- 1Medicine Department, Hamad Medical Corporation, Doha, Qatar
- 2Jaber AlAhmed Hospital, Ministry of Health, Kuwait City, Kuwait
- 3Department of Translational Research, Dasman Diabetes Institute, Kuwait City, Kuwait
- 4Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Dasman Diabetes Institute, Kuwait City, Kuwait
- 5Pharmacy Department, Hamad Medical Corporation, Doha, Qatar
- 6Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland, Medical University of Bahrain, Manama, Bahrain
- 7Pharmacology and Therapeutics Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, Kuwait University, Kuwait City, Kuwait
- 8Dasman Diabetes Institute, Kuwait City, Kuwait
- 9Division of Diabetes, University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, TX, United States
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, has emerged as a rapidly spreading contagious disease across the globe. Recent studies showed that people with diabetes mellitus, severe obesity, and cardiovascular disease are at higher risk of mortality from COVID-19. It has been suggested that the increased risk is due to the chronic inflammatory state associated with type 2 diabetes. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of pioglitazone, a strong insulin sensitizer with anti-inflammatory properties, in improving the clinical outcomes of patients with type 2 diabetes admitted with moderate–severe COVID-19.
Method: We enrolled 350 patients with type 2 diabetes who were admitted to hospitals in Qatar and Kuwait with COVID-19. Patients were randomized to receive, in a double-blind fashion, pioglitazone (n = 189) or a matching placebo (n = 161) for 28 days. The study had two primary outcomes: (1) the incidence of a composite outcome composed of (a) the requirement for mechanical ventilation, (b) death, and (c) myocardial damage; and (2) an increase in C-reactive protein (CRP) levels.
Results: The first primary outcome occurred in 28 participants (8%), and the secondary outcome occurred in 17. Treatment with pioglitazone showed a significant reduction in interleukin (IL)-3 levels compared with placebo treatment (mean (SD) 2.73 (± 2.14) [95% CI: 0.02, 1.1], p = 0.043 vs. 2.28 (± 1.67) [95% CI: − 0.23, 0.86], p = 0.3, respectively), with no effect seen in the levels of other inflammatory markers. Even though not significant, a few of the patients on pioglitazone exhibited serum troponin levels > 3 times higher than the normal range seen in patients on placebo. On the other hand, more patients on pioglitazone were admitted to the ICU than those with placebo, and no significant difference in the CRP reduction was observed between the two groups.
Conclusion: The results of the present study demonstrate that pioglitazone treatment did not independently provide any additional clinical benefit to patients with type 2 diabetes admitted with a COVID-19 infection.
Clinical trial registration: https://clinicaltrials.gov, identifier NCT04604223.
Introduction
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a type of acute respiratory syndrome that is caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus and has emerged as a fast-spreading communicable disease impacting most countries across the globe (1). Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the third coronavirus to cause serious human infections, following the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) in 2002 and the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) (2, 3). Coronaviruses are a family of enveloped viruses encoded by a large single-stranded positive-sense RNA genome and named for the crown-like appearance of their virions under electron microscopy. The key feature of SARS-CoV-2 that differentiates this virus from others is its ease of transmissibility combined with a greater risk of mortality from acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). The clinical manifestations of COVID-19 may range from asymptomatic infections to mild upper respiratory tract infections (20%–86% of all conditions). Approximately 10%–15% of patients with COVID-19 may develop a severe illness characterized by respiratory distress, an increased risk of clotting disease, myocardial damage, stroke, and mortality.
People with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), severe obesity, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and hypertension are at higher risk of developing severe COVID-19 infections and mortality (4–8). While the reasons behind this increased risk are yet to be discovered, a panoply of factors may contribute to the increased susceptibility of patients with T2DM to COVID-19 infection. Exuberant inflammatory and immune responses were primarily thought to be responsible for the etiology of severe COVID-19 disease and death. The increased chronic inflammatory state characteristic of T2DM could contribute to the increased risk of severe COVID-19 disease in these patients. Obese and obese-diabetic patients generally have impaired innate and adaptive immune responses, characterized by a state of chronic and low-grade inflammation (9). This may lead to abrupt systemic metabolic alterations characterized by higher leptin (a proinflammatory adipokine) and lower adiponectin (an anti-inflammatory adipokine) levels, which may lead to dysregulated immune responses (10). Furthermore, obese people have enhanced production of pro-inflammatory cytokines like tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), and interleukin (IL)-6 (11). Obesity-related chronic inflammation reduces macrophage activation and impairs proinflammatory cytokine production (12). This exceptional obesogenic milieu may partly explain the presence of antiviral-resistant and vaccine-escape deviations in the obese population (12, 13). Moreover, B- and T-cell responses are weakened in obese patients, and even more so in obese T2DM patients. After analyzing 70,000 people infected with COVID-19, the Chinese Centre for Disease Control and Prevention reported increased mortality in patients with T2DM (7.3%) compared to the general population (2.3%) (14).
Clinical studies have demonstrated that anti-inflammatory therapy with dexamethasone significantly improved the outcome of COVID-19-infected patients. Pioglitazone is a strong insulin sensitizer that reduces plasma glucose concentrations in T2DM patients. Several studies have demonstrated that pioglitazone treatment, besides improving insulin sensitivity, reduces chronic inflammation in T2DM patients, which is manifested by a decrease in the levels of TNF-α, IL-6, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (CRP) (hsCRP), leptin, and other inflammatory markers (15). Furthermore, pioglitazone enhances the plasma level of anti-inflammatory agents (16). For example, the plasma level of 15-epi-lipoxin A, a lipid mediator with strong anti-inflammatory and inflammation-resolving effects that have been reported to neutralize RNA-coated viruses, is significantly elevated by pioglitazone treatment in T2DM patients (17). Therefore, the aim of the present study is to test the hypothesis that administering pioglitazone to T2DM patients who have moderate-to-severe COVID-19 will improve their clinical outcomes.
Method
Study design
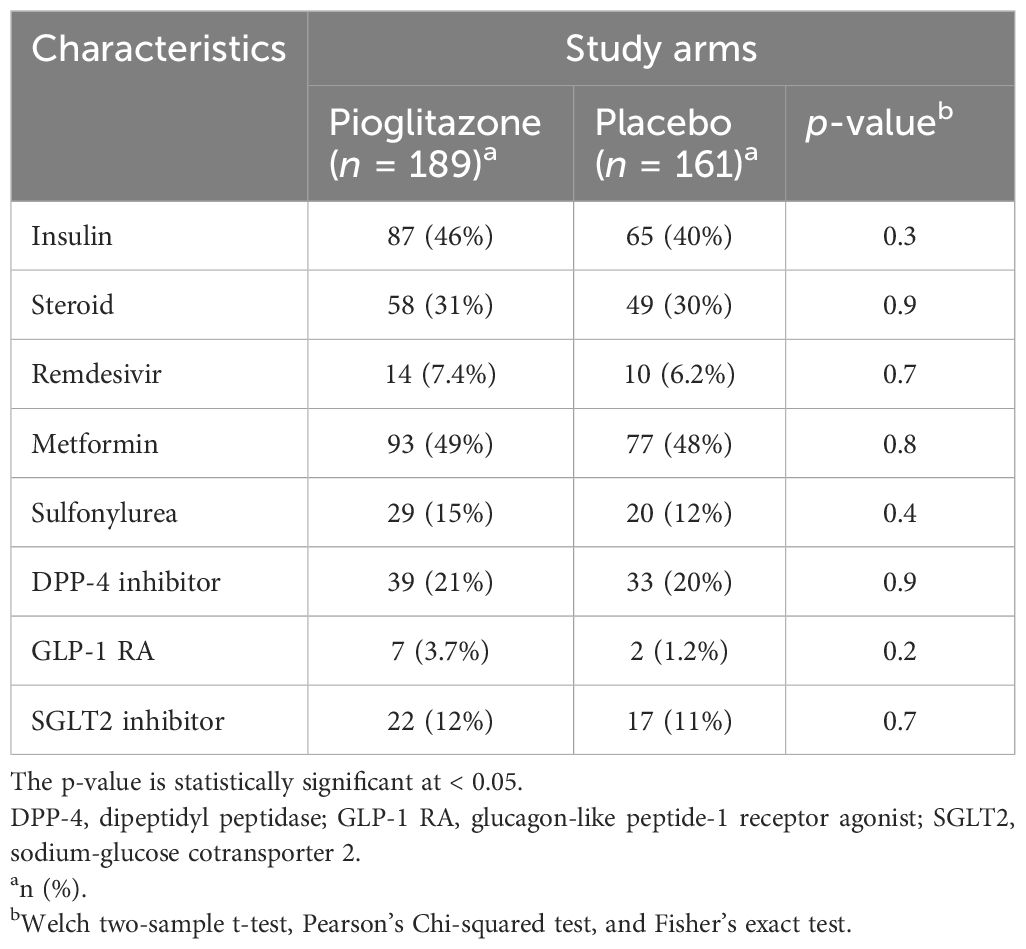
The study was a prospective, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial (NCT04604223) aimed at examining the effect of pioglitazone administration on COVID-19 outcome and inflammatory markers in T2DM patients admitted to the hospital because of COVID-19 infection. The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board at Dasman Diabetes Institute. Informed written consent was obtained from study participants prior to enrollment in the study. After evaluation for eligibility criteria (as listed in Supplementary Table S1), eligible subjects were randomized to receive for 28 days or upon discharge from the hospital the following: (1) pioglitazone 45 mg/day; or a (2) matching placebo. The randomization was done by the hospital pharmacist, and the randomization code was kept safe and confidential in the pharmacy. Patients were randomized according to age, gender, body mass index (BMI), baseline medications, background health conditions, diabetes duration, and respiratory rate. Through hospitalization, the investigators were instructed to lower the fasting plasma glucose concentration to 100–120 mg/dL and postprandial glucose to < 160 mg/dL with any glucose-lowering agent except thiazolidinedione.
Blood glucose was monitored daily, and blood samples were drawn at 3, 7, 14, 21, and 28 days for the measurement of CRP (coprimary outcome), other inflammatory markers, complete blood count (CBC), full chemistry panel including liver function test (LFT), renal function test (RFT), lipid profile, blood gases, HbA1c, CRP, troponin I, coagulation screen, d-dimers, and ferritin. Additional blood samples (panel 2, for research purposes) were drawn out; the plasma was separated and stored at − 80 for the measurement of the following biomarkers: TNF-α, interleukins 1, 2, 4, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 17, leptin, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), lipoxin A4, and resolvins.
The study had two primary outcomes: (1) clinical income that includes a difference in the incidence at 4 weeks of a composite outcome comprising the following: (a) requirement for mechanical ventilation (invasive [with tracheal tube] or noninvasive); (b) myocardial damage measured as plasma troponin I level > 3 times the upper normal limit; and (c) death; and (2) the difference in inflammatory response (measured as plasma hsCRP level) from baseline to 4 weeks between subjects receiving pioglitazone versus placebo. As a secondary outcome, hospitalization duration, the development of acute coronary syndrome (ACS), and mechanical ventilation (both invasive and noninvasive) were considered and recorded.
A previous study in Kuwait has demonstrated that around 24% of T2DM patients admitted to the hospital with COVID-19 symptoms required ICU admission (because of elevated troponin I or need for ventilation) (18). To detect a 25% reduction at study power of 90% by pioglitazone versus placebo in the admission of T2DM patients with COVID-19 admission to ICU at alpha < 0.05, we estimated a sample size of 753 subjects for each group. Thus, we have set the sample size of the study at 1,506. This number of participants provides > 99% power to see a 50% decrease in the plasma interleukin panel. However, due to the reduction in cases of hospitalization after COVID-19 vaccination, we only evaluated 350 cases.
The difference in hsCRP levels between the two treatment groups was compared using ANOVA with adjustments for baseline parameters. The time to the first clinical event (the composite clinical outcome) was analyzed with a Cox proportional hazards model with a factor for the treatment group. The hazard ratio for the occurrence of the composite outcome was compared between the two treatment arms. Statistical significance was set at a p-value ≤ 0.05. For patients who develop more than one event (e.g., have increased troponin and require mechanical ventilation), the time to the first event was used for analysis. A similar approach was used for the secondary outcome between the two treatment groups. Continues variables (such as change in SO2/FiO2 and length of stay in the ICU) were compared using ANOVA. However, discrete variables (such as the number of patients requiring mechanical ventilation and mortality) were compared with the Chi-squared test, and adjustments for multiple comparisons were performed using the Bonferroni test.
Results
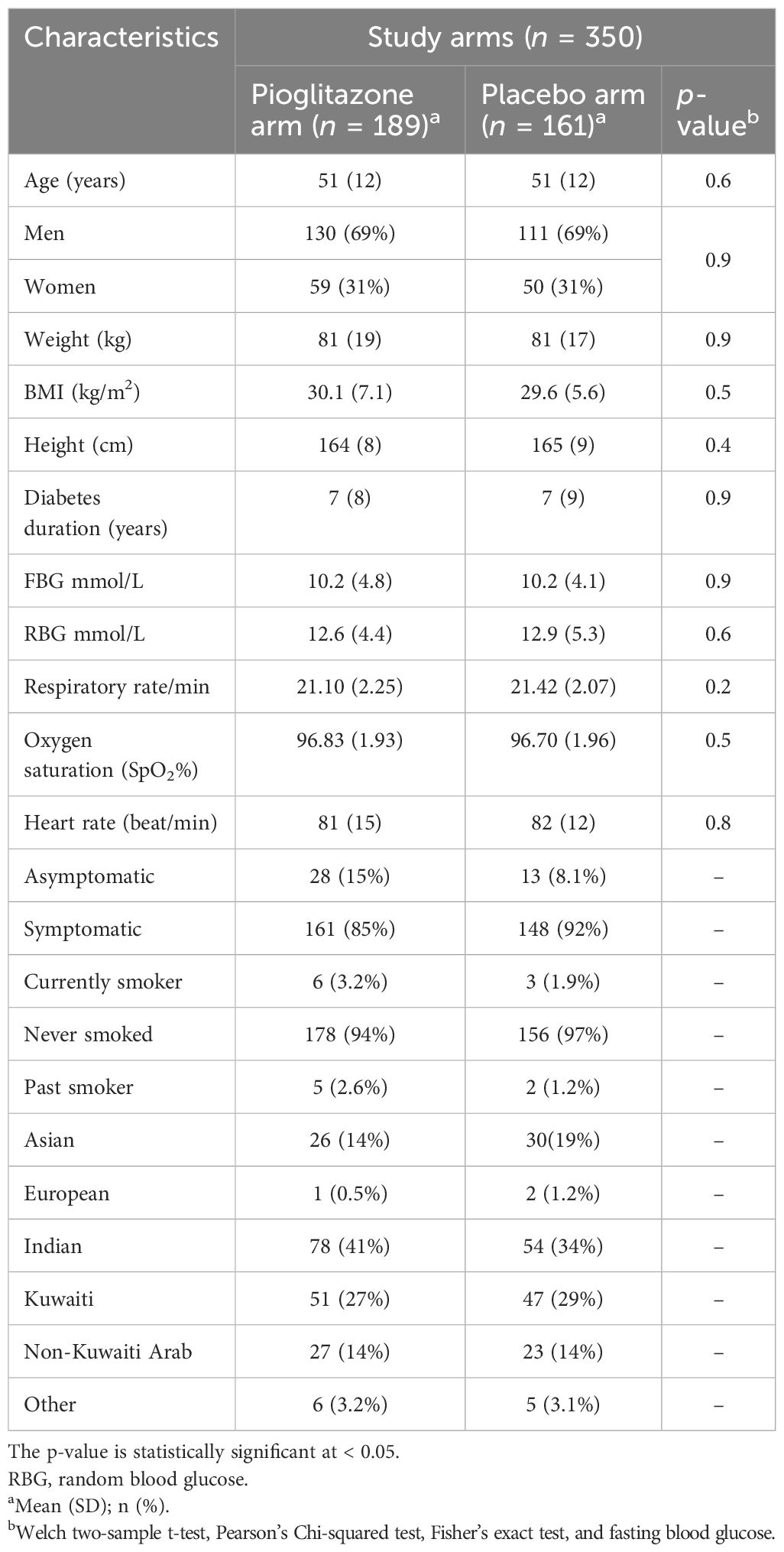
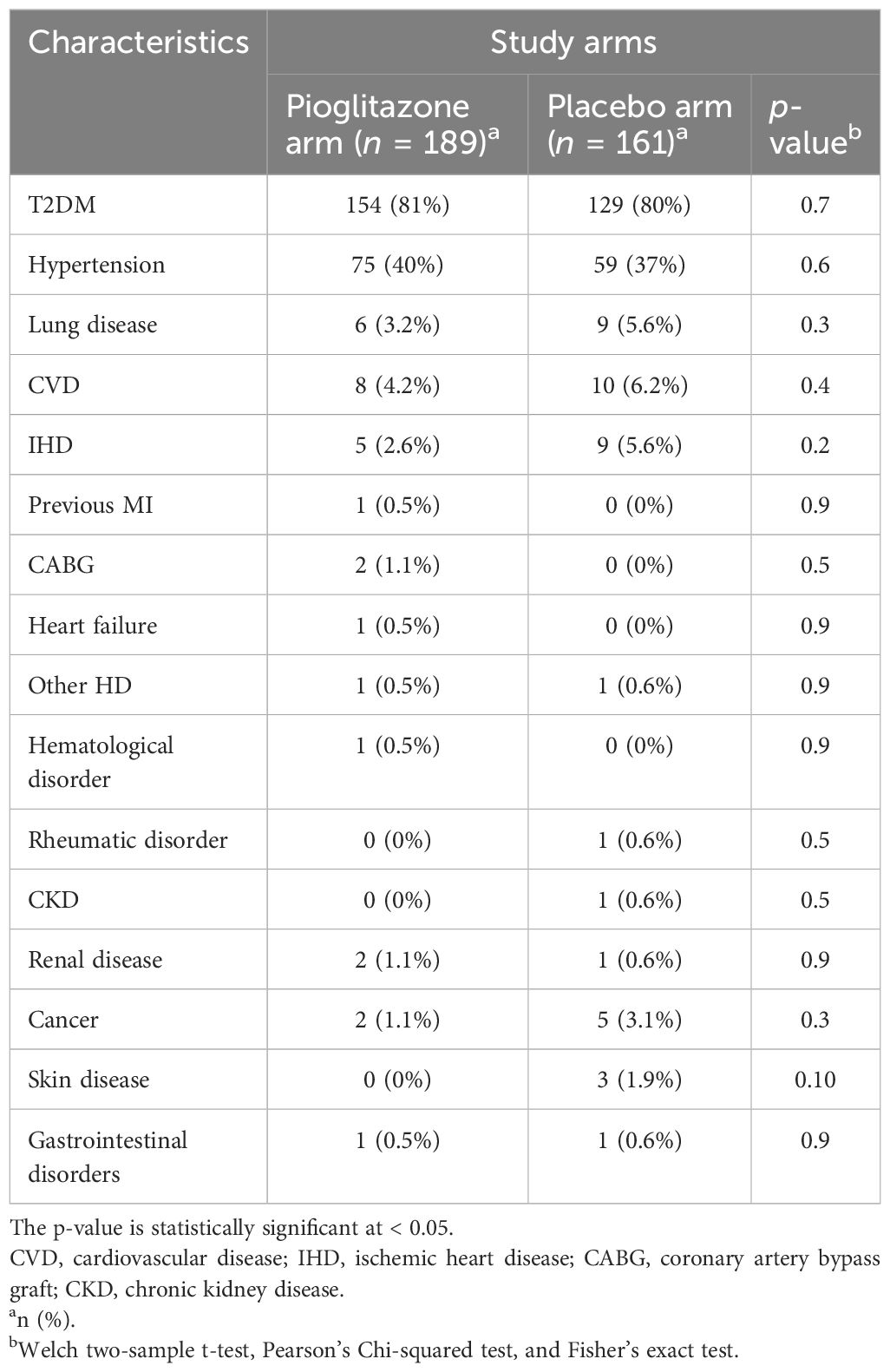
Between September 2020 and September 2021, 355 patients were enrolled in the study, with 189 receiving pioglitazone 45 mg/day and 161 receiving placebo. The baseline and clinical characteristics of the study participants are presented in Tables 1–3. In total, 61.5% of patients were enrolled in Hamad Medical Corporation (HMC), Qatar, and the other 38.5% were enrolled in Kuwait. Patients were largely of middle age and were overweight; two-thirds were men, and approximately 40% had hypertension. Patients in both arms were well-matched in age, gender, BMI, medical history, respiratory status, and baseline glucose-lowering therapy. The plasma glucose level at baseline for pioglitazone- and placebo-treated groups was 10.2 mmol/L and 10.2 mmol/L, respectively (p-value = 0.9).
Effect of pioglitazone on primary outcome
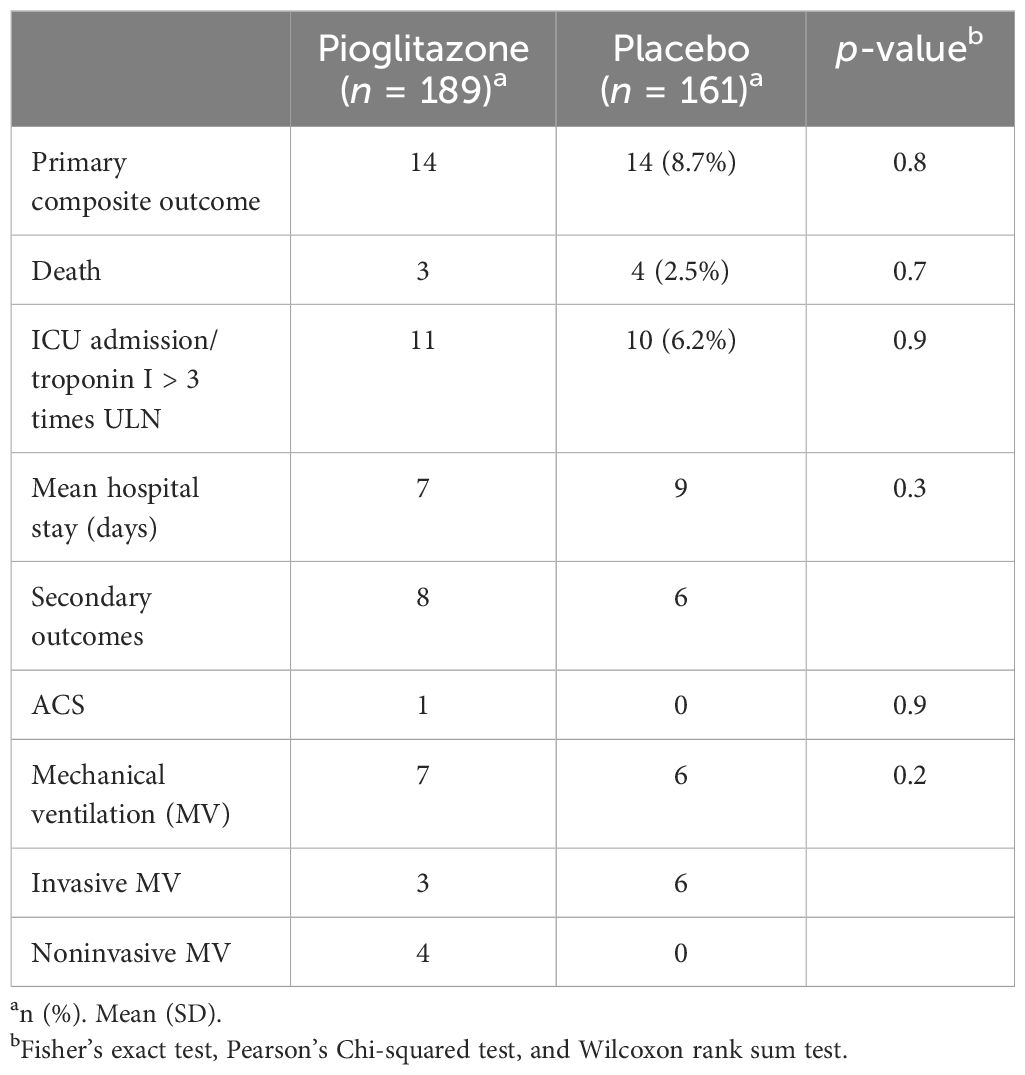
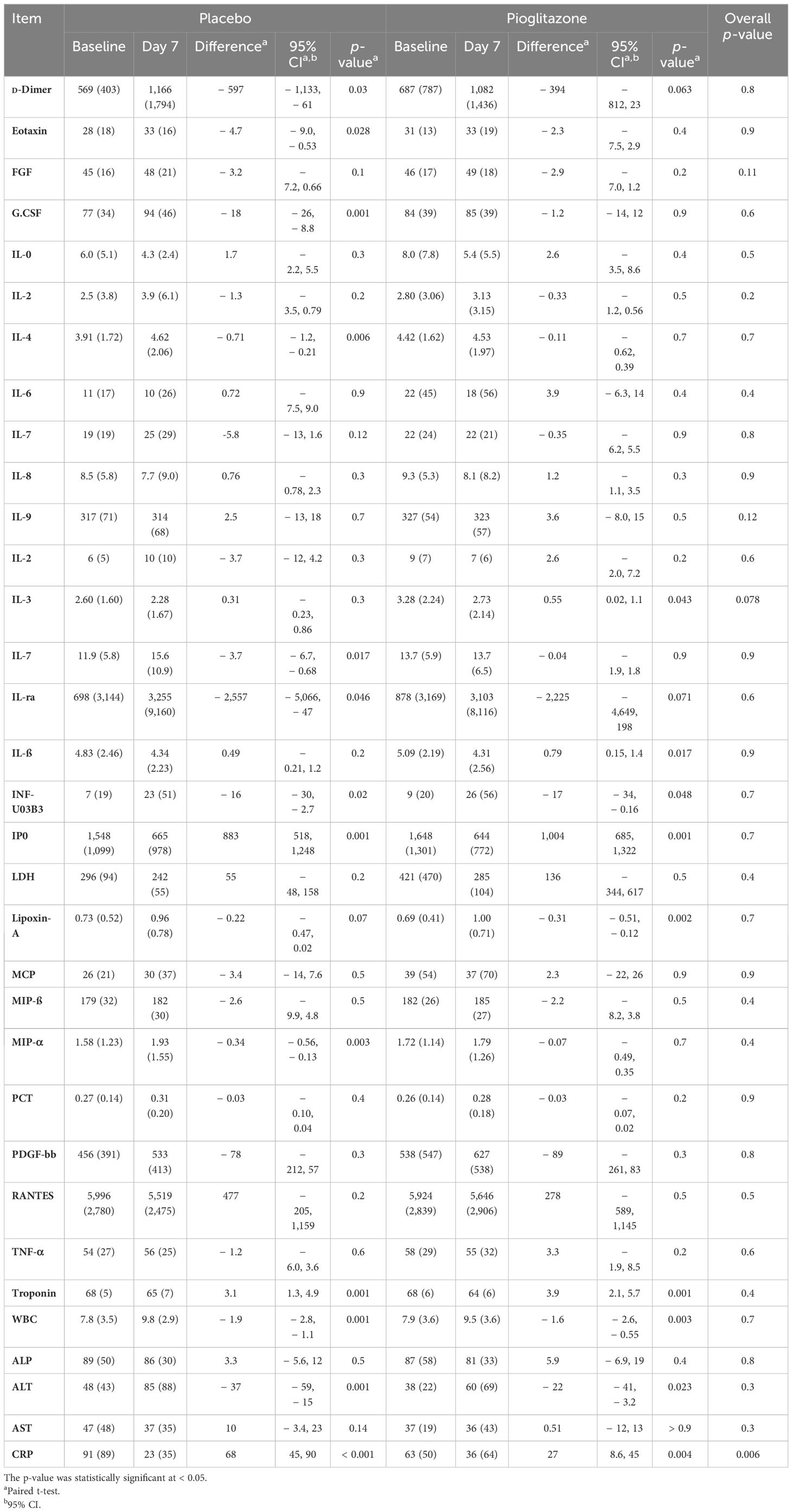
The primary composite outcome occurred in 14 patients receiving pioglitazone (7.8%) and in 14 patients receiving placebo (8.7%), with no significant difference between the two groups. Furthermore, because of the relatively small number of events, the individual components of the primary outcome did not differ. Plasma CRP (the coprimary outcome) decreased significantly from baseline to end of study in both the groups (from 63 ± to 36 ±, p < 0.05 in subjects receiving pioglitazone, and from 81 ± to 23 ± in subjects receiving placebo, p ≤ 0.05). However, the decrease in CRP did not significantly differ among the two groups (p = NS in two-way ANOVA). Likewise, no significant difference was observed in any of the secondary outcomes (Table 4).
Effect of pioglitazone on the inflammatory markers
We also examined the effect of pioglitazone versus placebo on other inflammatory markers. Pioglitazone caused a significant reduction in IL-3 compared to placebo (mean (SD) 2.73 (± 2.14) [95% CI: 0.02, 1.1], p = 0.043 vs. 2.28 (± 1.67) [95% CI: − 0.23, 0.86], p = 0.3, respectively), as seen in Table 5. However, no significant effect was observed on other inflammatory markers.
Discussion
The current study aimed to examine in a randomized, double-blinded fashion the hypothesis of whether pioglitazone will improve the clinical outcome in T2DM patients admitted with COVID-19 infection. The results of the present study failed to demonstrate a significant clinical benefit of pioglitazone on the clinical outcome (mortality, cardiac damage, or ICU admission) in T2DM patients admitted with COVID-19 infection. Moreover, the results of the present study failed to demonstrate a reduction in inflammatory markers in patients receiving pioglitazone versus placebo, despite the consistent reduction in inflammatory markers in T2DM patients receiving pioglitazone for glucose control. Because all participants in the present study had a more severe COVID-19 infection that required hospitalization and received therapy with dexamethasone, which is a powerful anti-inflammatory agent, it is likely that it masked the anti-inflammatory action of pioglitazone. Consistent with this notion, CRP was significantly and similarly reduced at the end of the study in both treatment groups.
Previous retrospective analysis has reported a 29% reduction in hospital admission in T2DM patients receiving pioglitazone compared to other glucose-lowering agents in T2DM patients with proven COVID-19 infection (19). Since participants in that study included individuals with a milder COVID-19 infection than those in the present study and none of the participants had received dexamethasone, pioglitazone had a positive effect on reducing the hospitalization rate. Thus, it is possible that the clinical benefit of pioglitazone is limited to patients with mild COVID-19 infection; however, its clinical efficacy is diminished in patients with severe COVID-19 infection receiving dexamethasone.
In a recent, multicenter retrospective cohort study of patients with T2DM infected with COVID-19, pioglitazone showed a significant reduction in the level of hospitalization and mortality when compared with other diabetes treatments (19). However, despite the previous COVID-19 pandemic, there is still no definitive treatment for COVID-19, and most of the published studies hypothesize that pioglitazone has an anti-inflammatory effect by regulating the inflammatory response (20). In a study of 66 patients with impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) who were randomized to receive pioglitazone or placebo for 4–5 months, treatment with pioglitazone was associated with a significant reduction in the monocytes and lymphocytes (21). Several pathways have been postulated for the inflammatory response to COVID-19. For example, lipoxins are endogenous mediators derived from arachidonic acid metabolism via the lipoxygenase pathway. In leukocytes (neutrophils), while interacting with endothelial cells, arachidonic acid, mainly leukotrienes (proinflammatory mediators) and lipoxins, may be generated via the lipoxygenase pathway. Lipoxin A4 (LXA4) is generated from arachidonic acid via two main pathways: via 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) conversion to leukotriene A4 (LTA4) and then 12-LO conversion; or via 15-LO conversion to 15-hydroxy-peroxy eicosatetraenoic acid (15-HPETE) and then 5-LO conversion. 15-epi-LXA4 is another lipoxin analog produced via arachidonic acid but involves a different pathway (22). Their anti-inflammatory effects are mediated via the dysregulation of TNF-α. In a rat model of sepsis, LXA4 administration improved their survival and reduced systemic inflammation by lowering blood bacterial load and the plasma levels of inflammatory markers such as IL-6, monocyte chemotactic protein 1, and IL-10 (22). Furthermore, LXA4 had other anti-inflammatory effects by reducing bacterial virulence and decreasing the release of exotoxin (23). Several studies have shown that the anti-inflammatory actions of LXA4 and analogs (including 15-epi-LXA4) are comparable to those of glucocorticoids and NSAIDs, yet at times more potent than NSAIDs, in various models of inflammation (24, 25).
In a multinational retrospective study in patients with type 2 diabetes, the use of pioglitazone 6 months prior to the diagnosis of COVID-19 was associated with a relative reduction of 29.2% in hospital admissions for COVID-19 but showed no effect on pulmonary complications or mortality (19). One postulated mechanism for the pioglitazone effect on COVID-19 is via inhibition of acyl-coenzyme A synthetase long-chain family member 4 (ACSL4), which is known to regulate an iron-dependent programmed cell death process called ferroptosis. ACSL4 is known to catalyze arachidonic acid into acyl-CoA and mediate eicosanoid biosynthesis. A recent study indicated that both coronaviruses and enteroviruses can induce ferroptosis via ACSL4 and that the use of pioglitazone or rosiglitazone (known ferroptosis inhibitors) decreased the viral titers of these two viruses, including SARS-CoV-2 (26). Similarly, in another in vitro study, pioglitazone significantly reduced the release of SARS-CoV-2 virion in several cell culture types, indicating its potential as an antiviral drug (27). Lastly, a recent study involving machine learning algorithms identified seven lipophagy-related biomarkers for COVID-19, with one gene called PLIN2. The study showed that PLIN2 gene expression was reduced significantly by treatment with pioglitazone and rosiglitazone (28).
The strength of the current study is that it was a prospective, randomized, double-blinded trial, eliminating any potential risk of bias influencing the results. Moreover, the study included a relatively large number of participants, making the outcome positively generalized and applicable. However, a more robust clinical trial with a larger cohort is still needed to add to the existing evidence.
In conclusion, the study hypothesized that pioglitazone could impact COVID-19-infected patients by reducing inflammatory markers such as IL-3 and CRP. However, the study found no significant independent effect of pioglitazone on COVID-19 patients with T2DM.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethical Review Committees of both Dasman Diabetes Institute, Kuwait, and Medical Research Center, Hamad Medical Corporation, Qatar. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
KB: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. TA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. MA-F: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. JA: Writing – review & editing. HAlh: Writing – review & editing. JF: Writing – review & editing. MH: Writing – review & editing. AO: Writing – review & editing. SA: Writing – review & editing. MZ-U: Writing – review & editing. AS: Writing – review & editing. BA: Writing – review & editing. MB: Writing – review & editing. AA: Writing – review & editing. HC: Writing – review & editing. EE: Writing – review & editing. IA-K: Writing – review & editing. PC: Writing – review & editing. LJ: Writing – review & editing. MA: Writing – review & editing. MQ: Writing – review & editing. SH: Writing – review & editing. AE: Writing – review & editing. AA-A: Writing – review & editing. AC: Writing – review & editing. SD: Writing – review & editing. HAli: Writing – review & editing. AT: Writing – review & editing. SA-S: Writing – review & editing. FA-M: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. MA-G: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AJ: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The authors declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This project was funded by the Kuwait Foundation for the Advancement of Sciences grant number RA HM 2020-011, and the Medical Research Center, Hamad Medical Corporation grant number MRC-01-20-784.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Jaber Hospital management and to Dr. Clara Garcia Enriquez, Mr. Yunel Gainza Matos, and Mr. Mario Esteban del Rey; Laboratory Department, Cuban Hospital, Hamad Medical Corporation, Doha, Qatar; and Qatar Biobank.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1369918/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Walls AC, Park YJ, Tortorici MA, Wall A, McGuire AT, Veesler D. Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-coV-2 spike glycoprotein. Cell. (2020). 181:281–92. doi: 10.1101/2020.02.19.956581
2. Zhou J, Chu H, Chan JF, Yuen KY. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection: virus-host cell interactions and implications on pathogenesis. Virol J. (2015) 12:218. doi: 10.1186/s12985-015-0446-6
3. Chan JF, Lau SK, To KK, Cheng VC, Woo PC, Yuen KY. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus: another zoonotic betacoronavirus causing SARS-like disease. Clin Microbiol Rev. (2015) 28:465–522. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00102-14
4. Muniyappa R, Gubbi S. COVID-19 pandemic, corona viruses, and diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2020) 318:E736–41. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00124.2020
5. Onder G, Rezza G, Brusaferro S. Case-fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy. JAMA. (2020) 323:1775–6. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4683
6. Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu Z, et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. (2020) 395:1054–62. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
7. Wu C, Chen X, Cai Y, Xia J, Zhou X, Xu S, et al. Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern Med. (2020) 180:934–43. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994
8. Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX, et al. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. (2020) 382:1708–20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2002032
9. Andersen CJ, Murphy KE, Fernandez ML. Impact of obesity and metabolic syndrome on immunity. Adv Nutr. (2016) 7:66–75. doi: 10.3945/an.115.010207
10. Ouchi N, Parker JL, Lugus JJ, Walsh K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat Rev Immunol. (2011) 11:85–97. doi: 10.1038/nri2921
11. Richard C, Wadowski M, Goruk S, Cameron L, Sharma AM, Field CJ. Individuals with obesity and type 2 diabetes have additional immune dysfunction compared with obese individuals who are metabolically healthy. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. (2017) 5:e000379. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2016-000379
12. Luzi L, Radaelli MG. Influenza and obesity: its odd relationship and the lessons for COVID-19 pandemic. Acta Diabetol. (2020) 57(6):759–764. doi: 10.1007/s00592-020-01522-8
13. Karlsson EA, Hertz T, Johnson C, Mehle A, Krammer F, Schultz-Cherry S. Obesity outweighs protection conferred by adjuvanted influenza vaccination. mBio. (2016) 7. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01144-16
14. Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention. JAMA. (2020) 323:1239–42. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.2648
15. Yu HJ, Wang LJ, Huang K, Guo QF, Lin BY, Liu YY, et al. PPAR-gamma agonist pioglitazone alleviates inflammatory response induced by lipopolysaccharides in osteoblast cells. J Orthop Res. (2022) 40:2471–9. doi: 10.1002/jor.25279
16. Kaplan J, Nowell M, Chima R, Zingarelli B. Pioglitazone reduces inflammation through inhibition of NF-kappaB in polymicrobial sepsis. Innate Immun. (2014) 20:519–28. doi: 10.1177/1753425913501565
17. Gutierrez AD, Sathyanarayana P, Konduru S, Ye Y, Birnbaum Y, Bajaj M. The effect of pioglitazone treatment on 15-epi-lipoxin A4 levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. Atherosclerosis. (2012) 223:204–8. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2012.04.016
18. Kipourou DK, Leyrat C, Alsheridah N, Almazeedi S, Al-Youha S, Jamal MH, et al. Probabilities of ICU admission and hospital discharge according to patient characteristics in the designated COVID-19 hospital of Kuwait. BMC Public Health. (2021) 21:799. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-10759-z
19. Nyland JE, Raja-Khan NT, Bettermann K, Haouzi PA, Leslie DL, Kraschnewski JL, et al. Diabetes, drug treatment, and mortality in COVID-19: A multinational retrospective cohort study. Diabetes. (2021) 70:2903–16. doi: 10.2337/db21-0385
20. Hasankhani A, Bahrami A, Tavakoli-Far B, Iranshahi S, Ghaemi F, Akbarizadeh MR, et al. The role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in the modulation of hyperinflammation induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection: A perspective for COVID-19 therapy. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1127358. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1127358
21. Zhang WY, Schwartz EA, Permana PA, Reaven PD. Pioglitazone inhibits the expression of inflammatory cytokines from both monocytes and lymphocytes in patients with impaired glucose tolerance. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2008) 28:2312–8. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.175687
22. Chandrasekharan JA, Sharma-Walia N. Lipoxins: nature’s way to resolve inflammation. J Inflammation Res. (2015) 8:181–92. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S90380
23. Walker J, Dichter E, Lacorte G, Kerner D, Spur B, Rodriguez A, et al. Lipoxin a4 increases survival by decreasing systemic inflammation and bacterial load in sepsis. Shock. (2011) 36:410–6. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e31822798c1
24. Liu X, Wang X, Duan X, Poorun D, Xu J, Zhang S, et al. Lipoxin A4 and its analog suppress inflammation by modulating HMGB1 translocation and expression in psoriasis. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:7100. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07485-1
25. Wu B, Walker JA, Temmermand D, Mian K, Spur B, Rodriguez A, et al. Lipoxin A(4) promotes more complete inflammation resolution in sepsis compared to stable lipoxin A(4) analog. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. (2013) 89:47–53. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2013.04.005
26. Kung YA, Chiang HJ, Li ML, Gong YN, Chiu HP, Hung CT, et al. Acyl-coenzyme A synthetase long-chain family member 4 is involved in viral replication organelle formation and facilitates virus replication via ferroptosis. mBio. (2022) 13:e0271721. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02717-21
27. Setz C, Grosse M, Auth J, Froba M, Rauch P, Bausch A, et al. Synergistic antiviral activity of pamapimod and pioglitazone against SARS-coV-2 and its variants of concern. Int J Mol Sci 23. (2022) 23. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126830
Keywords: COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, inflammation, type 2 diabetes, pioglitazone
Citation: Baagar K, Alessa T, Abu-Farha M, Abubaker J, Alhumaidi H, Franco Ceruto JA, Hamad MK, Omrani A, Abdelrahman S, Zaka-Ul Haq M, Safi AW, Alhariri B, Barman M, Abdelmajid A, Cancio HVD, Elmekaty E, Al-Khairi I, Cherian P, Jayyousi L, Ahmed M, Qaddoumi M, Hajji S, Esmaeel A, Al-Andaleeb A, Channanath A, Devarajan S, Ali H, Thanaraj TA, Al-Sabah S, Al-Mulla F, Abdul-Ghani M and Jayyousi A (2024) Effect of pioglitazone on inflammatory response and clinical outcome in T2DM patients with COVID-19: a randomized multicenter double-blind clinical trial. Front. Immunol. 15:1369918. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1369918
Received: 13 January 2024; Accepted: 12 August 2024;
Published: 06 September 2024.
Edited by:
Romina Salpini, University of Rome Tor Vergata, ItalyReviewed by:
Egidia Miftode, Grigore T. Popa University of Medicine and Pharmacy, RomaniaStelvio Tonello, University of Eastern Piedmont, Italy
Copyright © 2024 Baagar, Alessa, Abu-Farha, Abubaker, Alhumaidi, Franco Ceruto, Hamad, Omrani, Abdelrahman, Zaka-Ul Haq, Safi, Alhariri, Barman, Abdelmajid, Cancio, Elmekaty, Al-Khairi, Cherian, Jayyousi, Ahmed, Qaddoumi, Hajji, Esmaeel, Al-Andaleeb, Channanath, Devarajan, Ali, Thanaraj, Al-Sabah, Al-Mulla, Abdul-Ghani and Jayyousi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Amin Jayyousi, YWpheXlvdXNpQGhhbWFkLnFh; Muhammad Abdul-Ghani, YWJkdWxnaGFuaUB1dGhzY3NhLmVkdQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Khaled Baagar
Khaled Baagar Thamer Alessa
Thamer Alessa Mohamed Abu-Farha
Mohamed Abu-Farha Jehad Abubaker
Jehad Abubaker Heba Alhumaidi2
Heba Alhumaidi2 Jose Antonio Franco Ceruto
Jose Antonio Franco Ceruto Ali Omrani
Ali Omrani Bassem Alhariri
Bassem Alhariri Manish Barman
Manish Barman Alaaeldin Abdelmajid
Alaaeldin Abdelmajid Eman Elmekaty
Eman Elmekaty Irina Al-Khairi
Irina Al-Khairi Preethi Cherian
Preethi Cherian Mohammed Qaddoumi
Mohammed Qaddoumi Sulaiman Hajji
Sulaiman Hajji Arshad Channanath
Arshad Channanath Sriraman Devarajan
Sriraman Devarajan Hamad Ali
Hamad Ali Thangavel Alphonse Thanaraj
Thangavel Alphonse Thanaraj Salman Al-Sabah
Salman Al-Sabah Fahd Al-Mulla
Fahd Al-Mulla Muhammad Abdul-Ghani
Muhammad Abdul-Ghani Amin Jayyousi
Amin Jayyousi