Development of a Scrub Typhus Diagnostic Platform Incorporating Cell-Surface Display Technology
- 1Institute of Molecular Biology, Academia Sinica, Taipei, Taiwan
- 2Institute of Preventive Medicine, National Defense Medical Center, Taipei, Taiwan
- 3Department of Entomology, National Chung Hsing University, Taichung, Taiwan
- 4Department of Entomology, College of Bioresources and Agriculture, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan
- 5Department of Plant Pathology and Microbiology, College of Bioresources and Agriculture, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan
A Corrigendum on:
Development of a Scrub Typhus Diagnostic Platform Incorporating Cell-Surface Display Technology
By Liao C-C, Tsai C-H, Lo H-R, Lin P-R, Lin C-C and Chao Y-C (2021). Front. Immunol. 12:761136. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.761136
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 6 as published. The title of Figure 6D should be “ScaC-PD” instead of “Kato”. The corrected Figure 6 appears below.
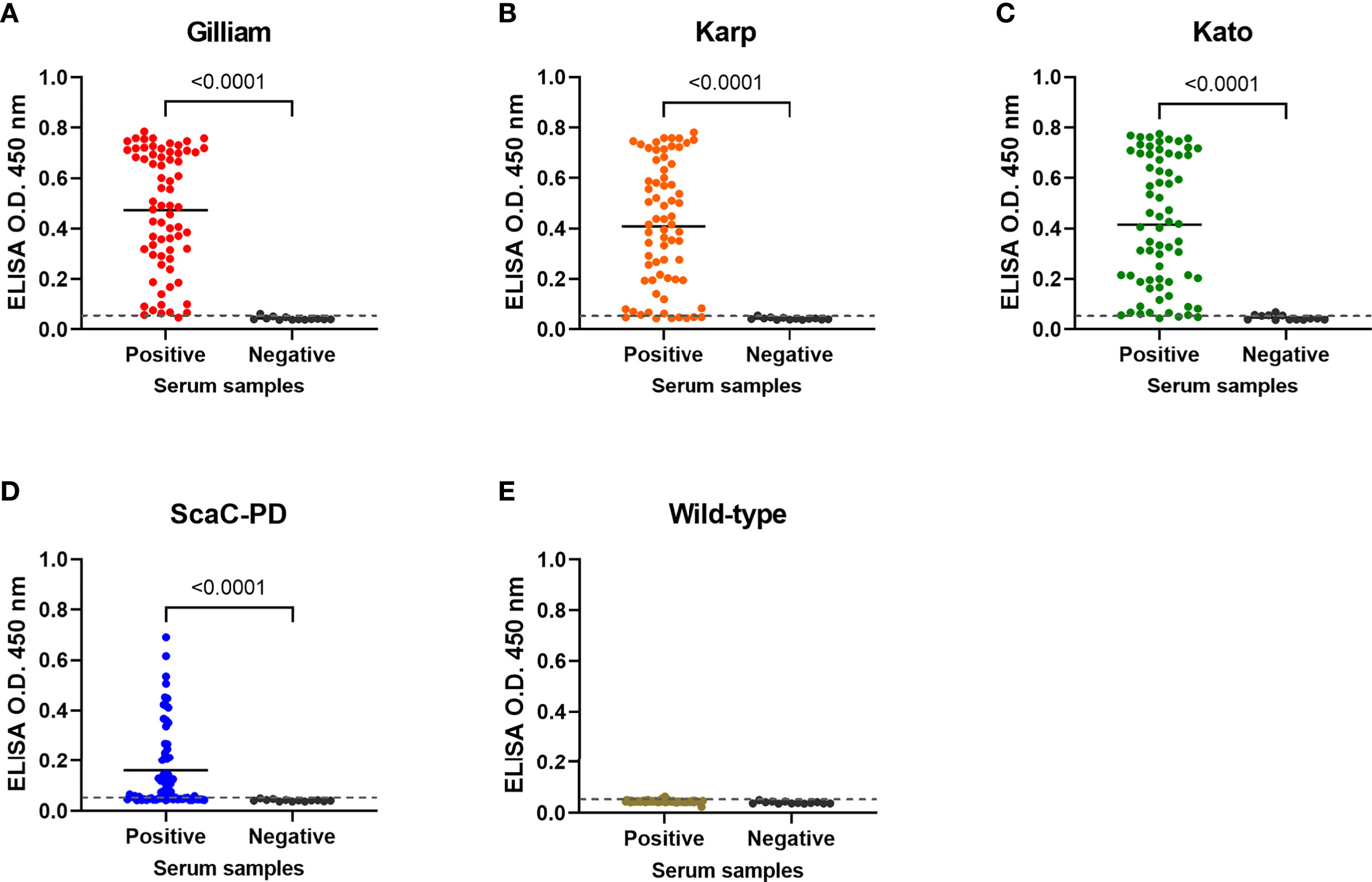
Figure 6 Cell-based ELISA detection of ST in serum samples obtained from field-caught or non-ST rats. Sixty-nine rat sera confirmed as having been infected with O. tsutsugamushi by IFA (Positive) and thirteen negative control rat sera (Negative) were subjected to cell-based ELISA using cells displaying Gilliam TSA56 (A), Karp TSA56 (B), Kato TSA56 (C), and ScaC-PD (D) antigens, and cells infected with wild-type baculovirus (E). Individual data points are shown and the solid line represents the mean value. Dotted line: cutoff value of 0.056 determined as the mean value of negative rat serum reactivities against each of the antigens plus two standard deviations. P-values determined by Welch’s t-test are displayed above the plots.
In the original article, there was an error in text. The term “His tag” should be “His-tag”.
A correction has been made to Discussion, paragraph 4:
“This outcome indicates that the His-tag may be inadequately exposed in the Gilliam TSA56 protein structure, so it is only partially recognized by anti-His antibody.”
The authors apologize for these errors and state that they do not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: baculovirus surface display, cell-based ELISA, Orientia tsutsugamushi, scrub typhus, serological diagnosis
Citation: Liao C-C, Tsai C-H, Lo H-R, Lin P-R, Lin C-C and Chao Y-C (2021) Corrigendum: Development of a Scrub Typhus Diagnostic Platform Incorporating Cell-Surface Display Technology. Front. Immunol. 12:803807. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.803807
Received: 28 October 2021; Accepted: 29 October 2021;
Published: 16 November 2021.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2021 Liao, Tsai, Lo, Lin, Lin and Chao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chang-Chi Lin, Y2hhbGluM0BuZG1jdHNnaC5lZHUudHc=; Yu-Chan Chao, bWJ5Y2NoYW9AaW1iLnNpbmljYS5lZHUudHc=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Chih-Chi Liao
Chih-Chi Liao Chih-Hsuan Tsai
Chih-Hsuan Tsai Huei-Ru Lo
Huei-Ru Lo Pey-Ru Lin
Pey-Ru Lin Chang-Chi Lin2*
Chang-Chi Lin2* Yu-Chan Chao
Yu-Chan Chao