- 1CIMMYT-China Specialty Maize Research Center, Crop Breeding and Cultivation Research Institute, Shanghai Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Shanghai, China
- 2National Research Center of Intercropping, The Islamia University of Bahawalpur, Bahawalpur, Pakistan
- 3International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), Nairobi, Kenya
- 4International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), Texcoco, Mexico
- 5Shenyang City Key Laboratory of Maize Genomic Selection Breeding, College of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Shenyang Agricultural University, Shenyang, China
Introduction: Maize (Zea mays L.) is one of the most important crops worldwide, the kernel size-related traits are the major components of maize grain yield.
Methods: To dissect the genetic architecture of four kernel-related traits of 100-kernel weight, kernel length, kernel width, and kernel diameter, a genome-wide association study (GWAS) was conducted in the waxy and sweet maize panel comprising of 447 maize inbred lines re-sequenced at the 5× coverage depth. GWAS analysis was carried out with the mixed linear model using 1,684,029 high-quality SNP markers.
Results: In total, 49 SNPs significantly associated with the four kernel-related traits were identified, including 46 SNPs on chromosome 3, two SNPs on chromosome 4, and one SNP on chromosome 7. Haplotype regression analysis identified 338 haplotypes that significantly affected these four kernel-related traits. Genomic selection (GS) results revealed that a set of 10,000 SNPs and a training population size of 30% are sufficient for the application of GS in waxy and sweet maize breeding for kernel weight and kernel size. Forty candidate genes associated with the four kernel-related traits were identified, including both Zm00001d000707 and Zm00001d044139 expressed in the kernel development tissues and stages with unknown functions.
Discussion: These significant SNPs and important haplotypes provide valuable information for developing functional markers for the implementation of marker-assisted selection in breeding. The molecular mechanism of Zm00001d000707 and Zm00001d044139 regulating these kernel-related traits needs to be investigated further.
1 Introduction
Maize (Zea mays L.) is one of the most important cereal crops globally. In 2022, maize production reached 1,163.5 million tons, surpassing other key crops such as rice (776.5 million tons) and wheat (880.4 million tons), according to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (https://www.fao.org/statistics/en/). Maize kernel size and weight are the two major components associated with grain yield. Specific kernel-related traits including 100-kernel weight (HKW), kernel length (KL), kernel width (KW), and kernel thickness (KT), play an important role in determining overall grain yield in maize (Gupta et al., 2006).
Genome-wide association study (GWAS) is a powerful approach to unravel the genetic basis of complex traits, which has been widely applied to various crops (Pang et al., 2020; Shikha et al., 2021; Shook et al., 2021; Soleimani et al., 2022). Maize has a high-level genetic diversity and harbors rare alleles in the genome. GWAS is an ideal tool to study the genetic architecture of complex traits in maize (Myles et al., 2009; Yan et al., 2009; Zhang X. et al., 2022). Over recent decades, numerous SNPs or candidate genes associated with these traits have been identified using this method. For example, Zhang et al. (2017) discovered 25 SNPs significantly associated with kernel weight (HKW), kernel row number (KRN), and kernel size in a study involving 240 maize inbred lines (Zhang et al., 2017). Moreover, GWAS was applied to identify 29 SNPs significantly associated with four kernel-related traits (Hao et al., 2019). Additionally, 21 SNPs and 7 SNPs were significantly associated with HKW and kernel weight efficiency (KWE), respectively (Zhang et al., 2020). Thus, exploring the genetic basis of kernel traits in maize using GWAS is crucial for enhancing crop improvement strategies.
The kernel size and weight are affected by key genes in the regulatory pathway involving cell proliferation and expansion at the kernel development stage, and several key regulatory factors involved in various signaling pathways have been identified in several previous studies. In the ubiquitin-proteasomal pathway, the GW2 gene encoding a RING-E3 ubiquitin ligase negatively affects maize kernel size and weight (Li et al., 2010a). A recent discovery highlighted the ZmKW1 gene, which codes for a SINA protein with E3 ubiquitin ligase activity, as a regulator of kernel weight and shape (Zhang et al., 2024). In the G-protein signaling pathway, the maize ortholog of the GS3 gene, which encodes the γ subunit of G-protein, negatively regulates kernel size and weight and also affects the GW2 gene (Li et al., 2010b). In the MAPK signaling pathway, the OPAQUE11 gene, which encodes an endosperm-specific bHLH transcription factor, activates the Zmyada gene upstream of MAPK (Feng et al., 2018). In the phytohormone pathway, the genes ZmYuc1/De18, ZmVPS29, and ZmSK2 have been proven to regulate kernel size and weight through the IAA signaling pathway (Bernardi et al., 2012; Chen et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2022).
Genomic Selection (GS) can help breeders improve breeding efficiency by saving phenotyping costs and reducing the breeding cycle time (Meuwissen et al., 2001; Crossa et al., 2014; Qu et al., 2022). GS utilizes a training population to estimate the effect of genetic markers based on phenotypic and genotypic data, which then helps predict the genomic estimated breeding values (GEBV) of individuals in the prediction population (Liu et al., 2023). GS has been extensively applied in maize to select desirable traits in inbred lines and to predict the performance of hybrids (Liu et al., 2017; Liu et al., 2021; Wang B. et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2020b; Song et al., 2024). The preliminary GS analysis is needed to better understand how to improve the kernel-related traits in waxy and sweet maize breeding.
In the present study, the genetic architecture of kernel-related traits in sweet and waxy maize was dissected in a GWAS including 230 waxy maize inbred lines, 112 sweet maize inbred lines, and 105 sweet-waxy maize inbred lines. The genetic loci and candidate genes regulating HKW, KL, KW, and kernel diameter (KD) were identified by GWAS, alongside a GS analysis was carried out. The present study aims to improve the understanding of the genetic architecture of kernel-related traits in waxy and sweet maize. Furthermore, it aims to contribute to the enhancement of kernel yield in both waxy and sweet maize breeding.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Plant materials, field planting, and phenotyping
In this study, 447 maize lines, including 230 sweet maize inbred lines, 112 waxy maize lines, and 105 sweet-waxy maize lines, were used for GWAS analysis. The plants were cultivated at the Shanghai Academy of Agricultural Sciences’ experimental stations in Linshui, Hainan (110°05′E, 18°55′N) in 2020 and Zhuanghang, Fengxian District, Shanghai (121°39′E, 30°89′N) in 2021. All experimental trials followed a randomized complete block design with three replications at each location. Approximately 50 seeds from each plant were collected to evaluate the four kernel-related traits, including HKW, KL, KW, and KD using the SC-G automatic seed tester and a thousand-kernel weight scale (http://www.wseen.com/ProductDetail.aspx?id=16&classid=28). For subsequent GWAS and GS analyses, the phenotypic values of each line were represented by the best linear unbiased prediction (BLUP) values, calculated using META-R (version: 6.0, http://hdl.handle.net/11529/10201) software (Alvarado et al., 2020).
2.2 Sequencing and SNP calling
For genotyping, next-generation sequencing (NGS) was employed to analyze the genotypes of 447 maize inbred lines. Genomic DNA was isolated using a modified CTAB method. Each inbred line of the associated population was genotyped using Illumina sequencing technology at a 5-fold depth by Novogene Co., Ltd., Beijing, China (https://cn.novogene.com/). The raw data from Novogene were initially processed using Fastp software (version: 0.20.1, https://github.com/OpenGene/fastp) with parameters set to “-q 20 --length_required = 50” (Chen et al., 2018). The processed data were then aligned to the Maize B73 RefGen_v4 reference genome using bwa-mem software (version: 0.7.17, https://github.com/lh3/bwa) with the ‘-M’ parameter (Chen et al., 2018). The alignment results were sorted, and duplicates were marked using samtools (version: 1.6, https://www.htslib.org/) and Picard (version: 2.18.29, https://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/) software, respectively (Danecek et al., 2021). SNPs were identified using Freebayes software (version: 1.3.6, https://github.com/freebayes/freebayes) with default parameters (Garrison and Marth, 2012). The raw SNPs were filtered to retain only those with a missing rate (MR) < 5%, minor allele frequency (MAF) > 0.05, and heterozygosity rate (HR) < 0.2, using an in-house Perl script. After filtering, 1,684,029 high-quality SNPs were retained for further analysis.
2.3 Genome-wide association analysis and haplotype analysis
A total of 1,684,029 high-quality SNPs, evenly distributed across the ten maize chromosomes, were retained for subsequent linkage disequilibrium (LD) calculation and GWAS analysis. LD analysis was conducted using TASSEL5 software (version: 5.2.90, https://tassel.bitbucket.io/), and LD decay visualization was achieved using an R programming script provided by Zhang X. et al. (2022) (Bradbury et al., 2007; Zhang A. et al., 2022). GWAS analysis on the four kernel-related traits including HKW, KL, KW, and KD was carried out with GEMMA software (version: 0.98.5, https://github.com/genetics-statistics/GEMMA) employing a mixed linear model (MLM) (Zhou and Stephens, 2012). The number of effective SNPs, calculated using GEC software (version: 1.0, https://pmglab.top/gec/#/), determined the p-value threshold (Li et al., 2012). Manhattan and QQ plots were generated using CMplot (https://github.com/YinLiLin/CMplot) packages in R.
SNPs with a p-value < 1 × 10−3 from the GWAS were used for developing haplotype and subsequent haplotype-trait regression analysis. The development of haplotype was performed using LDBlockShow software (version: 1.40, https://github.com/BGI-shenzhen/LDBlockShow) with default parameters (Dong et al., 2021). The identified haplotype blocks were used to carry out the haplotype-trait regression (HTR) analysis with four kernel-related traits using stepwise regression with forward elimination in R (Rashid et al., 2022).
2.4 Prediction and functional annotation analysis of candidate genes
Genes located within 106.12 kb (genome-wide average distance of LD decay to r2 = 0.2) around the significantly associated SNPs were selected as the candidate genes. Functional annotation of candidate genes was performed using files from MaizeGDB (https://maizegdb.org/) and agriGOV2 (http://systemsbiology.cau.edu.cn/agriGOv2/) for GO functional annotation (Tian et al., 2017). The expression level dataset was downloaded from the maizeGDB and filtered based on kernel-related tissues (Kakumanu et al., 2012; Johnston et al., 2014; Forestan et al., 2016; Stelpflug et al., 2016; Walley et al., 2016; Waters et al., 2017). The expression data of candidate genes were obtained from the filtered dataset. Finally, the expression results of candidate genes were visualized using the heatmap package in R.
2.5 Genomic selection analysis
The Ridge Regression Best Linear Unbiased Prediction (RRBLUP) model was employed for genomic prediction analysis (Endelman, 2011). Based on the phenotypic variation explained (PVE) values, the top 100, 500, 1,000, 3,000, 5,000, and 10,000 SNPs datasets were used to estimate the prediction accuracy for all four kernel-related traits. At each marker density, SNPs were randomly selected 500 times, and a five-fold cross-validation scheme with 500 repetitions was applied. In addition, 10%–90% of total population size, with a 10% interval, was set as the training population to explore the effect of training population size on the estimation of the prediction accuracy for all four kernel-related traits.
3 Results
3.1 Phenotypic variation and heritability of kernel size and weight
The HKW, KL, KW, and KD in the GWAS panel ranged from 9.24 to 26.80 g, 10.94–16.09 mm, 9.75–10.91 mm, and 10.32–12.32 mm, respectively, with averages of 17.44 g, 16.09 mm, 10.91 mm, and 12.32 mm (Table 1). Significant variation was observed in kernel size and weight. The broad-sense heritability (h2) for these traits ranged from 0.19 to 0.87 in the GWAS panel, i.e., 0.87 for HKW, 0.54 for KL, 0.19 for KW, and 0.29 for KD. This result shows HKW and KL exhibited higher heritability, whereas KW and KD had relatively lower values. These findings indicate that HKW and KL were under stronger genetic control, whereas KW and KD were influenced to a lesser extent by genetic factors. The differences in heritability among these traits may reflect the extent of genetic variation within the population, providing valuable insights to further understand the genetic mechanisms and breeding applications of these kernel-related traits.
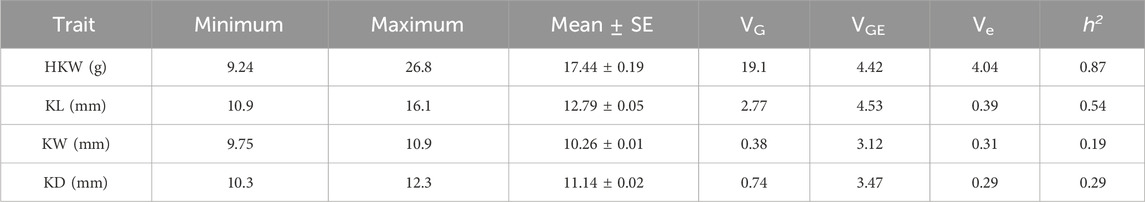
Table 1. The means and their standard errors (SE), genetic variances (VG), genotype-environment interaction variances (VGE), error variances (Ve), and heritability estimates (h2) for kernel-related traits across two environments in the associated panel.
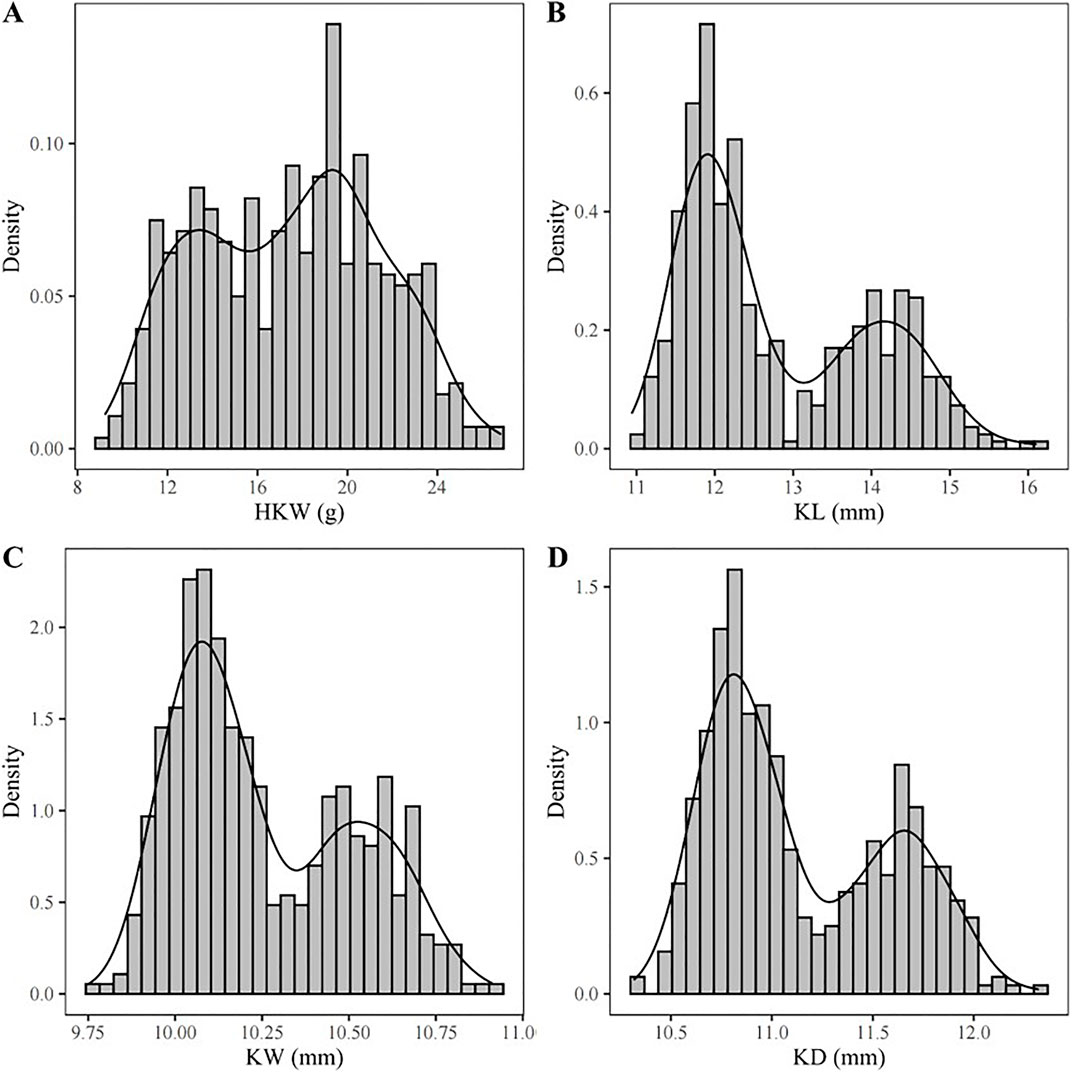
Density plots of the four kernel-related traits showed bimodal distributions (Figures 1A–D), suggesting major genes may regulate these traits in the associated panel. Additionally, the panel was divided into two subgroups based on the source information of sweet and waxy maize germplasm. Within each subgroup, correlation analyses of the traits were performed. In the waxy maize subgroup, the correlation coefficients between HKW and KL, KW, and KD were 0.61, 0.77, and 0.75, respectively (Figure 2A). In contrast, the sweet maize subgroup showed lower correlation coefficients of 0.22, 0.50, and 0.44, respectively (Figure 2B). This suggests that KL, KW, and KD were jointly contributed to regulating kernel weight in both sweet and waxy maize.
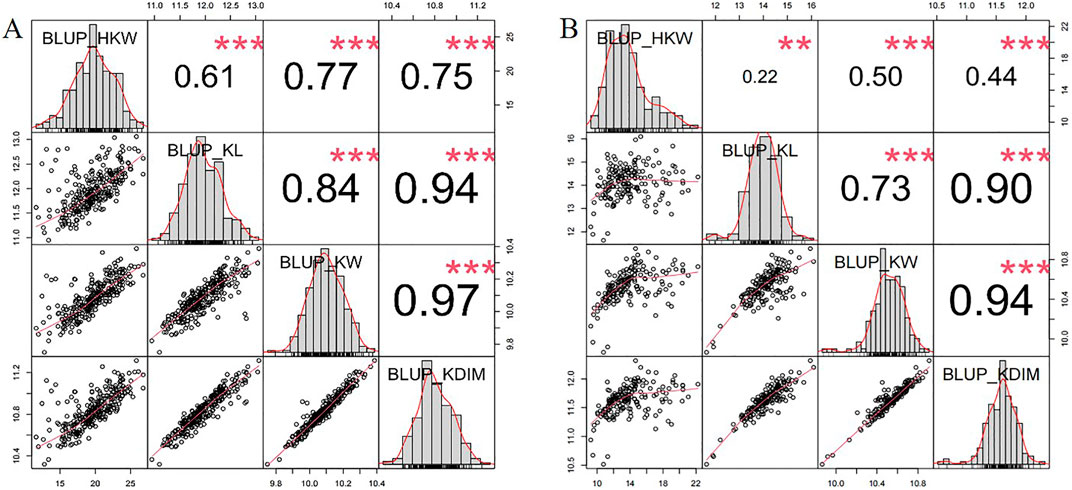
Figure 2. Frequency distribution and correlation analysis of HKW, KL, KW, and KD in waxy maize subgroup (A) and sweet maize subgroup (B) across two environments.
3.2 SNP calling, filtering, and characterizing
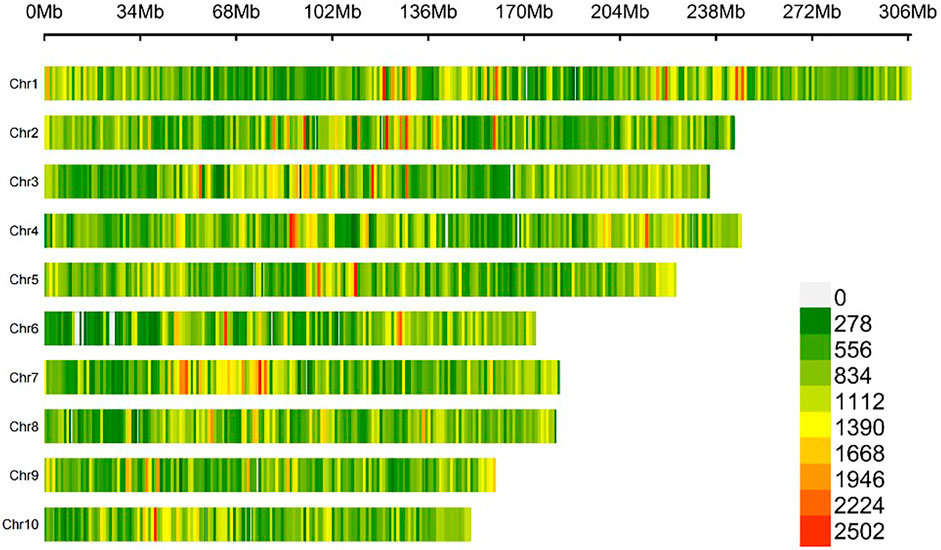
The raw sequencing data were filtered, aligned to the maize B73v4 genome, and PCR duplicates were removed. This process identified 45, 728, 361 raw SNPs using Freebayes software. After filtering, 1,684,029 SNPs were retained for further analysis. The number of high-quality SNPs ranged from 120,666 on chromosome 10 to 245,799 on chromosome 1, with an average of 168,402 SNPs per chromosome. The density of these SNPs varied from 732.20 SNPs per megabase (Mb) on chromosome 6 to 834.24 SNPs/Mb on chromosome 3, averaging 799.51 SNPs/Mb, as shown in Supplementary Table S1. The high-quality SNPs were distributed relatively evenly across all ten chromosomes of the maize B73v4 genome (Figure 3). The missing rate for SNPs across 447 maize inbred lines ranged from 0 to 0.05, with an average of 0.04 (Figure 4A), while SNP heterozygosity ranged from 0 to 0.1, averaging 0.02 (Figure 4B). The minor allele frequency (MAF) ranged from 0.05 to 0.5, with an average of 0.21 (Figure 4C). This SNP dataset was deemed suitable for subsequent GWAS analysis. Within this GWAS panel, the LD decay distance was 106.12 kb at r2 = 0.2, estimated with this high-quality SNP dataset (Figure 4F).
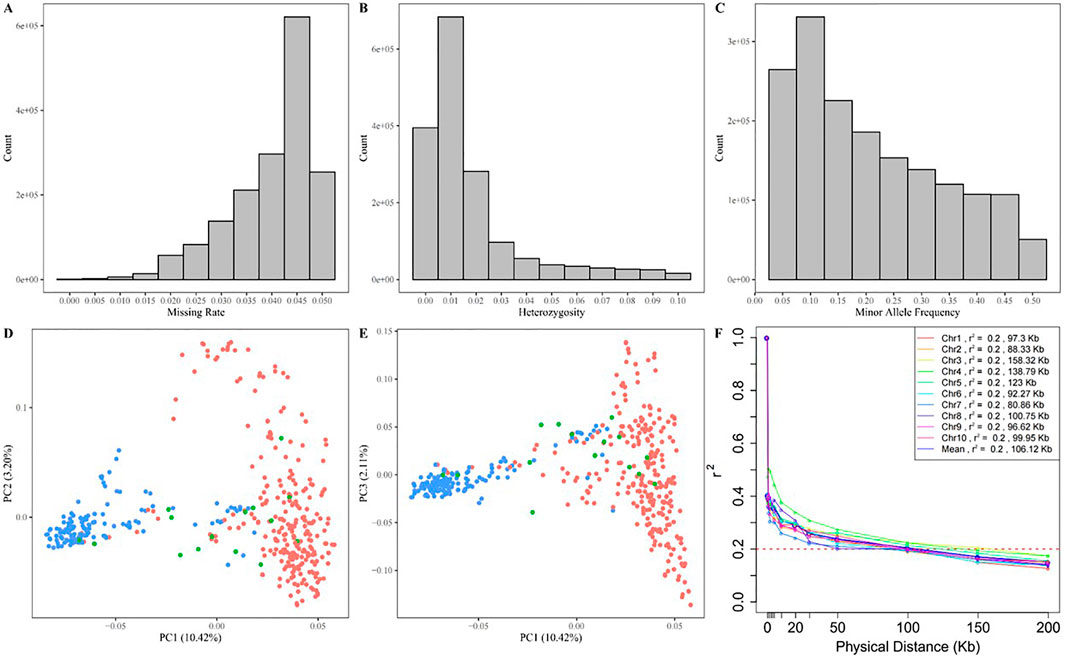
Figure 4. Distribution of the missing rate (A), heterozygosity rate (B), and minor allele frequency (C) of genotype. The scatter plot of the first three principal components of the GWAS panel (D, E), and the LD decay plot in GWAS panel (F).
Principal component analysis revealed that the first three components accounted for 15.73% of the total SNP variance (10.42% for PC1, 3.20% for PC2, and 2.11% for PC3), clearly classifying the 477 maize inbred lines into two subgroups corresponding to the original information of the sweet and waxy maize germplasm (Figures 4D, E). The sweet-waxy maize inbred lines were divided into either sweet maize subgroup or waxy maize subgroup, rather than being grouped into a separate subgroup. These findings reflect a correlation between domestication levels and selection intensity, leading to reduced genetic diversity.
3.3 Genome-wide association analysis and haplotype traits regression analysis
The GWAS analysis results from the GEMMA software showed that GWAS effects for HKW, KL, KW, and KD were 17.48, 12.77, 10.25, and 11.13, respectively. Meanwhile, the total PVE for HKW, KL, KW, and KD was 73.32%, 60.33%, 50.07%, and 52.05%, respectively (Table 2). After analyzing with the GEC software, the number of effective SNP in the association panel was 445,324. The threshold of p-value was set to 1.12 × 10−7, based on the number of effective SNPs and familywise error rate of α = 0.05. A total of 49 SNPs were significantly associated with the four kernel-related traits identified by GEMMA with the MLM model (Figures 5, 6). Out of these 49 SNPs, 19 were significantly associated with HKW, 19 with KL, 5 with KW, and 6 with KD (Supplementary Table S2). These significant SNPs were located on chromosome 3, 4, and 7, with counts of 46, 2, and 1, respectively. The PVE of these significant SNPs ranged from 6.27% to 12.33%, with an average value of 7.73%. The maximum PVE values were 12.33% (S3_220335807) for HKW, 9.25% (S3_220227161) for KL, 7.95% (S3_222360985) for KW, and 7.55% (S3_220227161) for KD. Meanwhile, the minimum p-values for HKW, KL, KW, and KD were 5.66 × 10−14, 1.30 × 10−10, 2.30 × 10−9, and 7.62 × 10−9, respectively.
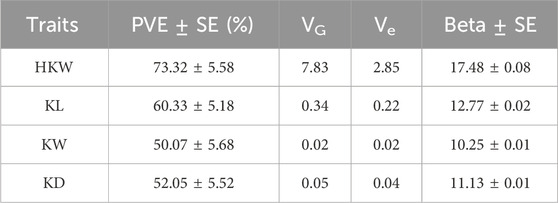
Table 2. The PVE and their standard errors (SE), genetic variances (VG), error variances (Ve), and Beta and their standard errors (SE) for GWAS using mix liner model in the associated panel.
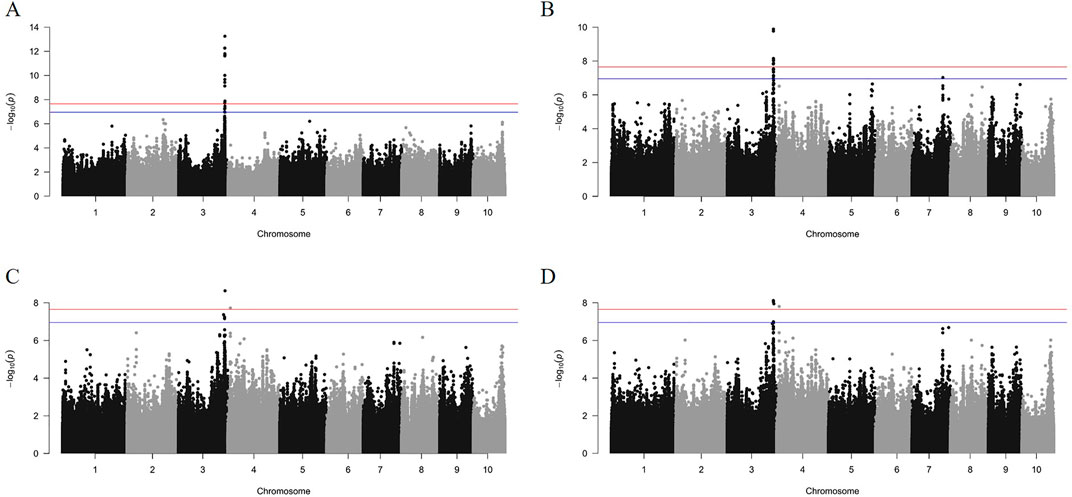
Figure 5. The Manhattan plots of GWAS results for HKW (A), KL (B), KW (C), and KD (D) using the mixed linear model. The cut-off of 0.01/number of effective SNPs and 0.05/number of effective SNPs are represented by red and blue parallel lines, respectively.
Figure 6. The quantile-quantile (QQ) plots of GWAS results for HKW (A), KL (B), KW (C), and KD (D) using the mixed linear model.
After applying a filtering criterion of p-value < 0.001, the numbers of retained SNPs were 1,808 for HKW, 3,213 for KL, 2,350 for KW, and 2,550 for KD. These were used in haplotype analyses conducted using the LDblockshow software. The analysis formed 316, 438, 338, and 370 haplotype blocks for HKW, KL, KW, and KD, respectively, which were then used for HTR analyses using BLUP for the kernel-related traits (Supplementary Table S4). The HTR analysis detected 61, 122, 66, and 89 significant haplotypes for HKW, KL, KW, and KD, respectively, with adjusted p-values < 0.05. The PVE values of the haplotypes ranged from 1.10% to 6.28% for HKW, 1.09%–11.76% for KL, 1.21%–6.78% for KW, and 1.17%–10.19% for KD (Supplementary Table S5). Notably, haplotype of hap6.16 for HKW on chromosome 6, comprising two SNPs at 142 Mb (S6_142324685 and S6_142324939), had the lowest adjusted p-value of 1.01 × 10−5. Similarly, haplotype of hap4.62 for KL on chromosome 4, formed by 51 SNPs at 239 Mb, had the lowest adjusted p-value of 4.19 × 10−11. Haplotype of hap3.10 for KW on chromosome 3, consisting of two SNPs at 161 Mb, and haplotype of hap9.23 for KD on chromosome 9, formed by six SNPs at 129 Mb, also demonstrated significantly low adjusted p-values of 4.19 × 10−11 and 2.20 × 10−9, respectively.
3.4 Functional annotation of candidate genes
In total, 40 candidate genes were identified in the genomic regions spanning 106.12 kb upstream and downstream of the significant associated SNPs, and the annotation of candidate genes was performed using the B73 RefGen_v4 as the reference genome. Among them, the number of candidate genes identified for HKW, KW, KL, and KD was 25, 20, 14, and 18, respectively (Figure 7A). A dataset comprising expression levels from 194 maize tissues was downloaded from MaizeGDB and refined to include data from 34 kernel-related tissues. From this refined dataset, expression data for 40 candidate genes were extracted (Figure 7B). The gene Zm00001d044129 exhibited the highest expression with an FPKM value of 1,599.63 in the endosperm tissue 16 days after pollination in the B73 inbred line. Among the 40 candidate genes, only Zm00001d000713, Zm00001d044149, and Zm00001d044123 did not exhibit expression in these kernel-related tissues. In contrast, the remaining 37 genes were expressed in these tissues (FPKM > 1).
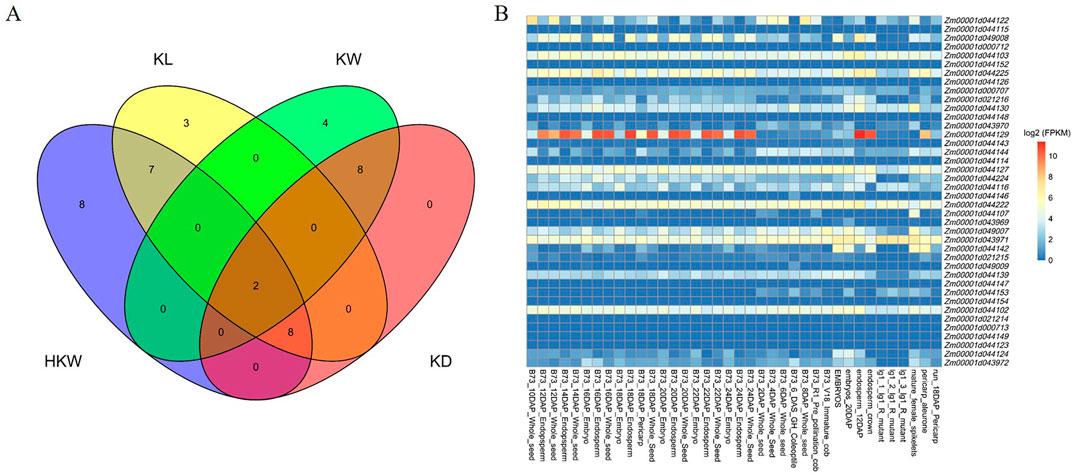
Figure 7. (A) Venn plot of candidate genes overlapping among the four kernel-related traits. (B) The expression heatmap of the candidate genes in kernel-related tissues.
Function annotations were available for 26 of the 40 candidate genes (Supplementary Table S3). Zm00001d000707 and Zm00001d044139 were associated with all four kernel-related traits. Notably, Zm00001d044129 and Zm00001d044143, encoding glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase and ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 27 respectively, have been reported for regulation of HKW and KL. Mutations in Zm00001d044129 caused maize kernel shrinkage. These genes can directly or indirectly regulate the weight and size of maize kernels.
Thirty-five candidate genes were annotated with 174 GO terms: 105 for biological processes, 35 for cellular components, and 34 for molecular functions (Supplementary Table S6). These terms include signal transduction (GO:0007165), multicellular organism development (GO:0007275), regulation of hormone levels (GO:0010817), signaling (GO:0023052), developmental processes (GO:0032502), hormone metabolic process (GO:0042445), and cellular developmental process (GO:0048869), which may be involved in maize kernel development.
3.5 Estimation of genomic prediction accuracies
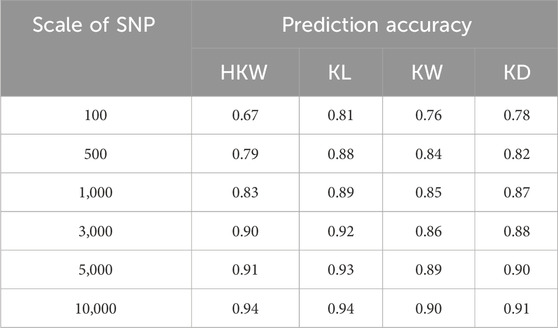
The accuracy of genomic prediction improves as the number of SNPs increases (Figure 8A). For HKW, the prediction accuracy increased from 0.67 with 100 SNPs to 0.94 with 10,000 SNPs. For KL, it rose from 0.81 with 100 SNPs to 0.94 with 10,000 SNPs. For KW, the prediction accuracy increased from 0.76 with 100 SNPs to 0.90 with 10,000 SNPs. For KD, it went from 0.78 with 100 SNPs to 0.91 with 10,000 SNPs (Table 3). At a scale of 10,000 SNPs, the prediction accuracy for all traits is consistently above 0.90.
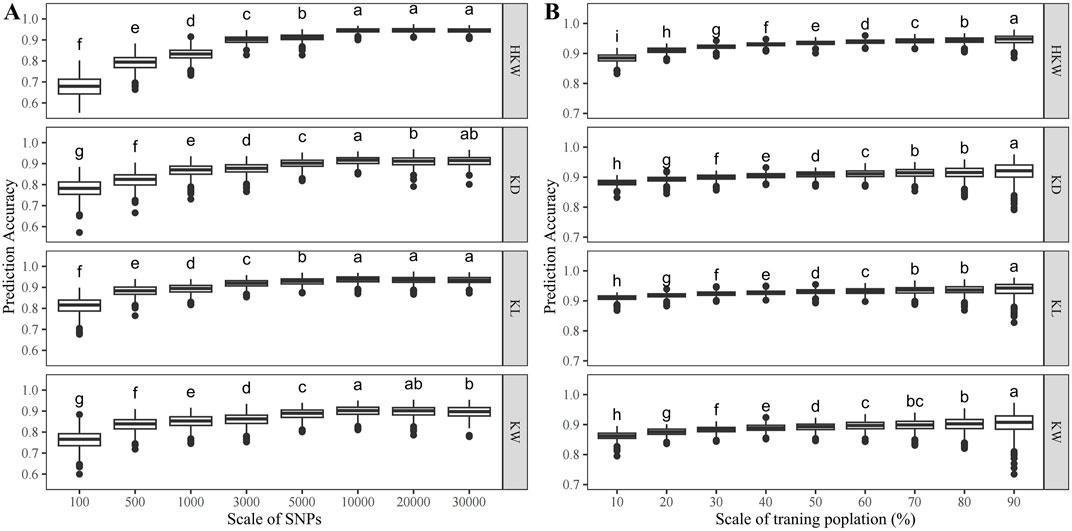
Figure 8. Genomic prediction accuracy of HKW, KL, KW, and KD in the population (A) when the number of SNPs varied from 100 to 30,000 with 8 scales, (B) when the training population size ranged from 10% to 90% of the total population size.
The accuracy of genomic prediction also improves with the increase of the training population size (Figure 8B). For HKW, the prediction accuracy increased from 0.88 with 10% of the GWAS panel as the training population to 0.95 with 90%. For KL, the prediction accuracy increased from 0.91 with 10% of the GWAS panel as the training population to 0.94 with 90% of the GWAS panel as the training population. For KW, it rose from 0.86 with 10% of the GWAS panel as the training population to 0.90 with 90% of the GWAS panel as the training population. For KD, the prediction accuracy increased from 0.88 with 10% of the GWAS panel as the training population to 0.92 with 90% of the GWAS panel as the training population (Table 4). The prediction accuracy for the four traits tends to saturate, when more than 60% of the GWAS panel was used as the training population.
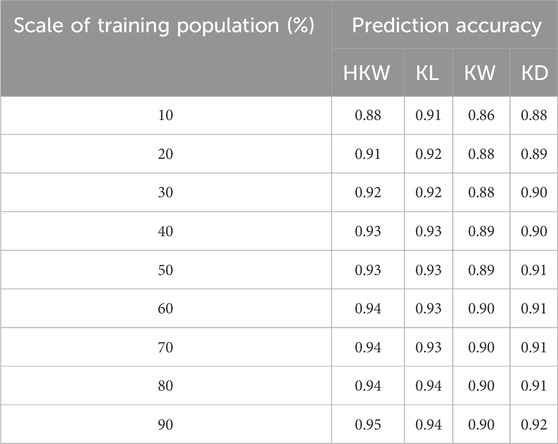
Table 4. Prediction accuracy for four maize kernel-related traits across different scale of training population.
These results revealed that a set of 10,000 SNPs and a training population size of 30% are sufficient for the application of GS in waxy and sweet maize breeding for kernel weight and kernel size.
4 Discussion
The kernel weight and size are among the most crucial factors influencing grain yield in maize (Liu et al., 2017). In the present study, GWAS, HTR, and GS analyses were conducted to dissect the genetic architecture of four kernel-related traits of HKW, KL, KW and KD in a representative sweet and waxy maize inbred line panel. The phenotypic analysis results of the four kernel-related traits across two environments revealed that the heritability of HKW and KL is moderately high, being 0.87 and 0.54, respectively. Both the genetic effects and genetic-environment interaction are significant, while the environmental effects are not significant, indicating that these two traits are primarily influenced by genetic factors. On the other hand, KW and KD exhibit lower heritability, with values of 0.19 and 0.29, respectively. This may be attributed to the relatively small phenotypic variation of these traits in this GWAS panel. The observed differences in heritability among these traits may reflect varying levels of genetic variation within the GWAS panel. Such insights are valuable for further understanding the genetic mechanisms underlying these kernel-related traits and can inform breeding strategies aimed at improving specific characteristics, particularly those with higher heritability like HKW and KL.
In GWAS, high-density and high-quality SNPs across the entire maize genome are essential to identify the SNPs significantly associated with the target traits. Genotyping by target sequencing (GBTS), genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS), and chip-based genotyping have been extensively utilized in the GWAS studies in maize (Xu et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2020c; Guo et al., 2021; Vinayan et al., 2021). Compared with these genotyping methods, whole-genome resequencing has a higher genome coverage and SNP density. With the dramatic decrease in the cost of whole-genome resequencing, this genotyping technique is being widely applied in GWAS analyses in maize (Xiao et al., 2017). In the present study, with the availability of the resequencing dataset of 447 sweet and waxy maize inbred lines, a saturated genome-wide dataset including 1,684,029 SNPs was used for GWAS analysis, the results showed the high-quality and high-density SNP dataset extracted from the re-sequencing data is powerful for obtaining more accurate results.
In this GWAS panel, PCA analysis distinctly divided the 447 maize inbred lines into two subgroups (Figures 4D,E). The results indicated that there was a very small partial germplasm exchange between sweet and waxy maize inbred lines in breeding selection. The main emphasis is on the improvement within each subgroup. Meanwhile, the LD decay distance at r2 = 0.2 was 106.12 kb, which is much greater than the LD decay distance of 33 kb in 350 modern maize lines developed from 2000 to 2010 in China (Wang B. et al., 2020), indicating lower genetic diversity of the GWAS panel used in the present study. Sweet and waxy maize are primarily cultivated for human consumption. The breeding process has historically emphasized traits linked to eating quality and nutritional value, resulting in decreased genetic diversity and increased linkage disequilibrium among genetic loci.
The GWAS has been shown to be an effective strategy for mining genetic loci for kernel weight and size (Liu et al., 2020). Due to the relatedness among maize inbred lines, the GWAS was conducted using the mixed linear model with the incorporation of the kinship matrices. The p-value of SNPs was the parameter to assess the association level between SNP and the trait. The smaller the p-value, the more significant the association between SNPs and the trait. To control the familywise error rate, 0.05/number of effective SNPs were used as the cut-off to ensure statistical significance for these SNPs (Li et al., 2022). In total, 49 SNPs were significantly associated with the four kernel-related traits based on the strict cut-off of the p-value. Candidate gene analysis revealed that 40 genes are the putative candidate genes for the four kernel-related traits. Out of these 40 genes, 37 genes were expressed in the kernel-related tissues of maize. Zm00001d044129 encodes the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase that affects starch metabolism in the maize endosperm (Bhave et al., 1990). Maize with mutations in the Zm00001d044129 gene exhibits a kernel shrunkage, affecting the weight and size of the maize kernel. Although the genes Zm00001d000707 and Zm00001d044139 lack functional annotations, they were found to be associated with all four kernel-related traits. Further experiments are needed to validate their functional characterization. Based on the GWAS results, functional markers can be developed, which will facilitate the marker-assisted selection to improve these kernel-related traits in sweet and waxy maize.
Genomic prediction has been successfully applied to several crops to accelerate the grain yield in maize breeding programs (Wang et al., 2020b). In the present study, the top 10,000 SNPs with the highest PVE values for each kernel-related trait were used for the GP analysis. In this GWAS panel, the predictive accuracy increased as the increase of the training population size. At a training population size of 10%, the lowest predictive accuracy for the four kernel-related traits, notably KW, reached 0.86. As the training population size increased, the prediction accuracy for HKW and KL stabilized around 0.94, while for KW and KD, it plateaued at approximately 0.91. Compared to previous approaches using SNPs significantly associated with the trait or random SNPs for GP analysis, this method exhibited higher predictive accuracy in GP analysis (Dang et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2023). Meanwhile, the predictive accuracy increased with the expansion of the SNPs from 100 to 10,000. At 500 SNPs, the predictive accuracy for the four kernel-related traits reached approximately 0.80. In this study, more than one and a half millions SNPs were used for GWAS analyses. However, our GS results showed that the prediction accuracies for all the kernel-related traits reached plateaus above 0.90, when 10,000 SNPs were used in prediction, these prediction accuracies are relatively high, indicating that using all the more than one million SNPs for prediction is not necessary. In practical applications, the KASP genotyping platform can be used (Semagn et al., 2014; Qu et al., 2022). This genotyping platform offers a faster and more cost-effective approach for low-density genotyping of a large number of individuals (500 SNPs). The prediction accuracies for four kernel-related traits were above 0.90 using 10,000 SNPs. In this case, the GBTS platform, suitable for medium-density genotyping, can be used (Guo et al., 2019).
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. This datasets have been deposited in the Genome Variation Map in National Genomics Data Center, Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences and China National Center for Bioinformation, under accession number GVM000854 (https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/gvm/getProjectDetail?project=GVM000854).
Author contributions
JQ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. DY: Data curation, Methodology, Software, Writing–review and editing. WG: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Resources, Writing–review and editing. MK: Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. HK: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing. DD: Data curation, Software, Writing–review and editing. HW: Methodology, Resources, Writing–review and editing. BP: Methodology, Resources, Writing–review and editing. XZ: Conceptualization, Software, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. AZ: Methodology, Software, Writing–review and editing. HZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. YG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 32172033, Shanghai Agriculture Applied Technology Development Program, grant number X2022-02-08-00-12-F01190, and the National Agricultural Science and Technology Major Projects, grant number NK202307040404.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Agricultural Science and Technology Major Projects. We also wish to thank Shanghai Engineering Research Center of Specialty Maize (20DZ2255300) and Shanghai Key Laboratory of Agricultural Genetics and Breeding (21DZ2271900) for providing us with experimental conditions.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fgene.2024.1431043/full#supplementary-material
References
Alvarado, G., Rodríguez, F. M., Pacheco, A., Burgueño, J., Crossa, J., Vargas, M., et al. (2020). META-R: a software to analyze data from multi-environment plant breeding trials. Crop J. 8, 745–756. doi:10.1016/j.cj.2020.03.010
Bernardi, J., Lanubile, A., Li, Q. B., Kumar, D., Kladnik, A., Cook, S. D., et al. (2012). Impaired auxin biosynthesis in the defective endosperm18 mutant is due to mutational loss of expression in the ZmYuc1 gene encoding endosperm-specific YUCCA1 protein in maize. Plant Physiol. 160, 1318–1328. doi:10.1104/pp.112.204743
Bhave, M. R., Lawrence, S., Barton, C., and Hannah, L. C. (1990). Identification and molecular characterization of shrunken-2 cDNA clones of maize. Plant Cell 2, 581–588. doi:10.1105/tpc.2.6.581
Bradbury, P. J., Zhang, Z., Kroon, D. E., Casstevens, T. M., Ramdoss, Y., and Buckler, E. S. (2007). TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23, 2633–2635. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm308
Chen, L., Li, Y. X., Li, C., Shi, Y., Song, Y., Zhang, D., et al. (2020). The retromer protein ZmVPS29 regulates maize kernel morphology likely through an auxin-dependent process(es). Plant Biotechnol. J. 18, 1004–1014. doi:10.1111/pbi.13267
Chen, S., Zhou, Y., Chen, Y., and Gu, J. (2018). Fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34, 884–890. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560
Crossa, J., Pérez, P., Hickey, J., Burgueño, J., Ornella, L., Cerón-Rojas, J., et al. (2014). Genomic prediction in CIMMYT maize and wheat breeding programs. Hered. (Edinb) 112, 48–60. doi:10.1038/hdy.2013.16
Danecek, P., Bonfield, J. K., Liddle, J., Marshall, J., Ohan, V., Pollard, M. O., et al. (2021). Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. Gigascience 10, giab008. doi:10.1093/gigascience/giab008
Dang, D., Guan, Y., Zheng, H., Zhang, X., Zhang, A., Wang, H., et al. (2023). Genome-wide association study and genomic prediction on plant architecture traits in sweet corn and waxy corn. Plants 12, 303. doi:10.3390/plants12020303
Dong, S. S., He, W. M., Ji, J. J., Zhang, C., Guo, Y., and Yang, T. L. (2021). LDBlockShow: a fast and convenient tool for visualizing linkage disequilibrium and haplotype blocks based on variant call format files. Brief. Bioinform. 22, 227. doi:10.1093/bib/bbaa227
Endelman, J. B. (2011). Ridge regression and other kernels for genomic selection with R package rrBLUP. Plant Genome 4, 250–255. doi:10.3835/plantgenome2011.08.0024
Feng, F., Qi, W., Lv, Y., Yan, S., Xu, L., Yang, W., et al. (2018). OPAQUE11 is a central hub of the regulatory network for maize endosperm development and nutrient metabolism. Plant Cell 30, 375–396. doi:10.1105/tpc.17.00616
Forestan, C., Aiese Cigliano, R., Farinati, S., Lunardon, A., Sanseverino, W., and Varotto, S. (2016). Stress-induced and epigenetic-mediated maize transcriptome regulation study by means of transcriptome reannotation and differential expression analysis. Sci. Rep. 6, 30446. doi:10.1038/srep30446
Garrison, E., and Marth, G. (2012). Haplotype-based variant detection from short-read sequencing. arXiv preprint arXiv 1207.3907.
Guo, Z., Wang, H., Tao, J., Ren, Y., Xu, C., Wu, K., et al. (2019). Development of multiple SNP marker panels affordable to breeders through genotyping by target sequencing (GBTS) in maize. Mol. Breed. 39, 37. doi:10.1007/s11032-019-0940-4
Guo, Z., Yang, Q., Huang, F., Zheng, H., Sang, Z., Xu, Y., et al. (2021). Development of high-resolution multiple-SNP arrays for genetic analyses and molecular breeding through genotyping by target sequencing and liquid chip. Plant Commun. 2, 100230. doi:10.1016/j.xplc.2021.100230
Gupta, P. K., Rustgi, S., and Kumar, N. (2006). Genetic and molecular basis of grain size and grain number and its relevance to grain productivity in higher plants. Genome 49, 565–571. doi:10.1139/G06-063
Hao, D., Xue, L., Zhang, Z., Cheng, Y., Chen, G., Zhou, G., et al. (2019). Combined linkage and association mapping reveal candidate loci for kernel size and weight in maize. Breed. Sci. 69, 420–428. doi:10.1270/jsbbs.18185
Johnston, R., Wang, M., Sun, Q., Sylvester, A. W., Hake, S., and Scanlon, M. J. (2014). Transcriptomic analyses indicate that maize ligule development recapitulates gene expression patterns that occur during lateral organ initiation. Plant Cell 26, 4718–4732. doi:10.1105/tpc.114.132688
Kakumanu, A., Ambavaram, M. M. R., Klumas, C., Krishnan, A., Batlang, U., Myers, E., et al. (2012). Effects of drought on gene expression in maize reproductive and leaf meristem tissue revealed by RNA-Seq. Plant Physiol. 160, 846–867. doi:10.1104/pp.112.200444
Li, H., Wang, S., Chai, S., Yang, Z., Zhang, Q., Xin, H., et al. (2022). Graph-based pan-genome reveals structural and sequence variations related to agronomic traits and domestication in cucumber. Nat. Commun. 13, 682. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-28362-0
Li, M. X., Yeung, J. M. Y., Cherny, S. S., and Sham, P. C. (2012). Evaluating the effective numbers of independent tests and significant p-value thresholds in commercial genotyping arrays and public imputation reference datasets. Hum. Genet. 131, 747–756. doi:10.1007/s00439-011-1118-2
Li, Q., Li, L., Yang, X., Warburton, M. L., Bai, G., Dai, J., et al. (2010a). Relationship, evolutionary fate and function of two maize co-orthologs of rice GW2 associated with kernel size and weight. BMC Plant Biol. 10, 143. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-10-143
Li, Q., Yang, X., Bai, G., Warburton, M. L., Mahuku, G., Gore, M., et al. (2010b). Cloning and characterization of a putative GS3 ortholog involved in maize kernel development. Theor. Appl. Genet. 120, 753–763. doi:10.1007/s00122-009-1196-x
Liu, J., Huang, J., Guo, H., Lan, L., Wang, H., Xu, Y., et al. (2017). The conserved and unique genetic architecture of kernel size and weight in maize and rice. Plant Physiol. 175, 774–785. doi:10.1104/pp.17.00708
Liu, M., Tan, X., Yang, Y., Liu, P., Zhang, X., Zhang, Y., et al. (2020). Analysis of the genetic architecture of maize kernel size traits by combined linkage and association mapping. Plant Biotechnol. J. 18, 207–221. doi:10.1111/pbi.13188
Liu, Y., Ao, M., Lu, M., Zheng, S., Zhu, F., Ruan, Y., et al. (2023). Genomic selection to improve husk tightness based on genomic molecular markers in maize. Front. Plant Sci. 14, 1252298. doi:10.3389/fpls.2023.1252298
Liu, Y., Hu, G., Zhang, A., Loladze, A., Hu, Y., Wang, H., et al. (2021). Genome-wide association study and genomic prediction of Fusarium ear rot resistance in tropical maize germplasm. Crop J. 9, 325–341. doi:10.1016/j.cj.2020.08.008
Meuwissen, T. H. E., Hayes, B. J., and Goddard, M. E. (2001). Prediction of total genetic value using genome-wide dense marker maps. Genetics 157, 1819–1829. doi:10.1093/genetics/157.4.1819
Myles, S., Peiffer, J., Brown, P. J., Ersoz, E. S., Zhang, Z., Costich, D. E., et al. (2009). Association mapping: critical considerations shift from genotyping to experimental design. Plant Cell 21, 2194–2202. doi:10.1105/tpc.109.068437
Pang, Y., Liu, C., Wang, D., St. Amand, P., Bernardo, A., Li, W., et al. (2020). High-resolution genome-wide association study identifies genomic regions and candidate genes for important agronomic traits in wheat. Mol. Plant 13, 1311–1327. doi:10.1016/j.molp.2020.07.008
Qu, J., Chassaigne-Ricciulli, A. A., Fu, F., Yu, H., Dreher, K., Nair, S. K., et al. (2022). Low-density reference fingerprinting SNP dataset of CIMMYT maize lines for quality control and genetic diversity analyses. Plants 11, 3092. doi:10.3390/plants11223092
Rashid, Z., Babu, V., Sharma, S. S., Singh, P. K., and Nair, S. K. (2022). Identification and validation of a key genomic region on chromosome 6 for resistance to Fusarium stalk rot in tropical maize. Theor. Appl. Genet. 135, 4549–4563. doi:10.1007/s00122-022-04239-0
Semagn, K., Babu, R., Hearne, S., and Olsen, M. (2014). Single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping using kompetitive allele specific PCR (KASP): overview of the technology and its application in crop improvement. Mol. Breed. 33, 1–14. doi:10.1007/s11032-013-9917-x
Shikha, K., Shahi, J. P., Vinayan, M. T., Zaidi, P. H., Singh, A. K., and Sinha, B. (2021). Genome-wide association mapping in maize: status and prospects. 3 Biotech. 11, 244. doi:10.1007/s13205-021-02799-4
Shook, J. M., Zhang, J., Jones, S. E., Singh, A., Diers, B. W., and Singh, A. K. (2021). Meta-GWAS for quantitative trait loci identification in soybean. G3 (Bethesda) 11, 117. doi:10.1093/g3journal/jkab117
Soleimani, B., Lehnert, H., Babben, S., Keilwagen, J., Koch, M., Arana-Ceballos, F. A., et al. (2022). Genome wide association study of frost tolerance in wheat. Sci. Rep. 12, 5275. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-08706-y
Song, J., Liu, Y., Guo, R., Pacheco, A., Muñoz-Zavala, C., Song, W., et al. (2024). Exploiting genomic tools for genetic dissection and improving the resistance to Fusarium stalk rot in tropical maize. Theor. Appl. Genet. 137, 109. doi:10.1007/s00122-024-04597-x
Stelpflug, S. C., Sekhon, R. S., Vaillancourt, B., Hirsch, C. N., Buell, C. R., de Leon, N., et al. (2016). An expanded maize gene expression atlas based on RNA sequencing and its use to explore root development. Plant Genome 9, 10. doi:10.3835/plantgenome2015.04.0025
Tian, T., Liu, Y., Yan, H., You, Q., Yi, X., Du, Z., et al. (2017). AgriGO v2.0: a GO analysis toolkit for the agricultural community, 2017 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 45, W122–W129. doi:10.1093/nar/gkx382
Vinayan, M. T., Seetharam, K., Babu, R., Zaidi, P. H., Blummel, M., and Nair, S. K. (2021). Genome wide association study and genomic prediction for stover quality traits in tropical maize (Zea mays L.). Sci. Rep. 11, 686. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-80118-2
Walley, J. W., Sartor, R. C., Shen, Z., Schmitz, R. J., Wu, K. J., Urich, M. A., et al. (2016). Integration of omic networks in a developmental atlas of maize. Science 353, 814–818. doi:10.1126/science.aag1125
Wang, B., Lin, Z., Li, X., Zhao, Y., Zhao, B., Wu, G., et al. (2020). Genome-wide selection and genetic improvement during modern maize breeding. Nat. Genet. 52, 565–571. doi:10.1038/s41588-020-0616-3
Wang, N., Wang, H., Zhang, A., Liu, Y., Yu, D., Hao, Z., et al. (2020b). Genomic prediction across years in a maize doubled haploid breeding program to accelerate early-stage testcross testing. Theor. Appl. Genet. 133, 2869–2879. doi:10.1007/s00122-020-03638-5
Wang, N., Yuan, Y., Wang, H., Yu, D., Liu, Y., Zhang, A., et al. (2020c). Applications of genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) in maize genetics and breeding. Sci. Rep. 10, 16308. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-73321-8
Wang, Y., Xu, J., Yu, J., Zhu, D., and Zhao, Q. (2022). Maize GSK3-like kinase ZmSK2 is involved in embryonic development. Plant Sci. 318, 111221. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2022.111221
Waters, A. J., Makarevitch, I., Noshay, J., Burghardt, L. T., Hirsch, C. N., Hirsch, C. D., et al. (2017). Natural variation for gene expression responses to abiotic stress in maize. Plant J. 89, 706–717. doi:10.1111/tpj.13414
Xiao, Y., Liu, H., Wu, L., Warburton, M., and Yan, J. (2017). Genome-wide association studies in maize: praise and stargaze. Mol. Plant 10, 359–374. doi:10.1016/j.molp.2016.12.008
Xu, C., Ren, Y., Jian, Y., Guo, Z., Zhang, Y., Xie, C., et al. (2017). Development of a maize 55 K SNP array with improved genome coverage for molecular breeding. Mol. Breed. 37, 20. doi:10.1007/s11032-017-0622-z
Yan, J., Shah, T., Warburton, M. L., Buckler, E. S., McMullen, M. D., and Crouch, J. (2009). Genetic characterization and linkage disequilibrium estimation of a global maize collection using SNP markers. PLOS ONE 4, 8451. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008451
Zhang A., A., Pérez-Rodríguez, P., San Vicente, F., Palacios-Rojas, N., Dhliwayo, T., Liu, Y., et al. (2022). Genomic prediction of the performance of hybrids and the combining abilities for line by tester trials in maize. Crop J. 10, 109–116. doi:10.1016/j.cj.2021.04.007
Zhang, C., Zhou, Z., Yong, H., Zhang, X., Hao, Z., Zhang, F., et al. (2017). Analysis of the genetic architecture of maize ear and grain morphological traits by combined linkage and association mapping. Theor. Appl. Genet. 130, 1011–1029. doi:10.1007/s00122-017-2867-7
Zhang, L., Fu, M., Li, W., Dong, Y., Zhou, Q., Wang, Q., et al. (2024). Genetic variation in ZmKW1 contributes to kernel weight and size in dent corn and popcorn. Plant Biotechnol. J. 22, 1453–1467. doi:10.1111/pbi.14279
Zhang, X., Guan, Z., Li, Z., Liu, P., Ma, L., Zhang, Y., et al. (2020). A combination of linkage mapping and GWAS brings new elements on the genetic basis of yield-related traits in maize across multiple environments. Theor. Appl. Genet. 133, 2881–2895. doi:10.1007/s00122-020-03639-4
Zhang, X., Ren, Z., Luo, B., Zhong, H., Ma, P., Zhang, H., et al. (2022). Genetic architecture of maize yield traits dissected by QTL mapping and GWAS in maize. Crop J. 10, 436–446. doi:10.1016/j.cj.2021.07.008
Keywords: kernel size, kernel weight, NGS, GWAS, GS
Citation: Qu J, Yu D, Gu W, Khalid MHB, Kuang H, Dang D, Wang H, Prasanna B, Zhang X, Zhang A, Zheng H and Guan Y (2024) Genetic architecture of kernel-related traits in sweet and waxy maize revealed by genome-wide association analysis. Front. Genet. 15:1431043. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1431043
Received: 11 May 2024; Accepted: 17 September 2024;
Published: 27 September 2024.
Edited by:
Deepmala Sehgal, Syngenta, United KingdomReviewed by:
Shibo Wang, University of California, Riverside, United StatesFahimeh Shahinnia, Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada (AAFC), Canada
Copyright © 2024 Qu, Yu, Gu, Khalid, Kuang, Dang, Wang, Prasanna, Zhang, Zhang, Zheng and Guan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hongjian Zheng, aGp6aDYxODhAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Yuan Guan, Z3Vhbnl1YW5Ac2Fhcy5zaC5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jingtao Qu
Jingtao Qu Diansi Yu
Diansi Yu Wei Gu1†
Wei Gu1† Muhammad Hayder Bin Khalid
Muhammad Hayder Bin Khalid Dongdong Dang
Dongdong Dang Boddupalli Prasanna
Boddupalli Prasanna Xuecai Zhang
Xuecai Zhang Ao Zhang
Ao Zhang Hongjian Zheng
Hongjian Zheng