
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
MINI REVIEW article
Front. Immunol. , 29 March 2019
Sec. Multiple Sclerosis and Neuroimmunology
Volume 10 - 2019 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00628
This article is part of the Research Topic The Anatomical Basis of the Cross Talk Between Immune System and Brain View all 8 articles
The wealth of recent evidence about a bi-directional communication between nerve- and immune- cells revolutionized the traditional concept about the brain as an “immune-privileged” organ while opening novel avenues in the pathophysiology of CNS disorders. In fact, altered communication between the immune and nervous system is emerging as a common hallmark in neuro-developmental, neurodegenerative, and neuro-immunological diseases. At molecular level, the ubiquitin proteasome machinery operates as a sentinel at the crossroad between the immune system and brain. In fact, the standard proteasome and its alternative/inducible counterpart, the immunoproteasome, operate dynamically and coordinately in both nerve- and immune- cells to modulate neurotransmission, oxidative/inflammatory stress response, and immunity. When dysregulations of the proteasome system occur, altered amounts of standard- vs. immune-proteasome subtypes translate into altered communication between neurons, glia, and immune cells. This contributes to neuro-inflammatory pathology in a variety of neurological disorders encompassing Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, and Huntingtin's diseases, brain trauma, epilepsy, and Multiple Sclerosis. In the present review, we analyze those proteasome-dependent molecular interactions which sustain communication between neurons, glia, and brain circulating T-lymphocytes both in baseline and pathological conditions. The evidence here discussed converges in that upregulation of immunoproteasome to the detriment of the standard proteasome, is commonly implicated in the inflammatory- and immune- biology of neurodegeneration. These concepts may foster additional studies investigating the role of immunoproteasome as a potential target in neurodegenerative and neuro-immunological disorders.
In the last decades, wide evidence about a bi-directional communication between nerve- and immune- cells led to connect the two systems within the branch of neuro-immunology (1, 2). The functional connections between the immune and nervous system are based on common phylogenetic and embryological roots (3, 4), which are evident at both anatomical and molecular levels. Grossly, this occurs through (i) the sympathetic, mainly catecholamine, innervation of both primary and secondary lymphoid organs (5–8), and (ii) the recently discovered lymphatic pathways operating in the perivascular and meningeal spaces (9–13). Catecholamine released from sympathetic nerve terminals modulates immune activity through binding to neurotransmitter receptors, which are abundantly expressed on lymphoid cells (5–8). The amount and duration of released catecholamine, mostly dopamine (DA), dictates the stimulation/expression pattern of DA-receptors expressed on T-cells. This is seminal to activate specific intracellular cascades which in turn foster T-cell activation or suppression, T-cell differentiation toward effector vs. regulatory or memory cells, as well as migration of T-cells to non-lymphoid organs (8). At the same time, macroscopic convective fluxes of the glymphatic system enable the brain to drain the interstitial fluid (ISF) into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF); CSF bearing soluble and cellular constituents is then drained into the bloodstream via arachnoid granulations and dural sinuses, and also directly into the deep cervical lymph nodes via dural lymphatic vessels (9–13). In this way, the clearance of potentially threatening interstitial solutes is achieved, and CNS-derived antigens (Ags) are drained to antigen presenting cells (APCs) in the choroid plexus, leptomeningeal spaces, and eventually, or even directly, in the deep cervical lymph nodes (14, 15). Within APCs, the ubiquitin proteasome (UP) and autophagy (ATG) machineries process endogenously- and exogenously- derived proteins into peptide determinants, which bind to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules class I and II, respectively. CNS-derived Ags bound to MHC-I and -II are then exposed on the plasma membrane of APCs for presentation to CD8+ and CD4+ T-lymphocytes, respectively (16). Nonetheless, alternative pathways exist through which exogenously-derived Ags are cross-processed by the UP to combine with MHC-I and stimulate CD8+ T-cells (17); vice versa, endogenously-derived Ags (e.g., self- and viral peptides) can access MHC-II groove for presentation to CD4+ T-cells (18). Following associative binding of MHC molecules with T-cells receptors (TCR), presentation of CNS-derived Ags fosters activation of T-cells in periphery, while mounting CNS-directed adaptive immune responses, which may have either beneficial or detrimental effects (14, 15, 19, 20). Peripherally activated T-cells can enter the brain parenchyma by crossing all CNS barriers including the blood-CSF, the blood-leptomeningeal, and the blood-brain barrier (19, 21). Along these barriers primed CD4+ and/or CD8+ T-cells encounter APCs which expose the cognate Ag complexed with MHC-II and/or MHC-I. In the presence of specific signals (e.g., co-stimulatory molecules, adhesion ligands and inflammatory cytokine mediators), re-activation of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells by APCs leads to the recruitment of their effector machinery to produce pro-inflammatory cytokine release and cytotoxicity, respectively (14, 15, 19–22). The foremost professional APCs which foster re-activation of T-cells in the CNS are dendritic cells (DCs) and macrophages in the CSF, perivascular space and choroid plexus stroma; nonetheless, choroid epithelial cells and endothelial cells of the CNS microvasculature also behave as CNS-resident APCs, thus providing a pathway for T-cell re-activation and infiltration in the brain (23, 24). It is remarkable that once in the CNS parenchyma, T-cells interact with, and may also target glia and neurons, which indeed are able to operate as APCs (15, 25). This is magnified under oxidative/pro-inflammatory conditions, where glia and neurons readily upregulate their ability to process, load and present Ags via MHC-I/-II and MHC-I molecules, respectively (15, 25). In this novel scenario, neurotransmitters and classic immune-related molecules co-operate at the level of a hybrid junction, the “neuro-immunological synapse,” where they adopt a common language to modulate both synaptic plasticity and neuro-immunity (26, 27). These findings have revolutionized the traditional concept of the brain as an “immune-privileged” organ while opening novel clues in the pathophysiology of CNS disorders (14, 28). In fact, defective or inappropriate communication between the immune and nervous system is emerging as a common hallmark in a number of etiologically different CNS diseases including neuro-developmental, neurodegenerative and neuro-immunological disorders (28). At molecular level, the UP represents an evolutionary preserved catalytic machinery operating at the cross-road between synaptic and immune activity (29–32). Dysregulations of the UP characterize a variety of neurological disorders where immune alterations occur, such Multiple Sclerosis (MS) and neuro-infectious diseases, but also classic neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, and Huntingtin's diseases (PD, AD, HD), epilepsy, brain stroke, and drug abuse (33–42). As such, the contribute of UP in the context of inflammatory- and immune-related biology of CNS disorders has been increasingly investigated (43, 44). The present mini-review analyzes those UP-related molecular mechanisms underpinning the shift from baseline neuro-immune surveillance to inflammatory and auto-immune neuropathology.
Proteasomes are ubiquitous multi-subunit proteases which ensure cell homeostasis. Such a task is achieved by removing unfolded, misfolded, oxidized, or disordered proteins to prevent their accumulation, aggregation, and spreading (45, 46). As actors of protein degradation, proteasomes regulate most cell functions encompassing cell cycle and division, cell differentiation and development, oxidative/inflammatory stress, and immune response. To optimize these different tasks according to specific cell demands, evolution has preserved alternative subtypes of proteasomes, which despite overlapping in structure and functions, differ for catalytic subunits and substrate specificity (29–32, 45–47). In the present review, we focus on two major proteasome isoforms, namely the standard 26S proteasome (SP) and its alternative/inducible counterpart, the immunoproteasome (IP), which operate dynamically and coordinately in nerve, glial, and immune cells to modulate neurotransmission, oxidative/inflammatory stress response and immunity. In the present section, we discuss the mechanisms through which SP and IP tune the repertoire of brain-circulating T-lymphocytes. Circulation of T-cells in the CNS occurs since the early development to guarantee both immune-surveillance and synaptic plasticity (48–50). On the other hand, alterations in CNS-circulating T-cell populations are emerging as a common signature in both classic and autoimmune degenerative disorders such as PD, AD, and MS (51).
The SP is ubiquitously expressed in non-immune cells including neurons, where it operates in the nucleus, cell body, and synapses to modulate oxidative stress, gene transcription, neurotransmitter release and synaptic plasticity (31, 52, 53). This is validated in a plethora of experimental models where SP inhibition profoundly alters neurotransmitter release and the expression of neurotransmitter receptors while producing ubiquitinated protein-aggregates, which recapitulate neurodegeneration (54–58). As a support to these findings, SP dysfunctions in human CNS disorders are bound to early synaptic alterations and/or protein aggregation (36–38, 59–61). Although detailing the mechanisms of SP in synaptic plasticity is beyond the aim of this brief review, we wish to mention that SP may modulate immune activity by modulating in turn, neurotransmitter release. For instance, SP modulates dopamine (DA) release (55–57), which is seminal for differentiation, maturation, selection, trafficking, and migration of T-lymphocytes (7, 8, 62–65). This occurs through the stimulation of DA receptors (D1–D5), which are all expressed on T-cells. Just like it occurs for neurons, the magnitude and duration of DA release are seminal to dictate the intracellular cascades placed downstream to DA receptors (DRs) in T-cells (8, 61–64). For instance, abnormal stimulation of D1/D5-DRs increases cAMP levels to inhibit activation of cytotoxic CD8+ T-lymphocytes (CTLs); again, it induces polarization of naïve CD4+ T cells toward T helper type17 phenotype (Th17) while suppressing differentiation and activity of T regulatory cells. On the other hand, stimulation of D3-DRs controls T-cell adhesion and migration and induces differentiation of naïve CD8+ T-cells into CTLs; again, it induces polarization of naïve CD4+ cells toward Th1 phenotype. Thus, SP-dependent surveillance of DA release and stimulation of DA-receptors at the level of the neuro-immunological synapse, in cooperation with CNS-derived Ag presentation, plays an active role in determining T-cells fate and activity, as well as their chemotactic migration and homing to the CNS. Emerging evidence indicates an association between T-cell-related pro-inflammatory and autoimmune mechanisms underlying neuropathology with abnormal DA levels and deregulation of DA receptors expressed on T-cells (64–69). It is remarkable that this occurs CNS disorders such as MS, PD, and stroke, where SP is impaired while its immune-related counterpart (the IP) is upregulated (34).
Besides the effects in lymphoid organs, DA release also modulates T-cells activity directly in the brain, including activation or suppression of naïve T-cells [for a review (8)]. In fact, despite the consensus view that only activated T-cells can migrate into the brain, a number of studies also revealed an unexpected ability of naïve CD4+ and CD8+ T cells to infiltrate the brain parenchyma (70–76). This is magnified during pro-inflammatory conditions, which enhance naïve T-cell recruitment in the CNS, while fostering their activation once they encounter the specific Ag (71, 74, 76–78). This was shown to occur upon interaction of naïve CD4+ and/or CD8+ T-cells with either activated microglia or oligodendrocytes [ODCs, (71, 74, 76, 77)]. However, the specific molecular mechanisms and functional significance underlying this phenomenon still remain to be elucidated. Recent in vitro studies demonstrated that exogenous administration of DA precursors to neurons which are co-cultured with activated CD8+ T-cells is sufficient to induce cognate Ag presentation via MHC-I and subsequent CTL-mediated neuronal death (79). Due to its intrinsic oxidative potential, DA is considered the primary candidate fostering SP disassembly and subsequent IP upregulation (40). This is supported by the effects of DA in enhancing neuronal Ag presentation via MHC-I (79), which is indeed the main task of IP (section Immunoproteasome in Constitutive and Adaptive Immunity). Thus, in a scenario in which dysfunctional SP alters DA release, the upregulation of IP renders neurons competent APCs for presentation to CD8+ T-cells; at the same time, abnormal stimulation of DA receptors (for instance D3-DRs) on CD8+ T-cells triggers metabolic downstream cascades which add on the recruitment of cytotoxic T cell effector machinery.
The IP is an alternative, cytokine-inducible form of the SP, which is mostly involved in inflammatory and immune response (80). All immune cells, including professional APCs (e.g., DCs) and lymphocytes, possess almost exclusively IP. Within APCs the IP generates defined T-cell epitopes which bind to MHC-I molecules (81–83). In detail, IP cleaves either endogenous or exogenous proteins to generate Ag peptides, which are firstly complexed to MHC-I in the endoplasmic reticulum and then exposed on the plasma membrane of APCs, for either direct or cross-presentation to CD8+ T-lymphocytes. This is accomplished at a higher rate and with greater efficacy by IP since it owns a selective enhancement of chymotrypsin-like activity and unique structural features compared with SP. In detail, within IP, β1, β2, and β5 subunits of the SP-20S catalytic core are replaced with β1i or low molecular mass protein 2 (LMP2), β2i or multi-catalytic endopeptidase complex subunit-1 (MECL-1) and β5i or LMP7, respectively (81–83). LMP2 possesses chymotrypsin-like activity contrarily to the standard β1 counterpart which possesses caspase-like activity. Moreover, LMP7 which possesses chymotrypsin activity similarly to the β5 subunit of SP, has a unique hydrophilic architecture which surrounds the LMP7-oxyanion hole (82). This facilitates the generation of peptides with C-terminal hydrophobic and basic amino acids, which better fit into the groove of MHC-I molecules (82, 84, 85). In this way, peptides bound to MHC-I are exposed extracellularly on the plasma membrane of DCs to be recognized by CD8+ T-cells as modified compared with “self” Ags. This is seminal to avoid auto-immunity while mounting T-cell mediated adaptive immune responses for the removal of pathogen-infected cells (86). Besides Ag presentation, the IP also operates within naïve T-cells to modulate metabolic cascades which orchestrate their differentiation and function (87). For instance, IP governs CD4+ T-cell differentiation toward T helper (Th1 and Th17) vs. T regulatory cell lineage (88). Likewise, IP regulates CD8+ T lymphocyte metabolism and differentiation toward memory vs. effector cells (89). IP also sustains the maturation process of stimulated DCs from an Ag-receptive state to a state of optimal stimulation of T-cells (90). Again, specialized and classic subtypes of IPs operate in thymic DCs, where together with SP, they regulate T-cell proliferation along with positive and negative T-cell selection (91, 92). SP-derived pool of peptides differs from that produced by IP degradation, and this is critical to avoid generation of auto-reactive T-cells. In this way, SP and IP coordinately shape the repertoire of immunocompetent T-cells, which are released in the bloodstream to reach secondary lymphoid organs and subsequently the brain via the CSF. Immune adaptation of the UP is a tightly regulated and transient response, which allows cells to rapidly switch back to SP once IP function is no longer required (93). In fact, production of IP in response to pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IFN-γ is four times faster than SP. This allows cells to quickly expand the peptides repertoire which is needed to aid immune defense in a challenged organism. Likewise, IP turnover is definitely faster compared with SP in order to avoid persistent immune activation (93). The transient induction of IP is seminal to protect the brain against microbial infections. In fact, IP inhibition may increase the susceptibility to either viral, fungal or bacterial neuro-infections (89, 94, 95). This correlates with profound alterations in T-cells differentiation and function along with altered cytokine release (89, 94–97). However, under persistent pro-inflammatory and/or oxidative stimuli, the balanced tuning between SP and IP fails to occur leading to an abnormal prevalence of IP over SP. In turn, abnormal IP upregulation enhances generation and MHC-I-dependent presentation of CNS-derived Ags within DCs while producing metabolic/transcriptional changes within both DCs and T-cells. These effects eventually synergize to produce CNS-directed auto-immune reactions. In the light of these findings, IP and/or SP inhibitors have been tested as a potential therapeutic strategy in CNS auto-immune disorders such as experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), and also in neurological disorders, which etiologically are not bound to auto-immunity [(98–127); Table 1; insert of Figure 1 for details]. Since IP operates in neurons and glia in addition to classic DCs, in the next paragraph we discuss evidence centered on IP expression within the CNS and its contribution to pro-inflammatory and auto-immune neuronal damage.
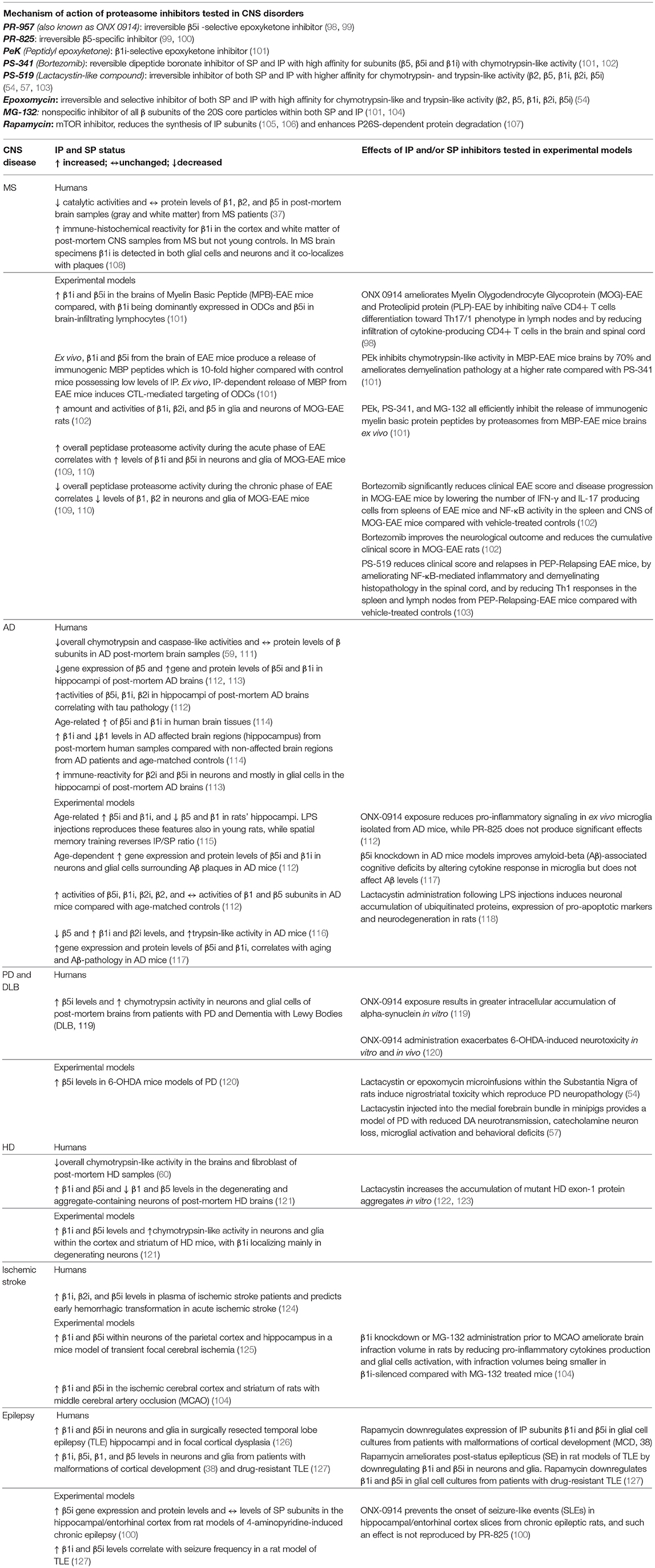
Table 1. Mechanisms of action of IP and/or SP inhibitors and their reference to IP and SP status in specific CNS disorders.
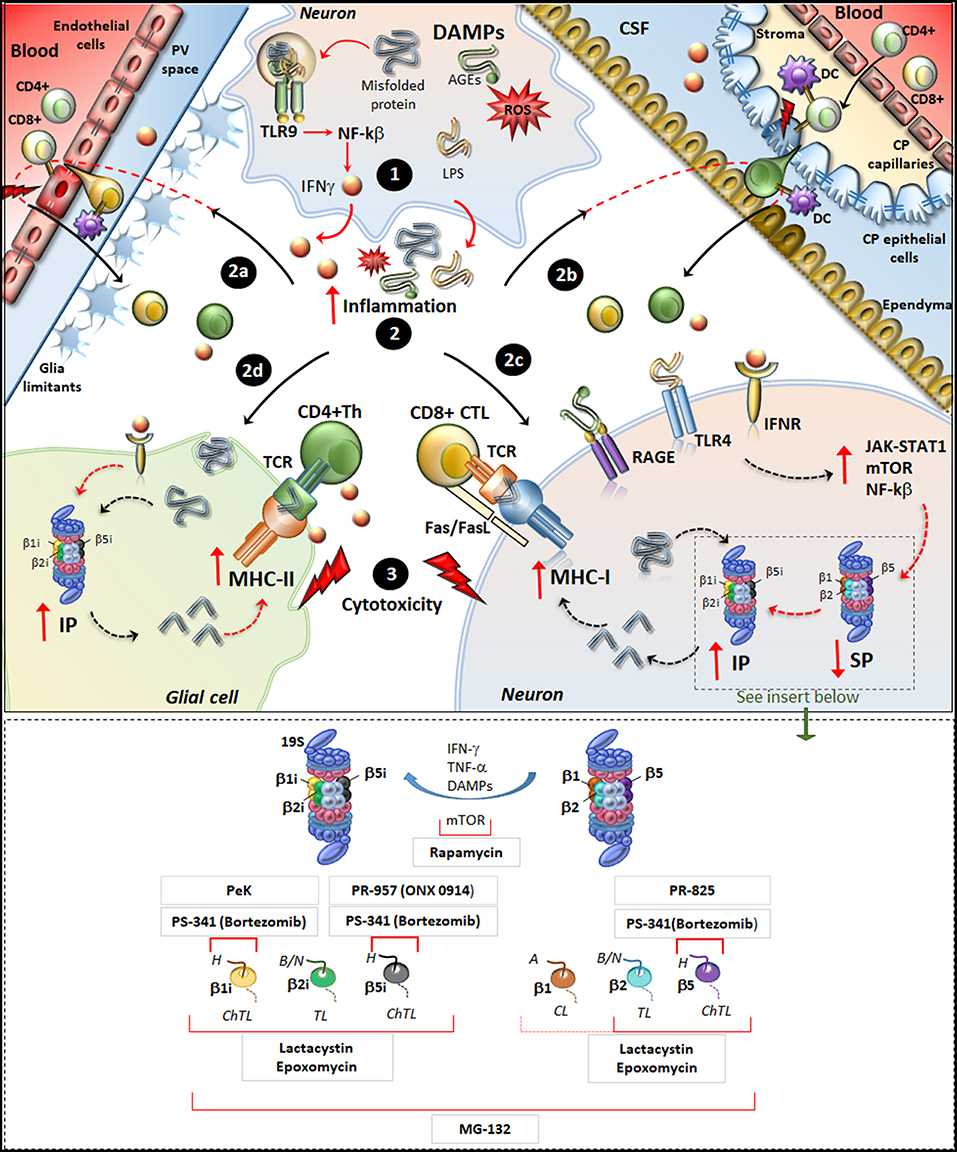
Figure 1. Molecular mechanisms underlying IP induction in neurons and glia in neurodegenerative disorders. (Upper panel) Within neurons, an oxidative/inflammatory challenge or the presence of misfolded proteins leads to the production of DAMPs such as ROS, LPS, and AGEs. DAMPs bind to TLR9 to activate NF-kb and produce pro-inflammatory cytokines (1). DAMPs and misfolded/oxidized proteins and cytokines are then released extracellularly, which triggers an inflammatory reaction within the brain parenchyma (2). This fosters the recruitment of peripherally primed T-cells which are reactivated by APCs along the blood-brain barrier (2a) and blood-CFS barrier (2b), including DCs in the perivascular space (PV), in the choroid plexus (CP) stroma and CSF, as well as CP epithelial cells and endothelial cells of the brain-blood-barrier. In this way auto-reactive CD4+ T cells (green) and CD8+ T-cells (yellowish) recruit their effector machineries to damage CNS barriers (flashlights) and infiltrate the brain parenchyma. At the same time, misfolded/oxidized proteins, DAMPs and IFNs spread throughout the brain parenchyma and they bind to their receptors IFNr, RAGEs and TLR4 which are expressed in glia and neurons (2c, 2d). These activate common intracellular pathways namely JAK/STAT, NF-kβ, and mTOR, which downregulate/disassembly SP to foster induction and de-novo synthesis of IP. Thus, IP produces Ag peptides which bind to MHC-I molecules in neurons (2c) or even to MHC-II in glia (2d). MHC-antigen complexes are then transported to the cell surface to be presented to auto-reactive CD8+ CTLs and CD4+ Th lymphocytes, which trigger cytotoxicity and cytokine-mediated damage in neurons and glia (3). Figure Insert. Schematic overview of the mechanism of action of various IP/SP inhibitors listed in Table 1. On the right, the SP with its subunits β1, β2, and β5 which possess caspase-like (CL), trypsin-like (TL) and chymotrypsin-like (ChTL) activity, respectively. Following inflammatory/oxidative stimuli (IFN-γ, TNF-α, or DAMPs release), SP subunits are replaced with IP subunits and de-novo synthesis of IP occurs. On the left, IP with its subunits β1i, β2i and β5i which possess ChTL, TL, and ChTL activity, respectively. Rapamycin, mTOR inhibitor, reduces the synthesis of IP subunits and enhances P26S-dependent protein degradation; PeK (Peptidyl epoxyketone), selective epoxyketone of inhibitor of β1i; PS-341 (Bortezomib), reversible dipeptide boronate inhibitor of SP and IP with high affinity for β5, β5i, and β1i; PR-957 (also known as ONX 0914), irreversible β5i -selective epoxyketone inhibitor; PR-825, irreversible β5-specific inhibitor; Epoxomycin, irreversible and selective inhibitor of both SP and IP with high affinity for β2, β5, β1i, β2i, β5i; Lactacystin, similar to Epoxomycin; MG-132, nonspecific inhibitor of all β subunits of the 20S core particles within both SP and IP. H, hydrophobic; B/N, basic/neutral; A, acidic substrates.
In neurons and glial cells, IP is generally induced by the pro-inflammatory cytokines IFNγ and TNFα, and by oxidative stress (42, 80, 82, 128). In these challenging conditions, SP disassembles to produce IP, which it is suggested to boost protein degradation and cope with protein overload (42, 119, 129, 130). Since IP owns enhanced catalytic activity, it produces immunogenic polypeptides from both microbial- and oxidized/aggregated-proteins. In fact, IP degrades aggregation-prone proteins such as alpha-synuclein with a similar or even higher rate and efficacy compared with SP (130, 131). Remarkably, IP cleaves alpha-synuclein specifically within immunogenic sites (119, 132), thus providing an oxidation-linked rationale for its Ag processing role in neuro-immune surveillance (32). This may explain why neurons and glia express low amounts of IP also in the absence of cytokine stimulation, which suggests a homeostatic role of IP in the CNS (133). One function consists in maintaining the expression of MHC-I molecules within specific neuronal populations and glia throughout the brain and spinal cord (133–135). The expression of MHC-I in the CNS extends beyond a classic Ag-presenting role. In fact, neuronal expression of MHC-I is bound to early neuronal development, axonal regeneration, synaptic plasticity, reward and memory (25, 136–138). Nonetheless, IP-dependent Ag processing and subsequent MHC-I-dependent Ag presentation to CD8+ T cells enable neurons and glia to behave just like professional APCs do. Thus, following vicious cycles of inflammatory/oxidative stress in the CNS, a persistent increase of IP to the detriment of SP may render neurons and glia susceptible to auto-immune damage.
The IP is significantly up-regulated in glia and neurons, in both patients and experimental models of HD (121, 139), AD (112–117), PD (119, 120), MS (41, 98–103, 108–110), ALS (134, 140), neurotrauma (129), ischemic stroke (104, 124, 125), and epilepsy (38, 100, 126, 127). In the context of PD, the induction of IP within glia and DA neurons was recently related to alpha-synuclein degradation and subsequent generation of self-Ag peptides for T-cell presentation by MHC-I (79, 119, 132). Since DA neurons of the Substantia Nigra (SN) possess an enhanced sensitivity to MHC-I upregulation, their susceptibility in PD may be related to CTL-mediated injury and death (79, 132). This hypothesis was tested by in vitro experiments showing that stem cell-derived DA neurons as well as murine primary catecholamine neurons can internalize, process and load Ags onto MHC-I just like professional APCs do (79). In detail, neuronal upregulation of Ag-loaded MHC-I can be induced by either microglial activation and subsequent IFN-γ release, or by administration of DA precursors even in the absence of microglia or exogenously administered IFN-γ. In the presence of activated CD8+ T-cells, the cognate Ag/MHC-I complex exposed on the neuronal plasma membrane induces proliferation of CD8+ T-cells, and most remarkably, it is sufficient to trigger CTL-mediated neuronal death via Fas/Fas ligand and perforin/granzyme pathways (79). Contrariwise, inflammatory-challenged neurons have no effects upon CD4+ T-cells, which specifically recognize MHC-II-bound Ags. This is in line with the lack of MHC-II expression in neurons either in baseline or inflammatory conditions. Nonetheless, Ag-peptides derived from alpha-synuclein degradation can presented via MHC-II molecules by glial cells for re-activation of CD4+ Th cells (119, 132). Thus, IP-dependent generation of Ag-peptides from alpha-synuclein may produce both pro-inflammatory and cytotoxic T-cell-mediated effects converging on DA neurons in PD. Despite being apparently detrimental, a balanced perspective emerges from experimental studies indicating a neuroprotective role for IP induction. In fact, the parkinsonian neurotoxin 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) increases IP and MHC-I expression in DA neurons in vitro and in vivo while IP inhibition exacerbates instead of preventing 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity (120). This suggests that in response to oxidative and inflammatory stimuli which foster protein-aggregation, transient induction of IP may compensate for SP downregulation to maintain cell-proteostasis. This is in line with studies on HD, showing that IP co-localizes with ubiquitinated aggregates in neurons from human and mouse brains (121). Noteworthy, a marked increase in IP induction takes place only at advanced stages of HD, when substantial proteinopathy develops along with SP downregulation. Subsequent studies demonstrated that protein-misfolding needs to synergize with pro-inflammatory cytokines in order to reproduce IP upregulation of HD brains (139). These results confirm that IP induction follows neuro-inflammation, which develops during protein aggregation. This is reproduced in experimental models of AD (117), ALS (134, 140), neurotrauma (129), ischemic stroke (104), epilepsy (100, 127), and MS (101), where the onset of inflammation accelerates IP expression and neuropathology. In neurodegenerative disorders, overlapping molecular mechanisms operate to foster neuro-inflammation and IP induction in either neurons or glia. For instance, misfolded or oxidized substrates may per se trigger inflammation through the release of danger-associated molecular pattern molecules (DAMPs) (141). Within neurons or glia, DAMPs bind to Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR-9) expressed in endosomes, which activates Nf-Kβ to foster the production of inflammatory cytokines including IFNγ (Figure 1). The inflammatory milieu promotes the recruitment, re-activation and infiltration of auto-reactive T-cells in the CNS parenchyma. At the same time, IFNγ induces upregulation of IP either locally or within neighboring cells, via autocrine or paracrine mechanisms. Induction of IP also occurs following binding of DAMPs to Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) as well as binding of advanced glycated end products (AGEs) to their receptors [RAGEs, (100, 118, 142, 143)]. Similarly to what occurs for IFNs receptors, activation of TLR4 and RAGEs is coupled to intracellular signaling cascades, which induce IP while downregulating SP. These consist of activation of JAK-STAT1, Nf-Kβ, and mTORC1 pathways, which trigger production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, replacement of SP with IP subunits and de novo synthesis of IP subunits (33, 100, 105, 106, 142, 143). In this way, IP upregulation leads to overproduction of neuronal and/or glial Ags co-expressed with MHC-I molecules to activate CD8+ CTLs. In glial cells, IP may also cross-process Ags which bind on MHC-II molecules to prime CD4+ Th lymphocytes and fuel production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (119, 132) (Figure 1). This eventual IP-related mechanism is reminiscent of what occurs in EAE, though IP induction within oligodendrocytes (ODCs) following IFNγ-mediated inflammatory reaction, seems be primarily involved in auto-immune demyelination rather than representing a compensatory response to proteinopathy as it occurs in neurodegenerative disorders (101). In fact, the specific up-regulation of the IP subunit LMP2 within ODCs leads to efficient production of myelin basic peptides (MBP) recognizable by CTLs, which may occur in the absence of, or at least prior to MBP cross-presentation to CD4+ Th cells (101). As a support to these findings, an LMP2 polymorphism, which alters production of MBP epitopes presented on MHC-I, associates with a reduced risk to develop MS in humans (108). At the same time, increased expression of LMP7 specifically in CD4+ CNS-infiltrating lymphocytes may facilitate Th17- and/or Th1-mediated damage in the CNS by stimulating their survival and proliferative capacity (88, 101, 108). The upregulation of IP in glial cells as well as in peripheral and CNS-circulating T-lymphocytes, joint to the beneficial effects observed upon selective IP inhibition in EAE, suggest that IP is mechanistically involved in the autoimmune nature of MS (41, 98, 101).
The evidence here reviewed converges that changes in UP β-subunit composition are largely responsible for the fluctuations in UP activities, which were described during the progression from inflammatory to neurodegenerative stages. Thus, characterizing UP subunit composition and IP/SP ratio appears seminal, since enzymatic assays do not permit to establish the molecular origin of UP activities. While some mechanisms underlying the over-expression of IP are emerging, those underlying changes in the expression of SP in various CNS disorders still remain to be fully established. Moreover, SP status and the IP/SP ratio varies not only among different CNS disorders, but also among various disease stages. For instance, beneficial effects in some EAE models are observed also following inhibition of both IP and SP subunits, while in classic neurodegenerative disorders SP inhibition appears detrimental (Table 1). In any case, IP upregulation occurs independently of disease etiology following oxidative/inflammatory reactions in the CNS. Again, the functional significance of IP induction differs between MS compared with classic neurodegenerative disorders, which is likely to underlie their different etiologies. In neurodegenerative disorders, upregulation of IP occurs as a compensatory response to cope with jeopardizing inflammatory conditions, which develop during proteinopathy (121, 139). In fact, selective IP inhibitors do not substantially modify the amount of Aβ despite ameliorating inflammation and cognitive abilities in AD models (117). Likewise, selective inhibition of IP does not protect DA neurons from 6-OHDA neurotoxicity (120). Thus, neuro-inflammatory and autoimmune reactions in these disorders may relate to concomitant SP dysfunction, which is further sustained by IP upregulation. This calls for a careful evaluation of SP status and activity in experimental approaches aimed at inhibiting the IP (see insert of Figure 1). For instance, targeting common pathways through which IP operates in the CNS may foster the naturally occurring switch from IP to SP. This is the case of mTOR inhibitors, which downregulate IP while counteracting protein aggregation and inflammation (38, 143–145). In addition to the effects upon SP and IP, mTOR is a well-known inhibitor of ATG, which is also involved in proteostasis, neurotransmission, and neuro-immunity (146, 147). In the last decades, evidence emerged indicating an intimate biochemical and morphological interplay between UP and ATG (107, 148, 149). In fact, UP and ATG-lysosomal pathway can be simultaneously modulated to prevent or slow down the disease process, as shown in experimental models (102, 148, 149). Recent studies showed that ATG-like vacuoles of choroid plexus epithelial cells release active UP subunits in the CSF (150). Since choroid cells express IP and MHC-I molecules to act as APCs, it is likely that IP is strategically placed at this level to modulate neuro-immunity during T-cell trafficking to the brain. The IP is also strategically placed within microvascular endothelial cells (151, 152). Here, the IP may modulate the luminal expression of MHC-I-bound CNS-derived Ags, which may preferentially drive the recruitment of CD8+ effector T-cells to the brain parenchyma (24). These findings open novel avenues to experimental studies aimed at dissecting the role of UP and the interplay with ATG in the context of neuro-immune pathophysiology.
FL wrote the article and made artwork. FB contributed to conceptualization. AG and CLB contributed to the literature review and artwork. FF coordinator of the paper, he drafted the article and critically revised the article for important intellectual content.
The present work was funded by Ministero della Salute (Ricerca Corrente 2019).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
1. Kerschensteiner M, Meinl E, Hohlfeld R. Neuro-immune crosstalk in CNS diseases. Neuroscience. (2009) 158:1122–32. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.09.009
2. Lorton D, Lubahn CL, Estus C, Millar BA, Carter JL, Wood CA, et al. Bidirectional communication between the brain and the immune system: implications for physiological sleep and disorders with disrupted sleep. Neuroimmunomodulation. (2006) 13:357–74. doi: 10.1159/000104864
3. Kioussis D, Pachnis V. Immune and nervous systems: more than just a superficial similarity? Immunity. (2009) 31:705–10. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.09.009
4. Hartenstein V, Giangrande A. Connecting the nervous and the immune systems in evolution. Commun Biol. (2018) 1:64. doi: 10.1038/s42003-018-0070-2
5. Mignini F, Streccioni V, Amenta F. Autonomic innervation of immune organs and neuroimmune modulation. Auton Autacoid Pharmacol. (2003) 23:1–25. doi: 10.1046/j.1474-8673.2003.00280.x
6. Mignini F, Sabbatini M, Capacchietti M, Amantini C, Bianchi E, Artico M, et al. T-cell subpopulations express a different pattern of dopaminergic markers in intra- and extra-thymic compartments. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. (2013) 27:463–75.
7. Levite M, Chowers Y, Ganor Y, Besser M, Hershkovits R, Cahalon L. Dopamine interacts directly with its D3 and D2 receptors on normal human T-cells, and activates beta1 integrin function. Eur J Immunol. (2001) 31:3504–12. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200112)31:12<3504::AID-IMMU3504>3.0.CO;2-F
8. Levite M. Neurotransmitters activate T-cells and elicit crucial functions via neurotransmitter receptors. Curr Opin Pharmacol. (2008) 8:460–71. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2008.05.001
9. Iliff JJ, Wang M, Liao Y, Plogg BA, Peng W, Gundersen GA, et al. A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid beta. Sci Transl Med. (2012) 4:147ra111. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003748
10. Plog BA, Nedergaard M. The glymphatic system in central nervous system health and disease: past, present, and future. Annu Rev Pathol. (2018) 24:379–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-051217-111018
11. Louveau A, Smirnov I, Keyes TJ, Eccles JD, Rouhani SJ, Peske JD, et al. Structural and functional features of central nervous system lymphatic vessels. Nature. (2015) 523:337–41. doi: 10.1038/nature14432
12. Da Mesquita S, Louveau A, Vaccari A, Smirnov I, Cornelison RC, Kingsmore KM, et al. Functional aspects of meningeal lymphatics in ageing and Alzheimer's disease. Nature. (2018) 560:185-91. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0368-8
13. Verheggen ICM, Van Boxtel MPJ, Verhey FRJ, Jansen JFA, Backes WH. Interaction between blood-brain barrier and glymphatic system in solute clearance. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. (2018) 90:26–33. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.03.028
14. Louveau A, Harris TH, Kipnis J. Revisiting the mechanisms of CNS immune privilege. Trends Immunol. (2015) 36:569–77. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2015.08.006
15. Schetters STT, Gomez-Nicola D, Garcia-Vallejo JJ, Van Kooyk Y. Neuroinflammation: microglia and T cells get ready to tango. Front Immunol. (2018) 8:1905. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01905
16. Harding CV. Phagocytic processing of antigens for presentation by MHC molecules. Trends Cell Biol. (1995) 5:105–9. doi: 10.1016/S0962-8924(00)88959-X
17. Palmowski MJ, Gileadi U, Salio M, Gallimore A, Millrain M, James E, et al. Role of immunoproteasomes in cross-presentation. J Immunol. (2006) 177:983–90. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.2.983
18. Leung CS. Endogenous antigen presentation of MHC class II epitopes through non-autophagic pathways. Front Immunol. (2015) 6:464. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00464
19. Shechter R, London A, Schwartz M. Orchestrated leukocyte recruitment to immune-privileged sites: absolute barriers versus educational gates. Nat Rev Immunol. (2013) 13:206–18. doi: 10.1038/nri3391
20. Riedhammer C, Weissert R. Antigen presentation, autoantigens, and immune regulation in multiple sclerosis and other autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. (2015) 6:322. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00322
21. Schwab N, Schneider-Hohendorf T, Wiendl H. Trafficking of lymphocytes into the CNS. Oncotarget. (2015) 6:17863–4. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5014
22. Goverman J. Autoimmune T cell responses in the central nervous system. Nat Rev Immunol. (2009) 9:393–407. doi: 10.1038/nri2550
23. Fisher Y, Strominger I, Biton S, Nemirovsky A, Baron R, Monsonego A. Th1 polarization of T cells injected into the cerebrospinal fluid induces brain immunosurveillance. J Immunol. (2014) 192:92–102. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301707
24. Galea I, Bernardes-Silva M, Forse PA, van Rooijen N, Liblau RS, Perry VH. An antigen-specific pathway for CD8 T cells across the blood-brain barrier. J Exp Med. (2007) 204:2023–30. doi: 10.1084/jem.20070064
25. Cebrián C, Loike JD, Sulzer D. Neuronal MHC-I expression and its implications in synaptic function, axonal regeneration and Parkinson's and other brain diseases. Front Neuroanat. (2014) 8:114. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2014.00114
26. Tournier JN, Hellmann AQ. Neuro-immune connections: evidence for a neuro-immunological synapse. Trends Immunol. (2003) 24:114–5. doi: 10.1016/S1471-4906(03)00002-4
27. Tian L, Rauvala H, Gahmberg CG. Neuronal regulation of immune responses in the central nervous system. Trends Immunol. (2009) 30:91–9. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2008.11.002
28. Schwartz M, Deczkowska A. Neurological disease as a failure of brain-immune crosstalk: the multiple faces of neuroinflammation. Trends Immunol. (2016) 37:668–79. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2016.08.001
29. Ferrington DA, Gregerson DS. Immunoproteasomes: structure, function, and antigen presentation. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. (2012) 109:75–112. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-397863-9.00003-1
30. Niedermann G, Grimm R, Geier E, Maurer M, Realini C, Gartmann C. et al. Potential immunocompetence of proteolytic fragments produced by proteasomes before evolution of the vertebrate immune system. J Exp Med. (1997) 186:209–220. doi: 10.1084/jem.186.2.209
31. Hegde AN. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and synaptic plasticity. Learn Mem. (2010) 17:314–27. doi: 10.1101/lm.1504010
32. Johnston-Carey HK, Pomatto LCD, Davies KJA. The immunoproteasome in oxidative stress, aging, and disease. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. (2015) 51:268–81. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2016.1172554
33. Thibaudeau TA, Anderson RT, Smith DM. A common mechanism of proteasome impairment by neurodegenerative disease-associated oligomers. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:1097. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03509-0
34. Jansen AHP, Reits EAJ, Hol EM. The ubiquitin proteasome system in glia and its role in neurodegenerative diseases. Front Mol Neurosci. (2014) 7:73. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2014.00073
35. Wang J, Wang CE, Orr A, Tydlacka S, Li SH, Li XJ. Impaired ubiquitin-proteasome system activity in the synapses of Huntington's disease mice. J Cell Biol. (2008) 180:1177–89. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200709080
36. McNaught KS, Belizaire R, Isacson O, Jenner P, Olanow CW. Altered proteasomal function in sporadic Parkinson's disease. Exp Neurol. (2003) 179:38–46. doi: 10.1006/exnr.2002.8050
37. Zheng J, Bizzozero OA. Decreased activity of the 20S proteasome in the brain white matter and gray matter of patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurochem. (2011) 117:143–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07182.x
38. van Scheppingen J, Broekaart DW, Scholl T, Zuidberg MR, Anink JJ, Spliet WG, et al. Dysregulation of the (immuno)proteasome pathway in malformations of cortical development. J Neuroinflamm. (2016) 13:202. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0662-z
39. Graham SH, Liu H. Life and death in the trash heap: the ubiquitin proteasome pathway and UCHL1 in brain aging, neurodegenerative disease and cerebral Ischemia. Ageing Res Rev. (2017) 34:30–38. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2016.09.011
40. Moszczynska A, Yamamoto BK. Methamphetamine oxidatively damages parkin and decreases the activity of 26S proteasome in vivo. J Neurochem. (2011) 116:1005–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07147.x
41. Bellavista E, Santoro A, Galimberti D, Comi C, Luciani F, Mishto M. Current understanding on the role of standard and immunoproteasomes in inflammatory/immunological pathways of multiple sclerosis. Autoimmune Dis. (2014) 2014:739705. doi: 10.1155/2014/739705
42. Kimura H, Caturegli P, Takahashi M, Suzuki K. New insights into the function of the immunoproteasome in immune and nonimmune cells. J Immunol Res. (2015) 2015:541984. doi: 10.1155/2015/541984
43. Miller Z, Ao L, Kim KB, Lee W. Inhibitors of the immunoproteasome: current status and future directions. Curr Pharm Des. (2013) 19:4140–51. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319220018
44. Myeku N, Duff KE. Targeting the 26S proteasome to protect against proteotoxic diseases. Trends Mol Med. (2017) 24:18–29. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2017.11.006
45. Davies KJ. Protein modification by oxidants and the role of proteolytic enzymes. Biochem Soc Trans. (1993) 21:346–53. doi: 10.1042/bst0210346
46. Coux O, Tanaka K, Goldberg AL. Structure and functions of the 20S and 26S proteasomes. Annu Rev Biochem. (1996) 65, 801–47. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.65.070196.004101
47. Humbard MA, Maupin-Furlow JA. Prokaryotic proteasomes: nanocompartments of degradation. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. (2013) 23:321–34. doi: 10.1159/000351348
48. Schwartz M, Shechter R. Protective autoimmunity functions by intracranial immunosurveillance to support the mind: the missing link between health and disease. Mol Psychiatry. (2010) 15:342–54. doi: 10.1038/mp.2010.31
49. Tanabe S, Yamashita T. The role of immune cells in brain development and neurodevelopmental diseases. Int Immunol. (2018) 30:437–44. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxy041
50. Smolders J, Heutinck KM, Fransen NL, Remmerswaal EBM, Hombrink P, Ten Berge IJM, et al. Tissue-resident memory T-cells populate the human brain. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:4593. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07053-9
51. Sommer A, Winner B, Prots I. The Trojan horse - neuroinflammatory impact of T-cells in neurodegenerative diseases. Mol Neurodegener. (2017) 12:78. doi: 10.1186/s13024-017-0222-8
52. Speese SD, Trotta N, Rodesch CK, Aravamudan B, Broadie K. The ubiquitin proteasome system acutely regulates presynaptic protein turnover and synaptic efficacy. Curr Biol. (2003) 13: 899–910. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(03)00338-5
53. Upadhya SC, Smith TK, Hegde AN. Ubiquitin-proteasome-mediated CREB repressor degradation during induction of long-term facilitation. J Neurochem. (2004) 91:210–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02707.x
54. Fornai F, Lenzi P, Gesi M, Ferrucci M, Lazzeri G, Busceti CL, et al. Fine structure and biochemical mechanisms underlying nigrostriatal inclusions and cell death after proteasome inhibition. J Neurosci. (2003) 23: 8955–66. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-26-08955.2003
55. Subramaniam M, Kern B, Vogel S, Klose V, Schneider G, Roeper J. Selective increase of in vivo firing frequencies in DA SN neurons after proteasome inhibition in the ventral midbrain. Eur J Neurosci. (2014) 40:2898–909. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12660
56. Konieczny J, Lenda T, Czarnecka A. Early increase in dopamine release in the ipsilateral striatum after unilateral intranigral administration of lactacystin produces spontaneous contralateral rotations in rats. Neuroscience. (2016) 324:92–106. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.02.072
57. Lillethorup TP, Glud AN, Alstrup AKO, Mikkelsen TW, Nielsen EH, Zaer H, et al. Nigrostriatal proteasome inhibition impairs dopamine neurotransmission and motor function in minipigs. Exp Neurol. (2018) 303:142–52. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2018.02.005
58. Bentea E, Verbruggen L, Massie A. The proteasome inhibition model of Parkinson's disease. J Parkinsons Dis. (2017) 7:31–63. doi: 10.3233/JPD-160921
59. Keller JN, Hanni KB, Marksberry WR. Impaired proteasome function in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. (2000) 75:436–9. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0750436.x
60. Seo H, Sonntag KC, Isacson O. Generalized brain and skin proteasome inhibition in Huntington's disease. Ann Neurol. (2004) 56:319–28. doi: 10.1002/ana.20207
61. Rubio MD, Wood K, Haroutunian V, Meador-Woodruff JH. Dysfunction of the ubiquitin proteasome and ubiquitin-like systems in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology. (2013) 38:1910–20. doi: 10.1038/npp.2013.84
62. Fiserová A, Starec M, Kuldová M, Kováru° H, Páv M, Vannucci L, et al. Effects of D2-dopamine and alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists in stress induced changes on immune responsiveness of mice. J Neuroimmunol. (2002) 130:55–65. doi: 10.1016/S0165-5728(02)00211-4
63. Sarkar C, Basu B, Chakroborty D, Dasgupta PS, Basu S. The immunoregulatory role of dopamine: an update. Brain Behav Immun. (2009) 24:525–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2009.10.015
64. Buttarelli FR, Fanciulli A, Pellicano C, Pontieri FE. The dopaminergic system in peripheral blood lymphocytes: from physiology to pharmacology and potential applications to neuropsychiatric disorders. Curr Neuropharmacol. (2011) 9:278–88. doi: 10.2174/157015911795596612
65. Levite M, Marino F, Cosentino M. Dopamine, T-cells and multiple sclerosis (MS). J Neural Transm. (Vienna). (2017) 124:525–42. doi: 10.1007/s00702-016-1640-4
66. Saunders JA, Estes KA, Kosloski LM, Allen HE, Dempsey KM, Torres-Russotto DR, et al. CD4+ regulatory and effector/memory T cell subsets profile motor dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. (2012) 7:927–38. doi: 10.1007/s11481-012-9402-z
67. González H, Contreras F, Prado C, Elgueta D, Franz D, et al. Dopamine receptor D3 expressed on CD4+ T-cells favors neurodegeneration of dopaminergic neurons during Parkinson's disease. J Immunol. (2013) 190:5048–56. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203121
68. Pacheco R, Contreras F, Zouali M. The dopaminergic system in autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. (2014) 5:117. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00117
69. Talhada D, Rabenstein M, Ruscher K. The role of dopaminergic immune cell signalling in poststroke inflammation. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. (2018) 11:1756286418774225. doi: 10.1177/1756286418774225
70. Brabb T, von Dassow P, Ordonez N, Schnabel B, Duke B, Goverman J. In situ tolerance within the central nervous system as a mechanism for preventing autoimmunity. J Exp Med. (2000) 192: 871–80. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.6.871
71. Krakowski ML, Owens T. Naive T lymphocytes traffic to inflamed central nervous system, but require antigen recognition for activation. Eur J Immunol. (2000) 30: 1002–9. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(200004)30:4<1002::AID-IMMU1002>3.0.CO;2-2
72. McMahon EJ, Bailey SL, Castenada CV, Waldner H, Miller SD. Epitope spreading initiates in the CNS in two mouse models of multiple sclerosis. Nat Med. (2005) 11:335–9. doi: 10.1038/nm1202
73. Cose S, Brammer C, Khanna KM, Masopust D, Lefrancois L. Evidence that a significant number of naive T cells enter non-lymphoid organs as part of a normal migratory pathway. Eur J Immunol. (2006) 36: 1423–33. doi: 10.1002/eji.200535539
74. Na SY, Cao Y, Toben C, Nitschke L, Stadelmann C, Gold R, et al. Naive CD8 T-cells initiate spontaneous autoimmunity to a sequestered model antigen of the central nervous system. Brain. (2008) 13:2353–65. doi: 10.1093/brain/awn148
75. Herz J, Paterka M, Niesner RA, Brandt AU, Siffrin V, Leuenberger T, et al. In vivo imaging of lymphocytes in the CNS reveals different behaviour of naive T cells in health and autoimmunity. J Neuroinflamm. (2011) 8:131. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-131
76. Jarry U, Jeannin P, Pineau L, Donnou S, Delneste Y, Couez D. Efficiently stimulated adult microglia cross-prime naive CD8+ T cells injected in the brain. Eur J Immunol. (2013) 43:1173-84. doi: 10.1002/eji.201243040
77. Chastain EM, Duncan DS, Rodgers JM, Miller SD. The role of antigen presenting cells in multiple sclerosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2010) 1812:265–74. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.07.008
78. Sosa RA, Forsthuber TG. The critical role of antigen-presentation-induced cytokine crosstalk in the central nervous system in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Interferon Cytokine Res. (2011) 31:753–68. doi: 10.1089/jir.2011.0052
79. Cebrián C, Zucca FA, Mauri P, Steinbeck JA, Studer L, Scherzer CR, et al. MHC-I expression renders catecholaminergic neurons susceptible to T-cell-mediated degeneration. Nat Commun. (2014) 5:3633. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4633
80. Krüger E, Kloetzel PM. Immunoproteasomes at the interface of innate and adaptive immune responses: two faces of one enzyme. Curr Opin Immunol. (2012) 24:77–83. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2012.01.005
81. Gaczynska M, Rock KL, Spies T, Goldberg AL. Peptidase activities of proteasomes are differentially regulated by the major histocompatibility complex-encoded genes for LMP2 and LMP7. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (1994) 91:9213–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.20.9213
82. Huber EM, Basler M, Schwab R, Heinemeyer W, Kirk CJ, Groettrup M. Immuno- and constitutive proteasome crystal structures reveal differences in substrate and inhibitor specificity. Cell. (2012) 148:727–38. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.12.030
83. Driscoll J, Brown MG, Finley D, Monaco JJ. MHC-linked LMP gene products specifically alter peptidase activities of the proteasome. Nature. (1993) 365:262–4. doi: 10.1038/365262a0
84. Chapiro J, Claverol S, Piette F, Ma W, Stroobant V, Guillaume B, et al. Destructive cleavage of antigenic peptides either by the immunoproteasome or by the standard proteasome results in differential antigen presentation. J Immunol. (2006) 176:1053–61. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.2.1053
85. Lei B, Abdul Hameed MD, Hamza A, Wehenkel M, Muzyka JL, Yao XJ, et al. Molecular basis of the selectivity of the immunoproteasome catalytic subunit LMP2-specific inhibitor revealed by molecular modeling and dynamics simulations. J Phys Chem B. (2010) 114:12333–9. doi: 10.1021/jp1058098
86. Andersen MH, Schrama D, Thor Straten P, Becker JC. Cytotoxic T-cells. J Invest Dermatol. (2006) 126:32–41. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700001
87. Basler M, Kirk CJ, Groettrup M. The immunoproteasome in antigen processing and other immunological functions. Curr Opin Immunol. (2013) 25:74–80. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2012.11.004
88. Kalim KW, Basler M, Kirk CJ, Groettrup M. Immunoproteasome subunit LMP7 deficiency and inhibition suppresses Th1 and Th17 but enhances regulatory T cell differentiation. J Immunol. (2012) 189:4182–93. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201183
89. Widjaja CE, Olvera JG, Metz PJ, Phan AT, Savas JN, de Bruin G, et al. Proteasome activity regulates CD8+ T lymphocyte metabolism and fate specification. J Clin Invest. (2017) 127:3609–23. doi: 10.1172/JCI90895
90. Macagno A, Gilliet M, Sallusto F, Lanzavecchia A, Nestle FO, Groettrup M. Dendritic cells up-regulate immunoproteasomes and the proteasome regulator PA28 during maturation. Eur J Immunol. (1999) 29:4037–42. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199912)29:12<4037::AID-IMMU4037>3.0.CO;2-T
91. Nil A, Firat E, Sobek V, Eichmann K, Niedermann G. Expression of housekeeping and immunoproteasome subunit genes is differentially regulated in positively and negatively selecting thymic stroma subsets. Eur J Immunol. (2004) 34:2681–9. doi: 10.1002/eji.200425032
92. Alexandropoulos K, Danzl NM. Thymic epithelial cells: antigen presenting cells that regulate T cell repertoire and tolerance development. Immunol Res. (2012) 54:177–90. doi: 10.1007/s12026-012-8301-y
93. Heink S, Ludwig D, Kloetzel PM, Krüger E. IFN-gamma-induced immune adaptation of the proteasome system is an accelerated and transient response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2005) 102:9241–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0501711102
94. Mundt S, Basler M, Buerger S, Engler H, Groettrup M. Inhibiting the immunoproteasome exacerbates the pathogenesis of systemic Candida albicans infection in mice. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:19434. doi: 10.1038/srep19434
95. Basler M, Moebius J, Elenich L, Groettrup M, Monaco JJ. An altered T cell repertoire in MECL-1-deficient mice. J Immunol. (2006) 176:6665–72. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.11.6665
96. Maseda D, Meister S, Neubert K, Herrmann M, Voll RE. Proteasome inhibition drastically but reversibly impairs murine lymphocyte development. Cell Death Differ. (2008) 15:600–12. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402297
97. Schmidt C, Berger T, Groettrup M, Basler M. Immunoproteasome inhibition impairs T and B cell activation by restraining ERK signaling and proteostasis. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:2386. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02386
98. Basler M, Mundt S, Muchamuel T, Moll C, Jiang J, Groettrup M, et al. Inhibition of the immunoproteasome ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. EMBO Mol Med. (2014) 6:226–38. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201303543
99. Muchamuel T, Basler M, Aujay MA, Suzuki E, Kalim KW, Lauer C, et al. A selective inhibitor of the immunoproteasome subunit LMP7 blocks cytokine production and attenuates progression of experimental arthritis. Nat Med. (2009) 15:781–7. doi: 10.1038/nm.1978
100. Mishto M, Raza ML, de Biase D, Ravizza T, Vasuri F, Martucci M, et al. The immunoproteasome beta5i subunit is a key contributor to ictogenesis in a rat model of chronic epilepsy. Brain Behav Immun. (2015) 49:188–96. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.05.007
101. Belogurov A Jr, Kuzina E, Kudriaeva A, Kononikhin A, Kovalchuk S, Surina Y, et al. Ubiquitin-independent proteosomal degradation of myelin basic protein contributes to development of neurodegenerative autoimmunity. FASEB J. (2015) 29:1901–13. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-259333
102. Fissolo N, Kraus M, Reich M, Ayturan M, Overkleeft H, Driessen C, et al. Dual inhibition of proteasomal and lysosomal proteolysis ameliorates autoimmune central nervous system inflammation. Eur J Immunol. (2008) 38:2401–11. doi: 10.1002/eji.200838413
103. Vanderlugt CL, Rahbe SM, Elliott PJ, Dal Canto MC, Miller SD. Treatment of established relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis with the proteasome inhibitor PS-519. J Autoimmun. (2000) 14:205–11. doi: 10.1006/jaut.2000.0370
104. Chen X, Zhang X, Wang Y, Lei H, Su H, Zeng J, et al. Inhibition of immunoproteasome reduces infarction volume and attenuates inflammatory reaction in a rat model of ischemic stroke. Cell Death Dis. (2015) 6:e1626. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.586
105. Yun YS, Kim KH, Tschida B, Sachs Z, Noble-Orcutt KE, Moriarity BS, et al. mTORC1 coordinates protein synthesis and immunoproteasome formation via PRAS40 to prevent accumulation of protein stress. Mol Cell. (2016) 61:625–39. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.01.013
106. Choi JH, Jo HS, Lim S, Kim HT, Lee KW, Moon KH, et al. mTORC1 accelerates retinal development via the immunoproteasome. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:2502. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04774-9
107. Zhao J, Zhai B, Gygi SP, Goldberg AL. mTOR inhibition activates overall protein degradation by the ubiquitin proteasome system as well as by autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2015) 112:15790–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1521919112
108. Mishto M, Bellavista E, Ligorio C, Textoris-Taube K, Santoro A, Giordano M, et al. Immunoproteasome LMP2 60HH variant alters MBP epitope generation and reduces the risk to develop multiple sclerosis in Italian female population. PLoS ONE. (2010) 5:e9287. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009287
109. Zheng J, Bizzozero OA. Reduced proteasomal activity contributes to the accumulation of carbonylated proteins in chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neurochem. (2010) 115:1556–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07062.x
110. Zheng J, Dasgupta A, Bizzozero OA. Changes in 20S subunit composition are largely responsible for altered proteasomal activities in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neurochem. (2012) 121:486–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07699.x
111. Keck S, Nitsch R, Grune T, Ullrich O. Proteasome inhibition by paired helical filament-tau in brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. (2003) 85:115–22. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01642.x
112. Orre M, Kamphuis W, Dooves S, Kooijman L, Chan ET, Kirk CJ, et al. Reactive glia show increased immunoproteasome activity in Alzheimer's disease. Brain. (2013) 136:1415–31. doi: 10.1093/brain/awt083
113. Nijholt DA, De Graaf TR, Van Haastert ES, Oliveira AO, Berkers CR, Zwart R, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress activates autophagy but not the proteasome in neuronal cells: implications for Alzheimer's disease. Cell Death Differ. (2011) 18:1071–81. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2010.176
114. Mishto M, Bellavista Santoro A, Stolzing A, Ligorio C, Nacmias B, et al. Immunoproteasome and LMP2 polymorphism in aged and Alzheimer's disease brains. Neurobiol Aging. (2006) 27:54–66. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.12.004
115. Gavilán MP, Castaño A, Torres M, Portavella M, Caballero C, Jiménez S, et al. Age-related increase in the immunoproteasome content in rat hippocampus: molecular and functional aspects. J Neurochem. (2009) 108:260–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05762.x
116. Aso E, Lomoio S, López-González I, Joda L, Carmona M, Fernández-Yagüe N. Amyloid generation and dysfunctional immunoproteasome activation with disease progression in animal model of familial Alzheimer's disease. Brain Pathol. (2012) 22:636–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2011.00560.x
117. Wagner LK, Gilling KE, Schormann E, Kloetzel PM, Heppner FL, Krüger E, et al. Immunoproteasome deficiency alters microglial cytokine response and improves cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease-like APPPS1 mice. Acta Neuropathol Commun. (2017) 5:52. doi: 10.1186/s40478-017-0453-5
118. Pintado C, Gavilan MP, Gavilan E, Garcia-Cuervo L, Gutierrez A, Vitorica J, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation leads to the accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins and increases susceptibility to neurodegeneration induced by proteasome inhibition in rat hippocampus. J Neuroinflamm. (2012) 9:87. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-87
119. Ugras S, Daniels MJ, Fazelinia H, Gould NS, Yocum AK, Luk KC, et al. Induction of the immunoproteasome subunit Lmp7 links proteostasis and immunity in α-synuclein aggregation disorders. EBioMedicine. (2018) 31:307–19. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.05.007
120. Mo MS, Li GH, Sun CC, Huang SX, Wei L, Zhang LM, et al. Dopaminergic neurons show increased low-molecular-mass protein 7 activity induced by 6-hydroxydopamine in vitro and in vivo. Transl Neurodegener. (2018) 7:19. doi: 10.1186/s40035-018-0125-9
121. Díaz-Hernández M, Hernández F, Martín-Aparicio E, Gómez-Ramos P, Morán MA, Castaño JG, et al. Neuronal induction of the immunoproteasome in Huntington's disease. J Neurosci. (2003) 23:11653–61. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-37-11653.2003
122. Wyttenbach A, Carmichael J, Swartz J, Furlong RA, Narain Y, Rankin J, et al. Effects of heat shock, heat shock protein 40 (HDJ-2), and proteasome inhibition on protein aggregation in cellular models of Huntington's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2000) 97:2898–903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.6.2898
123. Waelter S, Boeddrich A, Lurz R, Scherzinger E, Lueder G, Lehrach H, et al. Accumulation of mutant huntingtin fragments in aggresome-like inclusion bodies as a result of insufficient protein degradation. Mol Biol Cell. (2001) 12:1393–407. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.5.1393
124. Chen X, Wang Y, Fu M, Lei H, Cheng Q, Zhang X. Plasma immunoproteasome predicts early hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke patients. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. (2017) 26:49–56. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2016.08.027
125. Lu L, Wang H. Transient focal cerebral ischemia upregulates immunoproteasomal subunits. Cell Mol Neurobiol. (2012) 32:965–70. doi: 10.1007/s10571-012-9854-y
126. Mishto M, Ligorio C, Bellavista E, Martucci M, Santoro A, Giulioni M, et al. Immunoproteasome expression is induced in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2011) 408:65–70. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.03.117
127. Broekaart DWM, van Scheppingen J, Geijtenbeek KW, Zuidberg MRJ, Anink JJ, Baayen JC, et al. Increased expression of (immuno)proteasome subunits during epileptogenesis is attenuated by inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. Epilepsia. (2017) 58:1462–72. doi: 10.1111/epi.13823
128. Hallermalm K, Seki K, Wei C, Castelli C, Rivoltini L, Kiessling R, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces coordinated changes in major histocompatibility class I presentation pathway, resulting in increased stability of class I complexes at the cell surface. Blood. (2001) 98:1108–15. doi: 10.1182/blood.V98.4.1108
129. Moritz KE, McCormack NM, Abera MB, Viollet C, Yauger YJ, Sukumar G, et al. The role of the immunoproteasome in interferon-γ-mediated microglial activation. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:9365. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09715-y
130. Seifert U, Bialy LP, Ebstein F, Bech-Otschir D, Voigt A, Schröter F, et al. Immunoproteasomes preserve protein homeostasis upon interferon-induced oxidative stress. Cell. (2010) 142:613–24. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.07.036
131. Nathan JA, Spinnenhirn V, Schmidtke G, Basler M, Groettrup M, Goldberg AL. Immuno- and constitutive proteasomes do not differ in their abilities to degrade ubiquitinated proteins. Cell. (2013) 152:1184–94. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.01.037
132. Sulzer D, Alcalay RN, Garretti F, Cote L, Kanter E, Agin-Liebes J, et al. T-cells from patients with Parkinson's disease recognize α-synuclein peptides. Nature. (2017) 546:656–61. Erratum in: Nature (2017) 549:292. doi: 10.1038/nature22815
133. Piccinini M, Mostert M, Croce S, Baldovino S, Papotti M, Rinaudo MT. Interferon-gamma-inducible subunits are incorporated in human brain 20S proteasome. J Neuroimmunol. (2003) 135:135–40. doi: 10.1016/S0165-5728(02)00439-3
134. Nardo G, Trolese MC, Bendotti C. Major histocompatibility complex i expression by motor neurons and its implication in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front Neurol. (2016) 7:89. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2016.00089
135. Cullheim S, Thams S. Classic major histocompatibility complex class I molecules: new actors at the neuromuscular junction. Neuroscientist. (2010) 16: 600–7. doi: 10.1177/1073858410381534
136. Lazarczyk MJ, Kemmler JE, Eyford BA, Short JA, Varghese M, Sowa A, et al. Major Histocompatibility Complex class I proteins are critical for maintaining neuronal structural complexity in the aging brain. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:26199. doi: 10.1038/srep26199
137. Edamura M, Murakami G, Meng H, Itakura M, Shigemoto R, Fukuda A, et al. Functional deficiency of MHC class I enhances LTP and abolishes LTD in the nucleus accumbens of mice. PLoS ONE. (2014) 9:e107099. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107099
138. Murakami G, Edamura M, Furukawa T, Kawasaki H, Kosugi I, Fukuda A, et al. MHC class I in dopaminergic neurons suppresses relapse to reward seeking. Sci Adv. (2018) 4:eaap7388. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aap7388
139. Díaz-Hernández M, Martín-Aparicio E, Avila J, Hernández F, Lucas JJ. Enhanced induction of the immunoproteasome by interferon gamma in neurons expressing mutant Huntingtin. Neurotox Res. (2004) 6:463-8. doi: 10.1007/BF03033282
140. Puttaparthi K, Elliott JL. Non-neuronal induction of immunoproteasome subunits in an ALS model: possible mediation by cytokines. Exp Neurol. (2005) 196:441–51. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2005.08.027
141. Drouin-Ouellet J, Cicchetti F. Inflammation and neurodegeneration: the story ‘retolled'. Trends Pharmacol Sci. (2012) 33:542–51. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2012.07.002
142. Pla A, Pascual M, Renau-Piqueras J, Guerri C. TLR4 mediates the impairment of ubiquitin-proteasome and autophagy-lysosome pathways induced by ethanol treatment in brain. Cell Death Dis. (2014) 5:e1066. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.46
143. Grimm S, Ott C, Hörlacher M, Weber D, Höhn A, Grune T. Advanced-glycation-end-product-induced formation of immunoproteasomes: involvement of RAGE and Jak2/STAT1. Biochem J. (2012) 448:127–39. doi: 10.1042/BJ20120298
144. Ryskalin L, Limanaqi F, Frati A, Busceti CL, Fornai F. mTOR-related brain dysfunctions in neuropsychiatric disorders. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:2226. doi: 10.3390/ijms19082226
145. Zhang Y, He X, Wu X, Lei M, Wei Z, Zhang X, et al. Rapamycin upregulates glutamate transporter and IL-6 expression in astrocytes in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Cell Death Dis. (2017) 8:e2611. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.491
146. Rubinsztein DC, Bento CF, Deretic V. Therapeutic targeting of autophagy in neurodegenerative and infectious diseases. J Exp Med. (2015) 212:979–90. doi: 10.1084/jem.20150956
147. Limanaqi F, Biagioni F, Gambardella S, Ryskalin L, Fornai F. Interdependency between autophagy and synaptic vesicle trafficking: implications for dopamine release. Front Mol Neurosci. (2018) 11:299. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00299
148. Lazzeri G, Biagioni F, Fulceri F, Busceti CL, Scavuzzo MC, Ippolito C, et al. mTOR modulates methamphetamine-induced toxicity through cell clearing systems. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2018) 2018:6124745. doi: 10.1155/2018/6124745
149. Lenzi P, Lazzeri G, Biagioni F, Busceti CL, Gambardella S, Salvetti A, et al. The autophagoproteasome a novel cell clearing organelle in baseline and stimulated conditions. Front Neuroanat. (2016) 10:78. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2016.00078
150. Mueller O, Anlasik T, Wiedemann J, Thomassen J, Wohlschlaeger J, Hagel V, et al. Circulating extracellular proteasome in the cerebrospinal fluid: a study on concentration and proteolytic activity. J Mol Neurosci. (2012) 46:509–15. doi: 10.1007/s12031-011-9631-2
151. Howland SW, Poh CM, Rénia L. Activated brain endothelial cells cross-present malaria antigen. PLoS Pathog. (2015) 11:e1004963. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004963
Keywords: proteasome, immunoproteasome, T-cells, neuro-immunological synapse, cytokines, neurodegeneration, mTOR
Citation: Limanaqi F, Biagioni F, Gaglione A, Busceti CL and Fornai F (2019) A Sentinel in the Crosstalk Between the Nervous and Immune System: The (Immuno)-Proteasome. Front. Immunol. 10:628. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00628
Received: 16 January 2019; Accepted: 08 March 2019;
Published: 29 March 2019.
Edited by:
Robert Weissert, University of Regensburg, GermanyReviewed by:
Anna Fogdell-Hahn, Karolinska Institutet (KI), SwedenCopyright © 2019 Limanaqi, Biagioni, Gaglione, Busceti and Fornai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Francesco Fornai, ZnJhbmNlc2NvLmZvcm5haUBuZXVyb21lZC5pdA==; ZnJhbmNlc2NvLmZvcm5haUBtZWQudW5pcGkuaXQ=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.