
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Immunol. , 28 June 2023
Sec. Microbial Immunology
Volume 14 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1233307
This article is a correction to:
M(IL-4) Tissue Macrophages Support Efficient Interferon-Gamma Production in Antigen-Specific CD8+ T Cells with Reduced Proliferative Capacity
A Corrigendum on
M(IL-4) tissue macrophages support efficient interferon-gamma production in antigen-specific CD8+ T cells with reduced proliferative capacity
by Mulder R, Banete A, Seaver K and Basta S (2017) Front. Immunol. 8:1629. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01629
In the published article, there was an error in Name of Figure/Table as published. During the final version of figure submission, one plot labelled (TNF) was mistakenly duplicated in Figure 1C. The corrected Name of Figure/Table and its caption appear below. The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
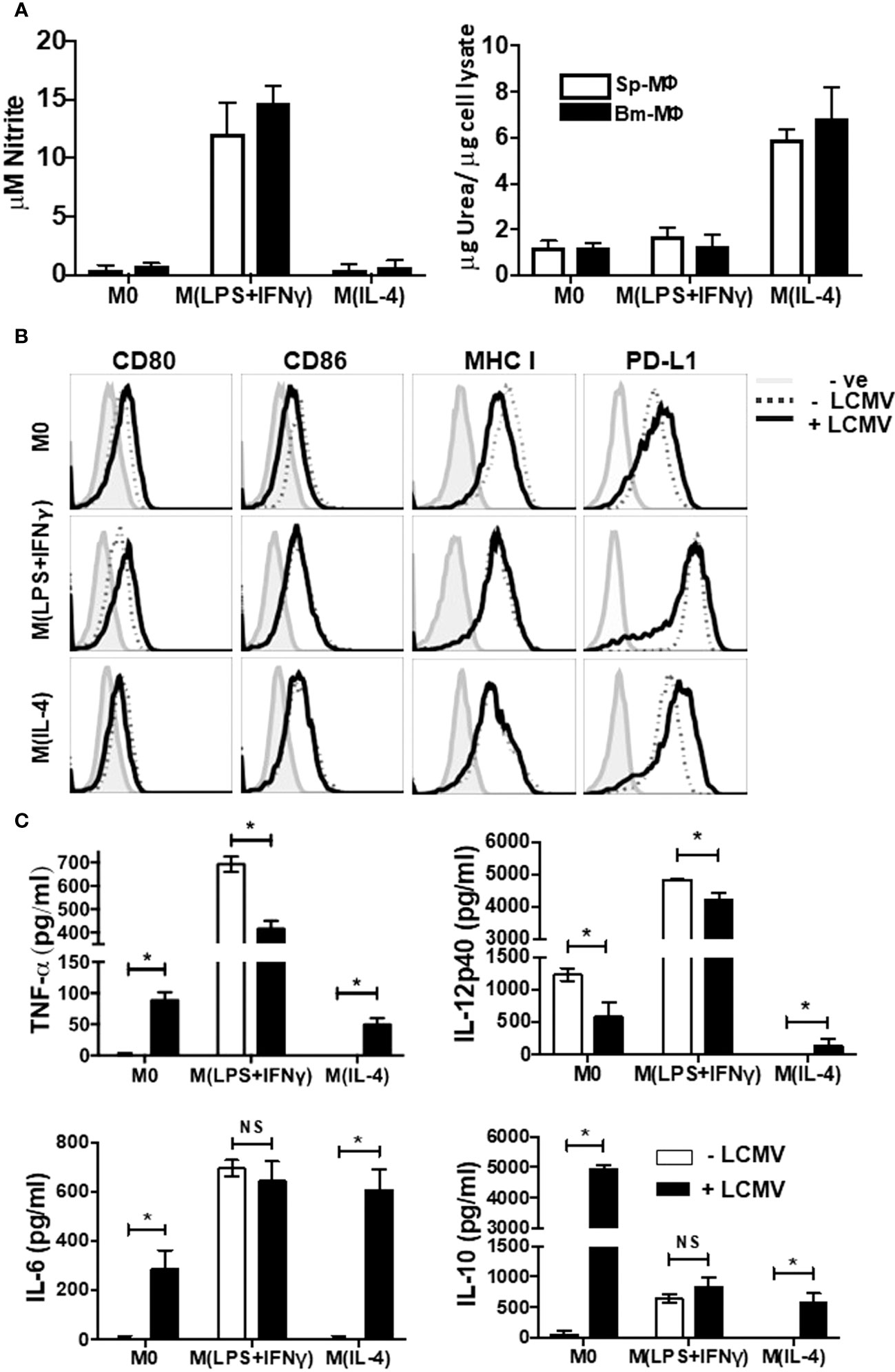
Figure 1 Immunophenotyping of Polarized Macrophages. Activated BM-MΦ or Sp-MΦ populations were polarized into M(LPS + IFN-γ) (25 ng/ml IFN-γ + 100 ng/ml LPS), or M(IL-4) (20 ng/ml IL4) or left un-stimulated. (A) Nitrite detection after BM-MΦ or Sp-MΦ were polarized into M(LPS + IFN-γ) or M(IL-4) or left un-stimulated (left panel). Supernatants were collected before testing them for nitrite production using the Greiss reaction. The OD was measured using Varioskan plate reader to quantify nitrite production after comparing the values to the standard curve. In the right panel, urea production was measured in polarized BMinfected with LCMV-WE (MOI 5M-MΦ and Sp-MΦ samples to monitor arginase activity indicative of M(IL-4) polarization. Values are represented as μg urea corrected to μg cell lysate. Data shown and error bars are the mean ± SD from one representative experiment out of three. (B) Staining profiles of activated polarized BM-MΦ and Sp-MΦ populations that were either controls or infected with LCMV-WE (MOI 5 for 24 h). Histograms show surface staining for CD80, CD86, MHC I or PD-L1 in the various MΦ populations compared to the isotype control (-ve). Data shown are representative from one of two experiments. (C) Cell supernatants from LCMV uninfected or LCMV infected (24 h) polarized Sp-MΦ were subjected to ELISA for quantification of TNF-α, IL-12p40, IL-6 and IL-10. Graphical data show mean ± SD from two independent experiments containing two experimental replicates.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: polarized macrophages, major histocompatibility complex, interleukin-4, interferon-gamma, T cells, lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection
Citation: Mulder R, Banete A, Seaver K and Basta S (2023) Corrigendum: M(IL-4) tissue macrophages support efficient interferon-gamma production in antigen-specific CD8+ T cells with reduced proliferative capacity. Front. Immunol. 14:1233307. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1233307
Received: 01 June 2023; Accepted: 14 June 2023;
Published: 28 June 2023.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Felix Ngosa Toka, Ross University School of Veterinary Medicine, Saint Kitts and NevisCopyright © 2023 Mulder, Banete, Seaver and Basta. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sameh Basta, YmFzdGFzQHF1ZWVuc3UuY2E=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.