Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Hyperactivation Associates With Follicular Helper T Cell Differentiation and Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- 1China-Australia Centre for Personalised Immunology, Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 2Department of Rheumatology, Shanghai Institute of Rheumatology, Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 3Hubei Provincial Key Laboratory of Occurrence and Intervention of Rheumatic Diseases, Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University for Nationalities, Enshi, China
- 4Department of Immunology and Infectious Disease, John Curtin School of Medical Research, The Australian National University, Canberra, ACT, Australia
- 5Laboratory of Immunology for Environment and Health, Shandong Analysis and Test Center, Qilu University of Technology, Shandong Academy of Sciences, Jinan, China
- 6Department of Rheumatology, Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University for Nationalities, Enshi, China
- 7Department of Laboratory Medicine, Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 8Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 9Guanghua Hospital of Integrative Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai, China
by Deng, J., Fan, C., Gao, X., Zeng, Q., Guo, R., Wei, Y., et al. (2018). Front. Immunol. 9:1226. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01226
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 2 as published. One diagram (DAS28 vs. Th2), was mistakenly duplicated from another diagram (DAS28 vs. Th1) during the figure preparation. The corrected Figure 2 appears below.
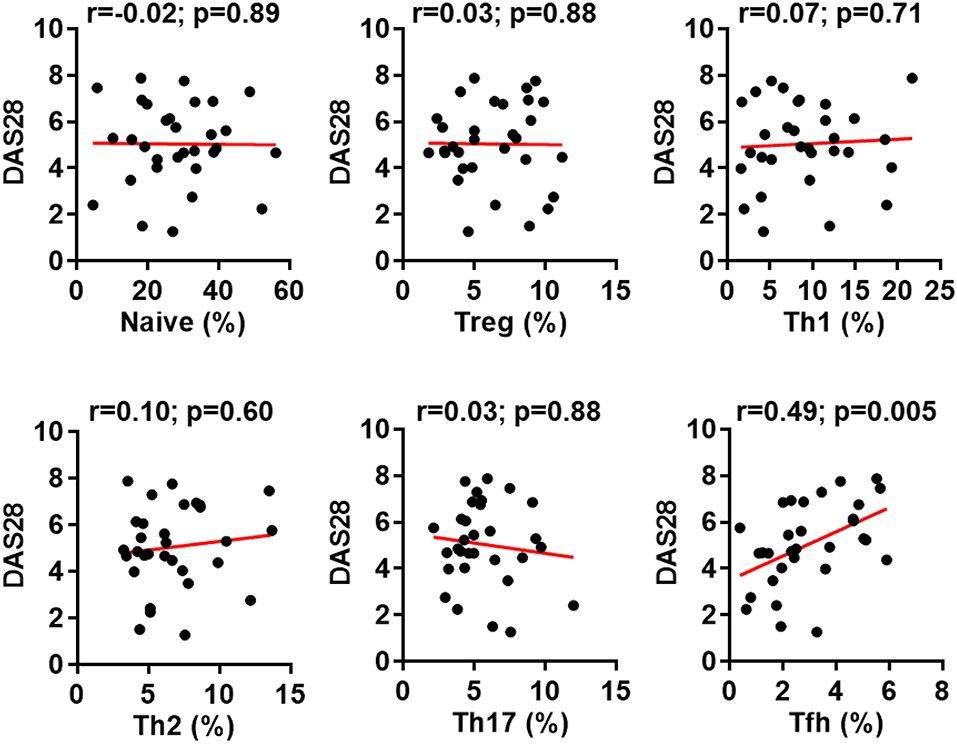
Figure 2. Increased follicular helper T (Tfh) cell differentiation correlates with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) disease activity. The percentages of CD4+ T cell subsets in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with RA were analyzed as Figure 1. The correlation between the frequencies of these subsets and the disease activities measured by DAS28 were determined using Spearman's correlation coefficient.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Keywords: rheumatoid arthritis, patient, follicular helper T cells, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, phosphorylation, IL-6
Citation: Deng J, Fan C, Gao X, Zeng Q, Guo R, Wei Y, Chen Z, Chen Y, Gong D, Feng J, Xia Y, Xiang S, Gong S, Yuan L, Shen W, Shen W, Lin L, Jiang T, He D, Lu L, Chen X and Yu D (2019) Corrigendum: Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Hyperactivation Associates With Follicular Helper T Cell Differentiation and Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 10:2008. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02008
Received: 17 March 2019; Accepted: 08 August 2019;
Published: 22 August 2019.
Edited by:
Raffi Gugasyan, Burnet Institute, AustraliaReviewed by:
Xing Chang, Westlake Institute for Advanced Study (WIAS), ChinaCopyright © 2019 Deng, Fan, Gao, Zeng, Guo, Wei, Chen, Chen, Gong, Feng, Xia, Xiang, Gong, Yuan, Shen, Shen, Lin, Jiang, He, Lu, Chen and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Liangjing Lu, bHVfX2xpYW5namluZ0AxNjMuY29t; Xiaoxiang Chen, eGlhb3hpYW5nMDcyMUAxMjYuY29t; Di Yu, ZGkueXVAYW51LmVkdS5hdQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jun Deng
Jun Deng Chaofan Fan2†
Chaofan Fan2† Ruru Guo
Ruru Guo Zhian Chen
Zhian Chen Dongyi He
Dongyi He Xiaoxiang Chen
Xiaoxiang Chen Di Yu
Di Yu