- 1Department of Molecular and Life Science, Hanyang University, Ansan, South Korea
- 2Depatment of Bionano Technology, Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) has complex and intricate interactions with host immune cells. Mtb can survive, persist, and grow within macrophages and thereby circumvent detection by the innate immune system. Recently, the field of immunometabolism, which focuses on the link between metabolism and immune function, has provided us with an improved understanding of the role of metabolism in modulating immune function. For example, host immune cells can switch from oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis in response to infection, a phenomenon known as the Warburg effect. In this state, immune cells are capable of amplifying production of both antimicrobial pro-inflammatory mediators that are critical for the elimination of bacteria. Also, cells undergoing the Warburg effect upregulate production of nitric oxide augment the synthesis of bioactive lipids. In this review, we describe our current understanding of the Warburg effect and discuss its role in promoting host immune responses to Mtb. In most settings, immune cells utilize the Warburg effect to promote inflammation and thereby eliminate invading bacteria; interestingly, Mtb exploits this effect to promote its own survival. A better understanding of the dynamics of metabolism within immune cells together with the specific features that contribute to the pathogenesis of tuberculosis (TB) may suggest potential host-directed therapeutic targets for promoting clearance of Mtb and limiting its survival in vivo.
Introduction
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by the pathogenic species, Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb); together with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV/AIDS) infection, TB is among the most prevalent and severe of the infectious diseases worldwide. In 2019, an estimated 10 million people developed active tuberculosis in association with 1.6 million deaths (1). Infection with Mtb triggers an immune response, however Mtb can survive and grow by circumventing the host immune detection. One of the pathological characteristics of the successful infection with Mtb is the formation of granulome, which are organized cellular structures that include a variety of innate and adaptive immune cells that surround the Mtb-infected phagocytes (2–5). During the formation of granulome, intricate host-Mtb interactions occur at the infectious site and this pathogen can escape various host immune responses, which ultimately prevent Mtb elimination by these systems. Once Mtb enters the host, its cell wall components and proteins are detected by Toll-like receptors (TLRs), primarily by TLR2 and TLR4. Mtb is engulfed by professional phagocytic cells such as a macrophage, dendritic cell (DC), or neutrophil, and becomes incorporated into the subcellular organelle formed by the fusion of the phagosome and lysosome to create the phagolysosome, however Mtb is able to manipulate the endocytic pathway by suppressing fusion of the phagosome containing the bacteria with lysosomes. Infected macrophages synthesize and release both inflammatory and antimicrobial genes and molecules, including interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-12, tumor necrosis factor (TNF), inducible nitric oxide synthase/nitric oxide synthase 2 (iNOS/NOS2), and chemokines which activate both the innate and adaptive immune systems. Activated immune cells secrete protective molecules to the extracellular space to promote recruitment of other immune cells to form a granuloma (4, 6). Interestingly, endogenous proteins expressed by Mtb serve to perturb the formation of phagolysosome, the permitting its survival and proliferation within macrophages. For preventing excessive lung damage during Mtb infection, Mtb also elicits the production of protective factors that promote its survival including anti-inflammatory mediators such as IL-4, IL-10, IL-13, and transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) (7–9) and several human TB studies show that these factors has been shown to be increased in the active TB patients (10, 11). These immunosuppressive factors play key roles in limits effective the immune defense to Mtb (12, 13). Mtb will persist and exacerbate pathophysiological manifestations within the granulome; this will ultimately result in progression of disease and dissemination to the other hosts (5, 14). As a major focus of this disease process, mycobacterial granulome have been the subject of intense scrutiny mainly focused on mechanisms of formation, function, maintenance, and evolution.
Recently, there has been an increasing appreciation of the important relationship that exists between essential metabolism and immune cell function. Metabolic reprogramming in immune cells, a phenomenon known as immunometabolism, focuses on unique cellular functions that are essential for the immune response. During TB infection, host cells undergo profound metabolic change, which results in differential control of various cytokines and chemokines associated with inflammation, clearance, inhibition, and progression of Mtb infection (15, 16). Specifically, a shift in the use of pathways promoting glucose and lipid metabolism can be an important feature for directing host cell function to promote mycobacterial survival with the granulome (17). At homeostasis, cells in “resting” condition utilize oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) to produce ATP from NADH and FADH2 by facilitating transfer of protons and electrons. Cells typically switch from OXPHOS to glycolysis in order to generate ATP under oxygen-depleted or hypoxic conditions (18). Similarly, glycolysis is main form of metabolism in immune cells that promote the inflammatory response in the immune system. This observation–that immune cells utilize glycolysis even in the presence of adequate concentrations of oxygen (i.e., aerobic glycolysis)– is known as the “Warburg effect.” To date, the Warburg effect has been explored primarily with respect to cancer metabolism. Although aerobic glycolysis generates fewer ATP molecules per cycle than does OXPHOS, this pathway is capable of rapid generation of ATP required by immune cells. Additionally, aerobic glycolysis requires a number of specific precursors, including nucleotides, amino acids, and lipids (19). Because metabolic reprogramming is essential for immune cell function, studies that explore this phenomenon in also provide new insight into the relationship between host immune cells and infection with Mtb. Furthermore, predisposing factors for TB, including diabetes, and HIV also related to immunometabolism against TB pathogenicity. Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a mainly risky factor for occurring active TB (20–22). In DM, innate immune cells undergo activation for releasing cytokines, recruiting neutrophils, upregulate T cell activation and antigen recognition (23, 24). Metabolism of DM is characterized by increasing glucose production and impairing glucose uptake. Expression of glucose transporter and glycolytic enzymes is elevated in DM (25). In DM, High glucose level increased IL-10 production, impaired macrophage phagocytic ability for promoting better milieu for survival and proliferation of TB (26, 27). Additionally, HIV is also other pathogen to be associated with pathogenicity of TB (28–30). In HIV-1-infected primary CD4+ T cells, glycolytic metabolism is induced with high pro-inflammatory response and increased production of virus (31, 32). Interestingly, glycolytic metabolism is regulated by HIV-1 infection in macrophage alleviated Warburg effects (33). These factors promote the activation of TB by reprogramming the metabolism.
A variety of antibiotics have been introduced for promoting eradication of Mtb infection, including 6–9 months courses of isoniazid, rifampicin, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide. However, the emergence of multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) or extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR-TB) has become a major challenge toward designing effective treatments and for eradication of this disease (34, 35). Among the approaches to this challenge, host-directed therapy (HDT) has been introduced as a means to potentiate and to amplify the effectiveness of current treatments used for TB (36). A clear understanding of the molecular interactions between host cell metabolism and accommodations made to Mtb may provide new strategies to combat infection. Here we review the current understanding of the metabolic relationship between the host and the Mtb pathogen. We also suggest several new strategies that may enhance host metabolic pathways and thereby promote protective antimicrobial functions in the setting of TB infection.
Metabolic Reprogramming in TB
Warburg Effect in Immune Cells
Immune cells provide critical protection and maintain homeostasis in the mammalian host. There are currently many studies that suggest that the functions of immune cells are largely reliant on specific aspects of host metabolism. These studies, which have generated a field known as immunometabolism, have provided us for a new focus for understanding how and why immune cells exist or persist in a specific metabolic state in order to support or direct functional changes. Several recent reports suggest that different metabolic signatures have a direct impact on specific effector functions characteristic of the innate and adaptive immune systems (37). As such, among the primary functions of immune cells, there are those that generate an inflammatory response, actions typically undertaken by M1-polarized macrophages, DCs, neutrophils, and effector T cells, and those that promote an anti- inflammatory response, which include M2-polarized macrophages, as well as regulatory and memory T cells. The basic metabolic profiles of these cells differ significantly from one another. Inflammatory immune cells generate energy in the form of ATP mainly via glycolytic metabolism; by contrast, immune cells that promote anti- inflammatory activities generate ATP via oxidative phosphorylation and fatty acid oxidation (38–43). These observations have been best characterized for polarized macrophages. The predominant phenotypes of macrophages are known as M1 and M2 (44, 45). M1 macrophages, activated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and IFN-γ, promote pro-inflammatory and antibacterial functions in immune system, and they produce nitric oxide (NO) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) which are fundamental components of the pathways used to eradicate bacteria. The main metabolic pathway used by these cells is glycolysis, which results in rapid production of ATP via inhibition of the trichloroacetic acid (TCA) cycle and OXPHOS in mitochondria; this is a critical factor due to the fact that M1 macrophages require rapid generation of ATP to activate inflammation. By contrast, M2 macrophages promote anti-inflammatory responses and tissue repair; these cells mainly utilize OXPHOS and fatty acid oxidation in order to generate ATP; this takes place via efficient pathways localized in the mitochondria (46–51). In T cells, metabolic state is reprogrammed according to T cell subsets. Naïve T cells mainly use OXPHOS for generating energy. Upon TCR stimulation, glycolytic metabolism is upregulated for differentiating into activated T cell. Th1, TH2, and Th17 effector cells mainly depend on aerobic glycolysis. While, regulatory and memory T cells use fatty acid oxidation and OXPHOS for differentiation and functions (52, 53). Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and AKT signaling is essential for regulating metabolism of T cells and cytokine responses (54). Recently, cyclophililn D (CypD) related to necrosis is a factor for regulating metabolic state and functions in T cells (55).
Pro-inflammatory immune cells generate ATP in high concentrations via glycolysis even when functioning in aerobic conditions; the phenomenon of aerobic glycolysis is also known as the “Warburg effect” (56). Hypoxia and inflammation are inherently linked to one another; upon activation, immune cells undergo considerable metabolic reprogramming to sustain energy needs and thus switch to predominantly aerobic glycolysis. Hypoxia-induced factor 1 (HIF-1), the main mediator of the Warburg effect, is expressed in response to hypoxia and controls expression of numerous glycolytic enzymes. HIF-1 has two subunits, α and β; regulation of HIF-1 is dependent on the α subunit. Post-translational regulation of HIF- 1 is modulated via the expression and stability of HIF-1α (56–58). Members of the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) family of transcription factors comprise the signaling pathway that is most closely involved in Hif-1α/HIF-1A expression (59, 60). Under conditions of physiologic oxygenation, prolyl hydrolases (PHD) degrade HIF-1α and target it for proteasome-mediated degradation. Inhibiting HIF (FIH) is an aspariginyl hydroxylase that also determines the level of active HIF-1α. Overall, hypoxia-inducible genes encode proteins involved in a myriad of cellular pathways that mediate cell survival, apoptosis, erythropoiesis, angiogenesis, glucose metabolism, and that regulate acid-base balance (61). HIF-1α is expressed in primary innate immune cells, including macrophages, DCs, neutrophils, and Th17 cells. Additional roles for HIF-1α in promoting macrophage differentiation and function have also been demonstrated. Most notably, HIF-1α-mediated metabolic reprogramming plays a significant role in modulating macrophage polarization toward the M1 or M2 phenotype (62).
Glycolysis Metabolism in TB
When the host is infected by bacteria, immune cells are activated; the characteristic immune response occur concomitant with a switch to glycolytic metabolism (Figure 1). Several recent studies that have focused on transcriptome data from mouse and rabbit lung as well as granulome from the lungs of TB patients suggest that the metabolic state of the TB-infected host includes modulation of glucose metabolism (63–66). The general metabolic characteristics in TB infection included enhanced expression of genes related to the Warburg effect including HIF-1α, glycolytic enzymes, the pentose phosphate pathway, and H+-ATPase. Additionally, 1H-NMR-based metabolomics profiled the increased accumulation of lactate due to the increased levels of glycolysis in the lungs of Mtb-infected mice (67). Likewise, host immune cells responded to Mtb infection with increased expression of pro- inflammatory and antimicrobial-related genes associated with the Warburg effect. These results highlighted the importance of metabolic reprogramming due to glycolysis and its relationship to protection against Mtb infection. Furthermore, analysis of the transcriptomes of bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM) infected with one of two clinical strains of Mtb (the immunogenic strain CDC1551 or the hypervirulent strain HN878) included elevated levels of expression of genes associated with the Warburg effect. Given that these two clinical strains are known for differential activation of immune responses during the course of BMDM infection, different metabolic responses were anticipated (64). Interestingly, BMDMs infected with each strain promoted upregulation of genes encoding enzymes associated with the Warburg effect together with HIF-1α-associated signaling, although specific differences were observed. Of note, at 6 h post-infection, the induction of the gene encoding 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3 (PFKFB3) a member of the of phosphofructokinase (PFK)-2 family, was more prominent in CDC1551-infected BMDMs (65). Pfkfb3 has the highest activity among the PFK-2 members, and fructose-2,6-diphosphate (F-2,6-BP), which is the product of Pfkfb3-mediated phosphorylation, is an essential component promoting regulation of glycolysis (68). CDC1551-infected BMDMs in a state of elevated glycolysis respond with a vigorous early pro-inflammatory response. By contrast, relatively limited activation of the Warburg effect together with high levels of glucose uptake were observed in response to Mtb. Furthermore, HN878-infection of BMDMs may result in dysregulated host cell lipid metabolism. Specifically, one study compared gene expression in response to Mtb H37Ra or H37Rv infection of human alveolar macrophage revealed strain-specific differences. Gene expression associated with inflammation, general metabolism, and lipid metabolism was downregulated in H37Rv infected macrophages (69). As suggested by the responses to infection with HN878, a virulent strain can have an impact on host metabolism gene by downregulating inflammatory responses that results in diminished the inflammation and prolonged Mtb survival. Another study compared the metabolic states elicited by macrophage challenge with Mtb, with the vaccine strain M. bovis BCG or with killed Mtb. Each strain promoted a unique pattern of energy modulation, as determined by XF (extracellular flux) analysis. Total metabolism in response to challenge with live Mtb including glucose utilization and OXPHOS is lower than that observed in response to BCG or dead Mtb (70). Also, CD8+ T cell showed similar results in Mtb or BCG infection. Through RNA-seq, glycolytic metabolism is upregulated by challenging Mtb in early and late phase. Surprisingly, Mtb triggered mitochondrial dysfunction, which downregulates OXPHOS metabolism, while upregulates mtROS, but metabolism is recovered against BCG (71). Thus, infection with live, virulent Mtb decelerated the shift to glycolytic and OXPHOS bioenergetics, and thereby limited the development of inflammatory effector functions.
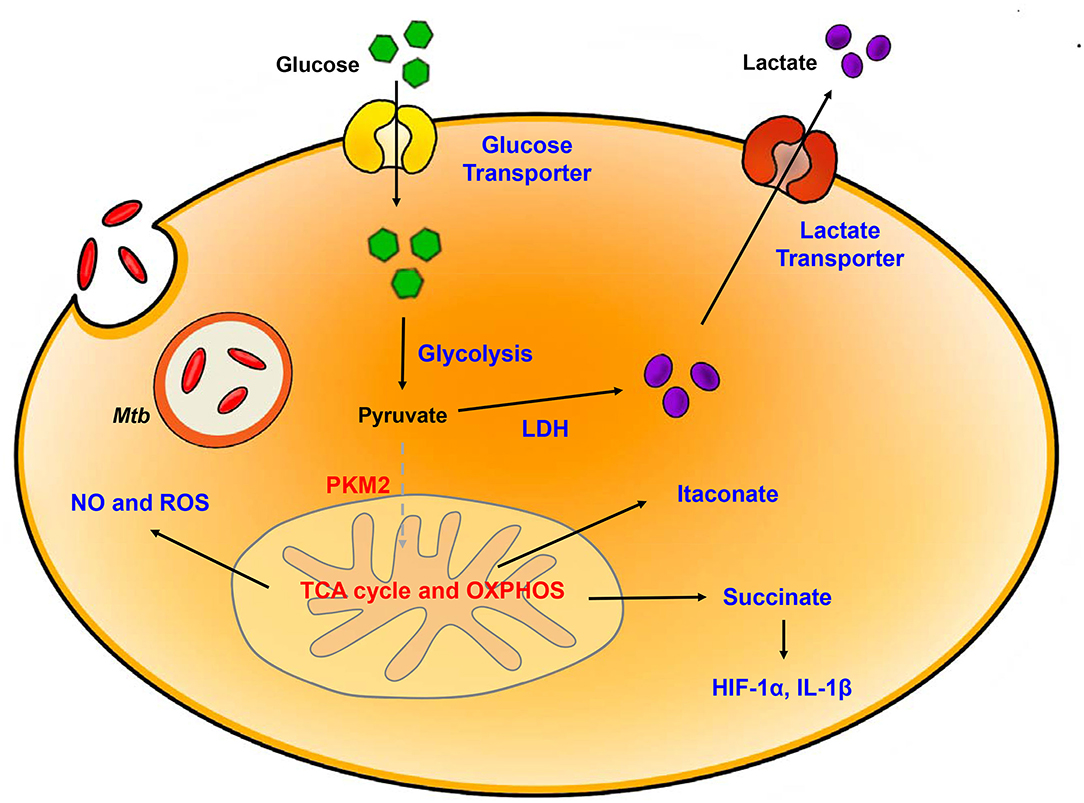
Figure 1. Metabolic reprogramming in Mtb-infected immune cells. Mtb infection in host is accompanied by upregulation of glycolysis and lactate production. Increased HIF-1α-induced Warburg effect enhance gene of glycolytic metabolism. In contrast, TCA cycle and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) is downregulated. Dysregulation of TCA cycle accumulates several intermediates in TCA cycle such as succinate and itaconate. Additionally, breakdown of OXPHOS increases NO and ROS level. Blue, increased expression/level; Red, decreased expression/level.
The switch to glycolytic metabolism resulted in the accumulation of several TCA intermediates that themselves function as a metabolic signal to link metabolism and immunity (Figure 2). Succinate, a prominent TCA intermediate, drives IL-1β production, inhibits the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, and enhances HIF-1α activity by inhibiting HIF-1α prolyl hydrolases (72–74). The succinate-induced pro-inflammatory response is directly dependent on the activity of succinate dehydrogenase (SDH). Inhibition of SDH activity via hydrolysis of dimethyl malonate to produce malonate, results in an attenuation of the activity of LPS-induced IL-1β, and likewise a boost in IL-10 production in BMDMs generated from C57BL/6 mice (75). In Mtb-infected murine macrophages, Sdh expression is downregulated; this leads to the induction of HIF-1α, the Warburg effect, and characteristic pro-inflammatory responses (76). Itaconate, a metabolite derived from the TCA cycle intermediate cis-aconitate, also regulates SDH activity in C57BL/6 BMDMs (77, 78). Breakdown of TCA cycle results in downregulation of mitochondrial isocitrate dehydrogenase (Idh)2 immediately following formation of itaconate. Aconitate decarboxylase 1 (ACOD1), is also known as immune-responsive gene (Irg)1; production of this mediator is related to generation of itaconate. ACOD1 is upregulated in Mtb-infected murine macrophages and lung tissue. Itaconate has antimicrobial functions via its capacity to inhibit isocitrate lyase, the essential enzyme in the glyoxylate shunt that is critical for bacterial growth. Itaconate inhibits SDH activity which results in the accumulation of succinate. Additionally, itaconate modulates pro- inflammatory responses in macrophage; Irg1−/− BMDMs from C57BL/6 mice maintain higher HIF-1α mRNA and protein levels, and produce more pro-inflammatory cytokines and antimicrobial factors including IL-6, IL-12, IL-1β, and NO in response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated activation (79). Thus, itaconate may be a critical link between the Warburg effect induced by Mtb infection, and the generation of anti-inflammatory responses to prevent damage to host cells.
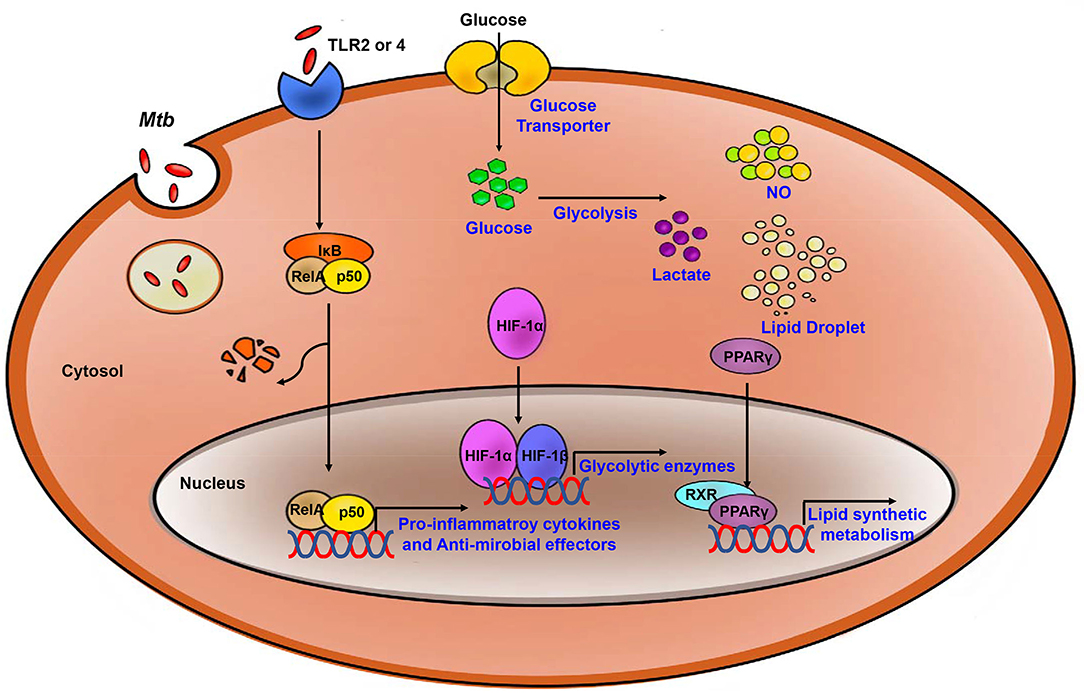
Figure 2. Process of the Immune response and metabolic reprogramming in Mtb- infected immune cells. After Mtb infection, inflammatory signaling is activated by TLR2 or 4. Also, Metabolism is switch to aerobic glycolysis mediated by HIF-1α which upregulates glycolytic enzymes. Increased glycolysis related to upregulate pro-inflammatory cytokines and anti-microbial effectors. PPARγ upregulates lipid synthetic gene for formation of lipid droplet which is exploited by Mtb for survival and growth. Blue, increased expression/level.
Upregulated expression of HIF-1α, the enhanced Warburg effect, and the antimicrobial response to Mtb infection of host immune cells are all linked to the actions of the glycolytic regulatory protein, pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2). Expression of PKM2, one of the two Pkm/PKM gene products, is upregulated in response to macrophage activation. In the cytoplasm, PKM2 maintains an enzymatically inactive state via its phosphorylation; the PKM2 dimer is transferred into the nucleus where it interacts with HIF-1α to activate target genes, including those encoding glycolytic enzymes and IL- 1β. In LPS-activated macrophages, small molecules such as TEPP-46 modulate PKM2 activation by preventing PKM2 translocation into the nucleus; consequently, results in a diminished Warburg effect and limited production of IL-1β. Inhibition of PKM2 translocation also promotes production of IL-10 and a decreased antimicrobial response in an S. typhimurinum infection model (80). In transcriptome analysis studies, upregulation of Pkm2/PKM2 was detected in Mtb- infected murine macrophages and in mouse lung tissue (65). These results suggest that, similar to itaconate, PKM2 promotes the HIF-1α-mediated Warburg effect and the associated antimicrobial response during Mtb infection. CypD, mitochondrial matrix protein, is regulator of metabolism in Mtb infection via upregulating mtROS in T cells. CypD-deficient T cells showed higher OXPHOS than wild-type T cells and more susceptible to Mtb (55).
In summary, metabolism in Mtb-infected host cells undergoes a switch from OXPHOS to glycolysis and generates a Warburg effect. The HIF-1α induced Warburg effect in the setting of TB infection plays an essential role in promoting upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokine and antimicrobial effector gene expression, both factors underlying the acute immune response. However, host immune responses were different depending on the virulence or avirulence of the Mtb-infecting strain. How and why immune responses are modulated by different strains of Mtb are not fully understood.
Arginine Metabolism in TB
Arginine, the key substrate for production of NO and other reactive nitrogen species, and also serves as a substrate for arginase. Arginine plays a distinct role in the host immune response. iNOS promotes one pathway that results in the generation of NO; the other pathway is via the arginase-mediated production of ornithine (16). iNOS is one of three NO synthase enzymes and the major isoform involved in immune cell functions. iNOS is inducible in immune cells, and is a prominent antimicrobial effector molecule produced by activated macrophages (81). The balance of arginine metabolism between the two competing pathways constitutes an important regulatory mechanism that modulates the polarization states of M1 and M2 macrophages. In M1 macrophages, arginine is in demand for protein synthesis, for production of NO, and for its antimicrobial roles; by contrast, in M2 macrophages, arginine is used for production of polyamines and proline. The iNOS pathway is in direct competition with the arginase pathway (82, 83). Two arginase isoforms exist in the cells. Cytosolic arginase ARG1 and mitochondrial arginase ARG2 are encoded by different genes and have different subcellular distributions (84, 85). ARG1 is mainly detected in murine myeloid cells, DCs, and granulocytes. ARG1 inhibits NO production from iNOS/NOS2 which is among the mechanisms used by Mtb for immune evasion. Mtb-infected Arg1 conditional gene-deleted mice were characterized with a diminished bacterial burden; Arg1-deficient macrophages were more capable of killing Mtb compared to their wild-type counterparts (86). ARG1 and iNOS are distributed in distinct patterns in human TB-associated granulome; expression of iNOS was highest in the central region, and ARG1 was more prominent at the periphery (87). The role of ARG1 in mediating immune cell function is directly dependent on the stage of Mtb infection. At initial stages of infection, the Mtb pathogen takes advantage of ARG1 activity by limiting macrophage immunity via competition with iNOS/NOS2. During the late stages of infection, ARG1 contributes to control of prolonged hyperinflammation; ARG1 also plays a role in regulating the progression of lung immunopathology in Mtb-infected, Nos2-deficient mice (87).
Lipid Metabolism in TB
Once glycolytic metabolism has been activated, the genes encoding pro- inflammatory mediators are synthesized, together with the synthesis of fatty acids and phospholipids. The TCA cycle and OXPHOS are inhibited, and several intermediates of the TCA cycle accumulate in situ (88). Similar to what has been observed for glucose metabolism, including the TCA cycle and OXPHOS, host lipid metabolism is also regulated in Mtb infection (Figure 2). There are master regulators that mediate lipid metabolism including the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), liver X receptor (LXR), sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs) and HIF (89–93). These factors work together to regulate processes including fatty acid uptake, lipid synthesis, the activities of lipolytic enzymes, and lipid droplet (LD) biogenesis (94). The activation of TLR signaling upregulates expression of several enzymes that promote synthesis of triglycerides and/or cholesterol ester, including fatty acid synthase (FASN), diacylglycerol O- acyltransferases (DGAT-1 and DGAT-2), and acyl-CoA:cholesterol O-acyltransferases (ACAT1 and ACAT2) (95–97). During lipid accumulation, increased expression of lipid uptake and transport-related genes is observed, and expression of genes involved in lipolysis is decreased. Perilipin-2 (Plin2) and Perilipin-3 (Plin3) are the main structural proteins of LDs that serve to promote lipid accumulation (96, 98, 99). These proteins are essential for the biogenesis and assembly of LDs (100).
PPARs are members of the ligand-activated transcription factor family (101). PPARs can have a direct impact on LD formation via the regulation of Plin2 expression. PPARs also regulate proteins associated with de novo lipogenesis, including fatty acid synthase and gene regulatory factors LXR and SREBPs (94). PPAR-γ is important for regulating lipid and glucose metabolism and other cellular process including inflammation (102). Host immune cells which are infected by Mtb exhibit increased PPAR-γ gene expression; this results in downregulation of NF-κB signaling and increases in production of prostaglandin (PG) E2; overall, this results in suppression of pro- inflammatory cytokines and Th1 responses (103, 104). Increased PPAR-γ expression in Mtb-infected macrophages is also associated with LD formation (105). Formation of LDs is critical for bacterial survival; the accumulated lipids in these infected cells provide nutrients and promote bacterial growth in host. Additionally, infection with M. bovis BCG results in upregulated expression and activation of PPAR-γ and the induction of lipid-loaded macrophages. In BCG-infected TLR2-deficient mice, production of TNF-α undergoes significant downregulation (104, 106). Taken together, these findings suggest that PPAR-γ accelerates intracellular lipid accumulation by modulating the expression of genes that modulate lipid absorption as well as those that promote fatty acid synthesis in response to Mtb infection.
PPAR-α is another isoform of the PPAR family. It is a transcription factor that modulates the expression of several genes involved in lipid oxidation and glucose metabolism (107). PPAR-α enhances fatty acid oxidation and ketogenesis while inhibiting fatty acid synthesis and glycolysis (108). As such, activation of PPAR-α may prevent lipid accumulation in Mtb-infected cells. PPAR-α activation also results in the upregulation of transcription factor EB (TFEB) and promotes host innate immunity and autophagy against Mtb infection. The induction of TFEB also promotes lipid catabolism which inhibited intracellular growth of Mtb growth in bone marrow-derived macrophages (109).
Metabolic HDT in TB
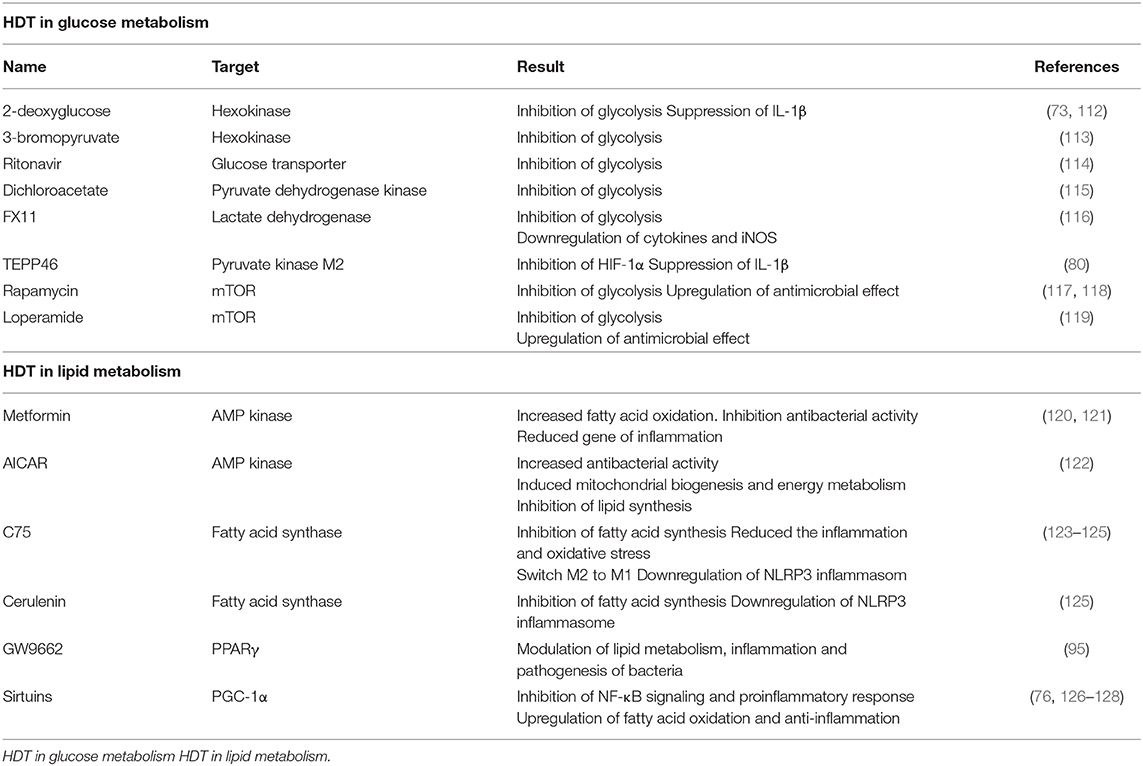
In recent years many researchers have demonstrated that changes in dynamic immunometabolism take place in response to infection with microbes; as such, studies focused on immunometabolism are important so as to provide a larger understanding of their role in promoting pathogenesis in host (110). Current clinical trials have limitations with respect to the elimination of Mtb infection, including the need for long-term use, severe side effects, and the emergence of drug-resistant strains (111). As noted above, Mtb infection can induce a Warburg effect in host immune cells, similar to that described in tumor tissue (65). Mtb exploits host metabolism in order to escape immune surveillance and modulates various responses to subvert their activities toward promoting its survival and longevity. We expect HDT to be a clinically-feasible approach toward readjusting uncontrolled immune responses in patients with infectious disorders. We discuss HDT drugs currently in use or under development that target host metabolism. We will also suggest novel candidate HDT pathways and agents that might be effective toward eradicating Mtb (Table 1).
HDT in Glucose Metabolism
In TB infection, metabolism switches to glycolysis in order to protect the host against early-phase Mtb responses. HIF-1-dependent glycolysis promotes various immune effector functions including production and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and NO. As noted earlier, virulent Mtb perturbs the glycolytic metabolism and thereby inhibits antimicrobial functions. These results suggest metabolic reprogramming to aerobic glycolysis is essential component of the anti-TB response. On the other hand, persistent inflammation can result in hyperinflammation and ultimately damage host cells and tissues. Among the featured mechanisms of HDT in TB, there is a focus on inhibition of glycolysis as well as modulation of mTOR and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathways. For example, 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG) and 3-bromopyruvate suppress activity of hexokinase which is a critical enzyme that catalyzes the first step of glycolysis (113). In LPS-activated macrophages, 2-DG suppresses the production of IL-1β and results in the accumulation of succinate (73). Additionally, LPS-induced acute lung injury is reduced by 2-DG-dependent inhibition of glycolysis (112). Among others under consideration is the HIV-protease inhibitor, ritonavir, which is an antagonist of glucose transporters (114), dichloroacetate, an inhibitor of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (115), and FX11, a specific inhibitor of lactate dehydrogenase. In LPS-activated RAW 264.7 mouse macrophages, FX11-mediated inhibition of lactate dehydrogenase resulted in the downregulation of cytokine and iNOS production (116). Likewise, TEPP46 is small molecule that inhibits the activity of pyruvate kinase M2; this inhibitor attenuates activation of PKM2 in LPS-induced macrophage in vivo and results in suppression of IL-1β production (80).
Induction of autophagy can be potential defense strategy used by cells to eradicate Mtb infection. The enzyme, mTOR kinase, negatively regulates autophagy; as such, mTOR kinase inhibitors may be potent candidates for HDT for the elimination of Mtb infection. Other mTOR inhibitors including rapamycin and torin serve to limit the increased levels of lactate detected in Mtb-infected macrophages (54). Rapamycin-mediated activation of autophagy results in acidification of mycobacterial phagosomes and thus decreased survival of BCG (117). Loperamide induces mTOR-independent autophagy and likewise controls intracellular Mtb burden in lung macrophages (119). However, the use of these inhibitors has several limitations. For example, rapamycin-induced autophagy resulted in enhanced intracellular bacterial replication in HIV/H37Rv co-infected cells (118). Therefore, pharmacological induction of autophagy should be carefully evaluated among the candidate drugs to be used for HDT.
HDT in Lipid Metabolism
Mtb exploits host lipid or fatty acid metabolism to promote its own survival and growth. Foamy macrophages are recruited to granulome where and are included in the barrier that forms around Mtb-infected phagocytic cells to which they provide support and nutrition. Toward this end, infection with Mtb induces the synthesis of LDs and fatty acids in host cell. Targeting the lipid synthesis may be a good strategy for initial HDT with the goal of eliminating Mtb. 5' AMPK is a highly conserved master regulator which can restore the energy balance by shifting cellular metabolism from one that consumes ATP to a catabolic mechanism that generates ATP (129). AMPK and other metabolic energy sensors are critical in maintaining various functions of Mtb-infected host immune cells, including autophagy, fatty acid β- oxidation, and metabolic reprogramming; the AMPK pathway also plays multi-faceted roles in promoting host defense against viral and bacterial infection. As such, molecules that are targeted by AMPK-targeted are considered to be effective adjuvant agents used to combat Mtb infection (130, 131). Metformin, a drug that is clinically-approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes functions by activating the AMPK-mediated signaling pathway (121). Treatment with metformin can limit intracellular Mtb growth in macrophages via induction mitochondrial ROS and can thereby reduce activation of inflammatory-related gene expression. Also, metformin shows some synergy with conventional anti-TB drugs, including isoniazid or ethionamide when evaluated in Mtb-infected mice. Metformin treatment also decreases the incidence of latent TB (120). AICAR (5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-β-D-ribofuranoside) is another agent that activates AMPK; AICAR activates autophagy pathways in macrophages and thus promotes antibacterial activity against Mtb. AICAR-mediated AMPK-activation also results in the activation of the PPARGC1 (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, coactivator 1) pathway; this latter pathway regulates mitochondrial biogenesis and energy metabolism in macrophages and in Drosophila melanogaster infected with M. marinum (122).
Factors that suppress lipid synthesis can limit inflammation and balance the inflammatory state of the host. Among several candidate molecules, C75 and cerulenin inhibit fatty acid synthase. C75 effectively lowers free fatty acid accumulation in mice with sepsis and limits inflammation and oxidative stress (123). Additionally, C75-mediated inhibition of lipid-derived droplet formation results in a switch from M2 to M1 macrophage polarization, resulting in enhanced production of both ROS and NO generation (124). Additionally, inhibition of fatty acid synthase by C75 and cerulenin results in downregulated uncoupling protein (UCP2)- mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation (125). GW9662, an antagonist of PPARγ, acts as a key modulator of lipid metabolism, inflammation, and pathogenesis in BCG-infected macrophages; this result suggests that regulation of lipid metabolism may be a strong potential host target for novel TB therapy (91). Likewise, sirtuins (SIRTs) have been recognized as potential targets for anti-TB therapeutics. Sirtuins are enzymes with deacetylase activity that modulate cellular process by inhibiting NF-κB signaling; this results in a downregulation of the pro-inflammatory response and upregulation of fatty acid oxidation and anti- inflammatory response by targeting Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α) (126, 127). SIRT1 expression is diminished in Mtb-infected THP-1 macrophages and in whole mouse lung tissue. SIRT1 promotes inflammatory resolution by downregulating the expression of the RelA/p65 unit of NF-κB (128). SIRT6 also suppress pro-inflammatory and antimicrobial responses at the early stages of Mtb infection (76).
Conclusion
Immunometabolism is among the critical features that define the intimate relationship between host and the Mtb pathogen; a clear understanding of these interactions will be essential for limiting the progression of the TB. Metabolic reprogramming from OXPHOS to glycolysis in Mtb infection results in the upregulated expression of numerous pro-inflammatory cytokines and antimicrobial effector molecules. Further investigation will be needed in order to understand more fully the relationship between Mtb and host metabolism. How and when Mtb exploit the host metabolism is not clearly understood at this time; clarification will be critical in order to identify the most appropriate candidates for HDT. Among those currently under consideration is Mtb-mediated modulation of glucose and/or lipid metabolism. Glucose metabolism might be targeted at the early stage, which would ultimately provide a boost to the Warburg effect. Thus, more efficient elimination of Mtb bacteria; by contrast, targeting glucose metabolism at a later stage may result in a much needed- alleviation of hyperinflammation. A better understanding of metabolic reprogramming in TB will provide further insights toward novel therapeutic strategies.
Author Contributions
J-SK, Y-RK, and C-SY designed, conceptualized, and wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This work was supported by the NRF grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (2016R1D1A1A02937312 and 2019R1I1A2A01064237); a grant from the KHIDI, funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (HI16C1653).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all members of the Infection Biology Lab for critical reading and discussion of the manuscript.
Abbreviations
Mtb, Mycobacterium tuberculosis; TB, Tuberculosis; HDT, Host-directed target; TLRs, Toll-like receptors; DC, Dendritic cell; IL, Interleukin; TNF, Tumor necrosis factor; iNOS/NOS2, inducible nitric oxide synthase/nitric oxide synthase 2; TGF-β, Transforming growth factor β; OXPHOS, Oxidative phosphorylation; DM, Diabetes mellitus; MDR-TB, Multidrug-resistant TB; XDR-TB, Extensively drug-resistance TB; NO, Nitric oxide; ROS, Reactive oxygen species; HIF-1, Hypoxia-induced factor 1; NF-κB, Nuclear factor-κB; CypD, Cyclophililn D; PHD, Prolyl hydrolases; FIH, Factor inhibiting HIF; PFKFB3, 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3; F-2,6-BP, Fructose-2,6-diphosphate; SDH, Succinate dehydrogenase; LPS, Lipopolysaccharide; ACOD1, Aconitate decarboxylase 1; Irg1, Immune-responsive gene1; PKM2, Pyruvate kinase M2; ARG, Arginase; PPARs, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors; LXR, Liver X receptor; SREBPs, Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins; LD, Lipid droplet; FASN, Fatty acid synthase; DGAT, Diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase; ACAT, Acyl-CoA:cholesterol O- acyltransferase; Plin, Perilipin; TFEB, Transcription factor EB; mTOR, Mammal target of rapamycin; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; 2-DG, 2-deoxyglucose; PPARGC1, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, coactivator 1; AICAR, 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-β-D-ribofuranoside; UCP2, Mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2; SIRTs, Sirtuins; PGC-1α, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha.
References
2. Saunders BM, Cooper AM. Restraining mycobacteria: role of granulomas in mycobacterial infections. Immunol Cell Biol. (2000) 78:334–41. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1711.2000.00933.x
3. Davis JM, Ramakrishnan L. The role of the granuloma in expansion and dissemination of early tuberculous infection. Cell. (2009) 136:37–49. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.11.014
4. Flynn JL, Chan J, Lin PL. Macrophages and control of granulomatous inflammation in tuberculosis. Mucosal Immunol. (2011) 4:271–8. doi: 10.1038/mi.2011.14
5. Ehlers S, Schaible U. The granuloma in tuberculosis: dynamics of a host–pathogen collusion. Front Immunol. (2013) 3:411. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00411
6. van Crevel R, Ottenhoff THM, van der Meer JWM. Innate immunity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. (2002) 15:294–309. doi: 10.1128/CMR.15.2.294-309.2002
7. Noss EH, Pai RK, Sellati TJ, Radolf JD, Belisle J, Golenbock DT, et al. Toll-like receptor 2-dependent inhibition of macrophage class II MHC expression and antigen processing by 19-kDa lipoprotein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. (2001) 167:910–8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.2.910
8. Pai RK, Convery M, Hamilton TA, Boom WH, Harding CV. Inhibition of IFN-γ- induced class II transactivator expression by a 19-kDa lipoprotein from Mycobacterium tuberculosis: a potential mechanism for immune evasion. J Immunol. (2003) 171:175–84. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.1.175
9. Richardson ET, Shukla S, Sweet DR, Wearsch PA, Tsichlis PN, Boom WH, et al. Toll-like receptor 2-dependent extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected macrophages drives anti-inflammatory responses and inhibits Th1 polarization of responding T cells. Infect Immunity. (2015) 83:2242–54. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00135-15
10. Barnes PF, Lu S, Abrams JS, Wang E, Yamamura M, Modlin RL. Cytokine production at the site of disease in human tuberculosis. Infect Immun. (1993) 61:3482–9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.61.8.3482-3489.1993
11. Verbon A, Juffermans N, Van Deventer SJ, Speelman P, Van Deutekom H, Van Der Poll T. Serum concentrations of cytokines in patients with active tuberculosis (TB) and after treatment. Clin Exp Immunol. (1999) 115:110–3. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00783.x
12. Redford PS, Murray PJ, O'Garra A. The role of IL-10 in immune regulation during M. tuberculosis infection. Mucosal Immunol. (2011) 4:261–70. doi: 10.1038/mi.2011.7
13. Wu M, Aung H, Hirsch CS, Toossi Z. Inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis- induced signalling by transforming growth factor-beta in human mononuclear phagocytes. Scand J Immunol. (2012) 75:301–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2011.02668.x
14. Cambier CJ, Falkow S, Ramakrishnan L. Host evasion and exploitation schemes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Cell. (2014) 159:1497–509. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.11.024
15. Gleeson LE, Sheedy FJ, Palsson-McDermott EM, Triglia D, O'Leary SM, O'Sullivan MP, et al. Cutting edge: Mycobacterium tuberculosis induces aerobic glycolysis in human alveolar macrophages that is required for control of intracellular bacillary replication. J Immunol. (2016) 196:2444–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501612
16. Qualls JE, Murray PJ. Immunometabolism within the tuberculosis granuloma: amino acids, hypoxia, and cellular respiration. Semin Immunopathol. (2016) 38:139–52. doi: 10.1007/s00281-015-0534-0
17. Shi L, Eugenin EA, Subbian S. Immunometabolism in tuberculosis. Front Immunol. (2016) 7:150. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00150
18. Escoll P, Buchrieser C. Metabolic reprogramming of host cells upon bacterial infection: Why shift to a Warburg-like metabolism? FEBS J. (2018) 285:2146–60. doi: 10.1111/febs.14446
19. Lunt SY, Heiden MGV. Aerobic glycolysis: meeting the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol. (2011) 27:441–64. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154237
20. Pérez A, Brown HS III, Restrepo BI. Association between tuberculosis and diabetes in the Mexican border and non-border regions of Texas. Am J Trop Med Hyg. (2006) 74:604–11. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2006.74.604
21. Dobler CC, Flack JR, Marks GB. Risk of tuberculosis among people with diabetes mellitus: an Australian nationwide cohort study. BMJ Open. (2012) 2:e000666. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2011-000666
22. Young F, Wotton CJ, Critchley JA, Unwin NC, Goldacre MJ. Increased risk of tuberculosis disease in people with diabetes mellitus: record-linkage study in a UK population. J Epidemiol Community Health. (2012) 66:519–23. doi: 10.1136/jech.2010.114595
23. Vallerskog T, Martens GW, Kornfeld H. Diabetic mice display a delayed adaptive immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. (2010) 184:6275–82. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000304
24. Hodgson K, Morris J, Bridson T, Govan B, Rush C, Ketheesan N. Immunological mechanisms contributing to the double burden of diabetes and intracellular bacterial infections. Immunology. (2015) 144:171–85. doi: 10.1111/imm.12394
25. Rosa LF, Cury Y, Curi R. Effects of insulin, glucocorticoids and thyroid hormones on the activities of key enzymes of glycolysis, glutaminolysis, the pentose-phosphate pathway and the Krebs cycle in rat macrophages. J Endocrinol. (1992) 135:213–9. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1350213
26. Ilyas R, Wallis R, Soilleux EJ, Townsend P, Zehnder D, Tan BK, et al. High glucose disrupts oligosaccharide recognition function via competitive inhibition: a potential mechanism for immune dysregulation in diabetes mellitus. Immunobiology. (2011) 216:126–31. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2010.06.002
27. Lachmandas E, Vrieling F, Wilson LG, Joosten SA, Netea MG, Ottenhoff TH, et al. The effect of hyperglycaemia on in vitro cytokine production and macrophage infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLoS ONE. (2015) 10:e0117941. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117941
28. Yogev O, Lagos D, Enver T, Boshoff C. Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus microRNAs induce metabolic transformation of infected cells. PLoS Pathog. (2014) 10:e1004400. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004400
29. Dagenais-Lussier X, Mouna A, Routy JP, Tremblay C, Sekaly RP, El-Far M, et al. Current topics in HIV-1 pathogenesis: the emergence of deregulated immuno-metabolism in HIV- infected subjects. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2015) 26:603–13. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2015.09.001
30. Aounallah M, Dagenais-Lussier X, El-Far M, Mehraj V, Jenabian MA, Routy JP, et al. Current topics in HIV pathogenesis, part 2: Inflammation drives a Warburg-like effect on the metabolism of HIV-infected subjects. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2016) 28:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2016.01.001
31. Hegedus A, Kavanagh Williamson M, Huthoff H. HIV-1 pathogenicity and virion production are dependent on the metabolic phenotype of activated CD4+ T cells. Retrovirology. (2014) 11:98. doi: 10.1186/s12977-014-0098-4
32. Palmer CS, Ostrowski M, Gouillou M, Tsai L, Yu D, Zhou J, et al. Increased glucose metabolic activity is associated with CD4+ T-cell activation and depletion during chronic HIV infection. Aids. (2014) 28:297–309. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000128
33. Sen S, Kaminiski R, Deshmane S, Langford D, Khalili K, Amini S, et al. Role of hexokinase- 1 in the survival of HIV-1-infected macrophages. Cell Cycle. (2015) 14:980–9. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1006971
34. Gandhi NR, Moll A, Sturm AW, Pawinski R, Govender T, Lalloo U, et al. Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis as a cause of death in patients co-infected with tuberculosis and HIV in a rural area of South Africa. Lancet. (2006) 368:1575–80. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69573-1
35. Shah NS, Wright A, Bai G-H, Barrera L, Boulahbal F, Martín-Casabona N, et al. Worldwide emergence of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Emerg Infect Dis. (2007) 13:380–7. doi: 10.3201/eid1303.061400
36. Tobin DM. Host-directed therapies for tuberculosis. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Med. (2015) 5:a021196. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a021196
37. O'Neill LAJ, Kishton RJ, Rathmell J. A guide to immunometabolism for immunologists. Nat Rev Immunol. (2016) 16:553–65. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.70
38. Doughty CA, Bleiman BF, Wagner DJ, Dufort FJ, Mataraza JM, Roberts MF, et al. Antigen receptor–mediated changes in glucose metabolism in B lymphocytes: role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling in the glycolytic control of growth. Blood. (2006) 107:4458–65. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-12-4788
39. Krawczyk CM, Holowka T, Sun J, Blagih J, Amiel E, DeBerardinis RJ, et al. Toll-like receptor-induced changes in glycolytic metabolism regulate dendritic cell activation. Blood. (2010) 115:4742–9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-10-249540
40. Michalek RD, Gerriets VA, Jacobs SR, Macintyre AN, MacIver NJ, Mason EF, et al. Cutting edge: distinct glycolytic and lipid oxidative metabolic programs are essential for effector and regulatory CD4+ T cell subsets. J Immunol. (2011) 186:3299–303. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003613
41. van der Windt GJ, Everts B, Chang CH, Curtis JD, Freitas TC, Amiel E, et al. Mitochondrial respiratory capacity is a critical regulator of CD8+ T cell memory development. Immunity. (2012) 36:68–78. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.12.007
42. Donnelly RP, Loftus RM, Keating SE, Liou KT, Biron CA, Gardiner CM, et al. mTORC1- dependent metabolic reprogramming is a prerequisite for NK cell effector function. J Immunol. (2014) 193:4477–84. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401558
43. O'Sullivan D, van der Windt GJ, Huang SC, Curtis JD, Chang CH, Buck MD, et al. Memory CD8(+) T cells use cell-intrinsic lipolysis to support the metabolic programming necessary for development. Immunity. (2014) 41:75–88. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.005
44. Gordon S. Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol. (2003) 3:23–35. doi: 10.1038/nri978
45. Gordon S, Taylor PR. Monocyte and macrophage heterogeneity. Nat Rev Immunol. (2005) 5:953–64. doi: 10.1038/nri1733
46. Mosser DM. The many faces of macrophage activation. J Leukoc Biol. (2003) 73:209–12. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0602325
47. Martinez FO, Gordon S, Locati M, Mantovani A. Transcriptional profiling of the human monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation and polarization: new molecules and patterns of gene expression. J Immunol. (2006) 177:7303–11. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.10.7303
48. Biswas SK, Mantovani A. Macrophage plasticity and interaction with lymphocyte subsets: cancer as a paradigm. Nat Immunol. (2010) 11:889–96. doi: 10.1038/ni.1937
49. Rodríguez-Prados J-C, Través PG, Cuenca J, Rico D, Aragonés J, Martín-Sanz P, et al. Substrate fate in activated macrophages: a comparison between innate, classic, and alternative activation. J Immunol. (2010) 185:605–14. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901698
50. Galvan-Pena S, O'Neill LA. Metabolic reprograming in macrophage polarization. Front Immunol. (2014) 5:420. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00420
51. Martinez FO, Gordon S. The M1 and M2 paradigm of macrophage activation: time for reassessment. F1000Prime Rep. (2014) 6:13. doi: 10.12703/P6-13
52. Patel CH, Powell JD. Targeting T cell metabolism to regulate T cell activation, differentiation and function in disease. Curr Opin Immunol. (2017) 46:82–8. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2017.04.006
53. Hu Z, Zou Q, Su B. Regulation of T cell immunity by cellular metabolism. Front Med. (2018) 12:463–72. doi: 10.1007/s11684-018-0668-2
54. Lachmandas E, Beigier-Bompadre M, Cheng SC, Kumar V, van Laarhoven A, Wang X, et al. Rewiring cellular metabolism via the AKT/mTOR pathway contributes to host defence against Mycobacterium tuberculosis in human and murine cells. Eur J Immunol. (2016) 46:2574–86. doi: 10.1002/eji.201546259
55. Tzelepis F, Blagih J, Khan N, Gillard J, Mendonca L, Roy DG, et al. Mitochondrial cyclophilin D regulates T cell metabolic responses and disease tolerance to tuberculosis. Sci Immunol. (2018) 3:eaar4135. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aar4135
56. Semenza GL. HIF-1: upstream and downstream of cancer metabolism. Curr Opin Genet Dev. (2010) 20:51–6. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2009.10.009
57. Semenza GL, Roth PH, Fang HM, Wang GL. Transcriptional regulation of genes encoding glycolytic enzymes by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem. (1994) 269:23757–63.
58. Wang GL, Semenza GL. Purification and characterization of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem. (1995) 270:1230–7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.3.1230
59. Rius J, Guma M, Schachtrup C, Akassoglou K, Zinkernagel AS, Nizet V, et al. NF-κB links innate immunity to the hypoxic response through transcriptional regulation of HIF-1α. Nature. (2008) 453:807–11. doi: 10.1038/nature06905
60. Nizet V, Johnson RS. Interdependence of hypoxic and innate immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. (2009) 9:609–17. doi: 10.1038/nri2607
61. Semenza GL. HIF-1: mediator of physiological and pathophysiological responses to hypoxia. J Appl Physiol. (2000) 88:1474–80. doi: 10.1152/jappl.2000.88.4.1474
62. Corcoran SE, O'Neill LAJ. HIF1α and metabolic reprogramming in inflammation. J Clin Investig. (2016) 126:3699–707. doi: 10.1172/JCI84431
63. Subbian S, Tsenova L, Yang G, O'Brien P, Parsons S, Peixoto B, et al. Chronic pulmonary cavitary tuberculosis in rabbits: a failed host immune response. Open Biol. (2011) 1:110016. doi: 10.1098/rsob.110016
64. Koo M-S, Subbian S, Kaplan G. Strain specific transcriptional response in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infected macrophages. Cell Commun Signal. (2012) 10:2. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-10-2
65. Shi L, Salamon H, Eugenin EA, Pine R, Cooper A, Gennaro ML. Infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis induces the Warburg effect in mouse lungs. Sci Rep. (2015) 5:18176. doi: 10.1038/srep18176
66. Subbian S, Tsenova L, Kim M-J, Wainwright HC, Visser A, Bandyopadhyay N, et al. Lesion-specific immune response in granulomas of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis: a pilot study. PLoS ONE. (2015) 10:e0132249. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132249
67. Shin J-H, Yang J-Y, Jeon B-Y, Yoon YJ, Cho S-N, Kang Y-H, et al. 1H NMR-based metabolomic profiling in mice infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Proteome Res. (2011) 10:2238–47. doi: 10.1021/pr101054m
68. Pilkis SJ, Claus TH, Kurland IJ, Lange AJ. 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase: a metabolic signaling enzyme. Annu Rev Biochem. (1995) 64:799–835. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.64.070195.004055
69. Silver RF, Walrath J, Lee H, Jacobson BA, Horton H, Bowman MR, et al. Human alveolar macrophage gene responses to Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains H37Ra and H37Rv. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2009) 40:491–504. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2008-0219OC
70. Cumming BM, Addicott KW, Adamson JH, Steyn AJC. Mycobacterium tuberculosis induces decelerated bioenergetic metabolism in human macrophages. eLife. (2018) 7:e39169. doi: 10.7554/eLife.39169.018
71. Russell SL, Lamprecht DA, Mandizvo T, Jones TT, Naidoo V, Addicott KW, et al. Compromised metabolic reprogramming is an early indicator of CD8(+) T cell dysfunction during chronic Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Cell Rep. (2019) 29:3564–79.e3565. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.11.034
72. Selak MA, Armour SM, MacKenzie ED, Boulahbel H, Watson DG, Mansfield KD, et al. Succinate links TCA cycle dysfunction to oncogenesis by inhibiting HIF-α prolyl hydroxylase. Cancer Cell. (2005) 7:77–85. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2004.11.022
73. Tannahill GM, Curtis AM, Adamik J, Palsson-McDermott EM, McGettrick AF, Goel G, et al. Succinate is an inflammatory signal that induces IL-1β through HIF-1α. Nature. (2013) 496:238–42. doi: 10.1038/nature11986
74. Mills E, O'Neill LAJ. Succinate: a metabolic signal in inflammation. Trends Cell Biol. (2014) 24:313–20. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2013.11.008
75. Mills EL, Kelly B, Logan A, Costa ASH, Varma M, Bryant CE, et al. Succinate dehydrogenase supports metabolic repurposing of mitochondria to drive inflammatory macrophages. Cell. (2016) 167:457–70.e413. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.08.064
76. Shi L, Jiang Q, Bushkin Y, Subbian S, Tyagi S. Biphasic dynamics of macrophage immunometabolism during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. mBio. (2019) 10:e02550–18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02550-18
77. Cordes T, Wallace M, Michelucci A, Divakaruni AS, Sapcariu SC, Sousa C, et al. Immunoresponsive gene 1 and itaconate inhibit succinate dehydrogenase to modulate intracellular succinate levels. J Biol Chem. (2016) 291:14274–84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.685792
78. Lampropoulou V, Sergushichev A, Bambouskova M, Nair S, Vincent E, Loginicheva E, et al. Itaconate links inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase with macrophage metabolic remodeling and regulation of inflammation. Cell Metab. (2016) 24:158–66. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.06.004
79. Michelucci A, Cordes T, Ghelfi J, Pailot A, Reiling N, Goldmann O, et al. Immune- responsive gene 1 protein links metabolism to immunity by catalyzing itaconic acid production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2013) 110:7820–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1218599110
80. Palsson-McDermott EM, Curtis AM, Goel G, Lauterbach MA, Sheedy FJ, Gleeson LE, et al. Pyruvate kinase M2 regulates Hif-1α activity and IL-1β induction and is a critical determinant of the warburg effect in LPS-activated macrophages. Cell Metab. (2015) 21:65–80. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.12.005
82. Munder M. Arginase: an emerging key player in the mammalian immune system. Br J Pharmacol. (2009) 158:638–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00291.x
83. Rath M, Müller I, Kropf P, Closs EI, Munder M. Metabolism via arginase or nitric oxide synthase: two competing arginine pathways in macrophages. Front Immunol. (2014) 5:532. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00532
84. Jenkinson CP, Grody WW, Cederbaum SD. Comparative properties of arginases. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B. (1996) 114:107–32. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(95)02138-8
85. Wu G, Morris SM Jr. Arginine metabolism: nitric oxide and beyond. Biochem J. (1998) 336:1–17. doi: 10.1042/bj3360001
86. El Kasmi KC, Qualls JE, Pesce JT, Smith AM, Thompson RW, Henao-Tamayo M, et al. Toll-like receptor–induced arginase 1 in macrophages thwarts effective immunity against intracellular pathogens. Nat Immunol. (2008) 9:1399–406. doi: 10.1038/ni.1671
87. Mattila JT, Ojo OO, Kepka-Lenhart D, Marino S, Kim JH, Eum SY, et al. Microenvironments in tuberculous granulomas are delineated by distinct populations of macrophage subsets and expression of nitric oxide synthase and arginase isoforms. J Immunol. (2013) 191:773–84. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300113
88. Roy S, Schmeier S, Kaczkowski B, Arner E, Alam T, Ozturk M, et al. Transcriptional landscape of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in macrophages. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:6758. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24509-6
89. Szatmari I, Torocsik D, Agostini M, Nagy T, Gurnell M, Barta E, et al. PPARgamma regulates the function of human dendritic cells primarily by altering lipid metabolism. Blood. (2007) 110:3271–80. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-06-096222
90. Mei CL, He P, Cheng B, Liu W, Wang YF, Wan JJ. Chlamydia pneumoniae induces macrophage-derived foam cell formation via PPAR alpha and PPAR gamma-dependent pathways. Cell Biol Int. (2009) 33:301–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cellbi.2008.12.002
91. Almeida PE, Roque NR, Magalhaes KG, Mattos KA, Teixeira L, Maya-Monteiro C, et al. Differential TLR2 downstream signaling regulates lipid metabolism and cytokine production triggered by Mycobacterium bovis BCG infection. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2014) 1841:97–107. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.10.008
92. McRae S, Iqbal J, Sarkar-Dutta M, Lane S, Nagaraj A, Ali N, et al. The Hepatitis C Virus- induced NLRP3 inflammasome activates the sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) and regulates lipid metabolism. J Biol Chem. (2016) 291:3254–67. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.694059
93. Knight M, Braverman J, Asfaha K, Gronert K, Stanley S. Lipid droplet formation in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infected macrophages requires IFN-gamma/HIF-1alpha signaling and supports host defense. PLoS Pathog. (2018) 14:e1006874. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006874
94. Pawlak M, Lefebvre P, Staels B. Molecular mechanism of PPARalpha action and its impact on lipid metabolism, inflammation and fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. (2015) 62:720–33. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.10.039
95. Nicolaou G, Goodall AH, Erridge C. Diverse bacteria promote macrophage foam cell formation via Toll-like receptor-dependent lipid body biosynthesis. J Atheroscler Thromb. (2012) 19:137–48. doi: 10.5551/jat.10249
96. Huang YL, Morales-Rosado J, Ray J, Myers TG, Kho T, Lu M, et al. Toll-like receptor agonists promote prolonged triglyceride storage in macrophages. J Biol Chem. (2014) 289:3001–12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.524587
97. Hu X, Binns D, Reese ML. The coccidian parasites Toxoplasma and Neospora dysregulate mammalian lipid droplet biogenesis. J Biol Chem. (2017) 292:11009–20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.768176
98. Silva AR, Pacheco P, Vieira-de-Abreu A, Maya-Monteiro CM, D'Alegria B, Magalhaes KG, et al. Lipid bodies in oxidized LDL-induced foam cells are leukotriene-synthesizing organelles: a MCP-1/CCL2 regulated phenomenon. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2009) 1791:1066–75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.06.004
99. Fan B, Gu JQ, Yan R, Zhang H, Feng J, Ikuyama S. High glucose, insulin and free fatty acid concentrations synergistically enhance perilipin 3 expression and lipid accumulation in macrophages. Metabolism. (2013) 62:1168–79. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.02.013
100. Brasaemle DL. Thematic review series: adipocyte biology. The perilipin family of structural lipid droplet proteins: stabilization of lipid droplets and control of lipolysis. J Lipid Res. (2007) 48:2547–59. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R700014-JLR200
101. Theocharis S, Margeli A, Vielh P, Kouraklis G. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ ligands as cell-cycle modulators. Cancer Treat Rev. (2004) 30:545–54. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2004.04.004
102. Almeida PE, Carneiro AB, Silva AR, Bozza PT. PPARgamma expression and function in mycobacterial infection: roles in lipid metabolism, immunity, and bacterial killing. PPAR Res. (2012) 2012:383829. doi: 10.1155/2012/383829
103. Almeida PE, Silva AR, Maya-Monteiro CM, Töröcsik D, D′Ávila H, Dezsö B, et al. Mycobacterium bovis bacillus calmette-guérin infection induces TLR2-dependent peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ expression and activation: functions in inflammation, lipid metabolism, and pathogenesis. J Immunol. (2009) 183:1337–45. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900365
104. Mahajan S, Dkhar HK, Chandra V, Dave S, Nanduri R, Janmeja AK, et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis modulates macrophage lipid-sensing nuclear receptors PPARγ and TR4 for survival. J Immunol. (2012) 188:5593–603. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103038
105. Larigauderie G, Furman C, Jaye M, Lasselin C, Copin C, Fruchart JC, et al. Adipophilin enhances lipid accumulation and prevents lipid efflux from THP-1 macrophages: potential role in atherogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2004) 24:504–10. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000115638.27381.97
106. Miyanari Y, Atsuzawa K, Usuda N, Watashi K, Hishiki T, Zayas M, et al. The lipid droplet is an important organelle for hepatitis C virus production. Nat Cell Biol. (2007) 9:1089–97. doi: 10.1038/ncb1631
107. Rakhshandehroo M, Knoch B, Muller M, Kersten S. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha target genes. PPAR Res. (2010) 2010:1–20. doi: 10.1155/2010/612089
108. Mandard S, Müller M, Kersten S. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α target genes. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS. (2004) 61:393–416. doi: 10.1007/s00018-003-3216-3
109. Kim YS, Lee H-M, Kim JK, Yang C-S, Kim TS, Jung M, et al. PPAR-α activation mediates innate host defense through induction of TFEB and lipid catabolism. J Immunol. (2017) 198:3283–95. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601920
110. Russell DG, Huang L, VanderVen BC. Immunometabolism at the interface between macrophages and pathogens. Nat Rev Immunol. (2019) 19:291–304. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0124-9
111. Sotgiu G, Centis R, D'Ambrosio L, Migliori GB. Tuberculosis treatment and drug regimens. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. (2015) 5:a017822. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a017822
112. Zhong WJ, Yang HH, Guan XX, Xiong JB, Sun CC, Zhang CY, et al. Inhibition of glycolysis alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in a mouse model. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:4641–54. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27261
113. Odçikin E, Ozdemir H, Ciftçi M, Capoglu I. Investigation of red blood cell carbonic anhydrase, glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase, hexokinase enzyme activities, and zinc concentration in patients with hyperthyroid diseases. Endocr Res. (2002) 28:61–8. doi: 10.1081/ERC-120004538
114. Hresko RC, Hruz PW. HIV protease inhibitors act as competitive inhibitors of the cytoplasmic glucose binding site of GLUTs with differing affinities for GLUT1 and GLUT4. PLoS ONE. (2011) 6:e25237. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025237
115. Tataranni T, Agriesti F, Pacelli C, Ruggieri V, Laurenzana I, Mazzoccoli C, et al. Dichloroacetate affects mitochondrial function and stemness-associated properties in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Cells. (2019) 8:478. doi: 10.3390/cells8050478
116. Song YJ, Kim A, Kim GT, Yu HY, Lee ES, Park MJ, et al. Inhibition of lactate dehydrogenase A suppresses inflammatory response in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Mol Med Rep. (2019) 19:629–37. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9678
117. Gutierrez MG, Master SS, Singh SB, Taylor GA, Colombo MI, Deretic V. Autophagy is a defense mechanism inhibiting BCG and Mycobacterium tuberculosis survival in infected macrophages. Cell. (2004) 119:753–66. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.038
118. Andersson AM, Andersson B, Lorell C, Raffetseder J, Larsson M, Blomgran R. Autophagy induction targeting mTORC1 enhances Mycobacterium tuberculosis replication in HIV co-infected human macrophages. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:28171. doi: 10.1038/srep28171
119. Juarez E, Carranza C, Sanchez G, Gonzalez M, Chavez J, Sarabia C, et al. Loperamide restricts intracellular growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in lung macrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2016) 55:837–47. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2015-0383OC
120. Singhal A, Jie L, Kumar P, Hong GS, Leow MK, Paleja B, et al. Metformin as adjunct antituberculosis therapy. Sci Transl Med. (2014) 6:263ra159. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3009885
121. Rena G, Hardie DG, Pearson ER. The mechanisms of action of metformin. Diabetologia. (2017) 60:1577–85. doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4342-z
122. Yang CS, Kim JJ, Lee HM, Jin HS, Lee SH, Park JH, et al. The AMPK-PPARGC1A pathway is required for antimicrobial host defense through activation of autophagy. Autophagy. (2014) 10:785–802. doi: 10.4161/auto.28072
123. Idrovo JP, Yang WL, Jacob A, Corbo L, Nicastro J, Coppa GF, et al. Inhibition of lipogenesis reduces inflammation and organ injury in sepsis. J Surg Res. (2016) 200:242–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2015.06.059
124. Bose D, Banerjee S, Chatterjee N, Das S, Saha M, Saha KD. Inhibition of TGF-β induced lipid droplets switches M2 macrophages to M1 phenotype. Toxicol In Vitro. (2019) 58:207–14. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2019.03.037
125. Moon JS, Lee S, Park MA, Siempos II, Haslip M, Lee PJ, et al. UCP2-induced fatty acid synthase promotes NLRP3 inflammasome activation during sepsis. J Clin Invest. (2015) 125:665–80. doi: 10.1172/JCI78253
126. Kauppinen A, Suuronen T, Ojala J, Kaarniranta K, Salminen A. Antagonistic crosstalk between NF-κB and SIRT1 in the regulation of inflammation and metabolic disorders. Cell Signal. (2013) 25:1939–48. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.06.007
127. Vachharajani VT, Liu T, Wang X, Hoth JJ, Yoza BK, McCall CE. Sirtuins link inflammation and metabolism. J Immunol Res. (2016) 2016:8167273. doi: 10.1155/2016/8167273
128. Cheng CY, Gutierrez NM, Marzuki MB, Lu X, Foreman TW, Paleja B, et al. Host sirtuin 1 regulates mycobacterial immunopathogenesis and represents a therapeutic target against tuberculosis. Sci Immunol. (2017) 2:eaaj1789. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aaj1789
129. Garcia D, Shaw RJ. AMPK: mechanisms of cellular energy sensing and restoration of metabolic balance. Mol Cell. (2017) 66:789–800. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.05.032
130. Silwal P, Kim JK, Yuk JM, Jo EK. AMP-activated protein kinase and host defense against infection. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:3495. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113495
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis, innate immunity, immunometabolism, host-directed therapy, inflammation
Citation: Kim J-S, Kim Y-R and Yang C-S (2020) Host-Directed Therapy in Tuberculosis: Targeting Host Metabolism. Front. Immunol. 11:1790. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01790
Received: 12 May 2020; Accepted: 06 July 2020;
Published: 13 August 2020.
Edited by:
Anca Dorhoi, Friedrich Loeffler Institute, GermanyReviewed by:
Arshad Khan, McGovern Medical School at UTHealth, United StatesElsa Anes, University of Lisbon, Portugal
Copyright © 2020 Kim, Kim and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chul-Su Yang, Y2h1bHN1eWFuZyYjeDAwMDQwO2hhbnlhbmcuYWMua3I=
 Jae-Sung Kim
Jae-Sung Kim Ye-Ram Kim
Ye-Ram Kim Chul-Su Yang
Chul-Su Yang