
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Immunol., 25 October 2024
Sec. Nutritional Immunology
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1406213
This article is part of the Research TopicEffects of Plant-Derived Bioactive Compounds as Nutritional Supplements on InflammationView all 3 articles
The great potential of polysaccharides in immunological regulation has recently been highlighted in pharmacological and clinical studies. Polysaccharides can trigger immunostimulatory responses through molecular identification, intra- and intercellular communication via direct or indirect interactions with the immune system. Various immunostimulatory polysaccharides or their derivative compounds interacts at cellular level to boost the immune system, including arabinogalactans, fucoidans, mannans, xylans, galactans, hyaluronans, fructans, pectin and arabinogalactans, etc. These natural polysaccharides are derived from various plants, animals and microbes. A unique structural diversity has been identified in polysaccharides, while monosaccharides and glucosidic bonds mainly confer diverse biological activities. These natural polysaccharides improve antioxidant capacity, reduce the production of pro-inflammatory mediators, strengthen the intestinal barrier, influence the composition of intestinal microbial populations and promote the synthesis of short-chain fatty acids. These natural polysaccharides are also known to reduce excessive inflammatory responses. It is crucial to develop polysaccharide-based immunomodulators that could be used to prevent or treat certain diseases. This review highlights the structural features, immunomodulatory properties, underlying immunomodulatory mechanisms of naturally occurring polysaccharides, and activities related to immune effects by elucidating a complex relationship between polysaccharides and immunity. In addition, the future of these molecules as potential immunomodulatory components that could transform pharmaceutical applications at clinical level will also be highlighted.
As the largest naturally occurring polymer in nature, polysaccharides exhibited a wide variety of structural and functional forms (1, 2). Advances and easy access to certain analytical tools help in the identification and quantification of polysaccharides, thereby supporting in-depth studies to determine the biological activities of polysaccharides. The polysaccharides shared certain structural features, just like other polymers such as proteins and nucleic acids (DNA, RNA), in which monosaccharide residues were linked together by glycosidic bonds (3). There are major differences in the structure of polysaccharides, which perform numerous biological functions at the cellular and tissue levels. In oligosaccharides and polysaccharides, the monosaccharide molecules can reassemble multiple times to form countless linear or branched structures, each with different functions. Polysaccharides, like proteins, exhibit the highest structural diversity ever known, with cosmopolitan distribution in nature, where they perform a variety of functions, as building blocks in cell membranes, energy storage, cell recognition, differentiation, proliferation and control of cell signaling (4–7). The biological properties of polysaccharides have attracted increasing attention in biochemistry and medicine in recent decades.
Polysaccharides exhibit a wide range of biological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antidiabetics, gut microbiota regulation and immunomodulatory effects (8, 9). Polysaccharides have emerged as significant players in the field of immunology due to enhancing the innate and adaptive immune response of the host. Polysaccharides stimulate immune cells via specific receptors, for example in necrophage and macrophage cells via bonds between functional groups of polysaccharides and groups of molecules on the cell surface. As soon as the polysaccharides bind to membrane receptors in the defense cells, the signaling pathways are activated and a cycle of biochemical processes begins, which leads to a positive regulation of gene expression in the ribosomes and initiates protein production. Moreover, polysaccharides influence immunity by modulating cytokines that have pro- and anti-inflammatory effects. They activate macrophages via signaling pathways such as TLRs and NF-κB and thus improve immunological functions. The ability of polysaccharides to enhance macrophage function is a crucial aspect of their immunomodulatory potential, as these cells are pivotal in the body’s defense mechanisms. Certain polysaccharides, such as those from Tinospora cordifolia, have been shown to increase macrophage activity, while Bupleurum polysaccharides have been shown to reduce inflammation (10). T lymphocytes produce cytokines that influence inflammatory responses, such as IL-10 and IL-4 (Th2) or TNF-α and IFN-γ (Th1). The mycelium of PhomaherbarumYS4108 contains polysaccharides that stimulate T cells via TLR2/4, improving immunological function. Polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum activate B cells, resulting in an increase in immunoglobulin synthesis. Neuroinflammation is reduced by fucoidan treatment, blocking the proinflammatory response of microglia (11). Additionally, the interaction between polysaccharides and the gut microbiota has garnered attention for its implications in immune health. Gut microbiota produces huge number of metabolites, consequently by metabolizing and anaerobic fermentation of complex polysaccharides. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) may help maintaining immunological homeostasis and immune cell functions both locally and systemically. Polysaccharides improve antioxidant capacity, reduce the production of pro-inflammatory mediators, strengthen the intestinal barrier, influence the composition of intestinal microbial populations, and promote the synthesis of SCFAs (12). The potential of polysaccharides not only as direct immunomodulators but also as agents that can influence the broader immune landscape through gut health.
This review highlights the structural features, immunomodulatory properties, underlying immunomodulatory mechanisms of naturally occurring polysaccharides, and activities related to immune effects by elucidating a complex relationship between polysaccharides and immunity.
Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates that play crucial roles in various biological processes across different organisms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms. Their structural differences significantly influence their biological activities, which can range from antioxidant properties to immunomodulatory effects. The molecular weight, number of branched chains, percentage of monosaccharides, and structural conformations of each polysaccharide source vary. As shown in Figure 1, types and structural arrangement of the common natural polysaccharides. Cellulose, starch, inulin and pectin are abundant in plant tissue. Animal polysaccharides include glycogen, chitosan and chitin. Glucan polysaccharides are widespread in mushrooms. Microbial polysaccharides include pullulan, xanthan gum, dextran, lentinan and curdlan. Exopolysaccharides are polysaccharides released by microorganisms. Polysaccharides from natural sources with structural diversity and different biological activities (Table 1). The structural differences among plant, animal, and microbial polysaccharides lead to distinct biological activities. Understanding these relationships is crucial for the development of polysaccharide-based therapeutics and functional foods, as their diverse structures can be tailored to enhance specific biological functions.
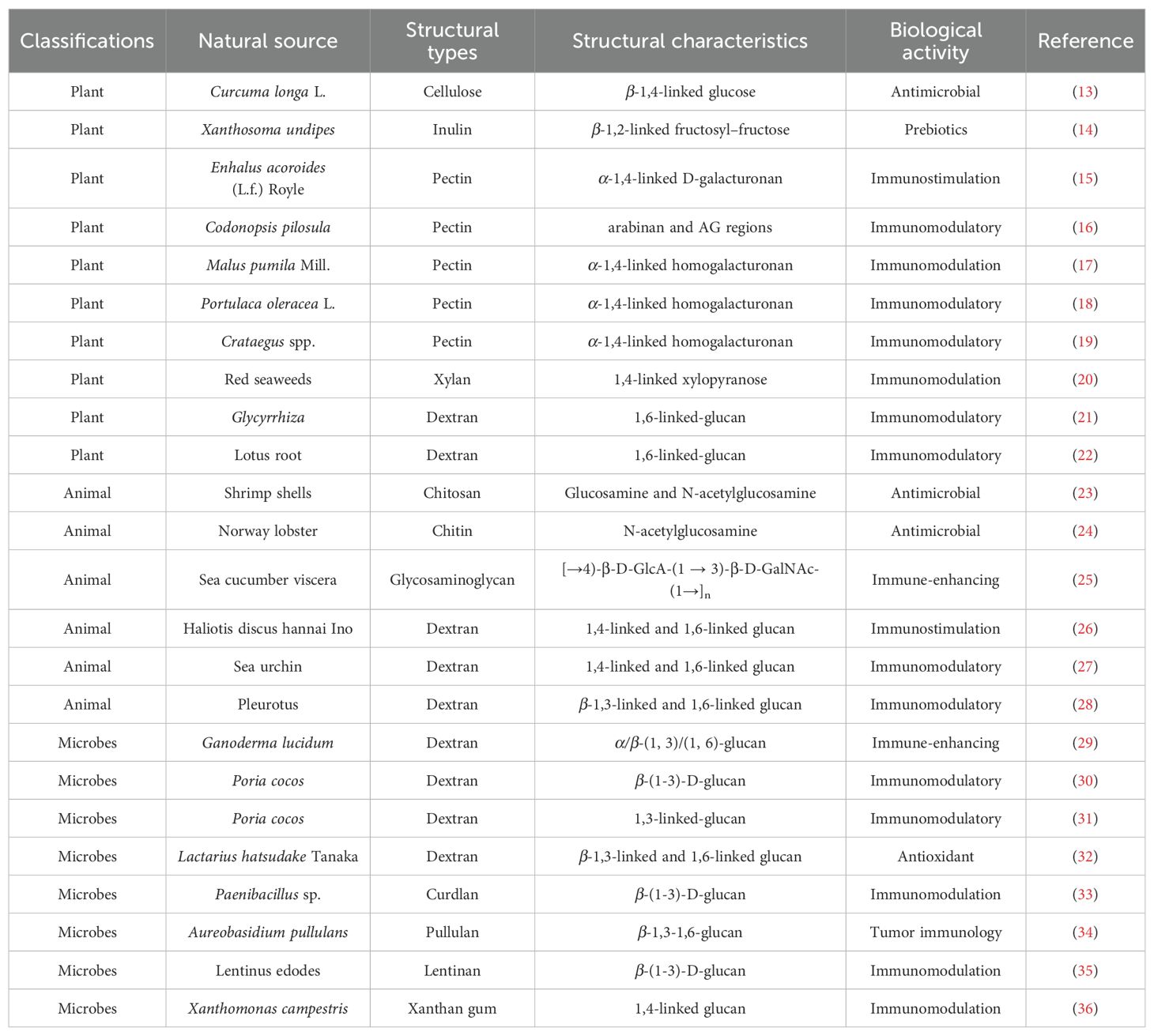
Table 1. Polysaccharides from natural sources with structural diversity and different biological activities.
Plant polysaccharides are primarily composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin, which are characterized by their linear and branched structures formed through various glycosidic linkages. Most plant polysaccharides are composed of glycosidic bonds such as β-(1→4)-D, α-(1→6)-D and α-(1→4)-D, which serve as links between various monosaccharides such as glucose, fructose and arabinose. A significant portion of cellulose, a biopolymer composed of chains of β-1,4-linked glucose units with a maximum length of millions of residues, is found in plant cell walls (37). Cellulose is the most important structural component of plants and is often used in the production of food, medicine and building materials (38). Furthermore, the combination of β-(1→2)-D-fructosyl-fructose bonds results in inulin, a diverse, water-soluble linear polymer (39). Inulin is an indigestible carbohydrate that occurs naturally in various forms, mostly as storage carbohydrates in plants (40). Pectin, the most complex polysaccharide found in plant cell walls, is mainly composed of branched rhamnogalacturonan segments (RG-I and RG-II) and linear 1,4-D-galacturonan segments (41). The diverse functional capabilities of pectin are influenced by its diverse structural features (42). According to research, plant polysaccharides are essential for immune modulation and other related diseases. Platycodon grandiflorum polysaccharide (PG) induced the phenotypic maturation of DCs, as evidenced by the increase in the expression of CD40, CD80, CD86 and major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-I/II on the cell surface (43). Furthermore, PG induces DC maturation by activating MAPK and NF-κB signaling downstream of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). The structural diversity in plant polysaccharides is also enhanced by modifications such as sulfation and phosphorylation, which can significantly alter their biological activities (44).
Animal polysaccharides are very widespread and are found in almost all animal tissues and organs, especially in marine animals. Compared to the plant polysaccharides, animal polysaccharides, particularly glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), exhibit linear polyanionic structures that are crucial for various physiological functions. Chitin is the only positively charged natural polymer in nature that belongs to the straight-chain aminoglycans. Chitin consists of N-acetylglucosamine units (GlcNAc) with β- (1, 4)-linked glycan, coupled with the presence of amino groups (at C-2) and hydroxyl groups (at C-3 and C-6) (45). Chitosan is a cationic polysaccharide formed by the deacetylation of chitin. Chitosan consists of N-acetyl-2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose (glucosamine, GlcN) and 2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose (N-acetyl-glucosamine, GlcNAc) monomer residues starting with β are linked (1→ 4) links (46). Chitin and chitosan activate peritoneal macrophages and NK cells to express a range of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), colony stimulating factor (CSF), and gamma interferon (IFN-γ) (47). Sulfated polysaccharides were isolated from sea cucumber viscera, which promoted the production of nitric oxide (NO) and cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α) by RAW 264.7 cells and also their phagocytic activity through TLR4-mediated activation increased MAPKs and NF-κB signaling pathways (25). Animal-derived polysaccharides, have been shown to play essential roles in cell signaling and tissue repair. Their ability to modulate immune responses and promote wound healing is well-documented, with studies indicating that modifications in their structure can enhance these biological activities (48). For example, the introduction of sulfate groups in polysaccharides can confer anticoagulant and anti-inflammatory properties, making them valuable in therapeutic applications (49).
Microbial polysaccharides, such as those derived from fungi and bacteria, display unique structural features that differ from both plant and animal polysaccharides. Some edible mushrooms like Ganodermalucidum, Poriacocos, and Ophiocordycepssinensis, contain polysaccharides, including glucans and heteropolysaccharides (50). In addition, among these polysaccharides there are large differences in molecular weight, type of chemical bonds and composition of monosaccharides (51). Over the last decade, observational studies have shown that polysaccharides from edible mushrooms have many biological effects, including regulating immunity, reducing obesity, and delaying aging (50, 52, 53). Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides (GLPs) may include α/β-(1, 3)/(1, 6)-glucans and other carbohydrates with various biological properties. There is evidence that GLPs can alleviate obesity, enhance immunity, and treat colorectal cancers by affecting a specific gut microbiota that includes Oscillopsia, Clostridium Cluster IV, and Eubacterium spp (29). Polysaccharides found in Poria cocos consist mainly of the primary (1→3)-β-glucan and side chains of (1→6)-β-glucose. Poria coco polysaccharides (PCPs) possess anti-cancer properties by enhancing host immunity against cancer, directly leading to tumor cell death, and helping to defend against harmful biological stresses (54). The structural complexity of these polysaccharides allows for interactions with various biological targets, leading to enhanced immune responses and potential therapeutic benefits (55).
The influence of natural polysaccharides on the immune system has received more attention. The ability of polysaccharides to alter immunity depends primarily on the presence of unique structures such as branching regions, molecular weight, acetyl or sulfate groups, conformation, monosaccharide composition, and glycosidic linkages (56). The molecular weight of polysaccharides plays a crucial role, while lower molecular weight polysaccharides often show stronger immunomodulatory effects. Each polysaccharide has a significant molecular weight, and different compounds with different molecular weights affect immune regulation in different ways. Research found that the ability of Schisandrachinensis polysaccharides to alter the immune system is inversely correlated with their molecular weight (57). The reduced molecular weight and simpler structures of polysaccharides provide an advantage over other types of molecules and can easily pass through cell barriers (58). The effect of different polysaccharide molecular weights on immunity is complex and important. Immune stimulation: Low molecular weight polysaccharides typically have stronger immune stimulating effects. They have a greater ability to activate immune cells, including natural killer cells, dendritic cells and macrophages, which increases the production of cytokines and other signaling molecules involved in immunological responses (59). Pattern recognition: Low molecular weight polysaccharides often have simple structures that may be found more easily by the pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) of immune cells. This identification triggers innate immune responses and allows the adaptive immune system to mount a stronger defense against infection (60). Phagocytosis Activation: Low polysaccharides can improve the ability of immune cells to absorb and clear infections through a process called phagocytosis (61). This increases the overall effectiveness of the immune response and helps remove pathogenic organisms. Antiviral and antitumor activity: Some low molecular weight polysaccharides have been demonstrated to have potent antiviral and anticancer properties (62, 63). They can both directly stop the growth of tumor cells and viruses and strengthen the immune system for an intensive attack on diseases or cancer cells. Immunomodulation: Polysaccharides of different molecular weights can regulate immunological reactions in different ways. Smaller polysaccharides can have immunosuppressive effects, but larger polysaccharides typically promote immunological activation (63, 64). In diseases such as autoimmune diseases, which are characterized by dysregulated immune responses, this regulation can be used therapeutically.
In addition, branched polysaccharides tend to have higher immunomodulatory activity compared to linear ones. The highly branched side chains of pectin may influence the immunological regulatory effects of pectin on LPS-induced IL-6 production, as shown in in vitro studies (65). Research has shown that pectin can have an even stronger inhibitory effect on LPS-induced cytokine production when its rhamnogalacturonan I side chains are removed (66). At the same time, it was found that pectin polysaccharides with sulfate groups stimulated a number of neutrophil and macrophage effector functions (67). Standard polysaccharide moieties are structurally linked to cores that have linked chains or linked monosaccharide residues (56). Different functional groups and patterns trigger different immune responses, but sometimes high levels of acetylation result in impaired immune activity (68). Depending on their solution conformation, polysaccharides can interact with immune system cells or other components in different ways. These interactions can be single, triple or random coils. For example, the researchers found that the triple helix conformation promoted the production of TNF-α by immune cells, which enhanced the immunomodulatory effect on β-glucans (69).
The composition of monosaccharides in polysaccharides plays a crucial role in determining their biological activities, particularly their immunomodulatory effects. The immunoenhancing activity of a novel heteropolysaccharide isolated from custard apple pulp was closely related to its monosaccharide composition, particularly noting that specific monosaccharides like glucose and rhamnose can enhance immune responses in mouse macrophages and dendritic cells (70). Moreover, the specific types of monosaccharides present in polysaccharides can dictate their interactions with immune cells. The polysaccharides from Ganoderma atrum could induce anti-tumor activity through the activation of host immune responses, with the composition of monosaccharides such as mannose and galactose being pivotal in mediating these effects (71). Another study result further supports this notion, indicating that polysaccharides containing domains of specific monosaccharides like galactose and mannose exhibit significant immunostimulatory activity (72). Moreover, wang reviewed the effects of monosaccharide composition and proportion on the bioactivity of polysaccharides, emphasizing that variations in these parameters can lead to significant differences in their immunomodulatory effects (73). the monosaccharide composition of polysaccharides is a fundamental determinant of their immune activity. Variations in the types and proportions of monosaccharides not only influence the structural characteristics of polysaccharides but also their interactions with immune cells, leading to diverse biological effects.
Glycosidic linkages are fundamental to the structure and function of polysaccharides, which play crucial roles in various biological processes, including immune responses. The type and configuration of glycosidic linkages significantly influence the immunogenicity and biological activity of polysaccharides. The polysaccharides with α-1,6-linkages have been shown to enhance immune responses, as seen in studies involving α-glucans derived from microbial sources, which are essential for macrophage phagocytosis and the induction of innate immune responses through Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) pathways (74). The structural diversity of glycosidic linkages also contributes to the functional variability of polysaccharides. For example, the presence of different glycosidic bonds, such as β-1,3 and β-1,4 linkages in galacto-oligosaccharides, has been associated with various biological activities, including prebiotic effects and modulation of immune responses (75). Furthermore, polysaccharides derived from plants, such as those from Radix Aconiti, have demonstrated immunostimulatory effects, enhancing the host’s immune response and showing potential as biological response modifiers (74). Glycosidic linkages are pivotal in determining the immune activity of polysaccharides. The type and configuration of these linkages influence the immunogenicity of polysaccharides, their ability to activate immune responses, and their potential applications in vaccine development and therapeutic interventions. Scientists have found a variety of potential sites for the production of immune-regulating polysaccharides that could be used in functional foods. Hopefully, further studies on the structure-function relationships of immunomodulation including polysaccharides will be carried out soon. Overall, the structural diversity of polysaccharides plays a significant role in modulating immunoregulatory functions (76).
Stimulating the complement system of dendritic cells and macrophages is the primary mechanism by which polysaccharides influence immunity (Figure 2). The increase in the number of lymphocytes and the immunological organ indices is within the scope of their possibilities. There are a number of signaling pathways and receptors on immune cells that also activate them (77). In addition to stimulating cytokines and complements, polysaccharides also stimulate the production of immune cells including macrophages, T cells, B lymphocytes, and (NK) cells, among others (78). Macrophages play a crucial role in the defense mechanisms of the host immune system (79, 80). In particular, polysaccharides influence the immunological responses of macrophages by increasing phagocytic activity, cell proliferation, ROS production and cytokine secretion (81).
Intercellular adhesions, cell division and cell proliferation are all regulated by cytokines. Interleukin (IL), colony stimulating factor (CSF), tumor necrosis factor (TNF), and interferons (IFN) are the four classes of cytokines. In addition to their essential functions in regulating inflammatory and immunological responses, polysaccharides also regulate adaptive and innate immunity (80). The polysaccharide component CPE-II can significantly increase the production of the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 as well as the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-12 in the macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 (82). Polysaccharides can simultaneously control the production of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines. The fact that IL-12 acts as a negative feedback mechanism during the hyperinflammatory response to prevent overactivation of macrophages lends credence to the idea that the body has a self-regulatory system that keeps everything in balance. Likewise, cytokine production by macrophages can be induced by polysaccharides (83, 84).
Natural polysaccharides and cytokines can combine to stimulate the immune response of macrophages. Macrophages can release many cytokines such as NO, IL-1β and TNF-α when the polysaccharides SHP and IFN-γ work together. The transcript levels of the cytokines IL-1 and TNF-α also increased significantly. The synergistic effect also altered the differentiation markers CD11b, CD18 and CD24 produced by macrophages (85). Complement, through its numerous common activation pathways, plays an essential role in immunological control and the body’s response to microbial defense. Immunological effects, control of the complement system, and complement modulators for complement-related diseases are all aspects of sulfated glycosaminoglycans (86, 87). Fruits of the species Capparis spinosa L. contain sulfated polysaccharides that can inhibit both traditional and nontraditional pathways of complement activation, making them a promising candidate for therapeutic complement suppression (88). These processes include the many complement pathways, the mannose-binding lectin (MBL) pathway, and classical complement (89). Ca+2 is essential for the MBL protein. By binding to the mannose receptors of certain pathogen cells, lectins activate the MBL complement system, which in turn generates immunity (90).
Biological response modifiers (BRMs) are polysaccharides that possess immunomodulatory properties (Figure 3), allowing them to simultaneously influence innate and adaptive immune responses (91). Molecular recognition of polysaccharide BRM is achieved by proteins such as plasma proteins and pattern recognition receptors (PRRs). Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) are PRRs – nonclonal immune proteins – that identify common molecular features among different microbes. Beginning with their binding to PRRs, ligands activate genes of innate immunity through signaling cascades regulated by Rel and NF-κB (92).
Two different types of PRRs can be used for polysaccharide BRMs: scavenger receptors (SRs) and toll-like receptors (TLRs) (93). In order for TLRs to interact with intracellular signaling proteins and accept ligands, they have two unique features: the Toll/IL-1 receptor-like domain and leucine-rich repeats (94). Recognizing both endogenous ligands that support tissue homeostasis and immune defense signaling is the role of multidomain and multiligand receptors (SRs). Both macrophages and dendritic cells (DCs) produce SRs (94). The BRMs are identified by class A SR, β-glucan receptors, mannose receptors and complement receptor type 3 (CR3). Fucoidan is a polysaccharide ligand related to class A SR (95). A recognized binding site for Dectin-1,3-Glucan is the glucan receptor/Dectin-1 (96). The mannose receptor requires calcium for binding of mannosyl/fucosyl or GlcNAc glycoconjugate ligands (97). Both the CR3 membrane receptor and the adhesion molecule are essential. As previously mentioned, β-glucan, fixed iC3b and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) are the ligands that CR3 recognizes as a receptor (98).
The MBL of the lectin-complement pathway and proteins from the alternative and conventional complement pathway are among the proteins in blood plasma that can recognize polysaccharide BRMs. As a multimericlectin, mannose-binding lectin can detect multiple diseases without the need for a specific antibody (99). Activation of the lectin complement cascade occurs upon MBL attachment to macromolecules containing fucose, mannose, N-acetylglucosamine, and glucose residues that are aligned and densely packed like microorganisms. As a result, the body begins to respond by releasing inflammatory chemicals (100).
Polysaccharide BRMs can trigger specific cellular and molecular events and produce specific expression patterns depending on the receptors and binding proteins to which they bind. The receptors and binding proteins present in polysaccharide BRMs, including mannose receptors, CR3, β-glucan receptors, TLRs, SRs, lectin-binding pathway binding proteins, and the alternative and classical complement pathways, originate from innate immunity, as previously mentioned. Not only mast cells, neutrophils and epithelial cells express TLRs, but also myeloid cells (monocytes, macrophages and dendritic cells) (101). Two Toll-like receptors, namely TLR-2 and TLR-4, are known to recognize polysaccharide BRMs, out of ten Toll-like receptors found in humans (102).
Endothelial cells, DCs, smooth muscle cells, and macrophages all express SRs (103). To SR’s knowledge, fucoidan is one of the polysaccharide BRMs. Various cell types, such as B and T lymphocytes, neutrophils, DC, eosinophils and monocytes, express the β-glucan receptor (95, 104). Certain cell types, including DCs, hepatic endothelial cells, renal mesangial cells, macrophages, and tracheal smooth muscle, express mannose receptors (105). The mannose receptor is bound by the mannan-type polysaccharide BRM. Cells that primarily express CR3 are macrophages and neutrophils. Furthermore, CR3 is expressed by a tiny percentage of B and T cells as well as non-NK cells (106). Myeloid cells are the main targets of polysaccharide BRMs as they are essential for innate and adaptive immunity (107). One of the most important types of myeloid cells, macrophages, are stimulated by BRMs to increase their phagocytosis, ROS production, cytokine release and activation marker expression (such as FcR and B-7) (108, 109). As a result, polysaccharide BRMs improve effector function, antigen processing ability and regulation of acquired immunity by promoting cytokinesis, antigen presentation and expression of macrophage cell adhesion molecules. Therefore, polysaccharide BRMs can secondarily or consequently directly stimulate other immune cells such as lymphocytes and NK cells. In many cases, BRMs containing polysaccharides are very potent mitogens (80, 110).
Activation of the polysaccharide BRM leads to an increase in macrophages, NK cells, T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes. This happens, among other things, through the binding of polysaccharides to their receptors. Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), involved in intracellular signaling events, are responsible for mitogen stimulation of macrophages (Figure 3), B lymphocytes, and NK cells by polysaccharide BRMs (111). Through their immunomodulatory function, BRMs promote the proliferation of immune cells and inhibit cell death (112). BRMs not only activate cells, they also stimulate the immune system’s complement pathways. One way the active complement system helps clear infections is by activating macrophages (113). Members of the β-glucan family comprise the polysaccharides with the greatest biological activity. Since they are PAMPs, glucans can be identified by various cell surface receptors on monocytes/macrophages, neutrophils, (NK) cells, DCs, T cells and B cells (114, 115).
In the presence of polysaccharides, interaction with CR3 leads to upregulation of NF-κB, activation of PI3K, and phosphorylation of Syk, the spleen tyrosine kinase. As a result of these events, cytokines such as interleukin IL-2, IL-10 and TNF-α are released (116). Various cells such as monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, T cells and dendritic cells are known to express Dectin-1. β-Glucans promote innate immune responses (phagocytosis, reactive oxygen species production, IL-12, IL-6, IL-10 and TNF-α synthesis) by activating many signaling pathways such as Syk, Akt, MAPK and nuclear factor activated T cells (NFAT) (116, 117). Another type of receptor that binds polysaccharides and can identify β-1,3-glucans is lactosylceramide or (LacCer). LacCer expression is abundant in neutrophils, dendritic cells and macrophages. Together, polysaccharide and LacCer enhance the oxidative burst response of neutrophils, stimulate macrophage inflammatory protein-2, and activate NF-κB (118). Dendritic cells and macrophages have scavenger receptors that can identify fungal β-glucans. However, the exact mechanism by which these receptors are triggered is still unknown. It is generally believed that activation of the MAPK and PI3K/Akt kinases occurs through ligand interaction (119, 120).
The immune activity of natural polysaccharides is closely related to intestinal immunity, anticancer, antigen recognition and presentation, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. As shown in Table 2, other effects of polysaccharides related to immunity. It not only helps maintain immune homeostasis and the body’s defense ability, but also provides a broad perspective for polysaccharides in the field of drug development and clinical application. The immune activity of natural polysaccharides allows the body to build a solid defense net.
The collection of bacteria that live and communicate in the human digestive tract is called the intestinal or gut microbiota (147). It is true that the microorganisms in our stomach have a remarkable ability to alter physiology in both healthy and sick states. Most human physiological systems are directly or indirectly influenced by intestinal bacteria. This includes the maturation of the immune system as well as metabolic and pathogenic processes (148). Due to their numerous biological applications, natural polysaccharides have gained interest and popularity as dietary nutrients in recent years. Polysaccharides, particularly those derived from dietary sources, have been shown to exert significant immunomodulatory effects through their interactions with gut microbiota and the metabolites produced therein. The mechanisms by which these polysaccharides influence immune responses are multifaceted and primarily involve the fermentation of indigestible carbohydrates by gut microbiota, leading to the production of SCFAs such as butyrate, propionate, and acetate. Natural polysaccharides can also reduce excessive inflammatory responses by altering the composition of the gut microbiota, promoting the production of SCFAs, strengthening the intestinal barrier, increasing antioxidant activity, and reducing pro-inflammatory mediators (149). These SCFAs play critical roles as signaling molecules that modulate host immunity by activating various G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and other immune pathways (150, 151). Colonocytes rapidly absorb SCFAs during their production, usually via sodium- or H+-dependent monocarboxylate transporters. Examples of GPCRs to which SCFAs bind and influence intestinal mucosal immunity, barrier integrity and function include free fatty acid receptors 2 and 3, GPR109a/HCAR2 and GPR164 (152, 153). Additionally, SCFAs have been reported to enhance the production of antibodies in B cells by promoting metabolic pathways that support energy production and cellular function (154). SCFAs play an important role in maintaining intestinal immunological homeostasis. The invasion of pathogens could be prevented by triggering immune responses and removing antigens from neutrophils and monocytes (115, 155, 156). These SCFAs control a variety of functions such as: glucose homeostasis, inflammatory reactions, energy absorption and gastrointestinal motility. They are quickly absorbed by the large intestine (157).
Prebiotics are made from polysaccharides and serve various biological purposes, including maintaining intestinal flora. In addition to its beneficial properties, the intestinal microbiota selectively degrades polysaccharides so that it can use them as energy to maintain physiological effects and control the composition of intestinal bacteria (158). Certain polysaccharides, such as fiber cannot be hydrolyzed by the human stomach or small intestine. A chronically low fiber intake can lead to dysbiosis in the intestine and permanently change the microbiota there (159). Unlike fermentable polysaccharides, which are broken down and fermented to form a variety of metabolites that provide energy to the host, non-fermentable polysaccharides are secreted in the large intestine (160, 161). As some diseases progress, certain polysaccharides act as immunomodulators and regulate the immune response. In addition, natural polysaccharides can improve immunity by strengthening the function of immune cells and helpful bacteria (149, 162).
Many polysaccharides, which come from natural herbs, mushrooms or yeasts, are used to treat intestinal disorders because they can repair damage to the intestinal lining (163). After an intestinal infection, free radicals accumulate in the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT). This negatively affects mucosal and systemic immune function and rapidly reduces the antioxidant activity of intestinal tissue. Nevertheless, consumption of a large amount of bioactive carbohydrates from food can increase the antioxidant activity of intestinal tissue, thereby strengthening the host’s immunity (164). The main effector molecule in response to gastrointestinal mucosal immunity is secretory IgA. Numerous polysaccharides can enhance the response of T and B cells to antigens, which in turn increases IgA synthesis and ultimately strengthens the immunity of the digestive tract, thereby increasing the immunological activity of the adaptive system in GALT (1). Damage to the intestinal mucosa occurs more quickly when intestinal epithelial cells undergo abnormal apoptosis. Polysaccharides can prevent the death of endothelial cells (ECs) because they can block the Fas/FasL pathway and the synthesis of caspase-3 (165). Exopolysaccharides can enhance the phagocytosis of intestinal macrophages and slightly increase the production of nitric oxide (NO), thereby stabilizing the balance of the intestinal environment (41, 166). Part of the disruption of physiological intestinal function can be attributed to the infiltration of inflammatory cells into the intestinal tissue and their sustained activation. In order to repair the damaged mucosa, it is therefore imperative to induce apoptosis of the inflammatory cells. Polysaccharides have the ability to both up- and down-regulate the expression of Bcl-2, Bax and caspase-3 while dramatically reducing the formation of inflammatory bodies (41). As a result, the intestine experiences a variety of immunological responses, many of which are closely linked to the host’s systemic immunity. These considerations support the idea that homeostasis of the gut microbial community is necessary for GALT function. Therefore, the role of dietary polysaccharides in general gut-associated immunity and their help in GALT improvement is described (Figure 4).
Polysaccharides are essential for intestinal protection as they support intestinal integrity and well-being (127). They support the intestinal mucosal barrier, which acts as the body’s first line of protection from dangerous chemicals. Polysaccharides support the integrity of this barrier by increasing mucus production and promoting the development of tight junctions between epithelial cells, keeping infections, toxins and allergens out of the bloodstream. The polysaccharides from Callicarpa nudiflora Hook (CNLP) alleviated the clinical symptoms such as loss of body weight (BW), pathological damage and systemic inflammation by regulating the intestinal flora and its metabolism (124). In addition, polysaccharides have immunomodulatory properties that help regulate the immune response in the intestine. They have the ability to control the activity of immune cells, including that of macrophages, dendritic cells and lymphocytes, which helps maintain a healthy immune system and reduce gastrointestinal inflammation. The polysaccharide purified from Alhagi camelorum fish promoted the secretion of serum LgG antibodies, intestinal LgA antibodies and intestinal cytokines, improved the morphology of intestinal villi and crypts, increased the amount of intestinal IELs and IgA+ cells, and activated T lymphocytes and DC cells in MLNs (126). In diseases like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that are marked by intestinal inflammation, this anti-inflammatory action is very helpful.
Despite the promising findings regarding the immunomodulatory effects of polysaccharides, there are notable shortcomings in the current research landscape. One significant limitation is the variability in the structural characteristics of polysaccharides, which can lead to inconsistent biological effects (167). Furthermore, the precise mechanisms through which different polysaccharides exert their effects remain poorly understood, necessitating further investigation into their bioavailability and the specific metabolic pathways involved (168, 169). Future research should focus on elucidating the complex interactions between polysaccharides, gut microbiota, and host immune systems, potentially employing advanced metabolomic and metagenomic approaches to track the effects of specific polysaccharide structures on microbial metabolism and immune modulation.
Polysaccharides have demonstrated potent anticancer activity against a range of cancer cell types. Their minimal dangerous side effects and their selectivity against tumor cells make them a viable replacement for current chemotherapeutic cancer drugs. Most polysaccharides derived from plants, microbes, fungi and marine sources have been discovered to cause apoptosis in cancer cells. Their mechanisms of action include DNA damage, cell cycle arrest, rupture of the mitochondrial membrane, and the production of nitric oxide, which kills cancer cells and prevents them from spreading (170). The mode of action of some polysaccharides was evaluated through in vitro research on cell lines, and the effectiveness of other polysaccharides was assessed through in vivo research on appropriate animal models (129, 171, 172). The most commonly observed mechanisms were immunomodulation, cell cycle arrest, and depolarization of the mitochondrial membrane nitric oxide pathway. Recent studies have shown that polysaccharides can inhibit tumor growth by stimulating the immune system, thereby promoting immune cell proliferation, increasing cytokine secretion, and regulating immune functions throughout the body. Lachnum polysaccharide led to the accumulation of anti-tumor immune cells and reduced the infiltration of immunosuppressive cells such as myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and Treg cells, thereby enhancing anti-cancer immunity (173). Sanghuangporus vaninii polysaccharides (SVPS2) could facilitate the initiation of immune response, promote the secretion of cytokines, and mediate the apoptosis of HT-29 cells by blocking them in S phase in vitro. The antitumor mechanism of SVPS2 may be associated with an enhancement of the immune response (134). Therefore, polysaccharides can improve the body’s immune functions and play an immunomodulatory role by activating the upstream immune cells and promoting the production of cytokines, thereby inhibiting the growth of tumors (174).
The most important causes of disease worldwide include encapsulated bacteria such as Neisseria meningitidis, Haemophilus influenzae serogroup B (Hib) and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Because disease-preventing anticapsular antibodies often provide protection, efforts to develop vaccines against these pathogens have focused on their capsular polysaccharides (CPS) (175). When administered to newborns or some immunocompromised individuals, the capsular polysaccharide immunizations currently available against these diseases are neither immunogenic nor protective. Polysaccharide antigens generally trigger a T-independent immune response, which is insufficiently immunogenic and lacks memory in extreme situations of life (176). Conjugate vaccines were developed to address the poor immunogenicity of CPS vaccinations. These antigens can trigger a T-dependent immune response by conjugating CPS to carrier proteins (177). The development of technical experiments to produce nanoparticles that can transport antigens is currently the focus of great attention worldwide. Vaccinations have become significantly safer and more effective thanks to polysaccharide nanoparticles. The use of these biopolymers has been shown in previous research to enhance the immune response, reduce side effects, accelerate immunomodulatory activity, and maintain antigens in an expanded and regulated state by encapsulating them in polysaccharides (178). Extensive testing has been carried out with polysaccharides, particularly lactic glycolic acid. However, issues with biocompatibility and biodegradability led researchers to conclude that innovative biomaterials should be used in vaccine development. Consequently, antigen engineering has recently dominated studies using natural polysaccharides. In addition to their influence on biofilm formation, cell walls, cell membranes, nucleic acids, mycoproteins and intracellular metabolic pathways, polysaccharides should also be investigated for their possible antibacterial potential. Polysaccharides can inhibit the antibacterial effects of other bioactive chemicals (135, 136). The antimicrobial peptide increases intracellular ROS, leading to intracellular DNA degradation and cell death. Stimulating the cell’s production of antimicrobial peptides and improving the cell’s immunity could potentially be how polysaccharides work as antibacterial agents (179, 180).
At the end of the last century, there was great interest worldwide in researching the anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory potential of polysaccharides (181). Wang et al. successfully isolated a sulfated polysaccharide from brown algae (Sargassum cristaefolium) and demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects in LPS-exposed RAW 264.7 cells (182). The polysaccharide in sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhomboids L.) berries can protect the liver of mice from CCL4-induced damage by reducing inflammation through antioxidant effects (183). Research has shown that cytokines, including TNF-α as well as IL-1β and IL-6, have a significant impact on pro-inflammatory responses. Endothelial cells lining blood vessels used the adhesion molecules produced by inflammatory cells to attract monocytes, lymphocytes and neutrophils. These cells traveled from the blood vessel to the damaged tissue, where they remained and caused hypotension, necrosis and death, symptoms similar to sepsis (184, 185). One approach to treating inflammation is to either prevent the generation of inflammatory mediators or ameliorate the dysregulation of proinflammatory (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α) and anti-inflammatory (IL-10) cytokines. Certain anti-inflammatory medications work in the following ways. Triggering of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) enables massive NO production in response to pro-inflammatory cytokines, LPS, bacteria or viruses. Among the many indicators of inflammatory diseases and inflammation, the molecule NO stands out. Inflammatory processes are also influenced by cyclooxygenase (COX). Activation of COX-2 and iNOS leads to the production of several mediators that promote inflammation (186, 187). Suppressing or downregulating their expression is more effective than reducing the severity of the inflammatory response (188). Purple sweet potatoes were used to extract a dilute alkali-soluble polysaccharide (ASPP), which was then purified using a Sephadex G-200 column with DEAE-52 cellulose. NO production in RAW264.7 cells was induced by LPS. The anti-inflammatory properties of ASPP were examined using a mouse model and seven different macrophage cell lines (189). Scientific studies have shown that ASPP can improve IL-10 synthesis by RAW 264.7 cells. In a dose-dependent manner, 7 types of alternatively activated macrophage cells were activated by LPS and simultaneously decreased the levels of NO, IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α. Furthermore, mice showed reduced levels of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α expression after ingesting LPS. Additional sulfated homopolysaccharide was also formed by flesh of Cipango paludinachinensis (CCPSn). The ratios of pro-/anti-inflammatory cytokine secretion such as TNF-α/IL-10, IL-6/IL-10 and IL-1β/IL-10 were significantly reduced as this chemical inhibited the expression of COX2 and NOS. A reduction in the release of nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) was also noted (190, 191). The use of natural polysaccharides from Pleurotus eryngi (PEPS) significantly and dose-dependently reduced the cytokine secretion ratios for IL-1β/IL-10, IL-6/IL-10 and TNF-α/IL-10 according to the research of Li et al. (192).
In conclusion, polysaccharides are vital biomacromolecules involved in many important biological activities. They have attracted great scientific interest due to their health benefits, including immune stimulation and immunomodulation, associated intestinal immunity, anticancer, antigenic, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activities. The wide variety of polysaccharides found in nature is due to the many different species of plants, animals and microbes. Polysaccharides provide a rich source of bioactive compounds with significant potential for health and medicine. Their non-toxic nature and significant influence on biological functions, especially on immunological cells, make them valuable for the treatment and prevention of diseases. Polysaccharides hold promise as modulators of the host’s defense and immune systems, and their immunoregulatory functions are highly dependent on their structural features. Polysaccharide structure, molecular weight, acetyl or sulfate groups, and branching areas greatly influence how they interact with immune cells and other components of the immune system. In addition, polysaccharides are essential for gut-associated immunity as they modulate inflammatory responses, improve the integrity of the intestinal barrier, influence the composition of the gut microbiota, and promote the formation of SCFAs. Due to their ability to alter immune responses, induce apoptosis, and reduce tumor cell proliferation, polysaccharides have shown promise as potential anticancer drugs in cancer immunotherapy. Polysaccharides also have antimicrobial properties. They prevent bacteria from multiplying by preventing them from forming biofilms, forming cell walls and blocking their intracellular metabolic processes. By regulating the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines, limiting the expression of inflammatory mediators, and modifying the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, they can also exert anti-inflammatory effects. Overall, polysaccharides represent a broad class of chemicals that have important implications for immunological function, host-microbiota interactions, cancer immunotherapy, antimicrobial defense, and inflammatory modulation. Further exploration of the structure-function relationships of polysaccharides and their medical applications promises to improve our understanding of immunology and develop new approaches to treating immune-related diseases.
YS: Writing – original draft. HBZ: Writing – original draft. SW: Writing – review & editing. XW: Writing – review & editing. YW: Writing – review & editing. CW: Writing – review & editing. YZ: Writing – review & editing. HZ: Writing – original draft.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the excellent youth project of Heilongjiang Natural Science Foundation (No. YQ2023H001), the North Medicine and Functional Food Characteristic Subject Project in Heilongjiang Province (No. HLJTSXK-2022-03), Basic Research Project of Fundamental Research Business Expenses of Education Department in Heilongjiang Province (NO. 2022-KYYWF-0641), Postdoctoral funded project of Heilongjiang Province (No.LBH-Z22292), “Dongji” Academic Team of Jiamusi University (No. DJXSTD202414), Doctoral Special Research Fund launch project of Jiamusi University (No. JMSUBZ2021-10), The Key Laboratory of New Drug Development and Drug Toxicology Evaluation in Heilongjiang Province (No. kfkt2022-14), Jiamusi University National Fund Cultivation Program (No. JMSUGPZR2023-001).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Huang X, Nie S, Xie M. Interaction between gut immunity and polysaccharides. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2015) 57:2943–55. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2015.1079165
2. Tabarsa M, You S, Yelithao K, Palanisamy S, Prabhu NM, Nan M. Isolation, structural elucidation and immuno-stimulatory properties of polysaccharides from Cuminum cyminum. Carbohydr Polym. (2020) 230:115636. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115636
3. Wang J, Hu S, Nie S, Yu Q, Xie M. Reviews on mechanisms ofIn vitroAntioxidant activity of polysaccharides. Oxid Med Cell Longevity. (2016) 2016:1–13. doi: 10.1155/2016/5692852
4. Descroix K, Ferrieres V, Jamois F, Yvin JC, Plusquellec D. Recent progress in the field of β-(1,3)-glucans and new applications. Mini Rev Med Chem. (2006) 6:1341–9. doi: 10.2174/138955706778993058
5. Stern R, Asari AA, Sugahara KN. Hyaluronan fragments: An information-rich system. Eur J Cell Biol. (2006) 85:699–715. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.05.009
6. Taylor KR, Gallo RL. Glycosaminoglycans and their proteoglycans: host-associated molecular patterns for initiation and modulation of inflammation. FASEB J. (2006) 20:9–22. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-4682rev
7. Whitelock JM, Iozzo RVJC. Heparan sulfate: A complex polymer charged with biological activity. Chem Rev. (2005) 105:2745–64. doi: 10.1002/chin.200542258
8. Zhang C, Pi X, Li X, Huo J, Wang W. Edible herbal source-derived polysaccharides as potential prebiotics: Composition, structure, gut microbiota regulation, and its related health effects. Food Chem. (2024) 458:140267. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.140267
9. Pillay LR, Olasehinde TA, Olofinsan KA, Erukainure OL, Islam MS, Olaniran AO. Antidiabetic potentials of crude and purified sulphated polysaccharides isolated from Gracilaria gracilis, a seaweed from South Africa. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e35729. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35729
10. Gupta PK, Rajan MGR, Kulkarni S. Activation of murine macrophages by G1-4A, a polysaccharide from Tinospora cordifolia, in TLR4/MyD88 dependent manner. Int Immunopharmacol. (2017) 50:168–77. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.06.025
11. Cui YQ, Zhang LJ, Zhang T, Luo DZ, Jia YJ, Guo ZX, et al. Inhibitory effect of fucoidan on nitric oxide production in lipopolysaccharide-activated primary microglia. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. (2010) 37:422–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2009.05314.x
12. Álvarez-Mercado AI, Plaza-Diaz J. Dietary polysaccharides as modulators of the gut microbiota ecosystem: an update on their impact on health. Nutrients. (2022) 14:4116. doi: 10.3390/nu14194116
13. Ilangovan M, Guna V, Hu C, Nagananda GS, Reddy N. Curcuma longa L. plant residue as a source for natural cellulose fibers with antimicrobial activity. Ind Crops Products. (2018) 112:556–60. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.12.042
14. Eris FR, Pamela VY, Kusumasari S, Meindrawan B. Extraction of inulin from Beneng tuber (Xanthosoma undipes) and its application to yogurt. Future Foods. (2024) 9:100339. doi: 10.1016/j.fufo.2024.100339
15. Thinh PD, Rasin AB, Silchenko AS, Trung VT, Kusaykin MI, Hang CTT, et al. Pectins from the sea grass Enhalus acoroides (L.f.) Royle: Structure, biological activity and ability to form nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol. (2023) 242:124714. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124714
16. Sun Q-L, Li Y-X, Cui Y-S, Jiang S-L, Dong C-X, Du J. Structural characterization of three polysaccharides from the roots of Codonopsis pilosula and their immunomodulatory effects on RAW264.7 macrophages. Int J Biol Macromol. (2019) 130:556–63. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.02.165
17. Guo H, Li H, Ran W, Yu W, Xiao Y, Gan R, et al. Structural and functional characteristics of pectins from three cultivars of apple (Malus pumila Mill.) pomaces. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 269:132002. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.132002
18. Li Y, Ren M, Yan H, Luo L, Fang X, He L, et al. Purification, structural characterization, and immunomodulatory activity of two polysaccharides from Portulaca oleracea L. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 264:130508. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130508
19. Liao Q, He Y, Wu C, Deng Z, Liu J. Hawthorn Fruit (Crataegus spp.) Polysaccharides Exhibit Immunomodulatory Activity on Macrophages via TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Activation. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. (2024) 79:367–73. doi: 10.1007/s11130-024-01160-3
20. Premarathna AD, Ahmed TAE, Rjabovs V, Hammami R, Critchley AT, Tuvikene R, et al. Immunomodulation by xylan and carrageenan-type polysaccharides from red seaweeds: Anti-inflammatory, wound healing, cytoprotective, and anticoagulant activities. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 260:129433. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129433
21. Song W, Wang Y, Li G, Xue S, Zhang G, Dang Y, et al. Modulating the gut microbiota is involved in the effect of low-molecular-weight Glycyrrhiza polysaccharide on immune function. Gut Microbes. (2023) 15:2276814. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2276814
22. Sun Y, Zhang M, Jiang X, Peng K, Yi Y, Meng Y, et al. Structural characterization and immunoregulatory mechanism of a low-molecular-weight polysaccharide from lotus root. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 280:135957. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135957
23. Abdel-Rahman RM, Hrdina R, Abdel-Mohsen AM, Fouda MMG, Soliman AY, Mohamed FK, et al. Chitin and chitosan from Brazilian Atlantic Coast: Isolation, characterization and antibacterial activity. Int J Biol Macromol. (2015) 80:107–20. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.06.027
24. Sayari N, Sila A, Abdelmalek BE, Abdallah RB, Ellouz-Chaabouni S, Bougatef A, et al. Chitin and chitosan from the Norway lobster by-products: Antimicrobial and anti-proliferative activities. Int J Biol Macromol. (2016) 87:163–71. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.02.057
25. Yang D, Lin F, Huang Y, Ye J, Xiao M. Separation, purification, structural analysis and immune-enhancing activity of sulfated polysaccharide isolated from sea cucumber viscera. Int J Biol Macromol. (2020) 155:1003–18. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.11.064
26. Shi L, Hao G, Chen J, Wang J, Weng W. Structural characterization and immunostimulatory activity of a water-soluble polysaccharide from abalone (Haliotis discus hannai Ino) muscle. Food Sci Hum Wellness. (2023) 12:495–502. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2022.07.051
27. Shang Z, Jiang Y, Yang F, Wu K, Zheng G, Lin Y, et al. A homologous series of α-glucans from Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus and their immunomodulatory activity. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 260:129657. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129657
28. Pérez-Bassart Z, Bäuerl C, Fabra MJ, Martínez-Abad A, Collado MC, López-Rubio A. Composition, structural properties and immunomodulatory activity of several aqueous Pleurotus β-glucan-rich extracts. Int J Biol Macromol. (2023) 253:127255. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127255
29. Chang C-J, Lin C-S, Lu C-C, Martel J, Ko Y-F, Ojcius DM, et al. Ganoderma lucidum reduces obesity in mice by modulating the composition of the gut microbiota. Nat Commun. (2015) 6:7489. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8489
30. Wang H, Mukerabigwi JF, Zhang Y, Han L, Jiayinaguli T, Wang Q, et al. In vivo immunological activity of carboxymethylated-sulfated (1→3)-β-d-glucan from sclerotium of Poria cocos. Int J Biol Macromol. (2015) 79:511–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.05.020
31. Zhang W, He J, Zheng D, Zhao P, Wang Y, Zhao J, et al. Immunomodulatory activity and its mechanisms of two polysaccharides from poria cocos. Molecules. (2023) 29:50. doi: 10.3390/molecules29010050
32. Yang Q, Chang S-L, Tian Y-M, Li W, Ren J-L. Glucan polysaccharides isolated from Lactarius hatsudake Tanaka mushroom: Structural characterization and in vitro bioactivities. Carbohydr Polym. (2024) 337:122171. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2024.122171
33. El-Sayed MH, Arafat HH, Elsehemy IA, Basha M. Optimization, purification and physicochemical characterization of curdlan produced by paenibacillus sp. Strain NBR-10. Biosci Biotechnol Res Asia. (2016) 13:901–9. doi: 10.13005/bbra/2113
34. Liao Y, Wang R, Qin X, Ma X, Liu X, Jia S, et al. A β-glucan from Aureobasidium pullulans enhanced the antitumor effect with rituximab against SU-DHL-8. Int J Biol Macromol. (2022) 220:1356–67. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.09.106
35. Rao Z, Dong Y, Zheng X, Tang K, Liu J. Extraction, purification, bioactivities and prospect of lentinan: A review. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. (2021) 37:102163. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2021.102163
36. Bhat IM, Wani SM, Mir SA, Masoodi FA. Advances in xanthan gum production, modifications and its applications. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. (2022) 42:102328. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2022.102328
37. Ye D, Rongpipi S, Kiemle SN, Barnes WJ, Chaves AM, Zhu C, et al. Preferred crystallographic orientation of cellulose in plant primary cell walls. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:4720. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18449-x
38. Klemm D, Heublein B, Fink HP, Bohn A. Cellulose: fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angewandte Chemie Int Edition. (2005) 44:3358–93. doi: 10.1002/anie.200460587
39. Roberfroid MB. Introducing inulin-type fructans. Br J Nutr. (2007) 93:S13–25. doi: 10.1079/bjn20041350
40. Ahmed W, Rashid S. Functional and therapeutic potential of inulin: A comprehensive review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2017) 59:1–13. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2017.1355775
41. Ching Y-P, Sliva D, Loganathan J, Jiang J, Jedinak A, Lamb JG, et al. Mushroom ganoderma lucidum prevents colitis-associated carcinogenesis in mice. PloS One. (2012) 7:e47873. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047873
42. Beukema M, Faas MM, de Vos P. The effects of different dietary fiber pectin structures on the gastrointestinal immune barrier: impact via gut microbiota and direct effects on immune cells. Exp Mol Med. (2020) 52:1364–76. doi: 10.1038/s12276-020-0449-2
43. Park MJ, Ryu HS, Kim JS, Lee HK, Kang JS, Yun J, et al. Platycodon grandiflorum polysaccharide induces dendritic cell maturation via TLR4 signaling. Food Chem Toxicol. (2014) 72:212–20. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2014.07.011
44. Gao Y, Liu Z, Dai S, Zhao J, Guo Y, Cai X, et al. Modification, structure identification, and biological activities of phosphorylated polysaccharides: A review. Starch - Stärke. (2024) 76:76. doi: 10.1002/star.202300223
45. Hou F, Gong Z, Jia F, Cui W, Song S, Zhang J, et al. Insights into the relationships of modifying methods, structure, functional properties and applications of chitin: A review. Food Chem. (2023) 409:135336. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135336
46. Mohan K, Rajan DK, Ganesan AR, Divya D, Johansen J, Zhang S. Chitin, chitosan and chitooligosaccharides as potential growth promoters and immunostimulants in aquaculture: A comprehensive review. Int J Biol Macromol. (2023) 251:126285. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126285
47. Lee CG, Da Silva CA, Lee J-Y, Hartl D, Elias JA. Chitin regulation of immune responses: an old molecule with new roles. Curr Opin Immunol. (2008) 20:684–9. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2008.10.002
48. Yang B, Yang C, Liu R, Sui W, Zhu Q, Jin Y, et al. The relationship between preparation and biological activities of animal-derived polysaccharides: A comprehensive review. Foods. (2024) 13:173. doi: 10.3390/foods13010173
49. Rcr O, Rr A, Ta G. A review of plant sulfated polysaccharides and their relations with anticoagulant activities. J Developing Drugs. (2016) 5:1000166. doi: 10.4172/2329-6631.1000166
50. Barbosa JR, de Carvalho Junior RN. Polysaccharides obtained from natural edible sources and their role in modulating the immune system: Biologically active potential that can be exploited against COVID-19. Trends Food Sci Technol. (2021) 108:223–35. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2020.12.026
51. Barbosa JR, d. Carvalho Junior RN. Occurrence and possible roles of polysaccharides in fungi and their influence on the development of new technologies. Carbohydr Polym. (2020) 246:10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116613. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116613
52. Huang S, Mao J, Ding K, Zhou Y, Zeng X, Yang W, et al. Polysaccharides from ganoderma lucidum promote cognitive function and neural progenitor proliferation in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Stem Cell Rep. (2017) 8:84–94. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.12.007
53. Tian H, Liu Z, Pu Y, Bao Y. Immunomodulatory effects exerted by Poria Cocos polysaccharides via TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB signaling in vitro and in vivo. Biomed Pharmacother. (2019) 112:108709. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108709
54. Li X, He Y, Zeng P, Liu Y, Zhang M, Hao C, et al. Molecular basis for Poria cocos mushroom polysaccharide used as an antitumour drug in China. J Cell Mol Med. (2018) 23:4–20. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13564
55. Yim S-K, Kim K, Kim I, Chun S, Oh T, Kim J-U, et al. Inhibition of SARS-coV-2 virus entry by the crude polysaccharides of seaweeds and abalone viscera in vitro. Mar Drugs. (2021) 19:219. doi: 10.3390/md19040219
56. Sasaki D, Sasaki K, Kondo A. Glycosidic linkage structures influence dietary fiber fermentability and propionate production by human colonic microbiota in vitro. Biotechnol J. (2020) 15:e1900523. doi: 10.1002/biot.201900523
57. Zhao T, Feng Y, Li J, Mao R, Zou Y, Feng W, et al. Schisandra polysaccharide evokes immunomodulatory activity through TLR 4-mediated activation of macrophages. Int J Biol Macromol. (2014) 65:33–40. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.01.018
58. Chen J-Y, Sun X-Y, Ouyang J-M. Modulation of calcium oxalate crystal growth and protection from oxidatively damaged renal epithelial cells of corn silk polysaccharides with different molecular weights. Oxid Med Cell Longevity. (2020) 2020:1–19. doi: 10.1155/2020/6982948
59. Jiang L, Yu Z, Lin Y, Cui L, Yao S, Lv L, et al. Low-molecular-weight polysaccharides from Agaricus blazei Murrill modulate the Th1 response in cancer immunity. Oncol Letters. (2018) 15:3429–36. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.7794
60. Cai Y, Si Z, Jiang Y, Ye M, Wang F, Yang X, et al. Structure-activity relationship of low molecular weight Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharides produced by Bacteroides. Carbohydr Polym. (2023) 316:121036. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.121036
61. Bi D, Yu B, Han Q, Lu J, White WL, Lai Q, et al. Immune activation of RAW264.7 macrophages by low molecular weight fucoidan extracted from New Zealand undaria pinnatifida. J Agric Food Chem. (2018) 66:10721–8. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b03698
62. Huo Y, Ding W-j, Liu Y-r, Li Z-t, Dai K-y, Liu C, et al. Selenochemical modification of low molecular weight polysaccharides from Grifola frondosa and the mechanism of their inhibitory effects on gastric cancer cells. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 269:131812. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131812
63. Kasai A, Arafuka S, Koshiba N, Takahashi D, Toshima K. Systematic synthesis of low-molecular weight fucoidan derivatives and their effect on cancer cells. Org Biomol Chem. (2015) 13:10556–68. doi: 10.1039/c5ob01634g
64. Jang J-Y, Moon S-Y, Joo H-G. Differential effects of fucoidans with low and high molecular weight on the viability and function of spleen cells. Food Chem Toxicol. (2014) 68:234–8. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2014.03.024
65. Ishisono K, Yabe T, Kitaguchi K. Citrus pectin attenuates endotoxin shock via suppression of Toll-like receptor signaling in Peyer’s patch myeloid cells. J Nutr Biochem. (2017) 50:38–45. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2017.07.016
66. do Nascimento GE, Winnischofer SMB, Ramirez MI, Iacomini M, Cordeiro LMC. The influence of sweet pepper pectin structural characteristics on cytokine secretion by THP-1 macrophages. Food Res Int. (2017) 102:588–94. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2017.09.037
67. Xie G, Schepetkin IA, Siemsen DW, Kirpotina LN, Wiley JA, Quinn MT. Fractionation and characterization of biologically-active polysaccharides from Artemisia tripartita. Phytochemistry. (2008) 69:1359–71. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2008.01.009
68. Wang X-S, Dong Q, Zuo J-P, Fang J-N. Structure and potential immunological activity of a pectin from Centellaasiatica (L.) Urban. Carbohydr Res. (2003) 338:2393–402. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(03)00380-x
69. Satitmanwiwat S, Ratanakhanokchai K, Laohakunjit N, Chao LK, Chen S-T, Pason P, et al. Improved purity and immunostimulatory activity of β-(1→3)(1→6)-glucan from pleurotus sajor-caju using cell wall-degrading enzymes. J Agric Food Chem. (2012) 60:5423–30. doi: 10.1021/jf300354x
70. Huang C, Tu W, Zhang M, Peng D, Guo Z, Huang W, et al. A novel heteropolysaccharide isolated from custard apple pulp and its immunomodulatory activity in mouse macrophages and dendritic cells. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e18521. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18521
71. Li WJ, Chen Y, Nie SP, Xie MY, He M, Zhang SS, et al. Ganoderma atrum polysaccharide induces anti-tumor activity via the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway related to activation of host immune response. J Cell Biochem. (2011) 112:860–71. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22993
72. Chen R, Xu J, Wu W, Wen Y, Lu S, El-Seedi HR, et al. Structure–immunomodulatory activity relationships of dietary polysaccharides. Curr Res Food Sci. (2022) 5:1330–41. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2022.08.016
73. Wang Z, Zheng Y, Lai Z, Hu X, Wang L, Wang X, et al. Effect of monosaccharide composition and proportion on the bioactivity of polysaccharides: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 254:127955. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127955
74. Boltje TJ, Kim J-H, Park J, Boons G-J. Chiral-auxiliary-mediated 1,2-cis-glycosylations for the solid-supported synthesis of a biologically important branched α-glucan. Nat Chem. (2010) 2:552–7. doi: 10.1038/nchem.663
75. Qamar T, Syed F, Nasir M, Rehman H, Zahid M, Liu R, et al. Novel combination of prebiotics galacto-oligosaccharides and inulin-inhibited aberrant crypt foci formation and biomarkers of colon cancer in wistar rats. Nutrients. (2016) 8:465. doi: 10.3390/nu8080465
76. Wang Z, Zhou X, Shu Z, Zheng Y, Hu X, Zhang P, et al. Regulation strategy, bioactivity, and physical property of plant and microbial polysaccharides based on molecular weight. Int J Biol Macromol. (2023) 244:125360. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125360
77. Hu Y, He Y, Niu Z, Shen T, Zhang J, Wang X, et al. A review of the immunomodulatory activities of polysaccharides isolated from Panax species. J Ginseng Res. (2022) 46:23–32. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2021.06.003
78. Kouakou K, Schepetkin IA, Yapi A, Kirpotina LN, Jutila MA, Quinn MT. Immunomodulatory activity of polysaccharides isolated from Alchornea cordifolia. J Ethnopharmacol. (2013) 146:232–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.12.037
79. Schepetkin IA, Quinn MT. Botanical polysaccharides: Macrophage immunomodulation and therapeutic potential. Int Immunopharmacol. (2006) 6:317–33. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2005.10.005
80. Cheng X-Q, Li H, Yue X-L, Xie J-Y, Zhang Y-Y, Di H-Y, et al. Macrophage immunomodulatory activity of the polysaccharides from the roots of Bupleurum smithii var. parvifolium. J Ethnopharmacol. (2010) 130:363–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.05.019
81. Gong W, Han R, Li H, Song J, Yan H, Li G, et al. Agronomic traits and molecular marker identification of wheat–aegilops caudata addition lines. Front Plant Sci. (2017) 8:1743. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01743
82. Shin M-S, Park SB, Shin K-S. Molecular mechanisms of immunomodulatory activity by polysaccharide isolated from the peels of Citrus unshiu. Int J Biol Macromol. (2018) 112:576–83. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.02.006
83. Műzes G. Changes of the cytokine profile in inflammatory bowel diseases. World J Gastroenterol. (2012) 18:10.3748/wjg.v18.i41.5848. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i41.5848
84. Deng C, Shang J, Fu H, Chen J, Liu H, Chen J. Mechanism of the immunostimulatory activity by a polysaccharide from Dictyophora indusiata. Int J Biol Macromol. (2016) 91:752–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.06.024
85. Im S-A, Lee Y-R, Lee Y-H, Oh S-T, Gerelchuluun T, Kim B-H, et al. Synergistic activation of monocytes by polysaccharides isolated from Salicornia herbacea and interferon-γ. J Ethnopharmacol. (2007) 111:365–70. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2006.11.027
86. Li L, Li Y, Ijaz M, Shahbaz M, Lian Q, Wang F. Review on complement analysis method and the roles of glycosaminoglycans in the complement system. Carbohydr Polym. (2015) 134:590–7. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.08.028
87. Pichert A, Schlorke D, Franz S, Arnhold J. Functional aspects of the interaction between interleukin-8 and sulfated glycosaminoglycans. Biomatter. (2014) 2:142–8. doi: 10.4161/biom.21316
88. Huang L, Shen M, Morris GA, Xie J. Sulfated polysaccharides: Immunomodulation and signaling mechanisms. Trends Food Sci Technol. (2019) 92:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2019.08.008
89. Ricklin D, Hajishengallis G, Yang K, Lambris JD. Complement: a key system for immune surveillance and homeostasis. Nat Immunol. (2010) 11:785–97. doi: 10.1038/ni.1923
90. Gadjeva M, Thiel S, Jensenius I. The mannan-binding-lectin pathway of the innate immune response. Curr Opin Immunol. (2001) 13:74–8. doi: 10.1016/s0952-7915(00)00185-0
91. Leung MYK, Liu C, Koon JCM, Fung KP. Polysaccharide biological response modifiers. Immunol Letters. (2006) 105:101–14. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2006.01.009
92. Kim Y-S, Ryu J-H, Han S-J, Choi K-H, Nam K-B, Jang I-H, et al. Gram-negative bacteria-binding protein, a pattern recognition receptor for lipopolysaccharide and β-1,3-glucan that mediates the signaling for the induction of innate immune genes in drosophila melanogaster cells. J Biol Chem. (2000) 275:32721–7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M003934200
93. Means TK, Golenbock DT, Fenton MJ. Structure and function of Toll-like receptor proteins. Life Sci. (2000) 68:241–58. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(00)00939-5
94. Schuster JM, Nelson PS. Toll receptors: an expanding role in our understanding of human disease. J Leukoc Biol. (2000) 67:767–73. doi: 10.1002/jlb.67.6.767
95. Kim WS, Ordija CM, Freeman MW. Activation of signaling pathways by putative scavenger receptor class A (SR-A) ligands requires CD14 but not SR-A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2003) 310:542–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.09.049
96. Brown GD, Taylor PR, Reid DM, Willment JA, Williams DL, Martinez-Pomares L, et al. Dectin-1 is A major β-glucan receptor on macrophages. J Exp Med. (2002) 196:407–12. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020470
97. Zamze S, Martinez-Pomares L, Jones H, Taylor PR, Stillion RJ, Gordon S, et al. Recognition of bacterial capsular polysaccharides and lipopolysaccharides by the macrophage mannose receptor. J Biol Chem. (2002) 277:41613–23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M207057200
98. Lamers C, Plüss CJ, Ricklin D. The promiscuous profile of complement receptor 3 in ligand binding, immune modulation, and pathophysiology. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:662164. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.662164
99. Fujita T, Matsushita M, Endo Y. The lectin-complement pathway – its role in innate immunity and evolution. Immunol Rev. (2004) 198:185–202. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.0123.x
100. Kilpatrick DC. Mannan-binding lectin and its role in innate immunity. Transfus Med. (2010) 12:335–52. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3148.2002.00408.x
101. Iwasaki A, Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptor control of the adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol. (2004) 5:987–95. doi: 10.1038/ni1112
102. Brown GD, Herre J, Williams DL, Willment JA, Marshall ASJ, Gordon S. Dectin-1 mediates the biological effects of β-glucans. J Exp Med. (2003) 197:1119–24. doi: 10.1084/jem.20021890
103. Peiser L, Mukhopadhyay S, Gordon S. Scavenger receptors in innate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. (2002) 14:123–8. doi: 10.1016/s0952-7915(01)00307-7
104. Willment JA, Marshall ASJ, Reid DM, Williams DL, Wong SYC, Gordon S, et al. The human β-glucan receptor is widely expressed and functionally equivalent to murine Dectin-1 on primary cells. Eur J Immunol. (2005) 35:1539–47. doi: 10.1002/eji.200425725
105. Linehan SA, Martínez-Pomares L, Stahl PD, Gordon S. Mannose receptor and its putative ligands in normal murine lymphoid and nonlymphoid organs: In situ expression of mannose receptor by selected macrophages, endothelial cells, perivascular microglia, and mesangial cells, but not dendritic cells. J Exp Med. (1999) 189:1961–72. doi: 10.1084/jem.189.12.1961
106. Ross GD, Vtvicka V. CR3 (CD11b, CD18): a phagocyte and NK cell membrane receptor with multiple ligand specificities and functions. Clin Exp Immunol. (2010) 92:181–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb03377.x
107. Shen J, Zhang M, Zhang K, Qin Y, Liu M, Liang S, et al. Effect of Angelica polysaccharide on mouse myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:989230. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.989230
108. Shin JY, Song JY, Yun YS, Yang HO, Pyo S. Immunostimulating effects of acidic polysaccharides extract of Panax ginseng on macrophage function. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. (2002) 24:469–82. doi: 10.1081/iph-120014730
109. Matsumoto T, Yamada H. Regulation of immune complexes binding of macrophages by pectic polysaccharide from bupleurum falcatum L.: pharmacological evidence for the requirement of intracellular calcium/calmodulin on fc receptor up-regulation by bupleuran 2IIb. J Pharm Pharmacol. (2011) 47:152–6. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1995.tb05769
110. Sierra-García GD, Castro-Ríos R, González-Horta A, Lara-Arias J. Acemannan, an extracted polysaccharide from Aloe vera: A literature review. Nat Prod Commun. (2014) 9:1217. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201300861
111. García-Lora A, Martinez M, Pedrinaci S, Garrido F. Different regulation of PKC isoenzymes and MAPK by PSK and IL-2 in the proliferative and cytotoxic activities of the NKL human natural killer cell line. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2003) 52:59–64. doi: 10.1007/s00262-002-0336-9
112. Hwang JS, Chung HK, Bae EK, Lee AY, Ji HJ, Park DW, et al. The polysaccharide fraction AIP1 from Artemisia iwayomogi suppresses apoptotic death of the mouse spleen cells in culture. Arch Pharm Res. (2003) 26:294–300. doi: 10.1007/bf02976958
113. Michaelsen TE, Gilje A, Samuelsen AB, Høgåsen K, Paulsen BS. Interaction between human complement and a pectin type polysaccharide fraction, PMII, from the leaves of plantago major L. Scand J Immunol. (2010) 52:483–90. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.2000.00801
114. Batbayar S, Lee D-H, Kim H-W. Immunomodulation of fungal β-glucan in host defense signaling by dectin-1. Biomol Ther. (2012) 20:433–45. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2012.20.5.433
115. Desalegn G, Pabst O. Inflammation triggers immediate rather than progressive changes in monocyte differentiation in the small intestine. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:3229. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11148-2
116. Chan GC-F, Chan WK, Sze DM-Y. The effects of β-glucan on human immune and cancer cells. J Hematol Oncol. (2009) 2:25. doi: 10.1186/1756-8722-2-25
117. Goodridge HS, Wolf AJ, Underhill DM. [amp]]beta;-glucan recognition by the innate immune system hhs public access. Immunol Rev. (2019) 230:38–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00793
118. Zimmerman JW, Lindermuth J, Fish PA, Palace GP, Stevenson TT, Demong DE. A novel carbohydrate-glycosphingolipid interaction between a β-(1–3)-glucan immunomodulator, PGG-glucan, and lactosylceramide of human leukocytes. J Biol Chem. (1998) 273:22014–20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.34.22014
119. Rice PJ, Kelley JL, Kogan G, Ensley HE, Kalbfleisch JH, Browder IW, et al. Human monocyte scavenger receptors are pattern recognition receptors for (1–>3)-beta-D-glucans. J Leukoc Biol. (2002) 72:140–6. doi: 10.1189/jlb.72.1.140
120. Lin Y-L, Liang Y-C, Lee S-S, Chiang B-L. Polysaccharide purified fromGanoderma luciduminduced activation and maturation of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells by the NF-κB and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. J Leuk Biol. (2005) 78:533–43. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0804481
121. Li X, Zhang M, Khoo HE, Jiang T, Guan Y, Li P. Effect of polysaccharides from enteromorpha intestinalis on intestinal function in sprague dawley rats. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 12:796734. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.796734
122. Wang Y, Sun W, Wu E, Wang K, Chen X, Cui Y, et al. Polysaccharides from abrus cantoniensis hance modulate intestinal microflora and improve intestinal mucosal barrier and liver oxidative damage induced by heat stress. Front Vet Sci. (2022) 9:868433. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.868433
123. Wu Y, Wu C, Che Y, Zhang T, Dai C, Nguyễn AD, et al. Effects of glycyrrhiza polysaccharides on chickens’ Intestinal health and homeostasis. Front Vet Sci. (2022) 9:891429. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.891429
124. Qin X, Nong K, Liu Z, Fang X, Zhang B, Chen W, et al. Regulation of the intestinal flora using polysaccharides from Callicarpa nudiflora Hook to alleviate ulcerative colitis and the molecular mechanisms involved. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 258:128887. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.128887
125. Huo J, Li M, Wei J, Wang Y, Hao W, Sun W, et al. RNA-seq based elucidation of mechanism underlying the protective effect of Huangshui polysaccharide on intestinal barrier injury in Caco-2 cells. Food Res Int. (2022) 162:112175. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.112175
126. Manafu Z, Du R, Kudereti T, Abulikemu G, Lakho SA, Xue L, et al. Structure characterization and intestinal immune promotion effect of polysaccharide purified from Alhagi camelorum Fisch. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 269:132077. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.132077
127. Fan X, Yu W, Wang Q, Yang H, Tan D, Yu B, et al. Protective effect of Broussonetia papyrifera leaf polysaccharides on intestinal integrity in a rat model of diet-induced oxidative stress. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 268:131589. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131589
128. Wu M, Lyu Y, Xu H, Luo H, Yin X, Zheng H. Raspberry polysaccharides attenuate hepatic inflammation and oxidative stress in diet-induced obese mice by enhancing butyrate-mediated intestinal barrier function. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 262:130007. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130007
129. Chen Y, Chen P, Liu H, Zhang Y, Zhang X. Penthorum chinense Pursh polysaccharide induces a mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis of H22 cells and activation of immunoregulation in H22 tumor-bearing mice. Int J Biol Macromol. (2023) 224:510–22. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.10.140
130. Cheng J, Wang Y, Song J, Liu Y, Ji W, He L, et al. Characterization, immunostimulatory and antitumor activities of a β-galactoglucofurannan from cultivated Sanghuangporus vaninii under forest. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:1058131. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1058131
131. Wang X, Li N, Li Y, Zhao Y, Zhang L, Sun Y, et al. A novel polysaccharide from Paeonia lactiflora exerts anti-tumor activity via immunoregulation. Arab J Chem. (2022) 15:104132. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.104132
132. Matsui R, Endo K, Saiki T, Haga H, Shen W, Wang X, et al. Characterization and anti-tumor activities of polysaccharide isolated from Brassica rapa L. via activation of macrophages through TLR2-and TLR4-Dependent pathways. Arch Biochem Biophys. (2024) 752:109879. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2023.109879
133. Tao S, Huang C, Tan Z, Duan S, Zhang X, Ren Z, et al. Effect of the polysaccharides derived from Dendrobium officinale stems on human HT-29 colorectal cancer cells and a zebrafish model. Food Biosci. (2021) 41:100995. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2021.100995
134. Liu M-Q, Bao C-J, Liang X-F, Ji X-Y, Zhao L-Q, Yao A-N, et al. Specific molecular weight of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide for robust breast cancer regression by repolarizing tumor-associated macrophages. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 261:129674. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129674
135. Baien SH, Seele J, Henneck T, Freibrodt C, Szura G, Moubasher H, et al. Antimicrobial and Immunomodulatory Effect of Gum Arabic on Human and Bovine Granulocytes Against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Front Immunol. (2020) 10:3119. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03119
136. Li X, Wei J, Lin L, Li J, Zheng G. Structural characterization, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of polysaccharide from Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz stem. Colloids Surf B: Biointerf. (2023) 231:113573. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2023.113573
137. Kungel PTAN, Correa VG, Corrêa RCG, Peralta RA, Soković M, Calhelha RC, et al. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of a purified polysaccharide from yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis). Int J Biol Macromol. (2018) 114:1161–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.04.020
138. Shao L-L, Xu J, Shi M-J, Wang X-L, Li Y-T, Kong L-M, et al. Preparation, antioxidant and antimicrobial evaluation of hydroxamated degraded polysaccharides from Enteromorpha prolifera. Food Chem. (2017) 237:481–7. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.05.119
139. Li Y-T, Chen B-J, Wu W-D, Ge K, Wei X-Y, Kong L-M, et al. Antioxidant and antimicrobial evaluation of carboxymethylated and hydroxamated degraded polysaccharides from Sargassum fusiforme. Int J Biol Macromol. (2018) 118:1550–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.06.196
140. Lu M-K, Lee M-H, Chao C-H, Hsu Y-C. Physiochemical changes and mechanisms of anti-inflammation effect of sulfated polysaccharides from ammonium sulfate feeding of Antrodia cinnamomea. Int J Biol Macromol. (2020) 148:715–21. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.110
141. Ji Y-p, Shi T-y, Zhang Y-y, Lin D, Linghu K-g, Xu Y-n, et al. Essential oil from Fructus Alpinia zerumbet (fruit of Alpinia zerumbet (Pers.) Burtt.et Smith) protected against aortic endothelial cell injury and inflammation in vitro and in vivo. J Ethnopharmacol. (2019) 237:149–58. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.03.011
142. Xu Y, Zhang Z, Feng H, Tang J, Peng W, Chen Y, et al. Scorias spongiosa polysaccharides promote the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacity and its effect on intestinal microbiota in mice. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:865396. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.865396
143. Ming K, Zhuang S, Ma N, Nan S, Li Q, Ding M, et al. Astragalus polysaccharides alleviates lipopolysaccharides-induced inflammatory lung injury by altering intestinal microbiota in mice. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:1033875. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1033875
144. Yan B, Wang R, Fu C, Huang C, Lai C, Yong Q. Procuring the polysaccharides with anti-inflammatory bioactivity from Russula vinosa Lindblad by citric acid extraction. Food Biosci. (2024) 59:104079. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2024.104079
145. Huang Y, Ye Y, Xu D, Ji J, Sun J, Xu M, et al. Structural characterization and anti-inflammatory activity of a novel neutral polysaccharide isolated from Smilax glabra Roxb. Int J Biol Macromol. (2023) 234:123559. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123559
146. Li Y, Sheng Y, Liu J, Xu G, Yu W, Cui Q, et al. Hair-growth promoting effect and anti-inflammatory mechanism of Ginkgo biloba polysaccharides. Carbohydr Polym. (2022) 278:118811. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118811
147. Qiu P, Ishimoto T, Fu L, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Liu Y. The gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2022) 12:733992. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.733992
148. Shreiner AB, Kao JY, Young VB. The gut microbiome in health and in disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. (2015) 31:69–75. doi: 10.1097/mog.0000000000000139
149. Tang C, Ding R, Sun J, Liu J, Kan J, Jin C. The impacts of natural polysaccharides on intestinal microbiota and immune responses – a review. Food Funct. (2019) 10:2290–312. doi: 10.1039/c8fo01946k
150. Sun J, Liu J, Ren G, Chen X, Cai H, Hong J, et al. Impact of purple sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) polysaccharides on the fecal metabolome in a murine colitis model. RSC Adv. (2022) 12:11376–90. doi: 10.1039/d2ra00310d
151. Xiao X-y, Guo Z-j, Li X, Chen P, Li Y, Zhang J-b, et al. Effects of wine processed Polygonatum polysaccharides on immunomodulatory effects and intestinal microecology in mice. Qual Assur Saf Crops Foods. (2023) 15:161–74. doi: 10.15586/qas.v15i2.1227
152. den Besten G, van Eunen K, Groen AK, Venema K, Reijngoud D-J, Bakker BM. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J Lipid Res. (2013) 54:2325–40. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R036012
153. Silva YP, Bernardi A, Frozza RL. The role of short-chain fatty acids from gut microbiota in gut-brain communication. Front Endocrinol. (2020) 11:25. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00025
154. Zhang J, Yang G, Wen Y, Liu S, Li C, Yang R, et al. Intestinal microbiota are involved in the immunomodulatory activities of longan polysaccharide. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2017) 61:1700466. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201700466
155. Holscher DH. Dietary fiber and prebiotics and the gastrointestinal microbiota. Gut Microbes. (2017) 8:172–84. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2017.1290756
156. Chen F, Yang W, Huang X, Cao AT, Bilotta AJ, Xiao Y, et al. Neutrophils promote amphiregulin production in intestinal epithelial cells through TGF-β and contribute to intestinal homeostasis. J Immunol. (2018) 201:2492–501. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800003
157. Cani PD, Everard A, Duparc T. Gut microbiota, enteroendocrine functions and metabolism. Curr Opin Pharmacol. (2013) 13:935–40. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2013.09.008
158. Zhang H, Jiang F, Zhang J, Wang W, Li L, Yan J. Modulatory effects of polysaccharides from plants, marine algae and edible mushrooms on gut microbiota and related health benefits: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. (2022) 204:169–92. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.01.166
159. Dolan KT, Chang EB. Diet, gut microbes, and the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2016) 61:129. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201600129
160. Slavin J. Fiber and prebiotics: mechanisms and health benefits. Nutrients. (2013) 5:1417–35. doi: 10.3390/nu5041417
161. Topping DL, Clifton P. Short-chain fatty acids and human colonic function: roles of resistant starch and nonstarch. Physiol Rev. (2001) 81:1031–1. doi: 10.1152/physrev.2001.81.3.1031
162. Tzianabos AO. Polysaccharide immunomodulators as therapeutic agents: structural aspects and biologic function. Clin Microbiol Rev. (2000) 13:523–33. doi: 10.1128/cmr.13.4.523-533.2000
163. Hur SJ, Kang SH, Jung HS, Kim SC, Jeon HS, Kim IH, et al. Review of natural products actions on cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nutr Res. (2012) 32:801–16. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2012.09.013
164. Chen L-h, Lin Z-b, Li W-d. Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides reduce methotrexate-induced small intestinal damage in mice via induction of epithelial cell proliferation and migration. Acta Pharmacol Sinica. (2011) 32:1505–12. doi: 10.1038/aps.2011.126
165. Zhang Y-S, Li W-J, Zhang X-Y, Yan Y-X, Nie S-P, Gong D-M, et al. Ganoderma atrum polysaccharide ameliorates anoxia/reoxygenation-mediated oxidative stress and apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Int J Biol Macromol. (2017) 98:398–406. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.071
166. Yasuda E, Serata M, Sako T. Suppressive effect on activation of macrophages by lactobacillus casei strain shirota genes determining the synthesis of cell wall-associated polysaccharides. Appl Environ Microbiol. (2008) 74:4746–55. doi: 10.1128/aem.00412-08
167. Wang Y, Song X, Wang Z, Li Z, Geng Y. Effects of pine pollen polysaccharides and sulfated polysaccharides on ulcerative colitis and gut flora in mice. Polymers. (2023) 15:1414. doi: 10.3390/polym15061414
168. Li Y, Li Q, Niu H, Li H, Jiao L, Wu W. UHPLC-MS-based metabolomics reveal the potential mechanism of armillaria mellea acid polysaccharide in and its effects on cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed mice. Molecules. (2023) 28:7944. doi: 10.3390/molecules28247944
169. Wassie T, Cheng B, Zhou T, Gao L, Lu Z, Xie C, et al. Microbiome-metabolome analysis reveals alterations in the composition and metabolism of caecal microbiota and metabolites with dietary Enteromorpha polysaccharide and Yeast glycoprotein in chickens. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:996897. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.996897
170. Khan T, Date A, Chawda H, Patel K. Polysaccharides as potential anticancer agents—A review of their progress. Carbohydr Polym. (2019) 210:412–28. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.01.064
171. O’Riordan K, Lee JC. Staphylococcus aureusCapsular polysaccharides. Clin Microbiol Rev. (2004) 17:218–34. doi: 10.1128/cmr.17.1.218-234.2004
172. Leene CHM, Dieleman LA. Inulin and oligofructose in chronic inflammatory bowel disease. J Nutr. (2007) 137:2572S–5S. doi: 10.1093/jn/137.11.2572S
173. Zong S, Li J, Ye Z, Zhang X, Yang L, Chen X, et al. Lachnum polysaccharide suppresses S180 sarcoma by boosting anti-tumor immune responses and skewing tumor-associated macrophages toward M1 phenotype. Int J Biol Macromol. (2020) 144:1022–33. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.09.179
174. Yang K, Chen J, Chen J, Wang Z, Song B, Li R, et al. The effect mechanism of polysaccharides inhibit tumor immune escape: A review. J Funct Foods. (2023) 107:105638. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2023.105638
175. Zhang Y, Wang D, Tan D, Zou A, Wang Z, Gong H, et al. Immune-enhancing activity of compound polysaccharide on the inactivated influenza vaccine. Carbohydr Polym. (2024) 336:122080. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2024.122080
176. Micoli F, Alfini R, Di Benedetto R, Necchi F, Schiavo F, Mancini F, et al. Generalized modules for membrane antigens as carrier for polysaccharides: impact of sugar length, density, and attachment site on the immune response elicited in animal models. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:719315. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.719315
177. Pletz MW, Bahrs C. Erratum zu: pneumokokkenimpfstoffe. Der Internist. (2021) 62:1256–6. doi: 10.1007/s00108-021-01175-x
178. Correia-Pinto JF, Csaba N, Alonso MJ. Vaccine delivery carriers: Insights and future perspectives. Int J Pharma. (2013) 440:27–38. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2012.04.047
179. Brogden KA. Antimicrobial peptides: pore formers or metabolic inhibitors in bacteria? Nat Rev Microbiol. (2005) 3:238–50. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1098
180. Reyes AWB, Hong TG, Hop HT, Arayan LT, Huy TXN, Min W, et al. The in vitro and in vivo protective effects of tannin derivatives against Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection. Microb Pathogen. (2017) 109:86–93. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.05.034
181. Guo L, Ma R, Sun H, Raza A, Tang J, Li Z. Anti-inflammatory activities and related mechanism of polysaccharides isolated from sargentodoxa cuneata. Chem Biodivers. (2018) 15:e1800343. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201800343
182. Wang C-Y, Wu T-C, Hsieh S-L, Tsai Y-H, Yeh C-W, Huang C-Y. Antioxidant activity and growth inhibition of human colon cancer cells by crude and purified fucoidan preparations extracted from Sargassum cristaefolium. J Food Drug Anal. (2015) 23:766–77. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2015.07.002
183. Zhang W, Zhang X, Zou K, Xie J, Zhao S, Liu J, et al. Seabuckthorn berry polysaccharide protects against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice via anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory activities. Food Funct. (2017) 8:3130–8. doi: 10.1039/c7fo00399d
184. Parida SK, Domann E, Rohde M, Müller S, Darji A, Hain T, et al. Internalin B is essential for adhesion and mediates the invasion of Listeria monocytogenes into human endothelial cells. Mol Microbiol. (1998) 28:81–93. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.00776
185. Abrams MT, Koser ML, Seitzer J, Williams SC, DiPietro MA, Wang W, et al. Evaluation of efficacy, biodistribution, and inflammation for a potent siRNA nanoparticle: effect of dexamethasone co-treatment. Mol Ther. (2010) 18:171–80. doi: 10.1038/mt.2009.208
186. Im D-S. Pro-resolving effect of ginsenosides as an anti-inflammatory mechanism of panax ginseng. Biomolecules. (2020) 10:444. doi: 10.3390/biom10030444
187. Park C-H, Min S-Y, Yu H-W, Kim K, Kim S, Lee H-J, et al. Effects of apigenin on RBL-2H3, RAW264.7, and haCaT cells: anti-allergic, anti-inflammatory, and skin-protective activities. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:4620. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134620
188. Zhu F, Du B, Xu B. Anti-inflammatory effects of phytochemicals from fruits, vegetables, and food legumes: A review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2017) 58:1260–70. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2016.1251390
189. Chen H, Sun J, Liu J, Gou Y, Zhang X, Wu X, et al. Structural characterization and anti-inflammatory activity of alkali-soluble polysaccharides from purple sweet potato. Int J Biol Macromol. (2019) 131:484–94. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.126
190. Shi Y, Xiong Q, Wang X, Li X, Yu C, Wu J, et al. Characterization of a novel purified polysaccharide from the flesh of Cipangopaludina chinensis. Carbohydr Polym. (2016) 136:875–83. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.09.062
191. Xiong Q, Hao H, He L, Jing Y, Xu T, Chen J, et al. Anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic activities of a purified polysaccharide from flesh of Cipangopaludina chinensis. Carbohydr Polym. (2017) 176:152–9. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.08.073
Keywords: polysaccharides, immunity, immune regulation, natural polysaccharides, gut microbiota, immunostimulatory activity
Citation: Shen Y, Zhao H, Wang X, Wu S, Wang Y, Wang C, Zhang Y and Zhao H (2024) Unraveling the web of defense: the crucial role of polysaccharides in immunity. Front. Immunol. 15:1406213. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1406213
Received: 24 March 2024; Accepted: 07 October 2024;
Published: 25 October 2024.
Edited by:
Genlin Zhang, Shihezi University, ChinaReviewed by:
Lanzhou Li, Jilin Agricultural University, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Shen, Zhao, Wang, Wu, Wang, Wang, Zhang and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hong Zhao, zhaohong1981@jmsu.edu.cn; Yu Zhang, zhangyu@jmsu.edu.cn
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.