
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Hum. Neurosci., 06 March 2025
Sec. Brain Imaging and Stimulation
Volume 19 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2025.1531123
 Daniel A. Monti1
Daniel A. Monti1 Nancy Wintering1
Nancy Wintering1 Faezeh Vedaei2
Faezeh Vedaei2 Alicia Steinmetz1
Alicia Steinmetz1 Feroze B. Mohamed2
Feroze B. Mohamed2 Andrew B. Newberg1,2*
Andrew B. Newberg1,2*Purpose: A growing number of research studies have explored the potential effects of vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) on brain physiology as well as clinical effects particularly related to stress and anxiety. However, there currently are limited studies showing functional changes during different frequencies of stimulation and laterality effects transcutaneous auricular VNS (TaVNS). In this study, we evaluated whether TaVNS alters functional connectivity in the brain of healthy controls. We hypothesized that TaVNS would significantly alter connectivity in areas involved with emotional processing and regulation including the limbic areas, insula, frontal lobe regions, and cerebellum.
Methods: We enrolled 50 healthy controls. Participants were placed in the MRI scanner with MRI compatible ear buds that provided TaVNS. Subjects underwent TaVNS in the left, right, and both ears in a randomized manner during the MRI session. Stimulation was provided for 5 min on and then there was a 5 min off period in between. To evaluate the primary outcome of neurophysiological effects, all participants received blood oxygen level dependent (BOLD) functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) during the TaVNS on and off states.
Results: The results demonstrated significant changes in functional connectivity during TaVNS that differed depending on the frequency of stimulation and which ear was stimulated. In general, areas of the brain that had altered functional connectivity included the frontoparietal regions, limbic regions, insula, and cerebellum. Interestingly, cognitive areas were also involved including parts of the temporal lobe, salience network, and default mode network.
Conclusion: This study is an initial step toward understanding the functional connectivity changes associated with TaVNS. The findings indicate significant brain changes, particularly in areas that are involved with emotional processing and regulation, as well as cognition. Future studies can expand on this data and focus on specific patient populations to determine the effects of TaVNS.
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is a rapidly expanding area of both treatment and research. It encompasses both invasive (implantable) and non-invasive (electro-simulative/physio-simulative) modalities such as transcutaneous auricular VNS (TaVNS). Non-invasive methods appear to be preferred in that they can be more readily modulated and do not bear the risks associated with surgical implantation of invasive systems, although they likely do not work for certain indications.
Studies have shown that VNS can reduce anxiety among patients suffering from an elevated state of arousal associated with PTSD (Wittbrodt et al., 2021). VNS is believed to trigger plasticity in brain areas such as the prefrontal cortex (PFC) and amygdala, increasing acetylcholine and reducing stress and anxiety (Hays et al., 2013). Furthermore, TaVNS has recently been shown to have effect in individuals suffering from various psychological conditions such as depression or anxiety (Ferstl et al., 2024). The potential advantages of TaVNS are: (1) it is designed specifically to address distressing stimuli and unresolved emotional memories; (2) it is a brief, time-limited intervention; and (3) its multi-modal design may appeal to and benefit a broader range of patients than a single mode intervention.
While there are a growing number of clinical studies exploring the potential benefit of TaVNS, there are few studies that have explored the neurophysiological effects. Furthermore, there are questions regarding optimal methods for using TaVNS which includes which ear to use and which frequency. While clinical trials could help explore such effects, neuroimaging can be beneficial in better determining how different TaVNS parameters might affect the brain. Such information could help guide future clinical trials.
The major goal of this study is to determine whether TaVNS alters brain function as measured by functional connectivity. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) with Blood Oxygen Level Dependent (BOLD) sequences allows for the determination of functional connectivity between brain structures to assess how these structures interact with each other. Studies have demonstrated that many neurological and psychological conditions (e.g., concussion, anxiety, depression, etc.) are associated with changes in functional connectivity since the brain has been altered physiologically either as part of or in response to the disorder (Vedaei et al., 2021; Gallo et al., 2023). Furthermore, interventions designed to improve these conditions, either pharmacological or non-pharmacological, can alter functional connectivity as part of their therapeutic effect (Monti et al., 2018; Vedaei et al., 2024).
We hypothesized that TaVNS would specifically alter functional connectivity primarily in the areas of the brain involved in emotional processing and regulation. These areas would include frontal regions, limbic regions, the insula, and cerebellum. These areas have been implicated in a wide range of emotional processes and emotional disorders.
If changes in the brain’s functional connectivity can be observed during TaVNS, this can contribute to future studies designed to take advantage of the brain regions affected by TaVNS. Specifically, if it can be shown that brain regions involved in emotions and emotional processing, such as the limbic structures, frontal regions, insula, and cerebellum, are affected by TaVNS, these findings would help guide future clinical studies to explore its use in emotional disorders. Such disorders might include depression, anxiety, or PTSD.
Fifty healthy controls were enrolled from the local community and provided informed consent approved by the Institutional Review Board of Thomas Jefferson University. This study was also posted on clinicaltrials.gov (NCT05132881). Exclusion criteria included any history of major psychiatric disorder such as post-traumatic stress disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, major depressive disorder, and substance abuse or dependence. In addition, potential participants were excluded for use of psychotropic medications or current use of medications that would interfere with autonomic nervous system measures.
The subjects consisted of 50 participants, 13 men and 37 women with an average age of 36.9 ± 19.4 years. Once enrolled, subjects underwent the TaVNS fMRI scanning procedure as described below.
The VNS procedure was developed to be used in the MRI scanner. Subjects were placed in the MRI scanner with an earbud in each ear connected to a commercially available VNS device (Xen by Neuvana, Boca Raton, FL, USA). The TaVNS device sits within the ear canal in each subject according to the device specifications. The TaVNS device specifically applies stimulation to the posterior tragus and the posterior external auditory meatus, both of which are areas that have been shown to stimulate the vagus nerve as it passes near the ear (Badran et al., 2018; Bretherton et al., 2019). The stimulator enabled for each earbud to be used for VNS either separately or together. The intensity of the stimulation was adjusted for each subject until they reported mild discomfort and then it was reduced until they reported barely sensing the stimulation. In addition, the stimulator was able to deliver the stimulation with one of two frequencies (30 Hz or 100 Hz). The selection of the two frequencies of 30 Hz and 100 Hz was based on prior research that has focused substantially on these frequencies. While other frequencies could have been considered, our review of the current research suggests that 100 Hz TaVNS has been most associated with locus coeruleus and nucleus tractus solitarius effects (Sclocco et al., 2020; Yokota et al., 2022). In the research literature, 30 Hz TaVNS has been associated with wellbeing, neuroplasticity, and mood modulation (Bretherton et al., 2019) and has been particularly used in studies on depression and epilepsy (Kong et al., 2018).
Subjects were randomized to receive all of their respective stimulation with either 30 Hz or 100 Hz. The 25 subjects receiving 30 Hz stimulation were 11 male and 14 female. Mean age is 37.5 ± 19.2, 4 were left handed, mean height is 67.4 ± 3.7 inches, and mean weight is 161 ± 39 pounds. The 25 subjects receiving 100 Hz stimulation were 2 male and 23 female. Mean age is 36.4 ± 20.0, 3 were left handed, mean height is 65.7 ± 3.4 inches, and mean weight is 154 ± 33 pounds.
While in the scanner, subjects underwent BOLD imaging throughout the time that the stimulator device was active. Subjects received LEFT or RIGHT ear stimulation first (in randomized order) and then BOTH ears stimulated in the final period. Each stimulation epoch lasted for 5 min with a 5 min off period in between (see Figure 1). It should be noted that subjects were not informed about whether they were randomized to LEFT or RIGHT first or to 30 Hz or 100 Hz.
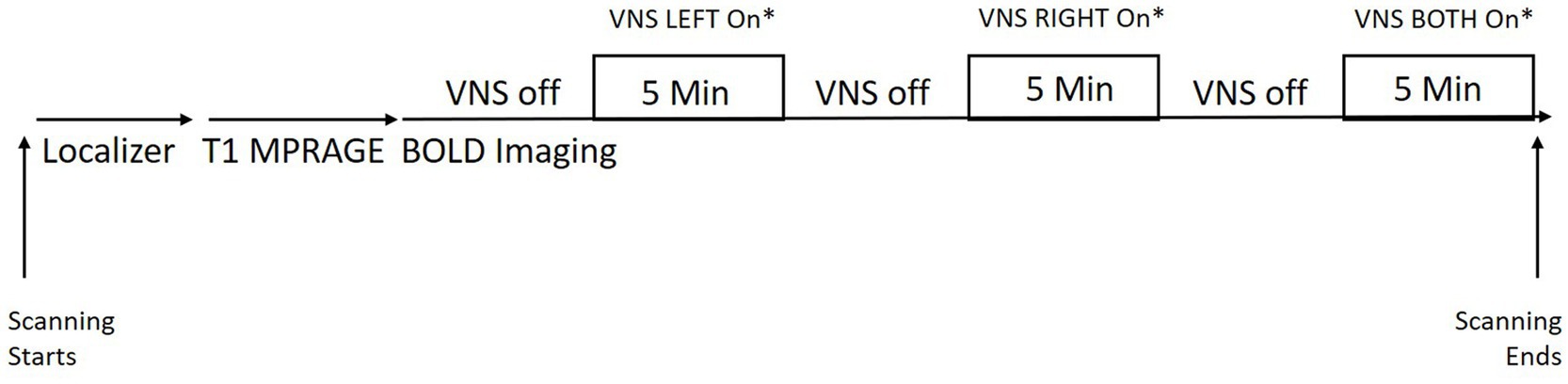
Figure 1. Scheme showing study set up with the TaVNS in the MRI scanner. *LEFT and RIGHT ordering was randomized within each subject. The stimulation frequency was randomized for each subject (subjects either received all stimulation at 30 Hz or 100 Hz).
fMRI data were obtained on all patients using a 3 T Siemens Biograph mMR PET-MR scanner with a 32-channel head coil. In order for further segmentation and registration steps during data pre-processing, an anatomical T1-image was obtained for all subjects. MRI parameters for the anatomical T1-weighted sequence were as follows: repetition time = 1.6 s, echo time = 2.46 ms, field of view = 250 × 250 mm, matrix = 512 × 512, voxel size = 0.49 × 0.49, 176 slices with slice thickness = 1 mm.
Next, BOLD scans were collected using the above described VNS paradigm with an Echo Planar Imaging (EPI) sequence to examine intrinsic FC of the brain regions. The following imaging parameters were used: FOV = 23.6 cm; voxel size = 3 × 3 × 4 mm3; TR = 2.0 s; TE = 30 ms; slice thickness = 4 mm; number of slices = 34; number of volumes = 300; and acquisition time = 600 s. During fMRI, the subjects were instructed to close their eyes, keep their heads still, and rest quietly without thinking about anything.
Data processing was performed using MATLAB-based programs, statistical parametric mapping1 and functional connectivity toolbox.2 The pre-processing was conducted using CONN default preprocessing pipeline. Initially, all the T1 structural data were oriented in the AC-PC line and their respective fMRI images reoriented to it using SPM12. All fMRI images were slice-timing corrected and realigned to the first volume using six-parameter rigid body transformation. The generated mean image was spatially normalized into standard stereotactic space, using the Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) echo planar image (EPI) template. Computed transformation parameters were applied to all functional images, and the resulting images were smoothed using an 8-mm full-width half-maximum (FWHM), isotropic Gaussian kernel. In addition, artifact detection toolbox (ART) was set to the 97th percentile setting with the mean global-signal deviation threshold set at z = ±5 and the subject-motion threshold set at 0.9 mm. The artifact detection implemented in CONN was utilized to detect framewise displacement (FD). The computed motion parameters were then used to exclude the outliers. Any volumes which exceeded a motion threshold of 2 mm (translation) and 1° rotation, or more, were excluded. After preprocessing, by applying linear regression and a band-pass filter of 0.008–0.09 Hz, data were denoised to remove the effects of low and high frequency oscillations such as scanner drift, head motion, heart rate, and respiration rate. Then, the anatomical component-based, noise correction strategy (aCompCor) for spatial and temporal processing was used to remove non-neuronal noise factors from BOLD signal before computing connectivity measures. This method extracted principal components from white matter and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) time series and used them as confounds during the denoising step (Behzadi et al., 2007). The implementation of aComCor along with the quantification of subject motion and the identification of outliers through (ART) allows for enhancement of specificity, sensitivity, and validity of first- and second-level connectivity analysis (Shirer et al., 2015).
After pre-processing steps, first-level and second-level functional connectivity analysis were conducted to generate ROI-based and Seed-based functional connectivity maps (Whitfield-Gabrieli and Nieto-Castanon, 2012). ROI-to-ROI analysis was performed by selecting a seed ROI, one by one, and the correlations of this seed with all other selected ROIs. The CONN toolbox provides predefined 164 ROIs composing an atlas of cortical and subcortical regions from the FSL Harvard-Oxford atlas, as well as cerebellar areas from the automated anatomical labeling (AAL) atlas. The atlas is normalized in MNI space and could be applied to the normalized data of the subject(s) (Rorden and Brett, 2000; Tzourio-Mazoyer et al., 2002). ROI-to-ROI analysis are Fisher z-transformed bivariate correlations between brain regions’ BOLD time-series that quantify associations in the activation at rest and serve as a proxy for connectivity. The time series were calculated by averaging voxel time series across all voxels within each ROI. For ROI-to-ROI analyses a threshold of p < 0.05 was used for bidirectional explorations of connectivity (i.e., positive and negative associations). Results of exploratory analyses were considered significant if they survived correction for multiple comparisons (p-FDR < 0.05). ROI-to-ROI analysis was executed separately for each condition of left, right, and bilateral stimulation each contrasted to no stimulation state fMRI data. Age, sex, and frequency used for the study were selected as the second-level covariates. Also, the same analysis was performed for subjects underwent stimulation with frequency 30 Hz and 100 Hz separately.
Further, seed-based functional connectivity was performed selecting brainstem since this region was found as the most common area with significant connectivity with other brain regions. So, the Fisher-transformed bivariate correlation coefficients between brainstem BOLD time series and each voxel BOLD timeseries were measured to generate brain functional connectivity maps. Cluster-level inferences on the between-group-level parametric statistics were based on false discovery rate multiple comparison correction with a voxel threshold p < 0.05 (uncorrected) and a cluster threshold p < 0.05 (cluster-size FDR corrected) for bidirectional explorations of connectivity (i.e., positive and negative associations). Seed-to-voxel connectivity was performed for each condition of left, right, and bilateral stimulation separately that each contrasted to no stimulation state fMRI data. In the next step, connectivity maps were generated for subjects underwent frequency 30 Hz and 100 Hz separately.
The ROI-to-ROI functional connectivity results showed a number of significant changes associated with the use of the TaVNS (see Tables 1, 2). The changes were distinguished between the left, right, and bilateral stimulation. Further, the changes were distinguished based on the frequency of the stimulation. The seed based analysis of functional connectivity using the brainstem as representative of the locus ceruleus is shown in Figure 2 and Table 3.
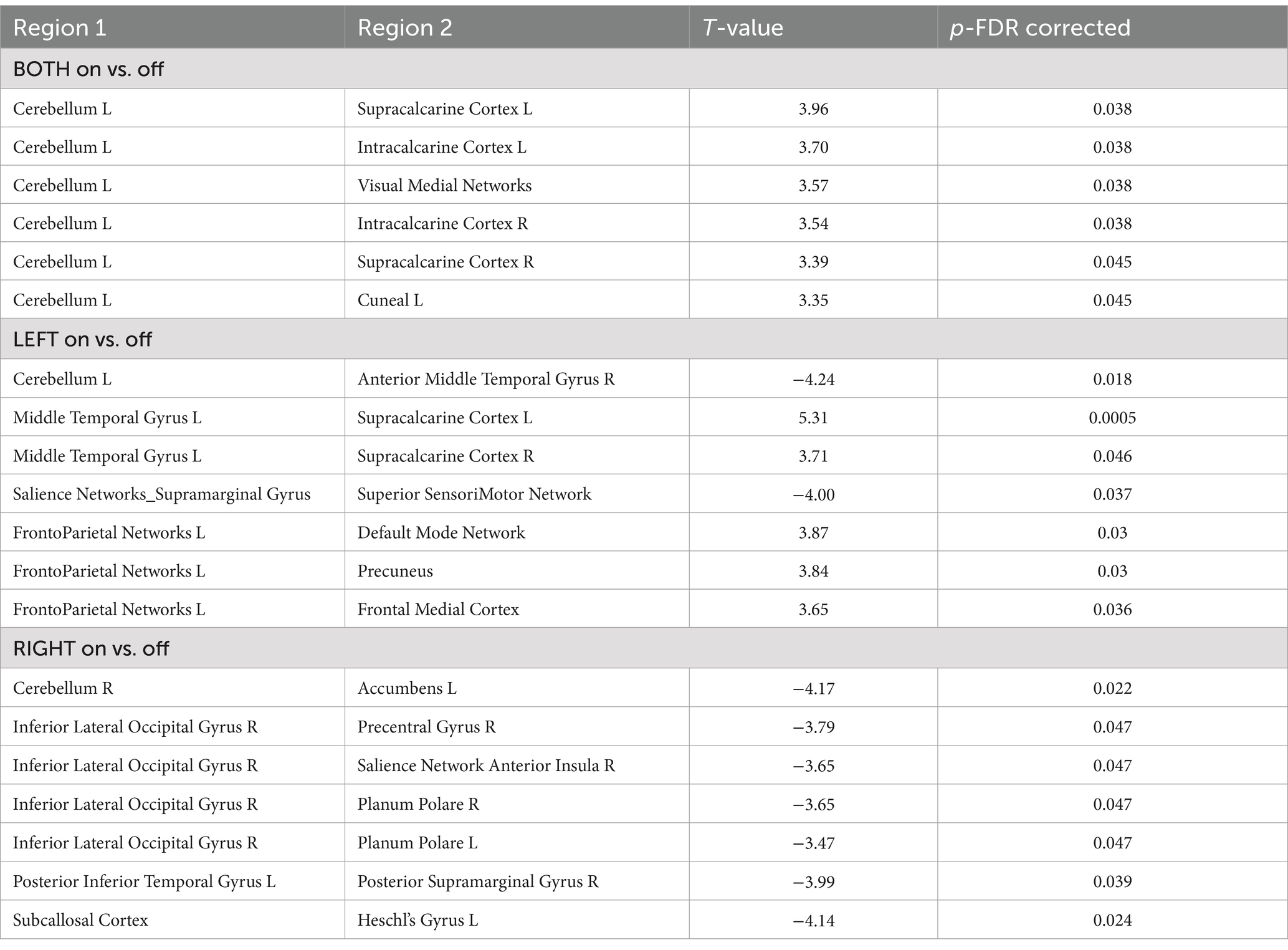
Table 1. ROI-to-ROI analysis TaVNS on vs off (for both frequencies) with significant functional connectivity between the Region 1 and Region 2, p-FDR < 0.05.
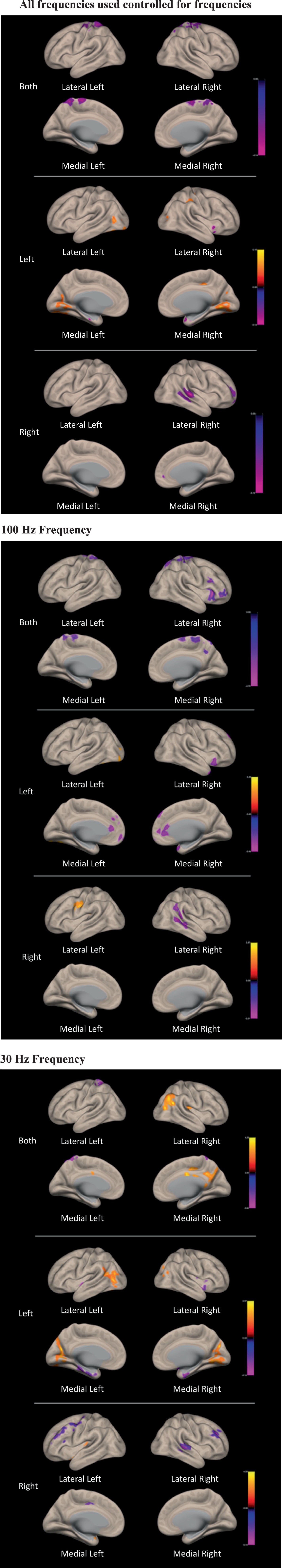
Figure 2. Figures for the functional connectivity changes associated with VNS when using the brainstem seed based analysis. There are three panels showing the changes associated with both frequencies on, and then the 100 Hz and the 30 Hz VNS.
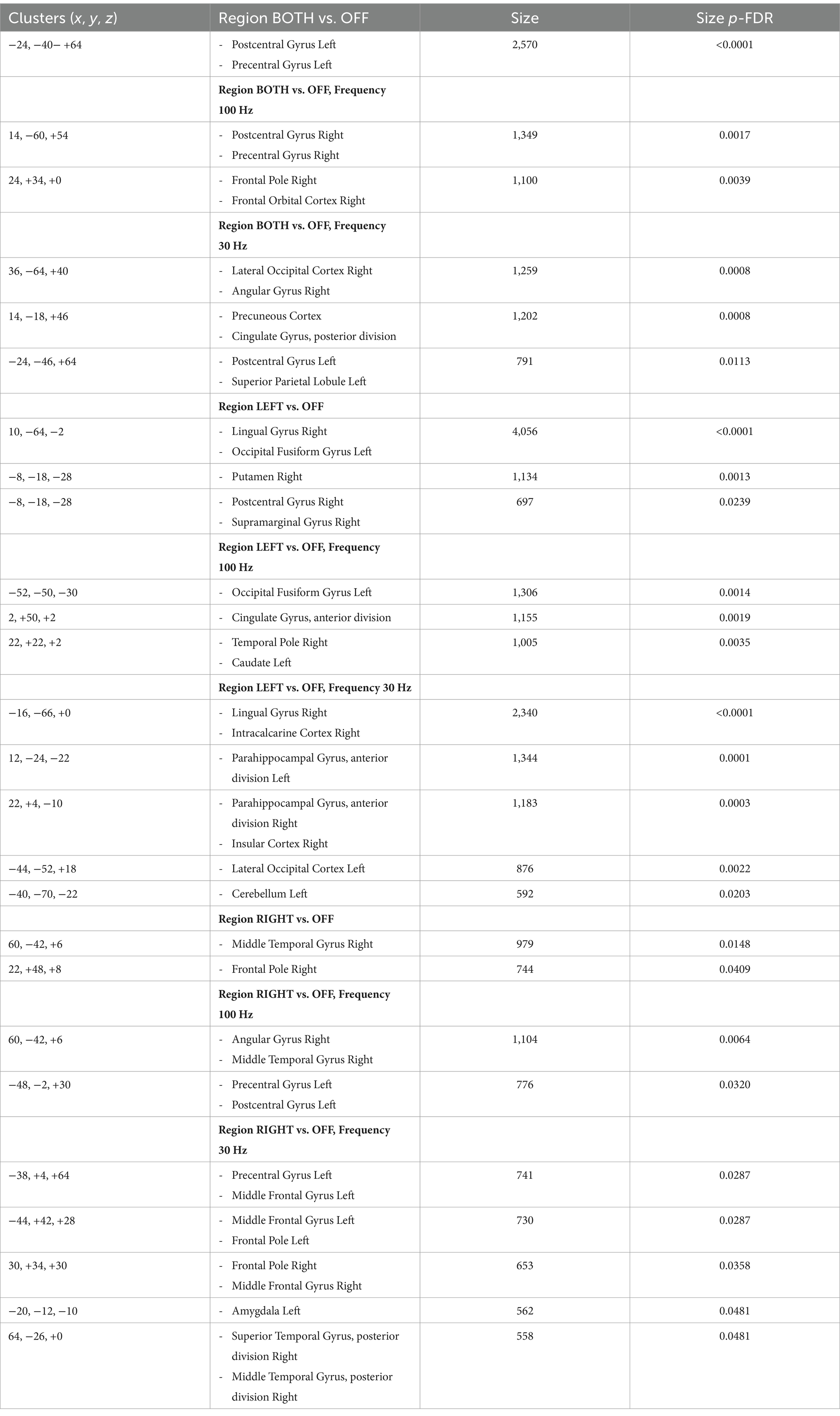
Table 3. Results from the seed-based analysis measuring the brainstem seed-to-voxel FC during TaVNS, p < 0.05 voxel and p-FDR < 0.05 at cluster level.
Overall, the TaVNS stimulation in this study resulted in altered functional connectivity between a number of important brain structures. The cerebellum had changes in functional connectivity with the visual areas. When the left vagus nerve was stimulated, there were changes in connectivity between the cerebellum and middle temporal gyrus, and the middle temporal gyrus and visual areas. There were also significant changes between the salience network and sensorimotor area as well as the frontoparietal network and the DMN, precuneus, and medial frontal cortex. When the right vagus nerve was stimulated, there were changes in connectivity between the cerebellum and nucleus accumbens, and between the visual areas of the occipital lobe and the salience network, precentral gyrus, and planum polare in the temporal lobe.
These findings are consistent with other studies evaluating TaVNS with fMRI which showed altered activity in the postcentral gyrus, insula, frontal cortex, right operculum, cingulate gyrus, and cerebellum (Badran et al., 2018). The insular connection with the frontal regions, particularly the medial PFC, has been found to be a focus of effect of TaVNS (Zhang et al., 2024). Other studies have found changes in limbic structures, temporal regions, thalamus, nucleus accumbens, and basal gangla (Dietrich et al., 2008; Kraus et al., 2013; Frangos et al., 2015; Yakunina et al., 2017). Such findings are consistent with our current study demonstrating changes in functional connectivity affecting most of these structures (see additional details below).
Additionally, EEG studies of TaVNS have yielded similar results to our current study (Gianlorenco et al., 2022). For example, an EEG study by Konakoğlu et al. (2023) showed that left-unilateral and right-unilateral auricular VNS causes delta and theta increase in the frontal regions, a finding supported by the current study showing important functional connectivity changes affecting the frontal regions. Another study of heart evoked potentials further implicated brain regions such as the orbitofrontal cortex, postcentral gyrus, precentral gyrus, insula, middle frontal gyrus, and temporal regions affected by TaVNS (Poppa et al., 2022).
There were distinctions between functional connectivity changes depending on the frequency of the stimulation as well. The 30 Hz frequency revealed changes in the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, temporal lobe, visual regions, and cerebellum. When the left vagus nerve was stimulated at 30 Hz, there were a number of changes involving the superior temporal lobe, cerebellum, angular gyrus, visual regions, caudate nucleus, and salience networks. When the right vagus nerve was stimulated at 30 Hz, there were changes involving the vermis, planum polare, salience networks, visual areas and amygdala.
The 100 Hz frequency TaVNS revealed changes particularly in the occipital-fusiform region and the precentral gyrus, sensorimotor regions, and salience network. Left TaVNS at 100 Hz revealed changes in the vermis and dorsal attention networks, while stimulation of the right vagus nerve resulted in changes involving the cerebellum, hippocampus, planum polare, dorsal attention network, and insula.
These differences in functional connectivity effects between the two frequencies respectively, and when analyzed together suggests some overlap and some distinctions. Thus, the results from the combined analysis suggests the overall effects of TaVNS, while the distinction between the two frequencies or the two sides suggests more specific changes. These more specific changes can become diluted or amplified when the entire group is evaluated.
Finally, since it is known that VNS is supposed to involve the locus ceruleus in the brainstem, we applied a specific seed based analysis to determine if there were any significant changes between this region and other brain regions. The results revealed altered functional connectivity with the precentral and postcentral gyrus and supplementary motor areas. There were distinctions between the left and right stimulation with the left involving changes in the visual cortex, cerebellum, basal ganglia, cingulate gyrus, frontal regions, and parahippocampus. Stimulation of the right vagus nerve was associated with changes to the temporal lobe, supramarginal gyrus, precentral and postcentral gyrus, basal ganglia, and amygdala. As with the general analysis, there were also subtle distinctions in functional connectivity between the brain stem and other brain regions depending on the frequency involved. Taken together, these findings suggest a possible neurobiological basis for regulating stress and anxiety through TaVNS that likely involves the locus ceruleus, particularly with regard to its functional connectivity with areas that regulate emotions.
From a therapeutic perspective, several studies have found that stimulation of the vagus nerve not only has clinical benefits, but alters functional connectivity in areas similar to those observed in the present study. For example, one study in patients with migraine showed TaVNS was associated with brain stem regions of the vagus nerve pathway and brain regions associated with the limbic system, pain processing areas such as the postcentral gyrus, thalamus, and PFC, and basal ganglia (Huang et al., 2023).
The results from our VNS study also suggest a laterality effect depending on which side of the vagus nerve is stimulated. This is consistent with previous clinical studies which have also suggested a distinction between left and right vagus nerve functions. Studies comparing left-sided and right-sided taVNS in patients with seizures have shown mixed results. Some studies suggest that left-sided stimulation is more effective in reducing seizure frequency, possibly due to its more direct influence on the left hemisphere, which is often the dominant hemisphere for controlling epileptic activity (Bauer et al., 2016). However, other research indicates that right-sided taVNS may be equally effective or could provide additional benefits in certain patients, such as those with right-hemispheric seizure foci or bilateral seizure activity (Yuan and Silberstein, 2016).
Additionally, individual differences in vagal nerve anatomy and brain connectivity could influence the response to taVNS, making personalized approaches to stimulation site selection important. The left vagus nerve may be particularly useful in patients with cognitive impairment, altering functional connectivity in structures such as the left hippocampus, left temporal regions, and salience networks (Murphy et al., 2023). We found similar alterations in left sided functional connectivity in this group of healthy individuals with left TaVNS. Stimulation of the right vagus nerve may be more effective for conditions involving motor activity or visuo-spatial processing.
We had hypothesized and found that areas affected by TaVNS in this study appear to be associated with emotional regulation and processing. This includes areas such as the insula and limbic regions. Altered functional connectivity associated with VNS stimulation may help understand some of the therapeutic trials in which the stimulation has improved anxiety, stress, and depression. For example, studies of depression have found that TaVNS was associated with alterations in functional connectivity in the precuneus and middle frontal gyrus, and the left posterior cingulate gyrus and the left angular gyrus (Sun et al., 2023). Future studies should explore the differential effects of left versus right versus bilateral stimulation of the vagus nerve in various therapeutic settings.
Another important area that appears to be associated with TaVNS in the present study is the cerebellum. Such an effect could have several clinical consequences. The cerebellum has long been considered the brain structure involved in motor coordination. Several studies have found that VNS can help improve motor coordination in stroke patients, especially when combined with physical therapy (Korupolu et al., 2024). Our finding of changes in functional connectivity, especially with respect to motor areas, may help provide an underlying neurobiological basis of this clinical finding.
In addition, recent research by our team, and others has found that the cerebellum is involved in the mediation of intense emotional reactions. The cerebellum may be integral to the experience of emotions and the development of emotional memories (Baumann and Mattingley, 2012). In fact, distinct subregions of the cerebellum are believed to be related to negative emotional processing (Park et al., 2008; Ferrucci et al., 2012). The potential role of the cerebellum in modulating emotions and autonomic reactivity has been supported by clinical and neuroimaging data (Stoodley and Schmahmann, 2009, 2010). The implication would be that stimulation of the vagus nerve, subsequently affects cerebellar function, and helps with emotional regulation.
Of particular relevance to the present study, prior fMRI studies show that negative emotional stimuli activate the cerebellum, posterior cingulate, and fusiform gyrus (Park et al., 2008; Schraa-Tam et al., 2012). In addition, reciprocal connections link the cerebellum with brainstem areas containing neurotransmitters involved in mood regulation, including serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine (Dempesy et al., 1983; Marcinkiewicz et al., 1989).
The cerebellum connects with the limbic structures both ipsilaterally and contralaterally (Cacciola et al., 2017). It has also been found that the vermis may be particularly connected to the limbic structures (Blatt et al., 2013). Using MRI techniques similar to the current study, several resting state functional connectivity studies have found functional coherence between the cerebellum and amygdala, hippocampus, hypothalamus, insula, and anterior cingulate (Seeley et al., 2007; Sang et al., 2012; Allen et al., 2005). Neuroimaging studies suggest the cerebellum is associated with emotional circuits such that positive emotions are associated with the left cerebral hemisphere and negative emotions are associated with the right hemisphere (Silberman and Weingartner, 1986; Lee et al., 2004). Finally, our research has found significant changes in the cerebellar functional connectivity when patients with traumatic memories were treated with a mind–body intervention (Monti et al., 2018). Thus, the finding of cerebellar effects resulting from TaVNS in the present study supports its potential use in patients trying to manage various traumatic events and emotions.
In addition to the laterality observed on the present study, we explored the effect of two different frequencies of stimulation. It has been hypothesized that altering the frequency of VNS may affect the overall physiological response as well as potential clinical effects. In our study, we found two different frequencies, one at 30 Hz and the other at 100 Hz, resulted in distinct changes in functional connectivity. These distinctions might also inform future therapeutic studies to try to affect areas most relevant for given conditions.
Our findings are consistent with the findings from previous studies utilizing different frequencies. For example, studies using 25 Hz frequency for TaVNS have found activation in areas of the brain responsible for cognitive & emotional processing and balance and GABAergic neuromodulation (Keute et al., 2018; Badran et al., 2018). The use of 30 Hz for TaVNS has been found to improve age-related autonomic, mood, and sleep changes, and reduce fatigue (Clancy et al., 2014; Bretherton et al., 2019; Aranow et al., 2021). TaVNS using a frequency of 100 Hz has been found to activate brainstem nuclei responsible for pain, learning, memory, and clinically has been shown to support healthy blood pressure, especially when combined with breathwork (Sclocco et al., 2020; Yokota et al., 2022).
This study is one of the largest we are aware of that uses fMRI to measure the effects of TaVNS. This larger sample size enabled us to explore laterality of vagus nerve simulation, as well as the effects of differential frequencies of simulation. Several limitations should be considered when evaluating the data. The BOLD imaging paradigm used was relatively brief in order to accomplish all of the imaging within a one-hour session. However, our prior research studies have suggested that this timeframe is able to provide significant findings, which is why this particular protocol was used.
In addition, since we were interested in observing stimulation of the left, right, and both sides, we included all three types of stimulation during the single imaging session with the left and right performed in a randomized order. We kept a 5 min off period between the stimulation periods to allow for a wash-out of any effects. However, it is not clear how long the VNS effect might last which could complicate interpretation of the findings. There are limited studies on the duration of the VNS effect when turned on for relatively short periods of time. For example, research on heart rate variability indicates that TaVNS induces immediate parasympathetic activation that is short-lived, occurring only during stimulation and not persisting after it stops (Keute et al., 2018). However, a study of TaVNS evaluated the P300 cognitive event-related potential (ERP) as an indirect marker that reflects NE brain activation and found persistent effects up to 28 min after stimulation for 7 min (Gurtubay et al., 2023). Future studies might explore a potential washout of the VNS effect and also include longer off periods between stimulations. This could be performed with longer off periods within a single imaging session, or with imaging on separate days. In addition, fMRI could be performed at several time points (e.g., 10 min, 30 min, and 60 min) after a single stimulation in order to determine how long the changes in functional connectivity persist. Another technical limitation was the selection of the frequency of TaVNS for the present study. As mentioned, we selected 30 Hz and 100 Hz based on existing literature suggesting these frequencies to be particularly effective both physiologically and clinically. However, future studies can expand upon the present data by exploring a broader range of frequencies to help determine those that produce the greatest effect on functional connectivity.
All subjects were healthy individuals, and while the subjects were randomized, it turned out that the group receiving 30 Hz stimulation had substantially more males compared to the group that received 100 Hz. It seems unlikely that such a difference in the group demographics would be responsible for the differences in the findings between the two stimulation frequencies. However, future studies might include larger populations to ascertain any differences in responses based on age, gender, or other factors, as well as whether the changes observed would be comparable in various patient populations. Thus, similar studies should be considered for patients with stroke, anxiety, and depression. Finally, future studies might also consider adding additional comparison groups such as a sham stimulation, in which the stimulation takes place, but at different locations. Such an approach could improve the accuracy of the findings and also could help identify potential side effects such as sensing the stimulation or stimulation artifacts. Any side effects could then be potentially eliminated from the evaluation of the real VNS.
Overall, the findings in this paper suggest that TaVNS appears to be associated with a number of changes in functional connectivity between brain structures. Several specific connections between cortical and limbic areas; cerebellum and limbic areas; and the brainstem and limbic areas; indicate important changes associated with TaVNS stimulation. These findings helped to demonstrate the neurobiological effects of TaVNS, but also generate hypotheses for future clinical trials, focusing on a variety of cognitive and emotional processes that might be addressed through TaVNS.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors without undue reservation.
The studies involving humans were approved by Thomas Jefferson University Institutional Review Board. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
DM: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft. NW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft. FV: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. AS: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. FM: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft. AN: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by a gift from Neuvana, LLC. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article, or the decision to submit it for publication.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. ^SPM12, https://www.fil.ion.ucl.ac.uk/spm/.
2. ^CONN22a, https://web.conn-toolbox.org/.
Allen, G., McColl, R., Barnard, H., Ringe, W. K., Fleckenstein, J., and Cullum, C. M. (2005). Magnetic resonance imaging of cerebellar-prefrontal and cerebellar-parietal functional connectivity. NeuroImage 28, 39–48. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.06.013
Aranow, C., Atish-Fregoso, Y., Lesser, M., Mackay, M., Anderson, E., Chavan, S., et al. (2021). Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation reduces pain and fatigue in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a randomised, double-blind, sham-controlled pilot trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 80, 203–208. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217872
Badran, B. W., Dowdle, L. T., Mithoefer, O. J., LaBate, N. T., Coatsworth, J., Brown, J. C., et al. (2018). Neurophysiologic effects of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation (taVNS) via electrical stimulation of the tragus: a concurrent taVNS/fMRI study and review. Brain Stimul. 11, 492–500. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2017.12.009
Bauer, S., Baier, H., Baumgartner, C., Bohlmann, K., Fauser, S., Graf, W., et al. (2016). Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (tVNS) for treatment of drug-resistant epilepsy: a randomized, double-blind clinical trial (cMPsE02). Brain Stimul. 9, 356–363. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2015.11.003
Baumann, O., and Mattingley, J. B. (2012). Functional topography of primary emotion processing in the human cerebellum. NeuroImage 61, 805–811. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.03.044
Behzadi, Y., Restom, K., Liau, J., and Liu, T. T. (2007). A component based noise correction method (CompCor) for BOLD and perfusion based fMRI. NeuroImage 37, 90–101. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.04.042
Blatt, G. J., Oblak, A. L., and Schmahmann, J. D. (2013). “Cerebellar connections with limbic circuits: anatomy and functional implications” in Handbook of the cerebellum and cerebellar disorders (New York: Springer), 479–496.
Bretherton, B., Atkinson, L., Murray, A., Clancy, J., Deuchars, S., and Deuchars, J. (2019). Effects of transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation in individuals aged 55 years or above: potential benefits of daily stimulation. Aging (Albany NY) 11, 4836–4857. doi: 10.18632/aging.102074
Cacciola, A., Milardi, D., Calamuneri, A., Bonanno, L., Marino, S., Ciolli, P., et al. (2017). Constrained spherical deconvolution tractography reveals cerebello-mammillary connections in humans. Cerebellum 16, 483–495. doi: 10.1007/s12311-016-0830-9
Clancy, J. A., Mary, D. A., Witte, K. K., Greenwood, J. P., Deuchars, S. A., and Deuchars, J. (2014). Non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation in healthy humans reduces sympathetic nerve activity. Brain Stimul. 7, 871–877. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2014.07.031
Dempesy, C. W., Tootle, D. M., Fontana, C. J., Fitzjarrell, A. T., Garey, R. E., and Heath, R. G. (1983). Stimulation of the paleocerebellar cortex of the cat: increased rate of synthesis and release of catecholamines at limbic sites. Biol. Psychiatry 18, 127–132
Dietrich, S., Smith, J., Scherzinger, C., Hofmann-Preiß, K., Freitag, T., Eisenkolb, A., et al. (2008). A novel transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation leads to brainstem and cerebral activations measured by functional MRI/Funktionelle magnet-resonanztomographie zeigt Aktivierungen des Hirnstamms und weiterer zerebraler Strukturen unter transkutaner Vagusnervstimulation. Biomed Tech/Biomed Eng 53, 104–111. doi: 10.1515/BMT.2008.022
Ferrucci, R., Giannicola, G., Rosa, M., Fumagalli, M., Boggio, P. S., Hallett, M., et al. (2012). Cerebellum and processing of negative facial emotions: cerebellar transcranial DC stimulation specifically enhances the emotional recognition of facial anger and sadness. Cognit. Emot. 26, 786–799. doi: 10.1080/02699931.2011.619520
Ferstl, M., Kühnel, A., Klaus, J., Lin, W. M., and Kroemer, N. B. (2024). Non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation conditions increased invigoration and wanting in depression. Compr. Psychiatry 132:152488. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2024.152488
Frangos, E., Ellrich, J., and Komisaruk, B. R. (2015). Non-invasive access to the vagus nerve central projections via electrical stimulation of the external ear: fMRI evidence in humans. Brain Stimul. 8, 624–636. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2014.11.018
Gallo, S., El-Gazzar, A., Zhutovsky, P., Thomas, R. M., Javaheripour, N., Li, M., et al. (2023). Functional connectivity signatures of major depressive disorder: machine learning analysis of two multicenter neuroimaging studies. Mol. Psychiatry 28, 3013–3022. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-01977-5
Gianlorenco, A. C. L., de Melo, P. S., Marduy, A., Kim, A. Y., Kim, C. K., Choi, H., et al. (2022). Electroencephalographic patterns in taVNS: a systematic review. Biomedicines. 10:2208. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092208
Gurtubay, I. G., Perez-Rodriguez, D. R., Fernandez, E., Librero-Lopez, J., Calvo, D., Bermejo, P., et al. (2023). Immediate effects and duration of a short and single application of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation on P300 event related potential. Front. Neurosci. 17:1096865. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1096865
Hays, S. A., Rennaker, R. L., and Kilgard, M. P. (2013). Targeting plasticity with vagus nerve stimulation to treat neurological disease. Prog. Brain Res. 207, 275–299. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63327-9.00010-2
Huang, Y., Zhang, Y., Hodges, S., Li, H., Yan, Z., Liu, X., et al. (2023). The modulation effects of repeated transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation on the functional connectivity of key brainstem regions along the vagus nerve pathway in migraine patients. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 16:1160006. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1160006
Keute, M., Ruhnau, P., Heinze, H. J., and Zaehle, T. (2018). Behavioral and electrophysiological evidence for GABAergic modulation through transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation. Clin. Neurophysiol. 129, 1789–1795. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2018.05.026
Konakoğlu, G., Özden, A. V., Solmaz, H., and Bildik, C. (2023). The effect of auricular vagus nerve stimulation on electroencephalography and electromyography measurements in healthy persons. Front. Physiol. 14:1215757. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1215757
Kong, J., Fang, J., Park, J., Li, S., and Rong, P. (2018). Treating depression with transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation: state of the art and future perspectives. Front. Psych. 9:20. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00020
Korupolu, R., Miller, A., Park, A., and Yozbatiran, N. (2024). Neurorehabilitation with vagus nerve stimulation: a systematic review. Front. Neurol. 15:1390217. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1390217
Kraus, T., Kiess, O., Hösl, K., Terekhin, P., Kornhuber, J., and Forster, C. (2013). CNS BOLD fMRI effects of sham-controlled transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in the left outer auditory canal–a pilot study. Brain Stimul. 6, 798–804. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2013.01.011
Lee, G. P., Meador, K. J., Loring, D. W., Allison, J. D., Brown, W. S., Paul, L. K., et al. (2004). Neural substrates of emotion as revealed by functional magnetic resonance imaging. Cogn. Behav. Neurol. 17, 9–17. doi: 10.1097/00146965-200403000-00002
Marcinkiewicz, M., Morcos, R., and Chretien, M. (1989). CNS connections with the median raphe nucleus: retrograde tracing with WGA-apoHRP-gold complex in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 289, 11–35. doi: 10.1002/cne.902890103
Monti, D. A., Tobia, A., Stoner, M., Wintering, N., Matthews, M., Conklin, C. J., et al. (2018). Changes in cerebellar functional connectivity and autonomic regulation in cancer patients treated with the neuro emotional technique for traumatic stress symptoms. J. Cancer Surviv. 12, 145–153. doi: 10.1007/s11764-017-0653-9
Murphy, A. J., O'Neal, A. G., Cohen, R. A., Lamb, D. G., Porges, E. C., Bottari, S. A., et al. (2023). The effects of transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation on functional connectivity within semantic and hippocampal networks in mild cognitive impairment. Neurotherapeutics 20, 419–430. doi: 10.1007/s13311-022-01318-4
Park, J. Y., Gu, B. M., Kang, D. H., Shin, Y. W., Choi, C. H., Lee, J. M., et al. (2008). Integration of cross-modal emotional information in the human brain: an fMRI study. Cortex 46, 161–169. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2008.06.008
Poppa, T., Benschop, L., Horczak, P., Vanderhasselt, M. A., Carrette, E., Bechara, A., et al. (2022). Auricular transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation modulates the heart-evoked potential. Brain Stimul. 15, 260–269. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2021.12.004
Rorden, C., and Brett, M. (2000). Stereotaxic display of brain lesions. Behav. Neurol. 12, 191–200. doi: 10.1155/2000/421719
Sang, L., Qin, W., Liu, Y., Zhang, Y., Jiang, T., and Yu, C. (2012). Resting-state functional connectivity of the vermal and hemispheric subregions of the cerebellum with both the cerebral cortical networks and subcortical structures. NeuroImage 61, 1213–1225. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.04.011
Schraa-Tam, C. K., Rietdijk, W. J., Verbeke, W. J., Dietvorst, R. C., van den Berg, W. E., Bagozzi, R. P., et al. (2012). fMRI activities in the emotional cerebellum: a preference for negative stimuli and goal-directed behavior. Cerebellum 11, 233–245. doi: 10.1007/s12311-011-0301-2
Sclocco, R., Garcia, R. G., Kettner, N. W., Fisher, H. P., Isenburg, K., Makarovsky, M., et al. (2020). Stimulus frequency modulates brainstem response to respiratory-gated transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation. Brain Stimul. 13, 970–978. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2020.03.011
Seeley, W. W., Menon, V., Schalzberg, A. F., Keller, J., Glover, G. H., Kenna, H., et al. (2007). Dissociable intrinsic connectivity networks for salience processing and executive control. J. Neurosci. 27, 2349–2356. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5587-06.2007
Shirer, W. R., Jiang, H., Price, C. M., Ng, B., and Greicius, M. D. (2015). Optimization of rs-fMRI pre-processing for enhanced signal-noise separation, test-retest reliability, and group discrimination. NeuroImage 117, 67–79. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.05.015
Silberman, E. K., and Weingartner, H. (1986). Hemispheric lateralization of functions related to emotion. Brain Cogn. 5, 322–353. doi: 10.1016/0278-2626(86)90035-7
Stoodley, C. J., and Schmahmann, J. D. (2009). Functional topography in the human cerebellum: a meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. NeuroImage 44, 489–501. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.08.039
Stoodley, C. J., and Schmahmann, J. D. (2010). Evidence for topographic organization in the cerebellum of motor control versus cognitive and affective processing. Cortex 46, 831–844. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2009.11.008
Sun, J., Guo, C., Ma, Y., Gao, S., Luo, Y., Chen, Q., et al. (2023). Immediate modulatory effects of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation on the resting state of major depressive disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 325, 513–521. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.01.035
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Landeau, B., Papathanassiou, D., Crivello, F., Etard, O., Delcroix, N., et al. (2002). Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. NeuroImage 15, 273–289. doi: 10.1006/nimg.2001.0978
Vedaei, F., Newberg, A. B., Alizadeh, M., Muller, J., Shahrampour, S., Middleton, D., et al. (2021). Resting-state functional MRI metrics in patients with chronic mild traumatic brain injury and their association with clinical cognitive performance. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 15:768485. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.768485
Vedaei, F., Newberg, A. B., Alizadeh, M., Zabrecky, G., Navarreto, E., Hriso, C., et al. (2024). Treatment effects of N-acetyl cysteine on resting-state functional MRI and cognitive performance in patients with chronic mild traumatic brain injury: a longitudinal study. Front. Neurol. 15:1282198. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1282198
Whitfield-Gabrieli, S., and Nieto-Castanon, A. (2012). Conn: a functional connectivity toolbox for correlated and anticorrelated brain networks. Brain Connect. 2, 125–141. doi: 10.1089/brain.2012.0073
Wittbrodt, M. T., Gurel, N. Z., Nye, J. A., Shandhi, M. M. H., Gazi, A. H., Shah, A. J., et al. (2021). Noninvasive cervical vagal nerve stimulation alters brain activity during traumatic stress in individuals with posttraumatic stress disorder. Psychosom. Med. 83, 969–977. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0000000000000987
Yakunina, N., Kim, S. S., and Nam, E. C. (2017). Optimization of transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation using functional MRI. Neuromodulation Technol. Neural Interface 20, 290–300. doi: 10.1111/ner.12541
Yokota, H., Edama, M., Hirabayashi, R., Sekine, C., Otsuru, N., Saito, K., et al. (2022). Effects of stimulus frequency, intensity, and sex on the autonomic response to transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation. Brain Sci. 12:1038. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12081038
Yuan, H., and Silberstein, S. D. (2016). Vagus Nerve and Vagus Nerve Stimulation, a Comprehensive Review: Part II. Headache, 56, 259–266. doi: 10.1111/head.12650
Keywords: transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation, fMRI, functional connectivity, cerebellum, amygdala, insula, frontal lobe, networks
Citation: Monti DA, Wintering N, Vedaei F, Steinmetz A, Mohamed FB and Newberg AB (2025) Changes in brain functional connectivity associated with transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation in healthy controls. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 19:1531123. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2025.1531123
Received: 20 November 2024; Accepted: 21 February 2025;
Published: 06 March 2025.
Edited by:
Jiu Chen, Nanjing University, ChinaReviewed by:
Gaoxiong Duan, Guangxi Academy of Medical Sciences, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Monti, Wintering, Vedaei, Steinmetz, Mohamed and Newberg. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Andrew B. Newberg, YW5kcmV3Lm5ld2JlcmdAamVmZmVyc29uLmVkdQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.