
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Immunol., 03 January 2022
Sec. B Cell Biology
Volume 12 - 2021 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.811632
 Zizhang Sheng1,2*†
Zizhang Sheng1,2*† Jude S. Bimela1†
Jude S. Bimela1† Phinikoula S. Katsamba1
Phinikoula S. Katsamba1 Saurabh D. Patel1
Saurabh D. Patel1 Yicheng Guo1,2
Yicheng Guo1,2 Haiqing Zhao3
Haiqing Zhao3 Youzhong Guo4,5
Youzhong Guo4,5 Peter D. Kwong6,7
Peter D. Kwong6,7 Lawrence Shapiro1,2,7*
Lawrence Shapiro1,2,7*Accumulation of somatic hypermutation (SHM) is the primary mechanism to enhance the binding affinity of antibodies to antigens in vivo. However, the structural basis of the effects of many SHMs remains elusive. Here, we integrated atomistic molecular dynamics (MD) simulation and data mining to build a high-throughput structural bioinformatics pipeline to study the effects of individual and combination SHMs on antibody conformation, flexibility, stability, and affinity. By applying this pipeline, we characterized a common mechanism of modulation of heavy-light pairing orientation by frequent SHMs at framework positions 39H, 91H, 38L, and 87L through disruption of a conserved hydrogen-bond network. Q39LH alone and in combination with light chain framework 4 (FWR4L) insertions further modulated the elbow angle between variable and constant domains of many antibodies, resulting in improved binding affinity for a subset of anti-HIV-1 antibodies. Q39LH also alleviated aggregation induced by FWR4L insertion, suggesting remote epistasis between these SHMs. Altogether, this study provides tools and insights for understanding antibody affinity maturation and for engineering functionally improved antibodies.
The affinity maturation process of antibodies or B cell receptors (BCRs) constitutes a microevolution system for antibody improvement (1). During affinity maturation, multiple types of somatic hypermutations (SHMs) (point mutations, insertions and deletions (indels), and sites for post-translational modifications) are incorporated in the BCR variable domain (2, 3). Beneficial SHMs are selected iteratively to optimize the properties of BCRs including antigen-binding affinity as well as the accommodation of antigen variability, flexibility, and physical stability (4–10). In previous studies (11, 12), we built gene-specific substitution profiles (GSSPs) to describe gene-specific hotspots and preferences of point SHMs. We found that SHMs are generated with strong preferences resulting in frequent or dominant convergent mutations, which are commonly observed amongst different antibody lineages (12, 13). Nevertheless, the functional impact and mechanistic basis of numerous SHMs and their combinations remain poorly understood. As mapping the development of functionally important antibody lineages has become commonplace, the need for a “dictionary” to interpret these developmental maps has become clear.
Structurally, the complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) from both heavy and light chains form a paratope, while framework regions (FWRs) of each chain form a 2-layered β-sandwich to present and stabilize the conformations of CDRs (14). SHMs in CDRs undergo frequent antigen-specific selection to optimize the physical non-covalent interactions between paratope and epitope. FWRs are more conserved than CDRs; however, new evidence demonstrates the critical roles of FWR SHMs in both in vivo and in vitro affinity maturation (15–18). In contrast to SHMs in CDRs, many beneficial SHMs in FWRs modulate antibody features remotely by altering the stability and conformations of CDRs, the pairing of specific VH-VL interactions, and the elbow angles between the variable and constant domains (VH-CH1 or VL-CL) (15, 18–23). Because many FWR residues are conserved among germline genes, a FWR SHM could affect antibody features consistently among antibodies with different gene origins, and we thus refer to such consistent affects as a common mechanism of modulation. For example, Koenig et al. showed that dominant SHMs at light chain position 83 [Kabat numbering (24)] alter the elbow angle and VH-VL angle in many antibodies, resulting in changes in antigen-binding affinity and stability (20).
Currently, approaches where structure determination is coupled to biophysical readouts [e.g. X-ray crystallography with surface plasmon resonance (SPR)] are used to characterize mechanisms of affinity improvement by SHMs. However, such approaches are time-consuming and expensive, and it is impractical to undertake such detailed experimental studies to characterize the effects of SHMs in all cases. With the development of high-performance graphics processing unit (GPU) computers, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations have proven effective at evaluating structural alterations by SHMs (25–28). In addition, about 6000 antibody structures are available in the Protein Data Bank (PDB), which form a valuable informative dataset to examine the effects of SHMs on antibody structure. A bioinformatics platform to interrogate this information could provide a fast and low-cost method, complementary to experimental approaches, for understanding the functions of SHMs and the process of antibody-affinity maturation.
In this study, we integrated MD simulation and a non-redundant antibody structure database to investigate SHM-induced conformation changes. We also applied SPR, thermostability measurement, and dynamic light scattering to evaluate the effects of SHMs on antigen-binding affinity, stability, and aggregation propensity respectively. We found a common mechanism of VH-VL conformation modulation by VH-VL interface and elbow interface SHMs and characterized epistasis effects between these SHMs.
To predict the effect of SHM on antibody conformation, we developed a script (MD.pl) to perform multiple steps of MD simulation from energy minimization, heating, equilibration, to production using Amber18 (Details see Materials and Methods) (Figure 1A). We also integrated multiple algorithms to develop a master script (Traj.R) to calculate structural features of antibodies from MD trajectory snapshots and to generate plots including root mean square deviation (RMSD), principle component analysis (PCA), VH-VL angle (six parameters, Figure S1A), elbow angle, buried accessible surface area (bASA), dynamics of hydrogen bonds, and root mean square flexibility (RMSF) (Figure 1A).
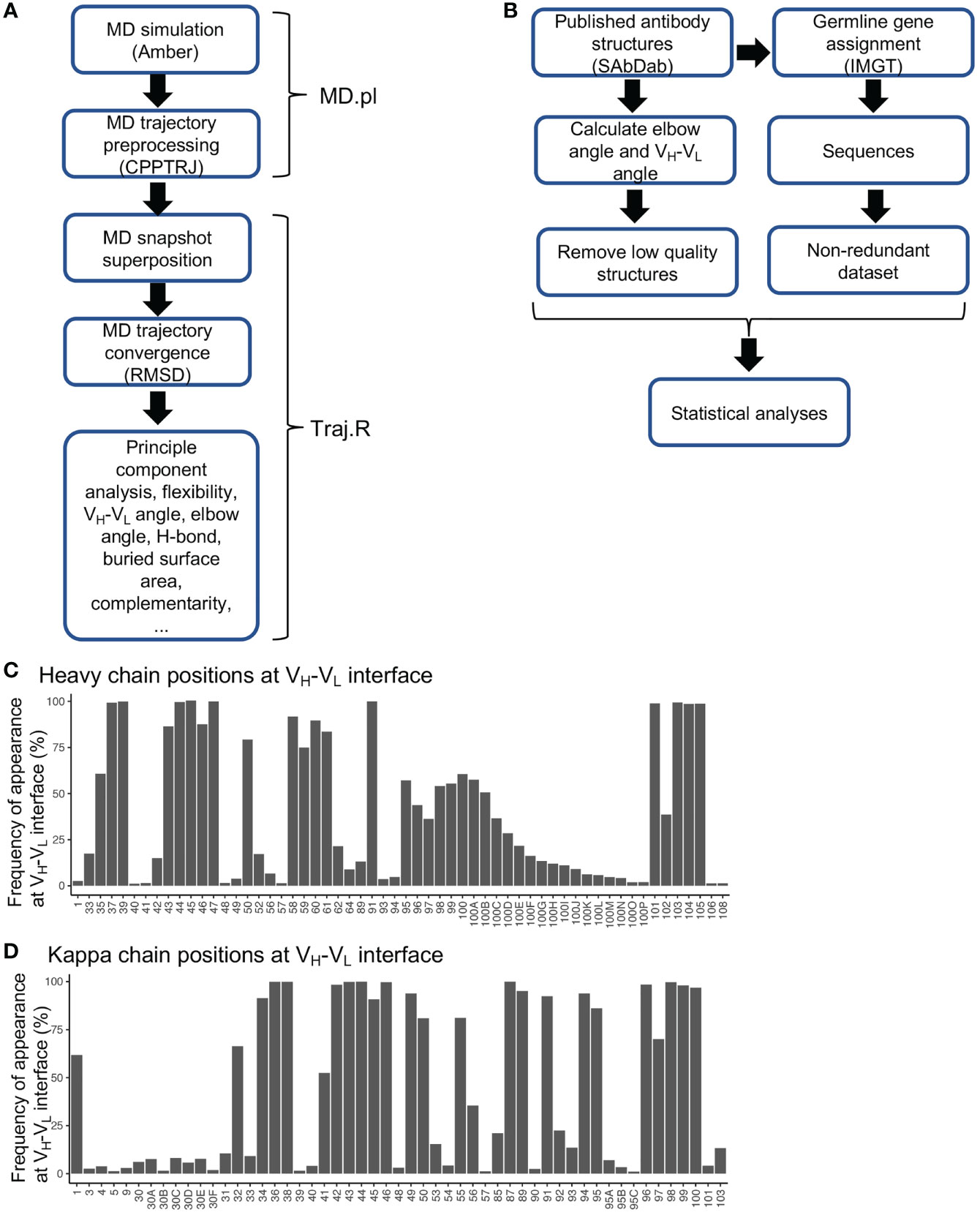
Figure 1 Diagrams for MD simulation and PDB structural analyses and frequencies of residues at VH-VL interface. (A) Diagram of MD simulation and analyses performed. (B) Diagram for analyzing antibody structures from the PDB database. (C) Frequencies of heavy chain variable domain residue positions at VH-VL interface. Residues with frequency less than 1% were omitted. (D) Frequencies of kappa chain variable domain residues at VH-VL interface. Residues with frequency less than 1% were omitted.
Antibody structures determined at the residue-level contain rich information for exploring conformational alterations induced by SHMs. To better utilize this dataset, we collected a total of 5994 experimentally determined antibody structures from the SAbDab database (29). We removed redundant structures with identical heavy and light chain variable domain sequences to identify 3163 unique structures, with 2651 having the antigen-binding fragment (Fab). For each structure, antibody positions were assigned according to the Chothia numbering scheme. We annotated each structure with various features including gene origin, amino acid sequence, SHM level, VH-VL angle, elbow angle, bASA at domain interfaces, and hydrogen bonds and salt bridges at domain interfaces (Figure 1B and Table S1). By utilizing this dataset, we identified residue positions frequently located at VH-VL and elbow interfaces (Figures 1C, D, S1B–E). One interesting observation is that many residue positions at the framework 2 (FWR2) and FWR4 regions contribute to either VH-VL or elbow interfaces (Figures S1F–I). In the gene-specific substitution profiles (GSSPs), which predict positional SHM preference, we found that many residue positions at the VH-VL and elbow interfaces mutate with high frequencies and strong substitution preference (Figures S1F–I), implying that SHMs at these positions are frequently used to modulate VH-VL and elbow conformations. However, for many of these positions, the effects of SHMs have not been elucidated.
VRC01 is a broadly HIV-1 neutralizing antibody (bnAb) which is an important template for antibody-targeted vaccine design. Currently, immunogens (eOD-GT6, eOD-GT8, etc.) have been designed to activate the precursors of VRC01-like antibodies for affinity maturation (30, 31). VRC01 accumulates a high level of SHMs (Figure 2A). However, the effects of many SHMs in VRC01, which are also observed in numerous other antibodies, are unknown. The germline reverted VRC01 (VRC01gl) in complex with eOD-GT6 and VRC01 in complex with gp120 form a good model system to characterize the effects of SHMs through forward and reversion mutagenesis.
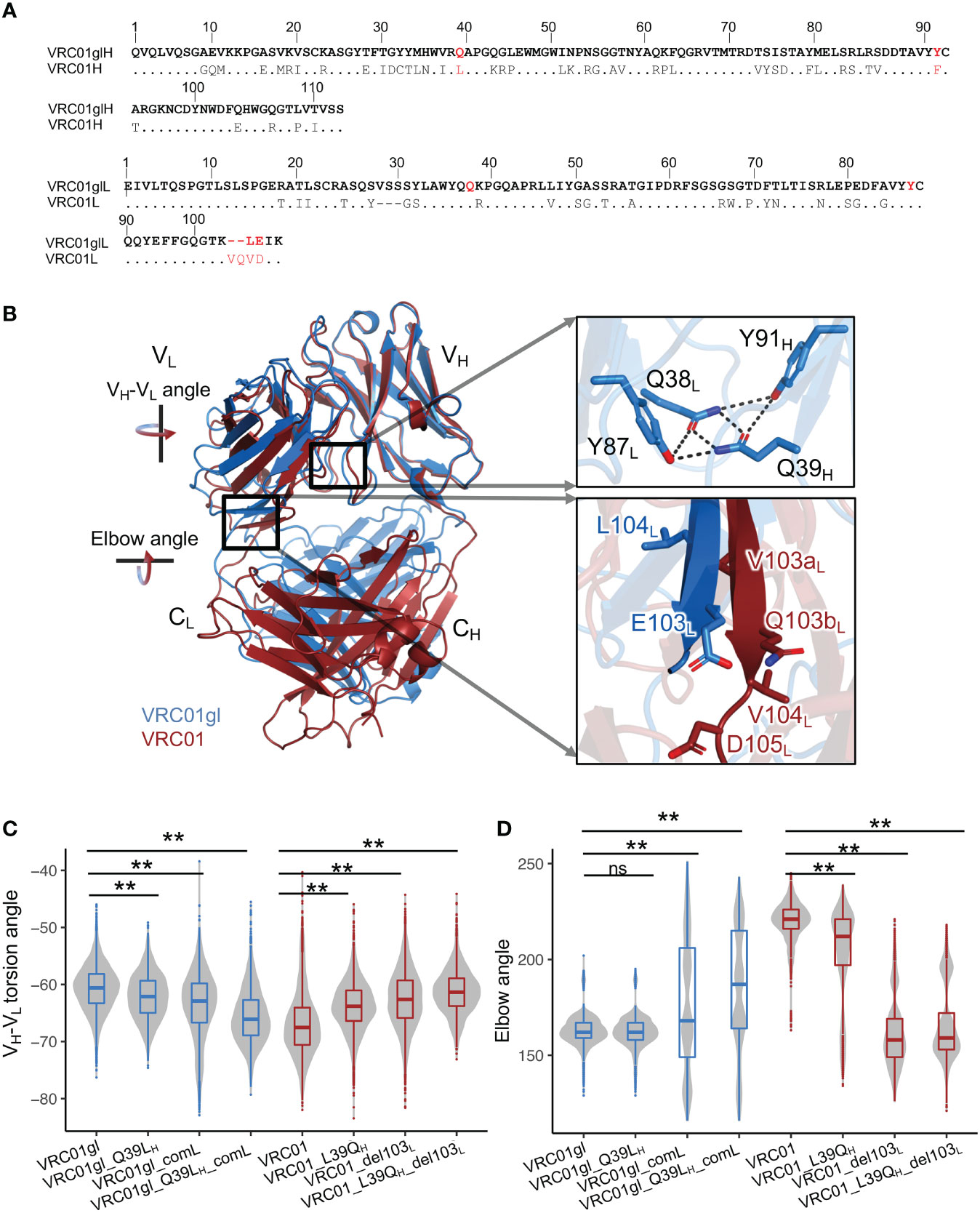
Figure 2 Somatic hypermutations involving Q39LH and FWR4L insertion modulate VH-VL and elbow angles. (A) Heavy and light chain sequence alignments of VRC01gl and VRC01. VRC01 residues identical to VRC01gl are shown in dots. (B) Superimposition of structures of VRC01gl and VRC01 using heavy chain variable domain shows that VH-VL and elbow conformation are changed in mature VRC01. (C) VH-VL angle distribution of VRC01gl and VRC01 mutants from MD simulation. Other parameters for measuring the VH-VL conformation are shown in Figure S2C. (D) Elbow angle distribution of VRC01gl and VRC01 mutants from MD simulation. Kolmogorov–Smirnov test is used to compare the significance of difference for VH-VL and elbow angles. P values less than 0.01 are labeled with two stars. We use Bonferroni Correction to control false discover rate of multiple test <0.01. ns, not significant.
In particular, the comparisons of X-ray crystal structures of VRC01gl and VRC01 revealed dramatic differences in both VH-VL and elbow angles (Figure 2B). To identify SHMs associated with the conformation changes, we introduced individual and combinations of a portion of SHMs observed at the VH-VL and elbow interfaces in VRC01 to VRC01gl, and performed MD simulations accordingly. Our analyses showed that SHM-induced conformation changes in VH-VL and elbow angles could be observed during long timescale (1μs) MD simulation (Figures S2A, B). Note, we referred to VH-VL and elbow angle changes as changes in the sampled distributions or propensity during MD simulation. We used the torsion angle (HL), and four tilting angles (HC1, HC2, LC1, LC2), and one distance parameter defined by ABangle to quantify the VH-VL angle (Figure S1A). We will mainly describe the VH-VL torsion angle changes in the following analyses. MD simulation successfully identified critical SHM events associated with the VRC01 conformation change: heavy chain Q39LH, light chain ‘VQ’ insertion at 103L, L104VL, and E105DL (Figures 2A–D, S2C–H). Q39H is involved in a hydrogen bond (HB) network at the VH-VL interface, which includes Q39H, Y91H, Q38L, and Y87L (Figure 2B). This HB network is completely disrupted in VRC01 by two SHMs: Q39LH and Y91FH (Figure 2A). MD simulation revealed that Q39LH increased the VH-VL torsion angle of VRC01gl (Figures 2C, S2C). Consistently, the revertant L39QH in VRC01 decreased the VH-VL torsion angle. However, substitutions at 39H alone do not alter the elbow angles of VRC01 and VRC01gl (Figure 2D). Further analysis revealed that the combination of ‘VQ’ insertion at 103aL and 103bL, L104VL, and E105DL (the combination defined as comL) at light chain FWR4 is critical for the increased elbow angle in VRC01 (Figure 2D). The deletion of 103aL and 103bL (del103L) reduced the elbow angle and VH-VL torsion angle of VRC01. Consistently, comL increased the VH-VL torsion angle of VRC01gl and modulated VRC01gl to sample multiple elbow angle states including a state similar to VRC01, suggesting that the insertion increases the flexibility of the elbow interface. Moreover, only the combination of Q39LH and comL but not individual mutations altered the VH-VL angle of VRC01gl to a level comparable to VRC01 (Figures S2C–H). Consistently, the combination of del103L and L39QH altered the VH-VL and elbow angles of VRC01 to levels comparable to those of VRC01gl. Moreover, we observed that the combination of Q39LH and comL increased the flexibility of heavy chain CDRs of VRC01gl, while the combination of L39QH and del103L reduced the flexibility of VRC01 CDRs (Figures S2I, J). In summary, the forward mutations in VRC01gl and reversion mutations in VRC01 consistently revealed the SHMs modulating VH-VL and elbow angles, with an additive effect between Q39LH and comL.
To further explore the effects of 39H and FWR4L SHMs individually and in combination, we produced forward mutants of VRC01gl (Q39LH and comL) and revertants of VRC01 (L39QH and del103L) and measured antigen-binding affinity, thermostability, and protein size. We measured KDs of VRC01gl and VRC01 variants against eOD-GT6 and BG505-DSSOSIP respectively using surface plasmon resonance (SPR). We used different antigens for VRC01gl and VRC01 because VRC01gl does not bind HIV-1 gp120/gp41 trimer. The SPR results revealed that Q39LH or comL alone had a mild effect on VRC01gl KD, but the combination improved KD by 4-fold (Figures 3A, S3A), primarily due to a slower reduced dissociation rate (kd). For VRC01, the revertant mutation L39QH decreased the KD of VRC01 by 3-fold due to faster kd, while del103L and the combination of L39QH and del103L showed moderate decrease on the KD (Figure 3A).
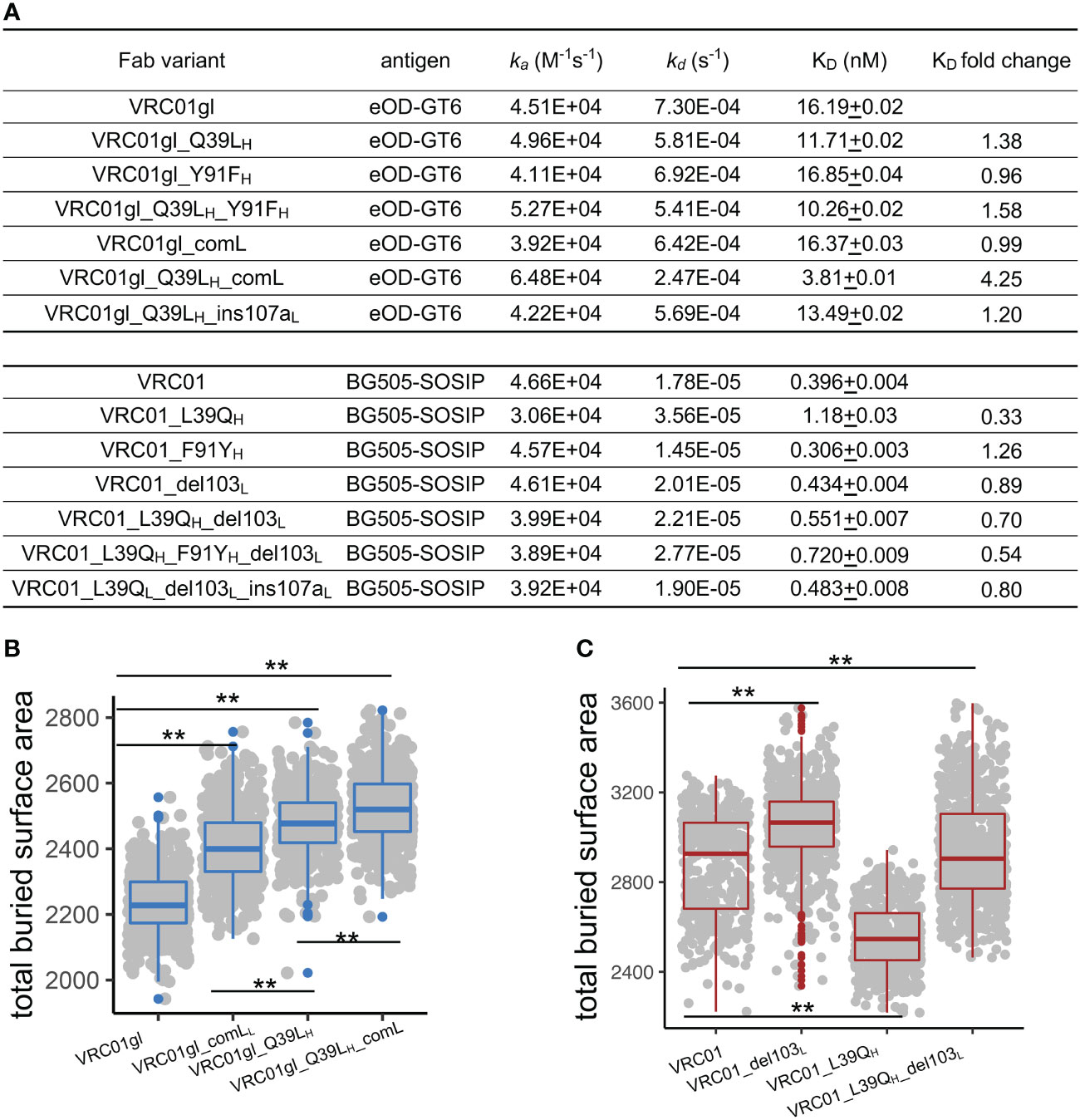
Figure 3 FWR somatic hypermutations improve antigen-binding affinity by increasing bASA between antibody and antigen. (A) Antigen-binding affinity of VRC01gl and VRC01 mutants measured by SPR. Q39LH and comL improves VRC01gl binding affinity against eOD-GT6. L39QH revertant reduces binding affinity of VRC01 against BG505-SOSIP. (B) Q39LH and comL increase bASA between VRC01gl and eOD-GT6. (C) L39QH and VRC01_del103L reduce bASA between VRC01 and gp120. Kolmogorov–Smirnov test is used to compare the significance of difference. P values less than 0.01 are labeled with two stars.
To understand the mechanism of binding affinity alteration by Q39LH and comL, we performed MD simulations of VRC01gl/eOD-GT6 and VRC01/gp120 with and without the mutations. We found that each of the VRC01gl and VRC01 variants sampled VH-VL torsion angle and elbow angle comparable to those observed in antigen-free MD simulations (Figures S3B-D), suggesting that the antibody variants undergo similar conformation changes in the presence of antigens. Both Q39LH and comL increased the bASA between VRC01gl and eOD-GT6 over 200 Ų, with the combination increasing the bASA the most (Figure 3B), consistent with the additive effect of the combination on VH-VL and elbow conformation change. For the three VRC01 reverteants, L39QH decreased the bASA between VRC01 and gp120 (Figure 3C) the most, which is consistent with the SPR results. Above all, these results suggested that modulation of bASA between epitope and paratope, which may alter kd, is one mechanism for improving KD by Q39LH and comL
We next measured melting temperature (Tm) to investigate the effects of 39H and FWR4L mutations on antibody stability. For VRC01gl, Q39LH and comL destabilized VRC01gl (Δ Tm -2.8°C and -14.0°C respectively, Figure 4A). Surprisingly, the destabilization effect of comL was alleviated by Q39LH. For VRC01, the reversion of L93QH had a minor effect on stability (Δ Tm 0.1°C), while del103L destabilized VRC01 by 7.4 °C. Interestingly, the destabilization effect of del103L was attenuated by L39QH.

Figure 4 Q39LH alleviates the stability and aggregation propensity of FWR4L insertion. (A) Effects of somatic hypermutations on VRC01gl and VRC01 melting temperature. Data are shown with mean and SD from two replicates. (B) Buried accessible surface area between VH and VL domains obtained from MD simulation. MD repeats were combined for each antibody variant. (C) Buried accessible surface area between variable and constant domains obtained from MD simulation. MD repeats were combined for each antibody variant. (D) Frequencies of hydrogen bonds at VH-VL interface in MD simulation. Median was highlighted by line. (E) Frequencies of salt bridges at elbow interface in MD simulation. Median was highlighted by line. (F) Effects of somatic hypermutations on VRC01gl and VRC01 Fab protein size. Data are shown with mean and SD from three replicates. Kolmogorov–Smirnov test is used to compare the significance of difference for panels (B, C). P values less than 0.01 are labeled with two stars. P values greater than 0.01 and less than 0.05 are labeled with one star.
Because the above mutations altered antibody conformation, we hypothesized that the observed stability changes may result from conformation change induced alterations in bASA and polar interactions in the VH-VL and elbow interfaces. To examine this hypothesis, we calculated bASA of the VH-VL and elbow interfaces as well as numbers of hydrogen bonds and salt bridges (SBs) in MD trajectories of each antibody variant. Note, stable SBs were not observed in the VH-VL interface and thus excluded from the analysis. For VRC01gl, we found that Q39LH reduced bASA of both VH-VL and elbow interfaces (Figures 4B, C). Q39LH also reduced the number of VH-VL HBs mainly due to the disruption of the HBs between Q39H and Q38L (Figures 4D, S4A). All these changes together may account for the observed destabilization effect of Q39LH. ComL showed reduced bASA of the VH-VL interface, increased bASA of the elbow interface, and reduced SBs at the elbow interface (Figures 4B–E). Interestingly, compared to comL alone, the combination of comL and Q39LH showed increased bASA at both VH-VL and elbow interfaces and SBs at elbow interface, consistent with the Tm measurement that Q39LH improved the stability of the comL mutant. For VRC01, L39QH reduced bASA of both interfaces which may counteract the effect of increased HBs at the VH-VL interface on stability (Figures 4B–D). The reduced bASA of elbow interface and number of SBs may be associated with the destabilization effect of del103L (Figures 4C, E). In contrast, the addition of L39QH recovered the bASA and the number of SB decreases in the del103L variant, coincided with the stability improvement (Figure 4A).
In addition, we noticed that VRC01gl with comL tended to precipitate, but the combination of comL and Q39LH did not. We suspected that comL could result in VRC01gl aggregation and therefore used dynamic light scattering (DLS) to measure the sizes of VRC01gl variants. The DLS results showed that VRC01gl with comL was about 4-fold larger than the wildtype (Figures 4F, S4C), confirming that comL led to aggregation in VRC01gl. Notably, such aggregation disappeared when comL was combined with Q39LH.
In addition, we also assessed the effect of Y91FH, another residue involved in the HB network between VH and VL. We found that Y91FH and its reversion had mild effects on VH-VL and elbow angles and binding affinities of VRC01gl and VRC01 variants (Figures 3A, S2C–H). Nonetheless, Y91FH and Q39LH and their reversions had an additive effect on VRC01gl and VRC01 stability (Figure 4A).
To understand whether SHMs at 39H and comL affect other antibodies, we first examined the conservation of all positions in germline genes. We observed Q39H, Y91H, Q38L, and Y87L to be conserved in many germline V genes of both BCR and T cell receptors across species (Figures 5A, S5A), suggesting a common mechanism for stabilizing interdomain interactions of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Our search of the cAb-Rep database revealed 39H to have a mutation frequency of approximately 4%, with Q39LH the most prevalent (Figure S1F).
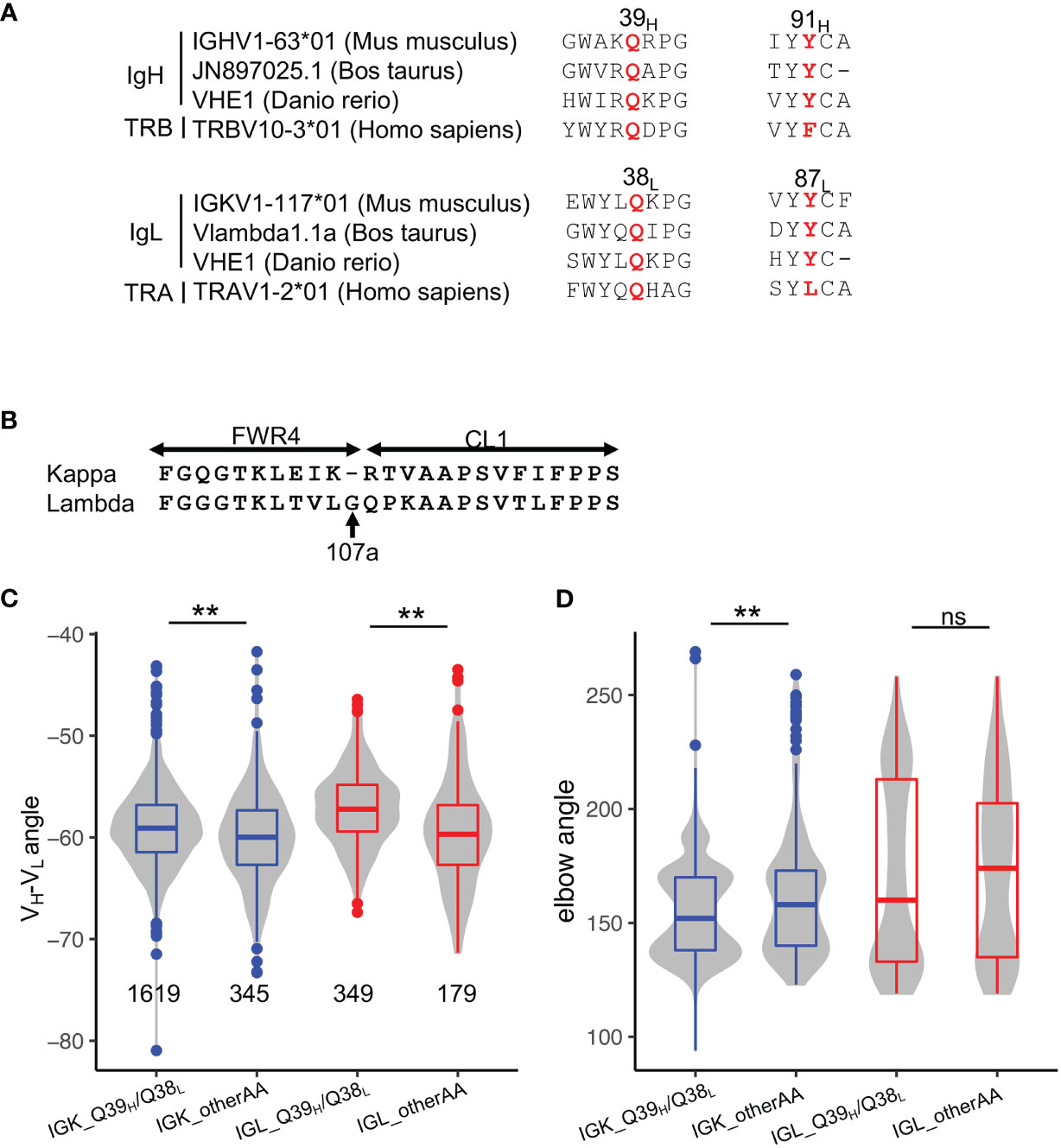
Figure 5 Disruption of the Q39H/Q38L hydrogen bonds represents a common mechanism for altering VH-VL conformation in affinity maturation. (A) Sequence alignment of Q39H, Y91H, Q38L, Y87L in antibody V genes of three species and T-cell receptor V genes of humans. (B) Sequence alignment of kappa and lambda FWR4 and constant regions. (C) VH-VL angles in PDB structures stratified by light chain isotype. Significance of the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test are shown on top. (D) Elbow angles in PDB structures stratified by light chain isotype. Significance of the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test are shown on top. P values less than 0.01 are labeled with two stars. ns, not significant.
To examine the commonality of the effect of Q39H/Q38L pairs on antibody conformation, we compared the VH-VL and elbow angles of antibodies with and without the residue pair. Because lambda light chain is one residue longer than kappa chain (Figure 5B, named 107aL according to kappa FWR4), resulting in increased elbow angle flexibility (32), we compared kappa and lambda chain antibodies separately. Overall, we found that both kappa and lambda antibodies with the Q39H/Q38L pair have a lower VH-VL torsion angle, consistent with the observation in VRC01gl (Figures 5C, D). However, the HC1, LC1, and LC2 angles of the two isotypes change in different directions (Figures S5B–F), with kappa antibodies showing directions of angle changes consistent with VRC01gl. Both kappa and lambda antibodies with the Q39H/Q38L pair tend to have lower elbow angles. In summary, the analysis indicated that SHMs at 39H and 38L broadly modulate conformations of many antibodies, with the conformation change genetic-context dependent.
No insertion is observed in light chain germline J genes. The search of antibody transcripts in the cAb-Rep database revealed a frequency of insertion less than 10-8 summed over all FWR4L positions, suggesting that comL is a rare event that is only observed in the VRC01 lineage. L104VL and E105DL are common individually (Figure S1I). To further examine whether the epistasis effect between 39H and comL is confined to the ‘VQ’ insertion at 103L, we introduced G107aL, frequently observed in lambda chain FWR4, to VRC01gl as well as VRC01 with del103L. We found that G107aL significantly destabilized VRC01gl and formed aggregation, but was further stabilized by Q39LH (Figures 4A, F, S4C). VRC01 with both del103L and G107aL could not be produced, but was expressed when combined with L39QH. Furthermore, G107aL did not affect the binding affinity of VRC01gl and VRC01 variants (Figure 3A). In summary, the results demonstrated again the remote interaction between VH-VL interface SHM and FWR4L insertions.
To further understand the commonality of the effects of 39H and 38L SHMs, we analyzed the frequencies of 39H and 38L SHMs in anti-HIV-1 neutralizing antibodies and anti-influenza antibodies. We found that the SHM frequencies of 39H and 38L are higher in anti-HIV-1 antibodies than in the general antibody repertoire and anti-influenza antibodies (Figures 6A, S6).
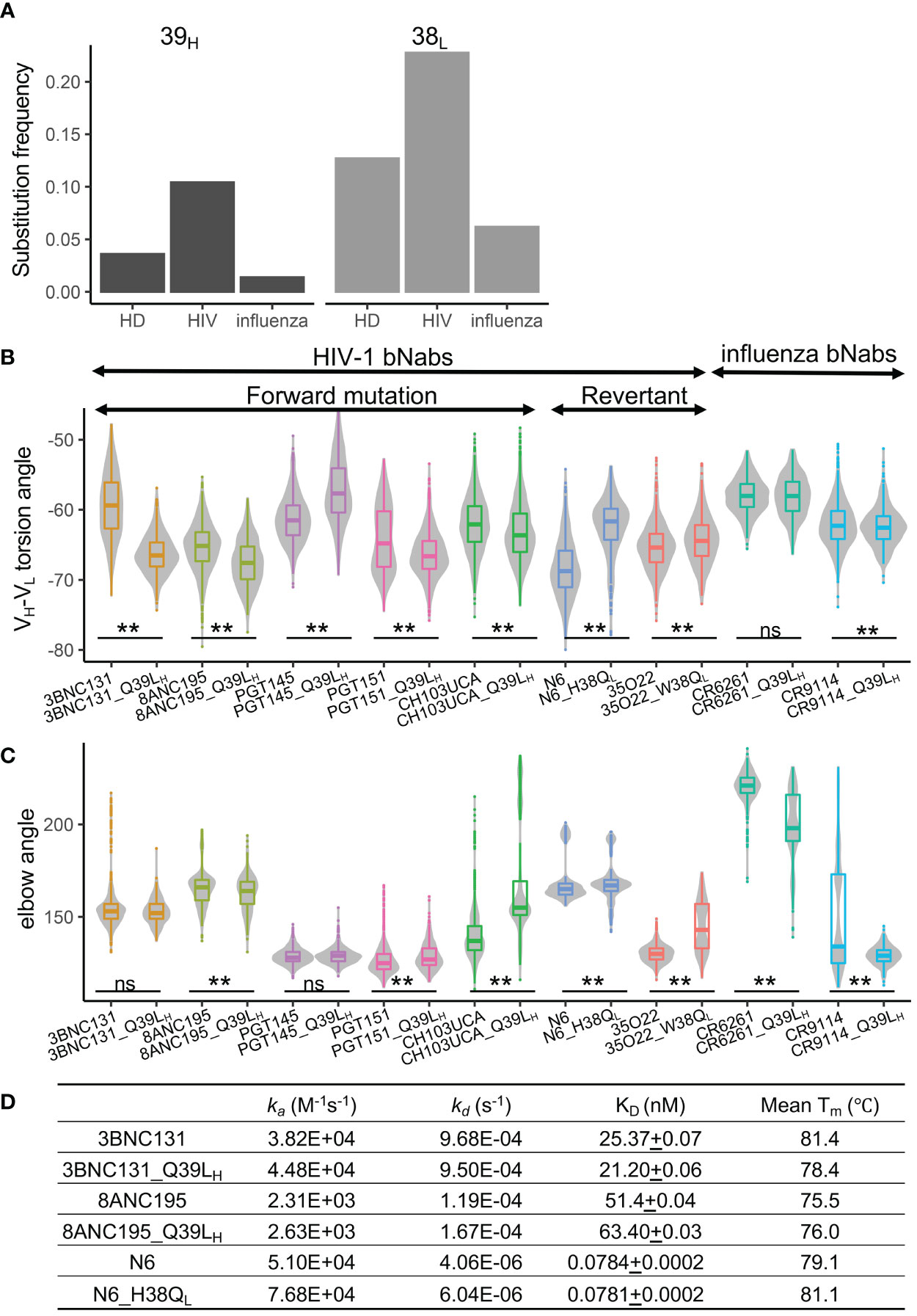
Figure 6 Somatic hypermutations at 39H and 38L are enriched in anti-HIV-1 antibodies. (A) Frequencies of somatic hypermutations at 39H and 38L increase in anti-HIV-1 antibodies. HD, healthy donor antibody repertoire. (B) Somatic hypermutations at 39H and 38L modulate the VH-VL conformation of bnAbs. (C) Somatic hypermutations at 39H and 38L modulate the elbow conformation of HIV-1 and influenza bnAbs. P values less than 0.01 are labeled with two stars. ns, not significant. We use Bonferroni Correction to control false discover rate of multiple test <0.01. (D) Somatic hypermutations at 39H and 38L do not affect the binding affinity of three HIV-1 bnAbs.
To understand whether the conformational changes of 39H and 38L SHMs can be observed in other HIV-1 and influenza antibodies, we introduced or reverted 39H and 38L substitutions in six selected HIV-1 bnAbs, one HIV-1 bnAb unmutated common ancestor (UCA), and two influenza bnAbs and performed MD simulations. The results revealed that the VH-VL angles of eight antibodies were affected by 39H or 38L mutations (Figures 6B, C). The direction of VH-VL torsion angle changes in the six HIV-1 bnAbs is consistent with that in VRC01gl, except PGT145. For five anti-HIV-1 antibodies and both anti-influenza antibodies, the elbow angles were also affected (Figure 6C).
We then selected three anti-HIV-1 bnAbs (3BNC131, 8ANC195, and N6) and measured their binding affinity against BG505-SOSIP and thermostability. We found that the three antibodies with 39H or 38L mutations showed no difference in KD compared to their respective wildtypes (Figure 6D). The stability changes in 3BNC131 and N6 were consistent with those observed in VRC01gl and VRC01. However, Q39LH did not impair the stability of 8ANC195, suggesting that the effect of Q39LH on stability is also context-dependent.
In this study, we established a structural bioinformatics pipeline to investigate the structural basis of the effects of somatic hypermutation. The pipeline was found to be successful at detecting SHM-induced conformational changes, with large conformation changes observed in MD simulation at a long timescale (μs). These conformation changes can be used to understand alterations in binding affinity, stability, flexibility, and other antibody features. With the development of high-performance GPUs, the pipeline paved the way for elucidating mechanisms of SHM effects in a high-throughput way. By using this pipeline, we revealed structural mechanisms of VH-VL and elbow conformation changes induced by SHMs at positions 39H, 91H, 38L, and 87L as well as FWR4L insertions. The stabilization of FWR4L insertion by alteration of VH-VL conformation suggested a remote synergy between VH-VL and elbow conformations. We also found that adjustment of VH-VL conformation is a strategy frequently used by anti-HIV-1 nAbs for affinity maturation.
In general, FWRs scaffold CDRs and many FWR positions are less tolerant of SHMs than CDR residues, which is one of the reasons that many FWR positions undergo strong purifying selection during affinity maturation (12). The GSSP profiles revealed that FWR positions close to VH-VL and elbow interfaces accumulate less SHMs than CDRs and loops in FWRs. Nonetheless, FWR SHMs are required for affinity maturation of numerous antibodies (16). In this study, we characterized the effects of SHMs involved in an HB-network at the VH-VL interface at positions 39H, 91H, 38L, and 87L. Although the importance of the HB network has been reported previously (33, 34), the structural basis, commonality, and genetic-context dependence of its roles have not been revealed. Through altering VH-VL orientation, SHMs at the four positions modulate multiple antibody features including binding affinity, stability, flexibility, and aggregation propensity. For individual antibodies, SHMs may be accumulated at these positions for some but not all of these effects. For example, Q38VL increases VH-VL torsion angle which reduces the steric clash between gp120 and anti-HIV-1 antibody CH103 UCA; Q39LH also improved the binding affinity of CH103 UCA, but the structural basis was not explored (34). In the current study, we found that CH103 UCA with Q39LH contained both VH-VL and elbow orientations more similar to those of matured CH103 characterized in a previous study (19), which could account for the binding affinity improvement. The current study also uncovered that the VH-VL orientation change induced by 39H can improve binding affinity by reducing the dissociation constant kd through increasing bASA between antibody and antigen. As a side effect, individual SHMs at 39H, 91H, 38L, and 87L destabilized antibodies by 1-3 °C. Furthermore, despite 39H and 38L forward and reverse mutations altered VH-VL orientation of anti-HIV-1 bnAbs (Figure 6B), we did not observe changes in binding affinity. It is possible that these SHMs cooperated with other SHMs for function similar to the observations in VRC01gl. Another possibility is that bnAbs may accumulate SHMs at 39H and 38L for stability or other beneficial effects at certain stages of the affinity maturation process. As more SHMs accumulate, the effects of individual 39H and 38L mutations may be counteracted in the matured bnAbs. Thus, antibodies with low or no SHM will be ideal for investigating the effect of individual SHMs. We acknowledge that the MD simulation predicted conformation changes induced by 39H and 38L SHMs were not validated by experimental approaches in this study, but the consistency between the predictions and the PDB dataset analysis suggests that the predictions are reliable.
The dynamics of VH-VL orientation tend to be interconnected with elbow orientation. Two previous studies revealed that mutations at the elbow interface increase VH-VL torsion angle through increasing elbow angle (19, 20). The current study showed that VH-VL interface SHMs can also increase elbow angle. Moreover, as kappa chains are one residue shorter in FWR4L, they tend to have a larger energy barrier to adopting elbow orientations with angles greater than 200 degrees than lambda chain (Figure 4). Insertions in FWR4L reduced the energy barrier and increased the flexibility of the elbow region, but resulted in destabilization and aggregation of VRC01gl. Nonetheless, we observed that introducing Q39LH alleviated the aggregation and improved the stability of VRC01gl, possibly because the VH-VL HB network rigidifies the VH-VL conformation to be incompatible with the large elbow angle. Surprisingly, we also observed that the VRC01 G107aL variant can only be produced in the presence of L39QH, which alters VRC01 antibody conformation. Thus, the alteration of VH-VL and elbow conformations may represent a general way to reduce aggregation propensity. Because the DLS results showed a single peak in the size measurement for VRC01gl with comL and G107aL, implying that the two variants form a stable Fab tetramer and dimer respectively. Although the structures of the polymers are unclear, they may not affect the SPR readout because the antibody variants were captured on the SPR chip surface through their constant domain and the paratopes are probably available for antigen-binding. Furthermore, the destabilization effect of FWR4L insertions suggested that its occurrence is limited to certain VH-VL conformation contexts, which may explain the rarity of indels in FWR4 regions of both heavy and light chains. Above all, there is a remote epistasis between mutations in the VH-VL and FWR4L interfaces. However, further study is required to address whether the destabilization effect is VRC01gl specific.
VH-VL orientation is essential for maintaining bioactivity when grafting CDRs of animal origins to the human FWR backbone (35, 36). We believe the pipeline established in this study provides an approach to predict VH-VL orientations. The combination of SHMs at 39H, 91H, 38L, and 87L and FWR4L insertion provides a new way to alter antibody conformation. This study also highlighted the importance of genetic context for interrogating the effects of SHMs in antibody affinity maturation. In addition, some antibodies require reduced VH-VL torsion angle and elbow angle for affinity improvement (20), a thorough understanding of the roles of many FWR SHMs, especially frequent SHMs, will help to generate a ‘dictionary’ for knowledge-based antibody engineering in different settings.
Antibody Fab structures for MD simulation were downloaded from PDB database (PDB IDs: VRC01gl, 4JPK; VRC01, 3NGB; CH103 UCA, 4QHK; PGT145, 3U1S; PGT151, 4NUG; 35O22, 4TOY; 3BNC131, 4RWY; 8ANC195, 4P9M; N6, 5TE7; CR9114, 4FQH; CR6261, 5C0S). We used FoldX (37) to introduce SHMs to antibody Fab structures. Modeller v9.16 with default parameters was used to model antibodies with insertion or deletion (38). For each Fab variant, we used tleap program to add a 10 angstrom (Å) cubic water box to the system, to neutralize the charge, and to generate topology and parameter files for MD simulation. For MD simulations of VRC01gl/eOD-GT6 and VRC01/gp120 complexes, to mimic the effects of N-glycosylation on antibody/antigen complexes, we built a MAN3 structure in tleap and replaced the crystal structure NAGs with MAN3 at N-glycosylation sites of eOD-GT6 and gp120 in PyMOL (39).
Amber18 with the amber14 and GLYCAM_06j-1 force fields was used for MD simulation (40, 41). We performed 1μs isothermal isobaric MD simulation per run (after 10,000 steps of solution energy minimization, 10,000 steps of whole system energy minimization, 5ns for heating from 0k to 300k, and 10ns of equilibration in the isothermal isovolumetric ensemble) on each Fab variant. 2-5 MD simulation repeats per Fab variant were performed with repeats not converged removed. A master MD script (MD.pl) was written to perform the above steps of MD simulation including energy minimization, heating, NPT and NVT ensembles.
Bio3D in R was used to perform most of the trajectory analyses. For each MD run, snapshots were superimposed to the first snapshot using Cα atoms of the heavy and light chain variable domains and root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) was calculated to determine simulation convergence (42). After confirming convergence, snapshots of about 500ns were used for analyzing antibody conformational features. Root-Mean-Square Fluctuations (RMSF) were then calculated for each variable domain residue to examine whether SHMs modulate antibody flexibility. For each snapshot, we quantified the sampled distributions of the torsion and tilting angles and distance between VH and VL using ABangle recompiled in R (43), elbow angle by PyMOL, buried ASA and HB networks between domain interfaces using PISA (44). All statistical analyses in this study were performed in R. A master analysis script (Traj.R) was used to perform the above analyses.
Experimentally determined antibody structures were downloaded from the SAbPred database (29). Gene origin and somatic hypermutation levels of each antibody were retrieved from the IMGT database (45). The elbow angle was calculated in PyMOL. bASA, hydrogen bonds at domain interfaces, and VH-VL and elbow interface residues were calculated using PISA. We removed antibodies with identical heavy and light chain variable domain sequences using USEARCH (46) to obtain a non-redundant dataset.
The GSSPs for V genes were obtained from the cAb-Rep database (11). We used the mGSSP program to generate GSSPs as well as to identify insertions and deletions for all human J genes using all curated human antibody transcripts (~306 million) in the cAb-Rep database (12).
Genes encoding for the heavy (VH & CH1 domains) and light (Kappa or Lambda VL & CL domains) chains of antibody Fabs were cloned in the mammalian expression plasmid pVRC8400. eOD-GT6 was cloned into the mammalian expression plasmid pHL-sec between the AgeI and KpnI sites. VRC01 heavy chain constructs were followed by a C-terminal octa-histidine tag and eOD-GT6 a hexa-histidine tag. The VRC01 light chain constructs had no tags.
Fabs mutants were generated using Pfu Ultra II polymerase in a protocol that employed both forward and reverse primers in the same PCR reaction for 18 cycles. The PCR products were denatured, and then reannealed. The non-mutated methylated parental plasmid was digested with DpnI and the remaining plasmids were transformed into E. coli cells. For each transformation, we selected five colonies at random and grew overnight in 5 ml LB + Kanamycin (pVRC8400) medium at 37°C. The plasmids were isolated using Spin miniprep kit (Qiagen, Germany) and sequenced to obtain the desired mutants.
Recombinant antibody Fabs were transiently expressed in FreeStyleTM 293F (Invitrogen) suspension cultures by co-transfection of pVRC8400 plasmids containing expression constructs for light chain and Fab heavy chain using polyethyleneimine (Polysciences). Cell growth was harvested on day 6 post transfection. eOD-GT6 was also produced in FreeStyleTM 293F (Invitrogen) suspension cultures by transient transfection using polyethyleneimine (Polysciences) of a pHLSec plasmid containing mammalian codon-optimized eOD-GT6 with a C-terminal Avi and His6x affinity tag. Proteins were harvested from the supernatant after 96 h.
The secreted proteins were purified by using Ni-NTA IMAC Sepharose 6 Fast Flow resin (GE Healthcare) nickel affinity chromatography followed by size exclusion chromatography (SEC) using a Superdex 200 26/600 (Fabs) or Superdex 75 26/600 (eOD) column (GE Healthcare) in 10 mM Tris pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl SEC buffer. Peak fractions containing Fabs or eOD-GT6 were pooled. Protein purity was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and concentrated where possible to ~10 mg/mL. BG505-SOSIP was requested from the Vaccine Research Center at the National Institute of Health (47).
Thermostability was measured by nano differential scanning fluorimetry on a Nanotemper Tycho NT. 6 instrument (NanoTemper Technologies) with a back-reflection aggregation detection at a range from 35 to 95°C and with a heating rate of 30°C/min. Protein unfolding was followed by tryptophan and tyrosine fluorescence intensity at 330 and 350 nm. The melting temperature (Tm) was determined by detecting the maximum of the first derivative of the fluorescence ratios (F350/F330) after fitting experimental data with a polynomial function. Each sample was measured in duplicate or triplicate.
SPR binding assays were performed using a Biacore T200 biosensor, equipped with a Series S CM5 chip, at 25°C in a HBS buffer, pH 7.4 (10mM HEPES pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl) supplemented with 0.1 mg/mL BSA and 0.005% (v/v) Tween-20.
For experiments involving the eOD-GT6 antigen, Fabs were captured to the chip surface using a human anti-Fab antibody (Human Fab Capture Kit, Cytiva), which was immobilized over all four flow cells of a chip using amine-coupling chemistry. Three different Fabs were captured over independent flow cells at 5-10 μg/mL at a capture level of approximately 400 RU. A surface without captured Fab served as a reference control. eOD-GT6 antigen was prepared in running buffer using a three-fold dilution series at six concentrations ranging from 2-486 nM, which were injected over all four flow cells simultaneously to increase concentration, using a 150s association time and 600s dissociation time at 50μL/min. At the end of each cycle the anti-Fab surface was regenerated using two consecutive 10s injections of 10 mM H3PO4 at 100μL/min, removing any Fab/eOD-GT6 bound complex, so that Fab can be re-captured in the next cycle. Buffer cycles instead of antigen samples were incorporated every two binding cycles to double reference the binding responses. Each concentration series was tested in triplicate.
BG505-SOSIP was tethered to the chip surface using the antibody 2G12 (NIH AIDS Reagent Program), which was immobilized over two flow cells of a Series S CM5 chip using amine-coupling chemistry. At the beginning of each cycle, BG505-SOSIP was captured over a single flow cell only, at 15ug/mL resulting in captures of approximately 400 RU, with the second flow cell used as a reference control. Fabs were used as the analyte at five concentrations ranging from 2.22-180 nM, with the exception of 8ANC195 and 8ANC195_Q39LH, which were tested at a 9-fold higher concentration range from 20-1620nM, to account for the slower association rate of the bound complex. Fab concentrations were prepared in running buffer using a three-fold dilution series and injected to increase concentration at 50μL/min for 150s association time and 900s dissociation time. 3BNC131 and 3BNC131_Q39LH, used dissociation times of 600s, and N6 and N6_Q39LH, used dissociation times of 2400s respectively to account for either a faster or a slower dissociating complex. The 2G12 surface was regenerated using a 10s pulse of 3M MgCl2 at 100μL/min, removing any bound BG505-SOSIP/Fab complex. Buffer cycles instead of antigen samples were incorporated every two binding cycles to double reference the binding responses. Each of concentration series was tested in triplicate.
Binding data were processed and fit to a simple 1:1 interaction model using the Scrubber 2.0 (BioLogic Software). The number in brackets reported with all kinetic parameters represents the error of the fit.
The sizes of antibody Fabs purified with the nickel affinity chromatography were measured using Malvern Nano-ZS with a 173° detection angle at 20°C. Zetasizer v7.13 was used to calculate the size of each Fab.
The computational codes used in this study are available at https://github.com/shengzizhang/Antibody_MD.git. The anti-HIV-1 and anti-influenza antibodies were downloaded from the HIV molecular immunology database (http://www.hiv.lanl.gov/content/immunology) and RAPID database respectively (48). Antibody repertoire dataset was obtained from the cAb-Rep database (11).
ZS and LS designed the research. ZS wrote the MD simulation pipeline. ZS, YCG, YZG, and HZ analyzed data. JB and SP produced the antibody and antigens and performed melting temperature analysis. ZS and JB performed Dynamics Light Scattering analysis. PSK and LS performed SPR measurement. PDK provided reagents. LS and ZS wrote the paper. All authors reviewed, commented on, and approved the manuscript.
Support for this work was provided by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) grant R21 1R21AI138024-01A1 and the startup fund UR010655/70003/ZS2248 to ZS; support was also provided by the Intramural Research Program of the Vaccine Research Center, NIAID, NIH.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2021.811632/full#supplementary-material
1. Victora GD, Nussenzweig MC. Germinal Centers. Annu Rev Immunol (2012) 30:429–57. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-075032
2. Muramatsu M, Kinoshita K, Fagarasan S, Yamada S, Shinkai Y, Honjo T. Class Switch Recombination and Hypermutation Require Activation-Induced Cytidine Deaminase (AID), A Potential RNA Editing Enzyme. Cell (2000) 102(5):553–63. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00078-7
3. Wood GS. The Immunohistology of Lymph Nodes in HIV Infection: A Review. Prog AIDS Pathol (1990) 2:25–32.
4. Cauerhff A, Goldbaum FA, Braden BC. Structural Mechanism for Affinity Maturation of an Anti-Lysozyme Antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (2004) 101(10):3539–44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400060101
5. Finlay WJ, Cunningham O, Lambert MA, Darmanin-Sheehan A, Liu XM, Fennell BJ, et al. Affinity Maturation of a Humanized Rat Antibody for Anti-RAGE Therapy: Comprehensive Mutagenesis Reveals a High Level of Mutational Plasticity Both Inside and Outside the Complementarity-Determining Regions. J Mol Biol (2009) 388(3):541–58. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.03.019
6. Wang F, Sen S, Zhang Y, Ahmad I, Zhu X, Wilson IA, et al. Somatic Hypermutation Maintains Antibody Thermodynamic Stability During Affinity Maturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (2013) 110(11):4261–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1301810110
7. Dimitrov JD, Kaveri SV, Lacroix-Desmazes S. Thermodynamic Stability Contributes to Immunoglobulin Specificity. Trends Biochem Sci (2014) 39(5):221–6. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2014.02.010
8. Manivel V, Sahoo NC, Salunke DM, Rao KVS. Maturation of an Antibody Response Is Governed by Modulations in Flexibility of the Antigen-Combining Site. Immunity (2000) 13(5):611–20. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)00061-3
9. Yin J, Beuscher A, Andryski SE, Stevens RC, Schultz PG. Structural Plasticity and the Evolution of Antibody Affinity and Specificity. J Mol Biol (2003) 330(4):651–6. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(03)00631-4
10. James LC, Roversi P, Tawfik DS. Antibody Multispecificity Mediated by Conformational Diversity. Science (2003) 299(5611):1362–7. doi: 10.1126/science.1079731
11. Guo Y, Chen K, Kwong PD, Shapiro L, Sheng Z. cAb-Rep: A Database of Curated Antibody Repertoires for Exploring Antibody Diversity and Predicting Antibody Prevalence. Front Immunol (2019) 10:2365. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02365
12. Sheng Z, Schramm CA, Kong R, Program NCS, Mullikin JC, Mascola JR, et al. Gene-Specific Substitution Profiles Describe the Types and Frequencies of Amino Acid Changes During Antibody Somatic Hypermutation. Front Immunol (2017) 8:537. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00537
13. Bonsignori M, Zhou T, Sheng Z, Chen L, Gao F, Joyce MG, et al. Maturation Pathway From Germline to Broad HIV-1 Neutralizer of a CD4-Mimic Antibody. Cell (2016) 165(2):449–63. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.02.022
14. Chothia C, Lesk AM. Canonical Structures for the Hypervariable Regions of Immunoglobulins. J Mol Biol (1987) 196(4):901–17. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90412-8
15. Ovchinnikov V, Louveau JE, Barton JP, Karplus M, Chakraborty AK. Role of Framework Mutations and Antibody Flexibility in the Evolution of Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies. eLife (2018) 7. doi: 10.7554/eLife.33038
16. Klein F, Diskin R, Scheid JF, Gaebler C, Mouquet H, Georgiev IS, et al. Somatic Mutations of the Immunoglobulin Framework Are Generally Required for Broad and Potent HIV-1 Neutralization. Cell (2013) 153(1):126–38. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.03.018
17. Simon T, Rajewsky K. A Functional Antibody Mutant With an Insertion in the Framework Region 3 Loop of the VH Domain: Implications for Antibody Engineering. Protein Eng (1992) 5(3):229–34. doi: 10.1093/protein/5.3.229
18. Burnett DL, Schofield P, Langley DB, Jackson J, Bourne K, Wilson E, et al. Conformational Diversity Facilitates Antibody Mutation Trajectories and Discrimination Between Foreign and Self-Antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (2020) 117(36):22341–50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2005102117
19. Henderson R, Watts BE, Ergin HN, Anasti K, Parks R, Xia SM, et al. Selection of Immunoglobulin Elbow Region Mutations Impacts Interdomain Conformational Flexibility in HIV-1 Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies. Nat Commun (2019) 10(1):654. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08415-7
20. Koenig P, Lee CV, Walters BT, Janakiraman V, Stinson J, Patapoff TW, et al. Mutational Landscape of Antibody Variable Domains Reveals a Switch Modulating the Interdomain Conformational Dynamics and Antigen Binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (2017) 114(4):E486–95. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1613231114
21. Abhinandan KR, Martin AC. Analysis and Prediction of VH/VL Packing in Antibodies. Protein Eng Des Sel (2010) 23(9):689–97. doi: 10.1093/protein/gzq043
22. Nakanishi T, Tsumoto K, Yokota A, Kondo H, Kumagai I. Critical Contribution of VH-VL Interaction to Reshaping of an Antibody: The Case of Humanization of Anti-Lysozyme Antibody, HyHEL-10. Protein Sci (2008) 17(2):261–70. doi: 10.1110/ps.073156708
23. Fernandez-Quintero ML, Kroell KB, Bacher LM, Loeffler JR, Quoika PK, Georges G, et al. Germline-Dependent Antibody Paratope States and Pairing Specific VH-VL Interface Dynamics. Front Immunol (2021) 12:675655. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.675655
24. Wu TT, Kabat EA. An Analysis of the Sequences of the Variable Regions of Bence Jones Proteins and Myeloma Light Chains and Their Implications for Antibody Complementarity. J Exp Med (1970) 132(2):211–50. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.211
25. Schmidt AG, Xu H, Khan AR, O’Donnell T, Khurana S, King LR, et al. Preconfiguration of the Antigen-Binding Site During Affinity Maturation of a Broadly Neutralizing Influenza Virus Antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (2013) 110(1):264–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1218256109
26. Xu HF, Schmidt AG, O’Donnell T, Therkelsen MD, Kepler TB, Moody MA, et al. Key Mutations Stabilize Antigen-Binding Conformation During Affinity Maturation of a Broadly Neutralizing Influenza Antibody Lineage. Proteins Structure Funct Bioinf (2015) 83(4):771–80. doi: 10.1002/prot.24745
27. Margreitter C, Mayrhofer P, Kunert R, Oostenbrink C. Antibody Humanization by Molecular Dynamics Simulations-in-Silico Guided Selection of Critical Backmutations. J Mol Recognit (2016) 29(6):266–75. doi: 10.1002/jmr.2527
28. Paci E, Caflisch A, Pluckthun A, Karplus M. Forces and Energetics of Hapten-Antibody Dissociation: A Biased Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. J Mol Biol (2001) 314(3):589–605. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.5103
29. Dunbar J, Krawczyk K, Leem J, Baker T, Fuchs A, Georges G, et al. SAbDab: The Structural Antibody Database. Nucleic Acids Res (2014) 42(Database issue):D1140–6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1043
30. Jardine JG, Kulp DW, Havenar-Daughton C, Sarkar A, Briney B, Sok D, et al. HIV-1 Broadly Neutralizing Antibody Precursor B Cells Revealed by Germline-Targeting Immunogen. Science (2016) 351(6280):1458–63. doi: 10.1126/science.aad9195
31. Jardine JG, Ota T, Sok D, Pauthner M, Kulp DW, Kalyuzhniy O, et al. Priming a Broadly Neutralizing Antibody Response to HIV-1 Using a Germline-Targeting Immunogen. Science (2015) 349(6244):156–61. doi: 10.1126/science.aac5894
32. Stanfield RL, Zemla A, Wilson IA, Rupp B. Antibody Elbow Angles Are Influenced by Their Light Chain Class. J Mol Biol (2006) 357(5):1566–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.01.023
33. Masuda K, Sakamoto K, Kojima M, Aburatani T, Ueda T, Ueda H. The Role of Interface Framework Residues in Determining Antibody V(H)/V(L) Interaction Strength and Antigen-Binding Affinity. FEBS J (2006) 273(10):2184–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05232.x
34. Zhou JO, Zaidi HA, Ton T, Fera D. The Effects of Framework Mutations at the Variable Domain Interface on Antibody Affinity Maturation in an HIV-1 Broadly Neutralizing Antibody Lineage. Front Immunol (2020) 11:1529. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01529
35. Bujotzek A, Lipsmeier F, Harris SF, Benz J, Kuglstatter A, Georges G. VH-VL Orientation Prediction for Antibody Humanization Candidate Selection: A Case Study. mAbs (2016) 8(2):288–305. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2015.1117720
36. Lord DM, Bird JJ, Honey DM, Best A, Park A, Wei RR, et al. Structure-Based Engineering to Restore High Affinity Binding of an Isoform-Selective Anti-TGFbeta1 Antibody. mAbs (2018) 10(3):444–52. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2018.1426421
37. Guerois R, Nielsen JE, Serrano L. Predicting Changes in the Stability of Proteins and Protein Complexes: A Study of More Than 1000 Mutations. J Mol Biol (2002) 320(2):369–87. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(02)00442-4
38. Eswar N, Webb B, Marti-Renom MA, Madhusudhan MS, Eramian D, Shen MY, et al. Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using MODELLER. Curr Protoc Protein Sci (2007) Chapter 2:Unit 2 9. doi: 10.1002/0471140864.ps0209s50
39. Schrodinger LLC. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.8. New York: Schrodinger LLC (2015).
40. Case DA, Cheatham TE, Darden T, Gohlke H, Luo R, Merz KM, et al. The Amber Biomolecular Simulation Programs. J Comput Chem (2005) 26(16):1668–88. doi: 10.1002/jcc.20290
41. Singh A, Tessier MB, Pederson K, Wang X, Venot AP, Boons GJ, et al. Extension and Validation of the GLYCAM Force Field Parameters for Modeling Glycosaminoglycans. Can J Chem (2016) 94(11):927–35. doi: 10.1139/cjc-2015-0606
42. Grossfield A, Zuckerman DM. Quantifying Uncertainty and Sampling Quality in Biomolecular Simulations. Annu Rep Comput Chem (2009) 5:23–48. doi: 10.1016/S1574-1400(09)00502-7
43. Dunbar J, Fuchs A, Shi J, Deane CM. ABangle: Characterising the VH-VL Orientation in Antibodies. Protein Eng Des Sel (2013) 26(10):611–20. doi: 10.1093/protein/gzt020
44. Krissinel E, Henrick K. Inference of Macromolecular Assemblies From Crystalline State. J Mol Biol (2007) 372(3):774–97. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.05.022
45. Lefranc MP, Giudicelli V, Ginestoux C, Jabado-Michaloud J, Folch G, Bellahcene F, et al. IMGT, the International ImMunoGeneTics Information System. Nucleic Acids Res (2009) 37(Database issue):D1006–12. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn838
46. Edgar RC. Search and Clustering Orders of Magnitude Faster Than BLAST. Bioinformatics (2010) 26(19):2460–1. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq461
47. Gulla K, Cibelli N, Cooper JW, Fuller HC, Schneiderman Z, Witter S, et al. A Non-Affinity Purification Process for GMP Production of Prefusion-Closed HIV-1 Envelope Trimers From Clades A and C for Clinical Evaluation. Vaccine (2021) 39(25):3379–87. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.04.063
Keywords: antibody, broadly HIV-1 neutralizing antibody, conformation modulation, epistasis, INDEL, molecular dynamics simulation, somatic hypermutation, stability
Citation: Sheng Z, Bimela JS, Katsamba PS, Patel SD, Guo Y, Zhao H, Guo Y, Kwong PD and Shapiro L (2022) Structural Basis of Antibody Conformation and Stability Modulation by Framework Somatic Hypermutation. Front. Immunol. 12:811632. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.811632
Received: 09 November 2021; Accepted: 07 December 2021;
Published: 03 January 2022.
Edited by:
Duane R. Wesemann, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, United StatesReviewed by:
Robyn Stanfield, The Scripps Research Institute, United StatesCopyright © 2021 Sheng, Bimela, Katsamba, Patel, Guo, Zhao, Guo, Kwong and Shapiro. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zizhang Sheng, enMyMjQ4QGN1bWMuY29sdW1iaWEuZWR1; Lawrence Shapiro, bHNzOEBjb2x1bWJpYS5lZHU=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.