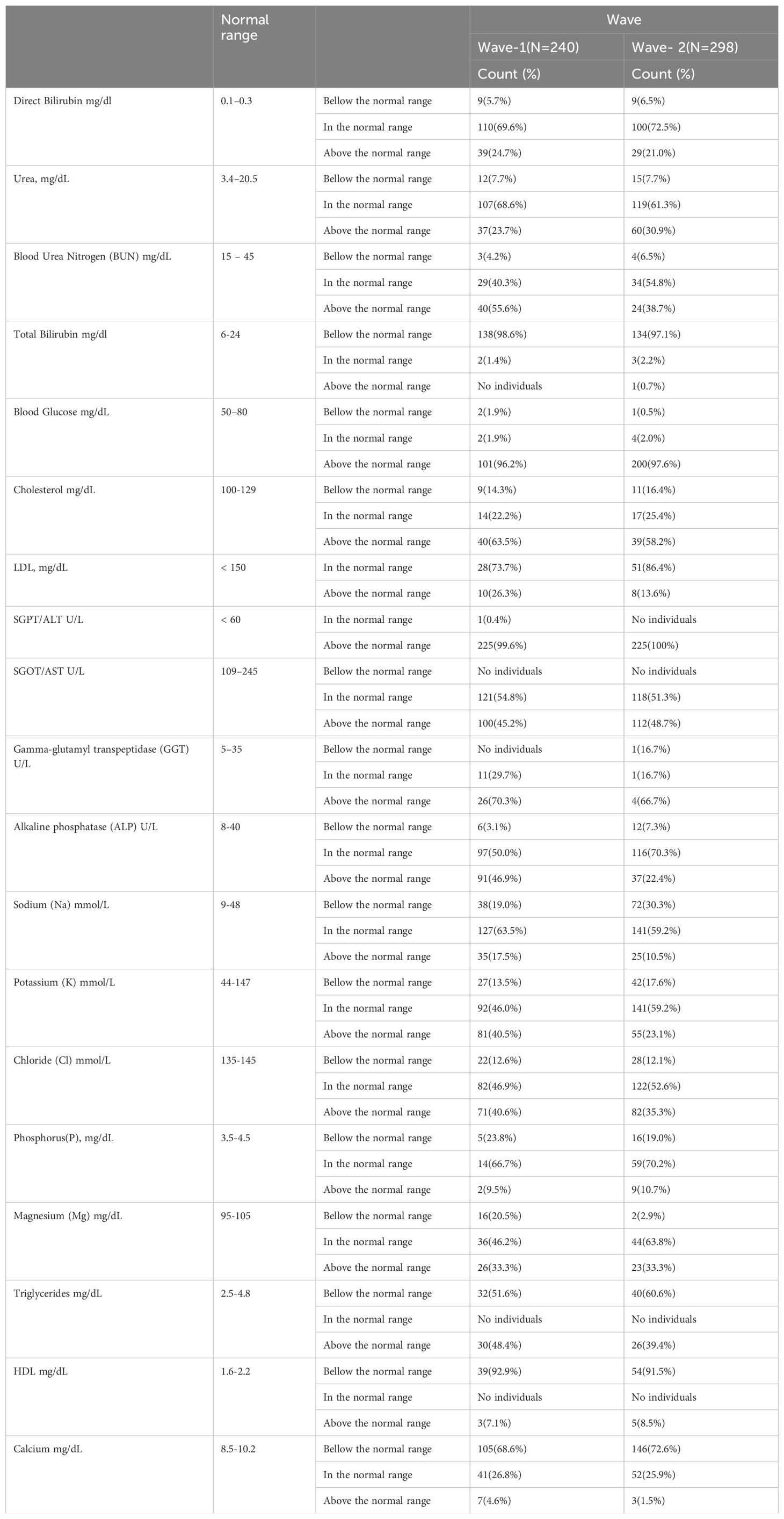
The distribution of patients in different WHO clinical stages (16) and across the first and second waves of COVID-19 in Ethiopia indicated that of 240 patients, 72 (30.10%) were in the moderate clinical stage, 132 (55.2%) were in the severe clinical stage, and 35 (14.6%) were in the critical stage during the first wave. Of the 298 patients in the second wave, 82 (27.2%) were in the moderate clinical stage, 173 (58.00%) were in the severe clinical stage, and the remaining 44 (4.8%) were in the critical stage (Figure 1). The biochemical parameters of the patients with COVID-19 in the selected COVID-19 treatment centers were analyzed. The biochemical parameter recorded in the highest number of patients was Na+ in the second wave, whereas the biochemical parameter recorded in the lowest number of patients was the Cl- level in the first wave. The Ca+ levels in the second wave were below the normal range. The K+ and Na+ levels in most patients during the second wave were within the normal range. In the first and second waves of COVID-19, 110 (69.6%) and 100 (72.5%) of the patients had direct bilirubin levels that were within the normal range, 9 (5.7%) and 9 (6.5%) were below the normal range, and 39 (24.7%) and 29 (21.0%) were above the normal range, respectively. The overall distributions of the biochemical parameters across the first two waves are shown in Table 2, Figure 2.
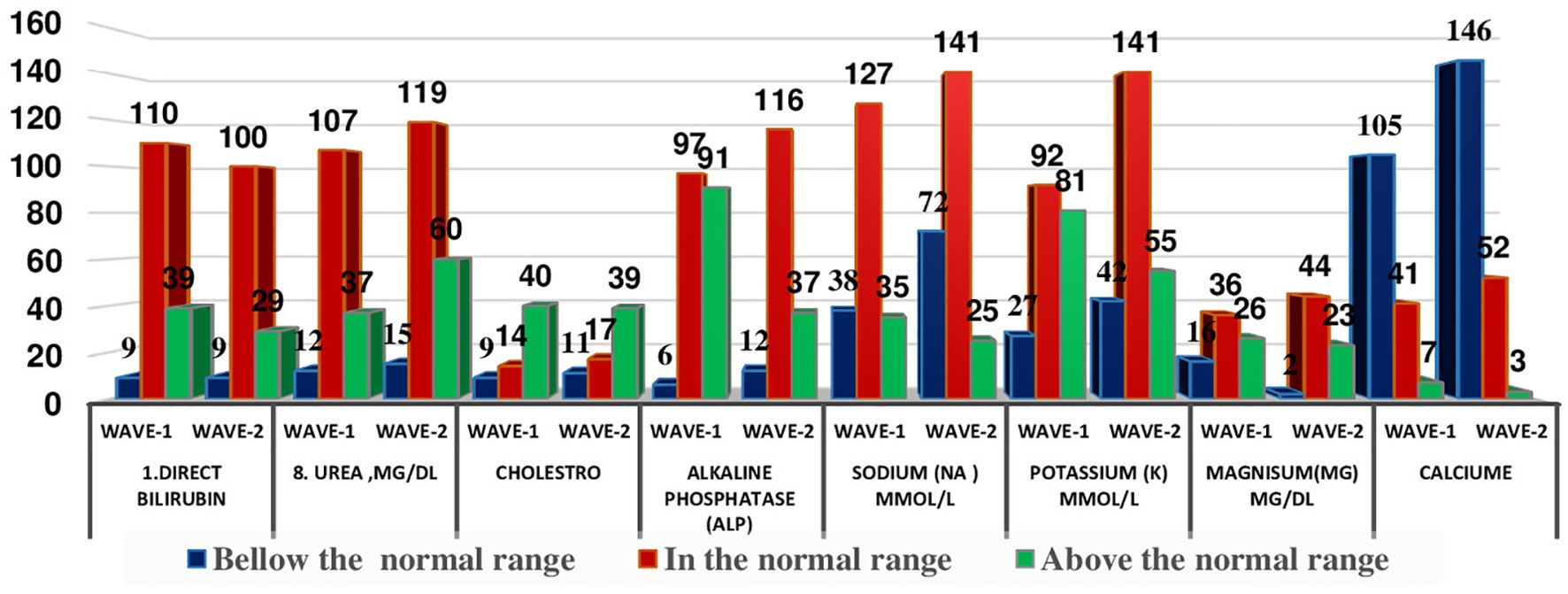
Figure 2. Distribution of some selected biochemical parameters across the two COVID-19 waves in Ethopia.
3.3 The clinical symptoms of patients with COVID-19 across waves
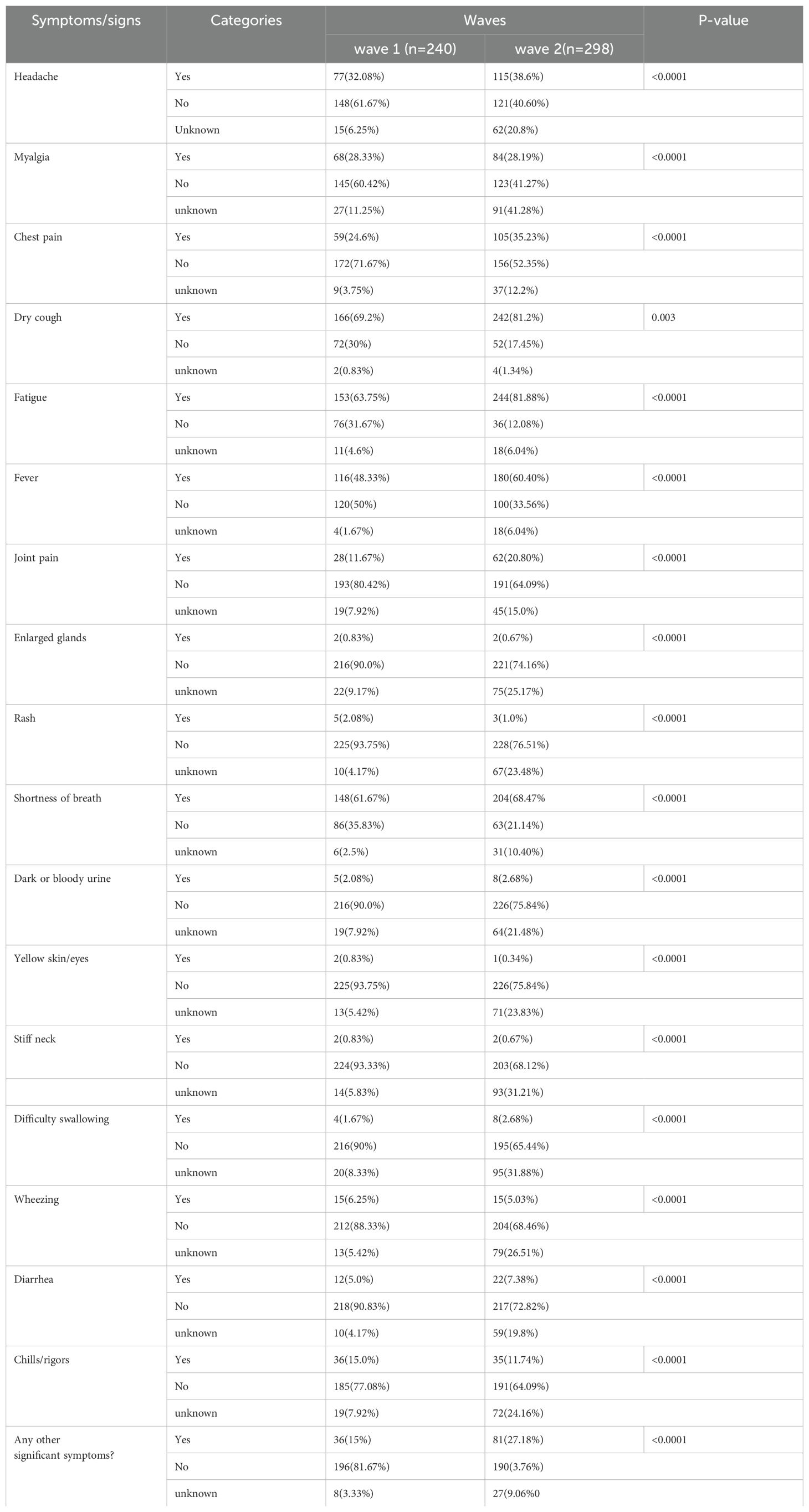
The most relevant clinical symptoms recorded during the first wave were dry cough (166; 69.2%), fatigue (153; 63.75%), shortness of breath (148; 61.67%), and fever (116; 48.33%). During the second wave, fatigue (244; 81.88%), dry cough (242; 81.2%), shortness of breath (204; 68.47%), and fever (180; 60.40%) were the most prevalent symptoms of COVID-19 infection in Ethiopia. A chi-square association test was conducted to identify whether the occurrence of COVID-19 symptoms and pandemic waves were associated. This revealed a significant association between the pandemic waves and headache, myalgia, chest pain, dry cough, fatigue, fever, joint pain, enlarged glands, rash, shortness of breath, dark or bloody urine, yellow skin/eyes, stiff neck, difficulty in swallowing, wheezing, diarrhea, and chills/rigors (Table 3).
3.4 Comparison of the biochemical profiles of patients with COVID-19 by independent t-test across waves in Ethiopia
The biochemical profiles of patients who were infected during the first and second waves of COVID-19 in Ethiopia were compared using an independent t-test to evaluate whether the mean biochemical profiles significantly differed across pandemic waves in Ethiopia. Accordingly, the mean alkaline phosphatase and sodium levels were identified as being significantly different between the first two waves of COVID-19. However, the other biochemical parameters did not significantly differ between the first two waves of the pandemic (Table 4).
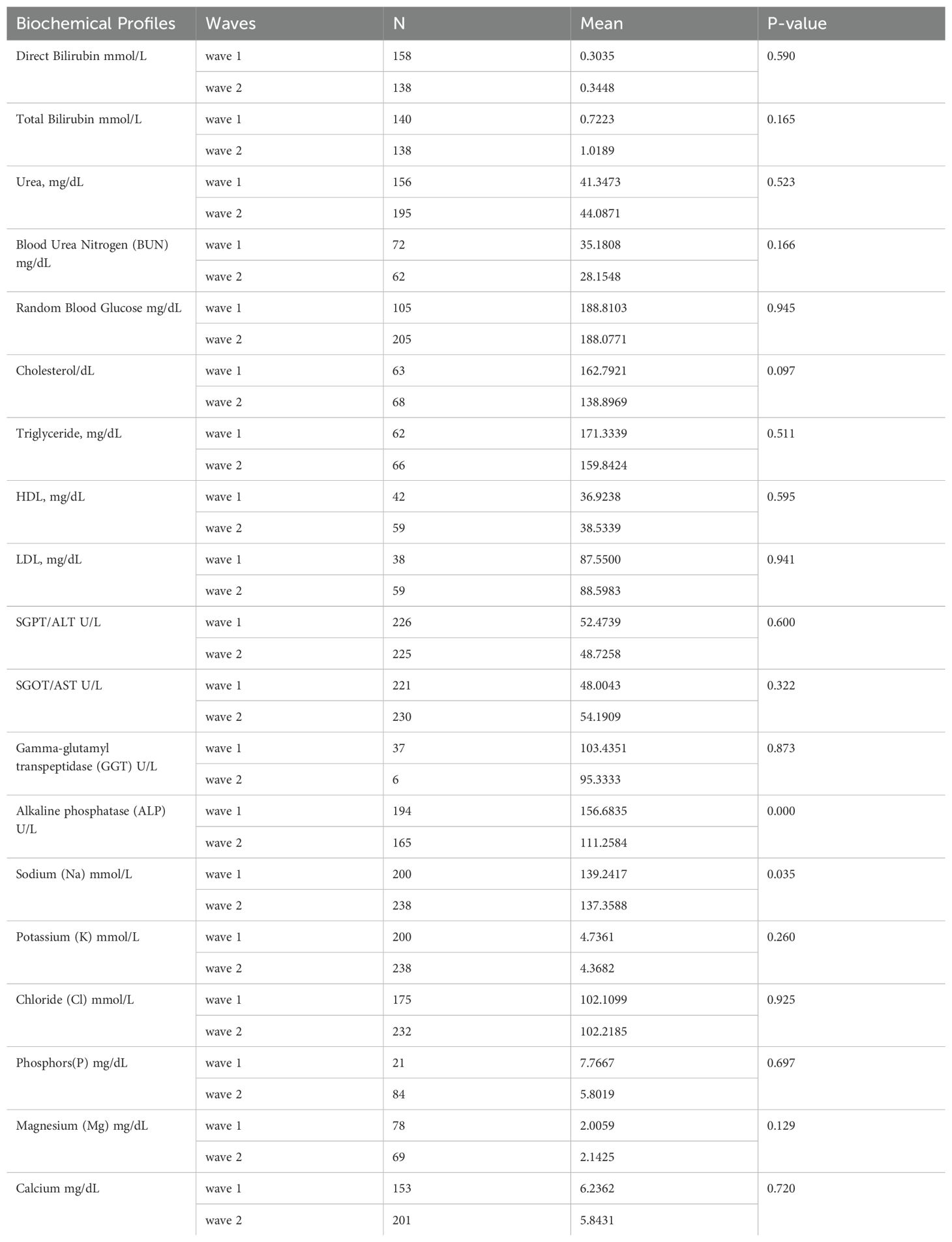
Table 4. Comparison of the biochemical profiles of COVID-19 patients by independent t-test across waves in Ethiopia.
4 Discussion
COVID-19 is an ongoing pandemic that continues to spread. According to WHO reports, more than 583 million cases have been confirmed globally while 6.44 million people have died as of 2 August 2022 (17). The WHO 2024 updates on COVID-19 have highlighted evolving trends and shifts in case numbers, as well as the development of variants globally. In early 2024, cases increased by 4% in January, showing sustained transmission in some areas despite a decline in deaths (7). After the initial spread of COVID-19 in China, it is evident that, together with age and other risk factors such as comorbidities, alterations in different biochemical biomarkers can be useful for assessing disease severity and the risk of evolution toward critical stages (17).
On 11 March 2022, the first case of COVID-19 was confirmed in Ethiopia. Several studies have shown that age, comorbidities, and abnormalities in various clinical biomarkers are essential for understanding disease severity (18, 19). SARS-CoV-2 infects people of all age groups; however, individuals aged >60 years, along with those with comorbidities such as diabetes, chronic respiratory disease, and cardiovascular diseases, are at a higher risk of developing the infection (19). Biochemical monitoring of patients with COVID-19 is critical for assessing disease severity and progression, as well as for monitoring therapeutic intervention (20).
An overview of the changes in the most common biochemical parameters observed in patients with COVID-19 across waves and multicenter studies is still lacking. Therefore, the present study presents the changes in biochemical profiles, medical histories, and symptoms of patients with COVID-19. In this report, a total of 240 and 298 patients with COVID-19 were studied during the first and second waves in Ethiopia, respectively.
This study found an association between the mean alkaline phosphatase levels of patients across the two waves of COVID-19 and the mean difference was -45.4. It shows that average alkaline phosphatase levels of patients decreased in the second wave. The other biochemical parameter of patients with COVID-19 where themean value significantly differed across the first two waves was the level of sodium. The mean significant difference in the sodium level was −1.883, indicating that the mean sodium level of patients with COVID had decreased in the second wave compared with that in the first wave. This might be due to the changing nature of the virus, population health, and healthcare factors. Several common biochemical parameters have been implicated in the progression of COVID-19, providing important prognostic information (20).
However, the other biochemical parameters of the patients did not significantly differ between the first two COVID waves. Thus, the mean biochemical profiles of patients in the first wave were similar to those of the patients in the second wave.
Chi-square analysis demonstrated that COVID-19 symptoms differed significantly across the waves of the pandemic in Ethiopia. This finding was consistent with that of Suleyman et al. (21).
4 Conclusion
This study found that >90% of patients in both the first and second waves of COVID-19 in Ethiopia were not comorbid with chronic lung disease. The mean alkaline phosphatase and sodium levels of the patients significantly differed across the first two waves of the pandemic. Headache, myalgia, chest pain, dry cough, fatigue, fever, joint pain, enlarged glands, rash, shortness of breath, dark or bloody urine, yellow skin/eyes, stiff neck, difficulty in swallowing, wheezing, diarrhea, and chills or rigors were the most common symptoms of COVID-19 in Ethiopia during the first and second waves of the pandemic.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Jimma University Institute of Health Institutional Review Board. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
HG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DD: Data curation, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. AL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AJ: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. IB: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. KA: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Resources, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. SH: Data curation, Resources, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. NS: Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. MF: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Jimma University Institute of Health (JUIH).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support provided by the Jimma University Institute of Health (JUIH). We would like to thank the medical directors and staff of Jimma University Medical Center (JUMC), St. Peter’s Specialized Hospital, EKA Kotebe General Hospital, Bethzatha General Hospital, Hallelujah General Hospital, and Bahir Dar University Tibebe Ghion Specialized Hospital) Ethiopia, for their positive and full collaboration and assistance during the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
ALT, alanine transaminase; APTT, activated partial thromboplastin time; AST, aspartate transferase; Ca+, calcium; CI-, chlorine; CRP, C-reactive protein; IL-6, interleukin-6; JUIRB, Jimma University Institutional Review Board, JUMC, Jimma University Medical Center; LDH, Lactate Dehydrogenase; PCR, Polymerase Chain Reaction; PLT, Platelet Count; RDT, rapid diagnostic tests; RNA, Ribonucleic Acid; WHO, World Health Organization; K+, potassium; Na+, sodium.
References
1. Organization WH. Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) weekly epidemiological update and weekly operational update. (2020) 2020:.
2. Fisher D, Heymann D. Q&A: The novel coronavirus outbreak causing COVID-19. BMC Med. (2020) 18:1–3. doi: 10.1186/s12916-020-01533-w
3. Buliva E, Elhakim M, Minh T, Nguyen N, Elkholy A, Mala P, et al. Emerging and reemerging diseases in the World Health Organization (WHO) Eastern Mediterranean Region—progress, challenges, and WHO initiatives. Front Public Health. (2017) 5:276. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2017.00276
4. Zhong B-L, Luo W, Li H-M, Zhang Q-Q, Liu X-G, Li W-T, et al. Knowledge, attitudes, and practices towards COVID-19 among Chinese residents during the rapid rise period of the COVID-19 outbreak: a quick online cross-sectional survey. Int J Biol Sci. (2020) 16:1745. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.45221
5. Organization WH. Rational use of personal protective equipment for coronavirus disease (COVID-19): interim guidance, 27 February 2020. World Health Organization (2020).
6. Organization WH. WHO director-general’s opening remarks at the media briefing on covid-19-11 march 2020, Vol. 2020. (2020).
8. Kumar R, Singh V, Mohanty A, Bahurupi Y, Gupta PK. Corona health-care warriors in India: knowledge, attitude, and practices during COVID-19 outbreak. (2021) 10:. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_524_20
10. Surveillances V. The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19)—China, 2020. China CDC Weekly. (2020) 2:113–22.
11. Yuan X, Huang W, Ye B, Chen C, Huang R, Wu F, et al. Changes of hematological and immunological parameters in COVID-19 patients. (2020) 112(4):553–9. doi: 10.1007/s12185-020-02930-w
12. Grasselli G, Greco M, Zanella A, Albano G, Antonelli M, Bellani G, et al. Risk factors associated with mortality among patients with COVID-19 in intensive care units in Lombardy, Italy. (2020) 180(10):1345–55.
13. Kunno J, Supawattanabodee B, Sumanasrethakul C, Wiriyasivaj B, Kuratong S, Kaewchandee C. Comparison of different waves during the COVID-19 pandemic: retrospective descriptive study in Thailand. (2021) 2021:. doi: 10.1155/2021/5807056
14. Wang C, Deng R, Gou L, Fu Z, Zhang X, Shao F, et al. Preliminary study to identify severe from moderate cases of COVID-19 using combined hematology parameters. (2020) 8(9):. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-3391
15. Moradi EV, Teimouri A, Rezaee R, Morovatdar N, Foroughian M, Layegh P, et al. Increased age, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and white blood cells count are associated with higher COVID-19 mortality. (2021) 40:11–4. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.12.003
16. Organization WH. Living guidance for clinical management of COVID-19: living guidance, 23 November 2021. World Health Organization (2021).
18. Sarhan AR, Hussein TA, Flaih MH, Hussein KR. A biochemical analysis of patients with COVID-19 infection. (2021) 2021:. doi: 10.1155/2021/1383830
19. Nayak AH, Kapote DS, Fonseca M, Chavan N, Mayekar R, Sarmalkar M, et al. Impact of the coronavirus infection in pregnancy: a preliminary study of 141 patients. (2020) 70(4):256–61. doi: 10.1007/s13224-020-01335-3
20. Hui DS, Azhar EI, Madani TA, Ntoumi F, Kock R, Dar O, et al. The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health—The latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China. (2020) 91:264–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.01.009
Keywords: biochemical profiles, waves, COVID-19, patients, Ethiopia
Citation: Getahun HA, Legesse A, Desta D, Johar A, Bekele I, Angasu K, Hunegnaw S, Simegnew N and Fekadie M (2024) Biochemical profiles of patients with COVID-19 during the first and second waves in Ethiopia. Front. Immunol. 15:1426413. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1426413
Received: 01 May 2024; Accepted: 19 November 2024;
Published: 10 December 2024.
Edited by:
Erika Paola Plata Menchaca, View Hospital, QatarReviewed by:
Angela Ostuni, University of Basilicata, ItalyMaria Antonietta Castiglione Morelli, University of Basilicata, Italy
Copyright © 2024 Getahun, Legesse, Desta, Johar, Bekele, Angasu, Hunegnaw, Simegnew and Fekadie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Habtamu Abebe Getahun, aGFidGllczIzQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==; aGFidGFtdS5hYmViZTFAanUuZWR1LmV0
†ORCID: Habtamu Abebe Getahun, orcid.org/0000-0002-3861-0782
 Habtamu Abebe Getahun
Habtamu Abebe Getahun Assefa Legesse
Assefa Legesse Diliab Desta
Diliab Desta Ahmed Johar4
Ahmed Johar4 Israel Bekele
Israel Bekele Samuel Hunegnaw
Samuel Hunegnaw Nebiyou Simegnew
Nebiyou Simegnew Minale Fekadie
Minale Fekadie