- 1Department of Applied Mathematics and Physics, Graduate School of Informatics, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan
- 2Department of Mathematics, Quaid-i-Azam University, Islamabad, Pakistan
- 3Graduate School of Advanced Integrated Studies in Human Survivability (Shishu-Kan), Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan
- 4Bioinformatics Center, Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University, Uji, Japan
Compound inference models are crucial for discovering novel drugs in bioinformatics and chemo-informatics. These models rely heavily on useful descriptors of chemical compounds that effectively capture important information about the underlying compounds for constructing accurate prediction functions. In this article, we introduce quadratic descriptors, the products of two graph-theoretic descriptors, to enhance the learning performance of a novel two-layered compound inference model. A mixed-integer linear programming formulation is designed to approximate these quadratic descriptors for inferring desired compounds with the two-layered model. Furthermore, we introduce different methods to reduce descriptors, aiming to avoid computational complexity and overfitting issues during the learning process caused by the large number of quadratic descriptors. Experimental results show that for 32 chemical properties of monomers and 10 chemical properties of polymers, the prediction functions constructed by the proposed method achieved high test coefficients of determination. Furthermore, our method inferred chemical compounds in a time ranging from a few seconds to approximately 60 s. These results indicate a strong correlation between the properties of chemical graphs and their quadratic graph-theoretic descriptors.
1 Introduction
In recent years, extensive studies have been done on the design of novel molecules using various machine learning techniques (Lo et al., 2018; Tetko and Engkvist, 2020; Gartner III et al., 2024). Computational molecular design also has a long history in the field of chemo-informatics and has been studied under the names of quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) (Cherkasov et al., 2014) and inverse quantitative structure-activity relationship (inverse QSAR) (Miyao et al., 2016; Ikebata et al., 2017; Rupakheti et al., 2015). This design problem has also become an important topic in both bioinformatics and machine learning.
The purpose of QSAR is to predict chemical activities from given chemical structures (Cherkasov et al., 2014). In most QSAR studies, a chemical structure is represented as a vector of real numbers called features or descriptors, and then a prediction function is applied to the vector, where a chemical structure is given as a chemical graph, which is defined by an undirected graph with an assignment of chemical elements to vertices and an assignment of bond multiplicities to edges. A prediction function is usually obtained from existing structure–activity relationship data. To this end, various regression-based methods have been utilized in traditional QSAR studies, whereas machine learning-based methods, including artificial neural network (ANN)-based methods, have recently been utilized (Ghasemi et al., 2018; Kim et al., 2021; Catacutan et al., 2024).
Conversely, the purpose of inverse QSAR is to predict chemical structures from given chemical activities (Miyao et al., 2016; Ikebata et al., 2017; Rupakheti et al., 2015; Miyao and Funatsu, 2024), where additional constraints may often be imposed to effectively restrict the possible structures. In traditional inverse QSAR, a feature vector is computed by applying some optimization or sampling method on the prediction function obtained by standard QSAR, and then chemical structures are reconstructed from the feature vector. However, the reconstruction itself is quite difficult due to the vast number of possible chemical graphs (Bohacek et al., 1996). In fact, inferring a chemical graph from a given feature vector, except for some simple cases, is an NP-hard problem (Akutsu et al., 2012). Due to this inherent difficulty, most existing methods employ heuristic methods for the reconstruction of chemical structures and thus do not guarantee optimal or exact solutions. On the other hand, one of the advantages of ANNs is that generative models, such as autoencoders and generative adversarial networks, are available. Furthermore, graph-structured data can be directly handled by using graph convolutional networks (Kipf and Welling, 2016). Therefore, it is reasonable to try to apply ANNs to inverse QSAR (Xiong et al., 2021). Various ANN models, including recurrent networks, autoencoders, generative networks, and invertible flow models, have been applied in this context (Segler et al., 2018; Yang et al., 2017; Gómez-Bombarelli et al., 2018; Kusner et al., 2017; De Cao and Kipf, 2018; Madhawa et al., 2019; Shi et al., 2020). However, the optimality or exactness of the solutions provided by these methods is not yet guaranteed.
A novel two-phase framework based on mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) and machine learning methods has been developed to infer chemical graphs (Shi et al., 2021; Zhu et al., 2022b; Ido et al., 2021; Azam et al., 2021a). The first phase constructs a prediction function
In the first phase, we introduce a feature function
The task of the second phase is to infer desired chemical graphs. This phase consists of three steps. For a given set of rules called topological specification
In the second and third steps of the process, we employ different techniques to generate additional desired chemical graphs based on the initial solution
Contribution: The feature vector
2 Quadratic descriptors and their approximation in an MILP
In the framework with the two-layered model (Shi et al., 2021), the feature vector consists of graph-theoretic descriptors that are mainly the frequencies of atoms, bonds, and edge configurations in the interior and exterior of the chemical compounds. See Zhu et al. (2022a) for the details of the interior and exterior of chemical compounds and all the descriptors
Given two real values
Constants:
-
-
variables:
-
-
constraints:
Note that the necessary number of integer variables for computing
3 Methods for reducing descriptors
The number of descriptors in the two-layered model increases drastically due to the quadratic descriptors. More precisely, if
Let
For given
3.1 A method based on lasso linear regression
Because the lasso linear regression finds some number of descriptors
LLR-Reduce
Input: A data set
Output: A subset
Initialize
while
Partition
for each
Choose a subset
end for;
end while;
Output
set
In this article, we set
3.2 A method based on the backward stepwise procedure
A backward stepwise procedure (Draper and Smith, 1998) reduces the number of descriptors one by one, choosing the one removal that maximizes the learning performance and outputs a subset with the maximum learning performance among all subsets during the reduction iteration.
For a subset
BS-Reduce
Input: A data set
Output: A subset
Compute
while
Compute
Set
Update:
if
end while;
Output
Based on the lasso linear regression and the backward stepwise procedure, we design the following method for choosing a subset
Select-Des-set
Input: A data set
Output: A subset
for each
Compute
end for;
Set
for each
Compute
if
else
Let
end if;
end for;
Output
In the computational experiment in this article, we set
4 Results and discussion
With our new method of choosing descriptors and formulating an MILP to treat quadratic descriptors in the two-layered model, we implemented the framework for inferring chemical graphs and conducted experiments to evaluate the computational efficiency.
4.1 Chemical properties
In the first phase, we used the following 32 chemical properties of monomers and ten chemical properties of polymers.
For monomers, we used the following data sets: biological half-life (BHL), boiling point (Bp), critical temperature (Ct), critical pressure (Cp), dissociation constants (Dc), flash point in closed cup (Fp), heat of combustion (Hc), heat of vaporization (Hv), octanol/water partition coefficient (Kow), melting point (Mp), optical rotation (OptR), refractive index of trees (RfIdT), vapor density (Vd) and vapor pressure (Vp) provided by HSDB from PubChem (2022); electron density on the most positive atom (EDPA) and Kovats retention index (Kov) provided by Jalali-Heravi and Fatemi (2001); entropy (ET) provided by Duchowicz et al. (2002); heat of atomization (Ha) and heat of formation (Hf) provided by Roy and Saha (2003); surface tension (SfT) by Goussard et al. (2017); viscosity (Vis) provided by Goussard et al. (2020); isobaric heat capacities liquid (LhcL) and isobaric heat capacities solid (LhcS) provided by Naef (2019); lipophilicity (Lp) provided by Xiao (2017); flammable limits lower of organics (FlmLO) provided by Yuan et al. (2019); molar refraction at 20° (Mr) provided by Ponce (2003); and solubility (Sl) provided by ESOL (MoleculeNet, 2022), and energy of highest occupied molecular orbital (Homo), energy of lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (Lumo), the energy difference between Homo and Lumo (Gap), isotropic polarizability (Alpha), heat capacity at 298.15 K (Cv), internal energy at 0 K (U0), and electric dipole moment (mu) provided by ESOL (MoleculeNet, 2022), where the properties from Homo to mu are based on a common data set QM9.
The data set QM9 contains more than 130,000 compounds. In our experiment, we used a set of 1,000 compounds randomly selected from the data set. For the Hv property, we removed the chemical compound with the compound identifier (CID)
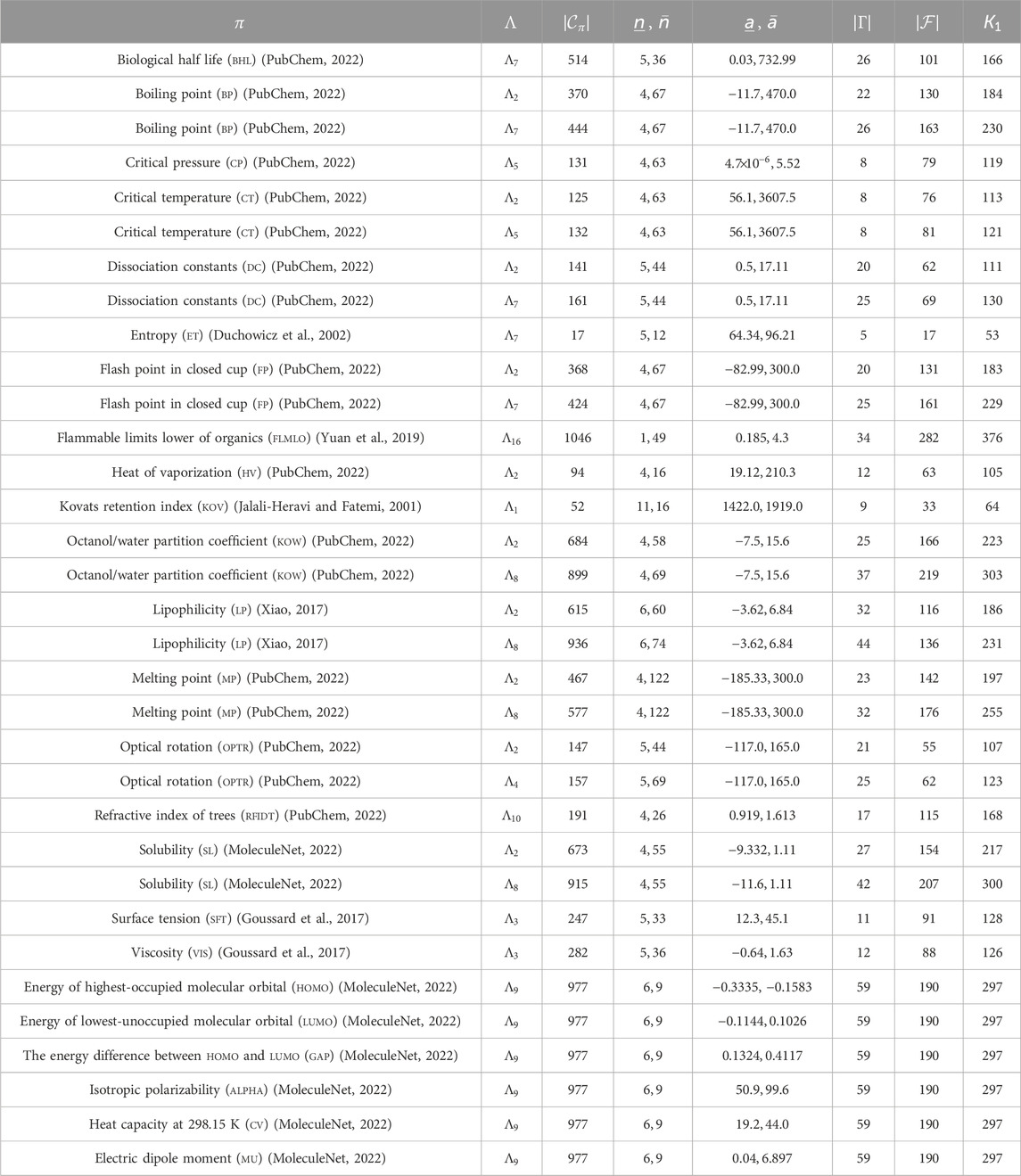
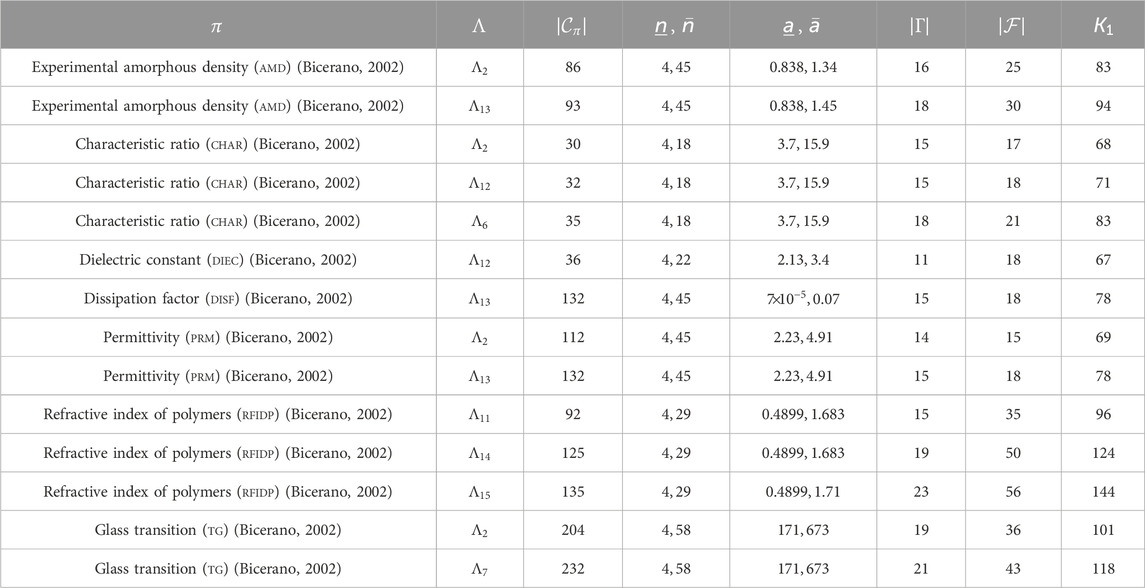
For polymers, we used the following data provided by Bicerano (2002): experimental amorphous density (AmD), characteristic ratio (ChaR), dielectric constant (DieC), dissipation factor (DisF), heat capacity in liquid (HcL), heat capacity in solid (HcS), mol volume (MlV), permittivity (Prm), refractive index of polymers (RfIdP), and glass transition (Tg), where we excluded from our test data set every polymer whose chemical formula could not be found by its name in the book (Bicerano, 2002). A summary of these properties is given in Tables 1, 2. We remark that the previous learning experiments for
4.2 Experimental setup and setting data set
We executed the experiments on a PC with a Core i7-9700 (3.0 GHz; 4.7 GHz at the maximum processor and 16 GB RAM DDR4 memory. Prediction functions were constructed using scikit-learn version 1.0.2 with Python 3.8.12, and MLPRegressor and rectified linear unit (ReLU) activation function were used for learning based on ANN. The prediction functions constructed by different machine learning models were evaluated using the coefficient of determination
For each property
We set a branch-parameter
Among the above properties, we found that the median of the test coefficient of determination
Tables 1, 2 show the size and range of data sets that we prepared for each chemical property to construct a prediction function, where we denote the following:
-
-
S(2), S(6),Br};
-
-
-
-
-
-
4.3 Results on the first phase of the framework
For each chemical property
(i) LLR: use lasso linear regression on the set
(ii) ANN: use ANN on the set
(iii) ALR: use adjustive linear regression on the set
(iv) R-MLR: apply our method (see Zhu et al. (2022a)) of reducing descriptors to the set
For methods (i)–(iii), we use the same implementation described in Zhu et al. (2022b) and Zhu et al. (2022c) and omit the details.
In method (iv), we apply LLR-Reduce
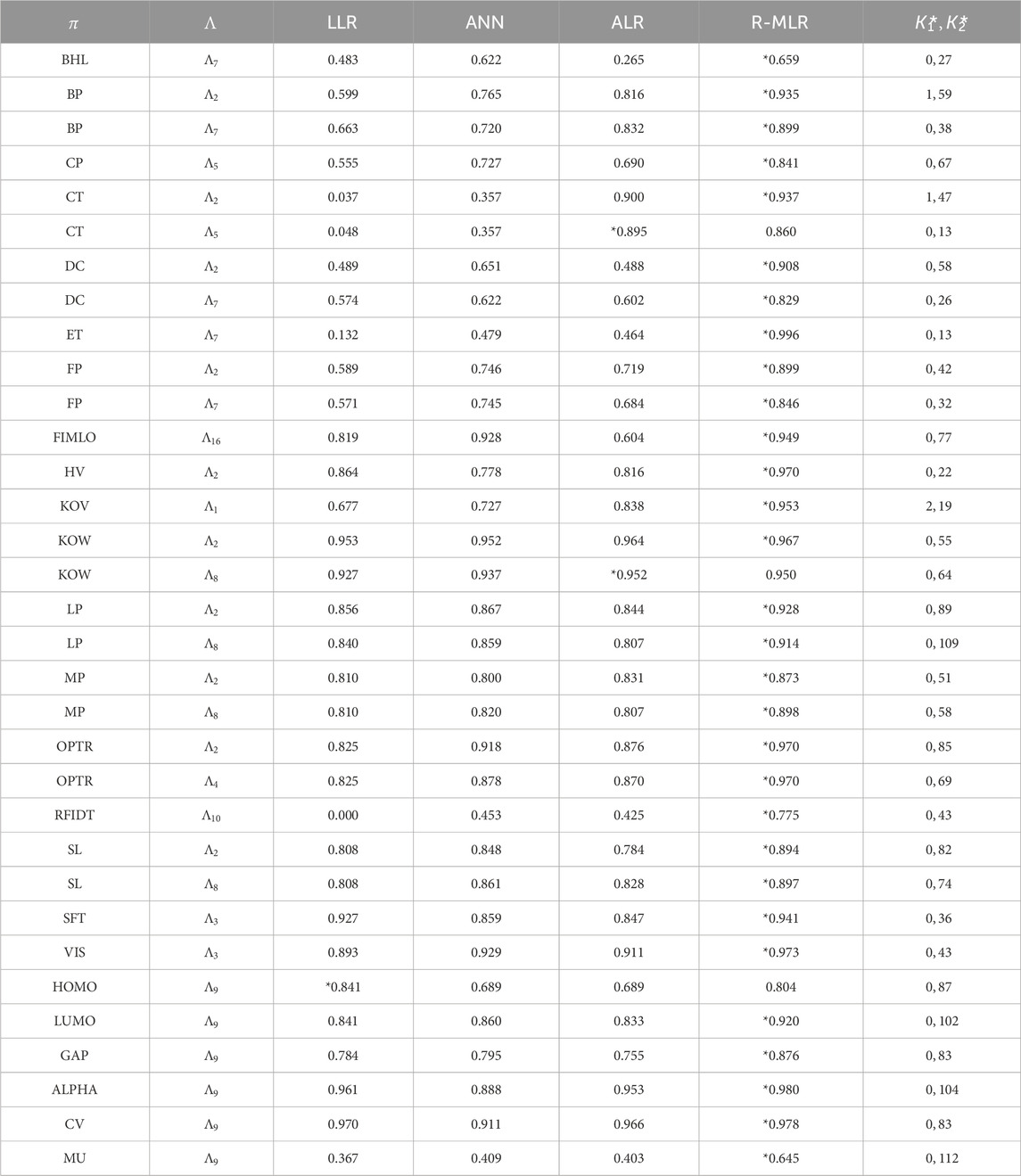
Results of the learning experiments are listed in Tables 3, 4, where:
-
-
- LLR, ANN, ALR, R-MLR: the median of test
- the best
-
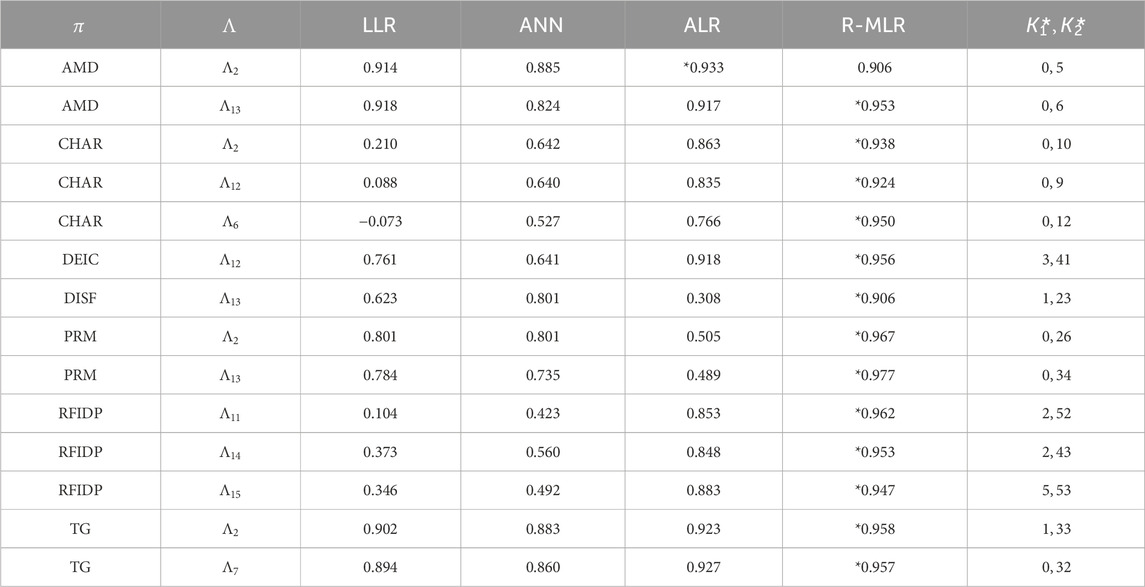
Table 4. Results of constructing prediction functions for polymers. The negative value shows that the respective model is arbitrarily worse.
The computation times of finding
Tables 3, 4 show that method (iv) significantly increased the learning performance of several properties and achieved the best scores among methods (i)–(iii) for 43 of 47 data sets. We also noticed that most of the selected descriptors in
4.4 Results on the second phase of the framework
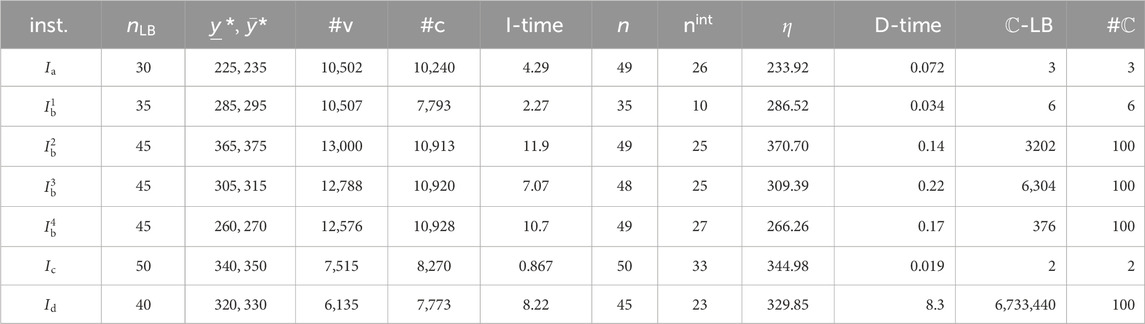
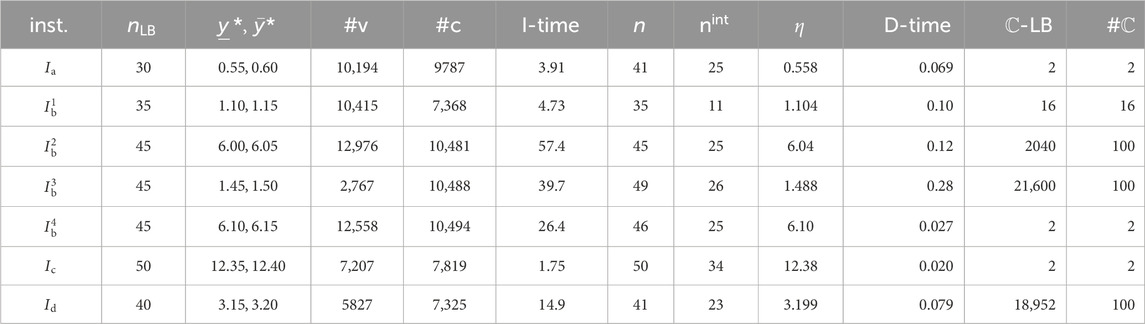
To execute the second phase, we used a set of seven instances
The seed graph
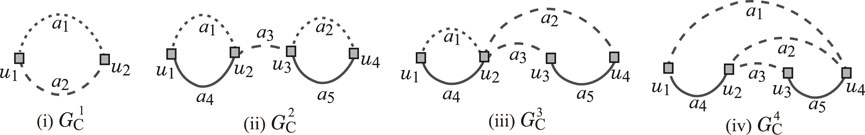
Figure 2. (i) Seed graph
Instance
- the core part of
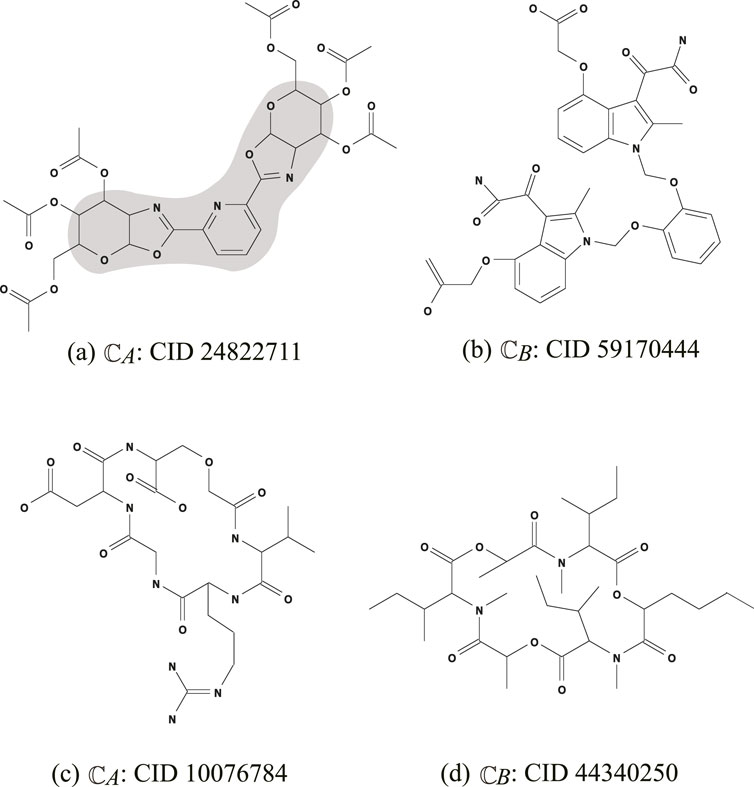
Figure 3. An illustration of chemical compounds for instances
- the frequencies of all edge-configurations of
Instance
-
- the frequency vector of edge configurations in
4.4.1 Solving an MILP for the inverse problem
We executed the stage of solving an MILP to infer a chemical graph for two properties
For the MILP formulation
-
-
-
- I-time: the time (sec.) to solve the MILP;
-
-
-
Figure 4A illustrates the chemical graph
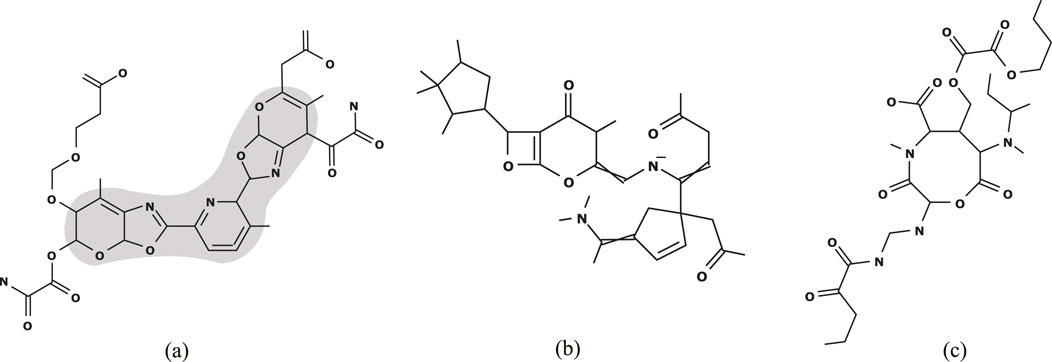
Figure 4. (A)
Figure 4B (resp., Figure 4C) illustrates the chemical graph
In this experiment, we prepared several different types of instances: instances
4.4.2 Generating recombination solutions
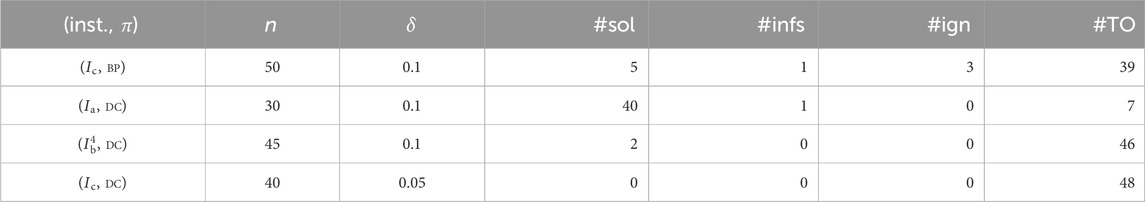
Let
We execute an algorithm for generating chemical isomers of
Tables 5, 6 show the computational results of the experiment in this stage for the two properties
- D-time: the running time (s) to execute the dynamic programming algorithm to compute a lower bound on the number of all chemical isomers
-
-
From Tables 5, 6, we observe the running time and the number of generated recombination solutions in this stage.
The chemical graph
4.4.3 Generating neighbor solutions
Let
We select an MILP for the inverse problem with a prediction function
In this experiment, we add to the MILP
Let
We regard each of
- (inst.,
-
-
- #sol: the number of new graphs inferred from 48 neighbors;
- #infs: the number of infeasible neighbors;
- #ign: the number of ignored neighbors;
- #TO: the number of neighbors for which the running time of the solver exceeds the time limit.
The branch-and-bound method for solving an MILP sometimes takes an extremely large execution time for the same size of instances. We introduce a time limit to bound an entire running time to skip such instances when testing the feasibility of neighbors in
5 Conclusion
In the framework of inferring chemical graphs, the descriptors of a prediction function were mainly defined to be the frequencies of local graph structures in the two-layered model, and such a definition was important to derive a compact MILP formulation for inferring a desired chemical graph. To improve the performance of prediction functions in the framework, this article introduced a multiplication of two of these descriptors as a new descriptor and examined the effectiveness of the new set of descriptors. For this, we designed a method for reducing the size of a descriptor set to not lose the learning performance in constructing prediction functions and gave a compact formulation to compute a product of two values in an MILP. From the results of our computational experiments, we observe that a prediction function constructed by our new method performs considerably better than the prediction functions constructed by the previous methods for several chemical properties. Furthermore, the modified MILP, with the computation of quadratic descriptors, was able to infer desired chemical graphs with up to 50 non-hydrogen atoms.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
JZ: data curation, funding acquisition, software, validation, and writing–review and editing. NA: data curation, formal analysis, software, validation, and writing–review and editing. SC: software, validation, and writing–review and editing. RI: software, validation, and writing–review and editing. KH: data curation, software, and writing–review and editing. LZ: data curation, software, and writing–review and editing. HN: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, methodology, project administration, and writing–original draft. TA: conceptualization, data curation, funding acquisition, methodology, and writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The publication cost of this article is funded by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Japan, under grant numbers 22H00532, 22K19830, and 22KJ1979. The funding agency has no role in the conceptualization, design, data collection, analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Akutsu, T., Fukagawa, D., Jansson, J., and Sadakane, K. (2012). Inferring a graph from path frequency. Discrete Appl. Math. 160, 1416–1428. doi:10.1016/j.dam.2012.02.002
Azam, N. A., Zhu, J., Haraguchi, K., Zhao, L., Nagamochi, H., and Akutsu, T. (2021a). “Molecular design based on artificial neural networks, integer programming and grid neighbor search,” in 2021 IEEE international Conference on Bioinformatics and biomedicine (BIBM) (IEEE), 360–363.
Azam, N. A., Zhu, J., Sun, Y., Shi, Y., Shurbevski, A., Zhao, L., et al. (2021b). A novel method for inference of acyclic chemical compounds with bounded branch-height based on artificial neural networks and integer programming. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 16, 18. doi:10.1186/s13015-021-00197-2
Bohacek, R. S., McMartin, C., and Guida, W. C. (1996). The art and practice of structure-based drug design: a molecular modeling perspective. Med. Res. Rev. 16, 3–50. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-1128(199601)16:1<3::AID-MED1>3.0.CO;2-6
Catacutan, D. B., Alexander, J., Arnold, A., and Stokes, J. M. (2024). Machine learning in preclinical drug discovery. Nat. Chem. Biol. 20, 960–973.
Cherkasov, A., Muratov, E. N., Fourches, D., Varnek, A., Baskin, I. I., Cronin, M., et al. (2014). Qsar modeling: where have you been? where are you going to? J. Med. Chem. 57, 4977–5010. doi:10.1021/jm4004285
De Cao, N., and Kipf, T. (2018). Molgan: an implicit generative model for small molecular graphs. arXiv Prepr. arXiv:1805.
Duchowicz, P., Castro, E. A., and Toropov, A. A. (2002). Improved qspr analysis of standard entropy of acyclic and aromatic compounds using optimized correlation weights of linear graph invariants. Comput. and Chem. 26, 327–332. doi:10.1016/s0097-8485(01)00121-8
Gartner III, T. E., Ferguson, A. L., and Debenedetti, P. G. (2024). Data-driven molecular design and simulation in modern chemical engineering. Nat. Chem. Eng. 1, 6–9.
Ghasemi, F., Mehridehnavi, A., Pérez-Garrido, A., and Pérez-Sánchez, H. (2018). Neural network and deep-learning algorithms used in qsar studies: merits and drawbacks. Drug Discov. today 23, 1784–1790. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2018.06.016
Gómez-Bombarelli, R., Wei, J. N., Duvenaud, D., Hernández-Lobato, J. M., Sánchez-Lengeling, B., Sheberla, D., et al. (2018). Automatic chemical design using a data-driven continuous representation of molecules. ACS central Sci. 4, 268–276. doi:10.1021/acscentsci.7b00572
Goussard, V., Duprat, F., Gerbaud, V., Ploix, J.-L., Dreyfus, G., Nardello-Rataj, V., et al. (2017). Predicting the surface tension of liquids: comparison of four modeling approaches and application to cosmetic oils. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 57, 2986–2995. doi:10.1021/acs.jcim.7b00512
Goussard, V., Duprat, F., Ploix, J.-L., Dreyfus, G., Nardello-Rataj, V., and Aubry, J.-M. (2020). A new machine-learning tool for fast estimation of liquid viscosity. application to cosmetic oils. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 60, 2012–2023. doi:10.1021/acs.jcim.0c00083
Ido, R., Cao, S., Zhu, J., Azam, N. A., Haraguchi, K., Zhao, L., et al. (2021). A method for inferring polymers based on linear regression and integer programming. arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.02628.
Ikebata, H., Hongo, K., Isomura, T., Maezono, R., and Yoshida, R. (2017). Bayesian molecular design with a chemical language model. J. computer-aided Mol. Des. 31, 379–391. doi:10.1007/s10822-016-0008-z
Jalali-Heravi, M., and Fatemi, M. H. (2001). Artificial neural network modeling of kovats retention indices for noncyclic and monocyclic terpenes. J. Chromatogr. A 915, 177–183. doi:10.1016/s0021-9673(00)01274-7
Kim, J., Park, S., Min, D., and Kim, W. (2021). Comprehensive survey of recent drug discovery using deep learning. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 9983. doi:10.3390/ijms22189983
Kipf, T. N., and Welling, M. (2016). Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. arXiv Prepr. arXiv:1609.02907.
Kusner, M. J., Paige, B., and Hernández-Lobato, J. M. (2017). “Grammar variational autoencoder,” in International conference on machine learning (Sydney, Australia: PMLR), 1945–1954.
Lo, Y.-C., Rensi, S. E., Torng, W., and Altman, R. B. (2018). Machine learning in chemoinformatics and drug discovery. Drug Discov. today 23, 1538–1546. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2018.05.010
Madhawa, K., Ishiguro, K., Nakago, K., and Abe, M. (2019). Graphnvp: an invertible flow model for generating molecular graphs. arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.11600.
Miyao, T., and Funatsu, K. (2024). Data-driven molecular structure generation for inverse qspr/qsar problem. In Drug Development Supported by Informatics (Springer). 47–59.
Miyao, T., Kaneko, H., and Funatsu, K. (2016). Inverse qspr/qsar analysis for chemical structure generation (from y to x). J. Chem. Inf. Model. 56, 286–299. doi:10.1021/acs.jcim.5b00628
MoleculeNet (2022). Available at: https://moleculenet.org/datasets-1.
Naef, R. (2019). Calculation of the isobaric heat capacities of the liquid and solid phase of organic compounds at and around 298.15 k based on their “true” molecular volume. Molecules 24, 1626. doi:10.3390/molecules24081626
Ponce, Y. M. (2003). Total and local quadratic indices of the molecular pseudograph’s atom adjacency matrix: applications to the prediction of physical properties of organic compounds. Molecules 8, 687–726. doi:10.3390/80900687
PubChem (2022). Annotations from hsdb. Available at: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/.
Roy, K., and Saha, A. (2003). Comparative qspr studies with molecular connectivity, molecular negentropy and tau indices: Part i: molecular thermochemical properties of diverse functional acyclic compounds. J. Mol. Model. 9, 259–270. doi:10.1007/s00894-003-0135-z
Rupakheti, C., Virshup, A., Yang, W., and Beratan, D. N. (2015). Strategy to discover diverse optimal molecules in the small molecule universe. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 55, 529–537. doi:10.1021/ci500749q
Segler, M. H., Kogej, T., Tyrchan, C., and Waller, M. P. (2018). Generating focused molecule libraries for drug discovery with recurrent neural networks. ACS central Sci. 4, 120–131. doi:10.1021/acscentsci.7b00512
Shi, C., Xu, M., Zhu, Z., Zhang, W., Zhang, M., and Tang, J. (2020). Graphaf: a flow-based autoregressive model for molecular graph generation. arXiv Prepr. arXiv:2001, 09382.
Shi, Y., Zhu, J., Azam, N. A., Haraguchi, K., Zhao, L., Nagamochi, H., et al. (2021). An inverse qsar method based on a two-layered model and integer programming. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 2847. doi:10.3390/ijms22062847
Tetko, I. V., and Engkvist, O. (2020). From big data to artificial intelligence: chemoinformatics meets new challenges. J. Cheminformatics 12, 1–3. doi:10.1186/s13321-020-00475-y
Xiong, J., Xiong, Z., Chen, K., Jiang, H., and Zheng, M. (2021). Graph neural networks for automated de novo drug design. Drug Discov. today 26, 1382–1393. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2021.02.011
Yang, X., Zhang, J., Yoshizoe, K., Terayama, K., and Tsuda, K. (2017). Chemts: an efficient python library for de novo molecular generation. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 18, 972–976. doi:10.1080/14686996.2017.1401424
Yuan, S., Jiao, Z., Quddus, N., Kwon, J. S.-I., and Mashuga, C. V. (2019). Developing quantitative structure–property relationship models to predict the upper flammability limit using machine learning. Industrial and Eng. Chem. Res. 58, 3531–3537. doi:10.1021/acs.iecr.8b05938
Zhu, J., Azam, N. A., Cao, S., Ido, R., Haraguchi, K., Zhao, L., et al. (2022a). Molecular design based on integer programming and quadratic descriptors in a two-layered model. arXiv Prepr. arXiv:2209.13527.
Zhu, J., Azam, N. A., Haraguchi, K., Zhao, L., Nagamochi, H., and Akutsu, T. (2022b). “A method for molecular design based on linear regression and integer programming,” in Proceedings of the 2022 12th international conference on bioscience, biochemistry and bioinformatics, 21–28.
Zhu, J., Haraguchi, K., Nagamochi, H., and Akutsu, T. (2022c). Adjustive linear regression and its application to the inverse qsar. BIOINFORMATICS, 144–151. doi:10.5220/0010853700003123
Glossary
Alpha isotropic polarizability
ALR adjustive linear regression
AmD experimental amorphous density
ANN artificial neural network
BHL biological half life
Bp boiling point
ChaR characteristic ratio
Cp critical pressure
Ct critical temperature
Cv heat capacity at 298.15 K
Dc dissociation constants
DieC dielectric constant
DisF dissipation factor
EDPA electron density on the most positive atom
ET entropy
FlmLO flammable limits lower of organics
Fp flash point in closed cup
Gap the energy difference between HOMO and LUMO
Ha heat of atomization
Hc heat of combustion
HcL heat capacity in liquid
HcS heat capacity in solid
Hf heat of formation
HOMO energy of highest-occupied molecular orbital
Hv heat of vaporization
Kov Kovats retention index
Kow octanol/water partition coefficient
LLR lasso linear regression
Lp lipophilicity
LUMO energy of lowest-unoccupied molecular orbital
MILP mixed-integer linear programming
MLR multidimensional linear regression
MlV mol volume
Mp melting point
Mr molar refraction at 20° degree
mu electric dipole moment
OptR optical rotation
Prm permittivity
QSAR quantitative structure–activity relationship
RfIdP refractive index of polymers
RfIdT refractive index of trees
SfT surface tension
Sl solubility
Tg glass transition
U0 internal energy at 0 K
Vd vapor density
Vis viscosity
Vp vapor pressure
Keywords: machine learning, integer programming, chemo-informatics, materials informatics, QSAR/QSPR, molecular design
Citation: Zhu J, Azam NA, Cao S, Ido R, Haraguchi K, Zhao L, Nagamochi H and Akutsu T (2025) Quadratic descriptors and reduction methods in a two-layered model for compound inference. Front. Genet. 15:1483490. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1483490
Received: 20 August 2024; Accepted: 30 December 2024;
Published: 29 January 2025.
Edited by:
Shoba Ranganathan, Macquarie University, AustraliaCopyright © 2025 Zhu, Azam, Cao, Ido, Haraguchi, Zhao, Nagamochi and Akutsu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Naveed Ahmed Azam, bmF2ZWVkYXphbUBxYXUuZWR1LnBr
 Jianshen Zhu1
Jianshen Zhu1 Naveed Ahmed Azam
Naveed Ahmed Azam Tatsuya Akutsu
Tatsuya Akutsu